Proceedings of the 34th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences
|
|
|
- Victor Elliott
- 3 years ago
- Views:
From this document you will learn the answers to the following questions:
What goals are first stage 3?
The role of IS is played by what level of IS?
What table describes the second stage of the planning?
Transcription
1 Integration between Business Planning and Information Systems Planning: An Analysis of Technology Exploration and Exploitation in Different Value Configurations Petter Gottschalk and Hans Solli-Sæther Norwegian School of Management, Sandvika, Norway Abstract Integration between business planning and information systems planning has been found to have a significant impact on the extent of information systems contribution to organizational performance. Based on a content analysis of strategic IS/IT plans in Norway, the extent of integration was studied. This paper evaluates ten integration mechanisms and four integration stages. Most of the organizations practiced sequential and reciprocal integration. Furthermore, this paper investigates technology exploration and exploitation in different value configurations. Statistical analysis indicates that value shops and value networks are more concerned with technology exploration than value chains. 1. Introduction Many firms make large investments in information technology (IT) and information systems (IS) [1], and yet executives often question whether these investments support their strategic objectives, and whether opportunities to exploit IS/IT for competitive advantage are being overlooked [2]. There are both enablers and inhibitors of business-it alignment [3], and one important area for improved alignment is integration of business planning and information systems planning [4]. This paper presents results from a content analysis of strategic IS/IT plan documents in Norway. The research focus is on identification of integration mechanisms in the plans in general and on technology exploration and exploitation in the plans in particular. Research questions can be stated as: 1) What integration mechanisms are found in strategic IS/IT plans, and 2) To what extent do the integration mechanisms found in strategic IS/IT plans indicate exploitation versus exploration? 2. Integration mechanisms Although no precise definition of strategic alignment of business and IS/IT strategies has gained widespread acceptance, many authors share a similar general interpretation of the term. Strategic alignment is said to be present when: i) business strategies are enabled, supported, and stimulated by information strategies [5]; ii) the goals and activities of the business are in harmony with the information systems that support them [6]; iii) information systems support organizational goals and activities at every level [7]; and iv) choices within content and process dimensions of IS/IT planning are mutually supportive and the two dimensions themselves are harmonized in a manner that is consistent with competitive strategy [8]. Integration between business planning and information system planning is one important enabler of business-it alignment [3, 4, 9]. Teo and King [9] found a significant positive relationship between the level of business planning (BP) and information systems planning (ISP) integration and the extent of information systems contribution to organizational performance. King and Teo [10] have suggested a stage of growth model for the evolution of strategic IS/IT planning integration. The first stage is a separate planning with administrative integration characterized by the integration mechanisms in table 1 such as a technically oriented and non-strategic role of the IS function. The second stage is a one-way linked planning with sequential integration characterized by integration mechanisms in table 1 such as performance criteria of business strategy contribution. The third stage is a two-way linked planning with reciprocal integration such as frequent IS executive participation in business planning. The fourth stage is integrated planning with full integration. 3. Value configurations In the research literature activities [11, 12], resources [13, 14] and technology [15] have been identified as important sources of competitive advantage. Grossmann and Helpman [16] state that the technology can be seen as the engine of growth. What we are about to see is a growing convergence of production, information, and communication technology. The increasing popularity of electronic communications (e.g. the Internet, ecommerce) represents new challenges to conventional exchange of information /01 $10.00 (c) 2001 IEEE 1
2 Table 1. Stages of integration [10] Integration Mechanisms Purpose of integration Role of IS function Primary role of IS executive Performance criteria for IS function Triggers for developing IS applications Stage 1 Administrative Integration Administrative and non strategic Technically oriented and non strategic Functional administrator responsible for back room support Operational efficiency and cost minimization Need to automate administrative work processes Stage 2 Sequential Integration Support business strategy Resource to support business strategy IS expert who formulates IS strategy to implement business strategy Contribution to business strategy implementation Business goals considered first Stage 3 Reciprocal Integration Support and influence business strategy Resource to support and influence business strategy IS expert who provides valuable inputs during strategy formulation and implementation Quality of IS inputs into business strategy formulation and implementation Business goals and IS capabilities considered jointly Stage 4 Full Integration Joint development of business and IS strategies Critical to long-term survival of organization Formal and integral member of top management who is involved in many business matters Long-term impact on organization IS applications are critical to success of business strategy Top management participation Seldom Infrequent Frequent Almost always in ISP User participation in ISP Seldom Infrequent Frequent Almost always IS executive participation in BP Seldom Infrequent Frequent Almost always Assessment of new technologies Seldom Infrequent Frequent Almost always Status of IS executive (Number of levels below CEO) Four or more Three Two One The evolution of customer demands can be seen as a result of the evolution of technology. The changing business environment will radically effect the nature of competition and will force a rethinking of some of the basic principles of strategy [17]. Thompson [15] describes three types of technology, which are important to the understanding of the rationality in organizations the long-linked technology, the mediating technology, and the intensive technology. The three types of technology offered have distinctive value creation logic. Where long-linked technologies focus on the transformation of inputs into outputs, mediating and intensive technologies focus on the linking of customers and the solving of customers problems, respectively. Different companies in different industries are likely to have different value creation sources [12]. Porter [11] addresses the interplay between the types of competitive advantage (cost and differentiation) and the scope of the firm s activities. As a general framework for systematically examining the activities of the firm, Porter [11] introduces the concept of the value chain, which models a long-linked technology quite well. But, differences in value creation logic indicate that Porter s value chain may not be optimal as an analytical framework for all kinds of businesses. Stabell and Fjeldstad [12] introduce the value shop and the value network as alternative value configurations. The analytical framework of the value shop relies on an intensive technology to solve a customer or client problem. Selection, combination, and order of application of resources and activities vary according to the problem at hand. The analytical framework of the value network relies on a mediating technology to link clients or customers who are or wish to be interdependent. The mediating technology facilitates exchange relationships among customers distributed in time and space. Some of the characteristics of the different value configurations are shown in table 2. Core technologies are important for internal efficiency and goal achievement, but it may also represent external opportunities and threats. Andrews [18] lists several environmental influences and states that changes are taking place in varying rates fastest in technology, less rapidly in politics. Porter [11] adds that of all things that can change the rules of competition, technological change is among the most prominent. The speed and prominence of technological change is recognized as important if it affects competitive advantage and industry structure. Technological developments are not only the fastest unfolding but also the most far-reaching in extending an established company. Today this change is driven by information and communication technologies. It is important to be aware of the different value configurations when developing and implementing new information technology /01 $ (c) 2001 IEEE 2
3 Table 2. Characteristics of the three value configurations [12] Chain Shop Network Value creation logic Transformation of input into (Re) solving customer problems Linking customers output Primary technology Long-linked Intensive Mediating Primary activities Inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, marketing, service Problem-finding, problem solving, choice, execution, control/evaluation Network promotion, service provisioning, infrastructure operation Main interactivity relationship Sequential Cyclic, spiraling Simultaneous, parallel logic Primary activity interdependence Pooled, sequential Pooled, sequential, reciprocal Pooled, reciprocal Key cost drivers Scale, capacity utilization Scale, capacity utilization Key value drivers Reputation Scale, capacity utilization Business value system structure Inter linked chains Referred shops Layered and interconnected networks 4. Exploration and exploitation According to March [19] exploration includes things captured by terms such as search, variation, risk taking, experimentation, play, flexibility, discovery, and innovation. Exploitation includes such things as refinement, choice, production, efficiency, selection, implementation, and execution [19]. These key terms of exploration and exploitation are used in the analysis and discussion of the integrative framework. Using the above definition, exploration is very much an issue of creating new activities, mixing technology and resources (both tangible and intangible). But organizations often fail to maintain an effective balance between exploitation and exploration. Knowing that innovation and change often fail, one realizes that it is a trade-off between exploration and exploitation [19, 20]. During the discussion of the integration mechanisms and the three value configurations, three research hypotheses are developed: Hypothesis 1: Value shops are more likely than value chains to facilitate technology exploration. Hypothesis 2: Value networks are more likely than value chains to facilitate technology exploration. Hypothesis 3: Value shops are more likely than value networks to facilitate technology exploration. Looking at the three value configurations presented in table 2, we will guess that the role of IS/IT in value chains are primarily concerned with operational efficiency and cost minimization (exploitation). In value shops IS/IT is a part of or co-performed with primary activities. We guess that solving unique customer or client problems requires innovative use of IS/IT (exploration). In value networks, where linking of customers is the value creation logic, IS/IT is a part of the basic infrastructure (e.g. telecommunications). We suggest that this will mean a balance between exploitation and exploration. 5. Methodology The initial research question in this research is: What integration mechanisms are found in strategic IS/IT plans? The form of the research question is what which can be explored using the research strategy of documentation and archival analysis [21]. Strengths of this form of evidence collection are stability (can be reviewed repeatedly), unobtrusiveness (not created as a result of the study), exact (contains exact names, references, and details), and coverage (all planning aspects). Specifically, this research applied content analysis, which is a research technique for making inferences by systematically and objectively identifying specified characteristics of messages [22, 23]. Content analysis classifies textual material, reducing it to more relevant, manageable bits of data [24]. According to Naccarato and Neuendorf [22], content analysis may be defined as the systematic, objective, quantitative analysis of message characteristics. There has been recognition of the difference between form variables; those that are linked to the formal features of the medium and cannot endure transfer to another media modality, and content or substance variables, and those that may exist independent of the medium. According to Weber [24], content analysis is a research method that uses a set of procedures to make valid inferences from text. A central idea in content analysis is that many words of the text are classified into much fewer content categories. The central problems of content analysis originate mainly in the data-reduction process. One set of problems concerns the consistency or reliability of text classification. Classification by multiple human coders permits the quantitative assessment of achieved reliability. A much more difficult set of problems concerns the validity of variables based on content classification. A content analysis variable is valid to the extent that it measures the construct the investigator intends it to measure [24] /01 $ (c) 2001 IEEE 3
4 In this research, content analysis was applied using key words [25, 26] for coding [27]. Key words concerning integration were treated as content constructs [22]. The model of analysis may be classified as hermeneutics. According to Lee [28], the motivating question in hermeneutics is: after a writer has implanted certain meanings in a text, how might readers of the text, especially those who belong to a different time and culture from the writer of the text, proceed to interpret the text for the meanings originally implanted in it, where other portions of the text itself are the primary, or sometimes the only, crossreferencing tools available? It can be argued that the meaning of a particular passage in a text as interpreted by the reader is related inextricably to the meanings of all other passages in the same text. In this research, manual inspection of all documents was performed to avoid this pitfall. Codes are tags or labels for assigning units of meaning to the descriptive information in collected information [27]. Codes usually are attached to words, phrases, sentences, or whole paragraphs, connected or unconnected to a specific setting. In this research, key words were derived from attributes in table 1 and table 2. The content analysis is designed to yield numerical data in terms of frequencies. This kind of quantification has the advantage that statistical methods provide a powerful set of tools not only for precise and parsimonious summary of findings, but also for improving the quality of interpretation and inference [29]. According to Krippendorf [30], by far the most common form of representation of data, serving primarily the summarizing function of analysis, is in terms of frequencies and their associations and correlation with other variables. 6. Results integration A letter asking for a copy of the IS/IT strategy was sent to 408 IS/IT managers in Norway in We received 41 IS/IT strategies in the mail (both paper mail and ), while we got messages from 15 organizations telling us that they were unable to send us their strategy for various reasons. Organization size ranged from 170 to employees. One plan was written in 1993, three in 1995, one in 1996, seven in 1997, nineteen in 1998 and ten in Time horizons ranged from two to five years. The shortest plan had 2 pages; the longest plan had 59 pages. Most organizations called their document an IT STRATEGY. Table 1 was used to identify integration stage. Specifically, for each strategic plan, a copy of the table was filled in by x-marking the most appropriate description for each of the ten integration mechanisms. The scale from 1 (administrative integration) to 4 (full integration) was kept. For example, by studying the plan document of a manufacturing company, the researcher found that the purpose of integration was support and influence of business strategy (3), the role of IS function was resource to support business strategy (2), the primary role of IS executive was formal and integral member of top management who is involved in many business matters (4), performance criteria for IS function was contribution to business strategy implementation (2), triggers for developing IS applications were business goals considered first (2), frequent top management participation in ISP (3), frequent user participation in ISP (3), frequent IS executive participation in business planning (3), infrequent assessment of new technologies (2), and IS executive one level below the CEO (4). Both the researcher and a doctoral student conducted the same coding, and the inter-rater reliability of 0.6 was considered low but acceptable to continue the research. In the following, the coding of the researcher is used in data analyses. Statistics for the ten items based on 41 observations are summarized in table 3. Assessment of new technologies achieves the highest score, while performance criteria for the IS function achieves the lowest score. The ten integration mechanisms in table 3 are treated as items on a multiple item scale. The reliability of the scale was measured using Cronbach s alpha. The scale achieves an acceptable reliability of Factor analysis was applied to investigate the existence of more than one scale. Three factors were identified as listed in table 4. Seven out of ten items load significantly on the same factor. Status of the IS executive, measured by the number of levels below the CEO, does not seem related to the other integration mechanisms since it loads on a separate factor. User participation also seems independent from other integration mechanisms since it loads on a separate factor. Findings in the available IS plans indicate that two organizations applied administrative integration, twentyseven organizations applied sequential integration, eleven organizations applied reciprocal integration while only one organization applied full integration. Integration between business planning and information systems planning was investigated in this research using four stages and ten integration mechanisms suggested by King and Teo [10]. In the following, each integration mechanism is discussed in light of the empirical results obtained. 6.1 Purpose of integration The purpose of integration varies at different stages of BP-ISP integration. At Stage 1, BP-ISP integration focuses primarily on the support of administrative work processes. This gradually changes as the IS function begins to support business strategy (Stage 2) or influence business strategy (Stage 3). At Stage 4, there is a joint /01 $ (c) 2001 IEEE 4
5 strategy development for both business and IS strategies. On average, the purpose of integration in the studied plans was to support business strategy (Stage 2). Only two plans out of forty-one plans had the ambition of full integration by documenting joint development of business and IS strategies. 6.2 Role of IS function The general transition from being technically oriented to business oriented is captured in this integration mechanism. At Stage 1, the IS function is viewed as being primarily technically oriented. Gradually, this role changes when the IS function is used as a resource to support the implementation (Stage 2) and formulation (Stage 3) of business strategies. At Stage 4, the IS function is viewed as critical to the long-term success of the organization. Again, only two out of forty-one plans defined the organization in Stage 4. Fifteen plans belonged to the first stage, while thirteen plans belonged to the second stage and eleven to the third stage. 6.3 Primary role of IS executive There seems to be a general decrease in the size of the central IS function due to end-user computing. This has resulted in a shift in the responsibilities of the IS function from systems design to systems integration, and from the role of a developer to that of an advisor. Due to increasing decentralization, the IS function will assume a staff role analogous to a federal government in coordinating the dispersed IS resources. The skill requirements of the senior IS executive have also changed over the years with increasing emphasis on both knowledge about changing technology and knowledge about the business. In addition, significant political and communication skills are required. Many IS executives perceive themselves as change leaders [31]. As shown in table 1, the role of the IS executive gradually changes from being a functional administrator responsible for providing back room support (Stage 1), to being an IS expert who formulates IS strategy to implement business objectives (Stage 3). Finally, in Stage 4, the IS executive becomes a formal and integral member of the top management team, and provides significant inputs in both IS and non-is related matters. Most of the IS executives (15) in the current study were functional administrators, quite a few (14) were IS experts who formulate IS strategy to implement business strategy, and a litter fewer (10) were IS experts who provide valuable inputs during strategy formulation and implementation. 6.4 Performance criteria for IS function As the IS function matures, the performance criteria for the IS function change from a structured focus on operational efficiency to a more unstructured concern for the impact of IS on strategic direction. It follows that the early performance criteria (Stage 1) delineated for the IS function are primarily concerned with operational efficiency and cost minimization. When the IS function begins to play a more strategic role, the emphasis gradually shifts to effective strategy implementation (Stage 2) and then to the quality of IS inputs into business strategy formulation and implementation (Stage 3). Ultimately, the performance criteria for the IS function should be its long-term impact (both financial and non financial) on the organization (Stage 4). Three out of forty-one organizations in the current study documented full integration in their plans by focusing on long-term impact on the organization from the performance of the IS function. The majority of the plans (21) focused on operational efficiency and cost minimization (Stage 1). 6.5 Triggers for developing IS applications Initially, the triggers for the development of new IS applications are opportunities for achieving greater efficiencies through process automation. As IS applications begin to be increasingly used to support business strategies, business goals become trigger mechanisms in deciding appropriate IS applications to be developed (Stage 2). At Stage 3, the joint consideration of business goals and IS capabilities becomes important as the firm attempts to develop systems for sustainable competitive advantage. Finally, in Stage 4, IS applications are developed because they are critical to the success of the firm's strategy and the creation of business value. The majority of plans (22) documented a Stage 2 perspective where business goals are considered first. 6.6 Top management participation in ISP Traditionally, as in Stage 1, top management had not paid great attention to the IS function because it was an overhead function that generated only cost. At Stage 2, greater top management participation in ISP begins when IS strategies come to be used to support business strategies. The realization that ISP can also influence business motivates top management to participate more actively in ISP (Stage 3). Finally, in Stage 4, when the IS function becomes critical for the survival of the organization, top management and the senior IS executive jointly formulate business and IS plans. None of the studied organizations defined themselves in Stage 4. Many (15) organizations seemed to have frequent top management participation in ISP /01 $ (c) 2001 IEEE 5
6 Table 3. Summary Statistics Integration Mechanism M. s.d Purpose of integration Role of IS function ** 3 Primary role of IS executive **.78** 4 Performance criteria for IS function **.60**.54** 5 Triggers for developing IS applications **.69**.52**.61** 6 Top management participation in ISP **.48**.49**.35*.35* 7 User participation in ISP IS executive participation in BP **.46**.58**.48**.46**.48**.04 9 Assessment of new technology *.49** Status of IS executive ** ** Table 4. Component matrix based on factor analysis Integration Mechanism Factor 1: Objectives Factor 2: CIO Factor 3: Users 1 Purpose of integration Role of IS function e Primary role of IS executive e e-02 4 Performance criteria for IS function Triggers for developing IS applications Top management participation in ISP User participation in ISP IS executive participation in BP E Assessment of new technology Status of IS executive Note: Extraction method: Principal component analysis, 3 components extracted. 6.7 User participation in ISP User participation in ISP is the seventh integration mechanism. Before the advent of end-user computing, user management is generally not significantly involved in ISP (Stage 1). However, as end-user computing begins to proliferate and the IS function begins to influence functional units in terms of its effects on business strategies, participation of user becomes more important in order to fully exploit the potential of information technology. User participation gradually increases through the stages. At Stage 4, users participate extensively in ISP. Most (27) studied organizations seemed to have frequent user participation in ISP. On average, user participation has highest score in table 3. Also, user participation loaded on a separate factor in table 4. It is interesting to note that although the organizations in this study seem to have a long way to go on integration, user participation seems to be strong. This is not surprising since the study was conducted in Norway. Sometimes called the Scandinavian school of information systems, user participation has for long been considered both a democratic necessity and a key to success. 6.8 IS executive participation in BP The mirror image of top business management participation in ISP is having senior IS executives participate in business planning. The traditional role of the IS function in providing administrative support does not require the senior IS executive to participate in BP (Stage 1). The senior IS executive reacts to business plans and does not have significant influence on their formulation. At Stage 2, the senior IS executive participation is initiated. As the IS function becomes more important in the achievement of business objectives, it becomes necessary to include more frequent participation of the senior IS executive in BP because the traditional participants are relatively unfamiliar with the potential of information technology (Stage 3). With greater participation, the senior IS executive becomes more informed about business objectives and is 1better able to provide higher quality inputs into the planning process. At Stage 4, the senior IS executive becomes an integral member of the top management team and participates extensively in both BP and ISP. None of the studied plans documented stage 4 integration. Most of the organizations seemed to have infrequent IS executive participation in business planning (Stage 2). 6.9 Assessment of new technologies During ISP, new technologies, which can impact on the firm, are usually assessed. The level of sophistication involved in assessing new technologies is the basis for the ninth integration mechanism. In the early stages of ISP (Stages 1 and 2), assessment of the impact of new technologies is usually done rather informally and infrequently. At Stage 3, the need for formal and frequent /01 $ (c) 2001 IEEE 6
7 procedures for assessing new technologies becomes apparent as the IS function begins to play a more important role in BP. At Stage 4, assessment of the impact of new technologies becomes an integral part of BP and ISP. Most studied organizations seem to be quite advanced in their assessment of new technologies, achieving the highest score in table 3. The majority of the organizations documented Stage 3 performance where new technologies are frequently assessed Status of IS executive The responsibilities of the IS function have changed over the years due to technological and conceptual changes that made information technology more important to organizations. IS line responsibilities are being rapidly distributed as the IS function begins to take on more staff responsibilities. With these changing responsibilities of the IS function, the status of the senior IS executive is likely to be elevated. The position of the senior IS executive (in terms of the number of levels below the CEO) can serve as an indication of the importance of the IS function to the firm s strategy. On average, the IS executive is 2.6 levels below the CEO, i.e. the CIO has often two and sometimes one executive level in between. In the factor analysis, this integration mechanism loaded on a separate factor. One explanation can be the relative size of Norwegian organizations compared with US organizations. Most Norwegian organizations are small [31], making a two level difference between CEO and CIO seem much more dramatic in Norway than in the US. 7. Results exploration Table 2 was used to classify companies according to their basic value configuration. Companies classified as chains are typically characterized as those transforming input into output, based on a long-linked type of technology. Examples from our sample are manufacturing companies producing food, drugs, paper and pulp. Companies classified as shops are typically characterized as solving (unique) customer problems using intensive technology. Examples of companies in our sample are hospitals, lawyers, and universities. Companies classified as networks are typically characterized by the linking of customers using mediating technologies. Examples of companies in our sample are telecommunications, postal services, insurance companies and banks. In our sample 14 companies where classified as value chains, 19 were classified as value shops, and 8 were classified as value networks. Operationalization of exploration and exploitation was done by selecting benchmark variable "Assessment of new technologies" (BMK9 in table 1) as the most feasible representation. Lower levels of BMK9 represent exploitation whereas higher values of BMK9 represent exploration. Hypothesis testing was carried out using t-statistic for different value configurations. While the average level of assessment of new technologies was 1.96 in value chains, it was significantly higher in both value shops and value networks. Hypothesis 1 is confirmed; value shops are more likely than value chains to facilitate technology exploration. Hypothesis 2 was also confirmed; value networks are more likely than value chains to facilitate technology exploration. Hypothesis 3 was not confirmed; the difference in BMK9 for value networks and value shops is not significant. Table 5. Significance of differences in technology assessment for value configurations Value Configuration BMK9 Shop Network Chain ** ** Shop Network 2.56 ** p<.01 The issue of technology policy, innovation and management is often forgotten in strategic management. Technically oriented ISP (e.g. search, experimentation, and play with technologies) isolated from BP might have little effect on business performance. But as we see a growing understanding of the importance of IS/IT, we will also see improved operational efficiency (exploitation). The understanding of the technological opportunities is of course essential. Recent development within production, information, and communication technology is extremely knowledge sensitive. Technologies are changing at unprecedented speed, replacing technologies that developed over centuries with new ones themselves have short life expectancies [32]. Bringing the knowledge of these technologies to business managers is a difficult but important task. Sharing of knowledge through integration of ISP and BP may facilitate assessment of new technologies, and by this exploration. In an environment with rapid technological obsolescence and rapidly changing industry settings, this requires a more entrepreneurial approach to identify new business opportunities. To avoid a technological lock-in, leadership must be build through learning, and through research and development. It is widely accepted that firms that invest in the creation of new knowledge and research perform better than those do which not [33]. Building knowledge, it is also important to be aware of the different value configurations and their different underlying technologies. If not, technology investments may be counterproductive /01 $ (c) 2001 IEEE 7
8 8. Conclusion Application of the integration mechanisms and stages suggested by King and Teo [10] confirm that these are useful concepts when doing empirical research. The study of forty-one strategic IS/IT plans in Norway indicates that integration between business planning and information systems planning is not advanced. There seems a long way to go to achieve full integration in Norwegian organizations. At the same time, there are explainable differences due to different activity configurations. Analysis of exploration and exploitation, in the three different value configurations suggested by Stabell and Fjeldstad [12], indicates that value shops and value networks are more concerned with technology exploration than value chains. 9. References [1] M. J. Earl and D. F. Feeny, Is Your CIO Adding Value?, Sloan Management Review, vol. 35, pp , [2] J. C. Henderson and N. Venkatraman, Strategic alignment: Leveraging information technology for transforming organizations, IBM Systems Journal, vol. 32, pp. 4-16, [3] J. N. Luftman, R. Papp, and T. Brier, Enablers and inhibitors of business-it alignment, Communications of AIS, vol. 1, [4] T. S. H. Teo and J. S. K. Ang, Critical success factors in the alignment of IS plans with business plans, International Journal of Information Management, vol. 19, pp , [5] M. Broadbent and P. Weill, Improving business and information strategy alignment: Learning from the banking industry, IBM Systems Journal, vol. 32, pp , [6] R. Woolfe, The path to strategic alignment, Information Strategy: The Executive's Journal, pp , [7] A. L. Lederer and A. L. Mendelow, Coordination of information systems plans with business plans, Journal of Management Information Systems, vol. 6, pp. 5-19, [8] S. R. Das, S. A. Zahra, and M. E. Warkentin, Integrating the content process of strategic MIS planning with competitive strategy, Decision Science, vol. 22, pp , [9] T. S. H. Teo and W. R. King, Integration between Business Planning and Information Systems Planning: An Evolutionary- Contingency Perspective, Journal of Management Information Systems, vol. 14, pp , [10] W. King and T. S. H. Teo, Integration Between Business Planning and Information Systems Planning: Validating a Stage Hypothesis, Decision Science, vol. 28, pp , [11] M. E. Porter, Competitive Advantage: Creating and Sustaining Competitive Performance: The Free Press, [12] C. B. Stabell and Ø. D. Fjeldstad, Configuring Value for Competitive Advantage: On Chains, Shops and Networks, Strategic Management Journal, vol. 19, pp , [13] J. Barney, Firm resources and sustained competitive advantage, Journal of Management, vol. 17, pp , [14] K. Haanes and Ø. Fjeldstad, Linking Intangible Resources and Competition, Forthcoming in the European Management Journal, [15] J. D. Thompson, Organizations in action: McGraw-Hill, [16] G. M. Grossmann and E. Helpman, Endogenous Innovation in the Theory of Growth, The Journal of Economic Perspectives, vol. 8, pp , [17] C. K. Prahalad and G. Hamel, Strategy as a field of study: Why search for a new paradigm?, Strategic Management Journal, vol. 14, pp. 5-16, [18] K. R. Andrews, The Concept of Corporate Strategy, Third Edition ed: The MacGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., [19] J. G. March, Exploration and Exploiting in Organizational Learning, Organization Science, vol. 2, pp , [20] M. B. Lieberman and D. B. Montgomery, First-mover Advantages, Strategic Management Journal, vol. 9, pp , [21] R. K. Yin, Case Study Research: Design and Methods, vol. 5, 2nd ed. ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, [22] J. L. Naccarato and K. A. Neuendorf, Content Analysis as a Predictive Methodology: Recall, Readership, and Evaluations of Business-to-Business Print Advertising, Journal of Advertising Research, pp , [23] D. Riffe and A. Freitag, A Content Analysis of Content Analyses: Twenty-Five Years of Journalism Quarterly, Journalism & Mass Communication Quarterly, vol. 74, pp , [24] R. P. Weber, Basic Content Analysis, 2nd ed. ed: Sage Publications, [25] K. R. Beattie and A. M. Sohal, Implementing ISO 9000: A study of its benefits among Australian organizations, Total Quality Management, vol. 10, pp , [26] A. Crouch and J. Basch, The Structure of Strategic Thinking: a lexical and content analysis, Journal of Applied Management Studies, vol. 6, pp , [27] M. B. Miles and A. M. Huberman, Qualitative data analysis: an expanded sourcebook. USA: Thousand Oaks: SAGE Publications, [28] A. S. Lee, Integrating positivist and interpretive approaches to organizational research, Organization Science, vol. 2, pp , /01 $ (c) 2001 IEEE 8
9 [29] O. R. Holsti, Content Analysis for the Social Sciences and Humanities. USA: Addison-Wesley Publishing, [30] K. Krippendorff, Content Analysis: An Introduction to Its Methodology, vol. 5: Sage Publications, [31] P. Gottschalk, Strategic Management of IS/IT functions: the role of the CIO in Norwegian organizations, International Journal of Information Systems, vol. 19, pp , [32] J. G. March, The Future: Disposable Organizations and the Rigidities of Imagination, Organization, vol. 2, pp , [33] M. H. Boisot, Knowledge Assets. Securing Competitive Advantage in the Information Economy: Oxford University Press, /01 $ (c) 2001 IEEE 9
Petter Gottschalk and Hans Solli-Sæther Norwegian School of Management BI, Sandvika, Norway. Abstract
 Informing Science Developing Effective Organizations Volume 4 No 1, 2001 Differences in Stage of Integration between Business Planning and Information Systems Planning according to Value Configurations
Informing Science Developing Effective Organizations Volume 4 No 1, 2001 Differences in Stage of Integration between Business Planning and Information Systems Planning according to Value Configurations
# # % &# # ( # ) + #, # #./0 /1 & 2 % 3 4 2 5 3 6 6 7 & 6 4 & 4 # 6 76 /0 / 6 7 & 6 4 & 4 # // 8 / 5 & /0 /# 6222 # /90 8 /9: ; & 0 0 6 76 /0 /!<!
 ! # # % &# # ( # ) + #, # #./0 /1 & 2 % 3 4 2 5 3 6 6 7 & 6 4 & 4 # 6 76 /0 / 6 7 & 6 4 & 4 # // 8 / 5 & /0 /# 6222 # /90 8 /9: ; & 0 0 6 76 /0 /!
! # # % &# # ( # ) + #, # #./0 /1 & 2 % 3 4 2 5 3 6 6 7 & 6 4 & 4 # 6 76 /0 / 6 7 & 6 4 & 4 # // 8 / 5 & /0 /# 6222 # /90 8 /9: ; & 0 0 6 76 /0 /!
THE CONTRIBUTION OF THE BALANCED SCORECARD AS A STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT TOOL IN MANAGEMENT SUPPORT
 Visión de Futuro Año 7, Nº1 Volumen Nº13, Enero - Junio 2010 URL de la Revista: www.fce.unam.edu.ar/revistacientifica/ URL del Documento: http://www.fce.unam.edu.ar/revistacientifica/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=184&itemid=51
Visión de Futuro Año 7, Nº1 Volumen Nº13, Enero - Junio 2010 URL de la Revista: www.fce.unam.edu.ar/revistacientifica/ URL del Documento: http://www.fce.unam.edu.ar/revistacientifica/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=184&itemid=51
A New Methodology For Developing The MIS Master Plan Mohammad Dadashzadeh, Ph.D., Oakland University, USA
 A New Methodology For Developing The MIS Master Plan Mohammad Dadashzadeh, Ph.D., Oakland University, USA ABSTRACT Organizations, small and large, for profit and non-profit, service oriented as well as
A New Methodology For Developing The MIS Master Plan Mohammad Dadashzadeh, Ph.D., Oakland University, USA ABSTRACT Organizations, small and large, for profit and non-profit, service oriented as well as
Benefits Realization from IS & IT, and Change Management of roles and the working practices of individuals and teams.
 : Delivering Value from IS & IT Investments John Ward and Elizabeth Daniel John Wiley & Son Ltd ISBN: 9780470094631, 399 pages Theme of the Book This book explores a process and practical tools and frameworks
: Delivering Value from IS & IT Investments John Ward and Elizabeth Daniel John Wiley & Son Ltd ISBN: 9780470094631, 399 pages Theme of the Book This book explores a process and practical tools and frameworks
Queensland recordkeeping metadata standard and guideline
 Queensland recordkeeping metadata standard and guideline June 2012 Version 1.1 Queensland State Archives Department of Science, Information Technology, Innovation and the Arts Document details Security
Queensland recordkeeping metadata standard and guideline June 2012 Version 1.1 Queensland State Archives Department of Science, Information Technology, Innovation and the Arts Document details Security
Developing an IS/IT Strategy: Establishing Effective Processes
 3 Developing an IS/IT Strategy: Establishing Effective Processes Developing an IS/IT strategy is taken to mean thinking strategically and planning for the effective long-term management and optimal impact
3 Developing an IS/IT Strategy: Establishing Effective Processes Developing an IS/IT strategy is taken to mean thinking strategically and planning for the effective long-term management and optimal impact
What is th of your St
 What is th of your St 18 Fall 2011 A Middle East Point of View Strategy e color rategy? A new dimension Over the past few decades, most strategists and corporate executives have been using a global classification
What is th of your St 18 Fall 2011 A Middle East Point of View Strategy e color rategy? A new dimension Over the past few decades, most strategists and corporate executives have been using a global classification
The Role of Controlled Experiments in Software Engineering Research
 The Role of Controlled Experiments in Software Engineering Research Victor R. Basili 1 The Experimental Discipline in Software Engineering Empirical studies play an important role in the evolution of the
The Role of Controlled Experiments in Software Engineering Research Victor R. Basili 1 The Experimental Discipline in Software Engineering Empirical studies play an important role in the evolution of the
Depth-of-Knowledge Levels for Four Content Areas Norman L. Webb March 28, 2002. Reading (based on Wixson, 1999)
 Depth-of-Knowledge Levels for Four Content Areas Norman L. Webb March 28, 2002 Language Arts Levels of Depth of Knowledge Interpreting and assigning depth-of-knowledge levels to both objectives within
Depth-of-Knowledge Levels for Four Content Areas Norman L. Webb March 28, 2002 Language Arts Levels of Depth of Knowledge Interpreting and assigning depth-of-knowledge levels to both objectives within
Operations and Supply Chain Management Prof. G. Srinivasan Department of Management Studies Indian Institute of Technology Madras
 Operations and Supply Chain Management Prof. G. Srinivasan Department of Management Studies Indian Institute of Technology Madras Lecture - 41 Value of Information In this lecture, we look at the Value
Operations and Supply Chain Management Prof. G. Srinivasan Department of Management Studies Indian Institute of Technology Madras Lecture - 41 Value of Information In this lecture, we look at the Value
Practical Research. Paul D. Leedy Jeanne Ellis Ormrod. Planning and Design. Tenth Edition
 Practical Research Planning and Design Tenth Edition Paul D. Leedy Jeanne Ellis Ormrod 2013, 2010, 2005, 2001, 1997 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter 1 The Nature and Tools of Research
Practical Research Planning and Design Tenth Edition Paul D. Leedy Jeanne Ellis Ormrod 2013, 2010, 2005, 2001, 1997 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter 1 The Nature and Tools of Research
BRAND MANAGEMENT AND MARKETING RESEARCH UNIT (BMMRU)
 BRAND MANAGEMENT AND MARKETING RESEARCH UNIT (BMMRU) THE CHALLENGE OF FINANCIAL SERVICES BRANDING: MAJORING ON CATEGORY OR BRAND VALUES? Leslie de Chernatony and Fiona Harris August 2000 00/6 ISBN 0 7492
BRAND MANAGEMENT AND MARKETING RESEARCH UNIT (BMMRU) THE CHALLENGE OF FINANCIAL SERVICES BRANDING: MAJORING ON CATEGORY OR BRAND VALUES? Leslie de Chernatony and Fiona Harris August 2000 00/6 ISBN 0 7492
The Role of Information Technology Studies in Software Product Quality Improvement
 The Role of Information Technology Studies in Software Product Quality Improvement RUDITE CEVERE, Dr.sc.comp., Professor Faculty of Information Technologies SANDRA SPROGE, Dr.sc.ing., Head of Department
The Role of Information Technology Studies in Software Product Quality Improvement RUDITE CEVERE, Dr.sc.comp., Professor Faculty of Information Technologies SANDRA SPROGE, Dr.sc.ing., Head of Department
Grounded Theory. 1 Introduction... 1. 2 Applications of grounded theory... 1. 3 Outline of the design... 2
 Grounded Theory Contents 1 Introduction... 1 2 Applications of grounded theory... 1 3 Outline of the design... 2 4 Strengths and weaknesses of grounded theory... 6 5 References... 6 1 Introduction This
Grounded Theory Contents 1 Introduction... 1 2 Applications of grounded theory... 1 3 Outline of the design... 2 4 Strengths and weaknesses of grounded theory... 6 5 References... 6 1 Introduction This
Universiteit Leiden. ICT in Business. Leiden Institute of Advanced Computer Science (LIACS) Capability Maturity Model for Software Usage
 Universiteit Leiden ICT in Business Capability Maturity Model for Software Usage Name: Yunwei Huang Student-no: s1101005 Date: 16/06/2014 1st supervisor: Dr. Luuk Groenewegen 2nd supervisor: Dr. Nelleke
Universiteit Leiden ICT in Business Capability Maturity Model for Software Usage Name: Yunwei Huang Student-no: s1101005 Date: 16/06/2014 1st supervisor: Dr. Luuk Groenewegen 2nd supervisor: Dr. Nelleke
Balanced Scorecard; a Tool for Measuring and Modifying IT Governance in Healthcare Organizations
 Balanced Scorecard; a Tool for Measuring and Modifying IT Governance in Healthcare Organizations Ehsan Borousan, Roozbeh Hojabri, Mahmoud Manafi and Aliread Hooman Abstract Nowadays healthcare organizations
Balanced Scorecard; a Tool for Measuring and Modifying IT Governance in Healthcare Organizations Ehsan Borousan, Roozbeh Hojabri, Mahmoud Manafi and Aliread Hooman Abstract Nowadays healthcare organizations
Don t just do it; Think IT: The IT Organization of the Future
 Don t just do it; Think IT: The IT Organization of the Future Today, technology has the potential to actually drive business strategy, and need no longer remain just an enabler of business. This means
Don t just do it; Think IT: The IT Organization of the Future Today, technology has the potential to actually drive business strategy, and need no longer remain just an enabler of business. This means
An Empirical Study of Software Process Maturity, TQM Practices and Organizational Characteristics in Taiwanese Companies
 Total Quality Management Vol. 16, No. 10, 1091 1102, December 2005 An Empirical Study of Software Process Maturity, TQM Practices and Organizational Characteristics in Taiwanese Companies SHIANG-HENG CHEN,
Total Quality Management Vol. 16, No. 10, 1091 1102, December 2005 An Empirical Study of Software Process Maturity, TQM Practices and Organizational Characteristics in Taiwanese Companies SHIANG-HENG CHEN,
Soft Skills Requirements in Software Architecture s Job: An Exploratory Study
 Soft Skills Requirements in Software Architecture s Job: An Exploratory Study 1 Faheem Ahmed, 1 Piers Campbell, 1 Azam Beg, 2 Luiz Fernando Capretz 1 Faculty of Information Technology, United Arab Emirates
Soft Skills Requirements in Software Architecture s Job: An Exploratory Study 1 Faheem Ahmed, 1 Piers Campbell, 1 Azam Beg, 2 Luiz Fernando Capretz 1 Faculty of Information Technology, United Arab Emirates
The fact is that 90% of business strategies are not implemented through operations as intended. Overview
 Overview It is important to recognize that a company s network determines its supply chain efficiency and customer satisfaction. Designing an optimal supply chain network means the network must be able
Overview It is important to recognize that a company s network determines its supply chain efficiency and customer satisfaction. Designing an optimal supply chain network means the network must be able
Service Quality Management The next logical step by James Lochran
 www.pipelinepub.com Volume 4, Issue 2 Service Quality Management The next logical step by James Lochran Service Quality Management (SQM) is the latest in the long list of buzz words floating around the
www.pipelinepub.com Volume 4, Issue 2 Service Quality Management The next logical step by James Lochran Service Quality Management (SQM) is the latest in the long list of buzz words floating around the
Becoming Agile: a getting started guide for Agile project management in Marketing, Customer Service, HR and other business teams.
 Becoming Agile: a getting started guide for Agile project management in Marketing, Customer Service, HR and other business teams. Agile for Business www.agilefluent.com Summary The success of Agile project
Becoming Agile: a getting started guide for Agile project management in Marketing, Customer Service, HR and other business teams. Agile for Business www.agilefluent.com Summary The success of Agile project
Center for Effective Organizations
 Center for Effective Organizations HR METRICS AND ANALYTICS USES AND IMPACTS CEO PUBLICATION G 04-8 (460) EDWARD E. LAWLER III ALEC LEVENSON JOHN BOUDREAU Center for Effective Organizations Marshall School
Center for Effective Organizations HR METRICS AND ANALYTICS USES AND IMPACTS CEO PUBLICATION G 04-8 (460) EDWARD E. LAWLER III ALEC LEVENSON JOHN BOUDREAU Center for Effective Organizations Marshall School
Aligning Technology and Business Strategy: Issues & Frameworks, A Field Study of 15 Companies
 Aligning Technology and Business Strategy: Issues & Frameworks, A Field Study of 15 Companies Joseph W. Weiss, Ph.D Bentley College Management Department 175 Forest St. Waltham, MA 02452 jweiss@bentley.edu
Aligning Technology and Business Strategy: Issues & Frameworks, A Field Study of 15 Companies Joseph W. Weiss, Ph.D Bentley College Management Department 175 Forest St. Waltham, MA 02452 jweiss@bentley.edu
School Psychology Doctoral Program Dissertation Outline 1 Final Version 6/2/2006
 School Psychology Doctoral Program Dissertation Outline 1 Final Version 6/2/2006 Instructions: Double Underline means the item should be a title or heading in your dissertation. Do not deviate from the
School Psychology Doctoral Program Dissertation Outline 1 Final Version 6/2/2006 Instructions: Double Underline means the item should be a title or heading in your dissertation. Do not deviate from the
IMPACT OF TRUST, PRIVACY AND SECURITY IN FACEBOOK INFORMATION SHARING
 IMPACT OF TRUST, PRIVACY AND SECURITY IN FACEBOOK INFORMATION SHARING 1 JithiKrishna P P, 2 Suresh Kumar R, 3 Sreejesh V K 1 Mtech Computer Science and Security LBS College of Engineering Kasaragod, Kerala
IMPACT OF TRUST, PRIVACY AND SECURITY IN FACEBOOK INFORMATION SHARING 1 JithiKrishna P P, 2 Suresh Kumar R, 3 Sreejesh V K 1 Mtech Computer Science and Security LBS College of Engineering Kasaragod, Kerala
2015 Global Identity and Access Management (IAM) Market Leadership Award
 2015 Global Identity and Access Management (IAM) Market Leadership Award 2015 Contents Background and Company Performance... 3 Industry Challenges... 3 Market Leadership of IBM... 3 Conclusion... 6 Significance
2015 Global Identity and Access Management (IAM) Market Leadership Award 2015 Contents Background and Company Performance... 3 Industry Challenges... 3 Market Leadership of IBM... 3 Conclusion... 6 Significance
CHAPTER 1. Introduction to CAD/CAM/CAE Systems
 CHAPTER 1 1.1 OVERVIEW Introduction to CAD/CAM/CAE Systems Today s industries cannot survive worldwide competition unless they introduce new products with better quality (quality, Q), at lower cost (cost,
CHAPTER 1 1.1 OVERVIEW Introduction to CAD/CAM/CAE Systems Today s industries cannot survive worldwide competition unless they introduce new products with better quality (quality, Q), at lower cost (cost,
Learning and Teaching
 B E S T PRACTICES NEA RESEARCH BRIEF Learning and Teaching July 2006 This brief outlines nine leading research-based concepts that have served as a foundation for education reform. It compares existing
B E S T PRACTICES NEA RESEARCH BRIEF Learning and Teaching July 2006 This brief outlines nine leading research-based concepts that have served as a foundation for education reform. It compares existing
Transforming Internal Audit: A Maturity Model from Data Analytics to Continuous Assurance
 ADVISORY SERVICES Transforming Internal Audit: A Model from Data Analytics to Assurance kpmg.com Contents Executive summary 1 Making the journey 2 The value of identifying maturity levels 4 Internal audit
ADVISORY SERVICES Transforming Internal Audit: A Model from Data Analytics to Assurance kpmg.com Contents Executive summary 1 Making the journey 2 The value of identifying maturity levels 4 Internal audit
THE EFFECT OF ORGANIZATIONAL CULTURE ON E-COMMERCE ADOPTION
 THE EFFECT OF ORGANIZATIONAL CULTURE ON E-COMMERCE ADOPTION David W. Nickels University of North Alabama, Box 5210 University of North Alabama Florence, AL 35632 Phone: (256) 765-4819 Fax: (256) 765-4811
THE EFFECT OF ORGANIZATIONAL CULTURE ON E-COMMERCE ADOPTION David W. Nickels University of North Alabama, Box 5210 University of North Alabama Florence, AL 35632 Phone: (256) 765-4819 Fax: (256) 765-4811
Organizational Learning and Knowledge Spillover in Innovation Networks: Agent-Based Approach (Extending SKIN Framework)
 Int. J. Manag. Bus. Res., 4 (3), 203-212, Summer 2014 IAU Organizational Learning and Knowledge Spillover in Innovation Networks: Agent-Based Approach (Extending SKIN Framework) * 1 M. Mahmoudzadeh, 2
Int. J. Manag. Bus. Res., 4 (3), 203-212, Summer 2014 IAU Organizational Learning and Knowledge Spillover in Innovation Networks: Agent-Based Approach (Extending SKIN Framework) * 1 M. Mahmoudzadeh, 2
Information Studies: Business Information Systems
 Master thesis Business Contribution to Successful Business-IT Alignment Jesse Piscaer SN: 10196749 University of Amsterdam Faculty of Science Information Studies: Business Information Systems Final version:
Master thesis Business Contribution to Successful Business-IT Alignment Jesse Piscaer SN: 10196749 University of Amsterdam Faculty of Science Information Studies: Business Information Systems Final version:
The Impact of Market Orientation and IT Management Orientation on Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Technology Adoption
 The Impact of Market Orientation and IT Management Orientation on Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Technology Adoption James E. Richard, Peter C. Thirkell and Sid L. Huff, Victoria University of
The Impact of Market Orientation and IT Management Orientation on Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Technology Adoption James E. Richard, Peter C. Thirkell and Sid L. Huff, Victoria University of
Analysis of the Relationship between Strategic Management and Human Resources Management in Informatics Services Company of Tehran Province
 Modern Applied Science; Vol. 10, No. 6; 2016 ISSN 1913-1844 E-ISSN 1913-1852 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Analysis of the Relationship between Strategic Management and Human Resources
Modern Applied Science; Vol. 10, No. 6; 2016 ISSN 1913-1844 E-ISSN 1913-1852 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Analysis of the Relationship between Strategic Management and Human Resources
INVESTIGATION OF EFFECTIVE FACTORS IN USING MOBILE ADVERTISING IN ANDIMESHK. Abstract
 INVESTIGATION OF EFFECTIVE FACTORS IN USING MOBILE ADVERTISING IN ANDIMESHK Mohammad Ali Enayati Shiraz 1, Elham Ramezani 2 1-2 Department of Industrial Management, Islamic Azad University, Andimeshk Branch,
INVESTIGATION OF EFFECTIVE FACTORS IN USING MOBILE ADVERTISING IN ANDIMESHK Mohammad Ali Enayati Shiraz 1, Elham Ramezani 2 1-2 Department of Industrial Management, Islamic Azad University, Andimeshk Branch,
Standardization, Value Configurations and Implications for Business Model Innovation
 Standardization, Value Configurations and Implications for Business Model Innovation Magnus Johansson Standardisation Research Centre, The Institute of Economic Research, School of Economics and Management,
Standardization, Value Configurations and Implications for Business Model Innovation Magnus Johansson Standardisation Research Centre, The Institute of Economic Research, School of Economics and Management,
5 Discussion and Implications
 5 Discussion and Implications 5.1 Summary of the findings and theoretical implications The main goal of this thesis is to provide insights into how online customers needs structured in the customer purchase
5 Discussion and Implications 5.1 Summary of the findings and theoretical implications The main goal of this thesis is to provide insights into how online customers needs structured in the customer purchase
Relationship Quality as Predictor of B2B Customer Loyalty. Shaimaa S. B. Ahmed Doma
 Relationship Quality as Predictor of B2B Customer Loyalty Shaimaa S. B. Ahmed Doma Faculty of Commerce, Business Administration Department, Alexandria University Email: Shaimaa_ahmed24@yahoo.com Abstract
Relationship Quality as Predictor of B2B Customer Loyalty Shaimaa S. B. Ahmed Doma Faculty of Commerce, Business Administration Department, Alexandria University Email: Shaimaa_ahmed24@yahoo.com Abstract
The Strategic Use of Supplier Price and Cost Analysis
 The Strategic Use of Supplier Price and Cost Analysis Michael E. Smith, Ph.D., C.Q.A. MBA Program Director and Associate Professor of Management & International Business Western Carolina University Lee
The Strategic Use of Supplier Price and Cost Analysis Michael E. Smith, Ph.D., C.Q.A. MBA Program Director and Associate Professor of Management & International Business Western Carolina University Lee
Five High Order Thinking Skills
 Five High Order Introduction The high technology like computers and calculators has profoundly changed the world of mathematics education. It is not only what aspects of mathematics are essential for learning,
Five High Order Introduction The high technology like computers and calculators has profoundly changed the world of mathematics education. It is not only what aspects of mathematics are essential for learning,
Business Architecture: a Key to Leading the Development of Business Capabilities
 Business Architecture: a Key to Leading the Development of Business Capabilities Brent Sabean Abstract: Relatively few enterprises consider themselves to be agile, i.e., able to adapt what they do and
Business Architecture: a Key to Leading the Development of Business Capabilities Brent Sabean Abstract: Relatively few enterprises consider themselves to be agile, i.e., able to adapt what they do and
Product Performance Based Business Models: A Service Based Perspective
 Product Performance Based Business Models: A Service Based Perspective Morris A. Cohen Panasonic Professor of Manufacturing and Logistics The Wharton School, University of Pennsylvania Abstract The migration
Product Performance Based Business Models: A Service Based Perspective Morris A. Cohen Panasonic Professor of Manufacturing and Logistics The Wharton School, University of Pennsylvania Abstract The migration
Interview studies. 1 Introduction... 1. 2 Applications of interview study designs... 2. 3 Outline of the design... 3
 Interview studies Contents 1 Introduction... 1 2 Applications of interview study designs... 2 3 Outline of the design... 3 4 Strengths and weaknesses of interview study designs... 6 5 References... 7 1
Interview studies Contents 1 Introduction... 1 2 Applications of interview study designs... 2 3 Outline of the design... 3 4 Strengths and weaknesses of interview study designs... 6 5 References... 7 1
Sales Management 101, Conducting Powerful Sales Review Meetings
 Sales Management 101, Conducting Powerful Sales Review Meetings Dave Brock, Partners In EXCELLENCE Dimensions of EXCELLENCE is based on the four dimensions of performance and organizational excellence.
Sales Management 101, Conducting Powerful Sales Review Meetings Dave Brock, Partners In EXCELLENCE Dimensions of EXCELLENCE is based on the four dimensions of performance and organizational excellence.
Which B2B E-Business Model To Adopt: The Case Of Taiwan Agribusiness Firms. Eric Ng, Les Brown, University of Southern Queensland.
 Which B2B E-Business Model To Adopt: The Case Of Taiwan Agribusiness Firms Eric Ng, Les Brown, University of Southern Queensland Abstract This research investigated the reasons which led Taiwanese agribusiness
Which B2B E-Business Model To Adopt: The Case Of Taiwan Agribusiness Firms Eric Ng, Les Brown, University of Southern Queensland Abstract This research investigated the reasons which led Taiwanese agribusiness
Does organizational culture cheer organizational profitability? A case study on a Bangalore based Software Company
 Does organizational culture cheer organizational profitability? A case study on a Bangalore based Software Company S Deepalakshmi Assistant Professor Department of Commerce School of Business, Alliance
Does organizational culture cheer organizational profitability? A case study on a Bangalore based Software Company S Deepalakshmi Assistant Professor Department of Commerce School of Business, Alliance
The Hidden Value of Enterprise Content Management Deliver business value by leveraging information
 The Hidden Value of Enterprise Content Management Deliver business value by leveraging information Introduction Enterprise Content Management (ECM) provides new information management tools, strategies
The Hidden Value of Enterprise Content Management Deliver business value by leveraging information Introduction Enterprise Content Management (ECM) provides new information management tools, strategies
Uncertainty as a key decision factor: evidence from the interaction between farmers and processors in the frozen vegetable agribusiness in Argentina
 Uncertainty as a key decision factor: evidence from the interaction between farmers and processors in the frozen vegetable agribusiness in Argentina Authors: Daziano, M.F.; Senesi, S.I.; Dulce, E.G. University
Uncertainty as a key decision factor: evidence from the interaction between farmers and processors in the frozen vegetable agribusiness in Argentina Authors: Daziano, M.F.; Senesi, S.I.; Dulce, E.G. University
Healthcare Measurement Analysis Using Data mining Techniques
 www.ijecs.in International Journal Of Engineering And Computer Science ISSN:2319-7242 Volume 03 Issue 07 July, 2014 Page No. 7058-7064 Healthcare Measurement Analysis Using Data mining Techniques 1 Dr.A.Shaik
www.ijecs.in International Journal Of Engineering And Computer Science ISSN:2319-7242 Volume 03 Issue 07 July, 2014 Page No. 7058-7064 Healthcare Measurement Analysis Using Data mining Techniques 1 Dr.A.Shaik
C. Wohlin, "Is Prior Knowledge of a Programming Language Important for Software Quality?", Proceedings 1st International Symposium on Empirical
 C. Wohlin, "Is Prior Knowledge of a Programming Language Important for Software Quality?", Proceedings 1st International Symposium on Empirical Software Engineering, pp. 27-36, Nara, Japan, October 2002.
C. Wohlin, "Is Prior Knowledge of a Programming Language Important for Software Quality?", Proceedings 1st International Symposium on Empirical Software Engineering, pp. 27-36, Nara, Japan, October 2002.
The impact of IT vendor to firm s IT outsourcing
 Association for Information Systems AIS Electronic Library (AISeL) PACIS 2007 Proceedings Pacific Asia Conference on Information Systems (PACIS) 1-1-2007 The impact of IT vendor to firm s IT outsourcing
Association for Information Systems AIS Electronic Library (AISeL) PACIS 2007 Proceedings Pacific Asia Conference on Information Systems (PACIS) 1-1-2007 The impact of IT vendor to firm s IT outsourcing
ASSESSING MIDDLE SCHOOL STUDENTS CONTENT KNOWLEDGE AND SCIENTIFIC
 ASSESSING MIDDLE SCHOOL STUDENTS CONTENT KNOWLEDGE AND SCIENTIFIC REASONING THROUGH WRITTEN EXPLANATIONS Joseph S. Krajcik and Katherine L. McNeill University of Michigan Modified from McNeill, K. L. &
ASSESSING MIDDLE SCHOOL STUDENTS CONTENT KNOWLEDGE AND SCIENTIFIC REASONING THROUGH WRITTEN EXPLANATIONS Joseph S. Krajcik and Katherine L. McNeill University of Michigan Modified from McNeill, K. L. &
STANDARD. Risk Assessment. Supply Chain Risk Management: A Compilation of Best Practices
 A S I S I N T E R N A T I O N A L Supply Chain Risk Management: Risk Assessment A Compilation of Best Practices ANSI/ASIS/RIMS SCRM.1-2014 RA.1-2015 STANDARD The worldwide leader in security standards
A S I S I N T E R N A T I O N A L Supply Chain Risk Management: Risk Assessment A Compilation of Best Practices ANSI/ASIS/RIMS SCRM.1-2014 RA.1-2015 STANDARD The worldwide leader in security standards
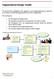
Organizational Design Toolkit
 Organizational Design Toolkit We provide below highlights of the approach to developing/confirming the preferred service delivery model and organizational structure for an organization. The key steps are:
Organizational Design Toolkit We provide below highlights of the approach to developing/confirming the preferred service delivery model and organizational structure for an organization. The key steps are:
Determinants of Organizational IT Infrastructure Capabilities: An Empirical Study
 Determinants of Organizational IT Infrastructure Capabilities: An Empirical Study by Weidong Xia Carlson School of Management University of Minnesota Minneapolis, MN 55455 (612) 626-9766 wxia@tc.umn.edu
Determinants of Organizational IT Infrastructure Capabilities: An Empirical Study by Weidong Xia Carlson School of Management University of Minnesota Minneapolis, MN 55455 (612) 626-9766 wxia@tc.umn.edu
CHAPTER 4 RESULTS. four research questions. The first section demonstrates the effects of the strategy
 CHAPTER 4 RESULTS This chapter presents the statistical analysis of the collected data based on the four research questions. The first section demonstrates the effects of the strategy instruction on the
CHAPTER 4 RESULTS This chapter presents the statistical analysis of the collected data based on the four research questions. The first section demonstrates the effects of the strategy instruction on the
IMPLEMENTATION NOTE. Validating Risk Rating Systems at IRB Institutions
 IMPLEMENTATION NOTE Subject: Category: Capital No: A-1 Date: January 2006 I. Introduction The term rating system comprises all of the methods, processes, controls, data collection and IT systems that support
IMPLEMENTATION NOTE Subject: Category: Capital No: A-1 Date: January 2006 I. Introduction The term rating system comprises all of the methods, processes, controls, data collection and IT systems that support
Managing Information Systems: Ten Essential Topics
 Preface Information systems have become an essential part and a major resource of the organization; and they can radically affect the structure of an organisation, the way it serves customers, and the
Preface Information systems have become an essential part and a major resource of the organization; and they can radically affect the structure of an organisation, the way it serves customers, and the
Optimizing Rewards and Employee Engagement
 Optimizing Rewards and Employee Engagement Improving employee motivation and engagement, and identifying the right total rewards strategy to influence workforce effectiveness. Kevin Aselstine, Towers Perrin
Optimizing Rewards and Employee Engagement Improving employee motivation and engagement, and identifying the right total rewards strategy to influence workforce effectiveness. Kevin Aselstine, Towers Perrin
Key Success Factors for Delivering Application Services
 Key Success Factors for Delivering Application Services George Feuerlicht University of Technology, Sydney jiri@it.uts.edu.au Jiri Vorisek Prague University of Economics vorisek@vse.cz Keywords: ASP, Application
Key Success Factors for Delivering Application Services George Feuerlicht University of Technology, Sydney jiri@it.uts.edu.au Jiri Vorisek Prague University of Economics vorisek@vse.cz Keywords: ASP, Application
Service Quality Value Alignment through Internal Customer Orientation in Financial Services An Exploratory Study in Indian Banks
 Service Quality Value Alignment through Internal Customer Orientation in Financial Services An Exploratory Study in Indian Banks Prof. Tapan K.Panda* Introduction A high level of external customer satisfaction
Service Quality Value Alignment through Internal Customer Orientation in Financial Services An Exploratory Study in Indian Banks Prof. Tapan K.Panda* Introduction A high level of external customer satisfaction
President & Group CEO Håkan Ericsson s speech to the PostNord Annual General Meeting on April 23, 2014. Chairman, valued meeting participants.
 President & Group CEO Håkan Ericsson s speech to the PostNord Annual General Meeting on April 23, 2014 NOTE: The speech as delivered orally supersedes this written script. Page 1/6 Chairman, valued meeting
President & Group CEO Håkan Ericsson s speech to the PostNord Annual General Meeting on April 23, 2014 NOTE: The speech as delivered orally supersedes this written script. Page 1/6 Chairman, valued meeting
Research of Female Consumer Behavior in Cosmetics Market Case Study of Female Consumers in Hsinchu Area Taiwan
 usiness, 2010, 2, 348-353 doi:10.4236/ib.2010.24045 Published Online December 2010 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ib) Research of Female Consumer Behavior in Cosmetics Market Case Study of Female Consumers
usiness, 2010, 2, 348-353 doi:10.4236/ib.2010.24045 Published Online December 2010 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ib) Research of Female Consumer Behavior in Cosmetics Market Case Study of Female Consumers
Facilitators and Inhibitors for Deploying Businessto-Business E-Commerce Applications: A Multi- Method, Cross-Cultural Study
 Association for Information Systems AIS Electronic Library (AISeL) ICIS 2001 Proceedings International Conference on Information Systems (ICIS) 12-31-2001 Facilitators and Inhibitors for Deploying Businessto-Business
Association for Information Systems AIS Electronic Library (AISeL) ICIS 2001 Proceedings International Conference on Information Systems (ICIS) 12-31-2001 Facilitators and Inhibitors for Deploying Businessto-Business
Identifying & Prioritizing of Electronic Commerce Factors in B2B Relationships using Fuzzy ANP (Case study: Nanotechnology High tech Organizations)
 Identifying & Prioritizing of Electronic Commerce Factors in B2B Relationships using Fuzzy ANP (Case study: Nanotechnology High tech Organizations) Zahra Javidian Department Of Engineering, Darab Branch,
Identifying & Prioritizing of Electronic Commerce Factors in B2B Relationships using Fuzzy ANP (Case study: Nanotechnology High tech Organizations) Zahra Javidian Department Of Engineering, Darab Branch,
Requirements Management in Global Software Development: Preliminary Findings from a Case Study in a SW-CMM context i
 Requirements Management in Global Software Development: Preliminary Findings from a Case Study in a SW-CMM context i Rafael Prikladnicki, Jorge Audy, Roberto Evaristo School of Computer Science, Pontifical
Requirements Management in Global Software Development: Preliminary Findings from a Case Study in a SW-CMM context i Rafael Prikladnicki, Jorge Audy, Roberto Evaristo School of Computer Science, Pontifical
REQUIREMENTS FOR THE MASTER THESIS IN INNOVATION AND TECHNOLOGY MANAGEMENT PROGRAM
 APPROVED BY Protocol No. 18-02-2016 Of 18 February 2016 of the Studies Commission meeting REQUIREMENTS FOR THE MASTER THESIS IN INNOVATION AND TECHNOLOGY MANAGEMENT PROGRAM Vilnius 2016-2017 1 P a g e
APPROVED BY Protocol No. 18-02-2016 Of 18 February 2016 of the Studies Commission meeting REQUIREMENTS FOR THE MASTER THESIS IN INNOVATION AND TECHNOLOGY MANAGEMENT PROGRAM Vilnius 2016-2017 1 P a g e
In mathematics, there are four attainment targets: using and applying mathematics; number and algebra; shape, space and measures, and handling data.
 MATHEMATICS: THE LEVEL DESCRIPTIONS In mathematics, there are four attainment targets: using and applying mathematics; number and algebra; shape, space and measures, and handling data. Attainment target
MATHEMATICS: THE LEVEL DESCRIPTIONS In mathematics, there are four attainment targets: using and applying mathematics; number and algebra; shape, space and measures, and handling data. Attainment target
THE MANAGEMENT OF INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL
 THE MANAGEMENT OF INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL Many companies have come to realize that market value multiples associated with its intangible assets (patents, trade-marks, trade secrets, brandings, etc.) are often
THE MANAGEMENT OF INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL Many companies have come to realize that market value multiples associated with its intangible assets (patents, trade-marks, trade secrets, brandings, etc.) are often
An Introduction to. Metrics. used during. Software Development
 An Introduction to Metrics used during Software Development Life Cycle www.softwaretestinggenius.com Page 1 of 10 Define the Metric Objectives You can t control what you can t measure. This is a quote
An Introduction to Metrics used during Software Development Life Cycle www.softwaretestinggenius.com Page 1 of 10 Define the Metric Objectives You can t control what you can t measure. This is a quote
Risk Knowledge Capture in the Riskit Method
 Risk Knowledge Capture in the Riskit Method Jyrki Kontio and Victor R. Basili jyrki.kontio@ntc.nokia.com / basili@cs.umd.edu University of Maryland Department of Computer Science A.V.Williams Building
Risk Knowledge Capture in the Riskit Method Jyrki Kontio and Victor R. Basili jyrki.kontio@ntc.nokia.com / basili@cs.umd.edu University of Maryland Department of Computer Science A.V.Williams Building
In recent years conversations among development
 Major gift metrics that matter By Thomas W. Grabau While the metrics used to measure development performance vary widely, clearly stated goals are essential. And thoughtful analysis of the metrics with
Major gift metrics that matter By Thomas W. Grabau While the metrics used to measure development performance vary widely, clearly stated goals are essential. And thoughtful analysis of the metrics with
PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT AND COST-EFFECTIVENESS OF PUBLIC SERVICES:
 PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT AND COST-EFFECTIVENESS OF PUBLIC SERVICES: EMPIRICAL EVIDENCE FROM DUTCH MUNICIPALITIES Hans de Groot (Innovation and Governance Studies, University of Twente, The Netherlands, h.degroot@utwente.nl)
PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT AND COST-EFFECTIVENESS OF PUBLIC SERVICES: EMPIRICAL EVIDENCE FROM DUTCH MUNICIPALITIES Hans de Groot (Innovation and Governance Studies, University of Twente, The Netherlands, h.degroot@utwente.nl)
Fairfield Public Schools
 Mathematics Fairfield Public Schools AP Statistics AP Statistics BOE Approved 04/08/2014 1 AP STATISTICS Critical Areas of Focus AP Statistics is a rigorous course that offers advanced students an opportunity
Mathematics Fairfield Public Schools AP Statistics AP Statistics BOE Approved 04/08/2014 1 AP STATISTICS Critical Areas of Focus AP Statistics is a rigorous course that offers advanced students an opportunity
BEPS ACTIONS 8-10. Revised Guidance on Profit Splits
 BEPS ACTIONS 8-10 Revised Guidance on Profit Splits DISCUSSION DRAFT ON THE REVISED GUIDANCE ON PROFIT SPLITS 4 July 2016 Public comments are invited on this discussion draft which deals with the clarification
BEPS ACTIONS 8-10 Revised Guidance on Profit Splits DISCUSSION DRAFT ON THE REVISED GUIDANCE ON PROFIT SPLITS 4 July 2016 Public comments are invited on this discussion draft which deals with the clarification
How To Develop Software
 Software Engineering Prof. N.L. Sarda Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture-4 Overview of Phases (Part - II) We studied the problem definition phase, with which
Software Engineering Prof. N.L. Sarda Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture-4 Overview of Phases (Part - II) We studied the problem definition phase, with which
CRITICAL SUCCESS FACTORS FOR SHARED SERVICES: A RESEARCH AGENDA
 CRITICAL SUCCESS FACTORS FOR SHARED SERVICES: A RESEARCH AGENDA Shouhong Wang Charlton College of Business, University of Massachusetts Dartmouth Dartmouth, MA 02747-2300 USA swang@umassd.edu Hai Wang
CRITICAL SUCCESS FACTORS FOR SHARED SERVICES: A RESEARCH AGENDA Shouhong Wang Charlton College of Business, University of Massachusetts Dartmouth Dartmouth, MA 02747-2300 USA swang@umassd.edu Hai Wang
Empirical study of Software Quality Evaluation in Agile Methodology Using Traditional Metrics
 Empirical study of Software Quality Evaluation in Agile Methodology Using Traditional Metrics Kumi Jinzenji NTT Software Innovation Canter NTT Corporation Tokyo, Japan jinzenji.kumi@lab.ntt.co.jp Takashi
Empirical study of Software Quality Evaluation in Agile Methodology Using Traditional Metrics Kumi Jinzenji NTT Software Innovation Canter NTT Corporation Tokyo, Japan jinzenji.kumi@lab.ntt.co.jp Takashi
IT Governance Issues in Korean Government Integrated Data Center 1
 IT Governance Issues in Korean Government Integrated Data Center 1 Mokpo National University, silee@mokpo.ac.kr Abstract Korean government established the GIDC (Government Integrated Data Center) as a
IT Governance Issues in Korean Government Integrated Data Center 1 Mokpo National University, silee@mokpo.ac.kr Abstract Korean government established the GIDC (Government Integrated Data Center) as a
Intercoder reliability for qualitative research
 Intercoder reliability for qualitative research You win some, but do you lose some as well? TRAIL Research School, October 2012 Authors Niek Mouter, MSc and Diana Vonk Noordegraaf, MSc Faculty of Technology,
Intercoder reliability for qualitative research You win some, but do you lose some as well? TRAIL Research School, October 2012 Authors Niek Mouter, MSc and Diana Vonk Noordegraaf, MSc Faculty of Technology,
HiTech. White Paper. A Next Generation Search System for Today's Digital Enterprises
 HiTech White Paper A Next Generation Search System for Today's Digital Enterprises About the Author Ajay Parashar Ajay Parashar is a Solution Architect with the HiTech business unit at Tata Consultancy
HiTech White Paper A Next Generation Search System for Today's Digital Enterprises About the Author Ajay Parashar Ajay Parashar is a Solution Architect with the HiTech business unit at Tata Consultancy
Examining the role of Electronic Customer Relationship Management (E-CRM) on Attracting Customers in Internet Marketing
 Examining the role of Electronic Customer Relationship Management (E-CRM) on Attracting Customers in Internet Marketing Vajihe Mogharabi M.A. Student of Information Technology Management, Shahid beheshti
Examining the role of Electronic Customer Relationship Management (E-CRM) on Attracting Customers in Internet Marketing Vajihe Mogharabi M.A. Student of Information Technology Management, Shahid beheshti
A Comparison of Common Business Modeling Approaches to GODS Generic Business Architecture
 A Comparison of Common Business Modeling Approaches to GODS Generic Business Architecture Adrian Grigoriu Contents GODS single page generic Business Architecture (gba), in brief... 2 Mapping scope and
A Comparison of Common Business Modeling Approaches to GODS Generic Business Architecture Adrian Grigoriu Contents GODS single page generic Business Architecture (gba), in brief... 2 Mapping scope and
History. Programme of study for key stage 3 and attainment target (This is an extract from The National Curriculum 2007)
 History Programme of study for key stage 3 and attainment target (This is an extract from The National Curriculum 2007) Crown copyright 2007 Qualifications and Curriculum Authority 2007 Curriculum aims
History Programme of study for key stage 3 and attainment target (This is an extract from The National Curriculum 2007) Crown copyright 2007 Qualifications and Curriculum Authority 2007 Curriculum aims
Organizational Change: Managing the Human Side
 Organizational Change: Managing the Human Side Based on findings from the American Productivity & Quality Center s 1997 Organizational Change consortium benchmarking study Changing Regulatory or Legal
Organizational Change: Managing the Human Side Based on findings from the American Productivity & Quality Center s 1997 Organizational Change consortium benchmarking study Changing Regulatory or Legal
CONFIGURING VALUE FOR COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE: ON CHAINS, SHOPS, AND NETWORKS
 Strategic Management Journal, Vol. 19, 413 437 (1998) CONFIGURING VALUE FOR COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE: ON CHAINS, SHOPS, AND NETWORKS CHARLES B. STABELL* and ØYSTEIN D. FJELDSTAD Norwegian School of Management,
Strategic Management Journal, Vol. 19, 413 437 (1998) CONFIGURING VALUE FOR COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE: ON CHAINS, SHOPS, AND NETWORKS CHARLES B. STABELL* and ØYSTEIN D. FJELDSTAD Norwegian School of Management,
RELEVANT TO FOUNDATION LEVEL PAPER FAB / ACCA QUALIFICATION PAPER F1
 RELEVANT TO FOUNDATION LEVEL PAPER FAB / ACCA QUALIFICATION PAPER F1 The role of marketing Section B2(e) of the Paper FAB Study Guide states that candidates should be able to describe the roles and functions
RELEVANT TO FOUNDATION LEVEL PAPER FAB / ACCA QUALIFICATION PAPER F1 The role of marketing Section B2(e) of the Paper FAB Study Guide states that candidates should be able to describe the roles and functions
ENTERPRISE RESOURCE PLANNING IN CONSTRUCTION: AN EVALUATION OF RECENT IMPLEMENTATIONS
 ENTERPRISE RESOURCE PLANNING IN CONSTRUCTION: AN EVALUATION OF RECENT IMPLEMENTATIONS Arjen van Leuven 1 and Hans Voordijk 2 1 Balance & Result, Dept. of Construction, P.O. Box 2382, 7500 CJ Enschede,
ENTERPRISE RESOURCE PLANNING IN CONSTRUCTION: AN EVALUATION OF RECENT IMPLEMENTATIONS Arjen van Leuven 1 and Hans Voordijk 2 1 Balance & Result, Dept. of Construction, P.O. Box 2382, 7500 CJ Enschede,
Strategic Brand Management Building, Measuring and Managing Brand Equity
 Strategic Brand Management Building, Measuring and Managing Brand Equity Part 1 Opening Perspectives 开 放 视 觉 Chapter 1 Brands and Brand Management ------------------------------------------------------------------------
Strategic Brand Management Building, Measuring and Managing Brand Equity Part 1 Opening Perspectives 开 放 视 觉 Chapter 1 Brands and Brand Management ------------------------------------------------------------------------
Strategic Information Systems Arrangement: (Business Strategy of IS/IT Arrangement)
 Asian Journal of Business Management 4(4): 327-332, 2012 ISSN: 2041-8752 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2012 Submitted: April 29, 2012 Accepted: May 23, 2012 Published: September 25, 2012 Strategic Information
Asian Journal of Business Management 4(4): 327-332, 2012 ISSN: 2041-8752 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2012 Submitted: April 29, 2012 Accepted: May 23, 2012 Published: September 25, 2012 Strategic Information
This software agent helps industry professionals review compliance case investigations, find resolutions, and improve decision making.
 Lost in a sea of data? Facing an external audit? Or just wondering how you re going meet the challenges of the next regulatory law? When you need fast, dependable support and company-specific solutions
Lost in a sea of data? Facing an external audit? Or just wondering how you re going meet the challenges of the next regulatory law? When you need fast, dependable support and company-specific solutions
ELA I-II English Language Arts Performance Level Descriptors
 Limited ELA I-II English Language Arts Performance Level Descriptors A student performing at the Limited Level demonstrates a minimal command of Ohio s Learning Standards for ELA I-II English Language
Limited ELA I-II English Language Arts Performance Level Descriptors A student performing at the Limited Level demonstrates a minimal command of Ohio s Learning Standards for ELA I-II English Language
How To Analyze The Benefits Of An Enterprise Resource Planning System
 JOURNAL OF EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES IN ACCOUNTING Vol. 1 2004 pp. 63 72 Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems: An Empirical Analysis of Benefits Daniel E. O Leary University of Southern California ABSTRACT:
JOURNAL OF EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES IN ACCOUNTING Vol. 1 2004 pp. 63 72 Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems: An Empirical Analysis of Benefits Daniel E. O Leary University of Southern California ABSTRACT:
MCQ: Unit -2: Operation processes
 MCQ: Unit -2: Operation processes 1.What type of process would a Cement plant be most likely to use? a. Continuous flow b. Project c c. Job shop d. Flow shop 2. Process selection is primarily considered
MCQ: Unit -2: Operation processes 1.What type of process would a Cement plant be most likely to use? a. Continuous flow b. Project c c. Job shop d. Flow shop 2. Process selection is primarily considered
A Risk Management System Framework for New Product Development (NPD)
 2011 International Conference on Economics and Finance Research IPEDR vol.4 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore A Risk Management System Framework for New Product Development (NPD) Seonmuk Park, Jongseong
2011 International Conference on Economics and Finance Research IPEDR vol.4 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore A Risk Management System Framework for New Product Development (NPD) Seonmuk Park, Jongseong
DIRECT MARKETING OF AGRO FOOD PRODUCTS ON VIRTUAL MARKET
 Universitatea de Ştiinţe Agricole şi Medicină Veterinară Iaşi DIRECT MARKETING OF AGRO FOOD PRODUCTS ON VIRTUAL MARKET Al. L. SIPICĂ 1 1 University of Agricultural Sciences and Veterinary Medicine, Bucharest
Universitatea de Ştiinţe Agricole şi Medicină Veterinară Iaşi DIRECT MARKETING OF AGRO FOOD PRODUCTS ON VIRTUAL MARKET Al. L. SIPICĂ 1 1 University of Agricultural Sciences and Veterinary Medicine, Bucharest
Research Design and Research Methods
 CHAPTER 3 Research Design and Research Methods Overview This chapter uses an emphasis on research design to discuss qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods research as three major approaches to research
CHAPTER 3 Research Design and Research Methods Overview This chapter uses an emphasis on research design to discuss qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods research as three major approaches to research
Optimization of Software Quality using Management and Technical Review Techniques
 Optimization of Software Quality using Management and Technical Review Techniques Inibehe Emmanuel Akpannah Post Graduate Student (MSc. Information Technology), SRM University, Chennai, India Abstract
Optimization of Software Quality using Management and Technical Review Techniques Inibehe Emmanuel Akpannah Post Graduate Student (MSc. Information Technology), SRM University, Chennai, India Abstract
