Ear study with 64 slices Multidetector CT
|
|
|
- Harvey Tyler
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cabeza y cuello Puesta al día Ear study with 64 slices Multidetector CT María Lourdes Mallo, Cecilia C. Giordanengo, Carlos A. Bertona, Juan José Bertona, Cecilia Gigena, María Paula Florez Abstract The ear is a complex anatomic structure. Its study and understanding represent a constant challenge for the radiologist. As a consequence, the computed tomography becomes an essential tool for its examination. The conventional tomographic examination with both axial and coronal reconstruction of the image allows a satisfactory visualization of different structures. However, the study requires long periods of time for its acquisition and uncomfortable or intolerable positions for some patients. Besides, the characterization of some ear s structures becomes limited. The 64 slices multidetector computed tomography enables an optimal study of the ear s small and complex anatomy, performing volumetric acquisitions with 0.5 mm slices, which leads to accurate multiplanar reconstructions in the three basic planes, in curved planes and three dimensional reconstructions. These make a detailed visualization of its structures in few seconds, avoiding discomfort in the patients. Our purpose in this article is to demonstrate the utility of reconstructions particularly in oblique planes, reaching an optimal visualization of the temporal bone. Key words: Inner ear. Multidetector computed tomography. Temporal bone. INTRODUCTION From the advent of Computed Tomography (CT), the study of temporal bone structures is limited to axial and coronal (1) orientations, with slices of the lowest thickness (usually of slices between 1 and 3 mm) (2,3). In that way, the identification of smallest and most complex anatomic ear structures is limited. Furthermore, it is necessary to consider time exploration in order to avoid movements and uncomfortable position in coronal plane orientations. The incorporation of 64 slices Multidetector Computed Tomography (64MDCT), by reconstructing the image in any space plane, with acquisition in few seconds and with a tolerable position for all patients, enables a detailed observation of the ear s anatomic repairs and progress in addressing different diseases (3). 64 MDCT PROTOCOL Data Acquisition: The temporal bone CT SCAN was performed in our institution using a 64 channels multidetector scanner Aquilion Toshiba. The exploration was conducted in the standard axial plane with helicoidal technique and volumetric acquisition (120 kv, 200 ma, rotation time of 0,5 seconds, thickness of the section of 0,5mm, matrix 512 l x 512). The head of the patient was located in a neutral position and the time of study was of 4 to 6 seconds. Image reconstruction and post-processing: The data analysis was performed in a Vítrea work station. The temporal bones were visualized in three basic planes (axial, sagital and coronal), reconstructed in isometric way (with the same resolution as the original acquisition) every 0,5, 1 or 2 mm. In addition, there were performed 3D reconstructions, multiplanar and oblique curves, and Maximum Intensity Projections (MIP), according to the structure of clinical interest or as the findings: ossicular chain, round and oval windows,the cochlea, vestibular aqueduct, semicircular canals and facial nerve canal. EXTERNAL EAR It comprises the pinna and external auditory canal (EAC). The EAC has an italic S shape on its way to the tympanic membrane. Its two internal thirds are osseous and slightly narrower than the lateral third, which is cartilaginous. The tympanic membrane shows the intermediate limit of EAC, separating the external ear from the tympanic cavity (2, 5, 6, 7). The exploration of these structures with 64 MDCT, with volumetric and 3D reconstructions allowed a very detailed view of them (Fig. 1), resulting a valuable help in the detection of pathological features (Fig. 2). Servicio de Diagnótico por Imágenes - Clínica Privada, Velez Sarfield, Córdoba - Argentina Correspondencia: María Lourdes Mallo marialma02@hotmail.com Recibido: agosto 2010; aceptado: septiembre 2010 Received: august 2010; accepted: september 2010 SAR-FAARDIT 2010 RAR - Volumen 74 - Número Página 1
2 Ear study with 64 slices Multidetector CT MIDDLE EAR Ossicular chain Hammer and incus The handle of the hammer and the incus are not clearly defined by conventional scan of the temporal bone, which consists on axial and coronal acquisitions (1). Oblique coronal planes (Figs. 3-4), oriented along long axis of these two ossicular structures provide a better identification of them. The oblique sagital plane (Fig. 5) also enables its visualization and provides an alternative to the axial plane for the examination of incude-maleolar joint (8). The reconstruction of this plane of hammer and incus, resemble a molar tooth (9-12) (Fig. 6). These reconstruction planes can be helpful for studying the erosions of the ossicular chain, colesteatoma, traumatic dislocations, and congenital anomalies of the ossicular chain and oval window (10-11). Stapes- oval window The oval window is located laterally to the vestibule, above and behind the promontory. It connects the tympanic cavity with the vestibule and it is occupied by the stapes footplate (2-3). Its longitudinal diameter is of 3-4 mm and its vertical is of 1,5-2 mm. Its conventional topographical visualization is optimum on the coronal plane, and it is not satisfactory visualized on the axial plane (1). A double-oblique orientation of the reconstruction s axial plane enables an optimum exhibition of the stapes and oval window (Fig. 7). An oblique sagital reconstruction is useful to confirm the presence of both branches of the stapes, next to the oval window. The combination of sagital, axial and oblique Fig. 1. 3D reconstruction of external ear with 64 MDCT. (A) skin, (B & C) bone. Fig. 2. 3D reconstruction of external ear with 64 MDCT. (A & B) Atresia of the external bone of EAC, occupied by compact bone (Arrows). (C) Skin fold. Página 2 RAR - Volumen 74 - Número
3 María Lourdes Mallo et al. Fig. 3. CT with Multiplanar Reconstruction (MPR) double oblique coronal of the hammer, shows hammer s head (C), handle (M) and neck (CU). Also, tensor timpani (TT). Fig. 4. CT with double oblique coronal MPR of incus, is visualized the body of the incus (C), short process (SP) and long process (LP). Fig. 6. Incude-malleolar joint, 3D bone reconstruction. Fig. 5. CT with oblique double sagital MPR of incude-malleolar joint (AIM). The incus body (CY), long process (LP); handle of hammer (MM). reconstructions can assist in the evaluation of congenital anomalies, in traumatic dislocations and in fixation of the stapes in patients with hearing loss (10). Round Window The round window is located behind and below the oval window, in a shallow pit. It corresponds to the tympanic orifice of the cochlea s tympanic scale and its diameter is 2 mm (2). It can be clearly represented on axial images (Fig. 8), while it is not possible to do it on the coronal plane, due to its orientation (1). It is more convenient to use oblique sagital reconstructions (Fig. 9). The radiological study of both windows is important in several pathologies, such as otosclerosis and malformations (13). INTERNAL EAR The internal ear is the bone labyrinth which contains the membranous labyrinth (2). Cochlea It is a spiral-shape structure with two and a half turns. It is located anterolateral to the IAC and contains the organ of Corti. Its long axis can be represented in axial or coronal standard images. The 64 MDCT, by oblique reconstructions (Fig. 10), enables the evaluation of superior, middle and inferior turns, as well as the evaluation of the opening of the cochlear nerve. Curve reconstructions enable to unroll the cochlea, getting insight into its morphology and dimensions. Finally, volumetric imaging provides morphological and anatomical detail, which allows to visualize the total of its turns (3-4). RAR - Volumen 74 - Número Página 3
4 Ear study with 64 slices Multidetector CT Semicircular Canals They are constituted by three conducts (superior, posterior and lateral), situated behind and above the vestibule. The superior semicircular canal is orientated in an approximately 90 angle to the long axis of the temporal bone. Coronary images are enough to determine its integrity (1-2-14). Vestibule and vestibular aqueduct The vestibule is part of the internal ear s labyrinth, situated between the semicircular conducts and the cochlea. It contains the utriculus and saculus, which are part of the membranous labyrinth. The aqueduct or vestibular conduct contains the endolymphatic conduct and communicates the vestbiule s saculus with the endolymphatic saculus (2). It is not usually visualized in coronary images and it is hard to see it in axial images (1) (Fig. 11). The vestibular conduct s course is better identified in the sagital plane (Fig. 12), which is useful in the diagnosis of dilated vestibular aqueduct syndrome, an anomaly more common of the osseous labyrinth observed in patients with a deep sensorineural hearing loss (15). Facial nerve canal It is a bony channel where the facial nerve is located in its intratemporal course. It starts at the back of the internal auditory canal. Its first portion, of 4 mm in length, is between the cochlea (front) and the semicircular canals (back). It is often injured in longitudinal bone fractures. The second portion or tympanic portion starts when it bends back, almost at right angle, to follow a parallel path to the lateral semicircular canal. It measures 10 mm long and may be dehiscent. The third portion or descending portion, is 15 mm long and continues to the stylomastoid foramen (2-16). With the image reconstruction in an oblique sagi- Fig. 7. CT with oblique double axial MPR of stapes (E) in the oval window (VO). Fig. 8. axial MPR of round window. Fig. 9. CT with sagital oblique MPR of round window (VR), carotid canal (CC), labyrinthic segment of facial nerve canal (NFL). Fig. 10. cochlea s short axis (Arrow), CT with oblique MPR, where the inferior turn can be observed. Página 4 RAR - Volumen 74 - Número
5 María Lourdes Mallo et al. tal plane (Figs ) and curve reconstructions, the whole longitude between the tympanic and mastoid segments of the facial nerve can be represented in just one image (8-9). The use of this reconstruction plane can help in the diagnosis of the nerve anomalies and fractures in the path of the facial nerve canal. Carotid conduct The intrapetrosal path of the internal carotid artery (ICA) is perfectly visible with a tomography regarding its bone repairs. With 64 MDCT it is also possible to perform angiographic reconstructions for suspected arterial injuries. This requires iodinated contrast injection (Figs. 16, 17 and 18). Cochlear implant 64 MDCT in presurgical study for cochlear implant is an excellent method for anatomical and pathological detail of the temporal bone region (Fig. 18). Volumetric images provide information about the anatomy of the ossicular chain, the inner ear and its relationship to vascular structures, the carotid artery and the internal jugular vein. Curve reconstructions enable to unroll the cochlea, getting insight into its morphology and dimensions. This information is very useful for the i surgeon. In the postsurgical study, 64 MDCT is an excellent method to control the correct positioning of the electrodes of the implant, since it avoids image artifices Fig. 11. CT, standard axial image. Vestibule (V) Posterior semicircular canal (CSP) and lateral (CSL). Fig. 12. CT with MPR, oblique sagital image, where the vestibular conduct is visualized (CV) in its origin, common area of CSS and CSP (ZC). Fig.13. 3D reconstruction: semicircular canals CCS: superior CCL: lateral CCP: posterior. Fig. 14. CT with MRP, oblique sagital image where superior semicircular conducts (CSS) and lateral (CSL) and facial nerve canal (NF) are visualized. RAR - Volumen 74 - Número Página 5
6 Ear study with 64 slices Multidetector CT with an acquisition of submillimetrical slices and optimum resolution (17) in just a few seconds. CONCLUSION 64 Channels MDCT is an excellent imaging method for the study of the ear s anatomy and pathology. It enables through volumetric acquisition with submillimetrical slices in a few seconds and with a comfortable position for the patient, a display on different planes of the space, with three dimensional reconstructions of the ear s anatomy. Therefore, they allow a more comprehensive approach to different pathologies and optimized the planning for possible surgery. Bibliography 1. Venema HW, Phoa SS, Mirck PG, Hulsmans FJ, Majoie CB, Verbeeten B Jr. Petrosal bone: coronal reconstructions from axial spiral CT data obtained with 0.5-mm collimation can replace direct coronal sequential CT scans. Radiology 1999;213(2): Williams PL, Warwick R, Dyson M, Bannister LH, eds. Gray s anatomy. New York: Churchill Livingstone Editors; 1989: Reisser C, Schubert O, Forsting M, Sartor K. Anatomy of the temporal bone: detailed three-dimensional display based on image data from high-resolution helical CT a preliminary report. Am J Otol 1996; 17(3): Calhoun PS, Kuszyk BS, Heath DG, Carley JC, Fishman EK. Three-dimensional volume rendering of spiral CT data: the- Fig. 15. CT with MPR, oblique sagital image where the facial nerve canal, tympanic (NFT) and mastoid (NFM) portions are visualized. Lateral semicircular conduct (CSL). Tensor timpani muscle (MTT). Fig. 16. CT, 3D reconstruction of aneurysm in intrapetrosal portion of ICA. Fig. 17. CT, 3D reconstruction of aneurysm in intrapetrosal portion of ICA. Bone lisis. Fig. 18. CT, MIP reconstruction of aneurysm in intrapetrosal portion of ICA. Página 6 RAR - Volumen 74 - Número
7 María Lourdes Mallo et al. ory and method. RadioGraphics 1999; 19(3): Fatterpekar GM, Doshi AH, Dugar M, Delman BN, Naidich TP, Peter M. Som PM. Continuing Medical Education: Role of 3D CT Evaluation of the Temporal in the Bone. RadioGraphics 2006; 26:S117-S Donaldson JA, Duckert LG, Lambert PM, Rubel EW. Surgical anatomy of the temporal bone. New York: Raven Edit.; 1992: S Curtin HD, Sanelli PC, Som PM. Temporal bone: embryology and anatomy. In: Som PM, Curtin HD, eds. Head and neck imaging. St. Louis: Mosby Edit; 2003: Chuang MT, Chiang IC, Liu GC, Lin WC. Multi-detector row CT demonstration of inner and middle ear structures. Clin Anat 2006; 19(4): Lane JI, Witte RJ, Driscoll CL, Camp JJ, Robb RA. Imaging microscopy of the middle and inner ear. I. CT microscopy. Clin Anat 2004; 17(8): Park K, Moon SK, Cho MJ, Won YY, Baek MG. 3D micro-ct images of ossicles destroyed by middle ear cholesteatoma. Acta Otolaryngol 2004; 124(4): Meriot P, Veillon F, Garcia JF, et al. CT appearance of ossicular injuries. Radiographics 1997; 17(6): Yamada M, Tsunoda A, Muraoka H, Komatsuzaki A. Threedimensional reconstruction of the incudostapedial joint with helical computed tomography. J Laryngol Otol 1999; 113(8): Zeifer B, Sabini P, Sonne J. Congenital absence of the oval window: radiologic diagnosis and associated anomalies. Am J Neuroradiol 2000; 21(2): Lemmerling M, Vanzieleghem B, Dhooge I, Van Cauwenberge P, Kunnen M. CT and MRI of the semicircular canals in the normal and diseased temporal bone. Eur Radiol 2001; 11(7): Berrettini S, Forli F, Bogazzi F, et al. Large vestibular aqueduct syndrome: audiological, radiological, clinical, and genetic features. Am J Otolaryngol 2005; 26(6): Tuccar E, Tekdemir I, Aslan A, Elhan A, Deda H. Radiological anatomy of the intratemporal course of facial nerve. Clin Anat 2000; 13(2): Manual de implante coclear. Medel Medical Electronics, Insbruck (Austria), Accesible en: Fig. 18. CT, 3D images and MPR. Cochlear implant. EXTERNAL: microphone, speech processor, transmitter. INTERNAL: receiver- stimulator: sends signals to the electrodes. Electrodes: stimulate nerve cells inside the cochlea. RAR - Volumen 74 - Número Página 7
A diagram of the ear s structure. The outer ear includes the portion of the ear that we see the pinna/auricle and the ear canal.
 A diagram of the ear s structure THE OUTER EAR The outer ear includes the portion of the ear that we see the pinna/auricle and the ear canal. The pinna or auricle is a concave cartilaginous structure,
A diagram of the ear s structure THE OUTER EAR The outer ear includes the portion of the ear that we see the pinna/auricle and the ear canal. The pinna or auricle is a concave cartilaginous structure,
Surgery for Conductive Hearing Loss
 Surgery for Conductive Hearing Loss What is conductive hearing loss Conductive hearing loss is a form of hearing loss due to abnormalities in mobile portions of the ear. Theses are the movable parts (including
Surgery for Conductive Hearing Loss What is conductive hearing loss Conductive hearing loss is a form of hearing loss due to abnormalities in mobile portions of the ear. Theses are the movable parts (including
Image. 3.11.3 SW Review the anatomy of the EAC and how this plays a role in the spread of tumors.
 Neoplasms of the Ear and Lateral Skull Base Image 3.11.1 SW What are the three most common neoplasms of the auricle? 3.11.2 SW What are the four most common neoplasms of the external auditory canal (EAC)
Neoplasms of the Ear and Lateral Skull Base Image 3.11.1 SW What are the three most common neoplasms of the auricle? 3.11.2 SW What are the four most common neoplasms of the external auditory canal (EAC)
SEMI-IMPLANTABLE AND FULLY IMPLANTABLE MIDDLE EAR HEARING AIDS
 Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Medical Coverage Guideline must be read in its
Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Medical Coverage Guideline must be read in its
GONCA SENNAROĞLU PhD LEVENT SENNAROĞLU MD. Department of Otolaryngology Hacettepe University ANKARA, TURKEY
 GONCA SENNAROĞLU PhD LEVENT SENNAROĞLU MD Department of Otolaryngology Hacettepe University ANKARA, TURKEY To present the audiological findings and rehabilitative outcomes of CI in children with cochlear
GONCA SENNAROĞLU PhD LEVENT SENNAROĞLU MD Department of Otolaryngology Hacettepe University ANKARA, TURKEY To present the audiological findings and rehabilitative outcomes of CI in children with cochlear
Auditory System. Chaos Healthcare
 Medical Coding Auditory System Chaos Healthcare AUDITORY SYSTEM: Anatomy AUDITORY SYSTEM: Physiology AUDITORY SYSTEM MYRINGOPLASTY: Myringoplasty is an operative procedure used in the reconstruction of
Medical Coding Auditory System Chaos Healthcare AUDITORY SYSTEM: Anatomy AUDITORY SYSTEM: Physiology AUDITORY SYSTEM MYRINGOPLASTY: Myringoplasty is an operative procedure used in the reconstruction of
Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing (added 09/06)
 Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing (added 09/06) 1. Briefly review the anatomy of the cochlea. What is the cochlear blood supply? SW 2. Discuss the effects of the pinna, head and ear canal on the transmission
Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing (added 09/06) 1. Briefly review the anatomy of the cochlea. What is the cochlear blood supply? SW 2. Discuss the effects of the pinna, head and ear canal on the transmission
Middle ear conditions
 Middle ear conditions Middle ear conditions This factsheet is part of our Ears and ear problems range. It is written for people who have been diagnosed with a condition that affects the middle ear. Read
Middle ear conditions Middle ear conditions This factsheet is part of our Ears and ear problems range. It is written for people who have been diagnosed with a condition that affects the middle ear. Read
Light wear for a powerful hearing. Bone Conduction Headset
 Light wear for a powerful hearing Bone Conduction Headset 2 Light wear for a powerful hearing Melody Flex, the new bone conduction headset is AUTEL s solution to improve hearing quality of those affected
Light wear for a powerful hearing Bone Conduction Headset 2 Light wear for a powerful hearing Melody Flex, the new bone conduction headset is AUTEL s solution to improve hearing quality of those affected
Diseases of the middle ear
 Diseases of the middle ear Acute Suppurative Otitis Media: Acute suppurative otitis media may be viral or bacterial and is accompanied by signs of pain, pressure sensation, diminished hearing and occasional
Diseases of the middle ear Acute Suppurative Otitis Media: Acute suppurative otitis media may be viral or bacterial and is accompanied by signs of pain, pressure sensation, diminished hearing and occasional
So, how do we hear? outer middle ear inner ear
 The ability to hear is critical to understanding the world around us. The human ear is a fully developed part of our bodies at birth and responds to sounds that are very faint as well as sounds that are
The ability to hear is critical to understanding the world around us. The human ear is a fully developed part of our bodies at birth and responds to sounds that are very faint as well as sounds that are
Less common vestibular disorders presenting with funny turns
 Less common vestibular disorders presenting with funny turns Charlotte Agrup, Department of Neuro-otology, The National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery, London Making the diagnosis Making the diagnosis
Less common vestibular disorders presenting with funny turns Charlotte Agrup, Department of Neuro-otology, The National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery, London Making the diagnosis Making the diagnosis
Voxar 3D TM. A suite of advanced visualization and analysis software tools
 Voxar 3D TM A suite of advanced visualization and analysis software tools The power to deliver advanced visualization throughout the enterprise To effectively manage the rapid growth of large volumetric
Voxar 3D TM A suite of advanced visualization and analysis software tools The power to deliver advanced visualization throughout the enterprise To effectively manage the rapid growth of large volumetric
Objectives AXIAL SKELETON. 1. Frontal Bone. 2. Parietal Bones. 3. Temporal Bones. CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired)
 Objectives AXIAL SKELETON SKULL 1. On a skull or diagram, identify and name the bones of the skull 2. Identify the structure and function of the bones of the skull 3. Describe how a fetal skull differs
Objectives AXIAL SKELETON SKULL 1. On a skull or diagram, identify and name the bones of the skull 2. Identify the structure and function of the bones of the skull 3. Describe how a fetal skull differs
Twelve. Figure 12.1: 3D Curved MPR Viewer Window
 Twelve The 3D Curved MPR Viewer This Chapter describes how to visualize and reformat a 3D dataset in a Curved MPR plane: Curved Planar Reformation (CPR). The 3D Curved MPR Viewer is a window opened from
Twelve The 3D Curved MPR Viewer This Chapter describes how to visualize and reformat a 3D dataset in a Curved MPR plane: Curved Planar Reformation (CPR). The 3D Curved MPR Viewer is a window opened from
Spiral CT: Single and Multiple Detector Systems. AAPM Refresher Course Nashville, TN July 28,1999
 Spiral CT: Single and Multiple Detector Systems AAPM Refresher Course Nashville, TN July 28,1999 Mike McNitt-Gray, PhD, DABR Assistant Professor UCLA Radiological Sciences mmcnittgray@mednet.ucla.edu X-Ray
Spiral CT: Single and Multiple Detector Systems AAPM Refresher Course Nashville, TN July 28,1999 Mike McNitt-Gray, PhD, DABR Assistant Professor UCLA Radiological Sciences mmcnittgray@mednet.ucla.edu X-Ray
DENTAL Cone beam 3D X-RAY SYSTEM with
 VERSATILE INTUITIVE efficient DENTAL Cone beam 3D X-RAY SYSTEM with dedicated panoramic imaging With thirty years of experience in designing and manufacturing state-of-the-art dental panoramic and tomographic
VERSATILE INTUITIVE efficient DENTAL Cone beam 3D X-RAY SYSTEM with dedicated panoramic imaging With thirty years of experience in designing and manufacturing state-of-the-art dental panoramic and tomographic
BONE-CONDUCTION HEARING AIDS
 BONE-CONDUCTION HEARING AIDS Introduction Conventional hearing aids fit in the ear canal and amplify sounds, which the hearing aid user then hears in the normal way. However, these hearing aids are not
BONE-CONDUCTION HEARING AIDS Introduction Conventional hearing aids fit in the ear canal and amplify sounds, which the hearing aid user then hears in the normal way. However, these hearing aids are not
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery
 Chapter 1 Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery 1 H.M. Mayer Primum non nocere First do no harm In the long history of surgery it always has been a basic principle to restrict the iatrogenic trauma done to
Chapter 1 Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery 1 H.M. Mayer Primum non nocere First do no harm In the long history of surgery it always has been a basic principle to restrict the iatrogenic trauma done to
Bone Anchored Hearing Aids B.A.H.A
 Bone Anchored Hearing Aids B.A.H.A Dr. Abdulrahman Hagr MBBS FRCS(c) Assistant Professor King Saud University Otolaryngology Consultant Otologist, Neurotologist & Skull Base Surgeon King Abdulaziz Hospital
Bone Anchored Hearing Aids B.A.H.A Dr. Abdulrahman Hagr MBBS FRCS(c) Assistant Professor King Saud University Otolaryngology Consultant Otologist, Neurotologist & Skull Base Surgeon King Abdulaziz Hospital
Student name: Lesson Objective(s):
 Lesson Objective(s): 1. Describe the processes at work in the vestibular system when the human body responds to circular motion. 2. Describe the role of the vestibular system when the human body responds
Lesson Objective(s): 1. Describe the processes at work in the vestibular system when the human body responds to circular motion. 2. Describe the role of the vestibular system when the human body responds
AP Psychology ~ Ms. Justice
 AP Psychology ~ Ms. Justice 8: What are the characteristics of air pressure waves that we hear as sound? Audition Audition, or hearing, is highly adaptive. We hear a wide range of sounds, but we hear best
AP Psychology ~ Ms. Justice 8: What are the characteristics of air pressure waves that we hear as sound? Audition Audition, or hearing, is highly adaptive. We hear a wide range of sounds, but we hear best
COCHLEAR NERVE APLASIA : THE AUDIOLOGIC PERSPECTIVE A CASE REPORT. Eva Orzan, MD Pediatric Audiology University Hospital of Padova, Italy
 COCHLEAR NERVE APLASIA : THE AUDIOLOGIC PERSPECTIVE A CASE REPORT Eva Orzan, MD Pediatric Audiology University Hospital of Padova, Italy Congenital absence or underdevelopment of the cochlear nerve has
COCHLEAR NERVE APLASIA : THE AUDIOLOGIC PERSPECTIVE A CASE REPORT Eva Orzan, MD Pediatric Audiology University Hospital of Padova, Italy Congenital absence or underdevelopment of the cochlear nerve has
Cochlear Implant, Bone Anchored Hearing Aids, and Auditory Brainstem Implant
 Origination: 06/23/08 Revised: 10/13/14 Annual Review: 11/12/15 Purpose: To provide cochlear implant, bone anchored hearing aids, and auditory brainstem implant guidelines for the Medical Department staff
Origination: 06/23/08 Revised: 10/13/14 Annual Review: 11/12/15 Purpose: To provide cochlear implant, bone anchored hearing aids, and auditory brainstem implant guidelines for the Medical Department staff
Imaging of Thoracic Endovascular Stent-Grafts
 Imaging of Thoracic Endovascular Stent-Grafts Tariq Hameed, M.D. Department of Radiology and Imaging Sciences, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, Indiana Disclosures: No relevant financial
Imaging of Thoracic Endovascular Stent-Grafts Tariq Hameed, M.D. Department of Radiology and Imaging Sciences, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, Indiana Disclosures: No relevant financial
Purchasing a cardiac CT scanner: What the radiologist needs to know
 Purchasing a cardiac CT scanner: What the radiologist needs to know Maria Lewis ImPACT St George s Hospital, London maria.lewis@stgeorges.nhs.uk CT scanner development Slice wars 1998 Increased z-coverage
Purchasing a cardiac CT scanner: What the radiologist needs to know Maria Lewis ImPACT St George s Hospital, London maria.lewis@stgeorges.nhs.uk CT scanner development Slice wars 1998 Increased z-coverage
COCHLEAR IMPLANTATION IN A PATIENT WITH LARGE VESTIBULAR AQUEDUCT SYNDROME: A CASE REPORT GENİŞ VESTİBÜLER SENDROMLU HASTADA KOKLEAR İMPLANTASYON
 CASE REPORT COCHLEAR IMPLANTATION IN A PATIENT WITH LARGE VESTIBULAR AQUEDUCT SYNDROME: A CASE REPORT Ufuk Derinsu, Ayça Çiprut, Sezer Külekçi, Ferda Akdaş Sub-department of Audiology, Department of Otorhinolaryngology,
CASE REPORT COCHLEAR IMPLANTATION IN A PATIENT WITH LARGE VESTIBULAR AQUEDUCT SYNDROME: A CASE REPORT Ufuk Derinsu, Ayça Çiprut, Sezer Külekçi, Ferda Akdaş Sub-department of Audiology, Department of Otorhinolaryngology,
Lecture 4: Jan 12, 2005
 EE516 Computer Speech Processing Winter 2005 Lecture 4: Jan 12, 2005 Lecturer: Prof: J. Bilmes University of Washington Dept. of Electrical Engineering Scribe: Scott Philips
EE516 Computer Speech Processing Winter 2005 Lecture 4: Jan 12, 2005 Lecturer: Prof: J. Bilmes University of Washington Dept. of Electrical Engineering Scribe: Scott Philips
Your Hearing ILLUMINATED
 Your Hearing ILLUMINATED INFORMATION FROM YOUR HEARING CARE PROFESSIONAL REDISCOVER your hearing and reconnect 1 with the important things you might have been missing. Your sense of hearing is a vital
Your Hearing ILLUMINATED INFORMATION FROM YOUR HEARING CARE PROFESSIONAL REDISCOVER your hearing and reconnect 1 with the important things you might have been missing. Your sense of hearing is a vital
Michigan Ear Institute. Cochlear Implant.
 Michigan Ear Institute Cochlear Implant www.michiganear.com DOCTORS Jack M. Kartush, MD Dennis I. Bojrab, MD Michael J. LaRouere, MD John J. Zappia, MD, FACS Eric W. Sargent, MD, FACS Seilesh C. Babu,
Michigan Ear Institute Cochlear Implant www.michiganear.com DOCTORS Jack M. Kartush, MD Dennis I. Bojrab, MD Michael J. LaRouere, MD John J. Zappia, MD, FACS Eric W. Sargent, MD, FACS Seilesh C. Babu,
Use of Three-Dimensional Computerized Tomography Reconstruction in Complex Facial Trauma
 Use of Three-Dimensional Computerized Tomography Reconstruction in Complex Facial Trauma Kapil Saigal, M.D., 1 Ronald S. Winokur, B.S., 2 Steven Finden, D.D.S., M.D., 3 Daniel Taub, D.D.S., M.D., 4 and
Use of Three-Dimensional Computerized Tomography Reconstruction in Complex Facial Trauma Kapil Saigal, M.D., 1 Ronald S. Winokur, B.S., 2 Steven Finden, D.D.S., M.D., 3 Daniel Taub, D.D.S., M.D., 4 and
Thinking ahead. Focused on life. REALIZED: GROUNDBREAKING RESOLUTION OF 80 µm VOXEL
 Thinking ahead. Focused on life. REALIZED: GROUNDBREAKING RESOLUTION OF 80 µm VOXEL X-ray ZOOM RECONSTRUCTION Flat Panel Detector (FPD) Automatic Positioning Function For ø 40 x H 40 mm, ø 60 x H 60 mm,
Thinking ahead. Focused on life. REALIZED: GROUNDBREAKING RESOLUTION OF 80 µm VOXEL X-ray ZOOM RECONSTRUCTION Flat Panel Detector (FPD) Automatic Positioning Function For ø 40 x H 40 mm, ø 60 x H 60 mm,
Enlarged Vestibular Aqueduct Syndrome
 PO BOX 13305 PORTLAND, OR 97213 FAX: (503) 229-8064 (800) 837-8428 INFO@VESTIBULAR.ORG WWW.VESTIBULAR.ORG Enlarged Vestibular Aqueduct Syndrome (EVAS) By Hamid, MD, PhD, EE, The Cleveland Hearing & Balance
PO BOX 13305 PORTLAND, OR 97213 FAX: (503) 229-8064 (800) 837-8428 INFO@VESTIBULAR.ORG WWW.VESTIBULAR.ORG Enlarged Vestibular Aqueduct Syndrome (EVAS) By Hamid, MD, PhD, EE, The Cleveland Hearing & Balance
C-shaped root canal system in mandibular second molars in a Chinese population evaluated by cone-beam computed tomography
 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2011.01896.x C-shaped root canal system in mandibular second molars in a Chinese population evaluated by cone-beam computed tomography Q. Zheng 1, L. Zhang 1, X. Zhou 2, Q. Wang
doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2011.01896.x C-shaped root canal system in mandibular second molars in a Chinese population evaluated by cone-beam computed tomography Q. Zheng 1, L. Zhang 1, X. Zhou 2, Q. Wang
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Bone Anchored Hearing Aids. April 2013. Reference: NHSCB/ D09/P/a
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Bone Anchored Hearing Aids April 2013 Reference: NHSCB/ D09/P/a NHS Commissioning Board Clinical Commissioning Policy: Bone Anchored Hearing Aids First published: April 2013
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Bone Anchored Hearing Aids April 2013 Reference: NHSCB/ D09/P/a NHS Commissioning Board Clinical Commissioning Policy: Bone Anchored Hearing Aids First published: April 2013
DURATION OF HEARING LOSS
 When your child is diagnosed with a hearing loss, it may be very overwhelming. This may be a difficult time for you and your family. However, gaining a greater knowledge in this area is crucial in helping
When your child is diagnosed with a hearing loss, it may be very overwhelming. This may be a difficult time for you and your family. However, gaining a greater knowledge in this area is crucial in helping
Quantitative Comparison of Conventional and Oblique MRI for Detection of Herniated Spinal Discs
 Quantitative Comparison of Conventional and Oblique MRI for Detection of Herniated Spinal Discs Doug Dean ENGN 2500: Medical Image Analysis Final Project Outline Introduction to the problem Based on paper:
Quantitative Comparison of Conventional and Oblique MRI for Detection of Herniated Spinal Discs Doug Dean ENGN 2500: Medical Image Analysis Final Project Outline Introduction to the problem Based on paper:
Hearing and Deafness 1. Anatomy & physiology
 Hearing and Deafness 1. Anatomy & physiology Chris Darwin Web site for lectures, lecture notes and filtering lab: http://www.lifesci.susx.ac.uk/home/chris_darwin/ safari 1 Outer, middle & inner ear Capture;
Hearing and Deafness 1. Anatomy & physiology Chris Darwin Web site for lectures, lecture notes and filtering lab: http://www.lifesci.susx.ac.uk/home/chris_darwin/ safari 1 Outer, middle & inner ear Capture;
Temporomandibular Joint Imaging Using CBCT: Technology Now Captures Reality!
 Temporomandibular Joint Imaging Using CBCT: Technology Now Captures Reality! Dale A. Miles BA, DDS, MS, FRCD (C) Diplomate, American Board of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology Diplomate, American Board
Temporomandibular Joint Imaging Using CBCT: Technology Now Captures Reality! Dale A. Miles BA, DDS, MS, FRCD (C) Diplomate, American Board of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology Diplomate, American Board
A MORPHOMETRIC STUDY OF THE PEDICLES IN DRY HUMAN TYPICAL THORACIC VERTEBRAE
 IJCRR Research Article A MORPHOMETRIC STUDY OF THE PEDICLES IN DRY HUMAN TYPICAL THORACIC VERTEBRAE Dhaval K. Patil, Pritha S. Bhuiyan Department of Anatomy, Seth G S Medical College, Parel, Mumbai-12,
IJCRR Research Article A MORPHOMETRIC STUDY OF THE PEDICLES IN DRY HUMAN TYPICAL THORACIC VERTEBRAE Dhaval K. Patil, Pritha S. Bhuiyan Department of Anatomy, Seth G S Medical College, Parel, Mumbai-12,
- Review ear anatomy. Evaluation of Hearing. - Specific causes of hearing loss
 Hearing Loss in Primary Care Aaron C. Moberly, MD Otolaryngologist Department of Otorhinolaryngology The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Overview - Review ear anatomy - Evaluation of hearing
Hearing Loss in Primary Care Aaron C. Moberly, MD Otolaryngologist Department of Otorhinolaryngology The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Overview - Review ear anatomy - Evaluation of hearing
What is the microbiology of acute otitis media for different age groups? Recommended therapy?
 Number Complications of Otitis Media 3.7.1 Matt What is the microbiology of acute otitis media for different age groups? Recommended therapy? 3.7.2 Matt What are the routes of spread of infection from
Number Complications of Otitis Media 3.7.1 Matt What is the microbiology of acute otitis media for different age groups? Recommended therapy? 3.7.2 Matt What are the routes of spread of infection from
Cochlear Implants, Osseointegrated Bone Conduction Hearing Devices, and Other Implantable Devices
 Chapter 15 Cochlear Implants, Osseointegrated Bone Conduction Hearing Devices, and Other Implantable Devices Seilesh Babu, Paulette McDonald, and Eric Sargent Introduction The cochlear implant is an electronic
Chapter 15 Cochlear Implants, Osseointegrated Bone Conduction Hearing Devices, and Other Implantable Devices Seilesh Babu, Paulette McDonald, and Eric Sargent Introduction The cochlear implant is an electronic
No conflicts of interest to disclose No off-label medication or device use to disclose Research support by NIH but not related to this presentation
 Pediatric Neuroradiology and Neuroanatomy for the Audiologist Matthew L. Bush, MD Assistant Professor, Division of Otology, Neurotology, and Cranial Base Surgery Dept. of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery
Pediatric Neuroradiology and Neuroanatomy for the Audiologist Matthew L. Bush, MD Assistant Professor, Division of Otology, Neurotology, and Cranial Base Surgery Dept. of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery
Acute abdominal pain in the elderly patient: Impact of early MDCT examination on diagnosis and management
 Acute abdominal pain in the elderly patient: Impact of early MDCT examination on diagnosis and management Poster No.: C-1464 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Scientific Exhibit GI Tract Authors: A. Pinto,
Acute abdominal pain in the elderly patient: Impact of early MDCT examination on diagnosis and management Poster No.: C-1464 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Scientific Exhibit GI Tract Authors: A. Pinto,
Getting a Cochlear Implant
 Cochlear Implants Getting a Cochlear Implant the journey to better hearing 1 All of life s journeys depend on taking the first step determining how to get from where you are to where you want to go. This
Cochlear Implants Getting a Cochlear Implant the journey to better hearing 1 All of life s journeys depend on taking the first step determining how to get from where you are to where you want to go. This
A new cone beam computerized tomography system for use in endodontic surgery
 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01198.x CASE REPORT A new cone beam computerized tomography system for use in endodontic surgery T. Tsurumachi 1 & K. Honda 2 1 Department of Endodontics, Division of Advanced
doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01198.x CASE REPORT A new cone beam computerized tomography system for use in endodontic surgery T. Tsurumachi 1 & K. Honda 2 1 Department of Endodontics, Division of Advanced
Ear, Nose, Throat, Teeth and the Jaw
 Many people suffer from ear related problems, such as ear pain, a feeling of pressure or fullness of the ear, or ringing of the ear. If you suffer from any of these symptoms, it may surprise you to learn
Many people suffer from ear related problems, such as ear pain, a feeling of pressure or fullness of the ear, or ringing of the ear. If you suffer from any of these symptoms, it may surprise you to learn
Audiology Services. Carolyn Dando Audiology Services Manager South Warwickshire NHS
 Audiology Services Carolyn Dando Audiology Services Manager South Warwickshire NHS What are we going to cover today? General overview of the ear Hearing loss Hearing assessments, results Hearing aids Paediatric
Audiology Services Carolyn Dando Audiology Services Manager South Warwickshire NHS What are we going to cover today? General overview of the ear Hearing loss Hearing assessments, results Hearing aids Paediatric
Autonomic Nervous System of the Neck. Adam Koleśnik, MD Department of Descriptive and Clinical Anatomy Center of Biostructure Research, MUW
 Autonomic Nervous System of the Neck Adam Koleśnik, MD Department of Descriptive and Clinical Anatomy Center of Biostructure Research, MUW Autonomic nervous system sympathetic parasympathetic enteric Autonomic
Autonomic Nervous System of the Neck Adam Koleśnik, MD Department of Descriptive and Clinical Anatomy Center of Biostructure Research, MUW Autonomic nervous system sympathetic parasympathetic enteric Autonomic
AI CPT Codes. x x. 70336 MRI Magnetic resonance (eg, proton) imaging, temporomandibular joint(s)
 Code Category Description Auth Required Medicaid Medicare 0126T IMT Testing Common carotid intima-media thickness (IMT) study for evaluation of atherosclerotic burden or coronary heart disease risk factor
Code Category Description Auth Required Medicaid Medicare 0126T IMT Testing Common carotid intima-media thickness (IMT) study for evaluation of atherosclerotic burden or coronary heart disease risk factor
DEVELOPMENT OF AN IMAGING SYSTEM FOR THE CHARACTERIZATION OF THE THORACIC AORTA.
 DEVELOPMENT OF AN IMAGING SYSTEM FOR THE CHARACTERIZATION OF THE THORACIC AORTA. Juan Antonio Martínez Mera Centro Singular de Investigación en Tecnoloxías da Información Universidade de Santiago de Compostela
DEVELOPMENT OF AN IMAGING SYSTEM FOR THE CHARACTERIZATION OF THE THORACIC AORTA. Juan Antonio Martínez Mera Centro Singular de Investigación en Tecnoloxías da Información Universidade de Santiago de Compostela
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)? Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a valuable diagnostic study that has been used
Magnetic Resonance Imaging North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)? Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a valuable diagnostic study that has been used
R/F. Efforts to Reduce Exposure Dose in Chest Tomosynthesis Targeting Lung Cancer Screening. 3. Utility of Chest Tomosynthesis. 1.
 R/F Efforts to Reduce Exposure Dose in Chest Tomosynthesis Targeting Lung Cancer Screening Department of Radiology, National Cancer Center Hospital East Kaoru Shimizu Ms. Kaoru Shimizu 1. Introduction
R/F Efforts to Reduce Exposure Dose in Chest Tomosynthesis Targeting Lung Cancer Screening Department of Radiology, National Cancer Center Hospital East Kaoru Shimizu Ms. Kaoru Shimizu 1. Introduction
 THE EARS IN CHARGE FOR THE PHYSICIAN Sandra L.H. Davenport, M.D. SensoryGenetic/Neuro-development, 5801 Southwood Drive, Bloomington MN 55437-1739 952-831-5522 slhdaven@tc.umn.edu Udayan K. Shah, M.D.
THE EARS IN CHARGE FOR THE PHYSICIAN Sandra L.H. Davenport, M.D. SensoryGenetic/Neuro-development, 5801 Southwood Drive, Bloomington MN 55437-1739 952-831-5522 slhdaven@tc.umn.edu Udayan K. Shah, M.D.
Vibrant Soundbridge Implantable Hearing System
 Vibrant Soundbridge Implantable Hearing System Kristin M. Avitabile, MS, CCC-A Clinical Manager, Southeastern U.S. MED-EL Corporation Hearing Technology Hearing Aids Mild to severe HL Problems with feedback
Vibrant Soundbridge Implantable Hearing System Kristin M. Avitabile, MS, CCC-A Clinical Manager, Southeastern U.S. MED-EL Corporation Hearing Technology Hearing Aids Mild to severe HL Problems with feedback
Multi-slice Helical CT Scanning of the Chest
 Multi-slice Helical CT Scanning of the Chest Comparison of different low-dose acquisitions Lung cancer is the main cause of deaths due to cancer in human males and the incidence is constantly increasing.
Multi-slice Helical CT Scanning of the Chest Comparison of different low-dose acquisitions Lung cancer is the main cause of deaths due to cancer in human males and the incidence is constantly increasing.
Construction of human knee bone joint model using FDM based 3D Printer from CT scan images.
 Biomedical Research 2015; 26 (4): S1-5 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Construction of human knee bone joint model using FDM based 3D Printer from CT scan images. Marlon Jones Louis a *, R. Malayalamurthi
Biomedical Research 2015; 26 (4): S1-5 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Construction of human knee bone joint model using FDM based 3D Printer from CT scan images. Marlon Jones Louis a *, R. Malayalamurthi
Sonographic Demonstration of Couinaud s Liver Segments
 PICTORIL ESSY Sonographic Demonstration of Couinaud s Liver Segments Dean Smith, MD, FRCPC, Donal Downey, M, Ch, FRCPC, lison Spouge, MD, FRCPC, Sue Soney, RT, RDMS, RCMS The segmental localization of
PICTORIL ESSY Sonographic Demonstration of Couinaud s Liver Segments Dean Smith, MD, FRCPC, Donal Downey, M, Ch, FRCPC, lison Spouge, MD, FRCPC, Sue Soney, RT, RDMS, RCMS The segmental localization of
CONVENTIONAL AND DIGITAL HEARING AIDS
 CONVENTIONAL AND DIGITAL HEARING AIDS Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Medical
CONVENTIONAL AND DIGITAL HEARING AIDS Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Medical
Help maintain homeostasis by capturing stimuli from the external environment and relaying them to the brain for processing.
 The Sense Organs... (page 409) Help maintain homeostasis by capturing stimuli from the external environment and relaying them to the brain for processing. Ex. Eye structure - protected by bony ridges and
The Sense Organs... (page 409) Help maintain homeostasis by capturing stimuli from the external environment and relaying them to the brain for processing. Ex. Eye structure - protected by bony ridges and
DISEASES OF THE EAR AND MASTOID PROCESS (380-389) 380.00 Perichondritis of pinna, unspecified
 DISEASES OF THE EAR AND MASTOID PROCESS (380-389) 380 Disorders of external ear 380.0 Perichondritis of pinna Perichondritis of auricle 380.00 Perichondritis of pinna, unspecified 380.01 Acute perichondritis
DISEASES OF THE EAR AND MASTOID PROCESS (380-389) 380 Disorders of external ear 380.0 Perichondritis of pinna Perichondritis of auricle 380.00 Perichondritis of pinna, unspecified 380.01 Acute perichondritis
X-Plain Perforated Ear Drum Reference Summary
 X-Plain Perforated Ear Drum Reference Summary Introduction Perforated eardrum is a common condition. The eardrum is a thin layer of tissue at the end of the ear canal inside the ear. Eardrum perforations
X-Plain Perforated Ear Drum Reference Summary Introduction Perforated eardrum is a common condition. The eardrum is a thin layer of tissue at the end of the ear canal inside the ear. Eardrum perforations
Why does my child have a hearing loss?
 Introduction This factsheet will tell you about the range of tests that can be carried out to try to find the cause of your child s hearing loss. The process to find out why a child is deaf is sometimes
Introduction This factsheet will tell you about the range of tests that can be carried out to try to find the cause of your child s hearing loss. The process to find out why a child is deaf is sometimes
Implantable Bone Conduction Clinical Coverage Policy No: 1A-36 Hearing Aids (BAHA) Amended Date: October 1, 2015.
 Implantable Bone Conduction Clinical Coverage Policy No: 1A-36 Table of Contents 1.0 Description of the Procedure, Product, or Service... 1 1.1 Conductive Hearing Loss... 1 1.2 Sensorineural Hearing Loss...
Implantable Bone Conduction Clinical Coverage Policy No: 1A-36 Table of Contents 1.0 Description of the Procedure, Product, or Service... 1 1.1 Conductive Hearing Loss... 1 1.2 Sensorineural Hearing Loss...
Cardiac CT for Calcium Scoring
 Scan for mobile link. Cardiac CT for Calcium Scoring Cardiac computed tomography (CT) for Calcium Scoring uses special x-ray equipment to produce pictures of the coronary arteries to determine if they
Scan for mobile link. Cardiac CT for Calcium Scoring Cardiac computed tomography (CT) for Calcium Scoring uses special x-ray equipment to produce pictures of the coronary arteries to determine if they
Noice induced hearing loss, Ototoxic drugs, Meniers disease, Rotataory vertigo, Sensorineural hearing loss, Tinnitis, Infections, Acoustic neuroma,
 Disorders of hearing and balance LEARNING OBJECTIVE At the end of lecture student must be able to know, Hearing disorders, Types of hearing disorders, Functional classification, Causes, Middle ear disorders,
Disorders of hearing and balance LEARNING OBJECTIVE At the end of lecture student must be able to know, Hearing disorders, Types of hearing disorders, Functional classification, Causes, Middle ear disorders,
Prevalence of otological disorders in diabetic patients with hearing loss
 Prevalence of otological disorders in diabetic patients with hearing loss Manche Santoshi Kumari *, Jangala Madhavi *, Koralla Raja Meganadh *, Akka Jyothy Institute of Genetics and Hospital for Genetic
Prevalence of otological disorders in diabetic patients with hearing loss Manche Santoshi Kumari *, Jangala Madhavi *, Koralla Raja Meganadh *, Akka Jyothy Institute of Genetics and Hospital for Genetic
Key words maxillary sinus, posterior teeth roots. Introduction. Tikrit Journal for Dental Sciences 1(2012)81-88
 Tikrit Journal for Dental Sciences 1(2012)81-88 The Relation of Maxillary Posterior Teeth Roots to the Maxillary Sinus Floor Using Panoramic and Computed Tomography Imaging in a Sample of Kurdish People
Tikrit Journal for Dental Sciences 1(2012)81-88 The Relation of Maxillary Posterior Teeth Roots to the Maxillary Sinus Floor Using Panoramic and Computed Tomography Imaging in a Sample of Kurdish People
X-ray (Radiography) - Bone
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Bone Bone x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of any bone in the body. It is commonly used to diagnose fractured bones or
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Bone Bone x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of any bone in the body. It is commonly used to diagnose fractured bones or
Simplified surgery. Personalized performance.
 Simplified surgery. Personalized performance. VISIONAIRE Patient Matched Technology Accuracy Advanced surgical precision, resulting in reproducible outcomes Efficiency Simplifying surgery, reducing costs,
Simplified surgery. Personalized performance. VISIONAIRE Patient Matched Technology Accuracy Advanced surgical precision, resulting in reproducible outcomes Efficiency Simplifying surgery, reducing costs,
SPECT/CT Wrist. Wrist pain 3/27/2012
 Wrist pain Wrist joint - complicated anatomy complex biomechanics Imaging and management of wrist pain presents a significant challenge Significant economic burden SPECT/CT Wrist HK Mohan GSTT London Intra-capsular
Wrist pain Wrist joint - complicated anatomy complex biomechanics Imaging and management of wrist pain presents a significant challenge Significant economic burden SPECT/CT Wrist HK Mohan GSTT London Intra-capsular
Jennifer A. Defant, M.S., C.G.C. Certified Genetic Counselor Division of Genetics and Metabolism University of Florida
 Jennifer A. Defant, M.S., C.G.C. Certified Genetic Counselor Division of Genetics and Metabolism University of Florida 60% of childhood hearing loss is genetic Syndromic Nonsyndromic 40% of childhood hearing
Jennifer A. Defant, M.S., C.G.C. Certified Genetic Counselor Division of Genetics and Metabolism University of Florida 60% of childhood hearing loss is genetic Syndromic Nonsyndromic 40% of childhood hearing
ANTERIOR CERVICAL DISCECTOMY AND FUSION. Basic Anatomical Landmarks: Anterior Cervical Spine
 Anterior In the human anatomy, referring to the front surface of the body or position of one structure relative to another Cervical Relating to the neck, in the spine relating to the first seven vertebrae
Anterior In the human anatomy, referring to the front surface of the body or position of one structure relative to another Cervical Relating to the neck, in the spine relating to the first seven vertebrae
Hearing Aids - Adult HEARING AIDS - ADULT HS-159. Policy Number: HS-159. Original Effective Date: 3/18/2010. Revised Date(s): 3/18/2011; 3/1/2012
 Harmony Behavioral Health, Inc. Harmony Behavioral Health of Florida, Inc. Harmony Health Plan of Illinois, Inc. HealthEase of Florida, Inc. Ohana Health Plan, a plan offered by WellCare Health Insurance
Harmony Behavioral Health, Inc. Harmony Behavioral Health of Florida, Inc. Harmony Health Plan of Illinois, Inc. HealthEase of Florida, Inc. Ohana Health Plan, a plan offered by WellCare Health Insurance
Oftentimes, as implant surgeons, we are
 CLINICAL AVOIDING INJURY TO THE INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE BY ROUTINE USE OF INTRAOPERATIVE RADIOGRAPHS DURING IMPLANT PLACEMENT Jeffrey Burstein, DDS, MD; Chris Mastin, DMD; Bach Le, DDS, MD Injury to the
CLINICAL AVOIDING INJURY TO THE INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE BY ROUTINE USE OF INTRAOPERATIVE RADIOGRAPHS DURING IMPLANT PLACEMENT Jeffrey Burstein, DDS, MD; Chris Mastin, DMD; Bach Le, DDS, MD Injury to the
Medical Benefit Effective Date: 07/01/12 Next Review Date: 03/13 Preauthorization* Yes Review Dates: 11/07, 07/08, 05/09, 03/10, 03/11, 03/12
 Protocol Implantable Bone-Conduction and Bone-Anchored Hearing Aids (70103) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 07/01/12 Next Review Date: 03/13 Preauthorization* Yes Review Dates: 11/07, 07/08, 05/09, 03/10,
Protocol Implantable Bone-Conduction and Bone-Anchored Hearing Aids (70103) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 07/01/12 Next Review Date: 03/13 Preauthorization* Yes Review Dates: 11/07, 07/08, 05/09, 03/10,
MDCT Technology. Kalpana M. Kanal, Ph.D., DABR Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Washington Seattle, Washington
 MDCT Technology Kalpana M. Kanal, Ph.D., DABR Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Washington Seattle, Washington ACMP Annual Meeting 2008 - Seattle, WA Educational Objectives Historical
MDCT Technology Kalpana M. Kanal, Ph.D., DABR Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Washington Seattle, Washington ACMP Annual Meeting 2008 - Seattle, WA Educational Objectives Historical
BODY BODY PEDICLE PEDICLE TRANSVERSE TRANSVERSE PROCESS PROCESS
 Learning Objective Radiology Anatomy of the Spine and Upper Extremity Identify anatomic structures of the spine and upper extremities on standard radiographic and cross-sectional images Timothy J. Mosher,
Learning Objective Radiology Anatomy of the Spine and Upper Extremity Identify anatomic structures of the spine and upper extremities on standard radiographic and cross-sectional images Timothy J. Mosher,
CT Angiography (CTA) What is CT Angiography?
 Scan for mobile link. CT Angiography (CTA) Computed tomography angiography (CTA) uses an injection of iodine-rich contrast material and CT scanning to help diagnose and evaluate blood vessel disease or
Scan for mobile link. CT Angiography (CTA) Computed tomography angiography (CTA) uses an injection of iodine-rich contrast material and CT scanning to help diagnose and evaluate blood vessel disease or
The multitude of symptoms following a whiplash injury has given rise to much discussion because of the lack of objective radiological findings.
 HELPFUL PERSONAL INJURY INFORMATION COURTESY OF RIVERVIEW CHIROPRACTIC FROM ABSTRACT: Dynamic kine magnetic resonance imaging in whiplash patients Pain Research and Management 2009 Nov-Dec 2009;Vol. 14,
HELPFUL PERSONAL INJURY INFORMATION COURTESY OF RIVERVIEW CHIROPRACTIC FROM ABSTRACT: Dynamic kine magnetic resonance imaging in whiplash patients Pain Research and Management 2009 Nov-Dec 2009;Vol. 14,
DISCUSSION TOPICS. Embryology Etiology Presentation Associated Anomalies Classification Management
 MICROTIA Emily Tignor, MD Faculty Advisor: Shraddha Mukerji, MD The University of Texas Medical Branch Department of Otolaryngology Grand Rounds Presentation October 30, 2013 DISCUSSION TOPICS Embryology
MICROTIA Emily Tignor, MD Faculty Advisor: Shraddha Mukerji, MD The University of Texas Medical Branch Department of Otolaryngology Grand Rounds Presentation October 30, 2013 DISCUSSION TOPICS Embryology
State-of-the-Art Technology in Cardiac CT
 1 2 Next Step Evolution or Revolution? State-of-the-Art Technology in Cardiac CT Stefan Ulzheimer, PhD Global Director of Collaborations CT Siemens Medical Solutions Major Innovations in CT Head The 80
1 2 Next Step Evolution or Revolution? State-of-the-Art Technology in Cardiac CT Stefan Ulzheimer, PhD Global Director of Collaborations CT Siemens Medical Solutions Major Innovations in CT Head The 80
Computed Tomography (CT) - Spine
 Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Spine Computed tomography (CT) of the spine is a diagnostic imaging test used to help diagnose or rule out spinal column damage in injured patients. CT
Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Spine Computed tomography (CT) of the spine is a diagnostic imaging test used to help diagnose or rule out spinal column damage in injured patients. CT
Diagnostic Tests for Vestibular Problems By the Vestibular Disorders Association
 PO BOX 13305 PORTLAND, OR 97213 FAX: (503) 229-8064 (800) 837-8428 INFO@VESTIBULAR.ORG WWW.VESTIBULAR.ORG Diagnostic Tests for Vestibular Problems By the Vestibular Disorders Association The inner ear
PO BOX 13305 PORTLAND, OR 97213 FAX: (503) 229-8064 (800) 837-8428 INFO@VESTIBULAR.ORG WWW.VESTIBULAR.ORG Diagnostic Tests for Vestibular Problems By the Vestibular Disorders Association The inner ear
1/26/2011. 50% of deafness and hearing impairment is avoidable through prevention, early diagnosis, and management.
 Hearing Impairment Roseann Mulligan, DDS, MS Herman Ostrow School of Dentistry of the University of Southern California 1 JAMA, July 4, 2007 Vol 298, No. 1 2 278 million - moderate to profound bilateral
Hearing Impairment Roseann Mulligan, DDS, MS Herman Ostrow School of Dentistry of the University of Southern California 1 JAMA, July 4, 2007 Vol 298, No. 1 2 278 million - moderate to profound bilateral
VERSYS HERITAGE CDH HIP PROSTHESIS. Surgical Technique for CDH Hip Arthroplasty
 VERSYS HERITAGE CDH HIP PROSTHESIS Surgical Technique for CDH Hip Arthroplasty SURGICAL TECHNIQUE FOR VERSYS HERITAGE CDH HIP PROSTHESIS CONTENTS ANATOMICAL CONSIDERATIONS....... 2 PREOPERATIVE PLANNING............
VERSYS HERITAGE CDH HIP PROSTHESIS Surgical Technique for CDH Hip Arthroplasty SURGICAL TECHNIQUE FOR VERSYS HERITAGE CDH HIP PROSTHESIS CONTENTS ANATOMICAL CONSIDERATIONS....... 2 PREOPERATIVE PLANNING............
3D volume rendering using multislice CT for dental implants
 (2002) 31, 218 ± 223 ã 2002 Nature Publishing Group. All rights reserved 0250 ± 832X/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/dmfr RESEARCH 3D volume rendering using multislice CT for dental implants MGP Cavalcanti*,1,
(2002) 31, 218 ± 223 ã 2002 Nature Publishing Group. All rights reserved 0250 ± 832X/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/dmfr RESEARCH 3D volume rendering using multislice CT for dental implants MGP Cavalcanti*,1,
DIAGNOSING SCAPHOID FRACTURES. Anthony Hewitt
 DIAGNOSING SCAPHOID FRACTURES Anthony Hewitt Introduction Anatomy of the scaphoid Resembles a deformed peanut Articular cartilage covers 80% of the surface It rests in a plane 45 degrees to the longitudinal
DIAGNOSING SCAPHOID FRACTURES Anthony Hewitt Introduction Anatomy of the scaphoid Resembles a deformed peanut Articular cartilage covers 80% of the surface It rests in a plane 45 degrees to the longitudinal
Paparella: Volume II: Otology and Neuro-Otology. Section 3: Diseases of the Ear. Part 1: General Problems. Chapter 15: Otologic Trauma
 Paparella: Volume II: Otology and Neuro-Otology Section 3: Diseases of the Ear Part 1: General Problems Chapter 15: Otologic Trauma J. V. D. Hough, Michael McGee Because of high-speed travel and activities
Paparella: Volume II: Otology and Neuro-Otology Section 3: Diseases of the Ear Part 1: General Problems Chapter 15: Otologic Trauma J. V. D. Hough, Michael McGee Because of high-speed travel and activities
What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)?
 What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair 1 What
What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair 1 What
Management of Deafness in the Elderly
 Management of Deafness in the Elderly Mrs R Kayarkar Consultant ENT Surgeon Mid Yorks NHS Trust British Geriatric Society Meeting 18.9.2013 Effects of hearing loss Embarrassment, loss of confidence, anger
Management of Deafness in the Elderly Mrs R Kayarkar Consultant ENT Surgeon Mid Yorks NHS Trust British Geriatric Society Meeting 18.9.2013 Effects of hearing loss Embarrassment, loss of confidence, anger
Preliminary Experience with Selective Laser Sintering Models of the Human Temporal Bone
 Preliminary Experience with Selective Laser Sintering Models of the Human Temporal Bone Richard A. Levy, Sashidhar Guduri, and Richard H. Crawford PURPOSE: To assess the accuracy of three-dimensional models
Preliminary Experience with Selective Laser Sintering Models of the Human Temporal Bone Richard A. Levy, Sashidhar Guduri, and Richard H. Crawford PURPOSE: To assess the accuracy of three-dimensional models
The essentials of managing. an important role at all stages of life. In. early childhood, near-normal hearing in
 MedicineToday 2015; 16(2): 31-42 PEER REVIEWED FEATURE 2 CPD POINTS The essentials of managing Hearing loss RICH LEGG/ISTOCKPHOTO Key points Hearing loss is very MELVILLE DA CRUZ FRACS, MSc, MD Hearing
MedicineToday 2015; 16(2): 31-42 PEER REVIEWED FEATURE 2 CPD POINTS The essentials of managing Hearing loss RICH LEGG/ISTOCKPHOTO Key points Hearing loss is very MELVILLE DA CRUZ FRACS, MSc, MD Hearing
The File-Card-Browser View for Breast DCE-MRI Data
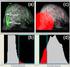 The File-Card-Browser View for Breast DCE-MRI Data Sylvia Glaßer 1, Kathrin Scheil 1, Uta Preim 2, Bernhard Preim 1 1 Department of Simulation and Graphics, University of Magdeburg 2 Department of Radiology,
The File-Card-Browser View for Breast DCE-MRI Data Sylvia Glaßer 1, Kathrin Scheil 1, Uta Preim 2, Bernhard Preim 1 1 Department of Simulation and Graphics, University of Magdeburg 2 Department of Radiology,
Cone Beam Imaging Why all the Fuss about the X-ray Dose? D.A. Miles BA, DDS, MS, FRCD(C) Dip. ABOM, Dip. ABOMR. Introduction
 Cone Beam Imaging Why all the Fuss about the X-ray Dose? D.A. Miles BA, DDS, MS, FRCD(C) Dip. ABOM, Dip. ABOMR Introduction The newest imaging modality to become available to dentists is making its impact
Cone Beam Imaging Why all the Fuss about the X-ray Dose? D.A. Miles BA, DDS, MS, FRCD(C) Dip. ABOM, Dip. ABOMR Introduction The newest imaging modality to become available to dentists is making its impact
Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (ALIF). Instrument set supports placement of ALIF spacers using anterior or anterolateral approach.
 Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (ALIF). Instrument set supports placement of ALIF spacers using anterior or anterolateral approach. Technique Guide Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation
Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (ALIF). Instrument set supports placement of ALIF spacers using anterior or anterolateral approach. Technique Guide Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation
Understanding Hearing Loss 404.591.1884. www.childrensent.com
 Understanding Hearing Loss 404.591.1884 www.childrensent.com You just found out your child has a hearing loss. You know what the Audiologist explained to you, but it is hard to keep track of all the new
Understanding Hearing Loss 404.591.1884 www.childrensent.com You just found out your child has a hearing loss. You know what the Audiologist explained to you, but it is hard to keep track of all the new
Computed Tomography (CT) - Sinuses
 Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Sinuses Computed tomography (CT) of the sinuses uses special x-ray equipment to evaluate the paranasal sinus cavities hollow, air-filled spaces within the
Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Sinuses Computed tomography (CT) of the sinuses uses special x-ray equipment to evaluate the paranasal sinus cavities hollow, air-filled spaces within the
SNHL is a major cause of childhood disability worldwide,
 Published May 12, 2011 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2498 REVIEW ARTICLE B.Y. Huang C. Zdanski M. Castillo Pediatric Sensorineural Hearing Loss, Part 1: Practical Aspects for Neuroradiologists SUMMARY: SNHL is a major
Published May 12, 2011 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2498 REVIEW ARTICLE B.Y. Huang C. Zdanski M. Castillo Pediatric Sensorineural Hearing Loss, Part 1: Practical Aspects for Neuroradiologists SUMMARY: SNHL is a major
