Association between Proton Pump Inhibitors and Clostridium difficile
|
|
|
- Dwayne Ross
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Association between Proton Pump Inhibitors and Clostridium difficile Lauren Petrik and Nicholas Hellebusch, Pharm.D. Candidates 2013, Tatum Mead, Pharm.D. UMKC School of Pharmacy Clostridium difficile, more commonly known as C. diff, is a gram positive anaerobic spore forming bacteria that is responsible for the most common cause of hospital associated diarrhea [1]. In 2005, eighty-four in every one-hundred thousand hospitalized patients developed C. diff and twenty thousand patients were diagnosed with C. diff in an outpatient setting [2]. The mortality rate for elderly, frail patients with a confirmed diagnosis of C. diff is estimated to be as high as 25%. In the general population, C. diff can lead to death, increased length of hospital stay and costs by as much as $5,000 per patient over the 180 days following the diagnosis of C. diff [3]. Established risk factors for the development of C. diff include recent antibiotic use ( previous 90 days; particularly exposure to antibiotics shown to increase the risk of C. diff such as clindamycin, fluroquinolones, 3 rd generation cephalosporins and ampicillin), an extended period of time spent in a healthcare facility (>14 days), increased age (>65 years old), serious underlying illness (immunocompromised patients such as those with HIV or receiving chemo), and proton pump inhibitor (PPI) use. The correlation between PPI use and greater patient susceptibility to the development of C. diff has been controversial. Data suggests there is a link between PPI use and both increased C. diff development and reoccurrence rates. A reoccurrence rate of up to 42% has been shown for patients exposed to PPIs and antibiotics within days following C. diff treatment [4]. On February 8, 2012 the FDA released a statement indicating an increased risk of C. diff associated with PPIs, ranging from 1.4 to 2.75 times greater risk for patients exposed to PPIs compared to patients who did not receive a PPI [5]. The basis for the increased risk is due to decreased acidity in the stomach, resulting from the blockage of the H + /K + ATPase enzyme (also known as a proton pump) in stomach parietal cells. The high acidity of the stomach, or low ph, is the main defense mechanism the body uses to inhibit the colonization and multiplication of bacteria associated with C. diff infections [1]. The higher the ph, the greater the number of bacteria capable of survival. PPIs are the most potent acid suppressing agents on the market and are often given in the hospital for stress ulcer prophylaxis and in the outpatient setting for gastroesophageal disease or dyspepsia. Histamine receptor antagonists (H2RA) have not been studied as thoroughly as PPIs, but are also believed to increase the risk of C. diff. Some studies have shown increased risks of developing C. diff as high as 2-fold for patients taking H2RAs and having risk factors such as gender, age, a hospital stay >7 days and recent antibiotic use, compared to patients not taking H2RAs [1]. Numerous studies conducted have shown an increased association of C. diff and PPIs. Some studies have shown increased risks of developing C. diff as high as 3-fold for patients taking PPIs and having risk factors such as gender, age, a hospital stay >7 days and recent antibiotic use, compared to patients not taking a PPI [1]. C. diff development is not only related to the use of PPIs, higher dosages have been shown to further increase the risk of C. diff development [6]. Patients receiving PPI therapy showed a greater chance of developing C. diff at 77% compared to control patients receiving no PPI therapy at 43% [1]. This compelling evidence should urge healthcare providers to review the necessity to initiate and/or continue PPI therapy. Table 1 [7] below provides appropriate indications, dosing and length of treatment for PPI therapies in accordance with the American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) guidelines. Table 2 [8] below indicates which patients should receive stress ulcer prophylaxis, also in accordance with the AGA guidelines [9]. Studies have shown that as many as 53% of patients on PPIs have no such indication [4]. Even if a patient has an appropriate indication for stress ulcer prophylaxis, it is important the patient be on the lowest effective dose 1
2 and the risks versus benefits for every patient should be evaluated before therapy initiation. Following the appropriate treatment duration and/or upon discharge from a healthcare facility, patients should be reassessed for such risk factors as recent antibiotic use, extended period of time spent in a healthcare facility, increasing age, serious underlying illness, and previous PPI use, when determining necessity for continuation of acid suppression therapy. Healthcare providers can consider tapering the patient off PPI therapy to avoid rebound hypersecretion and discomfort for the patient. Patients that take a moderate to high dose PPI should have the dose reduced 50 percent every week until on the lowest dose. After one week at the lowest dose the medication can be stopped [10]. While PPI use may be an appropriate choice, healthcare providers should remind patients that available over-the-counter PPIs are to be used for short intervals ( 14 days and for no >3 rounds per year). PPIs provide greater acid suppression compared to H2RAs, thus patients are more greatly predisposed to C. diff infection on PPI therapy. Since PPIs do not provide significant efficacy over H2RAs for the treatment of stress ulcer prophylaxis, H2RA therapy should be considered a possible alternative to PPIs [9]. Table 3 [11] below provides dosage recommendations for H2RA therapy. References: 1. Aseeri, M, T Schroeder, et al. "Gastric Acid Suppression by Proton Pump Inhibitors as a Risk Factor for Clostridium difficile-associated Diarrhea in Hospitalized Patients." American Journal of Gastroenterology 103. (2008): Medline. Database. 2 Feb Aberra, F., Katz, J., & Gronczewski, C. (2012). Clostridium difficile colitis. In J. Katz (Ed.), Medscape Reference Retrieved from 3. Dubberke ER, et al. Short- and long-term attributable costs of Clostridium difficile-associated disease in nonsurgical patients> Clin Infect Dis. 2008; 46: Linsky, A, G Kalpana, et al. "Proton Pump Inhibitors and Risk for Recurrent Clostridium difficile Infection." (2010): Medline. Database. 2 Feb PL Detail-Document, Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) and C. difficile. Pharmacist s Letter/Prescriber s Letter. March Howell, M, V Novack, et al. "Iatrogenic Gastric Acid Suppression and the Risk of Nosocomial Clostridium Difficlie Infection." Arch Intern Med (2010): Medline. Database.2 Feb Hester, S. Comparison of proton pump inhibitors. Pharmacist's Letter/Prescriber's Letter 2009;25(3): (Full update January 2010). 8. Hester, S. Overuse of acid suppressing drugs in the hospital. Pharmacist's Letter/Prescriber's Letter 2009;25(7): Guillamondegui, O et al. Practice management guidelines for stress ulcer prophylaxis. Chicago (IL): Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma (EAST); p. [58 references]. 10. Wolfe, M. "Overview and comparison of the proton pump inhibitors for the treatment of acid-related disorders." UpToDate Web.6 Mar < 11. Cupp, M. Histamine H 2 blocker oral dose comparison. Pharmacist's Letter/Prescriber's Letter 2009;25(8):
3 Table 1 Comparison of Proton Pump Inhibitors [7] Drug Indications and Adult Doses Drug Indications and Adult Doses Dexlansoprazole (Dexilant.) Omeprazole (Prilosec, Prilosec OTC) 60 mg QD for up to 8 weeks 30 mg QD for up to 6 months Symptoms from nonerosive GERD: 30 mg QD for 4 weeks for 4-8 weeks Healing gastric ulcers: 40 mg QD for 4-8 weeks for 4-8 weeks 20 mg BID for 10 days (triple therapy) or 40 mg QD for 14 days (dual therapy) Pathologic hypersecretory 60 mg QD. Max=360 mg/day Treatment of heartburn (OTC): for 14 days Omeprazole and sodium bicarbonate (Zegerid, Zegerid OTC) Pantoprazole (Protonix) EE=erosive esophagitis; GERD=gastroesophageal reflux disease Healing benign gastric ulcers: 40 mg QD for 4-8 weeks with EE: for 4-8 weeks Reduce risk of UGI bleeding in critically ill (suspension): 40 mg x1, then in 6-8 hours, then QD Treatment of heartburn (OTC): for 14 days PO: 40 mg QD for up to 8 weeks 40 mg QD Pathologic hypersecretory 40 mg BID. Max = 240 mg/day IV: with EE: 40 mg QD for 7-10 days Pathologic hypersecretory 80 mg Q12H. Max=240 mg/day 3
4 Table 1 Comparison of Proton Pump Inhibitors (continued) [7] Drug Esomeprazole (Nexium) Indications and Adult Doses PO: mg QD for 4-8 weeks 40 mg QD for 10 days (triple therapy) Reducing risk for ulcer with NSAIDs: mg QD for up to 6 months Pathologic hypersecretory 40 mg BID. Max=240 mg/day IV: 40 mg QD for 7-10 days Pathologic hypersecretory 80 mg Q12H. Max=240 mg/day Drug Indications and Adult Doses Drug Indications and Adult Doses Lansoprazole (Prevacid, Prevacid 24HR [OTC]) PO: 15 mg QD for 4 weeks Maintenance for duodenal ulcers: 15 mg QD 30 mg QD for up to 8 weeks Healing benign gastric ulcers: 30 mg QD for up to 8 weeks 15 mg QD for up to 8 weeks 30 mg Q12H for days(dual tx) or 30 mg Q8H for 14 days (triple tx) Reducing risk for ulcer with NSAIDs: 15 mg QD for up to 12 weeks Healing ulcers from NSAIDs: 30 mg QD for up to 8 weeks Treatment of heartburn (OTC): 15 mg QD for 14 days EE=erosive esophagitis; GERD=gastroesophageal reflux disease Rabeprazole (Aciphex) for up to 4 weeks Healing EE or ulcerative GERD: for 4-8 weeks Maintenance for EE or ulcerative GERD: 20 mg BID for 7 days Pathologic hypersecretory 60 mg QD. Max=120 mg/day 4
5 Table 2 - Patients Indicated for Stress Ulcer Prophylaxis [8] Coagulopathy (platelet count <50,000 mm 3, INR >1.5, or aptt >2 times control) Mechanical ventilation for >48 hours History of GI ulceration or bleeding within one year of admission Glasgow Coma score 10 Thermal injury to >35% of body surface area Partial hepatectomy Multiple trauma Transplantation perioperatively in the ICU Spinal cord injury Hepatic failure Two or more of the following risk factors: o Sepsis o ICU stay of more than one week o Occult bleeding lasting at least six days o High-dose corticosteroids (>250 mg/day of hydrocortisone) 5
6 Table 3 Histamine H 2 Blocker Oral Dose Comparison [11] Note: Dose comparison based on manufacturers' recommended oral dosing for patients with normal renal function. Consider indication, side effects, and drug interactions when choosing an H2 blocker. Doses in shaded column provide >80% duodenal or gastric ulcer healing at 8 weeks. 1-6 Abbreviations: BID=twice daily; CrCl=creatinine clearance; GERD=gastroesophageal reflux disease; HS=at bedtime; QID=four times daily Medication Maintenance, duodenal ulcer Active ulcer GERD/erosive esophagitis Cimetidine (Tagamet, generics) a 400 mg HS 800 mg HS (can divide BID for duodenal ulcer) up to 1600 mg HS (duodenal) or 300 mg QID (gastric) b 1600 mg divided BID or QID Famotidine (Pepcid, generics) c 20 mg HS 40 mg HS (can divide BID for duodenal ulcer) 20 mg BID (GERD); 20 or 40 mg BID (erosive esophagitis) Nizatidine (Axid, generics) 150 mg HS d 300 mg HS (duodenal ulcers) or divided BID (duodenal or gastric ulcers) e Ranitidine (Zantac, generics) f 150 mg HS 300 mg HS (duodenal ulcer) or 150 mg BID (duodenal or gastric ulcer) e 150 mg BID 150 mg BID (GERD); 150 mg QID (erosive esophagitis) a. Renal dosing, severe renal impairment: maximum dose 300 mg BID, increasing to TID with caution. 1 b. Optimal for most patients is 800 mg HS. Another regimen that has been used is 300 mg four times daily. A dose of 1600 mg HS may provide faster duodenal ulcer healing in smokers. 1 c. Renal dosing, CrCl <50 ml/min: reduce dose by 50% or extend dosing interval to every hours. 2 d. Renal dosing, CrCl ml/min: 150 mg every other day; CrCl <20 ml/min: 150 mg every third day. 3 e. Renal dosing, CrCl ml/min: 150 mg daily; CrCl <20 ml/min: 150 mg every other day. 3 f. Renal dosing, CrCl <50 ml/min: 150 mg QD, increasing to BID or even further with caution. 4 References for content contained within Table 3: 1. Product information for cimetidine. Mylan Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Morgantown, WV September Product information for Pepcid. Merck & Co., Inc. Whitehouse Station, NJ January Product information for Axid. Reliant Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Liberty Corner, NJ March Product information for Zantac. GlaxoSmithKline. Research Triangle Park, NC April Chase SL, Peterson AM, Wordell CJ. Therapeutic-interchange program for oral histamine H 2 -receptor antagonists. Am J Health Syst Pharm 1998;55: United States Department of Veterans Affairs. Pharmacy Benefits Management Services. Medical Advisory Panel. Drug class review. H 2 -receptor antagonists. Review.pdf. (Accessed July 6, 2009). 6
Inhibit terminal acid secretion from parietal cells by blocking H + /K + - ATPase pump
 Chris J. Taylor, Pharm.D., BCPS Clinical Pharmacist Phoenix VA Health Care System Review pharmacology of PPIs Discuss possible association between PPI use and development of the following: Pneumonia (community-acquired
Chris J. Taylor, Pharm.D., BCPS Clinical Pharmacist Phoenix VA Health Care System Review pharmacology of PPIs Discuss possible association between PPI use and development of the following: Pneumonia (community-acquired
National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Gastritis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is gastritis? Gastritis is a condition in which the stomach
Gastritis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is gastritis? Gastritis is a condition in which the stomach
The JPMorgan Chase Prescription Drug Plan Effective January 1, 2010 (CVS Caremark web site version)
 The JPMorgan Chase Prescription Drug Plan Effective January 1, 2010 (CVS Caremark web site version) OVERVIEW This Bulletin provides an overview of, as well as detail on changes to, the JPMorgan Chase Prescription
The JPMorgan Chase Prescription Drug Plan Effective January 1, 2010 (CVS Caremark web site version) OVERVIEW This Bulletin provides an overview of, as well as detail on changes to, the JPMorgan Chase Prescription
Improving Appropriate Use of Proton Pump Inhibitors as Gastrointestinal Prophylaxis in the Hospital Setting
 Improving Appropriate Use of Proton Pump Inhibitors as Gastrointestinal Prophylaxis in the Hospital Setting DATE Educating for Quality Improvement & Patient Safety 1 The Team Division CS&E Participants
Improving Appropriate Use of Proton Pump Inhibitors as Gastrointestinal Prophylaxis in the Hospital Setting DATE Educating for Quality Improvement & Patient Safety 1 The Team Division CS&E Participants
Awareness of the inappropriate use of GI prophylaxis and its cost. Adverse effects of proton pump inhibitor
 Understand the indication for stress ulcer/gi prophylaxis Awareness of the inappropriate use of GI prophylaxis and its cost Adverse effects of proton pump inhibitor A. 65yo w/ HTN and ESRD on HD p/w left
Understand the indication for stress ulcer/gi prophylaxis Awareness of the inappropriate use of GI prophylaxis and its cost Adverse effects of proton pump inhibitor A. 65yo w/ HTN and ESRD on HD p/w left
Digestive System (continued) Digestive System. Stomach. Peptic Ulcer Disease
 Digestive System Digestive System (continued) Responsible for breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, eliminating wastes Alimentary canal Also known as gastrointestinal tract Reaches from mouth to anus
Digestive System Digestive System (continued) Responsible for breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, eliminating wastes Alimentary canal Also known as gastrointestinal tract Reaches from mouth to anus
BYE-BYE, PPI. A toolkit for deprescribing proton pump inhibitors in EMR-enabled primary care settings
 BYE-BYE, PPI. A toolkit for deprescribing proton pump inhibitors in EMR-enabled primary care settings version 1.0 Don t maintain long-term Proton Pump Inhibitor (PPI) therapy for gastrointestinal symptoms
BYE-BYE, PPI. A toolkit for deprescribing proton pump inhibitors in EMR-enabled primary care settings version 1.0 Don t maintain long-term Proton Pump Inhibitor (PPI) therapy for gastrointestinal symptoms
GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)
 GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD) Gastroesophageal reflux disease is a clinical scenario where the gastric or duodenal contents reflux back up into the esophagus. Reflux esophagitis, however, is a
GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD) Gastroesophageal reflux disease is a clinical scenario where the gastric or duodenal contents reflux back up into the esophagus. Reflux esophagitis, however, is a
Heartburn and Stomach Acid Reflux
 Using the Proton Pump Inhibitors to Treat Heartburn and Stomach Acid Reflux Comparing Effectiveness, Safety, and Price Contents 2: Our Recommendations 4: Welcome 6: What Are PPIs and Who Needs Them? 8:
Using the Proton Pump Inhibitors to Treat Heartburn and Stomach Acid Reflux Comparing Effectiveness, Safety, and Price Contents 2: Our Recommendations 4: Welcome 6: What Are PPIs and Who Needs Them? 8:
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
 3702 Timberline Rd 2555 East 13th St Suite 220 Ft.Collins, CO 80525 Loveland, CO 80537 82001 7251 W. 20th St Greeley, CO 80634 4108 Laramie Cheyenne, WY Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Author(s): Peter
3702 Timberline Rd 2555 East 13th St Suite 220 Ft.Collins, CO 80525 Loveland, CO 80537 82001 7251 W. 20th St Greeley, CO 80634 4108 Laramie Cheyenne, WY Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Author(s): Peter
National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Barrett s Esophagus National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is Barrett s esophagus? Barrett s esophagus is
Barrett s Esophagus National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is Barrett s esophagus? Barrett s esophagus is
Public Assessment Report. Pharmacy to General Sales List Reclassification. Nexium Control 20mg Gastro-Resistant Tablets.
 Public Assessment Report Pharmacy to General Sales List Reclassification Nexium Control 20mg Gastro-Resistant Tablets (Esomeprazole) EMA Agency number: Pfizer Consumer Healthcare Ltd TABLE OF CONTENTS
Public Assessment Report Pharmacy to General Sales List Reclassification Nexium Control 20mg Gastro-Resistant Tablets (Esomeprazole) EMA Agency number: Pfizer Consumer Healthcare Ltd TABLE OF CONTENTS
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) and Barrett s Esophagus (BE)
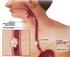 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) and Barrett s Esophagus (BE) Hashem El-Serag, M.D., M.P.H. Dan L. Duncan Professor of Medicine Chief, Gastroenterology and Hepatology Baylor College of Medicine Houston,
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) and Barrett s Esophagus (BE) Hashem El-Serag, M.D., M.P.H. Dan L. Duncan Professor of Medicine Chief, Gastroenterology and Hepatology Baylor College of Medicine Houston,
Research funding was provided by TAP Pharmaceutical Products, Inc.
 DOES THE DOSING FREQUENCY OF PROTON PUMP INHIBITORS (PPIs) AFFECT SUBSEQUENT RESOURCE UTILIZATION AND COSTS AMONG PATIENTS DIAGNOSED WITH GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)? Boulanger L 1, Mody R 2,
DOES THE DOSING FREQUENCY OF PROTON PUMP INHIBITORS (PPIs) AFFECT SUBSEQUENT RESOURCE UTILIZATION AND COSTS AMONG PATIENTS DIAGNOSED WITH GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)? Boulanger L 1, Mody R 2,
Medical Nutrition Therapy for Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Disorders. By: Jalal Hejazi PhD, MSc.
 Medical Nutrition Therapy for Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Disorders By: Jalal Hejazi PhD, MSc. Digestive Disorders Common problem; more than 50 million outpatient visits per year Dietary habits and nutrition
Medical Nutrition Therapy for Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Disorders By: Jalal Hejazi PhD, MSc. Digestive Disorders Common problem; more than 50 million outpatient visits per year Dietary habits and nutrition
A. Ketorolac*** B. Naproxen C. Ibuprofen D. Celecoxib
 1. A man, 66 years of age, with a history of knee osteoarthritis (OA) is experiencing increasing pain at rest and with physical activity. He also has a history of depression and coronary artery disease.
1. A man, 66 years of age, with a history of knee osteoarthritis (OA) is experiencing increasing pain at rest and with physical activity. He also has a history of depression and coronary artery disease.
Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) and Histamine-2 Antagonists (H2As)
 Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35, Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-945-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35, Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-945-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
The Proton Pump Inhibitors
 Drugs to Treat Heartburn and Stomach Acid Reflux: The Proton Pump Inhibitors Comparing Effectiveness, Safety, and Price Our Recommendations Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are a class of very effective and
Drugs to Treat Heartburn and Stomach Acid Reflux: The Proton Pump Inhibitors Comparing Effectiveness, Safety, and Price Our Recommendations Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are a class of very effective and
Medication Management Improvement System Protocol #4 Potentially Inappropriate Use of NSAIDs
 Medication Management Improvement System Protocol #4 Potentially Inappropriate Use of NSAIDs Problem: Use of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) in clients with any one of the following risk
Medication Management Improvement System Protocol #4 Potentially Inappropriate Use of NSAIDs Problem: Use of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) in clients with any one of the following risk
Drug Class Review Proton Pump Inhibitors
 Drug Class Review Proton Pump Inhibitors Final Report Update 5 May 2009 Update 4: May 2006 Update 3: May 2005 Update 2: April 2004 Update 1: April 2003 Original Report: November 2002 The literature on
Drug Class Review Proton Pump Inhibitors Final Report Update 5 May 2009 Update 4: May 2006 Update 3: May 2005 Update 2: April 2004 Update 1: April 2003 Original Report: November 2002 The literature on
Is H. pylori infection...
 Is H. pylori infection... the culprit behind your stomach symptoms? What s really going on in your stomach? You may often have stomach symptoms that you blame on certain foods or stress. You may take over-the-counter
Is H. pylori infection... the culprit behind your stomach symptoms? What s really going on in your stomach? You may often have stomach symptoms that you blame on certain foods or stress. You may take over-the-counter
Clostridium Difficile Colitis. Presented by Mark Skains August 2003
 Clostridium Difficile Colitis Presented by Mark Skains August 2003 What is Clostridium Difficile Gram positive rod Produces spores (hang out in diverticula) Forms Endotoxin A + B which cause diarrhea.
Clostridium Difficile Colitis Presented by Mark Skains August 2003 What is Clostridium Difficile Gram positive rod Produces spores (hang out in diverticula) Forms Endotoxin A + B which cause diarrhea.
Potential Savings from Generic Drugs in Upstate New York
 T H E F A C T S A B O U T Potential Savings from Generic Drugs in Upstate New York $880 Million in Potential Savings for Upstate New York Counties Finger Lakes Region $141 million Western New York Region
T H E F A C T S A B O U T Potential Savings from Generic Drugs in Upstate New York $880 Million in Potential Savings for Upstate New York Counties Finger Lakes Region $141 million Western New York Region
What can I eat? Peptic ulcers. What are peptic ulcers? What tests are needed? Will the ulcer come back? What causes a peptic ulcer?
 In association with: INFORMATION ABOUT Peptic ulcers www.corecharity.org.uk What are peptic ulcers? What causes a peptic ulcer? How are NSAIDs and aspirin involved? How do I know if I ve got an ulcer?
In association with: INFORMATION ABOUT Peptic ulcers www.corecharity.org.uk What are peptic ulcers? What causes a peptic ulcer? How are NSAIDs and aspirin involved? How do I know if I ve got an ulcer?
Tapered Withdrawal of a Proton Pump Inhibitor to Prevent Rebound Acid-Related Symptoms
 Akin Oyalowo CRC Rotation IRB Proposal August 8, 2012 Tapered Withdrawal of a Proton Pump Inhibitor to Prevent Rebound Acid-Related Symptoms A. Study Purpose and Rationale Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs)
Akin Oyalowo CRC Rotation IRB Proposal August 8, 2012 Tapered Withdrawal of a Proton Pump Inhibitor to Prevent Rebound Acid-Related Symptoms A. Study Purpose and Rationale Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs)
Ulcers and Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Protecting Your Health
 AMERICAN COLLEGE OF GASTROENTEROLOGY American College of Gastroenterology 6400 Goldsboro Road, Suite 450 Bethesda, MD 20817 www.acg.gi.org Ulcers and Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Protecting Your Health What
AMERICAN COLLEGE OF GASTROENTEROLOGY American College of Gastroenterology 6400 Goldsboro Road, Suite 450 Bethesda, MD 20817 www.acg.gi.org Ulcers and Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Protecting Your Health What
Proton pump inhibitors
 Proton pump inhibitors This brochure gives you information about acid reflux and some of the prescription medicines commonly used to manage it. You will learn how these medicines compare and get important
Proton pump inhibitors This brochure gives you information about acid reflux and some of the prescription medicines commonly used to manage it. You will learn how these medicines compare and get important
Audit of Six Ulcer Treatment Drugs Reimbursed Under the Indiana Medicaid Prescription Drug Program (A-06-92-00007)
 c \L.i( #I f: y**.a*, a ; % Q4 t im Wll DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Office of inspector General :, Memorandum ~~flpipqly. Principal Deputy inspector General To Audit of Six Ulcer Treatment Drugs
c \L.i( #I f: y**.a*, a ; % Q4 t im Wll DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Office of inspector General :, Memorandum ~~flpipqly. Principal Deputy inspector General To Audit of Six Ulcer Treatment Drugs
understanding GI bleeding
 understanding GI bleeding a consumer education brochure American College of Gastroenterology 4900B South 31st Street, Arlington, VA 22206 703-820-7400 www.acg.gi.org American College of Gastroenterology
understanding GI bleeding a consumer education brochure American College of Gastroenterology 4900B South 31st Street, Arlington, VA 22206 703-820-7400 www.acg.gi.org American College of Gastroenterology
Upper Endoscopy (EGD)
 Upper Endoscopy (EGD) Appointment Information: Patient Name: MRN: Physician Name: Location: _ For information on Directions, please visit: http://www.brighamandwomens.org/general/directions/directions.aspx
Upper Endoscopy (EGD) Appointment Information: Patient Name: MRN: Physician Name: Location: _ For information on Directions, please visit: http://www.brighamandwomens.org/general/directions/directions.aspx
Antimicrobial Stewardship for Hospital Acquired Infection Prevention: Focus on C. difficile infection
 Antimicrobial Stewardship for Hospital Acquired Infection Prevention: Focus on C. difficile infection Emi Minejima, PharmD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pharmacy USC School of Pharmacy [email protected]
Antimicrobial Stewardship for Hospital Acquired Infection Prevention: Focus on C. difficile infection Emi Minejima, PharmD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pharmacy USC School of Pharmacy [email protected]
Proton Pump Inhibitor Utilization Patterns in Infants
 Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 45:421 427 # 2007 by European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition and North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology,
Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 45:421 427 # 2007 by European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition and North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology,
PATIENTS AND METHODS
 symptoms 5. Heartburn is also common and the sufferers attribute symptoms to various lifestyle events, including diet and stress. In all these cases antacid usage is the commonest mode of therapy 6. Antacid
symptoms 5. Heartburn is also common and the sufferers attribute symptoms to various lifestyle events, including diet and stress. In all these cases antacid usage is the commonest mode of therapy 6. Antacid
Develop an understanding of the differential diagnosis of pseudomembranous colitis
 Update on Clostridium difficile Colitis Clostridium difficile infection has recently emerged in populations without any known risk factors. This presentation will focus on the historical background, diagnosis,
Update on Clostridium difficile Colitis Clostridium difficile infection has recently emerged in populations without any known risk factors. This presentation will focus on the historical background, diagnosis,
DVT/PE Management with Rivaroxaban (Xarelto)
 DVT/PE Management with Rivaroxaban (Xarelto) Rivaroxaban is FDA approved for the acute treatment of DVT and PE and reduction in risk of recurrence of DVT and PE. FDA approved indications: Non valvular
DVT/PE Management with Rivaroxaban (Xarelto) Rivaroxaban is FDA approved for the acute treatment of DVT and PE and reduction in risk of recurrence of DVT and PE. FDA approved indications: Non valvular
The author has no disclosures
 Mary Bradbury, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Pharmacy Specialist, Cardiac Surgery September 18, 2012 [email protected] This presentation will discuss unlabeled and investigational use of products The author
Mary Bradbury, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Pharmacy Specialist, Cardiac Surgery September 18, 2012 [email protected] This presentation will discuss unlabeled and investigational use of products The author
Treatment Guide Swallowing and Esophageal Disorders
 Treatment Guide Swallowing and Esophageal Disorders Esophageal disorders especially those involving swallowing problems affect more than 15 million Americans of all ages. For many, they re temporary issues
Treatment Guide Swallowing and Esophageal Disorders Esophageal disorders especially those involving swallowing problems affect more than 15 million Americans of all ages. For many, they re temporary issues
Dabigatran (Pradaxa) Guidelines
 Dabigatran (Pradaxa) Guidelines Dabigatran is a new anticoagulant for reducing the risk of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation. Dabigatran is a direct thrombin inhibitor, similar to warfarin, without
Dabigatran (Pradaxa) Guidelines Dabigatran is a new anticoagulant for reducing the risk of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation. Dabigatran is a direct thrombin inhibitor, similar to warfarin, without
Treatments, Tapers, and Transplants: Guidelines and Options for Complicated C. diff Patients MIA A. TAORMINA, DO, FACOI
 Treatments, Tapers, and Transplants: Guidelines and Options for Complicated C. diff Patients MIA A. TAORMINA, DO, FACOI DUPAGE MEDICAL GROUP INFECTIOUS DISEASE Objectives To discuss the epidemiology and
Treatments, Tapers, and Transplants: Guidelines and Options for Complicated C. diff Patients MIA A. TAORMINA, DO, FACOI DUPAGE MEDICAL GROUP INFECTIOUS DISEASE Objectives To discuss the epidemiology and
Pharmacy Benefit Program (Central Region Products)
 In this section Page General Information About Pharmaceuticals 6.1 Pharmaceutical services 6.1 Premier pharmacy networks 6.1 Pharmaceuticals: The Formulary 6.1 Drug formulary for physicians 6.1 The use
In this section Page General Information About Pharmaceuticals 6.1 Pharmaceutical services 6.1 Premier pharmacy networks 6.1 Pharmaceuticals: The Formulary 6.1 Drug formulary for physicians 6.1 The use
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are
 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY Proton Pump Inhibitors: An Update BRUCE T. VANDERHOFF, M.D., and RUNDSARAH M. TAHBOUB, M.D. Grant Medical Center, Columbus, Ohio Since their introduction in the late 1980s, proton
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY Proton Pump Inhibitors: An Update BRUCE T. VANDERHOFF, M.D., and RUNDSARAH M. TAHBOUB, M.D. Grant Medical Center, Columbus, Ohio Since their introduction in the late 1980s, proton
Clostridium difficile Infection (CDI) Gail Bennett, RN, MSN, CIC
 Clostridium difficile Infection (CDI) Gail Bennett, RN, MSN, CIC 1 Clostridium difficile (C.difficile) Antibiotic induced diarrhea Can cause pseudomembranous colitis Most common cause of acute infectious
Clostridium difficile Infection (CDI) Gail Bennett, RN, MSN, CIC 1 Clostridium difficile (C.difficile) Antibiotic induced diarrhea Can cause pseudomembranous colitis Most common cause of acute infectious
Long Term PPI Use and Associated Complications
 Long Term PPI Use and Associated Complications September 2014 Jessica Farrell, Pharm.D Co-Director Steffens Scleroderma Center Assistant Professor of Pharmacy Practice Albany College of Pharmacy and Health
Long Term PPI Use and Associated Complications September 2014 Jessica Farrell, Pharm.D Co-Director Steffens Scleroderma Center Assistant Professor of Pharmacy Practice Albany College of Pharmacy and Health
Update on Antiplatelets and anticoagulants. Outlines. Antiplatelets and Anticoagulants 1/23/2013. Timir Paul, MD, PhD
 Update on Antiplatelets and anticoagulants Timir Paul, MD, PhD Antiplatelets Indications Doses Long term use (beyond 12 months) ASA and combination use of NSAIDS ASA resistance Plavix resistance Plavix
Update on Antiplatelets and anticoagulants Timir Paul, MD, PhD Antiplatelets Indications Doses Long term use (beyond 12 months) ASA and combination use of NSAIDS ASA resistance Plavix resistance Plavix
Treatments for Barrett s Oesophagus
 Treatments for Barrett s Oesophagus Introduction This leaflet describes the various ways in which Barrett s Oesophagus is treated. It has been produced in association with Heartburn Cancer UK (HCUK), a
Treatments for Barrett s Oesophagus Introduction This leaflet describes the various ways in which Barrett s Oesophagus is treated. It has been produced in association with Heartburn Cancer UK (HCUK), a
Express Scripts/Medco Prescription Plan Information For Drug Coverage Review, Prior Authorization Process and Personalized Medicine Information
 Express Scripts/Medco Prescription Plan Information For Drug Coverage Review, Prior Authorization Process and Personalized Medicine Information The endowed health plan offers faculty and staff members
Express Scripts/Medco Prescription Plan Information For Drug Coverage Review, Prior Authorization Process and Personalized Medicine Information The endowed health plan offers faculty and staff members
Harvoni (Ledipasvir/Sofosbuvir) Treatment Agreement
 Harvoni (Ledipasvir/Sofosbuvir) Treatment Agreement Liver Disease & Hepatitis Program Providers: Brian McMahon, MD; Youssef Barbour, MD; Lisa Townshend-Bulson, FNP-C; Annette Hewitt, FNP-C; Prabhu Gounder,
Harvoni (Ledipasvir/Sofosbuvir) Treatment Agreement Liver Disease & Hepatitis Program Providers: Brian McMahon, MD; Youssef Barbour, MD; Lisa Townshend-Bulson, FNP-C; Annette Hewitt, FNP-C; Prabhu Gounder,
Scleroderma Education Program. Chapter 4. Gastrointestinal Tract
 Scleroderma Education Program Chapter 4 Gastrointestinal Tract Chapter 4-1 Chapter Highlights 1. Learn about how the GI tract works. 2. What happens when things go wrong? -Appetite loss -Difficulty chewing
Scleroderma Education Program Chapter 4 Gastrointestinal Tract Chapter 4-1 Chapter Highlights 1. Learn about how the GI tract works. 2. What happens when things go wrong? -Appetite loss -Difficulty chewing
Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea, Clostridium difficile- Associated Diarrhea and Colitis
 Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea, Clostridium difficile- Associated Diarrhea and Colitis ANTIBIOTIC-ASSOCIATED DIARRHEA Disturbance of the normal colonic microflora Leading to alterations in bacterial degradation
Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea, Clostridium difficile- Associated Diarrhea and Colitis ANTIBIOTIC-ASSOCIATED DIARRHEA Disturbance of the normal colonic microflora Leading to alterations in bacterial degradation
Drug Class Review Proton Pump Inhibitors
 Drug Class Review Proton Pump Inhibitors Preliminary Scan Report December 2014 The purpose of Drug Effectiveness Review Project reports is to make available information regarding the comparative clinical
Drug Class Review Proton Pump Inhibitors Preliminary Scan Report December 2014 The purpose of Drug Effectiveness Review Project reports is to make available information regarding the comparative clinical
Novel Oral Anticoagulants (NOACs) Prescriber Update 2013
 Novel Oral Anticoagulants (NOACs) Prescriber Update 2013 Indications/Contraindications Indications Orthopedic VTE Prophylaxis VTE Treatment Stroke Prevention for non-valvular AF Contraindications 150 mg
Novel Oral Anticoagulants (NOACs) Prescriber Update 2013 Indications/Contraindications Indications Orthopedic VTE Prophylaxis VTE Treatment Stroke Prevention for non-valvular AF Contraindications 150 mg
2.5mg SC daily. INR target 2-3 30 mg SC q 12 hr or 40mg daily. 10 mg PO q day (CrCl 30 ml/min). Avoid if < 30 ml/min. 2.
 Anticoagulation dosing at UCDMC (SC=subcutaneously; CI=continuous infusion) Indication Agent Dose Comments Prophylaxis Any or No bleeding risk factors see adult heparin (VTE prophylaxis) IV infusion order
Anticoagulation dosing at UCDMC (SC=subcutaneously; CI=continuous infusion) Indication Agent Dose Comments Prophylaxis Any or No bleeding risk factors see adult heparin (VTE prophylaxis) IV infusion order
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
 GERD Guideline Team Team Leader Joel J Heidelbaugh, MD Family Medicine Team Members R Van Harrison, PhD Medical Education Mark A McQuillan, MD General Medicine Timothy T Nostrant, MD Gastroenterology Initial
GERD Guideline Team Team Leader Joel J Heidelbaugh, MD Family Medicine Team Members R Van Harrison, PhD Medical Education Mark A McQuillan, MD General Medicine Timothy T Nostrant, MD Gastroenterology Initial
Guideline for the Prescribing of Novel Oral Anticoagulants (NOACs): Dabigatran (Pradaxa ), Rivaroxaban (Xarelto ), Apixaban (Eliquis )
 Guideline for the Prescribing of Novel Oral Anticoagulants (NOACs): Dabigatran (Pradaxa ), Rivaroxaban (Xarelto ), Apixaban (Eliquis ) The contents of this CPG are to be used as a guide. Healthcare professionals
Guideline for the Prescribing of Novel Oral Anticoagulants (NOACs): Dabigatran (Pradaxa ), Rivaroxaban (Xarelto ), Apixaban (Eliquis ) The contents of this CPG are to be used as a guide. Healthcare professionals
The Pharmacist s Role in Recognition and Management of Alzheimer s
 10:15am - 11:15am: Breakout 2 - Mental Health Option B: The Pharmacist s Role in Recognition and Management of Alzheimer s ACPE UAN 0107-0000-10-013-L01-P 0.1 CEU/1.0 Hr. Activity Type: Application-Based
10:15am - 11:15am: Breakout 2 - Mental Health Option B: The Pharmacist s Role in Recognition and Management of Alzheimer s ACPE UAN 0107-0000-10-013-L01-P 0.1 CEU/1.0 Hr. Activity Type: Application-Based
How To Treat Aneuricaagulation
 Speaker Introduction Jessica Wilhoite, PharmD, BCACP Doctor of Pharmacy: Purdue University Postgraduate Residency Training: PGY1 Pharmacy Practice St. Vincent Hospital PGY2 Ambulatory Care St. Vincent
Speaker Introduction Jessica Wilhoite, PharmD, BCACP Doctor of Pharmacy: Purdue University Postgraduate Residency Training: PGY1 Pharmacy Practice St. Vincent Hospital PGY2 Ambulatory Care St. Vincent
Omega-3 fatty acids improve the diagnosis-related clinical outcome. Critical Care Medicine April 2006;34(4):972-9
 Omega-3 fatty acids improve the diagnosis-related clinical outcome 1 Critical Care Medicine April 2006;34(4):972-9 Volume 34(4), April 2006, pp 972-979 Heller, Axel R. MD, PhD; Rössler, Susann; Litz, Rainer
Omega-3 fatty acids improve the diagnosis-related clinical outcome 1 Critical Care Medicine April 2006;34(4):972-9 Volume 34(4), April 2006, pp 972-979 Heller, Axel R. MD, PhD; Rössler, Susann; Litz, Rainer
Esomeprazole Versus Other Proton Pump Inhibitors in Erosive Esophagitis: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2006;4:1452 1458 Esomeprazole Versus Other Proton Pump Inhibitors in Erosive Esophagitis: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials IAN M. GRALNEK,*,,, GARETH
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2006;4:1452 1458 Esomeprazole Versus Other Proton Pump Inhibitors in Erosive Esophagitis: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials IAN M. GRALNEK,*,,, GARETH
4/18/14. Background. Evaluation of a Morphine Weaning Protocol in Pediatric Intensive Care Patients. Background. Signs and Symptoms of Withdrawal
 Background 1 Evaluation of a Morphine Weaning Protocol in Pediatric Intensive Care Patients Alyssa Cavanaugh, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Resident Children s Hospital of Michigan **The speaker has no actual or
Background 1 Evaluation of a Morphine Weaning Protocol in Pediatric Intensive Care Patients Alyssa Cavanaugh, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Resident Children s Hospital of Michigan **The speaker has no actual or
New Anticoagulation Options for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation. Joy Wahawisan, Pharm.D., BCPS April 25, 2012
 New Anticoagulation Options for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation Joy Wahawisan, Pharm.D., BCPS April 25, 2012 Stroke in Atrial Fibrillation % Stroke 1991;22:983. Age Range (years) CHADS 2 Risk
New Anticoagulation Options for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation Joy Wahawisan, Pharm.D., BCPS April 25, 2012 Stroke in Atrial Fibrillation % Stroke 1991;22:983. Age Range (years) CHADS 2 Risk
Enoxaparin for long term anticoagulation in patients unsuitable for oral anticoagulants
 Enoxaparin for long term anticoagulation in patients unsuitable for oral anticoagulants Traffic light classification- Amber 2 Information sheet for Primary Care Prescribers Relevant Licensed Indications
Enoxaparin for long term anticoagulation in patients unsuitable for oral anticoagulants Traffic light classification- Amber 2 Information sheet for Primary Care Prescribers Relevant Licensed Indications
Anticoagulation Dosing at UCDMC Indication Agent Standard Dose Comments and Dose Adjustments VTE Prophylaxis All Services UFH 5,000 units SC q 8 h
 Indication Agent Standard Dose Comments and Dose Adjustments VTE Prophylaxis All Services UFH 5,000 units SC q 8 h See EMR adult VTE prophylaxis CI order set Enoxaparin See service specific dosing Assess
Indication Agent Standard Dose Comments and Dose Adjustments VTE Prophylaxis All Services UFH 5,000 units SC q 8 h See EMR adult VTE prophylaxis CI order set Enoxaparin See service specific dosing Assess
Nash Heartburn Treatment Center
 Nash Heartburn Treatment Center a division of Nash Health Care NHCS Mission Statement: To provide superior quality health care services and to help improve the health of the community in a caring, efficient
Nash Heartburn Treatment Center a division of Nash Health Care NHCS Mission Statement: To provide superior quality health care services and to help improve the health of the community in a caring, efficient
New Anticoagulants and GI bleeding
 New Anticoagulants and GI bleeding DR DANNY MYERS MD FRCP(C) CLINICAL ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, UBC Conflicts of Interest None I am unbiased in the use of NOAC s vs Warfarin based on risk benefit
New Anticoagulants and GI bleeding DR DANNY MYERS MD FRCP(C) CLINICAL ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, UBC Conflicts of Interest None I am unbiased in the use of NOAC s vs Warfarin based on risk benefit
STROKE PREVENTION IN ATRIAL FIBRILLATION. TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: ABBREVIATIONS: BACKGROUND:
 STROKE PREVENTION IN ATRIAL FIBRILLATION TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: To guide clinicians in the selection of antithrombotic therapy for the secondary prevention
STROKE PREVENTION IN ATRIAL FIBRILLATION TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: To guide clinicians in the selection of antithrombotic therapy for the secondary prevention
MEDICAL ASSISTANCE HANDBOOK PRIOR AUTHORIZATION OF PHARMACEUTICAL SERVICES. A. Prescriptions That Require Prior Authorization
 MEDICAL ASSISTANCE HBOOK I. Requirements for Prior Authorization of Anticoagulants A. Prescriptions That Require Prior Authorization Prescriptions for Anticoagulants which meet any of the following conditions
MEDICAL ASSISTANCE HBOOK I. Requirements for Prior Authorization of Anticoagulants A. Prescriptions That Require Prior Authorization Prescriptions for Anticoagulants which meet any of the following conditions
Table 1: Approved Memantine Adult Dosage Recommendations 1-6
 About Information on indications for use or diagnosis is assumed to be unavailable. All criteria may be applied retrospectively; prospective application is indicated with an asterisk [*]. The information
About Information on indications for use or diagnosis is assumed to be unavailable. All criteria may be applied retrospectively; prospective application is indicated with an asterisk [*]. The information
MEDICAL ASSISTANCE BULLETIN
 ISSUE DATE June 22, 2015 SUBJECT EFFECTIVE DATE MEDICAL ASSISTANCE BULLETIN NUMBER *See below BY Prior Authorization of Anticoagulants Pharmacy Service Leesa M. Allen, Deputy Secretary Office of Medical
ISSUE DATE June 22, 2015 SUBJECT EFFECTIVE DATE MEDICAL ASSISTANCE BULLETIN NUMBER *See below BY Prior Authorization of Anticoagulants Pharmacy Service Leesa M. Allen, Deputy Secretary Office of Medical
1.1. (Es)omeprazole and vitamin B12 deficiency
 1.1. (Es)omeprazole and Introduction Omeprazole, a substituted benzimidazole, and esomeprazole, the S-isomere of omeprazole belong to the class of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) which strongly reduce gastric
1.1. (Es)omeprazole and Introduction Omeprazole, a substituted benzimidazole, and esomeprazole, the S-isomere of omeprazole belong to the class of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) which strongly reduce gastric
Probiotics for the Treatment of Adult Gastrointestinal Disorders
 Probiotics for the Treatment of Adult Gastrointestinal Disorders Darren M. Brenner, M.D. Division of Gastroenterology Northwestern University, Feinberg School of Medicine Chicago, Illinois What are Probiotics?
Probiotics for the Treatment of Adult Gastrointestinal Disorders Darren M. Brenner, M.D. Division of Gastroenterology Northwestern University, Feinberg School of Medicine Chicago, Illinois What are Probiotics?
CANDIDA INFECTIONS - TREATMENT GUIDELINES IN ADULT
 Page 1 of 6 TITLE: PATIENTS CANDIDA INFECTIONS - TREATMENT GUIDELINES IN ADULT GUIDELINES: These are the 2011 Guidelines for the Treatment of Candida species infections in adult patients. These recommendations
Page 1 of 6 TITLE: PATIENTS CANDIDA INFECTIONS - TREATMENT GUIDELINES IN ADULT GUIDELINES: These are the 2011 Guidelines for the Treatment of Candida species infections in adult patients. These recommendations
Memantine (Namenda ) [Developed, April 2010; Revised, March 2012; March 2014] MEDICAID DRUG USE REVIEW CRITERIA FOR OUTPATIENT USE
![Memantine (Namenda ) [Developed, April 2010; Revised, March 2012; March 2014] MEDICAID DRUG USE REVIEW CRITERIA FOR OUTPATIENT USE Memantine (Namenda ) [Developed, April 2010; Revised, March 2012; March 2014] MEDICAID DRUG USE REVIEW CRITERIA FOR OUTPATIENT USE](/thumbs/29/13621978.jpg) Memantine (Namenda ) [Developed, April 2010; Revised, March 2012; March 2014] MEDICAID DRUG USE REVIEW CRITERIA FOR OUTPATIENT USE Information on indications for use or diagnosis is assumed to be unavailable.
Memantine (Namenda ) [Developed, April 2010; Revised, March 2012; March 2014] MEDICAID DRUG USE REVIEW CRITERIA FOR OUTPATIENT USE Information on indications for use or diagnosis is assumed to be unavailable.
} Most common arrhythmia. } Incidence increases with age. } Anticoagulants approved for AF
 Deniz Yavas, PharmD PGY-2 Ambulatory Care Pharmacy Resident Detroit Veterans Affairs Medical Center } Most common arrhythmia 0.4-1% of Americans (2.2 mil people) 1,2 } Incidence increases with age 6% (65
Deniz Yavas, PharmD PGY-2 Ambulatory Care Pharmacy Resident Detroit Veterans Affairs Medical Center } Most common arrhythmia 0.4-1% of Americans (2.2 mil people) 1,2 } Incidence increases with age 6% (65
Kasey Crosby and Kathy Dexter, MLS, MHA, MPA, PA-C
 Kasey Crosby and Kathy Dexter, MLS, MHA, MPA, PA-C June 11, 2013 Clinical Feature Download: Figure 1. Diagnosis & treatment algorithm for PUD To start this activity, click Begin at the bottom of this page
Kasey Crosby and Kathy Dexter, MLS, MHA, MPA, PA-C June 11, 2013 Clinical Feature Download: Figure 1. Diagnosis & treatment algorithm for PUD To start this activity, click Begin at the bottom of this page
Over-Use of GERD Medications in the NICU
 Over-Use of GERD Medications in the NICU Anna Maria Hibbs, MD, MSCE [email protected] GERD Meds: What do nail polish and the laws of physics have to do with it? Disclosures I have no conflicts of
Over-Use of GERD Medications in the NICU Anna Maria Hibbs, MD, MSCE [email protected] GERD Meds: What do nail polish and the laws of physics have to do with it? Disclosures I have no conflicts of
Recommendations: Other Supportive Therapy of Severe Sepsis*
 Recommendations: Other Supportive Therapy of Severe Sepsis* K. Blood Product Administration 1. Once tissue hypoperfusion has resolved and in the absence of extenuating circumstances, such as myocardial
Recommendations: Other Supportive Therapy of Severe Sepsis* K. Blood Product Administration 1. Once tissue hypoperfusion has resolved and in the absence of extenuating circumstances, such as myocardial
FDA Approved Oral Anticoagulants
 FDA Approved Oral Anticoagulants Generic (Trade Name) Warfarin (Coumadin, Jantoven ) 1 FDA approved indication Prophylaxis and treatment of venous thromboembolism (VTE) Prophylaxis and treatment of thromboembolic
FDA Approved Oral Anticoagulants Generic (Trade Name) Warfarin (Coumadin, Jantoven ) 1 FDA approved indication Prophylaxis and treatment of venous thromboembolism (VTE) Prophylaxis and treatment of thromboembolic
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Overview A urine culture must ALWAYS be interpreted in the context of the urinalysis and patient symptoms. If a patient has no signs of infection on urinalysis, no symptoms of
Urinary Tract Infections Overview A urine culture must ALWAYS be interpreted in the context of the urinalysis and patient symptoms. If a patient has no signs of infection on urinalysis, no symptoms of
H. pylori Eradication Regimens
 H. pylori Eradication Regimens 1-2-3 Cured March 1999 Highlights H. pylori eradication drastically reduces ulcer recurrence in patients with duodenal or gastric ulcers. 7-day triple therapies with a proton
H. pylori Eradication Regimens 1-2-3 Cured March 1999 Highlights H. pylori eradication drastically reduces ulcer recurrence in patients with duodenal or gastric ulcers. 7-day triple therapies with a proton
Proton Pump Inhibitors vs. Histamine 2 -Receptor Antagonists for Stress Ulcer Prophylaxis Battle of the Acid Suppressants
 Proton Pump Inhibitors vs. Histamine 2 -Receptor Antagonists for Stress Ulcer Prophylaxis Battle of the Acid Suppressants Andrew J. Burris, Pharm.D. PGY1 Pharmacy Resident University Health System, San
Proton Pump Inhibitors vs. Histamine 2 -Receptor Antagonists for Stress Ulcer Prophylaxis Battle of the Acid Suppressants Andrew J. Burris, Pharm.D. PGY1 Pharmacy Resident University Health System, San
NHS FORTH VALLEY Guidelines for use of high dose Intravenous Esomeprazole in Adults (Previously called the Hong Kong Protocol)
 NHS FORTH VALLEY Guidelines for use of high dose Intravenous Esomeprazole in Adults (Previously called the Hong Kong Protocol) Date of First Issue 10/05/2010 Approved 16/06/2010 Current Issue Date 18/11/2015
NHS FORTH VALLEY Guidelines for use of high dose Intravenous Esomeprazole in Adults (Previously called the Hong Kong Protocol) Date of First Issue 10/05/2010 Approved 16/06/2010 Current Issue Date 18/11/2015
Patient Group Direction Hospital: Bristol Royal Infirmary Department: UHBristol Thrombosis Service University Hospitals Bristol NHS Foundation Trust.
 Patient Group Direction Hospital: Bristol Royal Infirmary Department: UHBristol Thrombosis Service University Hospitals Bristol NHS Foundation Trust. This Patient Group Direction (PGD) has been written
Patient Group Direction Hospital: Bristol Royal Infirmary Department: UHBristol Thrombosis Service University Hospitals Bristol NHS Foundation Trust. This Patient Group Direction (PGD) has been written
The Role of the Newer Anticoagulants
 The Role of the Newer Anticoagulants WARFARIN = Coumadin DAGIBATRAN = Pradaxa RIVAROXABAN = Xarelto APIXABAN = Eliquis INDICATION DABIGATRAN (Pradaxa) RIVAROXABAN (Xarelto) APIXABAN (Eliquis) Stroke prevention
The Role of the Newer Anticoagulants WARFARIN = Coumadin DAGIBATRAN = Pradaxa RIVAROXABAN = Xarelto APIXABAN = Eliquis INDICATION DABIGATRAN (Pradaxa) RIVAROXABAN (Xarelto) APIXABAN (Eliquis) Stroke prevention
