The main goal of endodontic therapy is to eradicate all vital and necrotic tissue, microorganisms,
|
|
|
- Shana Blair
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Efficacy and Safety of Various Active Irrigation Devices When Used with Either Positive or Negative Pressure: An In Vitro Study Augusto Malentacca, MD, DDS,* Umberto Uccioli, DDS, Dario Zangari, DDS,* Carlo Lajolo, MD, DDS, PhD, and Cristiano Fabiani, DDS, CAGS, MSD* Abstract Introduction: The purpose of this in vitro study was to evaluate and compare the efficacy and safety of different devices available for canal cleansing. Methods: The following systems were tested: passive ultrasonic irrigation, EndoVac (Discus Dental, Culver City, CA), and the irrigation ultrasonic needle (ProUltra PiezoFlow Irrigation Ultrasonic Needle; Dentsply Tulsa Dental Specialties, Tulsa, OK) used in both the injection mode (IUNI) and the aspiration mode (IUNA). In the control group, traditional irrigation with a syringe and side-vented needle was used. A resin model was used with 4 lateral canals (respectively at 2, 5, 8, and 11 mm from the apical foramen) filled with bovine pulp stained with fuchsin. The model also included a 2- mm chamber in communication with the apex, again filled with bovine pulp, which enabled the measurement of the extrusion of NaOCl beyond the apex. Results: With regard to efficacy, the most effective systems were found to be those using the ultrasonic needle, either in aspiration or injection modes; Endo- Vac was the least effective. Conversely, IUNI was found to bring the highest risk with regard to the extrusion of sodium hypochlorite beyond the apex. EndoVac was the safest but only by a slight margin compared with IUNA and passive ultrasonic irrigation. Conclusions: Based on this study, the system that best reconciles efficacy and safety appears to be IUNA. (J Endod 2012;38: ) Key Words Passive ultrasonic irrigation, sodium hypochlorite, ultrasonic needle From the *Private Practice, Rome Italy; Private Practice, Ferentino, Italy; and School of Dentistry, Catholic University, Rome, Italy. Address requests for reprints to Dr Cristiano Fabiani, Largo Belloni, 4, Rome, Italy. address: criendo@mac. com /$ - see front matter Copyright ª 2012 American Association of Endodontists. The main goal of endodontic therapy is to eradicate all vital and necrotic tissue, microorganisms, and products of microbial degradation from the canal system. The irrigation of root canals with an antibacterial solution is considered an essential phase of chemical/mechanical canal preparation (1); irrigation with a syringe and needle remains the most commonly used procedure (2, 3). Mechanical preparation, combined with the usual irrigation methods, is not capable of guaranteeing optimal cleansing of the endodontic system (4). The intricate nature of the root canal anatomy, with isthmi, fins, webs, anastomoses, and other irregularities, makes complete cleansing of all areas of the root canal a complex procedure because it hinders the irrigant from dissolving the organic tissues within the canal and destroying the bacterial biofilm (5, 6). The use of ultrasonic systems has been proposed as a possible solution to the problem of canal cleansing; their use after complete mechanical or manual instrumentation has been found to reduce the number of bacteria (7, 8). A marked efficacy in cleansing after the passive use of ultrasound has been reported (9 12). This technique using a file freely oscillating at ultrasonic frequencies in a root canal filled with sodium hypochlorite is known as passive ultrasonic irrigation (PUI) (9). In vivo histologic studies on the mesial roots of mandibular molars by Haidet et al (12) and by Archer et al (13) analyzed the removal of organic tissue with or without the use of ultrasound. These 2 studies reported that both canals and isthmi were significantly cleaner with the ultrasound method. Recent in vitro studies have confirmed the efficacy of PUI in removing pulp tissue from lateral canals (14 16) in straight canals and curved canals (17, 18). Also with this technique, the complete penetration of the irrigant cannot be achieved in all the phases of the root canal treatment (19). Gutarts et al (6) proposed the use of an ultrasonically-activated needle placed in the canal through which the sodium hypochlorite would flow, enabling the irrigant to be continually replaced. Studies by these researchers in vivo have shown this method to be remarkably effective at cleansing inaccessible zones of the endodontic system (20, 21). Conversely, it has been found that this method may push the action of irrigants beyond the distance at which the frontal pressure of a syringe normally operates when used for canal cleansing (22). Clearly, this might compromise the safety of the cleansing procedure because the severe consequences of the extrusion of sodium hypochlorite into the periapical tissue are well known (23). Different recent studies (22, 24) have shown the absolute safety of using negative-pressure cleansing systems compared with manual and ultrasonic irrigation with particular reference to the ultrasonic needle; however, no clear superiority of this latter system in terms of penetrating and cleansing the endodontic space has been reported. The dilemma remains that there is a need for an effective irrigation system that is able to penetrate in depth into the apical endodontic system but at the same time does not cause extrusion of irrigants beyond the apex. The aim of this study was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of an ultrasonic needle operating by aspirating sodium hypochlorite from the canal and to compare this with recently developed systems, namely PUI, EndoVac (Discus Dental, Culver City, CA), and the ultrasonic needle operating in injection mode Malentacca et al. JOE Volume 38, Number 12, December 2012
2 Materials and Methods Model Fabrication A customized transparent epoxy resin model was used, modifying a model developed by Al-Jadaa et al (15). Our model had lateral canals placed at different distances from the apex (ie, 11, 8, 5, and 2 mm); we added a cylindrical chamber of 0.3 ml to simulate an apical lesion. Once the model had been constructed, the main canal was instrumented with an F5 ProTaper file (Dentsply Maillefer, Ballaigues, Switzerland). To gain access to the lateral canals and the simulated lesion at the end of the main canal, external perforations were made with a calibrated tip from the MetaLift Kit (Classic Practice Resources Inc, Metalift, LLC, Baton Rouge, LA); these access holes could be sealed with corresponding screws from the same kit, thus creating a closed system. The assembled model is shown in Figure 1A. The same model could be used for the whole series of tests involved in this study because the canal system could be emptied, cleaned, and reused simply by unscrewing the calibrated screws. In order to verify any alterations that the model would undergo in repetitive trials, the model was tested in a pilot study. No alterations were observed in the 100-trial test. Bovine Pulp Tissue Preparation In order to simulate in vivo conditions, an artificial pulp tissue was prepared using pulp taken from bovine teeth as described by Al- Jadaa et al (15). Once a sufficient quantity of pulp had been obtained, it was stained with fuchsin and put into a syringe. The artificial pulp was injected into the lateral canals and into the apical cavity with a 22-G needle, leaving the main canal empty. After having sealed the access holes with the calibrated screws, the model was ready for the different systems to be tested. Main Experiment Five groups were set up (ie, irrigation ultrasonic needle in injection mode [IUNI], irrigation ultrasonic needle in aspiration mode [IUNA], PUI, EndoVac, and the control group). For the IUNI group, we used a ProUltra PiezoFlow Ultrasonic Irrigation 25-gauge Needle (Dentsply Tulsa Dental Specialties, Tulsa, OK) in the injection mode. For the IUNA group, the same needle as in group IUNI was used but in an off-label way (ie, in aspiration mode [the chair-side suction tube was attached to the Luer-Lock connection on the ProUltra Piezo- Flow Ultrasonic Irrigation Needle). For the PUI group, a passive ultrasonic ESI File (EMS, Nyon, Switzerland) was used. In the EndoVac group, the EndoVac irrigation system was used; in the negative control group, the irrigant was delivered with a 25-G side-vented needle. In all 4 groups, the irrigant solution used was 5.25% sodium hypochlorite at room temperature. In the IUNI group, the ultrasound source was activated for 3 minutes, with an irrigant flow of 10 ml solution every minute. In the IUNA group, the ultrasound source was activated for 3 minutes with an aspiration flow of 3 ml solution every minute. In the PUI group, the ultrasound source was activated in 3 steps of 1 minute each with irrigation of 10 ml with a 25-G side-vented needle after every activation. In the EndoVac group, the system was active for 3 minutes with an aspiration flow of 1.5 ml every minute. In the negative control group, the irrigant was left in place for 3 minutes, replacing 10 ml solution every minute. To replace the irrigant solution, the VATEA system (Re- Dent-Nova Ltd, Ra anana, Israel) was used. The ultrasound source (Suprasson PMax; Satelec Acteon, Merignac, France) was used at a power setting just sufficient to cause a drop of irrigant on the needle tip to be nebulized. In the case of the PUI group, the yellow 4 level of the Suprasson PMax device was used. For all the groups, the tip of the cleansing system was taken to a distance of 5, 3, or 1 mm from the apical foramen. During the experiment, the IUNI needle, the IUNA needle, and the ESI file (the PUI group) were moved back and forth within the canal, stopping at the predetermined distance from the apex, whereas in the case of the EndoVac group, the system was activated while keeping the tip stationery at the reference distance. There were no cases of breakage of any device during any of the tests. Photographs were taken with a 22-megapixel digital camera (5D; Canon, Tokyo, Japan) and macrolens (Canon 100 f2.8) at the beginning and 5 seconds after the end of each experiment. The photographs, bearing a digital code number, were analyzed randomly and blindly by 1 operator tested for his accuracy by analyzing the same images 5 times after different intervals. Both the penetration of the irrigant into the simulated lateral canals and the extrusion of sodium hypochlorite beyond the apex were measured. Thirty trials were recorded for each test group for a total of 150 trials. The mean value of extrusion beyond the apex in each group was calculated when the tip of the instrument was brought to 5, 3, or 1 mm from the apex. Tissue dissolution was measured from the Figure 1. (A) The assembled epoxy resin model used in the current study with tissue injected into the lateral canals and into the apical cavity, leaving the main canal empty. (B) A close up of a lateral canal with the artificial pulp partially dissolved. (C) A close up of the simulated apical lesion with the pulp partially dissolved. JOE Volume 38, Number 12, December 2012 Various Active Irrigation Devices 1623
3 canal entrance to the closest tissue-irrigant interface (Fig. 1B) for each of the 4 simulated lateral canals placed at 2, 5, 8, and 11 mm from the apex. The maximum value taken into consideration was 4 mm. The extrusion of sodium hypochlorite beyond the apex was analyzed on the photograph by calculating the area of the dissolved tissue (Fig. 1C). All images were analyzed using Adobe Photoshop CS5 software (Adobe Systems Inc, San Jose, CA), setting the same reference scale for all images. Statistical Analysis Quantitative variables were tested for normal distribution by a Shapiro-Wilk test. Because variables did not show a normal distribution, the Kruskal-Wallis nonparametric test was used to detect differences among devices and within the same device among lateral canals. Significance at the P #.01 level was used to determine statistical significance. Statistical analysis was performed using the software Intercooled Stata 8.0 (Stata Corp, College Station, TX). Results Apical Extrusion The mean values of extrusion (the area of dissolved tissue) beyond the apex when the tip of the different devices was placed at 5, 3, or 1 mm from the apex are shown in Table 1. Significant differences in the amount of extruded irrigant beyond the apex were observed among the different devices when placed at the same distance from the apex (P <.001). IUNI caused the most extrusion and EndoVac the least. EndoVac (same as the control) did not cause extrusion when placed at any distance from the apex, whereas IUNI, PUI, and IUNA caused some extrusion. When the tips were placed at varying depths of insertion, there were significant differences of extrusion within the same device (except EndoVac), with 5 mm from the apex being the safest (ie, the least amount of extrusion) and 1 mm from the apex being more dangerous (P <.001). IUNI showed extrusion of 0.5 mm 2 even when placed at 5 mm; when placed at 1 mm, it caused complete extrusion in all the samples. IUNA, among the devices that caused extrusion, was the safest at any working length. Even when the device was placed 1 mm from the apex, it showed extrusion of the irrigant for less than 1 mm 2. PUI showed extrusion of the irrigant for less than 1 mm 2 at 3 and 5 mm from the apex, whereas at 1 mm it showed extrusion of 2.04 mm 2. Accessory Canal Tissue Dissolution The values relating to the dissolution of tissue in the lateral canals are graphically presented in Figure 2. IUNI effectively dissolved tissue in all of the lateral canals regardless of its distance from the apex. IUNA was most effective when placed 1 mm from the apex with its effectiveness decreasing as it is moved coronally. PUI had similar results. EndoVac was almost ineffective at all depths. When the device tips were placed at 3 different working lengths, significant differences in lateral canal tissue dissolution were observed. At 1 mm from the apex, the IUNA group had the best results, and EndoVac was the least efficient device in dissolving lateral canal tissue (P <.001). At 3 and 5 mm from the apex, IUNI was the more efficient device. The control group had the worst results (P <.001). Within the same device, there were statistically significant differences in tissue dissolution when the tip of the device was placed at different depths. IUNI and IUNA were the most efficient devices at any depth, and the mean amount of dissolved tissue was more than 3 mm for both devices. PUI had a range between 1.5 and 1.8 mm, whereas EndoVac and the control group showed dissolution lower than 1 mm. Discussion Within the limitations of this in vitro study conducted on resin models, it can be stated that the ultrasonic systems based on the agitation of the irrigant are more effective in dissolving necrotic pulp than systems merely based on the replacement of the irrigant. The model used in this study was similar to the model used by Al-Jadaa et al (15) to assess the dissolution of artificial necrotic pulp tissue. However, their model was an open system. To simulate more accurately the conditions encountered in vivo, the resin model used here was hermetically sealed with screws inserted into the resin, ensuring a perfect seal of the system. However, in vivo it is not known whether at high pressures the biological system maintains a perfect hermetic seal because, unlike resin, the biological tissues are not rigid. Furthermore, dentin is markedly different from the material used to make the endoblocks used in most studies. The mechanisms of action of ultrasound (ie, cavitation, acoustic streaming, and so on) might be influenced by the different characteristics and hardness of the walls on which they act. The artificial pulp used in this study, lacking an intact fabric of collagen fibers holding it together, is easier to dissolve than natural pulp tissue either through chemical or mechanical action of the irrigant. Apart from these intrinsic limitations, the current model system allowed TABLE 1. Mean Values of Extrusion beyond the Apex When the Tip of the Different Devices Was Placed at 5, 3, or 1 mm from the Apex Distance from apex Device No. of samples Mean Standard deviation Minimum Maximum 1mm* IUNI A IUNA B PUI C mm* IUNI a IUNA b PUI c mm* IUNI a IUNA b PUI c Data are expressed in mm 2. Statistically significant differences were observed in IUNI ( a ), IUNA ( b ), and PUI ( c ) when irrigation was performed at different working lengths (1 mm vs 3 mm vs 5 mm) (Kruskal- Wallis test, P <.001). *Statistically significant differences in the amount of extruded irrigant beyond the apex were observed among the different devices when placed at the same distance from the apex (Kruskal-Wallis test, P <.001) Malentacca et al. JOE Volume 38, Number 12, December 2012
4 Figure 2. The mean dissolution of pulp in the lateral canals when the tip of the different devices was placed at 5, 3, or 1 mm from the apex. Brackets represent the standard deviation from the mean. a quantitative comparison of different devices used for cleansing of the endodontic system. The results of this study show that systems using ultrasound cleanse the endodontic space more efficaciously but that this cleansing action is also more difficult to control. There may be a risk of pushing the irrigant beyond the apex. From the resulting data, it emerged quite clearly that the use of an ultrasound needle in the aspiration mode offers an extremely advantageous efficacy-safety ratio. When operating at 5 mm from the apex, the IUNI system was generally the most effective, cleansing the lateral canals even in the most apical part of the root canal system with relative safety. However, this was not true if IUNI was used either at 3 mm or at 1 mm from the apex. At these distances, extrusion was observed in every sample. The PUI system showed absolute safety when used at 5 and at 3 mm, whereas at 1 mm in almost all tests there was some extrusion of sodium hypochlorite. With regard to efficacy, it had a cleansing action of the lateral canals that was less predictable than the other ultrasound systems tested; however, that action extended to all the lateral canals, independent of their position along the principal canal, in agreement with the results of the study by Jiang et al (25). The EndoVac system showed no extrusion of sodium hypochlorite beyond the apex in any of the trials, resulting in the safest system of all tested. However, the system s efficacy on the dissolution of simulated pulp into the lateral canals was only slightly above the values recorded for the control group. These results are in contrast with other studies showing good dissolution of tissue in isthmi of mandibular mesial canals (26). An isthmus is a communication between 2 canals, and so it is an open system within a closed one. Because in this study the lateral canals were closed at their ends, it may be speculated that the EndoVac system is able to promote flow, in a closed system, up to where the tip is placed and no further. When the IUNA system was used at 1 mm from the apex, the efficacy was comparable with that of the IUNI system, working in almost complete safety. In only one of the trials was there slight extrusion of sodium hypochlorite beyond the apex, thus resulting in a better efficacy/safety ratio. Considering that the diameter of the ultrasound needle is 0.51 mm, it is true that with apical preparations of 30 ISO or less it is impossible to reach the apical 2 mm. To get to this depth, the apical preparation should be at least 35 ISO; hence, for future clinical applications, it seems advisable to develop smaller ultrasound needles. Conclusions The present study analyzed 2 aspects of root canal irrigation: the efficacy of irrigation systems by measuring the dissolution of artificial pulp placed in lateral canals and the safety of these systems by measuring the amount of irrigant extruded beyond the apex. The safest system was found to be the EndoVac, which was also the least effective in dissolving tissue placed in lateral canals. The system most effective in dissolving tissue in lateral canals, the ProUltra ultrasound needle (IUNI group), was also the most risky if used at a distance of less than 5 mm from the apex. Within the limitations of this in vitro study, the system that appears to best reconcile efficacy and safety is the ultrasound needle working by aspirating sodium hypochlorite at a distance from the apex of more than 2 mm. Acknowledgments The authors deny any conflicts of interest related to this study. References 1. Haapasalo M, Endal U, Zandi H, Coil JM. Eradication of endodontic infection by instrumentation and irrigation solutions. Endod Topics 2005;10: Gu LS, Kim JR, Ling J, et al. Review of contemporary irrigant agitation techniques and devices. J Endod 2009;35: Haapasalo M, Shen Y, Qian W, Gao Y. Irrigation in endodontics. Dent Clin North Am 2010;54: Schafer E, Zapke K. A comparative scanning electron microscopic investigation of the efficacy of manual and automated instrumentation of root canals. J Endod 2000;26: Weller RN, Brady JM, Bernier WE. Efficacy of ultrasonic cleaning. J Endod 1980;6: Gutarts R, Nusstein J, Reader A, Beck M. In vivo debridement efficacy of ultrasonic irrigation following hand-rotary instrumentation in human mandibular molars. J Endod 2005;31: JOE Volume 38, Number 12, December 2012 Various Active Irrigation Devices 1625
5 7. DeNunzio MS, Hicks ML, Pelleu GB Jr, et al. Bacteriological comparison of ultrasonic and hand instrumentation of root canals in dogs. J Endod 1989; 15: Spoleti P, Siragusa M, Spoleti MJ. Bacteriological evaluation of passive ultrasonic activation. J Endod 2003;29: van der Sluis LW, Versluis M, Wu MK, Wesselink PR. Passive ultrasonic irrigation of the root canal: a review of the literature. Int Endod J 2007;40: Ahmad M, Pitt Ford TJ, Crum LA. Ultrasonic debridement of root canals: acoustic streaming and its possible role. J Endod 1987;13: Ahmad M, Pitt Ford TR, Crum LA, Walton AJ. Ultrasonic debridement of root canals: acoustic cavitation and its relevance. J Endod 1988;14: Haidet J, Reader A, Beck M, Meyers W. An in vivo comparison of the step-back technique versus a step-back/ultrasonic technique in human mandibular molars. J Endod 1989;15: Archer R, Reader A, Nist R, et al. An in vivo evaluation of the efficacy of ultrasound after step-back preparation in mandibular molars. J Endod 1992;18: van der Sluis LW, Wu MK, Wesselink PR. The efficacy of ultrasonic irrigation to remove artificially placed dentine debris from human root canals prepared using instruments of varying taper. Int Endod J 2005;38: Al-Jadaa A, Paque F, Attin T, Zehnder M. Necrotic pulp tissue dissolution by passive ultrasonic irrigation in simulated accessory canals: impact of canal location and angulation. Int Endod J 2009;42: Castelo-Baz P, Martin-Biedma B, Cantatore G, et al. In vitro comparison of passive and continuous ultrasonic irrigation in simulated lateral canals of extracted teeth. J Endod 2012;38: Al-Jadaa A, Paque F, Attin T, Zehnder M. Acoustic hypochlorite activation in simulated curved canals. J Endod 2009;35: Malki M, Verhaagen B, Jiang LM, et al. Irrigant flow beyond the insertion depth of an ultrasonically oscillating file in straight and curved root canals: visualization and cleaning efficacy. J Endod 2012;38: Vera J, Arias A, Romero M. Effect of maintaining apical patency on irrigant penetration into the apical third of root canals when using passive ultrasonic irrigation: an in vivo study. J Endod 2011;37: Carver K, Nusstein J, Reader A, Beck M. In vivo antibacterial efficacy of ultrasound after hand and rotary instrumentation in human mandibular molars. J Endod 2007; 33: Burleson A, Nusstein J, Reader A, Beck M. The in vivo evaluation of hand/rotary/ ultrasound instrumentation in necrotic, human mandibular molars. J Endod 2007;33: Desai P, Himel V. Comparative safety of various intracanal irrigation systems. J Endod 2009;35: Hulsmann M, Rodig T, Nordmeyer S. Complications during root canal irrigation. Endod Topics 2009;16: Fukumoto Y, Kikuchi I, Yoshioka T, et al. An ex vivo evaluation of a new root canal irrigation technique with intracanal aspiration. Int Endod J 2006;39: Jiang LM, Verhaagen B, Versluis M, et al. The influence of the ultrasonic intensity on the cleaning efficacy of passive ultrasonic irrigation. J Endod 2011;37: Susin L, Liu Y, Yoon JC, et al. Canal and isthmus debridement efficacies of two irrigant agitation techniques in a closed system. Int Endod J 2010;43: Malentacca et al. JOE Volume 38, Number 12, December 2012
Introduction. Abstract
 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01108.x The influence of volume, type of irrigant and flushing method on removing artificially placed dentine debris from the apical root canal during passive ultrasonic irrigation
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01108.x The influence of volume, type of irrigant and flushing method on removing artificially placed dentine debris from the apical root canal during passive ultrasonic irrigation
EndoActivator from Tulsa Dental
 EndoActivator from Tulsa Dental Irrigation-EndoActivator http://endoactivator.com/video3.html EndoActivator System did not enhance the removal of smear layer as compared with conventional Max-I-Probe irrigation
EndoActivator from Tulsa Dental Irrigation-EndoActivator http://endoactivator.com/video3.html EndoActivator System did not enhance the removal of smear layer as compared with conventional Max-I-Probe irrigation
Review of ultrasonic irrigation in endodontics: increasing action of irrigating solutions
 Journal section: Endodontics Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.17621 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.17621 Review of ultrasonic irrigation in endodontics: increasing action of irrigating
Journal section: Endodontics Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.17621 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.17621 Review of ultrasonic irrigation in endodontics: increasing action of irrigating
Removal of a fractured instrument with a new extractor: clinical cases
 Clinical Removal of a fractured instrument with a new extractor: clinical cases Dominique Martin 1 Introduction The fracture of a root canal instrument during endodontic treatment is a surgical accident
Clinical Removal of a fractured instrument with a new extractor: clinical cases Dominique Martin 1 Introduction The fracture of a root canal instrument during endodontic treatment is a surgical accident
C. Research Proposal 1. Introduction and Specific Aims of the Project 2. Previous Work and Background of the Project
 C. Research Proposal 1. Introduction and Specific Aims of the Project Endodontic success relies on thorough chemomechanical preparation of the root canal system (1-3). Adequate canal debridement is necessary
C. Research Proposal 1. Introduction and Specific Aims of the Project Endodontic success relies on thorough chemomechanical preparation of the root canal system (1-3). Adequate canal debridement is necessary
Endo Easy Efficient Sonic Powered Endo Irrigation
 Endo Easy Efficient Sonic Powered Endo Irrigation www.vdw-dental.com Naturally fascinating: gentle, yet powerful In our goal to provide easy and safe products and systems for endodontics which fulfil
Endo Easy Efficient Sonic Powered Endo Irrigation www.vdw-dental.com Naturally fascinating: gentle, yet powerful In our goal to provide easy and safe products and systems for endodontics which fulfil
ULTRASONIC TREATMENT ENDODONTICE
 ULTRASONIC TREATMENT ENDODONTICE Prof.Dr.Eng.Gheorghe AMZA, Dr. Eng. Oana Elena AMZA, Dr.Eng.Zoia APOSTOLESCU Department of Materials Technology and Welding - University Politehnica of Bucharest Abstract:
ULTRASONIC TREATMENT ENDODONTICE Prof.Dr.Eng.Gheorghe AMZA, Dr. Eng. Oana Elena AMZA, Dr.Eng.Zoia APOSTOLESCU Department of Materials Technology and Welding - University Politehnica of Bucharest Abstract:
Passive ultrasonic irrigation of the root canal: a review of the literature
 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2007.01243.x REVIEW Passive ultrasonic irrigation of the root canal: a review of the literature L. W. M. van der Sluis 1, M. Versluis 2,M.K.Wu 1 & P. R. Wesselink 1 1 Department
doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2007.01243.x REVIEW Passive ultrasonic irrigation of the root canal: a review of the literature L. W. M. van der Sluis 1, M. Versluis 2,M.K.Wu 1 & P. R. Wesselink 1 1 Department
BioRace NiTi system: biologically desirable apical sizes safely and efficiently
 BioRace NiTi system: biologically desirable apical sizes safely and efficiently Dr Martin Trope and Dr Gilberto Debelian explore the BioRace NiTi system, designed to achieve an apical preparation that
BioRace NiTi system: biologically desirable apical sizes safely and efficiently Dr Martin Trope and Dr Gilberto Debelian explore the BioRace NiTi system, designed to achieve an apical preparation that
Location of the apical foramen and its relationship with foraminal file size
 original article Location of the apical foramen and its relationship with foraminal file size Ronaldo Araújo Souza, DDS, MSc, PhD 1 José Antônio Poli de Figueiredo, DDS, MSc, PhD 2 Suely Colombo, DDS 1
original article Location of the apical foramen and its relationship with foraminal file size Ronaldo Araújo Souza, DDS, MSc, PhD 1 José Antônio Poli de Figueiredo, DDS, MSc, PhD 2 Suely Colombo, DDS 1
Contributions regarding FEM for an ultrasonic endodontic device and his appliance in the root canal treatments
 Contributions regarding FEM for an ultrasonic endodontic device and his appliance in the root canal treatments GHEORGHE AMZA, ROXANA YOLANDA ONEA, OANA ELENA AMZA, VICTOR CARP Department of Materials Technology
Contributions regarding FEM for an ultrasonic endodontic device and his appliance in the root canal treatments GHEORGHE AMZA, ROXANA YOLANDA ONEA, OANA ELENA AMZA, VICTOR CARP Department of Materials Technology
EFFECT OF PASSIVE ULTRASONIC IRRIGATION ON THE REMOVAL OF ROOT CANAL FILLING DURING RETREATMENT PROCEDURES
 Article Scientifique Scientific Article EFFECT OF PASSIVE ULTRASONIC IRRIGATION ON THE REMOVAL OF ROOT CANAL FILLING DURING RETREATMENT PROCEDURES Khaldoun AL-Naal* Mohammad Rekab** Abstract The aim of
Article Scientifique Scientific Article EFFECT OF PASSIVE ULTRASONIC IRRIGATION ON THE REMOVAL OF ROOT CANAL FILLING DURING RETREATMENT PROCEDURES Khaldoun AL-Naal* Mohammad Rekab** Abstract The aim of
The Benefits of Using Arap Locator in Root Canal Treatment
 UNSURPASSED ACCURACY UNRIVALED RELIABILITY 1 1. Data on file. Unsurpassed accuracy 1 with convenient, easy-to-read display Fully automatic multifrequency measurements Compact design with small footprint
UNSURPASSED ACCURACY UNRIVALED RELIABILITY 1 1. Data on file. Unsurpassed accuracy 1 with convenient, easy-to-read display Fully automatic multifrequency measurements Compact design with small footprint
Cleaning of Oval Canals Using Ultrasonic or Sonic Instrumentation
 0099-2399/93/1909-0453/$03.00/0 JOURNAL OF ENOOOONTICS Copyright 1993 by The American Association of Endoclontists Printed in U.S.A. VOL. 19, No. 9, SEPTEMBER 1993 Cleaning of Oval Canals Using Ultrasonic
0099-2399/93/1909-0453/$03.00/0 JOURNAL OF ENOOOONTICS Copyright 1993 by The American Association of Endoclontists Printed in U.S.A. VOL. 19, No. 9, SEPTEMBER 1993 Cleaning of Oval Canals Using Ultrasonic
Non-surgical management of a large periapical lesion using a simple aspiration technique: a case report
 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2010.01719.x CASE REPORT Non-surgical management of a large periapical lesion using a simple aspiration technique: a case report M. Fernandes & I. De Ataide Goa Dental College &
doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2010.01719.x CASE REPORT Non-surgical management of a large periapical lesion using a simple aspiration technique: a case report M. Fernandes & I. De Ataide Goa Dental College &
Endodontic treatment with MTA apical plugs: a case report
 325 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 49, No. 4, 325-329, 2007 Case Report Endodontic treatment with MTA apical plugs: a case report Pari Ghaziani 1), Navid Aghasizadeh 2) and Mahshid Sheikh-Nezami 1) 1) Department
325 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 49, No. 4, 325-329, 2007 Case Report Endodontic treatment with MTA apical plugs: a case report Pari Ghaziani 1), Navid Aghasizadeh 2) and Mahshid Sheikh-Nezami 1) 1) Department
Tooth anatomy risk factors influencing root canal working length accessibility
 Int J Oral Sci (2011) 3: 135-140. www.ijos.org.cn ORIGINAL ARTICLE Tooth anatomy risk factors influencing root canal working length accessibility Lu Tang 1,2, Tuo-qi Sun 1,2, Xiao-jie Gao 1, Xue-dong Zhou
Int J Oral Sci (2011) 3: 135-140. www.ijos.org.cn ORIGINAL ARTICLE Tooth anatomy risk factors influencing root canal working length accessibility Lu Tang 1,2, Tuo-qi Sun 1,2, Xiao-jie Gao 1, Xue-dong Zhou
The efficacy of gutta-percha removal using ProFiles
 Blackwell Science, Ltd The efficacy of gutta-percha removal using ProFiles J. J. Ferreira, J. S. Rhodes & T. R. Pitt Ford Department of Conservative Dentistry, Guy s, King s and St. Thomas Dental Institute,
Blackwell Science, Ltd The efficacy of gutta-percha removal using ProFiles J. J. Ferreira, J. S. Rhodes & T. R. Pitt Ford Department of Conservative Dentistry, Guy s, King s and St. Thomas Dental Institute,
Root Canal Retreatment: 2. Practical Solutions T.R. PITT FORD AND J.S. RHODES
 E N D O D O N T I CE SN D O D O N T I C S Root Canal Retreatment: 2. Practical Solutions T.R. PITT FORD AND J.S. RHODES Abstract: Root canal retreatment is often the preferred method of treating a tooth
E N D O D O N T I CE SN D O D O N T I C S Root Canal Retreatment: 2. Practical Solutions T.R. PITT FORD AND J.S. RHODES Abstract: Root canal retreatment is often the preferred method of treating a tooth
Air. Air and light. Light
 Air Air and light Light Light and Premiering The best quality light: Excellent visibility even in posterior areas, Cold light (6 000 7 000 K) for better tissue recognition, Ideal for working with loupes,
Air Air and light Light Light and Premiering The best quality light: Excellent visibility even in posterior areas, Cold light (6 000 7 000 K) for better tissue recognition, Ideal for working with loupes,
Analysis of forces developed during root canal filling by different operators
 original article Analysis of forces developed during root canal filling by different operators Maria Rosa Felix de Sousa G. GUIMARÃES, DDS, MSc 1 Henner Alberto GOMIDE, DDS, MSc, PhD 2 Maria Antonieta
original article Analysis of forces developed during root canal filling by different operators Maria Rosa Felix de Sousa G. GUIMARÃES, DDS, MSc 1 Henner Alberto GOMIDE, DDS, MSc, PhD 2 Maria Antonieta
Tissue Dissolution by Sodium Hypochlorite: Effect of Concentration, Temperature, Agitation, and Surfactant
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 Tissue Dissolution by Sodium Hypochlorite:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 Tissue Dissolution by Sodium Hypochlorite:
Case Report(s): Uncomplicated Crown Fractures
 Case Report(s): Uncomplicated Crown Fractures Tooth fractures can be classified as follows: Uncomplicated crown fracture = fracture limited to the crown of the tooth with dentin exposure but no pulp exposure.
Case Report(s): Uncomplicated Crown Fractures Tooth fractures can be classified as follows: Uncomplicated crown fracture = fracture limited to the crown of the tooth with dentin exposure but no pulp exposure.
Universal Endo System Directions for Use. ProTaper
 ProTaper Universal Endo System Directions for Use An instructional DVD is included with your system purchase. Please view this DVD, in addition to reading this booklet, to gain a complete understanding
ProTaper Universal Endo System Directions for Use An instructional DVD is included with your system purchase. Please view this DVD, in addition to reading this booklet, to gain a complete understanding
We make a point of ensuring safety.
 CAD/CAM SYSTEMS INSTRUMENTES HYGIENE SYSTEMS TREATMENT CENTERS IMAGING SYSTEMS INSTRUMENTS FOR EFFICIENT ROOT CANAL TREATMENT We make a point of ensuring safety. T h e D e n t a l C o m p a n y ENDODONTIC
CAD/CAM SYSTEMS INSTRUMENTES HYGIENE SYSTEMS TREATMENT CENTERS IMAGING SYSTEMS INSTRUMENTS FOR EFFICIENT ROOT CANAL TREATMENT We make a point of ensuring safety. T h e D e n t a l C o m p a n y ENDODONTIC
Oftentimes, as implant surgeons, we are
 CLINICAL AVOIDING INJURY TO THE INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE BY ROUTINE USE OF INTRAOPERATIVE RADIOGRAPHS DURING IMPLANT PLACEMENT Jeffrey Burstein, DDS, MD; Chris Mastin, DMD; Bach Le, DDS, MD Injury to the
CLINICAL AVOIDING INJURY TO THE INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE BY ROUTINE USE OF INTRAOPERATIVE RADIOGRAPHS DURING IMPLANT PLACEMENT Jeffrey Burstein, DDS, MD; Chris Mastin, DMD; Bach Le, DDS, MD Injury to the
Clinical Efficacy of Three Different Electronic Apex Locators in Comparison with Radiographic Working Length Determination
 Research Article Clinical Efficacy of Three Different Electronic Apex Locators in Comparison with Radiographic Working Length Determination Ayca Yilmaz, (contact author) aycasimsek@gmail.com Selçuk Gokyay
Research Article Clinical Efficacy of Three Different Electronic Apex Locators in Comparison with Radiographic Working Length Determination Ayca Yilmaz, (contact author) aycasimsek@gmail.com Selçuk Gokyay
Removal of a silver cone by using clinical microscope and ultrasound: Case report
 original article Removal of a silver cone by using clinical microscope and ultrasound: Case report Maíra do Prado 1 Marcos Cesar Pimenta de Araújo 2 Heloísa Carla Gusman 3 abstract Introduction: The retreatment
original article Removal of a silver cone by using clinical microscope and ultrasound: Case report Maíra do Prado 1 Marcos Cesar Pimenta de Araújo 2 Heloísa Carla Gusman 3 abstract Introduction: The retreatment
Revascularization of Immature Permanent Teeth With Apical Periodontitis: New Treatment Protocol?
 JOURNAL OF ENDODONTICS Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2004 by The American Association of Endodontists VOL. 30, NO. 4, APRIL 2004 CLINICAL RESEARCH Revascularization of Immature Permanent Teeth With Apical
JOURNAL OF ENDODONTICS Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2004 by The American Association of Endodontists VOL. 30, NO. 4, APRIL 2004 CLINICAL RESEARCH Revascularization of Immature Permanent Teeth With Apical
Jamia Millia Islamia: Performa for CV of Faculty/ Staff Members
 Curriculum Vitae Brief Profile: 1-2 paragraphs (not exceeding 500 words) 1. Name: Vivek Aggarwal 2. Designation: Assistant Professor 3. Office Address: Department of Conservative Dentistry & Endodontics,
Curriculum Vitae Brief Profile: 1-2 paragraphs (not exceeding 500 words) 1. Name: Vivek Aggarwal 2. Designation: Assistant Professor 3. Office Address: Department of Conservative Dentistry & Endodontics,
JMSCR Volume 03 Issue 05 Page 5590-5594 May 2015
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Nanoparticles in Irrigation and Disinfection of the Root Canal System A Review Authors Rucheet Purba 1, Snehal Sonarkar 2, Vidya Mokhade
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Nanoparticles in Irrigation and Disinfection of the Root Canal System A Review Authors Rucheet Purba 1, Snehal Sonarkar 2, Vidya Mokhade
The use of ultrasonics (US) or ultrasonic instrumentation was first introduced to
 Ultrasonics in Endodontics: A Review of the Literature Gianluca Plotino, DDS,* Cornelis H. Pameijer, DMD, DSc, PhD, Nicola Maria Grande, DDS,* and Francesco Somma, MD, DDS* Abstract During the past few
Ultrasonics in Endodontics: A Review of the Literature Gianluca Plotino, DDS,* Cornelis H. Pameijer, DMD, DSc, PhD, Nicola Maria Grande, DDS,* and Francesco Somma, MD, DDS* Abstract During the past few
Eliminating effect of Er, Cr: YSGG laser irradiation on the smear layer of dentin
 Eliminating effect of Er, Cr: YSGG laser irradiation on the smear layer of dentin Jingtao Yu, MD, DDS, and Lu Yan, MD, DDS College of Stomatology, China Medical University, Shenyang, P. R. China Purpose:
Eliminating effect of Er, Cr: YSGG laser irradiation on the smear layer of dentin Jingtao Yu, MD, DDS, and Lu Yan, MD, DDS College of Stomatology, China Medical University, Shenyang, P. R. China Purpose:
Pattern Classification Techniques for the Ultrasonographic Periodontal Probe Introduction Figure 1:
 Pattern Classification Techniques for the Ultrasonographic Periodontal Probe Crystal Bertoncini Nondestructive Evaluation Laboratory The College of William and Mary Introduction In the clinical practice
Pattern Classification Techniques for the Ultrasonographic Periodontal Probe Crystal Bertoncini Nondestructive Evaluation Laboratory The College of William and Mary Introduction In the clinical practice
The WaveOne single-file reciprocating system
 I clinical technique _ WaveOne The WaveOne single-file reciprocating system Authors_ Dr Julian Webber, UK; Drs Pierre Machtou & Wilhelm Pertot, France; Drs Sergio Kuttler, Clifford Ruddle & John West,
I clinical technique _ WaveOne The WaveOne single-file reciprocating system Authors_ Dr Julian Webber, UK; Drs Pierre Machtou & Wilhelm Pertot, France; Drs Sergio Kuttler, Clifford Ruddle & John West,
The Treatment of Traumatic Dental Injuries
 The Recommended Guidelines of the American Association of Endodontists for The Treatment of Traumatic Dental Injuries 2013 American Association of Endodontists Revised 9/13 The Recommended Guidelines of
The Recommended Guidelines of the American Association of Endodontists for The Treatment of Traumatic Dental Injuries 2013 American Association of Endodontists Revised 9/13 The Recommended Guidelines of
DENTAL ASSISTING CATEGORIES
 DENTAL ASSISTING CATEGORIES EFFECTIVE JANUARY 1, 2010 Starting January 1, 2010, the dental assisting scope of practice will include new duties and two new specialty permits in orthodontics and dental sedation
DENTAL ASSISTING CATEGORIES EFFECTIVE JANUARY 1, 2010 Starting January 1, 2010, the dental assisting scope of practice will include new duties and two new specialty permits in orthodontics and dental sedation
Precision Endodontic System. Precision Obturation System. So sophisticated, it s simple
 Precision Endodontic System Precision Obturation System So sophisticated, it s simple The EndoSequence File System and Brasseler USA Obturation Systems Work in Unison to Deliver What You ve Always Wanted
Precision Endodontic System Precision Obturation System So sophisticated, it s simple The EndoSequence File System and Brasseler USA Obturation Systems Work in Unison to Deliver What You ve Always Wanted
Fixing Dental Implant Component Failure and Fracture: Retrieving the Fractured Implant Abutment Screw. Charles A. Mastrovich, DDS
 Fixing Dental Implant Component Failure and Fracture: Retrieving the Fractured Implant Abutment Screw Charles A. Mastrovich, DDS cmastrovichdds@gmail.com www.mastrovichdental.com Evaluating component failure
Fixing Dental Implant Component Failure and Fracture: Retrieving the Fractured Implant Abutment Screw Charles A. Mastrovich, DDS cmastrovichdds@gmail.com www.mastrovichdental.com Evaluating component failure
Endodontic treatment outcome is related to treatment expectations of the operator
 Endodontic Treatment Outcome: Survey of Oral Health Care Professionals Ilan Rotstein, DDS,* Robert Salehrabi, DDS,* and Jane L. Forrest, BSDH, MS, EdD Abstract This study assessed the opinion of oral health
Endodontic Treatment Outcome: Survey of Oral Health Care Professionals Ilan Rotstein, DDS,* Robert Salehrabi, DDS,* and Jane L. Forrest, BSDH, MS, EdD Abstract This study assessed the opinion of oral health
Instruction manual. Safe and efficient NiTi rotary system. Fulfilling the biological requirement for successful endodontics
 Instruction manual Safe and efficient NiTi rotary system Fulfilling the biological requirement for successful endodontics FKG REF. - 99.7AA.50.04B.AN - 06/2010 BioRaCe kit 1 Educational CD 1 Endo Stand
Instruction manual Safe and efficient NiTi rotary system Fulfilling the biological requirement for successful endodontics FKG REF. - 99.7AA.50.04B.AN - 06/2010 BioRaCe kit 1 Educational CD 1 Endo Stand
Postendodontic Tooth Restoration - Part I: The Aim and the Plan of. the procedure.
 Postendodontic Tooth Restoration - Part I: The Aim and the Plan of the Procedure Sanja egoviê 1 Nada GaliÊ 1 Ana Davanzo 2 Boæidar PaveliÊ 1 1 Department of Dental Pathology School of Dental Medicine University
Postendodontic Tooth Restoration - Part I: The Aim and the Plan of the Procedure Sanja egoviê 1 Nada GaliÊ 1 Ana Davanzo 2 Boæidar PaveliÊ 1 1 Department of Dental Pathology School of Dental Medicine University
ULTRASONIC and SONIC INSTRUMENTATION FALL SEMESTER 2012
 ULTRASONIC and SONIC INSTRUMENTATION FALL SEMESTER 2012 PRINICPLES OF POWER- DRIVEN INSTRUMENTATION Ultrasonic/sonic and hand instrumentation are both utilized in initial and supportive periodontal therapy
ULTRASONIC and SONIC INSTRUMENTATION FALL SEMESTER 2012 PRINICPLES OF POWER- DRIVEN INSTRUMENTATION Ultrasonic/sonic and hand instrumentation are both utilized in initial and supportive periodontal therapy
INTRAOSSEOUS ANESTHESIA
 ENDODONTICS: Colleagues for Excellence Winter 2009 Bonus Material F INTRAOSSEOUS ANESTHESIA Intraosseous Anesthesia With the Stabident and X Tip Systems The intraosseous injection allows placement of a
ENDODONTICS: Colleagues for Excellence Winter 2009 Bonus Material F INTRAOSSEOUS ANESTHESIA Intraosseous Anesthesia With the Stabident and X Tip Systems The intraosseous injection allows placement of a
Rebilda DC. Rebilda Post System. Rebilda
 Rebilda DC Rebilda Post System Rebilda Rebilda DC Systematic coronal build-up reconstruction Nowadays, modern composite and adhesive systems enable the reconstruction of severely damaged teeth, even if
Rebilda DC Rebilda Post System Rebilda Rebilda DC Systematic coronal build-up reconstruction Nowadays, modern composite and adhesive systems enable the reconstruction of severely damaged teeth, even if
In vitro evaluation of shape changes in curved artificial root canals prepared with two rotary systems
 original article In vitro evaluation of shape changes in curved artificial root canals prepared with two rotary systems Benito André Silveira Miranzi, MSc, PhD 1 Almir José Silveira Miranzi, DDS 2 Luis
original article In vitro evaluation of shape changes in curved artificial root canals prepared with two rotary systems Benito André Silveira Miranzi, MSc, PhD 1 Almir José Silveira Miranzi, DDS 2 Luis
Mani Silk: A new and novel means of predictable canal shaping
 technique_ instrumentation I Mani Silk: A new and novel means of predictable canal shaping Author_Rich Mounce, DDS _Introduction Irrespective of how a root canal is shaped, the goals of canal shaping remain
technique_ instrumentation I Mani Silk: A new and novel means of predictable canal shaping Author_Rich Mounce, DDS _Introduction Irrespective of how a root canal is shaped, the goals of canal shaping remain
Root ZX II Endodontic Predictability Apex Locator with Low Speed Handpiece. Thinking ahead. Focused on life.
 Root ZX II Endodontic Predictability Apex Locator with Low Speed Handpiece Thinking ahead. Focused on life. Root ZX II Key Features Endodontic Predictability As the world s best selling apex locator, Root
Root ZX II Endodontic Predictability Apex Locator with Low Speed Handpiece Thinking ahead. Focused on life. Root ZX II Key Features Endodontic Predictability As the world s best selling apex locator, Root
DENTAL TRAUMATIC INJURIES
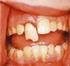 DENTAL TRAUMATIC INJURIES Nitrous Oxide Not Contraindicated Predisposing Factors > 90% of All Injuries Protrusion of Anterior Teeth Poor Lip Coverage Mouthguards Girls as Well as Boys Off - the - Shelf
DENTAL TRAUMATIC INJURIES Nitrous Oxide Not Contraindicated Predisposing Factors > 90% of All Injuries Protrusion of Anterior Teeth Poor Lip Coverage Mouthguards Girls as Well as Boys Off - the - Shelf
Statement on Lasers in Dentistry ADA Council on Scientific Affairs
 Statement on Lasers in Dentistry ADA Council on Scientific Affairs Introduction Applications for and research on lasers in dentistry continues to expand since their introduction to the dental profession.
Statement on Lasers in Dentistry ADA Council on Scientific Affairs Introduction Applications for and research on lasers in dentistry continues to expand since their introduction to the dental profession.
4-1-2005. Dental Clinical Criteria and Documentation Requirements
 4-1-2005 Dental Clinical Criteria and Documentation Requirements Table of Contents Dental Clinical Criteria Cast Restorations and Veneer Procedures... Pages 1-3 Crown Repair... Page 3 Endodontic Procedures...
4-1-2005 Dental Clinical Criteria and Documentation Requirements Table of Contents Dental Clinical Criteria Cast Restorations and Veneer Procedures... Pages 1-3 Crown Repair... Page 3 Endodontic Procedures...
Endodontics. Colleagues for Excellence. Root Canal Irrigants and Disinfectants
 Endodontics Colleagues for Excellence Winter 2011 Winter 2011 Root Canal Irrigants and Disinfectants Published for the Dental Professional Community by the American Association of Endodontists Cover artwork:
Endodontics Colleagues for Excellence Winter 2011 Winter 2011 Root Canal Irrigants and Disinfectants Published for the Dental Professional Community by the American Association of Endodontists Cover artwork:
CHAPTER 10 RESTS AND PREPARATIONS. 4. Serve as a reference point for evaluating the fit of the framework to the teeth.
 CHAPTER 10 RESTS AND DEFINITIONS A REST is any rigid part of an RPD framework which contacts a properly prepared surface of a tooth. A REST PREPARATION or REST SEAT is any portion of a tooth or restoration
CHAPTER 10 RESTS AND DEFINITIONS A REST is any rigid part of an RPD framework which contacts a properly prepared surface of a tooth. A REST PREPARATION or REST SEAT is any portion of a tooth or restoration
Telescopes or loupes have been readily available in
 THE USE OF MAGNIFICATION IN ENDODONTIC THERAPY: THE OPERATING MICROSCOPE Bertrand G. Khayat, DDS, MSD* KHAYAT Clinicians have recognized that the use of magnification can improve the performance of dental
THE USE OF MAGNIFICATION IN ENDODONTIC THERAPY: THE OPERATING MICROSCOPE Bertrand G. Khayat, DDS, MSD* KHAYAT Clinicians have recognized that the use of magnification can improve the performance of dental
C-shaped root canal system in mandibular second molars in a Chinese population evaluated by cone-beam computed tomography
 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2011.01896.x C-shaped root canal system in mandibular second molars in a Chinese population evaluated by cone-beam computed tomography Q. Zheng 1, L. Zhang 1, X. Zhou 2, Q. Wang
doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2011.01896.x C-shaped root canal system in mandibular second molars in a Chinese population evaluated by cone-beam computed tomography Q. Zheng 1, L. Zhang 1, X. Zhou 2, Q. Wang
Clinical Accuracy of Ipex Apex Locator for Measurement of Root Canal Length of Primary Molars
 Original Article Clinical Accuracy of Ipex Apex Locator for Measurement of Root Canal Length of Primary Molars M. Karami Nogorani 1, M. Zare Jahromi 2, Z. Dehghan 3, R. Talaei 4. 1 Associate Professor,
Original Article Clinical Accuracy of Ipex Apex Locator for Measurement of Root Canal Length of Primary Molars M. Karami Nogorani 1, M. Zare Jahromi 2, Z. Dehghan 3, R. Talaei 4. 1 Associate Professor,
Khaldoon G. Abu Afifeh, B.D.S, M. Sc in Prosthodontics
 Khaldoon G. Abu Afifeh, B.D.S, M. Sc in Prosthodontics Diagnosis Diagnosis Diagnosis Implantology Is a Prosthetically Driven Entity. Information Before Treatment is Diagnosis Information after Treatment
Khaldoon G. Abu Afifeh, B.D.S, M. Sc in Prosthodontics Diagnosis Diagnosis Diagnosis Implantology Is a Prosthetically Driven Entity. Information Before Treatment is Diagnosis Information after Treatment
Feel the Safety and Control
 e n d o d o n t i c f i l e s L i b e r a t o r N i t i r o t a r y f i l e s Liberator rotary nickel-titanium endodontic files are the result of years of research and development as well as feedback from
e n d o d o n t i c f i l e s L i b e r a t o r N i t i r o t a r y f i l e s Liberator rotary nickel-titanium endodontic files are the result of years of research and development as well as feedback from
Teeth and Dental Implants: When to save, and when to extract.
 Teeth and Dental Implants: When to save, and when to extract. One of the most difficult decisions a restorative dentist has to make is when to refer a patient for extraction and placement of dental implants.
Teeth and Dental Implants: When to save, and when to extract. One of the most difficult decisions a restorative dentist has to make is when to refer a patient for extraction and placement of dental implants.
Dentaport ZX Reliable Apex Location Perfect Endodontics Curing with High-Powered Parallel Precision
 Dentaport ZX Reliable Apex Location Perfect Endodontics Curing with High-Powered Parallel Precision Thinking ahead. Focused on life. Thinking ahead. Focused on life. 4 Key product features include the
Dentaport ZX Reliable Apex Location Perfect Endodontics Curing with High-Powered Parallel Precision Thinking ahead. Focused on life. Thinking ahead. Focused on life. 4 Key product features include the
Implants in your Laboratory: Abutment Design
 1/2 point CDT documented scientific credit. See Page 41. Implants in your Laboratory: Abutment Design By Leon Hermanides, CDT A patient s anatomical limitations have the greatest predictive value for successful
1/2 point CDT documented scientific credit. See Page 41. Implants in your Laboratory: Abutment Design By Leon Hermanides, CDT A patient s anatomical limitations have the greatest predictive value for successful
Color Coding System TipTi B pbook ook English
 Color Coding System Tip TipBook Book English 2 acteongroup.com Introduction Satelec has been manufacturing ultrasonic generators for over 40 years now and developed the first ever piezoelectric scaler
Color Coding System Tip TipBook Book English 2 acteongroup.com Introduction Satelec has been manufacturing ultrasonic generators for over 40 years now and developed the first ever piezoelectric scaler
Hypochlorite-induced severe cellulitis during endodontic treatment: case report
 ISSN: Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2014 Apr-Jun;11(2):199-203 Case Report Article Hypochlorite-induced severe cellulitis during endodontic treatment: case report Bernardo Almeida Aguiar 1 Fábio
ISSN: Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2014 Apr-Jun;11(2):199-203 Case Report Article Hypochlorite-induced severe cellulitis during endodontic treatment: case report Bernardo Almeida Aguiar 1 Fábio
Universal Crown and Bridge Preparation
 Universal Crown and Bridge Preparation The All-Ceramic Crown Preparation Technique for Predictable Success According to Dr. Ronald E. Goldstein Expect the Best. Buy Direct. The Universal * Crown and Bridge
Universal Crown and Bridge Preparation The All-Ceramic Crown Preparation Technique for Predictable Success According to Dr. Ronald E. Goldstein Expect the Best. Buy Direct. The Universal * Crown and Bridge
2015 Predoctoral Directors Workshop Clinical Curriculum Audience Response System Results Participants Include 65 Predoctoral Directors
 2015 Predoctoral Directors Workshop Clinical Curriculum Audience Response System Results Participants Include 65 Predoctoral Directors 1. Q: Did you attend the Predoctoral Director Workshop 3 years ago?
2015 Predoctoral Directors Workshop Clinical Curriculum Audience Response System Results Participants Include 65 Predoctoral Directors 1. Q: Did you attend the Predoctoral Director Workshop 3 years ago?
Straumann Dental Implant System. Implant Selection Guide.
 Straumann Dental Implant System. Implant Selection Guide. STRAUMANN's IMPLANT PORTFOLIO The Straumann Dental Implant System offers two implant lines with diverse body and neck designs ranging from the
Straumann Dental Implant System. Implant Selection Guide. STRAUMANN's IMPLANT PORTFOLIO The Straumann Dental Implant System offers two implant lines with diverse body and neck designs ranging from the
original article Keywords: Sodium hypochlorite. Chlorhexidine. Calcium hydroxide. Endodontic infection. Root canal medication.
 original article Efficacy of chemo-mechanical preparation with different substances and the use of a root canal medication in dog s teeth with induced periapical lesion Frederico C. Martinho, DDS, MSc
original article Efficacy of chemo-mechanical preparation with different substances and the use of a root canal medication in dog s teeth with induced periapical lesion Frederico C. Martinho, DDS, MSc
Histologic comparison of biologic width around teeth versus implants: The effect on bone preservation
 Clinical Histologic comparison of biologic width around teeth versus implants: The effect on bone preservation Kazuto Makigusa 1 Abstract Histological analysis of the biological width surrounding primate
Clinical Histologic comparison of biologic width around teeth versus implants: The effect on bone preservation Kazuto Makigusa 1 Abstract Histological analysis of the biological width surrounding primate
Develop a specialist who is capable of correlation of basic sciences and clinical sciences, and challenge the requirements for certification.
 Course Specification Faculty : Dentistry Department : Endodontics Program Specification: Diploma Degree A-Basic Information 1-Programme Title: Diploma in Endodontics 2-Departments (s): Endodontics 4-Coordinator:
Course Specification Faculty : Dentistry Department : Endodontics Program Specification: Diploma Degree A-Basic Information 1-Programme Title: Diploma in Endodontics 2-Departments (s): Endodontics 4-Coordinator:
MEDICAID DENTAL PROGRAMS CODING, POLICY AND RELATED FEE REVISION INFORMATION
 MEDICAID DENTAL PROGRAMS CODING, POLICY AND RELATED FEE REVISION INFORMATION Effective for dates of service on and after November 1, 2005, the following dental coding, policy and related fee revisions
MEDICAID DENTAL PROGRAMS CODING, POLICY AND RELATED FEE REVISION INFORMATION Effective for dates of service on and after November 1, 2005, the following dental coding, policy and related fee revisions
Table of Contents Section 6 Table of Contents
 Table of Contents Section Table of Contents Victory Series First Molar Bands...2 Victory Series Second Molar Bands... Unitek General Purpose Molar Bands...10 Unitek Pedodontic Molar Bands...11 Unitek Proportioned
Table of Contents Section Table of Contents Victory Series First Molar Bands...2 Victory Series Second Molar Bands... Unitek General Purpose Molar Bands...10 Unitek Pedodontic Molar Bands...11 Unitek Proportioned
KwikPen Insulin delivery device
 USER MANUAL KwikPen Insulin delivery device PLEASE READ THESE INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE USE Lilly Introduction The KwikPen is designed for ease of use. It is a disposable pen containing 3 ml (300 units) of U-
USER MANUAL KwikPen Insulin delivery device PLEASE READ THESE INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE USE Lilly Introduction The KwikPen is designed for ease of use. It is a disposable pen containing 3 ml (300 units) of U-
Endodontics. Colleagues for Excellence. Access Opening and Canal Location
 Endodontics Colleagues for Excellence Spring 2010 Access Opening and Canal Location Published for the Dental Professional Community by the American Association of Endodontists Cover artwork: Rusty Jones,
Endodontics Colleagues for Excellence Spring 2010 Access Opening and Canal Location Published for the Dental Professional Community by the American Association of Endodontists Cover artwork: Rusty Jones,
Doppler ultrasound to detect pulpal blood flow changes during local anaesthesia
 doi:1.1111/j.1365-2591.11.19.x Doppler ultrasound to detect pulpal blood flow changes during local anaesthesia M. J. Yoon, S. J. Lee, E. Kim & S. H. Park Department of Operative Dentistry, College of Dentistry,
doi:1.1111/j.1365-2591.11.19.x Doppler ultrasound to detect pulpal blood flow changes during local anaesthesia M. J. Yoon, S. J. Lee, E. Kim & S. H. Park Department of Operative Dentistry, College of Dentistry,
BioPure MTAD Antibacterial Root Canal Cleanser Research
 BioPure MTAD Antibacterial Root Canal Cleanser Research ANTIBACTERIAL 1. Torabinejad M, Shabahang S, Aprecio RM, Kettering JD. The antimicrobial effect of MTAD: An in vitro investigation. J Endodon 2003;
BioPure MTAD Antibacterial Root Canal Cleanser Research ANTIBACTERIAL 1. Torabinejad M, Shabahang S, Aprecio RM, Kettering JD. The antimicrobial effect of MTAD: An in vitro investigation. J Endodon 2003;
GC-xt. The most flexible GC /GC-MS liquid sample injector
 GC-xt Prep and Load Platform The most flexible GC /GC-MS liquid sample injector Environmental Foods/Beverages Consumer Products Forensics Petrochemicals/Polymers Pharmaceuticals GC-xt Liquid mode Prep
GC-xt Prep and Load Platform The most flexible GC /GC-MS liquid sample injector Environmental Foods/Beverages Consumer Products Forensics Petrochemicals/Polymers Pharmaceuticals GC-xt Liquid mode Prep
ENDODONTICS. Colleagues for Excellence. The Standard of Practice in Contemporary Endodontics. www.aae.org/colleagues
 ENDODONTICS Colleagues for Excellence Fall 2014 The Standard of Practice in Contemporary Endodontics Published for the Dental Professional Community by the American Association of Endodontists and the
ENDODONTICS Colleagues for Excellence Fall 2014 The Standard of Practice in Contemporary Endodontics Published for the Dental Professional Community by the American Association of Endodontists and the
POWER SCALING AIR-FLOW AIR POLISHING SOLUTIONS
 POWER SCALING AIR-FLOW AIR POLISHING SOLUTIONS ADVANCING PROPHYLAXIS PROTOCOL Introducing THE AIR-FLOW TECHNOLOGY AIR-FLOW PERIO units reach into periodontal pockets to remove biofilm. The new PERIO-FLOW
POWER SCALING AIR-FLOW AIR POLISHING SOLUTIONS ADVANCING PROPHYLAXIS PROTOCOL Introducing THE AIR-FLOW TECHNOLOGY AIR-FLOW PERIO units reach into periodontal pockets to remove biofilm. The new PERIO-FLOW
Totally lightweight, totally flexible, totally titanium.
 CAD/CAM SYSTEMS INSTRUMENTS HYGIENE SYSTEMS TREATMENT CENTERS IMAGING SYSTEMS CAD/CAM SYSTEMS INSTRUMENTS HYGIENE SYSTEMS TREATMENT CENTERS IMAGING SYSTEMS SIRONA UNIQUE WORLDWIDE SYSTEMS EXPERTISE IN
CAD/CAM SYSTEMS INSTRUMENTS HYGIENE SYSTEMS TREATMENT CENTERS IMAGING SYSTEMS CAD/CAM SYSTEMS INSTRUMENTS HYGIENE SYSTEMS TREATMENT CENTERS IMAGING SYSTEMS SIRONA UNIQUE WORLDWIDE SYSTEMS EXPERTISE IN
ENDODONTOLOGY. CALCIUM PHOSPHATE CEMENT: A NEW SAVIOUR FOR FURCATION PERFORATION? - An in-vitro study INTRODUCTION MATERIALS AND METHODS ABSTRACT
 CALCIUM PHOSPHATE CEMENT: A NEW SAVIOUR FOR FURCATION PERFORATION? - An in-vitro study SANOOP GEORGE * VASUNDHARA SHIVANNA ** DHANYAKUMAR N. M. *** ABSTRACT This study was conducted to evaluate the sealing
CALCIUM PHOSPHATE CEMENT: A NEW SAVIOUR FOR FURCATION PERFORATION? - An in-vitro study SANOOP GEORGE * VASUNDHARA SHIVANNA ** DHANYAKUMAR N. M. *** ABSTRACT This study was conducted to evaluate the sealing
Indications for Use: Contraindications: Benefits of Ultrasonics: Disadvantages: Some handpieces cannot be sterilized Portability Evacuation needed
 An Integral Part of Periodontal Therapy Indications for Use: Removal of calculus and stains Periodontal debridement Easier access to furcations Prior to oral surgery Removal of orthodontic cement & de
An Integral Part of Periodontal Therapy Indications for Use: Removal of calculus and stains Periodontal debridement Easier access to furcations Prior to oral surgery Removal of orthodontic cement & de
TABLE OF PERMITTED DUTIES (Rev. 1/1/10)
 TBLE OF PERMITTE UTIES (Rev. 1/1/10) Following is a table of duties which ental ssistants (), Registered ental ssistants (R), Registered ental ssistants in Extended Functions (REF), Orthodontic ssistants
TBLE OF PERMITTE UTIES (Rev. 1/1/10) Following is a table of duties which ental ssistants (), Registered ental ssistants (R), Registered ental ssistants in Extended Functions (REF), Orthodontic ssistants
RICHMOND CROWN - FOR RESTORATION OF BADLY MUTILATED POSTERIOR TEETH - A CASE REPORT
 RICHMOND CROWN - FOR RESTORATION OF BADLY MUTILATED POSTERIOR TEETH - A CASE REPORT 1. Dr. Yadav Chakravarthy, MDS* Professor and Head of The Department. Department of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics
RICHMOND CROWN - FOR RESTORATION OF BADLY MUTILATED POSTERIOR TEETH - A CASE REPORT 1. Dr. Yadav Chakravarthy, MDS* Professor and Head of The Department. Department of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics
Complications Associated with Tooth Extraction
 1 Complications Associated with Tooth Extraction Mark M. Smith, VMD, DACVS, DAVDC Center for Veterinary Dentistry and Oral Surgery 9041 Gaither Road Gaithersburg, MD 20877 Introduction Tooth extraction
1 Complications Associated with Tooth Extraction Mark M. Smith, VMD, DACVS, DAVDC Center for Veterinary Dentistry and Oral Surgery 9041 Gaither Road Gaithersburg, MD 20877 Introduction Tooth extraction
RomiApex A-15. APEX LOCATOR User Manual
 RomiApex A-15 APEX LOCATOR User Manual Table of Contents Introduction..... 2 1. Indications for use... 3 2. Precautions..... 3 3. Adverse Reactions...... 3 4. Package Contents........ 3 5. Getting Started.....
RomiApex A-15 APEX LOCATOR User Manual Table of Contents Introduction..... 2 1. Indications for use... 3 2. Precautions..... 3 3. Adverse Reactions...... 3 4. Package Contents........ 3 5. Getting Started.....
CDT 2015 Code Change Summary New codes effective 1/1/2015
 CDT 2015 Code Change Summary New codes effective 1/1/2015 Code Nomenclature Delta Dental Policy D0171 Re-Evaluation Post Operative Office Visit Not a Covered Benefit D0351 3D Photographic Image Not a Covered
CDT 2015 Code Change Summary New codes effective 1/1/2015 Code Nomenclature Delta Dental Policy D0171 Re-Evaluation Post Operative Office Visit Not a Covered Benefit D0351 3D Photographic Image Not a Covered
Ultrasound Phantoms: B-Mode, Doppler and Others. Heather M. Pierce, B.S. Norfolk, VA
 Ultrasound Phantoms: B-Mode, Doppler and Others Heather M. Pierce, B.S. Norfolk, VA Overview Design of ultrasound phantoms Types of phantoms available Use of phantoms in a QA/QC program Advantages and
Ultrasound Phantoms: B-Mode, Doppler and Others Heather M. Pierce, B.S. Norfolk, VA Overview Design of ultrasound phantoms Types of phantoms available Use of phantoms in a QA/QC program Advantages and
Dental Updates. Excerpted Article e-mail: re777@comcast.net. Why Implant Screws Loosen Part 1. Richard Erickson, MS, DDS
 ¼ ½ ¾ µ mw/cm 2 Volume 17; 2007 Dental Updates "CUTTING EDGE INFORMATION FOR THE DENTAL PROFESSIONAL " 200 SEMINARS AND 30 JOURNALS REVIEWED YEARLY FOR THE LATEST, CUTTING EDGE INFORMATION Excerpted Article
¼ ½ ¾ µ mw/cm 2 Volume 17; 2007 Dental Updates "CUTTING EDGE INFORMATION FOR THE DENTAL PROFESSIONAL " 200 SEMINARS AND 30 JOURNALS REVIEWED YEARLY FOR THE LATEST, CUTTING EDGE INFORMATION Excerpted Article
Osseointegrated implant connected with natural tooth using a semiprecision attachment: A clinical report
 Osseointegrated implant connected with natural tooth using a semiprecision attachment: A clinical report Yohsuke Taira, DDS, PhD, Kiyoshi Nagano, DT, and Mitsuru Atsuta, DDS, PhD Division of Fixed Prosthodontics
Osseointegrated implant connected with natural tooth using a semiprecision attachment: A clinical report Yohsuke Taira, DDS, PhD, Kiyoshi Nagano, DT, and Mitsuru Atsuta, DDS, PhD Division of Fixed Prosthodontics
Electronic Apex Locators
 Electronic Apex Locators This material is provided for information and education purposes only. No doctor/patient relationship has been established by the use of this site. No diagnosis or treatment is
Electronic Apex Locators This material is provided for information and education purposes only. No doctor/patient relationship has been established by the use of this site. No diagnosis or treatment is
Page 1 of 11 BDS FINAL PROFESSIONAL EXAMINATION 2007 OPERATIVE DENTISTRY (MCQs) Model Paper
 Page 1 of 11 Marks 45 Time 45 minutes Total No. of MCQs 45 One mark for each 01. Hand cutting instruments are composed of: A. Handle and neck. B. Handle and blade only. C. Handle, shank and blade. D. Handle,
Page 1 of 11 Marks 45 Time 45 minutes Total No. of MCQs 45 One mark for each 01. Hand cutting instruments are composed of: A. Handle and neck. B. Handle and blade only. C. Handle, shank and blade. D. Handle,
Svea Baumgarten, Dr. med. dent., M Sc, accredited implantologist as per the criteria of the DGZI (German Association of Dental Implantology) 1
 The use of ozone in dentistry a case study Svea Baumgarten, Dr. med. dent., M Sc, accredited implantologist as per the criteria of the DGZI (German Association of Dental Implantology) 1 Ozone gas is a
The use of ozone in dentistry a case study Svea Baumgarten, Dr. med. dent., M Sc, accredited implantologist as per the criteria of the DGZI (German Association of Dental Implantology) 1 Ozone gas is a
Dental Services. Dental Centre. HKSH Healthcare Medical Centre Dental Centre. For enquiries and appointments, please contact us
 Dental Services For enquiries and appointments, please contact us HKSH Healthcare Medical Centre Dental Centre Level 22, One Pacific Place 88 Queensway, Hong Kong (852) 2855 6666 (852) 2892 7589 dentalcentre@hksh.com
Dental Services For enquiries and appointments, please contact us HKSH Healthcare Medical Centre Dental Centre Level 22, One Pacific Place 88 Queensway, Hong Kong (852) 2855 6666 (852) 2892 7589 dentalcentre@hksh.com
Dentalworkers JOB DESCRIPTIONS Great Team Members make your Office function!
 Dentalworkers JOB DESCRIPTIONS Great Team Members make your Office function! Dental Assistant Registered Dental Assistant with Expanded Function: RDAEF Sterilization Assistant Dental Hygienist General
Dentalworkers JOB DESCRIPTIONS Great Team Members make your Office function! Dental Assistant Registered Dental Assistant with Expanded Function: RDAEF Sterilization Assistant Dental Hygienist General
Richmond Crown- A Conventional Approach for Restoration of Badly Broken Posterior Teeth
 Richmond Crown- A Conventional Approach for Restoration of Badly Broken Posterior Teeth Abhinav Agarwal 1, Manish Chadha 2, D.R.V.Kumar 3, Prakash Somani 4, Preet Jain 5 Abstract: Restoration of badly
Richmond Crown- A Conventional Approach for Restoration of Badly Broken Posterior Teeth Abhinav Agarwal 1, Manish Chadha 2, D.R.V.Kumar 3, Prakash Somani 4, Preet Jain 5 Abstract: Restoration of badly
Dental caries is an infectious disease caused
 Emerging Methods of Caries Diagnosis George K. Stookey, Ph.D.; Carlos González-Cabezas, D.D.S., Ph.D. Abstract: Current diagnostic tools used in dental caries detection are not sensitive enough to diagnose
Emerging Methods of Caries Diagnosis George K. Stookey, Ph.D.; Carlos González-Cabezas, D.D.S., Ph.D. Abstract: Current diagnostic tools used in dental caries detection are not sensitive enough to diagnose
TEPZZ 69 _ZA T EP 2 692 310 A2 (19) (11) EP 2 692 310 A2. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ 69 _ZA T (11) EP 2 692 3 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 0.02.14 Bulletin 14/06 (21) Application number: 1276632.0 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 69 _ZA T (11) EP 2 692 3 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 0.02.14 Bulletin 14/06 (21) Application number: 1276632.0 (22)
Friday 29 th April 2016
 8.00 9.00 Registration and coffee/bread 9.00 9.45 1. Status of Dental Traumatology worldwide. Is prevention realistic? Lars Andersson Presently almost all countries have published data on the dental trauma
8.00 9.00 Registration and coffee/bread 9.00 9.45 1. Status of Dental Traumatology worldwide. Is prevention realistic? Lars Andersson Presently almost all countries have published data on the dental trauma
ELECTRONIC METHODS IN THE DENTISTRY
 ELECTRONIC METHODS IN THE DENTISTRY THERAPY SET SCORPION DENTAL OPTIMA model 405-7A th 7 SERIES DENTAL THERAPY SET SCORPION DENTAL OPTIMA model 405-7A THE SET INCLUDES THE FOLLOWING DEVICSES FOR: Apex
ELECTRONIC METHODS IN THE DENTISTRY THERAPY SET SCORPION DENTAL OPTIMA model 405-7A th 7 SERIES DENTAL THERAPY SET SCORPION DENTAL OPTIMA model 405-7A THE SET INCLUDES THE FOLLOWING DEVICSES FOR: Apex
ENDO REMOVAL SYSTEM Set of endodontic micro instruments for removing broken canal instruments
 WWW.CERKAMED.COM ENDO REMOVAL SYSTEM Set of endodontic micro instruments for removing broken canal instruments by K. Gonczowski WWW.ENDO-RS.COM Krzysztof Gończowski DDS, PhD Specialist of Conservative
WWW.CERKAMED.COM ENDO REMOVAL SYSTEM Set of endodontic micro instruments for removing broken canal instruments by K. Gonczowski WWW.ENDO-RS.COM Krzysztof Gończowski DDS, PhD Specialist of Conservative
