Respiratory Assessment for Nurses (part two)
|
|
|
- Clementine Kennedy
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Respiratory Assessment for Nurses (part two) Introduction Part one of Respiratory Assessment for Nurses outlined the importance of appropriate respiratory assessment to improve care outcomes for the acutely ill ward patient. Moreover, it is recognised that deterioration in physiological status is often not appreciated, nor acted on in a timely manner (NICE 2007, Cioffi 2000b, Considine and Botti 2004, Franklin and Matthew 1994, Massey et al 2008). Evidence suggests that clinical staff may lack the required knowledge and skills to perform a comprehensive respiratory assessment which ultimately has a deleterious effect on the potential to minimise adverse patient events (Harrison et al 2006, Considine 2005, Kause et al 2004, Massey et al, 2008). In the first part of this article, respiratory inspection and palpation were described and discussed. In this second article the skills of percussion and auscultation will be explained in order to equip cardiac nurses with a comprehensive systematic model for respiratory assessment. Percussion Percussion is a key component of respiratory assessment that should be used in conjunction with auscultation to aid differential diagnosis (Mangione 2008). Percussion produces audible sounds (percussed notes) and palpable vibrations which can help to determine if the underlying lung tissue is filled with fluid, air or solid material (Douglas et al 2009). Pathophysiological changes occurring in the lungs as a result of conditions such as pneumothorax, pleural effusion and consolidation alter the characteristics of percussion notes which, when considered in the context of a comprehensive respiratory examination can assist with differential diagnosis. Percussion should be performed in sequence in the interspaces at 5cm intervals (avoiding the damping effect of the scapulae and ribs) over both sides of the chest, whilst paying close attention to the audible changes in percussion notes (Jarvis 2007) (figure 1). Percussion technique requires practice and can be difficult to master but good technique is important to extract accurate findings. Figure 1: Sequence for percussion a) posterior b) anterior Percussion of the anterior chest is usually carried out with the patient in a supine position, whereas the patient should be sitting upright (if possible) with their arms folded across the chest whilst examining the posterior chest wall. Correct technique involves hyperextending the middle finger of your dominant hand on the patient s chest with fingers slightly separated. With the tip (not the pad) of the opposite middle finger strike the middle finger placed on the chest wall with a loose swinging movement from the wrist (Douglas et al 2009) (figure 2). Remove the percussing finger quickly to avoid creating a dampened note.
2 Figure 2: Percussion technique A sound knowledge of the underlying structures within the thoracic cavity is essential in order to determine abnormal from normal findings. For example, percussion of normal lung tissue should produce a resonant note whereas percussion over solid structures like the liver or heart will produce a dull note (Jarvis 2007) (figure 3). Conversely, dull percussion notes found over lung tissue could be indicative of abnormal lung density found in atelectasis, tumour and plural effusion (figure 4). Obstructive atelectasis can be caused by secretions and or mucus plugs obstructing the bronchi resulting in collapsed, shrunken sections of alveoli (possibly an entire lung) that cannot take part in gaseous exchange, ultimately resulting in a ventilation/perfusion mismatch and hypoxaemia. Clinically, atelectic areas produce dull percussion notes and can be a common finding in cardiac patients due to chest pain, the use of opiate analgesia, surgical wound discomfort and immobility (Douglas et al 2009). Whilst percussion is an integral component of respiratory assessment, it is prudent to note that percussion alone only sets into motion approximately a 5-7cm depth of outer tissue; thus, it is not able to reveal any changes in tissue density deeper than 5-7cm (Bickley 2008). For example, scattered dullness can be heard over healthy lung tissue in people who are obese or in athletes with a heavily muscular chest wall. Figure 3: Expected percussion notes Figure 4: Percussion notes Resonant Hyperresonant Healthy lung tissue Too much air present Emphysema or pneumothorax Dull Abnormal lung density Pneumonia, pleural effusion, atelectasis or tumour Stoney dull Pleural effusion or haemothorax
3 Figure 4; Percussion notes adapted from Douglas et al (2009) Auscultation The final component required to complete a comprehensive respiratory assessment is auscultation of the anterior and posterior chest wall. When performed in conjunction with percussion, auscultation can help to assess the condition of the surrounding lungs and pleural space (Bickley 2008). Auscultation can provide important clues to the identification of disease such as early congestive heart failure, pleural effusion and atelectasis; as such, it remains a key component of respiratory evaluation (Mangione &Duffy 2003). Auscultation of the lungs comprises of three components (1) listening to the sounds created by air travelling through the tracheobronchial tree during normal, quiet breathing; (2) listening for any additional (adventitious) sounds and (3) listening to how the patient s spoken or whispered voice is transmitted through the chest wall when abnormalities are suspected (Bickley 2008). Auscultation of the posterior chest wall requires the patient to be sitting upright, leaning slightly forward with their arms resting comfortably across their lap. Anterior chest wall assessment can be performed with the patient supine or in a sitting position (Jarvis 2007). Both the anterior and posterior chest wall should be auscultated with the diaphragm of the stethoscope over a large number of equal positions to ensure that localised abnormalities are not missed (figure 5 a & b). The examination should, where possible, be conducted in a quiet environment with the examiner s stethoscope placed on bare skin to avoid misinterpreting the rubbing sound of clothes with abnormal breath sounds. During the examination patients should be as relaxed as possible and asked to breathe deeply through their mouth whilst avoiding unnecessary prolonged deep breathing which may result in the patient feeling light headed. Figure 5: sequence for auscultation of a) anterior b)posterior chest wall The key to effective respiratory auscultation is to listen to the intensity, pitch and duration of the inspiratory and expiratory sounds throughout a full inspiratory and expiratory cycle. There are three types of breath sounds normally heard in adults; bronchial, bronchovesicular and vesicular breath sounds (Jarvis 2007, Mangione 2008). Each of the three normal breath sounds has its own particular characteristics (figure 6) and should only be heard in certain locations over the chest wall (figure 7 a & b). For example, bronchial breathing is classified as an abnormal finding if it is heard over the peripheral lung fields (Mangione 2008). Bronchial breathing found in abnormal locations can occur as a result of fibrosis, consolidation or compression which alters lung density increasing transmission of sound from the bronchi (solids and liquid transmit sound better than gases) (Mangione 2008).Bronchial breath sounds would be evident in patients with pulmonary oedema due to fluid filled alveoli.
4 The intensity of breath sounds is directly related to air flow and the tissue through which the sound has to travel. Therefore, diminished or absent breath sounds can occur in obesity, pneumothorax, or when the bronchial tree is obstructed (Douglas et al 2009). If breath sounds are decreased as a result of secretions, asking the patient to cough may resolve this. Figure 6: Characteristics of breath sounds Figure 7: Location of normal breath sounds Added (adventitious) breath sounds are extra sounds that are heard over normal breath sounds. Adventitious sounds are generally categorised into three groups, crackles, wheezes and rhonchi (Bickley 2008, Jarvis 2007) (figure 8). The presence of added breath sounds frequently points to a diagnosis of pulmonary or cardiac conditions such as asthma, pulmonary oedema, early congestive heart failure and COPD (Mangione 2008). In the early stages of left sided heart failure, increased pressure within the pulmonary veins can cause interstitial oedema around the alveoli resulting in audible crackles in dependent lung regions (Bickley 2008). Course crackles result from air colliding with secretions and fluid in the trachea and bronchi and are commonly heard in patients with a depressed cough reflex such as the ventilated, post cardiac, surgical patient. Wheezes, when present, are commonly heard continuously throughout inspiration, expiration or both. Wheezes result from air being forced through narrowed or compressed airways as a result of swelling and inflammation classically seen in the asthmatic patient. Rhonchi are a lower pitched wheeze associated with secretions in the large airways as can be found in bronchitis. Adventitious breath sounds Crackles Discontinuous, brief, non musical Wheezes Fine (high pitched) Course (low pitched) Early, middle or late inspiration Musical, often prolonged High pitched, hissing or shrill quality May occur in inspiration and expiration Restrictive disease, pneumonia, heart failure and fibrosis Pulmonary oedema, pneumonia, secretions Diffuse airway obstruction in acute asthma or chronic emphysema Rhonchi Low pitched with snoring quality Secretions in large airways Figure 8: Characteristics of adventitious breath sounds adapted from Jarvis (2007) Transmitted voice sounds are not a routine part of respiratory assessment and are only assessed if abnormal bronchial or bronchovesicular breath sounds are heard. Transmitted voice sounds are assessed by asking the patient to say ninety-nine
5 and ee whilst listening in symmetric areas over the chest wall. Normally voice transmission is muffled and indistinct but pathology that increases lung density such as lobar pneumonia enhances the transmission of voice sounds (Mangione 2008). When listening to transmitted voice sounds, you are assessing for bronchophony, egophony and whispered pectoriloquy. Case study Gita Kumar is 68 yrs old. Two days ago she underwent coronary artery bypass (two saphenous vein grafts and one internal mammary artery). Post operatively she developed a chest infection. She has a history of emphysema. This morning she has had her pleural chest drains removed but has not yet had a CXR. Over the next twothree hours she becomes increasingly unwell. She is complaining of chest pain, shortness of breath and is becoming increasingly anxious. Your assessment of her vital signs reveals the following information: BP180/90 Heart Rate 150 BPM thready and weak pulse Respiratory rate 33 laboured and shallow Oxygen saturations 90% on four litres of oxygen Based on the knowledge you have gained about respiratory assessment, what aspects of the assessment framework would you apply to this patient? You would use a systematic and logical framework that included: Inspection Palpation Percussion Auscultation On inspection of Mrs Kumar you notice the following: She is sitting up and using her accessory muscles Chest expansion appears unequal and tachypnea and hyponea are evident. She has central cyanosis Based on the information gained from inspection, what aspect of the respiratory assessment would you perform next?
6 Palpation On palpation you identify the following: Unequal expansion of the left side of the chest Tactile fremitus is absent on the left side of the chest Right sided tracheal shift What is your differential diagnosis based on the information gained so far? Pneumonia Pleural effusion Emphysema Pneumothorax Atelectasis Percussion reveals the following: Hyperresonant on the left and resonant on the right What is your differential diagnosis based on the information gained so far? Emphysema Pneumothorax Auscultation reveals the following: Breath sounds absent and transmitted voice sounds on left side Decreased breath sounds with inspiratory wheeze over all zones on the right side. Based on the information gained what is your diagnosis? Left sided pnuemothorax. Conclusion This paper has described and discussed the skills of percussion and auscultation
7 which complete the systematic model of respiratory assessment outlined in part one of the series. Nurses close and continued monitoring of patients means that they are often the first to detect the early signs of physiological deterioration. Early identification of respiratory dysfunction plays an important role in preventing adverse events, promoting positive patient outcomes and improving patient care (Gardiner et al. 2007). A thorough and detailed respiratory assessment of patients is therefore essential in ensuring that a holistic and comprehensive model of care is delivered. Key Points Patients are more likely to deteriorate on wards and suffer a major adverse event. Changes in respiratory function are the most sensitive indicator of an impending adverse event. Auscultation and percussion skills are key components of respiratory assessment Respiratory assessment is now considered integral to the scope of practice of the cardiac practitioner
8 References Cioffi, J. (2000). Recognition of patients who require emergency assistance: A descriptive study. Heart & Lung, 29, Considine, J.(2005). The role of nurses in preventing adverse events related to respiratory dysfunction: literature review. J of Advan Nurs, 49, Considine, J. & Botti, M. (2004). Who, when and where? Identification of patients at risk of an in-hospital adverse event: implications for nursing practice. Int J Nurs Pract, 10, Jarvis C (2007) Physical Examination and Health Assessment 5 th Ed. Saunders Elsevier, St.Louis.Douglas G, Nicol F, Robertson C (2009) Macleod s Clinical Examination12th Ed. Elsevier. Churchill Livingstone, St Louis Bickley LS (2008) Bates Guide to Physical Examination and History Taking 10 th Ed. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia Franklin, C. & Matthew, J. (1994). Developing strategies to prevent inhospital cardiac arrest: analysing response of physicians and nurses in the hours before the event. Crit Care Med, 22, Harrison, G. A., T. Jacques, et al. (2006). "Combinations of early signs of critical illness predict in-hospital death-the SOCCER study (signs of critical conditions and emergency responses)." Resuscitation 71(3): Kause J., Smith, G., Prytherch, D., Parr, M., Flabouris, A. & Hillman, K.(2004). A comparison of antecedents to cardiac arrests, deaths and emergency intensive care admissions in Australia and New Zealand, and the United Kingdom - the ACADEMIA study. Resuscitation, 62, Gardiner et al (2007) Massey, D., Aitken, L. M. & Chaboyer, C What factors influence suboptimal ward care in the acutely ill ward patient? Australian Critical Care 21,
9 Mangione,S. (2008) Physical Diagnosis Secrets. Mosby Elsevier, Philadelphia Mangione S, Duffy D (2003) The Teaching of Chest Auscultation During Primary Care Training: Has Anything Changed in the 1990s? CHEST 124: National Institute of Health and clinical Excellence (2007) Acutely ill Patients in Hospital Recognition and responce to acute illness in adults in hosptial (accessed 24th September 2010)
Lung & Thorax Exams. Charlie Goldberg, M.D. Professor of Medicine, UCSD SOM [email protected]
 Lung & Thorax Exams Charlie Goldberg, M.D. Professor of Medicine, UCSD SOM [email protected] Lung Exam Includes Vital Signs & Cardiac Exam 4 Elements (cardiac & abdominal too) Observation Palpation Percussion
Lung & Thorax Exams Charlie Goldberg, M.D. Professor of Medicine, UCSD SOM [email protected] Lung Exam Includes Vital Signs & Cardiac Exam 4 Elements (cardiac & abdominal too) Observation Palpation Percussion
Pulmonary Auscultation
 Review of Clinical Signs Pulmonary Auscultation Series Editor: Bernard Karnath, MD Bernard Karnath, MD Michael C. Boyars, MD Pulmonary auscultation has been a principal feature of standard physical examinations
Review of Clinical Signs Pulmonary Auscultation Series Editor: Bernard Karnath, MD Bernard Karnath, MD Michael C. Boyars, MD Pulmonary auscultation has been a principal feature of standard physical examinations
Oxygen Therapy. Oxygen therapy quick guide V3 July 2012.
 PRESENTATION Oxygen (O 2 ) is a gas provided in a compressed form in a cylinder. It is also available in a liquid form. It is fed via a regulator and flow meter to the patient by means of plastic tubing
PRESENTATION Oxygen (O 2 ) is a gas provided in a compressed form in a cylinder. It is also available in a liquid form. It is fed via a regulator and flow meter to the patient by means of plastic tubing
HLTEN609B Practise in the respiratory nursing environment
 HLTEN609B Practise in the respiratory nursing environment Release: 1 HLTEN609B Practise in the respiratory nursing environment Modification History Not Applicable Unit Descriptor Descriptor This unit addresses
HLTEN609B Practise in the respiratory nursing environment Release: 1 HLTEN609B Practise in the respiratory nursing environment Modification History Not Applicable Unit Descriptor Descriptor This unit addresses
Respiratory Care. A Life and Breath Career for You!
 Respiratory Care A Life and Breath Career for You! Respiratory Care Makes a Difference At 9:32 am, Lori Moreno brought a newborn baby struggling to breathe back to life What have you accomplished today?
Respiratory Care A Life and Breath Career for You! Respiratory Care Makes a Difference At 9:32 am, Lori Moreno brought a newborn baby struggling to breathe back to life What have you accomplished today?
RESPIRATORY VENTILATION Page 1
 Page 1 VENTILATION PARAMETERS A. Lung Volumes 1. Basic volumes: elements a. Tidal Volume (V T, TV): volume of gas exchanged each breath; can change as ventilation pattern changes b. Inspiratory Reserve
Page 1 VENTILATION PARAMETERS A. Lung Volumes 1. Basic volumes: elements a. Tidal Volume (V T, TV): volume of gas exchanged each breath; can change as ventilation pattern changes b. Inspiratory Reserve
Oxygen - update April 2009 OXG
 PRESENTATION Oxygen (O 2 ) is a gas provided in compressed form in a cylinder. It is also available in liquid form, in a system adapted for ambulance use. It is fed via a regulator and flow meter to the
PRESENTATION Oxygen (O 2 ) is a gas provided in compressed form in a cylinder. It is also available in liquid form, in a system adapted for ambulance use. It is fed via a regulator and flow meter to the
Basic techniques of pulmonary physical therapy (I) 100/04/24
 Basic techniques of pulmonary physical therapy (I) 100/04/24 Evaluation of breathing function Chart review History Chest X ray Blood test Observation/palpation Chest mobility Shape of chest wall Accessory
Basic techniques of pulmonary physical therapy (I) 100/04/24 Evaluation of breathing function Chart review History Chest X ray Blood test Observation/palpation Chest mobility Shape of chest wall Accessory
Oxygenation. Chapter 21. Anatomy and Physiology of Breathing. Anatomy and Physiology of Breathing*
 Oxygenation Chapter 21 Anatomy and Physiology of Breathing Inspiration ~ breathing in Expiration ~ breathing out Ventilation ~ Movement of air in & out of the lungs Respiration ~ exchange of O2 & carbon
Oxygenation Chapter 21 Anatomy and Physiology of Breathing Inspiration ~ breathing in Expiration ~ breathing out Ventilation ~ Movement of air in & out of the lungs Respiration ~ exchange of O2 & carbon
written by Harvard Medical School COPD It Can Take Your Breath Away www.patientedu.org/copd
 written by Harvard Medical School COPD It Can Take Your Breath Away www.patientedu.org/copd What Is COPD? COPD stands for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. There are two major diseases included in
written by Harvard Medical School COPD It Can Take Your Breath Away www.patientedu.org/copd What Is COPD? COPD stands for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. There are two major diseases included in
Pulmonary Techniques. Anatomy Review. Anatomy Review. Chest Physical Therapy
 Pulmonary Techniques Chest Physical Therapy Anatomy Review Respiratory System Upper Tract Functions Warm moisten and filter inspired air Bacteria is trapped by nasal mucosa Respiratory System Middle Tract
Pulmonary Techniques Chest Physical Therapy Anatomy Review Respiratory System Upper Tract Functions Warm moisten and filter inspired air Bacteria is trapped by nasal mucosa Respiratory System Middle Tract
Tests. Pulmonary Functions
 Pulmonary Functions Tests Static lung functions volumes Dynamic lung functions volume and velocity Dynamic Tests Velocity dependent on Airway resistance Resistance of lung tissue to change in shape Dynamic
Pulmonary Functions Tests Static lung functions volumes Dynamic lung functions volume and velocity Dynamic Tests Velocity dependent on Airway resistance Resistance of lung tissue to change in shape Dynamic
2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system
 2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system 2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system Essential questions What are the functions of the respiratory
2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system 2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system Essential questions What are the functions of the respiratory
Emergency Scenario. Chest Pain
 Emergency Scenario Chest Pain This emergency scenario reviews chest pain in a primary care patient, and is set up for roleplay and case review with your staff. 1) The person facilitating scenarios can
Emergency Scenario Chest Pain This emergency scenario reviews chest pain in a primary care patient, and is set up for roleplay and case review with your staff. 1) The person facilitating scenarios can
CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE. Includes: Bronchitis (chronic and acute) Emphysema
 THE BASICS OF BREATHING: Assessment & Treatment Approaches for the Patient with COPD Jocelyn Alexander, MA CCC-SLP Director of Program Development Therapy Partners of Ohio LEARNER OBJECTIVES: Identify
THE BASICS OF BREATHING: Assessment & Treatment Approaches for the Patient with COPD Jocelyn Alexander, MA CCC-SLP Director of Program Development Therapy Partners of Ohio LEARNER OBJECTIVES: Identify
Cardiopulmonary Physical Therapy. Haneul Lee, DSc, PT
 Cardiopulmonary Physical Therapy Haneul Lee, DSc, PT Airway ClearanceTechniques Breathing Exercise SpecialConsiderations for MechanicallyVentilated Exercise Injury Prevention and Equipment provision Patient
Cardiopulmonary Physical Therapy Haneul Lee, DSc, PT Airway ClearanceTechniques Breathing Exercise SpecialConsiderations for MechanicallyVentilated Exercise Injury Prevention and Equipment provision Patient
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patient Guidebook
 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patient Guidebook The Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of the lungs and air passages. The lungs are the part of the body where gases are exchanged
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patient Guidebook The Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of the lungs and air passages. The lungs are the part of the body where gases are exchanged
Compare the physiologic responses of the respiratory system to emphysema, chronic bronchitis, and asthma
 Chapter 31 Drugs Used to Treat Lower Respiratory Disease Learning Objectives Describe the physiology of respirations Compare the physiologic responses of the respiratory system to emphysema, chronic bronchitis,
Chapter 31 Drugs Used to Treat Lower Respiratory Disease Learning Objectives Describe the physiology of respirations Compare the physiologic responses of the respiratory system to emphysema, chronic bronchitis,
Pulmonary Patterns VMA 976
 Pulmonary Patterns VMA 976 PULMONARY PATTERNS Which pulmonary patterns are commonly described in veterinary medicine? PULMONARY PATTERNS Normal Alveolar Interstitial Structured/Nodular Unstructured Bronchial
Pulmonary Patterns VMA 976 PULMONARY PATTERNS Which pulmonary patterns are commonly described in veterinary medicine? PULMONARY PATTERNS Normal Alveolar Interstitial Structured/Nodular Unstructured Bronchial
MOLLOY COLLEGE DIVISION OF NURSING NURSE PRACTITIONER PROGRAMS. Study Guide for the Basic Physical Assessment Exam
 DIVISION OF NURSING S Study Guide for the Basic Physical Assessment Exam Questions will be based on following chapters in, Bickley, L.S. (2009). (10 th ed). Bates guide to physical examination and history
DIVISION OF NURSING S Study Guide for the Basic Physical Assessment Exam Questions will be based on following chapters in, Bickley, L.S. (2009). (10 th ed). Bates guide to physical examination and history
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
Pneumonia Education and Discharge Instructions
 Pneumonia Education and Discharge Instructions Pneumonia Education and Discharge Instructions Definition: Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs. Many different organisms can cause it, including bacteria,
Pneumonia Education and Discharge Instructions Pneumonia Education and Discharge Instructions Definition: Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs. Many different organisms can cause it, including bacteria,
Asthma and COPD Awareness
 Asthma and COPD Awareness Molina Breathe with Ease sm and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Molina Healthcare of Michigan Fall 2012 Importance of Controller Medicines Asthma is a disease that causes
Asthma and COPD Awareness Molina Breathe with Ease sm and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Molina Healthcare of Michigan Fall 2012 Importance of Controller Medicines Asthma is a disease that causes
Pulmonary Diseases. Lung Disease: Pathophysiology, Medical and Exercise Programming. Overview of Pathophysiology
 Lung Disease: Pathophysiology, Medical and Exercise Programming Overview of Pathophysiology Ventilatory Impairments Increased airway resistance Reduced compliance Increased work of breathing Ventilatory
Lung Disease: Pathophysiology, Medical and Exercise Programming Overview of Pathophysiology Ventilatory Impairments Increased airway resistance Reduced compliance Increased work of breathing Ventilatory
Better Breathing with COPD
 Better Breathing with COPD People with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) often benefit from learning different breathing techniques. Pursed Lip Breathing Pursed Lip Breathing (PLB) can be very
Better Breathing with COPD People with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) often benefit from learning different breathing techniques. Pursed Lip Breathing Pursed Lip Breathing (PLB) can be very
Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System Basic functions of the respiratory system: as a Gas exchange supply oxygen to aerobic tissues in the body and remove carbon dioxide waste product. in-
Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System Basic functions of the respiratory system: as a Gas exchange supply oxygen to aerobic tissues in the body and remove carbon dioxide waste product. in-
Disease/Illness GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER. What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? www.simpsonmillar.co.uk Telephone 0844 858 3200
 GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
Chapter 26. Assisting With Oxygen Needs. Elsevier items and derived items 2014, 2010 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 26 Assisting With Oxygen Needs Oxygen (O 2 ) is a gas. Oxygen It has no taste, odor, or color. It is a basic need required for life. Death occurs within minutes if breathing stops. Brain damage
Chapter 26 Assisting With Oxygen Needs Oxygen (O 2 ) is a gas. Oxygen It has no taste, odor, or color. It is a basic need required for life. Death occurs within minutes if breathing stops. Brain damage
Wendy Sue Killham RN, BSN, MSN, FNP s
 We were never tired of visiting and examining and ausculting, and of examining and ausculting again and again, Peter Mere Latham (1789 8175) Wendy Sue Killham RN, BSN, MSN, FNP s Recognize system based
We were never tired of visiting and examining and ausculting, and of examining and ausculting again and again, Peter Mere Latham (1789 8175) Wendy Sue Killham RN, BSN, MSN, FNP s Recognize system based
Fourth Grade The Human Body: The Respiratory System Assessment
 Fourth Grade The Human Body: The Respiratory System Assessment 1a. The brings air in and out of the body. a. respiratory system b. circulatory system 1b. The system is the part of the body responsible
Fourth Grade The Human Body: The Respiratory System Assessment 1a. The brings air in and out of the body. a. respiratory system b. circulatory system 1b. The system is the part of the body responsible
Chapter 2 - Anatomy & Physiology of the Respiratory System
 Chapter 2 - Anatomy & Physiology of the Respiratory System Written by - AH Kendrick & C Newall 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Gross Anatomy of the Lungs, 2.3 Anatomy of the Thorax, 2.4 Anatomy and Histology of the
Chapter 2 - Anatomy & Physiology of the Respiratory System Written by - AH Kendrick & C Newall 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Gross Anatomy of the Lungs, 2.3 Anatomy of the Thorax, 2.4 Anatomy and Histology of the
COPD. Information brochure for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
 COPD Information brochure for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. CONTENTS What does COPD mean?...04 What are the symptoms of COPD?...06 What causes COPD?...09 Treating COPD...10 Valve therapy in COPD...12
COPD Information brochure for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. CONTENTS What does COPD mean?...04 What are the symptoms of COPD?...06 What causes COPD?...09 Treating COPD...10 Valve therapy in COPD...12
The Aged Lung per se and Chronic Pulmonary Diseases in and around the Aged Lung
 Special Article* The Aged Lung per se and Chronic Pulmonary Diseases in and around the Aged Lung Takashi Nakamura I. Introduction Professor of the First Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine,
Special Article* The Aged Lung per se and Chronic Pulmonary Diseases in and around the Aged Lung Takashi Nakamura I. Introduction Professor of the First Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine,
Acute Care Day Respiratory. SCENARIO The Patient with Acute Asthma
 Acute Care Day Respiratory SCENARIO The Patient with Acute Asthma Notes for the instructor not volunteered to students 30 minutes have been allocated to the running of the scenario with an additional 10
Acute Care Day Respiratory SCENARIO The Patient with Acute Asthma Notes for the instructor not volunteered to students 30 minutes have been allocated to the running of the scenario with an additional 10
SAM, Student Auscultation Manikin
 SAM, Student Auscultation Manikin Product: SAM, Student Auscultation Manikin Cat. No.: 718-9007 Price: (Call for latest pricing) 281-488-5901 or 1-800-364-5901 in US and Canada; Email: [email protected]
SAM, Student Auscultation Manikin Product: SAM, Student Auscultation Manikin Cat. No.: 718-9007 Price: (Call for latest pricing) 281-488-5901 or 1-800-364-5901 in US and Canada; Email: [email protected]
How To Treat A Heart Attack
 13 Resuscitation and preparation for anaesthesia and surgery Key Points 13.1 MANAGEMENT OF EMERGENCIES AND CARDIOPULMONARY RESUSCITATION ESSENTIAL HEALTH TECHNOLOGIES The emergency measures that are familiar
13 Resuscitation and preparation for anaesthesia and surgery Key Points 13.1 MANAGEMENT OF EMERGENCIES AND CARDIOPULMONARY RESUSCITATION ESSENTIAL HEALTH TECHNOLOGIES The emergency measures that are familiar
Department of Surgery
 What is emphysema? 2004 Regents of the University of Michigan Emphysema is a chronic disease of the lungs characterized by thinning and overexpansion of the lung-like blisters (bullae) in the lung tissue.
What is emphysema? 2004 Regents of the University of Michigan Emphysema is a chronic disease of the lungs characterized by thinning and overexpansion of the lung-like blisters (bullae) in the lung tissue.
PULMONARY PHYSIOLOGY
 I. Lung volumes PULMONARY PHYSIOLOGY American College of Surgeons SCC Review Course Christopher P. Michetti, MD, FACS and Forrest O. Moore, MD, FACS A. Tidal volume (TV) is the volume of air entering and
I. Lung volumes PULMONARY PHYSIOLOGY American College of Surgeons SCC Review Course Christopher P. Michetti, MD, FACS and Forrest O. Moore, MD, FACS A. Tidal volume (TV) is the volume of air entering and
University of Kansas. Respiratory Care Education
 University of Kansas Respiratory Care Education What is Respiratory Care? Respiratory Care is the health profession that specializes in the promotion of optimum cardiopulmonary function and health Respiratory
University of Kansas Respiratory Care Education What is Respiratory Care? Respiratory Care is the health profession that specializes in the promotion of optimum cardiopulmonary function and health Respiratory
Northwestern Health Sciences University. Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers
 Northwestern Health Sciences University Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest May 2005 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST for BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses Based
Northwestern Health Sciences University Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest May 2005 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST for BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses Based
404 Section 5 Shock and Resuscitation. Scene Size-up. Primary Assessment. History Taking
 404 Section 5 and Resuscitation Scene Size-up Scene Safety Mechanism of Injury (MOI)/ Nature of Illness (NOI) Ensure scene safety and address hazards. Standard precautions should include a minimum of gloves
404 Section 5 and Resuscitation Scene Size-up Scene Safety Mechanism of Injury (MOI)/ Nature of Illness (NOI) Ensure scene safety and address hazards. Standard precautions should include a minimum of gloves
April 2015 CALGARY ZONE CLINICAL REFERENCE PULMONARY CENTRAL ACCESS & TRIAGE
 April 2015 CALGARY ZONE CLINICAL REFERENCE CENTRAL ACCESS & TRIAGE Introduction Pulmonary consulting services are organized through the Calgary Zone Pulmonary Central Access and Triage (PCAT). Working
April 2015 CALGARY ZONE CLINICAL REFERENCE CENTRAL ACCESS & TRIAGE Introduction Pulmonary consulting services are organized through the Calgary Zone Pulmonary Central Access and Triage (PCAT). Working
Help Yourself Breathe. Tender Loving Care for Your Lungs. Department of Physiotherapy. PD 1359 (Rev 06-2009) File: peyles
 Help Yourself Breathe Tender Loving Care for Your Lungs PD 1359 (Rev 06-2009) File: peyles Department of Physiotherapy Why are you breathless? Chronic Airflow Limitation or Obstruction is a decrease in
Help Yourself Breathe Tender Loving Care for Your Lungs PD 1359 (Rev 06-2009) File: peyles Department of Physiotherapy Why are you breathless? Chronic Airflow Limitation or Obstruction is a decrease in
Your Lungs and COPD. Patient Education Pulmonary Rehabilitation. A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs
 Patient Education Your Lungs and COPD A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs Your lungs are organs that process every breath you take. They provide oxygen (O 2 ) to the blood and
Patient Education Your Lungs and COPD A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs Your lungs are organs that process every breath you take. They provide oxygen (O 2 ) to the blood and
Non-Cardiac Chest Pain in Athletes
 Non-Cardiac Chest Pain in Athletes Number of Contact Hours: ½ hour Description: Due to uncertainty and life-threatening conditions, chest pain can be a source of anxiety and concern for athletic trainers.
Non-Cardiac Chest Pain in Athletes Number of Contact Hours: ½ hour Description: Due to uncertainty and life-threatening conditions, chest pain can be a source of anxiety and concern for athletic trainers.
Pulmonary Ventilation
 Pulmonary Ventilation Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction Pulmonary ventilation, or breathing, is the
Pulmonary Ventilation Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction Pulmonary ventilation, or breathing, is the
PARAMEDIC TRAINING CLINICAL OBJECTIVES
 Page 1 of 21 GENERAL PATIENT UNIT When assigned to the General Patient unit paramedic student should gain knowledge and experience in the following: 1. Appropriate communication with patients and members
Page 1 of 21 GENERAL PATIENT UNIT When assigned to the General Patient unit paramedic student should gain knowledge and experience in the following: 1. Appropriate communication with patients and members
CLINICAL SKILLS: THE 'DR ABCDE' ASSESSMENT
 CLINICAL SKILLS: THE 'DR ABCDE' ASSESSMENT The 'DR ABCDE' approach to assessing an acutely unwell patient should be at the front of every junior doctor's mind whenever they get bleeped or asked to see
CLINICAL SKILLS: THE 'DR ABCDE' ASSESSMENT The 'DR ABCDE' approach to assessing an acutely unwell patient should be at the front of every junior doctor's mind whenever they get bleeped or asked to see
N26 Chest Tubes 5/9/2012
 Thoracic cavity, pleural space 1 Conditions requiring chest drainage_1 Air between the pleurae is a pneumothorax Occurs when there is an opening on the surface of the lung or in the airways, y, in the
Thoracic cavity, pleural space 1 Conditions requiring chest drainage_1 Air between the pleurae is a pneumothorax Occurs when there is an opening on the surface of the lung or in the airways, y, in the
Asbestos Related Diseases
 Asbestos Related Diseases Asbestosis Mesothelioma Lung Cancer Pleural Disease Asbestosis and Mesothelioma (LUNG CANCER) Support Group 1800 017 758 www.amsg.com.au ii Helping you and your family through
Asbestos Related Diseases Asbestosis Mesothelioma Lung Cancer Pleural Disease Asbestosis and Mesothelioma (LUNG CANCER) Support Group 1800 017 758 www.amsg.com.au ii Helping you and your family through
ENT Emergencies. Injuries of the Neck. Registrar Dept Trauma and emergency Medicine Tygerberg Hospital
 ENT Emergencies Injuries of the Neck Registrar Dept Trauma and emergency Medicine Tygerberg Hospital Neck Injuries Blunt and Penetrating Trauma Blunt Injuries Blunt trauma direct/indirect Trauma to larynx
ENT Emergencies Injuries of the Neck Registrar Dept Trauma and emergency Medicine Tygerberg Hospital Neck Injuries Blunt and Penetrating Trauma Blunt Injuries Blunt trauma direct/indirect Trauma to larynx
MECHINICAL VENTILATION S. Kache, MD
 MECHINICAL VENTILATION S. Kache, MD Spontaneous respiration vs. Mechanical ventilation Natural spontaneous ventilation occurs when the respiratory muscles, diaphragm and intercostal muscles pull on the
MECHINICAL VENTILATION S. Kache, MD Spontaneous respiration vs. Mechanical ventilation Natural spontaneous ventilation occurs when the respiratory muscles, diaphragm and intercostal muscles pull on the
Marilyn Borkgren-Okonek, APN, CCNS, RN, MS Suburban Lung Associates, S.C. Elk Grove Village, IL
 Marilyn Borkgren-Okonek, APN, CCNS, RN, MS Suburban Lung Associates, S.C. Elk Grove Village, IL www.goldcopd.com GLOBAL INITIATIVE FOR CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE LUNG DISEASE GLOBAL STRATEGY FOR DIAGNOSIS, MANAGEMENT
Marilyn Borkgren-Okonek, APN, CCNS, RN, MS Suburban Lung Associates, S.C. Elk Grove Village, IL www.goldcopd.com GLOBAL INITIATIVE FOR CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE LUNG DISEASE GLOBAL STRATEGY FOR DIAGNOSIS, MANAGEMENT
COPD It Can Take Your Breath Away www.patientedu.org
 written by Harvard Medical School COPD It Can Take Your Breath Away www.patientedu.org What Is COPD? COPD stands for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. There are 2 major diseases included in COPD:
written by Harvard Medical School COPD It Can Take Your Breath Away www.patientedu.org What Is COPD? COPD stands for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. There are 2 major diseases included in COPD:
Documenting & Coding. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Presented by: David S. Brigner, MLA, CPC
 Documenting & Coding Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Presented by: David S. Brigner, MLA, CPC Sr. Provider Training & Development Consultant Professional Profile David Brigner currently performs
Documenting & Coding Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Presented by: David S. Brigner, MLA, CPC Sr. Provider Training & Development Consultant Professional Profile David Brigner currently performs
NURSING CARE PLANS. mjmanalangquintornusrn
 NURSING CARE PLANS Nursing Care Plan Known to be the blueprint of the nursing process Used to identify the scope and depth of the nursing practice Evidenced by: Sufficient data collection At least one
NURSING CARE PLANS Nursing Care Plan Known to be the blueprint of the nursing process Used to identify the scope and depth of the nursing practice Evidenced by: Sufficient data collection At least one
Objectives COPD. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) 4/19/2011
 Objectives Discuss assessment findings and treatment for: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Bronchitis Emphysema Asthma Anaphylaxis Other respiratory issues Provide some definitions Chronic Obstructive
Objectives Discuss assessment findings and treatment for: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Bronchitis Emphysema Asthma Anaphylaxis Other respiratory issues Provide some definitions Chronic Obstructive
ASTHMA IN INFANTS AND YOUNG CHILDREN
 ASTHMA IN INFANTS AND YOUNG CHILDREN What is Asthma? Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways. Symptoms of asthma are variable. That means that they can be mild to severe, intermittent to
ASTHMA IN INFANTS AND YOUNG CHILDREN What is Asthma? Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways. Symptoms of asthma are variable. That means that they can be mild to severe, intermittent to
CPT codes are for information only; consult your payer organization for reimbursement information.
 CPT codes are for information only; consult your payer organization for reimbursement information. Coverage for Spirometry/Oximetry Spirometry is a component of pulmonary function testing (PFTs). PFTs
CPT codes are for information only; consult your payer organization for reimbursement information. Coverage for Spirometry/Oximetry Spirometry is a component of pulmonary function testing (PFTs). PFTs
Vtial sign #1: PULSE. Vital Signs: Assessment and Interpretation. Factors that influence pulse rate: Importance of Vital Signs
 Vital Signs: Assessment and Interpretation Elma I. LeDoux, MD, FACP, FACC Associate Professor of Medicine Vtial sign #1: PULSE Reflects heart rate (resting 60-90/min) Should be strong and regular Use 2
Vital Signs: Assessment and Interpretation Elma I. LeDoux, MD, FACP, FACC Associate Professor of Medicine Vtial sign #1: PULSE Reflects heart rate (resting 60-90/min) Should be strong and regular Use 2
81 First Responder Respiratory
 81 First Responder Medical Scenarios Asthma Scenario: You are called to a local house for a woman with trouble breathing. You arrive to find a 67-year-old woman sitting upright in a chair. She states she
81 First Responder Medical Scenarios Asthma Scenario: You are called to a local house for a woman with trouble breathing. You arrive to find a 67-year-old woman sitting upright in a chair. She states she
Diseases. Inflammations Non-inflammatory pleural effusions Pneumothorax Tumours
 Pleura Visceral pleura covers lungs and extends into fissures Parietal pleura limits mediastinum and covers dome of diaphragm and inner aspect of chest wall. Two layers between them (pleural cavity) contains
Pleura Visceral pleura covers lungs and extends into fissures Parietal pleura limits mediastinum and covers dome of diaphragm and inner aspect of chest wall. Two layers between them (pleural cavity) contains
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is the name for a group of lung diseases including chronic bronchitis, emphysema and chronic obstructive airways
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is the name for a group of lung diseases including chronic bronchitis, emphysema and chronic obstructive airways
Congestive Heart Failure
 William Herring, M.D. 2002 Congestive Heart Failure In Slide Show mode, to advance slides, press spacebar or click left mouse button Congestive Heart Failure Causes of Coronary artery disease Hypertension
William Herring, M.D. 2002 Congestive Heart Failure In Slide Show mode, to advance slides, press spacebar or click left mouse button Congestive Heart Failure Causes of Coronary artery disease Hypertension
Recurrent or Persistent Pneumonia
 Recurrent or Persistent Pneumonia Lower Respiratory Tract Dr T Avenant Recurrent or Persistent Pneumonia Definitions Recurrent pneumonia more than two episodes of pneumonia in 18 months Persistent pneumonia
Recurrent or Persistent Pneumonia Lower Respiratory Tract Dr T Avenant Recurrent or Persistent Pneumonia Definitions Recurrent pneumonia more than two episodes of pneumonia in 18 months Persistent pneumonia
Early Warning Scores (EWS) Clinical Sessions 2011 By Bhavin Doshi
 Early Warning Scores (EWS) Clinical Sessions 2011 By Bhavin Doshi What is EWS? After qualifying, junior doctors are expected to distinguish between the moderately sick patients who can be managed in the
Early Warning Scores (EWS) Clinical Sessions 2011 By Bhavin Doshi What is EWS? After qualifying, junior doctors are expected to distinguish between the moderately sick patients who can be managed in the
PROCEDURE - Chest Physiotherapy Chest Physiotherapy Effective: 10/12/94 Revised: 10/31/14 Chest Physiotherapy Purpose Policy Accountability/Training
 PROCEDURE - Page 1 of 10 Purpose Policy Physician's Order Indications Contraindications To standardize the use of chest physiotherapy as a form of therapy using one or more techniques to optimize the effects
PROCEDURE - Page 1 of 10 Purpose Policy Physician's Order Indications Contraindications To standardize the use of chest physiotherapy as a form of therapy using one or more techniques to optimize the effects
NEEDLE THORACENTESIS Pneumothorax / Hemothorax
 NEEDLE THORACENTESIS Pneumothorax / Hemothorax By: Steven Jones, NREMT-P Pneumothorax Pneumothorax is a collection of air or gas in the pleural space of the lung, causing the lung to collapse. Pneumothorax
NEEDLE THORACENTESIS Pneumothorax / Hemothorax By: Steven Jones, NREMT-P Pneumothorax Pneumothorax is a collection of air or gas in the pleural space of the lung, causing the lung to collapse. Pneumothorax
Asbestos Related Diseases. Asbestosis Mesothelioma Lung Cancer Pleural Disease. connecting raising awareness supporting advocating
 Asbestos Related Diseases Asbestosis Mesothelioma Lung Cancer Pleural Disease connecting raising awareness supporting advocating 1800 017 758 www.asbestosassociation.com.au Asbestos lagging was widely
Asbestos Related Diseases Asbestosis Mesothelioma Lung Cancer Pleural Disease connecting raising awareness supporting advocating 1800 017 758 www.asbestosassociation.com.au Asbestos lagging was widely
A. All cells need oxygen and release carbon dioxide why?
 I. Introduction: Describe how the cardiovascular and respiratory systems interact to supply O 2 and eliminate CO 2. A. All cells need oxygen and release carbon dioxide why? B. Two systems that help to
I. Introduction: Describe how the cardiovascular and respiratory systems interact to supply O 2 and eliminate CO 2. A. All cells need oxygen and release carbon dioxide why? B. Two systems that help to
Influenza (Flu) Influenza is a viral infection that may affect both the upper and lower respiratory tracts. There are three types of flu virus:
 Respiratory Disorders Bio 375 Pathophysiology General Manifestations of Respiratory Disease Sneezing is a reflex response to irritation in the upper respiratory tract and is associated with inflammation
Respiratory Disorders Bio 375 Pathophysiology General Manifestations of Respiratory Disease Sneezing is a reflex response to irritation in the upper respiratory tract and is associated with inflammation
Ventilation Perfusion Relationships
 Ventilation Perfusion Relationships VENTILATION PERFUSION RATIO Ideally, each alveolus in the lungs would receive the same amount of ventilation and pulmonary capillary blood flow (perfusion). In reality,
Ventilation Perfusion Relationships VENTILATION PERFUSION RATIO Ideally, each alveolus in the lungs would receive the same amount of ventilation and pulmonary capillary blood flow (perfusion). In reality,
Preoperative Laboratory and Diagnostic Studies
 Preoperative Laboratory and Diagnostic Studies Preoperative Labratorey and Diagnostic Studies The concept of standardized testing in all presurgical patients regardless of age or medical condition is no
Preoperative Laboratory and Diagnostic Studies Preoperative Labratorey and Diagnostic Studies The concept of standardized testing in all presurgical patients regardless of age or medical condition is no
Pediatric Respiratory System: Basic Anatomy & Physiology. Jihad Zahraa Pediatric Intensivist Head of PICU, King Fahad Medical City
 Pediatric Respiratory System: Basic Anatomy & Physiology Jihad Zahraa Pediatric Intensivist Head of PICU, King Fahad Medical City Outline Introduction Developmental Anatomy Developmental Mechanics of Breathing
Pediatric Respiratory System: Basic Anatomy & Physiology Jihad Zahraa Pediatric Intensivist Head of PICU, King Fahad Medical City Outline Introduction Developmental Anatomy Developmental Mechanics of Breathing
Cough, as a leading symptom, would certainly be in the top 10 of reasons for seeing a GP.
 COUGH Cough, as a leading symptom, would certainly be in the top 10 of reasons for seeing a GP. A cough in a child seems to cause more concern, even when it has not been present very long, whereas in adults
COUGH Cough, as a leading symptom, would certainly be in the top 10 of reasons for seeing a GP. A cough in a child seems to cause more concern, even when it has not been present very long, whereas in adults
SYMPTOMS OF RESPIRATORY DISORDERS THE PHYSICAL EXAMINATION AND THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. 134 The Body Systems: Clinical and Applied Topics
 34 The Body Systems: Clinical and Applied Topics The Respiratory System The anatomical components of the respiratory system can be divided into an upper respiratory system, which includes the nose, nasal
34 The Body Systems: Clinical and Applied Topics The Respiratory System The anatomical components of the respiratory system can be divided into an upper respiratory system, which includes the nose, nasal
Standard of Care: Pulmonary Physical Therapy Management of the patient with pulmonary disease
 BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL Department of Rehabilitation Services Physical Therapy Standard of Care: Pulmonary Case Type / Diagnosis: This standard of care applies to any patient with obstructive or restrictive
BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL Department of Rehabilitation Services Physical Therapy Standard of Care: Pulmonary Case Type / Diagnosis: This standard of care applies to any patient with obstructive or restrictive
2161-1 - Page 1. Name: 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. Questions 10 and 11 refer to the following:
 Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Lung Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand lung cancer and the treatment options that are available.
 Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
EUROPEAN LUNG FOUNDATION
 PULMONARY REHABILITATION understanding the professional guidelines This guide includes information on what the European Respiratory Society and the American Thoracic Society have said about pulmonary rehabilitation.
PULMONARY REHABILITATION understanding the professional guidelines This guide includes information on what the European Respiratory Society and the American Thoracic Society have said about pulmonary rehabilitation.
These factors increase your chance of developing emphysema. Tell your doctor if you have any of these risk factors:
 Emphysema Pronounced: em-fiss-see-mah by Debra Wood, RN En Español (Spanish Version) Definition Emphysema is a chronic obstructive disease of the lungs. The lungs contain millions of tiny air sacs called
Emphysema Pronounced: em-fiss-see-mah by Debra Wood, RN En Español (Spanish Version) Definition Emphysema is a chronic obstructive disease of the lungs. The lungs contain millions of tiny air sacs called
Understanding Hypoventilation and Its Treatment by Susan Agrawal
 www.complexchild.com Understanding Hypoventilation and Its Treatment by Susan Agrawal Most of us have a general understanding of what the term hyperventilation means, since hyperventilation, also called
www.complexchild.com Understanding Hypoventilation and Its Treatment by Susan Agrawal Most of us have a general understanding of what the term hyperventilation means, since hyperventilation, also called
American Heart Association. Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers
 American Heart Association Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest February 2001 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST for BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses 2001 American
American Heart Association Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest February 2001 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST for BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses 2001 American
Malignant Mesothelioma
 Malignant Malignant mesothelioma is a tumour originating from mesothelial cells. 85 95% of mesotheliomas are caused by asbestos exposure. It occurs much more commonly in the chest (malignant pleural mesothelioma)
Malignant Malignant mesothelioma is a tumour originating from mesothelial cells. 85 95% of mesotheliomas are caused by asbestos exposure. It occurs much more commonly in the chest (malignant pleural mesothelioma)
Malignant Mesothelioma
 Malignant mesothelioma is a tumour originating from mesothelial cells. 85 95% of mesotheliomas are caused by asbestos exposure. It occurs much more commonly in the chest (malignant pleural mesothelioma)
Malignant mesothelioma is a tumour originating from mesothelial cells. 85 95% of mesotheliomas are caused by asbestos exposure. It occurs much more commonly in the chest (malignant pleural mesothelioma)
GRADE 11F: Biology 3. UNIT 11FB.3 9 hours. Human gas exchange system and health. Resources. About this unit. Previous learning.
 GRADE 11F: Biology 3 Human gas exchange system and health UNIT 11FB.3 9 hours About this unit This unit is the third of six units on biology for Grade 11 foundation. The unit is designed to guide your
GRADE 11F: Biology 3 Human gas exchange system and health UNIT 11FB.3 9 hours About this unit This unit is the third of six units on biology for Grade 11 foundation. The unit is designed to guide your
Spinal Cord Injury Education. An Overview for Patients, Families, and Caregivers
 Spinal Cord Injury Education An Overview for Patients, Families, and Caregivers Spinal Cord Anatomy A major component of the Central Nervous System (CNS) It is 15 to 16 inches long, and weighs 1 to 2 ounces
Spinal Cord Injury Education An Overview for Patients, Families, and Caregivers Spinal Cord Anatomy A major component of the Central Nervous System (CNS) It is 15 to 16 inches long, and weighs 1 to 2 ounces
Emergency Medical Technician - Basic
 Washington State Specific Objectives for Emergency Medical Technician - Basic OFFICE OF EMERGENCY MEDICAL AND TRAUMA PREVENTION September 1996 Emergency Medical Technician - Basic Definition: Emergency
Washington State Specific Objectives for Emergency Medical Technician - Basic OFFICE OF EMERGENCY MEDICAL AND TRAUMA PREVENTION September 1996 Emergency Medical Technician - Basic Definition: Emergency
Pathophysiology of hypercapnic and hypoxic respiratory failure and V/Q relationships. Dr.Alok Nath Department of Pulmonary Medicine PGIMER Chandigarh
 Pathophysiology of hypercapnic and hypoxic respiratory failure and V/Q relationships Dr.Alok Nath Department of Pulmonary Medicine PGIMER Chandigarh Jan 2006 Respiratory Failure inadequate blood oxygenation
Pathophysiology of hypercapnic and hypoxic respiratory failure and V/Q relationships Dr.Alok Nath Department of Pulmonary Medicine PGIMER Chandigarh Jan 2006 Respiratory Failure inadequate blood oxygenation
Plank 1 Tool: Hypertension Medical Assistant Training (Providence Medical Group)
 Plank 1 Tool: Hypertension Medical Assistant Training (Providence Medical Group) Task Qualification Training Packet Volume 1 Date Performing Blood Pressure Checks SUBJECT AREA Vital Signs EQUIPMENT REQUIRED
Plank 1 Tool: Hypertension Medical Assistant Training (Providence Medical Group) Task Qualification Training Packet Volume 1 Date Performing Blood Pressure Checks SUBJECT AREA Vital Signs EQUIPMENT REQUIRED
Scope and Standards for Nurse Anesthesia Practice
 Scope and Standards for Nurse Anesthesia Practice Copyright 2013 222 South Prospect Ave. Park Ridge, IL 60068 www.aana.com Scope and Standards for Nurse Anesthesia Practice The AANA Scope and Standards
Scope and Standards for Nurse Anesthesia Practice Copyright 2013 222 South Prospect Ave. Park Ridge, IL 60068 www.aana.com Scope and Standards for Nurse Anesthesia Practice The AANA Scope and Standards
CERVICAL MEDIASTINOSCOPY WITH BIOPSY
 INFORMED CONSENT INFORMATION ADDRESSOGRAPH DATA CERVICAL MEDIASTINOSCOPY WITH BIOPSY You have decided to have an important procedure and we appreciate your selection of UCLA Healthcare to meet your needs.
INFORMED CONSENT INFORMATION ADDRESSOGRAPH DATA CERVICAL MEDIASTINOSCOPY WITH BIOPSY You have decided to have an important procedure and we appreciate your selection of UCLA Healthcare to meet your needs.
TRACHEOSTOMY TUBE PARTS
 Page1 NR 33 TRACHEOSTOMY CARE AND SUCTIONING Review ATI Basic skills videos: Tracheostomy care and Endotracheal suction using a closed suction set. TRACHEOSTOMY TUBE PARTS Match the numbers on the diagram
Page1 NR 33 TRACHEOSTOMY CARE AND SUCTIONING Review ATI Basic skills videos: Tracheostomy care and Endotracheal suction using a closed suction set. TRACHEOSTOMY TUBE PARTS Match the numbers on the diagram
PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS A Workshop on Simple Spirometry & Flow Volume Loops
 PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS A Workshop on Simple Spirometry & Flow Volume Loops YOU SHOULD READ THE FOLLOWING MATERIAL BEFORE Tuesday March 30 Interpretation of PFTs Learning Objectives 1. Specify the indications
PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS A Workshop on Simple Spirometry & Flow Volume Loops YOU SHOULD READ THE FOLLOWING MATERIAL BEFORE Tuesday March 30 Interpretation of PFTs Learning Objectives 1. Specify the indications
Measuring central venous pressure
 Elaine Cole Senior lecturer ED/Trauma, City University Barts and the London NHS Trust 1 Learning outcomes That the clinician can: Describe the sites of central venous catheterisation Understand why central
Elaine Cole Senior lecturer ED/Trauma, City University Barts and the London NHS Trust 1 Learning outcomes That the clinician can: Describe the sites of central venous catheterisation Understand why central
Airways Resistance and Airflow through the Tracheobronchial Tree
 Airways Resistance and Airflow through the Tracheobronchial Tree Lecturer: Sally Osborne, Ph.D. Department of Cellular & Physiological Sciences Email: [email protected] Useful links: www.sallyosborne.com
Airways Resistance and Airflow through the Tracheobronchial Tree Lecturer: Sally Osborne, Ph.D. Department of Cellular & Physiological Sciences Email: [email protected] Useful links: www.sallyosborne.com
Module 5 ADULT RECOvERY POSITION STEP 1 POSITION ThE victim
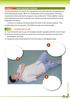 Module 5 ADULT RECOVERY POSITION The recovery position is used in the management of victims who are unresponsive but have breathing and pulse. When an unresponsive victim is lying supine, the airway may
Module 5 ADULT RECOVERY POSITION The recovery position is used in the management of victims who are unresponsive but have breathing and pulse. When an unresponsive victim is lying supine, the airway may
THE LUNGS IN MARFAN SYNDROME
 THE LUNGS IN MARFAN SYNDROME Many people with Marfan syndrome and some related disorders experience pulmonary complications, or problems with their lungs. If you have Marfan syndrome, it is important for
THE LUNGS IN MARFAN SYNDROME Many people with Marfan syndrome and some related disorders experience pulmonary complications, or problems with their lungs. If you have Marfan syndrome, it is important for
