Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Physician Performance Measurement Set
|
|
|
- Jack French
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 American Gastroenterological Association Institute/Physician Consortium for Performance Improvement Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Physician Performance Measurement Set October 2006 GERD Work Group Stuart Spechler, MD (Co-Chair) Josie Williams, MD, MMM (Co-Chair) Joel V. Brill, MD Cheri L. Canon, M.D. Donald O. Castell, MD Kedar Chintapalli, MD Kenneth DeVault, MD Glenn Eisen MD Scott Endsley, MD, MSc Gary W. Falk, MD Susan M. Harding, MD, FCCP Terri Herzog RN, C, CGRN Elizabeth Hodgson, MD John G. Hunter MD Peter J. Kahrilas, MD John Martin, MD Julie Parsonnet, MD Goutham Rao, MD Catherine Rees, MD Joel E. Richter, MD Sam JW Romeo, MD, MBA John F. Schneider, MD PhD Nicholas Shaheen, MD, MPH Prateek Sharma, MD Nathaniel Soper, MD Mark Stein, MD Monte Troutman, DO, FACOI Madhavi Vemireddy MD American Gastroenterological Association Institute Deborah Robin, MSN, RN, CHCQM American Medical Association Karen Kmetik, PhD Erin O. Kaleba, MPH Facilitators Timothy Kresowik, MD Rebecca Kresowik National Committee for Quality Assurance Sarah Sampsel, MPH Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations Kathy Domzalski Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services Susan Nedza, MD Latousha Leslie Measures including specifications American Medical Association and National Committee for Quality Assurance. 1
2 Intended Audience and Patient Population: These measures are intended for gastroenterologists, and any other physician managing the on-going care of patients with Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD). These clinical performance measures are designed for individual quality improvement. Some of the measures may also be appropriate for accountability if appropriate sample sizes and implementation rules are achieved. Accountability Measures: #1: Assessment for alarm symptoms #2: Endoscopy for patients with alarm symptoms #3: Biopsy for Barrett s esophagus #4: Barium swallow inappropriate use Quality Improvement Measure: #5: Medication Therapy - Assessment of GERD Symptoms 2
3 GERD Measure #1: Assessment for Alarm Symptoms This measure may be used as an Accountability measure Data Elements Clinical Performance Measure Feedback Per Patient, Per Year Yes/No documentation of the presence or absence of the following alarm symptoms: involuntary weight loss, dysphagia, and GI bleeding Yes/No Documentation of medical reason(s) for not assessing for alarm symptoms Sources Electronic medical record Paper medical record Flowsheet Administrative claims data* *adequate data source only if new codes are developed specific to the intent of this measure Numerator: Patients who were assessed for the presence or absence of the following alarm symptoms: involuntary weight loss, dysphagia, and GI bleeding Denominator: All patients aged 18 years and older with the diagnosis of GERD, seen for an initial evaluation Denominator Exclusion: Documentation of medical reason(s) for not assessing for alarm symptoms Measure: Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with diagnosis of GERD, seen for an initial evaluation, who were assessed for the presence or absence of the following alarm symptoms: involuntary weight loss, dysphagia, and GI bleeding Per Patient Whether or not the patient aged 18 years and older with diagnosis of GERD, seen for an initial evaluation, had an assessment for the presence or absence of the following alarm symptoms: involuntary weight loss, dysphagia, and GI bleeding Per Patient Population Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with diagnosis of GERD, seen for an initial evaluation, who had an assessment for the presence or absence of the following alarm symptoms: involuntary weight loss, dysphagia, and GI bleeding The following clinical recommendation statements are quoted verbatim from the referenced clinical guidelines and represent the evidence base for the measure: Further diagnostic testing (including endoscopy, proton pump inhibitor (PPI) trial, ambulatory ph monitoring, or other tests) is recommended in the following: Patients with alarm symptoms (referral for further testing should be immediate). Alarm symptoms are those that suggest cancer. Alarm symptoms include dysphagia, odynophagia, weight loss, hematemesis, black or bloody stools, chest pain, or choking (acid reflux causing coughing, hoarseness, or shortness of breath). (VHA 1 ) Alarm features should be sought in all patients presenting with dyspepsia. If alarm features are present, endoscopy should be performed (suggested time frames for urgency of endoscopy are provided with each of the alarm features listed). (ICSI 2 ) (Class A, C) Rationale for the measure: To determine a treatment plan for a patient with GERD, the physician should assess and document whether or not the patient has alarm symptoms. These symptoms are suggestive of possible cancer, and should be addressed with further diagnostic testing when present. Data are not readily available as to whether or not physicians are routinely assessing for alarm signs at the initial evaluation of a patient with GERD. 3
4 GERD Measure #2: Upper endoscopy for patients with alarm symptoms This measure may be used as an Accountability measure Data Elements Clinical Performance Measure Feedback Per Patient, Per Year Yes/No Patient had at least one alarm symptom (alarm symptoms include: involuntary weight loss, dysphagia, GI bleeding) Yes/No Documentation of referral for upper endoscopy Yes/No Patient had upper endoscopy performed Yes/No Documentation of medical reason(s) for not referring for upper endoscopy or performing an upper endoscopy Yes/No Documentation of patient reason(s) for not referring for upper endoscopy or performing an upper endoscopy Yes/No Documentation of system reason(s) for not referring for upper endoscopy or performing an upper endoscopy Sources Electronic medical record Paper medical record Flowsheet Administrative claims data* *adequate data source only if new codes are developed specific to the intent of this measure Numerator: Patients who were either referred for an upper endoscopy or had an upper endoscopy performed Denominator: All patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of GERD, seen for an initial evaluation, with documentation of at least one alarm symptom (involuntary weight loss, dysphagia, or GI bleeding) Denominator Exclusion: Documentation of medical reason(s) for not referring for or not performing an upper endoscopy Documentation of patient reason(s) for not referring for or not performing an upper endoscopy Documentation of system reason(s) for not referring for or not performing an upper endoscopy Measure: Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older seen for an initial evaluation of GERD with at least one alarm symptom who were either referred for upper endoscopy or had an upper endoscopy performed Per Patient Whether or not the patient aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of GERD, seen for an initial evaluation, with documentation of at least one alarm symptom who was either referred for upper endoscopy or had an upper endoscopy performed Per Patient Population Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of GERD, seen for an initial evaluation, with documentation of at least one alarm symptom, who were either referred for upper endoscopy or had an upper endoscopy performed 4
5 The following clinical recommendation statements are quoted verbatim from the referenced clinical guidelines and represent the evidence base for the measure: Further diagnostic testing (including endoscopy, proton pump inhibitor (PPI) trial, ambulatory ph monitoring, or other tests) is recommended in the following: Patients with alarm symptoms (referral for further testing should be immediate). Alarm symptoms are those that suggest cancer. Alarm symptoms include dysphagia, odynophagia, weight loss, hematemesis, black or bloody stools, chest pain, or choking (acid reflux causing coughing, hoarseness, or shortness of breath). (VHA) Send patients with dyspepsia plus one of the following alarm features for urgent endoscopic evaluation. Suggested time frames for the urgency of endoscopy are provided with each of the alarm features listed. (ICSI 3 ) (Class A, C) Melena (within 1 day if ill) Hematemesis (within 1 day if ill) Persistent vomiting (7-10 days) Anemia (7-10 days) Acute onset of total dysphagia (within 1 day) Weight loss greater than 5% (involuntary) (7-10 days) Rationale for the measure: This measure addresses the issue of when do perform an endoscopy by assessing whether an endoscopy was done for a patient with at least one alarm symptom. Alarm symptoms could indicate cancer, and further imaging is needed to rule out the diagnosis of cancer or other conditions. 5
6 GERD Measure #3: Biopsy for Barrett s esophagus This measure may be used as an Accountability measure Data Elements Clinical Performance Measure Feedback Per Patient, Per Procedure Yes/No Endoscopy report indicates a suspicion of Barrett s esophagus Yes/No Documentation of a forceps esophageal biopsy Date of endoscopy Yes/No Documentation of medical reason(s) for not performing a forceps esophageal biopsy Sources Electronic medical record Paper medical record Flowsheet Administrative claims data* Numerator: Patients who had a forceps esophageal biopsy performed Denominator: All patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of GERD or heartburn whose endoscopy report indicates a suspicion of Barrett s esophagus Denominator Exclusion: Documentation of medical reason(s) for not performing a forceps esophageal biopsy Measure: Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of GERD or heartburn whose endoscopy report indicates a suspicion of Barrett s esophagus who had a forceps esophageal biopsy performed Per Patient Whether or not the patient aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of GERD or heartburn whose endoscopy report indicates a suspicion of Barrett s esophagus had a forceps esophageal biopsy performed Per Patient Population Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of GERD or heartburn whose endoscopy report indicates a suspicion of Barrett s esophagus who had a forceps esophageal biopsy performed *adequate data source only if new codes are developed specific to the intent of this measure The following clinical recommendation statements are quoted verbatim from the referenced clinical guidelines and represent the evidence base for the measure: Endoscopy is the technique of choice used to identify suspected Barrett s esophagus and to diagnose complications of GERD. Biopsy must be added to confirm the presence of Barrett s epithelium and to evaluate for dysplasia. (ACG Error! Bookmark not defined. ) (Level III) Rationale for the measure: The official diagnosis of Barrett s esophagus is made by a pathologist. Therefore, if Barrett s esophagus is suspected upon endoscopic examination, a biopsy should be performed by the endoscopist and sent to pathology for diagnosis. 6
7 GERD Measure #4: Barium swallow inappropriate use This measure may be used as an Accountability measure Data Elements Clinical Performance Measure Feedback Per Patient, Per Year Yes/No Documentation that a Barium swallow test was ordered Date of Barium swallow test Yes/No Documentation of medical reason(s) for ordering a Barium swallow test Sources Electronic medical record Paper medical record Flowsheet Administrative claims data* Numerator: Patients who did not have Barium swallow test ordered Denominator: All patients aged 18 years and older seen for an initial evaluation of GERD Denominator Exclusion: Documentation of medical reason(s) for ordering a Barium swallow test Measure: Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older seen for an initial evaluation of GERD who did not have a Barium swallow test ordered Per Patient Whether or not the patient aged 18 years and older seen for an initial evaluation of GERD did not have a Barium swallow test ordered Per Patient Population Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older seen for an initial evaluation of GERD who did not have a Barium swallow test ordered *adequate data source only if new codes are developed specific to the intent of this measure The following clinical recommendation statements are quoted verbatim from the referenced clinical guidelines and represent the evidence base for the measure: Barium radiology has limited usefulness in the diagnosis of GERD and thus is not recommended. (UMHS 4 ) (Grade B) Rationale for the measure: This measure was written as an avoidance measure so that the performance goal is 100%, consistent with the other measures. Data elements required for the measure can be captured and the measure is actionable by the physician. 7
8 GERD Measure #5: Chronic Medication Therapy - Assessment of GERD Symptoms This measure may be used for Quality Improvement only Data Elements Clinical Performance Measure Feedback Per Patient, Per Year Date of initial acid suppression medication prescription Yes/No Patient had assessment for GERD symptoms Yes/No - Documentation of medical reason(s) for not assessing GERD symptoms Sources Electronic medical record Numerator: Patients who had an assessment of their GERD symptoms within 12 months Denominator: All patients aged 18 years and older patients with the diagnosis of GERD who have been prescribed chronic proton pump inhibitor (PPI) or histamine H2 receptor antagonist (H2RA) therapy Denominator exclusions: Documentation of medical reason(s) for not assessing GERD symptoms Per Patient Whether or not the patient aged 18 years and older with the diagnosis of GERD who have been prescribed chronic PPI or H2RA therapy who had an assessment of their GERD symptoms Per Patient Population All patients aged 18 years and older with the diagnosis of GERD who have been prescribed chronic PPI or H2RA therapy who received an assessment of their GERD symptoms Paper medical record Flowsheet Administrative claims data* *adequate data source only if new codes are developed specific to the intent of this measure Measure: All patients aged 18 years and older with the diagnosis of GERD who have been prescribed chronic proton pump inhibitor (PPI) or histamine H2 receptor antagonist (H2RA) therapy who received an assessment of their GERD symptoms within 12 months The following clinical recommendation statements are quoted verbatim from the referenced clinical guidelines and represent the evidence base for the measure: Because GERD is a chronic condition, continuous therapy to control symptoms and prevent complications is appropriate. (ACGError! Bookmark not defined.) (Level I) Nonresponders to adequate trials of drug therapy, particularly PPI therapy, should have their symptoms reassessed, undergo endoscopy if it was not previously done, and be considered for additional diagnostic work-up. (VHA/DOD) (OQ III, Grade C) Inadequate response to a 4- to 8- week course of standard-dose PPI may indicate longer treatment is needed, more severe disease, or incorrect diagnosis. If there is an inadequate response to a course of standard-dose PPI (the recommended duration of therapy for PPIs in the treatment of GERD is 4 to 8 weeks), extend treatment with either the same or double dose of PPI. (VHA/DOD) (OQ I, Grade B) Rationale for the measure: Many patients with GERD remain on medication therapy for years, and experts suspect that not all patients are being reassessed on a regular basis to determine whether the medication is still needed. This measure attempts to capture whether or not a patient on chronic medication have their GERD symptoms are assessed at least annually. Research indicates that patients on chronic therapy are able to have their dose modified or reduced based on the presence or absence of symptoms. 8
9 Evidence classification / rating scheme Veterans Health Administration (VHA)/Department of Defense (DoD) Evidence Rating Scale Quality of Evidence (QE) Level I Evidence obtained from at least one properly randomized controlled trial. Level II-1 Evidence obtained from well-designed controlled trials without randomization. Level II-2 Evidence obtained from well-designed cohort or case-controlled analytic studies, preferably from more than one center or research group. Level II-3 Evidence obtained from multiple time series with or without the intervention. Dramatic results in uncontrolled experiments could also be regarded as this type of evidence. Level III Opinion of respected authorities, based on clinical experience, descriptive studies and case reports, or reports of expert committees Overall Quality (OQ) Level I Good High-grade evidence (I or II-1) directly linked to health outcome Level II Fair High-grade evidence (I or II-1) linked to intermediate outcome OR Moderate-grade evidence (II-2 or II-3) directly linked to health outcome Level III Poor Level III evidence or no linkage of evidence to health outcome Level IV Insufficient evidence Grade for Strength of the Recommendation Grade A A strong recommendation that the intervention is always indicated and acceptable Grade B A recommendation that the intervention may be useful/effective Grade C A recommendation that the intervention may be considered Grade D A recommendation that a procedure may be considered not useful/effective, or may be harmful Grade I Insufficient evidence to recommend for or against the clinician will use their clinical judgment Institute for Clinical Systems Improvement (ICSI) 2 Classes of Research Reports: Primary Reports of New Data Collection: Class A: Randomized, controlled trial Class B: Cohort study Class C: Nonrandomized trial with concurrent or historical controls; Case-control study, Study of sensitivity and specificity of a diagnostic test; Population-based descriptive study Class D: Cross-sectional study, case series, case report Reports that Synthesize or Reflect upon Collections of Primary Reports: Class M: Meta-analysis; Systematic review; Decision analysis; Cost-effectiveness analysis Class R: Consensus statement; Consensus report; Narrative review Class X: Medical opinion American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) Rating of Levels of EvidenceError! Bookmark not defined. Level I Strong evidence from at least one published systematic review of multiple well-designed randomized controlled trials Level II Strong evidence from at least one published properly designed randomized controlled trial of appropriate size and in appropriate clinical setting Level III Evidence from published well-designed trials without randomization, single group prepost, cohort, time series or matched case-controlled studies Level IV Evidence from well-designed nonexperimental studies from more than one center or research group or opinion of respected authorities, based on clinical evidence, descriptive studies, or reports of expert consensus committees 9
10 University of Michigan Health System (UMHS) Evidence Grading System Levels of evidence reflect the best available literature in support of an intervention or test: A=randomized controlled trials B=controlled trials, no randomization C=observational trials D=opinion of expert pane References 1 VHA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Adults with Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Primary Care Practice. Washington, DC: Pharmacy Benefits Management Strategic Healthcare Group and the Medical Advisory Panel, Veterans Health Administration, Department of Veterans Affairs, and the Pharmacoeconomic Center, Department of Defense. March 12, PBM-MAP Publication No Institute for Clinical Systems Improvement (ICSI). Initial management of dyspepsia and GERD. Bloomington (MN): Institute for Clinical Systems Improvement (ICSI); 2006 July 3 Institute for Clinical Systems Improvement (ICSI). Initial management of dyspepsia and GERD. Bloomington (MN): Institute for Clinical Systems Improvement (ICSI); 2006 July 4 University of Michigan Health System (UMHS). Guidelines for clinical care. Management of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). March Available at: 10
What is Barrett s esophagus? How does Barrett s esophagus develop?
 Barrett s Esophagus What is Barrett s esophagus? Barrett s esophagus is a pre-cancerous condition affecting the lining of the esophagus, the swallowing tube that carries foods and liquids from the mouth
Barrett s Esophagus What is Barrett s esophagus? Barrett s esophagus is a pre-cancerous condition affecting the lining of the esophagus, the swallowing tube that carries foods and liquids from the mouth
GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)
 GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD) Gastroesophageal reflux disease is a clinical scenario where the gastric or duodenal contents reflux back up into the esophagus. Reflux esophagitis, however, is a
GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD) Gastroesophageal reflux disease is a clinical scenario where the gastric or duodenal contents reflux back up into the esophagus. Reflux esophagitis, however, is a
Research funding was provided by TAP Pharmaceutical Products, Inc.
 DOES THE DOSING FREQUENCY OF PROTON PUMP INHIBITORS (PPIs) AFFECT SUBSEQUENT RESOURCE UTILIZATION AND COSTS AMONG PATIENTS DIAGNOSED WITH GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)? Boulanger L 1, Mody R 2,
DOES THE DOSING FREQUENCY OF PROTON PUMP INHIBITORS (PPIs) AFFECT SUBSEQUENT RESOURCE UTILIZATION AND COSTS AMONG PATIENTS DIAGNOSED WITH GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)? Boulanger L 1, Mody R 2,
A. Ketorolac*** B. Naproxen C. Ibuprofen D. Celecoxib
 1. A man, 66 years of age, with a history of knee osteoarthritis (OA) is experiencing increasing pain at rest and with physical activity. He also has a history of depression and coronary artery disease.
1. A man, 66 years of age, with a history of knee osteoarthritis (OA) is experiencing increasing pain at rest and with physical activity. He also has a history of depression and coronary artery disease.
Figure 3: Dysphagia. 14 meets. esophageal. esophageal manometry +/- +/- impedance measurement. structural lesion? no. 19 yes
 Figure 3: Dysphagia 1 patient with dysphagia 2 history and physical exam. suggestive of nesophageal etiology? 3 evaluate and treat as as indicated 4 upper GI GI endoscopy with biopsies 15 achalasia, absent
Figure 3: Dysphagia 1 patient with dysphagia 2 history and physical exam. suggestive of nesophageal etiology? 3 evaluate and treat as as indicated 4 upper GI GI endoscopy with biopsies 15 achalasia, absent
1-800-HRT-BURN. understanding gerd. Is it just a little HEARTBURN. or something more serious? NEW
 Do you have GERD? Measure Yourself on the Richter Scale/Acid Test How significant is your heartburn? What are the chances that it is something more serious? If you need a yardstick, here s a simple self-test
Do you have GERD? Measure Yourself on the Richter Scale/Acid Test How significant is your heartburn? What are the chances that it is something more serious? If you need a yardstick, here s a simple self-test
National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Barrett s Esophagus National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is Barrett s esophagus? Barrett s esophagus is
Barrett s Esophagus National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is Barrett s esophagus? Barrett s esophagus is
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
 3702 Timberline Rd 2555 East 13th St Suite 220 Ft.Collins, CO 80525 Loveland, CO 80537 82001 7251 W. 20th St Greeley, CO 80634 4108 Laramie Cheyenne, WY Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Author(s): Peter
3702 Timberline Rd 2555 East 13th St Suite 220 Ft.Collins, CO 80525 Loveland, CO 80537 82001 7251 W. 20th St Greeley, CO 80634 4108 Laramie Cheyenne, WY Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Author(s): Peter
Treatments for Barrett s Oesophagus
 Treatments for Barrett s Oesophagus Introduction This leaflet describes the various ways in which Barrett s Oesophagus is treated. It has been produced in association with Heartburn Cancer UK (HCUK), a
Treatments for Barrett s Oesophagus Introduction This leaflet describes the various ways in which Barrett s Oesophagus is treated. It has been produced in association with Heartburn Cancer UK (HCUK), a
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) and Barrett s Esophagus (BE)
 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) and Barrett s Esophagus (BE) Hashem El-Serag, M.D., M.P.H. Dan L. Duncan Professor of Medicine Chief, Gastroenterology and Hepatology Baylor College of Medicine Houston,
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) and Barrett s Esophagus (BE) Hashem El-Serag, M.D., M.P.H. Dan L. Duncan Professor of Medicine Chief, Gastroenterology and Hepatology Baylor College of Medicine Houston,
Nash Heartburn Treatment Center
 Nash Heartburn Treatment Center a division of Nash Health Care NHCS Mission Statement: To provide superior quality health care services and to help improve the health of the community in a caring, efficient
Nash Heartburn Treatment Center a division of Nash Health Care NHCS Mission Statement: To provide superior quality health care services and to help improve the health of the community in a caring, efficient
Use of stents in esophageal cancer" Hans Gerdes, M.D. Director, GI Endoscopy Unit Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center
 Use of stents in esophageal cancer" Hans Gerdes, M.D. Director, GI Endoscopy Unit Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center Features of esophageal cancer Esophageal cancer is an abnormal growth that arises
Use of stents in esophageal cancer" Hans Gerdes, M.D. Director, GI Endoscopy Unit Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center Features of esophageal cancer Esophageal cancer is an abnormal growth that arises
American Gastroenterological Association Institute Technical Review on the Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2008;135:1392 1413 American Gastroenterological Association Institute Technical Review on the Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Learning Objectives At the end of this activity,
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2008;135:1392 1413 American Gastroenterological Association Institute Technical Review on the Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Learning Objectives At the end of this activity,
Figure 2: Recurrent chest pain of suspected esophageal origin
 Figure 2: Recurrent chest pain of suspected esophageal origin 1 patient with chest pain of suspected esophageal origin 2 history and physical exam. suggestive of n-esophageal etiology? 3 evaluate and treat
Figure 2: Recurrent chest pain of suspected esophageal origin 1 patient with chest pain of suspected esophageal origin 2 history and physical exam. suggestive of n-esophageal etiology? 3 evaluate and treat
John I Allen, MD, MBA
 Specialty Clinical Service Lines John I Allen, MD, MBA Minnesota Gastroenterology American Gastroenterological Association ICSI Accountable Care Organization Primary Care Specialty Care Outpatient Care
Specialty Clinical Service Lines John I Allen, MD, MBA Minnesota Gastroenterology American Gastroenterological Association ICSI Accountable Care Organization Primary Care Specialty Care Outpatient Care
Radiology Physician Performance Measurement Set
 American College of Radiology/ Physician Consortium for Performance Improvement / National Committee for Quality Assurance Radiology Physician Performance Measurement Set October 2007 Radiology Work Group
American College of Radiology/ Physician Consortium for Performance Improvement / National Committee for Quality Assurance Radiology Physician Performance Measurement Set October 2007 Radiology Work Group
Gastrointestinal Bleeding
 Gastrointestinal Bleeding Introduction Gastrointestinal bleeding is a symptom of many diseases rather than a disease itself. A number of different conditions can cause gastrointestinal bleeding. Some causes
Gastrointestinal Bleeding Introduction Gastrointestinal bleeding is a symptom of many diseases rather than a disease itself. A number of different conditions can cause gastrointestinal bleeding. Some causes
at our institution, was $1.8 million in 1999. While some patients require PPI therapy, many could control their symptoms with a histamine H 2
 A Practice-Based Approach for Converting from Proton Pump Inhibitors to Less Costly Therapy CASE REPORT LINDA M. LUCAS, MD MARTHA S. GERRITY, MD, PhD THOMAS ANDERSON, MD Department of Veterans Affairs
A Practice-Based Approach for Converting from Proton Pump Inhibitors to Less Costly Therapy CASE REPORT LINDA M. LUCAS, MD MARTHA S. GERRITY, MD, PhD THOMAS ANDERSON, MD Department of Veterans Affairs
Formulary Management
 Formulary Management Formulary management is an integrated patient care process which enables physicians, pharmacists and other health care professionals to work together to promote clinically sound, cost-effective
Formulary Management Formulary management is an integrated patient care process which enables physicians, pharmacists and other health care professionals to work together to promote clinically sound, cost-effective
Evidence Based Medicine Health Information Infrastructure Transparency and Payment Reform. Ward B. Hurlburt, M.D. October 12, 2002
 Evidence Based Medicine Health Information Infrastructure Transparency and Payment Reform Ward B. Hurlburt, M.D. October 12, 2002 Evidence-based medicine - EBM aims to apply the best available evidence
Evidence Based Medicine Health Information Infrastructure Transparency and Payment Reform Ward B. Hurlburt, M.D. October 12, 2002 Evidence-based medicine - EBM aims to apply the best available evidence
National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Gastritis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is gastritis? Gastritis is a condition in which the stomach
Gastritis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is gastritis? Gastritis is a condition in which the stomach
Clinical characteristics in patients with non-cardiac chest pain could favor gastroesophageal reflux disease diagnosis
 Original article Annals of Gastroenterology (2013) 26, 1-5 Clinical characteristics in patients with non-cardiac chest pain could favor gastroesophageal reflux disease diagnosis Anastasios Karlaftis a,b,
Original article Annals of Gastroenterology (2013) 26, 1-5 Clinical characteristics in patients with non-cardiac chest pain could favor gastroesophageal reflux disease diagnosis Anastasios Karlaftis a,b,
understanding HEARTBURN and reflux diseases A patient s guide from your doctor and
 understanding HEARTBURN and reflux diseases A patient s guide from your doctor and Heartburn Basics Heartburn is the most common symptom of a condition called gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), also
understanding HEARTBURN and reflux diseases A patient s guide from your doctor and Heartburn Basics Heartburn is the most common symptom of a condition called gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), also
Medical Nutrition Therapy for Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Disorders. By: Jalal Hejazi PhD, MSc.
 Medical Nutrition Therapy for Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Disorders By: Jalal Hejazi PhD, MSc. Digestive Disorders Common problem; more than 50 million outpatient visits per year Dietary habits and nutrition
Medical Nutrition Therapy for Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Disorders By: Jalal Hejazi PhD, MSc. Digestive Disorders Common problem; more than 50 million outpatient visits per year Dietary habits and nutrition
Attribute appropriate and inappropriate services to provider of initial visit
 Optimal Care for Acute Low Back Pain - Adults Primary Care Description The rate represents the percentage of members ages 18 and older with newly diagnosed acute low back pain who received optimal care
Optimal Care for Acute Low Back Pain - Adults Primary Care Description The rate represents the percentage of members ages 18 and older with newly diagnosed acute low back pain who received optimal care
Acute Abdominal Pain following Bariatric Surgery. Disclosure. Objectives 8/17/2015. I have nothing to disclose
 Acute Abdominal Pain following Bariatric Surgery Kathy J. Morris, DNP, APRN, FNP C, FAANP University of Nebraska Medical Center College of Nursing Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Objectives Pathophysiology
Acute Abdominal Pain following Bariatric Surgery Kathy J. Morris, DNP, APRN, FNP C, FAANP University of Nebraska Medical Center College of Nursing Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Objectives Pathophysiology
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
 GERD Guideline Team Team Leader Joel J Heidelbaugh, MD Family Medicine Team Members R Van Harrison, PhD Medical Education Mark A McQuillan, MD General Medicine Timothy T Nostrant, MD Gastroenterology Initial
GERD Guideline Team Team Leader Joel J Heidelbaugh, MD Family Medicine Team Members R Van Harrison, PhD Medical Education Mark A McQuillan, MD General Medicine Timothy T Nostrant, MD Gastroenterology Initial
Captivator EMR Device
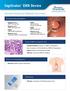 Device Clinical Article and Abstract Summary Endoscopic Mucosal Bergman et al: EMR Training Tips Bergman et al: EMR Learning Curve ASGE: EMR & ESD Guidelines Bergman et al: Captivator EMR vs Cook Duette
Device Clinical Article and Abstract Summary Endoscopic Mucosal Bergman et al: EMR Training Tips Bergman et al: EMR Learning Curve ASGE: EMR & ESD Guidelines Bergman et al: Captivator EMR vs Cook Duette
Chapter 6 Gastrointestinal Impairment
 Chapter 6 Gastrointestinal This chapter consists of 2 parts: Part 6.1 Diseases of the digestive system Part 6.2 Abdominal wall hernias and obesity PART 6.1: DISEASES OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Diseases of
Chapter 6 Gastrointestinal This chapter consists of 2 parts: Part 6.1 Diseases of the digestive system Part 6.2 Abdominal wall hernias and obesity PART 6.1: DISEASES OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Diseases of
HAWAII BOARD OF MEDICAL EXAMINERS PAIN MANAGEMENT GUIDELINES
 Pursuant to section 453-1.5, Hawaii Revised Statutes, the Board of Medical Examiners ("Board") has established guidelines for physicians with respect to the care and treatment of patients with severe acute
Pursuant to section 453-1.5, Hawaii Revised Statutes, the Board of Medical Examiners ("Board") has established guidelines for physicians with respect to the care and treatment of patients with severe acute
Esophageal Cancer. Understanding your diagnosis
 Esophageal Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Esophageal Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large
Esophageal Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Esophageal Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large
Gloucestershire Hospitals
 TRUST GUIDELINE In the case of hard copies of this policy the content can only be assured to be accurate on the date of issue marked on the document. The Policy framework requires that the policy is fully
TRUST GUIDELINE In the case of hard copies of this policy the content can only be assured to be accurate on the date of issue marked on the document. The Policy framework requires that the policy is fully
Michigan Guidelines for the Use of Controlled Substances for the Treatment of Pain
 Michigan Guidelines for the Use of Controlled Substances for the Treatment of Pain Section I: Preamble The Michigan Boards of Medicine and Osteopathic Medicine & Surgery recognize that principles of quality
Michigan Guidelines for the Use of Controlled Substances for the Treatment of Pain Section I: Preamble The Michigan Boards of Medicine and Osteopathic Medicine & Surgery recognize that principles of quality
MEDICAL ASSOCIATES HEALTH PLANS HEALTH CARE SERVI CES POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL POLICY NUMBER: PP 60
 POLICY TITLE: CRITERIA UTILIZED IN DETERMINATION OF MEDICAL NECESSITY. POLICY STATEMENT: MAHP utilizes evidence based medicine in its decision making process. This policy is to establish and maintain medical
POLICY TITLE: CRITERIA UTILIZED IN DETERMINATION OF MEDICAL NECESSITY. POLICY STATEMENT: MAHP utilizes evidence based medicine in its decision making process. This policy is to establish and maintain medical
The hidden endoscopic burden of sleeve gastrectomy and its comparison with Roux-en-Y gastric bypass
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Gastroenterology (2015) 28, 1-6 The hidden endoscopic burden of sleeve gastrectomy and its comparison with Roux-en-Y gastric bypass Katherine Arndtz a, Helen Steed b, James Hodson
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Gastroenterology (2015) 28, 1-6 The hidden endoscopic burden of sleeve gastrectomy and its comparison with Roux-en-Y gastric bypass Katherine Arndtz a, Helen Steed b, James Hodson
Patient information: Achalasia (Beyond the Basics)
 Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2012 UpToDate Patient information: Achalasia (Beyond the Basics) Author Stuart J Spechler, MD Section Editor J Thomas LaMont, MD Deputy Editor Shilpa Grover,
Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2012 UpToDate Patient information: Achalasia (Beyond the Basics) Author Stuart J Spechler, MD Section Editor J Thomas LaMont, MD Deputy Editor Shilpa Grover,
TREATMENT OF GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD) IN ADULTS
 TREATMENT OF GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD) IN ADULTS Clinical Practice Guideline January 2009 OBJECTIVE Alberta clinicians understand how to investigate and treat gastroesophageal reflux disease
TREATMENT OF GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD) IN ADULTS Clinical Practice Guideline January 2009 OBJECTIVE Alberta clinicians understand how to investigate and treat gastroesophageal reflux disease
BYE-BYE, PPI. A toolkit for deprescribing proton pump inhibitors in EMR-enabled primary care settings
 BYE-BYE, PPI. A toolkit for deprescribing proton pump inhibitors in EMR-enabled primary care settings version 1.0 Don t maintain long-term Proton Pump Inhibitor (PPI) therapy for gastrointestinal symptoms
BYE-BYE, PPI. A toolkit for deprescribing proton pump inhibitors in EMR-enabled primary care settings version 1.0 Don t maintain long-term Proton Pump Inhibitor (PPI) therapy for gastrointestinal symptoms
Original Article: http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/esophageal-spasms/ds00763
 MayoClinic.com reprints This single copy is for your personal, noncommercial use only. For permission to reprint multiple copies or to order presentation-ready copies for distribution, use the reprints
MayoClinic.com reprints This single copy is for your personal, noncommercial use only. For permission to reprint multiple copies or to order presentation-ready copies for distribution, use the reprints
EMR Decision Tool. Clinical and functional elements for EMR software
 EMR Decision Tool Clinical and functional elements for EMR software AGA Institute EMR Clinical and Functional Elements EMR Decision Tool To assist gastroenterologists in the decision process needed to
EMR Decision Tool Clinical and functional elements for EMR software AGA Institute EMR Clinical and Functional Elements EMR Decision Tool To assist gastroenterologists in the decision process needed to
Peptic Ulcer Disease and Dyspepsia. John M. Inadomi, MD Professor of Medicine UCSF Chief, Clinical Gastroenterology San Francisco General Hospital
 Peptic Ulcer Disease and Dyspepsia John M. Inadomi, MD Professor of Medicine UCSF Chief, Clinical Gastroenterology San Francisco General Hospital Case History 49 y/o woman complains of several months of
Peptic Ulcer Disease and Dyspepsia John M. Inadomi, MD Professor of Medicine UCSF Chief, Clinical Gastroenterology San Francisco General Hospital Case History 49 y/o woman complains of several months of
NURSE PRACTITIONER STANDARDS FOR PRACTICE
 NURSE PRACTITIONER STANDARDS FOR PRACTICE February 2012 Acknowledgement The Association of Registered Nurses of Prince Edward Island gratefully acknowledges permission granted by the Nurses Association
NURSE PRACTITIONER STANDARDS FOR PRACTICE February 2012 Acknowledgement The Association of Registered Nurses of Prince Edward Island gratefully acknowledges permission granted by the Nurses Association
Laparoscopic Anti-Reflux (GERD) Surgery Patient Information from SAGES
 Laparoscopic Anti-Reflux (GERD) Surgery Patient Information from SAGES Surgery for "Heartburn" If you suffer from moderate to severe "heartburn" your surgeon may have recommended Laparoscopic Antireflux
Laparoscopic Anti-Reflux (GERD) Surgery Patient Information from SAGES Surgery for "Heartburn" If you suffer from moderate to severe "heartburn" your surgeon may have recommended Laparoscopic Antireflux
03/20/12. Recognize the right of patients to appropriate assessment and management of pain
 Narcotic Bowel Syndrome Alvin Zfass M.D. M.D. Professor of Medicine Toufic Kachaamy M.D. GI Fellow Chronic Pain 110 million Americans suffer from chronic pain according to the NIH Cost of untreated t or
Narcotic Bowel Syndrome Alvin Zfass M.D. M.D. Professor of Medicine Toufic Kachaamy M.D. GI Fellow Chronic Pain 110 million Americans suffer from chronic pain according to the NIH Cost of untreated t or
PEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGY
 May 05 CLINICAL REFERENCE PEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGY INTRODUCTION Introduction Alberta Referral Pathways for Pediatric GI Services has been a collaborative project. The referral guidelines have considered
May 05 CLINICAL REFERENCE PEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGY INTRODUCTION Introduction Alberta Referral Pathways for Pediatric GI Services has been a collaborative project. The referral guidelines have considered
Chapter 4 Health Care Management Unit 1: Care Management
 Chapter 4 Health Care Unit 1: Care In This Unit Topic See Page Unit 1: Care Care 2 6 Emergency 7 4.1 Care Healthcare Healthcare (HMS), Highmark Blue Shield s medical management division, is responsible
Chapter 4 Health Care Unit 1: Care In This Unit Topic See Page Unit 1: Care Care 2 6 Emergency 7 4.1 Care Healthcare Healthcare (HMS), Highmark Blue Shield s medical management division, is responsible
Josephine Silvestre, RN, MSN The University of Chicago Medical Center. October 13, 2007
 Josephine Silvestre, RN, MSN The University of Chicago Medical Center October 13, 2007 A study in which people participate as volunteers. A clinical trial is conducted to develop potential new treatments
Josephine Silvestre, RN, MSN The University of Chicago Medical Center October 13, 2007 A study in which people participate as volunteers. A clinical trial is conducted to develop potential new treatments
Glossary of Methodologic Terms
 Glossary of Methodologic Terms Before-After Trial: Investigation of therapeutic alternatives in which individuals of 1 period and under a single treatment are compared with individuals at a subsequent
Glossary of Methodologic Terms Before-After Trial: Investigation of therapeutic alternatives in which individuals of 1 period and under a single treatment are compared with individuals at a subsequent
Is it time for a new drug development paradigm?
 Is it time for a new drug development paradigm? Robert McDonough, M.D. Senior Director, Clinical Policy Research and Development 1 The Aetna Way Our Cause To make quality health care more affordable and
Is it time for a new drug development paradigm? Robert McDonough, M.D. Senior Director, Clinical Policy Research and Development 1 The Aetna Way Our Cause To make quality health care more affordable and
Peptic Ulcer. Anatomy The stomach is a hollow organ. It is located in the upper abdomen, under the ribs.
 Peptic Ulcer Introduction A peptic ulcer is a sore in the lining of your stomach or duodenum. The duodenum is the first part of your small intestine. Peptic ulcers may also develop in the esophagus. Nearly
Peptic Ulcer Introduction A peptic ulcer is a sore in the lining of your stomach or duodenum. The duodenum is the first part of your small intestine. Peptic ulcers may also develop in the esophagus. Nearly
The Value of OTC Medicine to the United States. January 2012
 The Value of OTC Medicine to the United States January 2012 Table of Contents 3 Executive Summary 5 Study Methodology 7 Study Findings 10 Sources 2 Executive Summary For millions of Americans, over-the-counter
The Value of OTC Medicine to the United States January 2012 Table of Contents 3 Executive Summary 5 Study Methodology 7 Study Findings 10 Sources 2 Executive Summary For millions of Americans, over-the-counter
02 DEPARTMENT OF PROFESSIONAL AND FINANCIAL REGULATION
 Effective June 13, 2010 02-313, 02-373, 02-380, 02-383, 02-396 Chapter 21 page 1 02 DEPARTMENT OF PROFESSIONAL AND FINANCIAL REGULATION 313 BOARD OF DENTAL EXAMINERS 373 BOARD OF LICENSURE IN MEDICINE
Effective June 13, 2010 02-313, 02-373, 02-380, 02-383, 02-396 Chapter 21 page 1 02 DEPARTMENT OF PROFESSIONAL AND FINANCIAL REGULATION 313 BOARD OF DENTAL EXAMINERS 373 BOARD OF LICENSURE IN MEDICINE
Proton Pump Inhibitor Utilization Patterns in Infants
 Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 45:421 427 # 2007 by European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition and North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology,
Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 45:421 427 # 2007 by European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition and North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology,
PATIENT REPORTED OUTCOMES IN ESOPHAGEAL DISEASE: AN OPEN SOURCE WEB BASED FRAMEWORK
 Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine PATIENT REPORTED OUTCOMES IN ESOPHAGEAL DISEASE: AN OPEN SOURCE WEB BASED FRAMEWORK Andrew Gawron, MD, PhD Co-authors: Sherri LaVela, Jane Holl, David
Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine PATIENT REPORTED OUTCOMES IN ESOPHAGEAL DISEASE: AN OPEN SOURCE WEB BASED FRAMEWORK Andrew Gawron, MD, PhD Co-authors: Sherri LaVela, Jane Holl, David
Michigan Board of Nursing Guidelines for the Use of Controlled Substances for the Treatment of Pain
 JENNIFER M. GRANHOLM GOVERNOR STATE OF MICHIGAN DEPARTMENT OF COMMUNITY HEALTH LANSING JANET OLSZEWSKI DIRECTOR Michigan Board of Nursing Guidelines for the Use of Controlled Substances for the Treatment
JENNIFER M. GRANHOLM GOVERNOR STATE OF MICHIGAN DEPARTMENT OF COMMUNITY HEALTH LANSING JANET OLSZEWSKI DIRECTOR Michigan Board of Nursing Guidelines for the Use of Controlled Substances for the Treatment
Evolution of Barrett s esophagus
 Endoscopic Treatment and Surveillance of Esophageal Cancer: GI Perspective Charles J. Lightdale, MD Columbia University New York, NY Evolution of Barrett s esophagus Squamous esophagus Chronic inflammation
Endoscopic Treatment and Surveillance of Esophageal Cancer: GI Perspective Charles J. Lightdale, MD Columbia University New York, NY Evolution of Barrett s esophagus Squamous esophagus Chronic inflammation
Public Assessment Report. Pharmacy to General Sales List Reclassification. Nexium Control 20mg Gastro-Resistant Tablets.
 Public Assessment Report Pharmacy to General Sales List Reclassification Nexium Control 20mg Gastro-Resistant Tablets (Esomeprazole) EMA Agency number: Pfizer Consumer Healthcare Ltd TABLE OF CONTENTS
Public Assessment Report Pharmacy to General Sales List Reclassification Nexium Control 20mg Gastro-Resistant Tablets (Esomeprazole) EMA Agency number: Pfizer Consumer Healthcare Ltd TABLE OF CONTENTS
Treatment Guide Swallowing and Esophageal Disorders
 Treatment Guide Swallowing and Esophageal Disorders Esophageal disorders especially those involving swallowing problems affect more than 15 million Americans of all ages. For many, they re temporary issues
Treatment Guide Swallowing and Esophageal Disorders Esophageal disorders especially those involving swallowing problems affect more than 15 million Americans of all ages. For many, they re temporary issues
It s A Gut Feeling: Abdominal Pain in Children. David Deutsch, MD Pediatric Gastroenterology Rockford Health Physicians
 It s A Gut Feeling: Abdominal Pain in Children David Deutsch, MD Pediatric Gastroenterology Rockford Health Physicians Introduction Common Symptom Affects 10-15% of school-aged children Definition (Dr.
It s A Gut Feeling: Abdominal Pain in Children David Deutsch, MD Pediatric Gastroenterology Rockford Health Physicians Introduction Common Symptom Affects 10-15% of school-aged children Definition (Dr.
Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
 308 PRACTICE GUIDELINES nature publishing group see related editorial on page x CME Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Philip O. Katz, MD 1, Lauren B. Gerson,
308 PRACTICE GUIDELINES nature publishing group see related editorial on page x CME Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Philip O. Katz, MD 1, Lauren B. Gerson,
How To Be A Nurse Practitioner
 NURSE PRACTITIONER PROGRAM THE PENNSYLVANIA STATE UNIVERSITY College of Nursing Preceptor Evaluation of Student Clinical Performance: Adult Gerontology Acute Care Nurse Practitioner Option Nursing 863
NURSE PRACTITIONER PROGRAM THE PENNSYLVANIA STATE UNIVERSITY College of Nursing Preceptor Evaluation of Student Clinical Performance: Adult Gerontology Acute Care Nurse Practitioner Option Nursing 863
This is a prospective study that analyzed the factors associated with cancer progression after
 Sample Peer-Review of a Fictitious Manuscript Reviewer A s Comments to Authors: This is a prospective study that analyzed the factors associated with cancer progression after EMR of Barrett s esophagus
Sample Peer-Review of a Fictitious Manuscript Reviewer A s Comments to Authors: This is a prospective study that analyzed the factors associated with cancer progression after EMR of Barrett s esophagus
As the Director of The Clinical Center of Excellence at Rutgers University, I am speaking on
 Department of Environmental and Occupational Medicine Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey EOHSI 170 Frelinghuysen Road Piscataway, NJ 08540 Email: udasin@eohsi.rutgers.edu Phone: 848-445-6016 Fax:
Department of Environmental and Occupational Medicine Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey EOHSI 170 Frelinghuysen Road Piscataway, NJ 08540 Email: udasin@eohsi.rutgers.edu Phone: 848-445-6016 Fax:
of the Nurse Practitioner
 The Emerging Role of the Nurse Practitioner Rhonda Hettinger DNP, NP C, CLS Introduction The American health care system is in need of a fundamental change (Institute t of Medicine, 2001). Nurse practitioner
The Emerging Role of the Nurse Practitioner Rhonda Hettinger DNP, NP C, CLS Introduction The American health care system is in need of a fundamental change (Institute t of Medicine, 2001). Nurse practitioner
University College Hospital. Laparoscopic Fundoplication. Gastrointestinal Services Division
 University College Hospital Laparoscopic Fundoplication Gastrointestinal Services Division 2 3 If you need a large print, audio or translated copy of the document, please contact us on 020 3447 9202. We
University College Hospital Laparoscopic Fundoplication Gastrointestinal Services Division 2 3 If you need a large print, audio or translated copy of the document, please contact us on 020 3447 9202. We
Guidelines for Use of Controlled Substances for the Treatment of Pain
 1.0 Purpose: Use of Controlled Substances for the Treatment of Pain The Physicians Advisory Committee for Controlled Substances of the Medical Society of Delaware supports the Federation of State Medical
1.0 Purpose: Use of Controlled Substances for the Treatment of Pain The Physicians Advisory Committee for Controlled Substances of the Medical Society of Delaware supports the Federation of State Medical
POEM Procedure for. Esophageal Achalasia
 POEM Procedure for Esophageal Achalasia POEM (Per-Oral endoscopic myotomy) is an incisionless procedure to treat esophageal achalasia, totally performed by endoscopy, without cutting the surface of the
POEM Procedure for Esophageal Achalasia POEM (Per-Oral endoscopic myotomy) is an incisionless procedure to treat esophageal achalasia, totally performed by endoscopy, without cutting the surface of the
The Role of Industry Representatives in the Endoscopy Unit
 The Role of Industry Representatives in the Endoscopy Unit Vivek Kaul, MD 1 and Douglas Faigel, MD, FASGE 2 Introduction The modern endoscopy unit is a busy workplace environment. With the patient as the
The Role of Industry Representatives in the Endoscopy Unit Vivek Kaul, MD 1 and Douglas Faigel, MD, FASGE 2 Introduction The modern endoscopy unit is a busy workplace environment. With the patient as the
G E R D. (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease)
 G E R D (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease) What is GERD? Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a disorder caused by gastric acid flowing from the stomach into the esophagus. What are the symptoms of
G E R D (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease) What is GERD? Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a disorder caused by gastric acid flowing from the stomach into the esophagus. What are the symptoms of
Motility Disorders that are Commonly Mistaken for Reflux by Susan Agrawal
 www.complexchild.com Motility Disorders that are Commonly Mistaken for Reflux by Susan Agrawal A surprisingly large number of children with motility disorders experience the same progression of events
www.complexchild.com Motility Disorders that are Commonly Mistaken for Reflux by Susan Agrawal A surprisingly large number of children with motility disorders experience the same progression of events
Guidelines for the Use of Controlled Substances in the Treatment of Pain Adopted by the New Hampshire Medical Society, July 1998
 Guidelines for the Use of Controlled Substances in the Treatment of Pain Adopted by the New Hampshire Medical Society, July 1998 Section I: Preamble The New Hampshire Medical Society believes that principles
Guidelines for the Use of Controlled Substances in the Treatment of Pain Adopted by the New Hampshire Medical Society, July 1998 Section I: Preamble The New Hampshire Medical Society believes that principles
Reduction in Medication Errors due to Adoption of Computerized Provider Order Entry Systems
 UCSD Informatics Journal Club Webinar May 2, 2013 Reduction in Medication Errors due to Adoption of Computerized Provider Order Entry Systems David Radley, PhD Institute for Healthcare Improvement & The
UCSD Informatics Journal Club Webinar May 2, 2013 Reduction in Medication Errors due to Adoption of Computerized Provider Order Entry Systems David Radley, PhD Institute for Healthcare Improvement & The
GI Bleed. Steven Lichtenstein, D.O. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology Mercy Health System. Director, Endoscopy/GI Lab Mercy Fitzgerald Hospital
 October 3, 2015 GI Bleed Steven Lichtenstein, D.O. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology Mercy Health System Director, Endoscopy/GI Lab Mercy Fitzgerald Hospital Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine
October 3, 2015 GI Bleed Steven Lichtenstein, D.O. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology Mercy Health System Director, Endoscopy/GI Lab Mercy Fitzgerald Hospital Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine
Photodynamic Therapy for the Treatment of Barrett s Esophagus: A Systematic Review and Economic Evaluation
 Health Technology & Policy Series; 29:1 Photodynamic Therapy for the Treatment of Barrett s Esophagus: A Systematic Review and Economic Evaluation FINAL REPORT August 29 Submitted to: The Alberta Health
Health Technology & Policy Series; 29:1 Photodynamic Therapy for the Treatment of Barrett s Esophagus: A Systematic Review and Economic Evaluation FINAL REPORT August 29 Submitted to: The Alberta Health
Inhibit terminal acid secretion from parietal cells by blocking H + /K + - ATPase pump
 Chris J. Taylor, Pharm.D., BCPS Clinical Pharmacist Phoenix VA Health Care System Review pharmacology of PPIs Discuss possible association between PPI use and development of the following: Pneumonia (community-acquired
Chris J. Taylor, Pharm.D., BCPS Clinical Pharmacist Phoenix VA Health Care System Review pharmacology of PPIs Discuss possible association between PPI use and development of the following: Pneumonia (community-acquired
Ch. 14 - Medical Coding and Claims. A bill sent to the insurance carrier for payment related to patient care
 A bill sent to the insurance carrier for payment related to patient care A claim held or rejected by the insurance carrier due to problems or errors A coding system published by the US department of Health
A bill sent to the insurance carrier for payment related to patient care A claim held or rejected by the insurance carrier due to problems or errors A coding system published by the US department of Health
Arkansas Emergency Department Opioid Prescribing Guidelines
 Arkansas Emergency Department Opioid Prescribing Guidelines 1. One medical provider should provide all opioids to treat a patient s chronic pain. 2. The administration of intravenous and intramuscular
Arkansas Emergency Department Opioid Prescribing Guidelines 1. One medical provider should provide all opioids to treat a patient s chronic pain. 2. The administration of intravenous and intramuscular
DIABETIC ENTEROPATHY: TWO. Gary L. Cornette, D.O., F.A.C.O.I Medical Director Gastroenterology
 DIABETIC ENTEROPATHY: TWO DIFFICULT PROBLEMS DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT Gary L. Cornette, D.O., F.A.C.O.I Medical Director Gastroenterology Diabetic Enteropathy: What is it? Motility Disorders Esophageal
DIABETIC ENTEROPATHY: TWO DIFFICULT PROBLEMS DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT Gary L. Cornette, D.O., F.A.C.O.I Medical Director Gastroenterology Diabetic Enteropathy: What is it? Motility Disorders Esophageal
ECG may be indicated for patients with cardiovascular risk factors
 eappendix A. Summary for Preoperative ECG American College of Cardiology/ American Heart Association, 2007 A1 2002 A2 European Society of Cardiology and European Society of Anaesthesiology, 2009 A3 Improvement,
eappendix A. Summary for Preoperative ECG American College of Cardiology/ American Heart Association, 2007 A1 2002 A2 European Society of Cardiology and European Society of Anaesthesiology, 2009 A3 Improvement,
Use of routinely collected electronic healthcare data: Lessons Learned
 Use of routinely collected electronic healthcare data: Lessons Learned Massoud Toussi, MD, PhD, MBA European lead, Pharmacoepidemiology and Safety Real World Evidence Solutions, IMS Health, France ENCePP
Use of routinely collected electronic healthcare data: Lessons Learned Massoud Toussi, MD, PhD, MBA European lead, Pharmacoepidemiology and Safety Real World Evidence Solutions, IMS Health, France ENCePP
KENTUCKY ADMINISTRATIVE REGULATIONS TITLE 201. GENERAL GOVERNMENT CABINET CHAPTER 9. BOARD OF MEDICAL LICENSURE
 KENTUCKY ADMINISTRATIVE REGULATIONS TITLE 201. GENERAL GOVERNMENT CABINET CHAPTER 9. BOARD OF MEDICAL LICENSURE 201 KAR 9:260. Professional standards for prescribing and dispensing controlled substances.
KENTUCKY ADMINISTRATIVE REGULATIONS TITLE 201. GENERAL GOVERNMENT CABINET CHAPTER 9. BOARD OF MEDICAL LICENSURE 201 KAR 9:260. Professional standards for prescribing and dispensing controlled substances.
American College of Gastroenterology Guideline on the Management of Helicobacter pylori Infection
 American Journal of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270 C 2007 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2007.01393.x Published by Blackwell Publishing American College of Gastroenterology
American Journal of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270 C 2007 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2007.01393.x Published by Blackwell Publishing American College of Gastroenterology
Prevention of Medical Errors
 Prevention of Medical Errors FS 456.013(7) Florida Chapter of American College of Physicians St. Petersburg Beach, Florida October 5, 2013 Cliff Rapp, LHRM Regional Vice President Patient Safety Course
Prevention of Medical Errors FS 456.013(7) Florida Chapter of American College of Physicians St. Petersburg Beach, Florida October 5, 2013 Cliff Rapp, LHRM Regional Vice President Patient Safety Course
PTE Pediatric Asthma Metrics Reporting Updated January 2015
 PTE Pediatric Asthma Metrics Reporting Updated January 20 Introduction: The Maine Health Management Coalition s (MHMC) Pathways to Excellence (PTE) Program is preparing for its next round of PTE Pediatric
PTE Pediatric Asthma Metrics Reporting Updated January 20 Introduction: The Maine Health Management Coalition s (MHMC) Pathways to Excellence (PTE) Program is preparing for its next round of PTE Pediatric
Kaiser Permanente Southern California Depression Care Program
 Kaiser Permanente Southern California Depression Care Program Abstract In 2001, Kaiser Permanente of Southern California (KPSC) adopted the IMPACT model of collaborative care for depression, developed
Kaiser Permanente Southern California Depression Care Program Abstract In 2001, Kaiser Permanente of Southern California (KPSC) adopted the IMPACT model of collaborative care for depression, developed
Cenpatico STRS POLICIES & PROCEDURES. Effective Date: 07/11/11 Review/Revision Date: 07/11/11, 09/21/11
 Page 1 of 14 SCOPE: Clinical Department IMPORTANT REMINDER This Clinical Policy has been developed by appropriately experienced and licensed health care professionals based on a thorough review and consideration
Page 1 of 14 SCOPE: Clinical Department IMPORTANT REMINDER This Clinical Policy has been developed by appropriately experienced and licensed health care professionals based on a thorough review and consideration
Documentation Guidelines for Physicians Interventional Pain Services
 Documentation Guidelines for Physicians Interventional Pain Services Pamela Gibson, CPC Assistant Director, VMG Coding Anesthesia and Surgical Divisions 343.8791 1 General Principles of Medical Record
Documentation Guidelines for Physicians Interventional Pain Services Pamela Gibson, CPC Assistant Director, VMG Coding Anesthesia and Surgical Divisions 343.8791 1 General Principles of Medical Record
Fixing Mental Health Care in America
 Fixing Mental Health Care in America A National Call for Measurement Based Care in Behavioral Health and Primary Care An Issue Brief Released by The Kennedy Forum Prepared by: John Fortney PhD, Rebecca
Fixing Mental Health Care in America A National Call for Measurement Based Care in Behavioral Health and Primary Care An Issue Brief Released by The Kennedy Forum Prepared by: John Fortney PhD, Rebecca
Klinik für Kinder- und Jugendmedizin, Universitätsklinikum der RWTH Aachen, Aachen, Germany
 Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 49:498 547 # 2009 by European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition and North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology,
Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 49:498 547 # 2009 by European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition and North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology,
New Anticoagulants and GI bleeding
 New Anticoagulants and GI bleeding DR DANNY MYERS MD FRCP(C) CLINICAL ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, UBC Conflicts of Interest None I am unbiased in the use of NOAC s vs Warfarin based on risk benefit
New Anticoagulants and GI bleeding DR DANNY MYERS MD FRCP(C) CLINICAL ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, UBC Conflicts of Interest None I am unbiased in the use of NOAC s vs Warfarin based on risk benefit
Physician and other health professional services
 O n l i n e A p p e n d i x e s 4 Physician and other health professional services 4-A O n l i n e A p p e n d i x Access to physician and other health professional services 4 a1 Access to physician care
O n l i n e A p p e n d i x e s 4 Physician and other health professional services 4-A O n l i n e A p p e n d i x Access to physician and other health professional services 4 a1 Access to physician care
6. MEASURING EFFECTS OVERVIEW CHOOSE APPROPRIATE METRICS
 45 6. MEASURING EFFECTS OVERVIEW In Section 4, we provided an overview of how to select metrics for monitoring implementation progress. This section provides additional detail on metric selection and offers
45 6. MEASURING EFFECTS OVERVIEW In Section 4, we provided an overview of how to select metrics for monitoring implementation progress. This section provides additional detail on metric selection and offers
Association between Proton Pump Inhibitors and Clostridium difficile
 Association between Proton Pump Inhibitors and Clostridium difficile Lauren Petrik and Nicholas Hellebusch, Pharm.D. Candidates 2013, Tatum Mead, Pharm.D. UMKC School of Pharmacy Clostridium difficile,
Association between Proton Pump Inhibitors and Clostridium difficile Lauren Petrik and Nicholas Hellebusch, Pharm.D. Candidates 2013, Tatum Mead, Pharm.D. UMKC School of Pharmacy Clostridium difficile,
Pediatric Gastroenterology Fellowship Pediatric Nutrition Rotation Goals and Objectives - 1 st Year
 Pediatric Nutrition Rotation Goals and Objectives - 1 st Year Goal 1: Gain experience and competency in managing common and rare gastrointestinal, liver and nutritional problems. (Competencies: patient
Pediatric Nutrition Rotation Goals and Objectives - 1 st Year Goal 1: Gain experience and competency in managing common and rare gastrointestinal, liver and nutritional problems. (Competencies: patient
Overuse of PSA Screening for Prostate Cancer in Older Men. Elizabeth Jaramillo, MD January 17, 2014
 Overuse of PSA Screening for Prostate Cancer in Older Men Elizabeth Jaramillo, MD January 17, 2014 Screening Prostate cancer screening occurs in patients with no clinical sign or suspicion of disease Screening
Overuse of PSA Screening for Prostate Cancer in Older Men Elizabeth Jaramillo, MD January 17, 2014 Screening Prostate cancer screening occurs in patients with no clinical sign or suspicion of disease Screening
Doctor my belly hurts, what s wrong?
 Doctor my belly hurts, what s wrong? Luis Rivero Pinelo MD, LMCC, CCFP, FCFP, Fellow SRPC, CSPQ Shawville - Quebec Clinical Case 1 42 year old male with 1 year history of intermittent pain in the upper
Doctor my belly hurts, what s wrong? Luis Rivero Pinelo MD, LMCC, CCFP, FCFP, Fellow SRPC, CSPQ Shawville - Quebec Clinical Case 1 42 year old male with 1 year history of intermittent pain in the upper
GI Bleeding. Thomas S.Foster,Pharm.D. PHR 961 Integrated Therapeutics
 GI Bleeding Thomas S.Foster,Pharm.D. PHR 961 Integrated Therapeutics Overview Because GI bleeding is internal, it is possible for a person to have GI bleeding without symptoms. Important to recognize
GI Bleeding Thomas S.Foster,Pharm.D. PHR 961 Integrated Therapeutics Overview Because GI bleeding is internal, it is possible for a person to have GI bleeding without symptoms. Important to recognize
www.ghadialisurgery.com
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
Behavioral and Physical Treatments for Tension-type and Cervicogenic Headache
 Evidence Report: Behavioral and Physical Treatments for Tension-type and Cervicogenic Headache Douglas C. McCrory, MD, MHSc Donald B. Penzien, PhD Vic Hasselblad, PhD Rebecca N. Gray, DPhil Duke University
Evidence Report: Behavioral and Physical Treatments for Tension-type and Cervicogenic Headache Douglas C. McCrory, MD, MHSc Donald B. Penzien, PhD Vic Hasselblad, PhD Rebecca N. Gray, DPhil Duke University
410-127-0020 Definitions... 1. 410-127-0040 Coverage... 5. 410-127-0050 Client Copayments... 6. 410-127-0060 Reimbursement and Limitations...
 Home Health Services Administrative Rulebook Division of Medical Assistance Programs Policy and Planning Section Table of Contents Chapter 410, Division 127 Effective January 1, 2014 410-127-0020 Definitions...
Home Health Services Administrative Rulebook Division of Medical Assistance Programs Policy and Planning Section Table of Contents Chapter 410, Division 127 Effective January 1, 2014 410-127-0020 Definitions...
