An Assessment of the Burden of Arthritis in Utah
|
|
|
- Kelly Woods
- 3 years ago
- Views:
From this document you will learn the answers to the following questions:
What state has a higher incidence of arthritis among adults?
Who is the name of the person who edited this report?
Who provided funding for this report?
Transcription
1 An Assessment of the Burden of Arthritis in Utah Findings from the 2013 and 2014 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System Utah Arthritis Program
2 Table of contents Acknowledgments... Executive Summary... Arthritis Definition... Prevalence of Arthritis in Utah... Body Mass Index Rates Among People with and Without Arthritis... Arthritis and Activity Limitation... Management of Arthritis... Health Status, Physical Health, and Arthritis... Arthritis and Mental Health... Arthritis and Physical Inactivity... Health Care Access Among People with Arthritis... Health Care Access Among People with Arthritis by Age Groups... Prevalence of Arthritis by Education Level... Prevalence of Arthritis by Income... Prevalence of Arthritis by Ethnicity... Prevalence of Arthritis by Race... Rates of Arthritis and Coexisting Condition... Prevalence of Arthritis by Utah Small Areas... Prevalence of Arthritis by Local Health District... Age-adjusted Prevalence of Arthritis by Local Health District... Age-adjusted Prevalence of Arthritis Utah and U.S... Conclusions/References... Appendices
3 Acknowledgments Appreciation is extended to Randy Tanner, MPA who wrote this report, Shelly Wagstaff, BS who converted the BRFSS responses into meaningful data, and Keegan McCaffrey, BA whose design and layout skills enhanced the appearance of the document. We also express our appreciation to the following individuals for editing this report: Rebecca Castleton, BS Michael Friedrichs, MS Brenda Ralls, PhD Kim Neerings Wu Xu, PhD Jenny Johnson, MPH The Utah Arthritis Program also acknowledges the following individuals for their support in producing this report: Rebecca Castleton, MPH, CHES, Program Manager, Utah Arthritis Program Heather Borski, MPH, CHES, Director, Bureau of Health Promotion Funding for this publication was provided by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) through funding opportunity number CDC-RFA-DP , and the U.S. Administration for Community Living, Administration on Aging HHS ACL-AOA-CS-0094.The contents of this report are solely the responsibility of the Utah Arthritis Program (UAP) and do not represent the opinions of the CDC or the Administration on Aging. For more information contact: Utah Department of Health Bureau of Health Promotion Utah Arthritis Program PO Box Salt Lake City, Utah Phone (801)
4 Executive Summary This report examines the burden of doctor-diagnosed arthritis among adults in Utah using data primarily from the 2014 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS). The 2014 BRFSS data generated a sample of 3,892 Utah adults who reported having arthritis. The report describes the prevalence of arthritis in Utah overall and within specific demographic groups, such as sex, age, race/ethnicity, education, and income. Other factors such as activity limitation, physical activity, health status, health-related quality of life, and weight category were also examined. Finally, the report includes information about hospitalizations and hospital charges associated with arthritis in Utah. We hope the report will increase awareness of arthritis in Utah as a major public health issue and provide direction for implementing interventions needed to improve the health and quality-of-life for Utahns suffering from arthritis. The 2014 Utah BRFSS data demonstrated that: Approximately 410,000 (20.1%) of Utah adults had some form of arthritis. Higher rates of arthritis were present in women (23.7%) vs. men (16.4%). The prevalence of arthritis increased with age, from 4.9 percent among those aged to 52.4 percent among those aged 75 and older. Approximately 71.3 percent of adults with arthritis were overweight or obese compared to 56.5 percent of adults without arthritis. The percentage of adults who described their general health as fair or poor was 27.2 percent among those with arthritis compared to 8.2 percent among those without arthritis. Adults with arthritis reported being in poor physical health at a rate three times higher than adults without arthritis (31.1% vs. 9.9%). Adults with arthritis were twice as likely to report being inactive (23.3%) than adults without arthritis (15.0%). Among persons aged 25 and older, those with a college education or higher were least likely to have arthritis. Arthritis rates declined with increasing income; only 17.2 percent of adults in households with annual incomes of $75,000 or more reported they had arthritis. 2
5 Arthritis prevalence was highest among non-hispanic/latino Whites (21.7%), followed by15.8 percent for non-hispanic/latino non-whites, and 10.7 percent for Hispanic/Latinos. Arthritis affected all racial groups, but rates are highest for Whites (21.1%) and American Indians (20.0%). The prevalence of arthritis was significantly lower in Utah County Health District (17.6%) compared to the state rate (20.1%). Local health districts where arthritis prevalence was significantly higher than the state rate included Central Utah (27.5%), Southeastern (28.8%), Southwest (24.4%), Tooele County (26.1%), and Weber-Morgan (23.2%). In 2014, the age-adjusted prevalence of arthritis in Utah was 21.4 percent; which was slightly lower than the U.S. age-adjusted rate of 22.4 percent. The prevalence of arthritis among Utah Small Areas ranged from a low of 9.1 percent in Provo (South) to a high of 33.4 percent in Carbon/Emery Counties. Records from the 2013 Utah Hospital Inpatient Discharge Database also confirmed that arthritis is a major public health issue in Utah. There were 13,299 inpatient hospital visits with a primary diagnosis of arthritis in 2013, or 5.1 percent of all hospital visits in Utah. Total charges for patients with a primary diagnosis of arthritis were more than $535 million and the average charge per visit was $41,000. 3
6 Arthritis Definition The word arthritis means joint inflammation. The twelfth edition of The Primer on Rheumatic Diseases, an Arthritis Foundation publication, identifies more than 100 rheumatic diseases and conditions, including osteoarthritis (which is the most common), rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, gout, and bursitis. 1 Typically, rheumatic conditions are characterized by inflammation, pain, and stiffness in and around one or more joints, the tissues which surround the joint, and other connective tissues. Diagnosed arthritis or a diagnosis of arthritis is a term used in this report to describe persons who answer yes to the question, Have you ever been told by a doctor that you have arthritis? Therefore, arthritis refers to self-reported, doctor-diagnosed arthritis in this report. Although doctor-diagnosed arthritis is self-reported in the BRFSS and is not confirmed by a health care provider, such self-reports have been shown to be acceptable for surveillance purposes. NOTE: Unless otherwise noted, rates shown in this document are 2014 crude rates. Prevalence of Arthritis in Utah In 2014, about one of every five adults (20.1%), or approximately 410,000 individuals, aged 18 and over in Utah had arthritis. 2 While arthritis affects both men and women, nearly one-fourth (23.7%), of Utah women reported arthritis compared to 16.4 percent of Utah men. Based on the 2014 Utah population 18 and older, this represents 243,000 women and 167,000 men.2 Although arthritis affects Utahns of all ages, some age groups are more likely to be impacted. The prevalence of self-reported arthritis ranged from 4.9 percent among 18-to 34-year-olds, to 52.4 percent among those 75 and older. Among women 75 and older, 58.0 percent reported arthritis compared to 45.1 percent of men in the same age category (See Figure 1). Figure 1. Prevalence of Arthritis by Sex and Age Group Among Utah Adults, 2014 Percentage with Arthritis Age Group Source: Utah BRFSS 2014 Males Females 4
7 Body Mass Index Rates Among People with and Without Arthritis Obesity is a known risk factor for the development and progression of arthritis. Among adults with arthritis, 28.6 percent were at an ideal weight, 33.6 percent were overweight, and 37.7 percent were obese. This means that nearly three-fourths of adults with arthritis (71.3%) were overweight or obese. Among adults without arthritis 43.5 percent were ideal weight, 33.9 percent were overweight, and 22.6 percent were obese (See Figure 2). Figure 2. Body Mass Index Rates Among People with and Without Arthritis, Percentage of Adults Ideal Overweight Obese Weight Category Source: Utah BRFSS 2014 With Arthritis Without Arthritis 5
8 Arthritis and Activity Limitation When asked if arthritis or joint symptoms limited their activities, nearly one-half (46.7%) of Utah adults with arthritis or joint symptoms reported limiting their activities in Women with arthritis were more likely to have activity limitation due to arthritis and joint symptoms (49.4%) than men (42.7%). In addition to activity limitations, 34.7 percent of working age (18-64 years) Utah adults with arthritis reported being limited in their ability to work in Among working-age women with arthritis in 2013, 37.8 percent have some work limitation due to their arthritis, compared to 30.3 percent of working-age men. In 2013, pain played a leading role in limiting the activities of people with arthritis. Among Utahns with arthritis, 22.0 percent reported pain at a level of seven or higher, on a scale from 0 to 10, with 0 representing no pain, and 10 representing intense pain. In 2014, persons with arthritis had a rate of activity limitation four times higher because of a physical, mental, or emotional problem than persons without arthritis (45.0% vs. 10.9%). Management of Arthritis In 2013, among Utah adults with arthritis: 72.0 percent (273,000) could do everything or almost everything they would like to do; 33.9 percent (132,000) reported a doctor or other health professional had suggested they lose weight; 58.7 percent (229,000) were told by their doctor or other health professional to exercise; and 2.9 percent (50,000) reported attending a self-management class to learn how to deal with their arthritis. Persons with arthritis were six times more likely to report using special equipment such as a cane, wheelchair, or special bed compared to persons without arthritis (16.6% vs. 2.8%). 6
9 Health Status, Physical Health, and Arthritis Utah adults with arthritis reported fair or poor health at three times the rate as adults without arthritis (27.2% vs. 8.2%). For this report, poor physical health was defined as experiencing seven or more days in the last month when their physical health was not good. Adults with arthritis reported being in poor physical health at a rate three times higher than adults without arthritis (31.1% vs. 9.9%) (See Figure 3). Arthritis and Mental Health Poor mental health was defined as having seven or more days of poor mental health in the past month. The relationship between arthritis and poor mental health was less dramatic than it was for physical health; however, the pattern remained the same. One in five Utah adults with arthritis (21.8%) reported having poor mental health compared to one in seven adults (14.3%) without arthritis (See Figure 3). Arthritis and Physical Inactivity Although research shows physical activity can benefit people with arthritis, Utah adults with arthritis were more likely to report being inactive (23.3%) than persons without arthritis (15.0%) (See Figure 3). Figure 3. Impact of Arthritis on Health-Related Quality of Life Among Utah Adults, 2014 Percentage of Adults Fair or Poor Health Poor Physical Health Poor Mental Health Health Status No Leisure Time Activity With Arthritis Without Arthritis Source: Utah BRFSS
10 Health Care Access Among People with Arthritis Overall and by Age Groups Compared to individuals aged 65 and older with arthritis, health care access was more limited among individuals aged with arthritis (See Figure 4). Among all Utah adults with arthritis: 7.1 percent reported not having health care coverage; 12.8 percent reported not having a personal doctor or health care provider; 15.8 percent could not see a doctor when needed in the past 12 months because of the cost; and 28.1 percent did not have a routine medical checkup in the past 12 months. Among Utah adults with arthritis aged (See Figure 4): 10.7 percent reported not having health care coverage; 16.6 percent reported not having a doctor or health care provider; 21.6 percent could not see a doctor when needed in the past 12 months because of the cost; and 35.0 percent did not have a routine medical checkup in the past 12 months. Among Utah adults with arthritis aged 65 and older (See Figure 4): 1.0 percent reported they did not have health care coverage*; 6.8 percent did not have a personal doctor or health care provider; 5.8 percent could not see a doctor when needed in the past year because of the cost; and 16.6 percent did not have a routine medical checkup in the past 12 months. 50 Figure 4. Health Care Access Among Utah Adults with Arthritis by Age Group, 2014 Percentage of Adults * No Health Care Coverage 16.6 No Health Care Provider Could Not See Doctor No Medical Checkup Source: Utah BRFSS 2014 Aged Aged 65+ *Use caution in interpreting, the estimate has a relative standard error greater than 30 percent and does not meet Utah Department of Health standards for reliability. 8
11 Prevalence of Arthritis by Education Level Attained Because the majority of adults do not complete their highest level of education until age 25, data in Figure 5 focuses on the education level attained among adults aged 25 and older. Persons with a college education or higher were least likely to have arthritis (See Figure 5). Figure 5. Prevalence of Arthritis by Education Level among Utah Adults Aged 25+, 2014 Percentage of Adults Aged Source: Utah BRFSS Less than High School High School/GED 25.1 Some College Level of Education 18.8 College Graduate Prevalence of Arthritis by Income Arthritis rates declined with increasing income. Among persons with an annual income of less than $25,000 in 2014, 22.1 percent stated they had arthritis. Only 17.2 percent of adults in households with annual incomes of $75,000 or more reported they had arthritis (See Figure 6). Figure 6. Prevalence of Arthritis by Income Among Utah Adults, 2014 Percentage with Arthritis Source: Utah BRFSS < $24,999 $25,000 - $49,999 Income Level 19.7 $50,000 - $74, $75,000 9
12 Prevalence of Arthritis by Ethnicity Arthritis prevalence was highest among non-hispanic/latino Whites (21.7%), followed by 15.8 percent for non-hispanic/latino non-whites and 10.7 percent for Hispanic/Latinos (See Figure 7). The difference in the prevalence for the Hispanic/Latino population may be attributed to the fact that this population is younger overall. The age-adjusted estimate of arthritis among the Hispanic/Latino population was 18.5 percent. Figure 7. Prevalence of Arthritis by Ethnicity Among Utah Adults, 2014 Percentage with Arthritis Source: Utah BRFSS White non- Hispanic/Latinos 15.8 non-white/non Hispanic/Latinos Ethnicity 10.7 Hispanic/Latinos Prevalence of Arthritis by Race Arthritis affects all racial groups, but rates were highest for Whites (21.1%), followed by American Indians (20.0%) (See Figure 8). Figure 8. Prevalence of Arthritis by Race Among Utah Adults, 2014 Percentage with Arthritis White 20.0 American Indian/Alaskan Native Black Pacific Islander* 12.0 Asian 11.2 Other Source: Utah BRFSS 2014 Race *Use caution in interpreting, the estimate has a relative standard error greater than 30 percent and does not meet Utah Department of Health standards for reliability. 10
13 Arthritis and Coexisting Conditions Arthritis was frequently associated with other chronic health conditions such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol*. As seen in Figure 9, 36.2 percent of persons with high cholesterol, 42.2 percent with high blood pressure, 46.7 percent of adults with diabetes, and 50.0 percent of people with cardiovascular disease also had arthritis. Figure 9. Arthritis Prevalence Among Utah Adults with Selected Chronic Conditions, 2013 and Percentage with Arthritis High Cholesterol* Source: * Utah BRFSS 2013 ** Utah BRFSS 2014 High Blood Diabetes** Pressure** Condition Cardiovascular Disease** 11
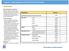
14 Prevalence of Arthritis by Utah Small Areas The prevalence of arthritis in Utah s Small Areas ranged from a low of 9.1 percent in Provo (South) to a high of 33.4 percent in Carbon/Emery Counties (See Table 1). Small Area Table 1. Prevalence of Arthritis by Utah Small Areas, 2014 Percentage with Arthritis Statistical Significance Compared to the State Rate Small Area Percentage with Arthritis Statistical Significance Compared to the State Rate State Total 20.1 Springville/Spanish Fork Provo (South) 9.1 Lower South Ogden West Jordan (West)/ Copperton 10.9 Lower Cache County (Other)/Rich County (All) SLC (Glendale) Roy/Hooper Orem (West) American Fork/Alpine Logan 13.4 Lower Orem (East) SLC (Foothill/U of U) Grand/San Juan Counties Pleasant Grove/Lindon 14.2 Lower West Jordan (Southeast) Provo North (BYU) Ben Lomond Midvale Ogden (Downtown) Riverton/Draper 15.3 Lower Southwest LHD (Other) West Jordan (Northeast)V Cedar City Lehi/Cedar Valley Box Elder Co. (Other) West Valley (West) Farmington/Centerville Summit County Washington Co. (Other) Clearfield/ Hill AFB Tooele County Millcreek St. George South Jordan Cottonwood South Salt Lake Taylorsville (East)/Murray (West) SLC (Downtown) Utah County (South) SLC (Avenues) West Valley East Version Syracuse/Kaysville Sandy (Northeast) SLC (Rose Park) Juab/Millard/Sanpete Counties 26.0 Higher Orem (North) Taylorsville (West) 26.9 Higher Magna Bountiful 27.1 Higher Sandy (SE) Holladay 27.5 Higher Wasatch County Woods Cross/ North Salt Lake 27.7 Higher TriCounty LHD Sandy (Center) 27.9 Higher Kearns V Riverdale 29.2 Higher Layton Sevier/Piute/Wayne Counties 31.0 Higher Morgan County (All)/ Weber County (East) Brigham City 31.8 Higher Murray Carbon/Emery Counties 33.4 Higher 12
15 Prevalence of Arthritis by Local Health District In 2014, the prevalence of arthritis was significantly lower in Utah County Health District (17.6%) than the state rate. Health districts that were significantly higher than the state rate were Central Utah (27.5%), Southeastern (28.8%), Southwest (24.4%), Tooele County (26.1%), and Weber-Morgan (23.2%) (See Figure 11). Bear River 20.0% Weber-Morgan 23.2% Davis 21.1% Salt Lake County 19.8% Tooele 26.1% Utah 17.6% Summit 18.4% Wasatch 20.1% TriCounty 20.7% Central 27.5% Southeastern 28.8% Southwest 24.4% 13
16 Figure 11. Percentage of Adults Reporting Arthritis by Local Health District, Percentage with Arthritis Source: Utah BRFSS 2014 Local Health District 14
17 Age-adjusted Prevalence of Arthritis by Local Health District Because age is a risk factor for arthritis, it is beneficial to adjust for the effect of age when comparing populations that may have strong differences in age distributions. This helps determine if a certain population has factors that contribute to arthritis prevalence in addition to the effect of age. In 2014, the age-adjusted prevalence of arthritis was significantly higher in Central Utah Health District (26.1%) than the state rate. (See Figure 12). Figure 12. Age-adjusted Percentage of Adults Reporting Arthritis by Local Health District, 2014 Percentage with Arthritis Local Health Department Source: Utah BRFSS 2014 Age-adjusted to the U.S standard population for comparison purposes. Age-adjusted rates are based on eight age groups: 18-24, 25-34, 35-44, 45-54, 55-64, 65-74, 75-84, and
18 Age-adjusted Prevalence of Arthritis Utah and U.S. The age-adjusted prevalence of arthritis in Utah has been consistently lower than the U.S. rate from 2011 to the present. In 2014, the age-adjusted prevalence of arthritis in Utah was 21.4 percent, which was slightly lower than the U.S. age-adjusted rate of 22.4 percent. Figure 13. Age-adjusted Prevalence of Arthritis, Utah and U.S Percentage of Adults Year Utah Sources: Utah and U.S. BRFSS datasets Age-adjusted to the U.S standard population for comparison purposes. Age-adjusted rates are based on eight age groups: 18-24, 25-34, 35-44, 45-54, 55-64, 65-74, 75-84, and 85+. U.S. 16
19 Conclusions Obtaining reliable arthritis data at state and local levels allows for accurate measurement of the prevalence of arthritis. Such data helps to set public health priorities and focus the use of limited public health resources in the most efficient way. It also helps us understand who is affected, who is at risk, what health behaviors increase that risk, and how the disease affects physical health, quality of life, and health care costs. Through awareness, education, and action, the public health concerns noted in this report could be addressed. Ultimately, adults with arthritis should learn about treatment options, attend self-management programs, participate in regular physical activity, and maintain appropriate body weight to relieve their symptoms. The data in this report also described a serious problem about the impact of arthritis on the quality of life. Adults with arthritis were more likely to have poor general, physical, and mental health and to be less physically active than adults without arthritis. The lack of access to medical care reported by some adults with arthritis also raises concerns about providing these individuals with adequate treatment and education. For those with access to care, physicians and health care providers could use more opportunities to recommend exercise and weight control to those who could benefit. References 1 Primer on the Rheumatic Diseases (Primer on Rheumatic Diseases (Klippel)) by John H. Klippel, John H. Stone, Leslie J. Crofford, and Patience H. White (Dec 12, 2007). 2 National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) through a collaborative agreement with the U.S. Census Bureau, IBIS Version
20 Appendix A: Arthritis-related Inpatient Hospital Visits and Costs Records from the 2013 Utah Hospital Inpatient Discharge Database confirmed that arthritis is a major public health issue in Utah. There were 13,299 inpatient hospital visits with a primary diagnosis of arthritis in 2013, or 5.1 percent of all hospital visits. Osteoarthritis accounted for 11,178 hospital visits or more than three-fourths (84.0%) of all hospital visits due to arthritis. Total charges for patients with a primary diagnosis of arthritis were more than $535 million and the average charge per visit was $40,737. The average inpatient length-of-stay for a patient with a primary diagnosis of arthritis was 2.9 days. Hospital visits for arthritis-associated knee and hip replacements accounted for 78.0 percent or 10,369 hospital visits due to arthritis in 2013, for a total cost of $424,791,915 or more than three-fourths (79.4%) of all hospital charges for arthritis (See Table 2). Table 2 Arthritis-related Inpatient Hospital Visits and Costs, Utah Residents, 2013 Average Diagnosis/Procedure Hospital Visits* Total Charges** Average Charge** Length of Stay Arthritis 13,299 $535,080,375 $40, days Knee Replacement 7,588 $306,148,929 $40, days Hip Replacement 2,781 $118,642,986 $43, days Age was associated with hospitalization of adults with arthritis. Of the 13,299 arthritis related inpatient visits in 2013, persons aged 55 and older accounted for more than three-fourths (81.4%) of arthritis-related hospital visits and 85.5 percent of knee and hip replacements due to arthritis. Total charges for persons aged 55 and older with arthritis accounted for 82.6 percent of all hospital charges due to arthritis and 85.3 percent of arthritis-associated knee and hip replacements (See Table 3). Table 3 Arthritis-related Inpatient Hospital Visits and Costs, Utah Residents Age 55 and Older, 2013 Diagnosis/Procedure Hospital Visits* Total Charges** Average Charge** Average Length of Stay Arthritis 10,828 $442,125,783 $41, days Knee Replacement 6,529 $262,651,735 $40, days Hip Replacement 2,335 $99,575,632 $43, days Source: Utah Inpatient Hospital Discharge Data, Office of Health Care Statistics, Utah Department of Health * Includes hospital visits with a primary diagnosis of arthritis using ICD-9 Codes 095.6, 095.7, 098.5, 099.3, 136.1, 274, 277.2, 287.0, 344.6, 353.0, 354.0, 355.5, 357.1, 390, 391, 437.4, 443.0, 446, 447.6, 696.0, 710, 711, 712, 713, 714, 715, 716, 719.0, , 720, 721, 725, 726, 727, , , 729.0, 729.1, The ICD-9 Procedure Codes for Knee and Hip Replacements are and 81.51, respectively. ** The charges shown differ from costs, reimbursement, price and payment. Different payers have different arrangements with each hospital for payment. Many factors affect the cost for a hospital stay, including a patient s health insurance, the type of insurance, and the billing procedures at the hospital. 18
21 Appendix B: What is Being Done to Address Arthritis in Utah? The UAP was established in 1999 with funding from the CDC. Since that time, the UAP and its partners have been working to: provide an effective public health program for arthritis;monitor the burden of arthritis within Utah; measure the impact of interventions; routinely update state plans targeting persons with arthritis; create sustainable partnerships to expand the reach of evidence-based interventions; collaborate with other chronic disease programs to promote systems change; and implement the CDC health communication campaign, Physical Activity. The Arthritis Pain Reliever. In an effort to improve the quality of life of Utahns affected by arthritis, the UAP supports the evidence-based programs listed in Table 4. Table 4 Evidence-based Intervention Delivery Programs Description of Program Demonstrated Benefits Arthritis Foundation Exercise Program (AFEP) This program uses low impact exercises to relieve stiffness, decrease pain, and restore or maintain muscle strength. Classes meet two or three times per week. Chronic Disease Self-Management Program (CDSMP) The CDSMP is for people with chronic health problems. The program was developed at Stanford University. Participants meet for 2 and 1/2 hours per week for six weeks. Workshop topics include: managing a chronic disease; appropriate exercise; managing medications; communicating with family, friends, and health professionals; nutrition; and how to evaluate new treatments. Tomando Control de su Salud - Tomando Control de su Salud is a self-management education program developed for Spanish-speaking people with a variety of chronic health problems. This program is similar in content and process to the English language version of CDSMP. EnhanceFitness (EF) Program instructors focus on stretching, flexibility, balance, low impact aerobics, and strength training exercises. Classes meet three times a week for one hour. Walk With Ease (WWE) WWE is a walking program offered by the Arthritis Foundation. Participants meet three times a week in groups of up to 30 participants under the supervision of a trained leader. Improved functional ability Decreased depression Increased confidence in being able to exercise Improved ability to exercise Improved ability to do social and household activities Less depression, fear, and frustration Less worry about personal health Reduced pain Increased confidence to manage a chronic condition Improved ability to exercise Improved ability to do social and household activities Less depression, fear, and frustration Less worry about personal health Reduced pain Increased confidence to manage a chronic condition Increased strength, flexibility, and balance Increased activity levels Elevated mood Increased fitness Improved ability to walk safely and comfortably Improved flexibility, strength, and stamina Reduced pain 19
22 Appendix C: Utah Arthritis Program Delivery Partners For information about evidence-based programs in Utah shown to reduce the burden of arthritis, visit During the last five years, the UAP has built an outstanding partner network. Currently the UAP partners with the following organizations to provide evidence-based programs to reduce the burden of arthritis in Utah (See Table 5). To learn more about our current partners, visit health.utah.gov/arthritis/currentpartners.html. Table 5 Utah Arthritis Program Intervention Delivery Partners Arthritis Foundation Great West Region Salt Lake County Active Aging Program Bear River Health Department Bear River Association of Governments Centers for Independent Living Central Utah Health Department Communidades en Accion Davis County Health Department Five County Area Agency on Aging Intermountain Healthcare Molina Healthcare National Tongan American Society San Juan Counseling The Orthopedic Specialty Hospital Tooele County Health Department University of Utah Community Clinics Utah County Health Department Utah Navajo Health System Veterans Administration Wasatch County Health Department Weber Human Services Weber-Morgan Health Department 20
23 Appendix D: Arthritis Program Delivery Model The Utah Arthritis Program works to Improve the Quality of Life for People Affected with Arthritis by partnering with Area Agencies on Aging Community- Based Health Care Local Health Departments to promote evidence-based interventions that Decrease Depression, Fear, and Frustration Improve Management of Chronic Conditions Decrease Pain and Disability Increase Physical, Social, and Work Capacity 21
24 Appendix E: Impact of Interventions in Utah The UAPs existing partners have successfully implemented the AFEP, CDSMP, EF, and Tomando Control de su Salud interventions in a way that has allowed for growth almost every year (See Figure 12). Figure 12. Participation in Evidence-based Programs by Calendar Year January December 2014 Number of Participants 2,400 1,933 1,663 1,622 1,600 1,384 1,356 1, AFEP ASMP CDSMP , ,027 1,139 EF WWE Total Participants 638 1,089 1,384 1,663 1,356 1,622 1,933 Source: Utah Arthritis Program participant reach data AFEP There are currently 14 ongoing Arthritis Foundation Exercise Program (AFEP) classes being offered in seven Utah counties. From 2008 through 2014, the Utah Arthritis Foundation enrolled 2,557 participants in the AFEP. For information about the AFEP, contact Randy Tanner at rtanner@utah.gov. Arthritis Self-Management Program (ASMP) At one time, the Arthritis Foundation offered the ASMP; however, because most individuals with arthritis have multiple chronic conditions, it was determined that the CDSMP was more suitable to our target population. 22
25 CDSMP and Tomando Control de su Salud From September 2008 through December 2014, 5,624 participants enrolled in the CDSMP workshops (English and Spanish). The number of participants grew from 102 in 2008, to a high of 1,139 in Since 2008, more than threefourths (79%) of participants attended a workshop in Davis, Salt Lake, Utah, or Weber Counties, which closely reflects the distribution of the state population. Eighteen host organizations provided workshops at 285 unique sites in 20 of Utah s 29 counties. The number of workshops increased from eight in 2008 to a high of 109 in For information about the CDSMP (Spanish and English) and a current list of classes, visit EnhanceFitness Since the Salt Lake County Active Aging Program implemented the EnhanceFitness Program in January 2009, they have enrolled 1,035 new participants at 16 senior centers. For information about the EnhanceFitness program, contact Nichole Shephard at NShepard@slco.org. Walk With Ease (WWE) From July 2012 through December 2014, 239 individuals participated in the WWE program. For information about the WWE program, contact Leslie Nelson at lrnelson@arthritis.org. 23
26 This Page Left Blank Intentionally
27 For more information contact: Utah Department of Health Bureau of Health Promotion Utah Arthritis Program PO Box Salt Lake City, Utah Phone (801) Utah Arthritis Program
Prostate Cancer: Stage of Disease at Diagnosis
 Bear River Health District 14% 3% 61% Bear River Health District 481 61.3 7830 64.5 173 22.0 2611 21.54% 23 2.93% 638 5.26% 107 13.6 1043 8. 40.6% 48. Bear River Health District Central Health District
Bear River Health District 14% 3% 61% Bear River Health District 481 61.3 7830 64.5 173 22.0 2611 21.54% 23 2.93% 638 5.26% 107 13.6 1043 8. 40.6% 48. Bear River Health District Central Health District
Chronic Disease Self Management Program
 Chronic Disease Self Management Program M I S S T Y L E C H N E R K A N S A S A R T H R I T I S P R O G R A M M A N A G E R B U R E A U O F H E A L T H P R O M O T I O N K A N S A S D E P A R T M E N T
Chronic Disease Self Management Program M I S S T Y L E C H N E R K A N S A S A R T H R I T I S P R O G R A M M A N A G E R B U R E A U O F H E A L T H P R O M O T I O N K A N S A S D E P A R T M E N T
TANF Grant Awards $50,000,000
 $50,000,000 Addiction Intervention Asian Association of Utah dba Refugee and Immigrant Center $388,801.00 Salt Lake City Addiction Intervention City of St. George $616,600.00 St. George Addiction Intervention
$50,000,000 Addiction Intervention Asian Association of Utah dba Refugee and Immigrant Center $388,801.00 Salt Lake City Addiction Intervention City of St. George $616,600.00 St. George Addiction Intervention
UTAH. Case Study Series
 Case Study Series UTAH MAP PAGE Nursing Homes and Hospitals Serving the Resident Population... 90 Major Cities............................................ 91 HAZMAT Response......................................
Case Study Series UTAH MAP PAGE Nursing Homes and Hospitals Serving the Resident Population... 90 Major Cities............................................ 91 HAZMAT Response......................................
Health Savings Account Eligible Plans
 Health Savings Account Eligible Plans Secure WELL TH Choices 100% PLAN PREMIUM SAVER NO WORRIES KNOW YOUR COSTS $0 copay yearly women s health checkup $0 copay routine pap smear and mammogram $0 copay
Health Savings Account Eligible Plans Secure WELL TH Choices 100% PLAN PREMIUM SAVER NO WORRIES KNOW YOUR COSTS $0 copay yearly women s health checkup $0 copay routine pap smear and mammogram $0 copay
STATE OF UTAH DIRECTORY OF COMMUNITY MENTAL HEALTH & SUBSTANCE ABUSE SERVICES March 2013
 STATE OF UTAH DIRECTORY OF COMMUNITY MENTAL HEALTH & SUBSTANCE ABUSE SERVICES March 2013 NAME & LOCATION PHONE FAX # UTAH DIVISION OF SUBSTANCE ABUSE AND MENTAL HEALTH 195 North 1950 West Salt Lake City
STATE OF UTAH DIRECTORY OF COMMUNITY MENTAL HEALTH & SUBSTANCE ABUSE SERVICES March 2013 NAME & LOCATION PHONE FAX # UTAH DIVISION OF SUBSTANCE ABUSE AND MENTAL HEALTH 195 North 1950 West Salt Lake City
Influenza Vaccination Coverage Report for Healthcare Workers in Utah Hospitals 2014-2015
 Influenza Vaccination Coverage Report for Healthcare Workers in Utah Hospitals 2014-2015 Utah Department of Health Division of Disease Control and Prevention Bureau of Epidemiology Influenza Vaccination
Influenza Vaccination Coverage Report for Healthcare Workers in Utah Hospitals 2014-2015 Utah Department of Health Division of Disease Control and Prevention Bureau of Epidemiology Influenza Vaccination
Connecticut Diabetes Statistics
 Connecticut Diabetes Statistics What is Diabetes? State Public Health Actions (1305, SHAPE) Grant March 2015 Page 1 of 16 Diabetes is a disease in which blood glucose levels are above normal. Blood glucose
Connecticut Diabetes Statistics What is Diabetes? State Public Health Actions (1305, SHAPE) Grant March 2015 Page 1 of 16 Diabetes is a disease in which blood glucose levels are above normal. Blood glucose
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Brief
 Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Brief What is Coronary Heart Disease? Coronary Heart Disease (CHD), also called coronary artery disease 1, is the most common heart condition in the United States. It occurs
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Brief What is Coronary Heart Disease? Coronary Heart Disease (CHD), also called coronary artery disease 1, is the most common heart condition in the United States. It occurs
16. ARTHRITIS, OSTEOPOROSIS, AND CHRONIC BACK CONDITIONS
 16. ARTHRITIS, OSTEOPOROSIS, AND CHRONIC BACK CONDITIONS Goal Reduce the impact of several major musculoskeletal conditions by reducing the occurrence, impairment, functional limitations, and limitation
16. ARTHRITIS, OSTEOPOROSIS, AND CHRONIC BACK CONDITIONS Goal Reduce the impact of several major musculoskeletal conditions by reducing the occurrence, impairment, functional limitations, and limitation
PHONE CALL AND OUTREACH VISIT SCRIPTS
 PHONE CALL AND OUTREACH VISIT SCRIPTS The scripts for phone calls to and outreach visits with primary care practices (PCPs) will help you prepare for contact with providers and office staff. You don t
PHONE CALL AND OUTREACH VISIT SCRIPTS The scripts for phone calls to and outreach visits with primary care practices (PCPs) will help you prepare for contact with providers and office staff. You don t
SAMPLE QUESTIONNAIRE
 Stanford Patient Education Research Center Stanford University School of Medicine SAMPLE QUESTIONNAIRE CHRONIC DISEASE August 2007 You may use all or parts of the questionnaire at no charge without permission
Stanford Patient Education Research Center Stanford University School of Medicine SAMPLE QUESTIONNAIRE CHRONIC DISEASE August 2007 You may use all or parts of the questionnaire at no charge without permission
 the Vocational Rehabilitation Program STATE OFFICE OF UTAH REHABILITATION Employment & Independence INTRODUCTION TO THE VOCATIONAL REHABILITATION PROGRAM VOCATIONAL REHABILITATION PROGRAM This booklet
the Vocational Rehabilitation Program STATE OFFICE OF UTAH REHABILITATION Employment & Independence INTRODUCTION TO THE VOCATIONAL REHABILITATION PROGRAM VOCATIONAL REHABILITATION PROGRAM This booklet
We would like to welcome you as a new customer of XFINITY Home!
 Comcast 9602 South 300 West Sandy, UT 84070 We would like to welcome you as a new customer of XFINITY Home! Certain municipalities in Utah require home security system users to obtain an alarm registration/user
Comcast 9602 South 300 West Sandy, UT 84070 We would like to welcome you as a new customer of XFINITY Home! Certain municipalities in Utah require home security system users to obtain an alarm registration/user
Kansas Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System Local Data, 2009
 Kansas Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System Local Data, 2009 Kansas BRFSS Bureau of Health Promotion Kansas Department of Health and Environment 1000 SW Jackson St., Suite 230 Topeka, Kansas 66612-1274
Kansas Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System Local Data, 2009 Kansas BRFSS Bureau of Health Promotion Kansas Department of Health and Environment 1000 SW Jackson St., Suite 230 Topeka, Kansas 66612-1274
Kansas Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System Local Data, 2009
 Kansas Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System Local Data, 2009 Kansas BRFSS Bureau of Health Promotion Kansas Department of Health and Environment 1000 SW Jackson St., Suite 230 Topeka, Kansas 66612-1274
Kansas Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System Local Data, 2009 Kansas BRFSS Bureau of Health Promotion Kansas Department of Health and Environment 1000 SW Jackson St., Suite 230 Topeka, Kansas 66612-1274
Star Ratings From Medicare For Utah Nursing Homes 2014
 Federal Provider Number Provider Name 6003 HERITAGE PARK CARE CENTER 6006 MT OLYMPUS REHABILITATION CENTER 6009 KINDRED NURSING & REHABILITATION - WASATCH CARE 6020 PIONEER CARE CENTER 609 SPRING CREEK
Federal Provider Number Provider Name 6003 HERITAGE PARK CARE CENTER 6006 MT OLYMPUS REHABILITATION CENTER 6009 KINDRED NURSING & REHABILITATION - WASATCH CARE 6020 PIONEER CARE CENTER 609 SPRING CREEK
Louisiana Report 2013
 Louisiana Report 2013 Prepared by Louisiana State University s Public Policy Research Lab For the Department of Health and Hospitals State of Louisiana December 2015 Introduction The Behavioral Risk Factor
Louisiana Report 2013 Prepared by Louisiana State University s Public Policy Research Lab For the Department of Health and Hospitals State of Louisiana December 2015 Introduction The Behavioral Risk Factor
The Burden of Pain Among Adults in the United States
 P F I Z E R F A C T S The Burden of Pain Among Adults in the United States Findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, the National Health Care Surveys, and the National Health
P F I Z E R F A C T S The Burden of Pain Among Adults in the United States Findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, the National Health Care Surveys, and the National Health
UT Based on Home Health Care - Patient survey (HHCAHPS)
 State CMS Certification Number (CCN)* Provider Name UT 467001 COMMUNITY NURSING SERVICES WEST VALLEY CITY UT 467004 INTERMOUNTAIN HOMECARE OGDEN OGDEN UT 467012 IRON COUNTY HOME HEALTH AGENCY CEDAR CITY
State CMS Certification Number (CCN)* Provider Name UT 467001 COMMUNITY NURSING SERVICES WEST VALLEY CITY UT 467004 INTERMOUNTAIN HOMECARE OGDEN OGDEN UT 467012 IRON COUNTY HOME HEALTH AGENCY CEDAR CITY
Overview. Chronic Disease Self-Management Program. Self-Management Support. Self-Management: What Is It? Self-Management and Patient Education
 Chronic Disease Kate Lorig, RN, DrPH Stanford Department of Medicine Stanford Patient Education Research Center Palo Alto, California http://patienteducation.stanford.edu Overview What is self-management?
Chronic Disease Kate Lorig, RN, DrPH Stanford Department of Medicine Stanford Patient Education Research Center Palo Alto, California http://patienteducation.stanford.edu Overview What is self-management?
Facts about Diabetes in Massachusetts
 Facts about Diabetes in Massachusetts Diabetes is a disease in which the body does not produce or properly use insulin (a hormone used to convert sugar, starches, and other food into the energy needed
Facts about Diabetes in Massachusetts Diabetes is a disease in which the body does not produce or properly use insulin (a hormone used to convert sugar, starches, and other food into the energy needed
2012 Georgia Diabetes Burden Report: An Overview
 r-,, 2012 Georgia Diabetes Burden Report: An Overview Background Diabetes and its complications are serious medical conditions disproportionately affecting vulnerable population groups including: aging
r-,, 2012 Georgia Diabetes Burden Report: An Overview Background Diabetes and its complications are serious medical conditions disproportionately affecting vulnerable population groups including: aging
Upstate New York adults with diagnosed type 1 and type 2 diabetes and estimated treatment costs
 T H E F A C T S A B O U T Upstate New York adults with diagnosed type 1 and type 2 diabetes and estimated treatment costs Upstate New York Adults with diagnosed diabetes: 2003: 295,399 2008: 377,280 diagnosed
T H E F A C T S A B O U T Upstate New York adults with diagnosed type 1 and type 2 diabetes and estimated treatment costs Upstate New York Adults with diagnosed diabetes: 2003: 295,399 2008: 377,280 diagnosed
2012 13 Fingertip UTAH STATE OFFICE OF EDUCATION. www.schools.utah.gov. 250 East 500 South P.O. Box 144200 Salt Lake City, UT 84114-4200
 2012 Thinkstock/iStockphoto UTAH STATE OFFICE OF EDUCATION FACTS UTAH STATE OFFICE OF EDUCATION 2012 13 Fingertip 250 East 500 South P.O. Box 144200 Salt Lake City, UT 84114-4200 www.schools.utah.gov CORE
2012 Thinkstock/iStockphoto UTAH STATE OFFICE OF EDUCATION FACTS UTAH STATE OFFICE OF EDUCATION 2012 13 Fingertip 250 East 500 South P.O. Box 144200 Salt Lake City, UT 84114-4200 www.schools.utah.gov CORE
A Health Profile of Older North Carolinians
 A Health Profile of Older North Carolinians A Joint Publication of the State Center for Health Statistics and Older Adult Health Branch North Carolina Division of Public Health and North Carolina Division
A Health Profile of Older North Carolinians A Joint Publication of the State Center for Health Statistics and Older Adult Health Branch North Carolina Division of Public Health and North Carolina Division
Texas Diabetes Fact Sheet
 I. Adult Prediabetes Prevalence, 2009 According to the 2009 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) survey, 984,142 persons aged eighteen years and older in Texas (5.4% of this age group) have
I. Adult Prediabetes Prevalence, 2009 According to the 2009 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) survey, 984,142 persons aged eighteen years and older in Texas (5.4% of this age group) have
The National Survey of Children s Health 2011-2012 The Child
 The National Survey of Children s 11-12 The Child The National Survey of Children s measures children s health status, their health care, and their activities in and outside of school. Taken together,
The National Survey of Children s 11-12 The Child The National Survey of Children s measures children s health status, their health care, and their activities in and outside of school. Taken together,
Payday lenders and small claims court cases in Utah: CORC
 Payday lenders and small claims court cases in Utah: CORC Overview The purpose of this study was to determine whether or not payday lenders were using a sizable portion of Utah small claims court resources
Payday lenders and small claims court cases in Utah: CORC Overview The purpose of this study was to determine whether or not payday lenders were using a sizable portion of Utah small claims court resources
A Population Based Risk Algorithm for the Development of Type 2 Diabetes: in the United States
 A Population Based Risk Algorithm for the Development of Type 2 Diabetes: Validation of the Diabetes Population Risk Tool (DPoRT) in the United States Christopher Tait PhD Student Canadian Society for
A Population Based Risk Algorithm for the Development of Type 2 Diabetes: Validation of the Diabetes Population Risk Tool (DPoRT) in the United States Christopher Tait PhD Student Canadian Society for
3.5% 3.0% 3.0% 2.4% Prevalence 2.0% 1.5% 1.0% 0.5% 0.0%
 S What is Heart Failure? 1,2,3 Heart failure, sometimes called congestive heart failure, develops over many years and results when the heart muscle struggles to supply the required oxygen-rich blood to
S What is Heart Failure? 1,2,3 Heart failure, sometimes called congestive heart failure, develops over many years and results when the heart muscle struggles to supply the required oxygen-rich blood to
Stickler Syndrome and Arthritis
 Stickler Syndrome and Arthritis Arthritis Foundation Pacific Region, Nevada Office Presented by: Crystal Schulz, MPH Community Development Manager Arthritis Foundation Improving lives through leadership
Stickler Syndrome and Arthritis Arthritis Foundation Pacific Region, Nevada Office Presented by: Crystal Schulz, MPH Community Development Manager Arthritis Foundation Improving lives through leadership
Diabetes. African Americans were disproportionately impacted by diabetes. Table 1 Diabetes deaths by race/ethnicity CHRONIC DISEASES
 Diabetes African Americans were disproportionately impacted by diabetes. African Americans were most likely to die of diabetes. People living in San Pablo, Pittsburg, Antioch and Richmond were more likely
Diabetes African Americans were disproportionately impacted by diabetes. African Americans were most likely to die of diabetes. People living in San Pablo, Pittsburg, Antioch and Richmond were more likely
The population with diabetes is less healthy than the population without it.
 Diabetes A drain on U.S. resources Some people with diabetes are able to control their condition and lead an active life. On the whole, however, people with diabetes are faced with many challenges. The
Diabetes A drain on U.S. resources Some people with diabetes are able to control their condition and lead an active life. On the whole, however, people with diabetes are faced with many challenges. The
Task 7: Study of the Uninsured and Underinsured
 75 Washington Avenue, Suite 206 Portland, Maine04101 Phone: 207-767-6440 Email: research@marketdecisions.com www.marketdecisions.com Task 7: Study of the Uninsured and Underinsured Vermont Office of Health
75 Washington Avenue, Suite 206 Portland, Maine04101 Phone: 207-767-6440 Email: research@marketdecisions.com www.marketdecisions.com Task 7: Study of the Uninsured and Underinsured Vermont Office of Health
What is a Heart Attack? 1,2,3
 S What is a Heart Attack? 1,2,3 Heart attacks, otherwise known as myocardial infarctions, are caused when the blood supply to a section of the heart is suddenly disrupted. Without the oxygen supplied by
S What is a Heart Attack? 1,2,3 Heart attacks, otherwise known as myocardial infarctions, are caused when the blood supply to a section of the heart is suddenly disrupted. Without the oxygen supplied by
Dental Resource Guide State of Utah
 Dental Resource Guide State of Utah UTAH DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH H ORAL HEALTH PROGRAM Last updated November 2013 http://www.insurekidsnow.gov/state/utah/utah_oral.html Table of Contents Table of Contents....2
Dental Resource Guide State of Utah UTAH DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH H ORAL HEALTH PROGRAM Last updated November 2013 http://www.insurekidsnow.gov/state/utah/utah_oral.html Table of Contents Table of Contents....2
Epi Research Report New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene May 2010
 Epi Research Report New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene May 2010 Including New Yorkers Who Can Be Reached Only by Cell Phone in the Community Health Survey: Results from the 2008 Cell
Epi Research Report New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene May 2010 Including New Yorkers Who Can Be Reached Only by Cell Phone in the Community Health Survey: Results from the 2008 Cell
Why Select Us? CONTACT US 2013 RATE INFORMATION FOR THE HIGH AND STANDARD OPTION SELECTHEALTH PLAN. for FEDERAL EMPLOYEES
 2013 RATE INFORMATION FOR THE HIGH AND STANDARD OPTION SELECTHEALTH PLAN These rates do not apply to all enrollees. If you are in a special enrollment category, please refer to your special FEHB Guide
2013 RATE INFORMATION FOR THE HIGH AND STANDARD OPTION SELECTHEALTH PLAN These rates do not apply to all enrollees. If you are in a special enrollment category, please refer to your special FEHB Guide
Educational Attainment of Veterans: 2000 to 2009
 Educational Attainment of Veterans: to 9 January 11 NCVAS National Center for Veterans Analysis and Statistics Data Source and Methods Data for this analysis come from years of the Current Population Survey
Educational Attainment of Veterans: to 9 January 11 NCVAS National Center for Veterans Analysis and Statistics Data Source and Methods Data for this analysis come from years of the Current Population Survey
Diabetes. Prevalence. in New York State
 Adult Diabetes Prevalence in New York State Diabetes Prevention and Control Program Bureau of Chronic Disease Evaluation and Research New York State Department of Health Authors: Bureau of Chronic Disease
Adult Diabetes Prevalence in New York State Diabetes Prevention and Control Program Bureau of Chronic Disease Evaluation and Research New York State Department of Health Authors: Bureau of Chronic Disease
9. Substance Abuse. pg 166-169: Self-reported alcohol consumption. pg 170-171: Childhood experience of living with someone who used drugs
 9. pg 166-169: Self-reported alcohol consumption pg 170-171: Childhood experience of living with someone who used drugs pg 172-173: Hospitalizations related to alcohol and substance abuse pg 174-179: Accidental
9. pg 166-169: Self-reported alcohol consumption pg 170-171: Childhood experience of living with someone who used drugs pg 172-173: Hospitalizations related to alcohol and substance abuse pg 174-179: Accidental
Addressing Racial/Ethnic Disparities in Hypertensive Health Center Patients
 Addressing Racial/Ethnic Disparities in Hypertensive Health Center Patients Academy Health June 11, 2011 Quyen Ngo Metzger, MD, MPH Data Branch Chief, Office of Quality and Data U.S. Department of Health
Addressing Racial/Ethnic Disparities in Hypertensive Health Center Patients Academy Health June 11, 2011 Quyen Ngo Metzger, MD, MPH Data Branch Chief, Office of Quality and Data U.S. Department of Health
Racial Disparities in US Healthcare
 Racial Disparities in US Healthcare Paul H. Johnson, Jr. Ph.D. Candidate University of Wisconsin Madison School of Business Research partially funded by the National Institute of Mental Health: Ruth L.
Racial Disparities in US Healthcare Paul H. Johnson, Jr. Ph.D. Candidate University of Wisconsin Madison School of Business Research partially funded by the National Institute of Mental Health: Ruth L.
Health Insurance Coverage: Estimates from the National Health Interview Survey, 2004
 Health Insurance Coverage: Estimates from the National Health Interview Survey, 2004 by Robin A. Cohen, Ph.D., and Michael E. Martinez, M.P.H., Division of Health Interview Statistics, National Center
Health Insurance Coverage: Estimates from the National Health Interview Survey, 2004 by Robin A. Cohen, Ph.D., and Michael E. Martinez, M.P.H., Division of Health Interview Statistics, National Center
531,000 adults in Virginia (8.7%) had diabetes that was diagnosed by a health professional. 1
 Percent of adults with diabetes Prevalence of Diabetes Prevalence refers to the total number of people with an existing condition or disease, including new diagnoses, at a point in time. All rates are
Percent of adults with diabetes Prevalence of Diabetes Prevalence refers to the total number of people with an existing condition or disease, including new diagnoses, at a point in time. All rates are
http://www.cdc.gov/nchs.
 As the Nation s principal health statistics agency, the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) compiles statistical information to guide actions and policies to improve the health of the population.
As the Nation s principal health statistics agency, the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) compiles statistical information to guide actions and policies to improve the health of the population.
No. 133 June 2002. Health Conditions and Behaviors Among North Carolina and United States Military Veterans Compared to Non-Veterans
 SCHS Studies North Carolina Public Health A Special Report Series by the 1908 Mail Service Center, Raleigh, N.C. 27699-1908 www.schs.state.nc.us/schs/ No. 133 June 2002 Health Conditions and Behaviors
SCHS Studies North Carolina Public Health A Special Report Series by the 1908 Mail Service Center, Raleigh, N.C. 27699-1908 www.schs.state.nc.us/schs/ No. 133 June 2002 Health Conditions and Behaviors
DEPRESSION AND ANXIETY STATUS IN KANSAS
 DEPRESSION AND ANXIETY STATUS IN KANSAS 2008 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System This report was prepared by the Bureau of Health Promotion, Kansas Department of Health and Environment December
DEPRESSION AND ANXIETY STATUS IN KANSAS 2008 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System This report was prepared by the Bureau of Health Promotion, Kansas Department of Health and Environment December
Shaping our future: a call to action to tackle the diabetes epidemic and reduce its economic impact
 Shaping our future: a call to action to tackle the diabetes epidemic and reduce its economic impact Task Force for the National Conference on Diabetes: The Task Force is comprised of Taking Control of
Shaping our future: a call to action to tackle the diabetes epidemic and reduce its economic impact Task Force for the National Conference on Diabetes: The Task Force is comprised of Taking Control of
How To Stop Smoking In Utah
 TOBACCO PREVENTION AND CONTROL IN UTAH Fourteenth Annual Report, August 2014 I quit smoking for my kids. Suelyn Springville 3 years tobacco-free Utah Department of Health Tobacco Prevention and Control
TOBACCO PREVENTION AND CONTROL IN UTAH Fourteenth Annual Report, August 2014 I quit smoking for my kids. Suelyn Springville 3 years tobacco-free Utah Department of Health Tobacco Prevention and Control
Health Care Access to Vulnerable Populations
 Health Care Access to Vulnerable Populations Closing the Gap: Reducing Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Florida Rosebud L. Foster, ED.D. Access to Health Care The timely use of personal health services
Health Care Access to Vulnerable Populations Closing the Gap: Reducing Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Florida Rosebud L. Foster, ED.D. Access to Health Care The timely use of personal health services
Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Women s Health Coverage and Access To Care Findings from the 2001 Kaiser Women s Health Survey
 March 2004 Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Women s Health Coverage and Access To Care Findings from the 2001 Kaiser Women s Health Survey Attention to racial and ethnic differences in health status and
March 2004 Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Women s Health Coverage and Access To Care Findings from the 2001 Kaiser Women s Health Survey Attention to racial and ethnic differences in health status and
Kansas Behavioral Health Risk Bulletin
 Kansas Behavioral Health Risk Bulletin Kansas Department of Health and Environment November 7, 1995 Bureau of Chronic Disease and Health Promotion Vol. 1 No. 12 Diabetes Mellitus in Kansas Diabetes mellitus
Kansas Behavioral Health Risk Bulletin Kansas Department of Health and Environment November 7, 1995 Bureau of Chronic Disease and Health Promotion Vol. 1 No. 12 Diabetes Mellitus in Kansas Diabetes mellitus
New York State s Racial, Ethnic, and Underserved Populations. Demographic Indicators
 New York State s Racial, Ethnic, and Underserved Populations While much progress has been made to improve the health of racial and ethnic populations, and increase access to care, many still experience
New York State s Racial, Ethnic, and Underserved Populations While much progress has been made to improve the health of racial and ethnic populations, and increase access to care, many still experience
Demographic Analysis of the Salt River Pima-Maricopa Indian Community Using 2010 Census and 2010 American Community Survey Estimates
 Demographic Analysis of the Salt River Pima-Maricopa Indian Community Using 2010 Census and 2010 American Community Survey Estimates Completed for: Grants & Contract Office The Salt River Pima-Maricopa
Demographic Analysis of the Salt River Pima-Maricopa Indian Community Using 2010 Census and 2010 American Community Survey Estimates Completed for: Grants & Contract Office The Salt River Pima-Maricopa
Appendix 1. Sociodemographic Characteristics for the Top and Bottom 10 States in the 2009 State Scorecard on Health System Performance
 Appendix 1. Sociodemographic Characteristics for the Top and Bottom 10 States in the 2009 State Scorecard on Health System Performance Resident Population in Millions (a) Median Annual Household Income
Appendix 1. Sociodemographic Characteristics for the Top and Bottom 10 States in the 2009 State Scorecard on Health System Performance Resident Population in Millions (a) Median Annual Household Income
Health Status, Health Insurance, and Medical Services Utilization: 2010 Household Economic Studies
 Health Status, Health Insurance, and Medical Services Utilization: 2010 Household Economic Studies Current Population Reports By Brett O Hara and Kyle Caswell Issued July 2013 P70-133RV INTRODUCTION The
Health Status, Health Insurance, and Medical Services Utilization: 2010 Household Economic Studies Current Population Reports By Brett O Hara and Kyle Caswell Issued July 2013 P70-133RV INTRODUCTION The
INTERIM REPORT June 9 th, 2010. Prepared By:
 County-Level Demographics, Health Characteristics and Health Behaviors of Florida Residents Aged 60 and over: Results from the 2007 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System INTERIM REPORT June 9 th,
County-Level Demographics, Health Characteristics and Health Behaviors of Florida Residents Aged 60 and over: Results from the 2007 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System INTERIM REPORT June 9 th,
King County City Health Profile Vashon Island
 King County City Health Profile Vashon Island West Seattle North Highline Burien SeaTac/Tukwila Vashon Island Des Moines/Normandy Park Kent-West East Federal Way Fed Way-Dash Point/Woodmont December, 212
King County City Health Profile Vashon Island West Seattle North Highline Burien SeaTac/Tukwila Vashon Island Des Moines/Normandy Park Kent-West East Federal Way Fed Way-Dash Point/Woodmont December, 212
Put Life Back In Your Life
 Put Life Back In Your Life Many Faces of Community Health October 29, 2010 Pam Van Zyl York, MPH, PhD, RD, LN Minnesota Department of Health The Chronic Disease Self-Management Program Agenda Benefits,
Put Life Back In Your Life Many Faces of Community Health October 29, 2010 Pam Van Zyl York, MPH, PhD, RD, LN Minnesota Department of Health The Chronic Disease Self-Management Program Agenda Benefits,
How To Get A Better Health Care Package For A Black Person
 Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes in Hispanics as Compared to the General Population in Massachusetts By Isabelle Pierre Krystal Amaral, and Ardrianna Howard, 2014 SEP Participants 1 TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS
Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes in Hispanics as Compared to the General Population in Massachusetts By Isabelle Pierre Krystal Amaral, and Ardrianna Howard, 2014 SEP Participants 1 TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS
Exploring Race & Ethnicity Health Insurance Coverage Differences: Results from the 2011 Oregon Health Insurance Survey
 Office for Oregon Health Policy and Research Exploring Race & Ethnicity Health Insurance Coverage Differences: Results from the 2011 Oregon Health Insurance Survey September 2012 Table of Contents Race
Office for Oregon Health Policy and Research Exploring Race & Ethnicity Health Insurance Coverage Differences: Results from the 2011 Oregon Health Insurance Survey September 2012 Table of Contents Race
Position (AIP): Utah! This program supports members serving in community health centers and other community
 General Information about AmeriCorps Internship Position (AIP): Utah Healthcare Corps (UHC) has contributed greatly to the improvement of health outcomes in the areas of immunization, diabetes, reproductive
General Information about AmeriCorps Internship Position (AIP): Utah Healthcare Corps (UHC) has contributed greatly to the improvement of health outcomes in the areas of immunization, diabetes, reproductive
Evaluations. Viewer Call-In. www.t2b2.org. Phone: 800-452-0662 Fax: 518-426-0696. Geriatric Mental Health. Thanks to our Sponsors: Guest Speaker
 Geriatric Mental Health June 1, 7 Guest Speaker Michael B. Friedman, LMSW Chairperson Geriatric Mental Health Alliance of New York Thanks to our Sponsors: School of Public Health, University at Albany
Geriatric Mental Health June 1, 7 Guest Speaker Michael B. Friedman, LMSW Chairperson Geriatric Mental Health Alliance of New York Thanks to our Sponsors: School of Public Health, University at Albany
State of Utah DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE Division of Corporations & Commercial Code BUSINESS LICENSING & REGISTRATION GUIDE
 State of Utah DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE Division of Corporations & Commercial Code BUSINESS LICENSING & REGISTRATION GUIDE All businesses operating in Utah must be registered with the Department of Commerce
State of Utah DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE Division of Corporations & Commercial Code BUSINESS LICENSING & REGISTRATION GUIDE All businesses operating in Utah must be registered with the Department of Commerce
The Burden of Diabetes in New Jersey: A Surveillance Report New Jersey Department of Health and Senior Services Division of Family Health Services
 The Burden of Diabetes in New Jersey: A Surveillance Report New Jersey Department of Health and Senior Services Division of Family Health Services Diabetes Control Program Section I : May 2005 Section
The Burden of Diabetes in New Jersey: A Surveillance Report New Jersey Department of Health and Senior Services Division of Family Health Services Diabetes Control Program Section I : May 2005 Section
A REGIONAL COMMUNITY NEEDS ASSESSMENT (CNA) UNDERTAKEN IN COLLABORATION WITH: WESTCHESTER MEDICAL CENTER, MONTEFIORE MEDICAL CENTER, REFUAH HEALTH
 A REGIONAL COMMUNITY NEEDS ASSESSMENT (CNA) UNDERTAKEN IN COLLABORATION WITH: WESTCHESTER MEDICAL CENTER, MONTEFIORE MEDICAL CENTER, REFUAH HEALTH CENTER AND HEALTH ALLIANCE OF THE HUDSON VALLEY 1 CNA
A REGIONAL COMMUNITY NEEDS ASSESSMENT (CNA) UNDERTAKEN IN COLLABORATION WITH: WESTCHESTER MEDICAL CENTER, MONTEFIORE MEDICAL CENTER, REFUAH HEALTH CENTER AND HEALTH ALLIANCE OF THE HUDSON VALLEY 1 CNA
2012/2013 Pulse of Pennsylvania s Registered Nurse Workforce. Bureau of Health Planning Division of Plan Development
 2012/2013 Pulse of Pennsylvania s Registered Nurse Workforce Bureau of Health Planning Division of Plan Development A Report on the 2012/2013 Survey of Registered Nurses Volume 6, March 2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS
2012/2013 Pulse of Pennsylvania s Registered Nurse Workforce Bureau of Health Planning Division of Plan Development A Report on the 2012/2013 Survey of Registered Nurses Volume 6, March 2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS
Diabetes: The Numbers
 Diabetes: The Numbers Changing the Way Diabetes is Treated. What is Diabetes? Diabetes is a group of diseases characterized by high levels of blood glucose (blood sugar) Diabetes can lead to serious health
Diabetes: The Numbers Changing the Way Diabetes is Treated. What is Diabetes? Diabetes is a group of diseases characterized by high levels of blood glucose (blood sugar) Diabetes can lead to serious health
Diversity in California s Mental Health Workforce and Education Pipeline
 Non-White Students Make up the Majority of Californians Pursuing Healthcare Education Diversity in California s Mental Health Workforce and Education Pipeline Tim Bates, MPP; Lisel Blash, MPA; Susan Chapman,
Non-White Students Make up the Majority of Californians Pursuing Healthcare Education Diversity in California s Mental Health Workforce and Education Pipeline Tim Bates, MPP; Lisel Blash, MPA; Susan Chapman,
Health Insurance Coverage: Estimates from the National Health Interview Survey, 2005
 Health Insurance Coverage: Estimates from the National Health Interview Survey, 2005 by Robin A. Cohen, Ph.D., and Michael E. Martinez, M.P.H., Division of Health Interview Statistics, National Center
Health Insurance Coverage: Estimates from the National Health Interview Survey, 2005 by Robin A. Cohen, Ph.D., and Michael E. Martinez, M.P.H., Division of Health Interview Statistics, National Center
INSIDE FRONT COVER INTENTIONALLY BLANK
 2014 Rankings Utah INSIDE FRONT COVER INTENTIONALLY BLANK INTRODUCTION The County Health Rankings & Roadmaps program helps communities identify and implement solutions that make it easier for people to
2014 Rankings Utah INSIDE FRONT COVER INTENTIONALLY BLANK INTRODUCTION The County Health Rankings & Roadmaps program helps communities identify and implement solutions that make it easier for people to
Diabetes Brief. Pre diabetes occurs when glucose levels are elevated in the blood, but are not as high as someone who has diabetes.
 Diabetes Brief What is Diabetes? Diabetes mellitus is a disease of abnormal carbohydrate metabolism in which the level of blood glucose, or blood sugar, is above normal. The disease occurs when the body
Diabetes Brief What is Diabetes? Diabetes mellitus is a disease of abnormal carbohydrate metabolism in which the level of blood glucose, or blood sugar, is above normal. The disease occurs when the body
Summary of health effects
 Review of Findings on Chronic Disease Self- Management Program (CDSMP) Outcomes: Physical, Emotional & Health-Related Quality of Life, Healthcare Utilization and Costs Summary of health effects The major
Review of Findings on Chronic Disease Self- Management Program (CDSMP) Outcomes: Physical, Emotional & Health-Related Quality of Life, Healthcare Utilization and Costs Summary of health effects The major
Access to Health Services
 Ah Access to Health Services Access to Health Services HP 2020 Goal Improve access to comprehensive, quality health care services. HP 2020 Objectives Increase the proportion of persons with a usual primary
Ah Access to Health Services Access to Health Services HP 2020 Goal Improve access to comprehensive, quality health care services. HP 2020 Objectives Increase the proportion of persons with a usual primary
Massachusetts Population
 Massachusetts October 2012 POLICY ACADEMY STATE PROFILE Massachusetts Population MASSACHUSETTS POPULATION (IN 1,000S) AGE GROUP Massachusetts is home to more than 6.5 million people. Of these, more than
Massachusetts October 2012 POLICY ACADEMY STATE PROFILE Massachusetts Population MASSACHUSETTS POPULATION (IN 1,000S) AGE GROUP Massachusetts is home to more than 6.5 million people. Of these, more than
Research. Dental Services: Use, Expenses, and Sources of Payment, 1996-2000
 yyyyyyyyy yyyyyyyyy yyyyyyyyy yyyyyyyyy Dental Services: Use, Expenses, and Sources of Payment, 1996-2000 yyyyyyyyy yyyyyyyyy Research yyyyyyyyy yyyyyyyyy #20 Findings yyyyyyyyy yyyyyyyyy U.S. Department
yyyyyyyyy yyyyyyyyy yyyyyyyyy yyyyyyyyy Dental Services: Use, Expenses, and Sources of Payment, 1996-2000 yyyyyyyyy yyyyyyyyy Research yyyyyyyyy yyyyyyyyy #20 Findings yyyyyyyyy yyyyyyyyy U.S. Department
New Jersey Population
 New Jersey October 2012 POLICY ACADEMY STATE PROFILE New Jersey Population NEW JERSEY POPULATION (IN 1,000S) AGE GROUP New Jersey is home to nearly9 million people. Of these, more than 2.9 million (33.1
New Jersey October 2012 POLICY ACADEMY STATE PROFILE New Jersey Population NEW JERSEY POPULATION (IN 1,000S) AGE GROUP New Jersey is home to nearly9 million people. Of these, more than 2.9 million (33.1
Stanford University s Chronic Disease Self-Management Program Curriculum and Evidence
 Stanford University s Chronic Disease Self-Management Program Curriculum and Evidence What is the Chronic Disease Self-Management Program? The Chronic Disease Self-Management Program (CDSMP), developed
Stanford University s Chronic Disease Self-Management Program Curriculum and Evidence What is the Chronic Disease Self-Management Program? The Chronic Disease Self-Management Program (CDSMP), developed
EMS Certficate Companies Utah
 County Service # Agency BEAVER 0101L BEAVER AMBULANCE SERVICE BEAVER 0102L MILFORD VALLEY AMBULANCE SERVICE BOX ELDER 0201L BRIGHAM CITY AMBULANCE BOX ELDER 0202L TREMONTON CITY FIRE DEPARTMENT BOX ELDER
County Service # Agency BEAVER 0101L BEAVER AMBULANCE SERVICE BEAVER 0102L MILFORD VALLEY AMBULANCE SERVICE BOX ELDER 0201L BRIGHAM CITY AMBULANCE BOX ELDER 0202L TREMONTON CITY FIRE DEPARTMENT BOX ELDER
Care Coordination in. the Health Home Program A benefit available to high risk Medicaid beneficiaries. Northwest Regional Council 1
 Care Coordination in the Health Home Program A benefit available to high risk Medicaid beneficiaries Northwest Regional Council 1 Northwest Regional Council Develops and advocates for a comprehensive and
Care Coordination in the Health Home Program A benefit available to high risk Medicaid beneficiaries Northwest Regional Council 1 Northwest Regional Council Develops and advocates for a comprehensive and
Report on the Burden of Chronic Diseases in Mississippi, 2014
 Report on the Burden of Chronic Diseases in Mississippi, 2014 AUTHOR Vanessa Short, PhD, MPH Senior Epidemiologist Mississippi State Department of Health ACKNOWLDEGMENTS Cassandra Dove, MPH Director, Chronic
Report on the Burden of Chronic Diseases in Mississippi, 2014 AUTHOR Vanessa Short, PhD, MPH Senior Epidemiologist Mississippi State Department of Health ACKNOWLDEGMENTS Cassandra Dove, MPH Director, Chronic
uninsured RESEARCH BRIEF: INSURANCE COVERAGE AND ACCESS TO CARE IN PRIMARY CARE SHORTAGE AREAS
 kaiser commission on medicaid and the uninsured RESEARCH BRIEF: INSURANCE COVERAGE AND ACCESS TO CARE IN PRIMARY CARE SHORTAGE AREAS Prepared by Catherine Hoffman, Anthony Damico, and Rachel Garfield The
kaiser commission on medicaid and the uninsured RESEARCH BRIEF: INSURANCE COVERAGE AND ACCESS TO CARE IN PRIMARY CARE SHORTAGE AREAS Prepared by Catherine Hoffman, Anthony Damico, and Rachel Garfield The
Population Percent C.I. All Hennepin County adults aged 18 and older 11.9% ± 1.1
 Overview ` Why Is This Indicator Important? Physical inactivity can lead to obesity and type 2 diabetes. Physical activity can help control weight, reduce the risk of heart disease and some cancers, strengthen
Overview ` Why Is This Indicator Important? Physical inactivity can lead to obesity and type 2 diabetes. Physical activity can help control weight, reduce the risk of heart disease and some cancers, strengthen
STATISTICAL BRIEF #113
 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey STATISTICAL BRIEF #113 Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality January 26 Children s Dental Care: Periodicity of Checkups and Access to Care, 23 May Chu Introduction
Medical Expenditure Panel Survey STATISTICAL BRIEF #113 Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality January 26 Children s Dental Care: Periodicity of Checkups and Access to Care, 23 May Chu Introduction
watch Introduction January 2012 No. 83
 AND health COLORADO DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC HEALTH AND ENVIRONMENT watch January 2012 No. 83 U N I O N CONSTITUTION Public versus Private Health Insurance in Colorado at a Glance: A Glimpse at Health Care
AND health COLORADO DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC HEALTH AND ENVIRONMENT watch January 2012 No. 83 U N I O N CONSTITUTION Public versus Private Health Insurance in Colorado at a Glance: A Glimpse at Health Care
Florida Population POLICY ACADEMY STATE PROFILE. Florida FLORIDA POPULATION (IN 1,000S) AGE GROUP
 Florida December 2012 POLICY ACADEMY STATE PROFILE Florida Population FLORIDA POPULATION (IN 1,000S) AGE GROUP Florida is home to more than 19 million people. Of these, more than 6.9 (36.9 percent) are
Florida December 2012 POLICY ACADEMY STATE PROFILE Florida Population FLORIDA POPULATION (IN 1,000S) AGE GROUP Florida is home to more than 19 million people. Of these, more than 6.9 (36.9 percent) are
INTRODUCING ARCHES HEALTH PLAN. For Nebo School District
 INTRODUCING ARCHES HEALTH PLAN For Nebo School District Who is Arches Health Plan? Who is Arches Health Plan? The only non-profit health insurance co-op in Utah (consumer operated and oriented plan) Unique
INTRODUCING ARCHES HEALTH PLAN For Nebo School District Who is Arches Health Plan? Who is Arches Health Plan? The only non-profit health insurance co-op in Utah (consumer operated and oriented plan) Unique
Arizona Living Well. Chronic Disease Self-Management Program Overview
 Arizona Living Well Chronic Disease Self-Management Program Overview What is CDSMP? CDSMP refers to Stanford University s Chronic Disease Self-Management Program developed by Dr. Kate Lorig. For more information
Arizona Living Well Chronic Disease Self-Management Program Overview What is CDSMP? CDSMP refers to Stanford University s Chronic Disease Self-Management Program developed by Dr. Kate Lorig. For more information
OHIO COUNTY. Demographic Data. Adult Behavioral Health Risk Factors: 2007-2011
 Prepared by the Department of Health and Human Resources Bureau for Behavioral Health and Health Facilities OHIO COUNTY February 14 Behavioral Health Epidemiological County Profile Demographic Data Ohio
Prepared by the Department of Health and Human Resources Bureau for Behavioral Health and Health Facilities OHIO COUNTY February 14 Behavioral Health Epidemiological County Profile Demographic Data Ohio
Information about the Developing Embryo and Fetus, about Abortion, and about Abortion Alternatives
 Information about the Developing Embryo and Fetus, about Abortion, and about Abortion Alternatives Published by: Utah Department of Health Division of Family Health and Preparedness September 2012 Prepared
Information about the Developing Embryo and Fetus, about Abortion, and about Abortion Alternatives Published by: Utah Department of Health Division of Family Health and Preparedness September 2012 Prepared
The ASMP/CDSMP Meta-Analysis Project Team thanks the group of subject matter experts that provided feedback on the project development.
 ASMP/CDSMP META-ANALYSIS PROJECT TEAM CENTERS FOR DISEASE CONTROL AND PREVENTION Teresa J. Brady, PhD Louise Murphy, PhD ICF MACRO Danielle Beauchesne, MPH Amee Bhalakia, MPH Doryn Chervin, DrPH, MEd Brandy
ASMP/CDSMP META-ANALYSIS PROJECT TEAM CENTERS FOR DISEASE CONTROL AND PREVENTION Teresa J. Brady, PhD Louise Murphy, PhD ICF MACRO Danielle Beauchesne, MPH Amee Bhalakia, MPH Doryn Chervin, DrPH, MEd Brandy
MASSACHUSETTS RESIDENTS NORTHEAST MA. Acute Care Hospital Utilization Trends in Massachusetts FY2009-2012
 ACUTE CARE HOSPITAL UTILIZATION TRENDS I N MASSACHUSETTS FY2009-2012 MASSACHUSETTS RESIDENTS NORTHEAST MA Introduction The Center for Health Information and Analysis (CHIA) is publishing these inpatient,
ACUTE CARE HOSPITAL UTILIZATION TRENDS I N MASSACHUSETTS FY2009-2012 MASSACHUSETTS RESIDENTS NORTHEAST MA Introduction The Center for Health Information and Analysis (CHIA) is publishing these inpatient,
Behavioral Health Barometer. United States, 2014
 Behavioral Health Barometer United States, 2014 Acknowledgments This report was prepared for the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) by RTI International under contract No.
Behavioral Health Barometer United States, 2014 Acknowledgments This report was prepared for the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) by RTI International under contract No.
The Use of Psychographic Data for Chronic Condition Self Management:
 The Use of Psychographic Data for Chronic Condition Self Management: Claims based study reveals health outcomes and economic returns Ninth Annual Population Health & DM Colloquium March 2 nd, 2010 Dr.
The Use of Psychographic Data for Chronic Condition Self Management: Claims based study reveals health outcomes and economic returns Ninth Annual Population Health & DM Colloquium March 2 nd, 2010 Dr.
HAWAI`I HEALTH SURVEY HHS INTRODUCTION 2002
 HAWAI`I HEALTH SURVEY HHS INTRODUCTION 2002 Hawai`i Department of Health Office of Health Status Monitoring Alvin T. Onaka, State Registrar, and Chief Brian Horiuchi, Supervisor Research & Statistics Honolulu,
HAWAI`I HEALTH SURVEY HHS INTRODUCTION 2002 Hawai`i Department of Health Office of Health Status Monitoring Alvin T. Onaka, State Registrar, and Chief Brian Horiuchi, Supervisor Research & Statistics Honolulu,
Three Common Types of Diabetes
 Diabetes Fact Sheet 1 ODPCP OHIO DIABETES PREVENTION AND CONTROL PROGRAM D O 1 Diabetes mellitus, or diabetes, is a disease in which a person has a high level of glucose (a type of sugar) in their blood.
Diabetes Fact Sheet 1 ODPCP OHIO DIABETES PREVENTION AND CONTROL PROGRAM D O 1 Diabetes mellitus, or diabetes, is a disease in which a person has a high level of glucose (a type of sugar) in their blood.
