Purpose of the System Components...5
|
|
|
- Gillian Collins
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Table of Contents Subject Page Purpose of the System... 3 Components...5 Integrated Control unit/hydraulic unit with CAN Interface... 6 Brake Pressure Sensor...6 Brake Light Switch...6 Charge pump...7 Hand Brake Switch...7 Integrated Rotation Rate/Lateral Acceleration Sensor...8 DSC Button...9 HDC Switch (Hill Descent Control) Four wheel speed sensors (Active Hall Effect)...9 Steering Angle Sensor...10 Brake Fluid Level Switch...11 DSC Warning Indicator CAN Interface (DME/AGS)...13 Principle of Operation...14 X5 DSC New Functions...27 Diagnosis...31 Review Questions...33 Initial Print Date:1/03 Revision Date:
2 Model: E53 X5 3.0i, 4.4i and 4.6is Production: All from Model Introduction Objectives: After completion of this module you will be able to: Understand X5 DSC operation Identify X5 DSC Components Understand HDC Operation 2
3 Purpose of System DSC for the X5 The X5 is equipped with DSC III for its stability control system. The components are the same as the DSC III system (version 5.7) currently installed in the E38/E39 vehicles. However the software and programming are changed to allow for new functions associated with all wheel drive and off-road use. New/changed functions of the DSC III include: New Hill Decent Control (HDC) function New Differential Brake Control (ABD) function Changed traction control function Changed ABS function The DSC system for the X5 provides all of the functions and features of the DSC III system currently in the E38/E39 vehicles. these functions/features include: Maintaining traction under all driving conditions Maintaining the directional Control (Longitudinal Stability) Providing Lateral Stability (Correction for oversteer/understeer) Providing Corner Braking Control (CBC) Providing Dynamic Braking System features of - Dynamic Braking Control and Maximum Braking Control (DBC and MBC) Providing Electronic Brake Proportioning (EBV) 3
4 4
5 Components The components of the X5 DSC III system are similar to the E39 with Bosch DSC III 5.7. The location of some components is slightly different than the E39. The components are as follows: Integrated Control unit/hydraulic unit with CAN Interface Charge pump Tandem Brake Master Cylinder Four wheel speed sensors (Active Hall Effect) Steering Angle Sensor Integrated Rotation Rate/Lateral Acceleration Sensor Brake Pressure Sensor Brake Fluid Level Switch Brake Light Switch Hand Brake Switch DSC Button DSC Warning Indicator CAN Interface (DME/AGS) HDC Switch (Hill Descent Control) 5
6 Components Control Module/Hydraulic Unit The control module is integrated into the hydraulic unit as one compact unit. This reduces the size and wiring required for DSC operation. Additionally the motor relay and valve relay have been replaced by solid state final stages in the control module. The hydraulic unit continues to use: Two pre-charge solenoid valves Two changeover solenoid valves Four intake solenoid valves Four outlet solenoid valves One return pump Brake Pressure Sensor A brake pressure sensor is installed in the hydraulic unit to determine the degree of pressure build-up for Dynamic Brake Control. It is installed in the front axle brake circuit. The sensor receives its power supply from the DSC control module and produces a linear voltage input signal ranging from 0.5 to 4.5 volts depending on how hard the brakes are applied. Brake Light Switch (BLS) The brake switch is an input to the DSC Module to inform it that the brakes are being applied. If the signal is received during an ASC regulation then brake regulation is interrupted. 6
7 Pre-Charge Pump (Bosch 5.7) The pre-charge pump is located below the master cylinder in the left side of the engine compartment. During ASC or DSC regulation with brake intervention, the DSC control unit activates the precharge pump. The pump delivers brake fluid at a pressure of 10 to 15 Bar to the front axle circuit of the master cylinder. The pressurized fluid also acts on the rear brake circuit of the master cylinder as well. The Pre-charge pump ensures that an adequate amount of brake fluid is available at the hydraulic unit during brake regulation. Handbrake Switch The Hand Brake Switch is a ground input to the DSC module. This DSC module will discontinue MSR regulation when the signal is present. DSC Module 7
8 Rotation Rate/Transverse Acceleration Sensor Located under the center console behind the MRS III control module, the rotation rate and transverse acceleration sensor provides two inputs to the DSC control module. The sensor is isolated from body/chassis vibrations through its rubber mounting. For rotational speed, the sensor produces a reference signal of 2.5 volts and a linear voltage signal from 0.7 to 4.3 volts. This linear voltage input signal is used by the DSC control module as the degree of rotational rate (yaw). The sensor also produces a linear voltage signal for the lateral acceleration (G-force) that ranges from 0.5 to 4.5 volts. The DSC control module uses this input to determine the side forces acting on the vehicle for DSC regulation. 8
9 DSC Switch The system is active whenever the ignition is switched on. When pressed, the switch provides a momentary 12 volt signal to the DSC III control module to switch the system off (DSC indicator in cluster illuminated.) When pressed again, the system switches back on (DSC Indicator in cluster goes off.) HDC Switch The hill decent control function is activated by pressing the HDC switch located in the center console. The LED will come on steady when the function is in standby and flash when HDC is regulating Wheel Speed Sensors 2 wire Hall Effect Sensor - Square wave generator. Stabilized 8 volt power supply to hall element on one wire, ground path for sensor through second wire back to control module. Signal is generated by the pulse wheel affecting voltage flow through hall element creating a low of.75 and a high of 2.5 volts. 48 pulse incremental wheel incorporated in wheel bearing cover for contaminant protection. 48 pulses = one complete wheel revolution. Sensors identical to DSC II and ASC V systems. Sensors provide immediate vehicle speed recognition. 9
10 Steering Angle Sensor (LEW) The Steering angle sensor is mounted at the bottom of the steering spindle (in front of the flex coupling). The sensor is equipped with a processor and is directly linked to the CAN bus to communicate with the DSC III module. The sensor still utilizes two potentiometers to determine the steering angle and the rate of steering. These are the raw signals the CAN Bus microprocessor utilizes to create the steering angle signal for broadcast on the CAN bus. The sensor requires calibration after repairs to the steering or suspension system (found in DIS Service Functions). Once the calibration is completed the sensor now also sends an identification number over the CAN bus to the DSC III module. The ID provides confirmation in the DSC module that the steering angle sensor is properly calibrated. If the ID differs due to component swapping it will not be possible to enter the DSC system for diagnosis. The DIS will request that the steering angle sensor be recalibrated using the service functions. Once complete a new ID number is generated and the DSC III control module and Steering angle sensor are properly mated. The DSC III logic checks the plausibility of the steering angle sensor against the other DSC III inputs (front wheel speeds, rotation and lateral acceleration sensors). If battery voltage is interrupted, the current steering wheel rotation is recalculated by the DSC module evaluating the front wheel speeds. Replacement steering angle sensors must be ZCS coded when installed in the vehicle prior to the calibration procedure. 10
11 Brake Fluid Level Warning Switch A new fluid level switch is incorporated into the reservoir cap. With sufficient fluid level the reed contact is closed. When level drops below allowable limits, switch opens. Since the normal position is closed, this circuit is monitored for shorts to + and ground. The LCM constantly monitors the input. If the ground signal is momentary, the LCM signals the Instrument cluster of the condition. The instrument cluster then informs the DSC III control module over the CAN bus. If the signal is received just prior to the activation of the charge pump, the charge pump activation is delayed. If the signal is present for more then 25 seconds, the LCM issues two I BUS message for the Instrument Cluster: 1. Post Brake Fluid Level in the Matrix display 2. Notify the DSC III via CAN that the Fluid level has been low for more than 25 seconds. The DSC III control module immediately switches DSC III functions off and continuously illuminates the DSC indicator in the cluster. 11
12 Instrument Cluster Warning Indicators km/h /min x MPH! SERVICE ENGINE SOON EML Mmiles BRAKE ABS Three warning indicator lamps are arranged in the instrument cluster: DSC lamp: Indicates fault in DSC or system disabled by the switch. ABS lamp: Indicates a fault in the ABS system. ABL BRAKE lamp: This lamp is a general brake warning and illuminates two different colors. Red indicates low brake fluid or hand brake engaged. Yellow indicates DSC/ABS fault or system disabled by the switch. The DSC and yellow ABL lamp are controlled by the DSC III control unit via the CAN bus. The ABS lamp is controlled directly by the DSC III control unit via hardwire. 12
13 CAN Interface The MK60 is connected to the CAN bus for communication with the AGS, DME control module, Steering Angle Sensor and the Instrument Cluster. The CAN bus allows all of the connected control modules to send and receive information and commands. Communication with the MK60 includes: DME - The DME sends current engine torque. MK60 commands the DME to reduce (ASC/DSC) or raise (MSR) engine torque. AGS - The MK60 commands the AGS to suppress shifts during regulation. LEW - The MK60 receives steering angle information. KOMBI - The MK60 commands the instrument cluster to activate or deactivate the warning lamps. All four wheels speed signals are sent over the CAN bus for use by other modules. INSTRUMENT CLUSTER GS 20 MS UNLEADED GASOLINE ONLY km/h /min x MPH Mmiles CAN BUS SPLICE CONNECTIONS FOR TWISTED PAIR CAN LEW MK 60 13
14 Principle of Operation The scope of control for the DSC III is comprised of three systems: ABS ASC+T DSC Based on signals coming from the various sensors the DSC III will determine which system is best suited to maintain control of the vehicle. In addition to the three basic systems, there are several sub-functions which are activated during very specific circumstances. The sub-functions are: CBC EBV MSR ADB DBC MBC The ABS system can prevent wheel lock when braking by comparing the four active wheel speed sensors to the average vehicle speed. If a wheel is locking during braking or has dropped below a speed threshold programmed in the control unit ABS, braking will begin. ABS braking is possible when vehicle speeds are above 12 km/h (7mph). The function of ABS for All-Wheel Drive use has an additional variation. During braking on loose surfaces the wedge effect is helpful. Gravel or dirt will build up in front of the tire when the wheel is locked, creating an increased braking effect. The system allows the locking of one or both front wheels up to approx. 20km/h (12mph). This poor road surface logic does not affect steerability. As soon as the control unit detects steering wheel change, the ABS system regulates normally again. 14
15 ABS regulation has three phases: Pressure Build Pressure Hold Pressure Release Pressure Build already occurs during normal braking, so when ABS first intervenes it will start holding pressure by energizing the Inlet Valve. For example, if the right rear wheel is locking up, both Inlet Valves will be energized, regulating both wheels together. This logic is known as Select Low. Front wheels can be regulated individually as needed to prevent lockup. Energizing the Inlet Valve closes the brake fluid passage to the calipers and traps the fluid at the current pressure, thus not allowing the brake pressure to rise any further. If the wheel speed does not increase, the Pressure Release phase begins. Pressure Release occurs when the control unit energizes the Outlet Valve while continuing XLE BRAKE CIRCUITS FRONT AXLE BRAKE CIRCUITS to hold the Inlet Valve closed. The trapped brake fluid is released out of the calipers reducing braking pressure. At the same time the pump is switched on which draws in the released brake fluid and pumps it back into the pressure build-up circuit restoring the volume of brake fluid again in front of the Inlet valve. Depending on conditions the ABS system may cycle between these three phases from 3 to 12 times a second to prevent wheel lock. 15
16 ABS Sub-functions Corner Brake Control (CBC) CBC can occur if the vehicle is cornering and ABS regulation is not taking place. If the control unit detects transverse acceleration in excess of 0.6g and the brakes are applied, CBC prevents a build up in brake pressure to the inside rear wheel. This prevents the vehicle from entering into an unstable situation that can lead to Oversteer. The DSC III accomplishes this by closing the Inlet Valve, thus not allowing brake pressure to increase at the brake caliper. The difference in braking force between the two rear wheels creates a yaw force that opposes the oversteer and allows the vehicle to handle neutrally. Weight of the vehicle Brake pressure allowed to increase Brake Pressure Held 16
17 Electronic Brake Force Distribution (EBV) EBV will adjust brake pressure to the rear axle based on the rate of slow-down of the rear wheels, ensuring even brake force between the front and rear of the vehicle. The control unit monitors the wheel speed when the brakes are applied and compares the deceleration rate of the front and rear axle to determine required regulation. If the vehicle is moderately to fully loaded, the rear axle will take longer to slow down, rear wheel brakes then can be applied at a higher pressure. If the vehicle is lightly loaded, a similar brake pressure would be too great and result in an unstable situation. If EBV control intervention is required, the control unit cycles the intake valve on the rear brake calipers to prevent further build-up. Benefits of EBV are Enhanced braking due to an even distribution of brake force. Rear wheel brake size can be increased. Front and rear brakes wear at a similar rate. 17
18 Automatic Stability Control (ASC+T) ASC prevents unintentional wheel slip of the drive wheels in every situation. The DSC III control unit determines if the vehicle is loosing traction due to excessive longitudinal wheel slip based on input from the wheel speed sensors. An ASC regulating sequence is initiated if the wheel slip exceeds the control units stored allowable values. The DSC III can control longitudinal wheel slip by two means: Automatic Stability Control ASC. Engine Intervention Automatic Differential Brake ADB. Brake intervention ASC Engine Intervention Engine torque may be reduced by: Reducing the throttle opening angle Retarding the ignition Canceling individual cylinders by fuel injection cutout. The DSC III control unit determines the amount of torque reduction that is necessary and sends the request for regulation to the DME via the CAN bus. ADB Brake Intervention The ADB is an automatic differential lock that improves traction. The slipping wheel is braked by pressure built up in the hydraulic unit. The drive torque can be transferred to the wheel with the greater traction, which can transmit drive power to the road. This function acts much like a limited slip differential. Brake intervention is applied to the individual wheel which is loosing traction by regulating the brake calipers in three phases: Pressure Build Pressure Hold Pressure Release 18
19 When brake intervention is necessary, the axle not being regulated must be isolated from the Pressure Build sequence in the hydraulic unit. This is accomplished by closing both Inlet Solenoid Valves for that axle. Here is an example of an ADB brake intervention at the left rear wheel: The Changeover Valve for the rear brake circuit, the right rear and both front Inlet Valves are energized and closed. The rear brake circuit Intake Valve is energized and opened. The Return/Pressure pump is activated and draws brake fluid through the open Intake Valve from the Master Cylinder (via the Central Valve) and delivers the pressurized fluid to the open Inlet Valve braking the left rear wheel. Pressure Hold and Pressure Release are done by cycling the Inlet and Outlet Valves similar to the ABS sequence described previously. The drive torque can be distributed to the wheels with high friction coefficients (traction). Transversal differential-lock function. 19
20 Longitudinal differential-lock function By performing brake intervention at the axle with a low friction coefficient, drive torque can be transmitted to the front wheels. Longitudinal and transversal differential-lock function By performing brake intervention at the diagonally opposing wheels with a low friction coefficient, drive torque can be transmitted to the two wheels with more traction. 20
21 ASC Sub-function Engine Drag Torque Reduction (MSR) If the vehicle is driven in low gear when coasting down hill, or if there is a sudden shift to a lower gear, the wheels may be slowed down by the engine braking effect to rapidly. This could result in an unstable situation. If the front wheels are turning faster than the rear wheels the DSC III control unit signals the DME via the CAN bus to raise the engine torque. DME cancels fuel cut-off and allows the engine speed to increase, this allows the drive wheels to accelerate to match the speed of the non-driven wheels. MSR regulation is cancelled if the brake pedal or hand brake is applied. Dynamic Stability Control (DSC) With the introduction of DSC systems, lateral dynamics were taken into account for the first time. The DSC III system will initiate a DSC regulation sequence if the control unit detects a difference between the drivers desired turning angle and the actual rotation angle of the vehicle. The control unit determines vehicle stability based on: Steering wheel angle Wheel speed Transverse acceleration forces Rotation angle and speed (yaw) Once the control unit determines that the vehicle is in an unstable situation, it also identifies whether it is oversteering or understeering. This distinction is important because it determines which control strategy should be used to help stabilize the vehicle. DSC regulation consist of : Engine intervention Engine and brake intervention (any wheel) Brake intervention 21
22 Understeer Understeer occurs when the driver wishes to turn a corner, but despite the front wheels being turned in the direction of the curve, the vehicle continues its forward track. This occurs when the front wheels no longer have sufficient lateral locating force (traction). The DSC III can identify the situation and initiate a corrective action based on engine torque reduction followed by a controlled brake intervention sequence if needed. Engine torque reduction is carried out by the DME from a request by the DSC via the CAN bus. The DME sends the torque reduction confirmation back to the DSC. Brake intervention is carried out by the DSC III hydraulic unit if the driver is not actively braking. An example of a brake intervention at the inside rear wheel is as follows: All Inlet Valves are closed except for the right rear inlet. Intake Valve for rear circuit is opened. Both Changeover Valves are closed. Return pump operated. 3. VEHICLE COMES OUT OF TURN SUCCES- FULLY UNDERSTEER CORRECTION WITH DSC III 1. VEHICLE APPROACHES TURN: - Driver steers into turn - Brakes are applied 3 2. DSC III detects an Understeer Condition based on vehicle speed, wheel speed differential, turning angle, lateral acceleration forces and yaw angle. - Engine torque reduction active - Inside rear wheel brake regulate 1 WITHOUT DSC III regulated brake slows wheel down (and helps to reduce vehicle speed). Wheel on outside of curve speeds up due to power transfer thru differential. Vehicle pivots in favor of curve. Combined, this forces the vehicle into the turn.
23 Just as an ASC regulation, DSC brake intervention carries out: Pressure Build Pressure Hold Pressure release 23
24 Oversteer Oversteer occurs when the driver wishes to turn a corner and the tail of the vehicle slides outward, leading the turn. This is caused by the rear tires loosing traction and not being able to hold against the centrifugal force acting upon the vehicle. The DSC III can identify the situation and initiate a corrective action based on engine torque reduction followed by a controlled brake intervention sequence if needed. Engine torque reduction is carried out by the DME from a request by the DSC via the CAN bus. The DME sends the torque reduction confirmation back to the DSC. 3. VEHICLE COMES OUT OF TURN SUCCESFULLY WITH DSC III OVERSTEER CORRECTION WITHOUT DSC III 1. VEHICLE APPROACES TURN AT HIGH RATE OF SPEED: - Driver steers into turn and applies brakes to slow down A. Lateral locating forces are diminished on rear wheels due to high speed and centrifugal force of vehicle in turn. 2 2D. The torque reduction and rear brake regulation should stabilize the vehicle at this point. If not the left front wheel has a high degree of lateral locating force and is momentarily regulated. This action deliberately causes the wheel to shed a calculated degree of it's locating force. This counteracts oversteer yaw at this wheel and also aids in slowing the vehicle down to correct it. 2B. Driver tries to compensate by oversteering which diminishes lateral locating force even further. Simultaneously, rear of car starts to slide out. 2C. DSC III determines an OVERSTEER condition. Engine torque is reduced via CAN Bus signalling. Outside rear wheel is momentarily regulated to counteract severe yaw angle (also helps to reduce drive torque further.) 24
25 DSC Sub-functions Dynamic Brake System (DBS) DBS is designed to assist the driver in emergency braking situations by automatically increasing pressure to the vehicles brake system. This allows the vehicle to stop in the shortest distance possible. DBS was first available in 1999 Bosch DSC III 5.7 systems. The DBS system contains two functions: Dynamic Brake Control and Maximum Brake Control. DBS functions are programmed into the DSC III control unit and require no additional hardware over conventional DSC. Dynamic Brake Control (DBC) The DBC function is designed to provide an increase in braking pressure up to the ABS threshold during rapid (emergency) braking situations. The DSC III control unit monitors the inputs from the brake light switch and the brake pressure sensor. The triggering criteria for activation of DBC is, how rapidly is the brake pressure increasing with an application of the brake pedal. The triggering conditions are: Brake light switch on. Brake pressure in the master cylinder above threshold. Brake pressure build-up speed above threshold. Vehicle road speed above 3mph (5km/h). Pressure sensor self test completed and sensor not faulted. Vehicle traveling forward. Not all of the wheels in ABS regulation range. If the threshold for DBC triggering is achieved, the DSC III control unit will activate a pressure build-up intervention by activating the pre-charge and return pump. The pressure at all wheels is increased up to the ABS regulation point. This ensures that the maximum brake force is applied to the vehicle. During DBC the rear axle is controlled with Select-Low logic and the front wheels are regulated individually. DBC will continue until: The driver releases the brake pedal. Brake pressure falls below threshold. Vehicle road speed below 3mph. DBC will also be switched off if a fault occurs in with any of the necessary input sensors. A fault in DBC will illuminate the BRAKE (ABL) lamp yellow to warn the driver, depending on the failure the DSC lamp may be illuminated as well. 25
26 Maximum Brake Control (MBC) The MBC function is designed to support driver initiated braking by building up pressure in the rear brake circuit when the front wheels are already in ABS regulation. The additional braking pressure is designed to bring the rear wheels up to the ABS regulation point shortening the stopping distance. The MBC function is triggered when the brakes are applied more slowly than the threshold needed for a DBC regulation. The triggering conditions are: Both front wheels in ABS regulation. Vehicle road speed above 3mph (5km/h). DBC and pressure sensor initialization test successful. Vehicle traveling forward. Rear wheels not in ABS regulation. If the threshold for MBC triggering is achieved, the DSC III control unit will activate a pressure build-up intervention by activating the return pump. The pressure at the rear wheels is increased up to the ABS regulation point. This ensures that the maximum brake force is applied to the vehicle. The MBC function will be switched off if: Front wheels drop out of ABS regulation. The driver releases the brake pedal. Brake pressure falls below threshold. Vehicle road speed below 3mph. MBC will also be switched off if a fault occurs in with any of the necessary input sensors. A fault in MBC will illuminate the BRAKE (ABL) lamp yellow to warn the driver, depending on the failure the DSC lamp may be illuminated as well. 26
27 X5 DSC New Functions Hill Descent Control Hill Decent Control (HDC) is designed for off road use to automatically slow the vehicle and maintain a steady speed on steep gradients. This function allows the driver to focus on steering and controlling the vehicle without having to use the brakes to slow the vehicle. HDC is activated manually through the push button switch located in the center switch panel located in the console. When activated, the vehicle s speed is held to approximately 5 MPH by the DSC system pulsing the brakes to maintain the speed. The following conditions must be met before the HDC will activate: Push button pressed - LED ON Vehicle speed: < 25 MPH Accelerator pedal pressed <15% Downhill driving recognized Downhill is recognized from the vehicle s speed and engine load from the engine control module. The accelerator pedal and engine load signals are passed over the CAN bus to the DSC control module. The HDC switch can be pressed at speeds < 37MPH and the LED will come on to indicate standby mode. However the system will not activate until the vehicle s speed is below 25. The driver can accelerate with HDC active up to approximately 20% engine load. The HDC will stop regulating as long as the driver is requesting a speed increase. If the vehicle s speed is > 37 MPH, the HDC function is automatically switched OFF. 27
28 Automatic Differential Braking On dry pavement with no wheel slip, the vehicle s driving torque is split 68% rear and 32% front through the planetary gear differential transfer case. If one or more wheels spin or slip, the DSC will activate a regulation process and the brakes on the effected wheel(s) will be pulsed. The driving torque will be distributed through the differential to the remaining wheels with a good coefficient of friction The driving torque will be applied through the differential as follows: Three wheels - with one wheel spinning. On two diagonal wheels with two wheels spinning on different axles. One axle only with two wheels spinning on the same axle. Once the spin or slip is under control, the drive torque will again be applied to all wheels. 28
29 29
30 Traction Control The traction control feature of the DSC III on the X5 cannot be switched OFF with the DSC switch. Pressing the button will only switch off the dynamic stability control function of the DSC. The traction control feature is needed at all times to provide anti-spin control especially when driving the vehicle off road. The DSC warning lamp in the instrument cluster will still come on when the system is switched off manually or there is a fault in the system. Off road traction control or HDC regulation places an additional load on the brakes. To prevent overheating of the brakes and rotors, the temperature of the rotors is calculated over time from the road speed and amount of brake application. If the temperature of one or more rotors goes above 600 o C, the traction control or HDC function for that wheel will be cancelled temporarily. Once the temperature of the rotor goes below 500 o C, the traction application will be re-activated. The normal braking function (including ABS) is always active at any temperatures. Off-Road ABS Control Module Programming The programming for ABS regulation have changed to allow a higher threshold for ABS regulation when driving off-road in loose gravel or dirt. A locked wheel is more effective in slowing or stopping the vehicle because of the wedge that is built up in front of the tire. The programming in the DSC control module allows one or both front wheel(s) to lock up to a speed of 12 MPH as long as the vehicle is traveling straight ahead. If the DSC control module receives a signal from the steering angle sensor indicating a turn, ABS regulation will activate to prevent the lock and allow the vehicle to be steered. 30 Braking Systems
31 Diagnosis The following diagnostic functions are available using the DISplus or GT-1. Control Unit Functions: Expert mode diagnosis available at any time during troubleshooting. To enter: press the Control Unit Functions button at the right lower corner of the screen. The contents are: Identification Delete Fault Memory Read Fault Memory Component Activation Status queries (requests) Service Functions: Provides access to specialized test modules used as post repair procedures. To enter: Function Selection Service Functions Chassis Dynamic Stability Control The contents are: Connection Speed Sensor: A test to verify the proper wiring to the wheel speed sensors Connection Brake Lines: A test to verify the proper brake pipe connections to the hydraulic unit. Adjustment Functions: Test modules to initialize certain components after repair work is performed Steering Angle Sensor Lateral Acceleration Sensor Pressure Sensors Test Modules: Faults with the MK60 system can be diagnosed using fault or symptom driven test modules. To begin diagnosis: Perform the Quick Test. Select Vehicle Symptom from the Symptom Selection page. Select Test Module from Test Plan page. Press the Test Schedule Button. Test Modules are configured in the E46 diagnosis concept. 31
32 Coding Coding must be performed after replacement of the DSC III control module or the steering angle sensor. ZCS coding is found in the Coding and Programming selection from the start screen or when pressing the Change button. Follow on-screen instructions for initialization of components after completing the coding process. Adjustment Functions Print Change End Services BMW Coding/programming SELECTION 1 CAR MEMORY 2 KEY MEMORY 3 ZCS CODING 4 PROGRAMMING 5 ALIGNMENT EWS-DME 6 ALIGNMENT EWS-DDE Note Adjustment (initialization) of certain components is required when: Replacing the DSC III Control Unit. Replacing/Re-coding the Steering Angle Sensor. Replacing Rotation/Lateral Acceleration Sensor. Steering Angle Sensor The steering angle sensor requires an offset adjustment after the sensor has been replaced, coded or after repairs to the steering or suspension system. The offset adjustment informs the steering angle sensor processor of the straight ahead position of the front wheels. The adjustment is performed by completing the Test Module found in Service Functions. Once the adjustment is complete, the sensor sends an identification number over the CAN bus to the DSC control unit. The ID provides confirmation that the steering angle sensor is coded and has successfully completed the adjustment procedure. Special Tools Special Tools available for the Bosch DSC III 5.7 consist of: 42 Pin V-Cable Pin Break-Out-Box 32
33 review Questions 1. Desribe the operation of the DSC button on the X5 DSC III system? _ 2. Describe the activation criteria for HDC: _ 3. What type of wheel speed sensors are used in the X5 DSC III system? _ 4. What is the difference in ABS control logic for the X5 DSC III in comparison to the 2wd models? _ 5. What service procedures are required when replacing a steering angle sensor? 6. Describe the operation of the Automatic Differential Lock function. 33
34 Review Questions 7. List the various sensors used to detect oversteer/understeer in the DSC III systems. 8. What is the purpose of the DBS sub-function? 9. What is the handbrake input signal used for? 10. What is the criteria for MBC activation? 11. Briefly explain Corner Braking Control (CBC): 34
Adaptive Cruise Control System Overview
 5th Meeting of the U.S. Software System Safety Working Group April 12th-14th 2005 @ Anaheim, California USA 1 Introduction Adaptive Cruise System Overview Adaptive Cruise () is an automotive feature that
5th Meeting of the U.S. Software System Safety Working Group April 12th-14th 2005 @ Anaheim, California USA 1 Introduction Adaptive Cruise System Overview Adaptive Cruise () is an automotive feature that
VEHICLE SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM
 PL VEHICLE SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM 8H - 1 VEHICLE SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM TABLE OF CONTENTS page DESCRIPTION AND SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM...1 SPEED CONTROL SERVO-PCM OUTPUT....2 SPEED CONTROL SWITCHES PCM INPUT...2
PL VEHICLE SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM 8H - 1 VEHICLE SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM TABLE OF CONTENTS page DESCRIPTION AND SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM...1 SPEED CONTROL SERVO-PCM OUTPUT....2 SPEED CONTROL SWITCHES PCM INPUT...2
Class 5 to 7 Truck and Bus Hydraulic Brake System
 Class 5 to 7 Truck and Bus Hydraulic Brake System Diagnostic Guide 1st Edition * 5+0 Important Service tes The information in this publication was current at the time of printing. The information presented
Class 5 to 7 Truck and Bus Hydraulic Brake System Diagnostic Guide 1st Edition * 5+0 Important Service tes The information in this publication was current at the time of printing. The information presented
Meritor WABCO Pneumatic Antilock Braking System (ABS) 42.22
 (ABS) 2.22 Troubleshooting WARNING Before testing a vehicle equipped with Automatic Traction Control (ATC) on a dynamometer, the ATC system must be disabled. See Subject 160 for instructions. Activation
(ABS) 2.22 Troubleshooting WARNING Before testing a vehicle equipped with Automatic Traction Control (ATC) on a dynamometer, the ATC system must be disabled. See Subject 160 for instructions. Activation
1. SYSTEM OVERVIEW. 1) Basic Theory of ABS Function 10-3 4891-01
 10-3 1. SYSTEM OVERVIEW When braking suddenly or braking on slippery roads, the vehicle keeps moving forward but the wheels are locking and not rotating. If these happen, the vehicle may lose stability
10-3 1. SYSTEM OVERVIEW When braking suddenly or braking on slippery roads, the vehicle keeps moving forward but the wheels are locking and not rotating. If these happen, the vehicle may lose stability
CHASSIS - 4WD SYSTEM. Realizes stable start-off and acceleration performance
 CH-66 CHASSIS - 4WD SYSTEM 4WD SYSTEM DESCRIPTION The 4WD system of the 06 RAV4 uses an active torque control 4WD system. It is a compact, lightweight, and high performance 4WD system that optimally controls
CH-66 CHASSIS - 4WD SYSTEM 4WD SYSTEM DESCRIPTION The 4WD system of the 06 RAV4 uses an active torque control 4WD system. It is a compact, lightweight, and high performance 4WD system that optimally controls
To help avoid personal injury due to poor braking. DO NOT Tap into the vehicle's brake system to operate a trailer brake system.
 489201 133 ANTIBRAKE SYSTEM GENERAL 489201 1. REPAIR INSTRUCTIONS 1) ONVEHICLE SERVICE (1) Service Precautions Brake Fluid may irritate eyes and skin. In case of contact, take the following actions: Eye
489201 133 ANTIBRAKE SYSTEM GENERAL 489201 1. REPAIR INSTRUCTIONS 1) ONVEHICLE SERVICE (1) Service Precautions Brake Fluid may irritate eyes and skin. In case of contact, take the following actions: Eye
Electronic Power Control
 Service. Self-Study Programme 210 Electronic Power Control Design and Function With the Electronic Power Control system, the throttle valve is actuated only by an electric motor. This eliminates the need
Service. Self-Study Programme 210 Electronic Power Control Design and Function With the Electronic Power Control system, the throttle valve is actuated only by an electric motor. This eliminates the need
TOYOTA ELECTRONIC CONTROL TRANSMISSION
 Electronic Control Transmission (ECT) The Electronic Control Transmission is an automatic transmission which uses modern electronic control technologies to control the transmission. The transmission itself,
Electronic Control Transmission (ECT) The Electronic Control Transmission is an automatic transmission which uses modern electronic control technologies to control the transmission. The transmission itself,
Tiguan Haldex All-Wheel Drive
 Service Training Self Study Program 861803 Tiguan Haldex All-Wheel Drive Volkswagen of America, Inc. Volkswagen Academy Printed in U.S.A. Printed 3/2008 Course Number 861803 2008 Volkswagen of America,
Service Training Self Study Program 861803 Tiguan Haldex All-Wheel Drive Volkswagen of America, Inc. Volkswagen Academy Printed in U.S.A. Printed 3/2008 Course Number 861803 2008 Volkswagen of America,
TOYOTA ELECTRONIC TRANSMISSION CHECKS & DIAGNOSIS
 Checks and Adjustments The transmission requires regular maintenance intervals if it is to continue to operate without failure. As we discussed in previous sections, transmission fluid loses certain properties
Checks and Adjustments The transmission requires regular maintenance intervals if it is to continue to operate without failure. As we discussed in previous sections, transmission fluid loses certain properties
Electronically Controlled Air Suspension (ECAS) for Trucks
 $2.50 Electronically Controlled Air Suspension (ECAS) for Trucks Maintenance Manual No. 36 Issued 7-99 ECAS System for 6 x 2 and 6 x 4 Vehicles with Rear Air Suspensions Service Notes Service Notes This
$2.50 Electronically Controlled Air Suspension (ECAS) for Trucks Maintenance Manual No. 36 Issued 7-99 ECAS System for 6 x 2 and 6 x 4 Vehicles with Rear Air Suspensions Service Notes Service Notes This
EBS Electronically controlled Brake system in the city bus CITARO / CITO
 Electronically controlled Brake system in the city bus CITARO / CITO System and functional description 1. Edition Copyright WABCO 2003 Vehicle Control Systems An American Standard Company 8150004073 The
Electronically controlled Brake system in the city bus CITARO / CITO System and functional description 1. Edition Copyright WABCO 2003 Vehicle Control Systems An American Standard Company 8150004073 The
Electrical/electronic components and installation locations
 Volkswagen Passat B5 - Electrical/electronic components and installation locations Page 1 / 24 45-3 Electrical/electronic components and installation locations ABS/EDL/ASR Bosch 5.3 ABS hydraulic unit
Volkswagen Passat B5 - Electrical/electronic components and installation locations Page 1 / 24 45-3 Electrical/electronic components and installation locations ABS/EDL/ASR Bosch 5.3 ABS hydraulic unit
Service Manual Trucks
 Service Manual Trucks Group 36 Vehicle Electronic Control Unit (MID 144), Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC), Guide From build date 1.2007 PV776-88951780 Foreword The descriptions and service procedures contained
Service Manual Trucks Group 36 Vehicle Electronic Control Unit (MID 144), Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC), Guide From build date 1.2007 PV776-88951780 Foreword The descriptions and service procedures contained
Signature and ISX CM870 Electronics
 Signature and ISX CM870 Electronics Cummins West Training Center System Description General Information The Signature and ISX CM870 engine control system is an electronically operated fuel control system
Signature and ISX CM870 Electronics Cummins West Training Center System Description General Information The Signature and ISX CM870 engine control system is an electronically operated fuel control system
BRAKE SYSTEMS 101. Energy Conversion Management. Presented by Paul S. Gritt
 Energy Conversion Management Presented by Paul S. Gritt Topics To Be Presented The Basic Concepts Hydraulic layouts Component functions Brake Balance Stopping Distance and Fade Formula SAE vs. Mini Baja
Energy Conversion Management Presented by Paul S. Gritt Topics To Be Presented The Basic Concepts Hydraulic layouts Component functions Brake Balance Stopping Distance and Fade Formula SAE vs. Mini Baja
SUSPENSION AND STEERING OVERVIEW
 SUSPENSION SUSPENSION AND STEERING OVERVIEW The S40/V50 has a wide track and a long wheelbase for its relative size and weight. This gives the car stable and predictable driving characteristics. It also
SUSPENSION SUSPENSION AND STEERING OVERVIEW The S40/V50 has a wide track and a long wheelbase for its relative size and weight. This gives the car stable and predictable driving characteristics. It also
Electronic Manual Gearbox
 Service. Self-Study Programme 221 Electronic Manual Gearbox Design and Function Taking the Lupo as the basis, Volkswagen has developed the world's first 3 L car that will also go into volume production.
Service. Self-Study Programme 221 Electronic Manual Gearbox Design and Function Taking the Lupo as the basis, Volkswagen has developed the world's first 3 L car that will also go into volume production.
Technical overview of the Carrera 4 AWD and Traction control system (PDAS) and all 964s ABS system. By Adrian Streather
 Technical overview of the Carrera 4 AWD and Traction control system (PDAS) and all 964s ABS system. By Adrian Streather The following information is a brief overview of the more complex 964 systems. Hopefully
Technical overview of the Carrera 4 AWD and Traction control system (PDAS) and all 964s ABS system. By Adrian Streather The following information is a brief overview of the more complex 964 systems. Hopefully
Troubleshooting & Diagnostic Procedures
 Troubleshooting & Diagnostic Procedures Subject Page Troubleshooting and Diagnostic Procedures......................2 Diagnositic Communication.................................. 3 CAN Bus Topology.........................................5
Troubleshooting & Diagnostic Procedures Subject Page Troubleshooting and Diagnostic Procedures......................2 Diagnositic Communication.................................. 3 CAN Bus Topology.........................................5
Adaptive cruise control (ACC)
 Adaptive cruise control (ACC) PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION The Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) system is designed to assist the driver in maintaining a gap from the vehicle ahead, or maintaining a set road speed,
Adaptive cruise control (ACC) PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION The Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) system is designed to assist the driver in maintaining a gap from the vehicle ahead, or maintaining a set road speed,
INSTRUMENT PANEL. 1995 Volvo 850 DESCRIPTION & OPERATION. 1995-96 ACCESSORIES & EQUIPMENT Volvo Instrument Panels
 INSTRUMENT PANEL 1995 Volvo 850 1995-96 ACCESSORIES & EQUIPMENT Volvo Instrument Panels 850 WARNING: When working around steering column and before performing repairs, disconnect and shield battery ground
INSTRUMENT PANEL 1995 Volvo 850 1995-96 ACCESSORIES & EQUIPMENT Volvo Instrument Panels 850 WARNING: When working around steering column and before performing repairs, disconnect and shield battery ground
Basic manual: Contents ELECTRONICALLY CONTROLLED HYDRAULIC SYSTEMS
 TECHNICAL NOTE Edition Anglaise 77 11 205 445 JUNE 1999 Type 3239A Service 0422 Sub-section JE0 X BOSCH 5.3 ABS WITH SPEED INFORMATION FUNCTION Engine: Gearbox: XXX XXX Basic manual: N.T. 3034A This note
TECHNICAL NOTE Edition Anglaise 77 11 205 445 JUNE 1999 Type 3239A Service 0422 Sub-section JE0 X BOSCH 5.3 ABS WITH SPEED INFORMATION FUNCTION Engine: Gearbox: XXX XXX Basic manual: N.T. 3034A This note
Electronic Brake Controller Hayes Brake Controller Company ENERGIZE III P/N # 81741B or ENERGIZE XPC P/N #81745 OPERATION MANUAL
 Electronic Brake Controller Hayes Brake Controller Company ENERGIZE III P/N # 81741B or ENERGIZE XPC P/N #81745 OPERATION MANUAL ENERGIZE III is for trailers with 2 or 4 electric brakes and vehicles with
Electronic Brake Controller Hayes Brake Controller Company ENERGIZE III P/N # 81741B or ENERGIZE XPC P/N #81745 OPERATION MANUAL ENERGIZE III is for trailers with 2 or 4 electric brakes and vehicles with
Longitudinal and lateral dynamics
 Longitudinal and lateral dynamics Lecturer dr. Arunas Tautkus Kaunas University of technology Powering the Future With Zero Emission and Human Powered Vehicles Terrassa 2011 1 Content of lecture Basic
Longitudinal and lateral dynamics Lecturer dr. Arunas Tautkus Kaunas University of technology Powering the Future With Zero Emission and Human Powered Vehicles Terrassa 2011 1 Content of lecture Basic
A Review of Antilock Braking and Traction Control Systems
 A Review of Antilock Braking and Traction Control Systems 4 4.1 BRAKING SYSTEM FUNDAMENTALS, FOUNDATION BRAKES THERE ARE TWO USUAL FORCE INPUTS to a motor vehicle: engine torque to provide acceleration
A Review of Antilock Braking and Traction Control Systems 4 4.1 BRAKING SYSTEM FUNDAMENTALS, FOUNDATION BRAKES THERE ARE TWO USUAL FORCE INPUTS to a motor vehicle: engine torque to provide acceleration
MASTER CYLINDER. Section 2. Master Cylinder. Tandem Master Cylinder. Master Cylinder
 MASTER CYLINDER Master Cylinder The master cylinder converts the motion of the brake pedal into hydraulic pressure. It consists of the reservoir tank, which contains the brake fluid; and the piston and
MASTER CYLINDER Master Cylinder The master cylinder converts the motion of the brake pedal into hydraulic pressure. It consists of the reservoir tank, which contains the brake fluid; and the piston and
TROUBLESHOOTING ABS DIAGNOSTIC CODES L20293, Rev. 1/13
 TROUBLESHOOTING ABS DIAGNOSTIC CODES L20293, Rev. 1/13 Additional information regarding complete ABS Systems can be found in the Haldex Service Manual L30041. This manual can be found on the Haldex website
TROUBLESHOOTING ABS DIAGNOSTIC CODES L20293, Rev. 1/13 Additional information regarding complete ABS Systems can be found in the Haldex Service Manual L30041. This manual can be found on the Haldex website
Volkswagen Golf 4 / Bora (1998-2005), GTI / Jetta (1998-2005), R32 (A4)
 Volkswagen Golf 4 / Bora (1998-2005), GTI / Jetta (1998-2005), R32 (A4) Note: For Guided Fault Finding information, refer to VAS 5051 Diagnostic Tester 01 - On Board Diagnostic (OBD) ABS ITT Mark 20 IE
Volkswagen Golf 4 / Bora (1998-2005), GTI / Jetta (1998-2005), R32 (A4) Note: For Guided Fault Finding information, refer to VAS 5051 Diagnostic Tester 01 - On Board Diagnostic (OBD) ABS ITT Mark 20 IE
04 13 ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM
 04 13 ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM ABS LOCATION INDEX............. 04 13 1 ABS SYSTEM DIAGRAM............ 04 13 2 ABS HYDRAULIC UNIT (HU)/ CONTROL MODULE (CM) SYSTEM INSPECTION............. 04 13 3 System Inspection................
04 13 ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM ABS LOCATION INDEX............. 04 13 1 ABS SYSTEM DIAGRAM............ 04 13 2 ABS HYDRAULIC UNIT (HU)/ CONTROL MODULE (CM) SYSTEM INSPECTION............. 04 13 3 System Inspection................
Stop Alert Flasher with G-Force sensor
 Stop Alert Flasher with G-Force sensor Stop Alert module creates brake light flashing effect to catch attention of the drivers behind to avoid dangerous rear end collision. The flasher module is a state
Stop Alert Flasher with G-Force sensor Stop Alert module creates brake light flashing effect to catch attention of the drivers behind to avoid dangerous rear end collision. The flasher module is a state
BL BOSCH 5.3 ABS. System Description of BL ABS
 System Description of BL ABS BL ABS Specification System - BOSCH ABS 5.3-4Sensor 4Channel - BRAKE Line : X Split - ABS with EBD Control Hydro-Electronic Control Unit (HECU ) - Hydraulic Modulator : Size(84
System Description of BL ABS BL ABS Specification System - BOSCH ABS 5.3-4Sensor 4Channel - BRAKE Line : X Split - ABS with EBD Control Hydro-Electronic Control Unit (HECU ) - Hydraulic Modulator : Size(84
Four-Wheel Drive with Haldex Coupling
 Service. Self-Study Programme 206 Four-Wheel Drive with Haldex Coupling Design and Function Volkswagen and Audi have been building permanent four-wheel drive systems for almost 15 years. In Volkswagen's
Service. Self-Study Programme 206 Four-Wheel Drive with Haldex Coupling Design and Function Volkswagen and Audi have been building permanent four-wheel drive systems for almost 15 years. In Volkswagen's
Introduction. In this Self-study Programme we will explain to you the design and function of the CAN data bus. SSP 186/01
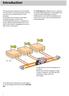 Introduction The requirements relating to driving safety, driving comfort, exhaust emissions and fuel economy are are becoming ever more stringent. This entails more intensive information exchange between
Introduction The requirements relating to driving safety, driving comfort, exhaust emissions and fuel economy are are becoming ever more stringent. This entails more intensive information exchange between
Note: This information obtained from internet sources and not verified- use at your own risk!!!!
 Cummins Engine Diagnostic Fault Codes for 2003 and later engines (generally for 2004 and later Alpines; see page 13 for earlier engine diagnostic codes): Note: This information obtained from internet sources
Cummins Engine Diagnostic Fault Codes for 2003 and later engines (generally for 2004 and later Alpines; see page 13 for earlier engine diagnostic codes): Note: This information obtained from internet sources
E70 Rear-view Camera (RFK)
 Table of Contents (RFK) Subject Page Introduction..................................................3 Rear-view Camera..............................................3 Input/Output...................................................4
Table of Contents (RFK) Subject Page Introduction..................................................3 Rear-view Camera..............................................3 Input/Output...................................................4
B777. Landing Gear DO NOT USE FOR FLIGHT
 B777 Landing Gear DO NOT USE FOR FLIGHT Introduction The airplane has two main landing gear and a single nose gear. The nose gear is a conventional steerable two wheel unit. Each main gear has six wheels
B777 Landing Gear DO NOT USE FOR FLIGHT Introduction The airplane has two main landing gear and a single nose gear. The nose gear is a conventional steerable two wheel unit. Each main gear has six wheels
Wynn s Extended Care
 Wynn s Extended Care Every car deserves to receive the very best care... especially yours. How Do You Keep Your Reliable Transportation Reliable? Count on Wynn s Because Wynn s has been caring for cars
Wynn s Extended Care Every car deserves to receive the very best care... especially yours. How Do You Keep Your Reliable Transportation Reliable? Count on Wynn s Because Wynn s has been caring for cars
User s Manual. Diagnostic and On-Screen Service Instructions For:
 Rev 01-04 User s Manual TOOLBOX TM SOFTWARE W H ME R I T O R A T Y O U WA B C O Diagnostic and On-Screen Service Instructions For: TOOLBOX Pneumatic ABS (D and E Versions) Trailer ABS (Easy-Stop TM and
Rev 01-04 User s Manual TOOLBOX TM SOFTWARE W H ME R I T O R A T Y O U WA B C O Diagnostic and On-Screen Service Instructions For: TOOLBOX Pneumatic ABS (D and E Versions) Trailer ABS (Easy-Stop TM and
Air conditioning, electrical testing
 just a test. Air conditioning, electrical testing 01-253 Wire and component test using VAG1598 A test box Special tools and equipment VAG 1598 A test box and VAG 1598/11 adapter cable and VAG 1598/12 VAG1526
just a test. Air conditioning, electrical testing 01-253 Wire and component test using VAG1598 A test box Special tools and equipment VAG 1598 A test box and VAG 1598/11 adapter cable and VAG 1598/12 VAG1526
TC Series Hydraulic Brake ABS System
 TC Series Hydraulic Brake ABS System Blue Bird Corporation assumes sole responsibility for ensuring that the information provided herein is accurate to the best of its knowledge at the time of printing.
TC Series Hydraulic Brake ABS System Blue Bird Corporation assumes sole responsibility for ensuring that the information provided herein is accurate to the best of its knowledge at the time of printing.
M.S Ramaiah School of Advanced Studies - Bangalore. On completion of this session, the delegate will understand and be able to appriciate:
 Transmission Control Lecture delivered by: Prof. Ashok C.Meti MSRSAS-Bangalore 1 Session Objectives On completion of this session, the delegate will understand and be able to appriciate: Rl Role of electronic
Transmission Control Lecture delivered by: Prof. Ashok C.Meti MSRSAS-Bangalore 1 Session Objectives On completion of this session, the delegate will understand and be able to appriciate: Rl Role of electronic
ABS Flash Code (Blink Code) Instructions
 ABS Flash Code (Blink Code) Instructions Innovative Products of America Incorporated Tinker Street, Woodsttock, NY 8 Local: 8-6-00 Toll Free: 888-86-8 Fax: 8-6-600 www.ipatools.com [email protected] ABS
ABS Flash Code (Blink Code) Instructions Innovative Products of America Incorporated Tinker Street, Woodsttock, NY 8 Local: 8-6-00 Toll Free: 888-86-8 Fax: 8-6-600 www.ipatools.com [email protected] ABS
Active Yaw Systems: Re-experience Front Wheel Drive with SCHNELLSTER and TWINSTER +
 Active Yaw Systems: Re-experience Front Wheel Drive with SCHNELLSTER and TWINSTER + Peter Obergünner 1 Content Introduction Investigation of different driveline configurations Functional Description -
Active Yaw Systems: Re-experience Front Wheel Drive with SCHNELLSTER and TWINSTER + Peter Obergünner 1 Content Introduction Investigation of different driveline configurations Functional Description -
Road Sensing Suspension System
 Knowles.CM-Ch_08.qxd 9/14/02 2:04 PM Page 202 Road Sensing Suspension System A continuously variable road sensing suspension () system adjusts shock absorber and strut damping in relation to road and driving
Knowles.CM-Ch_08.qxd 9/14/02 2:04 PM Page 202 Road Sensing Suspension System A continuously variable road sensing suspension () system adjusts shock absorber and strut damping in relation to road and driving
INTERACTIVE DISTANCE LEARNING ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SPECIALIST: KELSEY HAYES REAR WHEEL ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEMS (RWAL/RABS)
 INTERACTIVE DISTANCE LEARNING ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SPECIALIST: KELSEY HAYES REAR WHEEL ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEMS (RWAL/RABS) LEARNING GUIDE CARS KNOWLEDGE NETWORK 6 9120 Leslie Street Richmond Hill, ON L4B
INTERACTIVE DISTANCE LEARNING ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SPECIALIST: KELSEY HAYES REAR WHEEL ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEMS (RWAL/RABS) LEARNING GUIDE CARS KNOWLEDGE NETWORK 6 9120 Leslie Street Richmond Hill, ON L4B
ELECTRICAL WIRING (R.H. DRIVE VEHICLES)
 C-1 ELECTRICAL WIRING (R.H. DRIVE VEHICLES) CONTENTS GENERAL.......................... 3 WIRING HARNESS CONFIGURATION DIAGRAMS......................... 4 ENGINE COMPARTMENT................ 4 DASH PANEL...........................
C-1 ELECTRICAL WIRING (R.H. DRIVE VEHICLES) CONTENTS GENERAL.......................... 3 WIRING HARNESS CONFIGURATION DIAGRAMS......................... 4 ENGINE COMPARTMENT................ 4 DASH PANEL...........................
ILISC515-A Shift Interlock (Manual Lift Door) 2015 Ford Transit, 3.7L and 3.5L
 An ISO 9001:2008 Registered Company ILISC515-A Shift Interlock (Manual Lift Door) 2015 Ford Transit, 3.7L and 3.5L Introduction The ILISC515-A is a microprocessor driven system for controlling wheelchair
An ISO 9001:2008 Registered Company ILISC515-A Shift Interlock (Manual Lift Door) 2015 Ford Transit, 3.7L and 3.5L Introduction The ILISC515-A is a microprocessor driven system for controlling wheelchair
The Starting System. Section 4. Starting System Overview. Starter. The starting system:
 The Starting System Starter The starter motor drives the engine through a pinion gear that engages the ring gear on the flywheel. Fig. 4-01 TL623f401c Starting System Overview The starting system: Uses
The Starting System Starter The starter motor drives the engine through a pinion gear that engages the ring gear on the flywheel. Fig. 4-01 TL623f401c Starting System Overview The starting system: Uses
E/ECE/324/Rev.1/Add.12/Rev.7/Amend.4 E/ECE/TRANS/505/Rev.1/Add.12/Rev.7/Amend.4
 6 December 2012 Agreement Concerning the adoption of uniform technical prescriptions for wheeled vehicles, equipment and parts which can be fitted and/or be used on wheeled vehicles and the conditions
6 December 2012 Agreement Concerning the adoption of uniform technical prescriptions for wheeled vehicles, equipment and parts which can be fitted and/or be used on wheeled vehicles and the conditions
ANTI LOCK BRAKING SYSTEM MODELLING AND DEVELOPMENT
 ANTI LOCK BRAKING SYSTEM MODELLING AND DEVELOPMENT Aldi Manikanth ME10B004 A Manoj Kumar ME10B006 C Vijay Chauhan ME10B010 Nachiket Dongre ME10B013 Lithas ME10B020 Rajesh Kumar Meena ME10B030 Varada Karthik
ANTI LOCK BRAKING SYSTEM MODELLING AND DEVELOPMENT Aldi Manikanth ME10B004 A Manoj Kumar ME10B006 C Vijay Chauhan ME10B010 Nachiket Dongre ME10B013 Lithas ME10B020 Rajesh Kumar Meena ME10B030 Varada Karthik
CONTINUOUSLY VARIABLE TRANSMISSION (CVT)
 GROUP 23 CONTINUOUSLY VARIABLE TRANSMISSION (CVT) CONTENTS CVT........................... 23-2 GENERAL INFORMATION............. 23-2 ELECTRONIC CONTROL SYSTEM...... 23-3 EEPROM...........................
GROUP 23 CONTINUOUSLY VARIABLE TRANSMISSION (CVT) CONTENTS CVT........................... 23-2 GENERAL INFORMATION............. 23-2 ELECTRONIC CONTROL SYSTEM...... 23-3 EEPROM...........................
USER MANUAL OPERATION AND USE OF CAR WITH. Diego G3 / NEVO SEQUENTIAL GAS INJECTION SYSTEM
 USER MANUAL OPERATION AND USE OF CAR WITH Diego G3 / NEVO SEQUENTIAL GAS INJECTION SYSTEM Page 2 z 7 Table of contents 1. STARTING THE ENGINE... 3 2. CONTROL PANEL... 3 2.1 Indication of the current level
USER MANUAL OPERATION AND USE OF CAR WITH Diego G3 / NEVO SEQUENTIAL GAS INJECTION SYSTEM Page 2 z 7 Table of contents 1. STARTING THE ENGINE... 3 2. CONTROL PANEL... 3 2.1 Indication of the current level
PUSH BUTTON START INSTALLATION MANUAL
 PUSH BUTTON START INSTALLATION MANUAL ALTHOUGH THIS PRODUCT HAS BEEN THOROUGHLY TESTED KPIERSON TECHNOLOGIES ASSUMES NO RESPONSIBILITY FOR ANY DAMAGE THAT MAY RESULT BY THE INSTALLATION OF THIS PRODUCT.
PUSH BUTTON START INSTALLATION MANUAL ALTHOUGH THIS PRODUCT HAS BEEN THOROUGHLY TESTED KPIERSON TECHNOLOGIES ASSUMES NO RESPONSIBILITY FOR ANY DAMAGE THAT MAY RESULT BY THE INSTALLATION OF THIS PRODUCT.
Heater and Air Conditioner, Blend Air System, Troubleshooting 83.06
 A/C Performance Diagnosis Problem Warm Airflow When the Air Conditioner is On, A/C Not Working, or Poor A/C Performance (dash outlet temperature is too high) Problem Warm Airflow When the Air Conditioner
A/C Performance Diagnosis Problem Warm Airflow When the Air Conditioner is On, A/C Not Working, or Poor A/C Performance (dash outlet temperature is too high) Problem Warm Airflow When the Air Conditioner
Technical Service Information
 Technical Service Information COMPLAINT: CAUSE: 1996-20 DEFINITIONS When a VW/Audi vehicle is exhibiting a symptom or is in fail-safe, the technician, in many cases, is unable to communicate with the on-board
Technical Service Information COMPLAINT: CAUSE: 1996-20 DEFINITIONS When a VW/Audi vehicle is exhibiting a symptom or is in fail-safe, the technician, in many cases, is unable to communicate with the on-board
SD-13-4869. Bendix EC-60 ABS / ATC / ESP Controllers (Advanced Models) INTRODUCTION
 SD-13-4869 Bendix EC-60 ABS / ATC / ESP Controllers (Advanced Models) See SD-13-4863 for Standard and Premium Controllers FIGURE 1 - EC-60 ADVANCED CONTROLLER INTRODUCTION The Bendix EC-60 advanced controller
SD-13-4869 Bendix EC-60 ABS / ATC / ESP Controllers (Advanced Models) See SD-13-4863 for Standard and Premium Controllers FIGURE 1 - EC-60 ADVANCED CONTROLLER INTRODUCTION The Bendix EC-60 advanced controller
Diagnosing and Understanding Starting Problems on the ZR-1 Marc Haibeck 28-Sep-13
 Diagnosing and Understanding Starting Problems on the ZR-1 Marc Haibeck 28-Sep-13 There are three basic failure conditions: - A VATS security system lockout - A click from the starter solenoid but no engine
Diagnosing and Understanding Starting Problems on the ZR-1 Marc Haibeck 28-Sep-13 There are three basic failure conditions: - A VATS security system lockout - A click from the starter solenoid but no engine
E - THEORY/OPERATION
 E - THEORY/OPERATION 1995 Volvo 850 1995 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo - Theory & Operation 850 INTRODUCTION This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related systems and components.
E - THEORY/OPERATION 1995 Volvo 850 1995 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo - Theory & Operation 850 INTRODUCTION This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related systems and components.
OPTO-PLUS 204. Type DSX2
 1 OPTO-PLUS 204 Type DSX2 OPTO-ELECTRONIC LASER ALIGNER Operators manual 2 Operators manual for OPTO-PLUS wheel aligner Model 204 Type DSX2 (Dual Sensor Doubble Laser) INDEX Accessories and specifications
1 OPTO-PLUS 204 Type DSX2 OPTO-ELECTRONIC LASER ALIGNER Operators manual 2 Operators manual for OPTO-PLUS wheel aligner Model 204 Type DSX2 (Dual Sensor Doubble Laser) INDEX Accessories and specifications
E46 IHKA... 4. Control Panel... 4. Fresh Air Micro Filter... 5. Temperature Regulation - Heating... 6. Temperature Regulation - Cooling...
 Table of Contents E46 CLIMATE CONTROL Subject Page E46 IHKA................................................ 4 Control Panel........................................... 4 Fresh Air Micro Filter......................................
Table of Contents E46 CLIMATE CONTROL Subject Page E46 IHKA................................................ 4 Control Panel........................................... 4 Fresh Air Micro Filter......................................
Table of Contents. E70 Park Distance Control (PDC)
 Table of Contents (PDC) Subject Page Introduction..................................................4 Park Distance Control...........................................4 Input/Output - Park Distance Control..............................5
Table of Contents (PDC) Subject Page Introduction..................................................4 Park Distance Control...........................................4 Input/Output - Park Distance Control..............................5
Fire suppression system for engine compartments USER MANUAL
 Fire suppression system for engine compartments USER MANUAL Contractor s machinery/vehicles, tooling machines and special machines Edition 2011-3 Hydro pneumatic activation Mechanical activation Electrical
Fire suppression system for engine compartments USER MANUAL Contractor s machinery/vehicles, tooling machines and special machines Edition 2011-3 Hydro pneumatic activation Mechanical activation Electrical
Electronic Diesel Control EDC 16
 Service. Self-Study Programme 304 Electronic Diesel Control EDC 16 Design and Function The new EDC 16 engine management system from Bosch has its debut in the V10-TDI- and R5-TDI-engines. Increasing demands
Service. Self-Study Programme 304 Electronic Diesel Control EDC 16 Design and Function The new EDC 16 engine management system from Bosch has its debut in the V10-TDI- and R5-TDI-engines. Increasing demands
ELECTRONICALLY CONTROLLED BRAKE SYSTEM
 BRAKE CONTROL ELECTRONICALLY CONTROLLED BRAKE SYSTEM 1 ELECTRONICALLY CONTROLLED BRAKE SYSTEM PRECAUTION 1. TROUBLESHOOTING PRECAUTION When there is a malfunction with terminal contact points or part installation
BRAKE CONTROL ELECTRONICALLY CONTROLLED BRAKE SYSTEM 1 ELECTRONICALLY CONTROLLED BRAKE SYSTEM PRECAUTION 1. TROUBLESHOOTING PRECAUTION When there is a malfunction with terminal contact points or part installation
UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION TO AUTOMOBILE ENGINEERING
 UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION TO AUTOMOBILE ENGINEERING Introduction to Automobile Engineering Structure 1.1 Introduction Objectives 1.2 Definition 1.3 Classification of Vehicles 1.4 Layout of an Automobile Chassis
UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION TO AUTOMOBILE ENGINEERING Introduction to Automobile Engineering Structure 1.1 Introduction Objectives 1.2 Definition 1.3 Classification of Vehicles 1.4 Layout of an Automobile Chassis
Vario Roof. Model R171. 287 HO 04 Vario Roof (CrullG) 08-17-04
 Vario Roof Model R171 287 HO 04 Vario Roof (CrullG) 08-17-04 1 Objectives At the end of this session, you will be able to: 1. Explain how roof can be operated 2. Explain operation of front and rear windows
Vario Roof Model R171 287 HO 04 Vario Roof (CrullG) 08-17-04 1 Objectives At the end of this session, you will be able to: 1. Explain how roof can be operated 2. Explain operation of front and rear windows
Wheel speed sensors in motor vehicles. Function, diagnosis, troubleshooting. Thermal Management. Sales Support. Our Ideas, Your Success.
 Lighting Electrics Electronics Thermal Management Sales Support Technical Service Our Ideas, Your Success. Wheel speed sensors in motor vehicles Function, diagnosis, troubleshooting. Ideas today for the
Lighting Electrics Electronics Thermal Management Sales Support Technical Service Our Ideas, Your Success. Wheel speed sensors in motor vehicles Function, diagnosis, troubleshooting. Ideas today for the
Introduction to Electronic Signals
 Introduction to Electronic Signals Oscilloscope An oscilloscope displays voltage changes over time. Use an oscilloscope to view analog and digital signals when required during circuit diagnosis. Fig. 6-01
Introduction to Electronic Signals Oscilloscope An oscilloscope displays voltage changes over time. Use an oscilloscope to view analog and digital signals when required during circuit diagnosis. Fig. 6-01
Transmission electronic controls outline. Inputs- processing- outputs
 Transmission electronic controls outline Inputs- processing- outputs Inputs provide the system the environmental conditions that are needed to operate or check the operation of the transmission. Inputs
Transmission electronic controls outline Inputs- processing- outputs Inputs provide the system the environmental conditions that are needed to operate or check the operation of the transmission. Inputs
EVBIKE LCD Display Control User Guide. EVBIKE LCD Display Control User Guide WWW.EVBIKE.CZ - 1 -
 EVBIKE LCD Display Control User Guide WWW.EVBIKE.CZ - 1 - Table of Contents: 1) Description of the individual components and installation 2) Description of the measured quantities and user control display
EVBIKE LCD Display Control User Guide WWW.EVBIKE.CZ - 1 - Table of Contents: 1) Description of the individual components and installation 2) Description of the measured quantities and user control display
Fault codes DM1. Industrial engines DC09, DC13, DC16. Marine engines DI09, DI13, DI16 INSTALLATION MANUAL. 03:10 Issue 5.0 en-gb 1
 Fault codes DM1 Industrial engines DC09, DC13, DC16 Marine engines DI09, DI13, DI16 03:10 Issue 5.0 en-gb 1 DM1...3 Abbreviations...3 Fault type identifier...3...4 03:10 Issue 5.0 en-gb 2 DM1 DM1 Fault
Fault codes DM1 Industrial engines DC09, DC13, DC16 Marine engines DI09, DI13, DI16 03:10 Issue 5.0 en-gb 1 DM1...3 Abbreviations...3 Fault type identifier...3...4 03:10 Issue 5.0 en-gb 2 DM1 DM1 Fault
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS ZF 6HP26 TRANSMISSION
 ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS ZF 6HP26 TRANSMISSION Vehicle Coverage: XK8 from 2003 model year XJ Range from 2003 model year S-Type from 2003 model year Jaguar Cars Revision Date: October 2003 Page 1 of 30 1 Contents
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS ZF 6HP26 TRANSMISSION Vehicle Coverage: XK8 from 2003 model year XJ Range from 2003 model year S-Type from 2003 model year Jaguar Cars Revision Date: October 2003 Page 1 of 30 1 Contents
SMARTBOARD DRIVER MANUAL
 SMARTBOARD DRIVER MANUAL SMARTBOAD DRIVER MANUAL INTRODUCTION Monitoring a wide range of trailer s is important for improving the performance of haulage company operations and reducing the costs of the
SMARTBOARD DRIVER MANUAL SMARTBOAD DRIVER MANUAL INTRODUCTION Monitoring a wide range of trailer s is important for improving the performance of haulage company operations and reducing the costs of the
Operating Instructions Display, graphic. Numeric language
 Operating Instructions Display, graphic Numeric language Contents Numeric language, general... 1 Numeric language, general... 1 Display control stalk... 1 Text strings... 1 Stop message... 2 Change language...
Operating Instructions Display, graphic Numeric language Contents Numeric language, general... 1 Numeric language, general... 1 Display control stalk... 1 Text strings... 1 Stop message... 2 Change language...
TOYOTA TECHNICAL. An example of a tire pressure monitor valve sub-assembly. This mounts to a drop area in the wheel.
 TOYOTA TIRE PRESSURE WARNING SYSTEM Toyota uses various tire pressure warning systems. Here, we ll discuss the system featured on the 2006 Land Cruiser. Combination meter warning reset switch warning reset
TOYOTA TIRE PRESSURE WARNING SYSTEM Toyota uses various tire pressure warning systems. Here, we ll discuss the system featured on the 2006 Land Cruiser. Combination meter warning reset switch warning reset
PROCEDURES FOR SELF DIAGNOSTICS
 PROCEDURES FOR SELF DIAGNOSTICS Baum Tools Unlimited Inc. March 31, 1999 TAU 2.1 READING ACTUAL VALUES 1. Remove the operating console from the TAU 2. At the upper side of the operating consol there is
PROCEDURES FOR SELF DIAGNOSTICS Baum Tools Unlimited Inc. March 31, 1999 TAU 2.1 READING ACTUAL VALUES 1. Remove the operating console from the TAU 2. At the upper side of the operating consol there is
The Aftertreatment System Technician's Guide has been revised.
 NUMBER: 2 ATS 07 S.M. REF.: Listed in Table 1 ENGINE: ATS DATE: April 2007 SUBJECT: UPDATES TO AFTERTREATMENT SYSTEM TROUBLESHOOTING PUBLICATION: 7SE63 The Aftertreatment System Technician's Guide has
NUMBER: 2 ATS 07 S.M. REF.: Listed in Table 1 ENGINE: ATS DATE: April 2007 SUBJECT: UPDATES TO AFTERTREATMENT SYSTEM TROUBLESHOOTING PUBLICATION: 7SE63 The Aftertreatment System Technician's Guide has
Vario Tractors - Fault Codes. Faults. all Vario tractors Tractor / General system. EDC / EMR bus fault. Fault in ECU Programming errors in ECU.
 12/1999 f 1/58 Vario Tractors - Codes 0000 000001 Date Version Page Capitel Index Docu-No. FCT_InitPage 0.0.11 A021; A022 Id rief description Description Consequences Link FENDIAS / Note ECU, EDC; ECU,
12/1999 f 1/58 Vario Tractors - Codes 0000 000001 Date Version Page Capitel Index Docu-No. FCT_InitPage 0.0.11 A021; A022 Id rief description Description Consequences Link FENDIAS / Note ECU, EDC; ECU,
Fixed Right First Time. Volvo Technicians, Service and Parts Managers
 Tech-Net Notes Fixed Right First Time Volvo Technicians, Service and Parts Managers NO: 25-149-A DATE: 04-03-06 MODEL/YEAR: C70 1999-2002 S70 1999-2000 S60 2001 all engine variants, 2002 non-turbo only.
Tech-Net Notes Fixed Right First Time Volvo Technicians, Service and Parts Managers NO: 25-149-A DATE: 04-03-06 MODEL/YEAR: C70 1999-2002 S70 1999-2000 S60 2001 all engine variants, 2002 non-turbo only.
MEASURING WHEEL ALIGNMENT
 MEASURING WHEEL ALIGNMENT 2003-04 WHEEL ALIGNMENT Specifications & Procedures - Hummer - H2 Steering and vibration complaints are not always the result of improper alignment. One possible cause is wheel
MEASURING WHEEL ALIGNMENT 2003-04 WHEEL ALIGNMENT Specifications & Procedures - Hummer - H2 Steering and vibration complaints are not always the result of improper alignment. One possible cause is wheel
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle. Course Final Review
 Automatic Transmission/Transaxle Course Final Review An automatic transmission s torque converter connects and disconnects the engine and transmission. Pistons and servos, planetary gearsets & transmission
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle Course Final Review An automatic transmission s torque converter connects and disconnects the engine and transmission. Pistons and servos, planetary gearsets & transmission
BACK PRESSURE MONITOR Operator Display with Exhaust Temperature KIT 194-722
 HEWITT INDUSTRIES 5492 BOLSA AVE. HUNTINGTON BEACH, CA 92649 PH. (714) 891-9300 FAX. (714) 897-7632 WEBSITE: www.hewittindustries.com E-MAIL: [email protected] BACK PRESSURE MONITOR Operator Display
HEWITT INDUSTRIES 5492 BOLSA AVE. HUNTINGTON BEACH, CA 92649 PH. (714) 891-9300 FAX. (714) 897-7632 WEBSITE: www.hewittindustries.com E-MAIL: [email protected] BACK PRESSURE MONITOR Operator Display
Chapter 4 DEFENSIVE DRIVING
 Chapter 4 DEFENSIVE DRIVING Chapter 4 Table of Contents Chapter 4 DEFENSIVE DRIVING... 4-1 DEFENSIVE DRIVING... 4-3 Positioning The Bus... 4-3 When Making a Turn at an Intersection... 4-3 Making the perfect
Chapter 4 DEFENSIVE DRIVING Chapter 4 Table of Contents Chapter 4 DEFENSIVE DRIVING... 4-1 DEFENSIVE DRIVING... 4-3 Positioning The Bus... 4-3 When Making a Turn at an Intersection... 4-3 Making the perfect
TECHNICAL BULLETIN. Meritor WABCO Cab Leveling Valves and Chassis Leveling Valves. How the Cab Leveling and Chassis Leveling Valves Work
 Revised 02-00 TECHNICAL BULLETIN Meritor WABCO Cab Leveling Valves and Chassis Leveling Valves This technical bulletin covers both cab and chassis leveling valves manufactured by Meritor WABCO. While the
Revised 02-00 TECHNICAL BULLETIN Meritor WABCO Cab Leveling Valves and Chassis Leveling Valves This technical bulletin covers both cab and chassis leveling valves manufactured by Meritor WABCO. While the
ADVANCED BRAKE ALERT SYSTEM
 ADVANCED BRAKE ALERT SYSTEM Dr.A.Aruna Kumari 1, V.Siva Rama Krishna 2 Associate Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, JNTU College of Engineering Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh, India 1. Assistant
ADVANCED BRAKE ALERT SYSTEM Dr.A.Aruna Kumari 1, V.Siva Rama Krishna 2 Associate Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, JNTU College of Engineering Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh, India 1. Assistant
Troubleshooting Guide for Jacks Down LED Lights
 Troubleshooting Guide for Jacks Down LED Lights Equalizer Systems Auto-Level systems manufactured after 2005 feature a pressure switch system that monitors the retracted state of leveling jacks and any
Troubleshooting Guide for Jacks Down LED Lights Equalizer Systems Auto-Level systems manufactured after 2005 feature a pressure switch system that monitors the retracted state of leveling jacks and any
PART 2 FORKLIFT HYDRAULIC SYSTEM
 PART 2 FORKLIFT HYDRAULIC SYSTEM Chapter 1 Description and Operation Component Locations & Circuit Layouts 1 Hydraulic Pump 11 Control Valve 14 Valve Section Oil Flows 15 Anti-Cavitation Valve 22 Velocity
PART 2 FORKLIFT HYDRAULIC SYSTEM Chapter 1 Description and Operation Component Locations & Circuit Layouts 1 Hydraulic Pump 11 Control Valve 14 Valve Section Oil Flows 15 Anti-Cavitation Valve 22 Velocity
INSPECTION BEFORE RIDING
 INSPECTION BEFORE RIDING Check the following items before riding. ITEM Engine cum transmission oil Fuel Tyres Battery Speedometer Lighting Steering Throttle Clutch Brakes Wheels WHAT TO CHECK FOR Availability
INSPECTION BEFORE RIDING Check the following items before riding. ITEM Engine cum transmission oil Fuel Tyres Battery Speedometer Lighting Steering Throttle Clutch Brakes Wheels WHAT TO CHECK FOR Availability
Hybrid System Overview
 1 Hybrid System Overview January 31, 2004 2 Chevrolet Silverado / GMC Sierra Models: Extended Cab Short Box, 2WD & 4WD Engine: VORTEC 5.3 Liter V-8 Transmission: 4-speed auto transmission Power: 295 hp
1 Hybrid System Overview January 31, 2004 2 Chevrolet Silverado / GMC Sierra Models: Extended Cab Short Box, 2WD & 4WD Engine: VORTEC 5.3 Liter V-8 Transmission: 4-speed auto transmission Power: 295 hp
Electro-Mechanical Landing Gear System. Landing Gear and Brakes
 Electro-Mechanical Landing Gear System N O 2 D U A L F E D B U S LANDING RELAY 5A DOWN EMERGENCY EXTENSION DOWN LIMIT GROUND AIRBORNE DOWN LIMIT Landing Gear and Brakes DOWNLOCK HOOK ENGAGED GROUND AIRBORNE
Electro-Mechanical Landing Gear System N O 2 D U A L F E D B U S LANDING RELAY 5A DOWN EMERGENCY EXTENSION DOWN LIMIT GROUND AIRBORNE DOWN LIMIT Landing Gear and Brakes DOWNLOCK HOOK ENGAGED GROUND AIRBORNE
(A5) Brakes Sample Questions and Answers
 (A5) Brakes Sample Questions and Answers Answers to these questions are found beginning on page 4 of this document 1. Two technicians are discussing a problem where the brake pedal travels too far before
(A5) Brakes Sample Questions and Answers Answers to these questions are found beginning on page 4 of this document 1. Two technicians are discussing a problem where the brake pedal travels too far before
Octavia (1U) 17-Dashboard up to 00 identification Octavia (1U) 17-Dashboard up to 00 07 - Coding Octavia (1U) 17-Dashboard up to 00 10 - Adaptation
 Octavia (1U) 17-Dashboard up to 00 identification Octavia (1U) 17-Dashboard up to 00 07 - Coding Octavia (1U) 17-Dashboard up to 00 10 - Adaptation Octavia (1U) 17-Dashboard from 01 identification Octavia
Octavia (1U) 17-Dashboard up to 00 identification Octavia (1U) 17-Dashboard up to 00 07 - Coding Octavia (1U) 17-Dashboard up to 00 10 - Adaptation Octavia (1U) 17-Dashboard from 01 identification Octavia
Electrical Systems - IQAN Digital Control System. IQAN Control System Components... 5.1.3
 Section 5.1 Electrical Systems - IQAN Digital Control System IQAN Control System Components........................... 5.1.3 IQAN Operational Description: At Machine Startup.....................................
Section 5.1 Electrical Systems - IQAN Digital Control System IQAN Control System Components........................... 5.1.3 IQAN Operational Description: At Machine Startup.....................................
Installation Guide. Contents. D Version Hydraulic ABS
 Revised 0-00 Installation Guide Hydraulic Anti-Lock Braking System (HABS) Installation Guide for OEMs and Body Builders (Includes Body Builder Installation Information) D Version Hydraulic ABS This guide
Revised 0-00 Installation Guide Hydraulic Anti-Lock Braking System (HABS) Installation Guide for OEMs and Body Builders (Includes Body Builder Installation Information) D Version Hydraulic ABS This guide
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION IN-CAR DIAGNOSTICS
 Learning Guide CHASSIS ELECTRICAL SPECIALIST AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION IN-CAR DIAGNOSTICS COURSE NUMBER: C050-01 Notice Due to the wide range of vehicles makes and models, the information given during the
Learning Guide CHASSIS ELECTRICAL SPECIALIST AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION IN-CAR DIAGNOSTICS COURSE NUMBER: C050-01 Notice Due to the wide range of vehicles makes and models, the information given during the
Automotive Technician-Advanced
 Job Ready Assessment Blueprint Automotive Technician-Advanced Test Code: 4008 / Version: 01 Copyright 2006. All Rights Reserved. General Assessment Information Automotive Technician-Advanced Blueprint
Job Ready Assessment Blueprint Automotive Technician-Advanced Test Code: 4008 / Version: 01 Copyright 2006. All Rights Reserved. General Assessment Information Automotive Technician-Advanced Blueprint
Meritor WABCO Hydraulic Power Brake (HPB) System Bleeding Procedures
 Issued 03-10 Technical Bulletin Meritor WABCO Hydraulic Power Brake (HPB) System Bleeding Procedures Issued 1 Technical 03-10 Bulletin Hazard Alert Messages Read and observe all Warning and Caution hazard
Issued 03-10 Technical Bulletin Meritor WABCO Hydraulic Power Brake (HPB) System Bleeding Procedures Issued 1 Technical 03-10 Bulletin Hazard Alert Messages Read and observe all Warning and Caution hazard
Volkswagen Jetta, Golf, GTI 1999, 2000 Brake System 47 Brakes - Hydraulic Components (Page GR-47)
 47 Brakes - Hydraulic Components (Page GR-47) FS III front brake calipers, servicing Front brake caliper piston, removing and installing FN 3 front brake calipers, servicing Front caliper piston, removing
47 Brakes - Hydraulic Components (Page GR-47) FS III front brake calipers, servicing Front brake caliper piston, removing and installing FN 3 front brake calipers, servicing Front caliper piston, removing
