SIM/USIM cards. Samia Bouzefrane. CEDRIC Lab CNAM
|
|
|
- Camron Golden
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SIM/USIM cards Samia Bouzefrane CEDRIC Lab CNAM 1
2 Agenda - Introduction to GSM network - Introduction to SIM cards - SIM card services -Security - File systems of SIM cards 2
3 Introduction to GSM network 3
4 GSM - Early 1980 s, several cellular networks in Europe - the systems are incompatible from one country to another - Consequences : - mobile equipements are limited to the frontiers - limited market -Creation of «Group Special Mobile» to: Increase the quality of service international support : roaming new functionalities provide terminals and services with low cost 4
5 GSM Standardization in 1982 : called «Group Special Mobile» Since 1989, the ETSI (European Telecommunications Standard Institute) provides the spécifications of GSM and of UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunications System, 3rd generation ntework). ETSI is at Sophia Antipolis (Nice, France) : becomes an international standard called «Global System for Mobile communications» In Europe, the GSM standard uses frequency bandwidth of 9 MHz and 18 MHz. In US, the bandwidth used is of 19 MHz. Tri-band: cell phones are usable in Europe and US (3 frequencies) Bi-band : cell phones are usable only in Europe. The GSM standard allows a maximal rate of 9,6 kbps => transmission of voice, of data, text messages (SMS, Short Message Service) or multimedia messages (MMS, Multimedia Message Service). 5
6 Cell network principle A cellular network is based on cells, Each cell covers a geographical area. A cell: hundred of meters (urban zone), thirty kms (rural zone ). Each cell has a central transmitter-receiver called Base Transceiver Station, BTS. Over the radius of a cell is smaller, the available bandwidth is high. Each cell is surrounded by six neighboring cells. Adjacent cells can not use the same frequency. 6
7 Elements of the cellular network BSC, Base Station Controller that connects all the base stations. BSS Base Station Subsystem Base station controller + base stations. MSC, Mobile Switching Center, managed by the telecom operator, links the station controllers to the Internet and to the telephone network. NSS, Network Station Subsystem to which belongs the MSC, In charge of managing the user identities, their location and establishing of the communication with the other subscribers. 7
8 GSM Architecture 8
9 Involved Databases HLR, Home Location Register: the database of the subscribers linked to the MSC. It contains information (location, administrative information, etc.) VLR, Visitor Location Register: a database contains information on the local subscribers. The VLR retrieves data of new user from the HLR corresponding to its subscription area. The data is stored during the time of its presence in the area and are removed when he leaves or after a long period of inactivity (device off). EIR, Equipement Identity Register : a database of mobile equipments. AuC, Autentication Center : in charge of verifying the user identities (authentication). 9
10 Mobility The cellular network supports mobility by managing the handover, ie to pass from one cell to another. GSM networks also support the concept of roaming ie the passage of a network operator to another. 10
11 Mobile stations 11
12 Mobile Station Mobile Station : the terminal of the user Mobile Station composed of: SIM (Subscriber Identity Module) card, to identify a unique user. a mobile equipment identified with a unique number of 15 digits called IMEI (International Mobile Equipment Identity). Each SIM card owns a unique identity number (secret):imsi (International Mobile Subscriber Identity), which can be protected with a key called 4-digit PIN. Communication between a mobile station and a base station is done via a radio link, generally called over the air. 12
13 SIM card Initially introduced in billions of cards in 2011 Functional role in the network: - Contains details concerning the user subscription - Holds the secrets needed to prove the authenticity of the mobile and to quantify the exchange. - Loading new services. 13
14 SIM card: Mobility Subscription details stored on the card: - Unique identity of the subscriber (IMSI) - Telephone number of the subscriber (MSISDN) - Mobile equipment identity (IMEI) - Service Code (operator) and so on. 14
15 SIM card: Security Services The SIM card stores sensitive information: Secret codes: - User authentication: PIN (Personal Identification Code) - Authentication of the operator: PUK (Personal Unlock Code) Secret keys: - For authentication of the SIM card by the network - For encrypted communication 15
16 SIM Card: downloadable services The SIM card is a runtime environment for trusted applications able to interact with the mobile: * Display info on the mobile screen * Collect information for the user * Etc. Able to interact with the network: * Send and receive messages (SMS, GPRS, etc.). * geolocalization Able to interact with the system files from the SIM card * Write / read files from the SIM 16
17 Standardization and security 17
18 The standards GSM UMTS Universal Mobile Telecommunications System UICC: Universal Integrated Circuit Card 18
19 ETSI standards SIM File management and Authentication : 3 GPP TS (ETSI GSM 11.11) SIM Toolkit Applet Management : 3 GPP TS (ETSI GSM 11.14) SIM API for Java Card : 3 GPP TS USIM File management and Authentication : 3 GPP TS USIM Toolkit Applet Management : 3 GPP TS USIM API for Java Card : 3 GPP TS
20 Protection methods proposed in GSM / 1 1. Protecting the identity of a subscriber: The subscriber has an identifier (IMSI: International Mobile Subscriber Identity) to find the subscription settings in the HLR (Host Location Register): database of customer accounts. The network delivers a TMSI (Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity) a temporary identity that changes with each call to ban traceability of communications. 2. The authentication of a subscriber: Strong authentication is performed using the A3 algorithm associated with a 128-bit key Ki. GSM 02.09: "Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Security Aspects". 20
21 Protection methods proposed in GSM 02.09/2 3. The confidentiality of user data: In a cellular network, the information is transmitted by electromagnetic waves (Over The Air) between the mobile and base station (antenna). Exchange between mobile and base station are encrypted using A5 algorithm that uses an encryption key Kc. Kc is updated each call (authentication) with the algorithm A8 key generation. A3 and A8 are often confused (called A38 or A3A8). 4. The protection of certain information such as: IMSI, the serial number of the phone, IMEI (International Mobile Equipment Identity). 21
22 Authentication in GSM network There are 5 entities involved: - SIM card -Mobile -VLR (Visitor Location Register) -HLR (Host Location Register) : - AuC (Authentication Center). The standard 3GPP TS identifies a cell and a set of cells thanks to LAI (Location Area Identity). 3GPP TS Technical Specification Group Services & System Aspects; Security Related Network Functions (Release 5, 22). 22
23 Security Protocol of GSM/1 SIM card Mobile Base Station VLR HLR/AuC LAI, TMSI Identity request IMSI Authentication request RAND Triplet(RAND, SRES, Kc) Kc=A8(Ki,RAND) SRES =A3(Ki,RAND) Aknowledgment A5(Kc, TMSI) SRES =SRES? Switch to encrypted mode Aknowledgment RAND: randomnumberof 16 bytes SRES(Signed RESponse): SRES=A3(Ki, RAND) Kc: key of encryption of the communications, Kc=A8(Ki, RAND). 23
24 Security Protocol of GSM/2 1. The subscriber has the values (LAI, TMSI) stored in the SIM module, following a previous call. 2. The mobile sends the VLR values (LAI, TMSI). 3. If the VLR fails to retrieve the IMSI, it sends an identification request to the mobile 4. The VLR retrieves the IMSI stored in the SIM card 5. The VLR sends to the HLR / AuC an authentication request 6. GSM AuC produces a triplet (RAND, SRES, Kc) 7. Upon receipt of the triplet, the VLR sends RAND to the mobile 8. The SIM calculates SRES = A3 (K i, RAND) which is sent to the HLR. 9. The HLR compares SRES and SRES '=> authentication of the subscriber succeeds if SRES=SRES. 10. The VLR chooses a new TMSI encrypted with A5 algorithm and K c key and sends it to mobile. The operations of encryption and decryption are applied to radio signals performed by the mobile (not the SIM card). From the base stations to the network cable operator, there is no guarantee of confidentiality. 24
25 Cryptographical algorithms The SIM card performs the calculation A3A8 in a safe space. In 1998, Mark Briceno, Ian Goldberg and David Wagner (Researchers at the University of Berkeley) broke A3A8 algorithm. While GSM recommends any algorithm, the operators use a secret Algo COMP These researchers have also broken the algorithm by finding the key Ki after approximately 5 0 tests. For this reason, the components that integrate COMP128-1 limited the number of calls to 1 0. SIM modules are now based on the COMP128-2 algorithm which is currently secret. 25
26 File systems 26
27 SIM card characteristics In the 90 s: SIM card : CPU (8 bits), RAM (128 bytes), ROM (7 Kb), EEPROM (3 Kb). In 2011: SIM card : CPU (32 bits), RAM (16 Kb), ROM (512 Kb), EEPROM/FLASH (512 Ko), a dedicated processor for crypto-calculations. ROM (Read Only Memory) hosts the OS of the card, security mechanisms, API GSM. EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory) contains directories as defined in GSM standard and applications. RAM (Random Access Memory) allows computations. 27
28 SIM card structure 28
29 File system accordingto 3GPP TS
30 File system of the SIM card Dedicated File Elementary File Transparent file Linear-fixed file Cyclic file 30
31 Directories and files Root directory : 3F Principal sub-directories : GSM (DF GSM, 7F20) and TELECOM (DF TELECOM, 7F10). 1 st byte: - '3F': Master File; - '7F': 1st level Dedicated File; - '5F': 2nd level Dedicated File; - '2F': Elementary File under the Master File; - '6F': Elementary File under a 1st level Dedicated File; -'4F': Elementary File under 2nd level Dedicated File. After the reception of the ATR (Answer To Reset), the master file (MF) is selected automatically. 31
32 GSM directory File EF IMSI (6F07) contains IMSI code. File EF LOCI (6F 7E) contains : TMSI, LAI. EF LP (Language preference) EF Kc (Ciphering key Kc) contains Kc and the sequence number of the key. EF SST (SIM service table) : is the list of available services. Service n 1 : CHV1 disable function Service n 2 : Abbreviated Dialling Numbers (ADN) Service n 3 : Fixed Dialling Numbers (FDN) Service n 4 : Short Message Storage (SMS) etc. EF ACM (Accumulated call meter): contains the total number of units for the current call and the preceding calls. EF MSISDN (MSISDN): contains the phone number of the subscriber MSISDN. 32
33 TELECOM directory TELECOM directory has several files: EF FDN (6F3B) contains a phone book, EF SMS (6F3C) contains a list of sent/received SMS, etc. These files are accessible in read/write and are protected by the PIN code of the user. 33
34 Access conditions to files 5 levelsof priority: ALWays (code 0) : the file is always accessible CHV1 (code 1) : file is protected by the PIN code of the user CHV2 (code 2) : file protected by the PIN code of the telecom operator ADM (codes de 4 to E) : file managed by the administrative authority NEVER (code F) : inaccessible file. Level Access conditions 0 ALWays 1 CHV1 2 CHV2 3 Réservé 4 à 14 ADM 15 NEver 34
35 Access conditions to files ALWAYS : action executed without restriction ; (CardHolderVerification1) : the action is possible if the CHV1 has been presented to the SIM card successfully. CHV2 : the action is possible if the CHV1 has been presented to the SIM card with successfully. ADM : the attribution of these levels are under the responsability of the appropriate administrative authority. NEVER : the action cannot be executed. 35
36 APDU commands Mobile SIM 36
37 APDU commands The standard 3GPP TS (ex-gsm 11.11) defines 22 APDU commands gathered in 4 groups : Six commands of file management: SELECT, READ, WRITE Five commandsof PIN code management : verification, modification, activation, deletion and unlocking with PUK code. Executionof A3A8 algorithm thanks to the command RUN GSM ALGORITHM. Tendifferentcommands, some are related to SIM Tool Kit such that a program executed on a SIM card may access to the keyboard or the screen of the mobile, or communicate via SMS with outside. 37
38 APDU commands COMMAND INS P1 P2 P3 SELECT STATUS READ BINARY UPDATE BINARY READ RECORD UPDATE RECORD SEEK INCREASE VERIFY CHV CHANGE CHV DISABLE CHV ENABLE CHV UNBLOCK CHV INVALIDATE REHABILITATE A4 F2 B0 D6 B2 DC A C Offset high Offset high Rec N Rec N Offset low Offset low Mode Mode Type/mode CHV N CHV N Voir note RUN GSM ALGORITHM SLEEP FA GET RESPONSE TERMINAL PROFILE ENVELOPE FETCH TERMINAL RESPONSE C0 10 C Lgth lgth lgth lgth lgth lgth Lgth Lgth Lgth Lgth Lgth 38
39 SELECT command A0 A4 02 XX XX (XX XX : FID of the file/directory). When selecting a directory, a response may include the following information: - Memory size not used - The FID of the selected directory - The type of the directory (MF or not) - presentation of the PIN code -Number of the sub-directories 39
40 Reading files Reading the IMSI The file EF IMSI (6F07) of the GSM directory is transparent, it contains the IMSI. The selection of the file returns the size of the file. A0 B0 09 (READ BINARY 9 bytes, size of the IMSI). Reading the TMSI and LAI These parameters are read from the file EF LOCI (6F 7E) A0 B0 B (READ BINARY 11 bytes, 4 bytes for TSMI followed by 5 bytes for LAI,..) 40
41 Authentification algorithm Execution of the authentication algorithm UN-GSM-ALGORITHM executes the function A3A8 with as an argument The random number RAND of 16 bytes. The command returns the signature SRES (4 bytes) and the key Kc (8 bytes). Update of file EF Kc The file EF Kc is updated by the mobile thanks to the command UPDATE BINARY. Two values are stored in the file: the key and a validation byte(= if the key is valide else 07). 41
42 Reading the table of Services The file EF SIM-Service-Table (6F 38) contains the list of the services provided by the SIMcard. Each service is associated to two bits (bit1 =1 if service is present, bit2 =1 if the service is active). Example : Service n 1 allows the desactivation of the PIN code of the user, Service n 2 indicates the presence of a speed dial directory(fichier EF ADN ), Service n 3 notifies the presence of an unabridged directory numbers (fichier EF FDN ), Service n 4 indicates the presence of SMS file (fichier EF SMS ), etc. The files EF ADN, EF FDN, EF SMS belong to the directory DF TELECOM (7F 10). 42
43 The files directory and SMS SMS file: - EF SMS, has 6F 3C as FID, - a cyclic file, - read/write SMS withi n the SIM card. A contact-list file ADN EF ADN has 6F 3A as FID, - is a contact list. Cmd: A0 A4 02 6F 3A (SELECT EF-ADN) Resp: 9F 0F (the cards wants to send 0F data) Cmd : A0 C0 0F (GET RESPONSE 0F bytes) Resp: 1B 58 6F 3A C 90. File size : 1B 58 (7 0 bytes) and record size (1C : 28 bytes). The number of records : 70/28=250 bytes). Each number contains a label with a size of 14 (28-14=14). The label has 0 in the most significant bit. 43
44 Operations on PIN codes PIN coded on 8 bytes. The non significant bytes are coded with FF. VERIFY CHV : presenting PIN code A0 20 P2 0B PIN (P2=01 for CHV1 : user PIN code, = 02 for CHV2). DISABLE PIN cancels the use of PIN code. A PIN ENABLE PIN allows using the PIN code A PIN CHANGE CHV allows the modifiction of PIN code A Ancien_PIN Nouveau_PIN UNBLOCK CHV unlocks a blocked card after 3 three unsuccessful attempts of the PIN code (CHV1). A0 2C PUK PIN (PUK is a unique code of 8 bytes associated to the SIM card). 44
45 Comparison of the authentification SIM/USIM GSM UMTS Description Bits Alg Description Bits Alg Ki Subscriber authentication key 128 K Subscriber authentication key RAND random challenge 128 RAND random challenge 128 XRES exepected result 32 A3 XRES expected result f2 Kc cipher key 64 max A8 Ck cipher key 128 f3 128 IK integrity key 128 f4 AK anonimity key 48 f5 SQN sequence number 48 AMF authentication management field 16 MAC message auth. Code 64 f1 Example : algorithm COMP128-1 Example : algorithm Milenage 45
46 «Milenage» Algorithm SIM ME 46
47 SIM/USIM Comparison Characteristics SIM USIM Class used CLA= A0 CLA= Root directory MF (3F ) ADF USIM (7F FF) Multiple channels support No Yes Authentification command RUN GSM ALGORITHM AUTHENTICATE Used with GSM Yes Yes Used with 3G Yes Yes SIM Toolkit Yes Yes New standards stopped In progress Versions Release 1 à Release 4 Release 99 à Release 7 47
48 References Normes GSM : Article de Pascal Urien, «La carte SIM ou la sécurité du GSM par la pratique», Magazine MISC, hors Série «Cartes à puce», Nov. /Dec. 28. Article de Serge Chaumette et Jonathan Ouoba, «Java Card (U)SIM et Applications sécurisées sur téléphones mobiles», Magazine MISC, hors Série «Cartes à puce», Nov. /Dec. 28. Description des SMS : Smart Card Handbook, Third Edition, Wolfgang Rankl and Wolfgang Effing, Giesecke & Devrient GmbH, Munich, Germany, Translated by Kenneth Cox, John Wiley & Sons, 22. Rapport de stage Niang Souleymane réalisé chez Trusted Logics, Master SEM, septembre 28. Keith E. Mayes and Konstantinos Markantonakis, Smart Cards, Tokens, Security and Applications, Springer, 28, 392 pages. 3 GPP TS Specification of the SIM Application Toolkit for the Subscriber Identity Module-Mobile Equipement interface (Release 1999). 3 GPP TS Technical Specification Group Terminals Specification of the Subscriber Identity Module-ME interface (Release 1999). 3GPP TS V6.0.0 (24-12), Technical Specification, 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Terminals; Subscriber Identity Module Application Programming Interface, (SIM API) for Java Card, Stage 2, (Release 6), 3GPP TS V4.5.0 (24-12), Technical Specification, 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Specification of the SIM Application Toolkit for the Subscriber Identity Module - Mobile Equipment (SIM - ME) interface (Release 4) 3GPP TS V5.0.0 (21-12), Technical Specification, 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Terminals; Specification of the Subscriber Identity Module - Mobile Equipment (SIM - ME) interface, (Release 5) ETSI SAGE Task Force for 3GPP, Authentication Function Algorithms, VERSION 1.0, Security Algorithms Group of Experts (SAGE); General Report on the Design, Specification and Evaluation of The MILENAGE Algorithm Set: An Example Algorithm Set for the 3GPP, Authentication and Key Generation Functions, 20 ( 3GPP TS Technical Specification Group Services & System Aspects; Security Related Network Functions (Release 5, 22). 48
49 End 49
The GSM and GPRS network T-110.300/301
 The GSM and GPRS network T-110.300/301 History The successful analog 1:st generation mobile telephone systems proved that there is a market for mobile telephones ARP (AutoRadioPuhelin) in Finland NMT (Nordic
The GSM and GPRS network T-110.300/301 History The successful analog 1:st generation mobile telephone systems proved that there is a market for mobile telephones ARP (AutoRadioPuhelin) in Finland NMT (Nordic
Theory and Practice. IT-Security: GSM Location System Syslog XP 3.7. Mobile Communication. December 18, 2001. GSM Location System Syslog XP 3.
 Participant: Hack contacting... IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication December 18, 2001 Uwe Jendricke uwe@iig.uni-freiburg.de Lecture Homepage: http://www.informatik.uni-freiburg.de/~softech/teaching/ws01/itsec/
Participant: Hack contacting... IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication December 18, 2001 Uwe Jendricke uwe@iig.uni-freiburg.de Lecture Homepage: http://www.informatik.uni-freiburg.de/~softech/teaching/ws01/itsec/
UMTS security. Helsinki University of Technology S-38.153 Security of Communication Protocols k-p.perttula@hut.fi 15.4.2003
 UMTS security Helsinki University of Technology S-38.153 Security of Communication Protocols k-p.perttula@hut.fi 15.4.2003 Contents UMTS Security objectives Problems with GSM security UMTS security mechanisms
UMTS security Helsinki University of Technology S-38.153 Security of Communication Protocols k-p.perttula@hut.fi 15.4.2003 Contents UMTS Security objectives Problems with GSM security UMTS security mechanisms
Solution for Non-Repudiation in GSM WAP Applications
 Solution for Non-Repudiation in GSM WAP Applications CRISTIAN TOMA, MARIUS POPA, CATALIN BOJA Economic Informatics Department Academy of Economic Studies Romana Square No. 6, Bucharest ROMANIA cristian.toma@ie.ase.ro
Solution for Non-Repudiation in GSM WAP Applications CRISTIAN TOMA, MARIUS POPA, CATALIN BOJA Economic Informatics Department Academy of Economic Studies Romana Square No. 6, Bucharest ROMANIA cristian.toma@ie.ase.ro
3GPP 21.11 V1.1.0 (1999-01) Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP); USIM and IC Card Requirements TSGT3#1(99)032
 TSG-Terminals Working Group 3 (USIM) meeting #1 Nice 25 th - 27 th January, 1999 TSGT3#1(99)032 Technical Report Third Generation Partnership Project (); USIM and IC Card Requirements 2 Reference
TSG-Terminals Working Group 3 (USIM) meeting #1 Nice 25 th - 27 th January, 1999 TSGT3#1(99)032 Technical Report Third Generation Partnership Project (); USIM and IC Card Requirements 2 Reference
Authentication and Secure Communication in GSM, GPRS, and UMTS Using Asymmetric Cryptography
 ISSN (Online): 1694-0784 ISSN (Print): 1694-0814 10 Authentication and Secure Communication in GSM, GPRS, and UMTS Using Asymmetric Cryptography Wilayat Khan 1 and Habib Ullah 2 1 Department of Electrical
ISSN (Online): 1694-0784 ISSN (Print): 1694-0814 10 Authentication and Secure Communication in GSM, GPRS, and UMTS Using Asymmetric Cryptography Wilayat Khan 1 and Habib Ullah 2 1 Department of Electrical
Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM)
 Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) Nguyen Thi Mai Trang LIP6/PHARE Thi-Mai-Trang.Nguyen@lip6.fr UPMC/PUF - M2 Networks - PTEL 1 Outline Principles of cellular networks GSM architecture Security
Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) Nguyen Thi Mai Trang LIP6/PHARE Thi-Mai-Trang.Nguyen@lip6.fr UPMC/PUF - M2 Networks - PTEL 1 Outline Principles of cellular networks GSM architecture Security
2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems
 2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems Winter 2012/13 Integrated Communication Systems Group Ilmenau University of Technology Outline 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management
2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems Winter 2012/13 Integrated Communication Systems Group Ilmenau University of Technology Outline 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management
An Example of Mobile Forensics
 An Example of Mobile Forensics Kelvin Hilton K319 kchilton@staffsacuk k.c.hilton@staffs.ac.uk www.soc.staffs.ac.uk/kch1 Objectives The sources of evidence The subscriber The mobile station The network
An Example of Mobile Forensics Kelvin Hilton K319 kchilton@staffsacuk k.c.hilton@staffs.ac.uk www.soc.staffs.ac.uk/kch1 Objectives The sources of evidence The subscriber The mobile station The network
Mobile Communications
 October 21, 2009 Agenda Topic 2: Case Study: The GSM Network 1 GSM System General Architecture 2 GSM Access network. 3 Traffic Models for the Air interface 4 Models for the BSS design. 5 UMTS and the path
October 21, 2009 Agenda Topic 2: Case Study: The GSM Network 1 GSM System General Architecture 2 GSM Access network. 3 Traffic Models for the Air interface 4 Models for the BSS design. 5 UMTS and the path
GSM Databases. Virginia Location Area HLR Vienna Cell Virginia BSC. Virginia MSC VLR
 Update ( Update Procedure) Network Mobiles Maryland Maryland Other Rockville Bethesda Maryland Mobile Mobile Cell Cell HLR Vienna Cell 12-Jun-14 22:48 (Page 1) This sequence diagram was generated with
Update ( Update Procedure) Network Mobiles Maryland Maryland Other Rockville Bethesda Maryland Mobile Mobile Cell Cell HLR Vienna Cell 12-Jun-14 22:48 (Page 1) This sequence diagram was generated with
SIM Card Security. Sheng He 108005239797. Seminar Work. Chair for Communication Security Prof. Dr.-Ing. Christof Paar
 SIM Card Security Sheng He 108005239797 Seminar Work at Chair for Communication Security Prof. Dr.-Ing. Christof Paar advised through Thomas Eisenbarth 12.07.2007 Ruhr-University of Bochum Contents 1 Overview...3
SIM Card Security Sheng He 108005239797 Seminar Work at Chair for Communication Security Prof. Dr.-Ing. Christof Paar advised through Thomas Eisenbarth 12.07.2007 Ruhr-University of Bochum Contents 1 Overview...3
GSM and UMTS security
 2007 Levente Buttyán Why is security more of a concern in wireless? no inherent physical protection physical connections between devices are replaced by logical associations sending and receiving messages
2007 Levente Buttyán Why is security more of a concern in wireless? no inherent physical protection physical connections between devices are replaced by logical associations sending and receiving messages
Global System for Mobile Communication Technology
 Global System for Mobile Communication Technology Mobile Device Investigations Program Technical Operations Division DHS - FLETC GSM Technology Global System for Mobile Communication or Groupe Special
Global System for Mobile Communication Technology Mobile Device Investigations Program Technical Operations Division DHS - FLETC GSM Technology Global System for Mobile Communication or Groupe Special
Technical Specifications (GPGPU)
 TS 131 116 V6.7.0 (2005-03) Technical Specification Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); Remote APDU Structure for (Universal) Subscriber
TS 131 116 V6.7.0 (2005-03) Technical Specification Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); Remote APDU Structure for (Universal) Subscriber
2 System introduction
 2 System introduction Objectives After this chapter the student will: be able to describe the different nodes in a GSM network. be able to describe geographical subdivision of a GSM network. be able to
2 System introduction Objectives After this chapter the student will: be able to describe the different nodes in a GSM network. be able to describe geographical subdivision of a GSM network. be able to
!!! "# $ % & & # ' (! ) * +, -!!. / " 0! 1 (!!! ' &! & & & ' ( 2 3 0-4 ' 3 ' Giuseppe Bianchi
 !!! "# $ % & & # ' (! ) * +, -!!. / " 0! 1 (!!! ' &! & & & ' ( 2 3 0-4 ' 3 ' "#$!!% "&'! #&'!%! () *+,, 3 & 5 &,! #-!*! ' & '.! #%!* //!! & (0)/!&/, 6 5 /, "! First system: NMT-450 (Nordic Mobile Telephone)
!!! "# $ % & & # ' (! ) * +, -!!. / " 0! 1 (!!! ' &! & & & ' ( 2 3 0-4 ' 3 ' "#$!!% "&'! #&'!%! () *+,, 3 & 5 &,! #-!*! ' & '.! #%!* //!! & (0)/!&/, 6 5 /, "! First system: NMT-450 (Nordic Mobile Telephone)
Security features include Authentication and encryption to protect data and prevent eavesdropping.
 What is a SIM card? A SIM card, also known as a subscriber identity module, is a subscriber identity module application on a smartcard that stores data for GSM/CDMA Cellular telephone subscribers. Such
What is a SIM card? A SIM card, also known as a subscriber identity module, is a subscriber identity module application on a smartcard that stores data for GSM/CDMA Cellular telephone subscribers. Such
Study Paper on Security Accreditation Scheme for SIM
 May 2014 MOBILE Study Paper on Security Accreditation Scheme for SIM TEC TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING CENTRE KHURSHID LAL BHAWAN, JANPATH NEW DELHI - 110001 INDIA 1 Introduction... 4 2 Security Threats...
May 2014 MOBILE Study Paper on Security Accreditation Scheme for SIM TEC TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING CENTRE KHURSHID LAL BHAWAN, JANPATH NEW DELHI - 110001 INDIA 1 Introduction... 4 2 Security Threats...
Mobile Office Security Requirements for the Mobile Office
 Mobile Office Security Requirements for the Mobile Office S.Rupp@alcatel.de Alcatel SEL AG 20./21.06.2001 Overview Security Concepts in Mobile Networks Applications in Mobile Networks Mobile Terminal used
Mobile Office Security Requirements for the Mobile Office S.Rupp@alcatel.de Alcatel SEL AG 20./21.06.2001 Overview Security Concepts in Mobile Networks Applications in Mobile Networks Mobile Terminal used
3GPP TSG SA WG3 Security S3#30 S3-030534 6-10 October 2003 Povoa de Varzim, Portugal. Abstract
 3GPP TSG SA WG3 Security S3#30 S3-030534 6-10 October 2003 Povoa de Varzim, Portugal Source: Gemplus, Oberthur, Schlumberger Title: Over-The-Air (OTA) technology Document for: Discussion and decision Agenda
3GPP TSG SA WG3 Security S3#30 S3-030534 6-10 October 2003 Povoa de Varzim, Portugal Source: Gemplus, Oberthur, Schlumberger Title: Over-The-Air (OTA) technology Document for: Discussion and decision Agenda
ETSI TS 121 111 V8.0.1 (2008-01) Technical Specification
 TS 121 111 V8.0.1 (2008-01) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); USIM and IC card requirements (3GPP TS 21.111 version 8.0.1 Release 8) 1 TS 121 111 V8.0.1 (2008-01)
TS 121 111 V8.0.1 (2008-01) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); USIM and IC card requirements (3GPP TS 21.111 version 8.0.1 Release 8) 1 TS 121 111 V8.0.1 (2008-01)
ETSI TS 131 104 V11.1.0 (2012-10)
 TS 131 104 V11.1.0 (2012-10) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; Characteristics of the Hosting Party Subscription Identity Module (HPSIM) application (3GPP
TS 131 104 V11.1.0 (2012-10) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; Characteristics of the Hosting Party Subscription Identity Module (HPSIM) application (3GPP
Mobile Security. Practical attacks using cheap equipment. Business France. Presented the 07/06/2016. For. By Sébastien Dudek
 Mobile Security Practical attacks using cheap equipment Presented the 07/06/2016 Business France By Sébastien Dudek For Content Security measures Recent publications in the hacking community Practical
Mobile Security Practical attacks using cheap equipment Presented the 07/06/2016 Business France By Sébastien Dudek For Content Security measures Recent publications in the hacking community Practical
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems slides by Jochen Schiller with modifications by Emmanuel Agu
 Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems slides by Jochen Schiller with modifications by Emmanuel Agu Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems slides by Jochen Schiller with modifications by Emmanuel Agu Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen
IMSI Catcher. Daehyun Strobel. 13.Juli 2007. Seminararbeit Ruhr-Universität Bochum. Chair for Communication Security Prof. Dr.-Ing.
 IMSI Catcher Daehyun Strobel 13.Juli 2007 Seminararbeit Ruhr-Universität Bochum Chair for Communication Security Prof. Dr.-Ing. Christof Paar Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 GSM (Global System for Mobile
IMSI Catcher Daehyun Strobel 13.Juli 2007 Seminararbeit Ruhr-Universität Bochum Chair for Communication Security Prof. Dr.-Ing. Christof Paar Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 GSM (Global System for Mobile
Mobile Phone Security. Hoang Vo Billy Ngo
 Mobile Phone Security Hoang Vo Billy Ngo Table of Content 1. Introduction Page 2 1.1 Analog Network Page 2 1.2 Digital Network Page 2 2. Security Protocols Page 4 2.1 Analog Page 4 2.2 Digital Page 5 3.
Mobile Phone Security Hoang Vo Billy Ngo Table of Content 1. Introduction Page 2 1.1 Analog Network Page 2 1.2 Digital Network Page 2 2. Security Protocols Page 4 2.1 Analog Page 4 2.2 Digital Page 5 3.
How To Understand The Gsm And Mts Mobile Network Evolution
 Mobile Network Evolution Part 1 GSM and UMTS GSM Cell layout Architecture Call setup Mobility management Security GPRS Architecture Protocols QoS EDGE UMTS Architecture Integrated Communication Systems
Mobile Network Evolution Part 1 GSM and UMTS GSM Cell layout Architecture Call setup Mobility management Security GPRS Architecture Protocols QoS EDGE UMTS Architecture Integrated Communication Systems
GSM GPRS. Course requirements: Understanding Telecommunications book by Ericsson (Part D PLMN) + supporting material (= these slides)
 GSM Example of a PLMN (Public Land Mobile Network) At present most successful cellular mobile system (over 200 million subscribers worldwide) Digital (2 nd Generation) cellular mobile system operating
GSM Example of a PLMN (Public Land Mobile Network) At present most successful cellular mobile system (over 200 million subscribers worldwide) Digital (2 nd Generation) cellular mobile system operating
ETSI TS 133 102 V3.6.0 (2000-10)
 TS 133 102 V3.6.0 (2000-10) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); 3G Security; Security Architecture (3GPP TS 33.102 version 3.6.0 Release 1999) 1 TS 133 102 V3.6.0
TS 133 102 V3.6.0 (2000-10) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); 3G Security; Security Architecture (3GPP TS 33.102 version 3.6.0 Release 1999) 1 TS 133 102 V3.6.0
GSM Research. Chair in Communication Systems Department of Applied Sciences University of Freiburg 2010
 Chair in Communication Systems Department of Applied Sciences University of Freiburg 2010 Dennis Wehrle, Konrad Meier, Dirk von Suchodoletz, Klaus Rechert, Gerhard Schneider Overview 1. GSM Infrastructure
Chair in Communication Systems Department of Applied Sciences University of Freiburg 2010 Dennis Wehrle, Konrad Meier, Dirk von Suchodoletz, Klaus Rechert, Gerhard Schneider Overview 1. GSM Infrastructure
SPYTEC 3000 The system for GSM communication monitoring
 SPYTEC 3000 The system for GSM communication monitoring The SPYTEC 3000 system is intended for passive (if system encryption is absent of if A5.2 encryption is used) or semi-active (if A5.1 encryption
SPYTEC 3000 The system for GSM communication monitoring The SPYTEC 3000 system is intended for passive (if system encryption is absent of if A5.2 encryption is used) or semi-active (if A5.1 encryption
International Journal of Computing and Business Research (IJCBR)
 AN INVESTIGATION OF GSM ARCHITECTURE AND OVERLAYING WITH EFFICIENT SECURITY PROTOCOL Karun Madan, Surya World Institute of Engg. & Technology, Rajpura, Punjab ABSTRACT The Global System for Mobile Communications
AN INVESTIGATION OF GSM ARCHITECTURE AND OVERLAYING WITH EFFICIENT SECURITY PROTOCOL Karun Madan, Surya World Institute of Engg. & Technology, Rajpura, Punjab ABSTRACT The Global System for Mobile Communications
Security Evaluation of CDMA2000
 Security Evaluation of CDMA2000 L. Ertaul 1, S. Natte 2, and G. Saldamli 3 1 Mathematics and Computer Science, CSU East Bay, Hayward, CA, USA 2 Mathematics and Computer Science, CSU East Bay, Hayward,
Security Evaluation of CDMA2000 L. Ertaul 1, S. Natte 2, and G. Saldamli 3 1 Mathematics and Computer Science, CSU East Bay, Hayward, CA, USA 2 Mathematics and Computer Science, CSU East Bay, Hayward,
Evolution of the SIM to esim
 Evolution of the SIM to esim Elaheh Vahidian Master of Telematics - Communication Networks and Networked Services (2 Submission date: Januar 2013 Supervisor: Van Thanh Do, ITEM Norwegian University of
Evolution of the SIM to esim Elaheh Vahidian Master of Telematics - Communication Networks and Networked Services (2 Submission date: Januar 2013 Supervisor: Van Thanh Do, ITEM Norwegian University of
Ch 2.3.3 GSM PENN. Magda El Zarki - Tcom 510 - Spring 98
 Ch 2.3.3 GSM In the early 80 s the European community decided to work together to define a cellular system that would permit full roaming in all countries and give the network providers freedom to provide
Ch 2.3.3 GSM In the early 80 s the European community decided to work together to define a cellular system that would permit full roaming in all countries and give the network providers freedom to provide
3GPP TSG SA WG3 Security S3#20 S3-010580 27-30 November, 2001 Sophia Antipolis, France
 TSG SA WG3 Security S3#20 S3-010580 27-30 November, 2001 Sophia Antipolis, France Source : Subject : Gemplus ISIM Application The following document is a draft TS describing the ISIM characteristics. It
TSG SA WG3 Security S3#20 S3-010580 27-30 November, 2001 Sophia Antipolis, France Source : Subject : Gemplus ISIM Application The following document is a draft TS describing the ISIM characteristics. It
The GSM Standard (An overview of its security)
 Interested in learning more about security? SANS Institute InfoSec Reading Room This paper is from the SANS Institute Reading Room site. Reposting is not permitted without express written permission. The
Interested in learning more about security? SANS Institute InfoSec Reading Room This paper is from the SANS Institute Reading Room site. Reposting is not permitted without express written permission. The
GSM BASICS GSM HISTORY:
 GSM BASICS GSM HISTORY: In 1982 the Nordic PTTs sent a proposal to CEPT (Conference of European Postal & telegraph Administration) to study and to improve digital cellular technology by forming a team
GSM BASICS GSM HISTORY: In 1982 the Nordic PTTs sent a proposal to CEPT (Conference of European Postal & telegraph Administration) to study and to improve digital cellular technology by forming a team
9.1 Introduction. 9.2 Roaming
 9 Location Updating Objectives After this chapter the student will: be able to define the concepts of roaming and location updating. be able to name the different types of location updating and why they
9 Location Updating Objectives After this chapter the student will: be able to define the concepts of roaming and location updating. be able to name the different types of location updating and why they
Provides a communication link between MS and MSC; Manages DB for MS location. Controls user connection. Transmission.
 Provides a communication link between MS and MSC; Manages DB for MS location Controls user connection CM MM RR Transmission Several RR functions considered in previous part!"# Surprise! handover is part
Provides a communication link between MS and MSC; Manages DB for MS location Controls user connection CM MM RR Transmission Several RR functions considered in previous part!"# Surprise! handover is part
EAP-SIM Authentication using Interlink Networks RAD-Series RADIUS Server
 Application Note EAP-SIM Authentication using Interlink Networks RAD-Series RADIUS Server Introduction The demand for wireless LAN (WLAN) access to the public IP network is growing rapidly. It is only
Application Note EAP-SIM Authentication using Interlink Networks RAD-Series RADIUS Server Introduction The demand for wireless LAN (WLAN) access to the public IP network is growing rapidly. It is only
Formal Analysis of A Novel Mutual Authentication and Key Agreement Protocol
 Formal Analysis of A Novel Mutual Authentication and ey Agreement Protocol Ja'afer M. AL-Saraireh Applied Science University Amman 11961, Jordan Saleh S. Saraireh Philadelphia University Amman 11961, Jordan
Formal Analysis of A Novel Mutual Authentication and ey Agreement Protocol Ja'afer M. AL-Saraireh Applied Science University Amman 11961, Jordan Saleh S. Saraireh Philadelphia University Amman 11961, Jordan
Mobile Wireless Overview
 Mobile Wireless Overview A fast-paced technological transition is occurring today in the world of internetworking. This transition is marked by the convergence of the telecommunications infrastructure
Mobile Wireless Overview A fast-paced technological transition is occurring today in the world of internetworking. This transition is marked by the convergence of the telecommunications infrastructure
Wireless Telecommunication Systems GSM, GPRS, UMTS. GSM as basis of current systems Satellites and
 Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: Wireless Telecommunication Systems GSM, GPRS,
Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: Wireless Telecommunication Systems GSM, GPRS,
MOBILE COMPUTING AND M- COMMERCE SECURITY ISSUES
 MOBILE COMPUTING AND M- COMMERCE SECURITY ISSUES Krishna Prakash 1 and Balachandra 2 1,2 Department of Information and Communication Technology, MIT Manipal 1 kkp_prakash@yahoo.com, 2 bala_muniyal@yahoo.com
MOBILE COMPUTING AND M- COMMERCE SECURITY ISSUES Krishna Prakash 1 and Balachandra 2 1,2 Department of Information and Communication Technology, MIT Manipal 1 kkp_prakash@yahoo.com, 2 bala_muniyal@yahoo.com
GSM System Architecture
 Intersystem Operation and Mobility Management David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Program in Telecommunications and Networking University it of Pittsburgh Telcom 2700 Slides 6 http://www.tele.pitt.edu/tipper.html
Intersystem Operation and Mobility Management David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Program in Telecommunications and Networking University it of Pittsburgh Telcom 2700 Slides 6 http://www.tele.pitt.edu/tipper.html
ETSI TS 131 221 V9.0.0 (2010-02) Technical Specification
 TS 131 221 V9.0.0 (2010-02) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; Contact Manager Application Programming Interface (API); Contact Manager API for Java Card (3GPP
TS 131 221 V9.0.0 (2010-02) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; Contact Manager Application Programming Interface (API); Contact Manager API for Java Card (3GPP
3GPP TR 23.912 V3.1.0 (2001-12)
 TR 23.912 V3.1.0 (2001-12) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network; Technical report on Super-Charger (Release 1999) The present document
TR 23.912 V3.1.0 (2001-12) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network; Technical report on Super-Charger (Release 1999) The present document
Lecture overview. History of cellular systems (1G) GSM introduction. Basic architecture of GSM system. Basic radio transmission parameters of GSM
 Lecture overview History of cellular systems (1G) GSM introduction Basic architecture of GSM system Basic radio transmission parameters of GSM Analogue cellular systems 70 s In the early 70 s radio frequencies
Lecture overview History of cellular systems (1G) GSM introduction Basic architecture of GSM system Basic radio transmission parameters of GSM Analogue cellular systems 70 s In the early 70 s radio frequencies
Protocol of the Communication between SIM and mobile phone
 Protocol of the Communication between SIM and mobile phone This protocol oft the layer 7 (application layer) and the layer 2 (data transmission layer) was made with an Siemens SL55 mobile phone in the
Protocol of the Communication between SIM and mobile phone This protocol oft the layer 7 (application layer) and the layer 2 (data transmission layer) was made with an Siemens SL55 mobile phone in the
Forensics and the GSM mobile telephone system
 Forensics and the GSM mobile telephone system Abstract Svein Yngvar Willassen, M.Sc, Senior Investigator, Computer Forensics, Ibas AS The GSM system has become the most popular system for mobile communication
Forensics and the GSM mobile telephone system Abstract Svein Yngvar Willassen, M.Sc, Senior Investigator, Computer Forensics, Ibas AS The GSM system has become the most popular system for mobile communication
Worldwide attacks on SS7 network
 Worldwide attacks on SS7 network P1 Security Hackito Ergo Sum 26 th April 2014 Pierre-Olivier Vauboin (po@p1sec.com) Alexandre De Oliveira (alex@p1sec.com) Agenda Overall telecom architecture Architecture
Worldwide attacks on SS7 network P1 Security Hackito Ergo Sum 26 th April 2014 Pierre-Olivier Vauboin (po@p1sec.com) Alexandre De Oliveira (alex@p1sec.com) Agenda Overall telecom architecture Architecture
The Global System for Mobile communications (GSM) Overview
 The Global System for Mobile communications (GSM) Overview GSM D-AMPS Japan Digital PCS 1900 DCS 1800 CDMA Digital Cellular Systems World-wide Multiple Access Techniques In the GSM/DCS mobile system each
The Global System for Mobile communications (GSM) Overview GSM D-AMPS Japan Digital PCS 1900 DCS 1800 CDMA Digital Cellular Systems World-wide Multiple Access Techniques In the GSM/DCS mobile system each
ETSI TS 102 226 V9.2.0 (2010-04) Technical Specification. Smart Cards; Remote APDU structure for UICC based applications (Release 9)
 TS 102 226 V9.2.0 (2010-04) Technical Specification Smart Cards; Remote APDU structure for UICC based applications (Release 9) 2 TS 102 226 V9.2.0 (2010-04) Reference RTS/SCP-T02850v920 Keywords protocol,
TS 102 226 V9.2.0 (2010-04) Technical Specification Smart Cards; Remote APDU structure for UICC based applications (Release 9) 2 TS 102 226 V9.2.0 (2010-04) Reference RTS/SCP-T02850v920 Keywords protocol,
Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM)
 Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Li-Hsing Yen National University of Kaohsiung GSM System Architecture Um (ME/SIM) C E C PSTN, ISDN, PSPDN, CSPDN A-bis A F A-bis C B BTS BSS BSC HLR VLR EIR
Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Li-Hsing Yen National University of Kaohsiung GSM System Architecture Um (ME/SIM) C E C PSTN, ISDN, PSPDN, CSPDN A-bis A F A-bis C B BTS BSS BSC HLR VLR EIR
4th European Tcl/Tk User Meeting. Tcl used for testing in the mobile world
 4th European Tcl/Tk User Meeting Tcl used for testing in the mobile world Hans Banken, SIGOS GmbH May 2003 Klingenhofstraße 50d D-90411 Nürnberg Fon +49 911 95168-0 Fax +49 911 95 16 8-355 www.sigos.de
4th European Tcl/Tk User Meeting Tcl used for testing in the mobile world Hans Banken, SIGOS GmbH May 2003 Klingenhofstraße 50d D-90411 Nürnberg Fon +49 911 95168-0 Fax +49 911 95 16 8-355 www.sigos.de
3G USB Modem. Model AC327U. User Manual. February 2014 202-11356-01. 350 East Plumeria Drive San Jose, CA 95134 USA
 3G USB Modem Model AC327U User Manual February 2014 202-11356-01 350 East Plumeria Drive San Jose, CA 95134 USA Support Thank you for selecting NETGEAR products. After installing your device, locate the
3G USB Modem Model AC327U User Manual February 2014 202-11356-01 350 East Plumeria Drive San Jose, CA 95134 USA Support Thank you for selecting NETGEAR products. After installing your device, locate the
Development of Wireless Networks
 Development of Wireless Networks Cellular Revolution In 1990 mobile phone users populate 11 million. By 2004 the figure will become 1 billion Phones are most obvious sign of the success of wireless technology.
Development of Wireless Networks Cellular Revolution In 1990 mobile phone users populate 11 million. By 2004 the figure will become 1 billion Phones are most obvious sign of the success of wireless technology.
ETSI TS 123 251 V6.5.0 (2005-09)
 TS 123 251 V6.5.0 (2005-09) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); Network sharing; Architecture and functional description (3GPP TS 23.251 version 6.5.0 Release 6)
TS 123 251 V6.5.0 (2005-09) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); Network sharing; Architecture and functional description (3GPP TS 23.251 version 6.5.0 Release 6)
SOLUTIONS FOR ROAMING AND INTEROPERABILITY PROBLEMS BETWEEN LTE AND 2G OR 3G NETWORKS
 Review of the Air Force Academy No 2 (24) 2013 SOLUTIONS FOR ROAMING AND INTEROPERABILITY PROBLEMS BETWEEN LTE AND 2G OR 3G NETWORKS Radu CURPEN, Florin SANDU, Cosmin COSTACHE, Gabriel Mihail DANCIU Transilvania
Review of the Air Force Academy No 2 (24) 2013 SOLUTIONS FOR ROAMING AND INTEROPERABILITY PROBLEMS BETWEEN LTE AND 2G OR 3G NETWORKS Radu CURPEN, Florin SANDU, Cosmin COSTACHE, Gabriel Mihail DANCIU Transilvania
CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: GSM - In Detail
 CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: GSM - In Detail Professor Patrick Traynor 9/27/12 Cellular Telecommunications Architecture Background Air Interfaces Network Protocols Application: Messaging
CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: GSM - In Detail Professor Patrick Traynor 9/27/12 Cellular Telecommunications Architecture Background Air Interfaces Network Protocols Application: Messaging
GSM System. Global System for Mobile Communications
 GSM System Global System for Mobile Communications Introduced in 1991. Settings of standards under ETSI (European Telecommunication Standards Institute) Services - Telephone services - Data services -
GSM System Global System for Mobile Communications Introduced in 1991. Settings of standards under ETSI (European Telecommunication Standards Institute) Services - Telephone services - Data services -
3GPP TS 31.103 V5.13.1 (2007-06)
 TS 31.103 V5.13.1 (2007-06) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Characteristics of the IP Multimedia Services Identity
TS 31.103 V5.13.1 (2007-06) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Characteristics of the IP Multimedia Services Identity
Mobile Computing. Basic Call Calling terminal Network Called terminal 10/25/14. Public Switched Telephone Network - PSTN. CSE 40814/60814 Fall 2014
 Mobile Computing CSE 40814/60814 Fall 2014 Public Switched Telephone Network - PSTN Transit switch Transit switch Long distance network Transit switch Local switch Outgoing call Incoming call Local switch
Mobile Computing CSE 40814/60814 Fall 2014 Public Switched Telephone Network - PSTN Transit switch Transit switch Long distance network Transit switch Local switch Outgoing call Incoming call Local switch
GSM GSM 11.11 TECHNICAL December 1995 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0
 GSM GSM 11.11 TECHNICAL December 1995 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-091111Q ICS: 33.060.50 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
GSM GSM 11.11 TECHNICAL December 1995 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-091111Q ICS: 33.060.50 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
GSM v. CDMA: Technical Comparison of M2M Technologies
 GSM v. CDMA: Technical Comparison of M2M Technologies Introduction Aeris provides network and data analytics services for Machine-to- Machine ( M2M ) and Internet of Things ( IoT ) applications using multiple
GSM v. CDMA: Technical Comparison of M2M Technologies Introduction Aeris provides network and data analytics services for Machine-to- Machine ( M2M ) and Internet of Things ( IoT ) applications using multiple
MAP/C SEND ROUTING INFO FOR SM. Destination Mobile Number. Obtain the SS7 address of the MSC VLR currently serving the specified Mobile Number
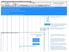 In this call flow we will look at how a terminating SMS is handled in GSM. Setting up a terminating SMS session is a multi-step process. (1) Interrogate the MSC to locate the subscriber (2)Setting SMS
In this call flow we will look at how a terminating SMS is handled in GSM. Setting up a terminating SMS session is a multi-step process. (1) Interrogate the MSC to locate the subscriber (2)Setting SMS
Cellular Network Organization. Cellular Wireless Networks. Approaches to Cope with Increasing Capacity. Frequency Reuse
 Cellular Network Organization Cellular Wireless Networks Use multiple low-power transmitters (100 W or less) Areas divided into cells Each served by its own antenna Served by base station consisting of
Cellular Network Organization Cellular Wireless Networks Use multiple low-power transmitters (100 W or less) Areas divided into cells Each served by its own antenna Served by base station consisting of
Using an approximated One-Time Pad to Secure Short Messaging Service (SMS)
 Using an approximated One-Time Pad to Secure Short Messaging Service (SMS) N.J Croft and M.S Olivier Information and Computer Security Architectures (ICSA) Research Group Department of Computer Science
Using an approximated One-Time Pad to Secure Short Messaging Service (SMS) N.J Croft and M.S Olivier Information and Computer Security Architectures (ICSA) Research Group Department of Computer Science
OVERCOMING CHANNEL BANDWIDTH CONSTRAINTS IN SECURE SIM APPLICATIONS
 OVERCOMING CHANNEL BANDWIDTH CONSTRAINTS IN SECURE SIM APPLICATIONS John A. MacDonald 1, William Sirett 2 and Chris J. Mitchell 1 1 Information Security Group, Royal Holloway, University of London, Egham,
OVERCOMING CHANNEL BANDWIDTH CONSTRAINTS IN SECURE SIM APPLICATIONS John A. MacDonald 1, William Sirett 2 and Chris J. Mitchell 1 1 Information Security Group, Royal Holloway, University of London, Egham,
Security Architecture in UMTS Third Generation Cellular Networks Tomás Balderas-Contreras René A. Cumplido-Parra
 Security Architecture in UMTS Third Generation Cellular Networks Tomás Balderas-Contreras René A. Cumplido-Parra Reporte Técnico No. CCC-04-002 27 de febrero de 2004 Coordinación de Ciencias Computacionales
Security Architecture in UMTS Third Generation Cellular Networks Tomás Balderas-Contreras René A. Cumplido-Parra Reporte Técnico No. CCC-04-002 27 de febrero de 2004 Coordinación de Ciencias Computacionales
Operator-based Over-the-air M2M Wireless Sensor Network Security
 Operator-based Over-the-air M2M Wireless Sensor Network Security Sachin Agarwal Christoph Peylo Deutsche Telekom A.G., Laboratories Ernst-Reuter-Platz 7 10587 Berlin DE Email: {sachin.agarwal, christoph.peylo}@telekom.de
Operator-based Over-the-air M2M Wireless Sensor Network Security Sachin Agarwal Christoph Peylo Deutsche Telekom A.G., Laboratories Ernst-Reuter-Platz 7 10587 Berlin DE Email: {sachin.agarwal, christoph.peylo}@telekom.de
GSM Architecture Training Document
 Training Document TC Finland Nokia Networks Oy 1 (20) The information in this document is subject to change without notice and describes only the product defined in the introduction of this documentation.
Training Document TC Finland Nokia Networks Oy 1 (20) The information in this document is subject to change without notice and describes only the product defined in the introduction of this documentation.
Sierra Wireless AirCard Watcher Help for Mac OS X
 Sierra Wireless AirCard Watcher Help for Mac OS X Sierra Wireless AirCard Watcher allows you to manage and monitor the connection between your modem and the network. With Watcher, you can: Determine signal
Sierra Wireless AirCard Watcher Help for Mac OS X Sierra Wireless AirCard Watcher allows you to manage and monitor the connection between your modem and the network. With Watcher, you can: Determine signal
Wireless Cellular Networks: 1G and 2G
 Wireless Cellular Networks: 1G and 2G Raj Jain Professor of Computer Science and Engineering Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available
Wireless Cellular Networks: 1G and 2G Raj Jain Professor of Computer Science and Engineering Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available
GSM GSM 03.13 TECHNICAL March 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0
 GSM GSM 03.13 TECHNICAL March 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-030313Q ICS: 33.060.50 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
GSM GSM 03.13 TECHNICAL March 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-030313Q ICS: 33.060.50 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
Product Description. HiLink E3531 HSPA+ USB Stick V100R001 HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Issue 01. Date 2013-6-13
 HiLink E3531 HSPA+ USB Stick V100R001 Issue 01 Date 2013-6-13 HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. provides customers with comprehensive technical support and service. Please feel
HiLink E3531 HSPA+ USB Stick V100R001 Issue 01 Date 2013-6-13 HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. provides customers with comprehensive technical support and service. Please feel
Authentication and Security in Mobile Phones
 Authentication and Security in Mobile Phones Greg Rose QUALCOMM Australia ggr@qualcomm.com ABSTRACT Mobile telephone systems have a checkered reputation regarding security and authentication features after
Authentication and Security in Mobile Phones Greg Rose QUALCOMM Australia ggr@qualcomm.com ABSTRACT Mobile telephone systems have a checkered reputation regarding security and authentication features after
Mobile Services (ST 2010)
 Mobile Services (ST 2010) Chapter 3: Mobility Management Axel Küpper Service-centric Networking Deutsche Telekom Laboratories, TU Berlin 1 Mobile Services Summer Term 2010 3 Mobility Management 3.1 Handover
Mobile Services (ST 2010) Chapter 3: Mobility Management Axel Küpper Service-centric Networking Deutsche Telekom Laboratories, TU Berlin 1 Mobile Services Summer Term 2010 3 Mobility Management 3.1 Handover
On the Security of 3GPP Networks
 On the Security of 3GPP Networks Michael Walker Vodafone AirTouch & Royal Holloway, University of London Chairman 3GPP SA3 - Security Eurocrypt 2000 Security of 3GPP networks 1 Acknowledgements This presentation
On the Security of 3GPP Networks Michael Walker Vodafone AirTouch & Royal Holloway, University of London Chairman 3GPP SA3 - Security Eurocrypt 2000 Security of 3GPP networks 1 Acknowledgements This presentation
In this Lecture" Access method CDMA" Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 2: Mobile Medium Access Control Layer and Telecommunications
 Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 2: Mobile Medium Access Control Layer and Telecommunications Dr. Cecilia Mascolo In this Lecture In this lecture we will discuss aspects related to the MAC Layer of wireless
Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 2: Mobile Medium Access Control Layer and Telecommunications Dr. Cecilia Mascolo In this Lecture In this lecture we will discuss aspects related to the MAC Layer of wireless
Privacy through Pseudonymity in Mobile Telephony Systems
 Privacy through Pseudonymity in Mobile Telephony Systems Eike Ritter University of Birmingham Joint work with Myrto Arapinis, Loretta Mancini and Mark Ryan Eike Ritter Privacy in Mobile Telephony Systems
Privacy through Pseudonymity in Mobile Telephony Systems Eike Ritter University of Birmingham Joint work with Myrto Arapinis, Loretta Mancini and Mark Ryan Eike Ritter Privacy in Mobile Telephony Systems
GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications
 GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN MS HLR 1) Overview of GSM architecture 2) GSM channel structure 05-1 GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN
GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN MS HLR 1) Overview of GSM architecture 2) GSM channel structure 05-1 GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN
Reprogrammable SIMs:
 Reprogrammable SIMs: Technology, Evolution and Implications Final Report Prepared for: Prepared by: CSMG Descartes House 8 Gate Street London WC2A 3HP United Kingdom www.csmg-global.com 25 September 2012
Reprogrammable SIMs: Technology, Evolution and Implications Final Report Prepared for: Prepared by: CSMG Descartes House 8 Gate Street London WC2A 3HP United Kingdom www.csmg-global.com 25 September 2012
Smart Card. Smart Card applications
 Smart Card Chip Plastic card A very secure way of storing a small amount of sensitive data 1 Smart Card applications Retail Sale of goods using Electronic Purses, Credit / Debit Vending machines Loyalty
Smart Card Chip Plastic card A very secure way of storing a small amount of sensitive data 1 Smart Card applications Retail Sale of goods using Electronic Purses, Credit / Debit Vending machines Loyalty
Security in the GSM Network
 Security in the GSM Network Ammar Yasir Korkusuz 2012 Bogazici University, Electrical-Electronics Engineering Department, MSc. Student EE 588 NETWORK SECURITY TERM PROJECT Abstract: GSM is the biggest
Security in the GSM Network Ammar Yasir Korkusuz 2012 Bogazici University, Electrical-Electronics Engineering Department, MSc. Student EE 588 NETWORK SECURITY TERM PROJECT Abstract: GSM is the biggest
Communication Infrastructure: GSM Communication
 Communication Infrastructure: GSM Communication Andreas Schöffl and Michael Irger Abstract. In this Paper we describe the GSM Standard of Mobile Phones. The Global System for Mobile communications is the
Communication Infrastructure: GSM Communication Andreas Schöffl and Michael Irger Abstract. In this Paper we describe the GSM Standard of Mobile Phones. The Global System for Mobile communications is the
GSM Security Claude Castelluccia INRIA
 GSM Security Claude Castelluccia INRIA Technology behind GSM 900 MHz (or 1800 MHz) band uplink frequency band 890-915 MHz downlink frequency band is 935-960 MHz 25 MHz subdivided into 124 carrier frequency
GSM Security Claude Castelluccia INRIA Technology behind GSM 900 MHz (or 1800 MHz) band uplink frequency band 890-915 MHz downlink frequency band is 935-960 MHz 25 MHz subdivided into 124 carrier frequency
Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM)
 Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Definition Global system for mobile communication (GSM) is a globally accepted standard for digital cellular communication. GSM is the name of a standardization
Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Definition Global system for mobile communication (GSM) is a globally accepted standard for digital cellular communication. GSM is the name of a standardization
Internet ID - Flexible Re-use of Mobile Phone Authentication Security for Service Access
 Internet ID - Flexible Re-use of Mobile Phone Authentication Security for Service Access Marko Schuba, Volker Gerstenberger, Paul Lahaije Abstract Identity management systems like.net Passport and the
Internet ID - Flexible Re-use of Mobile Phone Authentication Security for Service Access Marko Schuba, Volker Gerstenberger, Paul Lahaije Abstract Identity management systems like.net Passport and the
3G USB Modem. Model AC329U. User Manual. February 2014 202-11357-02. 350 East Plumeria Drive San Jose, CA 95134 USA
 3G USB Modem Model AC329U User Manual February 2014 202-11357-02 350 East Plumeria Drive San Jose, CA 95134 USA Support Thank you for selecting NETGEAR products. After installing your device, locate the
3G USB Modem Model AC329U User Manual February 2014 202-11357-02 350 East Plumeria Drive San Jose, CA 95134 USA Support Thank you for selecting NETGEAR products. After installing your device, locate the
What is telecommunication? electronic communications? What is telephony?
 What is telecommunication? Telecommunication: Any transmission, emission or reception of signs, signals, writing, images and sounds or intelligence of any nature by wire, radio, optical or other electromagnetic
What is telecommunication? Telecommunication: Any transmission, emission or reception of signs, signals, writing, images and sounds or intelligence of any nature by wire, radio, optical or other electromagnetic
Cellular Network Organization
 Cellular Networks Cellular Network Organization Use multiple low-power transmitters (100 W or less) Areas divided into cells o Each served by its own antenna o Served by base station consisting of transmitter,
Cellular Networks Cellular Network Organization Use multiple low-power transmitters (100 W or less) Areas divided into cells o Each served by its own antenna o Served by base station consisting of transmitter,
Smart Cards a(s) Safety Critical Systems
 Smart Cards a(s) Safety Critical Systems Gemplus Labs Pierre.Paradinas Paradinas@gemplus.com Agenda Smart Card Technologies Java Card TM Smart Card a specific domain Card Life cycle Our Technical and Business
Smart Cards a(s) Safety Critical Systems Gemplus Labs Pierre.Paradinas Paradinas@gemplus.com Agenda Smart Card Technologies Java Card TM Smart Card a specific domain Card Life cycle Our Technical and Business
Indian Journal of Advances in Computer & Information Engineering Volume.1 Number.1 January-June 2013, pp.1-5 @ Academic Research Journals.
 Cellular System Rajat Chugh, Parag Jasoria, Tushar Arora, Nitin Ginotra and Vivek Anand V Semester, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Dronacharya College of Engineering, Khentawas, Farukhnagar,
Cellular System Rajat Chugh, Parag Jasoria, Tushar Arora, Nitin Ginotra and Vivek Anand V Semester, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Dronacharya College of Engineering, Khentawas, Farukhnagar,
Wireless Mobile Telephony
 Wireless Mobile Telephony The Ohio State University Columbus, OH 43210 Durresi@cis.ohio-state.edu http://www.cis.ohio-state.edu/~durresi/ 1 Overview Why wireless mobile telephony? First Generation, Analog
Wireless Mobile Telephony The Ohio State University Columbus, OH 43210 Durresi@cis.ohio-state.edu http://www.cis.ohio-state.edu/~durresi/ 1 Overview Why wireless mobile telephony? First Generation, Analog
GSM GSM 08.52 TECHNICAL December 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0
 GSM GSM 08.52 TECHNICAL December 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-030852Q ICS: 33.020 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
GSM GSM 08.52 TECHNICAL December 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-030852Q ICS: 33.020 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
What is telecommunication? electronic communications. service?
 What is telecommunication? Telecommunication: Any transmission, emission or reception of signs, signals, writing, images and sounds or intelligence of any nature by wire, radio, optical or other electromagnetic
What is telecommunication? Telecommunication: Any transmission, emission or reception of signs, signals, writing, images and sounds or intelligence of any nature by wire, radio, optical or other electromagnetic
GSM GSM 03.07 TECHNICAL November 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0
 GSM GSM 03.07 TECHNICAL November 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-030307Q ICS: 33.020 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
GSM GSM 03.07 TECHNICAL November 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-030307Q ICS: 33.020 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
