PREGNANCY WEEK BY WEEK
|
|
|
- Nickolas Casey
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Department of Health PREGNANCY WEEK BY WEEK This section describes week by week the way that your baby develops during your pregnancy. During the 40 weeks or so of pregnancy, your baby will grow from a pinprick-sized cluster of cells to a baby boy or girl weighing an average of 3.4 kilograms. Pregnancy Week by Week also looks at some of the changes your body goes through at this time, and how your emotions and experiences may change as your pregnancy progresses. Each woman will experience pregnancy slightly differently so you should see the stages of pregnancy described here as just a guide. It lets you know what is likely to be happening to your body at each stage of your pregnancy and tells you about your baby's growth and development. Keep in mind that different pregnancies develop at different rates. The measurements given for weight and length are averages - this means that your baby may grow slower or faster and still be growing well. may like to think about keeping a diary during your pregnancy. r diary can become a special place to write down how you are feeling and the changes you are experiencing in your body as your baby grows. A pregnancy diary can be a wonderful record to look back on after your baby is born. CONCEPTION BABY S GROWTH IN THE FIRST 3 MONTHS BABY S GROWTH IN THE SECOND 3 MONTHS BABY S GROWTH IN THE LAST 3 MONTHS CONCEPTION Pregnancy begins when an egg (ovum) is released from your ovary about midway between menstrual periods, and is fertilised by a male cell (sperm). Fertilization usually takes place in the outer end of the Fallopian tube. Millions of sperm surround the ovum, but only one can enter it. As the head of the sperm enters the ovum its tail fall off. As the fertilized egg moves down the Fallopian tube, it divides into two cells. The cells keep dividing until a solid ball of cells has been formed. When it reaches the womb, this ball of cells becomes attached to the wall of the womb. Once the ball of cells is attached, the tissue surrounding produces hormones which help the pregnancy to continue. PREGNANCY WEEK BY WEEK - July 2004 Page 1
2 The ball of cells, which develops into the baby, is referred to as the embryo at this stage. The part of the ball of cells which attaches to the wall of your womb becomes three things the umbilical cord, the placenta, and the amniotic sac. These are all very important for the growth and protection of the baby. BABY S GROWTH IN THE FIRST 3 MONTHS During the first 12 weeks or 3 months of your pregnancy, you will usually only put on about 1 or 2 kilos, or possibly less if you have morning sickness. Most of this weight is in the placenta (the afterbirth) and in your breasts, uterus and in the extra blood your body will make. During pregnancy your body works harder, your heartbeat and breathing rate are faster. Hormones may make your breasts become tender to the touch, and become larger and heavier. r uterus will get bigger and put pressure on your bladder so that you need to urinate (pass water) more often. This section provides you with a week by week summary of what is happening to your body and to your baby. Don t worry if you think you are different from the week by week stages in this section, as every woman will experience her pregnancy slightly differently. Always discuss any concerns or worries you may have during your pregnancy with a doctor or midwife. may also like to link to other parts of this site to find more information on some of the issues that are important during you first trimester (3 months). For more information on healthy eating in pregnancy Preparing for Pregnancy - Watching what you eat. To find out more about smoking, alcohol, medicines and coffee in pregnancy, please see the section Staying well - Avoid smoking, alcohol and drugs. will find more information about folic acid (folate) in Preparing for Pregnancy - Folic acid (folate) Week 3 Each week of your pregnancy is numbered by the amount of weeks from the first day of your last period. This means that if you have a regular four week cycle, week 3 of your pregnancy will actually be the first week after your baby was conceived. At this stage, you will not have missed your period and won't know if you are pregnant. r baby During week 3 the fertilised egg burrows into the lining of your uterus and is the size of a full stop. PREGNANCY WEEK BY WEEK - July 2004 Page 2
3 Week 4 During week 4, you still haven't missed your period, but if you have been trying to conceive (get pregnant) you will probably be feeling very excited as you wonder if you have been successful this month. r baby Specialised layers of cells are beginning to develop, which will form your baby's vital organs, nervous system, bones, muscles and blood. Week 5 By week 5, your period is late so you may begin to think that you could be pregnant and you may notice that your breasts are slightly bigger and tender to touch. But you may simply feel as if your period is about to start (some women have called the first couple of weeks of pregnancy the 'longest stretch of PMS they have ever experienced'!). As soon as your period is a day late, you can do a urine pregnancy test. can go to a doctor for a pregnancy test or you can buy a pregnancy testing kit from your pharmacy. Some women may have already experienced nausea and vomiting by this time. This is known as morning sickness but can actually happen at any time of the day or night. The severity of morning sickness and how long into the pregnancy it lasts varies a great deal from one woman to another. For most women who do get morning sickness, the problem usually improves greatly by the end of the first three months, if not sooner. For information on how to manage morning sickness see Staying Well r baby At week 5, your baby is about 2 mm long. r baby's spine, brain, muscles and bone are already starting to form. Week 6 may be feeling very tired at this early stage of your pregnancy. Gentle, regular exercise such as swimming or walking will help you to feel less tired and more able to cope with the demands your pregnancy is making on your body. r baby By the end of this week, your baby (called an embryo) has a heartbeat. Blood is pumping around the baby and out along the umbilical cord to the placenta. The placenta is an organ that acts as a filter. It allows oxygen and nutrients to pass to the embryo, and carbon dioxide and waste products to be eliminated. The placenta is also called the afterbirth. r baby's head and body are now defined and tiny buds appear where their arms and legs will develop. r baby is now about 6 mm long about the length of a grain of rice. Week 7 Some women find that they are quite emotional during these early weeks of pregnancy, this is caused mainly by pregnancy hormones. Some women may notice that their breasts are bigger now and the dark area (areola) around their nipples has darkened. may see large 'goose bumps forming around the areola (called Montgomery's tubercules) and your nipples may become larger. r baby r baby's spinal cord and brain are developing and your baby lies within a sac of membranes and is PREGNANCY WEEK BY WEEK - July 2004 Page 3
4 supported by fluid known as amniotic fluid. Nostrils and lips now appear on your baby's face and the eyes can be seen under the skin. Week 8 may find that you have gone off certain foods that you used to like. Some women also have a taste like metal in their mouth, which is probably caused by pregnancy hormones. As your uterus is growing, you may need to urinate (pass water) more often because of the increased pressure on your bladder. Many women notice that they have more vaginal discharge at this stage. This is quite normal, unless the discharge is itchy, uncomfortable or has an unpleasant smell. If your discharge is causing you concern speak to your doctor or midwife, as this may be a sign of a vaginal infection or thrush. Thrush is a common problem during pregnancy, but can be easily treated. For more information, please see the section Staying Well - Common health problems in pregnancy - Vaginal thrush. r baby The baby now looks more human - your baby's limbs can be seen and their hands and feet are taking shape all this amazing growth, yet your baby is now around just 1.3 cm long! Week 9 Many people talk about 'the glow of pregnancy', referring to the way a pregnant woman's skin looks. This glow is caused by an increase in oil on skin due to pregnancy hormones. But not all women feel this glow, and some may notice pimples because of this extra oil. Some women have the opposite problem and their skin becomes very dry. Either way, make sure you drink plenty of water (6 8 glasses per day) which helps to purify the skin. r baby At the end of this week, your baby is now called a foetus, not an embryo. The limbs are growing quickly and the fingers and toes are forming. r baby s skeleton, which started as cartilage, is now changing to bone. Week 10 may find that your clothes are getting tighter around your waist and breasts. r abdomen may look bigger, but at this stage it is often due to changes in your bowel (rather than your uterus getting bigger) and is nothing to worry about. r uterus is now about the size of an orange and is still hidden within your pelvis. r baby r baby is now about 2.5 cm long and has tiny fingers and toes. Week 11 Some women find that constipation is a problem during pregnancy. Pregnancy hormones relax the bowel, which means that bowel motions don't pass through as quickly. Increasing the fibre in your diet and drinking plenty of water will usually help. If you are still having problems, please talk to your doctor, midwife or pharmacist about bulking laxatives that are suitable to use during pregnancy. For more information see Staying Well - Common health problems in pregnancy. r baby r baby's internal organs are now all formed including their ovaries or testicles. PREGNANCY WEEK BY WEEK - July 2004 Page 4
5 Week 12 Often by now morning sickness is much less of a problem and you are probably feeling less tired. r uterus is continuing to grow and is higher than your pelvis. From this stage on your baby's heartbeat may be able to be heard with a foetal heart detector. r baby r baby's head is becoming more rounded and the eyelids have formed and closed over the eyes. still can't feel it, but your baby is moving around constantly in your amniotic fluid they can now roll, stretch, yawn and wriggle their fingers. BABY S GROWTH IN THE SECOND 3 MONTHS During the next 3 months of your pregnancy you will probably put on about 6 kilograms, even though your unborn baby will only weigh about 1 kilogram. The other weight will be in the placenta, your uterus, breasts and extra blood. During this 3 month period some major tests may be done, especially if you are over 35 or there is a family medical problem. will probably also have an ultrasound scan to check on the baby s growth. will need to go to regular antenatal checkups with your doctor or midwife. Many women find that they feel great during this stage of their pregnancy. Much of the tiredness and morning sickness of the first trimester is behind you, and your baby is not yet so big that you are feeling exhausted from carrying it around. Remember to continue being careful with your diet, to look after yourself and to rest as much as possible. PREGNANCY WEEK BY WEEK - July 2004 Page 5
6 Week 13 If you have had morning sickness early in your pregnancy, this will usually settle about now. But some women will feel sick through their whole pregnancy. Talk to your midwife or doctor if morning sickness is still a problem for you. From now on your uterus will grow larger and your abdomen will become more noticeable. r baby r baby is now fully formed and looks like a tiny human being. Most of your baby s internal organs are working. Week 14 r uterus is now the size of a large grapefruit. A dark line down the centre of your abdomen may start to appear. This is called the Linea nigra. It is a dark pigmentation of your skin, and will usually fade after your baby is born. r baby r baby now has eyebrows and a small amount of hair on his or her head and measures about 12 cm long. r baby now gets all of their nourishment from the placenta they also drink some of the amniotic fluid around them and can pass urine. Week 15 There is more blood in your body now because your baby needs more oxygen as it is growing. r heart will need to work 20 per cent harder to pump this extra blood around your body. Some women find that they may forget things, have trouble concentrating and become clumsier. r baby The hair on your baby's head and eyebrows is becoming coarser. If your baby has an inherited or genetic tendency for dark hair, then the pigment is now forming in their hair follicles. Week 16 At your antenatal visit, the doctor will feel your abdomen to check the size of your uterus, which has now risen out of your pelvis. will have your blood pressure checked and hands and feet checked for swelling at each visit from now on. For information on antenatal tests see Checkups - Checking your baby's health before birth. r baby A fine downy hair (called lanugo) begins to form over your baby's body and they will begin to develop eyelashes. At this stage, your baby may even find and suck their thumb! r baby is now about 16 cm long and weighs about 135 g. Week 17 Some women find their nose becomes blocked up and sometimes bleeds for no obvious reason. This is a common problem during pregnancy and is probably because of pregnancy hormones, which cause the delicate nasal membranes to soften and swell. If your nose does become blocked, try not to blow it too hard, as this can cause nosebleeds. Many over the counter cold medicines are not suitable to use during pregnancy. Steam inhalations are a good alternative for clearing your nose while pregnant. PREGNANCY WEEK BY WEEK - July 2004 Page 6
7 r baby r growing baby has now pushed up the top of your uterus and this can be felt between your pubic bone and navel. From now on, your baby weighs more than the placenta (the afterbirth). Week 18 may notice your nipples are leaking small amounts of fluid, which is called colostrum. This is a sign that your breasts are developing so you can feed your baby. Many women do not notice any fluid during pregnancy but will find colostrum appears when their baby is born. r baby Measuring about 19 cm and weighing about 170 g, your baby is able to kick, grasp and suck. Week 19 Any time now, you may feel your baby moving or kicking, like a faint tickling or fluttering. If this is your second or third baby, you may have felt these movements earlier. To read more about the test you may have at this stage please see Check-ups - Ultrasound scans. r baby The baby's milk teeth are developing in the gums and so are the buds for permanent teeth. Week 20 The fundus (top of your uterus) is now at navel level and your doctor or midwife will palpate (feel) your abdomen to check the size of your uterus. r baby r baby's skin begins to form a white, waxy coating called vernix. The vernix clings to the lanugo (the fine downy hair) all over your baby's skin, to protect it and hold in moisture. Week 21 Some women begin having problems with heartburn or indigestion, which is quite uncomfortable and annoying. can relieve heartburn with an antacid solution or tablets - please ask your pharmacist, doctor or midwife to recommend a product that is suitable to use in pregnancy. For more information on dealing with this see Staying Well - Common health problems in pregnancy. r baby r baby weighs about 340 g and is moving around freely within the amniotic fluid in your uterus. Week 22 r gums may swell and bleed when you brush your teeth. The swelling is a result of more pregnancy hormones. Emotionally, you may have highs and lows and you may be more sensitive than usual. At this time of pregnancy your sleep patterns may change and you may find that you remember your dreams. r baby r baby is now about 25cm long and would fit into your cupped hands. PREGNANCY WEEK BY WEEK - July 2004 Page 7
8 Week 23 Some women get a stitch-like pain down one side of their abdomen. This is because your uterine ligaments are stretching as your uterus is enlarging. The pain will usually go away after you have rested and it is nothing to be worried about. However, if the pain does not go, or if you have any bleeding or vaginal discharge with the pain, then you should ring your doctor or midwife and talk about it. r baby r baby is now forming a pattern of activity and sleep, and this may be different from yours! r baby may be more active when you want to sleep. Week 24 may also start noticing Braxton Hicks contractions, which is your uterus practising for labour. r abdomen will feel hard when you have these contractions. This is a normal part of pregnancy and you may feel them occasionally from now on. If your contractions start to become stronger, increase in frequency and last longer, contact your doctor or midwife. r baby r baby is rapidly growing now and their internal organs are all formed and mature, except for the lungs. If your baby was born at this stage it may be mature enough to have a chance of survival in a neonatal intensive care unit. Week 25 When you go to bed at night, you may get leg cramps. This is a common problem during pregnancy It is not serious and will not harm your baby, but can become very uncomfortable for you. For information on dealing with cramps link to Staying Well - Common health problems in pregnancy. PREGNANCY WEEK BY WEEK - July 2004 Page 8
9 Week 26 may notice a rhythmic beating low in your abdomen that may last for 15 to 30 minutes. This is your baby hiccupping! If you haven't already done so now is a good time to be expertly fitted for a supportive maternity bra. Choose one made of cotton with adjustable straps so it remains comfortable as your breast size grows and fastenings with front opening for breastfeeding. r baby r baby is now about 33 cm long and weighs about 500 g. r baby may now be able to open and close its eyes. Week 27 As your baby is growing quickly during this time, you are likely to be putting on weight fairly regularly from now until you are about 36 weeks pregnant. Keep doing your best to follow a healthy eating plan. r baby The baby's skin is starting to change from being transparent (see-through) to opaque (can t see through). It is very wrinkled, but protected and nourished by the covering of vernix. Week 28 At your antenatal check, your doctor or midwife will palpate (feel) your abdomen your uterus will now be well above your navel. Remember to write down any questions you or your partner may have, as checkups are a good time to discuss queries or problems with the doctor or midwife. If you have a Pregnancy Hand-Held Record you can use the spaces provided in it to write down your questions. r baby r baby is now about 38 cm long, weighs around 900 g. At this antenatal check-up, your doctor or midwife will check the size of your baby and can often feel certain body parts, such as their head, bottom and limbs. BABY S GROWTH IN THE LAST 3 MONTHS During this last 3 months of pregnancy, you may be worried or anxious about labour and wish for the time before the birth to go quickly. will probably gain about 5 kilograms during this stage. Most of this weight will be from your baby, but you will also gain extra weight from the amniotic fluid, the placenta, your breasts, blood and your uterus. will need to have more frequent antenatal checkups during this time. Towards the end of your pregnancy you will need weekly checkups. r doctor or midwife will continue to monitor your progress to make sure all is going well. Problems which can make your life uncomfortable at this stage may include back pain, difficulty getting comfortable enough to sleep, and pressure on your lungs from the baby. may get more Braxton Hicks contractions and will probably begin to feel quite tired. Try to relax and get all the rest you can your baby's arrival is not far away. Week 29 probably feel as though the baby is pushing against all your internal organs. This is because your uterus is pushing up against your diaphragm, stomach, liver and intestines. Some women stop work around this time because they start to feel more tired. r baby r baby is now about two thirds of its birth size. PREGNANCY WEEK BY WEEK - July 2004 Page 9
10 Week 30 Pregnancy hormones have been softening your ligaments. The combination of this and your baby's increasing weight can cause problems with backache. It's therefore really important to maintain good posture when you are standing or sitting. Try putting a cushion behind the small of your back when you are sitting. Take care when lifting, and try to avoid wearing high heels from now on. r baby r baby's eyes are learning how to focus. Even if you don't notice regular Braxton Hicks contractions, your baby is becoming very aware of them. Week 31 may start to feel breathless at times because the baby is pushing up against your lungs, particularly when you are sitting. This feeling is normal and does not mean that you or your baby is getting less oxygen. It's good to know that changes to your respiratory system actually allow you to take in more air and use it more efficiently. r baby r baby's lungs are maturing, but they still need to develop surfactant, a substance that allows your baby to breathe after it is born. Week 32 Many babies will begin to settle into a head-down position in the uterus. This is because the top part of the uterus is larger and allows more room for the biggest part of the baby, which is baby s bottom and bent up legs. At this stage the baby still has plenty of room to move around in the uterus and the position is not important. r baby r baby now weighs about 1.8 kg, and is about 41 cm long. Week 33 will begin to feel your baby's movements more as prods and kicks and you may even be able to tell the difference between a foot, knee or your baby's bottom. r baby r baby is now beginning to form fat reserves under their skin, and is growing quickly. Week 34 At your checkups, the doctor or midwife will check on the growth of your baby and ask if your baby is moving or kicking regularly. It is important that you rest as much as you can with your feet elevated, especially if you have swelling in your feet or ankles. From now on you should avoid lying flat on your back because in this position the weight of the baby and the uterus place pressure on major blood vessels and may cause you to feel faint. r baby r baby can now tell the difference between dark and light and their skin is becoming smoother and less wrinkled. PREGNANCY WEEK BY WEEK - July 2004 Page 10
11 Week 35 may find that you need to urinate (pass water) more often as your baby's head is pushing on your bladder. When you laugh, sneeze or cough, you may lose a small amount of urine. It is important that you do pelvic floor tightening exercises, as these will help you control your bladder more quickly after the baby is born. If you don t know how to do pelvic floor exercises, your doctor or midwife can teach you. Physiotherapists also have a range of exercises for the pelvic floor. If you go to antenatal education classes these will be explained. It is important to do these exercises for the rest of your life. To find out more about pelvic floor exercises see Staying well - Pelvic floor exercises. r baby Measuring about 44 cm in length and weighing around 2.5 kg, your baby is now almost fully grown. Week 36 r baby s head may begin to move down or engage into your pelvis about this time. will find that breathing is easier once your baby s head is engaged, as your baby s bottom will no longer be pressing up against your lungs. Around 4 in every 100 babies remain in the breech position at the end of the pregnancy. A breech position means the baby has their bottom down instead of their head. If your baby stays in this position some doctors may attempt to turn the baby to a head down position for the birth. If the baby cannot be turned, the birth may need to be by Caesarean. r baby r baby is almost fully mature now. Week 37 r pattern of sleep may be troubled and you may find it hard to get comfortable in bed. It might be helpful to use pillows between your knees and to support your abdomen as you lie on your side. r baby r baby is now about 50 cm long, and may practise breathing movements, but of course there is no air in their lungs yet. PREGNANCY WEEK BY WEEK - July 2004 Page 11
12 Week 38 r baby may be moving a little less now and instead of whole body movements, you may only notice jabs from their foot or knee. may also feel a sensation inside your vagina as your baby's head is moving against your pelvic floor muscles. r baby r baby may be putting on 100 g a week at this stage, and now weighs around 2.9 kilograms. Week 39 r cervix is softening in readiness for labour. may also be experiencing quite strong Braxton Hicks contractions. may be feeling very heavy and weary and just waiting for the baby to hurry up and arrive. r baby r baby's sucking and breathing reflexes are now well established and they are fully ready for life in the outside world. Week 40 Although your due date has arrived remember that your labour may begin one or two weeks either side of this date. r baby By full-term, your baby should weight about 2.7 to 3.5 kg, although full-term babies can weight anything from 2.5 to 5 kg, and measure 35 to 38 cm from crown to rump and 44 to 55 cm from the baby's head to its toes. These are just average figures, and there can be wide variation in the measurements. PREGNANCY WEEK BY WEEK - July 2004 Page 12
Changes to Your Baby and Your Body During Pregnancy
 Changes to and Your Body During Pregnancy 1st Trimester: Conception to Week 16 Your baby s traits and sex are set when the sperm meets the egg. During this time: The brain, nerves, heart, lungs and bones
Changes to and Your Body During Pregnancy 1st Trimester: Conception to Week 16 Your baby s traits and sex are set when the sperm meets the egg. During this time: The brain, nerves, heart, lungs and bones
Human Growth and Reproduction
 Human Growth and Reproduction Sperm reach ovum and cluster around it Only one sperm is allowed to penetrate egg When the sperm penetrates the egg, the egg immediately releases a chemical creating a hard
Human Growth and Reproduction Sperm reach ovum and cluster around it Only one sperm is allowed to penetrate egg When the sperm penetrates the egg, the egg immediately releases a chemical creating a hard
Caring for your body. Antenatal exercises
 Caring for your body Antenatal exercises Antenatal Exercises FROM EARLY PREGNANCY TO DELIVERY INTRODUCTION.................................................3 DEEP BREATHING & FOOT AND ANKLE EXERCISES..................4
Caring for your body Antenatal exercises Antenatal Exercises FROM EARLY PREGNANCY TO DELIVERY INTRODUCTION.................................................3 DEEP BREATHING & FOOT AND ANKLE EXERCISES..................4
An overview from conception to birth
 An overview from conception to birth 1 Pregnancy Stages An overview from conception to birth Introduction This booklet has been prepared for you in consultation with midwives and current health care findings.
An overview from conception to birth 1 Pregnancy Stages An overview from conception to birth Introduction This booklet has been prepared for you in consultation with midwives and current health care findings.
LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-6.3:
 GRADE 6 FETAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 2 FETAL DEVELOPMENT Lesson 2 GRADE 6 LEARNER OUTCOME W-6.3: Identify and describe the stages and factors that can affect human development from conception through birth.
GRADE 6 FETAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 2 FETAL DEVELOPMENT Lesson 2 GRADE 6 LEARNER OUTCOME W-6.3: Identify and describe the stages and factors that can affect human development from conception through birth.
Common Concerns About Breastfeeding
 Patient Education Page 51 Caring for Yourself and Your New Baby Common Concerns About Breastfeeding Breastfeeding is healthy and natural. So are the questions and concerns that come with it. Whether you
Patient Education Page 51 Caring for Yourself and Your New Baby Common Concerns About Breastfeeding Breastfeeding is healthy and natural. So are the questions and concerns that come with it. Whether you
For the Patient: Dasatinib Other names: SPRYCEL
 For the Patient: Dasatinib Other names: SPRYCEL Dasatinib (da sa' ti nib) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. Tell your doctor if you have ever
For the Patient: Dasatinib Other names: SPRYCEL Dasatinib (da sa' ti nib) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. Tell your doctor if you have ever
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma)
 Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Caring for your perineum and pelvic floor after a 3rd or 4th degree tear
 Caring for your perineum and pelvic floor after a 3rd or 4th degree tear Most women, up to nine in ten (90%), tear to some extent during childbirth. Most tears occur in the perineum, the area between the
Caring for your perineum and pelvic floor after a 3rd or 4th degree tear Most women, up to nine in ten (90%), tear to some extent during childbirth. Most tears occur in the perineum, the area between the
STAGES OF PRE-NATAL DEVELOPMENT. During this presentation refer to the TIMELINE OF PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT.
 STAGES OF PRE-NATAL DEVELOPMENT During this presentation refer to the TIMELINE OF PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT. Day 1 - conception takes place. 7 days - tiny human implants in mother s uterus. 10 days - mother
STAGES OF PRE-NATAL DEVELOPMENT During this presentation refer to the TIMELINE OF PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT. Day 1 - conception takes place. 7 days - tiny human implants in mother s uterus. 10 days - mother
Human Embryonic Development. Human fetal development
 Human Embryonic Development Day 1: 1 st cleavage 1 cell becomes 2 (2-cell stage) Day 2: 2 nd cleavage 4-cell stage Day 3: 6-12 cell stage can test at this stage for genetic diseases if done by IVF Day
Human Embryonic Development Day 1: 1 st cleavage 1 cell becomes 2 (2-cell stage) Day 2: 2 nd cleavage 4-cell stage Day 3: 6-12 cell stage can test at this stage for genetic diseases if done by IVF Day
Your Recovery After a Cesarean Delivery
 Your Recovery After a Cesarean Delivery It is normal to have many questions about your care after delivery. Cesarean delivery is surgery and your body needs time to heal and recover for the next 6 weeks,
Your Recovery After a Cesarean Delivery It is normal to have many questions about your care after delivery. Cesarean delivery is surgery and your body needs time to heal and recover for the next 6 weeks,
Twins and Multiples. Monochorionic diamniotic twins, Monochorionic monoamniotic triplets or Higher order multiples. Oxford University Hospitals
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Twins and Multiples Monochorionic diamniotic twins, Monochorionic monoamniotic triplets or Higher order multiples How common are multiple pregnancies? Women who are
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Twins and Multiples Monochorionic diamniotic twins, Monochorionic monoamniotic triplets or Higher order multiples How common are multiple pregnancies? Women who are
Explore and Discover... Human growth. You have been asked to write a short leaflet for young people about growing up and puberty. Teacher information
 You have been asked to write a short leaflet for young people about growing up and puberty. Explore and Discover... Teacher information Gallery visited Human Biology Suitable for Key Stage 3 (ages 11 to
You have been asked to write a short leaflet for young people about growing up and puberty. Explore and Discover... Teacher information Gallery visited Human Biology Suitable for Key Stage 3 (ages 11 to
UNIT 3: Pregnancy to Birth
 UNIT 3: Pregnancy to Birth TOPICS: The Changing Body The Anatomy of Pregnancy The Gestational Period Common Discomforts of Pregnancy Preterm Labour and Birth Fetal Development GOAL: To increase knowledge
UNIT 3: Pregnancy to Birth TOPICS: The Changing Body The Anatomy of Pregnancy The Gestational Period Common Discomforts of Pregnancy Preterm Labour and Birth Fetal Development GOAL: To increase knowledge
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Menstruation
 Menstruation WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Menstruation is a normal and healthy part of growing up. The discharge of blood and tissue from the lining of your uterus each
Menstruation WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Menstruation is a normal and healthy part of growing up. The discharge of blood and tissue from the lining of your uterus each
Preterm Labour. Signs & Symptoms. Learn about the signs of preterm labour and what to do if it happens.
 An important message for pregnant women, their partners and families Preterm Labour Signs & Symptoms Learn about the signs of preterm labour and what to do if it happens. What is preterm labour? A normal,
An important message for pregnant women, their partners and families Preterm Labour Signs & Symptoms Learn about the signs of preterm labour and what to do if it happens. What is preterm labour? A normal,
Sexual reproduction in humans
 Sexual reproduction in humans Name: WHY DO HUMANS NEED TO REPRODUCE? The reason humans reproduce is to have children so that our species can continue to exist. Humans reproduce sexually, which means like
Sexual reproduction in humans Name: WHY DO HUMANS NEED TO REPRODUCE? The reason humans reproduce is to have children so that our species can continue to exist. Humans reproduce sexually, which means like
Female Reproductive System. Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued
 Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
How To Choose Between A Vaginal Birth Or A Cesarean Section
 Be informed. Know your rights. Protect yourself. Protect your baby. What Every Pregnant Woman Needs to Know About Cesarean Section 2012 Childbirth Connection If you re expecting a baby, there s a good
Be informed. Know your rights. Protect yourself. Protect your baby. What Every Pregnant Woman Needs to Know About Cesarean Section 2012 Childbirth Connection If you re expecting a baby, there s a good
Contents. Overview. Removing the womb (hysterectomy) Overview
 This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding womb (endometrial) cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 9. Overview Contents Overview Removing
This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding womb (endometrial) cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 9. Overview Contents Overview Removing
MEDICATION GUIDE ACTOPLUS MET (ak-tō-plus-met) (pioglitazone hydrochloride and metformin hydrochloride) tablets
 MEDICATION GUIDE (ak-tō-plus-met) (pioglitazone hydrochloride and metformin hydrochloride) tablets Read this Medication Guide carefully before you start taking and each time you get a refill. There may
MEDICATION GUIDE (ak-tō-plus-met) (pioglitazone hydrochloride and metformin hydrochloride) tablets Read this Medication Guide carefully before you start taking and each time you get a refill. There may
BLADDER CONTROL DURING PREGNANCY AND AFTER THE BIRTH OF YOUR BABY
 BLADDER CONTROL DURING PREGNANCY AND AFTER THE BIRTH OF YOUR BABY Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 8 Contents Stress incontinence... 3 Pelvic floor exercises... 3 Urgency and frequency...
BLADDER CONTROL DURING PREGNANCY AND AFTER THE BIRTH OF YOUR BABY Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 8 Contents Stress incontinence... 3 Pelvic floor exercises... 3 Urgency and frequency...
Pelvic Girdle Pain (PGP) Fact Sheet
 Pelvic Girdle Pain (PGP) Fact Sheet Physiotherapy PGP describes pain that is experienced in the front (symphysis pubis joint) and/or back (sacroiliac joints) of your pelvis. This is a common problem, affecting
Pelvic Girdle Pain (PGP) Fact Sheet Physiotherapy PGP describes pain that is experienced in the front (symphysis pubis joint) and/or back (sacroiliac joints) of your pelvis. This is a common problem, affecting
What Every Pregnant Woman Needs to Know About Cesarean Section. Be informed. Know your rights. Protect yourself. Protect your baby.
 Be informed. Know your rights. Protect yourself. Protect your baby. What Every Pregnant Woman Needs to Know About Cesarean Section 2012 Childbirth Connection If you re expecting a baby, there s a good
Be informed. Know your rights. Protect yourself. Protect your baby. What Every Pregnant Woman Needs to Know About Cesarean Section 2012 Childbirth Connection If you re expecting a baby, there s a good
Developing Human Fetus
 Period Date LAB. DEVELOPMENT OF A HUMAN FETUS After a human egg is fertilized with human sperm, the most amazing changes happen that allow a baby to develop. This amazing process, called development, normally
Period Date LAB. DEVELOPMENT OF A HUMAN FETUS After a human egg is fertilized with human sperm, the most amazing changes happen that allow a baby to develop. This amazing process, called development, normally
Labor is work, and it is hard work. Labor is an end to pregnancy and a beginning for a new human life in a newly shaped family."
 LABOR AND DELIVERY "The way we give birth to our young is that the muscular organ (the uterus) in which the offspring has been nurtured for nine months begins to contract. The contractions work to open
LABOR AND DELIVERY "The way we give birth to our young is that the muscular organ (the uterus) in which the offspring has been nurtured for nine months begins to contract. The contractions work to open
Pelvic Floor Exercises for Women
 Pelvic Floor Exercises for Women Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered What are pelvic floor muscles? They are layers of muscles stretching like a hammock from the pubic joint at the front of the
Pelvic Floor Exercises for Women Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered What are pelvic floor muscles? They are layers of muscles stretching like a hammock from the pubic joint at the front of the
For the Patient: Paclitaxel injection Other names: TAXOL
 For the Patient: Paclitaxel injection Other names: TAXOL Paclitaxel (pak'' li tax' el) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a clear liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell your
For the Patient: Paclitaxel injection Other names: TAXOL Paclitaxel (pak'' li tax' el) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a clear liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell your
STUDENT S WORKSHEETS. Eva M. Zamudio Zamudio
 STUDENT S WORKSHEETS January April 2009 HUMAN LIFE CYCLE HANDOUT 1 1. Write the name of each stage in the right order: retirement adolescence babyhood adulthood - childhood 2. What stage does it belong
STUDENT S WORKSHEETS January April 2009 HUMAN LIFE CYCLE HANDOUT 1 1. Write the name of each stage in the right order: retirement adolescence babyhood adulthood - childhood 2. What stage does it belong
Polycystic ovary syndrome
 Polycystic ovary syndrome All you need to know This resource is informed by the evidence-based guideline for the assessment and management of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), authored by the PCOS Australian
Polycystic ovary syndrome All you need to know This resource is informed by the evidence-based guideline for the assessment and management of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), authored by the PCOS Australian
Vaginal hysterectomy and vaginal repair
 Women s Service Vaginal hysterectomy and vaginal repair Information for patients Vaginal hysterectomy and vaginal repair This leaflet is for women who have been advised to have a vaginal hysterectomy.
Women s Service Vaginal hysterectomy and vaginal repair Information for patients Vaginal hysterectomy and vaginal repair This leaflet is for women who have been advised to have a vaginal hysterectomy.
Pelvic floor exercises for women. An information guide
 TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION Pelvic floor exercises for women An information guide Pelvic floor exercises for women Introduction Exercising the pelvic floor muscles
TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION Pelvic floor exercises for women An information guide Pelvic floor exercises for women Introduction Exercising the pelvic floor muscles
Ovarian cancer. Patient information from the BMJ Group. What is ovarian cancer? What are the symptoms?
 Patient information from the BMJ Group Ovarian cancer Ovarian cancer is a serious disease. If it s diagnosed at an early stage, ovarian cancer can usually be cured. But even cancers that are more advanced
Patient information from the BMJ Group Ovarian cancer Ovarian cancer is a serious disease. If it s diagnosed at an early stage, ovarian cancer can usually be cured. But even cancers that are more advanced
VAD Chemotherapy Regimen for Multiple Myeloma Information for Patients
 VAD Chemotherapy Regimen for Multiple Myeloma Information for Patients The Regimen contains: V = vincristine (Oncovin ) A = Adriamycin (doxorubicin) D = Decadron (dexamethasone) How Is This Regimen Given?
VAD Chemotherapy Regimen for Multiple Myeloma Information for Patients The Regimen contains: V = vincristine (Oncovin ) A = Adriamycin (doxorubicin) D = Decadron (dexamethasone) How Is This Regimen Given?
Work & Pregnancy Do Mix...
 Work & Pregnancy Do Mix... www.beststart.org PREGNANT AND WORKING Most women continue to work during their pregnancy, whether they work from home, or travel to a workplace. If you are pregnant or planning
Work & Pregnancy Do Mix... www.beststart.org PREGNANT AND WORKING Most women continue to work during their pregnancy, whether they work from home, or travel to a workplace. If you are pregnant or planning
Symphysis Pubis Dysfunction (SPD)
 Symphysis Pubis Dysfunction (SPD) Symphysis Pubis Dysfunction (SPD) Your health professional has given you this leaflet to explain and advise you about SPD, related to your pregnancy. SPD is a term used
Symphysis Pubis Dysfunction (SPD) Symphysis Pubis Dysfunction (SPD) Your health professional has given you this leaflet to explain and advise you about SPD, related to your pregnancy. SPD is a term used
Functional rehab after breast reconstruction surgery
 Functional rehab after breast reconstruction surgery UHN A guide for women who had DIEP, latissimus dorsi with a tissue expander or implant, or two-stage implant based breast reconstruction surgery Read
Functional rehab after breast reconstruction surgery UHN A guide for women who had DIEP, latissimus dorsi with a tissue expander or implant, or two-stage implant based breast reconstruction surgery Read
Pain Management for Labour & Delivery
 Pain Management for Labour & Delivery Departments of Anesthesia, Obstetrics, and Obstetrical Nursing December 2008 This pamphlet has been prepared to provide you, members of your family, and others who
Pain Management for Labour & Delivery Departments of Anesthesia, Obstetrics, and Obstetrical Nursing December 2008 This pamphlet has been prepared to provide you, members of your family, and others who
EARLY PREGNANCY LOSS A Patient Guide to Treatment
 EARLY PREGNANCY LOSS A Patient Guide to Treatment You have a pregnancy that has stopped growing, or you have started to miscarry and the process has not completed. If so, there are four ways to manage
EARLY PREGNANCY LOSS A Patient Guide to Treatment You have a pregnancy that has stopped growing, or you have started to miscarry and the process has not completed. If so, there are four ways to manage
Fetal Development, Abortion And Adoption
 INFORMATION ON Fetal Development, Abortion And Adoption Written Materials in Compliance with West Virginia Law [Section 16-2I-1, et. seq.] as enacted by Senate Bill No. 170 of the year 2003 WEST VIRGINIA
INFORMATION ON Fetal Development, Abortion And Adoption Written Materials in Compliance with West Virginia Law [Section 16-2I-1, et. seq.] as enacted by Senate Bill No. 170 of the year 2003 WEST VIRGINIA
10 Instructions Pregnant Women Should Follow for Safe and Effective Use of Medication
 10 Instructions Pregnant Women Should Follow for Safe and Effective Use of Medication 1. Check whether or not you are pregnant before taking medicines. Fertile women should check whether or not they could
10 Instructions Pregnant Women Should Follow for Safe and Effective Use of Medication 1. Check whether or not you are pregnant before taking medicines. Fertile women should check whether or not they could
Managing Constipation
 Managing Constipation The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your experience may be different. If you have any questions about what prostate cancer
Managing Constipation The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your experience may be different. If you have any questions about what prostate cancer
CVP Chemotherapy Regimen for Lymphoma Information for Patients
 CVP Chemotherapy Regimen for Lymphoma Information for Patients The Regimen Contains: C: Cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan ) V: Vincristine (Oncovin ) P: Prednisone How Is This Regimen Given? CVP is given every
CVP Chemotherapy Regimen for Lymphoma Information for Patients The Regimen Contains: C: Cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan ) V: Vincristine (Oncovin ) P: Prednisone How Is This Regimen Given? CVP is given every
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) in pregnancy
 Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) in pregnancy Information and advice for women and families Maternity What is a deep vein thrombosis (DVT)? A deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot that forms in a deep leg
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) in pregnancy Information and advice for women and families Maternity What is a deep vein thrombosis (DVT)? A deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot that forms in a deep leg
Patient Information Once Weekly FOSAMAX (FOSS-ah-max) (alendronate sodium) Tablets and Oral Solution
 Patient Information Once Weekly FOSAMAX (FOSS-ah-max) (alendronate sodium) Tablets and Oral Solution Read this information before you start taking FOSAMAX *. Also, read the leaflet each time you refill
Patient Information Once Weekly FOSAMAX (FOSS-ah-max) (alendronate sodium) Tablets and Oral Solution Read this information before you start taking FOSAMAX *. Also, read the leaflet each time you refill
Epidural Continuous Infusion. Patient information Leaflet
 Epidural Continuous Infusion Patient information Leaflet April 2015 Introduction You may already know that epidural s are often used to treat pain during childbirth. This same technique can also used as
Epidural Continuous Infusion Patient information Leaflet April 2015 Introduction You may already know that epidural s are often used to treat pain during childbirth. This same technique can also used as
Inducing your labour with Propess -
 Inducing your labour with Propess - going home during the process Parent Information If your baby is over-due You have agreed to have your labour induced. If you need more information about your options
Inducing your labour with Propess - going home during the process Parent Information If your baby is over-due You have agreed to have your labour induced. If you need more information about your options
Pregnancy and Substance Abuse
 Pregnancy and Substance Abuse Introduction When you are pregnant, you are not just "eating for two." You also breathe and drink for two, so it is important to carefully consider what you put into your
Pregnancy and Substance Abuse Introduction When you are pregnant, you are not just "eating for two." You also breathe and drink for two, so it is important to carefully consider what you put into your
Module 7 Talking With Mothers About Breastfeeding...During Pregnancy
 Module 7 Talking With Mothers About Breastfeeding...During Pregnancy Overview This seventh module introduces peer counselors to the various physical and emotional changes that occur throughout a woman
Module 7 Talking With Mothers About Breastfeeding...During Pregnancy Overview This seventh module introduces peer counselors to the various physical and emotional changes that occur throughout a woman
Why your weight matters during pregnancy and after birth
 Information for you Published in November 2011 (next review date: 2015) Why your weight matters during pregnancy and after birth Most women who are overweight have a straightforward pregnancy and birth
Information for you Published in November 2011 (next review date: 2015) Why your weight matters during pregnancy and after birth Most women who are overweight have a straightforward pregnancy and birth
Understanding Endometriosis - Information Pack
 What is endometriosis? Endometriosis (pronounced en- doh mee tree oh sis) is the name given to the condition where cells like the ones in the lining of the womb (uterus) are found elsewhere in the body.
What is endometriosis? Endometriosis (pronounced en- doh mee tree oh sis) is the name given to the condition where cells like the ones in the lining of the womb (uterus) are found elsewhere in the body.
Why is prematurity a concern?
 Prematurity What is prematurity? A baby born before 37 weeks of pregnancy is considered premature. Approximately 12% of all babies are born prematurely. Terms that refer to premature babies are preterm
Prematurity What is prematurity? A baby born before 37 weeks of pregnancy is considered premature. Approximately 12% of all babies are born prematurely. Terms that refer to premature babies are preterm
Total Abdominal Hysterectomy
 What is a total abdominal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through an abdominal incision (either an up and down or bikini cut). Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient.
What is a total abdominal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through an abdominal incision (either an up and down or bikini cut). Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient.
Premature Infant Care
 Premature Infant Care Introduction A premature baby is born before the 37th week of pregnancy. Premature babies are also called preemies. Premature babies may have health problems because their organs
Premature Infant Care Introduction A premature baby is born before the 37th week of pregnancy. Premature babies are also called preemies. Premature babies may have health problems because their organs
Dealing with Erectile Dysfunction During and After Prostate Cancer Treatment For You and Your Partner
 Dealing with Erectile Dysfunction During and After Prostate Cancer Treatment For You and Your Partner The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your
Dealing with Erectile Dysfunction During and After Prostate Cancer Treatment For You and Your Partner The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your
Headache after an epidural or spinal injection What you need to know. Patient information Leaflet
 Headache after an epidural or spinal injection What you need to know Patient information Leaflet April 2015 We have produced this leaflet to give you general information about the headache that may develop
Headache after an epidural or spinal injection What you need to know Patient information Leaflet April 2015 We have produced this leaflet to give you general information about the headache that may develop
Mini Medical School Lesson
 Mini Medical School Lesson The American Osteopathic Association s (AOA) Mini Medical School Lesson is designed to help educators teach children about health and fitness. This lesson is aimed towards elementary
Mini Medical School Lesson The American Osteopathic Association s (AOA) Mini Medical School Lesson is designed to help educators teach children about health and fitness. This lesson is aimed towards elementary
Living With Congestive Heart Failure
 Living With Congestive Heart Failure Information for patients and their families Patient information developed by EPICORE Centre, Division of Cardiology, University of Alberta The REACT study: supported
Living With Congestive Heart Failure Information for patients and their families Patient information developed by EPICORE Centre, Division of Cardiology, University of Alberta The REACT study: supported
Total Vaginal Hysterectomy
 What is a total vaginal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through the vagina. Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient. Why is this surgery used? To treat disease of
What is a total vaginal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through the vagina. Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient. Why is this surgery used? To treat disease of
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
Surgical removal of fibroids through an abdominal incision-either up and down or bikini cut. The uterus and cervix are left in place.
 What is an abdominal myomectomy? Surgical removal of fibroids through an abdominal incision-either up and down or bikini cut. The uterus and cervix are left in place. When is this surgery used? Treatment
What is an abdominal myomectomy? Surgical removal of fibroids through an abdominal incision-either up and down or bikini cut. The uterus and cervix are left in place. When is this surgery used? Treatment
Unit 3L.4: Body Parts and Functions
 Unit 3L.4: Organs in the Human body Keeping Healthy The Skeleton Science skills: Classification Observing Making models Data collection By the end of this unit you should: Compare the structure of humans
Unit 3L.4: Organs in the Human body Keeping Healthy The Skeleton Science skills: Classification Observing Making models Data collection By the end of this unit you should: Compare the structure of humans
Understanding Fertility
 Understanding Fertility 6 Introduction The word fertile means the ability to become pregnant or to cause pregnancy. Basic knowledge of both the male and female reproductive systems is important for understanding
Understanding Fertility 6 Introduction The word fertile means the ability to become pregnant or to cause pregnancy. Basic knowledge of both the male and female reproductive systems is important for understanding
Femoral artery bypass graft (Including femoral crossover graft)
 Femoral artery bypass graft (Including femoral crossover graft) Why do I need the operation? You have a blockage or narrowing of the arteries supplying blood to your leg. This reduces the blood flow to
Femoral artery bypass graft (Including femoral crossover graft) Why do I need the operation? You have a blockage or narrowing of the arteries supplying blood to your leg. This reduces the blood flow to
progestog progestogen stogen-only pill progestogen progestogen-only pill he progestogen-only pill progestogen-onl progestogen-o the progestogenonly
 your guide to the progestogenonly pill Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you the progestogen rogestogen-only the progestogen-only pill progestogen-only pill stogen-only progestoge
your guide to the progestogenonly pill Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you the progestogen rogestogen-only the progestogen-only pill progestogen-only pill stogen-only progestoge
Better Breathing with COPD
 Better Breathing with COPD People with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) often benefit from learning different breathing techniques. Pursed Lip Breathing Pursed Lip Breathing (PLB) can be very
Better Breathing with COPD People with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) often benefit from learning different breathing techniques. Pursed Lip Breathing Pursed Lip Breathing (PLB) can be very
Urinary Incontinence. Patient Information Sheet
 Urinary Incontinence Patient Information Sheet What is urinary incontinence (UI)? UI happens when you are not able to control when you urinate and you wet yourself. How common is urinary incontinence?
Urinary Incontinence Patient Information Sheet What is urinary incontinence (UI)? UI happens when you are not able to control when you urinate and you wet yourself. How common is urinary incontinence?
Stem cell transplant, you and your rehabilitation Information for patients and their carers
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Physiotherapy department Stem cell transplant, you and your rehabilitation Information for patients and their carers Stem cell transplant exercise handout Thank you
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Physiotherapy department Stem cell transplant, you and your rehabilitation Information for patients and their carers Stem cell transplant exercise handout Thank you
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH. Rheynn Slaynt. Jane Crookall Maternity Unit Noble s Hospital, Isle of Man INDUCTION OF LABOUR INFORMATION
 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH Rheynn Slaynt Jane Crookall Maternity Unit Noble s Hospital, Isle of Man INDUCTION OF LABOUR INFORMATION Mr T. Ghosh, Consultant Obstetrician & Gynaecologist NH367 INDUCTION OF LABOUR
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH Rheynn Slaynt Jane Crookall Maternity Unit Noble s Hospital, Isle of Man INDUCTION OF LABOUR INFORMATION Mr T. Ghosh, Consultant Obstetrician & Gynaecologist NH367 INDUCTION OF LABOUR
Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System
 Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Information for you A low-lying placenta (placenta praevia) after 20 weeks
 Information for you A low-lying placenta (placenta praevia) after 20 weeks Published in December 2011 Who is this information for? This information is intended to help you if you have, or have been told
Information for you A low-lying placenta (placenta praevia) after 20 weeks Published in December 2011 Who is this information for? This information is intended to help you if you have, or have been told
Blood Pressure Management and Your Pregnancy
 Patient Education Blood Pressure Management and Your Pregnancy This handout explains: How your blood pressure is checked during pregnancy. What preeclampsia is, including risk factors, treatments, and
Patient Education Blood Pressure Management and Your Pregnancy This handout explains: How your blood pressure is checked during pregnancy. What preeclampsia is, including risk factors, treatments, and
Total Vaginal Hysterectomy with an Anterior and Posterior Repair
 Total Vaginal Hysterectomy with an Anterior and Posterior Repair What is a total vaginal hysterectomy with an anterior and posterior repair? Total vaginal hysterectomy is the removal of the uterus and
Total Vaginal Hysterectomy with an Anterior and Posterior Repair What is a total vaginal hysterectomy with an anterior and posterior repair? Total vaginal hysterectomy is the removal of the uterus and
National 3- Multicellular Organisms Revision
 National 3- Multicellular Organisms Revision Key Area 1: Structure and function of organs and organ systems and their role in sustaining life. What you must know: The basic structure and functions of main
National 3- Multicellular Organisms Revision Key Area 1: Structure and function of organs and organ systems and their role in sustaining life. What you must know: The basic structure and functions of main
injections injections injections injections injections injection injections injections injections tions njections injections injections injections
 your guide to contraceptive Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you ions ections injection njections injection tions 2 Contraceptive Contraceptive contain a progestogen hormone
your guide to contraceptive Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you ions ections injection njections injection tions 2 Contraceptive Contraceptive contain a progestogen hormone
STAGES OF PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT
 STAGES OF PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT College of William and Mary Students for Life 2013 Germinal Period From conception to implantation Terms to Know Conception: the first stage in human development in which
STAGES OF PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT College of William and Mary Students for Life 2013 Germinal Period From conception to implantation Terms to Know Conception: the first stage in human development in which
implant contraceptiv contraceptive contraceptive raceptiv contraceptive implant contraceptive contraceptive ontraceptive implant ontraceptive im
 your guide to the contraceptive implant Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you contra ontraceptive im contraceptive implant mpl ceptive contraceptive contracepti ntraceptive
your guide to the contraceptive implant Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you contra ontraceptive im contraceptive implant mpl ceptive contraceptive contracepti ntraceptive
Red Flags that should not be ignored
 Pregnancy that should not be ignored If a pregnant woman tells you she is experiencing any of the following symptoms during pregnancy, assist her to contact her emergency care professional right away.
Pregnancy that should not be ignored If a pregnant woman tells you she is experiencing any of the following symptoms during pregnancy, assist her to contact her emergency care professional right away.
The Well Woman Centre. Adult Urinary Incontinence
 The Well Woman Centre Adult Urinary Incontinence 1 Adult Urinary Incontinence... 3 Stress Incontinence Symptoms... 3 Urge Incontinence Symptoms... 4 Mixed Incontinence Symptoms... 5 Where to Start?...
The Well Woman Centre Adult Urinary Incontinence 1 Adult Urinary Incontinence... 3 Stress Incontinence Symptoms... 3 Urge Incontinence Symptoms... 4 Mixed Incontinence Symptoms... 5 Where to Start?...
Post-natal period. You have one of the volumes of the Growth Guide in your hands. The Growth Guide consists of seven practical booklets:
 Post-natal period Dear (prospective) parents, You have one of the volumes of the Growth Guide in your hands. The Growth Guide consists of seven practical booklets: Planning for Parenthood Pregnancy Breastfeeding
Post-natal period Dear (prospective) parents, You have one of the volumes of the Growth Guide in your hands. The Growth Guide consists of seven practical booklets: Planning for Parenthood Pregnancy Breastfeeding
How babies' senses develop
 B2 There is much growth and change that must occur in your baby s body. For babies born full-term (37-40 weeks), this growth and change occurred within the warm, dark, watery womb. For the premature baby,
B2 There is much growth and change that must occur in your baby s body. For babies born full-term (37-40 weeks), this growth and change occurred within the warm, dark, watery womb. For the premature baby,
Having a companion you can lean on and who can support you during your labour can be helpful. It has been shown to reduce the need for pain relief.
 The pregnancy care planner Your NHS guide to having a baby www.nhs.uk/pregnancy My birth plan Name: Due date: Where to give birth You will have a choice about where to have your baby. Your midwife or doctor
The pregnancy care planner Your NHS guide to having a baby www.nhs.uk/pregnancy My birth plan Name: Due date: Where to give birth You will have a choice about where to have your baby. Your midwife or doctor
Prolapse of the Uterus, Bladder, Bowel, or Rectum
 Prolapse of the Uterus, Bladder, Bowel, or Rectum Broad bands of uterine ligaments provide structural support to the uterus and pelvis. The uterine ligaments may weaken, stretch, or spontaneously become
Prolapse of the Uterus, Bladder, Bowel, or Rectum Broad bands of uterine ligaments provide structural support to the uterus and pelvis. The uterine ligaments may weaken, stretch, or spontaneously become
FDA-Approved Patient Labeling IMPLANON (etonogestrel implant) Subdermal Use
 FDA-Approved Patient Labeling IMPLANON (etonogestrel implant) Subdermal Use IMPLANON does not protect against HIV infection (the virus that causes AIDS) or other sexually transmitted diseases. Read this
FDA-Approved Patient Labeling IMPLANON (etonogestrel implant) Subdermal Use IMPLANON does not protect against HIV infection (the virus that causes AIDS) or other sexually transmitted diseases. Read this
You will be having surgery to remove a tumour(s) from your liver.
 Liver surgery You will be having surgery to remove a tumour(s) from your liver. This handout will help you learn about the surgery, how to prepare for surgery and your care after surgery. Surgery can be
Liver surgery You will be having surgery to remove a tumour(s) from your liver. This handout will help you learn about the surgery, how to prepare for surgery and your care after surgery. Surgery can be
Staying on Track with TUBERCULOSIS. Medicine
 Staying on Track with TB TUBERCULOSIS Medicine What s Inside: Read this brochure to learn about TB and what you can do to get healthy. Put it in a familiar place to pull out and read when you have questions.
Staying on Track with TB TUBERCULOSIS Medicine What s Inside: Read this brochure to learn about TB and what you can do to get healthy. Put it in a familiar place to pull out and read when you have questions.
Adult Advisor: Plantar Fasciitis. Plantar Fasciitis
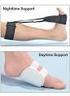 Adult Advisor: Plantar Fasciitis Page 1 of 3 Plantar Fasciitis What is plantar fasciitis? Plantar fasciitis is a painful inflammation of the bottom of the foot between the ball of the foot and the heel.
Adult Advisor: Plantar Fasciitis Page 1 of 3 Plantar Fasciitis What is plantar fasciitis? Plantar fasciitis is a painful inflammation of the bottom of the foot between the ball of the foot and the heel.
Copper intra-uterine device (IUD)
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Copper intra-uterine device (IUD) Page What is an inter-uterine device? 3 How does it work? 4 Would an IUD be suitable for me? 5 Are there any risks or complications?
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Copper intra-uterine device (IUD) Page What is an inter-uterine device? 3 How does it work? 4 Would an IUD be suitable for me? 5 Are there any risks or complications?
The Take-Apart Human Body
 The Take-Apart Human Body As any teacher knows, children are naturally curious about their bodies. Their questions are endless, and present a tremendous educational opportunity: How do my ears work? Where
The Take-Apart Human Body As any teacher knows, children are naturally curious about their bodies. Their questions are endless, and present a tremendous educational opportunity: How do my ears work? Where
IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD the IUD. the IUD. the the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD.
 your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you I the IUD 2 3 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that is put into your uterus (womb).
your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you I the IUD 2 3 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that is put into your uterus (womb).
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin
 Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Promoting recovery after sustaining a third and fourth degree tear
 Promoting recovery after sustaining a third and fourth degree tear Women s Health Physiotherapy Patient Information Page 2 Promoting recovery after sustaining a third and fourth degree tears What has happened?
Promoting recovery after sustaining a third and fourth degree tear Women s Health Physiotherapy Patient Information Page 2 Promoting recovery after sustaining a third and fourth degree tears What has happened?
Prenatal Testing Special tests for your baby during pregnancy
 English April 2006 [OTH-7750] There are a number of different prenatal (before birth) tests to check the development of your baby. Each test has advantages and disadvantages. This information is for people
English April 2006 [OTH-7750] There are a number of different prenatal (before birth) tests to check the development of your baby. Each test has advantages and disadvantages. This information is for people
Paclitaxel and Carboplatin
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu What is Paclitaxel (pak-li-tax-el) and how does it work? Paclitaxel is a chemotherapy drug known as an anti-microtubule inhibitor. Another name for this drug
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu What is Paclitaxel (pak-li-tax-el) and how does it work? Paclitaxel is a chemotherapy drug known as an anti-microtubule inhibitor. Another name for this drug
Get the Facts About Tuberculosis Disease
 TB Get the Facts About Tuberculosis Disease What s Inside: Read this brochure today to learn how to protect your family and friends from TB. Then share it with people in your life. 2 Contents Get the facts,
TB Get the Facts About Tuberculosis Disease What s Inside: Read this brochure today to learn how to protect your family and friends from TB. Then share it with people in your life. 2 Contents Get the facts,
