Endodontics. Colleagues for Excellence. Root Canal Irrigants and Disinfectants
|
|
|
- Wilfrid Woods
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Endodontics Colleagues for Excellence Winter 2011 Winter 2011 Root Canal Irrigants and Disinfectants Published for the Dental Professional Community by the American Association of Endodontists Cover artwork: Rusty Jones, MediVisuals, Inc.
2 D EndodoNtics: Colleagues for Excellence iagnosis, instrumentation, obturation and restoration are the main steps involved in the treatment of teeth with pulpal and periapical diseases. Elimination or significant reduction of irritants and prevention of recontamination of the root canal after treatment are the essential elements for successful outcomes. Although many advances have been made in different aspects of endodontics within the last few years to preserve natural dentition, the main objective of this field remains elimination of microorganisms from the root canal systems and prevention of recontamination after treatment. The common belief that inadequate obturation is the major cause of endodontic failures has been proven to be fallacious as obturation reflects the adequacy of cleaning and shaping. In other words, what you take out of a root canal may be more important than what you put in it. What are the Irritants for Pulpal and Periapical Tissues? The major causes of pulpal and periapical diseases are living and nonliving irritants. The latter group includes mechanical, thermal and chemical irritants. The living irritants include various microorganisms including bacteria, yeasts and viruses. When pathological changes occur in the dental pulp, the root canal space acquires the ability to harbor various irritants including several species of bacteria, along with their toxins and byproducts. Investigations in animals and patients have shown that pulpal and/or periradicular diseases do not develop without the presence of bacteria. 1,2 Advanced culturing and molecular biology techniques have shown that primary root canal infections are polymicrobial (10-30 bacterial species) in nature and are dominated by obligate anaerobic bacteria. 3 The variety of microorganisms present in root canal-treated teeth with persistent periapical lesions is more restricted (1-3 species) in comparison to primary root canal infections, which are dominated by E. faecalis, a facultative anaerobic gram-positive coccus that is resistant to intracanal medications, able to form biofilms and able to invade dentinal tubules. 4 Because the presence of bacteria negatively influences the outcome of root canal treatment, 4-6 every effort should be made to eradicate infections during treatment. What are the Obstacles in Removing Irritants From the Root Canal Systems? The complexity of the root canal system, presence of numerous dentinal tubules in the roots, invasion of the tubules by microorganisms, formation of smear layer during instrumentation and presence of dentin as a tissue are the major obstacles in achieving the primary objectives of complete cleaning and shaping of root canal systems. 7 Microscopic examinations of root canals show that they are irregular and complex systems with many cul-de-sacs, fins and lateral canals (Figures 1a and 1b). In the root, dentinal tubules extend from the pulp- to the cementum-dentin junction (Figure 2). Investigators have reported the presence of bacteria in the dentinal tubules (Figure 3) of infected teeth at approximately half the distance between the root canal walls and the cementum-dentin junction. 7 The presence of these natural complexities is important for clinicians to consider during cleaning and shaping of the root canal system. 8,9 In addition to these natural difficulties, it is known that a smear layer is created during cleaning and shaping that covers the instrumented root canal walls. 7 This smear layer (Figure 4) contains inorganic and organic substances as well Fig. 2. SEM of dentinal tubules running from the pre-dentin towards the cementum. Fig. 3. SEM of dentinal tubules containing microorganisms. Fig. 1a. Internal anatomy of a maxillary second molar after decalcification, dehydration and placement in India ink. Courtesy of Dr. JV Baroni Barbizam. Fig. 4. The smear layer consists of organic and inorganic substances as well as fragments of odontoblastic processes, various species of bacteria and necrotic debris. 2 Fig. 1b. Microcomputed tomography images of canal isthmuses in mesial roots of mandibular molars. Courtesy of Dr. L. Gu. as fragments of odontoblastic processes, microorganisms and necrotic debris. Intracanal irrigants and medications are used
3 during root canal treatment to reach the natural complexities and remove the smear layer. Intracanal irrigants exert their effects mechanically and chemically. Mechanical effects of irrigants are generated by the back and forth flow of the irrigation solution during cleaning and shaping of the infected root canals, significantly reducing the bacterial load. 10,11 Studies show that irrigants that possess antibacterial properties have clearly superior effectiveness in bacterial reduction and elimination when compared with saline solution. 11,12 What are the Ideal Properties of an Irrigant? To effectively clean and disinfect the root canal system, an irrigant should be able to disinfect and penetrate dentin and its tubules, offer long-term antibacterial effect (substantivity), remove the smear layer, and be nonantigenic, nontoxic and noncarcinogenic. In addition, it should have no adverse effects on dentin or the sealing ability of filling materials. 7 Furthermore, it should be relatively inexpensive, convenient to apply and cause no tooth discoloration. 7 Other desirable properties for an ideal irrigant include the ability to dissolve pulp tissue and inactivate endotoxins. 13 What are the Types, Advantages and Disadvantages of Current Irrigants? The irrigants that are currently used during cleaning and shaping can be divided into antibacterial and decalcifying agents or their combinations. They include sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl), chlorhexidine, ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), and a mixture of tetracycline, an acid and a detergent (MTAD). Sodium Hypochlorite (NaOCl) Sodium hypochlorite (household bleach) is the most commonly used root canal irrigant. It is an antiseptic and inexpensive lubricant that has been used in dilutions ranging from 0.5% to 5.25%. Free chlorine in NaOCl dissolves vital and necrotic tissue by breaking down proteins into amino acids. 14 Decreasing the concentration of the solution reduces its toxicity, antibacterial effect and ability to dissolve tissues. 14 Increasing its volume or warming it increases its effectiveness as a root canal irrigant. 14 Advantages of NaOCl include its ability to dissolve organic substances present in the root canal system and its affordability. The major disadvantages of this irrigant are its cytotoxicity when injected into periradicular tissues, foul smell and taste, ability to bleach clothes and ability to cause corrosion of metal objects. 15 In addition, it does not kill all bacteria, 12,16-18 nor does it remove all of the smear layer. 19 It also alters the properties of dentin. 20,21 The results of a recent in vitro study show that the most effective irrigation regimen is 5.25% at 40 minutes, whereas irrigation with 1.3% and 2.5% NaOCl for this same time interval is ineffective in removing E. faecalis from infected dentin cylinders. 22 Based on the findings of this study, the authors recommend the use of other irrigants to increase the antibacterial effects during cleaning and shaping of root canals. Sodium hypochlorite is generally not utilized in its most active form in a clinical setting. For proper antimicrobial activity, it must be prepared freshly just before its use. 23,24 In the majority of cases, however, it is purchased in large containers and stored at room temperature while being exposed to oxygen for extended periods of time. Exposure of the solution to oxygen, room temperature and light can inactivate it significantly. 24 Fig. 5a. NaOCl was inadvertently expressed into the periapical tissues through the apical foramen of the right maxillary cuspid during cleaning and shaping. Figure 5b. No treatment was necessary for the hematoma and swelling. Reprinted with permission from Endodontics: Principles and Practice 4 th ed., Torabinejad and Walton, Extrusion of NaOCl into periapical tissues (Figures 5a and 5b) can cause severe injury to the patient. 25,26 To minimize NaOCl accidents, the irrigating needle should be placed short of the working length, fit loosely in the canal and the solution must be injected using a gentle flow rate. Constantly moving the needle up and down during irrigation prevents wedging of the needle in the canal and provides better irrigation. The use of irrigation tips with sideventing reduces the possibility of forcing solutions into the periapical tissues. Treatment of NaOCl accidents is palliative and consists of observation of the patient as well as prescribing antibiotics and analgesics. Chlorhexidine Chlorhexidine gluconate has been used for the past 50 years for caries prevention, 27 in periodontal therapy and as an oral antiseptic mouthwash. 28 It has a 3 Continued on p. 4
4 broad-spectrum antibacterial action, sustained action and low toxicity. 14 Because of these properties, it has also been recommended as a potential root canal irrigant. 14,27 The major advantages of chlorhexidine over NaOCl are its lower cytotoxicity and lack of foul smell and bad taste. However, unlike NaOCl, it cannot dissolve organic substances and necrotic tissues present in the root canal system. In addition, like NaOCl, it is unable to kill all bacteria and cannot remove the smear layer. 29,30 Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid (EDTA) Chelating agents such as ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), citric acid and tetracycline are used for removal of the inorganic portion of the smear layer. 7 NaOCl is an adjunct solution for removal of the remaining organic components. Irrigation with 17% EDTA for one minute followed by a final rinse with NaOCl is the most commonly recommended method to remove the smear layer. 14 Longer exposures can cause excessive removal of both peritubular and intratubular dentin. 31 EDTA has little or no antibacterial effect. 32 MTAD An alternative solution to EDTA for removing the smear layer is the use of BioPure MTAD (DENTSPLY Tulsa Dental Specialties, Tulsa, Okla.), a mixture of a tetracycline isomer, an acid (citric acid) and a detergent. 33 MTAD was developed as a final rinse to disinfect the root canal system and remove the smear layer. The effectiveness of MTAD to completely remove the smear layer (Figure 6) is enhanced when a low concentration of NaOCl (1.3%) is used as an intracanal irrigant before placing 1 ml of MTAD in a canal for 5 minutes and rinsing it with an additional 4 ml of MTAD as the final rinse. 33 It appears to be superior to CHX in antimicrobial activity. 30 In addition, it has sustained antibacterial activity, is biocompatible and enhances bond strength. 14 Table 1 shows the advantages and disadvantages of current irrigants utilized during root canal treatment. Fig. 6. SEM of dentinal tubules after removal of the smear layer by MTAD. Irrigation Devices and Techniques For many years various methods have been proposed and developed to make root canal irrigants more effective in removing debris and bacteria from the root canal system. These techniques can be classified into two broad categories: manual and rotary agitation. 34 The manual irrigation techniques include irrigation with needles, agitation with brushes, and manual dynamic agitation with files or gutta-percha points. The rotary irrigation techniques include rotary brushes, continuous irrigation during instrumentation, sonic and ultrasonic vibrations, and application of negative pressure during irrigation of the root canal system. The use of these methods results in better canal cleanliness when compared with that of conventional syringe needle irrigation. However, there is no high level of evidence that correlates the clinical efficacy of these devices with better treatment outcomes. Clinical data are needed to support the use of these devices in endodontics. Table 1 Advantages and Disadvantages of Currently Used Intracanal Irrigants Characteristics MTAD NaOCI CHX EDTA Shelf life stability Antimicrobial activity Ability to remove smear layer Biocompatibility Ability to dissolve pulp tissue /- Dentin conditioning properties Positive effect on root canal seal Negative effect on dentin structure Upregulation of regional immune response / Application time (minutes) ? 1 31 Lasers Some investigators have reported that lasers can be used to vaporize tissues in the main canal, remove the smear layer and eliminate the residual tissue in the apical portion of the root canals. 7 Several investigators have reported that the efficacy of lasers depends on many factors including the power level, the duration of exposure, the absorption of light in the tissue, the geometry of the root canal and the tip-to-target distance The efficacy of the lasers to completely clean the root canals remains to be seen. The main difficulty continues to be access to small canal spaces with the relatively large probes that deliver the laser beams and the expense of these units. 4
5 Because current solutions and techniques cannot completely remove all irritants, dissolve all organic tissue or remove the smear layer, various methods have been employed to deliver irrigants more efficiently to the working length. These include sonic and ultrasonic vibrations as well as application of negative pressure to flush out the debris present in instrumented canals. EndoVac System The EndoVac system (Discus Dental, Culver City, Calif.) is a new irrigation system that consists of a delivery/evacuation tip attached to a syringe of irrigant and the high-speed suction source of the dental unit. As the cannulas are placed in the canal, negative pressure pulls irrigant from a fresh supply in the chamber down into the canal to the tip of the cannula, then into the cannula and finally out through the suction hose. 38 Investigators compared the efficacy of the EndoVac irrigation system with that of a needle irrigation system to clean root canals at 1 and 3mm from working length and found no significant difference between the two groups at the 3mm level. However, their results show significantly better debridement at 1mm from working length using the EndoVac compared with needle irrigation. 38 A recent in vitro study compared three agitation and two irrigation devices with ultrasonic agitation for mechanically removing bacteria from a plastic-simulated canal that was instrumented to a size 35 with a.06 taper. 39 The irrigation and agitation techniques evaluated were ultrasonic agitation, needle irrigation, EndoVac irrigation, EndoActivator (DENTSPLY Tulsa Dental Specialties, Tulsa, Okla.), F File (Plastic Endo, Lincolnshire, Ill) and sonic agitation. Based on the results of this investigation, the authors conclude that ultrasonic agitation is significantly more effective than needle irrigation and EndoVac irrigation at removing intracanal bacteria. Ultrasonic, EndoActivator, F File and sonic agitation are similar in their ability to remove bacteria in a plastic-simulated canal. These findings point to the importance of the use of antiseptic irrigants in addition to mechanical vibrations and application of negative pressure during cleaning and shaping of root canals. The results of a recent in vitro study using a combination of mechanical and chemical means to disinfect root canals showed that activation of MTAD with the EndoActivator system for 1.5 minutes was an effective method to completely inhibit the growth of E. faecali. 40 Intracanal Medicaments Intracanal medicaments have been used to disinfect root canals between appointments and reduce interappointment pain. 7 The disinfectants can be divided into phenolic compounds such as camphorated monochlorophenol, cresatin, aldehydes such as formocresol and glutaraldehyde, and halides, as well as other materials like calcium hydroxide [Ca(OH) 2 ] and some antibiotics. 14 These compounds are potent antibacterial agents under laboratory test conditions, but their efficacy in clinical use is unpredictable. 7 Some of the aldehyde de rivatives have been proposed to neutralize canal tissue remnants and to render them inert. These can be used to fix fresh tissues for histological examination, but they may not effectively fix necrotic or decomposed tissues. According to one report, 41 fixed tissues are not inert and may become more toxic and antigenic after fixation. Intracanal medications have also been used clinically to prevent post-treatment pain. Studies have shown, however, that routine use of these materials as intracanal medications has no significant effect on prevention of pain. 7 Calcium Hydroxide Ca(OH) 2 is a substance that inhibits microbial growth in canals. 42 The antibacterial effect of Ca(OH) 2 is due to its alkaline ph. It also dissolves necrotic tissue remnants and bacteria and their byproducts. 43 It can be placed as a dry powder, a powder mixed with a liquid such as water, saline, local anesthetic or glycerin, or a proprietary paste supplied in a syringe. 14 Because of its toxicity 44, Ca(OH) 2 should be placed within the canal with the aid of a file or a needle. Extrusion of the material into the periapical tissues can cause tissue necrosis and pain for the patient. Ca(OH) 2 can be removed from the canal by using irrigants such as saline, NaOCl, EDTA or MTAD. Corticosteroids Corticosteroids are anti-inflammatory agents that have been advocated as intracanal medicaments to reduce postoperative pain. 45 An animal study has shown a reduction of inflammatory cells in periapical tissues following supraperiosteal infiltration of dexamethasone into the buccal vestibule of rats. 46 There is no significant clinical evidence that suggests that they are effective in patients with very high pain levels. 47 The use of corticosteroids in patients with irreversible pulpitis and symptomatic apical periodontitis may be beneficial. 45,48 5 Continued on p. 6
6 Chlorhexidine Gel A 2% CHX gel has recently been advocated as an intracanal medicament. 49 It can be used alone in gel form or mixed with Ca(OH) 2. When used for seven days to medicate bovine teeth 50 or human teeth, 51 CHX gel provides antimicrobial activity for up to 21 days after contamination. When it is used in combination with Ca(OH) 2, the antimicrobial activity of this mixture is greater than the combination of Ca(OH) 2 and saline. 52 Summary Bacteria are the major cause of pulpal and periapical diseases. Complexity of the root canal system, invasion of the dentinal tubules by microorganisms, formation of smear layer during instrumentation and presence of dentin as a tissue are the major obstacles for complete elimination of bacteria during cleaning and shaping of root canal systems. The bacterial population of infected root canals can be significantly reduced by using saline irrigation; however, irrigants that have antibacterial effects have clearly superior effectiveness in bacterial elimination when compared with saline solution. The irrigants that are currently used during cleaning and shaping include NaOCl, CHX, EDTA and MTAD. None of these irrigants has all of the characteristics of an ideal irrigant. Sonic and ultrasonic vibrations alone or in combination with antibacterial irrigants as well as application of negative pressure have been used to increase the efficacy of these irrigants. Intracanal medicaments have been used to disinfect root canals between appointments and reduce interappointment pain. The major intracanal medications currently used in endodontics include Ca(OH) 2 and CH. The search for an ideal material and/or technique to completely clean infected root canals continues. The AAE wishes to thank Dr. Mahmoud Torabinejad for authoring this issue of the newsletter, as well as the following article reviewers: Drs. James A. Abbott, Peter J. Babick, James C. Kulild, Clara M. Spatafore and Susan L. Wolcott. References 1. Kakehashi S, Stanley HR, Fitzgerald RJ. The effects of surgical exposures of dental pulps in germ-free and conventional laboratory rats. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1965;20: Sundqvist G. Bacteriological studies of necrotic dental pulps. Umeå University Odontol Dissertation, No 7. University of Umeå, Sweden, Siqueira Jr JF, Rôças, IN. Endodontic Microbiology in: Endodontics: Principles and Practice 4 th ed. Saunders, Philadelphia, PA, Sjogren U, Figdor D, Persson, Sundqvist G. Influence of infection at the time of root filling on the outcome of endodontic treatment of teeth with apical periodontitis. Int Endod J 1997;30: Sundqvist G, Figdor D, Persson S, Sjogren U. Microbiologic analysis of teeth with failed endodontic treatment and the outcome of conservative re-treatment. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 1998;85: Waltimo T, Trope M, Haapasalo M, Ørstavik D. Clinical efficacy of treatment procedures in endodontic infection control and one year follow-up of periapical healing. J Endod 2005;31: Torabinejad M, Handysides R, Khademi A, Bakland LK. Clinical implications of the smear layer in endodontics: A review. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2002;94: Davis SR, Brayton S, Goldman M. The morphology of the prepared root canal: A study utilizing injectable silicone. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1972;34: Peters OA, Schönenberger K, Laib A. Effects of four NiTi preparation techniques on root canal geometry assessed by micro computed tomography. Int Endod J 2001;34: Byström A, Sundqvist G. Bacteriologic evaluation of the efficacy of mechanical root canal instrumentation in endodontic therapy. Scand J Dent Res 1981;89: Siqueira Jr JF, Rocas IN, Favieri A, Lima, KC. Chemomechanical reduction of the bacterial population in the root canal after instrumentation and irrigation with 1%, 2.5%, and 5.25% sodium hypochlorite. J Endod 2000;26: Siqueira Jr JF, Machado AG, Silveira RM, Lopes HP, de Uzeda M. Evaluation of the effectiveness of sodium hypochlorite used with three irrigation methods in the elimination of Enterococcus faecalis from the root canal, in vitro. Int Endod J 1997;30: Zehnder M. Root canal irrigants. J Endod 2006;32: Johnson WT, Noblett WC. Cleaning and Shaping in: Endodontics: Principles and Practice. 4 th ed. Saunders, Philadelphia, PA, Gomes BP, Ferraz CCR, Vianna ME, Berber VB, Teixeira FB, de Souza-Filho FJ. In vitro antimicrobial activity of several concentrations of sodium hypochlorite and chlorhexidine gluconate in the elimination of Enterococcus faecalis. Int Endod J 2001;34: Sjogren U, Figdor D, Persson S, Sundqvist G. Influence of infection at the time of root filling on the outcome of endodontic treatment of teeth with apical periodontitis. Int Endod J 1997;30:
7 17. Shuping GB, Ørstavik D, Sigurdsson A, Trope M. Reduction of intracanal bacteria using nickel-titanium rotary instrumentation and various medications. J Endod 2000;26: Shabahang S, Torabinejad M. Effect of MTAD on Enterococcus faecalis-contaminated root canals of extracted human teeth. J Endod 2003;29: McCome D, Smith DC. A preliminary scanning electron microscopic study of root canals after endodontic procedures. J Endod 1975;1: Sim TP, Knowles JC, Ng YL, Shelton J, Gulabivala K. Effect of sodium hypochlorite on mechanical properties of dentine and tooth surface strain. Int Endod J 2001;34: Grigoratos D, Knowles J, Ng YL, Gulabivala K. Effect of exposing dentine to sodium hypochlorite and calcium hydroxide on its flexural strength and elastic modulus. Int Endod J 2001;34: Retamozo B, Shabahang S, Johnson N, Aprecio RM, Torabinejad M. Minimum contact time and concentration of sodium hypochlorite required to eliminate Enterococcus faecalis. J Endod 2010;36: Clarkson RM, Moule AJ, Podlich HM. The shelf-life of sodium hypochlorite irrigating solutions. Aust Dent J 2001;46: Piskin B, Turkun M. Stability of various sodium hypochlorite solutions. J Endod 1995;21: Hülsmann M, Hahn W. Complications during root canal irrigation literature review and case reports. Int Endod J 2000;33: Reeh ES, Messer HH. Long-term paresthesia following inadvertent forcing of sodium hypochlorite through perforation in maxillary incisor. Endod Dent Traumatol 1989;5: Lee LW, Lan WH, Wang GY. An evaluation of chlorhexidine as an endodontic irrigant. J Formos Med Assoc 1990;89: Southard SR, Drisko CL, Killoy WJ, Cobb CM, Tira DE. The effect of 2.0% chlorhexidine digluconate irrigation on clinical parameters and the level of Bacteroides gingivalis in periodontal pockets. J Periodontol 1989;60: Estrela C et al. Efficacy of sodium hypochlorite and chlorhexidine against Enterococcus faecalis a systematic review. J Appl Oral Sci 2008;16: Shabahang S, Aslanyan J, Torabinejad M. The substitution of chlorhexidine for doxycycline in MTAD: the antibacterial efficacy against a strain of Enterococcus faecalis. J Endod 2008;34: Calt S, Serper A. Smear layer removal by EGTA. J Endod 2000;26: Torabinejad M, Shabahang S, Kettering J, Aprecio R. Effect of MTAD on E Faecalis: an in vitro investigation. J Endod 2003;29: Torabinejad M, Cho Y, Khademi AA, Bakland LK, Shabahang S. The effect of various concentrations of sodium hypochlorite on the ability of MTAD to remove the smear layer. J Endod 2003;29: Gu L, Kim JR, Ling J, Choi KK, Pashley DH, Tay FR et al. Review of Contemporary Irrigant Agitation Techniques and Devices. J Endod 2009;35: Dederich DN, Zakariasen KL, Tulip J. Scanning electron microscopic analysis of canal wall dentin following neodymium-yttrium-aluminum-garnet laser irradiation. J Endod 1984;10: Önal B, Ertl T, Siebert G, Müller G. Preliminary report on the application of pulsed CO 2 laser radiation on root canals with AgCl fibers: a scanning and transmission electron microscopic study. J Endod 1993;19: Moshonov J, Sion A, Kasirer J, Rotstein I, Stabholz A. Effect of argon laser irradiation in removing intracanal debris. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 1995;79: Nielsen BA, Baumgartner JC. Comparison of the EndoVac system to needle irrigation of root canals. J Endod 2007;33: Townsend C, Maki J. An in vitro comparison of new irrigation and agitation techniques to ultrasonic agitation in removing bacteria from a simulated root canal. J Endod 2009;35: Harhash AI, Shabahang S, Torabinejad M. Effect of EndoActivator System on Antibacterial Efficacy of MTAD. J Endod 2011;37:In press. 41. Wesselink PR, Thoden van Velzen SK, van den Hoof A. The tissue reaction to implantation of unfixed and glutaraldehyde fixed heterologous tissue. J Endod 1977;3: Law A, Messer H. An evidence-based analysis of the antibacterial effectiveness of intracanal medicaments. J Endod 2004;30: Yang SF, Rivera EM, Baumgardner KR, Walton RE, Stanford C. Anaerobic tissue-dissolving abilities of calcium hydroxide and sodium hypochlorite. J Endod 1995;21: Badr AE, Omar N, Badria FA. A laboratory evaluation of the antibacterial and cytotoxic effect of Liquorice when used as root canal medicament. Int Endod J 2011;44: Ehrmann EH, Messer HH, Adams GG. The relationship of intracanal medicaments to postoperative pain in endodontics. Int Endod J 2003;36: Nobuhara WK Carnes DL, Gilles JA. Anti-inflammatory effects of dexamethasone on periapical tissues following endodontic overinstrumentation. J Endod 1993;19: Trope M. Relationship of intracanal medicaments to endodontic flare-ups. Endod Dent Traumatol 1990;6: Chance KB, Lin L, Skribner JE. Corticosteroid use in acute apical periodontitis: a review with clinical implications. Clin Prev Dent 1988;10: Dametto FR, Ferraz CC, Gomes BP, Zaia AA, Teixeira FB, de Souza-Filho FJ. In vitro assessment of the immediate and prolonged antimicrobial action of chlorhexidine gel as an endodontic irrigant against Enterococcus faecalis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2005;99: Komorowski R, Grad H, Wu XY, Friedman S. Antimicrobial substantivity of chlorhexidine-treated bovine root dentin. J Endod 2000;26: Basrani B et al. Substantive antimicrobial activity in chlorhexidine-treated human root dentin. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2002;94: Gomes BP, Vianna ME, Sena NT, Zaia AA, Ferraz CC, de Souza-Filho FJ. In vitro evaluation of the antimicrobial activity of calcium hydroxide combined with chlorhexidine gel used as intracanal medicament. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2006;102:
8 Dental Dam as Standard of Care Presence of bacteria is the primary cause of pulpal and periapical diseases. Disinfection of the root canal system is accomplished mechanically and chemically. Isolation of a tooth using the dental dam during endodontic treatment provides a mechanical barrier against accidental mechanical and chemical mishaps. The use of the dental dam during endodontic treatment is mandatory in the United States and is considered the Standard of Care. 1 Application of a dental dam during endodontic treatment provides a physical barrier for the protection of the patient 2 from swallowing or aspirating instruments and materials 3 and confines the irrigating solutions to the field of operation. In addition, it provides a clean environment that enhances vision, retracts tissues and makes treatment more efficient. Other advantages of the use of the dental dam during root canal treatment include: protection of the dentists and their auxiliary members, 4 minimizing aerosols 5, 6 and decreasing the potential for transmission of systemic diseases such as HIV, hepatitis and tuberculosis. 4 The dental dam is manufactured from latex. Nonlatex dental dam material is available for patients with a latex allergy. It can be obtained in a variety of colors and thicknesses (light, medium, heavy and extra heavy). Application of the dental dam takes a few minutes to provide a clean field of operation, protect the patient and prevent legal actions against the dentist. In the absence of a dental dam, an expert testimony is not required when patients swallow or aspirate instruments or materials during endodontic treatment. For a copy of the AAE s position statement on the use of dental dams, visit References: 1. Cohen S, Schwartz S. Endodontic complications and the law. J Endod 1987;13: Huggins DR. The rubber dam an insurance policy against litigation. J Ind Dent Assoc 1986;65: Taintor JF, Biesterfeld RC. A swallowed endodontic file: case report. J Endod 1978;4: Forrest WR, Perez RS. AIDS and hepatitis prevention: the role of the rubber dam. Oper Dent 1986;11: Miller RL, Micik RE. Air pollution and its control in the dental office. Dent Clin North Am 1978;22: Wong RC. The rubber dam as a means of infection control in an era of AIDS and hepatitis. J Ind Dent Assoc 1988;67:41-3. Saving the Natural Tooth Just Got Easier Tough cases don t have to mean extracted teeth many endodontic treatments can save the natural tooth for a lifetime! Our handy Treatment Options for the Compromised Tooth Guide helps you evaluate a variety of conditions using: case examples with radiographs and clinical photographs; clinical considerations; and guidance for successful outcomes based on prognosis. Also available Treatment Options for the Diseased Tooth patient brochure! Describes endodontic treatment options in easyto-understand language Explains the benefits of implants when a tooth must be extracted Download your free copies today at EXCLUSIVE BONUS MATERIALS This issue of the ENDODONTICS: Colleagues for Excellence newsletter is available online at with the following exclusive bonus materials: Video: Removal of the Smear Layer Full-Text Article: Johnson WT, Noblett WC. Cleaning and Shaping in: Endodontics: Principles and Practice. 4 th ed. Saunders, Philadelphia, PA, Table: Properties of an Ideal Root Canal Irrigant Summary: Irrigation Agitation Techniques and Devices American Association of Endodontists 211 E. Chicago Ave., Suite 1100 Chicago, IL info@aae.org The information in this newsletter is designed to aid dentists. Practitioners must use their best professional judgment, taking into account the needs of each individual patient when making diagnosis/treatment plans. The AAE neither expressly nor implicitly warrants against any negative results associated with the application of this information. If you would like more information, consult your endodontic colleague or contact the AAE.
BioPure MTAD Antibacterial Root Canal Cleanser Research
 BioPure MTAD Antibacterial Root Canal Cleanser Research ANTIBACTERIAL 1. Torabinejad M, Shabahang S, Aprecio RM, Kettering JD. The antimicrobial effect of MTAD: An in vitro investigation. J Endodon 2003;
BioPure MTAD Antibacterial Root Canal Cleanser Research ANTIBACTERIAL 1. Torabinejad M, Shabahang S, Aprecio RM, Kettering JD. The antimicrobial effect of MTAD: An in vitro investigation. J Endodon 2003;
EndoActivator from Tulsa Dental
 EndoActivator from Tulsa Dental Irrigation-EndoActivator http://endoactivator.com/video3.html EndoActivator System did not enhance the removal of smear layer as compared with conventional Max-I-Probe irrigation
EndoActivator from Tulsa Dental Irrigation-EndoActivator http://endoactivator.com/video3.html EndoActivator System did not enhance the removal of smear layer as compared with conventional Max-I-Probe irrigation
Instruction manual. Safe and efficient NiTi rotary system. Fulfilling the biological requirement for successful endodontics
 Instruction manual Safe and efficient NiTi rotary system Fulfilling the biological requirement for successful endodontics FKG REF. - 99.7AA.50.04B.AN - 06/2010 BioRaCe kit 1 Educational CD 1 Endo Stand
Instruction manual Safe and efficient NiTi rotary system Fulfilling the biological requirement for successful endodontics FKG REF. - 99.7AA.50.04B.AN - 06/2010 BioRaCe kit 1 Educational CD 1 Endo Stand
BioRace NiTi system: biologically desirable apical sizes safely and efficiently
 BioRace NiTi system: biologically desirable apical sizes safely and efficiently Dr Martin Trope and Dr Gilberto Debelian explore the BioRace NiTi system, designed to achieve an apical preparation that
BioRace NiTi system: biologically desirable apical sizes safely and efficiently Dr Martin Trope and Dr Gilberto Debelian explore the BioRace NiTi system, designed to achieve an apical preparation that
original article Keywords: Sodium hypochlorite. Chlorhexidine. Calcium hydroxide. Endodontic infection. Root canal medication.
 original article Efficacy of chemo-mechanical preparation with different substances and the use of a root canal medication in dog s teeth with induced periapical lesion Frederico C. Martinho, DDS, MSc
original article Efficacy of chemo-mechanical preparation with different substances and the use of a root canal medication in dog s teeth with induced periapical lesion Frederico C. Martinho, DDS, MSc
Endodontic treatment with MTA apical plugs: a case report
 325 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 49, No. 4, 325-329, 2007 Case Report Endodontic treatment with MTA apical plugs: a case report Pari Ghaziani 1), Navid Aghasizadeh 2) and Mahshid Sheikh-Nezami 1) 1) Department
325 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 49, No. 4, 325-329, 2007 Case Report Endodontic treatment with MTA apical plugs: a case report Pari Ghaziani 1), Navid Aghasizadeh 2) and Mahshid Sheikh-Nezami 1) 1) Department
Revascularization of Immature Permanent Teeth With Apical Periodontitis: New Treatment Protocol?
 JOURNAL OF ENDODONTICS Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2004 by The American Association of Endodontists VOL. 30, NO. 4, APRIL 2004 CLINICAL RESEARCH Revascularization of Immature Permanent Teeth With Apical
JOURNAL OF ENDODONTICS Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2004 by The American Association of Endodontists VOL. 30, NO. 4, APRIL 2004 CLINICAL RESEARCH Revascularization of Immature Permanent Teeth With Apical
Removal of a fractured instrument with a new extractor: clinical cases
 Clinical Removal of a fractured instrument with a new extractor: clinical cases Dominique Martin 1 Introduction The fracture of a root canal instrument during endodontic treatment is a surgical accident
Clinical Removal of a fractured instrument with a new extractor: clinical cases Dominique Martin 1 Introduction The fracture of a root canal instrument during endodontic treatment is a surgical accident
The Treatment of Traumatic Dental Injuries
 The Recommended Guidelines of the American Association of Endodontists for The Treatment of Traumatic Dental Injuries 2013 American Association of Endodontists Revised 9/13 The Recommended Guidelines of
The Recommended Guidelines of the American Association of Endodontists for The Treatment of Traumatic Dental Injuries 2013 American Association of Endodontists Revised 9/13 The Recommended Guidelines of
Develop a specialist who is capable of correlation of basic sciences and clinical sciences, and challenge the requirements for certification.
 Course Specification Faculty : Dentistry Department : Endodontics Program Specification: Diploma Degree A-Basic Information 1-Programme Title: Diploma in Endodontics 2-Departments (s): Endodontics 4-Coordinator:
Course Specification Faculty : Dentistry Department : Endodontics Program Specification: Diploma Degree A-Basic Information 1-Programme Title: Diploma in Endodontics 2-Departments (s): Endodontics 4-Coordinator:
Endodontic treatment outcome is related to treatment expectations of the operator
 Endodontic Treatment Outcome: Survey of Oral Health Care Professionals Ilan Rotstein, DDS,* Robert Salehrabi, DDS,* and Jane L. Forrest, BSDH, MS, EdD Abstract This study assessed the opinion of oral health
Endodontic Treatment Outcome: Survey of Oral Health Care Professionals Ilan Rotstein, DDS,* Robert Salehrabi, DDS,* and Jane L. Forrest, BSDH, MS, EdD Abstract This study assessed the opinion of oral health
Endodontics. Colleagues for Excellence. Access Opening and Canal Location
 Endodontics Colleagues for Excellence Spring 2010 Access Opening and Canal Location Published for the Dental Professional Community by the American Association of Endodontists Cover artwork: Rusty Jones,
Endodontics Colleagues for Excellence Spring 2010 Access Opening and Canal Location Published for the Dental Professional Community by the American Association of Endodontists Cover artwork: Rusty Jones,
Tooth anatomy risk factors influencing root canal working length accessibility
 Int J Oral Sci (2011) 3: 135-140. www.ijos.org.cn ORIGINAL ARTICLE Tooth anatomy risk factors influencing root canal working length accessibility Lu Tang 1,2, Tuo-qi Sun 1,2, Xiao-jie Gao 1, Xue-dong Zhou
Int J Oral Sci (2011) 3: 135-140. www.ijos.org.cn ORIGINAL ARTICLE Tooth anatomy risk factors influencing root canal working length accessibility Lu Tang 1,2, Tuo-qi Sun 1,2, Xiao-jie Gao 1, Xue-dong Zhou
The main goal of endodontic therapy is to eradicate all vital and necrotic tissue, microorganisms,
 Efficacy and Safety of Various Active Irrigation Devices When Used with Either Positive or Negative Pressure: An In Vitro Study Augusto Malentacca, MD, DDS,* Umberto Uccioli, DDS, Dario Zangari, DDS,*
Efficacy and Safety of Various Active Irrigation Devices When Used with Either Positive or Negative Pressure: An In Vitro Study Augusto Malentacca, MD, DDS,* Umberto Uccioli, DDS, Dario Zangari, DDS,*
DENTAL TRAUMATIC INJURIES
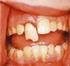 DENTAL TRAUMATIC INJURIES Nitrous Oxide Not Contraindicated Predisposing Factors > 90% of All Injuries Protrusion of Anterior Teeth Poor Lip Coverage Mouthguards Girls as Well as Boys Off - the - Shelf
DENTAL TRAUMATIC INJURIES Nitrous Oxide Not Contraindicated Predisposing Factors > 90% of All Injuries Protrusion of Anterior Teeth Poor Lip Coverage Mouthguards Girls as Well as Boys Off - the - Shelf
Non-surgical management of a large periapical lesion using a simple aspiration technique: a case report
 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2010.01719.x CASE REPORT Non-surgical management of a large periapical lesion using a simple aspiration technique: a case report M. Fernandes & I. De Ataide Goa Dental College &
doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2010.01719.x CASE REPORT Non-surgical management of a large periapical lesion using a simple aspiration technique: a case report M. Fernandes & I. De Ataide Goa Dental College &
Review of ultrasonic irrigation in endodontics: increasing action of irrigating solutions
 Journal section: Endodontics Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.17621 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.17621 Review of ultrasonic irrigation in endodontics: increasing action of irrigating
Journal section: Endodontics Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.17621 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.17621 Review of ultrasonic irrigation in endodontics: increasing action of irrigating
Eliminating effect of Er, Cr: YSGG laser irradiation on the smear layer of dentin
 Eliminating effect of Er, Cr: YSGG laser irradiation on the smear layer of dentin Jingtao Yu, MD, DDS, and Lu Yan, MD, DDS College of Stomatology, China Medical University, Shenyang, P. R. China Purpose:
Eliminating effect of Er, Cr: YSGG laser irradiation on the smear layer of dentin Jingtao Yu, MD, DDS, and Lu Yan, MD, DDS College of Stomatology, China Medical University, Shenyang, P. R. China Purpose:
Case Report(s): Uncomplicated Crown Fractures
 Case Report(s): Uncomplicated Crown Fractures Tooth fractures can be classified as follows: Uncomplicated crown fracture = fracture limited to the crown of the tooth with dentin exposure but no pulp exposure.
Case Report(s): Uncomplicated Crown Fractures Tooth fractures can be classified as follows: Uncomplicated crown fracture = fracture limited to the crown of the tooth with dentin exposure but no pulp exposure.
Introduction. Abstract
 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01108.x The influence of volume, type of irrigant and flushing method on removing artificially placed dentine debris from the apical root canal during passive ultrasonic irrigation
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01108.x The influence of volume, type of irrigant and flushing method on removing artificially placed dentine debris from the apical root canal during passive ultrasonic irrigation
Endodontics Colleagues for Excellence
 Endodontics Colleagues for Excellence Summer 2007 Treatment Planning: Comparing the Restored Endodontic Tooth and the Dental Implant Published for the Dental Professional Community by the American Association
Endodontics Colleagues for Excellence Summer 2007 Treatment Planning: Comparing the Restored Endodontic Tooth and the Dental Implant Published for the Dental Professional Community by the American Association
Quality guidelines for endodontic treatment: consensus report of the European Society of Endodontology
 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01180.x QUALITY GUIDELINES Quality guidelines for endodontic treatment: consensus report of the European Society of Endodontology Abstract. Quality guidelines for endodontic
doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01180.x QUALITY GUIDELINES Quality guidelines for endodontic treatment: consensus report of the European Society of Endodontology Abstract. Quality guidelines for endodontic
ENDODONTICS. Colleagues for Excellence. The Standard of Practice in Contemporary Endodontics. www.aae.org/colleagues
 ENDODONTICS Colleagues for Excellence Fall 2014 The Standard of Practice in Contemporary Endodontics Published for the Dental Professional Community by the American Association of Endodontists and the
ENDODONTICS Colleagues for Excellence Fall 2014 The Standard of Practice in Contemporary Endodontics Published for the Dental Professional Community by the American Association of Endodontists and the
The persistence of different calcium hydroxide paste medications in root canals: an SEM study
 original article The persistence of different calcium hydroxide paste medications in root canals: an SEM study Hélio Katsuya Onoda, DDS 1 Gerson Hiroshi Yoshinari, MSc, PhD 2 Key Fabiano Souza Pereira,
original article The persistence of different calcium hydroxide paste medications in root canals: an SEM study Hélio Katsuya Onoda, DDS 1 Gerson Hiroshi Yoshinari, MSc, PhD 2 Key Fabiano Souza Pereira,
Jamia Millia Islamia: Performa for CV of Faculty/ Staff Members
 Curriculum Vitae Brief Profile: 1-2 paragraphs (not exceeding 500 words) 1. Name: Vivek Aggarwal 2. Designation: Assistant Professor 3. Office Address: Department of Conservative Dentistry & Endodontics,
Curriculum Vitae Brief Profile: 1-2 paragraphs (not exceeding 500 words) 1. Name: Vivek Aggarwal 2. Designation: Assistant Professor 3. Office Address: Department of Conservative Dentistry & Endodontics,
The use of confocal laser scanning microscopy for the study of dentin infection
 The use of confocal laser scanning microscopy for the study of dentin infection R. Ordinola-Zapata 1, C. Monteiro Bramante 1, I. Gomes de Moraes 1, N. Bernardineli 1, V. Carvalho Porto 2, AP. Campanelli
The use of confocal laser scanning microscopy for the study of dentin infection R. Ordinola-Zapata 1, C. Monteiro Bramante 1, I. Gomes de Moraes 1, N. Bernardineli 1, V. Carvalho Porto 2, AP. Campanelli
Nature of Injury. Consequences of Trauma. Repair versus Regeneration. Repair versus Regeneration. Repair versus Regeneration
 Consequences of Trauma Nature of trauma Separation injury Crushing injury Early wound healing Late wound healing Nature of Injury Wound healing Control of hemmorage Establish line of defense against infection
Consequences of Trauma Nature of trauma Separation injury Crushing injury Early wound healing Late wound healing Nature of Injury Wound healing Control of hemmorage Establish line of defense against infection
Management of Avulsed Permanent Teeth
 Management of Avulsed Permanent Teeth Dr. Zuhair Al-Khatib Traumatic injuries to the teeth are so common among any community; trauma to the face especially to the oral region occurs frequently and comprises
Management of Avulsed Permanent Teeth Dr. Zuhair Al-Khatib Traumatic injuries to the teeth are so common among any community; trauma to the face especially to the oral region occurs frequently and comprises
Location of the apical foramen and its relationship with foraminal file size
 original article Location of the apical foramen and its relationship with foraminal file size Ronaldo Araújo Souza, DDS, MSc, PhD 1 José Antônio Poli de Figueiredo, DDS, MSc, PhD 2 Suely Colombo, DDS 1
original article Location of the apical foramen and its relationship with foraminal file size Ronaldo Araújo Souza, DDS, MSc, PhD 1 José Antônio Poli de Figueiredo, DDS, MSc, PhD 2 Suely Colombo, DDS 1
INTRAOSSEOUS ANESTHESIA
 ENDODONTICS: Colleagues for Excellence Winter 2009 Bonus Material F INTRAOSSEOUS ANESTHESIA Intraosseous Anesthesia With the Stabident and X Tip Systems The intraosseous injection allows placement of a
ENDODONTICS: Colleagues for Excellence Winter 2009 Bonus Material F INTRAOSSEOUS ANESTHESIA Intraosseous Anesthesia With the Stabident and X Tip Systems The intraosseous injection allows placement of a
Pain Management for the Periodontal Patient
 Pain Management for the Periodontal Patient Pain Control During Periodontal Treatment Methods of Pain Management General Anesthesia Nitrous Oxide Sedation Local Anesthesia Topical Anesthesia Selection
Pain Management for the Periodontal Patient Pain Control During Periodontal Treatment Methods of Pain Management General Anesthesia Nitrous Oxide Sedation Local Anesthesia Topical Anesthesia Selection
endodontic therapy combined to photo-disinfection on patients with periapical lesion. A 6-month follows up.
 Antimicrobial comparison on effectiveness of endodontic therapy and endodontic therapy combined to photo-disinfection on patients with periapical lesion. A 6-month follows up. Aguinaldo S Garcez a, Silvia
Antimicrobial comparison on effectiveness of endodontic therapy and endodontic therapy combined to photo-disinfection on patients with periapical lesion. A 6-month follows up. Aguinaldo S Garcez a, Silvia
Relationship between sealing ability of Activ GP and Gutta Flow and methods of calcium hydroxide removal
 Original Article Relationship between sealing ability of Activ GP and Gutta Flow and methods of calcium hydroxide removal Vineeta Nikhil, Vijay Singh 1, Simranjeet Singh 2 Department of Conservative Dentistry
Original Article Relationship between sealing ability of Activ GP and Gutta Flow and methods of calcium hydroxide removal Vineeta Nikhil, Vijay Singh 1, Simranjeet Singh 2 Department of Conservative Dentistry
STERILIZATION د STERILIZATION
 STERILIZATION. د STERILIZATION Is a term referring to any process that eliminates (removes) or kills all forms of microbial life, including transmissible agents (such as fungi, bacteria, viruses, spores
STERILIZATION. د STERILIZATION Is a term referring to any process that eliminates (removes) or kills all forms of microbial life, including transmissible agents (such as fungi, bacteria, viruses, spores
The WaveOne single-file reciprocating system
 I clinical technique _ WaveOne The WaveOne single-file reciprocating system Authors_ Dr Julian Webber, UK; Drs Pierre Machtou & Wilhelm Pertot, France; Drs Sergio Kuttler, Clifford Ruddle & John West,
I clinical technique _ WaveOne The WaveOne single-file reciprocating system Authors_ Dr Julian Webber, UK; Drs Pierre Machtou & Wilhelm Pertot, France; Drs Sergio Kuttler, Clifford Ruddle & John West,
The present study reports on the application of silver anode in root canals for disinfection of
 Murat AYDIN *, The antibacterial effect of silver anode in root canals Oral Microbiol Immunol Abstract The present study reports on the application of silver anode in root canals for disinfection of infected
Murat AYDIN *, The antibacterial effect of silver anode in root canals Oral Microbiol Immunol Abstract The present study reports on the application of silver anode in root canals for disinfection of infected
Friday 29 th April 2016
 8.00 9.00 Registration and coffee/bread 9.00 9.45 1. Status of Dental Traumatology worldwide. Is prevention realistic? Lars Andersson Presently almost all countries have published data on the dental trauma
8.00 9.00 Registration and coffee/bread 9.00 9.45 1. Status of Dental Traumatology worldwide. Is prevention realistic? Lars Andersson Presently almost all countries have published data on the dental trauma
ULTRASONIC and SONIC INSTRUMENTATION FALL SEMESTER 2012
 ULTRASONIC and SONIC INSTRUMENTATION FALL SEMESTER 2012 PRINICPLES OF POWER- DRIVEN INSTRUMENTATION Ultrasonic/sonic and hand instrumentation are both utilized in initial and supportive periodontal therapy
ULTRASONIC and SONIC INSTRUMENTATION FALL SEMESTER 2012 PRINICPLES OF POWER- DRIVEN INSTRUMENTATION Ultrasonic/sonic and hand instrumentation are both utilized in initial and supportive periodontal therapy
MEDICAID DENTAL PROGRAMS CODING, POLICY AND RELATED FEE REVISION INFORMATION
 MEDICAID DENTAL PROGRAMS CODING, POLICY AND RELATED FEE REVISION INFORMATION Effective for dates of service on and after November 1, 2005, the following dental coding, policy and related fee revisions
MEDICAID DENTAL PROGRAMS CODING, POLICY AND RELATED FEE REVISION INFORMATION Effective for dates of service on and after November 1, 2005, the following dental coding, policy and related fee revisions
Review: the use of sodium hypochlorite in endodontics potential complications and their management
 IN BRIEF Sodium hypochlorite is a commonly used irrigant in endodontic practice. It has many potential complications ranging from permanent bleaching of clothes to severe soft tissue damage. The complications
IN BRIEF Sodium hypochlorite is a commonly used irrigant in endodontic practice. It has many potential complications ranging from permanent bleaching of clothes to severe soft tissue damage. The complications
(a) The performance of intraoral tasks by dental hygienists or assistants shall be under the direct supervision of the employer-dentist;
 5-1-8. Expanded duties of dental hygienists and dental assistants. 8.1. General. Licensed dentists may assign to their employed dental hygienists or assistants intraoral tasks as set out in this section
5-1-8. Expanded duties of dental hygienists and dental assistants. 8.1. General. Licensed dentists may assign to their employed dental hygienists or assistants intraoral tasks as set out in this section
4-1-2005. Dental Clinical Criteria and Documentation Requirements
 4-1-2005 Dental Clinical Criteria and Documentation Requirements Table of Contents Dental Clinical Criteria Cast Restorations and Veneer Procedures... Pages 1-3 Crown Repair... Page 3 Endodontic Procedures...
4-1-2005 Dental Clinical Criteria and Documentation Requirements Table of Contents Dental Clinical Criteria Cast Restorations and Veneer Procedures... Pages 1-3 Crown Repair... Page 3 Endodontic Procedures...
Postendodontic Tooth Restoration - Part I: The Aim and the Plan of. the procedure.
 Postendodontic Tooth Restoration - Part I: The Aim and the Plan of the Procedure Sanja egoviê 1 Nada GaliÊ 1 Ana Davanzo 2 Boæidar PaveliÊ 1 1 Department of Dental Pathology School of Dental Medicine University
Postendodontic Tooth Restoration - Part I: The Aim and the Plan of the Procedure Sanja egoviê 1 Nada GaliÊ 1 Ana Davanzo 2 Boæidar PaveliÊ 1 1 Department of Dental Pathology School of Dental Medicine University
Hypochlorite-induced severe cellulitis during endodontic treatment: case report
 ISSN: Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2014 Apr-Jun;11(2):199-203 Case Report Article Hypochlorite-induced severe cellulitis during endodontic treatment: case report Bernardo Almeida Aguiar 1 Fábio
ISSN: Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2014 Apr-Jun;11(2):199-203 Case Report Article Hypochlorite-induced severe cellulitis during endodontic treatment: case report Bernardo Almeida Aguiar 1 Fábio
Complications Associated with Tooth Extraction
 1 Complications Associated with Tooth Extraction Mark M. Smith, VMD, DACVS, DAVDC Center for Veterinary Dentistry and Oral Surgery 9041 Gaither Road Gaithersburg, MD 20877 Introduction Tooth extraction
1 Complications Associated with Tooth Extraction Mark M. Smith, VMD, DACVS, DAVDC Center for Veterinary Dentistry and Oral Surgery 9041 Gaither Road Gaithersburg, MD 20877 Introduction Tooth extraction
Tissue Dissolution by Sodium Hypochlorite: Effect of Concentration, Temperature, Agitation, and Surfactant
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 Tissue Dissolution by Sodium Hypochlorite:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 Tissue Dissolution by Sodium Hypochlorite:
Dental implants or Endodontic Therapy: A review of factors affecting treatment planning
 TECHNOLOGY Dental implants or Endodontic Therapy: A review of factors Ankit Sharma, S Anil Kumar, M Venugopalan Nair* Department of Prosthodontics, Government Dental College, Kottayam, Kerala * Noor- Ul
TECHNOLOGY Dental implants or Endodontic Therapy: A review of factors Ankit Sharma, S Anil Kumar, M Venugopalan Nair* Department of Prosthodontics, Government Dental College, Kottayam, Kerala * Noor- Ul
Dental-based Injuries
 Dental-based Injuries LUXATIONS CROWN FRACTURE CROWN/ROOT FRACTURE ROOT FRACTURE ALVEOLAR BONE FRACTURE AVULSIONS LUXATIONS The tooth is loose, now what? 1. Concussive-not loose or displaced, but tender
Dental-based Injuries LUXATIONS CROWN FRACTURE CROWN/ROOT FRACTURE ROOT FRACTURE ALVEOLAR BONE FRACTURE AVULSIONS LUXATIONS The tooth is loose, now what? 1. Concussive-not loose or displaced, but tender
C. Research Proposal 1. Introduction and Specific Aims of the Project 2. Previous Work and Background of the Project
 C. Research Proposal 1. Introduction and Specific Aims of the Project Endodontic success relies on thorough chemomechanical preparation of the root canal system (1-3). Adequate canal debridement is necessary
C. Research Proposal 1. Introduction and Specific Aims of the Project Endodontic success relies on thorough chemomechanical preparation of the root canal system (1-3). Adequate canal debridement is necessary
Protocol for Disinfection of Cell Culture and Tissue Culture in Media:
 Protocol for Disinfection of Cell Culture and Tissue Culture in Media: Location: Hickory Hall 001 Director: Dr. Guido Verbeck DECONTAMINATION OF CELL CULTURE WASTE Cell culture has become a common laboratory
Protocol for Disinfection of Cell Culture and Tissue Culture in Media: Location: Hickory Hall 001 Director: Dr. Guido Verbeck DECONTAMINATION OF CELL CULTURE WASTE Cell culture has become a common laboratory
C HAPTER 4 O RAL AND M AXILLOFACIAL S URGERY
 C HAPTER 4 O RAL AND M AXILLOFACIAL S URGERY I. TREATMENT PLANNING GUIDELINES As part of informed consent, the clinician should carefully explain the risks and benefits of oral and maxillofacial surgery
C HAPTER 4 O RAL AND M AXILLOFACIAL S URGERY I. TREATMENT PLANNING GUIDELINES As part of informed consent, the clinician should carefully explain the risks and benefits of oral and maxillofacial surgery
ULTRASONIC TREATMENT ENDODONTICE
 ULTRASONIC TREATMENT ENDODONTICE Prof.Dr.Eng.Gheorghe AMZA, Dr. Eng. Oana Elena AMZA, Dr.Eng.Zoia APOSTOLESCU Department of Materials Technology and Welding - University Politehnica of Bucharest Abstract:
ULTRASONIC TREATMENT ENDODONTICE Prof.Dr.Eng.Gheorghe AMZA, Dr. Eng. Oana Elena AMZA, Dr.Eng.Zoia APOSTOLESCU Department of Materials Technology and Welding - University Politehnica of Bucharest Abstract:
Persistent infection in root-filled tooth: an SEM morphological analysis after apical microsurgery
 ISSN: Printed version: 1806-7727 Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2012 Oct-Dec;9(4):463-7 Case Report Article Persistent infection in root-filled tooth: an SEM morphological analysis after apical microsurgery
ISSN: Printed version: 1806-7727 Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2012 Oct-Dec;9(4):463-7 Case Report Article Persistent infection in root-filled tooth: an SEM morphological analysis after apical microsurgery
Oftentimes, as implant surgeons, we are
 CLINICAL AVOIDING INJURY TO THE INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE BY ROUTINE USE OF INTRAOPERATIVE RADIOGRAPHS DURING IMPLANT PLACEMENT Jeffrey Burstein, DDS, MD; Chris Mastin, DMD; Bach Le, DDS, MD Injury to the
CLINICAL AVOIDING INJURY TO THE INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE BY ROUTINE USE OF INTRAOPERATIVE RADIOGRAPHS DURING IMPLANT PLACEMENT Jeffrey Burstein, DDS, MD; Chris Mastin, DMD; Bach Le, DDS, MD Injury to the
Treatment of traumatically intruded permanent incisor teeth in children. BSPD reviewed guidelines
 Treatment of traumatically intruded permanent incisor teeth in children. BSPD reviewed guidelines Albadri S, Zaitoun H, Kinirons MJ Introduction Traumatic intrusion is a luxation injury where the tooth
Treatment of traumatically intruded permanent incisor teeth in children. BSPD reviewed guidelines Albadri S, Zaitoun H, Kinirons MJ Introduction Traumatic intrusion is a luxation injury where the tooth
PACUC Guidelines. Rodent Survival Surgery
 PACUC Guidelines Rodent Survival Surgery Guidelines for rodent survival surgery are based on the National Research Council Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals 8 th edition and the Animal Welfare
PACUC Guidelines Rodent Survival Surgery Guidelines for rodent survival surgery are based on the National Research Council Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals 8 th edition and the Animal Welfare
Removal of a silver cone by using clinical microscope and ultrasound: Case report
 original article Removal of a silver cone by using clinical microscope and ultrasound: Case report Maíra do Prado 1 Marcos Cesar Pimenta de Araújo 2 Heloísa Carla Gusman 3 abstract Introduction: The retreatment
original article Removal of a silver cone by using clinical microscope and ultrasound: Case report Maíra do Prado 1 Marcos Cesar Pimenta de Araújo 2 Heloísa Carla Gusman 3 abstract Introduction: The retreatment
Strong bone for beautiful teeth Patient Information I Bone reconstruction with Geistlich Bio-Oss and Geistlich Bio-Gide
 Strong bone for beautiful teeth Patient Information I Bone reconstruction with Geistlich Bio-Oss and Geistlich Bio-Gide Contents Smiling is the most beautiful way to show your teeth 3 What are the causes
Strong bone for beautiful teeth Patient Information I Bone reconstruction with Geistlich Bio-Oss and Geistlich Bio-Gide Contents Smiling is the most beautiful way to show your teeth 3 What are the causes
Contributions regarding FEM for an ultrasonic endodontic device and his appliance in the root canal treatments
 Contributions regarding FEM for an ultrasonic endodontic device and his appliance in the root canal treatments GHEORGHE AMZA, ROXANA YOLANDA ONEA, OANA ELENA AMZA, VICTOR CARP Department of Materials Technology
Contributions regarding FEM for an ultrasonic endodontic device and his appliance in the root canal treatments GHEORGHE AMZA, ROXANA YOLANDA ONEA, OANA ELENA AMZA, VICTOR CARP Department of Materials Technology
Svea Baumgarten, Dr. med. dent., M Sc, accredited implantologist as per the criteria of the DGZI (German Association of Dental Implantology) 1
 The use of ozone in dentistry a case study Svea Baumgarten, Dr. med. dent., M Sc, accredited implantologist as per the criteria of the DGZI (German Association of Dental Implantology) 1 Ozone gas is a
The use of ozone in dentistry a case study Svea Baumgarten, Dr. med. dent., M Sc, accredited implantologist as per the criteria of the DGZI (German Association of Dental Implantology) 1 Ozone gas is a
Root canal cleaning and disinfection during chemomechanical preparation relies
 Antagonistic Interactions between Sodium Hypochlorite, Chlorhexidine, EDTA, and Citric Acid Giampiero Rossi-Fedele, DDS, MClinDent,* Esma J. Dogramacı, BDS, MFDS (RCS Eng), Andrea R. Guastalli, PhD, Liviu
Antagonistic Interactions between Sodium Hypochlorite, Chlorhexidine, EDTA, and Citric Acid Giampiero Rossi-Fedele, DDS, MClinDent,* Esma J. Dogramacı, BDS, MFDS (RCS Eng), Andrea R. Guastalli, PhD, Liviu
JMSCR Volume 03 Issue 05 Page 5590-5594 May 2015
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Nanoparticles in Irrigation and Disinfection of the Root Canal System A Review Authors Rucheet Purba 1, Snehal Sonarkar 2, Vidya Mokhade
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Nanoparticles in Irrigation and Disinfection of the Root Canal System A Review Authors Rucheet Purba 1, Snehal Sonarkar 2, Vidya Mokhade
Comparison of Heart Rate and Blood Pressure administration of anesthesia agent with and without
 ISSN: 2347-3215 Volume 2 Number 9 (September-2014) pp. 153-158 www.ijcrar.com Comparison of Heart Rate and Blood Pressure administration of anesthesia agent with and without Mohammad Ali Ghavimi 1*, Javad
ISSN: 2347-3215 Volume 2 Number 9 (September-2014) pp. 153-158 www.ijcrar.com Comparison of Heart Rate and Blood Pressure administration of anesthesia agent with and without Mohammad Ali Ghavimi 1*, Javad
DENTAL TRAUMA GUIDELINES
 International Association of Dental Traumatology DENTAL TRAUMA GUIDELINES Revised 2012 CONTENT: Section 1. Fractures and luxations of permanent teeth Section 2. Avulsion of permanent teeth Section 3. Traumatic
International Association of Dental Traumatology DENTAL TRAUMA GUIDELINES Revised 2012 CONTENT: Section 1. Fractures and luxations of permanent teeth Section 2. Avulsion of permanent teeth Section 3. Traumatic
CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF THE AVULSED TOOTH: PRESENT STRATEGIES and FUTURE DIRECTIONS
 Dental Traumatology 2002: 18: 1 11 Copyright C Munksgaard 2002 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved DENTAL TRAUMATOLOGY ISSN 1600-4469 Editor s note After a year at the helm of Dental Traumatology I
Dental Traumatology 2002: 18: 1 11 Copyright C Munksgaard 2002 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved DENTAL TRAUMATOLOGY ISSN 1600-4469 Editor s note After a year at the helm of Dental Traumatology I
Replantation of Avulsed Permanent Anterior Teeth: A Case Report.
 RESEARCH AND REVIEWS: JOURNAL OF DENTAL SCIENCES Replantation of Avulsed Permanent Anterior Teeth: A Case Report. Abu-Hussein Muhamad 1 *, Watted Nezar 2, and Abdulgani Azzaldeen 3. 1 Department of Pediatric
RESEARCH AND REVIEWS: JOURNAL OF DENTAL SCIENCES Replantation of Avulsed Permanent Anterior Teeth: A Case Report. Abu-Hussein Muhamad 1 *, Watted Nezar 2, and Abdulgani Azzaldeen 3. 1 Department of Pediatric
Histologic comparison of biologic width around teeth versus implants: The effect on bone preservation
 Clinical Histologic comparison of biologic width around teeth versus implants: The effect on bone preservation Kazuto Makigusa 1 Abstract Histological analysis of the biological width surrounding primate
Clinical Histologic comparison of biologic width around teeth versus implants: The effect on bone preservation Kazuto Makigusa 1 Abstract Histological analysis of the biological width surrounding primate
WMI Mutual Insurance Company
 Dental Policy WMI Mutual Insurance Company PO Box 572450 Salt Lake City, UT 84157 (801) 263-8000 & (800) 748-5340 Fax: (801) 263-1247 DENTAL POLICY A. Schedule of Benefits: Annual Maximum Dental Benefit
Dental Policy WMI Mutual Insurance Company PO Box 572450 Salt Lake City, UT 84157 (801) 263-8000 & (800) 748-5340 Fax: (801) 263-1247 DENTAL POLICY A. Schedule of Benefits: Annual Maximum Dental Benefit
Factors Affecting the Long-term Results of Endodontic Treatment
 0099-2399/90/1610-0498/$02.00/0 JOURNAL OF ENDODONTICS Copyright 9 1990 by The American Association of Endodontists Printed in U.S.A. VOL. 16, NO. 10, OCTOBER 1990 Factors Affecting the Long-term Results
0099-2399/90/1610-0498/$02.00/0 JOURNAL OF ENDODONTICS Copyright 9 1990 by The American Association of Endodontists Printed in U.S.A. VOL. 16, NO. 10, OCTOBER 1990 Factors Affecting the Long-term Results
ELECTRONIC METHODS IN THE DENTISTRY
 ELECTRONIC METHODS IN THE DENTISTRY THERAPY SET SCORPION DENTAL OPTIMA model 405-7A th 7 SERIES DENTAL THERAPY SET SCORPION DENTAL OPTIMA model 405-7A THE SET INCLUDES THE FOLLOWING DEVICSES FOR: Apex
ELECTRONIC METHODS IN THE DENTISTRY THERAPY SET SCORPION DENTAL OPTIMA model 405-7A th 7 SERIES DENTAL THERAPY SET SCORPION DENTAL OPTIMA model 405-7A THE SET INCLUDES THE FOLLOWING DEVICSES FOR: Apex
The Benefits of Using Arap Locator in Root Canal Treatment
 UNSURPASSED ACCURACY UNRIVALED RELIABILITY 1 1. Data on file. Unsurpassed accuracy 1 with convenient, easy-to-read display Fully automatic multifrequency measurements Compact design with small footprint
UNSURPASSED ACCURACY UNRIVALED RELIABILITY 1 1. Data on file. Unsurpassed accuracy 1 with convenient, easy-to-read display Fully automatic multifrequency measurements Compact design with small footprint
Sore throat. Infection. Fungi: Viruses: Bacteria:
 Sore throat Infection Infection is an illness that is caused by germs or micro-organisms (tiny organisms) that invade the body. Micro-organisms include the like of viruses, bacteria and fungi.1 Bacteria:
Sore throat Infection Infection is an illness that is caused by germs or micro-organisms (tiny organisms) that invade the body. Micro-organisms include the like of viruses, bacteria and fungi.1 Bacteria:
CHLORHEXIDINE AS AN ADJUVANT IN ULTRASOUND SCALING
 Vol. 6, No. 3, July - September 14 CHLORHEXIDINE AS AN ADJUVANT IN ULTRASOUND SCALING Cristian Marin*, Vlad Popescu, Radu Costea Carol Davila" University of Medicine and Pharmacy - Bucharest, Romania,
Vol. 6, No. 3, July - September 14 CHLORHEXIDINE AS AN ADJUVANT IN ULTRASOUND SCALING Cristian Marin*, Vlad Popescu, Radu Costea Carol Davila" University of Medicine and Pharmacy - Bucharest, Romania,
Use of an Er:YAG Laser for Pulpotomies in Vital and Nonvital Primary Teeth Lawrence Kotlow, DDS, Albany, New York
 Use of an Er:YAG Laser for Pulpotomies in Vital and Nonvital Primary Teeth Lawrence, DDS, Albany, New York J Laser Dent 2008;16(2):75-79 SYNOPSIS A protocol for performing a primary tooth pulpotomy utilizing
Use of an Er:YAG Laser for Pulpotomies in Vital and Nonvital Primary Teeth Lawrence, DDS, Albany, New York J Laser Dent 2008;16(2):75-79 SYNOPSIS A protocol for performing a primary tooth pulpotomy utilizing
ORTHODONTIC TREATMENT
 ORTHODONTIC TREATMENT Informed Consent for the Orthodontic Patient As a general rule, positive orthodontic results can be achieved by informed and cooperative patients. Thus, the following information
ORTHODONTIC TREATMENT Informed Consent for the Orthodontic Patient As a general rule, positive orthodontic results can be achieved by informed and cooperative patients. Thus, the following information
Immediate Molar Implant Placement: A Private Practice Clinical Investigation. Abstract
 Immediate Molar Implant Placement: A Private Practice Clinical Investigation Gargiulo et al Alphonse Gargiulo, DDS, MS 1 Thomas Manos, DDS, MS 2 Mark Kolozenski, DDS, MS 3 Alex Tzanos, DDS, MSD 3 Michael
Immediate Molar Implant Placement: A Private Practice Clinical Investigation Gargiulo et al Alphonse Gargiulo, DDS, MS 1 Thomas Manos, DDS, MS 2 Mark Kolozenski, DDS, MS 3 Alex Tzanos, DDS, MSD 3 Michael
Semester I Dental Anatomy (Basic Orofacial Anatomy)
 Dental Assisting Curriculum Example The dentalcare.com CE library offers over 150 courses that can be used in conjunction with your dental assisting curriculum. The guide below recommends courses to assign,
Dental Assisting Curriculum Example The dentalcare.com CE library offers over 150 courses that can be used in conjunction with your dental assisting curriculum. The guide below recommends courses to assign,
RomiApex A-15. APEX LOCATOR User Manual
 RomiApex A-15 APEX LOCATOR User Manual Table of Contents Introduction..... 2 1. Indications for use... 3 2. Precautions..... 3 3. Adverse Reactions...... 3 4. Package Contents........ 3 5. Getting Started.....
RomiApex A-15 APEX LOCATOR User Manual Table of Contents Introduction..... 2 1. Indications for use... 3 2. Precautions..... 3 3. Adverse Reactions...... 3 4. Package Contents........ 3 5. Getting Started.....
Guide to Claims Submission and Payment
 Guide to Claims Submission and Payment The key to prompt and correct payment of dental benefit claims is filing complete and accurate claims forms. The following are tips to help that process run efficiently
Guide to Claims Submission and Payment The key to prompt and correct payment of dental benefit claims is filing complete and accurate claims forms. The following are tips to help that process run efficiently
Titanium versus Zirconium Implants
 Titanium versus Zirconium Implants A dental materials comparison Dr. Gerald Regni, DMD!!" Christian St. Phila. PA 1213" T: (""") %&'-!"#" E: Dr.Gerald_Regni@yahoo.com Titanium versus Zirconium Implants
Titanium versus Zirconium Implants A dental materials comparison Dr. Gerald Regni, DMD!!" Christian St. Phila. PA 1213" T: (""") %&'-!"#" E: Dr.Gerald_Regni@yahoo.com Titanium versus Zirconium Implants
DENTAL CLINIC. Policy and Procedure Oral Health Records Management. Responsible Party: Director of Dental Support Services
 Responsible Party: Director of Dental Support Services Policy: The oral health record is one of the most important documents in dental clinic. It must be accurately and concisely completed. In order to
Responsible Party: Director of Dental Support Services Policy: The oral health record is one of the most important documents in dental clinic. It must be accurately and concisely completed. In order to
Nu G Medical Waste System Technology (Pyrolysis / Thermal Decomposition)
 Product Description: Nu G Medical Waste System Technology (Pyrolysis / Thermal Decomposition) The NU G System uses pyrolysis thermal decomposition to treat infectious wastes typically generated in hospitals.
Product Description: Nu G Medical Waste System Technology (Pyrolysis / Thermal Decomposition) The NU G System uses pyrolysis thermal decomposition to treat infectious wastes typically generated in hospitals.
Guidelines for the management of traumatic dental injuries. II. Avulsion of permanent teeth
 Dental Traumatology 2007; doi: 10.1111/j.1600-9657.2007.00605.x DENTAL TRAUMATOLOGY Guidelines Guidelines for the management of traumatic dental injuries. II. Avulsion of permanent teeth Flores MT, Andersson
Dental Traumatology 2007; doi: 10.1111/j.1600-9657.2007.00605.x DENTAL TRAUMATOLOGY Guidelines Guidelines for the management of traumatic dental injuries. II. Avulsion of permanent teeth Flores MT, Andersson
CAMBRA is minimally invasive dentistry
 CAMBRA is minimally invasive dentistry CAMBRA stands for "CAries Management By Risk Assessment" and should be your standard for treating patients. In simple terms, here's why. By Drs. Douglas A. Young,
CAMBRA is minimally invasive dentistry CAMBRA stands for "CAries Management By Risk Assessment" and should be your standard for treating patients. In simple terms, here's why. By Drs. Douglas A. Young,
Ohio State Dental Board Permissible Duties of Dental Hygienists and Dental Assistants
 Ohio State Dental Board Permissible Duties of Dental Hygienists and Dental Assistants Pursuant to Ohio Administrative Code Section 4715-3-01 (C) which defines the following dental personnel as: Licensed
Ohio State Dental Board Permissible Duties of Dental Hygienists and Dental Assistants Pursuant to Ohio Administrative Code Section 4715-3-01 (C) which defines the following dental personnel as: Licensed
DENTAL ASSISTING CATEGORIES
 DENTAL ASSISTING CATEGORIES EFFECTIVE JANUARY 1, 2010 Starting January 1, 2010, the dental assisting scope of practice will include new duties and two new specialty permits in orthodontics and dental sedation
DENTAL ASSISTING CATEGORIES EFFECTIVE JANUARY 1, 2010 Starting January 1, 2010, the dental assisting scope of practice will include new duties and two new specialty permits in orthodontics and dental sedation
Root Canal Retreatment: 2. Practical Solutions T.R. PITT FORD AND J.S. RHODES
 E N D O D O N T I CE SN D O D O N T I C S Root Canal Retreatment: 2. Practical Solutions T.R. PITT FORD AND J.S. RHODES Abstract: Root canal retreatment is often the preferred method of treating a tooth
E N D O D O N T I CE SN D O D O N T I C S Root Canal Retreatment: 2. Practical Solutions T.R. PITT FORD AND J.S. RHODES Abstract: Root canal retreatment is often the preferred method of treating a tooth
STERILIZATION AND DISINFECTION
 STERILIZATION AND DISINFECTION Importance of hand washing shown by Semmelweis STERILIZATION A physical or chemical process that destroys or eliminates all forms of microbial life, including spores. A satisfactory
STERILIZATION AND DISINFECTION Importance of hand washing shown by Semmelweis STERILIZATION A physical or chemical process that destroys or eliminates all forms of microbial life, including spores. A satisfactory
Decontamination and Waste Management www.biosecurity.sandia.gov
 Decontamination and Waste Management www.biosecurity.sandia.gov SAND No. 2006-3684C Sandia is a multiprogram laboratory operated by Sandia Corporation, a Lockheed Martin Company, for the United States
Decontamination and Waste Management www.biosecurity.sandia.gov SAND No. 2006-3684C Sandia is a multiprogram laboratory operated by Sandia Corporation, a Lockheed Martin Company, for the United States
The use of the erbium, chromium:yttriumscandium-gallium-garnet ABSTRACT
 The use of the erbium, chromium:yttriumscandium-gallium-garnet laser in endodontic treatment The results of an in vitro study Ulrich Schoop, DDS, MD; Kawe Goharkhay, DMD, MD; Johannes Klimscha, DMD, MD;
The use of the erbium, chromium:yttriumscandium-gallium-garnet laser in endodontic treatment The results of an in vitro study Ulrich Schoop, DDS, MD; Kawe Goharkhay, DMD, MD; Johannes Klimscha, DMD, MD;
Oxivir Tb and Accelerated Hydrogen Peroxide (AHP) Frequently Asked Questions
 Oxivir Tb and Accelerated Hydrogen Peroxide (AHP) Frequently Asked Questions What is Accelerated Hydrogen Peroxide (AHP)? AHP is a patented synergistic blend of commonly used, safe ingredients that when
Oxivir Tb and Accelerated Hydrogen Peroxide (AHP) Frequently Asked Questions What is Accelerated Hydrogen Peroxide (AHP)? AHP is a patented synergistic blend of commonly used, safe ingredients that when
TREATMENT REFUSAL FORMS
 TREATMENT REFUSAL FORMS These forms are intended to be used when a patient refuses the treatment. These forms help confirm that the patient is informed and aware of the risks involved with not proceeding
TREATMENT REFUSAL FORMS These forms are intended to be used when a patient refuses the treatment. These forms help confirm that the patient is informed and aware of the risks involved with not proceeding
Endo Easy Efficient Sonic Powered Endo Irrigation
 Endo Easy Efficient Sonic Powered Endo Irrigation www.vdw-dental.com Naturally fascinating: gentle, yet powerful In our goal to provide easy and safe products and systems for endodontics which fulfil
Endo Easy Efficient Sonic Powered Endo Irrigation www.vdw-dental.com Naturally fascinating: gentle, yet powerful In our goal to provide easy and safe products and systems for endodontics which fulfil
Use of ultrasound Doppler to determine tooth vitality in a discolored tooth after traumatic injury: its prospects and limitations
 Case report ISSN 2234-7658 (print) / ISSN 2234-7666 (online) http://dx.doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.1.68 Use of ultrasound Doppler to determine tooth vitality in a discolored tooth after traumatic injury:
Case report ISSN 2234-7658 (print) / ISSN 2234-7666 (online) http://dx.doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.1.68 Use of ultrasound Doppler to determine tooth vitality in a discolored tooth after traumatic injury:
IMPLANT CONSENT FORM WHAT ARE DENTAL IMPLANTS?
 IMPLANT CONSENT FORM WHAT ARE DENTAL IMPLANTS? Dental implants are a very successful and accepted treatment option to replace lost or missing teeth. A dental implant is essentially an artificial tooth
IMPLANT CONSENT FORM WHAT ARE DENTAL IMPLANTS? Dental implants are a very successful and accepted treatment option to replace lost or missing teeth. A dental implant is essentially an artificial tooth
Analysis of pulp prognosis in 603 permanent teeth with uncomplicated crown fracture with or without luxation
 Dental Traumatology 2014; doi: 10.1111/edt.12099 Analysis of pulp prognosis in 603 permanent teeth with uncomplicated crown fracture with or without luxation Chao Wang, Man Qin, Yue Guan Department of
Dental Traumatology 2014; doi: 10.1111/edt.12099 Analysis of pulp prognosis in 603 permanent teeth with uncomplicated crown fracture with or without luxation Chao Wang, Man Qin, Yue Guan Department of
Endodontic Mishaps DETECTION OF MISHAPS ENDODONTIC MISHAPS
 8 Endodontic Mishaps DETECTION OF MISHAPS Endodontic mishaps or procedural accidents are those unfortunate accidents that happen during treatment, some owing to inattention to detail, others being totally
8 Endodontic Mishaps DETECTION OF MISHAPS Endodontic mishaps or procedural accidents are those unfortunate accidents that happen during treatment, some owing to inattention to detail, others being totally
SCOPE OF PRACTICE GENERAL DENTAL COUNCIL
 www.gdc-uk.org SCOPE OF PRACTICE Effective from 30 September 2013 2 SCOPE OF PRACTICE The scope of your practice is a way of describing what you are trained and competent to do. It describes the areas
www.gdc-uk.org SCOPE OF PRACTICE Effective from 30 September 2013 2 SCOPE OF PRACTICE The scope of your practice is a way of describing what you are trained and competent to do. It describes the areas
Rebilda DC. Rebilda Post System. Rebilda
 Rebilda DC Rebilda Post System Rebilda Rebilda DC Systematic coronal build-up reconstruction Nowadays, modern composite and adhesive systems enable the reconstruction of severely damaged teeth, even if
Rebilda DC Rebilda Post System Rebilda Rebilda DC Systematic coronal build-up reconstruction Nowadays, modern composite and adhesive systems enable the reconstruction of severely damaged teeth, even if
2015 Predoctoral Directors Workshop Clinical Curriculum Audience Response System Results Participants Include 65 Predoctoral Directors
 2015 Predoctoral Directors Workshop Clinical Curriculum Audience Response System Results Participants Include 65 Predoctoral Directors 1. Q: Did you attend the Predoctoral Director Workshop 3 years ago?
2015 Predoctoral Directors Workshop Clinical Curriculum Audience Response System Results Participants Include 65 Predoctoral Directors 1. Q: Did you attend the Predoctoral Director Workshop 3 years ago?
