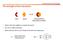
Quantifying Nucleophilicity and Electrophilicity: The Mayr Scales. log k = s(n + E)
|
|
|
- Randolf Damon Clarke
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Quantifying ucleophilicity and Electrophilicity: The Mayr Scales E k E R R log k = s( + E) Valerie Shurtleff MacMillan Group Meeting July 10, 2013
2 A Brief History of Polar Reactivity Scales 1920s: G.. Lewis presents valence bond theory LA LB 1930s: Ingold introduces the terms "electrophile" and "nucleophile" E u 1953: Swain and Scott introduce the first method for the quantification of nucleophilicity Br R u k u R log (k/k w ) = sn n = nucleophilicity parameter, =0 for H 2 O s = sensitivity of rate constant to changes in the nucleophile, =1 for MeBr k w = rate constant for reaction of RBr with H 2 O Mayr, H.; Patz, M. ACIE 1994, 33, 938. Ingold, C. K. Chem. Rev. 1934, 15, 225, 274. Swain, C. G.; Scott, C. B. JACS 1953, 75, 141.
3 The Ritchie Relationship 1972: Introduction of + for comparison of nucleophiles E u k u E log (k/k w ) = + + = nucleophilicity parameter, =0 for H 2 O k w = rate constant for reaction of E + with H 2 O + specific to a given solvent (n-nucleophiles) Slope represents selectivity of electrophile Same slope: "constant selectivity relationship" Mayr, H.; Patz, M. ACIE 1994, 33, 938. Ritchie, C. D. Acc. Chem. Res. 1972, 5, 348.
4 Kane-Maguire and Sweigart 1984: Application of Ritchie relationship to organometallic electrophiles u k ML n ML n u H log (k/k 0 ) = Fe Fe = nucleophilicity parameter, =0 for P(OBu) 3 k 0 = rate constant for reaction of L n MAr + with P(OBu) 3 Relative reactivities independent of electrophile Same relative reactivities found for carbocations Constant selectivity relationship Mayr, H.; Patz, M. ACIE 1994, 33, 938. Kane-Maguire, L. A. P.; Honig, E. D.; Sweigart, D. A. Chem. Rev. 1984, 84, 525.
5 An Aside: The Reactivity-Selectivity Principle "The more reactive a compound is, the less selective it is." Ritchie, 1972 Kane-Maguire, Sweigart, 1984 Virtually constant selectivity over reactivity spanning 4 orders of magnitude Virtually constant selectivity over reactivity spanning 9 orders of magnitude Giese, B. ACIE 1977, 16, 125. Mayr, H.; Ofial, A. R. ACIE 2006, 45, Ritchie, C. D. Acc. Chem. Res. 1972, 5, 348. Kane-Maguire, L. A. P.; Honig, E. D.; Sweigart, D. A. Chem. Rev. 1984, 84, 525.
6 Expanding the Utility of the Ritchie Relationship Can electrophiles also be characterized using constant selectivity relationships? E u k u E From the Ritchie relationship: log (k/k w ) = + log k - log k w = + log k = log k w + + (1) (2) (3) Recall, k w = the rate constant for the reaction of a given electrophile with H 2 O Thus, k w is independent of the nucleophile contributing to k and is characteristic of the electrophile Let log k w = E + in equation (3) above: log k = log k w + + log k w = E + log k = E Mayr, H.; Patz, M. ACIE 1994, 33, 938.
7 on-constant Selectivity Relationships Implications of the slope of correlation relationships k Ar Ar R Ar R Ar Mayr, H.; Patz, M. ACIE 1994, 33, 938.
8 The Mayr-Patz Equation Introduction of a third parameter to account for differences in selectivity E u k u E The Mayr-Patz equation: log k = s( + E) s = nucleophile-specific slope parameter = nucleophilicity parameter E = electrophilicity parameter Reference compounds: MeO OMe An 2 CH + E = 0 2-methyl-1-pentene s = 1 Mayr, H.; Patz, M. ACIE 1994, 33, 938.
9 Towards a Unified Reactivity Scale ucleophilicity parameters determined for 56 nucleophiles π-nucleophiles: alkenes, dienes, alkynes, allylsilanes, -germanes, -stannanes, arenes, enol ethers σ-nucleophiles: silanes, germanes, stannanes, BDHA (nicotinamide derivative) n-nucleophiles: phosphines, phosphites, alcohols, amines, heterocycles Conversions for electrophilicity terms determined by Richie and Kane-Maguire/Sweigart Richie: E = 1.24(log k w ) 5.80 Kane-Maguire/Sweigart: E = 1.38(log k 0 ) 18.2 Conversions for nucleophilicity parameters determined by Richie and Kane-Maguire/Sweigart Richie: = 1.20( + ) , s = 0.83 Kane-Maguire/Sweigart: = 1.51(log k) , s = 0.66 Mayr, H.; Patz, M. ACIE 1994, 33, 938.
10 Reference Scales for Parametrization of Polar Reactivity Rate constants measured for the reactions of 23 diarylcarbenium ions with 38 π-nucleophiles Pseudo-first-order conditions, [nucleophile] >>> [electrophile] R 1 R 6 R 7 R 2 R 3 R 4 R 5 R 8 R 9 electrophile nucleophile Measurement method dependent on the reaction rate: UV-Vis stopped -flow laser flash photolysis k Reactivity parameters s, E, determined by least-squares fitting from the Mayr-Patz equation s = 1 for 2-methyl-1-pentene, E = 0 for An 2 CH + Mayr, H., et al. JACS 2001, 123, Mayr, H., Ofial, A. R. J. Phys. Org. Chem. 2008, 21, 584.
11 Reference Scales for Parametrization of Polar Reactivity Mayr, H., Ofial, A. R. J. Phys. Org. Chem. 2008, 21, 584.
12 Mayr, H., Ofial, A. R. J. Phys. Org. Chem. 2005, 77, 1807.
13 Expansion of the Mayr Basis Set Determination of E for new electrophiles Measure rate constants for reaction with nucleophiles for which and s are known, then derive E Determination of and s for new nucleophiles Measure rate constants for reaction with a variety of electrophiles for which E is known, then derive and s "Quick and dirty" determination of for new nucleophiles 6 =? = 13.4 s 0.81 s = Assume s is similar to a that of a structurally analogous nucleophile Measure the rate constant for reaction with a single electrophile for which E is known log k 0-2 = E E Mayr, H.; Kempf, B.; Ofial, A. R. Acc. Chem. Res. 2003, 36, 66.
14 Mayr's Online Database of Reactivity Parameters, s parameters for 924 nucleophiles; E parameters for 235 electrophiles Searchable by molecule class, parameter, E parameter Enamines/Enamides: 42 entries currently listed
15 Utility of the Mayr Reactivity Scales Will a reaction happen? Consider a reaction at room temperature, 1 M in each reactant: u u Fe(CO) 3 Fe(CO) 3 E = 8.00 For 50% conversion in less than 3 h, k > 10-4 is required. Rule of thumb: An electrophile/nucleophile pair can be expected to react at room temperature if (E + ) > 5 Representative examples (reactions at 20 C): OTMS = 6.86 E + = 1.14 k = = 1.07 E + = 6.93 no reaction Birch, A. J.; Kelly, L. F.; arula, A. S. Tetrahedron 1982, 38, Mayr, H.; Patz, M. ACIE 1994, 33, 938.
16 Utility of the Mayr Reactivity Scales Comparison of nucleophilicity/electrophilicity of reaction partners Direct comparison of parameters if appropriate E or and s values are known "Semiquantitative" nucleophilicity comparison before addition 1 min. after addition Mayr, H.; Kempf, B.; Ofial, A. R. Acc. Chem. Res. 2003, 36, 66.
17 Utility of the Mayr Reactivity Scales Predicting selectivity Product ratios for reaction with competing nucleophiles A and B predicted by calculation of k A /k B As a corollary, selectivity for competing sites of electrophilic attack may be predicted: E + k A A O B k B R E + ucleophilicity requirement to outcompete solvent trapping π-nucleophile MeO S MeO k u Me S 2 u Me 2 MeO solvent S u with > 6 compete with solvent k solv solv Me 2 Richard, J. P.; Szymanski, P.; Williams, K. JACS 1998, 120, Mayr, H.; Kempf, B.; Ofial, A. R. Acc. Chem. Res. 2003, 36, 66.
18 Utility of the Mayr Reactivity Scales Correlation with Hammett parameters Few σ + parameters available for electron-donating groups stronger than alkoxy Strong correlation between σ + and E for symmetrical diarylcarbenium ions σ + = 0.134E r = Mayr, H., et al. JACS 2001, 123, 9500.
19 Solvent Effects Reactions of π-nucleophiles and σ-nucleophiles Changes in solvent have little effect on rate constants Presumably due to preservation of charge in the combination step solvent MeO OMe MeO OMe CHCl 3 : ε = 4.81, k = 2.63 CH 3 O 2 : ε = 35.9, k = k CHCl3 /k CH3O2 = 4.8 Reactions of n-nucleophiles Rate constants can be very different in aprotic vs. protic solvents due to H-bonding, s parameters are solvent-specific Reactions of diazonium electrophiles Electrophilicity dependent on donor number of solvent, E is solvent-specific Mayr, H.; Patz, M. ACIE 1994, 33, 938.
20 Temperature Effects ucleophilicity scales can be affected by changes in temperature MeO OMe TMS products C κ = k( TMS ) k( ) log κ /T T > 57 C: allyltrimethylsilane is more nucleophilic T < 57 C: 2-methyl-2-butene is more nucleophilic T = 57 C: aselective reaction ucleophiles with very different reaction enthalpies/entropies should be compared cautiously Reaction entropy seems to be influenced most heavily by nucleophile structure Mayr, H.; Patz, M. ACIE 1994, 33, 938.
21 A Few Caveats Rate constants for combination reactions, s, and E are kinetic parameters unfavorable equilibrium can prevent productive reaction Reactions for which electrophile nucleophile combination is not the RDS may not be amenable to analysis Steric effects and s reflect a combination of steric and electronic effects Reactions of bulky compounds can show deviation from linearity Very fast reactions Reactions with rates approaching diffusion control begin to deviate from linearity The Mayr-Patz equation holds only for k < Crossover in nucleophilicity scales ucleophiles with significantly different s values must be compared with caution Crossover is most likely to occur when values are very similar Mayr, H.; Patz, M. ACIE 1994, 33, 938. Mayr, H.; Kempf, B.; Ofial, A. R. Acc. Chem. Res. 2003, 36, 66.
22 ucleophilicity of Enamines and s determined using weak electrophiles = 16.3 = 14.9 = 13.4 = 12.5 = 11.4 s = 0.77 s = 0.86 s = 0.81 s = 0.80 s = 0.83 Me O O O more nucleophilic O less nucleophilic = 15.9 s = 0.86 = 15.1 s = 0.82 = 13.4 s = 0.82 Kempf, B. ; Hampel,.; Ofial, A. R.; Mayr, H. Chem. Eur. J. 2003, 9, 2209
23 ucleophilicity of Enamines Enamines derived from prolinol and imidazolidinone organocatalysts = 12.3 s = 0.99 = 10.6 s = 1.01 = 7.20 s = 1.14 = 5.80 s = 0.87 Ph Ph OTMS Ph O Me Me Me Ph O Me t Bu more nucleophilic Ph Ph OTMS Ph OTMS Ph less nucleophilic O = 10.6 s = 0.86 = 6.57 s = 0.93 Lakhdar, S.; Maji, B.; Mayr, H. ACIE 2012, 51, Mayr, H.; Kempf, B.; Ofial, A. R. Acc. Chem. Res. 2003, 36, 66.
24 Electrophilicity of α,β-unsaturated Iminiums Iminiums derived from prolinol and imidazolidinone organocatalysts E = 9.8 E = 8.2 E = 7.4 E = 5.5 Ph Ph OTMS Ph O Me Me Me Ph O Me t Bu less electrophilic Ph Ph Ph Ph more electrophilic Me E = 8.2 Me O E = 5.5 O Lakhdar, S.; Ammer, J.; Mayr, H. ACIE 2011, 50, Lakhdar, S.; Tokuyasu, T.; Mayr, H. ACIE 2008, 47, Mayr, H., et al. JACS 2001, 123, 9500.
25 And ow for Something (ot) Completely Different Design of electronically differentiated imidazolidinone catalysts E for 2 = 6.0 E for 6 = 7.0 Q zz = component of the traceless quadrupole moment orthogonal to the aromatic ring More EWG, Q zz more positive More EDG, Q zz more negative Electron-rich catalysts tend to populate conformation I preferentially (1, 4, 5, 6) Electron-poor catalysts tend to populate conformation III preferentially (2, 3) Holland, M. C.; Paul, S.; Schweizer, W. B.; Bergander, K. Mück-Lichtenfeld, C., Lakhdar, S.; Mayr, H.; Gilmour, R. ACIE 2013, 52, ASAP.
26 And ow for Something (ot) Completely Different Performance of new catalysts in an organocatalytic Friedel Crafts alkylation Using first generation imidazolidinone: 30 C, 42 h, 87% yield, 93% ee Reaction via iminium 6: rt, 3 h, "completion," 94% ee Significant correlation between Q zz and enantioselectivity Holland, M. C.; Paul, S.; Schweizer, W. B.; Bergander, K. Mück-Lichtenfeld, C., Lakhdar, S.; Mayr, H.; Gilmour, R. ACIE 2013, 52, ASAP.
Chapter 6 An Overview of Organic Reactions
 John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 6 An Overview of Organic Reactions Why this chapter? To understand organic and/or biochemistry, it is necessary to know: -What occurs -Why and
John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 6 An Overview of Organic Reactions Why this chapter? To understand organic and/or biochemistry, it is necessary to know: -What occurs -Why and
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions
 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions, Course Notes Archive, 1 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions An organic reaction in which an electrophile substitutes a hydrogen atom in an aromatic
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions, Course Notes Archive, 1 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions An organic reaction in which an electrophile substitutes a hydrogen atom in an aromatic
SN2 Ionic Substitution Reactions
 SN2 Ionic Substitution Reactions Chem 14D Winter 2005 SN2 Ionic Substitution Reactions Substitution can occur in organic compounds that have an electronegative atom or group bonded to an sp 3 hybridized
SN2 Ionic Substitution Reactions Chem 14D Winter 2005 SN2 Ionic Substitution Reactions Substitution can occur in organic compounds that have an electronegative atom or group bonded to an sp 3 hybridized
Writing a Correct Mechanism
 Chapter 2 1) Balancing Equations Writing a Correct Mechanism 2) Using Arrows to show Electron Movement 3) Mechanisms in Acidic and Basic Media 4) Electron rich Species: Nucleophile or Base? 5) Trimolecular
Chapter 2 1) Balancing Equations Writing a Correct Mechanism 2) Using Arrows to show Electron Movement 3) Mechanisms in Acidic and Basic Media 4) Electron rich Species: Nucleophile or Base? 5) Trimolecular
Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination
 Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination What does the term "nucleophilic substitution" imply? A nucleophile is an the electron rich species that will react with an electron poor species A substitution
Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination What does the term "nucleophilic substitution" imply? A nucleophile is an the electron rich species that will react with an electron poor species A substitution
Electrophilic Addition Reactions
 Electrophilic Addition Reactions Electrophilic addition reactions are an important class of reactions that allow the interconversion of C=C and C C into a range of important functional groups. Conceptually,
Electrophilic Addition Reactions Electrophilic addition reactions are an important class of reactions that allow the interconversion of C=C and C C into a range of important functional groups. Conceptually,
Willem Elbers. October 9, 2015
 S N 1 and S N 2 reactivity of 3 alkyl bromides Willem Elbers ctober 9, 2015 1 Abstract n this experiment, we investigate the relative reactivities of three alkyl bromides with increasing steric bulk. We
S N 1 and S N 2 reactivity of 3 alkyl bromides Willem Elbers ctober 9, 2015 1 Abstract n this experiment, we investigate the relative reactivities of three alkyl bromides with increasing steric bulk. We
CHEM 211 CHAPTER 16 - Homework
 CHEM 211 CHAPTER 16 - Homework SHORT ANSWER Consider the Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction below to answer the following question(s): 1. Refer to the reaction above. Draw the structure of the electrophilic
CHEM 211 CHAPTER 16 - Homework SHORT ANSWER Consider the Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction below to answer the following question(s): 1. Refer to the reaction above. Draw the structure of the electrophilic
Chapter 2 Polar Covalent Bonds: Acids and Bases
 John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 2 Polar Covalent Bonds: Acids and Bases Modified by Dr. Daniela R. Radu Why This Chapter? Description of basic ways chemists account for chemical
John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 2 Polar Covalent Bonds: Acids and Bases Modified by Dr. Daniela R. Radu Why This Chapter? Description of basic ways chemists account for chemical
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Electrophilic substitution is the typical reaction type for aromatic rings. Generalized electrophilic aromatic substitution: E E Electrophile Lewis acid: may be or neutral.
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Electrophilic substitution is the typical reaction type for aromatic rings. Generalized electrophilic aromatic substitution: E E Electrophile Lewis acid: may be or neutral.
Conjugation is broken completely by the introduction of saturated (sp3) carbon:
 Chapter 16 Conjugation, resonance, and dienes Conjugation relies on the partial overlap of p-orbitals on adjacent double or triple bonds. A common conjugated system involves 1,3-dienes, such as 1,3-butadiene.
Chapter 16 Conjugation, resonance, and dienes Conjugation relies on the partial overlap of p-orbitals on adjacent double or triple bonds. A common conjugated system involves 1,3-dienes, such as 1,3-butadiene.
Chapter 11 Homework and practice questions Reactions of Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitutions and Eliminations
 Chapter 11 Homework and practice questions Reactions of Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitutions and Eliminations SHORT ANSWER Exhibit 11-1 Circle your response in each set below. 1. Circle the least
Chapter 11 Homework and practice questions Reactions of Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitutions and Eliminations SHORT ANSWER Exhibit 11-1 Circle your response in each set below. 1. Circle the least
Benzene Benzene is best represented as a resonance hybrid:
 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution (EAS) is a substitution reaction usually involving the benzene ring; more specifically it is a reaction in which the hydrogen atom of an aromatic ring is replaced as
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution (EAS) is a substitution reaction usually involving the benzene ring; more specifically it is a reaction in which the hydrogen atom of an aromatic ring is replaced as
methyl RX example primary RX example secondary RX example secondary RX example tertiary RX example
 ucleophilic Substitution & Elimination hemistry 1 eginning patterns to knowfor S and E eactions - horizontal and vertical templates for practice Example 1 - two possible perspectives (deuterium and tritium
ucleophilic Substitution & Elimination hemistry 1 eginning patterns to knowfor S and E eactions - horizontal and vertical templates for practice Example 1 - two possible perspectives (deuterium and tritium
Addition Reactions of Carbon-Carbon Pi Bonds - Part 1
 Addition eactions of arbon-arbon Pi Bonds - Part 1 3 δ+ 2 δ 3 3 3 + 2 3 2 3 What Is an Addition eaction? Addition reaction: Atoms or groups are added to opposite ends of a pi bond. X Y Why should I study
Addition eactions of arbon-arbon Pi Bonds - Part 1 3 δ+ 2 δ 3 3 3 + 2 3 2 3 What Is an Addition eaction? Addition reaction: Atoms or groups are added to opposite ends of a pi bond. X Y Why should I study
CHEM 322 Organic Chemistry II - Professor Kathleen V. Kilway. CHAPTER 14 Substitution Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
 CHEM 322 Organic Chemistry II - Professor Kathleen V. Kilway "Organic Chemistry" by Maitland Jones, 4 th edition Chapter 14 Homework: 1, 2, 5, 7, 13, 19, 20, 23, 26, 27, 28, 30, 31, 34, 35, 36, 41, 46,
CHEM 322 Organic Chemistry II - Professor Kathleen V. Kilway "Organic Chemistry" by Maitland Jones, 4 th edition Chapter 14 Homework: 1, 2, 5, 7, 13, 19, 20, 23, 26, 27, 28, 30, 31, 34, 35, 36, 41, 46,
Organometallics Study Seminar Chapter 13: Metal-Ligand Multiple Bonds
 Organometallics Study Seminar Chapter 13: Metal-Ligand Multiple Bonds Contents 1. Carbene Complexes 2. Silylene Complexes 3. Metal-Heteroatom Multiple Bonds 1. Carbene Complexes 1.1 Classes of Carbene
Organometallics Study Seminar Chapter 13: Metal-Ligand Multiple Bonds Contents 1. Carbene Complexes 2. Silylene Complexes 3. Metal-Heteroatom Multiple Bonds 1. Carbene Complexes 1.1 Classes of Carbene
Q.1 Draw out some suitable structures which fit the molecular formula C 6 H 6
 Aromatic compounds GE 1 BENZENE Structure Primary analysis revealed benzene had an... empirical formula of and a molecular formula of 6 6 Q.1 Draw out some suitable structures which fit the molecular formula
Aromatic compounds GE 1 BENZENE Structure Primary analysis revealed benzene had an... empirical formula of and a molecular formula of 6 6 Q.1 Draw out some suitable structures which fit the molecular formula
 INTDUCTIN T LEWIS ACID-BASE CEMISTY DEINITINS Lewis acids and bases are defined in terms of electron pair transfers. A Lewis base is an electron pair donor, and a Lewis acid is an electron pair acceptor.
INTDUCTIN T LEWIS ACID-BASE CEMISTY DEINITINS Lewis acids and bases are defined in terms of electron pair transfers. A Lewis base is an electron pair donor, and a Lewis acid is an electron pair acceptor.
But in organic terms: Oxidation: loss of H 2 ; addition of O or O 2 ; addition of X 2 (halogens).
 Reactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. Normally: Oxidation
Reactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. Normally: Oxidation
EXPERIMENT 1: Survival Organic Chemistry: Molecular Models
 EXPERIMENT 1: Survival Organic Chemistry: Molecular Models Introduction: The goal in this laboratory experience is for you to easily and quickly move between empirical formulas, molecular formulas, condensed
EXPERIMENT 1: Survival Organic Chemistry: Molecular Models Introduction: The goal in this laboratory experience is for you to easily and quickly move between empirical formulas, molecular formulas, condensed
Molecular Spectroscopy
 Molecular Spectroscopy UV-Vis Spectroscopy Absorption Characteristics of Some Common Chromophores UV-Vis Spectroscopy Absorption Characteristics of Aromatic Compounds UV-Vis Spectroscopy Effect of extended
Molecular Spectroscopy UV-Vis Spectroscopy Absorption Characteristics of Some Common Chromophores UV-Vis Spectroscopy Absorption Characteristics of Aromatic Compounds UV-Vis Spectroscopy Effect of extended
4/18/2011. 9.8 Substituent Effects in Electrophilic Substitutions. Substituent Effects in Electrophilic Substitutions
 9.8 Substituent effects in the electrophilic substitution of an aromatic ring Substituents affect the reactivity of the aromatic ring Some substituents activate the ring, making it more reactive than benzene
9.8 Substituent effects in the electrophilic substitution of an aromatic ring Substituents affect the reactivity of the aromatic ring Some substituents activate the ring, making it more reactive than benzene
Survival Organic Chemistry Part I: Molecular Models
 Survival Organic Chemistry Part I: Molecular Models The goal in this laboratory experience is to get you so you can easily and quickly move between empirical formulas, molecular formulas, condensed formulas,
Survival Organic Chemistry Part I: Molecular Models The goal in this laboratory experience is to get you so you can easily and quickly move between empirical formulas, molecular formulas, condensed formulas,
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution: a reaction in which the hydrogen atom of an aromatic ring is replaced as a result of an electrophilic attack on the aromatic ring
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution: a reaction in which the hydrogen atom of an aromatic ring is replaced as a result of an electrophilic attack on the aromatic ring
ammonium salt (acidic)
 Chem 360 Jasperse Ch. 19 otes. Amines 1 eactions of Amines 1. eaction as a proton base (Section 19-5 and 19-6) amine base -X (proton acid) a X ammonium salt (acidic) Mechanism: equired (protonation) everse
Chem 360 Jasperse Ch. 19 otes. Amines 1 eactions of Amines 1. eaction as a proton base (Section 19-5 and 19-6) amine base -X (proton acid) a X ammonium salt (acidic) Mechanism: equired (protonation) everse
Reminder: These notes are meant to supplement, not replace, the textbook and lab manual. Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution notes
 Reminder: These notes are meant to supplement, not replace, the textbook and lab manual. Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution notes History and Application: The rate of a reaction directly impacts the commercial
Reminder: These notes are meant to supplement, not replace, the textbook and lab manual. Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution notes History and Application: The rate of a reaction directly impacts the commercial
Acids and Bases: Molecular Structure and Acidity
 Acids and Bases: Molecular Structure and Acidity Review the Acids and Bases Vocabulary List as needed. Tutorial Contents A. Introduction B. Resonance C. Atomic Radius D. Electronegativity E. Inductive
Acids and Bases: Molecular Structure and Acidity Review the Acids and Bases Vocabulary List as needed. Tutorial Contents A. Introduction B. Resonance C. Atomic Radius D. Electronegativity E. Inductive
Chapter 2 Polar Covalent Bonds; Acids and Bases
 John E. McMurry http://www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 2 Polar Covalent Bonds; Acids and Bases Javier E. Horta, M.D., Ph.D. University of Massachusetts Lowell Polar Covalent Bonds: Electronegativity
John E. McMurry http://www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 2 Polar Covalent Bonds; Acids and Bases Javier E. Horta, M.D., Ph.D. University of Massachusetts Lowell Polar Covalent Bonds: Electronegativity
Everything You Need to Know About Mechanisms. First rule: Arrows are used to indicate movement of electrons
 Everything You eed to Know About Mechanisms A) The orrect Use of Arrows to Indicate Electron Movement The ability to write an organic reaction mechanism properly is key to success in organic chemistry
Everything You eed to Know About Mechanisms A) The orrect Use of Arrows to Indicate Electron Movement The ability to write an organic reaction mechanism properly is key to success in organic chemistry
passing through (Y-axis). The peaks are those shown at frequencies when less than
 Infrared Spectroscopy used to analyze the presence of functional groups (bond types) in organic molecules The process for this analysis is two-fold: 1. Accurate analysis of infrared spectra to determine
Infrared Spectroscopy used to analyze the presence of functional groups (bond types) in organic molecules The process for this analysis is two-fold: 1. Accurate analysis of infrared spectra to determine
REACTIONS OF AROMATIC COMPOUNDS
 A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO: REACTIONS OF AROMATIC COMPOUNDS 1. Predict the product(s) of Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution (EAS), Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution (S N Ar) and Elimination-Addition
A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO: REACTIONS OF AROMATIC COMPOUNDS 1. Predict the product(s) of Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution (EAS), Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution (S N Ar) and Elimination-Addition
Part 2: Analysis of Relationship Between Two Variables
 Part 2: Analysis of Relationship Between Two Variables Linear Regression Linear correlation Significance Tests Multiple regression Linear Regression Y = a X + b Dependent Variable Independent Variable
Part 2: Analysis of Relationship Between Two Variables Linear Regression Linear correlation Significance Tests Multiple regression Linear Regression Y = a X + b Dependent Variable Independent Variable
EXPERIMENT 3 (Organic Chemistry II) Nitration of Aromatic Compounds: Preparation of methyl-m-nitrobenzoate
 EXPERIMENT 3 (Organic Chemistry II) Nitration of Aromatic Compounds: Preparation of methyl-m-nitrobenzoate Pahlavan/Cherif Purpose a) Study electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction (EAS) b) Study regioselectivity
EXPERIMENT 3 (Organic Chemistry II) Nitration of Aromatic Compounds: Preparation of methyl-m-nitrobenzoate Pahlavan/Cherif Purpose a) Study electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction (EAS) b) Study regioselectivity
CHEM 203 Exam 1. KEY Name Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 CHEM 203 Exam 1 KEY Name Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. _D C 1. Which of the following elements is a large percentage of both
CHEM 203 Exam 1 KEY Name Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. _D C 1. Which of the following elements is a large percentage of both
PTAC: Applied Chemistry COURSE OUTLINE & OBJECTIVES ESC Approved November 19, 2004
 INTRODUCTION PTAC: Applied Chemistry COURSE OUTLINE & OBJECTIVES ESC Approved November 19, 2004 A. Introduction to Chemistry Terms 1. Define basic terms associated with chemistry: Organic/inorganic/biochemistry/physical
INTRODUCTION PTAC: Applied Chemistry COURSE OUTLINE & OBJECTIVES ESC Approved November 19, 2004 A. Introduction to Chemistry Terms 1. Define basic terms associated with chemistry: Organic/inorganic/biochemistry/physical
Carboxylic Acid Structure and Chemistry: Part 2
 Principles of Drug Action 1, pring 2005, Carboxylic Acids Part 2 Carboxylic Acid tructure and Chemistry: Part 2 Jack Deuiter IV. eactions of the Carboxylic Acid eactions Depending on their overall structure,
Principles of Drug Action 1, pring 2005, Carboxylic Acids Part 2 Carboxylic Acid tructure and Chemistry: Part 2 Jack Deuiter IV. eactions of the Carboxylic Acid eactions Depending on their overall structure,
Allyl Metals. oxidative addition. transmet. + M(n) η 1 -allyl. n = 0, 1. base. X η 3 -allyl. Nuc. insertion. insertion. M(n+2)X MgX + MX2 MX 2
 Allyl tals Virtually all transition metals can form η 3 -allyl complexes, but few are synthetically useful. Pd is most widely studied and has broad utility. Allyl complexes of h, Ir, u and Mo are becoming
Allyl tals Virtually all transition metals can form η 3 -allyl complexes, but few are synthetically useful. Pd is most widely studied and has broad utility. Allyl complexes of h, Ir, u and Mo are becoming
Chemical Kinetics. Reaction Rate: The change in the concentration of a reactant or a product with time (M/s). Reactant Products A B
 Reaction Rates: Chemical Kinetics Reaction Rate: The change in the concentration of a reactant or a product with time (M/s). Reactant Products A B change in number of moles of B Average rate = change in
Reaction Rates: Chemical Kinetics Reaction Rate: The change in the concentration of a reactant or a product with time (M/s). Reactant Products A B change in number of moles of B Average rate = change in
The strength of the interaction
 The strength of the interaction Host Guest Supramolecule (host-guest complex) When is the host capable to recognize the guest? How do we define selectivity Which element will we use to design the host
The strength of the interaction Host Guest Supramolecule (host-guest complex) When is the host capable to recognize the guest? How do we define selectivity Which element will we use to design the host
Substitution and Elimination Reactions. 7.1. Definitions. In an acid base reaction such as CH 3 CO 2 H + NH 3 CH 3 CO 2 + NH 4
 Substitution and Elimination Reactions. 7.1. Definitions. In an acid base reaction such as CH 3 CO 2 H + NH 3 CH 3 CO 2 + NH 4 +, the N acts as a nucleophile (Greek for loving the nucleus), the H acts
Substitution and Elimination Reactions. 7.1. Definitions. In an acid base reaction such as CH 3 CO 2 H + NH 3 CH 3 CO 2 + NH 4 +, the N acts as a nucleophile (Greek for loving the nucleus), the H acts
SUBSTITUTION REACTION CHARACTERISTICS. Sn1: Substitution Nucleophilic, Unimolecular: Characteristics
 SUBSTITUTION EATION AATEISTIS Sn2: Substitution cleophilic, Bimolecular: haracteristics 1) The 2 means Bimolecular (or 2 nd order) in the rate-determining (slow) step: rate = k [: - ] [-X] or rate = k
SUBSTITUTION EATION AATEISTIS Sn2: Substitution cleophilic, Bimolecular: haracteristics 1) The 2 means Bimolecular (or 2 nd order) in the rate-determining (slow) step: rate = k [: - ] [-X] or rate = k
Activation of Carbon-Hydrogen Bonds at Transition Metal Centers!
 Activation of arbon-ydrogen Bonds at Transition Metal enters! Thanks to John Bercaw for many nice figures for this lecture! oxidative addition/reductive elimination [L n M q ] L n M q2 L n M q σ complex
Activation of arbon-ydrogen Bonds at Transition Metal enters! Thanks to John Bercaw for many nice figures for this lecture! oxidative addition/reductive elimination [L n M q ] L n M q2 L n M q σ complex
Experiment 11. Infrared Spectroscopy
 Chem 22 Spring 2010 Experiment 11 Infrared Spectroscopy Pre-lab preparation. (1) In Ch 5 and 12 of the text you will find examples of the most common functional groups in organic molecules. In your notebook,
Chem 22 Spring 2010 Experiment 11 Infrared Spectroscopy Pre-lab preparation. (1) In Ch 5 and 12 of the text you will find examples of the most common functional groups in organic molecules. In your notebook,
Brønsted-Lowry Acids and Bases
 Brønsted-Lowry Acids and Bases 1 According to Brønsted and Lowry, an acid-base reaction is defined in terms of a proton transfer. By this definition, the reaction of Cl in water is: Cl(aq) + Cl (aq) +
Brønsted-Lowry Acids and Bases 1 According to Brønsted and Lowry, an acid-base reaction is defined in terms of a proton transfer. By this definition, the reaction of Cl in water is: Cl(aq) + Cl (aq) +
Chemistry INDIVIDUAL PROGRAM INFORMATION 2015 2016. 866.Macomb1 (866.622.6621) www.macomb.edu
 Chemistry INDIVIDUAL PROGRAM INFORMATION 2015 2016 866.Macomb1 (866.622.6621) www.macomb.edu Chemistry PROGRAM OPTIONS CREDENTIAL TITLE CREDIT HOURS REQUIRED NOTES Associate of Science Chemistry 64 CONTACT
Chemistry INDIVIDUAL PROGRAM INFORMATION 2015 2016 866.Macomb1 (866.622.6621) www.macomb.edu Chemistry PROGRAM OPTIONS CREDENTIAL TITLE CREDIT HOURS REQUIRED NOTES Associate of Science Chemistry 64 CONTACT
Calorimetry: Heat of Vaporization
 Calorimetry: Heat of Vaporization OBJECTIVES INTRODUCTION - Learn what is meant by the heat of vaporization of a liquid or solid. - Discuss the connection between heat of vaporization and intermolecular
Calorimetry: Heat of Vaporization OBJECTIVES INTRODUCTION - Learn what is meant by the heat of vaporization of a liquid or solid. - Discuss the connection between heat of vaporization and intermolecular
A pure covalent bond is an equal sharing of shared electron pair(s) in a bond. A polar covalent bond is an unequal sharing.
 CHAPTER EIGHT BNDING: GENERAL CNCEPT or Review 1. Electronegativity is the ability of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself. Electronegativity is a bonding term. Electron affinity is the
CHAPTER EIGHT BNDING: GENERAL CNCEPT or Review 1. Electronegativity is the ability of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself. Electronegativity is a bonding term. Electron affinity is the
Chemical Bonds. Chemical Bonds. The Nature of Molecules. Energy and Metabolism < < Covalent bonds form when atoms share 2 or more valence electrons.
 The Nature of Molecules Chapter 2 Energy and Metabolism Chapter 6 Chemical Bonds Molecules are groups of atoms held together in a stable association. Compounds are molecules containing more than one type
The Nature of Molecules Chapter 2 Energy and Metabolism Chapter 6 Chemical Bonds Molecules are groups of atoms held together in a stable association. Compounds are molecules containing more than one type
partial positive an acid is a hydrogen ion donor, or proton donor base is a hydrogen ion acceptor, or proton acceptor acidic protons acid base
 INTRDUCTIN T INIC MECANISMS PART I: FUNDAMENTALS F BRNSTED-LWRY ACID-BASE CEMISTRY YDRGEN ATMS AND PRTNS IN RGANIC MLECULES - A hydrogen atom that has lost its only electron is sometimes referred to as
INTRDUCTIN T INIC MECANISMS PART I: FUNDAMENTALS F BRNSTED-LWRY ACID-BASE CEMISTRY YDRGEN ATMS AND PRTNS IN RGANIC MLECULES - A hydrogen atom that has lost its only electron is sometimes referred to as
for excitation to occur, there must be an exact match between the frequency of the applied radiation and the frequency of the vibration
 ! = 1 2"c k (m + M) m M wavenumbers! =!/c = 1/" wavelength frequency! units: cm 1 for excitation to occur, there must be an exact match between the frequency of the applied radiation and the frequency
! = 1 2"c k (m + M) m M wavenumbers! =!/c = 1/" wavelength frequency! units: cm 1 for excitation to occur, there must be an exact match between the frequency of the applied radiation and the frequency
AP Chemistry 2009 Scoring Guidelines
 AP Chemistry 2009 Scoring Guidelines The College Board The College Board is a not-for-profit membership association whose mission is to connect students to college success and opportunity. Founded in 1900,
AP Chemistry 2009 Scoring Guidelines The College Board The College Board is a not-for-profit membership association whose mission is to connect students to college success and opportunity. Founded in 1900,
Q.1 Carbonyl compounds are formed by oxidation of alcohols;
 arbonyl compounds 814 1 ARBYL MPUDS - Aldehydes and Ketones Q.1 arbonyl compounds are formed by oxidation of alcohols; a) Which type of alcohol is oxidised to an aldehyde? b) Which type of alcohol is oxidised
arbonyl compounds 814 1 ARBYL MPUDS - Aldehydes and Ketones Q.1 arbonyl compounds are formed by oxidation of alcohols; a) Which type of alcohol is oxidised to an aldehyde? b) Which type of alcohol is oxidised
ACID and BASES - a Summary
 AID and BASES - a Summary Stefan Svensson 2004 Brönsted-Lowry : Acids donate protons Lewis -acid : Electron pair acceptor Bases accept protons Lewis-base: Electron pair donator. Acetic acid ättiksyra 3
AID and BASES - a Summary Stefan Svensson 2004 Brönsted-Lowry : Acids donate protons Lewis -acid : Electron pair acceptor Bases accept protons Lewis-base: Electron pair donator. Acetic acid ättiksyra 3
UV-Visible Spectroscopy
 UV-Visible Spectroscopy UV-Visible Spectroscopy What is UV-Visible Spectroscopy? Molecular spectroscopy that involves study of the interaction of Ultra violet (UV)-Visible radiation with molecules What
UV-Visible Spectroscopy UV-Visible Spectroscopy What is UV-Visible Spectroscopy? Molecular spectroscopy that involves study of the interaction of Ultra violet (UV)-Visible radiation with molecules What
Conjugation is broken completely by the introduction of saturated (sp 3 ) carbon:
 Conjugation. Conjugation relies on the partial overlap of p-orbitals on adjacent double or triple bonds. ne of the simplest conjugated molecules is 1,3-butadiene. Conjugation comes in three flavors, the
Conjugation. Conjugation relies on the partial overlap of p-orbitals on adjacent double or triple bonds. ne of the simplest conjugated molecules is 1,3-butadiene. Conjugation comes in three flavors, the
Chemistry Notes for class 12 Chapter 13 Amines
 1 P a g e Chemistry Notes for class 12 Chapter 13 Amines Amines constitute an important class of organic compounds derived by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms ofnh 3 molecule by alkyl/aryl group(s).
1 P a g e Chemistry Notes for class 12 Chapter 13 Amines Amines constitute an important class of organic compounds derived by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms ofnh 3 molecule by alkyl/aryl group(s).
David W. C. MacMillan Career-in-Review. Sujun Wei BreslowGroup Columbia University September 28, 2007
 David W. C. MacMillan Career-in-Review Sujun Wei BreslowGroup Columbia University September 28, 2007 Biography 1968: Born in Bellshill, Scotland 1987-1991: B.S. at the University of Glasgow, Scotland 1991-1996:.D.
David W. C. MacMillan Career-in-Review Sujun Wei BreslowGroup Columbia University September 28, 2007 Biography 1968: Born in Bellshill, Scotland 1987-1991: B.S. at the University of Glasgow, Scotland 1991-1996:.D.
21.9 REDUCTION OF CARBOXYLIC ACID DERIVATIVES
 10 APTER 1 TE EMITRY F ARBXYLI AID DERIVATIVE TUDY GUIDE LIK 1.5 Esters and ucleophiles 1.17 Give the structure of the product in the reaction of each of the following esters with isotopically labeled
10 APTER 1 TE EMITRY F ARBXYLI AID DERIVATIVE TUDY GUIDE LIK 1.5 Esters and ucleophiles 1.17 Give the structure of the product in the reaction of each of the following esters with isotopically labeled
Chapter 5 Classification of Organic Compounds by Solubility
 Chapter 5 Classification of Organic Compounds by Solubility Deductions based upon interpretation of simple solubility tests can be extremely useful in organic structure determination. Both solubility and
Chapter 5 Classification of Organic Compounds by Solubility Deductions based upon interpretation of simple solubility tests can be extremely useful in organic structure determination. Both solubility and
Experiment #8 properties of Alcohols and Phenols
 Introduction Experiment #8 properties of Alcohols and Phenols As has been mentioned before, over 20 million organic compounds have been identified. If each substance had to be studied as an entity completely
Introduction Experiment #8 properties of Alcohols and Phenols As has been mentioned before, over 20 million organic compounds have been identified. If each substance had to be studied as an entity completely
10 Cl atoms. 10 H2O molecules. 8.3 mol HCN = 8.3 mol N atoms 1 mol HCN. 2 mol H atoms 2.63 mol CH2O = 5.26 mol H atoms 1 mol CH O
 Chem 100 Mole conversions and stoichiometry worksheet 1. How many Ag atoms are in.4 mol Ag atoms? 6.0 10 Ag atoms 4.4 mol Ag atoms = 1.46 10 Ag atoms 1 mol Ag atoms. How many Br molecules are in 18. mol
Chem 100 Mole conversions and stoichiometry worksheet 1. How many Ag atoms are in.4 mol Ag atoms? 6.0 10 Ag atoms 4.4 mol Ag atoms = 1.46 10 Ag atoms 1 mol Ag atoms. How many Br molecules are in 18. mol
acid: substance which gives up a proton base: substance which accepts a proton
 Acids & Bases Bronsted/Lowry: acid: substance which gives up a proton base: substance which accepts a proton A + B A - + B + acidgives + to B to form A- baseaccepts + from A to form B+ baseaccepts + from
Acids & Bases Bronsted/Lowry: acid: substance which gives up a proton base: substance which accepts a proton A + B A - + B + acidgives + to B to form A- baseaccepts + from A to form B+ baseaccepts + from
Lecture 15: Enzymes & Kinetics Mechanisms
 ROLE OF THE TRANSITION STATE Lecture 15: Enzymes & Kinetics Mechanisms Consider the reaction: H-O-H + Cl - H-O δ- H Cl δ- HO - + H-Cl Reactants Transition state Products Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2004
ROLE OF THE TRANSITION STATE Lecture 15: Enzymes & Kinetics Mechanisms Consider the reaction: H-O-H + Cl - H-O δ- H Cl δ- HO - + H-Cl Reactants Transition state Products Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2004
Summer Holidays Questions
 Summer Holidays Questions Chapter 1 1) Barium hydroxide reacts with hydrochloric acid. The initial concentration of the 1 st solution its 0.1M and the volume is 100ml. The initial concentration of the
Summer Holidays Questions Chapter 1 1) Barium hydroxide reacts with hydrochloric acid. The initial concentration of the 1 st solution its 0.1M and the volume is 100ml. The initial concentration of the
Write the acid-base equilibria connecting all components in the aqueous solution. Now list all of the species present.
 Chapter 16 Acids and Bases Concept Check 16.1 Chemists in the seventeenth century discovered that the substance that gives red ants their irritating bite is an acid with the formula HCHO 2. They called
Chapter 16 Acids and Bases Concept Check 16.1 Chemists in the seventeenth century discovered that the substance that gives red ants their irritating bite is an acid with the formula HCHO 2. They called
Chapter 22 Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactions
 John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 22 Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactions The α Position The carbon next to the carbonyl group is designated as being in the α position Electrophilic
John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 22 Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactions The α Position The carbon next to the carbonyl group is designated as being in the α position Electrophilic
Boston University Dresden Science Program ORGANIC CHEMISTRY CAS CH 203 Lecture
 Boston University Dresden Science Program ORGANIC CHEMISTRY CAS CH 203 Lecture Instructor: Professor Wolf D. Habicher, Professor Claus Rüger Meeting Times Lectures: twice a week at 90 minutes each Discussions:
Boston University Dresden Science Program ORGANIC CHEMISTRY CAS CH 203 Lecture Instructor: Professor Wolf D. Habicher, Professor Claus Rüger Meeting Times Lectures: twice a week at 90 minutes each Discussions:
Mass Spec - Fragmentation
 Mass Spec - Fragmentation An extremely useful result of EI ionization in particular is a phenomenon known as fragmentation. The radical cation that is produced when an electron is knocked out of a neutral
Mass Spec - Fragmentation An extremely useful result of EI ionization in particular is a phenomenon known as fragmentation. The radical cation that is produced when an electron is knocked out of a neutral
Carbonyl Chemistry (12 Lectures)
 arbonyl hemistry (12 Lectures) Aim of ourse Professor Donna G. Blackmond d.blackmond@imperial.ac.uk tel. 41193 oom 639 1 To build upon elements of Dr E.. Smith s and Dr. D.. Braddocks s course. To introduce
arbonyl hemistry (12 Lectures) Aim of ourse Professor Donna G. Blackmond d.blackmond@imperial.ac.uk tel. 41193 oom 639 1 To build upon elements of Dr E.. Smith s and Dr. D.. Braddocks s course. To introduce
CHEMISTRY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND BONDING
 CHEMISTRY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND BONDING Essential Standard: STUDENTS WILL UNDERSTAND THAT THE PROPERTIES OF MATTER AND THEIR INTERACTIONS ARE A CONSEQUENCE OF THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER,
CHEMISTRY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND BONDING Essential Standard: STUDENTS WILL UNDERSTAND THAT THE PROPERTIES OF MATTER AND THEIR INTERACTIONS ARE A CONSEQUENCE OF THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER,
Southeastern Louisiana University Dual Enrollment Program--Chemistry
 Southeastern Louisiana University Dual Enrollment Program--Chemistry The Southeastern Dual Enrollment Chemistry Program is a program whereby high school students are given the opportunity to take college
Southeastern Louisiana University Dual Enrollment Program--Chemistry The Southeastern Dual Enrollment Chemistry Program is a program whereby high school students are given the opportunity to take college
Syllabus for General Organic Chemistry M07A- Fall 2013 Prof. Robert Keil
 Syllabus for General Organic Chemistry M07A- Fall 2013 Prof. Robert Keil Textbook and Materials What you must buy: Organic Chemistry 4 th Ed. Janice G. Smith, McGraw Hill. (Older edition is fine) Chem
Syllabus for General Organic Chemistry M07A- Fall 2013 Prof. Robert Keil Textbook and Materials What you must buy: Organic Chemistry 4 th Ed. Janice G. Smith, McGraw Hill. (Older edition is fine) Chem
RESONANCE, USING CURVED ARROWS AND ACID-BASE REACTIONS
 RESONANCE, USING CURVED ARROWS AND ACID-BASE REACTIONS A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO: 1. Properly use curved arrows to draw resonance structures: the tail and the head of every arrow must be drawn in exactly
RESONANCE, USING CURVED ARROWS AND ACID-BASE REACTIONS A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO: 1. Properly use curved arrows to draw resonance structures: the tail and the head of every arrow must be drawn in exactly
Studying an Organic Reaction. How do we know if a reaction can occur? And if a reaction can occur what do we know about the reaction?
 Studying an Organic Reaction How do we know if a reaction can occur? And if a reaction can occur what do we know about the reaction? Information we want to know: How much heat is generated? How fast is
Studying an Organic Reaction How do we know if a reaction can occur? And if a reaction can occur what do we know about the reaction? Information we want to know: How much heat is generated? How fast is
CHEM 208(Organic Chemistry I) Instructor: Dr. Niranjan Goswami. Tel: (618)545-3361. Email: Ngoswami@kaskaskia.edu. Web: www.kc.cc.il.
 CHEM 208(Organic Chemistry I) Instructor: Dr. Niranjan Goswami Tel: (618)545-3361 Email: Ngoswami@kaskaskia.edu Web: www.kc.cc.il.us/ngoswami CHEM 208 COURSE SYLLABUS KASKASKIA COLLEGE NAME TERM YEAR TEXT:
CHEM 208(Organic Chemistry I) Instructor: Dr. Niranjan Goswami Tel: (618)545-3361 Email: Ngoswami@kaskaskia.edu Web: www.kc.cc.il.us/ngoswami CHEM 208 COURSE SYLLABUS KASKASKIA COLLEGE NAME TERM YEAR TEXT:
Acid-Base Chemistry. Brønsted-Lowry Acids & Bases
 Acid-Base Chemistry ν There are a couple of ways to define acids and bases ν Brønsted-Lowry acids and bases ν Acid: H + ion donor ν Base: H + ion acceptor ν Lewis acids and bases ν Acid: electron pair
Acid-Base Chemistry ν There are a couple of ways to define acids and bases ν Brønsted-Lowry acids and bases ν Acid: H + ion donor ν Base: H + ion acceptor ν Lewis acids and bases ν Acid: electron pair
ALKENES AND ALKYNES REACTIONS
 A STUDENT SHULD BE ABLE T: ALKENES AND ALKYNES REACTINS 1. Given the starting materials and reaction conditions, predict the products of the following reactions of alkenes and alkynes. Regioselective Markovnikov
A STUDENT SHULD BE ABLE T: ALKENES AND ALKYNES REACTINS 1. Given the starting materials and reaction conditions, predict the products of the following reactions of alkenes and alkynes. Regioselective Markovnikov
CHM220 Nucleophilic Substitution Lab. Studying S N 1 and S N 2 Reactions: Nucloephilic Substitution at Saturated Carbon*
 CHM220 Nucleophilic Substitution Lab Studying S N 1 and S N 2 Reactions: Nucloephilic Substitution at Saturated Carbon* Purpose: To convert a primary alcohol to an alkyl bromide using an S N 2 reaction
CHM220 Nucleophilic Substitution Lab Studying S N 1 and S N 2 Reactions: Nucloephilic Substitution at Saturated Carbon* Purpose: To convert a primary alcohol to an alkyl bromide using an S N 2 reaction
MOLECULAR REPRESENTATIONS AND INFRARED SPECTROSCOPY
 MLEULAR REPRESENTATINS AND INFRARED SPETRSPY A STUDENT SULD BE ABLE T: 1. Given a Lewis (dash or dot), condensed, bond-line, or wedge formula of a compound draw the other representations. 2. Give examples
MLEULAR REPRESENTATINS AND INFRARED SPETRSPY A STUDENT SULD BE ABLE T: 1. Given a Lewis (dash or dot), condensed, bond-line, or wedge formula of a compound draw the other representations. 2. Give examples
Saturated NaCl solution rubber tubing (2) Glass adaptor (2) thermometer adaptor heating mantle
 EXPERIMENT 5 (Organic Chemistry II) Pahlavan/Cherif Dehydration of Alcohols - Dehydration of Cyclohexanol Purpose - The purpose of this lab is to produce cyclohexene through the acid catalyzed elimination
EXPERIMENT 5 (Organic Chemistry II) Pahlavan/Cherif Dehydration of Alcohols - Dehydration of Cyclohexanol Purpose - The purpose of this lab is to produce cyclohexene through the acid catalyzed elimination
Chapter 10. Can You... 1. draw the Lewis structure for a given covalently bonded molecule?
 Chapter 10 Can You... 1. draw the Lewis structure for a given covalently bonded molecule? e.g. SF 6 and CH 3 Cl 2. identify and count the number of non-bonding and bonding domains within a given covalently
Chapter 10 Can You... 1. draw the Lewis structure for a given covalently bonded molecule? e.g. SF 6 and CH 3 Cl 2. identify and count the number of non-bonding and bonding domains within a given covalently
Suggested solutions for Chapter 3
 s for Chapter PRBLEM Assuming that the molecular ion is the base peak (00% abundance) what peaks would appear in the mass spectrum of each of these molecules: (a) C5Br (b) C60 (c) C64Br In cases (a) and
s for Chapter PRBLEM Assuming that the molecular ion is the base peak (00% abundance) what peaks would appear in the mass spectrum of each of these molecules: (a) C5Br (b) C60 (c) C64Br In cases (a) and
AP CHEMISTRY 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES. Question 6
 AP CHEMISTRY 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 6 Answer the following questions, which pertain to binary compounds. (a) In the box provided below, draw a complete Lewis electron-dot diagram for the IF 3
AP CHEMISTRY 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 6 Answer the following questions, which pertain to binary compounds. (a) In the box provided below, draw a complete Lewis electron-dot diagram for the IF 3
AROMATIC COMPOUNDS A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO:
 A STUDENT SHULD BE ABLE T: ARMATIC CMPUNDS 1. Name benzene derivatives given the structures, and draw the structures given the names. This includes: Monosubstituted benzenes named as derivatives of benzene:
A STUDENT SHULD BE ABLE T: ARMATIC CMPUNDS 1. Name benzene derivatives given the structures, and draw the structures given the names. This includes: Monosubstituted benzenes named as derivatives of benzene:
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I PRACTICE EXERCISE Sn1 and Sn2 Reactions
 ORGANIC CEMISTRY I PRACTICE EXERCISE Sn1 and Sn2 Reactions 1) Which of the following best represents the carbon-chlorine bond of methyl chloride? d d - d - d d d d - d - I II III IV V 2) Provide a detailed,
ORGANIC CEMISTRY I PRACTICE EXERCISE Sn1 and Sn2 Reactions 1) Which of the following best represents the carbon-chlorine bond of methyl chloride? d d - d - d d d d - d - I II III IV V 2) Provide a detailed,
Reminder: These notes are meant to supplement, not replace the laboratory manual. SN1 Reaction Notes
 Reminder: These notes are meant to supplement, not replace the laboratory manual. SN1 Reaction Notes Background and Application Substitution Nucleophilic First Order (SN1) reactions are one of the most
Reminder: These notes are meant to supplement, not replace the laboratory manual. SN1 Reaction Notes Background and Application Substitution Nucleophilic First Order (SN1) reactions are one of the most
Understanding Selectivity in Reversed Phase Chromatography A Simplified Look at Column Selection
 Understanding Selectivity in Reversed Phase Chromatography A Simplified Look at Column Selection Dr. Frank Dorman, Pennsylvania State University Ty Kahler, Randy Romesberg, Vernon Bartlett, Mike Wittrig,
Understanding Selectivity in Reversed Phase Chromatography A Simplified Look at Column Selection Dr. Frank Dorman, Pennsylvania State University Ty Kahler, Randy Romesberg, Vernon Bartlett, Mike Wittrig,
Benzene and Aromatic Compounds
 Benzene and Aromatic Compounds Benzene (C 6 H 6 ) is the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon (or arene). Benzene has four degrees of unsaturation, making it a highly unsaturated hydrocarbon. Whereas unsaturated
Benzene and Aromatic Compounds Benzene (C 6 H 6 ) is the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon (or arene). Benzene has four degrees of unsaturation, making it a highly unsaturated hydrocarbon. Whereas unsaturated
Chemical Kinetics. 2. Using the kinetics of a given reaction a possible reaction mechanism
 1. Kinetics is the study of the rates of reaction. Chemical Kinetics 2. Using the kinetics of a given reaction a possible reaction mechanism 3. What is a reaction mechanism? Why is it important? A reaction
1. Kinetics is the study of the rates of reaction. Chemical Kinetics 2. Using the kinetics of a given reaction a possible reaction mechanism 3. What is a reaction mechanism? Why is it important? A reaction
Physicochemical Properties of Drugs
 Therapeutics I Michael B. Bolger 1/3/02 bjectives: At the end of the next hour: Physicochemical Properties of Drugs 1. The student should be able to calculate the degree of ionization for an acidic or
Therapeutics I Michael B. Bolger 1/3/02 bjectives: At the end of the next hour: Physicochemical Properties of Drugs 1. The student should be able to calculate the degree of ionization for an acidic or
KINETIC DETERMINATION OF SELENIUM BY VISIBLE SPECTROSCOPY (VERSION 1.8)
 Selenium Determination, Page 1 KINETIC DETERMINATION OF SELENIUM BY VISIBLE SPECTROSCOPY I. BACKGROUND. (VERSION 1.8) The majority of reactions used in analytical chemistry possess the following characteristics:
Selenium Determination, Page 1 KINETIC DETERMINATION OF SELENIUM BY VISIBLE SPECTROSCOPY I. BACKGROUND. (VERSION 1.8) The majority of reactions used in analytical chemistry possess the following characteristics:
ALCOHOLS: Properties & Preparation
 ALLS: Properties & Preparation General formula: R-, where R is alkyl or substitued alkyl. Ar-: phenol - different properties. Nomenclature 1. ommon names: Name of alkyl group, followed by word alcohol.
ALLS: Properties & Preparation General formula: R-, where R is alkyl or substitued alkyl. Ar-: phenol - different properties. Nomenclature 1. ommon names: Name of alkyl group, followed by word alcohol.
Chapter 14 - Acids and Bases
 Chapter 14 - Acids and Bases 14.1 The Nature of Acids and Bases A. Arrhenius Model 1. Acids produce hydrogen ions in aqueous solutions 2. Bases produce hydroxide ions in aqueous solutions B. Bronsted-Lowry
Chapter 14 - Acids and Bases 14.1 The Nature of Acids and Bases A. Arrhenius Model 1. Acids produce hydrogen ions in aqueous solutions 2. Bases produce hydroxide ions in aqueous solutions B. Bronsted-Lowry
Use the Force! Noncovalent Molecular Forces
 Use the Force! Noncovalent Molecular Forces Not quite the type of Force we re talking about Before we talk about noncovalent molecular forces, let s talk very briefly about covalent bonds. The Illustrated
Use the Force! Noncovalent Molecular Forces Not quite the type of Force we re talking about Before we talk about noncovalent molecular forces, let s talk very briefly about covalent bonds. The Illustrated
Acids and Bases: A Brief Review
 Acids and : A Brief Review Acids: taste sour and cause dyes to change color. : taste bitter and feel soapy. Arrhenius: acids increase [H ] bases increase [OH ] in solution. Arrhenius: acid base salt water.
Acids and : A Brief Review Acids: taste sour and cause dyes to change color. : taste bitter and feel soapy. Arrhenius: acids increase [H ] bases increase [OH ] in solution. Arrhenius: acid base salt water.
Standard Free Energies of Formation at 298 K. Average Bond Dissociation Energies at 298 K
 1 Thermodynamics There always seems to be at least one free response question that involves thermodynamics. These types of question also show up in the multiple choice questions. G, S, and H. Know what
1 Thermodynamics There always seems to be at least one free response question that involves thermodynamics. These types of question also show up in the multiple choice questions. G, S, and H. Know what
Determination of Equilibrium Constants using NMR Spectrscopy
 CHEM 331L Physical Chemistry Laboratory Revision 1.0 Determination of Equilibrium Constants using NMR Spectrscopy In this laboratory exercise we will measure a chemical equilibrium constant using key proton
CHEM 331L Physical Chemistry Laboratory Revision 1.0 Determination of Equilibrium Constants using NMR Spectrscopy In this laboratory exercise we will measure a chemical equilibrium constant using key proton
Aldehydes can react with alcohols to form hemiacetals. 340 14. Nucleophilic substitution at C=O with loss of carbonyl oxygen
 340 14. Nucleophilic substitution at C= with loss of carbonyl oxygen Ph In Chapter 13 we saw this way of making a reaction go faster by raising the energy of the starting material. We also saw that the
340 14. Nucleophilic substitution at C= with loss of carbonyl oxygen Ph In Chapter 13 we saw this way of making a reaction go faster by raising the energy of the starting material. We also saw that the
CHEM 36 General Chemistry EXAM #1 February 13, 2002
 CHEM 36 General Chemistry EXAM #1 February 13, 2002 Name: Serkey, Anne INSTRUCTIONS: Read through the entire exam before you begin. Answer all of the questions. For questions involving calculations, show
CHEM 36 General Chemistry EXAM #1 February 13, 2002 Name: Serkey, Anne INSTRUCTIONS: Read through the entire exam before you begin. Answer all of the questions. For questions involving calculations, show
