ROLE OF MIDDLEWARE FOR INTERNET OF THINGS: A STUDY
|
|
|
- Estella Peters
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ROLE OF MIDDLEWARE FOR INTERNET OF THINGS: A STUDY Soma Bandyopadhyay, Munmun Sengupta, Souvik Maiti and Subhajit Dutta Innovation Lab, TATA Consultancy Services Ltd. Kolkata, India soma.bandyopadhyay@tcs.com, munmun.sengupta@tcs.com, s.maiti@tcs.com, subhajit.dutta@tcs.com ABSTRACT Internet of Things (IoT) has been recognized as a part of future internet and ubiquitous computing. It creates a true ubiquitous or smart environment. It demands a complex distributed architecture with numerous diverse components, including the end devices and application and association with their context. This article provides the significance of middleware system for (IoT). The middleware for IoT acts as a bond joining the heterogeneous domains of applications communicating over heterogeneous interfaces. First, to enable the better understanding of the current gap and future directions in this field a comprehensive review of the existing middleware systems for IoT is provided here. Second, fundamental functional blocks are proposed for this middleware system, and based on that feature wise classification is performed on the existing IoT-middleware. Third, open issues are analyzed and our vision on the research scope in this area is presented. KEYWORDS Internet of Things, middleware, semantic model, context-awareness, ubiquitous computing. 1. INTRODUCTION Internet of Things (IoT) is a combined part of future Internet and ubiquitous computing. It demands interactions with the heterogeneous raw sensors, aggregators, actuators and diverse domain of context aware applications, preserving the security and privacy. It comprises two definite components Internet and things. Internet is a global network infrastructure with self configuring, scalable, dynamic expansion capabilities based on standard and interoperable communication protocols whereas things are physical objects/devices or virtualobjects/devices/information having identities, physical attributes, and virtual personalities and use intelligent interfaces. Things are heterogeneous in nature and seamlessly integrated into the information network. In order to meet the above said demand IoT will require a software platform defined as middleware, fundamentally providing abstraction to applications from the things, and offering multiple services. Development of middleware in the domain of IoT is an active area of research. There have been a lot of researches towards building up this middleware addressing interoperability across heterogeneous devices serving diverse domains of applications, adaptation, context awareness, device discovery and management, scalability, managing a large data volumes and, privacy, security aspects of the said IoT environment. Therefore there is a strong need to understand how the existing IoT-middleware systems work and address the different requirements of ubiquity as well as IoT [14] and [15], and most importantly the existing issues and gaps. In this article focus has been given to study the existing IoT-middlewares, understanding its functional components and categorizing and comparing them as per the various features. The DOI : /ijcses
2 basic functional building blocks of IoT-middleware are proposed and discussed. Based on this review existing issues and gaps, and future research scope are also analyzed and presented. The remainder of this article is organized as follows. First, the related work in IoT-middleware is presented, followed by descriptions of the essential functional blocks and the system architecture of the IoT-middleware system. The feature wise classification of theirs along with the different interfaces and syntax and semantics strategies are described in detail in the next section. The final section concludes this article with future research scope, and analyzes the gaps of the existing IoT-middleware system. 2. RELATED WORK The common goal of all the middleware development initiatives is to develop a framework which can enable an adaptation layer in a plug-n-play mode. In recent past, many reviews have been made on different middleware, and on their basic features to support the important needs of the respective domains. Various kinds of middlewares based on their supported functionalities like adaptability, contextawareness and application domains like Wireless Sensor Network (WSN), Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) are studied. The surveys performed in [4] and [5] have studied the middleware based on context-awareness feature. The survey in [4] is based on the architectural aspects and provides taxonomy of the features of a generic context-aware middleware. Survey reported in [5] evaluates several context-aware architectures based on some relevant criteria from ubiquitous or pervasive computing perspective. In [6] middleware for WSN has been reviewed and a detailed analysis of the approaches and techniques offered by the middleware to meet the requirements of the WSN has been presented. It also discusses generic components of the middleware and reference model of WSN based middleware. In [7], middleware for WSN has been classified depending on their approaches, which can be database oriented, tuple space approaches, event based and service discovery based approaches [13]. It also narrates the challenges of WSN middleware and provides some suggestions for solving them. In [8] middleware has been surveyed from adaptability perspective. This review also presents taxonomy for adaptive middlewares, their application domains and provides details for one of each middleware categories. The survey presented in this article lists the overall features supported by the existing middleware in the IoT domain, with the proposal of the functional components and system architecture of IoT-middleware, and establishes the importance of middleware in IoT, whereas the rest of the surveys in this section depict how efficiently a particular feature is implemented in the middleware other than IoT domain. This is the basic difference between the present and the rest of the works. This article also analyses the issues and gaps on the existing middleware of IoT and explores the way forward on research scope. 3. FUNCTIONAL BLOCKS Middleware for IoT is required for various reasons. The summary of reasons is as follows: Difficult to define and enforce a common standard among all the diverse devices belonging to diverse domain in IoT. Middleware acts as a bond joining the heterogeneous components together. Applications of diverse domains demand abstraction /adaptation layer. Middleware provides API (application programming interfacing) for physical layer communications, and required services to the applications, hiding all the details of diversity. 95
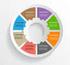
3 The above stated reasons generate the need for various functional components the IoTmiddleware must support. The functional components of the middleware as proposed here are portrayed in the current section. The functional component of an IoT-middleware is depicted in Fig. 1. The inner most circle shows the required functional blocks. The second circle encompasses the further division of the functional blocks, and the outermost circle shows the important modules interacting with the various functional components, but not part of the middleware example context processing, data storage and knowledge database. The functional components are as follows: Interoperation Context detection Device discovery and management Security and privacy Managing data volume Fig. 1. Functional Components of IoT-Middleware Functional components are discussed in the following subsections. The system architecture is depicted in Fig. 2. It presents a layered view of the IoT middleware architecture. The fundamental layers are interface protocols, device abstraction responsible for providing interoperation, resolving the syntax and semantics associated with devices, central and management module is the core component, which performs the device discovery, management and context detection. Application abstraction module provides the interface with local and remote application. Local applications mainly run as event driven services. The other components like context analysis, knowledge database may reside in remote system essentially generating a need of distributed architecture. 96
4 3.1 Interoperation Fig.2. Functional Components of IoT-Middleware Interoperation shares information and uses the same across diverse domains of applications using diverse communication interfaces. It can be further classified under three different categories like network, syntactic and semantics [11]. Network interoperation defines protocols for exchanging information among the various things across different communication networks, without considering the content of information. It covers the basic connectivity issues in physical and data-link to network, transport, session and sometimes application layer of TCP/IP stack. Syntactic interoperation deals with the format and structure of the encoding of the information exchanged among things. It includes the presentation and application of TCP/IP stack. Semantic interoperation defines the rules for understanding the meaning of the content of information, and creates a domain specific information model, known as semantic model. IoT-middleware exposes multiple APIs to perform these interoperation functionalities. SOAbased architecture [9], [18] and Ubiquitous Service-Discovery Service (ubisd-s) [22] are some of the common approaches adapted by the available IoT-middlewares for semantic interoperation whereas Home Audio/Video Interoperability (HAVi) [3] addresses network interoperation. IoT middleware particularly connecting the diverse sensors with the Internet uses sensorml (Sensor Model Language) [27] which provides standard models and XML schema for interoperating with sensors. This defines multiple models for various functionalities of the sensors, like actuation, aggregation, detection. 97
5 3.2 Context Detection Context is responsible for characterizing the situation of an entity where an entity can be person, place, or object relevant to the interaction between a user and an application, including the user and applications themselves. IoT-middleware must be context aware for working into smart environments. Context awareness can be achieved by context detection and context processing. Context detection collects data and identifies the factors that have significant impacts on the response. Context processing extracts the context data, processes it and performs or takes decision based on that. Both these functional modules are depicted in Fig. 1. A knowledge database is required for setting up a closed feedback path between these blocks to evaluate the effectiveness of context-aware systems and make some possible improvements. Among these, context-detection is a core component of IoT-middleware. The other two functional blocks residing outside the core components of IoT-middleware are mostly interacting with the IoT applications. Context detection and context processing have been implemented in different ways in existing IoT-middlewares. Each service supported by the middleware [9] can be registered with a context-dependent identifier. The context-dependent identifier gets changed with the change in end-point mobility. The network manager would maintain a data-structure like IDTable with the information of identifiers [10]. The middleware described in [11] performs context detection by collecting information from the sensor devices and extracts required context data by utilizing available data mining algorithms. Another approach towards context detection is incorporating semantic context-aware multimodal visualization approach [1]. This will enable users not only to get just raw data, but also information relevant to a particular context and also visualization in an adequate way. This type of framework contains context-aware A2H (Agent-to-Human) interaction which is termed as 4i (For Eye) technology. Optimized message communication between middleware users can be another notion of context awareness [12] where any event-response can first understand the intended recipient and can communicate among them. 3.3 Device Discovery and Management Device discovery and management enables any device in the IoT network to detect all its neighbouring devices and make its presence known to each neighbour in the network. Device ontology [26] is used for storing information about the heterogeneous devices. From IoT perspective, these modules need to be reliable, fault-tolerant, adaptive and optimized for resource consumption [21]. Few techniques adopted for device discovery and management of device information are listed below: Middleware described in [16], [8], [9], tries to extend the syntactic interoperability to semantic interoperability in application layer. This is done by combining the use of ontologies with semantic web services. Semantic Model Driven Architecture (Semantic MDA) is introduced to facilitate application development and to promote semantic interoperability for services and devices. It includes a set of models (Device ontology) and their usage in design time and run time. It introduces concept of semantic devices which are software representation of physical devices. Mapping of physical devices to semantic devices can be one-to-one or many-to-one depending on the application. Information and data about devices and device types are stored in device ontology. Semantic device description includes information regarding device capabilities, services, and device malfunction and security properties. Device Description includes information like device name, vendor details, hardware description and software description used to describe hardware and software resources of the device. Application 98
6 Ontology Manager provides interface for using Device Ontology. New devices can be included into the device ontology by adding sub-classes depending on specialized concepts and new properties. P2P (Point-to-Point) discovery is supported in various middleware systems. Middlewares described in [1] and [16] adopt this technique. As described in [12], peer-to-peer architecture is used in a system where devices support self-configurable services and scalability from tiny embedded devices to heterogeneous P2P networked systems. Using device ontology, sensor nodes are abstracted as virtual sensor node in middleware described in [2]. The virtual abstracted unit contains metadata used for identification and discovery of sensor nodes. It also contains information regarding the data stream, functional properties related to lifecycle management etc. Concept of hardware abstraction layer which creates new adaptor when newer devices are added to the network is described in [13]. Agent based architecture is used in middleware [1] and [11].Here it is assumed that agents are associated with all devices present in the network. Middleware described in [1] follows IEEE FIPA model, including a Directory Facilitator in the system which maintains mapping between agents and their roles. It helps one agent to find other suitable agent/agents. This introduces severe bottleneck in the system. To improve the survivability of these systems, a significant part of DF knowledge gets stored in local knowledge databases of different platform agents when the system becomes fully operational. The combination of the local storages presents a kind of distributed directory. Peer-to-Peer (P2P) mechanism implemented on such a distributed directory is another mechanism complementary to central DF. Also, sometimes some of the services might not prefer to advertise themselves through the central DF for security reasons. P2P discovery can be the option in such scenario. The objective here is the design of mechanisms which will extend the scale of semantic resource discovery with P2P discovery. Such mechanisms have to enable an agents for discovering other agents playing a certain organizational role, to discover an agent /agents possessing certain needed information, and to discover resources (through its agents) of certain type or possessing certain properties. Here the request is sent to all or some of the agents on the contact list of the agent who wants to communicate. Those agents can forward the request to all/some of the agents on their lists, and so on. Middleware in [11] includes agents for managing the repository of roles and scenarios. Agents are able to monitor data coming from the adapter about states of the resource, and take decisions depending on the data content. Agents also facilitate discovery of other agents in the environment. This approach facilitates service discovery, FIPA communication protocols utilization, and integration/composition of services. Agent-based layer includes an agent managing repository of roles and scenarios encoded in RDF-based Semantic Agent Programming Language (S-APL). Agents manage repository of atomic behaviours which are software components that agents can load depending on current scenario and the directory that facilitates flexible discovery of agents. S-APL [24] is a hybrid of semantics specification languages, semantic reasoners, and agent programming languages. It integrates the semantic description of domain resources with the semantic prescription of behaviour of agents in individual and collaborative level. Service discovery based approach is used to find services available in the system and then correspondingly binding to that target provider Middleware described in [22] introduces a service discovery protocol called ubiquitous Service-Discovery Service (ubisd-s) which provides dynamic, interoperable, context-aware service discovery. The middleware mentioned in [3] uses devices profile for Web Services (WS) which includes WS-Addressing, WS- Discovery, WS-Metadata exchange, and WS-Eventing for devices. The framework also includes device metadata management, and device lifecycle management containing information regarding the various devices in the network. 99
7 Monitoring and Inventory module of the middleware described in [18] includes sub-modules like Device Repository, Device Monitor, Middleware Historian and Discovery. Device Repository stores the static information about devices present in the network. For this purposes it clubs similar devices into Device Types. Device Type contains two fields: Properties and Features which describe common characteristics of a class of devices. Function of Device Monitor is to monitor devices and detect events like malfunction/faulty devices. As the devices are of varied nature, set of fault detection techniques are needed. These techniques can be driven by events generated by the devices or by invoking specific methods on the devices. New techniques can be used by implementing another monitoring method. Middleware Historian acts as an event archive for the architecture. Data from the devices (due to events or invocation), middleware system information, debugging messages, etc. can be stored there and are accessible for correlation of events. Discovery sub-module helps to find devices present on a network and retrieves information about them and their hosted services. Two functional modes are supported for discovery sub-module, passive discovery and active discovery. The passive discovery listens to the network for announcements from new devices that connect to the network, dynamically retrieves their metadata and notifies the systems about the devices and their hosted services. The active discovery, is responsible for dynamic search of specific devices or services, and is particularly suited for contexts where new devices with unknown capabilities continuously connect to the system. 3.4 Security and Privacy Security and privacy are responsible for confidentiality, authenticity, and non-repudiation. Security can be implemented in two ways (i) secure high-level peer communication which enables higher layer to communicate among peers in a secure and abstract way and (ii) secure topology management which deals with the authentication of new peers, permissions to access the network and protection of routing information exchanged in the network. Security has been considered in all the functional blocks of the existing IoT-middleware, from the user level application to the various parts of the functional blocks [12] with a view to build a trustworthy design [9] and [10]. Other approaches to implement security and privacy in IoTmiddleware are as follows. Middleware in [11] depicts the semantic ontology-based approach to build a universal trust management system, here trust descriptions are interpretable and processable by autonomous trust management procedures and modules, trust data should be given explicit meaning via semantic annotation. Semantic trust concepts and properties will be utilized and interpreted using common trust ontology. Trust information can be incorporated as part of semantic resource descriptions and stored in dedicated places within the platform. Communication and retrieval of trust information will be accomplished through corresponding agent-to-agent communication. Here agents represent communicating resources and required to be configured appropriately to handle all necessary trust management activities between the corresponding communication parties. Trust management procedures can be realized as a set of specific business scenarios in the form of agent configuration plans. Device authentication [18], integrity service and access control [2] are other techniques deployed for IoT. 3.5 Managing Data Volumes Managing data volumes is an integral part of IoT-middleware. It is believed that there will be trillions of objects which will be part of this enormous network and hundreds of Exabytes [20] will be stored or exchanged among the objects. In other words there will be Exaflood or Data deluge, i.e. explosion of the amount of data collected and exchanged. Therefore it is imperative to get novel methods to find, fetch, and transfer data. Here challenges involve in querying, indexing, process modelling, and transaction handling. These data can be identification data, positional data, environmental data, historical data and descriptive data as presented in [23]. 100
8 That is why managing these voluminous data is an important module of IoT-middleware. In addition storage and knowledge database plays an assistive role to the module as depicted in Fig. 1. The data volume management of various IoT-middlewares is discussed in the following sections. In [10] and [19] the Storage Manager module realizes the persistent storage and administration of information in the middleware. It can integrate any kind of storage into the middleware, address those storages as virtual devices and it stores the data as string. The main constraint of this middleware is that the storage device should also be running the same middleware. On the other hand, in [17] there is an existence of a RDBMS (Relational Data Base Management System). The Information Sharing Module of the middleware is responsible for collecting, filtering, storing and extracting queried data from the database. The agents in middleware, as proposed in [11], acquire knowledge by utilizing available data mining algorithms and dynamically reconfigure the data management architecture on the basis of this knowledge. These agents infer (also collaboratively) new configuration plan based on this acquired knowledge. Whereas in [2], storage layer is in-charge of providing and managing persistent storage for data streams. Query processing is done by the Query Manager (QM) which includes the query processor and query repository for efficient management of the data. The notification manager handles the delivery of events and query-results to the registered clients. 3. CLASSIFICATION OF THE IOT-MIDDLEWARE This section classifies the different IoT-middleware based on the various features like interoperation, device management, platform portability, context awareness, security and privacy, and the support of various interface protocols. Table 1 and Table 2 depict the classifications of various IoT-middleware systems based on the various features and interface protocol support respectively. IoT Middleware Device Management Table 1. IoT-middleware comparison. Features of Middleware Interoperation Platform Portability Context Awareness Security and Privacy HYDRA ISMB ASPIRE UBIWARE UBISOAP UBIROAD GSN SMEPP SOCRADES SIRENA WHEREX All the listed middlewares support device discovery and management. Context aware functionality is supported by HYDRA, UBIWARE, UBIROAD and SMEPP. On the other hand, SOCRADES, SMEPP, GSN, UBIROAD and HYDRA are some examples of middleware implementing security and user privacy in their architecture. Based on platform portability, syntactic resolution, HYDRA, SMEPP and ASPIRE are OSGi compliant, UBIROAD uses 101
9 JAVA and XML, UBISOAP uses J2SE and J2ME, GSN uses XML and SQL, SIRENA and SOCRADES use DPWS while SOCRADES also uses SAP NetWeaver [25] platform and ISMB uses any JAVA compliant platform. WhereX [28] is developed using J2EE architecture and is integrated with Oracle Application Server 10g.It also uses Rhino rule engine which is implementation of Java Script. IoT Middleware Table 2. IoT-middleware Interfaces. Interface protocols Zigbee RFID WiFi Bluetooth Sensor (others) HYDRA ISMB ASPIRE UBIWARE UBISOAP UBIROAD GSN IEEE-1451 SMEPP SOCRADES SIRENA WHEREX 4. CONCLUSION In this article the role of middleware system in IoT is presented. It has proposed the functional blocks of IoT-middleware, and discussed feature wise classifications among the existing IoTmiddleware. It has also presented the system architecture of IoT middleware. The current state-of-the-art of the middleware for IoT explores different approaches to support some of the functionalities to operate in IoT domain. But no one covers the full set of functionalities to meet the requirement of IoT-middleware as analyzed here for any smart or ubiquitous environment, except in [29]. Middlewares have several short comings or open issues. They are available for respective domains separately. ASPIRE, ISMB etc. address the RFID domain. GSN addresses the sensor networks in general. UBIROAD addresses smart vehicular systems. There exists no generic middleware which can be applicable across all possible smart environments- like smart home, smart vehicle, smart city[30] etc. including RFID domain, and can be customized as per the domain specific requirements. It has been observed from this study that to resolve scalability issues IPv6 is proposed but not yet resolved completely. Support for context detection and processing have not been achieved fully. Support of semantic modelling and managing of data volumes also fall in the open issues, particularly handling the crowd sourcing of diverse domain. There is a scope for research work in making a generic IoT-middleware system, which is applicable across all domains by making all the functional components reusable and can be added as add-on to the middleware system. The development of generic interfaces, as shown in interface1 and interface2 in Fig.2, are also open issues in this domain. We are continuing to carry researches on the above mentioned open issues to design and develop a layer based IoT-middleware for any smart environment. One of the contributions of this paper consists in this discussion on the open issues on middleware for IoT and that can be combined to define the future research scope on IoT-middleware. 102
10 REFERENCES [1] Katasonov, A., Kaykova, O., Khriyenko, O., Nikitin, S., Terziyan, V.: Smart Semantic Middleware for the Internet of Things. In: 5th Intl. Conf. Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO 08), pp Volume ICSO, (2008) [2] Aberer, K., Hauswirth, M., Salehi, A.: Middleware Support for the Internet of Things. In: 5th GI/ITG KuVS Fachgespr ach "Drahtlose Sensornetze", pp (2006 ) [3] Bohn, H., Bobek, A., Golatowski, F.: SIRENA - Service Infrastructure for Realtime Embedded Networked Devices: A Service Oriented Framework for Different Domains. In: International Conference on Systems and International Conference on Mobile Communications and Learning Technologies (ICNICONSMCL 06), pp. 43. IEEE Computer Society, Washington, DC, USA (2006) [4] Kjær, K., E.: A Survey of Context-Aware Middleware. In: 25th conference on IASTED International Multi-Conference: Software Engineering, pp ACTA Press (2007) [5] Miraoui, M., Tadj C., Amar, C. B.: Architectural Survey of Context-Aware Systems in Pervasive Computing Environment. In: Ubiquitous Computing and Communication Journal, vol. 3, no. 3 (2008) [6] Wang, M., M., Cao, J., N., Li, J., Das, S., K.: Middleware for Wireless Sensor Networks: A Survey. In: Journal of Computer Science and Technology, vol. 23, no. 3, pp (2008) [7] Henricksen, K., Robinson, R. A Survey of Middleware for Sensor Networks: State-of-the-Art and Future Directions. In: International Workshop on Middleware for Sensor Networks, pp Melbourne, Australia, November (2006) [8] Sadjadi, S. M., McKinley, P.: A Survey of Adaptive Middleware. Technical Report MSU-CSE ,Computer Science and Engineering, Michigan State University, East Lansing, Michigan (2003) [9] Eisenhauer, M., Rosengren, P., Antolin, P.: A Development Platform for Integrating Wireless Devices and Sensors into Ambient Intelligence Systems. In: 6th Annual IEEE Communications Society Conference on Sensor, Mesh and Ad Hoc Communications and Networks Workshops (SECON Workshops '09), pp (2009) [10] Badii, A., Khan, J., R., Crouch, M., Zickau, S.: Hydra: Networked Embedded System Middleware for Heterogeneous Physical Devices in a Distributed Architecture, Final External Developers Workshops Teaching Materials. (2010) [11] Terziyan, V., Kaykova, O., Zhovtobryukh, D.: UbiRoad: Semantic Middleware for Context- Aware Smart Road Environments. In: Fifth International Conference on Internet and Web Applications and Services (ICIW), pp , Barcelona (2010) [12] Albano et. al., M.: Towards Secure Middleware for Embedded Peer-to-Peer Systems: Objectives and Requirements. In: RSPSI, Innsbruck (2007) [13] Gelernter, D.: Generative Communication in Linda. In: ACM Transactions on Programming Languages and Systems (TOPLAS), vol. 7, issue 1, New York (1985) [14] Liu, D. -L. Y. F., Liang, Y. -D.: A Survey of the Internet of Things. In: The 2010 International Conference on Electronic-Business Intelligence (ICEBI) (2010) [15] Atzori, L., Iera, A., Morabito, G.: The Internet of Things: A Survey. In: Computer Networks, vol. 54, issue 15, pp (2010) [16] Vision and Challenges for Realising the Internet of Things, (2010) 103
11 [17] ASPIRE Architecture and Middleware, %20and%20Middleware.pdf [18] Spiess, P., Karnouskos, S., Guinard, D., Savio, D., Baecker, O., Souza, L., Trifa, V.: SOA-Based Integration of the Internet of Things in Enterprise Services. In: IEEE International Conference on Web Services (ICWS), pp Los Angeles (2009) [19] Reiners, R., Zimmermann, A., Jentsch, M., Zhang, Y.: Automizing Home Environments and Supervising Patients at Home with the Hydra Middleware: Application Scenarios using the Hydra Middleware for Embedded Systems. In: Proc. of the First International Workshop on Context-Aware Software Technology and Applications (CASTA), pp New York (2009) [20] [21] Ahamed, S. I.,Zulkernine, M.,Anamanamuri, S.: A Dependable Device Discovery Approach for Pervasive Computing Middleware. In: First International Conference on Availability, Reliability and Security (ARES '06), pp Vienna (2006) [22] Caporuscio, M., Raverdy, P. -G., Issarny, V.: ubisoap: A Service Oriented Middleware for Ubiquitous Networking. In: IEEE Transactions on Services Computing, IEEE computer Society Digital Library,(2010) [23] Cooper, J., James, A., Challenges for Database Management in the Internet of Things. In: IETE Technical Review, vol. 26, no. 5, pp (2009), [24] Katasonov, A., Terziyan, V.: Semantic Agent Programming Language (S- APL): A Middleware for the Semantic Web.In: IEEE International Conference on Semantic Computing, pp santa Clara (2008) [25] SAP NETWEAVER, [26] FIPA Device Ontology Specification (Approved for Experimental, as on 2002/05/10), [27] [28] [29] Soma Bandyopadhyay, Munmun Sengupta, Souvik Maiti, Subhajit Dutta A Survey of Middleware for Internet of Things CoNeCo 2011, Ankara, Turkey, June 26-28, [30] Authors Soma Bandyopadhyay has more than 13 years of industry experience in the area of Embedded Systems, Digital Signal Processor, Protocol and Wireless Communications and ubiquitous computing. Since 2003 has been associated with Innovation lab of TATA Consultancy Services (TCS) as senior scientist. Presently her prime focus area is ubiquitous and sensor network and computation, wireless communication- 4G-next generation broadband wireless MAC and Physical layer design, development & research activity. She has contributed towards the IEEE standard body on behalf of TCS. At present she is leading the research and development activity in interoperability and adaptability aspects of ubiquitous computing. Academically she is an M.Tech & B.Tech in Computer Science & Engineering from the University of Calcutta, India. She did her graduation in Physics (Hons.) from the same university. 104
12 Munmun Sengupta is working as a researcher in Innovation Lab of TATA Consultancy Services, India, in ubiquitous computing domain, mainly in middlewares with having 7 years of Industry experience. She has worked on the development of various wireless mobile communication technologies like WCDMA, UMTS, LTE. She has received her Bachelor of Technology degree in Electronics and Communication engineering from Sikkim Manipal University of Health, Medical and Technological Sciences, India in Souvik Maiti is working in the domain of media and informatics in TATA Consultancy Services, India, having 6 years of Industry experience. He has worked on various wireless communication technologies like LTE, WiMax, Bluetooth, n, and embedded platform development. He has received the Bachelor of Technology degree in Electronics and Communication engineering from the Sikkim Manipal University of Health, Medical and Technological Sciences, India and Diploma in Embedded System from the Jadavpur University in 2004 and 2005 respectively. Subhajit Dutta is working in the domain of Performance Optimization in Business Framework in TATA Consultancy Services, having 3 years of experience. He has worked on IPv6, OSGi platform, and interoperation aspects of middleware. He has received the Bachelor of Technology degree in Computer Science and Engineering from West Bengal University of Technology in
Middleware support for the Internet of Things
 Middleware support for the Internet of Things Karl Aberer, Manfred Hauswirth, Ali Salehi School of Computer and Communication Sciences Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) CH-1015 Lausanne,
Middleware support for the Internet of Things Karl Aberer, Manfred Hauswirth, Ali Salehi School of Computer and Communication Sciences Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) CH-1015 Lausanne,
ARCHITECTURE SUPPORTING DISCOVERY AND MANAGEMENT OF HETEROGENEOUS SENSORS FOR SMART SYSTEM USING GENERIC MIDDLEWARE
 ARCHITECTURE SUPPORTING DISCOVERY AND MANAGEMENT OF HETEROGENEOUS SENSORS FOR SMART SYSTEM USING GENERIC MIDDLEWARE Soma Bandyopadhyay 1 and Abhijan Bhattacharyya 1 1 Innovation Lab, Tata Consultancy Services
ARCHITECTURE SUPPORTING DISCOVERY AND MANAGEMENT OF HETEROGENEOUS SENSORS FOR SMART SYSTEM USING GENERIC MIDDLEWARE Soma Bandyopadhyay 1 and Abhijan Bhattacharyya 1 1 Innovation Lab, Tata Consultancy Services
NETCONF-based Integrated Management for Internet of Things using RESTful Web Services
 NETCONF-based Integrated Management for Internet of Things using RESTful Web Services Hui Xu, Chunzhi Wang, Wei Liu and Hongwei Chen School of Computer Science, Hubei University of Technology, Wuhan, China
NETCONF-based Integrated Management for Internet of Things using RESTful Web Services Hui Xu, Chunzhi Wang, Wei Liu and Hongwei Chen School of Computer Science, Hubei University of Technology, Wuhan, China
A Survey Study on Monitoring Service for Grid
 A Survey Study on Monitoring Service for Grid Erkang You erkyou@indiana.edu ABSTRACT Grid is a distributed system that integrates heterogeneous systems into a single transparent computer, aiming to provide
A Survey Study on Monitoring Service for Grid Erkang You erkyou@indiana.edu ABSTRACT Grid is a distributed system that integrates heterogeneous systems into a single transparent computer, aiming to provide
Secure Semantic Web Service Using SAML
 Secure Semantic Web Service Using SAML JOO-YOUNG LEE and KI-YOUNG MOON Information Security Department Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute 161 Gajeong-dong, Yuseong-gu, Daejeon KOREA
Secure Semantic Web Service Using SAML JOO-YOUNG LEE and KI-YOUNG MOON Information Security Department Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute 161 Gajeong-dong, Yuseong-gu, Daejeon KOREA
Performance Evaluation of Large-Scale Wireless Sensor Networks Communication Protocols that can be Integrated in a Smart City
 Performance Evaluation of Large-Scale Wireless Sensor Networks Communication Protocols that can be Integrated in a Smart City A. Lavric 1, V. Popa 2 PhD.,Computers, Department of Electronics and Automation,
Performance Evaluation of Large-Scale Wireless Sensor Networks Communication Protocols that can be Integrated in a Smart City A. Lavric 1, V. Popa 2 PhD.,Computers, Department of Electronics and Automation,
Combining SAWSDL, OWL DL and UDDI for Semantically Enhanced Web Service Discovery
 Combining SAWSDL, OWL DL and UDDI for Semantically Enhanced Web Service Discovery Dimitrios Kourtesis, Iraklis Paraskakis SEERC South East European Research Centre, Greece Research centre of the University
Combining SAWSDL, OWL DL and UDDI for Semantically Enhanced Web Service Discovery Dimitrios Kourtesis, Iraklis Paraskakis SEERC South East European Research Centre, Greece Research centre of the University
SOA-based Integration of the Internet of Things in Enterprise Services
 SOA-based Integration of the Internet of Things in Enterprise s Patrik Spiess 1, Stamatis Karnouskos 1, Dominique Guinard 1,2, Domnic Savio 1, Oliver Baecker 1,3, Luciana Moreira Sá de Souza 1, and Vlad
SOA-based Integration of the Internet of Things in Enterprise s Patrik Spiess 1, Stamatis Karnouskos 1, Dominique Guinard 1,2, Domnic Savio 1, Oliver Baecker 1,3, Luciana Moreira Sá de Souza 1, and Vlad
Principles and Foundations of Web Services: An Holistic View (Technologies, Business Drivers, Models, Architectures and Standards)
 Principles and Foundations of Web Services: An Holistic View (Technologies, Business Drivers, Models, Architectures and Standards) Michael P. Papazoglou (INFOLAB/CRISM, Tilburg University, The Netherlands)
Principles and Foundations of Web Services: An Holistic View (Technologies, Business Drivers, Models, Architectures and Standards) Michael P. Papazoglou (INFOLAB/CRISM, Tilburg University, The Netherlands)
The ebbits project: from the Internet of Things to Food Traceability
 The ebbits project: from the Internet of Things to Food Traceability Smart AgriMatics2014 Contribution to session 5.2 Meat Information Provenance 18-19 June 2014 Paolo Brizzi Istituto Superiore Mario Boella
The ebbits project: from the Internet of Things to Food Traceability Smart AgriMatics2014 Contribution to session 5.2 Meat Information Provenance 18-19 June 2014 Paolo Brizzi Istituto Superiore Mario Boella
Introduction to Service Oriented Architectures (SOA)
 Introduction to Service Oriented Architectures (SOA) Responsible Institutions: ETHZ (Concept) ETHZ (Overall) ETHZ (Revision) http://www.eu-orchestra.org - Version from: 26.10.2007 1 Content 1. Introduction
Introduction to Service Oriented Architectures (SOA) Responsible Institutions: ETHZ (Concept) ETHZ (Overall) ETHZ (Revision) http://www.eu-orchestra.org - Version from: 26.10.2007 1 Content 1. Introduction
Sensor Information Representation for the Internet of Things
 Sensor Information Representation for the Internet of Things Jiehan Zhou Jiehan.zhou@ee.oulu.fi University of Oulu, Finland Carleton University, Canada Agenda Internet of Things and Challenges Application
Sensor Information Representation for the Internet of Things Jiehan Zhou Jiehan.zhou@ee.oulu.fi University of Oulu, Finland Carleton University, Canada Agenda Internet of Things and Challenges Application
Research on the Model of Enterprise Application Integration with Web Services
 Research on the Model of Enterprise Integration with Web Services XIN JIN School of Information, Central University of Finance& Economics, Beijing, 100081 China Abstract: - In order to improve business
Research on the Model of Enterprise Integration with Web Services XIN JIN School of Information, Central University of Finance& Economics, Beijing, 100081 China Abstract: - In order to improve business
SIP Protocol as a Communication Bus to Control Embedded Devices
 229 SIP Protocol as a Communication Bus to Control Embedded Devices Ramunas DZINDZALIETA Institute of Mathematics and Informatics Akademijos str. 4, Vilnius Lithuania ramunas.dzindzalieta@gmail.com Abstract.
229 SIP Protocol as a Communication Bus to Control Embedded Devices Ramunas DZINDZALIETA Institute of Mathematics and Informatics Akademijos str. 4, Vilnius Lithuania ramunas.dzindzalieta@gmail.com Abstract.
BIG DATA IN THE CLOUD : CHALLENGES AND OPPORTUNITIES MARY- JANE SULE & PROF. MAOZHEN LI BRUNEL UNIVERSITY, LONDON
 BIG DATA IN THE CLOUD : CHALLENGES AND OPPORTUNITIES MARY- JANE SULE & PROF. MAOZHEN LI BRUNEL UNIVERSITY, LONDON Overview * Introduction * Multiple faces of Big Data * Challenges of Big Data * Cloud Computing
BIG DATA IN THE CLOUD : CHALLENGES AND OPPORTUNITIES MARY- JANE SULE & PROF. MAOZHEN LI BRUNEL UNIVERSITY, LONDON Overview * Introduction * Multiple faces of Big Data * Challenges of Big Data * Cloud Computing
Internet of Things (IoT): A vision, architectural elements, and future directions
 SeoulTech UCS Lab 2014-2 st Internet of Things (IoT): A vision, architectural elements, and future directions 2014. 11. 18 Won Min Kang Email: wkaqhsk0@seoultech.ac.kr Table of contents Open challenges
SeoulTech UCS Lab 2014-2 st Internet of Things (IoT): A vision, architectural elements, and future directions 2014. 11. 18 Won Min Kang Email: wkaqhsk0@seoultech.ac.kr Table of contents Open challenges
Overview of the Internet of things
 Overview of the Internet of things Tatiana Kurakova, International Telecommunication Union Place des Nations CH-1211 Geneva, Switzerland Abstract. This article provides an overview of the Internet of things
Overview of the Internet of things Tatiana Kurakova, International Telecommunication Union Place des Nations CH-1211 Geneva, Switzerland Abstract. This article provides an overview of the Internet of things
Horizontal IoT Application Development using Semantic Web Technologies
 Horizontal IoT Application Development using Semantic Web Technologies Soumya Kanti Datta Research Engineer Communication Systems Department Email: Soumya-Kanti.Datta@eurecom.fr Roadmap Introduction Challenges
Horizontal IoT Application Development using Semantic Web Technologies Soumya Kanti Datta Research Engineer Communication Systems Department Email: Soumya-Kanti.Datta@eurecom.fr Roadmap Introduction Challenges
A Semantic Marketplace of Peers Hosting Negotiating Intelligent Agents
 A Semantic Marketplace of Peers Hosting Negotiating Intelligent Agents Theodore Patkos and Dimitris Plexousakis Institute of Computer Science, FO.R.T.H. Vassilika Vouton, P.O. Box 1385, GR 71110 Heraklion,
A Semantic Marketplace of Peers Hosting Negotiating Intelligent Agents Theodore Patkos and Dimitris Plexousakis Institute of Computer Science, FO.R.T.H. Vassilika Vouton, P.O. Box 1385, GR 71110 Heraklion,
The Device Service Bus: A Solution for Embedded Device Integration through Web Services
 The Device Service Bus: A Solution for Embedded Device Integration through Web Services Gustavo Medeiros Araújo Federal University of Santa Catarina Informatics and Statistics Department Florianópolis,
The Device Service Bus: A Solution for Embedded Device Integration through Web Services Gustavo Medeiros Araújo Federal University of Santa Catarina Informatics and Statistics Department Florianópolis,
The Autonomic Management of Ubiquitous Systems meets the Semantic Web
 The Autonomic Management of Ubiquitous Systems meets the Semantic Web Steven Heeps 1, Naranker Dulay 2, Alberto Egon Schaeffer Filho 2, Emil Lupu 2, Morris Sloman 2, Stephen Strowes 1, Joe Sventek 1 1
The Autonomic Management of Ubiquitous Systems meets the Semantic Web Steven Heeps 1, Naranker Dulay 2, Alberto Egon Schaeffer Filho 2, Emil Lupu 2, Morris Sloman 2, Stephen Strowes 1, Joe Sventek 1 1
Myths and Realities of Sensor Network Data Management
 Myths and Realities of Sensor Network Data Management Gustavo Alonso Institute of Pervasive Computing Department of Computer Science Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETH Zurich) alonso@inf.ethz.ch
Myths and Realities of Sensor Network Data Management Gustavo Alonso Institute of Pervasive Computing Department of Computer Science Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETH Zurich) alonso@inf.ethz.ch
Remote Monitoring and Controlling System Based on ZigBee Networks
 Remote Monitoring and Controlling System Based on ZigBee Networks Soyoung Hwang and Donghui Yu* Department of Multimedia Engineering, Catholic University of Pusan, South Korea {soyoung, dhyu}@cup.ac.kr
Remote Monitoring and Controlling System Based on ZigBee Networks Soyoung Hwang and Donghui Yu* Department of Multimedia Engineering, Catholic University of Pusan, South Korea {soyoung, dhyu}@cup.ac.kr
MIDDLEWARE FOR INTERNET OF THINGS
 MASTER THESIS MIDDLEWARE FOR INTERNET OF THINGS Shirin Zarghami FACULTY OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING, MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE SOFTWARE ENGINEERING EXAMINATION COMMITTEE dr. Luís Ferreira Pires dr.
MASTER THESIS MIDDLEWARE FOR INTERNET OF THINGS Shirin Zarghami FACULTY OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING, MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE SOFTWARE ENGINEERING EXAMINATION COMMITTEE dr. Luís Ferreira Pires dr.
Building Web-based Infrastructures for Smart Meters
 Building Web-based Infrastructures for Smart Meters Andreas Kamilaris 1, Vlad Trifa 2, and Dominique Guinard 2 1 University of Cyprus, Nicosia, Cyprus 2 ETH Zurich and SAP Research, Switzerland Abstract.
Building Web-based Infrastructures for Smart Meters Andreas Kamilaris 1, Vlad Trifa 2, and Dominique Guinard 2 1 University of Cyprus, Nicosia, Cyprus 2 ETH Zurich and SAP Research, Switzerland Abstract.
A Generic Database Web Service
 A Generic Database Web Service Erdogan Dogdu TOBB Economics and Technology University Computer Engineering Department Ankara, Turkey edogdu@etu.edu.tr Yanchao Wang and Swetha Desetty Georgia State University
A Generic Database Web Service Erdogan Dogdu TOBB Economics and Technology University Computer Engineering Department Ankara, Turkey edogdu@etu.edu.tr Yanchao Wang and Swetha Desetty Georgia State University
Reducing Configuration Complexity with Next Gen IoT Networks
 Reducing Configuration Complexity with Next Gen IoT Networks Orama Inc. November, 2015 1 Network Lighting Controls Low Penetration - Why? Commissioning is very time-consuming & expensive Network configuration
Reducing Configuration Complexity with Next Gen IoT Networks Orama Inc. November, 2015 1 Network Lighting Controls Low Penetration - Why? Commissioning is very time-consuming & expensive Network configuration
Autonomic computing system for selfmanagement of Machine-to-Machine networks
 Self-IoT 2012, September 17th 2012, San Jose, California, USA in conjunction with ICAC 2012 Autonomic computing system for selfmanagement of Machine-to-Machine networks Mahdi BEN ALAYA, Salma MATOUSSI,Thierry
Self-IoT 2012, September 17th 2012, San Jose, California, USA in conjunction with ICAC 2012 Autonomic computing system for selfmanagement of Machine-to-Machine networks Mahdi BEN ALAYA, Salma MATOUSSI,Thierry
INTERNET OF THINGS 1
 INTERNET OF THINGS 1 OUTLINE Introduction to IoT Technologies Ubiquitous Network Network Management Technologies RFID WSN Embedded Nanotechnology IPv6 UPnP SNMP Challenging Problems Conclusions and Future
INTERNET OF THINGS 1 OUTLINE Introduction to IoT Technologies Ubiquitous Network Network Management Technologies RFID WSN Embedded Nanotechnology IPv6 UPnP SNMP Challenging Problems Conclusions and Future
Remote Sensitive Image Stations and Grid Services
 International Journal of Grid and Distributed Computing 23 Remote Sensing Images Data Integration Based on the Agent Service Binge Cui, Chuanmin Wang, Qiang Wang College of Information Science and Engineering,
International Journal of Grid and Distributed Computing 23 Remote Sensing Images Data Integration Based on the Agent Service Binge Cui, Chuanmin Wang, Qiang Wang College of Information Science and Engineering,
Mobile Devices: Server and Management Lesson 05 Service Discovery
 Mobile Devices: Server and Management Lesson 05 Service Discovery Oxford University Press 2007. All rights reserved. 1 Service discovery An adaptable middleware in a device (or a mobile computing system)
Mobile Devices: Server and Management Lesson 05 Service Discovery Oxford University Press 2007. All rights reserved. 1 Service discovery An adaptable middleware in a device (or a mobile computing system)
Vortex White Paper. Simplifying Real-time Information Integration in Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) Control Systems
 Vortex White Paper Simplifying Real-time Information Integration in Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) Control Systems Version 1.0 February 2015 Andrew Foster, Product Marketing Manager, PrismTech Vortex
Vortex White Paper Simplifying Real-time Information Integration in Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) Control Systems Version 1.0 February 2015 Andrew Foster, Product Marketing Manager, PrismTech Vortex
Setting Up an AS4 System
 INT0697_150625 Setting up an AS4 system V1r0 1 Setting Up an AS4 System 2 Version 1r0 ENTSOG AISBL; Av. de Cortenbergh 100, 1000-Brussels; Tel: +32 2 894 5100; Fax: +32 2 894 5101; info@entsog.eu, www.entsog.eu,
INT0697_150625 Setting up an AS4 system V1r0 1 Setting Up an AS4 System 2 Version 1r0 ENTSOG AISBL; Av. de Cortenbergh 100, 1000-Brussels; Tel: +32 2 894 5100; Fax: +32 2 894 5101; info@entsog.eu, www.entsog.eu,
Wireless Sensor Network: Challenges, Issues and Research
 ISBN 978-93-84468-20-0 Proceedings of 2015 International Conference on Future Computational Technologies (ICFCT'2015) Singapore, March 29-30, 2015, pp. 224-228 Wireless Sensor Network: Challenges, Issues
ISBN 978-93-84468-20-0 Proceedings of 2015 International Conference on Future Computational Technologies (ICFCT'2015) Singapore, March 29-30, 2015, pp. 224-228 Wireless Sensor Network: Challenges, Issues
Charith Pereral, Arkady Zaslavsky, Peter Christen, Ali Salehi and Dimitrios Georgakopoulos (IEEE 2012) Presented By- Anusha Sekar
 Charith Pereral, Arkady Zaslavsky, Peter Christen, Ali Salehi and Dimitrios Georgakopoulos (IEEE 2012) Presented By- Anusha Sekar Introduction Terms and Concepts Mobile Sensors Global Sensor Networks DAM4GSN
Charith Pereral, Arkady Zaslavsky, Peter Christen, Ali Salehi and Dimitrios Georgakopoulos (IEEE 2012) Presented By- Anusha Sekar Introduction Terms and Concepts Mobile Sensors Global Sensor Networks DAM4GSN
Towards service awareness and autonomic features in a SIPenabled
 features in a SIP-enabled network 1 Towards service awareness and autonomic features in a SIPenabled network Guillaume Delaire Laurent Walter Goix Giuseppe Valetto Telecom Italia Lab Outline 2 Context
features in a SIP-enabled network 1 Towards service awareness and autonomic features in a SIPenabled network Guillaume Delaire Laurent Walter Goix Giuseppe Valetto Telecom Italia Lab Outline 2 Context
Information Services for Smart Grids
 Smart Grid and Renewable Energy, 2009, 8 12 Published Online September 2009 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/sgre/). ABSTRACT Interconnected and integrated electrical power systems, by their very dynamic
Smart Grid and Renewable Energy, 2009, 8 12 Published Online September 2009 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/sgre/). ABSTRACT Interconnected and integrated electrical power systems, by their very dynamic
Design of Remote data acquisition system based on Internet of Things
 , pp.32-36 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.214.79.07 Design of Remote data acquisition system based on Internet of Things NIU Ling Zhou Kou Normal University, Zhoukou 466001,China; Niuling@zknu.edu.cn
, pp.32-36 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.214.79.07 Design of Remote data acquisition system based on Internet of Things NIU Ling Zhou Kou Normal University, Zhoukou 466001,China; Niuling@zknu.edu.cn
Classic Grid Architecture
 Peer-to to-peer Grids Classic Grid Architecture Resources Database Database Netsolve Collaboration Composition Content Access Computing Security Middle Tier Brokers Service Providers Middle Tier becomes
Peer-to to-peer Grids Classic Grid Architecture Resources Database Database Netsolve Collaboration Composition Content Access Computing Security Middle Tier Brokers Service Providers Middle Tier becomes
IEEE International Conference on Computing, Analytics and Security Trends CAST-2016 (19 21 December, 2016) Call for Paper
 IEEE International Conference on Computing, Analytics and Security Trends CAST-2016 (19 21 December, 2016) Call for Paper CAST-2015 provides an opportunity for researchers, academicians, scientists and
IEEE International Conference on Computing, Analytics and Security Trends CAST-2016 (19 21 December, 2016) Call for Paper CAST-2015 provides an opportunity for researchers, academicians, scientists and
Using Multi-Agent Systems to Simulate Dynamic Infrastructures Populated with Large Numbers of Web Service Enabled Devices
 Using Multi-Agent Systems to Simulate Dynamic Infrastructures Populated with Large Numbers of Web Service Enabled Devices Stamatis Karnouskos SAP Research Vincenz-Priessnitz-Str 1, D-76131, Karlsruhe,
Using Multi-Agent Systems to Simulate Dynamic Infrastructures Populated with Large Numbers of Web Service Enabled Devices Stamatis Karnouskos SAP Research Vincenz-Priessnitz-Str 1, D-76131, Karlsruhe,
Application of ontologies for the integration of network monitoring platforms
 Application of ontologies for the integration of network monitoring platforms Jorge E. López de Vergara, Javier Aracil, Jesús Martínez, Alfredo Salvador, José Alberto Hernández Networking Research Group,
Application of ontologies for the integration of network monitoring platforms Jorge E. López de Vergara, Javier Aracil, Jesús Martínez, Alfredo Salvador, José Alberto Hernández Networking Research Group,
ActiveVOS Server Architecture. March 2009
 ActiveVOS Server Architecture March 2009 Topics ActiveVOS Server Architecture Core Engine, Managers, Expression Languages BPEL4People People Activity WS HT Human Tasks Other Services JMS, REST, POJO,...
ActiveVOS Server Architecture March 2009 Topics ActiveVOS Server Architecture Core Engine, Managers, Expression Languages BPEL4People People Activity WS HT Human Tasks Other Services JMS, REST, POJO,...
Automatic Configuration and Service Discovery for Networked Smart Devices
 Automatic Configuration and Service Discovery for Networked Smart Devices Günter Obiltschnig Applied Informatics Software Engineering GmbH St. Peter 33 9184 St. Jakob im Rosental Austria Tel: +43 4253
Automatic Configuration and Service Discovery for Networked Smart Devices Günter Obiltschnig Applied Informatics Software Engineering GmbH St. Peter 33 9184 St. Jakob im Rosental Austria Tel: +43 4253
UIMA and WebContent: Complementary Frameworks for Building Semantic Web Applications
 UIMA and WebContent: Complementary Frameworks for Building Semantic Web Applications Gaël de Chalendar CEA LIST F-92265 Fontenay aux Roses Gael.de-Chalendar@cea.fr 1 Introduction The main data sources
UIMA and WebContent: Complementary Frameworks for Building Semantic Web Applications Gaël de Chalendar CEA LIST F-92265 Fontenay aux Roses Gael.de-Chalendar@cea.fr 1 Introduction The main data sources
A Peer-to-Peer Approach to Content Dissemination and Search in Collaborative Networks
 A Peer-to-Peer Approach to Content Dissemination and Search in Collaborative Networks Ismail Bhana and David Johnson Advanced Computing and Emerging Technologies Centre, School of Systems Engineering,
A Peer-to-Peer Approach to Content Dissemination and Search in Collaborative Networks Ismail Bhana and David Johnson Advanced Computing and Emerging Technologies Centre, School of Systems Engineering,
Integration Platforms Problems and Possibilities *
 BULGARIAN ACADEMY OF SCIENCES CYBERNETICS AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES Volume 8, No 2 Sofia 2008 Integration Platforms Problems and Possibilities * Hristina Daskalova, Tatiana Atanassova Institute of Information
BULGARIAN ACADEMY OF SCIENCES CYBERNETICS AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES Volume 8, No 2 Sofia 2008 Integration Platforms Problems and Possibilities * Hristina Daskalova, Tatiana Atanassova Institute of Information
INTERNET OF THE THINGS (IoT): An introduction to wireless sensor networking middleware
 1 INTERNET OF THE THINGS (IoT): An introduction to wireless sensor networking middleware Dr Antoine Bagula ISAT Laboratory, University of Cape Town, South Africa Goal of the lecture 2 The lecture intends
1 INTERNET OF THE THINGS (IoT): An introduction to wireless sensor networking middleware Dr Antoine Bagula ISAT Laboratory, University of Cape Town, South Africa Goal of the lecture 2 The lecture intends
Wireless Sensor Networks Database: Data Management and Implementation
 Sensors & Transducers 2014 by IFSA Publishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com Wireless Sensor Networks Database: Data Management and Implementation Ping Liu Computer and Information Engineering Institute,
Sensors & Transducers 2014 by IFSA Publishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com Wireless Sensor Networks Database: Data Management and Implementation Ping Liu Computer and Information Engineering Institute,
SERVICE DISCOVERY AND MOBILITY MANAGEMENT
 Objectives: 1) Understanding some popular service discovery protocols 2) Understanding mobility management in WLAN and cellular networks Readings: 1. Fundamentals of Mobile and Pervasive Computing (chapt7)
Objectives: 1) Understanding some popular service discovery protocols 2) Understanding mobility management in WLAN and cellular networks Readings: 1. Fundamentals of Mobile and Pervasive Computing (chapt7)
Ontology for Home Energy Management Domain
 Ontology for Home Energy Management Domain Nazaraf Shah 1,, Kuo-Ming Chao 1, 1 Faculty of Engineering and Computing Coventry University, Coventry, UK {nazaraf.shah, k.chao}@coventry.ac.uk Abstract. This
Ontology for Home Energy Management Domain Nazaraf Shah 1,, Kuo-Ming Chao 1, 1 Faculty of Engineering and Computing Coventry University, Coventry, UK {nazaraf.shah, k.chao}@coventry.ac.uk Abstract. This
In ediscovery and Litigation Support Repositories MPeterson, June 2009
 XAM PRESENTATION (extensible TITLE Access GOES Method) HERE In ediscovery and Litigation Support Repositories MPeterson, June 2009 Contents XAM Introduction XAM Value Propositions XAM Use Cases Digital
XAM PRESENTATION (extensible TITLE Access GOES Method) HERE In ediscovery and Litigation Support Repositories MPeterson, June 2009 Contents XAM Introduction XAM Value Propositions XAM Use Cases Digital
Development of Integrated Management System based on Mobile and Cloud service for preventing various dangerous situations
 Development of Integrated Management System based on Mobile and Cloud service for preventing various dangerous situations Ryu HyunKi, Moon ChangSoo, Yeo ChangSub, and Lee HaengSuk Abstract In this paper,
Development of Integrated Management System based on Mobile and Cloud service for preventing various dangerous situations Ryu HyunKi, Moon ChangSoo, Yeo ChangSub, and Lee HaengSuk Abstract In this paper,
Open Sensor Web Architecture: Core Services
 Open Web Architecture: Core s Xingchen Chu 1, Tom Kobialka 2, Bohdan Durnota 1, and Rajkumar Buyya 1 GRIDS Lab 1 and NICTA Victoria Lab 2 Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering The University
Open Web Architecture: Core s Xingchen Chu 1, Tom Kobialka 2, Bohdan Durnota 1, and Rajkumar Buyya 1 GRIDS Lab 1 and NICTA Victoria Lab 2 Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering The University
A Catechistic Method for Traffic Pattern Discovery in MANET
 A Catechistic Method for Traffic Pattern Discovery in MANET R. Saranya 1, R. Santhosh 2 1 PG Scholar, Computer Science and Engineering, Karpagam University, Coimbatore. 2 Assistant Professor, Computer
A Catechistic Method for Traffic Pattern Discovery in MANET R. Saranya 1, R. Santhosh 2 1 PG Scholar, Computer Science and Engineering, Karpagam University, Coimbatore. 2 Assistant Professor, Computer
A very short history of networking
 A New vision for network architecture David Clark M.I.T. Laboratory for Computer Science September, 2002 V3.0 Abstract This is a proposal for a long-term program in network research, consistent with the
A New vision for network architecture David Clark M.I.T. Laboratory for Computer Science September, 2002 V3.0 Abstract This is a proposal for a long-term program in network research, consistent with the
FIPA agent based network distributed control system
 FIPA agent based network distributed control system V.Gyurjyan, D. Abbott, G. Heyes, E. Jastrzembski, C. Timmer, E. Wolin TJNAF, Newport News, VA 23606, USA A control system with the capabilities to combine
FIPA agent based network distributed control system V.Gyurjyan, D. Abbott, G. Heyes, E. Jastrzembski, C. Timmer, E. Wolin TJNAF, Newport News, VA 23606, USA A control system with the capabilities to combine
Lightweight Data Integration using the WebComposition Data Grid Service
 Lightweight Data Integration using the WebComposition Data Grid Service Ralph Sommermeier 1, Andreas Heil 2, Martin Gaedke 1 1 Chemnitz University of Technology, Faculty of Computer Science, Distributed
Lightweight Data Integration using the WebComposition Data Grid Service Ralph Sommermeier 1, Andreas Heil 2, Martin Gaedke 1 1 Chemnitz University of Technology, Faculty of Computer Science, Distributed
PSG College of Technology, Coimbatore-641 004 Department of Computer & Information Sciences BSc (CT) G1 & G2 Sixth Semester PROJECT DETAILS.
 PSG College of Technology, Coimbatore-641 004 Department of Computer & Information Sciences BSc (CT) G1 & G2 Sixth Semester PROJECT DETAILS Project Project Title Area of Abstract No Specialization 1. Software
PSG College of Technology, Coimbatore-641 004 Department of Computer & Information Sciences BSc (CT) G1 & G2 Sixth Semester PROJECT DETAILS Project Project Title Area of Abstract No Specialization 1. Software
Session Initiation Protocol Deployment in Ad-Hoc Networks: a Decentralized Approach
 Session Initiation Protocol Deployment in Ad-Hoc Networks: a Decentralized Approach Simone Leggio, Jukka Manner, Antti Hulkkonen, Kimmo Raatikainen Department of Computer Science University of Helsinki,
Session Initiation Protocol Deployment in Ad-Hoc Networks: a Decentralized Approach Simone Leggio, Jukka Manner, Antti Hulkkonen, Kimmo Raatikainen Department of Computer Science University of Helsinki,
Enterprise Application Integration (EAI) Techniques
 Enterprise Application Integration (EAI) Techniques The development of technology over the years has led to most systems within an organisation existing in heterogeneous environments. That is to say, different
Enterprise Application Integration (EAI) Techniques The development of technology over the years has led to most systems within an organisation existing in heterogeneous environments. That is to say, different
Designing a Smart Multisensor framework based on Beaglebone Black board
 Designing a Smart Multisensor framework based on Beaglebone Black board Angelo Chianese, Francesco Piccialli, and Giuseppe Riccio Department of Electrical Engineering and Information Technologies University
Designing a Smart Multisensor framework based on Beaglebone Black board Angelo Chianese, Francesco Piccialli, and Giuseppe Riccio Department of Electrical Engineering and Information Technologies University
COBASEN (COntext-BAsed Search ENgine) Framework: Discovery of Computing Devices in IoT Environments
 COBASEN (COntext-BAsed Search ENgine) Framework: Discovery of Computing Devices in IoT Environments Willian T. Lunardi 1, Everton de Matos 1, Ramão Tiburski 1, Leonardo A. Amaral 1, Sabrina Marczak 2,
COBASEN (COntext-BAsed Search ENgine) Framework: Discovery of Computing Devices in IoT Environments Willian T. Lunardi 1, Everton de Matos 1, Ramão Tiburski 1, Leonardo A. Amaral 1, Sabrina Marczak 2,
An Approach for FIPA Agent Service Discovery in Mobile Ad Hoc Environments
 An Approach for FIPA Agent Service Discovery in Mobile Ad Hoc Environments Michael Pirker 1, Michael Berger 2, Michael Watzke 2 1 Profactor Produktionsforschungs GmbH, Im Stadtgut A2, 4407 Steyr, Austria
An Approach for FIPA Agent Service Discovery in Mobile Ad Hoc Environments Michael Pirker 1, Michael Berger 2, Michael Watzke 2 1 Profactor Produktionsforschungs GmbH, Im Stadtgut A2, 4407 Steyr, Austria
IOT ARCHITECTURE: A SURVEY
 IOT ARCHITECTURE: A SURVEY 1 SRINJOY NAG CHOWDHURY, 2 KSHITIJ MANOHAR KUHIKAR, 3 SANIYA DHAWAN 1,2,3 ECE Department, Manipal University, Manipal, Karnataka, India Abstract- The Internet of Things, popularly
IOT ARCHITECTURE: A SURVEY 1 SRINJOY NAG CHOWDHURY, 2 KSHITIJ MANOHAR KUHIKAR, 3 SANIYA DHAWAN 1,2,3 ECE Department, Manipal University, Manipal, Karnataka, India Abstract- The Internet of Things, popularly
Open Access Research and Design for Mobile Terminal-Based on Smart Home System
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae The Open Automation and Control Systems Journal, 2015, 7, 479-484 479 Open Access Research and Design for Mobile Terminal-Based on Smart Home System
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae The Open Automation and Control Systems Journal, 2015, 7, 479-484 479 Open Access Research and Design for Mobile Terminal-Based on Smart Home System
Device-centric Code is deployed to individual devices, mostly preprovisioned
 Programming Device Ensembles in the Web of Things A Position Paper for the W3C Workshop on the Web of Things Matias Cuenca, Marcelo Da Cruz, Ricardo Morin Intel Services Division (ISD), Software and Services
Programming Device Ensembles in the Web of Things A Position Paper for the W3C Workshop on the Web of Things Matias Cuenca, Marcelo Da Cruz, Ricardo Morin Intel Services Division (ISD), Software and Services
Chapter 17: M2M-Based Metropolitan Platform for IMS-Enabled Road Traffic Management in IoT
 Chapter 17: M2M-Based Metropolitan Platform for IMS-Enabled Road Traffic Management in IoT Chih-Yuan Lee Department of CSIE National Taipei University 1 Outline Abstract Introduction Background System
Chapter 17: M2M-Based Metropolitan Platform for IMS-Enabled Road Traffic Management in IoT Chih-Yuan Lee Department of CSIE National Taipei University 1 Outline Abstract Introduction Background System
Oracle Data Integrator 11g: Integration and Administration
 Oracle University Contact Us: Local: 1800 103 4775 Intl: +91 80 4108 4709 Oracle Data Integrator 11g: Integration and Administration Duration: 5 Days What you will learn Oracle Data Integrator is a comprehensive
Oracle University Contact Us: Local: 1800 103 4775 Intl: +91 80 4108 4709 Oracle Data Integrator 11g: Integration and Administration Duration: 5 Days What you will learn Oracle Data Integrator is a comprehensive
3rd International Symposium on Big Data and Cloud Computing Challenges (ISBCC-2016) March 10-11, 2016 VIT University, Chennai, India
 3rd International Symposium on Big Data and Cloud Computing Challenges (ISBCC-2016) March 10-11, 2016 VIT University, Chennai, India Call for Papers Cloud computing has emerged as a de facto computing
3rd International Symposium on Big Data and Cloud Computing Challenges (ISBCC-2016) March 10-11, 2016 VIT University, Chennai, India Call for Papers Cloud computing has emerged as a de facto computing
Hybrid Software Architecture Design Pattern Model
 Hybrid Software Architecture Design Pattern Model Asebe Jeware VisionFund Ethiopia, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia asebejeware@yahoo.com Nassir Dino HiLCoE School of Computer Science and Technology, Addis Ababa,
Hybrid Software Architecture Design Pattern Model Asebe Jeware VisionFund Ethiopia, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia asebejeware@yahoo.com Nassir Dino HiLCoE School of Computer Science and Technology, Addis Ababa,
Flattening Enterprise Knowledge
 Flattening Enterprise Knowledge Do you Control Your Content or Does Your Content Control You? 1 Executive Summary: Enterprise Content Management (ECM) is a common buzz term and every IT manager knows it
Flattening Enterprise Knowledge Do you Control Your Content or Does Your Content Control You? 1 Executive Summary: Enterprise Content Management (ECM) is a common buzz term and every IT manager knows it
Design for Management Information System Based on Internet of Things
 Design for Management Information System Based on Internet of Things * School of Computer Science, Sichuan University of Science & Engineering, Zigong Sichuan 643000, PR China, 413789256@qq.com Abstract
Design for Management Information System Based on Internet of Things * School of Computer Science, Sichuan University of Science & Engineering, Zigong Sichuan 643000, PR China, 413789256@qq.com Abstract
Challenges. Department of Informatics University of Oslo. Presenter. kashifd@ifi.uio.no. October 25, 2011
 Internet t of Things: Applications and Challenges Presenter Kashif Dar kashifd@ifi.uio.no INF9910: Cyber Physical Systems Department of Informatics University of Oslo October 25, 2011 Overview Internet
Internet t of Things: Applications and Challenges Presenter Kashif Dar kashifd@ifi.uio.no INF9910: Cyber Physical Systems Department of Informatics University of Oslo October 25, 2011 Overview Internet
STANDARDS FOR AGENTS AND AGENT BASED SYSTEMS (FIPA)
 Course Number: SENG 609.22 Session: Fall, 2003 Course Name: Agent-based Software Engineering Department: Electrical and Computer Engineering Document Type: Tutorial Report STANDARDS FOR AGENTS AND AGENT
Course Number: SENG 609.22 Session: Fall, 2003 Course Name: Agent-based Software Engineering Department: Electrical and Computer Engineering Document Type: Tutorial Report STANDARDS FOR AGENTS AND AGENT
Achieving Semantic Interoperability By UsingComplex Event Processing Technology
 Achieving Semantic Interoperability By UsingComplex Event Processing Technology Margarete Donovang-Kuhlisch Geschäftsbereich Verteidigung IBMDeutschlandGmbH Gorch-Fock-Str. 4 D-53229Bonn mdk@de.ibm.com
Achieving Semantic Interoperability By UsingComplex Event Processing Technology Margarete Donovang-Kuhlisch Geschäftsbereich Verteidigung IBMDeutschlandGmbH Gorch-Fock-Str. 4 D-53229Bonn mdk@de.ibm.com
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Introduction Service Discovery Protocols (SDPs) are network protocols which allow automatic detection of devices and services offered by these devices on a computer network [1].
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Introduction Service Discovery Protocols (SDPs) are network protocols which allow automatic detection of devices and services offered by these devices on a computer network [1].
Pragmatic Web 4.0. Towards an active and interactive Semantic Media Web. Fachtagung Semantische Technologien 26.-27. September 2013 HU Berlin
 Pragmatic Web 4.0 Towards an active and interactive Semantic Media Web Prof. Dr. Adrian Paschke Arbeitsgruppe Corporate Semantic Web (AG-CSW) Institut für Informatik, Freie Universität Berlin paschke@inf.fu-berlin
Pragmatic Web 4.0 Towards an active and interactive Semantic Media Web Prof. Dr. Adrian Paschke Arbeitsgruppe Corporate Semantic Web (AG-CSW) Institut für Informatik, Freie Universität Berlin paschke@inf.fu-berlin
The Ubiquitous Web, UPnP and Smart Homes
 The Ubiquitous Web, UPnP and Smart Homes Franklin Reynolds Nokia Research Center, Cambridge franklin.reynolds@nokia.com 1 NOKIA PCG.PPT / 15 6 2004 / Franklin Reynolds Our Vision "The essence of this vision
The Ubiquitous Web, UPnP and Smart Homes Franklin Reynolds Nokia Research Center, Cambridge franklin.reynolds@nokia.com 1 NOKIA PCG.PPT / 15 6 2004 / Franklin Reynolds Our Vision "The essence of this vision
Towards Secure Middleware for Embedded Peer-to-Peer Systems: Objectives & Requirements
 Michele Albano Antonio Brogi Razvan Popescu Manuel Díaz José A. Dianes Towards Secure Middleware for Embedded Peer-to-Peer Systems: Objectives & Requirements Received: June 1st, 2007 / Accepted: July 2nd,
Michele Albano Antonio Brogi Razvan Popescu Manuel Díaz José A. Dianes Towards Secure Middleware for Embedded Peer-to-Peer Systems: Objectives & Requirements Received: June 1st, 2007 / Accepted: July 2nd,
Event based Enterprise Service Bus (ESB)
 Event based Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) By: Kasun Indrasiri 128213m Supervised By: Dr. Srinath Perera Dr. Sanjiva Weerawarna Abstract With the increasing adaptation of Service Oriented Architecture for
Event based Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) By: Kasun Indrasiri 128213m Supervised By: Dr. Srinath Perera Dr. Sanjiva Weerawarna Abstract With the increasing adaptation of Service Oriented Architecture for
Data Integration Hub for a Hybrid Paper Search
 Data Integration Hub for a Hybrid Paper Search Jungkee Kim 1,2, Geoffrey Fox 2, and Seong-Joon Yoo 3 1 Department of Computer Science, Florida State University, Tallahassee FL 32306, U.S.A., jungkkim@cs.fsu.edu,
Data Integration Hub for a Hybrid Paper Search Jungkee Kim 1,2, Geoffrey Fox 2, and Seong-Joon Yoo 3 1 Department of Computer Science, Florida State University, Tallahassee FL 32306, U.S.A., jungkkim@cs.fsu.edu,
Exploiting peer group concept for adaptive and highly available services
 Exploiting peer group concept for adaptive and highly available services Muhammad Asif Jan Centre for European Nuclear Research (CERN) Switzerland Fahd Ali Zahid, Mohammad Moazam Fraz Foundation University,
Exploiting peer group concept for adaptive and highly available services Muhammad Asif Jan Centre for European Nuclear Research (CERN) Switzerland Fahd Ali Zahid, Mohammad Moazam Fraz Foundation University,
The Interoperability of Wireless Sensor Networks
 The Interoperability of Wireless Sensor Networks Daniela Ballari, Miguel Angel Manso-Callejo, Monica Wachowicz Technical University of Madrid daniela@topografia.upm.es; m.manso@upm.es; m.wachowicz@topografia.upm.es
The Interoperability of Wireless Sensor Networks Daniela Ballari, Miguel Angel Manso-Callejo, Monica Wachowicz Technical University of Madrid daniela@topografia.upm.es; m.manso@upm.es; m.wachowicz@topografia.upm.es
Implementation of Information Integration Platform in Chinese Tobacco Industry Enterprise Based on SOA. Hong-lv Wang, Yong Cen
 Implementation of Information Integration Platform in Chinese Tobacco Industry Enterprise Based on SOA Hong-lv Wang, Yong Cen Information Center, China Tobacco Zhejiang Industrial Co., Ltd Hangzhou, China,
Implementation of Information Integration Platform in Chinese Tobacco Industry Enterprise Based on SOA Hong-lv Wang, Yong Cen Information Center, China Tobacco Zhejiang Industrial Co., Ltd Hangzhou, China,
Sentinet for BizTalk Server SENTINET
 Sentinet for BizTalk Server SENTINET Sentinet for BizTalk Server 1 Contents Introduction... 2 Sentinet Benefits... 3 SOA and APIs Repository... 4 Security... 4 Mediation and Virtualization... 5 Authentication
Sentinet for BizTalk Server SENTINET Sentinet for BizTalk Server 1 Contents Introduction... 2 Sentinet Benefits... 3 SOA and APIs Repository... 4 Security... 4 Mediation and Virtualization... 5 Authentication
TOPOLOGIES NETWORK SECURITY SERVICES
 TOPOLOGIES NETWORK SECURITY SERVICES 1 R.DEEPA 1 Assitant Professor, Dept.of.Computer science, Raja s college of Tamil Studies & Sanskrit,Thiruvaiyaru ABSTRACT--In the paper propose about topology security
TOPOLOGIES NETWORK SECURITY SERVICES 1 R.DEEPA 1 Assitant Professor, Dept.of.Computer science, Raja s college of Tamil Studies & Sanskrit,Thiruvaiyaru ABSTRACT--In the paper propose about topology security
Overview of the Internet of Things {adapted based on Things in 2020 Roadmap for the Future by EU INFSO D.4 NETWORKED ENTERPRISE & RFID}
 Overview of the Internet of Things {adapted based on Things in 2020 Roadmap for the Future by EU INFSO D.4 NETWORKED ENTERPRISE & RFID} John Soldatos Associate Professor, Athens Information Technology
Overview of the Internet of Things {adapted based on Things in 2020 Roadmap for the Future by EU INFSO D.4 NETWORKED ENTERPRISE & RFID} John Soldatos Associate Professor, Athens Information Technology
Development of Integrated Management System based on Mobile and Cloud Service for Preventing Various Hazards
 , pp. 143-150 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijseia.2015.9.7.15 Development of Integrated Management System based on Mobile and Cloud Service for Preventing Various Hazards Ryu HyunKi 1, Yeo ChangSub 1, Jeonghyun
, pp. 143-150 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijseia.2015.9.7.15 Development of Integrated Management System based on Mobile and Cloud Service for Preventing Various Hazards Ryu HyunKi 1, Yeo ChangSub 1, Jeonghyun
RFID. Radio Frequency IDentification: Concepts, Application Domains and Implementation LOGO SPEAKER S COMPANY
 RFID Radio Frequency IDentification: Concepts, Application Domains and Implementation Dominique Guinard, Patrik Fuhrer and Olivier Liechti University of Fribourg, Switzerland Submission ID: 863 2 Agenda
RFID Radio Frequency IDentification: Concepts, Application Domains and Implementation Dominique Guinard, Patrik Fuhrer and Olivier Liechti University of Fribourg, Switzerland Submission ID: 863 2 Agenda
Context Model Based on Ontology in Mobile Cloud Computing
 Context Model Based on Ontology in Mobile Cloud Computing Changbok Jang, Euiin Choi * Dept. Of Computer Engineering, Hannam University, Daejeon, Korea chbjang@dblab.hannam.ac.kr, eichoi@hnu.kr Abstract.
Context Model Based on Ontology in Mobile Cloud Computing Changbok Jang, Euiin Choi * Dept. Of Computer Engineering, Hannam University, Daejeon, Korea chbjang@dblab.hannam.ac.kr, eichoi@hnu.kr Abstract.
Understanding Web personalization with Web Usage Mining and its Application: Recommender System
 Understanding Web personalization with Web Usage Mining and its Application: Recommender System Manoj Swami 1, Prof. Manasi Kulkarni 2 1 M.Tech (Computer-NIMS), VJTI, Mumbai. 2 Department of Computer Technology,
Understanding Web personalization with Web Usage Mining and its Application: Recommender System Manoj Swami 1, Prof. Manasi Kulkarni 2 1 M.Tech (Computer-NIMS), VJTI, Mumbai. 2 Department of Computer Technology,
I. INTRODUCTION NOESIS ONTOLOGIES SEMANTICS AND ANNOTATION
 Noesis: A Semantic Search Engine and Resource Aggregator for Atmospheric Science Sunil Movva, Rahul Ramachandran, Xiang Li, Phani Cherukuri, Sara Graves Information Technology and Systems Center University
Noesis: A Semantic Search Engine and Resource Aggregator for Atmospheric Science Sunil Movva, Rahul Ramachandran, Xiang Li, Phani Cherukuri, Sara Graves Information Technology and Systems Center University
Service-Oriented Architecture and its Implications for Software Life Cycle Activities
 Service-Oriented Architecture and its Implications for Software Life Cycle Activities Grace A. Lewis Software Engineering Institute Integration of Software-Intensive Systems (ISIS) Initiative Agenda SOA:
Service-Oriented Architecture and its Implications for Software Life Cycle Activities Grace A. Lewis Software Engineering Institute Integration of Software-Intensive Systems (ISIS) Initiative Agenda SOA:
Reverse Engineering in Data Integration Software
 Database Systems Journal vol. IV, no. 1/2013 11 Reverse Engineering in Data Integration Software Vlad DIACONITA The Bucharest Academy of Economic Studies diaconita.vlad@ie.ase.ro Integrated applications
Database Systems Journal vol. IV, no. 1/2013 11 Reverse Engineering in Data Integration Software Vlad DIACONITA The Bucharest Academy of Economic Studies diaconita.vlad@ie.ase.ro Integrated applications
Remote support for lab activities in educational institutions
 Remote support for lab activities in educational institutions Marco Mari 1, Agostino Poggi 1, Michele Tomaiuolo 1 1 Università di Parma, Dipartimento di Ingegneria dell'informazione 43100 Parma Italy {poggi,mari,tomamic}@ce.unipr.it,
Remote support for lab activities in educational institutions Marco Mari 1, Agostino Poggi 1, Michele Tomaiuolo 1 1 Università di Parma, Dipartimento di Ingegneria dell'informazione 43100 Parma Italy {poggi,mari,tomamic}@ce.unipr.it,
WBAN Beaconing for Efficient Resource Sharing. in Wireless Wearable Computer Networks
 Contemporary Engineering Sciences, Vol. 7, 2014, no. 15, 755-760 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ces.2014.4686 WBAN Beaconing for Efficient Resource Sharing in Wireless Wearable
Contemporary Engineering Sciences, Vol. 7, 2014, no. 15, 755-760 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ces.2014.4686 WBAN Beaconing for Efficient Resource Sharing in Wireless Wearable
VStore++: Virtual Storage Services for Mobile Devices
 VStore++: Virtual Storage Services for Mobile Devices Sudarsun Kannan, Karishma Babu, Ada Gavrilovska, and Karsten Schwan Center for Experimental Research in Computer Systems Georgia Institute of Technology
VStore++: Virtual Storage Services for Mobile Devices Sudarsun Kannan, Karishma Babu, Ada Gavrilovska, and Karsten Schwan Center for Experimental Research in Computer Systems Georgia Institute of Technology
2.1. The Notion of Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
 Int. J. Innovative Ideas (IJII) www.publishtopublic.com A Review on CRM and CIS: A Service Oriented Approach A Review on CRM and CIS: A Service Oriented Approach Shadi Hajibagheri 1, *, Babak Shirazi 2,
Int. J. Innovative Ideas (IJII) www.publishtopublic.com A Review on CRM and CIS: A Service Oriented Approach A Review on CRM and CIS: A Service Oriented Approach Shadi Hajibagheri 1, *, Babak Shirazi 2,
Getting Started with Service- Oriented Architecture (SOA) Terminology
 Getting Started with - Oriented Architecture (SOA) Terminology Grace Lewis September 2010 -Oriented Architecture (SOA) is a way of designing, developing, deploying, and managing systems it is neither a
Getting Started with - Oriented Architecture (SOA) Terminology Grace Lewis September 2010 -Oriented Architecture (SOA) is a way of designing, developing, deploying, and managing systems it is neither a
