Ulcerative Colitis. National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
|
|
|
- Flora Parks
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
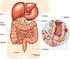
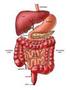
1 Ulcerative Colitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse What is ulcerative colitis? Ulcerative colitis is a chronic, or long lasting, disease that causes inflammation irritation or swelling and sores called ulcers on the inner lining of the large intestine. Ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammatory disease of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, called inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Crohn s disease and microscopic colitis are the other common IBDs. Read more in Crohn s Disease and Microscopic Colitis: Collagenous Colitis and Lymphocytic Colitis at IBD.aspx. Ulcerative colitis most often begins gradually and can become worse over time. Symptoms can be mild to severe. Most people have periods of remission times when symptoms disappear that can last for weeks or years. The goal of care is to keep people in remission long term. Most people with ulcerative colitis receive care from a gastroenterologist, a doctor who specializes in digestive diseases. What is the large intestine? The large intestine is part of the GI tract, a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus an opening through which stool leaves the body. The last part of the GI tract, called the lower GI tract, consists of the large intestine which includes the appendix, cecum, colon, and rectum and anus. The intestines are sometimes called the bowel. Small intestine Large intestine Cecum Appendix Anus The large intestine is part of the GI tract. Sigmoid colon Rectum Colon The large intestine is about 5 feet long in adults and absorbs water and any remaining nutrients from partially digested food passed from the small intestine. The large intestine changes waste from liquid to a solid matter called stool. Stool passes from the colon to the rectum. The rectum is located between the lower, or sigmoid, colon and the anus. The rectum stores stool prior to a bowel movement, when stool moves from the rectum to the anus and out of a person s body.
2 What causes ulcerative colitis? The exact cause of ulcerative colitis is unknown. Researchers believe the following factors may play a role in causing ulcerative colitis: overactive intestinal immune system genes environment Overactive intestinal immune system. Scientists believe one cause of ulcerative colitis may be an abnormal immune reaction in the intestine. Normally, the immune system protects the body from infection by identifying and destroying bacteria, viruses, and other potentially harmful foreign substances. Researchers believe bacteria or viruses can mistakenly trigger the immune system to attack the inner lining of the large intestine. This immune system response causes the inflammation, leading to symptoms. Genes. Ulcerative colitis sometimes runs in families. Research studies have shown that certain abnormal genes may appear in people with ulcerative colitis. However, researchers have not been able to show a clear link between the abnormal genes and ulcerative colitis. Environment. Some studies suggest that certain things in the environment may increase the chance of a person getting ulcerative colitis, although the overall chance is low. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, 1 antibiotics, 1 and oral contraceptives 2 may slightly increase the chance of developing ulcerative colitis. A high-fat diet may also slightly increase the chance of getting ulcerative colitis. 3 Some people believe eating certain foods, stress, or emotional distress can cause ulcerative colitis. Emotional distress does not seem to cause ulcerative colitis. A few studies suggest that stress may increase a person s chance of having a flare-up of ulcerative colitis. Also, some people may find that certain foods can trigger or worsen symptoms. Who is more likely to develop ulcerative colitis? Ulcerative colitis can occur in people of any age. However, it is more likely to develop in people between the ages of 15 and 30 4 older than 60 1 who have a family member with IBD of Jewish descent 2 Ulcerative Colitis
3 What are the signs and symptoms of ulcerative colitis? The most common signs and symptoms of ulcerative colitis are diarrhea with blood or pus and abdominal discomfort. Other signs and symptoms include an urgent need to have a bowel movement feeling tired nausea or loss of appetite weight loss fever anemia a condition in which the body has fewer red blood cells than normal Less common symptoms include joint pain or soreness eye irritation certain rashes The symptoms a person experiences can vary depending on the severity of the inflammation and where it occurs in the intestine. When symptoms first appear, most people with ulcerative colitis have mild to moderate symptoms about 10 percent of people can have severe symptoms, such as frequent, bloody bowel movements; fevers; and severe abdominal cramping 1 How is ulcerative colitis diagnosed? A health care provider diagnoses ulcerative colitis with the following: medical and family history physical exam lab tests endoscopies of the large intestine The health care provider may perform a series of medical tests to rule out other bowel disorders, such as irritable bowel syndrome, Crohn s disease, or celiac disease, that may cause symptoms similar to those of ulcerative colitis. Read more about these conditions at Medical and Family History Taking a medical and family history can help the health care provider diagnose ulcerative colitis and understand a patient s symptoms. The health care provider will also ask the patient about current and past medical conditions and medications. Physical Exam A physical exam may help diagnose ulcerative colitis. During a physical exam, the health care provider most often checks for abdominal distension, or swelling listens to sounds within the abdomen using a stethoscope taps on the abdomen to check for tenderness and pain 3 Ulcerative Colitis
4 Lab Tests A health care provider may order lab tests to help diagnose ulcerative colitis, including blood and stool tests. Blood tests. A blood test involves drawing blood at a health care provider s office or a lab. A lab technologist will analyze the blood sample. A health care provider may use blood tests to look for anemia inflammation or infection somewhere in the body markers that show ongoing inflammation low albumin, or protein common in patients with severe ulcerative colitis Stool tests. A stool test is the analysis of a sample of stool. A health care provider will give the patient a container for catching and storing the stool at home. The patient returns the sample to the health care provider or to a lab. A lab technologist will analyze the stool sample. Health care providers commonly order stool tests to rule out other causes of GI diseases, such as infection. Endoscopies of the Large Intestine Endoscopies of the large intestine are the most accurate methods for diagnosing ulcerative colitis and ruling out other possible conditions, such as Crohn s disease, diverticular disease, or cancer. Endoscopies of the large intestine include colonoscopy Colonoscopy. Colonoscopy is a test that uses a long, flexible, narrow tube with a light and tiny camera on one end, called a colonoscope or scope, to look inside the rectum and entire colon. In most cases, light anesthesia and pain medication help patients relax for the test. The medical staff will monitor a patient s vital signs and try to make him or her as comfortable as possible. A nurse or technician places an intravenous (IV) needle in a vein in the patient s arm or hand to give anesthesia. For the test, the patient will lie on a table or stretcher while the gastroenterologist inserts a colonoscope into the patient s anus and slowly guides it through the rectum and into the colon. The scope inflates the large intestine with air to give the gastroenterologist a better view. The camera sends a video image of the intestinal lining to a monitor, allowing the gastroenterologist to carefully examine the tissues lining the colon and rectum. The gastroenterologist may move the patient several times and adjust the scope for better viewing. Once the scope has reached the opening to the small intestine, the gastroenterologist slowly withdraws it and examines the lining of the colon and rectum again. A colonoscopy can show irritated and swollen tissue, ulcers, and abnormal growths such as polypsextra pieces of tissue that grow on the inner lining of the intestine. If the gastroenterologist suspects ulcerative colitis, he or she will biopsy the patient s colon and rectum. A biopsy is a procedure that involves taking small pieces of tissue for examination with a microscope. flexible sigmoidoscopy 4 Ulcerative Colitis
5 A health care provider will give patients written bowel prep instructions to follow at home before the test. The health care provider will also give patients information about how to care for themselves following the procedure. Flexible sigmoidoscopy. Flexible sigmoidoscopy is a test that uses a flexible, narrow tube with a light and tiny camera on one end, called a sigmoidoscope or scope, to look inside the rectum, the sigmoid colon, and sometimes the descending colon. In most cases, a patient does not need anesthesia. For the test, the patient will lie on a table or stretcher while the health care provider inserts the sigmoidoscope into the patient s anus and slowly guides it through the rectum, the sigmoid colon, and sometimes the descending colon. The scope inflates the large intestine with air to give the health care provider a better view. The camera sends a video image of the intestinal lining to a monitor, allowing the health care provider to examine the tissues lining the sigmoid colon and rectum. The health care provider may ask the patient to move several times and adjust the scope for better viewing. Once the scope reaches the end of the sigmoid colon, the health care provider slowly withdraws it while examining the lining of the colon and rectum again. The health care provider will look for signs of bowel diseases and conditions such as irritated and swollen tissue, ulcers, and polyps. If the health care provider suspects ulcerative colitis, he or she will biopsy the patient s colon and rectum. A health care provider will give patients written bowel prep instructions to follow at home before the test. The health care provider will also give patients information about how to care for themselves following the procedure. How is ulcerative colitis treated? A health care provider treats ulcerative colitis with medications surgery Which treatment a person needs depends on the severity of the disease and the symptoms. Each person experiences ulcerative colitis differently, so health care providers adjust treatments to improve the person s symptoms and induce, or bring about, remission. Medications While no medication cures ulcerative colitis, many can reduce symptoms. The goals of medication therapy are inducing and maintaining remission improving the person s quality of life Many people with ulcerative colitis require medication therapy indefinitely, unless they have their colon and rectum surgically removed. 5 Ulcerative Colitis
6 Health care providers will prescribe the medications that best treat a person s symptoms: aminosalicylates corticosteroids immunomodulators biologics, also called anti-tnf therapies other medications Depending on the location of the symptoms in the colon, health care providers may recommend a person take medications by enema, which involves flushing liquid medication into the rectum using a special wash bottle. The medication directly treats inflammation of the large intestine. rectal foam a foamy substance the person puts into the rectum like an enema. The medication directly treats inflammation of the large intestine. suppository a solid medication the person inserts into the rectum to dissolve. The intestinal lining absorbs the medication. mouth. IV. Aminosalicylates are medications that contain 5-aminosalicyclic acid (5-ASA), which helps control inflammation. Health care providers typically use aminosalicylates to treat people with mild or moderate symptoms or help people stay in remission. Aminosalicylates can be prescribed as an oral medication or a topical medication by enema or suppository. Combination therapy oral and rectal is most effective, even in people with extensive ulcerative colitis. 5 Aminosalicylates are generally well tolerated. Aminosalicylates include balsalazide mesalamine olsalazine sulfasalazine a combination of sulfapyridine and 5-ASA Some of the common side effects of aminosalicylates include abdominal pain diarrhea headaches nausea Health care providers may order routine blood tests for kidney function, as aminosalicylates can cause a rare allergic reaction in the kidneys. 6 Ulcerative Colitis
7 Corticosteroids, also known as steroids, help reduce the activity of the immune system and decrease inflammation. Health care providers prescribe corticosteroids for people with more severe symptoms and people who do not respond to aminosalicylates. Health care providers do not typically prescribe corticosteroids for long-term use. Corticosteroids are effective in bringing on remission; however, studies have not shown that the medications help maintain long-term remission. Corticosteroids include budesonide hydrocortisone methylprednisone prednisone Side effects of corticosteroids include acne a higher chance of developing infections bone mass loss death of bone tissue high blood glucose high blood pressure mood swings weight gain People who take budesonide may have fewer side effects than with other steroids. Immunomodulators reduce immune system activity, resulting in less inflammation in the colon. These medications can take several weeks to 3 months to start working. Immunomodulators include azathioprine 6-mercaptopurine, or 6-MP Health care providers prescribe these medications for people who do not respond to 5-ASAs. People taking these medications may have the following side effects: abnormal liver tests feeling tired infection low white blood cell count, which can lead to a higher chance of infection nausea and vomiting pancreatitis slightly increased chance of lymphoma slightly increased chance of nonmelanoma skin cancers Health care providers routinely test blood counts and liver function of people taking immunomodulators. People taking these medications should also have yearly skin cancer exams. People should talk with their health care provider about the risks and benefits of immunomodulators. 7 Ulcerative Colitis
8 Biologics including adalimumab, golimumab, infliximab, and vedolizumab are medications that target a protein made by the immune system called tumor necrosis factor (TNF). These medications decrease inflammation in the large intestine by neutralizing TNF. Anti-TNF therapies work quickly to bring on remission, especially in people who do not respond to other medications. Infliximab and vedolizumab are given through an IV; adalimumab and golimumab are given by injection. Health care providers will screen patients for tuberculosis and hepatitis B before starting treatment with anti-tnf medications. Side effects of anti-tnf medications may include a higher chance of developing infections especially tuberculosis or fungal infection skin cancer melanoma psoriasis Other medications to treat symptoms or complications may include acetaminophen for mild pain. People with ulcerative colitis should avoid using ibuprofen, naproxen, and aspirin since these medications can make symptoms worse. loperamide to help slow or stop diarrhea. In most cases, people only take this medication for short periods of time since it can increase the chance of developing megacolon. People should check with a health care provider before taking loperamide, because those with significantly active ulcerative colitis should not take this medication. 6 cyclosporine health care providers prescribe this medication only for people with severe ulcerative colitis because of the side effects. People should talk with their health care provider about the risks and benefits of cyclosporine. Surgery Some people will need surgery to treat their ulcerative colitis when they have colon cancer dysplasia, or precancerous cells in the colon complications that are life threatening, such as megacolon or bleeding no improvement in symptoms or condition despite treatment continued dependency on steroids side effects from medications that threaten their health antibiotics to prevent or treat infections. 8 Ulcerative Colitis
9 Removal of the entire colon, including the rectum, cures ulcerative colitis. A surgeon performs the procedure at a hospital. A surgeon can perform two different types of surgery to remove a patient s colon and treat ulcerative colitis: proctocolectomy and ileostomy proctocolectomy and ileoanal reservoir Full recovery from both operations may take 4 to 6 weeks. Proctocolectomy and ileostomy. A proctocolectomy is surgery to remove a patient s entire colon and rectum. An ileostomy is a stoma, or opening in the abdomen, that a surgeon creates from a part of the ileum the last section of the small intestine. The surgeon brings the end of the ileum through an opening in the patient s abdomen and attaches it to the skin, creating an opening outside of the patient s body. The stoma most often is located in the lower part of the patient s abdomen, just below the beltline. A removable external collection pouch, called an ostomy pouch or ostomy appliance, connects to the stoma and collects intestinal contents outside the patient s body. Intestinal contents pass through the stoma instead of passing through the anus. The stoma has no muscle, so it cannot control the flow of intestinal contents, and the flow occurs whenever peristalsis occurs. Peristalsis is the movement of the organ walls that propels food and liquid through the GI tract. People who have this type of surgery will have the ileostomy for the rest of their lives. Stoma Ileostomy Anus Colon Ileum Rectum 9 Ulcerative Colitis
10 Proctocolectomy and ileoanal reservoir. An ileoanal reservior is an internal pouch made from the patient s ileum. This surgery is a common alternative to an ileostomy and does not have a permanent stoma. Ileoanal reservoir is also known as a J-pouch, a pelvic pouch, or an ileoanal pouch anastamosis. The ileoanal reservior connects the ileum to the anus. The surgeon preserves the outer muscles of the patient s rectum during the proctocolectomy. Next, the surgeon creates the ileal pouch and attaches it to the end of the rectum. Waste is stored in the pouch and passes through the anus. Ileoanal reservoir Anus Colon (removed) Ileum After surgery, bowel movements may be more frequent and watery than before the procedure. People may have fecal incontinence the accidental passing of solid or liquid stool or mucus from the rectum. Medications can be used to control pouch function. Women may be infertile following the surgery. Many people develop pouchitis in the ileoanal reservoir. Pouchitis is an irritation or inflammation of the lining of the ileoanal reservoir. A health care provider treats pouchitis with antibiotics. Rarely, pouchitis can become chronic and require long-term antibiotics or other medications. The surgeon will recommend one of the operations based on a person s symptoms, severity of disease, expectations, age, and Ileoanal reservoir lifestyle. Before making a decision, the person should get as much information as possible by talking with health care providers enterostomal therapists, nurses who work with colon-surgery patients people who have had one of the surgeries Patient-advocacy organizations can provide information about support groups and other resources. Read more about ostomy surgery at 10 Ulcerative Colitis
11 Eating, Diet, and Nutrition Researchers have not found that eating, diet, and nutrition play a role in causing ulcerative colitis symptoms. Good nutrition is important in the management of ulcerative colitis, however. Dietary changes can help reduce symptoms. A health care provider may recommend dietary changes such as avoiding carbonated drinks avoiding popcorn, vegetable skins, nuts, and other high-fiber foods while a person has symptoms drinking more liquids eating smaller meals more often keeping a food diary to help identify troublesome foods Health care providers may recommend nutritional supplements and vitamins for people who do not absorb enough nutrients. To help ensure coordinated and safe care, people should discuss their use of complementary and alternative medical practices, including their use of dietary supplements and probiotics, with their health care provider. Read more at Depending on a person s symptoms or medications, a health care provider may recommend a specific diet, such as a high-calorie diet lactose-free diet low-fat diet low-fiber diet low-salt diet People should speak with a health care provider about specific dietary recommendations and changes. What are the complications of ulcerative colitis? Complications of ulcerative colitis can include rectal bleeding when ulcers in the intestinal lining open and bleed. Rectal bleeding can cause anemia, which health care providers can treat with diet changes and iron supplements. People who have a large amount of bleeding in the intestine over a short period of time may require surgery to stop the bleeding. Severe bleeding is a rare complication of ulcerative colitis. dehydration and malabsorbtion, which occur when the large intestine is unable to absorb fluids and nutrients because of diarrhea and inflammation. Some people may need IV fluids to replace lost nutrients and fluids. 11 Ulcerative Colitis
12 changes in bones. Some corticosteroid medications taken to treat ulcerative colitis symptoms can cause osteoporosis the loss of bone osteopenia low bone density Health care providers will monitor people for bone loss and can recommend calcium and vitamin D supplements and medications to help prevent or slow bone loss. inflammation in other areas of the body. The immune system can trigger inflammation in the joints eyes skin liver Health care providers can treat inflammation by adjusting medications or prescribing new medications. megacolon a serious complication that occurs when inflammation spreads to the deep tissue layers of the large intestine. The large intestine swells and stops working. Megacolon can be a lifethreatening complication and most often requires surgery. Megacolon is a rare complication of ulcerative colitis. Ulcerative Colitis and Colon Cancer People with ulcerative colitis may be more likely to develop colon cancer when ulcerative colitis affects the entire colon a person has ulcerative colitis for at least 8 years inflammation is ongoing people also have primary sclerosing cholangitis, a condition that affects the liver a person is male People who receive ongoing treatment and remain in remission may reduce their chances of developing colon cancer. People with ulcerative colitis should talk with their health care provider about how often they should get screened for colon cancer. Screening can include colonoscopy with biopsies or a special dye spray called chromoendoscopy. Health care providers may recommend colonoscopy every 1 to 3 years for people with ulcerative colitis who have the disease in one-third or more or of their colon had ulcerative colitis for 8 years Such screening does not reduce a person s chances of developing colon cancer. Instead, screening can help diagnose cancer early and improve chances for recovery. Surgery to remove the entire colon eliminates the risk of colon cancer. 12 Ulcerative Colitis
13 Points to Remember Ulcerative colitis is a chronic, or long lasting, disease that causes inflammation irritation or swelling and sores called ulcers on the inner lining of the large intestine. The exact cause of ulcerative colitis is unknown. Researchers believe that factors such as an overactive intestinal immune system, genes, and environment may play a role in causing ulcerative colitis. Ulcerative colitis can occur in people of any age. However, it is more likely to develop in people between the ages of 15 and 30 older than 60 who have a family member with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) of Jewish descent The most common signs and symptoms of ulcerative colitis are diarrhea with blood or pus and abdominal discomfort. A health care provider diagnoses ulcerative colitis with the following: medical and family history physical exam lab tests endoscopies of the large intestine Which treatment a person needs depends on the severity of the disease and symptoms. Good nutrition is important in the management of ulcerative colitis. A health care provider may recommend that a person make dietary changes. People with ulcerative colitis should talk with their health care provider about how often they should get screened for colon cancer. 13 Ulcerative Colitis
14 Hope through Research The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK s) Division of Digestive Diseases and Nutrition conducts and supports basic and clinical research into many digestive disorders. Clinical trials are research studies involving people. Clinical trials look at safe and effective new ways to prevent, detect, or treat disease. Researchers also use clinical trials to look at other aspects of care, such as improving the quality of life for people with chronic illnesses. To learn more about clinical trials, why they matter, and how to participate, visit the NIH Clinical Research Trials and You website at clinicaltrials. For information about current studies, visit References 1. Shanahan F. Ulcerative colitis. In: Hawkey CJ, Bosch J, Richter JE, Garcia- Tsao G, Chan FKL, eds. Textbook of Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 2nd ed. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell; 2012: Ko Y, Butcher R, Leong RW. Epidemiological studies of migration and environmental risk factors in the inflammatory bowel diseases. World Journal of Gastroenterology. 2014;20(5): Hou JK, Abraham B, El-Serag H. Dietary intake and risk of developing inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review of the literature. American Journal of Gastroenterology. 2011;106(4): Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. Updated January 14, Accessed July 23, Kornbluth A, Sachar DB. Ulcerative colitis practice guidelines in adults: American College of Gastroenterology, Practice Parameters Committee. American Journal of Gastroenterology. 2010;105(3): Walfish AE, Sachar DB. Ulcerative colitis. The Merck Manual website. gastrointestinal_disorders/inflammatory_ bowel_disease_ibd/ulcerative_colitis. html. Updated December Accessed July 23, Ulcerative Colitis
15 For More Information Center for the Study of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Ramnik Xavier, M.D., Ph.D., Director Phone: Internet: Crohn s & Colitis Foundation of America 733 Third Avenue, Suite 510 New York, NY Phone: info@ccfa.org Internet: United Ostomy Associations of America, Inc Rice Street, Suite 275 Roseville, MN Phone: info@ostomy.org Internet: Acknowledgments Publications produced by the Clearinghouse are carefully reviewed by both NIDDK scientists and outside experts. This publication was originally reviewed by the Crohn s & Colitis Foundation of America. Adam Cheifetz, M.D., Beth Israel Deaconness Medical Center and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, reviewed the updated version of this publication. You may also find additional information about this topic by visiting MedlinePlus at This publication may contain information about medications and, when taken as prescribed, the conditions they treat. When prepared, this publication included the most current information available. For updates or for questions about any medications, contact the U.S. Food and Drug Administration toll-free at INFO FDA ( ) or visit Consult your health care provider for more information. 15 Ulcerative Colitis
16 National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse 2 Information Way Bethesda, MD Phone: TTY: Fax: nddic@info.niddk.nih.gov Internet: The National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse (NDDIC) is a service of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK). The NIDDK is part of the National Institutes of Health of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Established in 1980, the Clearinghouse provides information about digestive diseases to people with digestive disorders and to their families, health care professionals, and the public. The NDDIC answers inquiries, develops and distributes publications, and works closely with professional and patient organizations and Government agencies to coordinate resources about digestive diseases. This publication is not copyrighted. The Clearinghouse encourages users of this publication to duplicate and distribute as many copies as desired. This publication is available at NIH Publication No September 2014 The NIDDK prints on recycled paper with bio-based ink.
Ulcerative Colitis. National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse. What is ulcerative colitis (UC)?
 Ulcerative Colitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is ulcerative colitis (UC)? Ulcerative colitis is
Ulcerative Colitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is ulcerative colitis (UC)? Ulcerative colitis is
Microscopic Colitis: Collagenous Colitis and Lymphocytic Colitis
 Microscopic Colitis: Collagenous Colitis and Lymphocytic Colitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is
Microscopic Colitis: Collagenous Colitis and Lymphocytic Colitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is
Flexible Sigmoidoscopy
 Flexible Sigmoidoscopy National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is flexible sigmoidoscopy? Flexible sigmoidoscopy
Flexible Sigmoidoscopy National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is flexible sigmoidoscopy? Flexible sigmoidoscopy
Crohn s Disease. What I need to know about. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services
 What I need to know about Crohn s Disease NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services What I need to know about Crohn
What I need to know about Crohn s Disease NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services What I need to know about Crohn
Understanding Colitis and Crohn s Disease
 Improving life for people affected by Colitis and Crohn s Disease Understanding Colitis and Crohn s Disease 1 Understanding Colitis and Crohn s Disease Understanding Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn s Disease...
Improving life for people affected by Colitis and Crohn s Disease Understanding Colitis and Crohn s Disease 1 Understanding Colitis and Crohn s Disease Understanding Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn s Disease...
Chronic Diarrhea in Children
 Chronic Diarrhea in Children National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse What is chronic diarrhea? Diarrhea is loose, watery stools. Chronic, or long lasting, diarrhea typically lasts for more
Chronic Diarrhea in Children National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse What is chronic diarrhea? Diarrhea is loose, watery stools. Chronic, or long lasting, diarrhea typically lasts for more
Complications that may occur with ulcerative colitis:
 Ulcerative Colitis What is ulcerative colitis? Ulcerative colitis is one of the major forms of inflammatory bowel disease. The other major form is Crohn s disease. Ulcerative colitis is felt to be due
Ulcerative Colitis What is ulcerative colitis? Ulcerative colitis is one of the major forms of inflammatory bowel disease. The other major form is Crohn s disease. Ulcerative colitis is felt to be due
Colon and Rectal Cancer
 Colon and Rectal Cancer What is colon or rectal cancer? Colon or rectal cancer is the growth of abnormal cells in your large intestine, which is also called the large bowel. The colon is the last 5 feet
Colon and Rectal Cancer What is colon or rectal cancer? Colon or rectal cancer is the growth of abnormal cells in your large intestine, which is also called the large bowel. The colon is the last 5 feet
Colon Polyps. What I need to know about. National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH
 What I need to know about Colon Polyps U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse What I need to know about Colon
What I need to know about Colon Polyps U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse What I need to know about Colon
Gastrointestinal Bleeding
 Gastrointestinal Bleeding Introduction Gastrointestinal bleeding is a symptom of many diseases rather than a disease itself. A number of different conditions can cause gastrointestinal bleeding. Some causes
Gastrointestinal Bleeding Introduction Gastrointestinal bleeding is a symptom of many diseases rather than a disease itself. A number of different conditions can cause gastrointestinal bleeding. Some causes
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
 What I need to know about Irritable Bowel Syndrome NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services What I need to know
What I need to know about Irritable Bowel Syndrome NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services What I need to know
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
 Irritable Bowel Syndrome National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)? Irritable
Irritable Bowel Syndrome National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)? Irritable
Laparoscopic Colectomy. What do I need to know about my laparoscopic colorectal surgery?
 Laparoscopic Colectomy What do I need to know about my laparoscopic colorectal surgery? Traditionally, colon & rectal surgery requires a large, abdominal and/or pelvic incision, which often requires a
Laparoscopic Colectomy What do I need to know about my laparoscopic colorectal surgery? Traditionally, colon & rectal surgery requires a large, abdominal and/or pelvic incision, which often requires a
Ulcerative Colitis & Proctitis. About Ulcerative Colitis & Proctitis
 Ulcerative Colitis & Proctitis About Ulcerative Colitis & Proctitis When you first learn that you have ulcerative colitis, you will probably feel overwhelmed. You may not even have heard of ulcerative
Ulcerative Colitis & Proctitis About Ulcerative Colitis & Proctitis When you first learn that you have ulcerative colitis, you will probably feel overwhelmed. You may not even have heard of ulcerative
Laparoscopic Surgery of the Colon and Rectum (Large Intestine) A Simple Guide to Help Answer Your Questions
 Laparoscopic Surgery of the Colon and Rectum (Large Intestine) A Simple Guide to Help Answer Your Questions What are the Colon and Rectum? The colon and rectum together make up the large intestine. After
Laparoscopic Surgery of the Colon and Rectum (Large Intestine) A Simple Guide to Help Answer Your Questions What are the Colon and Rectum? The colon and rectum together make up the large intestine. After
Problems of the Digestive System
 The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists f AQ FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS FAQ120 WOMEN S HEALTH Problems of the Digestive System What are some common digestive problems? What is constipation?
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists f AQ FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS FAQ120 WOMEN S HEALTH Problems of the Digestive System What are some common digestive problems? What is constipation?
Hepatitis C. What I need to know about. National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH
 What I need to know about Hepatitis C U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse What I need to know about Hepatitis
What I need to know about Hepatitis C U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse What I need to know about Hepatitis
Living with Ulcerative Colitis
 Living with Ulcerative Colitis What s Inside? Understanding the diagnosis 1 What is ulcerative colitis? 2 Will it ever go away? 3 A brief introduction to the 3 gastrointestinal (GI) tract Who gets ulcerative
Living with Ulcerative Colitis What s Inside? Understanding the diagnosis 1 What is ulcerative colitis? 2 Will it ever go away? 3 A brief introduction to the 3 gastrointestinal (GI) tract Who gets ulcerative
Bile Duct Diseases and Problems
 Bile Duct Diseases and Problems Introduction A bile duct is a tube that carries bile between the liver and gallbladder and the intestine. Bile is a substance made by the liver that helps with digestion.
Bile Duct Diseases and Problems Introduction A bile duct is a tube that carries bile between the liver and gallbladder and the intestine. Bile is a substance made by the liver that helps with digestion.
Hepatitis A. What I need to know about. National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH
 What I need to know about Hepatitis A U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse What I need to know about Hepatitis
What I need to know about Hepatitis A U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse What I need to know about Hepatitis
What Is Clostridium Difficile (C. Diff)? CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE (C. DIFF)
 What Is Clostridium Difficile (C. Diff)? Clostridium difficile, or C. diff for short, is an infection from a bacterium, or bug, that can grow in your intestines and cause bad GI symptoms. The main risk
What Is Clostridium Difficile (C. Diff)? Clostridium difficile, or C. diff for short, is an infection from a bacterium, or bug, that can grow in your intestines and cause bad GI symptoms. The main risk
Hepatitis B. What I need to know about. National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH
 What I need to know about Hepatitis B U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse What I need to know about Hepatitis
What I need to know about Hepatitis B U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse What I need to know about Hepatitis
Wilson Disease. National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Wilson Disease National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is Wilson disease? Wilson disease is a genetic disorder
Wilson Disease National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is Wilson disease? Wilson disease is a genetic disorder
Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection
 Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is pyelonephritis? Pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is pyelonephritis? Pyelonephritis
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE. Multiple Technology Appraisal
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Multiple Technology Appraisal Infliximab, adalimumab and golimumab for treating moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis after the failure of conventional
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Multiple Technology Appraisal Infliximab, adalimumab and golimumab for treating moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis after the failure of conventional
Understanding Laparoscopic Colorectal Surgery
 Understanding Laparoscopic Colorectal Surgery University Colon & Rectal Surgery A Problem with Your Colon Your doctor has told you that you have a colon problem. Now you ve learned that surgery is needed
Understanding Laparoscopic Colorectal Surgery University Colon & Rectal Surgery A Problem with Your Colon Your doctor has told you that you have a colon problem. Now you ve learned that surgery is needed
National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Gastritis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is gastritis? Gastritis is a condition in which the stomach
Gastritis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is gastritis? Gastritis is a condition in which the stomach
Arthritis and Rheumatology Clinics of Kansas Patient Education. Reactive Arthritis (ReA) / Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Arthritis
 Arthritis and Rheumatology Clinics of Kansas Patient Education Reactive Arthritis (ReA) / Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Arthritis Introduction: For as long as scientists have studied rheumatic disease,
Arthritis and Rheumatology Clinics of Kansas Patient Education Reactive Arthritis (ReA) / Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Arthritis Introduction: For as long as scientists have studied rheumatic disease,
Diverticulosis and Diverticulitis
 Diverticulosis and Diverticulitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What are diverticulosis and diverticulitis?
Diverticulosis and Diverticulitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What are diverticulosis and diverticulitis?
Patients who fail to bring a driver/someone to stay with them for the night will have their procedure cancelled immediately.
 Preparing for your Colonoscopy You must have someone and/or a driver accompany you and stay with you for 24 hours after your procedure. Patients who fail to bring a driver/someone to stay with them for
Preparing for your Colonoscopy You must have someone and/or a driver accompany you and stay with you for 24 hours after your procedure. Patients who fail to bring a driver/someone to stay with them for
The degree of liver inflammation or damage (grade) Presence and extent of fatty liver or other metabolic liver diseases
 ilearning about your health Liver Biopsy www.cpmc.org/learning What is a Liver Biopsy? A liver biopsy is a procedure where a specially trained doctor (typically a hepatologist, radiologist, or gastroenterologist)
ilearning about your health Liver Biopsy www.cpmc.org/learning What is a Liver Biopsy? A liver biopsy is a procedure where a specially trained doctor (typically a hepatologist, radiologist, or gastroenterologist)
The Digestive System
 School of Social Work The Digestive System Undergraduate researcher: Nancy D. Bergerson (2010). 1 The Digestive System breaks down and absorbs food. When food is eaten, it is not in a form the body can
School of Social Work The Digestive System Undergraduate researcher: Nancy D. Bergerson (2010). 1 The Digestive System breaks down and absorbs food. When food is eaten, it is not in a form the body can
By Anne C. Travis, M.D., M.Sc. and John R. Saltzman, M.D., FACG Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA
 SMALL BOWEL BLEEDING: CAUSES, DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT By Anne C. Travis, M.D., M.Sc. and John R. Saltzman, M.D., FACG Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA 1. What is the small
SMALL BOWEL BLEEDING: CAUSES, DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT By Anne C. Travis, M.D., M.Sc. and John R. Saltzman, M.D., FACG Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA 1. What is the small
Presence and extent of fatty liver or other metabolic liver diseases
 UC San Diego Health System Patient Information Sheet: Liver Biopsy What is a Liver Biopsy? A liver biopsy is a procedure where a qualified doctor (typically a hepatologist, radiologist or gastroenterologist)
UC San Diego Health System Patient Information Sheet: Liver Biopsy What is a Liver Biopsy? A liver biopsy is a procedure where a qualified doctor (typically a hepatologist, radiologist or gastroenterologist)
Peptic Ulcer. Anatomy The stomach is a hollow organ. It is located in the upper abdomen, under the ribs.
 Peptic Ulcer Introduction A peptic ulcer is a sore in the lining of your stomach or duodenum. The duodenum is the first part of your small intestine. Peptic ulcers may also develop in the esophagus. Nearly
Peptic Ulcer Introduction A peptic ulcer is a sore in the lining of your stomach or duodenum. The duodenum is the first part of your small intestine. Peptic ulcers may also develop in the esophagus. Nearly
COLORECTAL CANCER SCREENING
 COLORECTAL CANCER SCREENING By Douglas K. Rex, M.D., FACG & Suthat Liangpunsakul, M.D. Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Medicine Indiana University School of Medicine Indianapolis,
COLORECTAL CANCER SCREENING By Douglas K. Rex, M.D., FACG & Suthat Liangpunsakul, M.D. Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Medicine Indiana University School of Medicine Indianapolis,
Managing Flares. and Other IBD Symptoms. Information Resource Center (888.694.8872)
 Managing Flares and Other IBD Symptoms Information Resource Center 888.MY.GUT.PAIN (888.694.8872) www.ccfa.org What s Inside? What is a flare? 3 What can cause a flare? 5 Flares from ulcerative colitis
Managing Flares and Other IBD Symptoms Information Resource Center 888.MY.GUT.PAIN (888.694.8872) www.ccfa.org What s Inside? What is a flare? 3 What can cause a flare? 5 Flares from ulcerative colitis
C. difficile Infections
 C. difficile Infections Introduction C. difficile is a type of bacteria that can cause diarrhea and infection of the colon. This bacterium is more likely to infect patients at hospitals and other healthcare
C. difficile Infections Introduction C. difficile is a type of bacteria that can cause diarrhea and infection of the colon. This bacterium is more likely to infect patients at hospitals and other healthcare
Multiple Myeloma. This reference summary will help you understand multiple myeloma and its treatment options.
 Multiple Myeloma Introduction Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells. Each year, thousands of people find out that they have multiple myeloma. This reference summary will help
Multiple Myeloma Introduction Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells. Each year, thousands of people find out that they have multiple myeloma. This reference summary will help
Once the immune system is triggered, cells migrate from the blood into the joints and produce substances that cause inflammation.
 HealthExchange Points For Your Joints An Arthritis Talk Howard Epstein, MD Orthopaedic & Rheumatologic Institute Rheumatic & Immunologic Disease Cleveland Clinic Beachwood Family Health & Surgery Center
HealthExchange Points For Your Joints An Arthritis Talk Howard Epstein, MD Orthopaedic & Rheumatologic Institute Rheumatic & Immunologic Disease Cleveland Clinic Beachwood Family Health & Surgery Center
Biologic Treatments for Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Biologic Treatments Rheumatoid Arthritis (also known as cytokine inhibitors, TNF inhibitors, IL 1 inhibitor, or Biologic Response Modifiers) Description Biologics are new class of drugs that have been
Biologic Treatments Rheumatoid Arthritis (also known as cytokine inhibitors, TNF inhibitors, IL 1 inhibitor, or Biologic Response Modifiers) Description Biologics are new class of drugs that have been
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Xofigo Therapy. For metastatic prostate cancer. What is Xofigo? How does it work?
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Xofigo Therapy For metastatic prostate cancer This handout explains how the drug Xofigo is used to treat metastatic prostate cancer. What is Xofigo? Xofigo is a radioactive
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Xofigo Therapy For metastatic prostate cancer This handout explains how the drug Xofigo is used to treat metastatic prostate cancer. What is Xofigo? Xofigo is a radioactive
Chemotherapy Side Effects Worksheet
 Page 1 of 6 Chemotherapy Side Effects Worksheet Medicines or drugs that destroy cancer cells are called cancer chemotherapy. It is sometimes the first choice for treating many cancers. Chemotherapy differs
Page 1 of 6 Chemotherapy Side Effects Worksheet Medicines or drugs that destroy cancer cells are called cancer chemotherapy. It is sometimes the first choice for treating many cancers. Chemotherapy differs
Medical Tests for Prostate Problems
 Medical Tests for Prostate Problems National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is the prostate? The
Medical Tests for Prostate Problems National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is the prostate? The
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
 Irritable Bowel Syndrome National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH U.S. Department of Health and
Irritable Bowel Syndrome National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH U.S. Department of Health and
University of California, Berkeley 2222 Bancroft Way Berkeley, CA 94720 Appointments 510/642-2000 Online Appointment www.uhs.berkeley.
 Constipation Why Am I Constipated? Constipation is passage of small amounts of hard, dry bowel movements, usually fewer than three times a week. People who are constipated may find it difficult and painful
Constipation Why Am I Constipated? Constipation is passage of small amounts of hard, dry bowel movements, usually fewer than three times a week. People who are constipated may find it difficult and painful
Colorectal Cancer Screening
 Colorectal Cancer Screening Introduction Colorectal cancer (cancer of the large intestine) is the second most common cause of death from cancer in the United States, after lung cancer. However, colorectal
Colorectal Cancer Screening Introduction Colorectal cancer (cancer of the large intestine) is the second most common cause of death from cancer in the United States, after lung cancer. However, colorectal
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/pmh0001295/?report=printable
 of 13 Crohn's disease - PubMed Health PubMed Health. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health. A.D.A.M. Medical Encyclopedia. Atlanta (GA): A.D.A.M.; 2011. Crohn's disease
of 13 Crohn's disease - PubMed Health PubMed Health. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health. A.D.A.M. Medical Encyclopedia. Atlanta (GA): A.D.A.M.; 2011. Crohn's disease
EVIDENCE BASED TREATMENT OF CROHN S DISEASE. Dr E Ndabaneze
 EVIDENCE BASED TREATMENT OF CROHN S DISEASE Dr E Ndabaneze PLAN 1. Case presentation 2. Topic on Evidence based Treatment of Crohn s disease - Introduction pathology aetiology - Treatment - concept of
EVIDENCE BASED TREATMENT OF CROHN S DISEASE Dr E Ndabaneze PLAN 1. Case presentation 2. Topic on Evidence based Treatment of Crohn s disease - Introduction pathology aetiology - Treatment - concept of
MANAGING ANEMIA. When You Have Kidney Disease or Kidney Failure. www.kidney.org
 MANAGING ANEMIA When You Have Kidney Disease or Kidney Failure www.kidney.org About the Information in this Booklet Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation (NKF) offers guidelines and commentaries
MANAGING ANEMIA When You Have Kidney Disease or Kidney Failure www.kidney.org About the Information in this Booklet Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation (NKF) offers guidelines and commentaries
Colorectal Cancer Care A Cancer Care Map for Patients
 Colorectal Cancer Care A Cancer Care Map for Patients Understanding the process of care that a patient goes through in the diagnosis and treatment of colorectal cancer in BC. Colorectal Cancer Care Map
Colorectal Cancer Care A Cancer Care Map for Patients Understanding the process of care that a patient goes through in the diagnosis and treatment of colorectal cancer in BC. Colorectal Cancer Care Map
Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis
 Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis Summary Crohn s disease and ulcerative colitis are collectively known as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Crohn s disease can appear in any part of a person s digestive
Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis Summary Crohn s disease and ulcerative colitis are collectively known as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Crohn s disease can appear in any part of a person s digestive
Guide to Abdominal or Gastroenterological Surgery Claims
 What are the steps towards abdominal surgery? Investigation and Diagnosis It is very important that all necessary tests are undertaken to investigate the patient s symptoms appropriately and an accurate
What are the steps towards abdominal surgery? Investigation and Diagnosis It is very important that all necessary tests are undertaken to investigate the patient s symptoms appropriately and an accurate
Quick Facts about Appendix Cancer
 Quick Facts about Appendix Cancer What is the appendix? The appendix is a pouch-like tube attached to the first part of the large intestine (cecum). The appendix is about 10 centimetres long and has no
Quick Facts about Appendix Cancer What is the appendix? The appendix is a pouch-like tube attached to the first part of the large intestine (cecum). The appendix is about 10 centimetres long and has no
Lawyers / Attorneys: Evaluation of Nationwide Accutane Accidents, Injuries & Death
 The Fox Law Firm is Reviewing Potential ACCUTANE Claims. In the United States, jury trials have awarded at least $33 million dollars to patients as compensation for injuries attributed to Accutane use.
The Fox Law Firm is Reviewing Potential ACCUTANE Claims. In the United States, jury trials have awarded at least $33 million dollars to patients as compensation for injuries attributed to Accutane use.
Medicines for Psoriatic Arthritis. A Review of the Research for Adults
 Medicines for Psoriatic Arthritis A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor* has told you that you have psoriatic (pronounced
Medicines for Psoriatic Arthritis A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor* has told you that you have psoriatic (pronounced
You may have the following signs and symptoms, depending on which part of the colon is inflamed:
 Diseases and Conditions Ulcerative colitis By Mayo Clinic Staff Ulcerative colitis (UL-sur-uh-tiv koe-lie-tis) is an inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that causes long-lasting inflammation and ulcers (sores)
Diseases and Conditions Ulcerative colitis By Mayo Clinic Staff Ulcerative colitis (UL-sur-uh-tiv koe-lie-tis) is an inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that causes long-lasting inflammation and ulcers (sores)
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
 Irritable Bowel Syndrome National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)? Irritable
Irritable Bowel Syndrome National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)? Irritable
Crohn s Disease. What is Crohn s Disease? ho gets Crohn s Disease? hat are the symptoms? What causes Crohn s Disease?
 In association with: Primary Care Society for Gastroenterology INFORMATION ABOUT Crohn s Disease What is Crohn s Disease? ho gets Crohn s Disease? What causes Crohn s Disease? hat does it do to the intestine?
In association with: Primary Care Society for Gastroenterology INFORMATION ABOUT Crohn s Disease What is Crohn s Disease? ho gets Crohn s Disease? What causes Crohn s Disease? hat does it do to the intestine?
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer
 Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
Ulcerative Colitis. Living with
 Living with Ulcerative Colitis Our Mission: To cure and prevent Crohn s disease and ulcerative colitis through research, and to improve the quality of life of children and adults affected by these digestive
Living with Ulcerative Colitis Our Mission: To cure and prevent Crohn s disease and ulcerative colitis through research, and to improve the quality of life of children and adults affected by these digestive
Colonoscopy Preparation Instructions with PEG-3350 (TriLyte, Colyte, NuLytely or GoLytely)
 Colonoscopy Preparation Instructions with PEG-3350 (TriLyte, Colyte, NuLytely or GoLytely) IMPORTANT: For best results and to prevent the need to cancel or reschedule your colonoscopy: Only follow department
Colonoscopy Preparation Instructions with PEG-3350 (TriLyte, Colyte, NuLytely or GoLytely) IMPORTANT: For best results and to prevent the need to cancel or reschedule your colonoscopy: Only follow department
PATIENT CONSENT TO PROCEDURE - ROUX-EN-Y GASTRIC BYPASS
 As a patient you must be adequately informed about your condition and the recommended surgical procedure. Please read this document carefully and ask about anything you do not understand. Please initial
As a patient you must be adequately informed about your condition and the recommended surgical procedure. Please read this document carefully and ask about anything you do not understand. Please initial
Appendicitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
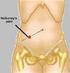 Appendicitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH The appendix is a small, tube-like structure
Appendicitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH The appendix is a small, tube-like structure
Care and Problems of the Digestive System. Chapter 18 Lesson 2
 Care and Problems of the Digestive System Chapter 18 Lesson 2 Care of the Digestive System Good eating habits are the best way to avoid or minimize digestive system problems. Eat a variety of foods Avoid
Care and Problems of the Digestive System Chapter 18 Lesson 2 Care of the Digestive System Good eating habits are the best way to avoid or minimize digestive system problems. Eat a variety of foods Avoid
Surgical Weight Loss. Mission Bariatrics
 Surgical Weight Loss Mission Bariatrics Obesity is a major health problem in the United States, with more than one in every three people suffering from this chronic condition. Obese adults are at an increased
Surgical Weight Loss Mission Bariatrics Obesity is a major health problem in the United States, with more than one in every three people suffering from this chronic condition. Obese adults are at an increased
TREATING INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE (IBD) BACKGROUNDER
 Press information for journalists only TREATING INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE (IBD) BACKGROUNDER Why treat IBD? IBD describes a range of chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal system, encompassing Ulcerative
Press information for journalists only TREATING INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE (IBD) BACKGROUNDER Why treat IBD? IBD describes a range of chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal system, encompassing Ulcerative
Patient Information Once Weekly FOSAMAX (FOSS-ah-max) (alendronate sodium) Tablets and Oral Solution
 Patient Information Once Weekly FOSAMAX (FOSS-ah-max) (alendronate sodium) Tablets and Oral Solution Read this information before you start taking FOSAMAX *. Also, read the leaflet each time you refill
Patient Information Once Weekly FOSAMAX (FOSS-ah-max) (alendronate sodium) Tablets and Oral Solution Read this information before you start taking FOSAMAX *. Also, read the leaflet each time you refill
Surgery. for Crohn s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis
 Surgery for Crohn s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis What s Inside? About Crohn s disease and 2 ulcerative colitis When is surgery necessary? 3 Reasons for elective surgery 3 Conditions that require 5 immediate
Surgery for Crohn s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis What s Inside? About Crohn s disease and 2 ulcerative colitis When is surgery necessary? 3 Reasons for elective surgery 3 Conditions that require 5 immediate
Teachers. Other School Personnel. and. A Guide for. 800.932.2423 www.ccfa.org
 800.932.2423 www.ccfa.org National Headquarters 386 Park Avenue South 17th Floor New York, NY 10016-8804 A Guide for Teachers and Other School Personnel A Guide for Teachers and Other School Personnel
800.932.2423 www.ccfa.org National Headquarters 386 Park Avenue South 17th Floor New York, NY 10016-8804 A Guide for Teachers and Other School Personnel A Guide for Teachers and Other School Personnel
Bowel Control Problems
 Bowel Control Problems WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Bowel control problems affect at least 1 million people in the United States. Loss of normal control of the bowels is
Bowel Control Problems WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Bowel control problems affect at least 1 million people in the United States. Loss of normal control of the bowels is
Urinary Diversion: Ileovesicostomy/Ileal Loop/Colon Loop
 Urinary Diversion: Ileovesicostomy/Ileal Loop/Colon Loop Why do I need this surgery? A urinary diversion is a surgical procedure that is performed to allow urine to safely pass from the kidneys into a
Urinary Diversion: Ileovesicostomy/Ileal Loop/Colon Loop Why do I need this surgery? A urinary diversion is a surgical procedure that is performed to allow urine to safely pass from the kidneys into a
Medical Therapy for IBD
 CHILDREN S DIGESTIVE HEALTH & NUTRITION FOUNDATION NORTH AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR PEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGY, HEPATOLOGY AND NUTRITION Medical Therapy for IBD I. INTRODUCTION The treatment of Crohn s disease
CHILDREN S DIGESTIVE HEALTH & NUTRITION FOUNDATION NORTH AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR PEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGY, HEPATOLOGY AND NUTRITION Medical Therapy for IBD I. INTRODUCTION The treatment of Crohn s disease
Bowel cancer: should I be screened?
 Patient information from the BMJ Group Bowel cancer: should I be screened? Bowel cancer is a serious condition, but there are good treatments. Treatment works best if it's started early.to pick up early
Patient information from the BMJ Group Bowel cancer: should I be screened? Bowel cancer is a serious condition, but there are good treatments. Treatment works best if it's started early.to pick up early
Arthritis www.patientedu.org
 written by Harvard Medical School Arthritis www.patientedu.org Arthritis is the most common chronic disease in the world, and it s the leading cause of disability in the United States. There are more than
written by Harvard Medical School Arthritis www.patientedu.org Arthritis is the most common chronic disease in the world, and it s the leading cause of disability in the United States. There are more than
Treating Chronic Hepatitis C. A Review of the Research for Adults
 Treating Chronic Hepatitis C A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor* has told you that you have chronic hepatitis C.
Treating Chronic Hepatitis C A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor* has told you that you have chronic hepatitis C.
Millions of Americans suffer from abdominal pain, bloating, constipation and diarrhea. Now new treatments can relieve your pain and discomfort.
 3888-IBS Consumer Bro 5/8/03 10:38 AM Page 1 TAKE THE IBS TEST Do you have recurrent abdominal pain or discomfort? YES NO UNDERSTANDING IRRITABLE BOWEL SYNDROME A Consumer Education Brochure Do you often
3888-IBS Consumer Bro 5/8/03 10:38 AM Page 1 TAKE THE IBS TEST Do you have recurrent abdominal pain or discomfort? YES NO UNDERSTANDING IRRITABLE BOWEL SYNDROME A Consumer Education Brochure Do you often
IMMUNOTHERAPY FOR THE TREATMENT OF LUNG CANCER
 IMMUNOTHERAPY FOR THE TREATMENT OF LUNG CANCER BOOKLET SUPPLEMENT Immunotherapy Immunotherapy is one of the most exciting new approaches for treating several types of cancer, including lung cancer. Immunotherapies
IMMUNOTHERAPY FOR THE TREATMENT OF LUNG CANCER BOOKLET SUPPLEMENT Immunotherapy Immunotherapy is one of the most exciting new approaches for treating several types of cancer, including lung cancer. Immunotherapies
Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy
 Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy What is Intraperitoneal (IP) Chemotherapy? Intraperitoneal (IP) chemotherapy is a way to put some of your chemotherapy into your abdomen (also called the peritoneal cavity)
Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy What is Intraperitoneal (IP) Chemotherapy? Intraperitoneal (IP) chemotherapy is a way to put some of your chemotherapy into your abdomen (also called the peritoneal cavity)
MEDICATION GUIDE REMICADE (Rem-eh-kaid) (infliximab) Read the Medication Guide that comes with REMICADE before you receive the first treatment, and
 MEDICATION GUIDE REMICADE (Rem-eh-kaid) (infliximab) Read the Medication Guide that comes with REMICADE before you receive the first treatment, and before each time you get a treatment of REMICADE. This
MEDICATION GUIDE REMICADE (Rem-eh-kaid) (infliximab) Read the Medication Guide that comes with REMICADE before you receive the first treatment, and before each time you get a treatment of REMICADE. This
I can t empty my rectum without pressing my fingers in or near my vagina
 Since the birth of my baby, I can t control my bowel movements Normally bowel movements (stools) are stored in the rectum until the bowel sends a message to the brain that it is full, and the person finds
Since the birth of my baby, I can t control my bowel movements Normally bowel movements (stools) are stored in the rectum until the bowel sends a message to the brain that it is full, and the person finds
MEDICATION GUIDE KOMBIGLYZE XR (kom-be-glyze X-R) (saxagliptin and metformin HCl extended-release) tablets
 MEDICATION GUIDE KOMBIGLYZE XR (kom-be-glyze X-R) (saxagliptin and metformin HCl extended-release) tablets Read this Medication Guide carefully before you start taking KOMBIGLYZE XR and each time you get
MEDICATION GUIDE KOMBIGLYZE XR (kom-be-glyze X-R) (saxagliptin and metformin HCl extended-release) tablets Read this Medication Guide carefully before you start taking KOMBIGLYZE XR and each time you get
Pancreatic Cancer Understanding your diagnosis
 Pancreatic Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Let s Make Cancer History 1 888 939-3333 cancer.ca Pancreatic Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer you may feel alone
Pancreatic Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Let s Make Cancer History 1 888 939-3333 cancer.ca Pancreatic Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer you may feel alone
Crohn's and Colitis UK Information Sheet. Students with IBD: a guide for universities and colleges
 Crohn's and Colitis UK Information Sheet Improving life for people affected by inflammatory bowel diseases Students with IBD: a guide for universities and colleges Introduction It is very likely that several
Crohn's and Colitis UK Information Sheet Improving life for people affected by inflammatory bowel diseases Students with IBD: a guide for universities and colleges Introduction It is very likely that several
Blood Transfusion. Red Blood Cells White Blood Cells Platelets
 Blood Transfusion Introduction Blood transfusions are very common. Each year, almost 5 million Americans need a blood transfusion. Blood transfusions are given to replace blood lost during surgery or serious
Blood Transfusion Introduction Blood transfusions are very common. Each year, almost 5 million Americans need a blood transfusion. Blood transfusions are given to replace blood lost during surgery or serious
Bone Marrow or Blood Stem Cell Transplants in Children With Severe Forms of Autoimmune Disorders or Certain Types of Cancer
 Bone Marrow or Blood Stem Cell Transplants in Children With Severe Forms of Autoimmune Disorders or Certain Types of Cancer A Review of the Research for Parents and Caregivers Is This Information Right
Bone Marrow or Blood Stem Cell Transplants in Children With Severe Forms of Autoimmune Disorders or Certain Types of Cancer A Review of the Research for Parents and Caregivers Is This Information Right
Thymus Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand what thymus cancer is and what treatment options are available.
 Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
The Hereditary Colorectal Cancer Website has been sponsored by the Robert Rauschenberg Foundation
 Introduction The Hereditary Colorectal Cancer Website has been sponsored by the Robert Rauschenberg Foundation Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC) syndrome was first described over 100 years
Introduction The Hereditary Colorectal Cancer Website has been sponsored by the Robert Rauschenberg Foundation Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC) syndrome was first described over 100 years
Medicines for Rheumatoid. Arthritis. A Review of the Research for Adults
 Medicines for Rheumatoid Arthritis A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, this summary is for you if: Your doctor* has told you that you have rheumatoid (pronounced
Medicines for Rheumatoid Arthritis A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, this summary is for you if: Your doctor* has told you that you have rheumatoid (pronounced
Flexible sigmoidoscopy the procedure explained Please bring this booklet with you
 Flexible sigmoidoscopy the procedure explained Please bring this booklet with you Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Introduction You have been advised by your GP or hospital doctor to have an
Flexible sigmoidoscopy the procedure explained Please bring this booklet with you Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Introduction You have been advised by your GP or hospital doctor to have an
Medication Guide. Serious loss of body fluid (dehydration) and changes in blood salts (electrolytes) in your blood.
 Medication Guide MoviPrep (moo-vee-prěp) (PEG 3350, sodium sulfate, sodium chloride, potassium chloride, sodium ascorbate, and ascorbic acid for oral solution) Read this Medication Guide before you start
Medication Guide MoviPrep (moo-vee-prěp) (PEG 3350, sodium sulfate, sodium chloride, potassium chloride, sodium ascorbate, and ascorbic acid for oral solution) Read this Medication Guide before you start
Hemochromatosis. National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Hemochromatosis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse What is hemochromatosis? Hemochromatosis is the most common form of iron overload disease. Too much iron in the body causes hemochromatosis.
Hemochromatosis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse What is hemochromatosis? Hemochromatosis is the most common form of iron overload disease. Too much iron in the body causes hemochromatosis.
FUNCTIONAL BOWEL DISORDERS
 FUNCTIONAL BOWEL DISORDERS Contributed by the International Foundation for Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (IFFGD) and edited by the Patient Care Committee of the ACG. INTRODUCTION Doctors use the
FUNCTIONAL BOWEL DISORDERS Contributed by the International Foundation for Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (IFFGD) and edited by the Patient Care Committee of the ACG. INTRODUCTION Doctors use the
Inflammatory Bowel Disease. (Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn s Disease)
 Ministry of Defence Synopsis of Causation Inflammatory Bowel Disease (Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn s Disease) Authors: Dr Hazel Younger, Ninewells Hospital and Medical School, Dundee and Dr Craig Mowat,
Ministry of Defence Synopsis of Causation Inflammatory Bowel Disease (Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn s Disease) Authors: Dr Hazel Younger, Ninewells Hospital and Medical School, Dundee and Dr Craig Mowat,
Arthritis in Children: Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis By Kerry V. Cooke
 Reading Comprehension Read the following essay on juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Then use the information in the text to answer the questions that follow. Arthritis in Children: Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis
Reading Comprehension Read the following essay on juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Then use the information in the text to answer the questions that follow. Arthritis in Children: Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis
Probiotics for the Treatment of Adult Gastrointestinal Disorders
 Probiotics for the Treatment of Adult Gastrointestinal Disorders Darren M. Brenner, M.D. Division of Gastroenterology Northwestern University, Feinberg School of Medicine Chicago, Illinois What are Probiotics?
Probiotics for the Treatment of Adult Gastrointestinal Disorders Darren M. Brenner, M.D. Division of Gastroenterology Northwestern University, Feinberg School of Medicine Chicago, Illinois What are Probiotics?
The Burden of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) in Canada
 Final Report and Recommendations The Burden of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) in Canada Approved by the Board of Directors of the Crohn s and Colitis Foundation of Canada September 13, 2008 Crohn s and
Final Report and Recommendations The Burden of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) in Canada Approved by the Board of Directors of the Crohn s and Colitis Foundation of Canada September 13, 2008 Crohn s and
Colorectal Cancer: Preventable, Beatable, Treatable. American Cancer Society
 Colorectal Cancer: Preventable, Beatable, Treatable American Cancer Society Reviewed January 2016 What we ll be talking about How common is colorectal cancer? What is colorectal cancer? What causes it?
Colorectal Cancer: Preventable, Beatable, Treatable American Cancer Society Reviewed January 2016 What we ll be talking about How common is colorectal cancer? What is colorectal cancer? What causes it?
Weight-Loss Surgery for Adults With Diabetes or Prediabetes Who Are at the Lower Levels of Obesity
 Weight-Loss Surgery for Adults With Diabetes or Prediabetes Who Are at the Lower Levels of Obesity A Review of the Research for Adults With a BMI Between 30 and 35 Is This Information Right for Me? If
Weight-Loss Surgery for Adults With Diabetes or Prediabetes Who Are at the Lower Levels of Obesity A Review of the Research for Adults With a BMI Between 30 and 35 Is This Information Right for Me? If
Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Treatment with Rivaroxaban
 Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Treatment with Rivaroxaban Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn: about venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism how the medicine Rivaroxaban
Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Treatment with Rivaroxaban Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn: about venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism how the medicine Rivaroxaban
