A Syllabus for the Education and Training of Radiation Oncology Nurses
|
|
|
- Josephine Bryan
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A Syllabus for the Education and Training of Radiation Oncology Nurses VIENNA, 2008 TRAINING COURSE SERIES28
2 TRAINING COURSE SERIES No. 28 A Syllabus for the Education and Training of Radiation Oncology Nurses INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY, VIENNA, 2008
3 The originating Section of this publication in the IAEA was: Applied Radiation Biology and Radiotherapy Section International Atomic Energy Agency Wagramer Strasse 5 P.O. Box 100 A-1400 Vienna, Austria A SYLLABUS FOR THE EDUCATION AND TRAINING OF RADIATION ONCOLOGY NURSES IAEA, VIENNA, 2008 IAEA-TCS-28 ISSN IAEA, 2008 Printed by the IAEA in Austria February 2008
4 FOREWORD A dramatic rise in cancer incidence across the developing world is stretching already limited resources and equipment. Shortages of qualified staff and equipment are growing constraints to treating cancer efficiently. More than 5000 radiotherapy machines are presently needed to help patients fight cancer, yet the entire developing world has only about 2200 such machines. Experts predict a long term crisis in managing cancer, with an estimated five million new patients requiring radiotherapy every year. Meeting the challenge is not simply a matter of providing appropriate equipment. There must be sufficient trained and knowledgeable staff with clinical and medical physics expertise to deliver a safe and effective radiation dose. Appropriate facilities and radiation protection infrastructure for monitoring and regulatory control are needed. Cancer treatment must be carried out in a comprehensive context of prevention, early diagnosis and palliative care. In the early stages of development of a radiotherapy department or unit, the staffing needs of radiotherapy services should also be specifically and carefully addressed. To make radiotherapy available to all patients who need it, human resources should be urgently expanded globally, along with the rational acquisition of additional equipment. The recommended staffing for a basic radiotherapy facility with 1 teletherapy machine, simulator and high dose rate brachytherapy (HDR) should be: 5 radiation oncologists, 4 medical physicists, 7 8 radiotherapy technologists (RTTs), 3 oncology nurses and 1 maintenance engineer. Where possible, training should be undertaken in centres with patient populations, equipment and training programmes relevant to the needs of the country. Radiotherapy staff should also be required to obtain a qualification adequate for registration in their own country. The human resources listed above could treat on average about 1000 patients per year by extending operations to a minimum of 12 hours per day. The equipment and staffing indicated would be sufficient to start operations, but certainly would not be sustainable without adding a training component. Hence, to qualify as a centre of competence a clinic should provide training to replace its own radiotherapy technologists and radiation oncology nurses. In addition, it should be able to provide financial resources to enable academic training for replacement of radiation oncologists and medical physicists as well as on-site clinical training for these professionals. This IAEA syllabus provides the basic contents of an education course for radiation oncology nurses. It is a minimally essential syllabus which can and should be adapted to the particular needs and characteristics of the centre and country. It should be translated and used in a local language version for the training of nurses who plan to join a radiotherapy team. Special thanks are due to A. Berniger, Rambam Medical Center Oncology Institute (Israel); N. El-Khateb, Technical Institute of Nursing (Egypt); M. Fitch, International Society of Nurses in Cancer Care (Canada); A. Kurashima, Hospital do Cancer A.C. Carmargo (Brazil); A. Moret, National Institute of Oncology and Radiobiology (INOR) (Cuba); and D. Tadic, Institute of Oncology and Radiology of Serbia, for their substantial contribution to the drafting and review of this publication. The IAEA officer responsible for this publication was E. Rosenblatt of the Division of Human Health.
5 EDITORIAL NOTE The use of particular designations of countries or territories does not imply any judgement by the publisher, the IAEA, as to the legal status of such countries or territories, of their authorities and institutions or of the delimitation of their boundaries. The mention of names of specific companies or products (whether or not indicated as registered) does not imply any intention to infringe proprietary rights, nor should it be construed as an endorsement or recommendation on the part of the IAEA.
6 CONTENTS 1. GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS The role of the radiation oncology nurse Standards of care Course description Course objectives Participants qualifications Course duration Student evaluation CURRICULUM Role of the radiation oncology nurse Standards of care Standards of professional performance Evidence-based practice Clinical practice Introduction to oncology Pathophysiology Types of cancer Second primary malignant tumours Principles of management Importance of follow-up Psychosocial impact and consequences of cancer diagnosis and treatment Radiotherapy (RT) Historical development of RT Radiotherapy department Quality assurance Principles of radiation Radiotherapy planning process Treatment delivery techniques External beam radiotherapy (Teletherapy) Brachytherapy Combined modality therapy Tissue/organ response General symptoms management Site specific management Radiation induced malignancies Paediatric radiation oncology Common paediatric malignancies treated with RT Special techniques and approaches Dose/technique modifications in children Sedation and anaesthesia Acute effects (site dependent) Late effects Nursing considerations Palliative radiotherapy Definition and purpose... 17
7 Decision making Quality of life (QOL) issues End-of-life care Do-not-resuscitate (DNR) orders Radiotherapy emergencies Spinal cord compression Superior vena cava syndrome Increased intracranial pressure Bleeding Counselling Patient and family education Psychosocial responses Emotional distress Coping, body image Sexuality and sexual dysfunction Spiritual needs Complementary forms of healing Nutrition Ethical considerations Assessment Management Radiation protection Absorbed dose and units ALARA Time: how to minimize exposure time Distance: how to maximize distance Shielding: how to optimize shielding Hazards of radiation exposure Radiation protection committee Radiation monitoring devices Discharge regulations Discharge regulations for patients with permanent prostate implants Patient, family and the general public concerns about radiation Emergency situations Documentation Quality assurance (QA) programme Components of a QA programme RT treatment chart Nursing record (inpatients) or checklist Skin/wound assessment and care Assessment and management of the oral cavity Assessment and management of fatigue Assessment and management of the nutritional status Assessment of the patient to receive brachytherapy or unsealed radionuclides Counselling in brachytherapy Care for the brachytherapy patient treated with sealed or unsealed sources... 22
8 Counselling in external beam radiotherapy Counselling for children and their family Assessment and management of psychosocial/ emotional distress Assessment and evaluation of patient learning Stoma care Assistance in the performance of gynaecological and other brachytherapy procedures Paediatric catheters care Handling of radiotherapy emergencies Lymphoedema care Care of the laryngectomy patient End-of-life care Application of radiation protection principles APPENDIX I: GLOSSARY APPENDIX II: STANDARDIZED NURSING CARE PLANS APPENDIX III: NUTRITIONAL ADVICE APPENDIX IV: PATIENT EDUCATION TOOLS APPENDIX V: GUIDELINES FOR WRITING A CASE STUDY ON A PATIENT RECEIVING RADIOTHERAPY APPENDIX VI: STUDENT EVALUATION SHEET APPENDIX VII: COMMON TERMINOLOGY CRITERIA FOR ADVERSE EVENTS (CTCAE) APPENDIX VIII: RTOG/EORTC LATE MORBIDITY SCORING SCHEME APPENDIX IX: PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF CURRENTLY USED SEALED RADIOACTIVE SOURCES BIBLIOGRAPHY ABBREVIATIONS... 51
9
10 1. GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS 1.1. The role of the radiation oncology nurse The American College of Radiology (ACR) defined the radiation oncology nursing role: The nurse will assess and provide appropriate nursing intervention for the actual and potential problems that the patient and family may experience related to the disease process, treatment course and follow-up period. This role includes the teaching, counselling and support functions needed to assist the patient and family to cope with and adjust to the diagnosis and treatment of cancer. The radiation oncology nurse is a registered professional nurse who functions independently and interdependently with the radiation oncology team in providing quality patient care. The radiation oncology nurse provides clinical care, consultation and education. The radiation oncology nurse may participate in the leadership roles of clinician, educator, consultant, and/or researcher. Using an evidence-based model for practice, the radiation oncology nurse will provide assessment, diagnosis, outcome identification, planning, implementation and evaluation, focusing on the continuum of care to support the patients receiving radiotherapy, their families and caregivers. It is recommended that the minimal background education for the radiation oncology nurse is a baccalaureate degree in nursing. Subsequent training should include a week course, covering the theoretical aspects described in the syllabus as well as clinical practice in a radiation oncology department or unit under the direct supervision of the programme coordinator. All nurses should be licensed to practice nursing in their respective countries. In addition, radiation oncology nursing certification is also recommended Standards of care According to D. Watkins Bruner, M. Haas and T.K. Gosselin-Acomb (see bibliography) Standards of Care pertain to professional nursing activities demonstrated by the radiation oncology nurse through the nursing process. The nursing process is the foundation of clinical decision making and encompasses all significant action taken by nurses in providing oncology care to all patients and families. The overall goal is to influence the overall health, wellbeing and quality of life of patients and families/caregivers across the radiotherapy continuum. Standard I Assessment The radiation oncology nurse assesses the needs of the patient and family throughout the continuum of care. Standard II Diagnosis The radiation oncology nurse collaborates with other disciplines to analyse the assessment data and identify patient and family problems. Standard III Outcome identification The radiation oncology nurse identifies expected, evidence-based nursing interventions, which will guide patient and family outcomes. 1
11 Standard IV Planning The radiation oncology nurse develops and communicates an individualized, comprehensive, measurable plan for interventions to attain expected outcomes. Standard V Implementation The radiation oncology nurse uses evidence-based information to implement the plan of care to achieve the expected outcomes. Standard VI Evaluation The radiation oncology nurse systematically evaluates patient and family responses to interventions and the process of care. Standards of Professional Performance Standards of Professional Performance describe a competent level of behaviour in the professional nursing role. The radiation oncology nurse should be self-directed and purposeful in seeking the necessary knowledge and skills to enhance professional development and clinical outcomes. Standard I Quality of care The radiation oncology nurse systematically evaluates and documents the effectiveness of clinical care. Standard II Accountability The radiation oncology nurse evaluates his or her own nursing practice in relation to professional practice standards, relevant statutes and regulations. Standard III Education The radiation oncology nurse, building upon the fundamentals of nursing, will participate in ongoing education activities and update knowledge pertaining to basic and behavioural sciences, technology and information systems. Standard IV Leadership The radiation oncology nurse serves as a leader, role model, and mentor for the professional development of peers and colleagues. Standard V Ethics The radiation oncology nurse serves as patient and family advocate, protecting personal health information and patient autonomy, dignity and rights in a manner sensitive to spiritual, cultural and ethnic practices. Standard VI Collaboration The radiation oncology nurse collaborates and consults with patient and family, along with the multidisciplinary team, to enhance desired clinical outcomes. Standard VII Research The radiation oncology nurse uses research as the scientific base for all nursing practice and participates in the conduct of research to improve patient outcomes. 2
12 Standard VII Resource utilization The radiation oncology nurse strives to maintain the clinical aspect of the role, ensuring his or her expertise is primarily used for direct patient care, and healthcare institutions should recognize their expertise in allowing them to function at the highest level of patient care. Consideration will be given to patient and family safety, effectiveness of care, and securing of appropriate services and financial resources as needed Course description The didactic portion of this course is designed to prepare the registered nurse to practice in a radiation oncology setting. Course topics include the following: Principles and properties of ionizing radiation and basic concepts of radiobiology; The purposes of radiotherapy as a cancer treatment modality; General principles of patient and family education (radiotherapy specific); Nursing assessment and management of site-specific cancers; Nursing assessment and management of radiotherapy-related symptoms; Psychosocial and supportive care issues; Description of modality-specific management, including newer and specialized techniques; Principles of radiation protection; Radiotherapy palliative care; Radiation oncology resources Course objectives At the completion of the didactic portion of this course, the nurse will be able to: Discuss the principles and purposes of radiotherapy; Describe the basic principles of radiobiology; Assess patients undergoing radiotherapy for actual or potential problems and for general and site-specific side effects; Assess the psychosocial impact of cancer diagnosis and treatment on the patient and family; Formulate a plan of care for a patient receiving radiotherapy, including patient assessment, symptom management, patient/family education, measurable outcomes and evaluation criteria; Teach the patient and family about the radiotherapy procedures and their potential side effects, and provide instruction on appropriate self-care measures; Describe the nursing management of the patient receiving external beam radiotherapy, low dose rate and high dose rate intracavitary brachytherapy Participants qualifications It is recommended that the minimal education for the radiation oncology nurse is a baccalaureate degree in nursing. Subsequent education should include a week course, 3
13 covering the theoretical aspects described in the syllabus as well as clinical practice in a radiation oncology department or unit under the direct supervision of the programme coordinator Course duration weeks, 5 days per week (depending on the local needs of the oncology setting) Student evaluation The final student s evaluation should include all or some of the following elements: Student s assessment sheet of special competencies and practical skills; Submission and approval of a Patient Case Study ; Multiple choice questionnaire (MCQ) final examination; Evaluation of professional development. 4
14 2.1. Role of the radiation oncology nurse Definition of terms Standards of care 2. CURRICULUM Standards of professional performance Evidence-based practice Clinical practice Recommended sources for teaching: WATKINS BRUNER, D., Manual for Radiation Oncology Nursing Practice and Education, (WATKINS BRUNER, D., HAAS, M.L., GOSSELIN-ACOMB, T.K., eds) Oncology Nursing Society, Pittsburgh, PA, 3rd ed (2004) Introduction to oncology Definition of terms Pathophysiology Epidemiology Carcinogenesis Principles of staging Mechanisms of cancer spread Types of cancer Second primary malignant tumours Principles of management Importance of follow-up Psychosocial impact and consequences of cancer diagnosis and treatment Recommended sources for teaching: JONES & BARLETT, A Cancer Source Book for Nurses, American Cancer Society, 8 th Ed. Sundbury, M.A. (2004). LENHARD JR, R.E., OSTEEN, R.T., GENSLER, T., Clinical Oncology, American Cancer Society, Atlanta, GA (2001) Radiotherapy (RT) Radiotherapy is a clinical modality dealing with the use of ionizing radiation in the management of patients with malignant neoplasias (and occasionally benign disease). 5
15 Historical development of RT Radiotherapy department Radiotherapy team Clinical service role of each member of the RT team Quality assurance Principles of radiation Goals of treatment approaches curative vs. palliative Basic concepts of medical radiation physics Radiobiology Radiobiology is the study of events that occur after ionizing radiation is absorbed by a living organism. Ionizing radiation can result in breaking of chemical bonds and, eventually, in biological change. The nature and severity of effects and the time in which they appear depend on the amount and type of radiation absorbed and the rate at which it is administered. Early- and late-responding tissues are affected differently by these factors. Interaction of radiation in cells is random and has no selectivity for any structure or site. Radiosensitivity Cell response Chemical and thermal modifiers of radiation Ionizing radiation Photons Electrons Heavier particles Radiotherapy planning process Treatment plan Simulation process Patient positioning and immobilization techniques Treatment delivery techniques RT machines Cobalt-60 Linacs HDR brachytherapy 6
16 External beam radiotherapy (Teletherapy) External beam radiotherapy (EBRT) is the delivery of radiation from a specified distance to a defined target volume to cure, control or palliate a tumour within the defined field or in special cases as an adjuvant to surgery. The student should be able to describe the basic differences between cobalt-60 and linear accelerator teletherapy units. The principles of external beam radiotherapy techniques and dose prescription should be discussed. Principles Special techniques of radiation delivery Total body irradiation (TBI) Definition Principles and rationale Indications Techniques and doses Toxicity: acute and late Intraoperative radiotherapy (IORT) Image guided radiotherapy (IGRT) Three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy (3D-CRT) Intensity modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) Stereotactic radiotherapy Radiosurgery Recommended sources for teaching: MIESKALSKI, G.B., BRADY, L.W., YAEGER, T.E., CLASS, R., Radiotherapy in Clinical Oncology. (LENHARD Jr., R.E., OSTEEB, R.T., GENSLEER, T., eds) American Cancer Society, Atlanta, GA (2001) Brachytherapy Brachytherapy (BT) is the temporary or permanent placement of a radioactive source into a body cavity (intracavitary), into a hollow organ (intraluminal) or into the tissue (interstitial). Brachytherapy may be used by itself or as an adjunctive treatment in combination with external beam therapy to increase the total dose to a specified target. Brachytherapy is the optimal way of delivering conformal radiotherapy tailored to the shape of the tumour while sparing surrounding normal tissues. Knowledge of specific radionuclide types and techniques is important to the radiation oncology nurse. With temporary sealed source implants, the patient is not radioactive, only the source is radioactive. Once the implanted source is removed, the patient no longer needs to be treated with any special precautions. 7
17 Principles Low dose rate (LDR)/High dose rate (HDR) brachytherapy. Radioactive source therapy Commonly used radioactive elements Special techniques Sealed sources: Co-60, Cs-137, Ir-192, I-125 Unsealed sources: I-131, P-32, Sr-90 Gynaecology (GYN) Prostate Breast Head-and-neck Soft-tissue Sarcomas Nursing considerations Acute and late effects Coordination activities Operating room (OR) techniques and principles Familiarity with GYN applicators and procedures Pain control and anaesthesia Counselling the BT patient and family Recommended sources for teaching: WATKINS BRUNER, D., Radiation Oncology Nursing Practice and Education: Manual for Radiation Oncology Nursing Practice and Education, (WATKINS BRUNER, D., HAAS, M.L., GOSSELIN-ACOMB, T.K., eds) Oncology Nursing Society, Pittsburgh, PA, 3rd ed (2004) Combined modality therapy Concurrent (also called concomitant) chemotherapy is chemotherapy given at the same time as radiotherapy, resulting in a greater effect on the tumour cells than either agent given alone, with acceptable toxicity. The concomitant administration of chemotherapy and radiotherapy has yielded better clinical results than induction or adjuvant chemotherapy. Since the radiation oncology nurse will often be managing the toxicity of these combined modality therapies, she/he should be familiar with this treatment approach and its possible adverse effects. 8
18 Basic concepts in cancer chemotherapy Commonly used chemotherapeutic drugs and radiosensitizers Surgery and radiotherapy Pre-operative Post-operative Recommended sources for teaching: WATKINS BRUNER, D., Radiation Oncology Nursing Practice and Education: Manual for Radiation Oncology Nursing Practice and Education, (WATKINS BRUNER, D., HAAS, M.L., GOSSELIN-ACOMB, T.K., eds) Oncology Nursing Society, Pittsburgh, PA, 3rd ed (2004). Radiation adverse events (Toxicities) Tumours as well as normal tissues are affected by ionizing radiation. The time in which toxicities appear and the severity of effects depend on the amount of radiation absorbed, fractionation and rate at which it is administered. Acute (early) and late toxicities are to be expected. The radiation oncology nurse should be familiar with the identification and management of acute and late adverse events of radiotherapy in the various organs and systems Tissue/organ response Acute effects Sub-acute effects Late effects Generic Consequential General symptoms management Acute skin and mucosal reactions Myelosuppression Fatigue Nutritional status 9
19 Site specific management Central nervous system (CNS) Overview Common cancers Signs and symptoms Diagnoses Treatment approach Prognosis Acute toxicity Alopecia and scalp erythema Ear and external auditory canal Cerebral oedema Nausea and vomiting Late toxicity Cognitive dysfunction Neurological deficits Hearing deficits Visual deficits Brain necrosis Head and Neck Overview Common cancers Signs and symptoms Diagnoses Treatment approach Prognosis 10
20 Acute toxicity Mucositis Dermatitis Oral infections Xerostomia Oesophagitis/pharyngitis Taste changes Late toxicity Taste changes Xerostomia Dental caries Fibrosis Hypothyroidism Radiation myelitis Osteoradionecrosis Breast Overview Common cancers Signs and symptoms Diagnoses Treatment approach Prognosis Acute toxicity Skin reaction Dysphagia Arm oedema Shoulder dysfunction Radiation pneumonitis 11
21 Late toxicity Skin fibrosis Telangiectasia Rib fractures Cardiotoxicity Cosmetic defects Thoracic Overview Common cancers Signs and symptoms Diagnoses Treatment approach Prognosis Acute toxicity Oesophagitis/pharyngitis Taste changes Pneumonitis (acute or sub-acute) Late toxicity Radiation pneumonitis Cardiotoxicity Neurotoxicity Skin fibrosis Gastrointestinal and abdomen Overview Common cancers Signs and symptoms Diagnoses 12
22 Treatment approach Prognosis Acute toxicity Nausea and vomiting Weakness Diarrhoea and enteritis Late toxicity Chronic enteritis Renal dysfunction Liver failure Pelvic Overview Common cancers Signs and symptoms Diagnoses Treatment approach Prognosis Acute toxicity Weakness Diarrhoea and proctitis Cystitis and haematuria Late toxicity Vaginal dryness Chronic enteritis Chronic cystitis Chronic proctitis Infertility 13
23 Sexual dysfunction: male/female Pelvic fibrosis Eyes Overview Common cancers Signs and symptoms Diagnoses Treatment approach Prognosis Acute toxicity Conjunctival oedema and tearing Late toxicity Cataract Retinopathy Soft tissue sarcoma Overview Common types Signs and symptoms Diagnoses Treatment approach Prognosis Acute toxicity Skin reaction Late toxicity Fibrosis Telangiectasia Ulceration 14
24 Skin Overview Deformities Joint dysfunctions Common cancers Signs and symptoms Diagnoses Treatment approach Prognosis Acute toxicity Epilation Erythema Desquamation Dryness Ulceration Late toxicity Hyperpigmentation Fibrosis Telangiectasia Chronic ulceration Recommended sources for teaching: ROSENTHAL, P.E., Complications of Cancer and Cancer Treatment in Clinical Oncology, (LENHARD Jr, R.E., OSTEEN, R.T., GENSLER, T., eds), American Cancer Society, Atlanta, GA (2001) Radiation induced malignancies Definition and criteria Management and prognosis 15
25 2.4. Paediatric radiation oncology Radiotherapy has a significant role in the modern management of a number of paediatric tumours. These include tumours of the central nervous system, Wilm s tumour, neuroblastoma, rhabdomyosarcoma, Ewing s sarcoma and lymphomas. Childhood cancers differ from those that occur in the adult. The majority of childhood cancers arise from the mesodermal germ layer giving rise to sarcomas, while the majority of adult cancers arise from tissue of epithelial origin giving rise to carcinomas. There are special issues associated with treating children with radiation: these include developmental considerations, psychosocial issues, nutritional problems, immobilization and sedation issues and the potential for late radiation effects Common paediatric malignancies treated with RT Special techniques and approaches Dose/technique modifications in children Sedation and anaesthesia Acute effects (site dependent) Late effects Growth retardation Cognitive dysfunctions Organ failure Infertility Cosmetic defects Radiation induced malignancies Nursing considerations Coordination activities Counselling of the paediatric patient and family Recommended sources for teaching: MARCUS, K.C., Pediatric Solid Tumors in Clinical Oncology, (LENHARD Jr, R.E., OSTEEN, R.T., GENSLER, T., eds), American Cancer Society, Atlanta, GA (2001). KLINE, N.E., TOMLINSON, D., (Eds), Pediatric Oncology Nursing: Advanced Clinical Handbook, Springer Publishing Co, New York (2004). 16
26 2.5. Palliative radiotherapy There are many clinical settings in oncology where radiotherapy can either prevent serious clinical problems (paraplegia, blindness) or alleviate the symptoms produced by the tumour or its metastasis (pain, bleeding and obstruction). Palliative radiotherapy is of value in lifethreatening situations, such as profuse bleeding from a tumour or compression of the superior vena cava, in cases of pain secondary to bone metastasis, spinal cord compression or cerebral metastasis. A single treatment or a small number of treatments will often have a significant palliative effect while at the same time being the most cost-effective form of palliation Definition and purpose Decision making Quality of life (QOL) issues Pain Fatigue Comfort Daily activities End-of-life care Do-not-resuscitate (DNR) orders Recommended sources for teaching: KUEBLE, K.K., ESPER, P., (Eds), Palliative Practices from A Z for the Bedside Clinician, Oncology Nursing Society, Pittsburgh, PA (2002). O CONNOR, M., ARANDA, S., Palliative Care Nursing: A Guide to Practice, 2nd ed, Ausmed Publications, London (2003). FAITHFULL, S., WELLS M., Supportive Care in Radiotherapy, Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, UK (2003). KING CR., HINDS, P.S., (Eds), Quality of Life: From Nursing and Patient Perspectives, St. Jude Children s Research Hospital, Jones and Bartlett Publishers, Sudbury MA. 2nd ed, (2003) 2.6. Radiotherapy emergencies An oncological emergency is defined as a potential life-threatening or function-threatening event directly or indirectly related to a patient s neoplasm or subsequent to its treatment. The emergency could be due to direct or indirect compression of organs, occlusion of vital structures such as blood vessels, nerves or airway. Radiotherapy plays a significant role in the acute treatment of these clinical situations. Radiotherapy relieves symptoms by local cytoreduction of the tumour, thereby removing compression to the affected organ or structure. 17
Basic Radiation Therapy Terms
 Basic Radiation Therapy Terms accelerated radiation: radiation schedule in which the total dose is given over a shorter period of time. (Compare to hyperfractionated radiation.) adjuvant therapy (add-joo-vunt):
Basic Radiation Therapy Terms accelerated radiation: radiation schedule in which the total dose is given over a shorter period of time. (Compare to hyperfractionated radiation.) adjuvant therapy (add-joo-vunt):
Radiation therapy involves using many terms you may have never heard before. Below is a list of words you could hear during your treatment.
 Dictionary Radiation therapy involves using many terms you may have never heard before. Below is a list of words you could hear during your treatment. Applicator A device used to hold a radioactive source
Dictionary Radiation therapy involves using many terms you may have never heard before. Below is a list of words you could hear during your treatment. Applicator A device used to hold a radioactive source
Smoking and misuse of certain pain medicines can affect the risk of developing renal cell cancer.
 Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer
 Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
Understanding brachytherapy
 Understanding brachytherapy Brachytherapy Cancer Treatment Legacy Cancer Institute Your health care provider has requested that you receive a type of radiation treatment called brachytherapy as part of
Understanding brachytherapy Brachytherapy Cancer Treatment Legacy Cancer Institute Your health care provider has requested that you receive a type of radiation treatment called brachytherapy as part of
GYNECOLOGIC CANCERS Facts to Help Patients Make an Informed Decision
 RADIATION THERAPY FOR GYNECOLOGIC CANCERS Facts to Help Patients Make an Informed Decision TARGETING CANCER CARE AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR RADIATION ONCOLOGY FACTS ABOUT GYNECOLOGIC CANCERS Gynecologic cancers
RADIATION THERAPY FOR GYNECOLOGIC CANCERS Facts to Help Patients Make an Informed Decision TARGETING CANCER CARE AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR RADIATION ONCOLOGY FACTS ABOUT GYNECOLOGIC CANCERS Gynecologic cancers
FAQ About Prostate Cancer Treatment and SpaceOAR System
 FAQ About Prostate Cancer Treatment and SpaceOAR System P. 4 Prostate Cancer Background SpaceOAR Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) 1. What is prostate cancer? The vast majority of prostate cancers develop
FAQ About Prostate Cancer Treatment and SpaceOAR System P. 4 Prostate Cancer Background SpaceOAR Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) 1. What is prostate cancer? The vast majority of prostate cancers develop
Small cell lung cancer
 Small cell lung cancer Small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs that are found within
Small cell lung cancer Small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs that are found within
Brain Tumor Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumor Treatment Brain Tumors Overview A brain tumor is a group of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. Tumors can directly destroy healthy brain cells. They can
Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumor Treatment Brain Tumors Overview A brain tumor is a group of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. Tumors can directly destroy healthy brain cells. They can
There must be an appropriate administrative structure for each residency program.
 Specific Standards of Accreditation for Residency Programs in Radiation Oncology 2015 VERSION 3.0 INTRODUCTION The purpose of this document is to provide program directors and surveyors with an interpretation
Specific Standards of Accreditation for Residency Programs in Radiation Oncology 2015 VERSION 3.0 INTRODUCTION The purpose of this document is to provide program directors and surveyors with an interpretation
Report series: General cancer information
 Fighting cancer with information Report series: General cancer information Eastern Cancer Registration and Information Centre ECRIC report series: General cancer information Cancer is a general term for
Fighting cancer with information Report series: General cancer information Eastern Cancer Registration and Information Centre ECRIC report series: General cancer information Cancer is a general term for
Proton Therapy. What is proton therapy and how is it used?
 Scan for mobile link. Proton Therapy Proton therapy delivers radiation to tumor tissue in a much more confined way than conventional photon therapy thus allowing the radiation oncologist to use a greater
Scan for mobile link. Proton Therapy Proton therapy delivers radiation to tumor tissue in a much more confined way than conventional photon therapy thus allowing the radiation oncologist to use a greater
Esophageal Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Esophageal Cancer Treatment What is Esophageal Cancer? Esophageal cancer occurs when cancer cells develop in the esophagus, a long, tube-like structure that connects the throat and
Scan for mobile link. Esophageal Cancer Treatment What is Esophageal Cancer? Esophageal cancer occurs when cancer cells develop in the esophagus, a long, tube-like structure that connects the throat and
Colorectal Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Treatment Colorectal cancer overview Colorectal cancer, also called large bowel cancer, is the term used to describe malignant tumors found in the colon and rectum.
Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Treatment Colorectal cancer overview Colorectal cancer, also called large bowel cancer, is the term used to describe malignant tumors found in the colon and rectum.
Thymus Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand what thymus cancer is and what treatment options are available.
 Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too.
 Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
Janusz Skowronek MD, PhD
 Janusz Skowronek MD, PhD Greatpoland Cancer Center Pozna, January 2004 1 1. About Brachytherapy Derived from ancient Greek words for short distance (brachios) and treatment (therapy) and refers to the
Janusz Skowronek MD, PhD Greatpoland Cancer Center Pozna, January 2004 1 1. About Brachytherapy Derived from ancient Greek words for short distance (brachios) and treatment (therapy) and refers to the
PSA Screening for Prostate Cancer Information for Care Providers
 All men should know they are having a PSA test and be informed of the implications prior to testing. This booklet was created to help primary care providers offer men information about the risks and benefits
All men should know they are having a PSA test and be informed of the implications prior to testing. This booklet was created to help primary care providers offer men information about the risks and benefits
Prostate Cancer. What is prostate cancer?
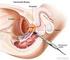 Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam, prostate-specific
Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam, prostate-specific
CMScript. Member of a medical scheme? Know your guaranteed benefits! Issue 7 of 2014
 Background CMScript Member of a medical scheme? Know your guaranteed benefits! Issue 7 of 2014 Prostate cancer is second only to lung cancer as the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in men. It is
Background CMScript Member of a medical scheme? Know your guaranteed benefits! Issue 7 of 2014 Prostate cancer is second only to lung cancer as the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in men. It is
Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT)
 Scan for mobile link. Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) Intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) uses linear accelerators to safely and painlessly deliver precise radiation doses to a tumor while
Scan for mobile link. Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) Intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) uses linear accelerators to safely and painlessly deliver precise radiation doses to a tumor while
RADIATION THERAPY & CANCER
 CANCERCARE MANITOBA Mission Statement CancerCare Manitoba, by an act of the legislature, is responsible for cancer prevention, detection, care, research and education throughout Manitoba. RADIATION THERAPY
CANCERCARE MANITOBA Mission Statement CancerCare Manitoba, by an act of the legislature, is responsible for cancer prevention, detection, care, research and education throughout Manitoba. RADIATION THERAPY
Multiple Myeloma. This reference summary will help you understand multiple myeloma and its treatment options.
 Multiple Myeloma Introduction Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells. Each year, thousands of people find out that they have multiple myeloma. This reference summary will help
Multiple Myeloma Introduction Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells. Each year, thousands of people find out that they have multiple myeloma. This reference summary will help
Prostate Cancer. There is no known association with an enlarged prostate or benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
 Prostate Cancer Definition Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate gland. The prostate is a small, walnut-sized structure that makes up part of a man's reproductive system. It wraps around
Prostate Cancer Definition Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate gland. The prostate is a small, walnut-sized structure that makes up part of a man's reproductive system. It wraps around
Prostate Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Treatment Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam,
Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Treatment Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam,
Brain Cancer. This reference summary will help you understand how brain tumors are diagnosed and what options are available to treat them.
 Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
1400 Telegraph Bloomfield Hills, MI 48302 248-334-6877-Phone number/248-334-6877-fax Number CANCER TREATMENT
 1400 Telegraph Bloomfield Hills, MI 48302 248-334-6877-Phone number/248-334-6877-fax Number CANCER TREATMENT Learning that your pet has a diagnosis of cancer can be overwhelming. We realize that your pet
1400 Telegraph Bloomfield Hills, MI 48302 248-334-6877-Phone number/248-334-6877-fax Number CANCER TREATMENT Learning that your pet has a diagnosis of cancer can be overwhelming. We realize that your pet
M6-1 NOTE. Each major learning point is clearly identified by boldface type throughout the guide and emphasized in the PowerPoint presentation.
 Basics of Cancer Treatment Module 6 Basics of Cancer Treatment Target Audience: Community members Staff of Indian health programs, including Community Health Representatives Contents of Learning Module:
Basics of Cancer Treatment Module 6 Basics of Cancer Treatment Target Audience: Community members Staff of Indian health programs, including Community Health Representatives Contents of Learning Module:
Lung Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand lung cancer and the treatment options that are available.
 Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Inova. Breast Care Institute
 Inova Breast Care Institute At the Inova Breast Care Institute, our commitment is to provide expert care for you, every step of the way. Our multidisciplinary team of more than 80 experts provides a full
Inova Breast Care Institute At the Inova Breast Care Institute, our commitment is to provide expert care for you, every step of the way. Our multidisciplinary team of more than 80 experts provides a full
Early Prostate Cancer: Questions and Answers. Key Points
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Early Prostate Cancer:
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Early Prostate Cancer:
Understanding. Pancreatic Cancer
 Understanding Pancreatic Cancer Understanding Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreas The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your
Understanding Pancreatic Cancer Understanding Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreas The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your
dedicated to curing BREAST CANCER
 dedicated to curing BREAST CANCER When you are diagnosed with breast cancer, you need a team of specialists who will share their knowledge of breast disease and the latest treatments available. At Cancer
dedicated to curing BREAST CANCER When you are diagnosed with breast cancer, you need a team of specialists who will share their knowledge of breast disease and the latest treatments available. At Cancer
RADIATION THERAPY IN THE MANAGEMENT OF CANCER
 RADIATION THERAPY IN THE MANAGEMENT OF CANCER G K Rath Introduction Radiotherapy or radiation treatment is defined as the treatment of diseases (mostly malignant) with ionizing radiation. The various types
RADIATION THERAPY IN THE MANAGEMENT OF CANCER G K Rath Introduction Radiotherapy or radiation treatment is defined as the treatment of diseases (mostly malignant) with ionizing radiation. The various types
An Introduction to PROSTATE CANCER
 An Introduction to PROSTATE CANCER Being diagnosed with prostate cancer can be a life-altering experience. It requires making some very difficult decisions about treatments that can affect not only the
An Introduction to PROSTATE CANCER Being diagnosed with prostate cancer can be a life-altering experience. It requires making some very difficult decisions about treatments that can affect not only the
PRINIPLES OF RADIATION THERAPY Adarsh Kumar. The basis of radiation therapy revolve around the principle that ionizing radiations kill cells
 PRINIPLES OF RADIATION THERAPY Adarsh Kumar The basis of radiation therapy revolve around the principle that ionizing radiations kill cells Radiotherapy terminology: a. Radiosensitivity: refers to susceptibility
PRINIPLES OF RADIATION THERAPY Adarsh Kumar The basis of radiation therapy revolve around the principle that ionizing radiations kill cells Radiotherapy terminology: a. Radiosensitivity: refers to susceptibility
INTENSITY MODULATED RADIATION THERAPY (IMRT) FOR PROSTATE CANCER PATIENTS
 INTENSITY MODULATED RADIATION THERAPY (IMRT) FOR PROSTATE CANCER PATIENTS HOW DOES RADIATION THERAPY WORK? Cancer is the unrestrained growth of abnormal cells within the body. Radiation therapy kills both
INTENSITY MODULATED RADIATION THERAPY (IMRT) FOR PROSTATE CANCER PATIENTS HOW DOES RADIATION THERAPY WORK? Cancer is the unrestrained growth of abnormal cells within the body. Radiation therapy kills both
Goals and Objectives: Breast Cancer Service Department of Radiation Oncology
 Goals and Objectives: Breast Cancer Service Department of Radiation Oncology The breast cancer service provides training in the diagnosis, management, treatment, and follow-up of breast malignancies, including
Goals and Objectives: Breast Cancer Service Department of Radiation Oncology The breast cancer service provides training in the diagnosis, management, treatment, and follow-up of breast malignancies, including
Disease/Illness GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER. What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? www.simpsonmillar.co.uk Telephone 0844 858 3200
 GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
Preface to Practice Standards
 0 0 0 0 Preface to Practice Standards A profession s practice standards serve as a guide for appropriate practice. The practice standards define the practice and establish general criteria to determine
0 0 0 0 Preface to Practice Standards A profession s practice standards serve as a guide for appropriate practice. The practice standards define the practice and establish general criteria to determine
Radiation Therapy for Cancer Treatment
 Radiation Therapy for Cancer Treatment Guest Expert: Kenneth, MD Associate Professor of Therapeutic Radiology www.wnpr.org www.yalecancercenter.org Welcome to Yale Cancer Center Answers with Dr. Ed and
Radiation Therapy for Cancer Treatment Guest Expert: Kenneth, MD Associate Professor of Therapeutic Radiology www.wnpr.org www.yalecancercenter.org Welcome to Yale Cancer Center Answers with Dr. Ed and
General Information About Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 General Information About Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Non-small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing
General Information About Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Non-small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing
95% of childhood kidney cancer cases are Wilms tumours. Childhood kidney cancer is extremely rare, with only 90 cases a year in
 James Whale Fund for Kidney Cancer Childhood kidney cancer factsheet Kidney cancer rarely afflicts children and about 90 paediatric cases are diagnosed in the UK each year. About 75% of childhood kidney
James Whale Fund for Kidney Cancer Childhood kidney cancer factsheet Kidney cancer rarely afflicts children and about 90 paediatric cases are diagnosed in the UK each year. About 75% of childhood kidney
Understanding Your Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE
 Understanding Your Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE Introduction This guide is designed to help you clarify and understand the decisions that need to be made about your care for the
Understanding Your Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE Introduction This guide is designed to help you clarify and understand the decisions that need to be made about your care for the
Radiation Oncology Nursing Care. Helen Lusby Radiation Oncology Nurse BAROC 2012
 Radiation Oncology Nursing Care Helen Lusby Radiation Oncology Nurse BAROC 2012 Definitions Radiation Therapy: Treatment of cancer using x- ray particles that cause ionisation within the cells. External
Radiation Oncology Nursing Care Helen Lusby Radiation Oncology Nurse BAROC 2012 Definitions Radiation Therapy: Treatment of cancer using x- ray particles that cause ionisation within the cells. External
Our Facility. Advanced clinical center with the newest and highly exact technology for treatment of patients with cancer pencil beam
 PTC Czech The main goal of radiotherapy is to irreversibly damage tumor cells, whereas the cells of healthy tissue are damaged only reversibly or not at all. Proton therapy currently comes closest to this
PTC Czech The main goal of radiotherapy is to irreversibly damage tumor cells, whereas the cells of healthy tissue are damaged only reversibly or not at all. Proton therapy currently comes closest to this
A Woman s Guide to Prostate Cancer Treatment
 A Woman s Guide to Prostate Cancer Treatment Supporting the man in your life Providing prostate cancer support and resources for women and families WOMEN AGAINST PROSTATE CANCER A Woman s Guide to Prostate
A Woman s Guide to Prostate Cancer Treatment Supporting the man in your life Providing prostate cancer support and resources for women and families WOMEN AGAINST PROSTATE CANCER A Woman s Guide to Prostate
Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer
 Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 gerri@gomezhowardgroup.com Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 gerri@gomezhowardgroup.com Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Acute Myeloid Leukemia
 Acute Myeloid Leukemia Introduction Leukemia is cancer of the white blood cells. The increased number of these cells leads to overcrowding of healthy blood cells. As a result, the healthy cells are not
Acute Myeloid Leukemia Introduction Leukemia is cancer of the white blood cells. The increased number of these cells leads to overcrowding of healthy blood cells. As a result, the healthy cells are not
Brachytherapy: Low Dose Rate (LDR) Radiation Interstitial Implant
 Brachytherapy: Low Dose Rate (LDR) Radiation Interstitial Implant Goal of the Procedure Brachytherapy, or internal radiation therapy, is a way of giving a higher dose of radiation to the tumor area while
Brachytherapy: Low Dose Rate (LDR) Radiation Interstitial Implant Goal of the Procedure Brachytherapy, or internal radiation therapy, is a way of giving a higher dose of radiation to the tumor area while
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML)
 Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) Adult acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes abnormal myeloblasts (a type of white blood cell), red blood cells, or platelets. Adult
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) Adult acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes abnormal myeloblasts (a type of white blood cell), red blood cells, or platelets. Adult
Breast Cancer. Sometimes cells keep dividing and growing without normal controls, causing an abnormal growth called a tumor.
 Breast Cancer Introduction Cancer of the breast is the most common form of cancer that affects women but is no longer the leading cause of cancer deaths. About 1 out of 8 women are diagnosed with breast
Breast Cancer Introduction Cancer of the breast is the most common form of cancer that affects women but is no longer the leading cause of cancer deaths. About 1 out of 8 women are diagnosed with breast
Lung cancer forms in tissues of the lung, usually in the cells lining air passages.
 Scan for mobile link. Lung Cancer Lung cancer usually forms in the tissue cells lining the air passages within the lungs. The two main types are small-cell lung cancer (usually found in cigarette smokers)
Scan for mobile link. Lung Cancer Lung cancer usually forms in the tissue cells lining the air passages within the lungs. The two main types are small-cell lung cancer (usually found in cigarette smokers)
Guide to Understanding Breast Cancer
 An estimated 220,000 women in the United States are diagnosed with breast cancer each year, and one in eight will be diagnosed during their lifetime. While breast cancer is a serious disease, most patients
An estimated 220,000 women in the United States are diagnosed with breast cancer each year, and one in eight will be diagnosed during their lifetime. While breast cancer is a serious disease, most patients
Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults
 Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults Is this information right for me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor * said all tests show you have localized
Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults Is this information right for me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor * said all tests show you have localized
METASTASES TO THE BONE
 RADIATION THERAPY FOR METASTASES TO THE BONE Facts to Help Patients Make an Informed Decision TARGETING CANCER CARE AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR RADIATION ONCOLOGY WHAT ARE BONE METASTASES? Cancer that starts
RADIATION THERAPY FOR METASTASES TO THE BONE Facts to Help Patients Make an Informed Decision TARGETING CANCER CARE AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR RADIATION ONCOLOGY WHAT ARE BONE METASTASES? Cancer that starts
Mesothelioma: Questions and Answers
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Mesothelioma: Questions
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Mesothelioma: Questions
Prostate Cancer Guide. A resource to help answer your questions about prostate cancer
 Prostate Cancer Guide A resource to help answer your questions about prostate cancer Thank you for downloading this guide to prostate cancer treatment. We know that all the information provided online
Prostate Cancer Guide A resource to help answer your questions about prostate cancer Thank you for downloading this guide to prostate cancer treatment. We know that all the information provided online
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options
 AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
Radiation Therapy. What to expect
 Radiation Therapy What to expect This booklet was made possible through the generosity of BC Cancer Foundation donors. The BC Cancer Foundation is the fundraising partner of the BC Cancer Agency, supporting
Radiation Therapy What to expect This booklet was made possible through the generosity of BC Cancer Foundation donors. The BC Cancer Foundation is the fundraising partner of the BC Cancer Agency, supporting
Patient Guide: Your Radiation Therapy Treatment
 Patient Guide: Your Radiation Therapy Treatment Hours of Operation Regular Business Hours: CancerCare Manitoba (CCMB) Radiation Therapy Department 675 McDermot Avenue, Winnipeg, MB 204-787-2252 Treatment
Patient Guide: Your Radiation Therapy Treatment Hours of Operation Regular Business Hours: CancerCare Manitoba (CCMB) Radiation Therapy Department 675 McDermot Avenue, Winnipeg, MB 204-787-2252 Treatment
at a critical moment Physician Suggestion Line...
 Radiation Oncology Exceptional care at a critical moment When your patients require radiation therapy, they deserve the very best care available to them. The Department of Radiation Oncology provides exceptional
Radiation Oncology Exceptional care at a critical moment When your patients require radiation therapy, they deserve the very best care available to them. The Department of Radiation Oncology provides exceptional
Patient Guide. Brachytherapy: The precise answer for tackling breast cancer. Because life is for living
 Patient Guide Brachytherapy: The precise answer for tackling breast cancer Because life is for living This booklet is designed to provide information that helps women who have been diagnosed with early
Patient Guide Brachytherapy: The precise answer for tackling breast cancer Because life is for living This booklet is designed to provide information that helps women who have been diagnosed with early
Radiotherapy for vulval cancer
 This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding cancer of the vulva. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 6. Contents External radiotherapy Internal
This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding cancer of the vulva. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 6. Contents External radiotherapy Internal
PROTON THERAPY FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
 PROTON THERAPY FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS Table of contents 1. What is cancer?... 2 2. How is cancer treated?... 3 3. What is proton therapy?... 4 4. What are the clinical benefits of proton therapy?...
PROTON THERAPY FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS Table of contents 1. What is cancer?... 2 2. How is cancer treated?... 3 3. What is proton therapy?... 4 4. What are the clinical benefits of proton therapy?...
Benign (beh-nine): Not cancerous. Benign tumors may grow larger but do not spread to other parts of the body.
 Cancer Glossary Source: National Cancer Institute: What You Need to Know About Cancer Adenoma (ad-in-oh-ma): A noncancerous tumor. Adjuvant therapy (AD-joo-vant): Treatment given after the primary treatment
Cancer Glossary Source: National Cancer Institute: What You Need to Know About Cancer Adenoma (ad-in-oh-ma): A noncancerous tumor. Adjuvant therapy (AD-joo-vant): Treatment given after the primary treatment
RADIATION THERAPY FOR LYMPHOMA. Facts to Help Patients Make an Informed Decision TARGETING CANCER CARE AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR RADIATION ONCOLOGY
 RADIATION THERAPY FOR Facts to Help Patients Make an Informed Decision TARGETING CANCER CARE AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR RADIATION ONCOLOGY FACTS ABOUT The lymphatic system is a network of tiny vessels extending
RADIATION THERAPY FOR Facts to Help Patients Make an Informed Decision TARGETING CANCER CARE AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR RADIATION ONCOLOGY FACTS ABOUT The lymphatic system is a network of tiny vessels extending
Interstitial Breast Brachytherapy
 Patient Education Questions? Your questions are important. Call your doctor or health care provider if you have questions or concerns. UWMC clinic staff are also available to help at any time. During normal
Patient Education Questions? Your questions are important. Call your doctor or health care provider if you have questions or concerns. UWMC clinic staff are also available to help at any time. During normal
Rotation Specific Goals & Objectives: University Health Network-Princess Margaret Hospital/ Sunnybrook Breast/Melanoma
 Rotation Specific Goals & Objectives: University Health Network-Princess Margaret Hospital/ Sunnybrook Breast/Melanoma Medical Expert: Breast Rotation Specific Competencies/Objectives 1.0 Medical History
Rotation Specific Goals & Objectives: University Health Network-Princess Margaret Hospital/ Sunnybrook Breast/Melanoma Medical Expert: Breast Rotation Specific Competencies/Objectives 1.0 Medical History
Follow-Up Care for Breast Cancer
 A Patient s Guide Follow-Up Care for Breast Cancer Recommendations of the American Society of Clinical Oncology The American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) is a nonprofit organization which represents
A Patient s Guide Follow-Up Care for Breast Cancer Recommendations of the American Society of Clinical Oncology The American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) is a nonprofit organization which represents
Skin cancer Patient information
 Skin cancer Patient information What is cancer? The human body is made up of billions of cells. In healthy people, cells grow, divide and die. New cells constantly replace old ones in an orderly way. This
Skin cancer Patient information What is cancer? The human body is made up of billions of cells. In healthy people, cells grow, divide and die. New cells constantly replace old ones in an orderly way. This
RADIATION THERAPY FOR BRAIN METASTASES. Facts to Help Patients Make an Informed Decision TARGETING CANCER CARE AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR RADIATION ONCOLOGY
 RADIATION THERAPY FOR BRAIN METASTASES Facts to Help Patients Make an Informed Decision TARGETING CANCER CARE AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR RADIATION ONCOLOGY FACTS ABOUT BRAIN METASTASIS Brain metastases are clusters
RADIATION THERAPY FOR BRAIN METASTASES Facts to Help Patients Make an Informed Decision TARGETING CANCER CARE AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR RADIATION ONCOLOGY FACTS ABOUT BRAIN METASTASIS Brain metastases are clusters
Quick Facts about Appendix Cancer
 Quick Facts about Appendix Cancer What is the appendix? The appendix is a pouch-like tube attached to the first part of the large intestine (cecum). The appendix is about 10 centimetres long and has no
Quick Facts about Appendix Cancer What is the appendix? The appendix is a pouch-like tube attached to the first part of the large intestine (cecum). The appendix is about 10 centimetres long and has no
Objectives of Training in Radiation Oncology
 Objectives of Training in Radiation Oncology 2008 This document applies to those who begin training on or after July 1 st, 2009. (Please see also the Policies and Procedures. ) DEFINITION Radiation Oncologists
Objectives of Training in Radiation Oncology 2008 This document applies to those who begin training on or after July 1 st, 2009. (Please see also the Policies and Procedures. ) DEFINITION Radiation Oncologists
Kidney Cancer. Understanding your diagnosis
 Kidney Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Kidney Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
Kidney Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Kidney Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
Adjuvant Therapy for Breast Cancer: Questions and Answers
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Adjuvant Therapy for Breast
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Adjuvant Therapy for Breast
WHEN PROSTATE CANCER RETURNS: ADVANCED PROSTATE CANCER. How Will I Know If My Prostate Cancer Returns?
 WHEN PROSTATE CANCER RETURNS: ADVANCED PROSTATE CANCER (The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your experience may be different.) How Will I Know
WHEN PROSTATE CANCER RETURNS: ADVANCED PROSTATE CANCER (The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your experience may be different.) How Will I Know
Cervical Cancer. Cervical smear test. The cervix. Dysplasia. Cervical cancer. The female reproductive system
 INFORMATION SHEET Cervical Cancer This information sheet has been written to provide you with information about cervical cancer (cancer of the cervix). The sheet has information about the different types
INFORMATION SHEET Cervical Cancer This information sheet has been written to provide you with information about cervical cancer (cancer of the cervix). The sheet has information about the different types
Brain Tumor Center. A Team Approach to Treating Brain Tumors
 Brain Tumor Center A Team Approach to Treating Brain Tumors Introducing Our Brain Tumor Center Making an appointment with the Brain Tumor Center at the Center for Advanced Medicine is the important first
Brain Tumor Center A Team Approach to Treating Brain Tumors Introducing Our Brain Tumor Center Making an appointment with the Brain Tumor Center at the Center for Advanced Medicine is the important first
Radiation Therapy and Prostate Cancer
 Radiation Therapy and Prostate Cancer The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your experience may be different. If you have any questions about what
Radiation Therapy and Prostate Cancer The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your experience may be different. If you have any questions about what
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Proton Beam Radiotherapy (High Energy) for Paediatric Cancer Treatment
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Proton Beam Radiotherapy (High Energy) for Paediatric Cancer Treatment Reference: NHS England xxx/x/x 1 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Proton Beam Radiotherapy (High Energy)
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Proton Beam Radiotherapy (High Energy) for Paediatric Cancer Treatment Reference: NHS England xxx/x/x 1 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Proton Beam Radiotherapy (High Energy)
Multiple Myeloma Understanding your diagnosis
 Multiple Myeloma Understanding your diagnosis Multiple Myeloma Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
Multiple Myeloma Understanding your diagnosis Multiple Myeloma Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
Radiation Therapy for Cancer: Questions and Answers. Key Points
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Radiation Therapy for
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Radiation Therapy for
to Know About Your Partner s
 What You Need to Know About Your Partner s Prostate Cancer. A Guide for Wives, Partners, and the Men They Love. Providing Support for Your Partner Prostate cancer can be a physical and emotional challenge
What You Need to Know About Your Partner s Prostate Cancer. A Guide for Wives, Partners, and the Men They Love. Providing Support for Your Partner Prostate cancer can be a physical and emotional challenge
Cancer of the Cervix
 Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE
 HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE Prostate comes from the Greek meaning to stand in front of ; this is very different than prostrate which means to lie down flat. The prostate is a walnut-sized
HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE Prostate comes from the Greek meaning to stand in front of ; this is very different than prostrate which means to lie down flat. The prostate is a walnut-sized
Cancer is the leading cause of death for Canadians aged 35 to 64 and is also the leading cause of critical illness claims in Canada.
 Underwriting cancer In this issue of the Decision, we provide an overview of Canadian cancer statistics and the information we use to make an underwriting decision. The next few issues will deal with specific
Underwriting cancer In this issue of the Decision, we provide an overview of Canadian cancer statistics and the information we use to make an underwriting decision. The next few issues will deal with specific
Acute Care Pediatric Nurse Practitioner Certification Exam. Detailed Content Outline
 Acute Care Pediatric Nurse Practitioner Certification Exam Description of the Specialty This exam is for the pediatric nurse practitioner (PNP) who has graduated from a formal acute care PNP program with
Acute Care Pediatric Nurse Practitioner Certification Exam Description of the Specialty This exam is for the pediatric nurse practitioner (PNP) who has graduated from a formal acute care PNP program with
Uterine Cancer. Understanding your diagnosis
 Uterine Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Uterine Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
Uterine Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Uterine Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
Radiation Fibrosis Fact Sheet
 Radiation Fibrosis Fact Sheet What is Radiation Fibrosis Syndrome (RFS), and when can it occur? Radiation Fibrosis Syndrome (RFS) is a term used to describe the multiple clinical symptoms associated with
Radiation Fibrosis Fact Sheet What is Radiation Fibrosis Syndrome (RFS), and when can it occur? Radiation Fibrosis Syndrome (RFS) is a term used to describe the multiple clinical symptoms associated with
How To Treat Lung Cancer At Cleveland Clinic
 Treatment Guide Lung Cancer Management The Chest Cancer Center at Cleveland Clinic, which includes specialists from the Respiratory Institute, Taussig Cancer Institute and Miller Family Heart & Vascular
Treatment Guide Lung Cancer Management The Chest Cancer Center at Cleveland Clinic, which includes specialists from the Respiratory Institute, Taussig Cancer Institute and Miller Family Heart & Vascular
Colorectal Cancer Care A Cancer Care Map for Patients
 Colorectal Cancer Care A Cancer Care Map for Patients Understanding the process of care that a patient goes through in the diagnosis and treatment of colorectal cancer in BC. Colorectal Cancer Care Map
Colorectal Cancer Care A Cancer Care Map for Patients Understanding the process of care that a patient goes through in the diagnosis and treatment of colorectal cancer in BC. Colorectal Cancer Care Map
X-Plain Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer - Adriamycin, Cytoxan, and Tamoxifen Reference Summary
 X-Plain Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer - Adriamycin, Cytoxan, and Tamoxifen Reference Summary Introduction Breast cancer is a common condition that affects one out of every 11 women. Your doctor has recommended
X-Plain Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer - Adriamycin, Cytoxan, and Tamoxifen Reference Summary Introduction Breast cancer is a common condition that affects one out of every 11 women. Your doctor has recommended
Guidance on competencies for management of Cancer Pain in adults
 Guidance on competencies for management of Cancer Pain in adults Endorsed by: Contents Introduction A: Core competencies for practitioners in Pain Medicine B: Competencies for practitioners in Pain Medicine
Guidance on competencies for management of Cancer Pain in adults Endorsed by: Contents Introduction A: Core competencies for practitioners in Pain Medicine B: Competencies for practitioners in Pain Medicine
Treating Oesophageal Cancer A Quick Guide
 Treating Oesophageal Cancer A Quick Guide Contents This is a brief summary of the information on Treating from our website. You will find more detailed information on the website. In this information there
Treating Oesophageal Cancer A Quick Guide Contents This is a brief summary of the information on Treating from our website. You will find more detailed information on the website. In this information there
Surgery. Wedge resection only part of the lung, not. not a lobe, is removed. Cancer Council NSW
 The treatment you receive will depend on your lung cancer type, for example, whether you have a non-small cell lung cancer Adenocarcinoma or Squamous cell carcinoma, and if this is a sub-type with a mutation.
The treatment you receive will depend on your lung cancer type, for example, whether you have a non-small cell lung cancer Adenocarcinoma or Squamous cell carcinoma, and if this is a sub-type with a mutation.
Prostate Cancer. Understanding your diagnosis
 Prostate Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Prostate Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
Prostate Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Prostate Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal
 Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? An inferior vena cava filter placement procedure involves an interventional radiologist (a specialist doctor)
Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? An inferior vena cava filter placement procedure involves an interventional radiologist (a specialist doctor)
Department of Radiation Oncology
 Department of Radiation Oncology Welcome to Radiation Oncology at Emory Clinic Every member of Emory Clinic Department of Radiation Oncology strives to provide the highest quality of care for you as our
Department of Radiation Oncology Welcome to Radiation Oncology at Emory Clinic Every member of Emory Clinic Department of Radiation Oncology strives to provide the highest quality of care for you as our
CEU Update. Pancreatic Cancer
 CEU Update A semi-annual publication of the National Association for Health Professionals June 2015 Issue #0615 Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreatic Cancer Action Network, Inc. (PanCAN), established in 1999,
CEU Update A semi-annual publication of the National Association for Health Professionals June 2015 Issue #0615 Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreatic Cancer Action Network, Inc. (PanCAN), established in 1999,
