Atrial Fibrillation Roger Hefflinger, Pharm.D. Clinical Associate Professor Idaho State University COP Family Medicine Residency of Idaho
|
|
|
- Annabella Briggs
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Atrial Fibrillation 2016 Roger Hefflinger, Pharm.D. Clinical Associate Professor Idaho State University COP Family Medicine Residency of Idaho
2 Disclosures: The planners and presenter have disclosed no conflict of interest, including no relevant financial relationships with any commercial interests pertaining to this activity.
3 Objectives for Pharmacists and Prescribers: Analyze rationale for stroke risk stratification and options for anticoagulation Describe viable intravenous and oral ratecontrolling therapy options Recognize conditions in which chemical cardioversion should be considered
4 Objectives for Pharmacy Technicians and Nurses: Describe types of atrial fibrillation Identify anticoagulant therapy options for patients with atrial fibrillation List medications for atrial fibrillation with high risk for drug interactions and adverse effects
5 Atrial Fibrillation Guidelines
6
7 What Controls SA Automaticity? Sympathetic tone Parasympathetic tone Hormones Steroids Thyroxine Electrolytes sodium, potassium, magnesium, chloride, phosphorus Tissue Hypoxia
8 Where does the Impulse go next? Atrial Myocardium Sodium dependent tissue AV Node Calcium Dependent tissue Adrenergic sensitive HIS Purkinje See SA node Ventricular Myocardium Ectopic focci and reentrant circuits primarily generated in sodium dependent tissue- Atrial myocardium
9
10 Definition of Atrial Fibrillation Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation: AF that terminates spontaneously or with intervention within 7 days Episodes may recur with variable frequency Persistent Atrial Fibrillation: Continuous AF that is sustained > 7 days Long-Standing Persistent AF: Continuous AF > 12 months duration
11 Definition of Atrial Fibrillation Permanent Atrial Fibrillation: The term permanent AF is used when the patient and clinician make a joint decision to stop further attempts to restore and/or maintain sinus rhythm Acceptance of AF represents a therapeutic attitude on the part of the patient and the clinician than an inherent pathophysiologic attribute of AF. Acceptance of AF may change as symptoms, efficacy of therapeutic interventions and patient and clinician preferences evolve
12 Definition of Atrial Fibrillation Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation: AF in the absence of rheumatic mitral stenosis, a mechanical or bioprosthetic heart valve, or mitral valve repair
13 Pathophysiology
14 Selected Risk Factors and Biomarkers for AF: Increasing Age, Hypertension, Diabetes Mellitus, Hyperthyroidism CHF, MI, Valvular heart disease, Cardiothoracic surgery Obesity, Sleep Apnea Smoking, Exercise, Alcohol Use European ancestry, Family History, Genetic Variants EKG: Left ventricular hypertrophy Echocardiographic: Left atrial enlargement Decrease LV fractional shortening Increased LV thickness Biomarkers: Increase CRP Increase BNP
15 What are our Goals of therapy? Thromboembolic Risk and Treatment: Risk Stratification Considerations in selecting Anticoagulants What are the factors that influence your selection of one drug over another? - rgh Rate Control: Recommendations Rhythm Control: Recommendations Prevent Thromboembolism Direct Current Cardioversion Pharmacologic Cardioversion Chemical Cardioversion Drugs to Maintain Sinus Rhythm
16 What are our Goals of therapy? Specific Patient Groups AF: Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy AF Complicating Acute Coronary Syndromes Hyperthyroidism Pulmonary Disease Wolf-Parkinson Whit and Pre-Excitation Syndromes Heart Failure Familial (Genetic) AF Post operative Cardiac and Thoracic Surgery
17 Goal Number One- Thromboembolic Event Prevention Issues- Antiplatelet therapy enough? Anticoagulation therapy Acute- Un-fractionated Heparin Low molecular weight heparins Injectable Xa Inhibitors Chronic- Vitamin K antagonists- Coumadin with bridge or without? Thrombin Inhibitor Factor Xa inhibitors
18 It used to be easy! Risk Stratification <65 = ASA, ASA or Warfarin, >75 Warfarin
19 CHADS 2
20 Now Preferred = CHA 2 DS 2 -VASc
21 Thromboembolism Prevention: Selection of antithrombotic therapy should be based on the risk of thromboembolism irrespective of whether the AF pattern is paroxysmal, persistent or permanent Patients with nonvalvular AF with prior stroke, TIA, or a CHA 2 DS 2 -VASc score of 2 or greater, oral anticoagulants are recommended Warfarin (INR 2-3): Level A or Dabigatran, Rivoroxaban, Apixaban: Level B
22
23 Vitamin K Antagonists Warfarin Coumadin
24 Warfarin Pharmacokinetics Food- no effects on absorption Protein Binding: 99% Extensive p-450 metabolism CYP2C9- primarily responsible for inactivation of more active s-warfarin T ½- 40 hours Terminal T-1/2- About 7 days
25 Mechanism of Vitamin K Antagonists Protein C Protein S Factor VII Factor IX Factor X Factor II
26 Gut absorption- Binding GI bacteria- K Warfarin Interactions Diet changes Liver metabolism Protein displacement
27 2009 FDA Warfarin Labeling Change CYP2C9 and VKORC1 Polymorphisms The S-enantiomer of warfarin is mainly metabolized to 7-hydroxywarfarin by CYP2C9, a polymorphic enzyme. The variant alleles, CYP2C9*2 and CYP2C9*3, result in decreased in vitro CYP2C9 enzymatic 7-hydroxylation of S-warfarin. The frequencies of these alleles in Caucasians are approximately 11% and 7% for CYP2C9*2 and CYP2C9*3, respectively. Other CYP2C9 alleles associated with reduced enzymatic activity occur at lower frequencies, including *5, *6, and *11 alleles in populations of African ancestry and *5, *9, and *11 alleles in Caucasians. Warfarin reduces the regeneration of vitamin K from vitamin K epoxide in the vitamin K cycle through inhibition of VKOR, a multiprotein enzyme complex. Certain single nucleotide polymorphisms in the VKORC1 gene (e.g., 1639G>A) have been associated with variable warfarin dose requirements. VKORC1 and CYP2C9 gene variants generally explain the largest proportion of known variability in warfarin dose requirements. CYP2C9 and VKORC1 genotype information, when available, can assist in selection of the initial dose of warfarin
28 Genetic testing does it help? 2007 FDA Coumadin warning of genetic mutations 2009 made the dosing recommendation changes;
29 Signal Interaction Everything interacts with Warfarin
30 Think/Pair/Share Discuss with the person on your right: What are the potential advantages and disadvantages of using warfarin as an anticoagulant? Discuss with the person on your left: When do you anticipate the major potential drug interactions with warfarin to present? What should you do about it?
31 Direct Thrombin Inhibitor: Dabigatran Pradaxa Dabigatran etexilate mesylate is indicated to reduce the risk of stroke and systemic embolism in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation 150 mg BID Renal Dosing: CrCl no change CrCl consider decreasing to 75 BID CrCl mg BID CrCl <15- Dosing recommendations can not be provided
32 Pharmacokinetics Xa Inhibitors Abixaban Eliquis 50% Bioavailable Food Delays Tmax 1 hour 87% Protein Bound Metabolism 3A4, Pgp = Look for inhibitors Not Dialyzable Rivoroxaban Xarelto % Bioavailable Food- no effect 10 mg 15, 20 mg WITH food Evening Meal Inc Bioava Metabolism 3A4, Pgp Inhibitors increase AUC T ½ 5-9 hours Longer in elderly NOT dialyzable
33 Factor Xa Inhibitors: 2015 January 9 th 2015 Edoxaban Savaysa ENGAGE AF-TIMI 48 (ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT ) 21,105 Afib- CHADs score 2.8 Low dose edoxaban- 30 mg/day High dose edoxaban- 60 mg/day Standard warfarin 3.5 years Primary endpoint- Thromboembolic event Percent Renal elimination- 50% T ½- Normal GFR- 12 hours T ½ GFR<30-17 hours Liver 3A4 substrateminimal Time to peak 1-2 hours Effects food- minimal N Engl J Med 2013;369:
34 Edoxaban Savaysa Afib: N Engl J Med 2013;369:
35 Atrial Fibrillation: SE Stroke Systemic Embolism Major Bleeding Intracranial hemorrhage All Cause Mortality
36 Anticoagulation Renal Recommendations:
37 Fresh Frozen Plasma Reversing Agents? Human Prothrombin Complex Concentrate: Kcentra Recombinant active Factor VIIa: Prothrombin Complex Concentrate:
38 Xa Inhibitor Reversing Agent: Antidote Andexanet Alpha Annexa Portola Rx Coming Soon????
39 Think/Pair/Share Work with the person on your right: What are the advantages and potential disadvantages of the Novel Oral Anticoagulants?
40 Goal of Therapy Two: Rate Control Control of the ventricular rate using a beta blocker or non-dihydropyridine calcium channel antagonist is recommended for patients with paroxysmal, persistent or permanent AF. Intravenous administration of a BB or CCB is recommended to slow the ventricular heart rate in the acute setting. In patients experiencing AF related symptoms during activity, the adequacy of the heart rate control should be assed during exertion.
41 What is the desired heart rate? A heart rate control (resting heart rate <80 beats per minute strategy is reasonable for symptomatic management of AF. A lenient rate-control strategy (resting heart rate < 110 bpm) may be reasonable as long as patients remain asymptomatic and left ventricular systolic function is preserved
42 Beta Adrenergic Blocking Medications:
43 Limitations BB Blood pressure reduction Adrenergic blockade Decrease exercise ability Shortness of breath NOT contraindicated in COPD or Asthma Caution- may want to rate control with different class Tartrate Succinate
44 Calcium Channel Antagonists Diltiazem 0.25 mg/kg loading dose ( ) then in 20 minutes if needed 0.35 mg/kg (25 mg) then Continuous infusion (5-10mg/hour) then PO IR mg Q 6 hours then SR QD Verapamil 5-10 mg IV then repeat in minutes then IR mg Q 6 hours then SR QD
45 Limitations NDPCCB Nondihydropyridine calcium channel antagonists should not be used in patients with decompensated HF as these may lead to further hemodynamic compromise. (Level of Evidence: C) Negative Inotropes Blood pressure reduction Statin interactions: Lovastatin, Simvastatin (NMT mg) others caution
46 BB vs CCB vs Dig vs BB + Dig vs CCB + Dig
47 CCB or BB NOT Appropriately Controlling Rate: Digitalize Loading dose normal sized adult about 1 mg ½ dose first time 0.5mg over 5 minutes 6 hours later: ¼ dose 0.25mg over 5 minutes 6 hours later: ¼ dose 0.25mg over 5 minutes 6 hours later Maintenance dose PO mg Check level in 5-7 days
48 STILL not to adequate rate control: Rate and Cardioversion considerations: Amiodarone: mg IV over 1 hour 50mg/hour for 24 hours then PO: mg a day or mg a day
49 Think/Pair/Share Work with the person on your left: What are the advantages and disadvantages of the various medications used for rate control?
50 Goal of Therapy Three: Cardioversion: Direct Current Cardioversion: For patients with AF of 48 hours duration or longer or duration unknown- Anticoagulation is recommended for 3 weeks before and 4 weeks after cardioversion. (Electrical or Chemical) If needing urgent cardioversion and not anticoagulated a transesophageal echocardiography before cardioversion to look for left atrial thrombus
51 Chemical Cardioversion When and why did we stop trying to chemically cardiovert ALL patients with AF
52 Chemical Cardioversion: Class 1 Evidence A Recommendations: Flecainide, dofetilide, propafenone and intravenous ibutilide are useful for pharmacologic cardioversion of AF or atrial flutter, provided contraindications to the selected drug are absent Class 2a- Recommendation: Amiodarone orally is a reasonable option for cardioversion
53 What- PRN antiarrythmics Pill in the Pocket Propafenone or flecanide in addition to BB or NDPCCB is reasonable to terminate AF outside the hospital once this treatment has been observed to be safe in a monitored setting for selected patients
54 Pill in the Pocket Data: In-hospital administration of flecainide and propafenone in a single oral loading dose has been shown to be effective and superior to placebo in terminating atrial fibrillation 210 Patients, /- 5 months follow-up 165 pts (79%) had 619 events 569 events (92%) treated within 36 minutes Treatment successful in 534 episodes (94%) within 113 minutes N Engl J Med 2004;351:
55 Antiarrhythmics to Maintain Sinus Rhythm
56 Amiodarone Class 3: Phase 3 (Potassium channel blocker) Pharmacologic Cardioversion Guideline dose (Initial): 600 to 800 mg/day orally in divided doses until a total loading dose of 10 g Guideline dose (Maintenance): 200 mg orally daily Maintenance of Sinus Rhythm Guideline dose (Initial): 400 to 600 mg/day orally in divided doses for 2 to 4 weeks Guideline (Maintenance): 100 to 200 mg orally daily
57 Amiodarone Side Effects:
58 Dronedarone Multaq Exact MOA unknown Non-Iodinated amiodarone Important note: Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (eg, ketoconazole) and Class I or III antiarrhythmics (eg, amiodarone, flecainide, propafenone, quinidine, disopyramide, dofetilide, sotalol) must be discontinued prior to initiating dronedarone hydrochloride 400 mg BID with food 2x increased risk of heart failure and cardiovascular death
59 Flecanide Tambocor Class 1c (Sodium channel blocker) Flecainide has a long half-life (12 to 27 hours). Steady-state plasma levels in normal renal and hepatic function may not be achieved until 3 to 5 days of therapy at a given dose. Therefore, do not increase dosage more frequently than once every 4 days, because optimal effect may not be achieved during the first 2 to 3 days of therapy. Ventricular proarrythmic effects Facts and Comparisons
60 Sotolol Betapace Recommended Hospitalized: Initial dosage: Step 1: Prior to administration of the first dose, the QT interval must be determined using an average of 5 beats. If the baseline QT is greater than 450 msec (JT greater than or equal to 330 msec if QRS over 100 msec), use is contraindicated. Step 2: Prior to the administration of the first dose, the patient's CrCl should be calculated. Step 3: 80 mg twice daily (CrCl greater than 60 ml/minute); 80 mg once daily (CrCl 40 to 60 ml/minute); contraindicated (CrCl less than 40 ml/minute). Step 4: Administer the appropriate daily dose and begin continuous ECG monitoring with QT interval measurements 2 to 4 hours after each dose Step 5: If the 80 mg dose level is tolerated and the QT interval remains less than 500 msec after at least 3 days (after 5 or 6 doses if patient receives once-daily dosing), the patient can be discharged. Alternatively, during hospitalization, the dose can be increased to 120 mg twice daily and the patient followed for 3 days on this dose (followed for 5 or 6 doses if patient receives once-daily doses
61 Propafenone Rythmol Class 1c (sodium channel blocker) Chemical Cardioversion IV 2mg/kg may repeat with 1-2mg/kg in 6-8 hours Oral Cardioversion IR 150, 225, mg PO x once 150mg TID Oral Cardioversion ER 225, 325, BID increase every 3-5 days
62
63 Conclusion: Anti-coagulate Vitamin K Antagonist- Warfarin Thrombin Inhibitor- Dabigatran Pradaxa Xa Inhibitors- Xarelto, Eliquis, Savaysa Rate Control BB, NDHPCCB, Dig, Amiodarone Chemical Cardioversion Amiodarone, Flecanide, Sotalol, Propafenone
64
65 Questions
Treating AF: The Newest Recommendations. CardioCase presentation. Ethel s Case. Wayne Warnica, MD, FACC, FACP, FRCPC
 Treating AF: The Newest Recommendations Wayne Warnica, MD, FACC, FACP, FRCPC CardioCase presentation Ethel s Case Ethel, 73, presents with rapid heart beating and mild chest discomfort. In the ED, ECG
Treating AF: The Newest Recommendations Wayne Warnica, MD, FACC, FACP, FRCPC CardioCase presentation Ethel s Case Ethel, 73, presents with rapid heart beating and mild chest discomfort. In the ED, ECG
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION IN THE 21 ST CENTURY TIMOTHY DOWLING, D.O. FAMILY PHYSICIAN
 ATRIAL FIBRILLATION IN THE 21 ST CENTURY TIMOTHY DOWLING, D.O. FAMILY PHYSICIAN GOALS AND OBJECTIVES At The end of this talk you should understand: What is Atrial Fibrillation Causes of Atrial Fibrillation
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION IN THE 21 ST CENTURY TIMOTHY DOWLING, D.O. FAMILY PHYSICIAN GOALS AND OBJECTIVES At The end of this talk you should understand: What is Atrial Fibrillation Causes of Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial Fibrillation Peter Santucci, MD Revised May, 2008
 Atrial Fibrillation Peter Santucci, MD Revised May, 2008 Atrial fibrillation (AF) is an irregular, disorganized rhythm characterized by a lack of organized mechanical atrial activity. The atrial rate is
Atrial Fibrillation Peter Santucci, MD Revised May, 2008 Atrial fibrillation (AF) is an irregular, disorganized rhythm characterized by a lack of organized mechanical atrial activity. The atrial rate is
Current Management of Atrial Fibrillation DISCLOSURES. Heart Beat Anatomy. I have no financial conflicts to disclose
 Current Management of Atrial Fibrillation Mary Macklin, MSN, APRN Concord Hospital Cardiac Associates DISCLOSURES I have no financial conflicts to disclose Book Women: Fit at Fifty. A Guide to Living Long.
Current Management of Atrial Fibrillation Mary Macklin, MSN, APRN Concord Hospital Cardiac Associates DISCLOSURES I have no financial conflicts to disclose Book Women: Fit at Fifty. A Guide to Living Long.
Analyzing Clinical Trial Findings of the Efficacy and Safety Profiles of Novel Anticoagulants for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation
 Analyzing Clinical Trial Findings of the Efficacy and Safety Profiles of Novel Anticoagulants for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation Drew Baldwin, MD Virginia Mason Seattle, Washington NCVH May 29,
Analyzing Clinical Trial Findings of the Efficacy and Safety Profiles of Novel Anticoagulants for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation Drew Baldwin, MD Virginia Mason Seattle, Washington NCVH May 29,
Atrial Fibrillation Management Across the Spectrum of Illness
 Disclosures Atrial Fibrillation Management Across the Spectrum of Illness NONE Barbara Birriel, MSN, ACNP-BC, FCCM The Pennsylvania State University Objectives AF Discuss the pathophysiology, diagnosis,
Disclosures Atrial Fibrillation Management Across the Spectrum of Illness NONE Barbara Birriel, MSN, ACNP-BC, FCCM The Pennsylvania State University Objectives AF Discuss the pathophysiology, diagnosis,
The author has no disclosures
 Mary Bradbury, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Pharmacy Specialist, Cardiac Surgery September 18, 2012 Mary.bradbury@inova.org This presentation will discuss unlabeled and investigational use of products The author
Mary Bradbury, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Pharmacy Specialist, Cardiac Surgery September 18, 2012 Mary.bradbury@inova.org This presentation will discuss unlabeled and investigational use of products The author
3/25/14. To Clot or Not What s New In Anticoagulation? Clotting Cascade. Anticoagulant drug targets. Anita Ralstin, MS CNS CNP. Heparin.
 To Clot or Not What s New In Anticoagulation? Anita Ralstin, MS CNS CNP 1 Clotting Cascade 2 Anticoagulant drug targets Heparin XI VIII IX V X VII LMWH II Warfarin Fibrin clot 1 Who Needs Anticoagulation
To Clot or Not What s New In Anticoagulation? Anita Ralstin, MS CNS CNP 1 Clotting Cascade 2 Anticoagulant drug targets Heparin XI VIII IX V X VII LMWH II Warfarin Fibrin clot 1 Who Needs Anticoagulation
Managing the Patient with Atrial Fibrillation
 Pocket Guide Managing the Patient with Atrial Fibrillation Updated April 2012 Editor Stephen R. Shorofsky, MD, Ph.D. Assistant Editors Anastasios Saliaris, MD Shawn Robinson, MD www.hrsonline.org DEFINITION
Pocket Guide Managing the Patient with Atrial Fibrillation Updated April 2012 Editor Stephen R. Shorofsky, MD, Ph.D. Assistant Editors Anastasios Saliaris, MD Shawn Robinson, MD www.hrsonline.org DEFINITION
Antiplatelet and Antithrombotic Therapy. Dr Curry Grant Stroke Prevention Clinic Quinte Health Care
 Antiplatelet and Antithrombotic Therapy Dr Curry Grant Stroke Prevention Clinic Quinte Health Care Disclosure of Potential for Conflict of Interest Dr. F.C. Grant Atrial Fibrillation FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE:
Antiplatelet and Antithrombotic Therapy Dr Curry Grant Stroke Prevention Clinic Quinte Health Care Disclosure of Potential for Conflict of Interest Dr. F.C. Grant Atrial Fibrillation FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE:
Recurrent AF: Choosing the Right Medication.
 In the name of God Shiraz E-Medical Journal Vol. 11, No. 3, July 2010 http://semj.sums.ac.ir/vol11/jul2010/89015.htm Recurrent AF: Choosing the Right Medication. Basamad Z. * Assistant Professor, Department
In the name of God Shiraz E-Medical Journal Vol. 11, No. 3, July 2010 http://semj.sums.ac.ir/vol11/jul2010/89015.htm Recurrent AF: Choosing the Right Medication. Basamad Z. * Assistant Professor, Department
Atrial Fibrillation Based on ESC Guidelines. Moshe Swissa MD Kaplan Medical Center
 Atrial Fibrillation Based on ESC Guidelines Moshe Swissa MD Kaplan Medical Center Epidemiology AF affects 1 2% of the population, and this figure is likely to increase in the next 50 years. AF may long
Atrial Fibrillation Based on ESC Guidelines Moshe Swissa MD Kaplan Medical Center Epidemiology AF affects 1 2% of the population, and this figure is likely to increase in the next 50 years. AF may long
Anticoagulants in Atrial Fibrillation
 Anticoagulants in Atrial Fibrillation Starting and Stopping Them Safely Carmine D Amico, D.O. Overview Learning objectives Introduction Basic concepts Treatment strategy & options Summary 1 Learning objectives
Anticoagulants in Atrial Fibrillation Starting and Stopping Them Safely Carmine D Amico, D.O. Overview Learning objectives Introduction Basic concepts Treatment strategy & options Summary 1 Learning objectives
Anticoagulation in Atrial Fibrillation
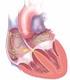 Anticoagulation in Atrial Fibrillation Parag P. Patel, MD FACC Disclosures Eliquis Speakers Bureau 1 Clinical Scenario Ms. L is a 76F admitted to the stroke service with a dense right sided hemiparesis
Anticoagulation in Atrial Fibrillation Parag P. Patel, MD FACC Disclosures Eliquis Speakers Bureau 1 Clinical Scenario Ms. L is a 76F admitted to the stroke service with a dense right sided hemiparesis
Non- Valvular Atrial Fibrillation and Stroke Prevention: Which OAC Do I Choose. Warfarin vs the NOACs
 Non- Valvular Atrial Fibrillation and Stroke Prevention: Which OAC Do I Choose Warfarin vs the NOACs Dr. Lori McIntosh D.O. Board Certified Neurologist Objectives Be able to list the current options of
Non- Valvular Atrial Fibrillation and Stroke Prevention: Which OAC Do I Choose Warfarin vs the NOACs Dr. Lori McIntosh D.O. Board Certified Neurologist Objectives Be able to list the current options of
Cardiology Update 2014
 Cardiology Update 2014 Update on the Novel Oral Anticoagulants (NOACS) Raymond Kawasaki, MD AMG Cardiology December 6, 2014 Disclosures I have no disclosures relevant to this presentation Contents I. The
Cardiology Update 2014 Update on the Novel Oral Anticoagulants (NOACS) Raymond Kawasaki, MD AMG Cardiology December 6, 2014 Disclosures I have no disclosures relevant to this presentation Contents I. The
1/7/2012. Objectives. Epidemiology of Atrial Fibrillation(AF) Stroke in AF. Stroke Risk Stratification in AF
 Objectives Atrial Fibrillation and Prevention of Thrombotic Complications: Therapeutic Update Andrea C. Flores Pharm.D Pharmacy Resident at the Miami VA Healthcare System Review the epidemiology, pathophysiology
Objectives Atrial Fibrillation and Prevention of Thrombotic Complications: Therapeutic Update Andrea C. Flores Pharm.D Pharmacy Resident at the Miami VA Healthcare System Review the epidemiology, pathophysiology
Anticoagulation: How Do I Pick From All the Choices? Jeffrey H. Neuhauser, DO, FACC BHHI Primary Care Symposium February 28, 2014
 Anticoagulation: How Do I Pick From All the Choices? Jeffrey H. Neuhauser, DO, FACC BHHI Primary Care Symposium February 28, 2014 Atrial Fibrillation 2 Atrial Fibrillation The most common arrhythmia encountered
Anticoagulation: How Do I Pick From All the Choices? Jeffrey H. Neuhauser, DO, FACC BHHI Primary Care Symposium February 28, 2014 Atrial Fibrillation 2 Atrial Fibrillation The most common arrhythmia encountered
New Treatments for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation. John C. Andrefsky, MD, FAHA NEOMED Internal Medicine Review course May 5 th, 2013
 New Treatments for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation John C. Andrefsky, MD, FAHA NEOMED Internal Medicine Review course May 5 th, 2013 Classification Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (AF) Last < 7
New Treatments for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation John C. Andrefsky, MD, FAHA NEOMED Internal Medicine Review course May 5 th, 2013 Classification Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (AF) Last < 7
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) MANAGEMENT of Atrial Fibrillation (AF)
 DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) MANAGEMENT of Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Key priorities Identification and diagnosis Treatment for persistent AF Treatment for permanent AF Antithrombotic
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) MANAGEMENT of Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Key priorities Identification and diagnosis Treatment for persistent AF Treatment for permanent AF Antithrombotic
FDA Approved Oral Anticoagulants
 FDA Approved Oral Anticoagulants Generic (Trade Name) Warfarin (Coumadin, Jantoven ) 1 FDA approved indication Prophylaxis and treatment of venous thromboembolism (VTE) Prophylaxis and treatment of thromboembolic
FDA Approved Oral Anticoagulants Generic (Trade Name) Warfarin (Coumadin, Jantoven ) 1 FDA approved indication Prophylaxis and treatment of venous thromboembolism (VTE) Prophylaxis and treatment of thromboembolic
Long term anticoagulant therapy in patients with atrial fibrillation at high risk of stroke: a new scenario after RE-LY trial
 Long term anticoagulant therapy in patients with atrial fibrillation at high risk of stroke: a new scenario after RE-LY trial Camillo Autore Università di Roma Sapienza II Facoltà di Medicina e Chirurgia
Long term anticoagulant therapy in patients with atrial fibrillation at high risk of stroke: a new scenario after RE-LY trial Camillo Autore Università di Roma Sapienza II Facoltà di Medicina e Chirurgia
Speaker Disclosure. Outline. Pharmacist Objectives. Patient Case. Outline 9/4/2014
 Speaker Disclosure Matthew K. Pitlick, Pharm.D., BCPS St. Louis College of Pharmacy/VA St. Louis HCS mpitlick@stlcop.edu Matthew K. Pitlick, Pharm.D., BCPS declares no conflicts of interest, real or apparent,
Speaker Disclosure Matthew K. Pitlick, Pharm.D., BCPS St. Louis College of Pharmacy/VA St. Louis HCS mpitlick@stlcop.edu Matthew K. Pitlick, Pharm.D., BCPS declares no conflicts of interest, real or apparent,
Atrial fibrillation (AF) care pathways. for the primary care physicians
 Atrial fibrillation (AF) care pathways for the primary care physicians by University of Minnesota Physicians Heart, October, 2011 Evaluation by the primary care physician: 1. Comprehensive history and
Atrial fibrillation (AF) care pathways for the primary care physicians by University of Minnesota Physicians Heart, October, 2011 Evaluation by the primary care physician: 1. Comprehensive history and
TSOAC Initiation Checklist
 Task Establish appropriate dose based on anticoagulant selected, indication and patient factors such as renal function. Evaluate for medication interactions that may necessitate TSOAC dose adjustment.
Task Establish appropriate dose based on anticoagulant selected, indication and patient factors such as renal function. Evaluate for medication interactions that may necessitate TSOAC dose adjustment.
The Role of the Newer Anticoagulants
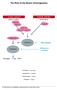 The Role of the Newer Anticoagulants WARFARIN = Coumadin DAGIBATRAN = Pradaxa RIVAROXABAN = Xarelto APIXABAN = Eliquis INDICATION DABIGATRAN (Pradaxa) RIVAROXABAN (Xarelto) APIXABAN (Eliquis) Stroke prevention
The Role of the Newer Anticoagulants WARFARIN = Coumadin DAGIBATRAN = Pradaxa RIVAROXABAN = Xarelto APIXABAN = Eliquis INDICATION DABIGATRAN (Pradaxa) RIVAROXABAN (Xarelto) APIXABAN (Eliquis) Stroke prevention
New in Atrial Fibrillation
 New in Atrial Fibrillation September 2011 Stroke prevention more options Rhythm Control -drugs - alternatives to drugs; ablation Rate Control - pace + ablate A-FIB Dell Stroke Risk AFib Two Principles
New in Atrial Fibrillation September 2011 Stroke prevention more options Rhythm Control -drugs - alternatives to drugs; ablation Rate Control - pace + ablate A-FIB Dell Stroke Risk AFib Two Principles
Practical Rate and Rhythm Management of Atrial Fibrillation
 Practical Rate and Rhythm Management of Atrial Fibrillation pocket guide UPDATED FEBRUARY 2013 Adapted from the ACCF/AHA/HRS 2011 Focused Updates Incorporated into the ACC/AHA/ESC Guidelines for the Management
Practical Rate and Rhythm Management of Atrial Fibrillation pocket guide UPDATED FEBRUARY 2013 Adapted from the ACCF/AHA/HRS 2011 Focused Updates Incorporated into the ACC/AHA/ESC Guidelines for the Management
The speakers have attested that their presentation will be free of all commercial bias toward a specific company and its products.
 Update on New Anticoagulants (Apixaban, Dabigatran and Rivaroxaban) Patient Safety Daniel B. DiCola, MD and Paul Ament,, Pharm.D Excela Heath, Latrobe, PA Disclosures: Paul Ament discloses that he receives
Update on New Anticoagulants (Apixaban, Dabigatran and Rivaroxaban) Patient Safety Daniel B. DiCola, MD and Paul Ament,, Pharm.D Excela Heath, Latrobe, PA Disclosures: Paul Ament discloses that he receives
Atrial Fibrillation The Basics
 Atrial Fibrillation The Basics Family Practice Symposium Tim McAveney, M.D. 10/23/09 Objectives Review the fundamentals of managing afib Discuss the risks for stroke and the indications for anticoagulation
Atrial Fibrillation The Basics Family Practice Symposium Tim McAveney, M.D. 10/23/09 Objectives Review the fundamentals of managing afib Discuss the risks for stroke and the indications for anticoagulation
Comparison between New Oral Anticoagulants and Warfarin
 Comparison between New Oral Anticoagulants and Warfarin Warfarin was the mainstay of oral anticoagulant therapy until the recent discovery of more precise targets for therapy. In recent years, several
Comparison between New Oral Anticoagulants and Warfarin Warfarin was the mainstay of oral anticoagulant therapy until the recent discovery of more precise targets for therapy. In recent years, several
STROKE PREVENTION IN ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 STROKE PREVENTION IN ATRIAL FIBRILLATION OBJECTIVE: To guide clinicians in the selection of antithrombotic therapy for the secondary prevention of ischemic stroke and arterial thromboembolism in patients
STROKE PREVENTION IN ATRIAL FIBRILLATION OBJECTIVE: To guide clinicians in the selection of antithrombotic therapy for the secondary prevention of ischemic stroke and arterial thromboembolism in patients
2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS, REGISTRY
 Measure #326 (NQF 1525): Atrial Fibrillation and Atrial Flutter: Chronic Anticoagulation Therapy National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS,
Measure #326 (NQF 1525): Atrial Fibrillation and Atrial Flutter: Chronic Anticoagulation Therapy National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS,
DOACs. What s in a name? or TSOACs. Blood Clot. Darra Cover, Pharm D. Clot Formation DOACs work here. Direct Oral AntiCoagulant
 DOACs NOACs or TSOACs Generic Name DOACs Brand Name Mechanism of Action Direct Xa Inhibitor Direct Thrombin Inhibitor Dabigatran Pradaxa X Rivaroxaban Xarelto X Darra Cover, Pharm D Apixaban Eliquis X
DOACs NOACs or TSOACs Generic Name DOACs Brand Name Mechanism of Action Direct Xa Inhibitor Direct Thrombin Inhibitor Dabigatran Pradaxa X Rivaroxaban Xarelto X Darra Cover, Pharm D Apixaban Eliquis X
Atrial Fibrillation An update on diagnosis and management
 Dr Arvind Vasudeva Consultant Cardiologist Atrial Fibrillation An update on diagnosis and management Atrial fibrillation (AF) remains the commonest disturbance of cardiac rhythm seen in clinical practice.
Dr Arvind Vasudeva Consultant Cardiologist Atrial Fibrillation An update on diagnosis and management Atrial fibrillation (AF) remains the commonest disturbance of cardiac rhythm seen in clinical practice.
Novel oral anticoagulant (NOAC) for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation Special situations
 Novel oral anticoagulant (NOAC) for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation Special situations Dardo E. Ferrara MD Cardiac Electrophysiology North Cascade Cardiology PeaceHealth Medical Group Which anticoagulant
Novel oral anticoagulant (NOAC) for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation Special situations Dardo E. Ferrara MD Cardiac Electrophysiology North Cascade Cardiology PeaceHealth Medical Group Which anticoagulant
Atrial Fibrillation. Management Strategies Marc D. Schrode, D.O., F.A.C.C.,F.A.C.O.I.
 Atrial Fibrillation Management Strategies Marc D. Schrode, D.O., F.A.C.C.,F.A.C.O.I. Atrial Fibrillation Estimated that 2.6 to 6.1 million people in the U.S. with Afib as of 2010 By 2050 it is expected
Atrial Fibrillation Management Strategies Marc D. Schrode, D.O., F.A.C.C.,F.A.C.O.I. Atrial Fibrillation Estimated that 2.6 to 6.1 million people in the U.S. with Afib as of 2010 By 2050 it is expected
Management of ATRIAL FIBRILLATION. in general practice. 22 BPJ Issue 39
 Management of ATRIAL FIBRILLATION in general practice 22 BPJ Issue 39 What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common cardiac arrhythmia encountered in primary care. It is often
Management of ATRIAL FIBRILLATION in general practice 22 BPJ Issue 39 What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common cardiac arrhythmia encountered in primary care. It is often
New Anticoagulation Options for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation. Joy Wahawisan, Pharm.D., BCPS April 25, 2012
 New Anticoagulation Options for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation Joy Wahawisan, Pharm.D., BCPS April 25, 2012 Stroke in Atrial Fibrillation % Stroke 1991;22:983. Age Range (years) CHADS 2 Risk
New Anticoagulation Options for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation Joy Wahawisan, Pharm.D., BCPS April 25, 2012 Stroke in Atrial Fibrillation % Stroke 1991;22:983. Age Range (years) CHADS 2 Risk
Three new/novel oral anticoagulants (NOAC) have been licensed in Ireland since 2008:
 Key Points to consider when prescribing NOACs Introduction Three new/novel oral anticoagulants (NOAC) have been licensed in Ireland since 2008: Dabigatran Etexilate (Pradaxa ) 75mg, 110mg, 150mg. Rivaroxaban
Key Points to consider when prescribing NOACs Introduction Three new/novel oral anticoagulants (NOAC) have been licensed in Ireland since 2008: Dabigatran Etexilate (Pradaxa ) 75mg, 110mg, 150mg. Rivaroxaban
Dabigatran (Pradaxa) Guidelines
 Dabigatran (Pradaxa) Guidelines Dabigatran is a new anticoagulant for reducing the risk of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation. Dabigatran is a direct thrombin inhibitor, similar to warfarin, without
Dabigatran (Pradaxa) Guidelines Dabigatran is a new anticoagulant for reducing the risk of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation. Dabigatran is a direct thrombin inhibitor, similar to warfarin, without
Atrial Fibrillation The High Risk Obese Patient
 Atrial Fibrillation The High Risk Obese Patient Frederick Schaller, D.O.,F.A.C.O.I. Professor and Vice Dean Touro University Nevada A 56 year old male with a history of hypertension and chronic stable
Atrial Fibrillation The High Risk Obese Patient Frederick Schaller, D.O.,F.A.C.O.I. Professor and Vice Dean Touro University Nevada A 56 year old male with a history of hypertension and chronic stable
Atrial Fibrillation: Drugs, Ablation, or Benign Neglect. Robert Kennedy, MD October 10, 2015
 Atrial Fibrillation: Drugs, Ablation, or Benign Neglect Robert Kennedy, MD October 10, 2015 Definitions 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS Guideline for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: Executive Summary.
Atrial Fibrillation: Drugs, Ablation, or Benign Neglect Robert Kennedy, MD October 10, 2015 Definitions 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS Guideline for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: Executive Summary.
Goals 6/6/2014. Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation: New Oral Anti-Coagulants No More INRs. Ashkan Babaie, MD
 Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation: New Oral Anti-Coagulants No More INRs Ashkan Babaie, MD Arrhythmia Service Providence Heart Clinic June 8 th, 2014 Goals Discuss the data behind approval of NOACs
Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation: New Oral Anti-Coagulants No More INRs Ashkan Babaie, MD Arrhythmia Service Providence Heart Clinic June 8 th, 2014 Goals Discuss the data behind approval of NOACs
How To Compare The New Oral Anticoagulants
 Disclosures The New Oral Anticoagulants: Are they better than Warfarin? Alan P. Agins, Ph.D. does not have any actual or potential conflicts of interest in relation to this CE activity. Alan Agins, Ph.D.
Disclosures The New Oral Anticoagulants: Are they better than Warfarin? Alan P. Agins, Ph.D. does not have any actual or potential conflicts of interest in relation to this CE activity. Alan Agins, Ph.D.
Anticoagulation Therapy Update
 Anticoagulation Therapy Update JUDY R. WALLING, FNP-BC ARRHYTHMIA MANAGEMENT MUSC CARDIOLOGY Outline Who do we anticoagulate? Review classes of Anticoagulants Review examples of Anticoagulants Review CHADS2
Anticoagulation Therapy Update JUDY R. WALLING, FNP-BC ARRHYTHMIA MANAGEMENT MUSC CARDIOLOGY Outline Who do we anticoagulate? Review classes of Anticoagulants Review examples of Anticoagulants Review CHADS2
Rx Updates New Guidelines, New Medications What You Need to Know
 Rx Updates New Guidelines, New Medications What You Need to Know Maria Pruchnicki, PharmD, BCPS, BCACP, CLS Associate Professor of Clinical Pharmacy OSU College of Pharmacy Background scope and impact
Rx Updates New Guidelines, New Medications What You Need to Know Maria Pruchnicki, PharmD, BCPS, BCACP, CLS Associate Professor of Clinical Pharmacy OSU College of Pharmacy Background scope and impact
Episode 20 Atrial fibrillation Prepared by Dr. Lucas Chartier
 Episode 20 Atrial fibrillation Prepared by Dr. Lucas Chartier Most common dysrhythmia seen in ED, and incidence increasing with ageing population Presentation Common presentations: younger patients often
Episode 20 Atrial fibrillation Prepared by Dr. Lucas Chartier Most common dysrhythmia seen in ED, and incidence increasing with ageing population Presentation Common presentations: younger patients often
STROKE PREVENTION IN ATRIAL FIBRILLATION. TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: ABBREVIATIONS: BACKGROUND:
 STROKE PREVENTION IN ATRIAL FIBRILLATION TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: To guide clinicians in the selection of antithrombotic therapy for the secondary prevention
STROKE PREVENTION IN ATRIAL FIBRILLATION TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: To guide clinicians in the selection of antithrombotic therapy for the secondary prevention
New Oral Anticoagulants
 New Oral Anticoagulants Tracy Minichiello, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Chief, San FranciscoVA Anticoagulation and Thrombosis Service Ansell, J. Hematology Copyright 2010 American Society of Hematology.
New Oral Anticoagulants Tracy Minichiello, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Chief, San FranciscoVA Anticoagulation and Thrombosis Service Ansell, J. Hematology Copyright 2010 American Society of Hematology.
AHA/ASA Scientific Statement Oral Antithrombotic Agents for the Prevention of Stroke in Atrial Fibrillation
 AHA/ASA Scientific Statement Oral Antithrombotic Agents for the Prevention of Stroke in Atrial Fibrillation A Statement for Healthcare Professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke
AHA/ASA Scientific Statement Oral Antithrombotic Agents for the Prevention of Stroke in Atrial Fibrillation A Statement for Healthcare Professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke
How To Treat Aneuricaagulation
 Speaker Introduction Jessica Wilhoite, PharmD, BCACP Doctor of Pharmacy: Purdue University Postgraduate Residency Training: PGY1 Pharmacy Practice St. Vincent Hospital PGY2 Ambulatory Care St. Vincent
Speaker Introduction Jessica Wilhoite, PharmD, BCACP Doctor of Pharmacy: Purdue University Postgraduate Residency Training: PGY1 Pharmacy Practice St. Vincent Hospital PGY2 Ambulatory Care St. Vincent
Venous Thromboembolism: Long Term Anticoagulation. Dan Johnson, Pharm.D.
 Venous Thromboembolism: Long Term Anticoagulation Dan Johnson, Pharm.D. Disclosures No financial relationships with products discussed Off-label use of drug therapy always discussed Objectives Review clinical
Venous Thromboembolism: Long Term Anticoagulation Dan Johnson, Pharm.D. Disclosures No financial relationships with products discussed Off-label use of drug therapy always discussed Objectives Review clinical
Optimizing Anticoagulation Selection for Your Patient. C. Andrew Brian MD, FACC NCVH 2015
 Optimizing Anticoagulation Selection for Your Patient C. Andrew Brian MD, FACC NCVH 2015 Who Needs to Be Anticoagulated and What is the Patient s Risk? 1. Atrial Fibrillation ( nonvalvular ) 2. What regimen
Optimizing Anticoagulation Selection for Your Patient C. Andrew Brian MD, FACC NCVH 2015 Who Needs to Be Anticoagulated and What is the Patient s Risk? 1. Atrial Fibrillation ( nonvalvular ) 2. What regimen
NnEeWw DdEeVvEeLlOoPpMmEeNnTtSs IiıNn OoRrAaLl AaNnTtIiıCcOoAaGgUuLlAaTtIiıOoNn AaNnDd RrEeVvEeRrSsAaLl
 NnEeWw DdEeVvEeLlOoPpMmEeNnTtSs IiıNn OoRrAaLl AaNnTtIiıCcOoAaGgUuLlAaTtIiıOoNn AaNnDd RrEeVvEeRrSsAaLl Mikele Wissing, RN June 2014 Introduction until recently, was the unrivaled medication for treatment
NnEeWw DdEeVvEeLlOoPpMmEeNnTtSs IiıNn OoRrAaLl AaNnTtIiıCcOoAaGgUuLlAaTtIiıOoNn AaNnDd RrEeVvEeRrSsAaLl Mikele Wissing, RN June 2014 Introduction until recently, was the unrivaled medication for treatment
Xarelto (Rivaroxaban)
 Xarelto (Rivaroxaban) Hightly selective, reversible, direct oral FXa inhibitor Maxium concentratiion after 2 to 4 hrs High bioavailability(66%),increase with food ( suggest with food) 1/3 from renal excretion,
Xarelto (Rivaroxaban) Hightly selective, reversible, direct oral FXa inhibitor Maxium concentratiion after 2 to 4 hrs High bioavailability(66%),increase with food ( suggest with food) 1/3 from renal excretion,
Palpitations & AF. Richard Grocott Mason Consultant Cardiologist THH NHS Foundation Trust & Royal Brompton & Harefield NHS Foundation Trust
 Palpitations & AF Richard Grocott Mason Consultant Cardiologist THH NHS Foundation Trust & Royal Brompton & Harefield NHS Foundation Trust Palpitations Frequent symptom Less than 50% associated with arrhythmia
Palpitations & AF Richard Grocott Mason Consultant Cardiologist THH NHS Foundation Trust & Royal Brompton & Harefield NHS Foundation Trust Palpitations Frequent symptom Less than 50% associated with arrhythmia
Atrial Fibrillation: Stroke and Thromboprophylaxis. Derek Waller
 Atrial Fibrillation: Stroke and Thromboprophylaxis Derek Waller Atrial Fibrillation in the Elderly: Risk of Stroke Framingham study AGE 50-59 60-69 70-79 80-89 Prevalence of AF % Attributable Risk of AF
Atrial Fibrillation: Stroke and Thromboprophylaxis Derek Waller Atrial Fibrillation in the Elderly: Risk of Stroke Framingham study AGE 50-59 60-69 70-79 80-89 Prevalence of AF % Attributable Risk of AF
Practical everyday use of NOACs. Dr. Elisabetta Toso SOC Cardiologia Ospedale Cardinal Massaia - Asti
 Practical everyday use of NOACs Dr. Elisabetta Toso SOC Cardiologia Ospedale Cardinal Massaia - Asti THE NEW ANTICOAGULANTS HISTORY Oral Inhibitors Edoxaban Apixaban Betrixaban EXPLORE-Xa Phase II trial
Practical everyday use of NOACs Dr. Elisabetta Toso SOC Cardiologia Ospedale Cardinal Massaia - Asti THE NEW ANTICOAGULANTS HISTORY Oral Inhibitors Edoxaban Apixaban Betrixaban EXPLORE-Xa Phase II trial
Comparative Anticoagulation
 Comparative Anticoagulation Laurajo Ryan, PharmD, MSc, BCPS, CDE Clinical Associate Professor The University of Texas at Austin College of Pharmacy The University of Texas Health Science Center Pharmacotherapy
Comparative Anticoagulation Laurajo Ryan, PharmD, MSc, BCPS, CDE Clinical Associate Professor The University of Texas at Austin College of Pharmacy The University of Texas Health Science Center Pharmacotherapy
PRACTICAL APPROACH TO SVT. Graham C. Wong MD MPH Division of Cardiology Vancouver General Hospital University of British Columbia
 PRACTICAL APPROACH TO SVT Graham C. Wong MD MPH Division of Cardiology Vancouver General Hospital University of British Columbia CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF THE HEART SA node His bundle Left bundle AV node Right
PRACTICAL APPROACH TO SVT Graham C. Wong MD MPH Division of Cardiology Vancouver General Hospital University of British Columbia CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF THE HEART SA node His bundle Left bundle AV node Right
Novel Anticoagulation Agents DISCLOSURES. Objectives ATRIAL FIBRILLATION TRIALS. NOAC Comparison 6/12/2015
 Novel Anticoagulation Agents DISCLOSURES James W. Haynes, MD Department of Family Medicine Univ of TN Health Science Center (Chattanooga) Objectives Understand mechanism of action behind the NOAC agents
Novel Anticoagulation Agents DISCLOSURES James W. Haynes, MD Department of Family Medicine Univ of TN Health Science Center (Chattanooga) Objectives Understand mechanism of action behind the NOAC agents
Anticoagulation at the end of life. Rhona Maclean Rhona.maclean@sth.nhs.uk
 Anticoagulation at the end of life Rhona Maclean Rhona.maclean@sth.nhs.uk Content Anticoagulant Therapies Indications for anticoagulation Venous thromboembolism (VTE) Atrial Fibrillation Mechnical Heart
Anticoagulation at the end of life Rhona Maclean Rhona.maclean@sth.nhs.uk Content Anticoagulant Therapies Indications for anticoagulation Venous thromboembolism (VTE) Atrial Fibrillation Mechnical Heart
Presenter Disclosure Information
 2:15 3 pm Managing Arrhythmias in Primary Care Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Raul Mitrani, MD, FACC, FHRS: Speakers Bureau for Medtronic.
2:15 3 pm Managing Arrhythmias in Primary Care Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Raul Mitrani, MD, FACC, FHRS: Speakers Bureau for Medtronic.
Bridging the Gap: How to Transition from the NOACs to Warfarin
 Bridging the Gap: How to Transition from the NOACs to April 24 th 2015 UAN: 0048-0000-15-034-L01-P Amanda Styer, Pharm.D. Marion General Hospital, OhioHealth Objectives: 1. Review labeling regarding transition
Bridging the Gap: How to Transition from the NOACs to April 24 th 2015 UAN: 0048-0000-15-034-L01-P Amanda Styer, Pharm.D. Marion General Hospital, OhioHealth Objectives: 1. Review labeling regarding transition
National Medicines Information Centre
 National Medicines Information Centre ST. JAMES S HOSPITAL DUBLIN 8 TEL 01-4730589 or 1850-727-727 FAX 01-4730596 www.nmic.ie THE CONTEMPORARY MANAGEMENT OF ATRIAL FIBRILLATION VOLUME 12 NUMBER 3 2006
National Medicines Information Centre ST. JAMES S HOSPITAL DUBLIN 8 TEL 01-4730589 or 1850-727-727 FAX 01-4730596 www.nmic.ie THE CONTEMPORARY MANAGEMENT OF ATRIAL FIBRILLATION VOLUME 12 NUMBER 3 2006
Kevin Saunders MD CCFP Rivergrove Medical Clinic Wellness Institute @ SOGH April 17 2013
 Kevin Saunders MD CCFP Rivergrove Medical Clinic Wellness Institute @ SOGH April 17 2013 Family physician with Rivergrove Medical Clinic Practice in the north end since 1985 Medical Director of the Wellness
Kevin Saunders MD CCFP Rivergrove Medical Clinic Wellness Institute @ SOGH April 17 2013 Family physician with Rivergrove Medical Clinic Practice in the north end since 1985 Medical Director of the Wellness
Anticoagulation and Reversal
 Anticoagulation and Reversal John Howard, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Pharmacist Internal Medicine Affiliate Associate Clinical Professor South Carolina College of Pharmacy Disclosures I have no Financial, Industry,
Anticoagulation and Reversal John Howard, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Pharmacist Internal Medicine Affiliate Associate Clinical Professor South Carolina College of Pharmacy Disclosures I have no Financial, Industry,
Reversing the New Anticoagulants
 Reversing the New Anticoagulants Disclosure Susan C. Lambe, MD Assistant Clinical Professor Department of Emergency Medicine University of California, San Francisco Roadmap for today 1 Roadmap for today
Reversing the New Anticoagulants Disclosure Susan C. Lambe, MD Assistant Clinical Professor Department of Emergency Medicine University of California, San Francisco Roadmap for today 1 Roadmap for today
Devang M. Desai, MD, FACC, FSCAI Chief of Interventional Cardiology Director of Cardiac Catheterization Lab St. Mary s Hospital and Regional Medical
 Devang M. Desai, MD, FACC, FSCAI Chief of Interventional Cardiology Director of Cardiac Catheterization Lab St. Mary s Hospital and Regional Medical Center A.Fib affects 2.2 million Americans. The lifetime
Devang M. Desai, MD, FACC, FSCAI Chief of Interventional Cardiology Director of Cardiac Catheterization Lab St. Mary s Hospital and Regional Medical Center A.Fib affects 2.2 million Americans. The lifetime
New Oral Anticoagulants for VTE, A-fib, and ACS
 New Oral Anticoagulants for VTE, A-fib, and ACS KCUMB Fall CME 2014 September 18, 2014 Schoen W. Kruse, Ph.D. Assistant Dean Associate Professor of Pharmacology KCUMB An 82 y/o male presents to the ED
New Oral Anticoagulants for VTE, A-fib, and ACS KCUMB Fall CME 2014 September 18, 2014 Schoen W. Kruse, Ph.D. Assistant Dean Associate Professor of Pharmacology KCUMB An 82 y/o male presents to the ED
Management of Antithrombotics with Procedures. Jordan Weinstein, MD
 Management of Antithrombotics with Procedures Jordan Weinstein, MD Presenter Disclosure Information Cardiology Update 2013 I have no relevant financial interest and/or arrangement with industry. Novel
Management of Antithrombotics with Procedures Jordan Weinstein, MD Presenter Disclosure Information Cardiology Update 2013 I have no relevant financial interest and/or arrangement with industry. Novel
Cardiovascular Disease
 Cardiovascular Disease 1 Cardiovascular Disease 1. More target specific oral anticoagulants (TSOAC) 2. Vorapaxar (Zonivity) 3. Continued noise about a polypill 4. WATCHMAN 3 1 2 3 4 Left Atrial Appendage
Cardiovascular Disease 1 Cardiovascular Disease 1. More target specific oral anticoagulants (TSOAC) 2. Vorapaxar (Zonivity) 3. Continued noise about a polypill 4. WATCHMAN 3 1 2 3 4 Left Atrial Appendage
New Treatment Guidelines in Atrial Fibrillation and Updates on NOACs
 New Treatment Guidelines in Atrial Fibrillation and Updates on NOACs Dean Schillinger MD Professor of Medicine University of California, San Francisco San Francisco General Hospital & Trauma Center Disclosures
New Treatment Guidelines in Atrial Fibrillation and Updates on NOACs Dean Schillinger MD Professor of Medicine University of California, San Francisco San Francisco General Hospital & Trauma Center Disclosures
NOAC S For Stroke Prevention in. Atrial Fibrillation. Peter Cohn M.D FACC Associate Physician in Chief Cardiovascular Care Center Southcoast Health
 NOAC S For Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation Peter Cohn M.D FACC Associate Physician in Chief Cardiovascular Care Center Southcoast Health New Oral Anti Coagulant Formal Definition: Atrial Fibrillation
NOAC S For Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation Peter Cohn M.D FACC Associate Physician in Chief Cardiovascular Care Center Southcoast Health New Oral Anti Coagulant Formal Definition: Atrial Fibrillation
Practical Management of Atrial Fibrillation
 Practical Management of Atrial Fibrillation UPDATED JULY 2014 Adapted from the AHA/ACC/HRS 2014 Guideline for the Management of Patients with Atrial Fibrillation Editor: Bradley P. Knight, MD, FACC, FHRS
Practical Management of Atrial Fibrillation UPDATED JULY 2014 Adapted from the AHA/ACC/HRS 2014 Guideline for the Management of Patients with Atrial Fibrillation Editor: Bradley P. Knight, MD, FACC, FHRS
Atrial Fibrillation New Treatment, New Hope. Atrial Fibrillation It Just Sucks. Atrial Fibrillation Disclosure Information 1/30/2014
 New Treatment, New Hope Emerging Concepts And Novel Management Strategies James J. Merrill, MD February 1, 2014 Wellmont CVA Heart Institute Kingsport, TN It Just Sucks We Don t Know What Causes It Or
New Treatment, New Hope Emerging Concepts And Novel Management Strategies James J. Merrill, MD February 1, 2014 Wellmont CVA Heart Institute Kingsport, TN It Just Sucks We Don t Know What Causes It Or
Antiplatelet and Antithrombotics From clinical trials to guidelines
 Antiplatelet and Antithrombotics From clinical trials to guidelines Ashraf Reda, MD, FESC Prof and head of Cardiology Dep. Menofiya University Preisedent of EGYBAC Chairman of WGLVR One of the big stories
Antiplatelet and Antithrombotics From clinical trials to guidelines Ashraf Reda, MD, FESC Prof and head of Cardiology Dep. Menofiya University Preisedent of EGYBAC Chairman of WGLVR One of the big stories
Anticoagulation before and after cardioversion; which and for how long
 Anticoagulation before and after cardioversion; which and for how long Sameh Samir, MD Cardiovascular medicine dept. Tanta faculty of medicine Atrial fibrillation goals of management Identify and treat
Anticoagulation before and after cardioversion; which and for how long Sameh Samir, MD Cardiovascular medicine dept. Tanta faculty of medicine Atrial fibrillation goals of management Identify and treat
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (RATE VS RHYTHM CONTROL)
 ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (RATE VS RHYTHM CONTROL) By Prof. Dr. Helmy A. Bakr Mansoura Universirty 2014 AF Classification: Mechanisms of AF : Selected Risk Factors and Biomarkers for AF: WHY AF? 1. Atrial fibrillation
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (RATE VS RHYTHM CONTROL) By Prof. Dr. Helmy A. Bakr Mansoura Universirty 2014 AF Classification: Mechanisms of AF : Selected Risk Factors and Biomarkers for AF: WHY AF? 1. Atrial fibrillation
Dabigatran: Amber Drug Guidance for the prevention of stroke and systemic embolism in patients with non-valvular AF
 Leeds Dabigatran: Amber Drug Guidance for the prevention of stroke and systemic embolism in patients with non-valvular AF Amber Drug Level 3 (amber drug with monitoring requirements) We have started your
Leeds Dabigatran: Amber Drug Guidance for the prevention of stroke and systemic embolism in patients with non-valvular AF Amber Drug Level 3 (amber drug with monitoring requirements) We have started your
A PRACTICAL REVIEW OF THE NOVEL ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS
 A PRACTICAL REVIEW OF THE NOVEL ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS BRIAN CRYDER, PHARMD BCACP LEARNING OBJECTIVES AS A RESULT OF THIS PRESENTATION, THE AUDIENCE WILL BE ABLE TO 1. DISCUSS THE KEY DIFFERENCES BETWEEN
A PRACTICAL REVIEW OF THE NOVEL ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS BRIAN CRYDER, PHARMD BCACP LEARNING OBJECTIVES AS A RESULT OF THIS PRESENTATION, THE AUDIENCE WILL BE ABLE TO 1. DISCUSS THE KEY DIFFERENCES BETWEEN
Time of Offset of Action The Trial
 New Antithrombotic Agents DISCLOSURE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) Speaker Bureau - None Consultant Amgen Tom DeLoughery, MD FACP FAWM Oregon Health and Sciences University What I am Talking About
New Antithrombotic Agents DISCLOSURE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) Speaker Bureau - None Consultant Amgen Tom DeLoughery, MD FACP FAWM Oregon Health and Sciences University What I am Talking About
Anticoagulation Dosing at UCDMC Indication Agent Standard Dose Comments and Dose Adjustments VTE Prophylaxis All Services UFH 5,000 units SC q 8 h
 Indication Agent Standard Dose Comments and Dose Adjustments VTE Prophylaxis All Services UFH 5,000 units SC q 8 h See EMR adult VTE prophylaxis CI order set Enoxaparin See service specific dosing Assess
Indication Agent Standard Dose Comments and Dose Adjustments VTE Prophylaxis All Services UFH 5,000 units SC q 8 h See EMR adult VTE prophylaxis CI order set Enoxaparin See service specific dosing Assess
New Anticoagulants: Are we Ready to Replace Warfarin? Carole Goodine, RPh Horizon Health Network Stroke Conference 2011
 New Anticoagulants: Are we Ready to Replace Warfarin? Carole Goodine, RPh Horizon Health Network Stroke Conference 2011 Warfarin Decreases stroke risk by 60-70% Superior to ASA and ASA plus clopidogrel
New Anticoagulants: Are we Ready to Replace Warfarin? Carole Goodine, RPh Horizon Health Network Stroke Conference 2011 Warfarin Decreases stroke risk by 60-70% Superior to ASA and ASA plus clopidogrel
ACCIDENT AND EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT/CARDIOLOGY
 Care Pathway Triage category ATRIAL FIBRILLATION PATHWAY ACCIDENT AND EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT/CARDIOLOGY AF/ FLUTTER IS PRIMARY REASON FOR PRESENTATION YES NO ONSET SYMPTOMS OF AF./../ TIME DURATION OF AF
Care Pathway Triage category ATRIAL FIBRILLATION PATHWAY ACCIDENT AND EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT/CARDIOLOGY AF/ FLUTTER IS PRIMARY REASON FOR PRESENTATION YES NO ONSET SYMPTOMS OF AF./../ TIME DURATION OF AF
NORTH WEST LONDON GUIDANCE ANTITHROMBOTIC MANAGEMENT OF ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 North West London CardioVascular & Stroke Network NORTH WEST LONDON GUIDANCE ON ANTITHROMBOTIC MANAGEMENT OF ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Key Messages 1. Efforts should be made to identify patients with Atrial
North West London CardioVascular & Stroke Network NORTH WEST LONDON GUIDANCE ON ANTITHROMBOTIC MANAGEMENT OF ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Key Messages 1. Efforts should be made to identify patients with Atrial
Appendix C Factors to consider when choosing between anticoagulant options and FAQs
 Appendix C Factors to consider when choosing between anticoagulant options and FAQs Choice of anticoagulant for non-valvular* atrial fibrillation: Clinical decision aid Patients should already be screened
Appendix C Factors to consider when choosing between anticoagulant options and FAQs Choice of anticoagulant for non-valvular* atrial fibrillation: Clinical decision aid Patients should already be screened
DVT/PE Management with Rivaroxaban (Xarelto)
 DVT/PE Management with Rivaroxaban (Xarelto) Rivaroxaban is FDA approved for the acute treatment of DVT and PE and reduction in risk of recurrence of DVT and PE. FDA approved indications: Non valvular
DVT/PE Management with Rivaroxaban (Xarelto) Rivaroxaban is FDA approved for the acute treatment of DVT and PE and reduction in risk of recurrence of DVT and PE. FDA approved indications: Non valvular
Atrial fibrillation. Quick reference guide. Issue date: June 2006. The management of atrial fibrillation
 Quick reference guide Issue date: June 2006 Atrial fibrillation The management of atrial fibrillation Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Chronic Conditions Contents Contents Patient-centred
Quick reference guide Issue date: June 2006 Atrial fibrillation The management of atrial fibrillation Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Chronic Conditions Contents Contents Patient-centred
Anticoagulant therapy
 Anticoagulation: The risks Anticoagulant therapy 1990 2002: 600 incidents reported 120 resulted in death of patient 92 deaths related to warfarin usage 28 reports related to heparin usage Incidents in
Anticoagulation: The risks Anticoagulant therapy 1990 2002: 600 incidents reported 120 resulted in death of patient 92 deaths related to warfarin usage 28 reports related to heparin usage Incidents in
NIL. Dr Chuks Ajaero FMCP FRACP Cardiologist QEH, NALHN, SA Heart & Central Districts. Approach. Approach. 06-Nov-14
 Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation: Commencing Non- Oral Anticoagulants in GP setting Dr Chuks Ajaero FMCP FRACP Cardiologist QEH, NALHN, SA Heart & Central Districts Disclosures NIL Classification
Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation: Commencing Non- Oral Anticoagulants in GP setting Dr Chuks Ajaero FMCP FRACP Cardiologist QEH, NALHN, SA Heart & Central Districts Disclosures NIL Classification
4/9/2015. Risk Stratify Our Patients. Stroke Risk in AF: CHADS2 Scoring system JAMA 2001; 285: 2864-71
 Anticoagulation in the 21 st Century Adam Karpman, D.O. Saint Francis Medical Center/Oklahoma State University Medical Center Disclosures: None Atrial Fibrillation Most common arrhythmia in clinical practice.
Anticoagulation in the 21 st Century Adam Karpman, D.O. Saint Francis Medical Center/Oklahoma State University Medical Center Disclosures: None Atrial Fibrillation Most common arrhythmia in clinical practice.
The Emerging Atrial Fibrillation Epidemic: Treat It, Leave It or Burn It?
 The Emerging Atrial Fibrillation Epidemic: Treat It, Leave It or Burn It? Indiana Chapter-ACC 17 th Annual Meeting Indianapolis, Indiana October 19, 2013 Deepak Bhakta MD FACC FACP FAHA FHRS CCDS Associate
The Emerging Atrial Fibrillation Epidemic: Treat It, Leave It or Burn It? Indiana Chapter-ACC 17 th Annual Meeting Indianapolis, Indiana October 19, 2013 Deepak Bhakta MD FACC FACP FAHA FHRS CCDS Associate
Failure or significant adverse effects to all of the alternatives: Eliquis and Xarelto
 This policy has been developed through review of medical literature, consideration of medical necessity, generally accepted medical practice standards, and approved by the IEHP Pharmacy and Therapeutics
This policy has been developed through review of medical literature, consideration of medical necessity, generally accepted medical practice standards, and approved by the IEHP Pharmacy and Therapeutics
New Anticoagulants: When and Why Should I Use Them? Disclosures
 Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University New Anticoagulants: When and Why Should I Use Them? Christine L. Kempton, MD, MSc Associate Professor of Pediatrics and Hematology and Medical Oncology Hemophilia
Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University New Anticoagulants: When and Why Should I Use Them? Christine L. Kempton, MD, MSc Associate Professor of Pediatrics and Hematology and Medical Oncology Hemophilia
Atrial Fibrillation Centre
 About this guide We have prepared this guide to help you to: learn about atrial fibrillation manage atrial fibrillation and reduce the risk of stroke find out about medicines and other treatment options
About this guide We have prepared this guide to help you to: learn about atrial fibrillation manage atrial fibrillation and reduce the risk of stroke find out about medicines and other treatment options
MCHENRY WESTERN LAKE COUNTY EMS SYSTEM OPTIONAL CE ADVANCED LEVEL (EMTP, PHRN, ECRN) August 2013. Anticoagulants
 MCHENRY WESTERN LAKE COUNTY EMS SYSTEM OPTIONAL CE ADVANCED LEVEL (EMTP, PHRN, ECRN) August 2013 Anticoagulants Anticoagulants are agents that prevent the formation of blood clots. Before we can talk about
MCHENRY WESTERN LAKE COUNTY EMS SYSTEM OPTIONAL CE ADVANCED LEVEL (EMTP, PHRN, ECRN) August 2013 Anticoagulants Anticoagulants are agents that prevent the formation of blood clots. Before we can talk about
Thrombosis and Hemostasis
 Thrombosis and Hemostasis Wendy Lim, MD, MSc, FRCPC Associate Professor, Department of Medicine McMaster University, Hamilton, ON Overview To review the important developments in venous thromboembolism
Thrombosis and Hemostasis Wendy Lim, MD, MSc, FRCPC Associate Professor, Department of Medicine McMaster University, Hamilton, ON Overview To review the important developments in venous thromboembolism
New anticoagulants: Monitoring or not Monitoring? Not Monitoring
 The 2 nd World Congress on CONTROVERSIES IN HEMATOLOGY (COHEM) Barcelona, Spain September 6 8, 2012 New anticoagulants: Monitoring or not Monitoring? Not Monitoring Anna Falanga, MD Immunohematology and
The 2 nd World Congress on CONTROVERSIES IN HEMATOLOGY (COHEM) Barcelona, Spain September 6 8, 2012 New anticoagulants: Monitoring or not Monitoring? Not Monitoring Anna Falanga, MD Immunohematology and
