TITLE: Botulinum Toxin A for Headaches in Adults: A Review of Clinical-Effectiveness and Safety
|
|
|
- Scott Turner
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TITLE: Botulinum Toxin A for Headaches in Adults: A Review of Clinical-Effectiveness and Safety DATE: 28 July 2009 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES: Botulinum toxin is a neurotoxin that causes muscle paralysis by blocking the release of acetylcholine at neuromuscular junctions. 1 Although botulinum toxin subtypes A to G exist, only subtypes A and B are used in clinical practice. In Canada, botulinum toxin A (BTA) is marketed as Botox and Botox Cosmetic by Allergan Inc., 2 and as Xeomin by Merz Pharmaceuticals 3. Botox Cosmetic (Allergan Inc.) 4 and Dysport (Ipsen Biopharm Ltd) 5 are available in the United States. Approved indications include the treatment of focal spasticity, blepharospasm, strabismus, and cervical dystonia. 1 Treatment involves local intramuscular. Effects may last from several weeks to several months. 1,2 In Canada, BTA is not currently indicated for the management of headaches and governmentsponsored drug plans are receiving requests for coverage. To better guide off-label coverage decisions, information is required on the clinical benefits and harm of BTA when used for the management of headaches in adults, including chronic tension-type headache (CTTH), chronic daily headache (CDH), and cluster headache. RESEARCH QUESTIONS: What is the clinical benefit and harm of botulinum toxin A for the management of headaches in adults? METHODS: A limited literature search was conducted on key health technology assessment resources, including OVID Medline, The Cochrane Library (Issue 3, 2009), University of York Centre for Reviews and Dissemination (CRD) databases, ECRI, EuroScan, international health technology Disclaimer: The Health Technology Inquiry Service (HTIS) is an information service for those involved in planning and providing health care in Canada. HTIS responses are based on a limited literature search and are not comprehensive, systematic reviews. The intent is to provide a list of sources and a summary of the best evidence on the topic that CADTH could identify using all reasonable efforts within the time allowed. HTIS responses should be considered along with other types of information and health care considerations. The information included in this response is not intended to replace professional medical advice, nor should it be construed as a recommendation for or against the use of a particular health technology. Readers are also cautioned that a lack of good quality evidence does not necessarily mean a lack of effectiveness particularly in the case of new and emerging health technologies, for which little information can be found, but which may in future prove to be effective. While CADTH has taken care in the preparation of the report to ensure that its contents are accurate, complete and up to date, CADTH does not make any guarantee to that effect. CADTH is not liable for any loss or damages resulting from use of the information in the report. Copyright: This report contains CADTH copyright material. It may be copied and used for non-commercial purposes, provided that attribution is given to CADTH. Links: This report may contain links to other information available on the websites of third parties on the Internet. CADTH does not have control over the content of such sites. Use of third party sites is governed by the owners own terms and conditions.
2 agencies, and a focused Internet search. The search was limited to English language articles published between 2004 and July Filters were applied to limit the retrieval to health technology assessments, systematic reviews, meta-analyses, randomized controlled trials (RCTs), controlled clinical trials, and observational studies. HTIS reports are organized so that the higher quality evidence is presented first. Therefore, health technology assessment reports, systematic reviews and meta-analysis are presented first. These are followed by randomized controlled trials, controlled clinical trials, and observational studies. SUMMARY OF FINDINGS: One health technology assessment 6 (Table 1) and six systematic reviews 7-12 (Table 2) assessing BTA for the management of headaches were found. Nine RCTs and one subgroup analysis 22 were retrieved (Tables 3 and 4). Given the wealth of information, controlled clinical trials and observational studies were excluded. Health technology assessments A health technology assessment on the use of BTA for the management of primary chronic headache disorders, including migraines, chronic or episodic tension headaches, and cluster headaches, was published in 2004 (Table 1). 6 For the prophylaxis of tension headaches, the evidence (eight RCTs; n=348) was insufficient to support the use of BTA. No evidence was identified to support the use of BTA in the prevention of cluster headaches. Systematic reviews and meta-analysis Cluster headaches A systematic review (2008) on the various treatments used in cluster headaches found no evidence for the use of BTA in the prevention of cluster headaches (Table 2). 7 Chronic tension-type and chronic daily headaches A systematic review (2007) on the effects of treatments used in CTTH examined four RCTs (n=285) from a previous systematic review and a subsequent RCT (n=40), all published in or before 2004 (Table 2). 8 showed that compared to placebo, BTA may be no more effective for improving the symptoms of CTTH. Reported adverse events (AEs) included facial weakness, difficulty in swallowing, and disturbed local sensation. A systematic review (2008) published by the American Academy of Neurology evaluated the benefits and harm of BTA in the treatment of various autonomic and pain disorders, including CDH and CTTH (Table 2). 9 Based on four RCTs (total sample size not specified), there was insufficient evidence to support or refute a benefit in using BTA for the treatment of CDH. Four RCTs (total sample size not specified) indicated that BTA is ineffective and should not be considered for patients with CTTH. Transient and mild muscle weakness was the most commonly reported AE, occurring in 2.5% to 25% of patients. Two systematic reviews on the use of BTA in headache disorders were retrieved (Table 2). 10,11 The first (2008) 10 included three RCTs (n=1,117) on CDH and five RCTs (n=533) on CTTH. Findings did not support the clinical effectiveness of BTA when compared to placebo for CDH or Botulinum Toxin A for Headaches 2
3 CTTH. 10 The second systematic review (2009) 11 included three RCTs (n=1,115) on CDH and six RCTs (n=651) on CTTH. The study results did not support the use of BTA for CDH. In CTTH, the studies suggested that BTA is ineffective, regardless of injection site, dosage or injection regimen. 11 Harm The safety of BTA when used for various conditions (not limited to headaches) was examined in a systematic review (2004) that included a meta-analysis of the number and the frequency of adverse events (AEs) (Table 2). 12 Thirty-six studies with 2,309 participants, of which 1,425 received BTA (Botox ), met the inclusion criteria. There were no severe AEs reported. Mild-tomoderate AEs were reported at a rate of 24.8% (353/1,425) in the BTA group compared to 15.0% (133/884) in the control group (p<0.001). The adjusted, weighted-risk difference was 9% and the number-needed-to-harm was 11. Focal weakness was reported with significantly greater frequency in BTA-treated patients when compared with patients in the control group (p< ). There were no significant differences between groups in other AEs including pain or reaction at injection the site, headache, back pain, neck pain, or ptosis. Randomized controlled trials Chronic tension-type headaches Six randomized, placebo controlled studies were identified, of which five were double-blinded 13-16,18 and one was single-blinded 17 (Table 3). With the exception of the single-blinded study that showed a statistically significant improvement in two end-points, all studies were negative for their primary end-point. Chronic daily headaches Three randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled studies were identified (Table 4) One sub-group analysis 22 of a larger trial 20 was also retrieved. All RCTs reported negative results. The sub-group analysis showed a significant improvement in patients not taking concurrent prophylactic medications. 22 Limitations The RCTs on CTTH used different products (Botox or Dysport ), doses, and injection sites (follow the pain approach versus fixed injection sites) making comparisons difficult. With the exception of one study, 15 CTTH studies did not include enough study participants to detect a clinically important difference between the treatment and control group. CDH consists of different types of primary headaches, which may have different pathophysiological profiles. 11 A clear definition for CDH has not been established by the International Headache Society. 23 The RCTs on CDH included patients with a diagnosis of chronic migraine, CTTH, new daily persistent headache, and hemicrania continua. 20 Furthermore, a sub-group analysis 22 of patients not receiving prophylactic medications showed positive results in favor of BTA. The heterogeneous nature of the included patients may affect the results. It is possible that BTA may be effective in more homogenous groups of patients; but this has yet to be determined in RCTs. Botulinum Toxin A for Headaches 3
4 CONCLUSIONS AND IMPLICATIONS FOR DECISION OR POLICY MAKING: Compared to placebo, there is evidence that BTA is not effective in the management of CTTH or CDH. These results need to be interpreted in light of the fact that CDH includes different types of primary headaches. In addition, one RCT showed significant improvement in a subgroup of patients not receiving concurrent prophylactic medications. 22 There may be sub-groups of patients that benefit from BTA who have not yet been identified in RCTs. In CTTH, all, but one study, 15 were underpowered to detect a clinical difference. No information about the clinical effectiveness of BTA for the management of cluster headaches was found. In summary, evidence from systematic reviews and RCTs indicates that BTA may not be effective for the treatment of CTTH or CDH when compared with placebo. Furthermore, BTA may be associated with adverse effects including focal weakness. PREPARED BY: Christine Perras, B.Sc. Phm., MPH, Research Officer Michelle Clark, B.Sc., Research Assistant Jessie Cunningham, M.I.St., Information Specialist Health Technology Inquiry Service htis@cadth.ca Tel: Botulinum Toxin A for Headaches 4
5 PREFERENCES: 1. Taylor P. Agents acting at the neuromuscular junction and automomic ganglia. In: Brunton LL, editor. Goodman and Gilman's the pharmacological basis of therapeutics. 11th ed. New York (NY): McGraw-Hill; p Botox. In: e-theraputics+. [database online]. Ottawa (ON): Canadian Pharmacists Association; Available: (accessed 2009 Jul 15). 3. Xeomin. In: e-theraputics+. [database online]. Ottawa (ON): Canadian Pharmacists Association; Available: (accessed 2009 Jul 15). 4. Botox cosmetic. In: [database online]. Bethesda (MD): Food and Drug Administration; Available: gdetails (accessed 2009 Jul 15). 5. Dysport. In: [database online]. Bethesda (MD): Food and Drug Administration; Available: gdetails (accessed 2009 Jul 15). 6. Samson D. Botulinum toxin for treatment of primary chronic headache disorders. Technol Eval Cent Asses Program Exec Summ 2004;19(10): Matharu M, Silver N. Cluster headache. BMJ Clin Evid (Online) 2008;2: Available: (accessed 2009 Jul 28). 8. Krishnan A, Silver N. Headache (chronic tension-type). BMJ Clin Evid (Online) 2009;7: Available: (accessed 2009 Jul 28). 9. Naumann M, So Y, Argoff CE, Childers MK, Dykstra DD, Gronseth GS, et al. Assessment: Botulinum neurotoxin in the treatment of autonomic disorders and pain (an evidence-based review): report of the Therapeutics and Technology Assessment Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2008;70(19): Schulte-Mattler WJ, Leinisch E. Evidence based medicine on the use of botulinum toxin for headache disorders. J Neural Transm 2008;115(4): Obermann M, Diener HC. Is botulinum toxin useful in treating headache? No. Curr Treat Options Neurol 2009;11(1): Naumann M, Jankovic J. Safety of botulinum toxin type A: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Curr Med Res Opin 2004;20(7): Schulte-Mattler WJ, Krack P, BoNTTH Study Group. Treatment of chronic tension-type headache with botulinum toxin A: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled multicenter study. Pain 2004;109(1-2): Botulinum Toxin A for Headaches 5
6 14. Padberg M, de Bruijn SF, de Haan RJ, Tavy DL. Treatment of chronic tension-type headache with botulinum toxin: a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Cephalalgia 2004;24(8): Silberstein SD, Göbel H, Jensen R, Elkind AH, DeGryse R, Walcott JM, et al. Botulinum toxin type A in the prophylactic treatment of chronic tension-type headache: a multicentre, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study. Cephalalgia 2006;26(7): Straube A, Empl M, Ceballos-Baumann A, Tölle T, Stefenelli U, Pfaffenrath V, et al. Pericranial injection of botulinum toxin type A (Dysport) for tension-type headache - a multicentre, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Eur J Neurol 2008;15(3): Hamdy SM, Samir H, El-Sayed M, Adel N, Hasan R. Botulinum toxin: could it be an effective treatment for chronic tension-type headache? J Headache Pain 2009;10(1): Harden RN, Cottrill J, Gagnon CM, Smitherman TA, Weinland SR, Tann B, et al. Botulinum toxin a in the treatment of chronic tension-type headache with cervical myofascial trigger points: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study. Headache 2009;49(5): Ondo WG, Vuong KD, Derman HS. Botulinum toxin A for chronic daily headache: a randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel design study. Cephalalgia 2004;24(1): Mathew NT, Frishberg BM, Gawel M, Dimitrova R, Gibson J, Turkel C, et al. Botulinum toxin type A (BOTOX) for the prophylactic treatment of chronic daily headache: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Headache 2005;45(4): Silberstein SD, Stark SR, Lucas SM, Christie SN, Degryse RE, Turkel CC, et al. Botulinum toxin type A for the prophylactic treatment of chronic daily headache: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Mayo Clin Proc 2005;80(9): Dodick DW, Mauskop A, Elkind AH, DeGryse R, Brin MF, Silberstein SD, et al. Botulinum toxin type a for the prophylaxis of chronic daily headache: subgroup analysis of patients not receiving other prophylactic medications: a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Headache 2005;45(4): Olesen J, Bousser M, Diener H, Dodick D, First M, Goadsby PJ, et al. The international classification of headache disorders. 2nd ed. Oxford (UK): International Headache Society; Available: (accessed 2009 Jul 15). Botulinum Toxin A for Headaches 6
7 APPENDIX: Table 1: Health Technology Assessment on Botulinum Toxin A in the Management of Primary Chronic Headache Disorders Reference Search methods Samson Update to an HTA published in Medline 2002 to 2004 and handsearching. Study selection and indications RCT, DB, PC. Migraines; chronic or episodic tension-type headaches; cluster headaches. Health outcomes Headache frequency, severity and duration; disability; AEs. 4 studies from the original 2002 HTA and 4 additional studies found with new search; n= studies rated fair quality; 6 studies rated poor quality. The 2 better-rated studies did not find significant differences between placebo and BTA in the prevention of tension headaches. No information found on cluster headaches. Minor AEs include ptosis, acute headache, neck weakness, nausea, pain at injection site and diplopia. AEs=adverse events; BTA=botulinum toxin A; DB=double-blind; PC=placebo-controlled; RCT=randomized controlled trial Botulinum Toxin A for Headaches 7
8 Table 2: Systematic Reviews on the Benefits and Harm of Botulinum Toxin A versus Placebo in the Management of Cluster, Chronic Tension-Type, and Chronic Daily Headaches Reference Search methods Cluster headache Matharu Medline to September 2006; Embase 1980 to September 2006; Cochrane library; various websites. Study selection SRs and RCTs in any language. Health outcomes Headache relief measured by headache frequency, severity, and duration. No studies identified on the effects of BTA for the prevention of cluster headaches. Chronic tension-type headache Silver Medline 1966 to March 2006; Embase 1980 to March 2006; Cochrane library; various websites. SRs and RCTs in any language. Headache frequency, severity, and duration. One SR (search date 2004; includes 4 RCTs; n=285) and one RCT; n=40 were found. 3 of the 4 RCTs included in the SR found no significant difference between BTA and placebo in headache frequency, while 1 RCT reported a significant reduction from baseline in headache intensity and days without pain after BTA treatment (p value not reported and no between group comparison). One subsequent RCT reported no significant difference between BTA and placebo. BTA may be no more effective than placebo at improving the symptoms of CTTH and has been associated with AEs. AEs=facial weakness, difficulty in swallowing, and disturbed local sensation. Botulinum Toxin A for Headaches 8
9 Reference Search methods Naumann Not described. Health outcomes VAS; area under the headache curve, proportion of severe headaches posttreatment. Schulte- Mattler Medline (search timeframe not specified). Obermann Medline (search timeframe not specified). Study selection Not described. 4 RCTs (total sample size not specified), 2 of which were of higher quality. Based on these 2 studies, the authors concluded that BTA is probably ineffective for CTTH. AEs=transient weakness of neck muscle, local skin tension, ptosis, flulike reaction. RCT, PC. Not reported. 5 RCTs; n=533. No significant difference between BTA and placebo. No serious AEs reported. RCT, PC. Not reported. 6 RCTs; n=651. The authors concluded that BTA is probably ineffective for CTTH. AEs not reported. Chronic daily headache Naumann Not described. Not described. Change in headachefree days. 4 RCTs (sample size not specified), all of lower quality. A large number of patients had a diagnosis of transformed migraines. The authors concluded that, based on inconsistent results, there is insufficient evidence to support or refute a benefit of BTA in CDH. AEs=ptosis, weakness of neck, flu-like reaction. Schulte- Mattler Medline (search timeframe not specified). Obermann Medline (search timeframe not specified). RCT, PC. Not reported. 3 RCTs; n=1,117. Primary outcome criteria not met. No serious AEs reported. RCT, PC. Not reported. 3 RCTs; n=1,115. The authors concluded that BTA is probably ineffective for CDH. AEs not reported. Botulinum Toxin A for Headaches 9
10 Reference Search Study Health methods selection outcomes Harm (Botox used in various conditions and not limited to headaches) Naumann Medline, Embase, Cochrane library for the years 1966 to RCT, PC, other active comparators, DB. Number and frequency of AEs and complications. 36 RCTs; n=2,309. (1,425 participants received Botox ). 24.8% (353/1,425) AEs for BTA vs. 15.0% (133/884) for control group (p<0.001). Adjusted, weighted-risk difference=9%. Number-needed-to-harm=11. AEs= focal weakness, pain or reaction at injection site, headache, back pain, neck pain, and ptosis. AEs=adverse events; BTA=botulinum toxin A; CDH=chronic daily headache; CTTH=chronic tension-type headache; DB=double-blind; PC=placebo-controlled; RCT=randomized controlled trial; SR=systematic review; VAS=visual analogue scale Botulinum Toxin A for Headaches 10
11 Table 3: Randomized, placebo-controlled studies* of botulinum toxin A in the management of chronic tension-type headache (one injection session and final evaluation at week-12) Reference Administration (brand, dose, injection site) Schulte-Mattler Dysport U fixed site Padberg Botox U per kg; maximum 100 U follow the pain approach for Silberstein Botox up to 150 U fixed site Number of participants Primary end-points 112 Headache diary used to calculate the area under the headache curve at 6 weeks before and 12 weeks after treatment. 40 Headache intensity on VAS at 12 weeks; mean number of headache days; headache hours per day. 300 Mean change from baseline in the number of headache-free days per month, for 3 months. No statistically significant difference. AE=transient weakness of the eyelids, neck or both. No statistically significant difference. 8 minor AEs in BTA group: pain at injection site, muscle weakness, numbness in the neck, and nausea. Placebo more effective than 150 U (p=0.007). No statistically significant difference for other doses. Straube Dysport 210 U or 420 U fixed site 125 (118 evaluated) Change in the number of headache-free days at weeks after treatment compared to 4 weeks before treatment. AEs were mild and transient and included muscle weakness, neck pain or rigidity, hypertonia, pain or burning at injection site. No statistically significant difference. Significantly more AEs in BTA group at week 12 (p=0.02). AEs=muscle weakness and dysphagia. Botulinum Toxin A for Headaches 11
12 Reference Hamdy Administration (brand, dose, injection site) Botox 2 to 12 U injected into tender points (mean total dose=50 U) fixed site and follow the pain approach Number of participants Primary end-points 28 Number of headache days per month, headache severity assessed by VAS and HDI at 30 and 90 days compared to baseline. Changes from baseline at 90 days: 37.5% reduction in headache days (treatment group) vs % reduction (placebo) p=0.000; 43.68% decrease in headache severity assessed by VAS (treatment group) vs % (placebo) p=0.001; 40.74% decrease in HDI (treatment group) vs. 6.60% (placebo) p= Harden Botox 25 U per trigger points, up to 4 trigger points (maximum dose of 100 U) follow the pain approach for 23 Headache frequency; headache intensity and range of motion at baseline and at 12 weeks. 3 types of AEs reported in BTA group: hematoma at injection site, blepharoptosis, and itching and pain at the site of injection. No statistically significant difference. One mild and transient AE reported in BTA group (head extensor weakness). AEs=adverse events; BTA= botulinum toxin A; HDI=headache disability inventory; U=unit; VAS=visual analog scale * all trials were double-blinded except for a single-blinded study 17 Botulinum Toxin A for Headaches 12
13 Table 4: Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Studies on Botulinum Toxin A in the Management of Chronic Daily Headache Reference Ondo Dodick Administration (brand, dose, injection site) Botox 200 U single injection session follow the pain approach for Botox every 90 days for 9 months (mean dose=190 U) follow the pain approach for Matthew Botox every 90 days for 9 months (mean dose=190 U) follow the pain approach for Number of Participants Primary end-point 60 Number of headache-free days as assessed by diary for 12 weeks. 228 sub-group analysis of patients not taking concurrent prophylactic medications (see Matthew ) Change from baseline in the frequency of headache-free days per 30-day period. 355 Change from baseline in the frequency of headache-free days in a 30-day period at day 180. No statistically significant difference. AEs were mild with no significant differences between groups (33 AEs with BTA vs. 39 with placebo). One patient in BTA group experienced ptosis. Statistically significant difference in favor BTA (p=0.032 at 6 months and p=0.023 at 9 months). Four patients in the BTA group discontinued study due to AEs. Most frequently reported AEs with BTA=muscle weakness, neck pain, headache, and blepharoptosis. No statistically significant difference. Significantly more AEs in BTA group (76.1% vs. 63.1% in placebo group; p=0.033): muscle weakness, neck pain, blepharoptosis, and skin tightness. Botulinum Toxin A for Headaches 13
14 Reference Administration (brand, dose, injection site) Silberstein Botox U, 150 U or 225 U every 90 days for 9 months fixed site Number of Participants AEs=adverse events; BTA= botulinum toxin A; U=unit Primary end-point 702 Mean change from baseline in the frequency of headache-free days in a 30-day period at day 180. No statistically significant difference. 27 patients in the BTA group withdrew from the study due to AEs. Most frequently reported AEs=muscle weakness, neck pain or rigidity, pain at injection site, hypertonia, headache, shoulder and arm pain, and hypersthesia. Botulinum Toxin A for Headaches 14
PROCEEDINGS BOTULINUM TOXIN: PARADIGMS FOR TREATMENT * Benjamin M. Frishberg, MD ABSTRACT
 BOTULINUM TOIN: PARADIGMS FOR TREATMENT Benjamin M. Frishberg, MD ABSTRACT Botulinum toxin type A has been studied for the treatment of headache disorders since the early 1990s when its usefulness for
BOTULINUM TOIN: PARADIGMS FOR TREATMENT Benjamin M. Frishberg, MD ABSTRACT Botulinum toxin type A has been studied for the treatment of headache disorders since the early 1990s when its usefulness for
TITLE: Cannabinoids for the Treatment of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder: A Review of the Clinical Effectiveness and Guidelines
 TITLE: Cannabinoids for the Treatment of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder: A Review of the Clinical Effectiveness and Guidelines DATE: 27 June 2012 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES In 2009, CADTH reviewed the clinical
TITLE: Cannabinoids for the Treatment of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder: A Review of the Clinical Effectiveness and Guidelines DATE: 27 June 2012 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES In 2009, CADTH reviewed the clinical
BOTOX Injection (Onabotulinumtoxin A) for Migraine Headaches [Preauthorization Required]
![BOTOX Injection (Onabotulinumtoxin A) for Migraine Headaches [Preauthorization Required] BOTOX Injection (Onabotulinumtoxin A) for Migraine Headaches [Preauthorization Required]](/thumbs/29/13417512.jpg) BOTOX Injection (Onabotulinumtoxin A) for Migraine Headaches [Preauthorization Required] Medical Policy: MP-RX-01-11 Original Effective Date: March 24, 2011 Reviewed: Revised: This policy applies to products
BOTOX Injection (Onabotulinumtoxin A) for Migraine Headaches [Preauthorization Required] Medical Policy: MP-RX-01-11 Original Effective Date: March 24, 2011 Reviewed: Revised: This policy applies to products
Neurotoxins and headache: A review of the evidence. Alan G Finkel MD FAHS FAAN Carolina Headache Institute University of North Carolina
 Neurotoxins and headache: A review of the evidence Alan G Finkel MD FAHS FAAN Carolina Headache Institute University of North Carolina Disclosures Allergan: Trainer 2010 present Glaxo Smith Kline: Speaker
Neurotoxins and headache: A review of the evidence Alan G Finkel MD FAHS FAAN Carolina Headache Institute University of North Carolina Disclosures Allergan: Trainer 2010 present Glaxo Smith Kline: Speaker
Onabotulinumtoxin in the Preventive Treatment of Chronic Migraine and Other Headaches
 Onabotulinumtoxin in the Preventive Treatment of Chronic Migraine and Other Headaches While BoNTA shows promise in the management of chronic migraine, optimal outcomes will be acheived when clinicians
Onabotulinumtoxin in the Preventive Treatment of Chronic Migraine and Other Headaches While BoNTA shows promise in the management of chronic migraine, optimal outcomes will be acheived when clinicians
Botulinum toxin for the treatment of headache: a promising path on a dead end road?
 Acta Neurol. Belg., 2010, 110, 221-229 Review article Botulinum toxin for the treatment of headache: a promising path on a dead end road? Stephanie DELSTANCHE and Jean SCHOENEN Headache Research Unit.
Acta Neurol. Belg., 2010, 110, 221-229 Review article Botulinum toxin for the treatment of headache: a promising path on a dead end road? Stephanie DELSTANCHE and Jean SCHOENEN Headache Research Unit.
TITLE: Acupuncture for Management of Addictions Withdrawal: Clinical Effectiveness
 TITLE: Acupuncture for Management of Addictions Withdrawal: Clinical Effectiveness DATE: 09 October 2008 RESEARCH QUESTION: What is the clinical effectiveness of auricular acupuncture in the management
TITLE: Acupuncture for Management of Addictions Withdrawal: Clinical Effectiveness DATE: 09 October 2008 RESEARCH QUESTION: What is the clinical effectiveness of auricular acupuncture in the management
botulinum toxin type A, 50 unit, 100 unit and 200 unit powder for solution for injection (Botox ) SMC No. (692/11) Allergan Ltd
 Resubmission botulinum toxin type A, 50 unit, 100 unit and 200 unit powder for solution for injection (Botox ) SMC No. (692/11) Allergan Ltd 08 March 2013 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed
Resubmission botulinum toxin type A, 50 unit, 100 unit and 200 unit powder for solution for injection (Botox ) SMC No. (692/11) Allergan Ltd 08 March 2013 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed
Botulinum Toxin: Could It Be An Effective Treatment For Chronic Tension Type Headache?
 Sherif M. Hamdy et al. Botulinum Toxin: Could It Be An Effective Treatment For Chronic Tension Type Headache? Sherif M. Hamdy 1, Hatem Samir 1, M. El-Sayed 1, Nermin Adel 1, Rasha Hassan 2 Department of
Sherif M. Hamdy et al. Botulinum Toxin: Could It Be An Effective Treatment For Chronic Tension Type Headache? Sherif M. Hamdy 1, Hatem Samir 1, M. El-Sayed 1, Nermin Adel 1, Rasha Hassan 2 Department of
Will Botox help your migraines?
 Will Botox help your migraines? In case you hadn t heard, Botox can now be used and potentially claimed on insurance for migraines. Surprising I know. You re probably wondering how will an injection of
Will Botox help your migraines? In case you hadn t heard, Botox can now be used and potentially claimed on insurance for migraines. Surprising I know. You re probably wondering how will an injection of
TITLE: Cannabinoids for the Treatment of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder: A Review of the Clinical Effectiveness and Guidelines
 TITLE: Cannabinoids for the Treatment of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder: A Review of the Clinical Effectiveness and Guidelines DATE: 01 December 2009 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES: Post-traumatic stress disorder
TITLE: Cannabinoids for the Treatment of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder: A Review of the Clinical Effectiveness and Guidelines DATE: 01 December 2009 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES: Post-traumatic stress disorder
New appendix criteria open for a broader concept of chronic migraine
 Blackwell Publishing LtdOxford, UKCHACephalalgia0333-1024Blackwell Science, 20062006266742746Original ArticleA broader concept of chronic migrainej Olesen et al. BRIEF REPORT New appendix criteria open
Blackwell Publishing LtdOxford, UKCHACephalalgia0333-1024Blackwell Science, 20062006266742746Original ArticleA broader concept of chronic migrainej Olesen et al. BRIEF REPORT New appendix criteria open
BOTOX Injection (Onabotulinumtoxin A) for Chronic Migraine Headaches
 BOTOX Injection (Onabotulinumtoxin A) for Chronic Migraine Headaches [For the list of services and procedures that need preauthorization, please refer to www.mcs.com.pr go to Comunicados a Proveedores,
BOTOX Injection (Onabotulinumtoxin A) for Chronic Migraine Headaches [For the list of services and procedures that need preauthorization, please refer to www.mcs.com.pr go to Comunicados a Proveedores,
OnabotulinumtoxinA 155 U in medication overuse headache: a two years prospective study
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-015-1636-9 RESEARCH Open Access OnabotulinumtoxinA 155 U in medication overuse headache: a two years prospective study Andrea Negro 1,2,6*, Martina Curto 2,3,4, Luana Lionetto 5, Dorotea
DOI 10.1186/s40064-015-1636-9 RESEARCH Open Access OnabotulinumtoxinA 155 U in medication overuse headache: a two years prospective study Andrea Negro 1,2,6*, Martina Curto 2,3,4, Luana Lionetto 5, Dorotea
Drugs for MS.Drug fact box cannabis extract (Sativex) Version 1.0 Author
 Version History Policy Title Drugs for MS.Drug fact box cannabis extract (Sativex) Version 1.0 Author West Midlands Commissioning Support Unit Publication Date Jan 2013 Review Date Supersedes/New (Further
Version History Policy Title Drugs for MS.Drug fact box cannabis extract (Sativex) Version 1.0 Author West Midlands Commissioning Support Unit Publication Date Jan 2013 Review Date Supersedes/New (Further
Research Submissions. ISSN 0017-8748 doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.2010.01678.x Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
 Headache 21 American Headache Society ISSN 17-8748 doi: 1.1111/j.1526-461.21.1678.x Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Research Submissions OnabotulinumtoxinA for Treatment of Chronic Migraine: Pooled
Headache 21 American Headache Society ISSN 17-8748 doi: 1.1111/j.1526-461.21.1678.x Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Research Submissions OnabotulinumtoxinA for Treatment of Chronic Migraine: Pooled
Treatment of Tension-Type Headache with Botox:
 Treatment of Tension-Type Headache with Botox: A Review of the Literature DIMA ROZEN, M.D. 1, AND JOYTI SHARMA, M.D. 2 Abstract Botulinum toxin has been shown to effectively treat several types of neurological
Treatment of Tension-Type Headache with Botox: A Review of the Literature DIMA ROZEN, M.D. 1, AND JOYTI SHARMA, M.D. 2 Abstract Botulinum toxin has been shown to effectively treat several types of neurological
33 % of whiplash patients develop. headaches originating from the upper. cervical spine
 33 % of whiplash patients develop headaches originating from the upper cervical spine - Dr Nikolai Bogduk Spine, 1995 1 Physical Treatments for Headache: A Structured Review Headache: The Journal of Head
33 % of whiplash patients develop headaches originating from the upper cervical spine - Dr Nikolai Bogduk Spine, 1995 1 Physical Treatments for Headache: A Structured Review Headache: The Journal of Head
Tension Type Headaches
 Tension Type Headaches Research Review by : Dr. Ian MacIntyre Physiotherapy for tension-type Headache: A Controlled Study P. Torelli, R. Jenson, J. Olsen: Cephalalgia, 2004, 24, 29-36 Tension-type headache
Tension Type Headaches Research Review by : Dr. Ian MacIntyre Physiotherapy for tension-type Headache: A Controlled Study P. Torelli, R. Jenson, J. Olsen: Cephalalgia, 2004, 24, 29-36 Tension-type headache
BOTOX Treatment. for Chronic Migraine. Information for patients and their families. Botulinum Toxin Type A
 BOTOX Treatment Botulinum Toxin Type A for Chronic Migraine Information for patients and their families. Is Chronic Migraine the same as Migraine? Chronic Migraine is similar to migraine as sufferers experience
BOTOX Treatment Botulinum Toxin Type A for Chronic Migraine Information for patients and their families. Is Chronic Migraine the same as Migraine? Chronic Migraine is similar to migraine as sufferers experience
Chronic daily headache
 Chronic daily headache Chronic daily headache (CDH) is defined as any headache syndrome affecting more than half of the month, i.e. a headache on more than 15 days per month. It is also known as daily
Chronic daily headache Chronic daily headache (CDH) is defined as any headache syndrome affecting more than half of the month, i.e. a headache on more than 15 days per month. It is also known as daily
Botulinum neurotoxin for the treatment of migraine and other primary headache disorders
 Dermatol Clin 22 (2004) 167 175 Botulinum neurotoxin for the treatment of migraine and other primary headache disorders Andrew M. Blumenfeld, MD a, *, David W. Dodick, MD, FRCP(C), FACP b,c, Stephen D.
Dermatol Clin 22 (2004) 167 175 Botulinum neurotoxin for the treatment of migraine and other primary headache disorders Andrew M. Blumenfeld, MD a, *, David W. Dodick, MD, FRCP(C), FACP b,c, Stephen D.
Which injectable medication should I take for relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis?
 Which injectable medication should I take for relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis? A decision aid to discuss options with your doctor This decision aid is for you if you: Have multiple sclerosis Have
Which injectable medication should I take for relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis? A decision aid to discuss options with your doctor This decision aid is for you if you: Have multiple sclerosis Have
Botulinum toxin in the treatment of chronic migraine. Gregory P. Hanes, MD Neuroscience Summit 5/14/15
 Botulinum toxin in the treatment of chronic migraine Gregory P. Hanes, MD Neuroscience Summit 5/14/15 Primary Headache Disorders: Frequency Classification After Secondary Causes Are Ruled Out Short-Duration
Botulinum toxin in the treatment of chronic migraine Gregory P. Hanes, MD Neuroscience Summit 5/14/15 Primary Headache Disorders: Frequency Classification After Secondary Causes Are Ruled Out Short-Duration
TITLE: Naltrexone in Combination with Acamprosate for the Treatment of Alcohol Dependence: A Review of the Clinical and Cost-Effectiveness
 TITLE: Naltrexone in Combination with Acamprosate for the Treatment of Alcohol Dependence: A Review of the Clinical and Cost-Effectiveness DATE: 08 October 2009 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES: Alcohol dependence
TITLE: Naltrexone in Combination with Acamprosate for the Treatment of Alcohol Dependence: A Review of the Clinical and Cost-Effectiveness DATE: 08 October 2009 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES: Alcohol dependence
TITLE: Metal-Ceramic and Porcelain Dental Crowns: A Review of Clinical and Cost- Effectiveness
 TITLE: Metal-Ceramic and Porcelain Dental Crowns: A Review of Clinical and Cost- Effectiveness DATE: 23 June 2009 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES: Dental ceramics are widely used to repair damaged teeth and
TITLE: Metal-Ceramic and Porcelain Dental Crowns: A Review of Clinical and Cost- Effectiveness DATE: 23 June 2009 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES: Dental ceramics are widely used to repair damaged teeth and
When the Pain Won t Stop: Managing Chronic Daily Headache
 When the Pain Won t Stop: Managing Chronic Daily Headache Arnolda Eloff, MB, ChB, Mmed Presented at the University of Calgary s Wednesday Evening Course Program, Calgary, Alberta. Copyright Chronic daily
When the Pain Won t Stop: Managing Chronic Daily Headache Arnolda Eloff, MB, ChB, Mmed Presented at the University of Calgary s Wednesday Evening Course Program, Calgary, Alberta. Copyright Chronic daily
Botulinum Neurotoxin for Chronic Migraine and Trigeminal Neuralgia
 Botulinum Neurotoxin for Chronic Migraine and Trigeminal Neuralgia David W. Dodick Professor Department of Neurology, Mayo Clinic Phoenix Arizona, USA Onabotulinumtoxin A is the only botulinum toxin serotype
Botulinum Neurotoxin for Chronic Migraine and Trigeminal Neuralgia David W. Dodick Professor Department of Neurology, Mayo Clinic Phoenix Arizona, USA Onabotulinumtoxin A is the only botulinum toxin serotype
New daily persistent headache in the paediatric population
 doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2008.01647.x New daily persistent headache in the paediatric population E Kung 1, SJ Tepper 2, AM Rapoport 3, FD Sheftell 4 & ME Bigal 1,5 1 Department of Neurology, Albert Einstein
doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2008.01647.x New daily persistent headache in the paediatric population E Kung 1, SJ Tepper 2, AM Rapoport 3, FD Sheftell 4 & ME Bigal 1,5 1 Department of Neurology, Albert Einstein
Evidence based medicine on the use of botulinum toxin for headache disorders
 J Neural Transm (2007) DOI 10.1007/s00702-007-0832-3 Printed in The Netherlands Evidence based medicine on the use of botulinum toxin for headache disorders W. J. Schulte-Mattler, E. Leinisch Department
J Neural Transm (2007) DOI 10.1007/s00702-007-0832-3 Printed in The Netherlands Evidence based medicine on the use of botulinum toxin for headache disorders W. J. Schulte-Mattler, E. Leinisch Department
Address all correspondence to A. Blumenfeld, Headache Center, The Headache Center of Southern CA, 320 Santa Fe Drive, Encinitas, CA 92024, USA.
 Headache 2010 American Headache Society ISSN 0017-8748 doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.2010.01766.x Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Research Submissions Method of Injection of OnabotulinumtoxinA for Chronic
Headache 2010 American Headache Society ISSN 0017-8748 doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.2010.01766.x Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Research Submissions Method of Injection of OnabotulinumtoxinA for Chronic
Updated guidelines on headache management for use by the pharmacist
 M I P C A MIGRAINE IN PRIMARY CARE ADVISORS Updated guidelines on headache management for use by the pharmacist Introduction N U M B E R 2 1, O C T O B E R 2 0 1 2 Headache is a major public health problem,
M I P C A MIGRAINE IN PRIMARY CARE ADVISORS Updated guidelines on headache management for use by the pharmacist Introduction N U M B E R 2 1, O C T O B E R 2 0 1 2 Headache is a major public health problem,
Classification of Chronic Headache
 Chronic Headache Classification of Chronic Headache JMAJ 47(3): 112 117, 2004 Mitsunori MORIMATSU Professor, Department of Neurology and Clinical Neuroscience, Yamaguchi University School of Medicine Abstract:
Chronic Headache Classification of Chronic Headache JMAJ 47(3): 112 117, 2004 Mitsunori MORIMATSU Professor, Department of Neurology and Clinical Neuroscience, Yamaguchi University School of Medicine Abstract:
Botulinum toxins in the treatment of migraine and tension-type headaches
 Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am 14 (2003) 885 899 Botulinum toxins in the treatment of migraine and tension-type headaches Paul Winner, DO, FAAN a,b,* a Palm Beach Headache Center, Premiere Research Institute,
Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am 14 (2003) 885 899 Botulinum toxins in the treatment of migraine and tension-type headaches Paul Winner, DO, FAAN a,b,* a Palm Beach Headache Center, Premiere Research Institute,
Tension-type headache Non-pharmacological and pharmacological treatment
 Danish Headache Center Tension-type headache Non-pharmacological and pharmacological treatment Lars Bendtsen Associate professor, MD, PhD, Dr Med Sci Danish Headache Center, Department of Neurology Glostrup
Danish Headache Center Tension-type headache Non-pharmacological and pharmacological treatment Lars Bendtsen Associate professor, MD, PhD, Dr Med Sci Danish Headache Center, Department of Neurology Glostrup
Botox treatment for chronic migraine
 University Teaching Trust Botox treatment for chronic migraine Humphrey Booth Building Neurosciences 0161 206 2563 0161 206 2427 All Rights Reserved 2016. Document for issue as handout.. This information
University Teaching Trust Botox treatment for chronic migraine Humphrey Booth Building Neurosciences 0161 206 2563 0161 206 2427 All Rights Reserved 2016. Document for issue as handout.. This information
Guidance for Industry Migraine: Developing Drugs for Acute Treatment
 Guidance for Industry Migraine: Developing Drugs for Acute Treatment DRAFT GUIDANCE This guidance document is being distributed for comment purposes only. Comments and suggestions regarding this draft
Guidance for Industry Migraine: Developing Drugs for Acute Treatment DRAFT GUIDANCE This guidance document is being distributed for comment purposes only. Comments and suggestions regarding this draft
Tension-type headache Non-pharmacological and pharmacological treatment
 Danish Headache Center Tension-type headache Non-pharmacological and pharmacological treatment Lars Bendtsen Associate professor, MD, PhD, Dr Med Sci Danish Headache Center, Department of Neurology Glostrup
Danish Headache Center Tension-type headache Non-pharmacological and pharmacological treatment Lars Bendtsen Associate professor, MD, PhD, Dr Med Sci Danish Headache Center, Department of Neurology Glostrup
DATE: 29 August 2012 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES
 TITLE: Dual Antiplatelet Therapy and Enoxaparin or Unfractionated Heparin for patients with ST-elevation Myocardial Infarction: A Review of the Clinical Evidence DATE: 29 August 2012 CONTEXT AND POLICY
TITLE: Dual Antiplatelet Therapy and Enoxaparin or Unfractionated Heparin for patients with ST-elevation Myocardial Infarction: A Review of the Clinical Evidence DATE: 29 August 2012 CONTEXT AND POLICY
Introduction. Jean-Christophe Cuvellier 1 Frédéric Couttenier 2 Stéphane Auvin 1 Louis Vallée 1 ORIGINAL RESEARCH
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH The classifi cation of chronic daily headache in French children and adolescents: A comparison between the second edition of the International Classifi cation of Headache Disorders and
ORIGINAL RESEARCH The classifi cation of chronic daily headache in French children and adolescents: A comparison between the second edition of the International Classifi cation of Headache Disorders and
Natural Modality in the Treatment of Primary Headaches. William S. Mihin, D.C. Catharine Helms, M.S. Michelle M. Anderson, M.S.N., F.N.P.
 Natural Modality in the Treatment of Primary Headaches William S. Mihin, D.C. Catharine Helms, M.S. Michelle M. Anderson, M.S.N., F.N.P. Abstract Headaches are both a prevalent and disabling condition.
Natural Modality in the Treatment of Primary Headaches William S. Mihin, D.C. Catharine Helms, M.S. Michelle M. Anderson, M.S.N., F.N.P. Abstract Headaches are both a prevalent and disabling condition.
Botulinum Toxin. Policy MEDICAL POLICY. Focal dystonias
 MEDICAL POLICY POLICY RELATED POLICIES POLICY GUIDELINES DESCRIPTION SCOPE BENEFIT APPLICATION RATIONALE REFERENCES CODING APPENDIX HISTORY Botulinum Toxin Number 5.01.512 Effective Date July 14, 2015
MEDICAL POLICY POLICY RELATED POLICIES POLICY GUIDELINES DESCRIPTION SCOPE BENEFIT APPLICATION RATIONALE REFERENCES CODING APPENDIX HISTORY Botulinum Toxin Number 5.01.512 Effective Date July 14, 2015
Version History. Previous Versions. Drugs for MS.Drug facts box fampridine Version 1.0 Author
 Version History Policy Title Drugs for MS.Drug facts box fampridine Version 1.0 Author West Midlands Commissioning Support Unit Publication Date Jan 2013 Review Date Supersedes/New (Further fields as required
Version History Policy Title Drugs for MS.Drug facts box fampridine Version 1.0 Author West Midlands Commissioning Support Unit Publication Date Jan 2013 Review Date Supersedes/New (Further fields as required
Behavioral and Physical Treatments for Tension-type and Cervicogenic Headache
 Evidence Report: Behavioral and Physical Treatments for Tension-type and Cervicogenic Headache Douglas C. McCrory, MD, MHSc Donald B. Penzien, PhD Vic Hasselblad, PhD Rebecca N. Gray, DPhil Duke University
Evidence Report: Behavioral and Physical Treatments for Tension-type and Cervicogenic Headache Douglas C. McCrory, MD, MHSc Donald B. Penzien, PhD Vic Hasselblad, PhD Rebecca N. Gray, DPhil Duke University
Is Botox-A Effective For Headaches and Neck Pain?
 0008-3194/2006/263 270/$2.00/ JCCA 2006 The use of botulinum neurotoxin type A (Botox) for headaches: a case review Mia Oliver, BA, DC* Joanna MacDonald, BHK, DC* Moez Rajwani, DC** Chiropractic care is
0008-3194/2006/263 270/$2.00/ JCCA 2006 The use of botulinum neurotoxin type A (Botox) for headaches: a case review Mia Oliver, BA, DC* Joanna MacDonald, BHK, DC* Moez Rajwani, DC** Chiropractic care is
CONSUMER MEDICINE INFORMATION
 CONSUMER MEDICINE INFORMATION BOTOX (botulinum toxin, type A) purified neurotoxin complex The information in this leaflet is ONLY a summary and is not a complete statement about BOTOX injection. Your doctor
CONSUMER MEDICINE INFORMATION BOTOX (botulinum toxin, type A) purified neurotoxin complex The information in this leaflet is ONLY a summary and is not a complete statement about BOTOX injection. Your doctor
Prednisone for the treatment of withdrawal headache in patients with medication overuse headache: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study
 Brief Report Prednisone for the treatment of withdrawal headache in patients with medication overuse headache: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study Cephalalgia 33(3) 202 207! International
Brief Report Prednisone for the treatment of withdrawal headache in patients with medication overuse headache: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study Cephalalgia 33(3) 202 207! International
Handicap after acute whiplash injury A 1-year prospective study of risk factors
 1 Handicap after acute whiplash injury A 1-year prospective study of risk factors Neurology 2001;56:1637-1643 (June 26, 2001) Helge Kasch, MD, PhD; Flemming W Bach, MD, PhD; Troels S Jensen, MD, PhD From
1 Handicap after acute whiplash injury A 1-year prospective study of risk factors Neurology 2001;56:1637-1643 (June 26, 2001) Helge Kasch, MD, PhD; Flemming W Bach, MD, PhD; Troels S Jensen, MD, PhD From
Chronic migraine and medication overuse headache: clarifying the current International Headache Society classification criteria
 Chronic migraine and medication overuse headache: clarifying the current International Headache Society classification criteria doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2008.01753.x C Sun-Edelstein 1, ME Bigal 2 & AM Rapoport
Chronic migraine and medication overuse headache: clarifying the current International Headache Society classification criteria doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2008.01753.x C Sun-Edelstein 1, ME Bigal 2 & AM Rapoport
Views and Perspectives
 Headache 2010 American Headache Society ISSN 0017-8748 doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.2010.01764.x Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Views and Perspectives Defining the Pharmacologically Intractable Headache
Headache 2010 American Headache Society ISSN 0017-8748 doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.2010.01764.x Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Views and Perspectives Defining the Pharmacologically Intractable Headache
Version History. Previous Versions. for secondary progressive MS (SPMS) Policy Title. Drugs for MS.Drug facts box Interferon beta 1b
 Version History Policy Title Drugs for MS.Drug facts box Interferon beta 1b for secondary progressive MS (SPMS) Version 1.0 Author West Midlands Commissioning Support Unit Publication Date Jan 2013 Review
Version History Policy Title Drugs for MS.Drug facts box Interferon beta 1b for secondary progressive MS (SPMS) Version 1.0 Author West Midlands Commissioning Support Unit Publication Date Jan 2013 Review
Evidence review group report: Botulinum toxin type A for the prophylaxis of headaches in adults with chronic migraine
 Evidence review group report: Botulinum toxin type A for the prophylaxis of headaches in adults with chronic migraine Produced by Warwick Evidence Authors: Dr Pamela Royle, senior research fellow Dr Ewen
Evidence review group report: Botulinum toxin type A for the prophylaxis of headaches in adults with chronic migraine Produced by Warwick Evidence Authors: Dr Pamela Royle, senior research fellow Dr Ewen
How Is OnabotulinumtoxinA Reimbursed For Chronic Migraine? Impact Of FDA Approval And The New CPT Code
 How Is OnabotulinumtoxinA Reimbursed For Chronic Migraine? Impact Of FDA Approval And The New CPT Code Effective January 1, 2013, physicians will be able to report the new CPT code 64615 when performing
How Is OnabotulinumtoxinA Reimbursed For Chronic Migraine? Impact Of FDA Approval And The New CPT Code Effective January 1, 2013, physicians will be able to report the new CPT code 64615 when performing
Botulinum Toxins. Policy # 00012 Original Effective Date: 01/28/2003 Current Effective Date: 02/19/2014
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
DATE: 06 May 2013 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES
 TITLE: Low Molecular Weight Heparins versus New Oral Anticoagulants for Long-Term Thrombosis Prophylaxis and Long-Term Treatment of DVT and PE: A Review of the Clinical and Cost-Effectiveness DATE: 06
TITLE: Low Molecular Weight Heparins versus New Oral Anticoagulants for Long-Term Thrombosis Prophylaxis and Long-Term Treatment of DVT and PE: A Review of the Clinical and Cost-Effectiveness DATE: 06
Headaches when to worry is a scan always needed? Regan Solomons
 Headaches when to worry is a scan always needed? Regan Solomons Introduction o Headache is a common problem in childhood o Up to 25% of school children suffer from chronic recurrent headaches o Primary
Headaches when to worry is a scan always needed? Regan Solomons Introduction o Headache is a common problem in childhood o Up to 25% of school children suffer from chronic recurrent headaches o Primary
MEDICAL POLICY. I. POLICY Top BOTULINUM TOXIN MP-2.006 POLICY TITLE POLICY NUMBER
 Original Issue Date (Created): July 1, 2002 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): November 25, 2014 Effective Date: April 1, 2015 POLICY PRODUCT VARIATIONS DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND RATIONALE DEFINITIONS BENEFIT
Original Issue Date (Created): July 1, 2002 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): November 25, 2014 Effective Date: April 1, 2015 POLICY PRODUCT VARIATIONS DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND RATIONALE DEFINITIONS BENEFIT
Appendix 1 (as supplied by the authors): Framework and content of the intervention of the LIMIT study
 Appendix 1 (as supplied by the authors): Framework and content of the intervention of the LIMIT study Background The training was based on the learning cycle of Kolb 1. According to this cycle effective
Appendix 1 (as supplied by the authors): Framework and content of the intervention of the LIMIT study Background The training was based on the learning cycle of Kolb 1. According to this cycle effective
TITLE: Diabetic Diets for Frail Elderly Long-Term Care Residents with Type II Diabetes Mellitus: A Review of Guidelines
 TITLE: Diabetic Diets for Frail Elderly Long-Term Care Residents with Type II Diabetes Mellitus: A Review of Guidelines DATE: 15 June 2015 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES People with type 2 diabetes, also known
TITLE: Diabetic Diets for Frail Elderly Long-Term Care Residents with Type II Diabetes Mellitus: A Review of Guidelines DATE: 15 June 2015 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES People with type 2 diabetes, also known
BEST in MH clinical question-answering service
 Best Evidence Summaries of Topics in Mental Healthcare BEST in MH clinical question-answering service Question In people with PTSD (including single and multiple event trauma) how effective is prazosin
Best Evidence Summaries of Topics in Mental Healthcare BEST in MH clinical question-answering service Question In people with PTSD (including single and multiple event trauma) how effective is prazosin
WAT ALS HOOFDPIJN CHRONISCH WORDT? Prof Jan Versijpt, MD PhD Kliniek voor Hoofd- en Aangezichtspijn Neurologie, UZ Brussel
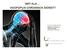 WAT ALS HOOFDPIJN CHRONISCH WORDT? Prof Jan Versijpt, MD PhD Kliniek voor Hoofd- en Aangezichtspijn Neurologie, UZ Brussel Stovner, IHC 2009 New daily persistent headache Primair = dagelijkse and continue
WAT ALS HOOFDPIJN CHRONISCH WORDT? Prof Jan Versijpt, MD PhD Kliniek voor Hoofd- en Aangezichtspijn Neurologie, UZ Brussel Stovner, IHC 2009 New daily persistent headache Primair = dagelijkse and continue
Informed Consent BOTOX / DYSPORT / XEOMIN Injection for
 Fresno Laser Aesthetics 1105 E. Spruce Ph (559) 432-3492 Suite 203 Fax (559) 256-7711 Fresno, CA 93720 Informed Consent BOTOX / DYSPORT / XEOMIN Injection for INSTRUCTIONS This is an informed-consent document
Fresno Laser Aesthetics 1105 E. Spruce Ph (559) 432-3492 Suite 203 Fax (559) 256-7711 Fresno, CA 93720 Informed Consent BOTOX / DYSPORT / XEOMIN Injection for INSTRUCTIONS This is an informed-consent document
Guidelines for controlled trials of prophylactic treatment of chronic migraine in adults
 doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2008.01555.x REVIEW Guidelines for controlled trials of prophylactic treatment of chronic migraine in adults S Silberstein 1 (Chairman, USA), P Tfelt-Hansen 2 (Co-Chairman, Denmark),
doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2008.01555.x REVIEW Guidelines for controlled trials of prophylactic treatment of chronic migraine in adults S Silberstein 1 (Chairman, USA), P Tfelt-Hansen 2 (Co-Chairman, Denmark),
Chander Sehgal, MD, MBA Director, Common Drug Review (CDR) Taipei, Taiwan July 23 26, 2012
 Chander Sehgal, MD, MBA Director, Common Drug Review (CDR) Taipei, Taiwan July 23 26, 2012 CANADIAN PERSPECTIVE Common Drug review: A *pan-canadian process CANADA: 33 M people; area 10 M km 2 DIVERSITY!
Chander Sehgal, MD, MBA Director, Common Drug Review (CDR) Taipei, Taiwan July 23 26, 2012 CANADIAN PERSPECTIVE Common Drug review: A *pan-canadian process CANADA: 33 M people; area 10 M km 2 DIVERSITY!
Frustrated with your Overactive Bladder (OAB) medication not working? Can t handle the side effects?
 Frustrated with your Overactive Bladder (OAB) medication not working? Can t handle the side effects? BOTOX treats adults with the OAB symptoms of leaking, going too often, and the strong sudden need to
Frustrated with your Overactive Bladder (OAB) medication not working? Can t handle the side effects? BOTOX treats adults with the OAB symptoms of leaking, going too often, and the strong sudden need to
TITLE: Suboxone for Short-term Detoxification: A Review of the Clinical Evidence
 TITLE: Suboxone for Short-term Detoxification: A Review of the Clinical Evidence DATE: 7 September 2011 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES: Opioid dependence is defined as a strong desire to use the substance,
TITLE: Suboxone for Short-term Detoxification: A Review of the Clinical Evidence DATE: 7 September 2011 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES: Opioid dependence is defined as a strong desire to use the substance,
BOTOX is the first and only preventive treatment proven to reduce headache days every month.
 For adults with Chronic Migraine, 15 or more headache days a month, each lasting 4 hours or more, is the first and only preventive treatment proven to reduce headache days every month. prevents up to 9
For adults with Chronic Migraine, 15 or more headache days a month, each lasting 4 hours or more, is the first and only preventive treatment proven to reduce headache days every month. prevents up to 9
How To Write A Systematic Review
 Formulating the Review Question & Writing a Protocol Madhukar Pai, MD, PhD Associate Professor Department of Epidemiology & Biostatistics McGill University, Montreal, Canada Email: madhukar.pai@mcgill.ca
Formulating the Review Question & Writing a Protocol Madhukar Pai, MD, PhD Associate Professor Department of Epidemiology & Biostatistics McGill University, Montreal, Canada Email: madhukar.pai@mcgill.ca
Neck Pain & Cervicogenic Headache Integrating Research into Practice: San Luis Sports Therapy s Approach to Evidence-Based Practice
 Neck Pain & Cervicogenic Headache Integrating Research into Practice: San Luis Sports Therapy s Approach to Evidence-Based Practice PROBLEM: Neck Pain and Cervicogenic Headache 66% Proportion of individuals
Neck Pain & Cervicogenic Headache Integrating Research into Practice: San Luis Sports Therapy s Approach to Evidence-Based Practice PROBLEM: Neck Pain and Cervicogenic Headache 66% Proportion of individuals
A Guide to Urinary Incontinence (UI) in Adults With Overactive Bladder (OAB) Due to a Neurologic Condition
 A Guide to Urinary Incontinence (UI) in Adults With Overactive Bladder (OAB) Due to a Neurologic Condition Information and treatment options BOTOX is a prescription medicine that is injected into muscles
A Guide to Urinary Incontinence (UI) in Adults With Overactive Bladder (OAB) Due to a Neurologic Condition Information and treatment options BOTOX is a prescription medicine that is injected into muscles
Multimodal manual therapy vs. pharmacological care for management of tension type headache: A meta-analysis of randomized trials
 Review Article Multimodal manual therapy vs. pharmacological care for management of tension type headache: A meta-analysis of randomized trials Cephalalgia 2015, Vol. 35(14) 1323 1332! International Headache
Review Article Multimodal manual therapy vs. pharmacological care for management of tension type headache: A meta-analysis of randomized trials Cephalalgia 2015, Vol. 35(14) 1323 1332! International Headache
15 or more headache days a month, each headache lasting 4 hours or more. Isn t it time to reduce those headache days?
 15 or more headache days a month, each headache lasting 4 hours or more (onabotulinumtoxina) is a prescription medicine that is injected to prevent headaches in adults with chronic migraine who have 15
15 or more headache days a month, each headache lasting 4 hours or more (onabotulinumtoxina) is a prescription medicine that is injected to prevent headaches in adults with chronic migraine who have 15
Cervicogenic Headaches
 Cervicogenic Headaches Definition/Description Cervicogenic headaches refer to headache type sensations felt in the head and/face that originates from the neck, most commonly the upper cervical zygapophyseal
Cervicogenic Headaches Definition/Description Cervicogenic headaches refer to headache type sensations felt in the head and/face that originates from the neck, most commonly the upper cervical zygapophyseal
Review for NHS Surrey Prescribing Clinical Network. Treatment: Botox for chronic migraine. Prepared by: Victoria Overland
 Review for NHS Surrey Prescribing Clinical Network Treatment: Botox for chronic migraine Prepared by: Victoria Overland Date: To be considered at September 2012 PCN meeting 1. Purpose of the Review NICE
Review for NHS Surrey Prescribing Clinical Network Treatment: Botox for chronic migraine Prepared by: Victoria Overland Date: To be considered at September 2012 PCN meeting 1. Purpose of the Review NICE
A chiropractic approach to managing migraine
 A chiropractic approach to managing migraine What is chiropractic? Chiropractic is a primary healthcare profession that specialises in the diagnosis, treatment and overall management of conditions that
A chiropractic approach to managing migraine What is chiropractic? Chiropractic is a primary healthcare profession that specialises in the diagnosis, treatment and overall management of conditions that
Migraine and the greater occipital nerve
 Migraine and the greater occipital nerve What is the greater occipital nerve? The nerves that travel from your spine (in the neck) to the back of the head and scalp are known as the occipital nerves. There
Migraine and the greater occipital nerve What is the greater occipital nerve? The nerves that travel from your spine (in the neck) to the back of the head and scalp are known as the occipital nerves. There
Guidelines for trials of drug treatments in tension-type headache
 Guidelines for trials of drug treatments in tension-type headache First Edition: International Headache Society Committee on Clinical Trials in Tension-type Headache COMMITTEE MEMBERS J SCHOENEN, Belgium
Guidelines for trials of drug treatments in tension-type headache First Edition: International Headache Society Committee on Clinical Trials in Tension-type Headache COMMITTEE MEMBERS J SCHOENEN, Belgium
Frequent headache is defined as headaches 15 days/month and daily. Course of Frequent/Daily Headache in the General Population and in Medical Practice
 DISEASE STATE REVIEW Course of Frequent/Daily Headache in the General Population and in Medical Practice Egilius L.H. Spierings, MD, PhD, Willem K.P. Mutsaerts, MSc Department of Neurology, Brigham and
DISEASE STATE REVIEW Course of Frequent/Daily Headache in the General Population and in Medical Practice Egilius L.H. Spierings, MD, PhD, Willem K.P. Mutsaerts, MSc Department of Neurology, Brigham and
Dry Needling Corporate Medical Policy
 Dry Needling Corporate Medical Policy File name: Dry Needling File code: UM.REHAB.09 Origination: 04/2015 Last Review: New policy Next Review: 04/2016 Effective Date: 9/1/2015 Description Myofascial pain
Dry Needling Corporate Medical Policy File name: Dry Needling File code: UM.REHAB.09 Origination: 04/2015 Last Review: New policy Next Review: 04/2016 Effective Date: 9/1/2015 Description Myofascial pain
Version History. Previous Versions. Policy Title. Drugs for MS.Drug facts box Glatiramer Acetate Version 1.0 Author
 Version History Policy Title Drugs for MS.Drug facts box Glatiramer Acetate Version 1.0 Author West Midlands Commissioning Support Unit Publication Date Jan 2013 Review Date Supersedes/New (Further fields
Version History Policy Title Drugs for MS.Drug facts box Glatiramer Acetate Version 1.0 Author West Midlands Commissioning Support Unit Publication Date Jan 2013 Review Date Supersedes/New (Further fields
Prior Authorization Guideline
 Prior Authorization Guideline Guideline: MEDPD SPAP Inj - Botox Therapeutic Class: Musculoskeletal Agents Therapeutic Sub-Class: Musculoskeletal Relaxant Agents Client: PDP SPAP Inj Approval Date: 3/17/2000
Prior Authorization Guideline Guideline: MEDPD SPAP Inj - Botox Therapeutic Class: Musculoskeletal Agents Therapeutic Sub-Class: Musculoskeletal Relaxant Agents Client: PDP SPAP Inj Approval Date: 3/17/2000
Whiplash and Cervical Spine Disorders: Evaluation and Management
 Whiplash and Cervical Spine Disorders: Evaluation and Management Dr. Corrie Graboski Definition by Quebec Task Force Pain Generators an acceleration-deceleration mechanism of energy transfer to the neck
Whiplash and Cervical Spine Disorders: Evaluation and Management Dr. Corrie Graboski Definition by Quebec Task Force Pain Generators an acceleration-deceleration mechanism of energy transfer to the neck
Ultrasound guided onabotulinum injection in chronic migraine: a case series
 Ultrasound guided onabotulinum injection in chronic migraine: a case series L. Di Lorenzo 1, F. Di Stani 2, D. Santopadre 3, C. Foti 4 1 Department of Rehabilitation, Hospital G. Rummo, Benevento, Italy
Ultrasound guided onabotulinum injection in chronic migraine: a case series L. Di Lorenzo 1, F. Di Stani 2, D. Santopadre 3, C. Foti 4 1 Department of Rehabilitation, Hospital G. Rummo, Benevento, Italy
OnabotulinumtoxinA for treatment of chronic migraine: Results from the double-blind, randomized, placebocontrolled phase of the PREEMPT 1 trial
 Original Article OnabotulinumtoxinA for treatment of chronic migraine: Results from the double-blind, randomized, placebocontrolled phase of the PREEMPT 1 trial Cephalalgia 30(7) 793 803! International
Original Article OnabotulinumtoxinA for treatment of chronic migraine: Results from the double-blind, randomized, placebocontrolled phase of the PREEMPT 1 trial Cephalalgia 30(7) 793 803! International
CHRONIC MIGRAINE TACKLED HEAD-ON
 MEDIA RELEASE [Insert embargo time and date] March 2014 CHRONIC MIGRAINE TACKLED HEAD-ON BOTOX (botulinum toxin type A) receives government subsidy for debilitating condition Sydney, Australia, [insert
MEDIA RELEASE [Insert embargo time and date] March 2014 CHRONIC MIGRAINE TACKLED HEAD-ON BOTOX (botulinum toxin type A) receives government subsidy for debilitating condition Sydney, Australia, [insert
Botulinum Toxins A and B
 DRUG POLICY Botulinum Toxins A and B Policy Number: 2015D0017P Effective Date: 11/1/2015 Table of Contents Page Related Medical or Drug Policies: Temporomandibular Joint Disorders COVERAGE RATIONALE...
DRUG POLICY Botulinum Toxins A and B Policy Number: 2015D0017P Effective Date: 11/1/2015 Table of Contents Page Related Medical or Drug Policies: Temporomandibular Joint Disorders COVERAGE RATIONALE...
THE COMMONWEALTH OF MASSACHUSETTS Department of Industrial Accidents
 THE COMMONWEALTH OF MASSACHUSETTS Department of Industrial Accidents 1 Congress Street, Suite 100 Boston, Massachusetts 02114-2017 DEVAL L. PATRICK Governor PHILIP L. HILLMAN Director TIMOTHY P. MURRAY
THE COMMONWEALTH OF MASSACHUSETTS Department of Industrial Accidents 1 Congress Street, Suite 100 Boston, Massachusetts 02114-2017 DEVAL L. PATRICK Governor PHILIP L. HILLMAN Director TIMOTHY P. MURRAY
Presented by: Jean Yoo-Campbell, Matthew Konerman, Monica Konerman, Jean Yoo Campbell, Christian Gocke, Eunpi Cho Donald Lynch
 Bass N.M., et. al. N Engl J Med 2010; 362:1071-1081 Presented by: Jean Yoo-Campbell, Matthew Konerman, Monica Konerman, Jean Yoo Campbell, Christian Gocke, Eunpi Cho Donald Lynch Faculty Advisor: Dr. Fred
Bass N.M., et. al. N Engl J Med 2010; 362:1071-1081 Presented by: Jean Yoo-Campbell, Matthew Konerman, Monica Konerman, Jean Yoo Campbell, Christian Gocke, Eunpi Cho Donald Lynch Faculty Advisor: Dr. Fred
Chronic Daily Headache in a Patient With Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
 CASE REPORT Chronic Daily Headache in a Patient With Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Jiann-Jy Chen 1,2,3, Dem-Lion Chen 4 * 1 Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Taoyuan Hospital, Department of Health, Executive
CASE REPORT Chronic Daily Headache in a Patient With Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Jiann-Jy Chen 1,2,3, Dem-Lion Chen 4 * 1 Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Taoyuan Hospital, Department of Health, Executive
Is manual physical therapy more effective than other physical therapy approaches in reducing pain and disability in adults post whiplash injury?
 Is manual physical therapy more effective than other physical therapy approaches in reducing pain and disability in adults post whiplash injury? Clinical Bottom Line Manual therapy may have a role in the
Is manual physical therapy more effective than other physical therapy approaches in reducing pain and disability in adults post whiplash injury? Clinical Bottom Line Manual therapy may have a role in the
The Prevalence of Neck Pain in Migrainehead_1608
 1..5 Headache 2010 the Authors Journal compilation 2010 American Headache Society ISSN 0017-8748 doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.2009.01608.x Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Research Submission The Prevalence
1..5 Headache 2010 the Authors Journal compilation 2010 American Headache Society ISSN 0017-8748 doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.2009.01608.x Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Research Submission The Prevalence
Headache - What is Your Migraine Size?
 Headache The Pharmacist s Role in Assessment & Peter Loewen, B.Sc.(Pharm), Pharm.D. Vancouver Hospital & Health Sciences Centre University of British Columbia ETC, Headache. Nan Quintin www.vhpharmsci.com
Headache The Pharmacist s Role in Assessment & Peter Loewen, B.Sc.(Pharm), Pharm.D. Vancouver Hospital & Health Sciences Centre University of British Columbia ETC, Headache. Nan Quintin www.vhpharmsci.com
Version History. Previous Versions. Drugs for MS.Drug facts box fingolimod Version 1.0 Author
 Version History Policy Title Drugs for MS.Drug facts box fingolimod Version 1.0 Author West Midlands Commissioning Support Unit Publication Date Jan 2013 Review Date Supersedes/New (Further fields as required
Version History Policy Title Drugs for MS.Drug facts box fingolimod Version 1.0 Author West Midlands Commissioning Support Unit Publication Date Jan 2013 Review Date Supersedes/New (Further fields as required
Post Traumatic and other Headache Syndromes. Danielle L. Erb, MD Brain Rehabilitation Medicine, LLC Brain Injury Rehab Center, PRA
 Post Traumatic and other Headache Syndromes Danielle L. Erb, MD Brain Rehabilitation Medicine, LLC Brain Injury Rehab Center, PRA Over 45 million Americans have chronic, recurring headaches 62% of these
Post Traumatic and other Headache Syndromes Danielle L. Erb, MD Brain Rehabilitation Medicine, LLC Brain Injury Rehab Center, PRA Over 45 million Americans have chronic, recurring headaches 62% of these
Manual therapies for primary chronic headaches: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials
 Chaibi and Russell The Journal of Headache and Pain 2014, 15:67 REVIEW ARTICLE Open Access Manual therapies for primary chronic headaches: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials Aleksander
Chaibi and Russell The Journal of Headache and Pain 2014, 15:67 REVIEW ARTICLE Open Access Manual therapies for primary chronic headaches: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials Aleksander
PROTOCOL SYNOPSIS Evaluation of long-term opioid efficacy for chronic pain
 P a g e 1 PROTOCOL SYNOPSIS Evaluation of long-term opioid efficacy for chronic pain Clinical Phase 4 Study Centers Study Period 25 U.S. sites identified and reviewed by the Steering Committee and Contract
P a g e 1 PROTOCOL SYNOPSIS Evaluation of long-term opioid efficacy for chronic pain Clinical Phase 4 Study Centers Study Period 25 U.S. sites identified and reviewed by the Steering Committee and Contract
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery. Migraine associated dizziness Department of Neuro-otology
 National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Migraine associated dizziness Department of Neuro-otology If you would like this document in another language or format or if you require the services of
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Migraine associated dizziness Department of Neuro-otology If you would like this document in another language or format or if you require the services of

![Bell s Palsy ]]> <![CDATA[Bell's Palsy]]> Bell s Palsy ]]> <![CDATA[Bell's Palsy]]>](/thumbs/27/10105461.jpg)