Sonography of Abdominal Wall Hernias
|
|
|
- Rafe Beasley
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Thomas Rettenbacher 1 Alois Hollerweger 2 Peter Macheiner 2 Norbert Gritzmann 2 Thaddeus Gotwald 1 Robert Frass 3 Barbara Schneider 4 Received March 19, 2001; accepted after revision May 11, Department of Radiology II, University Hospital Innsbruck, Anichstr. 35, 6020 Innsbruck, Austria. Address correspondence to T. Rettenbacher. 2 Department of Radiology, Hospital Barmherzige Brueder, Kajetanerplatz 1, 5010 Salzburg, Austria. 3 Department of Surgery, Hospital Barmherzige Brueder, 5010 Salzburg, Austria. 4 Institute of Medical Statistics, University of Vienna, Schwarzspanierstr. 17, 1090 Wien, Austria. AJR 2001;177: X/01/ American Roentgen Ray Society Abdominal Wall Hernias: Cross- Sectional Imaging Signs of Incarceration Determined with Sonography OBJECTIVE. The aim of this study was to determine with sonography whether distinct cross-sectional imaging signs exist that may differentiate between incarcerated and nonincarcerated abdominal wall hernias. SUBJECTS AND METHODS. The sonographic appearance of 149 consecutive abdominal wall hernias was prospectively investigated and correlated with subsequent surgical results. Commercially available 4- to 10-MHz linear transducers and 2- to 5-MHz curved transducers were used to evaluate the hernias. RESULTS. Surgery revealed 126 nonincarcerated and 23 incarcerated hernias. The sonographic signs suggestive of incarceration that we identified included free fluid in the hernia sac, which was observed in 91% of the incarcerated hernias and in 3% of the nonincarcerated hernias; bowel wall thickening in the hernia, which was detected in 88% of the incarcerated hernias and in none of the nonincarcerated hernias; fluid in the herniated bowel loop, which was detected in 82% of the incarcerated hernias and in 3% of the nonincarcerated hernias; and dilated bowel loops in the abdomen, which occurred in 65% of the incarcerated hernias and in none of the nonincarcerated hernias. These imaging findings allowed the identification of incarceration in all 23 cases and led to a false-positive result in two of 126 nonincarcerated hernias. CONCLUSION. Cross-sectional imaging signs indicating hernial incarceration included free fluid in the hernial sac, bowel wall thickening in the hernia, fluid in the herniated bowel loop, and dilated bowel loops in the abdomen. Sonography is an appropriate cross-sectional imaging modality for detecting these signs that are helpful in diagnosing patients with atypical clinical presentations. A bdominal wall hernias are usually suggested by the patient s clinical history and confirmed by findings from a physical examination. The patient s clinical history, however, may be atypical and the physical examination may be limited in obese patients, in patients with severe abdominal pain and distention, and in patients with small hernias or with hernias located in uncommon sites [1 14]. In these instances, diagnostic imaging is necessary. Herniography, sonography, and CT are the established imaging methods for confirming or excluding suspected abdominal wall hernias [1 11, 15 25]. In addition, the cross-sectional imaging modalities, sonography and CT, can aid in the differential diagnosis of palpable abdominal wall masses and can help to define hernial contents such as fatty tissue, bowel, other organs, or fluid [1 9, 15 19, 26, 27]. Hernial complications such as incarceration are also usually detected at clinical presentation. Cross-sectional imaging, however, is required when the clinical presentation is misleading or inconclusive, or when the surgeon believes it is important to preoperatively assess the contents of an incarcerated hernia [1, 12, 13]. Radiologists, therefore, should be familiar with the imaging findings of both incarcerated and nonincarcerated hernias. Several years ago, we observed that an incarcerated abdominal wall hernia was usually associated with a sonographic appearance that clearly differed from the sonographic appearance of a nonincarcerated hernia. To our knowledge, no crosssectional imaging studies in the literature have examined the spectrum of imaging signs of hernial incarceration and their frequencies in a substantial patient population. The aim of this study was to investigate with sonography whether distinct cross-sectional imaging signs exist to differentiate incarcerated and nonincarcerated abdominal wall hernias. AJR:177, November
2 Rettenbacher et al. Subjects and Methods Patient Population The prospective part of this study includes 236 consecutive patients (102 females and 134 males; years old; mean age, 57 years) who underwent diagnostic sonography between May 1997 and September These patients were referred by the surgery department for sonography of the abdominal wall and the abdomen when their clinical presentations were suggestive of an abdominal wall hernia but their physical examinations were inconclusive (n = 187), or when the surgeon believed it was important to preoperatively determine the contents of a suspected hernia (n = 49). This procedure has been a common practice at our hospital since Also included in our study were six patients in whom sonography revealed complicated abdominal wall hernias that were clinically not suspected. Three of the patients were referred for sonography because of abdominal pain and vomiting of unclear origin; two patients, because of a clinically unclear abdominal wall mass; and one patient, because of suspicion for acute appendicitis. Imaging Techniques All sonographic examinations included in this study were performed by four radiologists experienced in gastrointestinal sonography. The patients were not specially prepared for the sonographic examination. Sonography was performed on patients in a supine position, and the Valsalva s or coughing maneuvers were almost always performed during the examination to confirm or exclude a hernia. At least four images on several planes were obtained of each hernia and documented on film with a multiformat camera. Commercially available sonographic equipment included an HDI 3000 unit with 2- to 4-MHz curved array, 4- to 7-MHz linear array, and 5- to 10-MHz linear array transducers (Advanced Technology Laboratories, Bothell, WA) and an AU4 unit with 3.5- to 5.0-MHz curved array and 7.5- to 10.0-MHz linear array transducers (Esaote, Florence, Italy). Color Doppler sonography was performed using the previously mentioned linear array transducers. Color Doppler settings were adjusted for maximal blood flow sensitivity. These settings included a wall filter of 50 Hz, a pulse repetition frequency of 1000, maximum power, and the highest possible gain at a usable ratio of signalto-background noise. To evaluate the peristalsis of herniated bowel loops, the sonographic transducer was held motionless over the hernia for approximately 2 min. Interpretation of Sonographic Findings In this study, the sonographic detection of bowel, other abdominal organs, or fatty tissue in the abdominal wall, as well as the sonographic visualization of a lesion connecting with the abdomen, was required to interpret a lesion as an abdominal wall hernia. Several years before the study began, the authors observed on sonography that incarcerated abdominal wall hernias were often associated with distinct imaging signs. On the basis of this experience, a study protocol was designed in which the investigators were requested to prospectively evaluate the following points by sonography: the contents of the hernias, such as fatty tissue, bowel, or other organs; the presence or absence of free fluid in the hernial sac; the wall thickness of the herniated bowel loop; the presence or absence of fluid in the herniated bowel loop; the diameter of small bowel in the abdomen; the presence or absence of color Doppler signals in the hernial contents; and the presence or absence of peristalsis in the herniated bowel loop. Immediately after the imaging was performed, the cross-sectional signs were noted on a prepared sheet of paper. In addition, the sonographic signs were then independently reviewed by the four investigating radiologists, and a consensus opinion regarding the signs was made. The study protocol was approved by the ethics committee. Statistical Analysis Surgical results were considered the gold standard for this study. A hernia was diagnosed as incarcerated at surgery if there was evidence of a compromise in the blood supply of the hernial contents. To enable statistical correlation of imaging signs with surgical results in all patients, we evaluated only those hernias in which sonography was performed and the diagnosis was confirmed by surgery. For each sonographic sign, 2 2 contingency tables were used to calculate the estimates for sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values, and accuracy. Data analyses were performed using the statistical software package version 8.0 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC) for Windows (Microsoft, Redmond, CA). Results In 141 of 236 prospectively investigated patients, sonography revealed one lesion (n = 117) and two lesions (n = 24) suggestive of abdominal wall hernias. One hundred twenty-nine of the 141 patients with sonographically diagnosed hernias underwent surgical hernia repair, with a total of 147 hernias repaired. In 143 of 147 hernias with surgical treatment, sonographic diagnosis of a hernia was correct, whereas four of the 147 presented as an extraperitoneal lipoma at surgery. In 77 of 236 prospectively imaged patients, sonography did not reveal any abnormal findings. Sixteen of the patients underwent surgery despite normal findings on sonography because the clinical presentation remained suggestive of a hernia. Surgery revealed a nonincarcerated hernia in six patients and no abnormal findings in 10 patients. In 18 of 236 patients, sonography revealed an abdominal wall lesion other than a hernia, including a lipoma in five patients, an enlarged lymph node in five patients, a metastasis in three patients, a suture granuloma in three patients, and an abscess in two patients. The statistical analysis of imaging signs included 149 hernias in 131 patients in whom sonography and surgery were performed. A final diagnosis based on the surgical results included 126 nonincarcerated hernias and 23 incarcerated hernias. The location of all 149 abdominal wall hernias is given in Table 1. The contents of the nonincarcerated hernias were fatty tissue alone in 54 patients, fatty tissue and bowel in 47 patients (Fig. 1), bowel alone in 16 patients, and urinary bladder in three patients. The contents of the incarcerated hernias were fatty tissue alone in six patients, fatty tissue and bowel in four patients, and bowel alone in 13 patients. In 15 of 17 patients with incarcerated hernias containing bowel, blood circulation improved during surgery. Therefore, resection of the incarcerated bowel loop was necessary in only two patients. In three of six patients with incarcerated hernias containing only fatty tissue, resection of the fatty tissue was performed. The sonographic signs of incarceration investigated for this study and their frequencies are given in Table 2. The sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values, and accuracy of each sonographic sign as a finding positive for hernial incarceration are shown in Table 3. Concomitant free fluid in the hernia was the only sonographic sign of incarceration that we found when fatty tissue alone was present in a hernial sac (Fig. 2). In these cases, this finding indicated incarceration with a sensitivity of 100% (6/6) and a specificity of 96% (52/54) because free fluid was found in two of 54 nonincarcerated hernias containing fatty tissue alone. If bowel was present in a Location of 23 Incarcerated TABLE 1 and 126 Nonincarcerated Abdominal Wall Hernias Location I Hernias NI Hernias Right groin 3 50 Left groin 5 48 Right thigh 6 7 Left thigh 1 5 Right obturator 1 0 Umbilicus 5 10 Incisional 2 6 Note. I = Incarcerated, NI = Nonincarcerated AJR:177, November 2001
3 Sonography of Abdominal Wall Hernias hernia, all four sonographic signs of incarceration could be applied (Figs. 3 and 4). Each of the incarcerated hernias with bowel displayed at least two signs of incarceration. The combination of at least two of the four identified signs allowed the detection of incarceration with a sensitivity of 100% (17/17) and a specificity of 100% (63/63) because the combined signs were never observed in nonincarcerated hernias in our series. All 23 incarcerated abdominal wall hernias were correctly interpreted preoperatively as incarcerated by the investigating radiologists, whereas two of 126 nonincarcerated hernias were considered incarcerated and were therefore false-positive for incarceration on sonography. During the time of the study, no incarcerated hernias were overlooked on sonography. In the six patients in whom sonography diagnosed an incarcerated hernia that was clinically not suspected and who underwent surgical repair, the sonographic signs included free fluid in the hernia sac in five patients, bowel wall thickening in the hernia in four patients, fluid in the herniated bowel loop in five patients, dilated bowel loops in the abdomen in three patients, absence of blood flow in the hernial contents in two patients, and absence of peristalsis in the hernia in four patients (Fig. 3). Fig year-old man with nonincarcerated left inguinal hernia. Longitudinal sonogram shows fatty tissue (short arrows) and gas-filled bowel loop (curved arrows). Note reverberation artifacts behind gas surface (long straight arrows). Fig year-old woman with incarcerated umbilical hernia. Longitudinal sonogram shows hernia containing fatty tissue (long arrows) and considerable amount of septate collection of free fluid (short arrows). Discussion Although hernial incarceration was usually assessed accurately by the clinician, its diagnosis may be difficult when the clinical presentation is atypical or when the physical examination is limited. During a period of 3 years, we registered six patients with incarcerated hernias that were not suspected by the clinician and in whom sonography helped to establish the correct preoperative diagnosis of this life-threatening condition (Fig. 3). Because an incarcerated hernia presents as a complex mass on cross-sectional imaging and usually differs considerably in appearance from a nonincarcerated hernia, radiologists performing abdominal imaging should be familiar with the spectrum of imaging signs of this entity. In addition, cross-sectional imaging is necessary when the surgeon believes it is important to preoperatively define the contents of an incarcerated hernia to determine the timing of surgery. If fatty tissue, fluid, or both are present in the incarcerated hernia, time is not a limiting factor in preparing a patient for surgery. This finding is especially an advantage in elderly and multimorbid patients. In contrast, incarcerated bowel calls for immediate surgery to prevent bowel necrosis and the subsequent necessity to resect the affected bowel loop. Although several studies, predominantly case reports, noted that sonography and CT can identify complications such as hernial incarceration [1, 2, 12, 15, 17, 27 29], no study, to our knowledge, has evaluated the spectrum of imaging signs of incarcerated hernias in a substantial patient population. Free fluid in the hernia sac was a sensitive and specific criterion of incarceration in our series (Tables 2 and 3 and Figs. 2 5). Free fluid is an eye-catching finding on sonography because of the great difference in echogenicity between the usually echo-free fluid and the other hernial contents or surrounding tissue (Figs. 2 5). This single sign immediately indicated TABLE 2 Frequency of Occurrence of Each Sonographic Sign as Criterion of Hernial Incarceration in 126 Nonincarcerated and 23 Incarcerated Hernias Sonographic Sign Incarcerated (%) Nonincarcerated (%) Free fluid in hernial sac 91 (21/23) 3 (4/126) Bowel wall thickness in hernia 4 mm 88 (15/17) 0 (0/63) Fluid within herniated bowel loop 82 (14/17) 3 (2/63) Dilated bowel loops in abdomen 65 (11/17) 0 (0/63) Absence of blood flow within hernia 22 (5/23) 25 (31/126) Absence of peristalsis within hernia 76 (13/17) 38 (24/63) Note. Seventeen of 23 incarcerated hernias and 63 of 126 nonincarcerated hernias contained bowel. Numbers in parentheses represent cases. 1 2 AJR:177, November
4 Rettenbacher et al. Fig year-old woman with incarcerated right femoral hernia. Longitudinal sonogram shows fluidfilled small-bowel loop with moderate wall thickening (long arrows) and small amount of free fluid in hernia (short arrows). Patient suffered from vomiting and diffuse abdominal pain. Incarcerated hernia was clinically not suspected. Surgery confirmed sonographic findings. to the investigator that a hernial complication had a high probability of being present. In the literature, we found two sonographic studies mentioning that an incarcerated hernia may contain free fluid [1, 15]. Motta et al. [27] reported three cases determined by sonography of torsion of an inguinal hernial sac filled with only a multiseptate fluid. Several cross-sectional imaging studies dealing with imaging signs of hernial incarceration [1, 2, 12, 17, 28] did not mention free fluid as a sign, although three of them [1, 2, 17] showed images of incarcerated hernias with a considerable amount of free fluid in the hernial sac without describing this as a criterion of incarceration. In our series, two of four patients with free fluid in a nonincarcerated hernia had free fluid in the abdomen and also in the hernia caused by liver cirrhosis. This finding can be a pitfall. Free fluid in an incarcerated hernia may be explained by transudation into the hernial sac caused by the compromised blood supply of hernial contents. The fluid in the hernial sac may be clear or sanguineous at surgery [27]. Wall thickening of herniated bowel was another important sonographic sign of incarceration in our patients (Fig. 3). Wall thickening indicated incarceration of the hernias containing bowel with an excellent specificity but with limited sensitivity (Table 3). A cutoff point of 4 mm for wall thickening in this study was obtained for nondilated bowel loops in particular. In dilated bowel loops, wall thickening may sometimes remain undiagnosed with a cutoff point of 4 mm (Fig. 4) and result in a reduced sensitivity. Some sonographic and CT studies reported in the literature state that wall thickening of the herniated bowel loop is suggestive of hernial incarceration [1, 15, 17, 28]. Percentages of occurrence, to our knowledge, are not available. Wall thickening of incarcerated bowel may be predominantly explained by blood congestion and edema. Another sign of hernial incarceration that we investigated was fluid in the herniated bowel loop (Figs. 3 and 4). The free fluid indicated incarceration of the hernias containing bowel with high specificity but limited sensitivity (Table 3). To our knowledge, this sign has not been reported previously in the literature. However, we found a sonographic image in a study showing fluid in an incarcerated bowel loop that was not mentioned in the text [2]. This sonographic image of an incarcerated hernia shows fluid in the herniated bowel loop with bowel wall thickening and free fluid in the hernial sac [2]. The reason for the presence of fluid in an incarcerated bowel loop may be exudation into the bowel lumen, causing excess fluid in the bowel in cases of bowel obstruction. An indirect sign of an incarcerated hernia was evidence of dilated, fluid-filled bowel loops in the abdomen. This sign indicated incarceration of the hernias containing bowel with excellent specificity but limited sensitivity (Table 3). Despite the relatively low percentage of occurrence A B Fig year-old man with incarcerated right inguinal hernia. A and B, Longitudinal (A) and transverse (B) sonograms show dilated, fluid-filled small-bowel loop (long arrows) and considerable amount of free fluid in hernia (short arrows) AJR:177, November 2001
5 Sonography of Abdominal Wall Hernias TABLE 3 Sensitivity, Specificity, Positive and Negative Predictive Values, and Accuracy of Each Sonographic Sign as Criterion of Hernial Incarceration in 126 Nonincarcerated and 23 Incarcerated Hernias Sonographic Sign Sensitivity (%) Specificity (%) Positive Predictive Value (%) Negative Predictive Value (%) Accuracy (%) Free fluid in hernia sac 91 (21/23) 97 (122/126) 51 (21/41) 100 (610/612) 96 (143/149) Bowel wall thickening within hernia 88 (15/17) 100 (63/63) 100 (15/15) 99 (315/317) 97 (78/80) Fluid within herniated bowel loop 82 (14/17) 97 (61/63) 58 (14/24) 99 (305/308) 94 (75/80) Dilated bowel loops in abdomen 65 (11/17) 100 (63/63) 100 (11/11) 98 (315/321) 92 (74/80) Absence of blood flow within hernia 22 (5/23) 75 (95/126) 3 (5/160) 96 (475/493) 67 (100/149) Absence of peristalsis within hernia 76 (13/17) 62 (39/63) 10 (13/133) 98 (195/199) 65 (52/80) Note. Seventeen of 23 incarcerated hernias and 63 of 126 nonincarcerated hernias contained bowel. Numbers in parentheses represent cases. Fig year-old man with nonincarcerated right inguinal hernia. Longitudinal sonogram shows fatty tissue (short arrows) and small amount of free fluid (long arrows). in our series, dilated, fluid-filled bowel loops are worth mentioning as an important sign because they may be the only conspicuous cross-sectional imaging finding in patients who clinically present exclusively with vomiting, diffuse abdominal pain, or both. We observed this situation in three patients. Almost all patients with an incarcerated hernia containing bowel can be expected to have complete bowel obstruction. For the absence of this sign in a relatively high percentage of patients (35% in the present study), we suggest the following explanations: incarceration is not complete and some chyme passes through, the time from the onset of incarceration to diagnostic imaging is too short to develop dilatation of bowel loops in the abdomen, and a Richter s hernia is present in which only part of the bowel wall is herniated. Evidence of bowel obstruction in the abdomen in patients with incarcerated hernias containing bowel is described in detail in the literature [12, 17, 18, 28 31]. To our knowledge, however, percentages of occurrence are not available. Our data suggest that the absence of blood flow in the contents of a hernia should not be taken as a sign of incarceration because most incarcerated hernias in our series (78%) had detectable blood flow on color Doppler sonography (Tables 2 and 3). The patients in whom color Doppler sonography did not detect blood flow in the incarcerated bowel loop included the two patients with incarcerated hernia and bowel necrosis. Our study results show that the absence of peristalsis should not be considered a sign of incarceration because nonincarcerated hernias did not show peristalsis during the sonographic investigation in a relatively high percentage of patients (Table 2). Our data, however, suggest that if peristalsis is present in an incarcerated hernia on sonography, bowel resection at surgery is probably not necessary. Gas in the bowel wall or free gas, either in the abdomen or the hernia sac, was considered a sign of a complicated hernia [17, 28]. In our series, however, no patient had such an advanced stage of an incarcerated hernia. A limitation of our study was that we had only two incarcerated hernias with bowel necrosis. The spectrum of imaging signs of incarcerated hernias with this advanced stage of disease could therefore not be assessed adequately. Another limitation could be that the investigators were aware of the results of the physical examination and the clinical presentation of patients at the time of sonographic imaging. In summary, several cross-sectional imaging signs of hernial incarceration, such as free fluid in the hernial sac, bowel wall thickening in the hernia, fluid in the herniated bowel loop, and dilated bowel loops in the abdomen are identifiable on sonography. These signs, indicating hernial incarceration in a high percentage of cases, are helpful in patients whose clinical presentations are inconclusive or misleading. References 1. Yokoyama T, Munakata Y, Ogiwara M, Kamijima T, Kitamura H, Kawasaki S. Preoperative diagnosis of strangulated obturator hernia using ultrasonography. Am J Surg 1997;174: Truong S, Pfingsten FP, Dreuw B, Schumpelick V. Stellenwert der Sonographie in der Diagnostik von unklaren Befunden der Bauchwand und Leistenregion. Chirurg 1993;64: Mufid MM, Abu-Yousef MM, Kakish ME, Urdaneta LF, Al-Jurf AS. Spigelian hernia: diagnosis by high-resolution real-time sonography. J Ultrasound Med 1997;16: Krone KD, Carroll BA. Scrotal ultrasound. Radiol Clin N Am 1985;23: Hricak H, Jeffrey RB. Sonography of acute scrotal abnormalities. Radiol Clin N Am 1983;21: Harrison LA, Keesling CA, Martin NL, Lee KR, Wetzel LH. Abdominal wall hernias: review of herniography and correlation with cross-sectional imaging. RadioGraphics 1995;15: Goodman P, Raval B. CT of the abdominal wall. AJR 1990;154: Lee GM, Cohen AJ. CT imaging of abdominal hernias. AJR 1993;161: Van den Berg JC, Strijk SP. Groin hernia: role of herniography. Radiology 1992;184: Spangen L. Ultrasound as a diagnostic aid in ventral abdominal hernia. J Clin Ultrasound 1975;3: Ekberg O, Fork FT, Aspelin P. Herniography in anterior abdominal wall hernia. ROFO Fortschr Geb Rontgenstr Nuklearmed 1985;143: Zalel Y, Shalev E, Romano S, Ben-Ami M, Dan AJR:177, November
6 Rettenbacher et al. U, Weiner E. Incarcerated spigelian hernia in pregnancy: an ultrasonic diagnosis. J Clin Ultrasound 1992;20: Glicklich M, Eliasoph J. Incarcerated obturator hernia: case diagnosed at barium enema fluoroscopy. Radiology 1989;172: Sutphen JH, Hitchcock DA, King DC. Ultrasonic demonstration of spigelian hernia. AJR 1980;134: Engel JM, Deitch EE. Sonography of the anterior abdominal wall. AJR 1981;137: Subramanyam BR, Balthazar EJ, Raghavendra NB, Horii SC, Hilton S. Sonographic diagnosis of scrotal hernia. AJR 1982;139: Stabile Ianora AA, Midiri M, Vinci R, Rotondo A, Angelelli G. Abdominal wall hernias: imaging with spiral CT. Eur Radiol 2000;10: Miller PA, Mezwa DG, Feczko PJ, Jafri ZH, Madrazo BL. Imaging of abdominal hernias. RadioGraphics 1995;15: Chou TY, Chu CC, Diau GY, Wu CJ, Gueng MK. Inguinal hernia in children: US versus exploratory surgery and intraoperative contralateral laparoscopy. Radiology 1996;201: Hojer AM, Rygaard H, Jess P. CT in the diagnosis of abdominal wall hernias: a preliminary study. Eur Radiol 1997;7: Ekberg O. Inguinal herniography in adults: technique, normal anatomy, and diagnostic criteria for hernias. Radiology 1981;138: Oh KS, Condon VR, Dorst JP, Grajo G. Peritoneographic demonstration of femoral hernia. Radiology 1978;127: Wechsler RJ, Kurtz AB, Needleman L, et al. Cross-sectional imaging of abdominal wall hernias. AJR 1989;153: Fried AM, Meeker WR. Incarcerated spigelian hernia: ultrasonic differential diagnosis. AJR 1979;133: Ghahremani GG, Jimenez MA, Rosenfeld M, Rochester D. CT diagnosis of occult incisional hernias. AJR 1987;148: Catalano O. US evaluation of inguinoscrotal bladder hernias: report of three cases. Clin Imaging 1997;21: Motta J, Bagli DJ, Savage JV, Khoury AE, McLorie G, Salle JP. Torsion of an indirect hernia sac: an unusual cause of acute scrotal swelling in children. Urology 1997;50: Zarvan NP, Lee FT, Yandow DR, Unger JS. Abdominal hernias: CT findings. AJR 1995;164: Schiller VL, Joyce PW, Sarti DA. Small-bowel obstruction due to hernia through the primary laparoscopic port: a complication of laparoscopic cholecystectomy. AJR 1994;163: Maglinte DDT, Miller RE, Lappas JC. Radiologic diagnosis of occult incisional hernias of the small intestine. AJR 1984;142: Megibow AJ, Balthazar EJ, Cho KC, Medwid SW, Birnbaum BA, Noz ME. Bowel obstruction: evaluation with CT. Radiology 1991;180: For the convenience of AJR authors, a standardized form requesting permission to reprint from other publications is now available via the ARRS Web site at AJR:177, November 2001
Sonography of Hernias
 Sonography of Hernias Cindy Rapp BS, RDMS, FAIUM, FSDMS Sr. Clinical Marketing Manager Toshiba America Medical Systems Tustin, California What is a hernia? A hernia is a protrusion of an organ or tissue
Sonography of Hernias Cindy Rapp BS, RDMS, FAIUM, FSDMS Sr. Clinical Marketing Manager Toshiba America Medical Systems Tustin, California What is a hernia? A hernia is a protrusion of an organ or tissue
Prosthetic mesh used for inguinal and ventral hernia repair: normal appearance and complications in ultrasound and CT
 The British Journal of Radiology, 77 (2004), 261 265 DOI: 10.1259/bjr/63333975 E 2004 The British Institute of Radiology Pictorial review Prosthetic mesh used for inguinal and ventral hernia repair: normal
The British Journal of Radiology, 77 (2004), 261 265 DOI: 10.1259/bjr/63333975 E 2004 The British Institute of Radiology Pictorial review Prosthetic mesh used for inguinal and ventral hernia repair: normal
KEYHOLE HERNIA SURGERY
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage a hernia or abdominal pain. All decisions about the management of a hernia must be made in conjunction with your Physician
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage a hernia or abdominal pain. All decisions about the management of a hernia must be made in conjunction with your Physician
Torsed Appendix Testis
 Article Torsed Appendix Testis Gray Scale and Color Doppler Sonographic Findings Compared With Normal Appendix Testis Dal Mo Yang, MD, Joo Won Lim, MD, Jee Eun Kim, MD, Ji Hye Kim, MD, Hyuni Cho, MD Objective.
Article Torsed Appendix Testis Gray Scale and Color Doppler Sonographic Findings Compared With Normal Appendix Testis Dal Mo Yang, MD, Joo Won Lim, MD, Jee Eun Kim, MD, Ji Hye Kim, MD, Hyuni Cho, MD Objective.
Abdominal Wall Hernias: Classic and Unusual
 Abdominal Wall Hernias: Classic and Unusual Arash Bedayat, MD; Hemang Kotecha, DO; Matthew L. Hoimes, MD; Byron Y. Chen, MD; Hao S. Lo, MD; Adib R. Karam, MD Objectives Review the radiologic anatomy and
Abdominal Wall Hernias: Classic and Unusual Arash Bedayat, MD; Hemang Kotecha, DO; Matthew L. Hoimes, MD; Byron Y. Chen, MD; Hao S. Lo, MD; Adib R. Karam, MD Objectives Review the radiologic anatomy and
The sensitivity and specificity of ultrasound in diagnosis of acute appendicitis Abstract Key words: Introduction 132
 The sensitivity and specificity of ultrasound in diagnosis of acute Mohaed B. Hassan*, Ahmed S. Tawfiq*, Adnan M. Brayyich**, Lubna A. Aljabbar Yaseen*** *Dept. of Radiology, College of Medicine, Tikrit
The sensitivity and specificity of ultrasound in diagnosis of acute Mohaed B. Hassan*, Ahmed S. Tawfiq*, Adnan M. Brayyich**, Lubna A. Aljabbar Yaseen*** *Dept. of Radiology, College of Medicine, Tikrit
Interim Clinical Commissioning Insert heading depending. cover options once
 Interim Clinical Commissioning Insert heading depending Insert Policy: Insert heading Abdominal depending Wall Hernia on line on on Management line length; length; please please delete delete on line line
Interim Clinical Commissioning Insert heading depending Insert Policy: Insert heading Abdominal depending Wall Hernia on line on on Management line length; length; please please delete delete on line line
Sonographic Features of Internal Hernia
 Case Series Sonographic Features of Internal Hernia S. Boopathy Vijayaraghavan, MD, DMRD Objective. The purpose of this series is to describe the sonographic findings in 4 patients with intestinal obstruction
Case Series Sonographic Features of Internal Hernia S. Boopathy Vijayaraghavan, MD, DMRD Objective. The purpose of this series is to describe the sonographic findings in 4 patients with intestinal obstruction
Ovarian Torsion: Sonographic Evaluation
 J Clin Ultrasound 17:327-332, June 1989 Ovarian Torsion: Sonographic Evaluation Mark A. Helvie, MD,* and Terry M. Silver, MDI Abstract: The sonographic and clinical findings of 13 patients with surgically
J Clin Ultrasound 17:327-332, June 1989 Ovarian Torsion: Sonographic Evaluation Mark A. Helvie, MD,* and Terry M. Silver, MDI Abstract: The sonographic and clinical findings of 13 patients with surgically
Acute Abdominal Pain following Bariatric Surgery. Disclosure. Objectives 8/17/2015. I have nothing to disclose
 Acute Abdominal Pain following Bariatric Surgery Kathy J. Morris, DNP, APRN, FNP C, FAANP University of Nebraska Medical Center College of Nursing Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Objectives Pathophysiology
Acute Abdominal Pain following Bariatric Surgery Kathy J. Morris, DNP, APRN, FNP C, FAANP University of Nebraska Medical Center College of Nursing Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Objectives Pathophysiology
Laparoscopic Repair of Hernias. A simple guide to help answer your questions
 Laparoscopic Repair of Hernias A simple guide to help answer your questions What is a hernia? A hernia is defined as a hole or defect in the abdominal (belly) wall. A hernia can either be congenital (a
Laparoscopic Repair of Hernias A simple guide to help answer your questions What is a hernia? A hernia is defined as a hole or defect in the abdominal (belly) wall. A hernia can either be congenital (a
Contents. 1. Milestones in Hernia Surgery 1. 2. Surgical Anatomy of Hernia Sites 5. 3. Incidence, Prevalence of Hernia 32
 1. Milestones in Hernia Surgery 1 History of the Procedure 3 2. Surgical Anatomy of Hernia Sites 5 Surgical Anatomy of Hernia Sites 5 External Anatomy of Abdominal Wall The Surface Markings 6 The Fascia
1. Milestones in Hernia Surgery 1 History of the Procedure 3 2. Surgical Anatomy of Hernia Sites 5 Surgical Anatomy of Hernia Sites 5 External Anatomy of Abdominal Wall The Surface Markings 6 The Fascia
The TV Series. www.healthybodyhealthymind.com INFORMATION TELEVISION NETWORK
 The TV Series www.healthybodyhealthymind.com Produced By: INFORMATION TELEVISION NETWORK ONE PARK PLACE 621 NW 53RD ST BOCA RATON, FL 33428 1-800-INFO-ITV www.itvisus.com 2005 Information Television Network.
The TV Series www.healthybodyhealthymind.com Produced By: INFORMATION TELEVISION NETWORK ONE PARK PLACE 621 NW 53RD ST BOCA RATON, FL 33428 1-800-INFO-ITV www.itvisus.com 2005 Information Television Network.
Gallstone Ileus. Audrey C. Durrant,, M.D. SUNY Downstate Medical Center May 20, 2005
 Gallstone Ileus Audrey C. Durrant,, M.D. SUNY Downstate Medical Center May 20, 2005 Gallstone Ileus Diagnosis and Management Background Misnomer coined by Bartolin in 1654 Not a true ileus True mechanical
Gallstone Ileus Audrey C. Durrant,, M.D. SUNY Downstate Medical Center May 20, 2005 Gallstone Ileus Diagnosis and Management Background Misnomer coined by Bartolin in 1654 Not a true ileus True mechanical
Sonographic Features Related to Volvulus in Neonatal Intestinal Malrotation
 Sonographic Features Related to Volvulus in Neonatal Intestinal Malrotation Hsun-Chin Chao, MD, Man-Shan Kong, MD, Ju-Yi Chen, MD, Syh-Jae Lin, MD, Jer-Nan Lin, MD This 3 year prospective study evaluated
Sonographic Features Related to Volvulus in Neonatal Intestinal Malrotation Hsun-Chin Chao, MD, Man-Shan Kong, MD, Ju-Yi Chen, MD, Syh-Jae Lin, MD, Jer-Nan Lin, MD This 3 year prospective study evaluated
Beverly E Hashimoto, M.D. Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, WA
 Pelvic Floor Relaxation Beverly E Hashimoto, M.D. Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, WA Disclosures Beverly Hashimoto: GE Medical Systems: research support and consultant (all fees given to Virginia
Pelvic Floor Relaxation Beverly E Hashimoto, M.D. Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, WA Disclosures Beverly Hashimoto: GE Medical Systems: research support and consultant (all fees given to Virginia
False reduction of an inguinal hernia treated by Kugel patch repair via an anterior. 1) Department of Surgery, Asahi General Hospital, Chiba, Japan
 Case Report False reduction of an inguinal hernia treated by Kugel patch repair via an anterior approach Naoya Yamada 1, Atsushi Akai 1, Akihiko Seo 1, Yukihiro Nomura 1, Nobutaka Tanaka 1 1) Department
Case Report False reduction of an inguinal hernia treated by Kugel patch repair via an anterior approach Naoya Yamada 1, Atsushi Akai 1, Akihiko Seo 1, Yukihiro Nomura 1, Nobutaka Tanaka 1 1) Department
Emergencies in Post- Bariatric Surgery Patients
 Emergencies in Post- Patients Disclosures Dr. Birnbaumer has no financial disclosures Diane M. Birnbaumer, M.D., FACEP Professor of Medicine University of California, Los Angeles Senior Clinical Educator
Emergencies in Post- Patients Disclosures Dr. Birnbaumer has no financial disclosures Diane M. Birnbaumer, M.D., FACEP Professor of Medicine University of California, Los Angeles Senior Clinical Educator
The Abdominal Wall And Hernias. Stanley Kurek, DO, FACS Associate Professor of Surgery UTMCK
 The Abdominal Wall And Hernias Stanley Kurek, DO, FACS Associate Professor of Surgery UTMCK The Abdominal Wall The structure of the abdominal wall is similar in principle to the thoracic wall. There are
The Abdominal Wall And Hernias Stanley Kurek, DO, FACS Associate Professor of Surgery UTMCK The Abdominal Wall The structure of the abdominal wall is similar in principle to the thoracic wall. There are
Facing a Hernia Repair? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery
 Facing a Hernia Repair? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Hernia A hernia happens when part of an internal organ or tissue bulges through a hole or weak area in the belly wall
Facing a Hernia Repair? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Hernia A hernia happens when part of an internal organ or tissue bulges through a hole or weak area in the belly wall
X-Plain Inguinal Hernia Repair Reference Summary
 X-Plain Inguinal Hernia Repair Reference Summary Introduction Hernias are common conditions that affect men and women of all ages. Your doctor may recommend a hernia operation. The decision whether or
X-Plain Inguinal Hernia Repair Reference Summary Introduction Hernias are common conditions that affect men and women of all ages. Your doctor may recommend a hernia operation. The decision whether or
Amir Kashefi 1, MD Marc A Friedman 1, MD Alan V Krauthamer 1, MD Anthony G Gilet 1, MD Bijan Bijan 2, MD, MBA
 Amir Kashefi 1, MD Marc A Friedman 1, MD Alan V Krauthamer 1, MD Anthony G Gilet 1, MD Bijan Bijan 2, MD, MBA 1. Harlem Hospital Center, Radiology Dep. 506 Lenox Ave, New York, NY 10037 2. UC Davis Medical
Amir Kashefi 1, MD Marc A Friedman 1, MD Alan V Krauthamer 1, MD Anthony G Gilet 1, MD Bijan Bijan 2, MD, MBA 1. Harlem Hospital Center, Radiology Dep. 506 Lenox Ave, New York, NY 10037 2. UC Davis Medical
M O V I N G F R E E LY. HerniaCenter. The Columbia Hernia Center at ColumbiaDoctors Midtown
 M O V I N G F R E E LY HerniaCenter The Columbia Hernia Center at ColumbiaDoctors Midtown Director, Dr. Peter L. Geller The Columbia Hernia Center brings together a group of surgeons adept in using the
M O V I N G F R E E LY HerniaCenter The Columbia Hernia Center at ColumbiaDoctors Midtown Director, Dr. Peter L. Geller The Columbia Hernia Center brings together a group of surgeons adept in using the
Evaluation and Follow-up of Fetal Hydronephrosis
 Evaluation and Follow-up of Fetal Hydronephrosis Deborah M. Feldman, MD, Marvalyn DeCambre, MD, Erin Kong, Adam Borgida, MD, Mujgan Jamil, MBBS, Patrick McKenna, MD, James F. X. Egan, MD Objective. To
Evaluation and Follow-up of Fetal Hydronephrosis Deborah M. Feldman, MD, Marvalyn DeCambre, MD, Erin Kong, Adam Borgida, MD, Mujgan Jamil, MBBS, Patrick McKenna, MD, James F. X. Egan, MD Objective. To
ABThera Open Abdomen Negative Pressure Therapy for Active Abdominal Therapy. Case Series
 ABThera Open Abdomen Negative Pressure Therapy for Active Abdominal Therapy Case Series Summary of Cases: USER EXPERIENCE The ABThera OA NPT system was found by surgeons to be a convenient and effective
ABThera Open Abdomen Negative Pressure Therapy for Active Abdominal Therapy Case Series Summary of Cases: USER EXPERIENCE The ABThera OA NPT system was found by surgeons to be a convenient and effective
Title : Small bowel strangulation due to Peritoneopericardial diaphragmatic hernia
 (TITLE PAGE) Title : Small bowel strangulation due to Peritoneopericardial diaphragmatic hernia Jang-Hoon Lee 1, Se-Won Kim 2 1 Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, College of Medicine, Yeungnam
(TITLE PAGE) Title : Small bowel strangulation due to Peritoneopericardial diaphragmatic hernia Jang-Hoon Lee 1, Se-Won Kim 2 1 Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, College of Medicine, Yeungnam
Diagnostic Accuracy of Sonographic Criteria for Evaluation of Cervical Lymphadenopathy
 Diagnostic Accuracy of Sonographic Criteria for Evaluation of Cervical Lymphadenopathy Michael Ying, MPhil, Anil Ahuja, FRCR, Constantine Metreweli, FRCR Although ultrasonographic criteria for abnormal
Diagnostic Accuracy of Sonographic Criteria for Evaluation of Cervical Lymphadenopathy Michael Ying, MPhil, Anil Ahuja, FRCR, Constantine Metreweli, FRCR Although ultrasonographic criteria for abnormal
Femoral Hernia Repair
 Femoral Hernia Repair WHAT IS A FEMORAL HERNIA REPAIR? 2 WHAT CAUSES A FEMORAL HERNIA? 2 WHAT DOES TREATMENT/ MANAGEMENT INVOLVE? 3 DAY SURGERY MANAGEMENT 3 SURGICAL REPAIR 4 WHAT ARE THE RISKS/COMPLICATIONS
Femoral Hernia Repair WHAT IS A FEMORAL HERNIA REPAIR? 2 WHAT CAUSES A FEMORAL HERNIA? 2 WHAT DOES TREATMENT/ MANAGEMENT INVOLVE? 3 DAY SURGERY MANAGEMENT 3 SURGICAL REPAIR 4 WHAT ARE THE RISKS/COMPLICATIONS
Laparoscopic hernia repair GEORGIOS SAMPALIS GENERAL SURGEON. Director of surgical department of Lefkos Stavros of Athens
 Laparoscopic hernia repair GEORGIOS SAMPALIS GENERAL SURGEON Director of surgical department of Lefkos Stavros of Athens About 600,000 surgical hernia repair procedures are performed every year... Many
Laparoscopic hernia repair GEORGIOS SAMPALIS GENERAL SURGEON Director of surgical department of Lefkos Stavros of Athens About 600,000 surgical hernia repair procedures are performed every year... Many
Guide to Abdominal or Gastroenterological Surgery Claims
 What are the steps towards abdominal surgery? Investigation and Diagnosis It is very important that all necessary tests are undertaken to investigate the patient s symptoms appropriately and an accurate
What are the steps towards abdominal surgery? Investigation and Diagnosis It is very important that all necessary tests are undertaken to investigate the patient s symptoms appropriately and an accurate
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
WHAT S WRONG WITH MY GALL BLADDER? GALL BLADDER POLYPS
 WHAT S WRONG WITH MY GALL BLADDER? GALL BLADDER POLYPS This is a patient information booklet providing specific practical information about gall bladder polyps in brief. Its aim is to provide the patient
WHAT S WRONG WITH MY GALL BLADDER? GALL BLADDER POLYPS This is a patient information booklet providing specific practical information about gall bladder polyps in brief. Its aim is to provide the patient
Sonography of Partial-Thickness Quadriceps Tendon Tears With Surgical Correlation
 Article Sonography of Partial-Thickness Quadriceps Tendon Tears With Surgical Correlation Samuel La, MD, David P. Fessell, MD, John E. Femino, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, David Jamadar, MB, BS, Curtis Hayes,
Article Sonography of Partial-Thickness Quadriceps Tendon Tears With Surgical Correlation Samuel La, MD, David P. Fessell, MD, John E. Femino, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, David Jamadar, MB, BS, Curtis Hayes,
Inguinal Hernia (Female)
 Inguinal Hernia (Female) WHAT IS AN INGUINAL HERNIA? 2 WHAT CAUSES AN INGUINAL HERNIA? 2 WHAT DOES TREATMENT / MANAGEMENT INVOLVE? 3 DAY SURGERY MANAGEMENT 3 SURGICAL REPAIR 4 WHAT ARE THE RISKS/COMPLICATIONS
Inguinal Hernia (Female) WHAT IS AN INGUINAL HERNIA? 2 WHAT CAUSES AN INGUINAL HERNIA? 2 WHAT DOES TREATMENT / MANAGEMENT INVOLVE? 3 DAY SURGERY MANAGEMENT 3 SURGICAL REPAIR 4 WHAT ARE THE RISKS/COMPLICATIONS
Bochdalek hernia of adult in emergency situation
 O P E N A C C E S S Case study Bochdalek hernia of adult in emergency situation Nooruldin F Shakir*, Warda Alsaad, Saad Mahi Emergency Department, Hamad General Hospital, Doha, Qatar * Email: nshakir@hmc.org.qa
O P E N A C C E S S Case study Bochdalek hernia of adult in emergency situation Nooruldin F Shakir*, Warda Alsaad, Saad Mahi Emergency Department, Hamad General Hospital, Doha, Qatar * Email: nshakir@hmc.org.qa
Dept. of Medical Imaging University of Ottawa
 ED Visits Related to Bariatric Surgery: Review of Normal Post-Surgical Anatomy as Well as Complications Dept. of Medical Imaging University of Ottawa Disclosures Background Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Surgery
ED Visits Related to Bariatric Surgery: Review of Normal Post-Surgical Anatomy as Well as Complications Dept. of Medical Imaging University of Ottawa Disclosures Background Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Surgery
C A R O L I N A S. Hernia Handbook ( C H A P T E R 2 ) B. Todd Heniford, MD
 C A R O L I N A S Hernia Handbook ( C H A P T E R 2 ) B. Todd Heniford, MD C H A P T E R 2 Umbilical Hernias C A R O L I N A S H E R N I A H A N D B O O K 17 Umbilical Hernias W H AT I S A N U M B I L
C A R O L I N A S Hernia Handbook ( C H A P T E R 2 ) B. Todd Heniford, MD C H A P T E R 2 Umbilical Hernias C A R O L I N A S H E R N I A H A N D B O O K 17 Umbilical Hernias W H AT I S A N U M B I L
BERGEN COMMUNITY COLLEGE DIAGNOSTIC MEDICAL SONOGRAPHY PROGRAM Division of Health Professions DMS 213 SYLLABUS
 BERGEN COMMUNITY COLLEGE DIAGNOSTIC MEDICAL SONOGRAPHY PROGRAM Division of Health Professions DMS 213 SYLLABUS Course Title: DMS 213 - Abdominal Sonography 2 2 lec. 3 lab. 3 credits (5 hours) Required
BERGEN COMMUNITY COLLEGE DIAGNOSTIC MEDICAL SONOGRAPHY PROGRAM Division of Health Professions DMS 213 SYLLABUS Course Title: DMS 213 - Abdominal Sonography 2 2 lec. 3 lab. 3 credits (5 hours) Required
Appendicitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Appendicitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH The appendix is a small, tube-like structure
Appendicitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH The appendix is a small, tube-like structure
If Your Child has an Inguinal Hernia, Hydrocele or Undescended Testicles. A Guide for Parents
 Introduction Urology Clinic If Your Child has an Inguinal Hernia, Hydrocele or Undescended Testicles A Guide for Parents Three of the most common birth defects in males are an inguinal hernia, hydrocele,
Introduction Urology Clinic If Your Child has an Inguinal Hernia, Hydrocele or Undescended Testicles A Guide for Parents Three of the most common birth defects in males are an inguinal hernia, hydrocele,
Lower Extremity Venous Duplex Evaluation
 VASCULAR TECHNOLOGY PROFESSIONAL PERFORMANCE GUIDELINES Lower Extremity Venous Duplex Evaluation This Guideline was prepared by the Professional Guidelines Subcommittee of the Society for Vascular Ultrasound
VASCULAR TECHNOLOGY PROFESSIONAL PERFORMANCE GUIDELINES Lower Extremity Venous Duplex Evaluation This Guideline was prepared by the Professional Guidelines Subcommittee of the Society for Vascular Ultrasound
Laparoscopic Surgery of the Colon and Rectum (Large Intestine) A Simple Guide to Help Answer Your Questions
 Laparoscopic Surgery of the Colon and Rectum (Large Intestine) A Simple Guide to Help Answer Your Questions What are the Colon and Rectum? The colon and rectum together make up the large intestine. After
Laparoscopic Surgery of the Colon and Rectum (Large Intestine) A Simple Guide to Help Answer Your Questions What are the Colon and Rectum? The colon and rectum together make up the large intestine. After
Ultrasound in Vascular Surgery. Torbjørn Dahl
 Ultrasound in Vascular Surgery Torbjørn Dahl 1 The field of vascular surgery Veins dilatation and obstruction (varicose veins and valve dysfunction) Arteries dilatation and narrowing (aneurysms and atherosclerosis)
Ultrasound in Vascular Surgery Torbjørn Dahl 1 The field of vascular surgery Veins dilatation and obstruction (varicose veins and valve dysfunction) Arteries dilatation and narrowing (aneurysms and atherosclerosis)
Healthletter. Hernias They Should not be Ignored. August 2009
 Healthletter August 2009 Hernias They Should not be Ignored Did you know that over five million Americans suffer from some type of hernia? For many of these people, this condition causes substantial pain
Healthletter August 2009 Hernias They Should not be Ignored Did you know that over five million Americans suffer from some type of hernia? For many of these people, this condition causes substantial pain
Duplication Images in Vascular Sonography
 Article Duplication Images in Vascular Sonography Jonathan M. Rubin, MD, PhD, Jing Gao, MD, Keith Hetel, MD, Robert Min, MD Objective. The purpose of this study was to determine the characteristics and
Article Duplication Images in Vascular Sonography Jonathan M. Rubin, MD, PhD, Jing Gao, MD, Keith Hetel, MD, Robert Min, MD Objective. The purpose of this study was to determine the characteristics and
Pediatric Upper GI Series New Patient
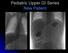 Pediatric Upper GI Series New Patient Upper GI Series Thought to be malrotation, no evidence of midgut volvulus Needed to repeat UGI Series WHY? Repeat UGI Series Repeat UGI Series Repeat UGI Series No
Pediatric Upper GI Series New Patient Upper GI Series Thought to be malrotation, no evidence of midgut volvulus Needed to repeat UGI Series WHY? Repeat UGI Series Repeat UGI Series Repeat UGI Series No
MUSCULOSKELETAL ULTRASOUND EVALUATION OF THE PLANTAR PLATE FOR IDENTIFICATION OF PLANTAR PLATE TEARS
 MUSCULOSKELETAL ULTRASOUND EVALUATION OF THE PLANTAR PLATE FOR IDENTIFICATION OF PLANTAR PLATE TEARS Erin E. Klein, DPM, MS Lowell Weil, Jr., DPM, MBA Lowell Scott Weil, Sr., DPM Jessica Knight, DPM Weil
MUSCULOSKELETAL ULTRASOUND EVALUATION OF THE PLANTAR PLATE FOR IDENTIFICATION OF PLANTAR PLATE TEARS Erin E. Klein, DPM, MS Lowell Weil, Jr., DPM, MBA Lowell Scott Weil, Sr., DPM Jessica Knight, DPM Weil
An abdominal ultrasound produces a picture of the organs and other structures in the upper abdomen.
 Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Abdomen Ultrasound imaging of the abdomen uses sound waves to produce pictures of the structures within the upper abdomen. It is used to help diagnose pain or distention
Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Abdomen Ultrasound imaging of the abdomen uses sound waves to produce pictures of the structures within the upper abdomen. It is used to help diagnose pain or distention
Abdominal CT scan findings in Acute Appendicitis
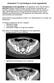 Abdominal CT scan findings in Acute Appendicitis Pathophysiology of acute appendicitis. Acute appendicitis occurs when the lumen is obstructed, leading to fluid accumulation, luminal distention, inflammation
Abdominal CT scan findings in Acute Appendicitis Pathophysiology of acute appendicitis. Acute appendicitis occurs when the lumen is obstructed, leading to fluid accumulation, luminal distention, inflammation
Characterization of small renal lesions: Problem solving with MRI Gary Israel, MD
 Characterization of small renal lesions: Problem solving with MRI Gary Israel, MD With the widespread use of cross-sectional imaging, many renal masses are incidentally found. These need to be accurately
Characterization of small renal lesions: Problem solving with MRI Gary Israel, MD With the widespread use of cross-sectional imaging, many renal masses are incidentally found. These need to be accurately
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones. Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke
 Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
da Vinci Prostatectomy Information Guide (Robotically-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy)
 da Vinci Prostatectomy Information Guide (Robotically-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy) Prostate Cancer Overview Prostate cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the
da Vinci Prostatectomy Information Guide (Robotically-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy) Prostate Cancer Overview Prostate cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the
Open Ventral Hernia Repair
 Ventral Hernias Open Ventral Hernia Repair UCSF Postgraduate Course in General Surgery Maui, HI March 21, 2011 Hobart W. Harris, MD, MPH Ventral Hernias: National Experience Occur following 11-23% of laparotomies,
Ventral Hernias Open Ventral Hernia Repair UCSF Postgraduate Course in General Surgery Maui, HI March 21, 2011 Hobart W. Harris, MD, MPH Ventral Hernias: National Experience Occur following 11-23% of laparotomies,
AORTOENTERIC FISTULA. Mark H. Tseng MD Brooklyn VA Hospital February 11, 2005
 AORTOENTERIC FISTULA Mark H. Tseng MD Brooklyn VA Hospital February 11, 2005 AORTOENTERIC FISTULA diagnosis and management Mark H. Tseng MD Brooklyn VA Hospital February 11, 2005 AORTOENTERIC FISTULA Aortoenteric
AORTOENTERIC FISTULA Mark H. Tseng MD Brooklyn VA Hospital February 11, 2005 AORTOENTERIC FISTULA diagnosis and management Mark H. Tseng MD Brooklyn VA Hospital February 11, 2005 AORTOENTERIC FISTULA Aortoenteric
A Left Paraduodenal Hernia Causing Recurrent Small Bowel Obstruction : A Case Report
 Article ID: WMC001308 2046-1690 A Left Paraduodenal Hernia Causing Recurrent Small Bowel Obstruction : A Case Report Corresponding Author: Dr. Prashanth Shetty, Associate Professor, Kasturba Medical College,
Article ID: WMC001308 2046-1690 A Left Paraduodenal Hernia Causing Recurrent Small Bowel Obstruction : A Case Report Corresponding Author: Dr. Prashanth Shetty, Associate Professor, Kasturba Medical College,
Inguinal hernia repair
 Inguinal hernia repair A hernia is an abnormal protrusion on an organ through a weakness in the abdominal wall. The abdominal muscles are usually strong enough to keep your internal organs in place, when
Inguinal hernia repair A hernia is an abnormal protrusion on an organ through a weakness in the abdominal wall. The abdominal muscles are usually strong enough to keep your internal organs in place, when
Seeing the Unseen New Techniques in Vascular Imaging
 M edical R eview Seeing the Unseen New Techniques in Vascular Imaging Superb Micro-Vascular Imaging M edical R eview Seeing the Unseen New Techniques in Vascular Imaging Superb Micro-Vascular Imaging Dr.
M edical R eview Seeing the Unseen New Techniques in Vascular Imaging Superb Micro-Vascular Imaging M edical R eview Seeing the Unseen New Techniques in Vascular Imaging Superb Micro-Vascular Imaging Dr.
1. Use Radiographic Findings
 Top 5 Tips on Radiographic Diagnosis of Obstructive Foreign Bodies Nathalie Rademacher, Dr. med. vet., DECVDI, DACVR Louisiana State University Ileus can be functional or mechanical. In functional ileus,
Top 5 Tips on Radiographic Diagnosis of Obstructive Foreign Bodies Nathalie Rademacher, Dr. med. vet., DECVDI, DACVR Louisiana State University Ileus can be functional or mechanical. In functional ileus,
Ultrasonographic Determination of Equine Fetal Gender (31 Mar 2000)
 In: Recent Advances in Equine Theriogenology, B.A. Ball (Ed.) Publisher: International Veterinary Information Service (www.ivis.org) Ultrasonographic Determination of Equine Fetal Gender (31 Mar 2000)
In: Recent Advances in Equine Theriogenology, B.A. Ball (Ed.) Publisher: International Veterinary Information Service (www.ivis.org) Ultrasonographic Determination of Equine Fetal Gender (31 Mar 2000)
First floor, Main Hospital North Services provided 24/7 365 days per year
 First floor, Main Hospital North Services provided 24/7 365 days per year General Radiology (X-ray) Fluoroscopy Ultrasound (Sonography) Nuclear Medicine P.E.T. imaging Computed Tomography (CT scan) Magnetic
First floor, Main Hospital North Services provided 24/7 365 days per year General Radiology (X-ray) Fluoroscopy Ultrasound (Sonography) Nuclear Medicine P.E.T. imaging Computed Tomography (CT scan) Magnetic
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
 Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Gallbladder removal is one of the most commonly performed surgical procedures in the United States. Today,gallbladder surgery is performed laparoscopically. The medical name
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Gallbladder removal is one of the most commonly performed surgical procedures in the United States. Today,gallbladder surgery is performed laparoscopically. The medical name
Acute abdominal conditions Key Points
 7 Acute abdominal conditions Key Points 7.1 ASSESSMENT AND DIAGNOSIS Referred abdominal pain Fore gut pain (stomach, duodenum, gall bladder) is referred to the upper abdomen Mid gut pain (small intestine,
7 Acute abdominal conditions Key Points 7.1 ASSESSMENT AND DIAGNOSIS Referred abdominal pain Fore gut pain (stomach, duodenum, gall bladder) is referred to the upper abdomen Mid gut pain (small intestine,
OVARIAN CYSTS. Types of Ovarian Cysts There are many types of ovarian cysts and these can be categorized into functional and nonfunctional
 OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography
 Semester 1 Orientation - 101 This class is an introduction to sonography which includes a basic anatomy review, introduction to sonographic scanning techniques and physical principles. This curriculum
Semester 1 Orientation - 101 This class is an introduction to sonography which includes a basic anatomy review, introduction to sonographic scanning techniques and physical principles. This curriculum
Three-Dimensional Inversion Rendering
 Image Presentation Three-Dimensional Inversion Rendering New Sonographic Technique and Its Use in Gynecology Ilan E. Timor-Tritsch, MD, RDMS, na Monteagudo, MD, RDMS, Tanya Tsymbal,, RDMS, Irina Strok,
Image Presentation Three-Dimensional Inversion Rendering New Sonographic Technique and Its Use in Gynecology Ilan E. Timor-Tritsch, MD, RDMS, na Monteagudo, MD, RDMS, Tanya Tsymbal,, RDMS, Irina Strok,
How to Detect a Thyroid Pyramidal Lobes
 ORIGINL RESERCH Sonographic Detection of Thyroid Pyramidal Lobes Before Thyroid Surgery Prospective Single-Center Study Dong Wook Kim, MD, Tae Kwun Ha, MD, Ha Kyoung Park, MD, Taewoo Kang, MD Received
ORIGINL RESERCH Sonographic Detection of Thyroid Pyramidal Lobes Before Thyroid Surgery Prospective Single-Center Study Dong Wook Kim, MD, Tae Kwun Ha, MD, Ha Kyoung Park, MD, Taewoo Kang, MD Received
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS CONSIDERING LAPAROSCOPIC INGUINAL HERNIA REPAIR
 INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS CONSIDERING A LAPAROSCOPIC INGUINAL HERNIA REPAIR Prepared By Mr Peter Willson Consultant Surgeon Contents 1. Background... 3 2. What is an inguinal Hernia?... 3 3. What are the
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS CONSIDERING A LAPAROSCOPIC INGUINAL HERNIA REPAIR Prepared By Mr Peter Willson Consultant Surgeon Contents 1. Background... 3 2. What is an inguinal Hernia?... 3 3. What are the
Only about 15% of patients presenting
 CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION Imaging in appendicitis: CT and sonography By Philip W. Ralls, M.D. Earn 1.0 hours of AMA PRA Category 1 Credits through March 2009 Upon completion of this activity, participants
CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION Imaging in appendicitis: CT and sonography By Philip W. Ralls, M.D. Earn 1.0 hours of AMA PRA Category 1 Credits through March 2009 Upon completion of this activity, participants
Laparoscopic Gallbladder Removal (Cholecystectomy) Patient Information from SAGES
 Laparoscopic Gallbladder Removal (Cholecystectomy) Patient Information from SAGES Gallbladder removal is one of the most commonly performed surgical procedures. Gallbladder removal surgery is usually performed
Laparoscopic Gallbladder Removal (Cholecystectomy) Patient Information from SAGES Gallbladder removal is one of the most commonly performed surgical procedures. Gallbladder removal surgery is usually performed
Guideline for the Imaging of Patients Presenting with Breast Symptoms incorporating the guideline for the use of MRI in breast cancer
 Guideline for the Imaging of Patients Presenting with Breast Symptoms incorporating the guideline for the use of MRI in breast cancer Version History Version Date Summary of Change/Process 0.1 09.01.11
Guideline for the Imaging of Patients Presenting with Breast Symptoms incorporating the guideline for the use of MRI in breast cancer Version History Version Date Summary of Change/Process 0.1 09.01.11
10/10/2013. Pediatric Hernias: When to Refer. Disclosures. Outline. Nothing to disclose. Inguinal Hernias. Epigastric Hernias.
 Pediatric Hernias: When to Refer Katrina Cardenas, MMS, PA-C October 12, 2013 http://lifestyle-advertising-photographer-la.blogspot.com/ Disclosures Nothing to disclose Outline Inguinal Hernias Epigastric
Pediatric Hernias: When to Refer Katrina Cardenas, MMS, PA-C October 12, 2013 http://lifestyle-advertising-photographer-la.blogspot.com/ Disclosures Nothing to disclose Outline Inguinal Hernias Epigastric
Preparation iagnostic Medical Sonographer Overview"
 Diagnostic Medical Sonographer Overview The Field - Preparation - Specialty Areas - Day in the Life - Earnings - Employment - Career Path Forecast - Professional Organizations The Field Diagnostic imaging
Diagnostic Medical Sonographer Overview The Field - Preparation - Specialty Areas - Day in the Life - Earnings - Employment - Career Path Forecast - Professional Organizations The Field Diagnostic imaging
Lenox Hill Hospital Department of Surgery General Surgery Goals and Objectives
 Lenox Hill Hospital Department of Surgery General Surgery Goals and Objectives Medical Knowledge and Patient Care: Residents must demonstrate knowledge and application of the pathophysiology and epidemiology
Lenox Hill Hospital Department of Surgery General Surgery Goals and Objectives Medical Knowledge and Patient Care: Residents must demonstrate knowledge and application of the pathophysiology and epidemiology
Metastatic Cervical Cancer s/p Radiation Therapy, Radical Hysterectomy and Attempted Modified Internal Hemipelvectomy
 Metastatic Cervical Cancer s/p Radiation Therapy, Radical Hysterectomy and Attempted Modified Internal Hemipelvectomy Sarah Hutto,, MSIV Marc Underhill, M.D. January 27, 2009 Past History 45 yo female
Metastatic Cervical Cancer s/p Radiation Therapy, Radical Hysterectomy and Attempted Modified Internal Hemipelvectomy Sarah Hutto,, MSIV Marc Underhill, M.D. January 27, 2009 Past History 45 yo female
Recanalized Umbilical Vein in the Presence of Cirrhosis-Induced Portal Hypertension
 Recanalized Umbilical Vein in the Presence of Cirrhosis-Induced Portal Hypertension Audrey Galey RDMS, RVT, Mary Grace Renfro RDSM, RVT, Lindsey Simon, RVT March 22, 2013 2 Abstract A recanalized umbilical
Recanalized Umbilical Vein in the Presence of Cirrhosis-Induced Portal Hypertension Audrey Galey RDMS, RVT, Mary Grace Renfro RDSM, RVT, Lindsey Simon, RVT March 22, 2013 2 Abstract A recanalized umbilical
Internal Hernia After Gastric Bypass: Sensitivity and Specificity of Seven CT Signs with Surgical Correlation and Controls
 CT of Hernia After Gastric Bypass Abdominal Imaging Original Research Mark E. Lockhart 1 Franklin N. Tessler 1 Cheri L. Canon 1 J. Kevin Smith 1 Matthew C. Larrison 1 Naomi S. Fineberg 2 Brandon P. Roy
CT of Hernia After Gastric Bypass Abdominal Imaging Original Research Mark E. Lockhart 1 Franklin N. Tessler 1 Cheri L. Canon 1 J. Kevin Smith 1 Matthew C. Larrison 1 Naomi S. Fineberg 2 Brandon P. Roy
Abdomen X-Ray (AXR) Collimation is ideally from diaphragms to lower border of the symphysis pubis and the lateral skin margins.
 Abdomen X-Ray (AXR) Collimation is ideally from diaphragms to lower border of the symphysis pubis and the lateral skin margins. LMP of child-bearing age female patients should be checked. 1. Acute abdomen
Abdomen X-Ray (AXR) Collimation is ideally from diaphragms to lower border of the symphysis pubis and the lateral skin margins. LMP of child-bearing age female patients should be checked. 1. Acute abdomen
RBH GUIDELINES FOR ULTRASOUND REFERRAL
 RBH GUIDELINES FOR ULTRASOUND REFERRAL Introduction Ultrasound can be very useful as a first line investigation; it is typically non-invasive and does not involve ionising radiation. However, a significant
RBH GUIDELINES FOR ULTRASOUND REFERRAL Introduction Ultrasound can be very useful as a first line investigation; it is typically non-invasive and does not involve ionising radiation. However, a significant
Sonography of Wrist Ganglion Cysts
 CME Article Sonography of Wrist Ganglion Cysts Variable and Noncystic Appearances George Wang, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, Felix Y. Feng, MD, Gandikota Girish, MBBS, FRCS, FRCR, Elaine M. Caoili, MD, Catherine
CME Article Sonography of Wrist Ganglion Cysts Variable and Noncystic Appearances George Wang, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, Felix Y. Feng, MD, Gandikota Girish, MBBS, FRCS, FRCR, Elaine M. Caoili, MD, Catherine
Ultrasonography of the Adrenal Glands CVM 6105 Kari L. Anderson, DVM, Diplomate ACVR Associate Clinical Professor of Veterinary Radiology
 1: US of adrenal glands, KLA Ultrasonography of the Adrenal Glands CVM 6105 Kari L. Anderson, DVM, Diplomate ACVR Associate Clinical Professor of Veterinary Radiology Ultrasound has quickly become an important
1: US of adrenal glands, KLA Ultrasonography of the Adrenal Glands CVM 6105 Kari L. Anderson, DVM, Diplomate ACVR Associate Clinical Professor of Veterinary Radiology Ultrasound has quickly become an important
Strangulated Epigastric Hernia Mimicking Abdominal Wall Carbuncle: Report of a Case
 Formos J Surg 2009;42:219-223 219 Strangulated Epigastric Hernia Mimicking Abdominal Wall Carbuncle: Report of a Case Hsien Liu 1,2, Chih-Kun Huang 1, Po-Chin Yu 1, Pei-Min Hsieh 1, Chao-Ming Hung 1, Yaw-Sen
Formos J Surg 2009;42:219-223 219 Strangulated Epigastric Hernia Mimicking Abdominal Wall Carbuncle: Report of a Case Hsien Liu 1,2, Chih-Kun Huang 1, Po-Chin Yu 1, Pei-Min Hsieh 1, Chao-Ming Hung 1, Yaw-Sen
SAMSUNG ULTRASOUND RS80A
 Samsung Medison is a global leading medical device company. Founded in 1985, the company sells cutting-edge diagnostic ultrasound devices around the world in various medical fields. The company has attracted
Samsung Medison is a global leading medical device company. Founded in 1985, the company sells cutting-edge diagnostic ultrasound devices around the world in various medical fields. The company has attracted
en-y Y Gastric Bypass Types of Bariatric Surgery Gastric Bypass BARIATRIC SURGERY PROCEDURES Imaging the Gastric Bypass Patient
 I have no financial disclosures Imaging the Gastric Bypass Patient Christine O. Menias, MD Associate Professor of Radiology Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology Washington University St Louis, Missouri,
I have no financial disclosures Imaging the Gastric Bypass Patient Christine O. Menias, MD Associate Professor of Radiology Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology Washington University St Louis, Missouri,
Diagnostic accuracy of shoulder ultrasound performed by a single operator
 Radiology Australasian Radiology (2007) 51, 226 229 Diagnostic accuracy of shoulder ultrasound performed by a single operator DM Cullen, WH Breidahl and GC Janes Perth Orthopaedic and Sports Medicine Centre,
Radiology Australasian Radiology (2007) 51, 226 229 Diagnostic accuracy of shoulder ultrasound performed by a single operator DM Cullen, WH Breidahl and GC Janes Perth Orthopaedic and Sports Medicine Centre,
Free Echogenic Pelvic Fluid: Correlation with Hemoperitoneum
 Free Echogenic Pelvic Fluid: Correlation with Hemoperitoneum G. Kimberly Sickler, MD, Phebe C. Chen, MD, Theodore J. Dubinsky, MD, Nabil Maklad, MD, PhD Echogenic fluid is an important extrauterine finding
Free Echogenic Pelvic Fluid: Correlation with Hemoperitoneum G. Kimberly Sickler, MD, Phebe C. Chen, MD, Theodore J. Dubinsky, MD, Nabil Maklad, MD, PhD Echogenic fluid is an important extrauterine finding
Ultrasound and colour Doppler sonography in acute osteomyelitis in children
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2005, 71, 590-596 ORIGINAL STUDY Ultrasound and colour Doppler sonography in acute osteomyelitis in children Quamar AZAM, Ibne AHMAD, Mazhar ABBAS, Anjum SYED, Faisal HAQUE From the
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2005, 71, 590-596 ORIGINAL STUDY Ultrasound and colour Doppler sonography in acute osteomyelitis in children Quamar AZAM, Ibne AHMAD, Mazhar ABBAS, Anjum SYED, Faisal HAQUE From the
Acute abdominal pain in the elderly patient: Impact of early MDCT examination on diagnosis and management
 Acute abdominal pain in the elderly patient: Impact of early MDCT examination on diagnosis and management Poster No.: C-1464 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Scientific Exhibit GI Tract Authors: A. Pinto,
Acute abdominal pain in the elderly patient: Impact of early MDCT examination on diagnosis and management Poster No.: C-1464 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Scientific Exhibit GI Tract Authors: A. Pinto,
Sandwich technique of closure of lumbar hernia: A novel technique
 CASE SERIES 243 OPEN ACCESS Sandwich technique of closure of lumbar hernia: A novel technique Manash Ranjan Sahoo, Anil Kumar T ABSTRACT Background: Lumbar hernia is a rare hernia which accounts for less
CASE SERIES 243 OPEN ACCESS Sandwich technique of closure of lumbar hernia: A novel technique Manash Ranjan Sahoo, Anil Kumar T ABSTRACT Background: Lumbar hernia is a rare hernia which accounts for less
Sonographic Diagnosis of Ureteral Tumors
 Sonographic Diagnosis of Ureteral Tumors Irith Hadas-Halpern, MD, micur Farkas, MD, Michael Patlas, MD, Ibrahim Zaghal, MD, Shoshana Sabag-Gottschalk, MD, Drora Fisher, MD We present our experience with
Sonographic Diagnosis of Ureteral Tumors Irith Hadas-Halpern, MD, micur Farkas, MD, Michael Patlas, MD, Ibrahim Zaghal, MD, Shoshana Sabag-Gottschalk, MD, Drora Fisher, MD We present our experience with
Ileal intussusception due to a parasite egg: A case report
 Submit a Manuscript: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ Help Desk: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/helpdesk.aspx DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i36.13191 World J Gastroenterol 2014 September 28; 20(36): 13191-13194 ISSN 1007-9327
Submit a Manuscript: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ Help Desk: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/helpdesk.aspx DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i36.13191 World J Gastroenterol 2014 September 28; 20(36): 13191-13194 ISSN 1007-9327
What to Expect from Intestinal Ultrasonography
 261) What to Expect from Intestinal Ultrasonography Červenková J., Steyerová P. Charles University in Prague, First Faculty of Medicine and General Teaching Hospital, Department of Radiology, Prague, Czech
261) What to Expect from Intestinal Ultrasonography Červenková J., Steyerová P. Charles University in Prague, First Faculty of Medicine and General Teaching Hospital, Department of Radiology, Prague, Czech
KIDNEY FUNCTION RELATION TO SIZE OF THE TUMOR IN RENAL CELL CANCINOMA
 KIDNEY FUNCTION RELATION TO SIZE OF THE TUMOR IN RENAL CELL CANCINOMA O.E. Stakhvoskyi, E.O. Stakhovsky, Y.V. Vitruk, O.A. Voylenko, P.S. Vukalovich, V.A. Kotov, O.M. Gavriluk National Canсer Institute,
KIDNEY FUNCTION RELATION TO SIZE OF THE TUMOR IN RENAL CELL CANCINOMA O.E. Stakhvoskyi, E.O. Stakhovsky, Y.V. Vitruk, O.A. Voylenko, P.S. Vukalovich, V.A. Kotov, O.M. Gavriluk National Canсer Institute,
III. REPORTING SYSTEM
 ACR BI-RADS ATLAS BREAST III. REPORTING SYSTEM American College of Radiology 121 2013 122 American College of Radiology ACR BI-RADS ATLAS BREAST A. REPORT ORGANIZATION The report should be concise and
ACR BI-RADS ATLAS BREAST III. REPORTING SYSTEM American College of Radiology 121 2013 122 American College of Radiology ACR BI-RADS ATLAS BREAST A. REPORT ORGANIZATION The report should be concise and
A912: Kidney, Renal cell carcinoma
 A912: Kidney, Renal cell carcinoma General facts of kidney cancer Renal cell carcinoma, a form of kidney cancer that involves cancerous changes in the cells of the renal tubule, is the most common type
A912: Kidney, Renal cell carcinoma General facts of kidney cancer Renal cell carcinoma, a form of kidney cancer that involves cancerous changes in the cells of the renal tubule, is the most common type
Abdominal Wall Endometriosis: Case Report and Review of Literature
 In the name of God Shiraz E-Medical Journal Vol. 13, No. 4, October 2012 http://semj.sums.ac.ir/vol13/oct2012/91001.htm Abdominal Wall Endometriosis: Case Report and Review of Literature Jafar Malmir1,
In the name of God Shiraz E-Medical Journal Vol. 13, No. 4, October 2012 http://semj.sums.ac.ir/vol13/oct2012/91001.htm Abdominal Wall Endometriosis: Case Report and Review of Literature Jafar Malmir1,
Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system.
 Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Women s Health Laparoscopy Information for patients
 Women s Health Laparoscopy Information for patients This leaflet is for women who have been advised to have a laparoscopy. It outlines the common reasons doctors recommend this operation, what will happen
Women s Health Laparoscopy Information for patients This leaflet is for women who have been advised to have a laparoscopy. It outlines the common reasons doctors recommend this operation, what will happen
Accepted Article. Case report: Amyand s hernia, diagnosis to consider in a routine procedure
 Accepted Article Case report: Amyand s hernia, diagnosis to consider in a routine procedure Diana Fernanda Benavides de la Rosa, Íñigo López de Cenarruzabeitia, Francisca Moreno Racionero, Luis María Merino
Accepted Article Case report: Amyand s hernia, diagnosis to consider in a routine procedure Diana Fernanda Benavides de la Rosa, Íñigo López de Cenarruzabeitia, Francisca Moreno Racionero, Luis María Merino
Medical Surgical Procedures - Laparoscopy
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
