First Aid Worksheet. A. Primary Survey - Critical Intervention
|
|
|
- Aubrey Silas Ferguson
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 First Aid Worksheet A. Primary Survey - Critical Intervention 1. The purpose of the primary survey is to: a) get an accurate account of the patient s injuries b) locate all the bleeding and fracture sites c) check for and control all the life-threatening problems d) restore breathing 2. To maintain an open airway for an unconscious patient with a suspected spinal injury, one could do all of the following EXCEPT: a) jaw thrust b) roll lateral without moving the head c) head tilt with C-spine control d) inserting an oral airway 3. The difference between a partial and a complete airway obstruction is: a) assisted ventilations are not required for a partial obstruction b) a partial airway obstruction does not have to be referred to medical aid c) with a partial airway obstruction the patient is able to get some air into the lungs d) a partial obstruction is easier to clear with abdominal thrusts than a complete obstruction 4. The most common cause of airway obstruction in an unconscious patient is: a) swelling of the throat b) the tongue c) foreign bodies or material d) patient s own blood or vomit 5. To maintain a clear air passage for a person you suspect has a spinal injury you would: a) perform a tracheotomy b) use the jaw thrust technique c) hyperextend the neck d) do a head tilt chin lift 6. Your patient s breathing is very shallow, ineffective with little chest movement. You would: a) give them oxygen at a 10 lpm flow with a simple face mask b) assist their breathing with a pocket mask and oxygen c) assist their breathing with a pocket mask d) assist their breathing with a bag valve mask 7. Which of the following would NOT provide you with information about a patient s circulation? a) the patient s hands feel cold to touch b) the pulses on the wrist are hard to find c) the patient feels clammy to touch d) the patient can not feel what finger you are touching 8. A non-breathing patient has no radial pulses but a slow, weak and irregular carotid pulse. You should: a) start CPR b) breathe for the patient and assist the heartbeat with compressions c) ventilate the patient every 5 seconds d) attempt 15 quick compressions to restore a regular heart rhythm 9. CPR should be performed when the patient: a) is not breathing and has a faint heartbeat of less than 50 bpm. b) is not breathing and has a serious head injury c) has an absent radial pulse and is in severe shock d) is not breathing and has no pulse 10. External chest compressions, when efficiently performed will provide approximately: a) 10% of normal blood flow to the brain b) 15% of normal blood flow to the brain c) 25% of normal blood flow to the brain d) 50% of normal blood flow to the brain 11. Any action taken by a lifeguard when correcting life-threatening conditions is referred to as: a) EMS b) a critical intervention c) the priority action approach d) the primary survey 1
2 12. A boy fell from the top of the 3 metre diving board ladder. He is prone (face down) and does not respond to verbal stimuli (voice). When should you establish C-spine control? a) immediately after the scene assessment b) after rolling the patient into lateral position c) after the patient is on the spine board d) after the patient s breathing has been checked B. Deadly Bleeding 13. To control bleeding from a severed carotid artery, you would: a) lie the patient down, put dressings on the bleed, and secure with a tie b) lie the patient down, put pressure above the cut and below the cut c) let the patient control the bleeding d) apply the appropriate pressure point 14. If direst pressure does not control bleeding you would control bleeding by a) using a tourniquet b) using the indirect pressure point c) elevating the part d) dressing and bandaging the wound 15. A bleed that requires a pressure point must be initially maintained for a) 5 minutes b) 15 minutes c) 30 minutes d) indefinitely C. Shock 16. Shock is: a) adequate perfusion of blood b) inadequate perfusion of blood c) nothing to worry about if recognized right away d) always reversible 17. Shock that is caused by blood loss is called: a) hypovolemic shock b) anaphylactic shock c) respiratory shock d) cardiogenic shock D. Oxygen Therapy - Oral Airways 18. Exhaled air contains what percentage of oxygen? a) 10% b) 16% c) 21% d) 80% 19. Several safety systems have been developed to prevent the connection of the wrong type of cylinder to an oxygen regulator, tubing and mask. When hooking up a D size cylinder, the best safeguard is the: a) colour of the cylinder b) overall height of the cylinder c) pin indexing d) size of the regulator threads 20. When is an oropharyngeal airway required? a) all patients who have a decreased LOC (no obstruction) b) all patients who do not respond to verbal stimuli (no obstruction) c) patients who do respond to verbal stimuli (no obstruction) d) patients who do not respond to pain stimuli only (no obstruction) 21. If the oral airway has been inserted in a patient and becomes obstructed with foreign matter or blood clots, the first thing you should do is: a) remove the airway and position the patient lateral b) leave the airway in and position the patient lateral c) leave the airway in to hold the tongue forward d) quickly remove, clean and replace the airway 22. What is the danger of inserting an oral airway that is too small? a) the patient will gag b) it will prevent a proper seal with a pocket mask c) it could dislodge dentures d) it may cause an airway obstruction E. Secondary Survey 2
3 23. The secondary survey consists of: a) vitals, history and head to toe b) vitals and head to toe c) vitals, history and treatment d) head to toe 24. The bluish colour sometimes seen on the trauma patient is called: a) cyanosis b) dyspnea c) apnea d) hypoxia F. Head and Spinal Cord Injuries 25. Which of the following symptoms would indicate spinal cord injury rather that a spinal column injury? a) point tenderness b) deformity c) numbness d) pain on movement 26. A large object fell and knocked somebody down. Before getting to the patient, what injury do you know you will have to treat, other than the head injury? a) injury to facial bones b) abdominal injury c) injury to the airway d) cervical injury 27. Which of the following would provide you with information about a suspected spinal injury? a) the patient can not identify which toe you touch b) the patient s feet feel cool to the touch c) the pulses in the feet are hard to find d) the patient s feet look very pale 28. A slow and strong pulse in a casualty with a head injury is a strong indication of: a) brain damage b) intracranial pressure c) shock d) blood loss from other injuries 29. What is the most important guide to gauging the severity of a brain injury? a) the patient s response to pain stimulus b) level of consciousness c) draining of cerebrospinal fluid d) paralysis of the limbs 30. The first thing to do in the care of all unwitnessed unconscious patients is to: a) suspect a possible spinal injury and act accordingly b) keep the patient in the supine position if he does not have a spinal injury c) check vital signs d) establish and maintain adequate ventilations 31. A good sign of possible brain damage is: a) pain and swelling b) bruises under the eyes c) unequal pupils d) none of the above 32. Two complications that may develop with spinal cord injuries are: a) bleeding and hypovolemic shock b) inadequate breathing and neurogenic shock c) transient vasodilation and psychogenic shock d) infection and septic shock G. CardioRespiratory Emergencies 33. Which of the following symptoms are generally associated with heart attack: a) radiating chest pain lasting longer than 30 minutes b) chest pain that increases with the patient coughs, moves, or breathes deeply c) squeezing, substernal chest pain decreases when the patient is resting d) oxygen relieves the pain within five minutes 34. The management of a heart attack patient should include: a) completion of the primary and secondary survey before calling EMS 3
4 b) assisting the patient to take nitroglycerin c) walking the patient to the first aid room for rest d) calling EMS, then monitoring vitals closely 35. In most cases, the pain of Myocardial infarction feels like it is: a) located beneath the breastbone and feels like someone is squeezing the chest b) very sharp, especially during inhalation c) in the upper abdomen and feels like indigestion d) between the shoulder blades in the back 36. This heart condition is often mistaken for indigestion and is brought on by emotional stress, strenuous exercise or agitation. It is characterized by pain in the chest and/or arm, and is relieved by rest. This condition is known as: a) chronic heart failure b) myocardial infarction c) stroke d) angina pectoris 37. If a patient with a previous cardiac history is complaining of chest pain, which of the following questions would help you decide if it was a heart attack or angina? (1) where is the pain located? (2) is the pain relieved by oxygen? (3) how long has the pain lasted? (4) how would you describe the pain? (5) what is the quality of the pain? a) 1 and 2 b) 2 and 3 c) 3 and 4 d) 2 and The term for shortness of breath is: a) apnea b) cyanosis c) dyspnea d) hypoxia 39. A harsh high pitched sound heard on inspiration is called: a) crowing b) stridor c) wheezing d) rales 40. Suffocation due to decreased oxygen and increased carbon dioxide in the blood is: a) arrythmia b) asthma c) aspiration d) asphyxia 41. The lining of the chest cavity is: a) periosteum b) peritoneum c) pleura d) pia matter H. Fractures - Sprains - Dislocations 42. Which of the following is the correct treatment for an open fracture? a) apply traction to fix any overlying bones b) never splint directly over the wound c) wrap the break with a tensor before putting the splint on d) always apply ice 43. Which of the following signs will best help distinguish a simple fracture from a bad sprain? a) point tenderness and crepitis b) level of pain c) amount of swelling d) distal circulation 44. The function of the tendons is to: a) connect bone to bone b) connect muscle to bone c) connect muscle to muscle d) connect joint to joint I. Chest and Abdominal Injuries 45. Which of the following will help determine how severe a chest injury is? 4
5 (1) determine the rate and quality of breathing (2) identify the mechanism of injury (3) determine the patient s past medical history (4) expose and examine the chest (5) determine the presence of a radial pulse (6) determine the patient s level of consciousness a) 1, 3, and 5 b) 1, 2, and 4 c) 3, 4, and 6 d) 2, 5, and 6 1. Which of the following signs and symptoms would indicate a simple rib fracture? (1) stridor (2) coughing (3) pain worsens on inhalation (4) paradoxal movement of the chest wall (5) point tenderness a) 1 and 2 b) 2 and 3 c) 3 and 5 d) 4 and 5 1. If you discover an open wound with blood stained bubbles when you expose the chest, you must immediately: a) cover the wound with a gloved hand b) apply sterile air tight dressing and bandage c) ensure the wound stays open d) apply a tourniquet 0. The signs and symptoms of a tension pneumothorax are: a) over expansion of the uninjured side, trachea out of alignment, distended neck veins, subcutaneous emphysema and distressed breathing b) over expansion of the injured side, trachea out of alignment, distended neck veins, subcutaneous emphysema and distressed breathing c) laboured and distressed breathing d) laboured and distressed breathing greater than 30 bpm 1. A casualty with a sealed sucking chest wound shows signs and symptoms of a tension pneumothorax. You would a) release one side of the airtight dressing on inhalation b) ensure that the dressing is still airtight c) start assisted ventilations d) release one side of the airtight dressing on exhalation 2. Which of the following would indicate internal bleeding? (1) rigidity and/or guarding of the abdominal muscles (2) bruising in the abdominal area (3) restlessness and air hunger (4) distention of the abdomen (5) numbness and tingling in the pelvic area (6) chest pain a) 1, 2, and 4 b) 2, 3, and 4 c) 1, 5, and 6 d) 2, 5, and 6 J. Diabetic Emergencies 1. A patient who has diabetes can develop hypoglycemia (insulin shock) by: (1) not eating enough (2) exercising too much (3) taking too much insulin (4) not taking enough insulin (5) eating too much a) 1, 2, and 3 b) 1, 3, and 4 c) 2, 3, and 5 d) 2, 4, and 5 2. Which of the following signs and symptoms would indicate that a victim is suffering from hypoglycemia: (1) pale, clammy skin (2) breath has a fruity odour (3) deep rapid breathing (4) complains about being hungry (5) confusion (6) flushed and dry skin a) 1, 2, and 5 b) 2, 3, and 6 c) 1, 4, and 5 d) 3, 4, and 5 5
6 1. The earliest signs of hypoglycemia are: a) hunger, pale clammy skin, dizziness, trembling, weakness, confusion, restlessness, and irrational behaviour b) thirst, excessive urination, loss of appetite, weakness, and dizziness c) nausea, vomiting, deep rapid breathing, dry mouth, fruity breath, weak and rapid pulse, warm and dry skin d) pale cool and clammy skin, confusion and irrational behaviour, excessive urination 2. What is the greatest risk in giving glucose to an unconscious diabetic patient? a) the patient may be hyperglycemic b) it may make the patient vomit c) the patient may be hypoglycemic d) it may obstruct the patient s airway K. Seizure Management 55. A grand mal seizure in the water: a) causes muscles to relax: patient is likely to float b) causes muscles to relax: patient is likely to sink c) causes muscles to tense: patient is likely to float d) causes muscles to tense: patient is likely to sink 56. A person is having a grand mal seizure on the pool deck, and their head is repeatedly hitting the hard surface. You should: a) never touch a person having a seizure b) put your hands under the patient s head c) get a bystander to hold the patient s head down so that it doesn t move d) grab a pool mat, and put it under the patient s head L. Hypo/Hyperthermia 57. Why is it important to make a careful and lengthy check for a carotid pulse when assessing a hypothermic patient? a) the warmth from your fingers will transfer to the artery and increase blood flow to the brain b) blood vessels constrict and the heart rate slows giving the impression the heart is not beating c) the chemical changes within the tissues, as they become colder, may result in stimulation to nerves controlling the contraction of blood vessels giving the false impression the patient has a pulse d) it is possible to collapse the carotid artery if too much pressure is applied 58. What is the most reliable indicator in determining whether a patient is suffering from heat exhaustion or heat stroke? a) heat cramps b) level of consciousness c) sweating d) vomiting 59. What is the priority in treating a patient suffering from heat stroke? a) cool the body and replenish fluids, give cold water or juice, prevent further exposure to heat b) immediate cooling of the patient and continued cooling until EMS arrives c) replace water and salt in the patient s system d) wait for EMS before starting any cooling M. Minor Bleeding 60. Bleeding from an artery would a) flow b) ooze c) squirt d) drip 61. Infection is the result of: a) inflammation in a wound b) the healing process c) bacterial growth in an injury d) dirt in the wound 62. Which of the following signs would indicate the most advanced sign of infection a) red streaks extending from the wound b) aching and local tenderness around the wound c) pus draining from the wound d) redness in the area surrounding the wound N. Facial Injuries 63. The major concern for an unconscious patient with a facial injury is: a) C-spine injury b) facial fractures 6
7 c) airway problems d) nerve damage 64. The irreplaceable fluid contained in the eyeball is: a) cornea b) sclera c) conjunctiva d) vitreous humor 65. The treatment for a nosebleed includes: (1) stand the patient over a sink to avoid getting blood everywhere (2) apply a cold pack to the back of the neck (3) apply constant pressure by pinching the nostrils (4) sit the patient with the head forward (5) tilt the patients head back a) 3 and 4 b) 1 and 2 c) 2 and 5 d) 3 and Which of the following would be appropriate for a patient with a nosebleed? a) place the patient supine and apply direct pressure to the nose b) sit the patient down and apply cold to the back of the neck c) sit the patient down with the head bent forward and apply direct pressure to the nose d) place the patient in the position of most comfort and insert a small gauze wad into the nostril O. Burns 67. Which of the following describes a first degree burn? a) the outer layer of skin is damages allowing blisters to form b) reddening of one layer of skin c) appears charred and pain is severe d) results in plasma loss as the blisters are formed 68. Which of the following describes a second degree burn? a) reddening of one layer of skin b) appears yellowish and pain is not prominent c) both layers of skin are involved and there are blisters d) appears charred and pain is severe P. Drugs - Poisons - Chemicals 69. What is the treatment for a chemical splashed in the eye: (1) flush the eyes for 30 minutes with a neutralizing agent (2) conduct the secondary survey before treating the injury (3) flush the eyes for 30 minutes with saline or water (4) examine the eyes for looses chemical particles (5) send patient to the doctor if the patient s eyes appear normal (6) apply an eye anesthetic a) 1, 4, 6 b) 3, 4, 5 c) 1, 2, 5, 6 d) 1, 4, What is the treatment for chlorine gas inhalation? a) oxygen at 10 lpm b) assisted ventilation with 100% oxygen flow c) inhalation of amyl nitrate d) supine position, encouraging the patient to cough 71. If chlorine does not immediately affect someone, what could make it deadly over time? a) the gas blocks the cells ability to receive oxygen b) the gas inflames lung tissue causing fluid to collect in the lungs over time c) exposure may initially impair judgment and eventually have a toxic effect d) chlorine gas displaces oxygen in the bloodstream causing hypoxia 72. The treatment for a dry chemical spill on the body is: a) flush with water for 30 minutes b) brush off the chemical, them flush for 30 minutes c) wait for EMS before treating d) brush off the chemical, then cover with sterile gauze 7
8 Q. Protection from Disease 73. Lifeguards must use gloves: a) with victims who are HIV positive b) with victims who have Hepatitis c) with all victims d) whenever there is a possibility of coming into contact with bodily fluids 74. What is the most effective method a lifeguard can use to prevent the transfer of infection when dealing with minor injuries? a) use sterile bandages b) wash hands with soap and water before and after every treatment c) disinfect equipment and work surfaces with soap and water d) wear disposable medical gloves 75. A fellow lifeguard is treating a patron for a bleed and splashes some blood in their eye. You should: a) Flush the eyes with water for 30 minutes b) Flush the eyes with water for one minute, then get them to go to the hospital within two hours c) Flush the eyes with water for one minute, then get them to go to the hospital after their shift is over d) Flush the eyes for 30 minutes, then send them to the hospital 8
9 True/False Questions 1. Non-prescription drugs may be kept in the first aid room and patrons or lifeguards can help themselves as needed. 2. The signs and symptoms of critical incident stress are only emotional in nature. 3. Treatment for a nosebleed includes sitting a patient down with the head tilted back and an icepack on the bridge of the nose. 4. With any penetrating wound there is danger of infection due to the likelihood of contamination below the surface. 5. Any open wounds associated with a fracture should not be treated until after splinting the limb. 6. Petit Mal seizures are common in adults and are often mistaken for epilepsy. 7. Grand Mal seizures follow a classic pattern and the patient will have an aura just prior to the seizure. 8. It is important to place a bite stick in the mouth of a patient having convulsions. 9. After a seizure the patient is usually confused, with no memory of the seizure. 10. Diabetes is a disease of the pancreas and does not affect any other area of the body. 11. Hypoglycemia is a result of low blood sugar, and the patient requires glucose (or a substance containing glucose). 12. Diabetes is an incurable disease but can be controlled through diet and medication. 13. Among injury victims, shock is almost always caused by the patient s emotional response to the pain of the injuries. 14. There may only be a short time between the onset of shock, and the point where it becomes irreversible, leading to death. 15. It is important to keep a patient who is suffering from shock active, for this will keep the blood flowing through the body and help tissue perfusion. 16. Asthma most commonly results from traumatic chest injuries. 17. Asthma is a narrowing of the airways (bronchospasm) that results in wheezing and whistling noises when the patient breathes. 18. A person suffering an asthma attack has the greatest difficulty with inspiration or getting air into the lungs. 19. Asthmatic attacks may be a result of a serious allergic reaction and can progress to anaphylactic shock. 20. Electrical burns can appear quite small, but there may be extensive internal damage. 21. Heat cramps result from salt imbalances in the muscles, heat exhaustion results from salt and water depletion. 22. Shivering is one of the earliest signs of hypothermia, and as the condition worsens it will stop. 23. Hand washing is one of the best defenses against spreading infections. 24. Latex gloves can be washed and reused as long as there are no tears in them. 25. The effects of drugs and alcohol can make the interpretation of signs and symptoms difficult. 9
10 Short Answers 1. List the steps of the primary survey (starting with scene assessment and ending with shock management) and describe the critical intervention that may be necessary at each step. 2. List the parts of the secondary survey and their components. 3. What is gastric distension? 4. What do we do if direct pressure does not control a bleed? 5. What is the difference between 3/4 prone and lateral position? 6. What is the difference between regurgitation and vomit? 7. When do you put in an oral airway? 8. Why is it important to use a pocket mask? 9. What are the key signs of a possible concussion? 10. In what position should a stroke victim probably be placed? 11. What is the treatment for anaphylactic shock? 12. What happens to the CO 2 and O 2 levels in hyperventilation? 13. What does COPD have to do with oxygen therapy? 14. How often should an angina patient take their medication in an emergency? 15. What are the key differences between an angina attack and a heart attack? 16. When would you treat a patient as a suspected c-spine injury? 17. How do you tell the difference between a sprain and a fracture? 18. Why is important to assess the distal circulation for a fracture injury? 19. What is the difference between diabetic coma and insulin shock? 20. How do you treat a semi-conscious diabetic patient? 21. What is the difference between a laceration, abrasion, avulsion and a puncture injury? 22. What is the treatment for a 2 nd or 3 rd degree burn? 23. In what position should someone with a serious eye injury be placed? 24. How long should a patient hold their nose for a nosebleed? 25. What does a flail chest injury look like? 26. What is the treatment for an open pneumothorax? 27. What are the symptoms of a tension pneumothorax? 28. How do you recognize internal bleeding? 29. What is heat syncope? 30. What are the symptoms of heat exhaustion? 31. What is the treatment for heat stroke? 32. What are the phases of a grand mal seizure? 33. What are some things to consider when treating drugs or poison situations? 10
11 First Aid Answer Key Multiple Choice 1. C 2. C 3. C 4. B 5. B 6. B 7. D 8. C 9. D 10. C 11. B 12. A 13. B 14. B 15. A 16. B 17. A 18. B 19. C 20. B 21. A 22. D 23. A 24. A 25. C 26. D 27. A 28. B 29. B 30.A 31. C 32. B 33. A 34. D 35. A 36. D 37. B 38. C 39. B 40. D 41. C 42. B 43. A 44. B 45. B 46. C 47. A 48. B 49. D 50. A 51. A 52. C 53. A 54. D 55. D 56. D 57. B 58. C 59. B 60. C 61. D 62. A 63. C 64. D 65. A 66. C 67. B 68. C 69. B 70. A 71. B 72. B 73. D 74. B 75. B True/False 1. F 2. F 3. F 4. T 5. F 6. F 7. T 8. F 9. T 10. F 11. T 12. T 13. F 14. T 15. F 16. F 17. T 18. T 19. T 20. T 21. T 22. T 23. T 24. F 25. T 11
First Responder (FR) and Emergency Medical Responder (EMR) Progress Log
 First Responder (FR) and Emergency Medical Responder (EMR) Progress Log Note: Those competencies that are for EMR only are denoted by boldface type. For further details on the National Occupational Competencies
First Responder (FR) and Emergency Medical Responder (EMR) Progress Log Note: Those competencies that are for EMR only are denoted by boldface type. For further details on the National Occupational Competencies
WET, COUGHING AND COLD NEAR RIVER BANK STUNG BY BEE CAUSING ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK TO WRIST
 GRIT IN EYE BROKEN LEG BONE WET, COUGHING AND COLD NEAR RIVER BANK STUNG BY BEE CAUSING ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK HEART ATTACK SUFFERING FROM SHOCK CHOKING SEVERE BLEEDING TO WRIST HYPOTHERMIA ANGINA Localised
GRIT IN EYE BROKEN LEG BONE WET, COUGHING AND COLD NEAR RIVER BANK STUNG BY BEE CAUSING ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK HEART ATTACK SUFFERING FROM SHOCK CHOKING SEVERE BLEEDING TO WRIST HYPOTHERMIA ANGINA Localised
EYE, EAR, NOSE, and THROAT INJURIES
 T6 EYE, EAR, NOSE, and THROAT INJURIES Management of injuries of the eyes, ears, nose, and throat focuses on airway management and initial stabilization of the injury. Bilateral comparisons can assist
T6 EYE, EAR, NOSE, and THROAT INJURIES Management of injuries of the eyes, ears, nose, and throat focuses on airway management and initial stabilization of the injury. Bilateral comparisons can assist
404 Section 5 Shock and Resuscitation. Scene Size-up. Primary Assessment. History Taking
 404 Section 5 and Resuscitation Scene Size-up Scene Safety Mechanism of Injury (MOI)/ Nature of Illness (NOI) Ensure scene safety and address hazards. Standard precautions should include a minimum of gloves
404 Section 5 and Resuscitation Scene Size-up Scene Safety Mechanism of Injury (MOI)/ Nature of Illness (NOI) Ensure scene safety and address hazards. Standard precautions should include a minimum of gloves
American Heart Association
 American Heart Association Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest April 2006 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST For BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses 2006 American Heart
American Heart Association Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest April 2006 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST For BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses 2006 American Heart
First Aid Multiple Choice Test
 First Aid Multiple Choice Test Answer all 25 questions by circling the correct answer. This is an open-book test. Answers are contained in The Boy Scout Handbook. Patrol Troop 1. When making a 911 call,
First Aid Multiple Choice Test Answer all 25 questions by circling the correct answer. This is an open-book test. Answers are contained in The Boy Scout Handbook. Patrol Troop 1. When making a 911 call,
What Medical Emergencies Should a Dental Office be Prepared to Handle?
 What Medical Emergencies Should a Dental Office be Prepared to Handle? Gary Cuttrell, DDS, JD, University of NM Division of Dental Services Santiago Macias, MD, First Choice Community Healthcare Dentists
What Medical Emergencies Should a Dental Office be Prepared to Handle? Gary Cuttrell, DDS, JD, University of NM Division of Dental Services Santiago Macias, MD, First Choice Community Healthcare Dentists
Northwestern Health Sciences University. Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers
 Northwestern Health Sciences University Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest May 2005 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST for BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses Based
Northwestern Health Sciences University Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest May 2005 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST for BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses Based
American Heart Association. Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers
 American Heart Association Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest February 2001 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST for BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses 2001 American
American Heart Association Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest February 2001 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST for BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses 2001 American
American Red Cross First Aid EXAMPLE ANSWER SHEET
 American Red Cross First Aid Exam A IMPORTANT: Read all instructions before beginning the exam. INSTRUCTIONS: Do not write on this exam. Mark all answers in pencil on the separate answer sheet as directed
American Red Cross First Aid Exam A IMPORTANT: Read all instructions before beginning the exam. INSTRUCTIONS: Do not write on this exam. Mark all answers in pencil on the separate answer sheet as directed
CASAID THE AIMS OF FIRST AID, INCIDENT ACTION PLAN, INITIAL ASSESSMENT AND THE RECOVERY POSITION. Airway must be open so oxygen can enter the body.
 CASAID THE AIMS OF FIRST AID, INCIDENT ACTION PLAN, INITIAL ASSESSMENT AND THE RECOVERY POSITION The Aims of First Aid The aims of first aid (the three Ps) are to: Preserve the casualty s life. Prevent
CASAID THE AIMS OF FIRST AID, INCIDENT ACTION PLAN, INITIAL ASSESSMENT AND THE RECOVERY POSITION The Aims of First Aid The aims of first aid (the three Ps) are to: Preserve the casualty s life. Prevent
FIRST AID TEST. 367 West Robles Ave Santa Rosa, CA 95407 707-206-9988. www.schoolbusing.com. Revised April 21, 2008 - 1 -
 FIRST AID TEST 367 West Robles Ave Santa Rosa, CA 95407 707-206-9988 www.schoolbusing.com Revised April 21, 2008-1 - West County Transportation Agency This test was developed to help school bus driver
FIRST AID TEST 367 West Robles Ave Santa Rosa, CA 95407 707-206-9988 www.schoolbusing.com Revised April 21, 2008-1 - West County Transportation Agency This test was developed to help school bus driver
HEAT ILLNESS PREVENTION PLAN FOR SUTTER COUNTY SUPERINTENDENT OF SCHOOLS
 HEAT ILLNESS PREVENTION PLAN FOR SUTTER COUNTY SUPERINTENDENT OF SCHOOLS TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 Purpose... 1 2.0 Heat Illness Prevention... 2 2.1 Heat Stroke... 2 2.2 Heat Exhaustion... 2 2.3 Heat Cramps...
HEAT ILLNESS PREVENTION PLAN FOR SUTTER COUNTY SUPERINTENDENT OF SCHOOLS TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 Purpose... 1 2.0 Heat Illness Prevention... 2 2.1 Heat Stroke... 2 2.2 Heat Exhaustion... 2 2.3 Heat Cramps...
Adult First Aid/CPR/AEd. Ready Reference
 Adult First Aid/CPR/AEd Ready Reference Contents Checking an Injured or Ill Adult 3 CPR 4 AED Adult or Child 5 Conscious Choking 7 Controlling External Bleeding 8 Burns 9 Poisoning 10 Head, Neck or Spinal
Adult First Aid/CPR/AEd Ready Reference Contents Checking an Injured or Ill Adult 3 CPR 4 AED Adult or Child 5 Conscious Choking 7 Controlling External Bleeding 8 Burns 9 Poisoning 10 Head, Neck or Spinal
CHAPTER 6 HEAD INJURY AND UNCONSCIOUSNESS
 CHAPTER 6 HEAD INJURY AND UNCONSCIOUSNESS BRAIN INJURY Injury to the brain is one of the more serious outcomes that occur due to injury or illness. The first aider plays a major role in limiting damage
CHAPTER 6 HEAD INJURY AND UNCONSCIOUSNESS BRAIN INJURY Injury to the brain is one of the more serious outcomes that occur due to injury or illness. The first aider plays a major role in limiting damage
The Family Library. Understanding Diabetes
 The Family Library Understanding Diabetes What is Diabetes? Diabetes is caused when the body has a problem in making or using insulin. Insulin is a hormone secreted by the pancreas and is needed for the
The Family Library Understanding Diabetes What is Diabetes? Diabetes is caused when the body has a problem in making or using insulin. Insulin is a hormone secreted by the pancreas and is needed for the
2. (U4C2L3:F2) If your friend received a deep cut on her wrist, what would you do?
 Cadet Name: Date: 1. (U4C2L3:F1) Your friend receives a deep cut on her wrist while washing dishes. She asks for your help. How confident are you that you could provide appropriate aid? A) My friend is
Cadet Name: Date: 1. (U4C2L3:F1) Your friend receives a deep cut on her wrist while washing dishes. She asks for your help. How confident are you that you could provide appropriate aid? A) My friend is
12/5/2012. Introduction. Head, Neck, and Spine Injuries. Recognizing and Caring for Serious Head, Neck and Back Injuries
 Head, Neck, and Spine Injuries Identify the most common causes of head, neck and spinal injuries. List 10 situations that might indicate serious head, neck and spinal injuries. List the signals of head,
Head, Neck, and Spine Injuries Identify the most common causes of head, neck and spinal injuries. List 10 situations that might indicate serious head, neck and spinal injuries. List the signals of head,
Fainting - Syncope. This reference summary explains fainting. It discusses the causes and treatment options for the condition.
 Fainting - Syncope Introduction Fainting, also known as syncope, is a temporary loss of consciousness. It is caused by a drop in blood flow to the brain. You may feel dizzy, lightheaded or nauseous before
Fainting - Syncope Introduction Fainting, also known as syncope, is a temporary loss of consciousness. It is caused by a drop in blood flow to the brain. You may feel dizzy, lightheaded or nauseous before
FIRST AID FOR BASEBALL COACHES
 FIRST AID FOR BASEBALL COACHES Liability Issues. Do the right thing State provides qualified immunity Chapter 258 C, Section 13. Good Samaritan Law: No person who, in good faith, provides or obtains, or
FIRST AID FOR BASEBALL COACHES Liability Issues. Do the right thing State provides qualified immunity Chapter 258 C, Section 13. Good Samaritan Law: No person who, in good faith, provides or obtains, or
COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL. Effective Date: August 31, 2006
 COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION Emergency Procedures POLICY NUMBER: 715 Effective Date: August 31, 2006 SUBJECT: EMERGENCY CARE OF HEMORRHAGE 1. PURPOSE: The management
COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION Emergency Procedures POLICY NUMBER: 715 Effective Date: August 31, 2006 SUBJECT: EMERGENCY CARE OF HEMORRHAGE 1. PURPOSE: The management
Types of electrical injuries
 Types of electrical injuries Electrical injury is a term for all injuries caused by contact with electrical energy. Electrical contact can cause a wide variety of injuries involving most organ systems.
Types of electrical injuries Electrical injury is a term for all injuries caused by contact with electrical energy. Electrical contact can cause a wide variety of injuries involving most organ systems.
Heat Illness Prevention Program
 I. Policy Heat Illness Prevention Program Responsible Executive: Vice President for Administration and Finance Responsible Office: Environmental Health and Instructional Safety Originally Issued: February
I. Policy Heat Illness Prevention Program Responsible Executive: Vice President for Administration and Finance Responsible Office: Environmental Health and Instructional Safety Originally Issued: February
Emergency Medical Responder Mid-Course Knowledge Evaluation
 Emergency Medical Responder Mid-Course Knowledge Evaluation Please do not write on this sheet. Indicate your answers on the answer sheet provided. 1. Medical control is the process by which a physician
Emergency Medical Responder Mid-Course Knowledge Evaluation Please do not write on this sheet. Indicate your answers on the answer sheet provided. 1. Medical control is the process by which a physician
BLS TREATMENT GUIDELINES - CARDIAC
 BLS TREATMENT GUIDELINES - CARDIAC CARDIOPULMONARY ARREST - NON-TRAUMATIC (SJ-B101) effective 07/01/99 Defibrillation CPR Apply S-AED and assess rhythm as trained. Defib as indicated Simultaneous OXYGEN:
BLS TREATMENT GUIDELINES - CARDIAC CARDIOPULMONARY ARREST - NON-TRAUMATIC (SJ-B101) effective 07/01/99 Defibrillation CPR Apply S-AED and assess rhythm as trained. Defib as indicated Simultaneous OXYGEN:
Objectives. Burn Assessment and Management. Questions Regarding the Case Study. Case Study. Patient Assessment. Patient Assessment
 Objectives Burn Assessment and Management Discuss the mechanisms and complications of a thermal burn, electrical burn and an inhalation burn Explain the factors to consider when determining the severity
Objectives Burn Assessment and Management Discuss the mechanisms and complications of a thermal burn, electrical burn and an inhalation burn Explain the factors to consider when determining the severity
CHAPTER 1 DISASTER FIRST AID INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 1 DISASTER FIRST AID INTRODUCTION This chapter will cover the following topics: Introduction: The basic concepts of providing disaster first aid and the equipment required to safely respond to
CHAPTER 1 DISASTER FIRST AID INTRODUCTION This chapter will cover the following topics: Introduction: The basic concepts of providing disaster first aid and the equipment required to safely respond to
Heat Illness Prevention Program
 Heat Illness Prevention Program I. Policy Employees working in outdoor places of employment or in other areas at times when the environmental risk factors for heat illness are present, are at risk for
Heat Illness Prevention Program I. Policy Employees working in outdoor places of employment or in other areas at times when the environmental risk factors for heat illness are present, are at risk for
Eye Injuries. The Eyes The eyes are sophisticated organs. They collect light and focus it on the back of the eye, allowing us to see.
 Eye Injuries Introduction The design of your face helps protect your eyes from injury. But injuries can still damage your eyes. Sometimes injuries are severe enough that you could lose your vision. Most
Eye Injuries Introduction The design of your face helps protect your eyes from injury. But injuries can still damage your eyes. Sometimes injuries are severe enough that you could lose your vision. Most
Emergency Action Plans
 Emergency Action Plans Clearly the most effective way to deal with an injury- emergency is to plan ahead and to practice the appropriate procedures. An emergency action plan is a written plan of action
Emergency Action Plans Clearly the most effective way to deal with an injury- emergency is to plan ahead and to practice the appropriate procedures. An emergency action plan is a written plan of action
Basic First Aid Tutorial
 Basic First Aid Tutorial 1 Overview: 1-Introduction 2-Emergency Response 3-Bleeding, Shock, & Soft-Tissue Injuries 4-Bone, Joint, & Muscle Injuries 5-Medical Emergencies 6-Heat & Cold-Related Illness/Injury
Basic First Aid Tutorial 1 Overview: 1-Introduction 2-Emergency Response 3-Bleeding, Shock, & Soft-Tissue Injuries 4-Bone, Joint, & Muscle Injuries 5-Medical Emergencies 6-Heat & Cold-Related Illness/Injury
Lesson 7: Respiratory and Skeletal Systems and Tuberculosis
 Glossary 1. asthma: when the airways of the lungs narrow, making breathing difficult 2. bacteria: tiny living creatures that can only be seen with a microscope; some bacteria help the human body, and other
Glossary 1. asthma: when the airways of the lungs narrow, making breathing difficult 2. bacteria: tiny living creatures that can only be seen with a microscope; some bacteria help the human body, and other
HOW TO CARE FOR A PATIENT WITH DIABETES
 HOW TO CARE FOR A PATIENT WITH DIABETES INTRODUCTION Diabetes is one of the most common diseases in the United States, and diabetes is a disease that affects the way the body handles blood sugar. Approximately
HOW TO CARE FOR A PATIENT WITH DIABETES INTRODUCTION Diabetes is one of the most common diseases in the United States, and diabetes is a disease that affects the way the body handles blood sugar. Approximately
Low Blood Pressure. This reference summary explains low blood pressure and how it can be prevented and controlled.
 Low Blood Pressure Introduction Low blood pressure, or hypotension, is when your blood pressure reading is 90/60 or lower. Some people have low blood pressure all of the time. In other people, blood pressure
Low Blood Pressure Introduction Low blood pressure, or hypotension, is when your blood pressure reading is 90/60 or lower. Some people have low blood pressure all of the time. In other people, blood pressure
NEEDLE THORACENTESIS Pneumothorax / Hemothorax
 NEEDLE THORACENTESIS Pneumothorax / Hemothorax By: Steven Jones, NREMT-P Pneumothorax Pneumothorax is a collection of air or gas in the pleural space of the lung, causing the lung to collapse. Pneumothorax
NEEDLE THORACENTESIS Pneumothorax / Hemothorax By: Steven Jones, NREMT-P Pneumothorax Pneumothorax is a collection of air or gas in the pleural space of the lung, causing the lung to collapse. Pneumothorax
CHAPTER 21 QUIZ. Handout 21-1. Write the letter of the best answer in the space provided.
 Handout 21-1 QUIZ Write the letter of the best answer in the space provided. 1. A severe form of allergic reaction is called A. an allergen. C. epinephrine. B. anaphylaxis. D. an immune reaction. 2. Harmless
Handout 21-1 QUIZ Write the letter of the best answer in the space provided. 1. A severe form of allergic reaction is called A. an allergen. C. epinephrine. B. anaphylaxis. D. an immune reaction. 2. Harmless
BROCKTON AREA MULTI-SERVICES, INC. MEDICAL PROCEDURE GUIDE. Date(s) Reviewed/Revised:
 Page 1 of 5 PROCEDURE FOR: MAP-certified staff and RN/LPN MAP-certified staff are to be trained in the use of epinephrine administration via pre-filled autoinjector devices(s) annually. Certified staff
Page 1 of 5 PROCEDURE FOR: MAP-certified staff and RN/LPN MAP-certified staff are to be trained in the use of epinephrine administration via pre-filled autoinjector devices(s) annually. Certified staff
Injury Law Center OTHER INJURIES
 Injury Law Center Note: This information is provided to give you a basic understanding of the injury. It is not intended as medical advice. You should consult a qualified medical provider. OTHER INJURIES
Injury Law Center Note: This information is provided to give you a basic understanding of the injury. It is not intended as medical advice. You should consult a qualified medical provider. OTHER INJURIES
NEW YORK STATE DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH BUREAU OF EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES
 NEW YORK STATE DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH BUREAU OF EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES TRAINING PROGRAM OUTLINE FOR UNLICENSED OR UNCERTIFIED PERSONNEL TO ADMINISTER EPINEPHRINE BY AUTO-INJECTOR IN LIFE-THREATENING
NEW YORK STATE DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH BUREAU OF EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES TRAINING PROGRAM OUTLINE FOR UNLICENSED OR UNCERTIFIED PERSONNEL TO ADMINISTER EPINEPHRINE BY AUTO-INJECTOR IN LIFE-THREATENING
Frontline First Aid EMR Scenario Examples
 Course Type: Start Date: Instructors initial scenarios as they are completed CPR-AED Scenarios CPR with Hypothermia Load and Go CPR with Obstructed Airway Continue CPR after airway clears with NO obvious
Course Type: Start Date: Instructors initial scenarios as they are completed CPR-AED Scenarios CPR with Hypothermia Load and Go CPR with Obstructed Airway Continue CPR after airway clears with NO obvious
Heat Production and Loss. Environmental Emergencies. Heat Regulation. Body Temperature Ranges. Focused Assessment: Your Patient: Heat Production
 Heat Production and Loss Environmental Emergencies Messing with Mother Nature Heat Production Basal Metabolism processes in the body that generate heat through nominal functions Activity, fever, metabolic
Heat Production and Loss Environmental Emergencies Messing with Mother Nature Heat Production Basal Metabolism processes in the body that generate heat through nominal functions Activity, fever, metabolic
81 First Responder Respiratory
 81 First Responder Medical Scenarios Asthma Scenario: You are called to a local house for a woman with trouble breathing. You arrive to find a 67-year-old woman sitting upright in a chair. She states she
81 First Responder Medical Scenarios Asthma Scenario: You are called to a local house for a woman with trouble breathing. You arrive to find a 67-year-old woman sitting upright in a chair. She states she
LEGAL PROTECTION. Good Samaritan Law RCW 4.24.300
 GOALS This course is designed to instruct coach very basic first aid techniques to protect the players under your guidance. This presentation only provides a brief overview of the issues that you may face
GOALS This course is designed to instruct coach very basic first aid techniques to protect the players under your guidance. This presentation only provides a brief overview of the issues that you may face
Tired, Aching Legs? Swollen Ankles? Varicose Veins?
 Tired, Aching Legs? Swollen Ankles? Varicose Veins? Healthy Legs 2006 http://healthylegs.com Page 1 Venous disorders are widespread Leg problems are widespread throughout the world, but what most people
Tired, Aching Legs? Swollen Ankles? Varicose Veins? Healthy Legs 2006 http://healthylegs.com Page 1 Venous disorders are widespread Leg problems are widespread throughout the world, but what most people
Epinephrine Administration Training for Unlicensed School Personnel
 Epinephrine Administration Training for Unlicensed School Personnel Management of Life-Threatening Allergies in the School Setting Dover and Sherborn Schools EpiPen Administration This program is designed
Epinephrine Administration Training for Unlicensed School Personnel Management of Life-Threatening Allergies in the School Setting Dover and Sherborn Schools EpiPen Administration This program is designed
X-Plain Diabetes - Introduction Reference Summary
 X-Plain Diabetes - Introduction Reference Summary Introduction Diabetes is a disease that affects millions of Americans every year. Your doctor may have informed you that you have diabetes. Although there
X-Plain Diabetes - Introduction Reference Summary Introduction Diabetes is a disease that affects millions of Americans every year. Your doctor may have informed you that you have diabetes. Although there
2 CHECKING AN INJURED OR ILL ATHLETE
 American Red Cross 2 CHECKING AN INJURED OR ILL ATHLETE ~~~'1'H ~.. 2 CHECKING AN INJURED OR III ATHLETE Checking the scene for safety and checking an injured or ill athlete is the first action to take,
American Red Cross 2 CHECKING AN INJURED OR ILL ATHLETE ~~~'1'H ~.. 2 CHECKING AN INJURED OR III ATHLETE Checking the scene for safety and checking an injured or ill athlete is the first action to take,
INTERNATIONAL TRAUMA LIFE SUPPORT
 INTERNATIONAL TRAUMA LIFE SUPPORT What to wear STUDENT GUIDE TO INTERNATIONAL TRAUMA LIFE SUPPORT ITLS is a practical course that stresses hands-on teaching. You should wear comfortable clothes that you
INTERNATIONAL TRAUMA LIFE SUPPORT What to wear STUDENT GUIDE TO INTERNATIONAL TRAUMA LIFE SUPPORT ITLS is a practical course that stresses hands-on teaching. You should wear comfortable clothes that you
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary
 X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR
 Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
Adult, Child, and Infant Written Exam CPR Pro for the Professional Rescuer
 Adult, Child, and Infant Written Exam CPR Pro for the Professional Rescuer Instructions: Read each of the following questions carefully and then place an X over the correct answer on the separate answer
Adult, Child, and Infant Written Exam CPR Pro for the Professional Rescuer Instructions: Read each of the following questions carefully and then place an X over the correct answer on the separate answer
3/24/2014. Waubonsee Community College Safety Day 2014. Why do we need a First Aid Program?
 Waubonsee Community College Safety Day 2014 Why do we need a First Aid Program? 4,383 workers were killed on the job in 2012 Total recordable non fatal cases: 2,976,400 in 2012 Cases involving days away
Waubonsee Community College Safety Day 2014 Why do we need a First Aid Program? 4,383 workers were killed on the job in 2012 Total recordable non fatal cases: 2,976,400 in 2012 Cases involving days away
MRC Medical Jeopardy Feud List of Treatments for Possible Injuries/Conditions
 List of Treatments for Possible Injuries/Conditions A. Apply cold compresses to affected area; elevate the area to reduce swelling and possible bleeding B. Apply direct pressure to wound area with sterile
List of Treatments for Possible Injuries/Conditions A. Apply cold compresses to affected area; elevate the area to reduce swelling and possible bleeding B. Apply direct pressure to wound area with sterile
Southern Stone County Fire Protection District Emergency Medical Protocols
 TITLE Pediatric Medical Assessment PM 2.4 Confirm scene safety Appropriate body substance isolation procedures Number of patients Nature of illness Evaluate the need for assistance B.L.S ABC s & LOC Focused
TITLE Pediatric Medical Assessment PM 2.4 Confirm scene safety Appropriate body substance isolation procedures Number of patients Nature of illness Evaluate the need for assistance B.L.S ABC s & LOC Focused
Facial Sports Injuries
 Facial Sports Injuries Playing catch, shooting hoops, bicycling on a scenic path or just kicking around a soccer ball have more in common than you may think. On the up side, these activities are good exercise
Facial Sports Injuries Playing catch, shooting hoops, bicycling on a scenic path or just kicking around a soccer ball have more in common than you may think. On the up side, these activities are good exercise
How To Treat A Heart Attack
 13 Resuscitation and preparation for anaesthesia and surgery Key Points 13.1 MANAGEMENT OF EMERGENCIES AND CARDIOPULMONARY RESUSCITATION ESSENTIAL HEALTH TECHNOLOGIES The emergency measures that are familiar
13 Resuscitation and preparation for anaesthesia and surgery Key Points 13.1 MANAGEMENT OF EMERGENCIES AND CARDIOPULMONARY RESUSCITATION ESSENTIAL HEALTH TECHNOLOGIES The emergency measures that are familiar
EXTREME HEAT OR COLD
 Responsibility Never hesitate to call 911 Life Safety is most important! It is the responsibility of every individual to learn to recognize the warning signs of a medical emergency. Warning Signs and Symptoms
Responsibility Never hesitate to call 911 Life Safety is most important! It is the responsibility of every individual to learn to recognize the warning signs of a medical emergency. Warning Signs and Symptoms
Pesticide Harmful Effects And Emergency Response
 Pesticide Harmful Effects And Emergency Response Most pesticides are designed to harm or kill pests. Because some pests have systems similar to the human system, some pesticides also can harm or kill humans.
Pesticide Harmful Effects And Emergency Response Most pesticides are designed to harm or kill pests. Because some pests have systems similar to the human system, some pesticides also can harm or kill humans.
Heart information. CPR cardiopulmonary resuscitation
 Heart information CPR cardiopulmonary resuscitation Contents 3 What is CPR? 3 What is cardiac arrest? 4 Heart attack and cardiac arrest 4 Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) 5 Danger 6 Response 7 Send
Heart information CPR cardiopulmonary resuscitation Contents 3 What is CPR? 3 What is cardiac arrest? 4 Heart attack and cardiac arrest 4 Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) 5 Danger 6 Response 7 Send
CPR/AED for Professional Rescuers and Health Care Providers HANDBOOK
 CPR/AED for Professional Rescuers and Health Care Providers HANDBOOK TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION 1: THE PROFESSIONAL RESCUER The Duty to Respond 2 Preventing the Spread of Bloodborne Pathogens 3 Taking Action
CPR/AED for Professional Rescuers and Health Care Providers HANDBOOK TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION 1: THE PROFESSIONAL RESCUER The Duty to Respond 2 Preventing the Spread of Bloodborne Pathogens 3 Taking Action
JAC-CEN-DEL COMMUNITY SCHOOLS BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS UNIVERSAL PRECAUTIONS A BACK TO SCHOOL TRADITION
 JAC-CEN-DEL COMMUNITY SCHOOLS BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS UNIVERSAL PRECAUTIONS A BACK TO SCHOOL TRADITION UNIVERSAL PRECAUTIONS AGAINST BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS Employees working in a school system are potentially
JAC-CEN-DEL COMMUNITY SCHOOLS BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS UNIVERSAL PRECAUTIONS A BACK TO SCHOOL TRADITION UNIVERSAL PRECAUTIONS AGAINST BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS Employees working in a school system are potentially
National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians Emergency Medical Technician Psychomotor Examination BLEEDING CONTROL/SHOCK MANAGEMENT
 BLEEDING CONTROL/SHOCK MANAGEMENT Candidate: Examiner: Date: Signature: Possible Applies direct pressure to the wound 1 NOTE: The examiner must now inform the candidate that the wound continues to bleed.
BLEEDING CONTROL/SHOCK MANAGEMENT Candidate: Examiner: Date: Signature: Possible Applies direct pressure to the wound 1 NOTE: The examiner must now inform the candidate that the wound continues to bleed.
Diuretics: You may get diuretic medicine to help decrease swelling in your brain. This may help your brain get better blood flow.
 Hemorrhagic Stroke GENERAL INFORMATION: What is a hemorrhagic stroke? A hemorrhagic stroke happens when a blood vessel in the brain bursts. This may happen if the blood vessel wall is weak, or sometimes
Hemorrhagic Stroke GENERAL INFORMATION: What is a hemorrhagic stroke? A hemorrhagic stroke happens when a blood vessel in the brain bursts. This may happen if the blood vessel wall is weak, or sometimes
Enables MDA Medical Teams to categorize victims in mass casualty scenarios, in order to be able to triage and treat casualties
 MDA Disposable ALS + BLS Medical Ambulance Equipment Prices shown in CDN. Funds Items Description Picture Mass Casualty ID tag 1000 units = $350 Enables MDA Medical Teams to categorize victims in mass
MDA Disposable ALS + BLS Medical Ambulance Equipment Prices shown in CDN. Funds Items Description Picture Mass Casualty ID tag 1000 units = $350 Enables MDA Medical Teams to categorize victims in mass
MEDICATION ADMINISTRATION TO STUDENTS
 540 540 SECTION 540 MEDICATION AND FIRST AID SECTION 540A - MEDICATION MEDICATION ADMINISTRATION TO STUDENTS Medications are given to students in the school setting to continue or maintain a medical therapy
540 540 SECTION 540 MEDICATION AND FIRST AID SECTION 540A - MEDICATION MEDICATION ADMINISTRATION TO STUDENTS Medications are given to students in the school setting to continue or maintain a medical therapy
Module 5 ADULT RECOvERY POSITION STEP 1 POSITION ThE victim
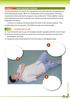 Module 5 ADULT RECOVERY POSITION The recovery position is used in the management of victims who are unresponsive but have breathing and pulse. When an unresponsive victim is lying supine, the airway may
Module 5 ADULT RECOVERY POSITION The recovery position is used in the management of victims who are unresponsive but have breathing and pulse. When an unresponsive victim is lying supine, the airway may
Adult Choking and CPR Manual
 Adult Choking and CPR Manual 2009 Breath of Life Home Medical Equipment and Respiratory Services CHOKING Description: Choking is the coughing spasm and sputtering that happen when liquids or solids get
Adult Choking and CPR Manual 2009 Breath of Life Home Medical Equipment and Respiratory Services CHOKING Description: Choking is the coughing spasm and sputtering that happen when liquids or solids get
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) for Outpatient
 Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) for Outpatient Introduction A Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter, or PICC line, is a thin, long, soft plastic tube inserted into a vein of the arm. It
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) for Outpatient Introduction A Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter, or PICC line, is a thin, long, soft plastic tube inserted into a vein of the arm. It
CHAPTER 32 QUIZ. Handout 32-1. Write the letter of the best answer in the space provided.
 Handout 32-1 QUIZ Write the letter of the best answer in the space provided. 1. All of the following are signs and symptoms in patients with spinal injuries except A. paralysis. C. hyperglycemia. B. priapism.
Handout 32-1 QUIZ Write the letter of the best answer in the space provided. 1. All of the following are signs and symptoms in patients with spinal injuries except A. paralysis. C. hyperglycemia. B. priapism.
N E B R A S K A JAIL BULLETIN NUMBER 102 OCTOBER 1993
 N E B R A S K A JAIL BULLETIN NUMBER 102 OCTOBER 1993 The Jail Bulletin is a monthly feature of the Crime Commission Update. The Bulletin may be used as a supplement to your jail in-service training program
N E B R A S K A JAIL BULLETIN NUMBER 102 OCTOBER 1993 The Jail Bulletin is a monthly feature of the Crime Commission Update. The Bulletin may be used as a supplement to your jail in-service training program
American Heart Association. BLS Instructor Course. Written Examination. July 2003
 American Heart Association BLS Instructor Course Written Examination July 2003 Basic Life Support Instructor Exam Part I Please do not mark on this examination. Record the best answer on the separate answer
American Heart Association BLS Instructor Course Written Examination July 2003 Basic Life Support Instructor Exam Part I Please do not mark on this examination. Record the best answer on the separate answer
Adult Forearm Fractures
 Adult Forearm Fractures Your forearm is made up of two bones, the radius and ulna. In most cases of adult forearm fractures, both bones are broken. Fractures of the forearm can occur near the wrist at
Adult Forearm Fractures Your forearm is made up of two bones, the radius and ulna. In most cases of adult forearm fractures, both bones are broken. Fractures of the forearm can occur near the wrist at
Diabetes Hypoglycemia/Hyperglycemia Reaction
 Diabetes Hypoglycemia/Hyperglycemia Reaction Hypoglycemic Reaction (Insulin Shock) A. Hypoglycemic reactions (insulin reactions) should be treated according to current nursing and medical recommendations.
Diabetes Hypoglycemia/Hyperglycemia Reaction Hypoglycemic Reaction (Insulin Shock) A. Hypoglycemic reactions (insulin reactions) should be treated according to current nursing and medical recommendations.
Accident/Injury Reporting, Investigation, & Basic First Aid Plan
 Accident/Injury Reporting, Investigation, & Basic First Aid Plan Environmental Health, Safety, and Risk Management Department Box 6113, SFA Station Nacogdoches, Texas 75962-6113 Revised: January 2011 Purpose
Accident/Injury Reporting, Investigation, & Basic First Aid Plan Environmental Health, Safety, and Risk Management Department Box 6113, SFA Station Nacogdoches, Texas 75962-6113 Revised: January 2011 Purpose
PICC & Midline Catheters Patient Information Guide
 PICC & Midline Catheters Patient Information Guide medcompnet.com 1 table of contents Introduction 4 What is a PICC or Midline Catheter? 4 How is the PICC or Midline Catheter Inserted? 6 Catheter Care
PICC & Midline Catheters Patient Information Guide medcompnet.com 1 table of contents Introduction 4 What is a PICC or Midline Catheter? 4 How is the PICC or Midline Catheter Inserted? 6 Catheter Care
National Registry Skill Sheets
 Bleeding Control/Shock Management BVM Ventilation of an Apneic Adult Patient Cardiac Arrest Management/AED Joint Immobilization Long Bone Immobilization Oxygen Administration By Non-Rebreather Mask Patient
Bleeding Control/Shock Management BVM Ventilation of an Apneic Adult Patient Cardiac Arrest Management/AED Joint Immobilization Long Bone Immobilization Oxygen Administration By Non-Rebreather Mask Patient
Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy
 Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain centralized around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. Health care providers
Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain centralized around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. Health care providers
Understanding your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Patient Information
 Understanding your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Patient Information The Purpose of this Information Sheet This information sheet has been written by patients, members of the public and
Understanding your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Patient Information The Purpose of this Information Sheet This information sheet has been written by patients, members of the public and
CBT/OTEP 450 Diabetic Emergencies
 Seattle-King County EMS Seattle-King County Emergency Medical Services Division Public Health - Seattle/King County 401 5th Avenue, Suite 1200 Seattle, WA 98104 (206) 296-4693 January 2009 CBT/OTEP 450
Seattle-King County EMS Seattle-King County Emergency Medical Services Division Public Health - Seattle/King County 401 5th Avenue, Suite 1200 Seattle, WA 98104 (206) 296-4693 January 2009 CBT/OTEP 450
Basic First Aid for the Community and Workplace
 A M E R I C A N S A F E T Y & H E A LT H I N S T I T U T E Basic First Aid for the Community and Workplace Student Handbook This handbook serves as a reference guide for basic first aid. For the purpose
A M E R I C A N S A F E T Y & H E A LT H I N S T I T U T E Basic First Aid for the Community and Workplace Student Handbook This handbook serves as a reference guide for basic first aid. For the purpose
100018 100016 100017. Scope of Course Public Safety First Aid and CPR Course Content. (a) The initial course of instruction shall at a minimum
 100018 100016 100017. Scope of Course Public Safety First Aid and CPR Course Content. (a) The initial course of instruction shall at a minimum consist of not less than fifteen (15) hours in first aid and
100018 100016 100017. Scope of Course Public Safety First Aid and CPR Course Content. (a) The initial course of instruction shall at a minimum consist of not less than fifteen (15) hours in first aid and
Pattern Identification According to Qi and Blood
 CHAPTER EIGHT Pattern Identification According to Qi and Blood Pattern identification according to qi and blood is a commonly used method for pattern identification which analyzes manifestations obtained
CHAPTER EIGHT Pattern Identification According to Qi and Blood Pattern identification according to qi and blood is a commonly used method for pattern identification which analyzes manifestations obtained
THERAPEUTIC USE OF HEAT AND COLD
 THERAPEUTIC USE OF HEAT AND COLD INTRODUCTION Heat and cold are simple and very effective therapeutic tools. They can be used locally or over the whole body, and the proper application of heat and cold
THERAPEUTIC USE OF HEAT AND COLD INTRODUCTION Heat and cold are simple and very effective therapeutic tools. They can be used locally or over the whole body, and the proper application of heat and cold
Epidural Continuous Infusion. Patient information Leaflet
 Epidural Continuous Infusion Patient information Leaflet April 2015 Introduction You may already know that epidural s are often used to treat pain during childbirth. This same technique can also used as
Epidural Continuous Infusion Patient information Leaflet April 2015 Introduction You may already know that epidural s are often used to treat pain during childbirth. This same technique can also used as
EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER (EMR) PRACTICAL SKILLS EXAMINATION REPORT State Form 54407 (R / 5-13)
 EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER (EMR) PRACTICAL SKILLS EXAMINATION REPT State Form 54407 (R / 5-3) INDIANA DEPARTMENT OF HOMELAND SECURITY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES CERTIFICATION 302 West Washington Street,
EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER (EMR) PRACTICAL SKILLS EXAMINATION REPT State Form 54407 (R / 5-3) INDIANA DEPARTMENT OF HOMELAND SECURITY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES CERTIFICATION 302 West Washington Street,
Oxygen Therapy. Oxygen therapy quick guide V3 July 2012.
 PRESENTATION Oxygen (O 2 ) is a gas provided in a compressed form in a cylinder. It is also available in a liquid form. It is fed via a regulator and flow meter to the patient by means of plastic tubing
PRESENTATION Oxygen (O 2 ) is a gas provided in a compressed form in a cylinder. It is also available in a liquid form. It is fed via a regulator and flow meter to the patient by means of plastic tubing
How To Manage A Catastrophic Injury
 Report #14 CATASTROPHIC INJURIES: Paralysis, Amputation, Burns Overview: A catastrophic injury or illness usually occurs suddenly and without warning. Injuries may be considered catastrophic when they
Report #14 CATASTROPHIC INJURIES: Paralysis, Amputation, Burns Overview: A catastrophic injury or illness usually occurs suddenly and without warning. Injuries may be considered catastrophic when they
5420-R STUDENT HEALTH SERVICES REGULATION NORTH COLONIE CENTRAL SCHOOLS NEWTONVILLE, NEW YORK Emergency Procedures and Approved First Aid Methods
 STUDENT HEALTH SERVICES REGULATION NORTH COLONIE CENTRAL SCHOOLS NEWTONVILLE, NEW YORK Emergency Procedures and Approved First Aid Methods EMERGENCY PROCEDURES Contact parents and cooperate with them in
STUDENT HEALTH SERVICES REGULATION NORTH COLONIE CENTRAL SCHOOLS NEWTONVILLE, NEW YORK Emergency Procedures and Approved First Aid Methods EMERGENCY PROCEDURES Contact parents and cooperate with them in
For the Patient: Dasatinib Other names: SPRYCEL
 For the Patient: Dasatinib Other names: SPRYCEL Dasatinib (da sa' ti nib) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. Tell your doctor if you have ever
For the Patient: Dasatinib Other names: SPRYCEL Dasatinib (da sa' ti nib) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. Tell your doctor if you have ever
Oxygen - update April 2009 OXG
 PRESENTATION Oxygen (O 2 ) is a gas provided in compressed form in a cylinder. It is also available in liquid form, in a system adapted for ambulance use. It is fed via a regulator and flow meter to the
PRESENTATION Oxygen (O 2 ) is a gas provided in compressed form in a cylinder. It is also available in liquid form, in a system adapted for ambulance use. It is fed via a regulator and flow meter to the
Scenario 2 Is it ever safe enough?
 IRECA BLS Competition 2011 Scenario 2 Is it ever safe enough? Team Name Captain Name Judge 1 Judge 2 The Event: You are dispatched to a shooting for two injured at a local bar. Witnesses have told police
IRECA BLS Competition 2011 Scenario 2 Is it ever safe enough? Team Name Captain Name Judge 1 Judge 2 The Event: You are dispatched to a shooting for two injured at a local bar. Witnesses have told police
Neck Injuries and Disorders
 Neck Injuries and Disorders Introduction Any part of your neck can be affected by neck problems. These affect the muscles, bones, joints, tendons, ligaments or nerves in the neck. There are many common
Neck Injuries and Disorders Introduction Any part of your neck can be affected by neck problems. These affect the muscles, bones, joints, tendons, ligaments or nerves in the neck. There are many common
Understanding Diabetes
 Patient Education Understanding Diabetes This handout describes diabetes, the complications related to the disease, and how you can prevent these complications. Blood Sugar Control Diabetes is a disease
Patient Education Understanding Diabetes This handout describes diabetes, the complications related to the disease, and how you can prevent these complications. Blood Sugar Control Diabetes is a disease
Chapter 11. Everting skin edges
 Chapter 11 PRIMARY WOUND CLOSURE KEY FIGURE: Everting skin edges In primary wound closure, the skin edges of the wound are sutured together to close the defect. Whenever possible and practical, primary
Chapter 11 PRIMARY WOUND CLOSURE KEY FIGURE: Everting skin edges In primary wound closure, the skin edges of the wound are sutured together to close the defect. Whenever possible and practical, primary
CBT/OTEP 243 Aspirin Administration for ACS
 Seattle-King County EMS Seattle-King County Emergency Medical Services Division Public Health - Seattle/King County 401 5th Avenue, Suite 1200 Seattle, WA 98104 (206) 296-4693 February 2009 CBT/OTEP 243
Seattle-King County EMS Seattle-King County Emergency Medical Services Division Public Health - Seattle/King County 401 5th Avenue, Suite 1200 Seattle, WA 98104 (206) 296-4693 February 2009 CBT/OTEP 243
X-Plain Sinus Surgery Reference Summary
 X-Plain Sinus Surgery Reference Summary Introduction Sinus surgery is a very common and safe operation. Your doctor may recommend that you have sinus surgery. The decision whether or not to have sinus
X-Plain Sinus Surgery Reference Summary Introduction Sinus surgery is a very common and safe operation. Your doctor may recommend that you have sinus surgery. The decision whether or not to have sinus
Provided by the American Venous Forum: veinforum.org
 CHAPTER 1 NORMAL VENOUS CIRCULATION Original author: Frank Padberg Abstracted by Teresa L.Carman Introduction The circulatory system is responsible for circulating (moving) blood throughout the body. The
CHAPTER 1 NORMAL VENOUS CIRCULATION Original author: Frank Padberg Abstracted by Teresa L.Carman Introduction The circulatory system is responsible for circulating (moving) blood throughout the body. The
Be Safe! Manage Heat Stress. Be Safe! Manage Heat Stress.
 Be Safe! Manage Heat Stress. Be Safe! Manage Heat Stress. Overview Workers who are exposed to extreme heat or work in hot environments may be at risk of heat stress. Exposure to extreme heat can result
Be Safe! Manage Heat Stress. Be Safe! Manage Heat Stress. Overview Workers who are exposed to extreme heat or work in hot environments may be at risk of heat stress. Exposure to extreme heat can result
Certified Athletic trainers should follow a 10-step process of evaluation for orthopedic injuries, which includes but is not limited to:
 Acute Care Policy Acute Care Policy and Procedures Athletic training students within Winona State University s Athletic Training Education Program have the opportunity to evaluate acute athletic injuries
Acute Care Policy Acute Care Policy and Procedures Athletic training students within Winona State University s Athletic Training Education Program have the opportunity to evaluate acute athletic injuries
American Red Cross CPR Adult EXAMPLE ANSWER SHEET
 American Red Cross CPR Adult IMPORTANT: Read all instructions before beginning the exam. INSTRUCTIONS: Do not write on this exam. Mark all answers in pencil on the separate answer sheet as directed by
American Red Cross CPR Adult IMPORTANT: Read all instructions before beginning the exam. INSTRUCTIONS: Do not write on this exam. Mark all answers in pencil on the separate answer sheet as directed by
