Policy and Procedure Manual
|
|
|
- Andrea York
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Policy and Procedure Manual Diagnostic Services Radiology DS-R SUBJECT/TITLE: PURPOSE: INTRAVENOUS CONTRAST ADMINISTRATION 1) Ensure appropriate premedication in patients with known/suspected allergic reactions; 2) Ensure contrast administration is performed according to hospital and departmental protocols with appropriate supervision by a licensed independent practitioner (LIP). 3) Ensure appropriate actions are undertaken in case of contrast reactions and extravasation of contrast. 4) Ensure laboratory testing requirements conducted in patients in whom contrast administration is considered. DEFINITION: BACKGROUND: None The policy will be based on the Manual on Contrast Media (ACR, 2012) and other relevant literature. CONTENTS: A. Intravenous Iodinated Contrast Preparation for Contrast Administration Indications for Serum Creatinine Contrast Reactions to Iodinated IV Contrast Premedication for Iodinated IV contrast B. Intravenous Gadolinium Based Contrast Administration of Gadolinium Magnetic Resonance (MR) Screening for Impaired Renal Function Emergency MR Exams Premedication for Gadolinium contrast C. Intra-arterial Iodinated Contrast Administration D. Non-Intravenous Contrast Agents E. Ultrasound Contrast Agents F. Pediatric IV Contrast Administration G. Treatment of Contrast Reaction Table 1: Suggested Treatments for Contrast Reaction H. Treatment and Prevention of Contrast Extravasation I. Pregnancy and Breast Feeding Precautions J. Appendix A: Patient Information Sheet for Contrast Enhanced MRI K. Appendix B: Patient information Sheet for Breast Feeding after Contrast Enhanced MRI
2 POLICY: Guidelines for administration of Intravenous contrast: 1. A radiologic technologist or radiology nurse may administer intravenous contrast under the supervision of a licensed independent practitioner (LIP) and in accordance with procedure defined in this policy and following protocols used for contrast administration that are based upon the type of examination ordered and define the type, dose and route of contrast. 2. The supervising LIP or his/her physician designee must be available to respond promptly to an adverse event related to contrast administration. 3. Protocols for administration of intravenous contrast must be reviewed by the Department of Pharmaceutical Care Drug Information Center and approved by the P&T Subcommittee and by the Contrast Committee of the Department of Radiology when the standards of care and application change or when the characteristics of the intravenous contrast change. 4. An LIP reviews all requests for radiology procedures with intravenous contrast to determine and/or modify the appropriate protocol based on the clinical indications for the examination and patient status. The assigned protocol is indicated in the radiology information system (RIS) or electronic medical record (EMR). 5. A radiologic technologist or radiology nurse will review patient s current medications and clinical conditions for contraindications related to intravenous contrast administration. These include allergy to contrast, use of particular medications (e.g., metformin see below), and general physical condition which may impact risks for patient, such as heart failure and asthma. 6. If contraindications are identified, the supervising LIP will be contacted to determine appropriate IV contrast use. 7. Type of contrast and dose information is recorded in the EMR by the nurse or technologist. 8. Contrast doses that are prepared and NOT immediately administered to patient by the person who prepared the dose must be labeled with: Drug name, strength and amount (if not apparent from container) Initials or name of the person preparing the syringe Name of patient, medical record number, date of birth and location of the patient, if contrast dose is prepared based upon specific patient information. The dose should be used immediately and not stored. Page 2 of 19
3 PROCEDURE: A. INTRAVENOUS IODINATED CONTRAST All intravenous contrast utilized for CT and fluoroscopic exams at UIHC utilize iodine. The differing contrast agents will vary based on the form that the iodine is organically bound. Other variables in the type of iodinated contrast include ionic vs. nonionic, high osmolar (HOCM) vs. low osmolar (LOCM), and iso-osmolar contrast media. Preparation for Contrast Administration 1. Pre-administration Checks (4 Hs) The ACR manual describes the 4 Hs a. History b. Hydration c. Have equipment and expertise ready d. Heads up These checks have an effect on both the need for premedication, the risk of contrast extravasation, and the need for laboratory testing. 2. Renal failure-related issues with iodinated contrast a. Iodinated contrast has been implicated in causing significant decreased renal function in some patients following its administration, an effect called contrast media nephrotoxicity. b. Significant contrast media induced nephrotoxicity may be defined as: a >25% rise in serum creatinine from baseline (if < 1.5 mg/dl) OR an absolute elevation of >1.0 mg/dl from baseline (if > 1.5 mg/dl) within 72 hours following contrast administration. 3. Risk factors for contrast induced renal failure include: a. Pre-existing renal insufficiency b. History of kidney disease as an adult, including tumor and transplant c. Diabetes mellitus d. Dehydration e. Cardiovascular disease and use of diuretics f. Age > 60 years g. Multiple myeloma or paraproteinemia syndromes/diseases h. Uncontrolled Hypertension i. Hyperuricemia (gout) 4. Medications which may increase the risk of iodinated contrast-induced renal failure. a. Metformin (oral hypoglycemic agent for diabetes): This drug is excreted by the kidneys, and may accumulate resulting in severe (even fatal) lactic acidosis. b. NSAIDs including COX-2 selective agents (e.g., ibuprofen, naproxen, ketorolac, fenoprofen, indomethacin, celecoxib, etc.) c. Nephrotoxic antimicrobials (e.g., gentamicin, tobramycin, amikacin, amphotericin B, cidofovir) Page 3 of 19
4 5. Indications for serum creatinine prior to iodinated contrast exam The following patients must have a serum creatinine within 60 days prior to the exam: Age > 60 History of renal disease, including: Dialysis Kidney transplant Single kidney Renal cancer Renal surgery History of hypertension requiring medical therapy History of diabetes mellitus Metformin or metformin-containing drug combinations 6. Measures to Prevention/Ameliorate Nephrotoxicity a. Hydration if required. Normally, this can be achieved by oral administration of 1-2 liters of extra fluids in the 24 hours prior to contrast injection. In some cases, this can be achieved using 0.45% or 0.9% saline, 100 ml/hr from 12 hours before until 12 hours after contrast administration. b. Withhold furosemide. c. Withhold metformin for 48 hours after contrast administration and reinstitute only after repeat renal function tests (creatinine) had been obtained and determined to be normal. d. In patients with risk factors for contrast-induced renal failure, administer acetylcysteine, 600 mg by mouth twice daily on the day before and on the day of contrast administration (4 total doses). e. In patients who present acutely and who have an indication for acetylcysteine in patients with an adynamic ileus or non-intact GI tract, or patients who are unable to swallow and have no NG tube, two options are allowed: No contrast is administered; this is the preferred option for patients who present acutely) In life-threatening situations where a contrast-enhanced CT is required immediately (e.g., suspected pulmonary embolism, suspected aortic dissection, suspected aortic rupture, immediate requirement for vascular intervention), and where a 24-hour delay is unacceptable based on clinical grounds, one may consider administration of IV acetylcysteine (Acetadote 150 mg/kg over 30 minutes immediately prior contrast administration, followed by 50 mg/kg over 4 hours after). If IV acetylcysteine is administered, one must to be prepared for anaphylactic reactions and appropriate precautions much be taken. 7. Patients on Dialysis Patients on dialysis can receive IV contrast, and early post-procedural dialysis is NOT routinely required in every case. The Nephrology Service should be consulted for these cases. The fact that a patient is on dialysis should NOT be regarded as automatically allowing the administration IV contrast. Page 4 of 19
5 CONTRAST REACTIONS TO IODINATED IV CONTRAST Reactions to iodinated IV contrast occur in 1-3% of nonionic low-osmolar contrast injections. These range from mild urticaria (hives) to severe and life-threatening events. The severe lifethreatening reactions are relatively rare. Although overall adverse reactions are decreased following steroid premedication, the incidence of severe life-threatening adverse events has not been affected. Therefore, administration of IV contrast in patients with previous severe reactions should be done only in exceptional circumstances with full agreement by the patient, attending physician(s) and radiologist. 1. Premedication The following regimens are suggested based on the ACR Manual on Contrast media version : a. Planned contrast administration in patients with previous documented/suspected reaction: Two frequently used regimens are: 1. Prednisone 50 mg by mouth at 13 hours, 7 hours, and 1 hour before contrast media injection, plus diphenhydramine (Benadryl ) 50 mg intravenously, intramuscularly, or by mouth 1 hour before contrast medium. or 2. Methylprednisolone (Medrol ) 32 mg by mouth 12 hours and 2 hours before contrast media injection. An antihistamine (as in option 1) can also be added to this regimen injection. If the patient is unable to take oral medication, 200 mg of hydrocortisone intravenously may be substituted for oral prednisone. b. (Semi-) acute investigations in patients with previous documented/suspected reaction: The ordering physicians are encouraged to discuss the indication for contrast administration with the radiologist for alternative imaging. In decreasing order of desirability: 1. Methylprednisolone sodium succinate (Solu-Medrol ) 40 mg or hydrocortisone sodium succinate (Solu-Cortef ) 200 mg intravenously every 4 hours (q4h) until contrast study required plus diphenhydramine 50 mg IV 1 hour prior to contrast injection. 2. Dexamethasone sodium phosphate (Decadron ) 7.5 mg or betamethasone 6 mg intramuscularly q4h until contrast study must be done in patent with known allergy to methylprednisolone, aspirin, or non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs, especially if asthmatic. Also diphenhydramine 50 mg IV 1 hour prior to contrast injection. 3. Omit steroids entirely and give diphenhydramine 50 mg IV. Note: IV steroids have been shown to be less effective when administered less than 4 to 6 hours prior to contrast injection. c. Pediatric pre-medication Prednisone mg/kg PO (up to 50 mg) 13 hours, 7 hours, and 1 hour prior to contrast administration AND Diphenhydramine (Benadryl ) 1.25 mg/kg PO (up to 50 mg) 1 hour prior to contrast administration Page 5 of 19
6 d. Use of these pre-medication regimens may result in impairments that affect the patient s ability to drive. Appropriate precautions are advised i.e., designated driver. e. The non-emergent patients with contrast allergy, severe enough to require premedication may not be scanned after hours. The pre medication may be scheduled in such a way that the patient is scanned the first thing next morning, when we have full manpower to handle any breakthrough reactions. f. If clinical situation warrants emergent scanning after hours in a patient who has received either the premedication for prior contrast allergy: The afterhours scanning of the premedicated patient should be approved by the faculty member during the day. The on-call 5-6 PM, long or short call resident (as applicable) is to be informed by the day team about the scanning of premedicated patient. The technologist will page the on-call resident before administering the contrast. The on-call resident may request a LIP from the medical team to be present with the patient at the time of scanning g. On call and on weekends, any case with contrast allergy should go through the on-call resident to determine if the study needs to be done after hours or to suggest alternative method of scanning vs. premedication. h. For CT studies, imaging of premedicated patients after hours may be done on the ETC scanner if possible. 2. Emergent contrast administration in life-threatening situations In cases of life-threatening emergency requiring administration of IV contrast and where the ordering provider cannot wait for the premedication by the acute/semi-acute protocol requiring administration of steroids 4 hours and 1 hour prior to the procedure and the alternative test is not acceptable: a. The ordering physician must add a note in the medical record of the patient prior to the contrast administration which clearly states the following: Indication of the urgent study. Reason why the alternative exam (if offered by the radiologist) is not acceptable. Ensure that sufficient staff capable of handling the severe contrast reaction; including intubation and administration of life support drugs will be available during and after the procedure. b. You may consider giving hydrocortisone 200 mg IV AND diphenhydramine (Benadryl ) 50 mg IV stat prior to contrast administration and 4 hours later to cover delayed reaction, although according to the ACR manual IV steroids have not been shown to be effective when administered less than 4 to 6 hours prior to contrast injection. Page 6 of 19
7 B. INTRAVENOUS GADOLINIUM BASED CONTRAST AGENTS Patients with impaired renal function who receive IV gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCA) for MRI or MRA exams are at risk for developing a serious side effect called nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF), previously known as nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy (NFD). Patients at risk for NSF are those with severe or end-stage chronic kidney disease (CKD 4 or 5) or acute kidney injury (AKI). However, the greatest risk occurs in patients with end-stage kidney disease on renal dialysis. Patients with AKI, the group at next greatest risk, account for 12-20% of NSF cases. The exact NSF risk is unknown, but is probably in the range of 1-7% after one or more exposures to IV GBCA. The FDA has issued a black box warning for GBCA, which requires patients to be screened for acute kidney injury and other conditions that may reduce renal function. In addition, IV GBCA can cause allergic reactions, which are biologically similar to those observed with IV iodinated contrast agents formulated for use in CT, but are less frequent. 1. Screening for impaired renal function a. Patients with the conditions below are at risk for impaired renal function and must have a serum creatinine with estimated GFR (egfr) checked prior to administration of IV GBCA: Age > 60 years old Diabetes Mellitus (insulin-dependent, oral hypoglycemic or diet-controlled) History of renal disease (includes renal insufficiency or failure, solitary kidney, renal transplant, renal tumor) Other conditions as deemed appropriate by the responsible radiologist b. For outpatients with risk factors described above in subheading a, an acceptable time window for prior egfr laboratory testing, if available, is outlined in the table below (adapted from the ACR Manual on Contrast Media, Version 8, 2012): c. For all inpatients, egfr level should be obtained within two days prior to GBCA administration. Page 7 of 19
8 d. Identify risk factors for AKI, including recent surgery, severe infection, severe trauma and nephrotoxic drugs egfr is not a reliable indicator of AKI. e. Patients currently on dialysis (hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis or continuous dialysis) do not need to have their egfr checked. Dialysis patients represent 80% of all reported NSF cases. The ordering provider should indicate if the patient is on continuous dialysis (CVVHD, etc.) as these patients are at high risk for NSF, but may appear to have an egfr >30 ml/min/1.73m Administration of Gadolinium contrast agents for patients with impaired renal function a. Whenever possible, MR with IV GBCA should be avoided in patients on dialysis or with AKI or CKD stage 4 or 5 (egfr <30 ml/min/1.73m 2 ). However, if imaging with GBCA is essential and no suitable alternative is available, the following procedure must be followed: The responsible radiologist and ordering physician must discuss the clinical appropriateness, alternatives and urgency of the proposed MR exam and agree that the benefits outweigh the risks. The patient will be given copy of Information Sheet for Patients Scheduled for Contrast-Enhanced MRI. (Appendix A). The responsible radiologist will explain the risks and benefits of the proposed MRI exam and the patient will have an opportunity to discuss any concerns. If the patient agrees to proceed with the MRI exam, the radiologist will obtain verbal informed consent. The ordering physician must add a note in the medical record of the patient prior to the contrast administration which clearly states the benefit outweighs the risk. The radiology report must document the above discussions and verbal informed consent. The MR exam should be performed with the smallest possible dose of GBCA necessary to obtain a diagnostic study. The only permissible IV GBCA is Gadavist (gadobutrol)). The contrast agent can be administered only once during an imaging session. Omniscan (gadodiamide), Magnevist (gadopentetate dimeglumine) and OptiMARK (gadoversetamide) are contraindicated in patients on dialysis or with AKI or CKD stage 4 or 5 (per FDA warning dated 9/10/2010). b. Try to limit the cumulative dose of GBCA over several MR exams because this may increase NSF risk. c. For current hemodialysis patients, dialysis should be performed as soon as possible, but no later than 24 hours, after an MRI exam with IV gadolinium-based contrast agent. To date, hemodialysis has NOT been proven to decrease NSF risk. Page 8 of 19
9 3. Administration of Gadolinium contrast agents for various MRI exams a. Most contrast-enhanced MRI exams will be performed with single dose IV Gadavist (gadobutrol) 0.1 mmol/kg (0.1 ml/kg) body weight. If a patient has had previous contrast reactions or nausea/vomiting to Gadavist (gadobutrol), use Magnevist (gadopentetate dimeglumine) at 0.1 mmol/kg (0.2 ml/kg) if no risk of NSF. b. Some abdominal MRI exams of the liver and biliary tree may be performed with IV Eovist (gadoxetate disodium) (0.2 ml/kg). c. MR Enterography exams will be performed IV Gadavist (gadobutrol) at 0.15 ml/kg. If patient has a history of contrast reactions or nausea/vomiting to Gadavist (gadobutrol), use Magnevist (gadopentetate dimeglumine) at 0.3 ml/kg. d. Contrast-enhanced MRA exams will be performed with IV Gadavist (gadobutrol) as follows: Single station MRA 10 ml Gadavist (gadobutrol). Two or three station MRA 15 ml Gadavist (gadobutrol) diluted with 25 ml saline to 40 ml total volume. e. Contrast-enhanced cardiac MRI exams for myocardial viability will be performed with IV Gadavist (gadobutrol) 0.2 ml/kg. f. Pediatric Patients: Contrast-enhanced MRI exams will be performed with single dose IV Gadavist (gadobutrol): 0.1 ml/kg body weight in patients over 50 kg (110 lbs). Contrast-enhanced MRI exams will be performed with single dose IV Magnevist (gadopentetate): 0.2 ml/kg body weight in patients under 50 kg (110 lbs). MRA Neck, Brain, and MRV Brain will be performed with single dose IV Gadavist (gadobutrol): 0.1 ml/kg body weight in all patients diluted with saline to equal the dose of Gadavist (gadobutrol) for patients less than 50 kg (110 lbs). All other MRA s below neck will be performed with double dose IV Gadavist (gadobutrol) for patients less than 50 kg (110 lbs): 0.2 ml/kg body weight in all patients dilute with saline < dose of Gadavist (gadobutrol) so the total volume injected is no more than 10 ml. Contrast-enhanced MRA exams for patients over 50 kg (110 lbs) will be performed with IV Gadavist (gadobutrol) as follows: 1. Single station MRA - 10 ml Gadavist (gadobutrol) 2. Two or three station MRA 15 ml Gadavist (gadobutrol) diluted to 40 ml with saline. MR Enterography exams will be performed IV Gadavist (gadobutrol) at 0.15 ml/kg or Magnevist (gadopentetate) 0.3 ml/kg if patient has had previous contrast reactions to Gadavist (gadobutrol) or nausea/vomiting. Page 9 of 19
10 4. Prevention of Contrast Reactions Allergic-type reactions to GBCA are rare and severe or anaphylactoid reactions are extremely rare. In patients who have previously reacted to a GBCA or experienced nausea/vomiting, there are no definitive studies to support the efficacy of premedication in reducing the incidence of subsequent reactions. Nonetheless, in the absence of such data, it is reasonable to follow a common sense approach. a. Use a different gadolinium-based agent. b. At the discretion of the radiologist, premedicate the patient with steroids and antihistamine in accordance with the policy for iodinated contrast may be considered: Premedication for Iodinated IV contrast (page 5) 5. Emergency MR exams (with contrast) This section pertains to the following circumstances: a. Request is for an emergency MR study or studies b. Patient would ordinarily require egfr screening for renal insufficiency c. No current serum egfr is available d. The referring physician believes that a delay in performing the MR study due to obtaining a serum egfr would compromise patient care. e. At the discretion of the responsible radiologist, such patients may undergo an MR exam with Gadavist (gadobutrol) without a current egfr. f. The ordering physician must add a note in the medical record of the patient prior to the contrast administration which clearly states the benefit outweighs the risk. g. The radiology report must document the above discussions and verbal informed consent. Page 10 of 19
11 C. INTRA-ARTERIAL IODINATED CONTRAST ADMINISTRATION 1. For intra-arterial iodinated contrast injections, the same general rules apply as for intravenous iodinated contrast injections. 2. For run-off angiograms for peripheral vascular disease, use of Visipaque (iodixanol) may be preferred by some (compared to Isovue [iopamidol]) in effort to decrease the somatic effects typical of iodinated contrast. 3. In patients with severe contrast allergy, gadolinium may be used per protocol in section B. D. NON-INTRAVENOUS CONTRAST AGENTS 1. Oral contrast agents such as barium and diatrizoate sodium-meglumine (MD-Gastroview, Gastrografin ) are medications and preparation and administration must be under the supervision of a licensed independent practitioner. 2. All procedures requiring the administration of oral contrast agents must have a written Radiology procedure protocol that is developed by a radiologist. 3. For swallow studies, where there is an inherent risk for aspiration, non-ionic, iso-osmolar contrast Visipaque (iodixanol) is preferred. 4. Protocols for administration and preparation of oral contrast must be reviewed by the Drug Information Center and approved by the P&T Subcommittee and by the appropriate radiologist or radiologists when the standards of care and application change or when the characteristics of the oral contrast agent change. 5. Orders for contrast administration are reviewed by a radiologist or licensed independent practitioner to determine appropriateness. The currently used oral contrast preparations for CT, MRI, and fluoro procedures have minimal adverse effects. A pharmacist is available on the 4JP satellite to answer any questions the radiologist or licensed independent practitioner may have. 6. Oral contrast agents that are sent to the in-patient floor by radiology technicians must include the following information: a. Drug name, strength, and amount (if not apparent from the container) b. Time and date the contrast was prepared, an expiration date, and initials of the person who prepared the container. c. Name of patient, medical record number, date of birth, and location of the patient. d. Directions for use and any applicable cautionary statements. Instructions on administration times in relation to Radiology procedure. 7. Quality control procedures are implemented to prevent retrieval errors. a. Oral contrast is stored segregated from other medications and clearly labeled. 8. A percentage of records for cases that did not have a pharmacy review prior to dispensing are sampled quarterly per protocol to determine if the system functions successfully as designed. Page 11 of 19
12 E. ULTRASOUND CONTRAST AGENTS Currently, there is no FDA approved ultrasound contrast agent. However, at UIHC, clinical studies are performed under IRB and FDA guidance, for which patients will receive separate informed consent and detailed information. Should a clinician wish to discuss such studies, he should be directed to the responsible radiologist. F. PEDIATRIC IV CONTRAST ADMINISTRATION 1. For iodinated contrast media agents, the same principles apply in adults as in children. The dose of contrast is delivered based on weight of the patient (2 ml/kg). 2. For gadolinium agents, a dose is similarly prescribed based on body weight (see point 3 in gadolinium administration paragraph). Pediatric patients (page 9) References for pediatric contrast media use: a. Manual/Contrast%20Media%20in%20Children.pdf b. c. d. e. Page 12 of 19
13 G. TREATMENT OF CONTRAST MEDIA REACTION In all cases, treatment should begin with: IV access and monitor frequent vitals Maintain the ABCs (airway, breathing, circulation) Notify the radiologist Call Code Blue, Rapid Response or 911 (at IRL) for severe reactions Complete contrast reaction note and document allergy in EMR Follow up call to patient the next day (done by nursing staff and documented in EMR) Table 1: Suggested Treatments for Adults w/ Adverse Effects to Contrast Agents Hives Mild None Observe until resolving (Scattered & transient) Moderate (numerous & bothersome to the patient) Diphenhydramine (Benadryl ) OR mg oral (causes drowsiness; patient will need a designated driver) Fexofenadine 180 mg po (for patients without a driver) Severe (profound) Secure IV access 50 mg IV Diphenhydramine (Benadryl ) Diffuse erythema Mild Severe Laryngeal edema Bronchospasm Secure IV access, IV fluids Consider: diphenhydramine Consider: hydrocortisone Epinephrine CALL CODE Secure IV access, O 2 by mask 10 l/min O 2 Epinephrine CALL CODE Hydrocortisone 0.9% NaCl or Lactated Ringer s 1-2 liters IV 50 mg oral or IV 200 mg IV 0.3 mg /0.3 ml IM (1:1,000), if inadequate response; 0.1 mg/1 ml (1:10,000) slow IV; repeat as needed up to 1 mg/10 ml total dose 0.1 mg/1 ml (1:10,000) slow IV; repeat as needed up to 1 mg/10 ml total dose 200 mg IV, repeat if necessary Mild Albuterol inhaler 2 puffs, repeat as necessary Secure IV access, O 2 by mask 10 l/min O 2 Moderate Epinephrine IM* 0.3 mg/0.3 ml (1:1,000) IM; may repeat once Severe Epinephrine IV 0.1 mg/1 ml (1:10,000) slow IV; repeat as needed up to 1 mg/10 ml total dose CALL CODE Page 13 of 19
14 Table 1 (cont): Suggested Treatments for Adults w/ Adverse Effects to Contrast Agents Pulmonary Edema Secure IV access O 2 by mask 10 l/min O 2 Elevate head of bed Furosemide Morphine CALL CODE Hypotension with Bradycardia mg IV, slowly ( 10 mg/minute) 1-3 mg IV, repeat every 5-10 min as needed Mild Elevate legs Secure IV access, IV fluids 0.9% NaCl or Lactated Ringer s 1-2 liters O 2 by mask 10 l/min O 2 Severe Atropine 0.6 mg 1 mg IV, slow; up to 2-3 mg total dose (0.04 mg/kg) Hypotension with Tachycardia Mild Severe Elevate legs Secure IV access IV fluids O 2 by mask 10 l/min O 2 Epinephrine 0.9% NaCl or Lactated Ringer s 1-2 liters 0.1 mg/1 ml (1:10,000) slow IV; repeat as needed up to 1 mg (10 ml total dose) CALL RAPID RESPONSE Hypertension Crisis (diastolic BP > 120 mmhg) Secure IV access O 2 by mask 10 l/min O 2 Labetalol (first choice) 20mg IV over 2 minutes, may repeat q 10 minutes 40 mg IV slowly (over at least 4 minutes) Furosemide (if labetalol is not available) Nitroglycerin 0.4 mg sublingual; repeat after 5-10 min x 3 CALL RAPID RESPONSE Hypoglycemia (blood sugar below 50-60) If patient is able to swallow safely If patient is unable to swallow safely Secure IV access O 2 by mask 6-10 L/min O 2 Administer oral glucose 15 grams of glucose tablet/gel or ½ cup (4 oz) of fruit juice If IV access present, administer Dextrose 50% IV If IV access not present, administer Glucagon D50W IV 1 ampule (25 grams) IV push over 2 minutes (rate 100 ml/hr) 1 mg (1 mg/ml) IM/SQ Following Glucagon treatment provide a snack * In hypotensive patients, the preferred route of epinephrine delivery is IV as the extremities may not be perfused sufficiently to allow adequate absorption of IM administration Page 14 of 19
15 H. TREATMENT AND PREVENTION OF CONTRAST EXTRAVASATION Methods to Decrease the Risk of Extravasation during Injection of Contrast Media 1. Most CT and MRI protocols use power injectors. In angiography/intervention there is a mix of power and hand injections. There is preference for 20-gauge or larger catheters/cannulas with flow rates of 3 ml/second or higher. 2. Extravasations have incidence of 1/1000 to 1/106 patients when a power injector is used. 3. Patients should be instructed about potential extravasation and how to alert the technician. All injections should be monitored during the first seconds of injection to ensure no extravasation occurs early. Communication with the patient should continue via intercom during injection. 4. Use of standard central venous catheters should be discouraged, but Power PICC lines (purple) and Power Ports may be used for contrast injection should the situation demand it. 5. Extravasation of MRI contrast media is rare and generally constitutes relatively small quantities, thus limiting the risk for compartment syndrome. 6. Extravasation of any contrast volume should be treated in accordance with the following paragraphs. 7. Risk factors that have been identified for contrast extravasation include: a. Inadequate communication (elderly, altered consciousness) b. Severely ill/debilitated patients c. Patients with abnormal circulation to limb to be injected (atherosclerosis, Raynaud s disease, venous thrombosis/insufficiency, prior radiation therapy, previous [axillary] surgery) d. More peripheral injection sites (hand, wrist, foot, ankle) e. Injection through line that has been present >24 hrs Treatment of Extravasation of IV Contrast Media 1. Observation is required if extravasation <100 ml low osmolar contrast media: a. Notify radiologist. b. Elevate affected limb above the heart. Check the pulses and sensations. c. No clear evidence favoring the use of warm or cold packs ( ACR manual 2010). Suggested applying cold pack for immediate relief of pain and burning x 30 minutes followed by warm pack x hours to facilitate absorption of the contrast. d. If >5 ml extravasated: observation for 2-4 hours. e. The radiologist may at his/her discretion discharge a patient less than 2-4 hours with gadolinium agent extravasation. The guidelines for IV contrast media extravasation may be referred to as needed. f. Watch for increasing pain, swelling, blisters, numbness or tingling. g. Disposition to be determined by the radiologist or the LIP. h. Record the event and the treatment in the patients chart. 2. Surgical (plastic surgery) consultation is required in the following situations: a. Extravasation >100 ml low-osmolar contrast media. b. Increased swelling or pain after 2-4 hours. c. Altered tissue perfusion. d. Change in sensation or temperature. e. Development of skin ulceration or blistering. Page 15 of 19
16 I. PREGNANCY AND BREAST FEEDING Pregnancy 1. During pregnancy, it is safe practice to limit ionizing radiation as well as MRI investigations as much as possible. Nevertheless, the risk of missing a diagnosis or mismanagement in the absence of a significant diagnosis will take precedent over any risks to the mother and fetus. 2. The administration of iodinated contrast and oral contrast agents has no known risks during any trimester. 3. For gadolinium-based contrast agents there is insufficient data at present, and therefore these agents should NOT be routinely administered during pregnancy. a. The decision to use intravenous contrast must be made on a case-by case basis by the attending radiologist, who will confer with the referring physician to assess the risk benefit tradeoffs for that patient. The medical necessity to use contrast during pregnancy must be documented in the patient s medical record by the attending physician who requested the study must be in the patient s medical record before procedure can be performed. b. If it is determined that contrast is needed, the patient or legal guardian must sign a procedural consent form (G-2d 2 ) after they are made aware of the potential risks and benefits of the proposed MR procedure and the availability of alternative diagnostic tests (if any). Breast Feeding The literature on the excretion into breast milk of iodinated and gadolinium-based contrast media and the gastrointestinal absorption of these agents from breast milk is very limited; however, several studies have shown that 1) less than 1% of the administered maternal dose of contrast medium is excreted into breast milk; and 2) less than 1% of the contrast medium in breast milk ingested by an infant is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, the expected dose of contrast medium absorbed by an infant from ingested breast milk is extremely low. 1. Iodinated contrast agents are excreted rapidly through the kidneys, and less than 1% is excreted into breast milk during the first 24 hours. Therefore, it is considered safe for the mother to continue breast feeding after receiving iodinated contrast. 2. Gadolinium contrast is excreted rapidly through the kidneys, and less than 0.04% is excreted into breast milk during the first 24 hours. Therefore, it is considered safe to continue breast feeding after receiving Gadolinium contrast. Patients will be given the Breast Feeding Information Form (Appendix B) prior to their MRI procedure. 3. If the patient has any question or concerns they can speak to a radiologist. 4. If the patient still has concerns they can pump and throw their milk away for the next 24 hours after their injection of gadolinium. Page 16 of 19
17 J. APPENDIX A: INFORMATION SHEET FOR CONTRAST ENHANCED MRI Information Sheet for Patients Scheduled for Contrast-Enhanced MRI Your doctor or health care provider has ordered a Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) test with intravenous contrast to help evaluate your medical condition. The MRI contrast contains a metal called gadolinium, which increases the diagnostic capability of MRI. Unlike the x-ray dyes used for CT scans, MRI contrast agents do not contain iodine and have enjoyed a generally excellent safety profile after 20 years and more than 200 million doses worldwide. However, recent reports in the medical literature have identified an association between gadolinium contrast and a rare, debilitating disease called Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis (NSF). First described in 1997, NSF can affect the skin, muscles, and internal organs. The skin can become thick, hard, tight, dark and itchy. NSF occurs exclusively in patients with severely impaired kidney function, particularly those on kidney dialysis. The disease is rarely fatal, but there is no consistently successful treatment. The cause of NSF and the exact role of gadolinium contrast are unknown. In patients with severely impaired kidney function, the risk of developing NSF from gadolinium contrast is not precisely known, but is probably small (3-7%). After carefully considering your medical condition, your doctor and the supervising radiologist believe that an MRI with gadolinium contrast is medically indicated and is more likely to provide important diagnostic information than alternative imaging tests. Also, your doctors believe that the potential benefits of MRI with gadolinium contrast outweigh the risks. To minimize your chances of developing NSF, your radiologist will perform the MRI with one of three gadolinium contrast agents thought to pose a smaller risk of NSF. We will use the lowest possible contrast dose consistent with making a diagnostic study. If you are currently on hemodialysis, you will be dialyzed promptly after your MRI to help remove the gadolinium contrast from your body. The US Food and Drug administration (FDA) cautions that all gadolinium contrast agents may pose a risk of NSF. Your radiologist, who is a physician with expertise in medical imaging, will be glad to answer any questions or concerns that you may have about your MRI or the intravenous contrast agent. Page 17 of 19
18 K. APPENDIX B: BREAST FEEDING INFORMATION FORM University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinic Department of Radiology MRI 0440 JCP 200 Hawkins Drive Iowa City, Iowa / / Fax Your doctor as ordered an MRI exam that requires us to give you a gadolinium contrast agent for this exam. Gadolinium is a type of contrast agent that will be injected in a vein in your arm and will give the radiologist additional information when reading your images. After injection of the gadolinium contrast agent a tiny amount will be excreted into your breast milk. A review of the literature shows there is no evidence to suggest that the oral intake of your breast milk by your baby that contains the tiny amount of gadolinium would cause toxic effects to your baby. It is believed that the available data suggest that it is safe for you to have your baby continue breast feeding after receiving an injection of gadolinium contrast agent. If you remain concerned about any potential ill effects, you can speak to a radiologist so you can make an informed decision as to whether to continue breast-feeding or temporarily stop breastfeeding after receiving a gadolinium contrast agent. If you so desire, you can stop breast-feeding for 24 hours and pump both breasts if needed and throw the pumped breast milk away. After 24 hours you can resume normal breast feeding. If you have any questions and would like to speak to a radiologist please ask the receptionist. Page 18 of 19
19 Reviewed by Department of Pharmaceutical Care (March 2012, March 2013) Reviewed by Department of Anesthesiology (April 2005) Approved by the Pharmacy and Therapeutics Subcommittee (March 2012, March 2013) Approved by Radiology Quality Assurance Committee (March 2012, January 2013) Page 19 of 19
UC San Diego Health System Intravenous Contrast Media Guidelines Adult Approved by P&T Committee 6/18/2014
 UC San Diego Health System Intravenous Contrast Media Guidelines Adult Approved by P&T Committee 6/18/2014 Policy Statement To establish guidelines for the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of contrast
UC San Diego Health System Intravenous Contrast Media Guidelines Adult Approved by P&T Committee 6/18/2014 Policy Statement To establish guidelines for the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of contrast
8. Strategies in Patients at Risk for Allergic Reactions to IV Contrast for CT
 Updated 7/14/09 UAB Department of Radiology Guidelines for Administering Gadolinium-based and Iodine-based Intravenous Contrast Agents in Patients with Renal Dysfunction or at Risk for Adverse Reactions
Updated 7/14/09 UAB Department of Radiology Guidelines for Administering Gadolinium-based and Iodine-based Intravenous Contrast Agents in Patients with Renal Dysfunction or at Risk for Adverse Reactions
Positron Emission Tomography - For Patients
 Positron Emission Tomography - For Patients A physician s written order is required for any PET-CT tests. How should I prepare for my PET-CT? PET-CT is more complicated than most other tests you may be
Positron Emission Tomography - For Patients A physician s written order is required for any PET-CT tests. How should I prepare for my PET-CT? PET-CT is more complicated than most other tests you may be
Protocol for the safe administration of iodinated contrast media in diagnostic radiology
 Protocol for the safe administration of iodinated contrast media in diagnostic radiology Protocol statement: This protocol applies to all staff within Radiology Departments at Heart of England NHS Foundation
Protocol for the safe administration of iodinated contrast media in diagnostic radiology Protocol statement: This protocol applies to all staff within Radiology Departments at Heart of England NHS Foundation
What are contrast materials and how do they work? Contrast materials enter the body in one of three ways. They can be:
 Scan for mobile link. Contrast Materials What are contrast materials and how do they work? Contrast materials, also called contrast agents or contrast media, are used to improve pictures of the inside
Scan for mobile link. Contrast Materials What are contrast materials and how do they work? Contrast materials, also called contrast agents or contrast media, are used to improve pictures of the inside
Allergy Emergency Treatment Protocol
 Allergy Emergency Treatment Protocol I. Initial evaluation of possible allergic reaction a. Cease administration of allergenic extracts b. Notify physician c. Record vital signs: blood pressure, pulse,
Allergy Emergency Treatment Protocol I. Initial evaluation of possible allergic reaction a. Cease administration of allergenic extracts b. Notify physician c. Record vital signs: blood pressure, pulse,
Influenza Vaccine Protocol Agreement (O.C.G.A. Section 43-34-26.1)
 Influenza Vaccine Protocol Agreement (O.C.G.A. Section 43-34-26.1) This Influenza Vaccine Protocol Agreement (the "Protocol") authorizes the Georgia licensed pharmacists (the "Pharmacists") or nurses (
Influenza Vaccine Protocol Agreement (O.C.G.A. Section 43-34-26.1) This Influenza Vaccine Protocol Agreement (the "Protocol") authorizes the Georgia licensed pharmacists (the "Pharmacists") or nurses (
POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE
 POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE Acute Pylonephritis DIAGNOSIS COMPLICATED PYELONEPHRITIS EXCLUSION CRITERIA: Male Known or suspected renal impairment (egfr < 60) Abnormality of renal tract Known or suspected renal
POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE Acute Pylonephritis DIAGNOSIS COMPLICATED PYELONEPHRITIS EXCLUSION CRITERIA: Male Known or suspected renal impairment (egfr < 60) Abnormality of renal tract Known or suspected renal
Care Pathway for the Administration of Intravenous Iron Sucrose (Venofer )
 Departments of Haematology, Nephrology and Pharmacy Care Pathway for the Administration of Intravenous Iron Sucrose (Venofer ) [Care Pathway Review Date] Guidance for use This Care Pathway is intended
Departments of Haematology, Nephrology and Pharmacy Care Pathway for the Administration of Intravenous Iron Sucrose (Venofer ) [Care Pathway Review Date] Guidance for use This Care Pathway is intended
SMO: Anaphylaxis and Allergic Reactions
 REGION I EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES STANDING MEDICAL ORDERS EMT Basic SMO: Anaphylaxis and Allergic Reactions Overview: Allergic reactions can vary in severity from a mild reaction consisting of hives
REGION I EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES STANDING MEDICAL ORDERS EMT Basic SMO: Anaphylaxis and Allergic Reactions Overview: Allergic reactions can vary in severity from a mild reaction consisting of hives
Liver Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE) Cancer treatment
 Patient Education Liver Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE) Cancer treatment This handout explains what liver transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) is and what to expect with this cancer treatment.
Patient Education Liver Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE) Cancer treatment This handout explains what liver transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) is and what to expect with this cancer treatment.
CH CONSCIOUS SEDATION
 Summary: CH CONSCIOUS SEDATION It is the policy of Carondelet Health that moderate conscious sedation of patients will be undertaken with appropriate evaluation and monitoring. Effective Date: 9/4/04 Revision
Summary: CH CONSCIOUS SEDATION It is the policy of Carondelet Health that moderate conscious sedation of patients will be undertaken with appropriate evaluation and monitoring. Effective Date: 9/4/04 Revision
Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal
 Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? An inferior vena cava filter placement procedure involves an interventional radiologist (a specialist doctor)
Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? An inferior vena cava filter placement procedure involves an interventional radiologist (a specialist doctor)
IV Contrast Extravasation PQI Project Feed-Back Document from the Society of Abdominal Radiology & American College of Radiology
 IV Contrast Extravasation PQI Project Feed-Back Document from the Society of Abdominal Radiology & American College of Radiology This performance feedback document and the accompanying spreadsheet include
IV Contrast Extravasation PQI Project Feed-Back Document from the Society of Abdominal Radiology & American College of Radiology This performance feedback document and the accompanying spreadsheet include
LOUISIANA STATE UNIVERSITY HEALTH SCIENCES CENTER - SHREVEPORT MEDICAL RECORDS CONTENT/DOCUMENTATION
 LOUISIANA STATE UNIVERSITY HEALTH SCIENCES CENTER - SHREVEPORT MEDICAL RECORDS CONTENT/DOCUMENTATION Hospital Policy Manual Purpose: To define the components of the paper and electronic medical record
LOUISIANA STATE UNIVERSITY HEALTH SCIENCES CENTER - SHREVEPORT MEDICAL RECORDS CONTENT/DOCUMENTATION Hospital Policy Manual Purpose: To define the components of the paper and electronic medical record
1. Dosing Schedule: your customized schedule of your weekly injections as provided by the center.
 Home Immunotherapy Raza Pasha, MD Congratulations. You are now on the path to better control of your allergies. The following is your instruction guide to allow you to become more familiar with proper
Home Immunotherapy Raza Pasha, MD Congratulations. You are now on the path to better control of your allergies. The following is your instruction guide to allow you to become more familiar with proper
Pain Management after Surgery Patient Information Booklet
 Pain Management after Surgery Patient Information Booklet PATS 509-15-05 Your Health Care Be Involved Be involved in your healthcare. Speak up if you have questions or concerns about your care. Tell a
Pain Management after Surgery Patient Information Booklet PATS 509-15-05 Your Health Care Be Involved Be involved in your healthcare. Speak up if you have questions or concerns about your care. Tell a
The patient s response to therapy within the first hour in the Emergency Room is one of the most reliable ways to predict need for hospitalization.
 Emergency Room Asthma Management Algorithm The Emergency Room Asthma Management Algorithm is to be used for any patient seen in the Emergency Room with the diagnosis of asthma. (The initial history should
Emergency Room Asthma Management Algorithm The Emergency Room Asthma Management Algorithm is to be used for any patient seen in the Emergency Room with the diagnosis of asthma. (The initial history should
Yttrium-90 Radiotherapy Treatment for liver tumors
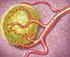 Patient Education Yttrium-90 Radiotherapy Treatment for liver tumors This handout explains what Yttrium-90 radiotherapy is and what to expect when you have it done. Why do I need this treatment? Your doctors
Patient Education Yttrium-90 Radiotherapy Treatment for liver tumors This handout explains what Yttrium-90 radiotherapy is and what to expect when you have it done. Why do I need this treatment? Your doctors
Upstate University Health System Medication Exam - Version A
 Upstate University Health System Medication Exam - Version A Name: ID Number: Date: Unit: Directions: Please read each question below. Choose the best response for each of the Multiple Choice and Medication
Upstate University Health System Medication Exam - Version A Name: ID Number: Date: Unit: Directions: Please read each question below. Choose the best response for each of the Multiple Choice and Medication
Vaccine Protocol Agreement. Name of Pharmacy: Address: City, State, Zip:
 Vaccine Protocol Agreement Name of Pharmacy: Address: City, State, Zip: This Vaccine Protocol Agreement (the "Protocol") authorizes the Georgia licensed pharmacists (the "Pharmacists") or nurses ( Nurses
Vaccine Protocol Agreement Name of Pharmacy: Address: City, State, Zip: This Vaccine Protocol Agreement (the "Protocol") authorizes the Georgia licensed pharmacists (the "Pharmacists") or nurses ( Nurses
MARYLAND STATE SCHOOL HEALTH SERVICES GUIDELINES
 Department of Health and Mental Hygiene Maryland State Department of Education Maryland State School Health Council MARYLAND STATE SCHOOL HEALTH SERVICES GUIDELINES Emergency Management Guidelines for
Department of Health and Mental Hygiene Maryland State Department of Education Maryland State School Health Council MARYLAND STATE SCHOOL HEALTH SERVICES GUIDELINES Emergency Management Guidelines for
Suspected pulmonary embolism (PE) in pregnant women
 Suspected pulmonary embolism (PE) in pregnant women What is a pulmonary embolus? A deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot that forms in one of the deep veins of the leg. If the clot moves to the lung,
Suspected pulmonary embolism (PE) in pregnant women What is a pulmonary embolus? A deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot that forms in one of the deep veins of the leg. If the clot moves to the lung,
PROPHYLACTIC TREATMENT PREVIOUS HISTORY OF REACTIONS
 Management of Contrast Media Reactions - Adult Page 1 of 10 Any signs or symptoms of HSR/allergic reaction, notify Radiologist and consider notifying the Diagnostic Imaging Urgent Response Team. If patient
Management of Contrast Media Reactions - Adult Page 1 of 10 Any signs or symptoms of HSR/allergic reaction, notify Radiologist and consider notifying the Diagnostic Imaging Urgent Response Team. If patient
PARENT/GUARDIAN REQUEST: ADMINISTRATION OF EMERGENCY EPINEPHRINE, ANAPHYLAXIS CARE PLAN/ IHP & IEHP
 IEF Elementary School 105 Andrew Street, Green Brook, N.J. 08812 School Nurse: Mrs. Ostrander Office Phone: 732-9681052 ext. # 3 Fax: 732-968-0791 Green Brook Township Public Schools Green Brook Middle
IEF Elementary School 105 Andrew Street, Green Brook, N.J. 08812 School Nurse: Mrs. Ostrander Office Phone: 732-9681052 ext. # 3 Fax: 732-968-0791 Green Brook Township Public Schools Green Brook Middle
Beaumont Hospital Department of Nephrology and Renal Nursing. Guideline for administering Ferinject
 Beaumont Hospital Department of Nephrology and Renal Nursing Guideline Name: Guideline for administering Ferinject Guideline Number: 18 Guideline Version: a Developed By: Louise Kelly CNM 1 Renal Day Care
Beaumont Hospital Department of Nephrology and Renal Nursing Guideline Name: Guideline for administering Ferinject Guideline Number: 18 Guideline Version: a Developed By: Louise Kelly CNM 1 Renal Day Care
RENAL ANGIOMYOLIPOMA EMBOLIZATION
 RENAL ANGIOMYOLIPOMA EMBOLIZATION The information about renal angiomyolipomas on the next several pages includes questions commonly asked about the embolization procedure. Please take a few moments to
RENAL ANGIOMYOLIPOMA EMBOLIZATION The information about renal angiomyolipomas on the next several pages includes questions commonly asked about the embolization procedure. Please take a few moments to
Emergency Treatment for Vaccine Reactions
 Massachusetts Department of Public Health Division of Epidemiology and Immunization Model Standing Orders Emergency Treatment for Vaccine Reactions Note: These model standing orders are current as of December
Massachusetts Department of Public Health Division of Epidemiology and Immunization Model Standing Orders Emergency Treatment for Vaccine Reactions Note: These model standing orders are current as of December
MEDICATION MANUAL Policy & Procedure
 MEDICATION MANUAL Policy & Procedure TITLE: Section: Initial Management of Anaphylaxis Following Immunization Medication Specific NUMBER: MM 20-005 Date Issued: October 2009 Source: Distribution: Capital
MEDICATION MANUAL Policy & Procedure TITLE: Section: Initial Management of Anaphylaxis Following Immunization Medication Specific NUMBER: MM 20-005 Date Issued: October 2009 Source: Distribution: Capital
Diabetic nephropathy is detected clinically by the presence of persistent microalbuminuria or proteinuria.
 Kidney Complications Diabetic Nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy is detected clinically by the presence of persistent microalbuminuria or proteinuria. The peak incidence of nephropathy is usually 15-25 years
Kidney Complications Diabetic Nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy is detected clinically by the presence of persistent microalbuminuria or proteinuria. The peak incidence of nephropathy is usually 15-25 years
Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty (PTA) and Stenting For PVS Patients
 Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty (PTA) and Stenting For PVS Patients There are two types of blood vessels in the body arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood rich in oxygen from the heart to all
Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty (PTA) and Stenting For PVS Patients There are two types of blood vessels in the body arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood rich in oxygen from the heart to all
ANAPHYLAXIS. Introduction. Differential Diagnosis. Starship Children s Health Clinical Guideline
 Introduction Differential Diagnosis Management Treatment of Anaphylaxis (Flow Chart) Disposition from Emergency Department Adrenaline Autoinjectors Action Plan Adrenaline Autoinjector Information Sheet
Introduction Differential Diagnosis Management Treatment of Anaphylaxis (Flow Chart) Disposition from Emergency Department Adrenaline Autoinjectors Action Plan Adrenaline Autoinjector Information Sheet
Community Ambulance Service of Minot ALS Standing Orders Legend
 Legend Indicates General Information and Guidelines Indicates Procedures Indicates Medication Administration Indicates Referral to Other Protocol Indicates Referral to Online Medical Direction Pediatric
Legend Indicates General Information and Guidelines Indicates Procedures Indicates Medication Administration Indicates Referral to Other Protocol Indicates Referral to Online Medical Direction Pediatric
Percutaneous Abscess Drainage
 Scan for mobile link. Percutaneous Abscess Drainage An abscess is an infected fluid collection within the body. Percutaneous abscess drainage uses imaging guidance to place a thin needle through the skin
Scan for mobile link. Percutaneous Abscess Drainage An abscess is an infected fluid collection within the body. Percutaneous abscess drainage uses imaging guidance to place a thin needle through the skin
patient group direction
 DICLOFENAC v01 1/8 DICLOFENAC PGD Details Version 1.0 Legal category Staff grades Approved by POM Paramedic (Non-ECP) Nurse (Non-ECP) Emergency Care Practitioner (Paramedic) Emergency Care Practitioner
DICLOFENAC v01 1/8 DICLOFENAC PGD Details Version 1.0 Legal category Staff grades Approved by POM Paramedic (Non-ECP) Nurse (Non-ECP) Emergency Care Practitioner (Paramedic) Emergency Care Practitioner
The degree of liver inflammation or damage (grade) Presence and extent of fatty liver or other metabolic liver diseases
 ilearning about your health Liver Biopsy www.cpmc.org/learning What is a Liver Biopsy? A liver biopsy is a procedure where a specially trained doctor (typically a hepatologist, radiologist, or gastroenterologist)
ilearning about your health Liver Biopsy www.cpmc.org/learning What is a Liver Biopsy? A liver biopsy is a procedure where a specially trained doctor (typically a hepatologist, radiologist, or gastroenterologist)
EFFIMET 1000 XR Metformin Hydrochloride extended release tablet
 BRAND NAME: Effimet XR. THERAPEUTIC CATEGORY: Anti-Diabetic PHARMACOLOGIC CLASS: Biguanides EFFIMET 1000 XR Metformin Hydrochloride extended release tablet COMPOSITION AND PRESENTATION Composition Each
BRAND NAME: Effimet XR. THERAPEUTIC CATEGORY: Anti-Diabetic PHARMACOLOGIC CLASS: Biguanides EFFIMET 1000 XR Metformin Hydrochloride extended release tablet COMPOSITION AND PRESENTATION Composition Each
Medications or therapeutic solutions may be injected directly into the bloodstream
 Intravenous Therapy Medications or therapeutic solutions may be injected directly into the bloodstream for immediate circulation and use by the body. State practice acts designate which health care professionals
Intravenous Therapy Medications or therapeutic solutions may be injected directly into the bloodstream for immediate circulation and use by the body. State practice acts designate which health care professionals
Provision of Intravenous EDTA Chelation as a Complementary and Alternative Medicine
 Provision of Intravenous EDTA Chelation as a Complementary and Alternative Medicine Guideline Updated: August 2010 Replaced: November 1998 To serve the public and guide the medical profession EDTA Chelation
Provision of Intravenous EDTA Chelation as a Complementary and Alternative Medicine Guideline Updated: August 2010 Replaced: November 1998 To serve the public and guide the medical profession EDTA Chelation
What Medical Emergencies Should a Dental Office be Prepared to Handle?
 What Medical Emergencies Should a Dental Office be Prepared to Handle? Gary Cuttrell, DDS, JD, University of NM Division of Dental Services Santiago Macias, MD, First Choice Community Healthcare Dentists
What Medical Emergencies Should a Dental Office be Prepared to Handle? Gary Cuttrell, DDS, JD, University of NM Division of Dental Services Santiago Macias, MD, First Choice Community Healthcare Dentists
Section II When you are finished with this section, you will be able to: Define medication (p 2) Describe how medications work (p 3)
 Section II When you are finished with this section, you will be able to: Define medication (p 2) Describe how medications work (p 3) List the different medication effects (p5) List the ways that medications
Section II When you are finished with this section, you will be able to: Define medication (p 2) Describe how medications work (p 3) List the different medication effects (p5) List the ways that medications
RADIOLOGY HOUSE STAFF MANUAL
 RADIOLOGY HOUSE STAFF MANUAL The Department of Radiology offers a wide range of services/procedures and operates 12 divisions/sections, which are listed separately below. The procedures offered are listed
RADIOLOGY HOUSE STAFF MANUAL The Department of Radiology offers a wide range of services/procedures and operates 12 divisions/sections, which are listed separately below. The procedures offered are listed
PRIMARY CARE PRACTICE GUIDELINES
 1 of 6 1. OUTCOME To identify anaphylaxis in the primary care setting and provide an evidence informed emergency response utilizing the most current provincial and federal practice guidelines. 2. DEFINITIONS
1 of 6 1. OUTCOME To identify anaphylaxis in the primary care setting and provide an evidence informed emergency response utilizing the most current provincial and federal practice guidelines. 2. DEFINITIONS
Adult Drug Reference. Dopamine Drip Chart. Pediatric Drug Reference. Pediatric Drug Dosage Charts DRUG REFERENCES
 Adult Drug Reference Dopamine Drip Chart Pediatric Drug Reference Pediatric Drug Dosage Charts DRUG REFERENCES ADULT DRUG REFERENCE Drug Indication Adult Dosage Precautions / Comments ADENOSINE Paroxysmal
Adult Drug Reference Dopamine Drip Chart Pediatric Drug Reference Pediatric Drug Dosage Charts DRUG REFERENCES ADULT DRUG REFERENCE Drug Indication Adult Dosage Precautions / Comments ADENOSINE Paroxysmal
PERIPHERAL STEM CELL TRANSPLANT INTRODUCTION
 PERIPHERAL STEM CELL TRANSPLANT INTRODUCTION This booklet was designed to help you and the important people in your life understand the treatment of high dose chemotherapy with stem cell support: a procedure
PERIPHERAL STEM CELL TRANSPLANT INTRODUCTION This booklet was designed to help you and the important people in your life understand the treatment of high dose chemotherapy with stem cell support: a procedure
IVC Filter Insertion PROCEDURAL CONSENT FORM. A. Interpreter / cultural needs. B. Procedure. C. Risks of the procedure
 DO NOT WRITE IN THIS BINDING MARGIN V4.00-03/2011 SW9264 Facility: A. Interpreter / cultural needs An Interpreter Service is required? Yes No If Yes, is a qualified Interpreter present? Yes No A Cultural
DO NOT WRITE IN THIS BINDING MARGIN V4.00-03/2011 SW9264 Facility: A. Interpreter / cultural needs An Interpreter Service is required? Yes No If Yes, is a qualified Interpreter present? Yes No A Cultural
Anaphylaxis: Treatment in the Community
 : Treatment in the Community is likely if a patient who, within minutes of exposure to a trigger (allergen), develops a sudden illness with rapidly progressing skin changes and life-threatening airway
: Treatment in the Community is likely if a patient who, within minutes of exposure to a trigger (allergen), develops a sudden illness with rapidly progressing skin changes and life-threatening airway
X-ray (Radiography) - Chest
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Chest What is a Chest X-ray (Chest Radiography)? The chest x-ray is the most commonly performed diagnostic x-ray examination. A chest x-ray produces images of
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Chest What is a Chest X-ray (Chest Radiography)? The chest x-ray is the most commonly performed diagnostic x-ray examination. A chest x-ray produces images of
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE: ANAPHYLAXIS REGISTERED NURSE INITIATED MANAGEMENT AUTHORIZATION: Effective Date: Integrated Professional Practice
 CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE: ANAPHYLAXIS REGISTERED NURSE INITIATED MANAGEMENT AUTHORIZATION: Integrated Professional Practice Council Page 1 of 10 ADAPTED from BC Health Authorities Provincial Decision
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE: ANAPHYLAXIS REGISTERED NURSE INITIATED MANAGEMENT AUTHORIZATION: Integrated Professional Practice Council Page 1 of 10 ADAPTED from BC Health Authorities Provincial Decision
Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal
 Scan for mobile link. Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? In an inferior vena cava filter placement procedure, interventional radiologists
Scan for mobile link. Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? In an inferior vena cava filter placement procedure, interventional radiologists
ANNE ARUNDEL MEDICAL CENTER CRITICAL CARE MEDICATION MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF NURSING AND PHARMACY. Guidelines for Use of Intravenous Isoproterenol
 ANNE ARUNDEL MEDICAL CENTER CRITICAL CARE MEDICATION MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF NURSING AND PHARMACY Guidelines for Use of Intravenous Isoproterenol Major Indications Status Asthmaticus As a last resort for
ANNE ARUNDEL MEDICAL CENTER CRITICAL CARE MEDICATION MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF NURSING AND PHARMACY Guidelines for Use of Intravenous Isoproterenol Major Indications Status Asthmaticus As a last resort for
Lindenwold Board File Code # 5141.21 Of Education Page 1 of 7
 Of Education Page 1 of 7 The Board of Education disclaims any and all responsibility for the diagnosis and treatment of the illness be contingent upon the timely administration of medication duly prescribed
Of Education Page 1 of 7 The Board of Education disclaims any and all responsibility for the diagnosis and treatment of the illness be contingent upon the timely administration of medication duly prescribed
Paramedic Pediatric Medical Math Test
 Paramedic Pediatric Medical Math Test Name: Date: Problem 1 Your 4 year old pediatric patient weighs 40 pounds. She is febrile. You need to administer acetaminophen (Tylenol) 15mg/kg. How many mg will
Paramedic Pediatric Medical Math Test Name: Date: Problem 1 Your 4 year old pediatric patient weighs 40 pounds. She is febrile. You need to administer acetaminophen (Tylenol) 15mg/kg. How many mg will
University College Hospital. Contrast agent for radiotherapy CT (computed tomography) scans. Radiotherapy Department Patient information series
 University College Hospital Contrast agent for radiotherapy CT (computed tomography) scans Radiotherapy Department Patient information series 11 2 If you need a large print, audio or translated copy of
University College Hospital Contrast agent for radiotherapy CT (computed tomography) scans Radiotherapy Department Patient information series 11 2 If you need a large print, audio or translated copy of
Medicines Management
 Medicines Management Patient Group Direction for the Supply/administration of Adrenaline (Epinephrine) for Treatment of Anaphylaxis by accredited community Pharmacists. Rationale To enable a pharmacist,
Medicines Management Patient Group Direction for the Supply/administration of Adrenaline (Epinephrine) for Treatment of Anaphylaxis by accredited community Pharmacists. Rationale To enable a pharmacist,
CT scans and IV contrast (radiographic iodinated contrast) utilization in adults
 CT scans and IV contrast (radiographic iodinated contrast) utilization in adults At United Radiology Group, a majority of CT exams are performed either with IV contrast or without while just a few exams
CT scans and IV contrast (radiographic iodinated contrast) utilization in adults At United Radiology Group, a majority of CT exams are performed either with IV contrast or without while just a few exams
Nursing 113. Pharmacology Principles
 Nursing 113 Pharmacology Principles 1. The study of how drugs enter the body, reach the site of action, and are removed from the body is called a. pharmacotherapeutics b. pharmacology c. pharmacodynamics
Nursing 113 Pharmacology Principles 1. The study of how drugs enter the body, reach the site of action, and are removed from the body is called a. pharmacotherapeutics b. pharmacology c. pharmacodynamics
Yes This controlled document shall not be copied in part or whole without the express permission of the author or the author s representative.
 Title: Patient Group Direction for the administration of lidocaine hydrochloride 1% injection as infiltration anaesthesia for insertion/removal of central venous catheters by nurses/radiographers working
Title: Patient Group Direction for the administration of lidocaine hydrochloride 1% injection as infiltration anaesthesia for insertion/removal of central venous catheters by nurses/radiographers working
Update on Contrast Material Use in Children Jonathan R. Dillman, M.D.
 Update on Contrast Material Use in Children Jonathan R. Dillman, M.D. Assistant Professor University of Michigan Health System Department of Radiology Section of Pediatric Radiology Disclosures Research
Update on Contrast Material Use in Children Jonathan R. Dillman, M.D. Assistant Professor University of Michigan Health System Department of Radiology Section of Pediatric Radiology Disclosures Research
MODERATE SEDATION RECORD (formerly termed Conscious Sedation)
 (POLICY #DOC-051) Page 1 of 6 WELLSPAN HEALTH - YORK HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE Dates: Original Issue: September 1998 Annual Review: March 2012 Revised: March 2010 Submitted by: Brenda Artz
(POLICY #DOC-051) Page 1 of 6 WELLSPAN HEALTH - YORK HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE Dates: Original Issue: September 1998 Annual Review: March 2012 Revised: March 2010 Submitted by: Brenda Artz
Section 400: Code # 453.4R
 Section 400: Code # 453.4R Administering Medication Conditions for Administering Prescription Drugs Except as otherwise specifically provided by law, a school bus driver, employee, or volunteer that has
Section 400: Code # 453.4R Administering Medication Conditions for Administering Prescription Drugs Except as otherwise specifically provided by law, a school bus driver, employee, or volunteer that has
Enoxaparin for long term anticoagulation in patients unsuitable for oral anticoagulants
 Enoxaparin for long term anticoagulation in patients unsuitable for oral anticoagulants Traffic light classification- Amber 2 Information sheet for Primary Care Prescribers Relevant Licensed Indications
Enoxaparin for long term anticoagulation in patients unsuitable for oral anticoagulants Traffic light classification- Amber 2 Information sheet for Primary Care Prescribers Relevant Licensed Indications
Adverse Events in Clinical Trials: Definitions and Documentation
 Clinical and Translational Science Institute / CTSI at the University of California, San Francisco Welcome to Online Training for Clinical Research Coordinators Adverse Events in Clinical Trials: Definitions
Clinical and Translational Science Institute / CTSI at the University of California, San Francisco Welcome to Online Training for Clinical Research Coordinators Adverse Events in Clinical Trials: Definitions
Emergency Medical Services Advanced Level Competency Checklist
 Emergency Services Advanced Level Competency Checklist EMS Service: Current License in State of Nebraska: # (Copy of license kept in file at station) Date of joining EMS Service: EMS Service Member Name:
Emergency Services Advanced Level Competency Checklist EMS Service: Current License in State of Nebraska: # (Copy of license kept in file at station) Date of joining EMS Service: EMS Service Member Name:
Diabetic Nephropathy
 Diabetic Nephropathy Kidney disease is common in people affected by diabetes mellitus Definition Urinary albumin excretion of more than 300mg in a 24 hour collection or macroalbuminuria Abnormal renal
Diabetic Nephropathy Kidney disease is common in people affected by diabetes mellitus Definition Urinary albumin excretion of more than 300mg in a 24 hour collection or macroalbuminuria Abnormal renal
X-ray (Radiography), Chest
 X-ray (Radiography), Chest What is a Chest X-ray (Chest Radiography)? The chest x-ray is the most commonly performed diagnostic x-ray examination. A chest x-ray makes images of the heart, lungs, airways,
X-ray (Radiography), Chest What is a Chest X-ray (Chest Radiography)? The chest x-ray is the most commonly performed diagnostic x-ray examination. A chest x-ray makes images of the heart, lungs, airways,
Procedure -8. Intraosseous Infusion Adult and Pediatric EZIO. Page 1 of 7 APPROVED:
 Page 1 of 7 Intraosseous Infusion Adult and Pediatric APPROVED: EMS Medical Director EMS Administrator 1. Goals/Introduction: 1.1 Intraosseous (IO) infusion provides an effective alternative means of providing
Page 1 of 7 Intraosseous Infusion Adult and Pediatric APPROVED: EMS Medical Director EMS Administrator 1. Goals/Introduction: 1.1 Intraosseous (IO) infusion provides an effective alternative means of providing
Herniated Cervical Disc
 Herniated Cervical Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The backbone, or spine, is composed of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The vertebrae
Herniated Cervical Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The backbone, or spine, is composed of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The vertebrae
BEAUMONT HOSPITAL DEPARTMENT OF NEPHROLOGY RENAL BIOPSY
 1 BEAUMONT HOSPITAL DEPARTMENT OF NEPHROLOGY GUIDELINES ON ADMINISTRATION OF INTRAVENOUS IRON SUCROSE (VENOFER) AS A BOLUS DOSE IN THE RENAL OUTPATIENT SETTING Date Developed: August- October 2007 RENAL
1 BEAUMONT HOSPITAL DEPARTMENT OF NEPHROLOGY GUIDELINES ON ADMINISTRATION OF INTRAVENOUS IRON SUCROSE (VENOFER) AS A BOLUS DOSE IN THE RENAL OUTPATIENT SETTING Date Developed: August- October 2007 RENAL
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER. VITAMINE B12 STEROP 1mg/1ml Solution for injection / oral solution. Cyanocobalamin
 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER VITAMINE B12 STEROP 1mg/1ml Solution for injection / oral solution Cyanocobalamin Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER VITAMINE B12 STEROP 1mg/1ml Solution for injection / oral solution Cyanocobalamin Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because
Hypoglycemia (Technician-Paramedic) Protocol revised October 2008
 Hypoglycemia (Technician-Paramedic) Protocol revised October 2008 Preamble Prolonged hypoglycemia may result in serious neurologic complications and death. Glucose and glucagon can be administered to correct
Hypoglycemia (Technician-Paramedic) Protocol revised October 2008 Preamble Prolonged hypoglycemia may result in serious neurologic complications and death. Glucose and glucagon can be administered to correct
Inpatient Anticoagulation Safety. To provide safe and effective anticoagulation therapy through a collaborative approach.
 Inpatient Anticoagulation Safety Purpose: Policy: To provide safe and effective anticoagulation therapy through a collaborative approach. Upon the written order of a physician, Heparin, Low Molecular Weight
Inpatient Anticoagulation Safety Purpose: Policy: To provide safe and effective anticoagulation therapy through a collaborative approach. Upon the written order of a physician, Heparin, Low Molecular Weight
PHYSICIAN SIGNATURE DATE TIME DRUG ALLERGIES WT: KG
 MED Hospitalist Stroke-TIA Vital Signs Vital Signs Q4H (DEF)* Q2H Q1H Vital Signs Orthostatic Activity Activity Bedrest, for 12 hours then Up ad lib (DEF)* Bedrest, for 24 hours then Up ad lib Up Ad Lib
MED Hospitalist Stroke-TIA Vital Signs Vital Signs Q4H (DEF)* Q2H Q1H Vital Signs Orthostatic Activity Activity Bedrest, for 12 hours then Up ad lib (DEF)* Bedrest, for 24 hours then Up ad lib Up Ad Lib
Radiation Exposure in X-ray and CT Examinations
 Patient Safety-Xray: Radiation Exposure in X-ray and CT Examinations What are x-rays and what do they do? X-rays are forms of radiant energy, like light or radio waves. Unlike light, x-rays can penetrate
Patient Safety-Xray: Radiation Exposure in X-ray and CT Examinations What are x-rays and what do they do? X-rays are forms of radiant energy, like light or radio waves. Unlike light, x-rays can penetrate
3% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP 5% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP
 PRESCRIBING INFORMATION 3% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP 5% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP IV Fluid and Electrolyte Replenisher Baxter Corporation Mississauga, Ontario L5N 0C2 Canada Date of Revision:
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION 3% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP 5% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP IV Fluid and Electrolyte Replenisher Baxter Corporation Mississauga, Ontario L5N 0C2 Canada Date of Revision:
Acute Myocardial Infarction (the formulary thrombolytic for AMI at AAMC is TNK, please see the TNK monograph in this manual for information)
 ANNE ARUNDEL MEDICAL CENTER CRITICAL CARE MEDICATION MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF NURSING AND PHARMACY Guidelines for Use of Intravenous Alteplase (Tissue Plasminogen Activator (t-pa)), Activase in the Treatment
ANNE ARUNDEL MEDICAL CENTER CRITICAL CARE MEDICATION MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF NURSING AND PHARMACY Guidelines for Use of Intravenous Alteplase (Tissue Plasminogen Activator (t-pa)), Activase in the Treatment
MEDICATION GUIDE ACTOPLUS MET (ak-tō-plus-met) (pioglitazone hydrochloride and metformin hydrochloride) tablets
 MEDICATION GUIDE (ak-tō-plus-met) (pioglitazone hydrochloride and metformin hydrochloride) tablets Read this Medication Guide carefully before you start taking and each time you get a refill. There may
MEDICATION GUIDE (ak-tō-plus-met) (pioglitazone hydrochloride and metformin hydrochloride) tablets Read this Medication Guide carefully before you start taking and each time you get a refill. There may
SLIDING SCALE INSULIN ASPART PROTOCOL PLAN
 Weight Allergies Patient Care Accucheck Per Sliding Scale Insulin Frequency AC & HS AC & HS 3 days TID BID q12h q6h q6h 24 hr q4h q2h Sliding Scale Insulin Protocol Follow SSI Reference Text Medications
Weight Allergies Patient Care Accucheck Per Sliding Scale Insulin Frequency AC & HS AC & HS 3 days TID BID q12h q6h q6h 24 hr q4h q2h Sliding Scale Insulin Protocol Follow SSI Reference Text Medications
Brewton City Schools Anaphylaxis Preparedness Guidelines
 Brewton City Schools Anaphylaxis Preparedness Guidelines Background In response to Act#2014-405 by the Alabama Legislature, the Brewton City School System recognizes the growing concern with severe life-threatening
Brewton City Schools Anaphylaxis Preparedness Guidelines Background In response to Act#2014-405 by the Alabama Legislature, the Brewton City School System recognizes the growing concern with severe life-threatening
table of contents drug reference
 table of contents drug reference ADULT DRUG REFERENCE...155 161 PEDIATRIC DRUG REFERENCE...162 164 PEDIATRIC WEIGHT-BASED DOSING CHARTS...165 180 Adenosine...165 Amiodarone...166 Atropine...167 Defibrillation...168
table of contents drug reference ADULT DRUG REFERENCE...155 161 PEDIATRIC DRUG REFERENCE...162 164 PEDIATRIC WEIGHT-BASED DOSING CHARTS...165 180 Adenosine...165 Amiodarone...166 Atropine...167 Defibrillation...168
ADMINISTRATION OF MEDICATIONS POLICY
 Policy 6.007. ADMINISTRATION OF MEDICATIONS POLICY It is the policy of Cooperative Educational Services (C.E.S.) that students who require any medications to be administered during school hours, including
Policy 6.007. ADMINISTRATION OF MEDICATIONS POLICY It is the policy of Cooperative Educational Services (C.E.S.) that students who require any medications to be administered during school hours, including
MEDICATION GUIDE. PROCRIT (PRO KRIT) (epoetin alfa)
 MEDICATION GUIDE PROCRIT (PROKRIT) (epoetin alfa) Read this Medication Guide: before you start PROCRIT. if you are told by your healthcare provider that there is new information about PROCRIT. if you are
MEDICATION GUIDE PROCRIT (PROKRIT) (epoetin alfa) Read this Medication Guide: before you start PROCRIT. if you are told by your healthcare provider that there is new information about PROCRIT. if you are
GUIDELINES FOR CONTRAST MEDIA PRE-MEDICATION
 GUIDELINES FOR CONTRAST MEDIA PRE-MEDICATION Purpose To produce pre-medication guidelines for CDHA to minimize patient risk from acute allergic-like contrast reactions while performing necessary diagnostic
GUIDELINES FOR CONTRAST MEDIA PRE-MEDICATION Purpose To produce pre-medication guidelines for CDHA to minimize patient risk from acute allergic-like contrast reactions while performing necessary diagnostic
Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Xultophy (insulin degludec / liraglutide)
 EMA/467911/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Xultophy (insulin degludec / liraglutide) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Xultophy, which details the measures to be
EMA/467911/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Xultophy (insulin degludec / liraglutide) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Xultophy, which details the measures to be
Medical Direction and Practices Board WHITE PAPER
 Medical Direction and Practices Board WHITE PAPER Use of Pressors in Pre-Hospital Medicine: Proper Indication and State of the Science Regarding Proper Choice of Pressor BACKGROUND Shock is caused by a
Medical Direction and Practices Board WHITE PAPER Use of Pressors in Pre-Hospital Medicine: Proper Indication and State of the Science Regarding Proper Choice of Pressor BACKGROUND Shock is caused by a
Ureteral Stenting and Nephrostomy
 Scan for mobile link. Ureteral Stenting and Nephrostomy Ureteral stenting and nephrostomy help restore urine flow through blocked ureters and return the kidney to normal function. Ureters are long, narrow
Scan for mobile link. Ureteral Stenting and Nephrostomy Ureteral stenting and nephrostomy help restore urine flow through blocked ureters and return the kidney to normal function. Ureters are long, narrow
Care of Gastrostomy Tubes for Adults with IDD in Community Settings: The Nurse s Role. Lillian Khalil, BSN, RN Volunteers of America, Chesapeake
 Care of Gastrostomy Tubes for Adults with IDD in Community Settings: The Nurse s Role Lillian Khalil, BSN, RN Volunteers of America, Chesapeake Objectives The participants will be able to identify the
Care of Gastrostomy Tubes for Adults with IDD in Community Settings: The Nurse s Role Lillian Khalil, BSN, RN Volunteers of America, Chesapeake Objectives The participants will be able to identify the
Appendix 7 Anaphylaxis Management
 Appendix 7 Anaphylaxis Management Anaphylaxis: Initial Management in Non-Hospital Settings This section is intended for the initial management of patients in a public health clinic, medical office or similar
Appendix 7 Anaphylaxis Management Anaphylaxis: Initial Management in Non-Hospital Settings This section is intended for the initial management of patients in a public health clinic, medical office or similar
Humulin (HU-mu-lin) R
 1 PATIENT INFORMATION Humulin (HU-mu-lin) R Regular U-500 (Concentrated) insulin human injection, USP (rdna origin) Read the Patient Information that comes with Humulin R U-500 before you start taking
1 PATIENT INFORMATION Humulin (HU-mu-lin) R Regular U-500 (Concentrated) insulin human injection, USP (rdna origin) Read the Patient Information that comes with Humulin R U-500 before you start taking
Paracetamol apollo +9191 46 950 950. Paracetamol apollo +9191 46 950 950. Paracetamol
 Paracetamol apollo +9191 46 950 950 Paracetamol apollo +9191 46 950 950 Paracetamol CAS Number : 103-90-2 Molecular Weight : 151.17 g/mol Molecular Formula : C8H9NO2 Systematic (IUPAC) : N-(4- hydroxyphenyl)ethanamide
Paracetamol apollo +9191 46 950 950 Paracetamol apollo +9191 46 950 950 Paracetamol CAS Number : 103-90-2 Molecular Weight : 151.17 g/mol Molecular Formula : C8H9NO2 Systematic (IUPAC) : N-(4- hydroxyphenyl)ethanamide
I B2.4. Design of the patient information leaflet for VariQuin
 (English translation of official Dutch version) I B2.4. Design of the patient information leaflet for VariQuin Information for the Patient: Read this package leaflet carefully when you have some time to
(English translation of official Dutch version) I B2.4. Design of the patient information leaflet for VariQuin Information for the Patient: Read this package leaflet carefully when you have some time to
UBISTESIN 1:200,000 and UBISTESIN FORTE 1:100,000
 UBISTESIN 1:200,000 and UBISTESIN FORTE 1:100,000 Articaine hydrochloride and adrenaline hydrochloride Consumer Medicine Information WHAT IS IN THIS LEAFLET Please read this leaflet carefully before you
UBISTESIN 1:200,000 and UBISTESIN FORTE 1:100,000 Articaine hydrochloride and adrenaline hydrochloride Consumer Medicine Information WHAT IS IN THIS LEAFLET Please read this leaflet carefully before you
PHENYLEPHRINE HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION USP
 PRESCRIBING INFORMATION PHENYLEPHRINE HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION USP 10 mg/ml Sandoz Canada Inc. Date of Preparation: September 1992 145 Jules-Léger Date of Revision : January 13, 2011 Boucherville, QC, Canada
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION PHENYLEPHRINE HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION USP 10 mg/ml Sandoz Canada Inc. Date of Preparation: September 1992 145 Jules-Léger Date of Revision : January 13, 2011 Boucherville, QC, Canada
SLIDING SCALE INSULIN REGULAR PLAN
 PHYSICIAN S Weight Allergies DETAILS Patient Care POC Blood Sugar Check Per Sliding Scale Insulin Frequency AC & HS AC & HS 3 days TID BID q12h q6h q6h 24 hr q4h q2h Sliding Scale Insulin Regular Guidelines
PHYSICIAN S Weight Allergies DETAILS Patient Care POC Blood Sugar Check Per Sliding Scale Insulin Frequency AC & HS AC & HS 3 days TID BID q12h q6h q6h 24 hr q4h q2h Sliding Scale Insulin Regular Guidelines
105 CMR: DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC HEALTH 105 CMR 210.000: THE ADMINISTRATION OF PRESCRIPTION MEDICATIONS IN PUBLIC AND PRIVATE SCHOOLS
 105 CMR 210.000: THE ADMINISTRATION OF PRESCRIPTION MEDICATIONS IN PUBLIC AND PRIVATE SCHOOLS Section 210.001: Purpose 210.002: Definitions 210.003: Policies Governing the Administration of Prescription
105 CMR 210.000: THE ADMINISTRATION OF PRESCRIPTION MEDICATIONS IN PUBLIC AND PRIVATE SCHOOLS Section 210.001: Purpose 210.002: Definitions 210.003: Policies Governing the Administration of Prescription
