Can we achieve health information for all by 2015?
|
|
|
- Sharleen Terry
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Can we achieve health information for all by 2015? Fiona Godlee, Neil Pakenham-Walsh, Dan Ncayiyana, Barbara Cohen, Abel Packer Universal access to information for health professionals is a prerequisite for meeting the Millennium Development Goals and achieving Health for All. However, despite the promises of the information revolution, and some successful initiatives, there is little if any evidence that the majority of health professionals in the developing world are any better informed than they were 10 years ago. Lack of access to information remains a major barrier to knowledge-based health care in developing countries. The development of reliable, relevant, usable information can be represented as a system that requires cooperation among a wide range of professionals including health-care providers, policy makers, researchers, publishers, information professionals, indexers, and systematic reviewers. The system is not working because it is poorly understood, unmanaged, and under-resourced. This Public Health article proposes that WHO takes the lead in championing the goal of Universal access to essential health-care information by 2015 or Health Information for All. Strategies for achieving universal access include funding for research into barriers to use of information, evaluation and replication of successful initiatives, support for interdisciplinary networks, information cycles, and communities of practice, and the formation of national policies on health information. 10 years ago, a meeting to review global access to health information concluded that most health professionals in developing countries had inadequate access to information and that the information available to them was often unreliable or irrelevant. 1 At that time, there was optimism that, by 2004, all or nearly all health professionals in developing countries would have access to the information they needed to provide the most effective health care possible with the resources available. The world was at the cusp of the information age: information and communication technologies would mean that lack of access to reliable relevant information would no longer be a barrier to effective health care. Although other factors such as lack of drugs and infrastructure might hinder provision of health care, this would not be the case with information. What then has been achieved in the past 10 years? What have we learnt? And if providing access to reliable information is the single most cost-effective and achievable strategy for sustainable improvement in health care, 2 what steps can we now take to bring us nearer to health information for all (panel)? information is recognised in the latest draft of WHO s World Report on Knowledge for Better Health 3 as an important part of worldwide strategies to reduce global disparities in health and to achieve the health-related Millennium Development Goals. Progress has been patchy, both geographically (with sub-saharan Africa generally falling far behind most other regions) and across different health sectors (specialist and academic health care is much better served with information than rural primary care), and overall there is little if any evidence that the majority of health professionals, especially those working in primary health care, are any better informed than they were 10 years ago. The few empirical studies we identified 4 7 and many anecdotal reports suggest that lack of physical access to information (absent, slow, or unreliable internet connectivity, expensive paper, and high subscription cost of products) remains the major barrier to knowledge-based health care in developing countries. However, there are now many successful initiatives that could be extended or replicated. An example is BIREME ( the Latin American Published online July 9, extras/04art6112web.pdf See Comment BMJ Knowledge, BMA House, Tavistock Square, London WC1H 9JR, UK (F Godlee MRCP); INASP, Suite B, 58 St Aldates, Oxford OX1 1ST, UK (N Pakenham-Walsh MBBS); Durban Institute of Technology, PO Box 1334, Durban 4000, South Africa (Prof D Ncayiyana PhD Med); Public Library of Science, 185 Berry Street, Suite 1300, San Francisco, CA 94107, USA (B Cohen PhD); and BIREME, Rua Botucatu 862, Sao Paulo, Brazil (A Packer MLS) Correspondence to: Dr Fiona Godlee, Head of BMJ Knowledge, BMJ Publishing Group, London WC1H 9JR, UK fgodlee@bmjgroup.com What has been achieved? Important progress has undoubtedly been made. Information and communication technologies are increasingly available; more and better content is available to a growing number of people, especially those in tertiary hospitals, academic institutions, and urban settings; there are more and better free resources on the internet; there is a larger and wider range of healthinformation support programmes; an international community has evolved that is committed to improving health-care information, with governments and other bodies in developing countries playing an increasingly active part; and politically, access to health-care information has become a key international development issue. Equitable and universal access to health-care Panel: Background This paper is adapted from a discussion paper commissioned by WHO in preparation for the Mexico Summit on Health Research in November, Publication in The Lancet coincides with the launch of the Global Review of Access to Health Information in Developing Countries ( globalreview). Building on a series of existing conferences worldwide in , the review will bring together people from all stages of knowledge creation and dissemination, to understand more about progress, lessons learned, and ways forward. To get involved, join the forum HIF-net at WHO (health@inasp.info). Published online July 9,
2 and Caribbean Centre For Health Sciences Information. Established in 1967 following an agreement between the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO)/WHO and the Brazilian Government, BIREME has shown how significant government funding across a region can successfully overcome the phenomenon of the lost science of the Third World. 8 In collaboration with the Foundation for the Support of Science of São Paulo (FAPESP) and the Chilean National Council of Sciences, BIREME set up SciELO (the Scientific Electronic Library Online, which was the first and is now one of the largest sources of free full-text access to health research information. BIREME also set up LILACS ( which indexes journals from Latin America and the Caribbean, and the Virtual Health Library ( which provides free online access to a range of evidence-based resources that support health-care decisions. EMRO (World Health Organization Eastern Mediterranean Regional Office) has also developed a raft of initiatives to improve access to health information and to build capacity in health research and the production and dissemination of healthinformation materials. It provides training for researchers at country and regional level, helps countries develop research policies, directly sponsors research, and has developed a regional journal as an avenue for dissemination and academic recognition. EMRO Index Medicus indexes over 310 journals in the region and is published in print, CD-ROM, and on the internet. EMRO maintains a database of locally produced books and journals from the region, maintains a core list of recommended resources for small libraries, and provides financial support for libraries to procure such core resources. These initiatives, and many others, show what is possible given political support, international cooperation, clear leadership, good management, and adequate funds and what might be possible for important initiatives such as the Association for Health Information and Libraries in Africa ( org) and the African Index Medicus ( int/library), which are currently struggling partly through lack of sustained national and international political and financial commitment. What have we learnt? The past 10 years have taught some crucial lessons. One is that pull is better than push when it comes to information transfer. The meeting 10 years ago to review global access to health information recognised the huge importance of information flows within and among developing countries and the limitations of pushing information to health-care professionals. A report of the meeting concluded that: People in the developing world should be given the chance to say what they want rather than simply be sent information. 1 Despite growing understanding of the need for exchange of knowledge between countries and within regions, there is a continuing tendency to push information out to people rather than strengthening and responding to the pull of their information needs. Another lesson is that sustainable development is achieved only through building local capacity. More and more initiatives have shown the wisdom of acting locally. Healthlink Worldwide ( org.uk) has shifted from being a publisher and distributor of international newsletters (Dialogue on Diarrhoea, AIDS Action, etc) to enabling developing country producers and distributors (publishers, ministries of health, library services, local and regional non-governmental organisations) to publish and distribute their own health learning materials. The Effective Health Care Alliance Programme 9 helps individuals and groups in middle and low-income countries to prepare and update systematic reviews. INCLEN (the International Clinical Epidemiology Network; provides long-term funds, training, peer support, and mentoring to build capacity in clinical epidemiology in developing countries. Thanks to the Council on Health Research for Development (COHRED) and the Global Forum for Health Research, we have learnt that less than 10% of health-research funding is targeted to the health problems that account for 90% of the global disease burden. 10 This 10/90 gap is a fundamental cause of lack of access to relevant health information. It is exacerbated by problems in getting developing world research published, indexed, incorporated into systematic reviews, and integrated into accessible learning and reference materials. The 10/90 gap in research probably translates into a 1/99 gap in health information. We have learnt that most health professionals still prefer print. 7,11,12 We have also learnt that most health workers in developing countries will not or cannot pay for information themselves and that as much information as possible should therefore be free to use. In its draft report, WHO argues that knowledge must be accessible to all in a form which is useful and can be acted upon by different people and groups. 2 Free access and open access initiatives have greatly improved availability of the biomedical literature, 13 which is the crucial building block for evidence-based health care. In particular, HINARI (Health InterNetwork Access to Research Initiative; a partnership initiative led by WHO, now provides developing countries with access to nearly 2300 online journals. But we have also learnt that journals are one of the least useful information sources for health professionals in 2 Published online July 9,
3 practice. 4,11,12 In information-rich industrialised countries, clinicians often rely largely on two or three essential information resources basic reference and learning materials such as handbooks and drug formularies. A community health worker may find a single copy of Where there is no doctor, 14 adapted and written in the local language more useful than access to thousands of international journals. More attention is needed to ensure free access to such resources for the vast majority of developing-world health professionals who work in primary and district care. We have learnt that funders behaviour is critical. Despite increasing recognition of the importance of information, communication, and networking, many funding agencies are reluctant to support these types of activity, whose impacts are more diffuse and less easy to define and measure than those of discrete, short-term practical projects. Funding agencies tend not to like providing small grants, and they often prefer to fund new rather than established programmes, even where these have been successful. As a result, health-information funding often falls between the cracks: between project-based and infrastructural support, between health and education, and between international and country approaches. Finally, we have learnt about the existence and importance of local information cycles or communities of practice. Complete sustainable information cycles are those in which readers/users are also writers/ contributors. A completely inclusive information cycle exists within the world of academic research, where all authors are readers and all readers are potential authors. But information cycles also exist, or can be established, between researchers, scientific publishers and editors, systematic reviewers, funders of research, health professionals, policy makers, and patients. These information cycles have the potential to greatly increase the relevance and reliability of information about health care, and to build skills, understanding, and ownership that will help to increase the use of that information. Experience at BIREME and elsewhere shows that local information cycles and communities of practice can be facilitated and strengthened by giving people the chance to use virtual forums, chat rooms, and discussion lists. HIF-net at WHO ( inasp.info/health/hif-net) and the World Association of Medical Editors ( are examples of virtual communities of practice that have the potential to build local capacity in the developing world. What needs to happen now? It is not the place of this article to make detailed recommendations on the way forward. However, we suggest four broad issues around which future activity could be focused, and we propose a framework within which more detailed ideas could be formulated, implemented, and evaluated. The first issue is improved access to essential information for health professionals, such as drug formularies and evidence-based handbooks. This may best be achieved through strengthening of local and regional publishers, libraries, and information services. With access to electronic resources (and adequate financial support for training and equipment), libraries can make information available to end-users in a range of formats (printed, electronic, digital, and broadcast media). At the moment there are stark regional differences in library support. In many developing countries it is difficult, if not impossible, for librarians and others to find out and certainly to afford the full range of relevant publications available nationally or internationally. But much has been learned about the development of libraries and resource centres, particularly through the work of Healthlink Worldwide and its partners. WHO s Blue Trunk Library may be a model that should be replicated more widely; it has provided over 1000 minilibraries for use by district hospitals and other frontline facilities, providing access to a selection of essential health-information materials. The second issue is improved connectivity. Clinicians may still generally prefer paper, but among currently available technologies only the internet has the potential to deliver universal access to up-to-date health-care information. Connectivity is vital for efficient information flows among librarians, publishers, and all others responsible for developing and distributing materials. Internet connectivity has increased dramatically over the past 10 years, but it is still unavailable to most health professionals. 15 Access to is spreading faster than the internet, especially in Africa. provides new possibilities for publishing and distributing practical health-care information and for networking with other health professionals, as evidenced by the success of regional networks (eg, AFRO-Nets; publisher networks (eg, Forum for African Medical Editors), 16 librarian networks, and multidisciplinary health-information development networks (eg, HIF-net at WHO). has also enabled one-to-one communications, both professional and personal, facilitating development of relationships and reducing professional isolation. Significant problems to overcome in some countries include inadequate power supply; lack of computer equipment and information technology support; the fact that the necessary software is mainly in English; lack of computer skills; and resistance to use of technology among health professionals. Improvements in connectivity will require a major global information communication technology initiative, which itself will require substantial and sustained financing. The third issue is the need to identify and overcome barriers to the use of information in different settings. Published online July 9,
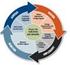
4 Evidence-based materials made available Generic information localised Generic information materials produced Evidence-based materials field tested Localise knowledge Systematic reviews produced (or updated) New questions generated Identify needs Synthesise relevant knowledge Related research identified Search for answers in systematic reviews Add to body of biomedical knowledge Research papers indexed Knowledge gaps identified Decisions made to undertake new research Research completed and written up Research papers peer reviewed and disseminated Figure: Evidence-based knowledge system for developing reliable, relevant, usable information on health care A growing body of evidence, mainly from the developed world, suggests that access to information is necessary but not sufficient to change practice. Changing practice is by no means simple and remains a major challenge in the information-rich industrialised world. 17 A survey in 2003 of nearly 7000 people in the USA, and review of their medical records, found that, over 2 years, participants received only 54% of recommended care. 18 There is plenty of anecdotal evidence to suggest that this know-do gap is at least as great in developing as in developed countries. Known and assumed barriers to using information in practice (many of which are also experienced by health professionals in developed countries) include: lack of awareness of what is available; lack of relevance of available information (not meeting people s needs in terms of scope, style, language, or format); lack of time and incentives to use information; and lack of interpretation skills. 4,5,7,11,12,17,19 There are no simple solutions. Any attempts to overcome barriers to use of information should be based on good research into the nature of the barriers and evaluations of planned interventions. Training and peer support is likely to be key. As the amount of information available increases, health professionals will need critical appraisal skills to be able to distinguish unreliable from reliable sources of information. Librarians and producers of health-care materials need searching, critical appraisal, and computer skills. Researchers, systematic reviewers, journal editors, and indexers need to understand research design and to have skills in searching, critical appraisal, writing, and editing. Software and interface designers need to empower users so that they can exploit technologies to combine and mediate information and knowledge. Achieving all of this on a global scale will require major investment within countries, and the use of effective learning and peer support methodologies, whether face-to-face or virtual. Our final issue on which future activity should focus is the need to improve the quality of health-care information in terms of its reliability, relevance, and usability. One barrier to use of information in practice which may be more apparent in developing countries, but is still by no means unique to them is the lack of demand for information. This may be related to factors such as a lack of reading culture; low motivation associated with poor working conditions and poor prospects for career development; lack of awareness of evidence-based health care; long-term professional isolation; or long-term lack of access to information leading to the view that whatever is available is adequate. But anecdotal evidence also suggests that lack of demand is related in part to the poor quality of much of the information available. Creating reliable, relevant, and usable information for health professionals requires a series of activities. Within an evidence-based paradigm these can be represented as forming a virtuous cycle or system, each activity being dependent for its success on the activities before, each contributing to the success of the activities that follow (figure). The figure is highly simplified; at every step there are various inputs and outputs, drivers and constraints, strengths and weaknesses. The system is not managed either locally or globally; it is largely unrecognised as a system and is severely under-resourced. As a result, the system is not working. Individual activities within it are taking place but haphazardly and in isolation, with many short circuits that significantly reduce the reliability, relevance, and usability of the information reaching health professionals and policy makers. For example, much research is still undertaken without a prior systematic review to check that the research is necessary, to learn from the methodology of previous studies, or to focus the research question; completed research is often disseminated without proper peer review; individual research studies are distributed to health professionals without being put into context of other related research; many systematic reviews are still undertaken without careful consultation with health professionals and patients about which questions are most urgently in need of answers; many information resources are poorly evidence based and are not field tested on end-users to check that they meet their information needs; most of the information reaching health professionals in developing countries 4 Published online July 9,
5 comes from producers in industrialised countries, without any attempt at localisation. We suggest four main reasons for these short circuits. The first is lack of understanding about how the various actors can work together more effectively. Education and consultation among groups may be the best way to tackle this. The second reason is lack of capacity in the system eg, the lack of systematic reviews addressing health-care issues in the developing world, 20 the lack of good research on these issues (the 10/90 gap), and the shortage of people adequately trained and resourced to adapt material for local needs. This problem could be tackled by identifying and specifically supporting activities where local capacity is lacking. The third reason is the market. Commercial players in the system focus their efforts, for obvious reasons, on where the money is in providing endproducts to health professionals. Business models need to be found that distribute revenue more evenly around the system, reflecting the distribution of costs, to establish robust intermediate markets. The fourth reason is a lack of national public policies on health information that define national goals and priorities as well as promoting convergence of initiatives and resources. The system is, in reality, a series of potential and actual local information cycles. These bring together (or could bring together) people working at different stages in the creation and dissemination of knowledge, within a hospital, a country, regionally, or globally. Support for such local information cycles would bring greater understanding of how to make the knowledge system work better in different settings and for different groups of people, and so improve the quality of information reaching health professionals. A proposal As a framework for taking things forward, we propose that WHO takes the lead in championing the goal of Universal access to essential health-care information by 2015 or Health information for All. We suggest that WHO and its partners establish an international collaborative group along the lines of the Global Fund for AIDS, TB, and Malaria, which is coordinated by the UN, or the Global AIDS Vaccine Initiative coordinated by the Rockefeller Foundation. We envision that this group, which should include representatives of the major global funders, would create a pot of money like a lottery fund to be allocated to initiatives on a competitive basis in line with an overall strategy to achieve health information for all. This strategy could include calls for research into information needs and barriers to use of information; evaluation and replication of successful initiatives; support for local information cycles and communities of practice; and the formulation and establishment of national public policies on health information. The international collaborative group could be assisted by an independent advisory board made up of key representatives from all stages in the knowledge system, with the majority from developing countries. A small part of the fund could be devoted to networking and learning among the thousands of stakeholders worldwide who are working to improve access to health information in developing countries. This is important for many reasons: to strengthen cooperation, reduce duplication of effort, and to develop a shared understanding of the system in which we operate. Such networks are already in place at global (eg, HIFnet at WHO) and regional (eg, AHILA-net) levels, and country networks are now beginning to emerge (eg, Senegal-AHILA). We call upon WHO and other organisations to commit to universal access to essential health-care information by We believe such access is a prerequisite to meeting the Millennium Development Goals and achieving Health for All; moreover, it is now, for the first time, realistically achievable. Contributors F Godlee and N Pakenham-Walsh wrote the report and devised the knowledge system diagram, with detailed input from all other authors. A Packer contributed the concept of local information cycles. All authors reviewed the final version. Conflict of interest statement FG is executive editor of Clinical Evidence, a compendium of evidence syntheses on the effects of health-care interventions, which is published by the BMJ Publishing Group and is available free online to users in low and very low income countries through the HINARI initiative. NP-W runs the INASP-Health programme, which aims to support cooperation, analysis, and advocacy among those working to improve access to reliable information for health-care workers in developing and transitional countries. INASP-Health is a programme of INASP (International Network for the Availability of Scientific Publications), a non-governmental organisation founded by the International Council for Science in INASP-Health activities are supported by the BMJ, Exchange (a UK Department for Internal Development-funded networking and learning programme on health communications), and WHO. DJN is editor of the South African Medical Journal, which is owned by the South African Medical Association. BC is senior editor on PLoS Biology and PLoS Medicine, two open-access journals published by the Public Library of Science, a not-for-profit organisation that is committed to making the scientific and medical literature a public resource. AP is director of BIREME/PAHO/WHO and operational coordinator of SciELO. Acknowledgments The authors would like to thank all those who kindly reviewed drafts of the WHO discussion paper on which this article is based. Many thanks also to Tamara Rader for literature search and appraisal and to Sam Knottenbelt for research and administrative support. WHO provided funding for research and administrative support, but had no other role in the writing of the report. References 1 Kale R. Health information for the developing world. BMJ 1994; 309: Pakenham-Walsh N, Priestly C, Smith R. Meeting the information needs of health workers in developing countries. BMJ 1997; 314: WHO. World report on knowledge for better health. Geneva: World Health Organization, Available at: (accessed June 21, 2004). Published online July 9,
6 4 Adamson S, Muula AS, Misiri H, et al. What is the access to continued professional education among health workers in Blantyre, Malawi? docs/malawihealtheducat.pdf (accessed June 21, 2004). 5 Health InterNetwork (HIN) India. Web based initiatives: health workers needs assessment summary report of findings. (accessed June 21, 2004). 6 Horton R. North and South: bridging the information gap. Lancet 2000; 355: Health information needs and services in Cameroon. Afr JLibr Arch Info Sci 1998; 8: Gibbs WW. Lost science in the Third World. Sci Am 1995; Aug: Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine. Effective health care alliance programme (EHCAP). introduction.htm (accessed June 21, 2004). 10 Global Forum on Health Research. 10/90 report on health research pages/index.asp (accessed June 21, 2004). 11 Dawes M, Sampson U. Knowledge management in clinical practice: a systematic review of information seeking behavior in physicians. Int J Med Inf 2003; 71: Smith R. What information do doctors need? BMJ 1996; 313: Tamber PS, Godlee F, Newmark P. Open access to peer-reviewed research: making it happen. Lancet 2003; 362: Werner D, Thuman C, Maxwell J. Where there is no doctor, revised 1992, updated Berkeley: The Hesperian Foundation ( 15 Tan-Torres Edejer T. Disseminating health information in developing countries: the role of the internet. BMJ 2000; 321: TDR. FAME constitution. publications/fame_constitution.htm (accessed July 1, 2004). 17 Haines A, Donald A. Getting research into practice, 2nd edn. London: BMJ Books, McGlynn EA, Asch SM, Adams J, et al. The quality of health care delivered to adults in the United States. N Engl J Med 2003; 348: Hunt JM. Barriers to research utilization. J Adv Nurs 1996; 23: Swingler GH, Volmink J, Ioannidis JPA. Number of published systematic reviews and global burden of disease: database analysis. BMJ 2003; 327: Published online July 9,
Improving access to healthcare information in resource poor settings
 Improving access to healthcare information in resource poor settings A position paper for WHO April 2004 Fiona Godlee, Neil Pakenham-Walsh, Dan Ncayiyana, Barbara Cohen, Abel Packer Why improve access?
Improving access to healthcare information in resource poor settings A position paper for WHO April 2004 Fiona Godlee, Neil Pakenham-Walsh, Dan Ncayiyana, Barbara Cohen, Abel Packer Why improve access?
National Health Research Policy
 National Health Research Policy The establishment of a Department of Health Research (DHR) in the Ministry of Health is recognition by the GOI of the key role that health research should play in the nation.
National Health Research Policy The establishment of a Department of Health Research (DHR) in the Ministry of Health is recognition by the GOI of the key role that health research should play in the nation.
Developing Excellence in Leadership, Training and Science
 DELTAS Africa Initiative Outline Developing Excellence in Leadership, Training and Science August 2014 Improving School Governance 1 The Wellcome Trust and its partners have launched an initiative with
DELTAS Africa Initiative Outline Developing Excellence in Leadership, Training and Science August 2014 Improving School Governance 1 The Wellcome Trust and its partners have launched an initiative with
How To Write The Who Disability And Rehabilitation Guidelines
 WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION CONCEPT PAPER WHO Guidelines on Health-Related Rehabilitation (Rehabilitation Guidelines) MANDATE The World Health Assembly Resolution on "Disability, including prevention, management
WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION CONCEPT PAPER WHO Guidelines on Health-Related Rehabilitation (Rehabilitation Guidelines) MANDATE The World Health Assembly Resolution on "Disability, including prevention, management
Components of Geonomics and Bio-Informatics
 Components of Geonomics and Bio-Informatics Shankar Srinivasan, PhD Department of Health Informatics University of Medicine and Dentistry of New Jersey Newark, New Jersey World Health Organization (WHO)
Components of Geonomics and Bio-Informatics Shankar Srinivasan, PhD Department of Health Informatics University of Medicine and Dentistry of New Jersey Newark, New Jersey World Health Organization (WHO)
World Health Organization
 March 1, 2005 Proposed Networks to Support Health Decision-Making and Health Policy Formulation in Low and Lower Middle Income Countries & Considerations for Implementation World Health Organization A
March 1, 2005 Proposed Networks to Support Health Decision-Making and Health Policy Formulation in Low and Lower Middle Income Countries & Considerations for Implementation World Health Organization A
Findings and Recommendations
 6 Findings and Recommendations The committee s review of current research, models for collaboration between research and practice, community-based organizations, and dissemination strategies led to findings
6 Findings and Recommendations The committee s review of current research, models for collaboration between research and practice, community-based organizations, and dissemination strategies led to findings
Better Skills Better Jobs Better Health. National occupational standards for the practice of public health guide
 Better Skills Better Jobs Better Health National occupational standards for the practice of public health guide March 2004 Acknowledgements These national occupational standards describe good practice
Better Skills Better Jobs Better Health National occupational standards for the practice of public health guide March 2004 Acknowledgements These national occupational standards describe good practice
Research is everybody s business
 Research and Development Strategy (DRAFT) 2013-2018 Research is everybody s business 1 Information Reader Box to be inserted for documents six pages and over. (To be inserted in final version, after consultation
Research and Development Strategy (DRAFT) 2013-2018 Research is everybody s business 1 Information Reader Box to be inserted for documents six pages and over. (To be inserted in final version, after consultation
Agriculture, Nutrition & Health (ANH) Academy Draft Concept Note
 Agriculture, Nutrition & Health (ANH) Academy Draft Concept Note 1. Background and rationale There is a growing need for methods and tools to evaluate the impact of agricultural practices on nutrition
Agriculture, Nutrition & Health (ANH) Academy Draft Concept Note 1. Background and rationale There is a growing need for methods and tools to evaluate the impact of agricultural practices on nutrition
Building Partnerships for Aid Effectiveness. 1. Introduction
 Building Partnerships for Aid Effectiveness 1. Introduction I would like to begin by expressing my gratitude to the Ugandan National Academy of Sciences for according me the honour of addressing this important
Building Partnerships for Aid Effectiveness 1. Introduction I would like to begin by expressing my gratitude to the Ugandan National Academy of Sciences for according me the honour of addressing this important
Integrated Healthcare Technology Package: Introduction. Peter Heimann World Health Organization, Genève
 Integrated Healthcare Technology Package: Introduction Peter Heimann World Health Organization, Genève Why ihtp MILLENNIUM DEVELOPMENT GOALS T0 BE ACHIEVED BY 2015 1. Halve extreme poverty and hunger 2.
Integrated Healthcare Technology Package: Introduction Peter Heimann World Health Organization, Genève Why ihtp MILLENNIUM DEVELOPMENT GOALS T0 BE ACHIEVED BY 2015 1. Halve extreme poverty and hunger 2.
Turku School of Economics: Strategy for 2010 2015
 Turku School of Economics: Strategy for 2010 2015 Appendix A TURKU SCHOOL OF ECONOMICS STRATEGY FOR 2010 2015 1 The strategic position of the Turku School of Economics... 1 1.1 Operating environment...
Turku School of Economics: Strategy for 2010 2015 Appendix A TURKU SCHOOL OF ECONOMICS STRATEGY FOR 2010 2015 1 The strategic position of the Turku School of Economics... 1 1.1 Operating environment...
MAKING YOUR ORGANISATION S INFORMATION ACCESSIBLE FOR ALL IMPLEMENTING THE GUIDELINES FOR ACCESSIBLE INFORMATION
 MAKING YOUR ORGANISATION S INFORMATION ACCESSIBLE FOR ALL IMPLEMENTING THE GUIDELINES FOR ACCESSIBLE INFORMATION project has been funded with support from the European Union. publication reflects the views
MAKING YOUR ORGANISATION S INFORMATION ACCESSIBLE FOR ALL IMPLEMENTING THE GUIDELINES FOR ACCESSIBLE INFORMATION project has been funded with support from the European Union. publication reflects the views
Systematic review of a health system intervention:
 Systematic review of a health system intervention: lessons learnt from a review of results-based financing approaches in Africa and Asia. Emma Jolley, Juliet Milgate and Elena Schmidt Format 1. Introduction
Systematic review of a health system intervention: lessons learnt from a review of results-based financing approaches in Africa and Asia. Emma Jolley, Juliet Milgate and Elena Schmidt Format 1. Introduction
Lessons Learned from MDG Monitoring From A Statistical Perspective
 Lessons Learned from MDG Monitoring From A Statistical Perspective Report of the Task Team on Lessons Learned from MDG Monitoring of the IAEG-MDG United Nations March 2013 The views expressed in this paper
Lessons Learned from MDG Monitoring From A Statistical Perspective Report of the Task Team on Lessons Learned from MDG Monitoring of the IAEG-MDG United Nations March 2013 The views expressed in this paper
Systematic Reviews. knowledge to support evidence-informed health and social care
 Systematic Reviews knowledge to support evidence-informed health and social care By removing uncertainties in science and research, systematic reviews ensure that only the most effective and best-value
Systematic Reviews knowledge to support evidence-informed health and social care By removing uncertainties in science and research, systematic reviews ensure that only the most effective and best-value
Requirements for Drug Information Centres
 FIP Pharmacy Information Section Requirements for Drug Information Centres Summary All countries should provide drug information services either independently or as part of a regional network. The service
FIP Pharmacy Information Section Requirements for Drug Information Centres Summary All countries should provide drug information services either independently or as part of a regional network. The service
DEVELOPING WORLD HEALTH PARTNERSHIPS DIRECTORY
 DEVELOPING WORLD HEALTH PARTNERSHIPS DIRECTORY OVER 250 HEALTH PARTNERSHIPS THAT MAKE A DIFFERENCE TO PEOPLE S LIVES The global health community needs to overcome both new and current challenges in the
DEVELOPING WORLD HEALTH PARTNERSHIPS DIRECTORY OVER 250 HEALTH PARTNERSHIPS THAT MAKE A DIFFERENCE TO PEOPLE S LIVES The global health community needs to overcome both new and current challenges in the
A proposal for measures under Norwegian foreign and international development policy to combat the global health workforce crisis
 A proposal for measures under Norwegian foreign and international development policy to combat the global health workforce crisis Report by the workgroup headed by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, with
A proposal for measures under Norwegian foreign and international development policy to combat the global health workforce crisis Report by the workgroup headed by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, with
THE INFORMATION AUDIT AS A FIRST STEP TOWARDS EFFECTIVE KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT: AN OPPORTUNITY FOR THE SPECIAL LIBRARIAN * By Susan Henczel
 INSPEL 34(2000)3/4, pp. 210-226 THE INFORMATION AUDIT AS A FIRST STEP TOWARDS EFFECTIVE KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT: AN OPPORTUNITY FOR THE SPECIAL LIBRARIAN * By Susan Henczel Introduction Knowledge is universally
INSPEL 34(2000)3/4, pp. 210-226 THE INFORMATION AUDIT AS A FIRST STEP TOWARDS EFFECTIVE KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT: AN OPPORTUNITY FOR THE SPECIAL LIBRARIAN * By Susan Henczel Introduction Knowledge is universally
First World Summit Award Mobile Content
 UNITED NATIONS EDUCATIONAL, SCIENTIFIC AND CULTURAL ORGANIZATION First World Summit Award Mobile Content Releasing mobile potential for development Keynote Address by Mr. Jānis Kārkliņš Assistant Director
UNITED NATIONS EDUCATIONAL, SCIENTIFIC AND CULTURAL ORGANIZATION First World Summit Award Mobile Content Releasing mobile potential for development Keynote Address by Mr. Jānis Kārkliņš Assistant Director
Post Graduate Diploma in Public Mental Health
 Post Graduate Diploma in Public Mental Health The Centre for Public Mental Health (CPMH) is a joint initiative of the Department of Psychology at Stellenbosch University (SU) and The Department of Psychiatry
Post Graduate Diploma in Public Mental Health The Centre for Public Mental Health (CPMH) is a joint initiative of the Department of Psychology at Stellenbosch University (SU) and The Department of Psychiatry
WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION
 WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION FIFTY-SIXTH WORLD HEALTH ASSEMBLY A56/27 Provisional agenda item 14.18 24 April 2003 International Conference on Primary Health Care, Alma-Ata: twenty-fifth anniversary Report
WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION FIFTY-SIXTH WORLD HEALTH ASSEMBLY A56/27 Provisional agenda item 14.18 24 April 2003 International Conference on Primary Health Care, Alma-Ata: twenty-fifth anniversary Report
Stakeholder Guide 2014 www.effectivehealthcare.ahrq.gov
 Stakeholder Guide 2014 www.effectivehealthcare.ahrq.gov AHRQ Publication No. 14-EHC010-EF Replaces Publication No. 11-EHC069-EF February 2014 Effective Health Care Program Stakeholder Guide Contents Introduction...1
Stakeholder Guide 2014 www.effectivehealthcare.ahrq.gov AHRQ Publication No. 14-EHC010-EF Replaces Publication No. 11-EHC069-EF February 2014 Effective Health Care Program Stakeholder Guide Contents Introduction...1
WHO Consultation on the Zero Draft Global Mental Health Action Plan 2013-2020 International Diabetes Federation (IDF) Submission
 WHO Consultation on the Zero Draft Global Mental Health Action Plan 2013-2020 International Diabetes Federation (IDF) Submission The International Diabetes Federation (IDF), an umbrella organisation of
WHO Consultation on the Zero Draft Global Mental Health Action Plan 2013-2020 International Diabetes Federation (IDF) Submission The International Diabetes Federation (IDF), an umbrella organisation of
Guide for Documenting and Sharing Best Practices. in Health Programmes
 Guide for Documenting and Sharing Best Practices in Health Programmes Guide for Documenting and Sharing Best Practices in Health Programmes WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION Regional Office for Africa Brazzaville
Guide for Documenting and Sharing Best Practices in Health Programmes Guide for Documenting and Sharing Best Practices in Health Programmes WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION Regional Office for Africa Brazzaville
Mobile health: scaling the value chain
 32 Linklaters / Generation Next: Five pathways to TMT growth in emerging markets / Mobile health Mobile health: scaling the value chain Mobile health is set to generate around $8.8bn of annual revenues
32 Linklaters / Generation Next: Five pathways to TMT growth in emerging markets / Mobile health Mobile health: scaling the value chain Mobile health is set to generate around $8.8bn of annual revenues
North South Experiences of Doctoral Training for Development in Africa: The Impact of Partnerships Thomas Quinn, M.D., M.Sc.
 North South Experiences of Doctoral Training for Development in Africa: The Impact of Partnerships Thomas Quinn, M.D., M.Sc. Director of Global Health, Johns Hopkins University Associate Director for International
North South Experiences of Doctoral Training for Development in Africa: The Impact of Partnerships Thomas Quinn, M.D., M.Sc. Director of Global Health, Johns Hopkins University Associate Director for International
Synthesis Report. Towards an effective monitoring and accountability framework for the post-2015 development agenda: perspectives from the regions.
 Synthesis Report Towards an effective monitoring and accountability framework for the post-2015 development agenda: perspectives from the regions. In response to the emphasis and strong recognition by
Synthesis Report Towards an effective monitoring and accountability framework for the post-2015 development agenda: perspectives from the regions. In response to the emphasis and strong recognition by
TORONTO CALL TO ACTION. 2006-2015 Towards a decade of Human Resources in Health for the Americas
 TORONTO CALL TO ACTION 2006-2015 Towards a decade of Human Resources in Health for the Americas Regional Meeting of the Observatory of Human Resources in Health 4-7 October, 2005 TOWARDS A DECADE OF HUMAN
TORONTO CALL TO ACTION 2006-2015 Towards a decade of Human Resources in Health for the Americas Regional Meeting of the Observatory of Human Resources in Health 4-7 October, 2005 TOWARDS A DECADE OF HUMAN
ETI PERSPECTIVE 2020: A FIVE YEAR STRATEGY
 ETI PERSPECTIVE 2020: A FIVE YEAR STRATEGY Introduction This document is the final and Board approved version of ETI s strategic directions based on the ETI Board meeting discussion of 12 th March 2015.
ETI PERSPECTIVE 2020: A FIVE YEAR STRATEGY Introduction This document is the final and Board approved version of ETI s strategic directions based on the ETI Board meeting discussion of 12 th March 2015.
Technical guidance note for Global Fund HIV proposals in Round 11
 Technical guidance note for Global Fund HIV proposals in Round 11 UNAIDS I World Health Organization I August 2011 Rationale for including the development of a system in the proposal With the global momentum
Technical guidance note for Global Fund HIV proposals in Round 11 UNAIDS I World Health Organization I August 2011 Rationale for including the development of a system in the proposal With the global momentum
Partnering with Physicians
 policy paper: Partnering with Physicians January 2014 doctors of bc Policy: Partnering with Physicians Policy Statement: The Doctors of BC supports the development of collaborative and constructive partnerships
policy paper: Partnering with Physicians January 2014 doctors of bc Policy: Partnering with Physicians Policy Statement: The Doctors of BC supports the development of collaborative and constructive partnerships
How To Run A Virtual Health Library
 Ten years ago, on March 27, 1998, the proposal for the Virtual Health Library was publicly launched in Costa Rica, with the "Declaration of San Jose towards the Virtual Health Library", formulated around
Ten years ago, on March 27, 1998, the proposal for the Virtual Health Library was publicly launched in Costa Rica, with the "Declaration of San Jose towards the Virtual Health Library", formulated around
Knowledge Management and Communication Strategy
 2011 Knowledge Management and Communication Strategy Knowledge Management and Communications Deputy Directors Office (DD) PAHO/WHO 1 3/7/2011 This will be the century of networks, connectivity and interdependency,
2011 Knowledge Management and Communication Strategy Knowledge Management and Communications Deputy Directors Office (DD) PAHO/WHO 1 3/7/2011 This will be the century of networks, connectivity and interdependency,
Monitoring, Evaluation and Learning Plan
 Monitoring, Evaluation and Learning Plan Cap-Net International Network for Capacity Building in Sustainable Water Management November 2009 The purpose of this document is to improve learning from the Cap-Net
Monitoring, Evaluation and Learning Plan Cap-Net International Network for Capacity Building in Sustainable Water Management November 2009 The purpose of this document is to improve learning from the Cap-Net
Middlesbrough Manager Competency Framework. Behaviours Business Skills Middlesbrough Manager
 Middlesbrough Manager Competency Framework + = Behaviours Business Skills Middlesbrough Manager Middlesbrough Manager Competency Framework Background Middlesbrough Council is going through significant
Middlesbrough Manager Competency Framework + = Behaviours Business Skills Middlesbrough Manager Middlesbrough Manager Competency Framework Background Middlesbrough Council is going through significant
Decision PC.2/dc.1 on the Interim Work Programme 2009/2010
 PREPARATORY COMMISSION FOR THE INTERNATIONAL RENEWABLE ENERGY AGENCY Annex 8: Decision on the Interim Work Programme 2009/2010 Report Annex 7 Second session Monday, 29 June 2009 Sharm El Sheikh International
PREPARATORY COMMISSION FOR THE INTERNATIONAL RENEWABLE ENERGY AGENCY Annex 8: Decision on the Interim Work Programme 2009/2010 Report Annex 7 Second session Monday, 29 June 2009 Sharm El Sheikh International
SKILLS AND ENTREPRENEURSHIP
 PARTNERS FOR CHANGE SKILLS AND ENTREPRENEURSHIP SUB-SAHARAN AFRICA PARTNERS FOR CHANGE SKILLS AND ENTREPRENEURSHIP PARTNERS FOR CHANGE The British Council works with governments, businesses, training and
PARTNERS FOR CHANGE SKILLS AND ENTREPRENEURSHIP SUB-SAHARAN AFRICA PARTNERS FOR CHANGE SKILLS AND ENTREPRENEURSHIP PARTNERS FOR CHANGE The British Council works with governments, businesses, training and
NATIONAL NURSING RESEARCH STRATEGY OF SOUTH AFRICA
 NATIONAL NURSING RESEARCH STRATEGY OF SOUTH AFRICA developed collaboratively by a group of stakeholders committed to improving the health of the people of South Africa enhancing collaborative rigorous
NATIONAL NURSING RESEARCH STRATEGY OF SOUTH AFRICA developed collaboratively by a group of stakeholders committed to improving the health of the people of South Africa enhancing collaborative rigorous
Helping TANZANIA Fight Injection Drug Use and HIV
 Helping TANZANIA Fight Injection Drug Use and HIV Pharmacist dispensing methadone at Mwananyamala Regional Hospital Pangaea Global AIDS Foundation 436 Fourteenth Street, Suite 920, Oakland, CA 94612 Phone
Helping TANZANIA Fight Injection Drug Use and HIV Pharmacist dispensing methadone at Mwananyamala Regional Hospital Pangaea Global AIDS Foundation 436 Fourteenth Street, Suite 920, Oakland, CA 94612 Phone
Aids Fonds funding for programmes to prevent HIV drug resistance
 funding for programmes to prevent HIV drug resistance Call for proposals July 2012 Page 1 van 10 grants@aidsfonds.nl Documentnumber 20120719/JKA/RAP Universal Access Lifting barriers to universal access
funding for programmes to prevent HIV drug resistance Call for proposals July 2012 Page 1 van 10 grants@aidsfonds.nl Documentnumber 20120719/JKA/RAP Universal Access Lifting barriers to universal access
IGF Policy Options for Connecting the Next Billion
 Introduction IGF Policy Options for Connecting the Next Billion - A Synthesis - More than three billion people will be connected to the Internet by the end of 2015. This is by all standards a great achievement,
Introduction IGF Policy Options for Connecting the Next Billion - A Synthesis - More than three billion people will be connected to the Internet by the end of 2015. This is by all standards a great achievement,
STATEMENT ON MANAGED PUBLIC HEALTH NETWORKS
 Faculty of Public Health Medicine PUBLIC HEALTH AND Health Development Agency PRIMARY CARE GROUP STATEMENT ON MANAGED PUBLIC HEALTH NETWORKS Public health programmes within a public health service supported
Faculty of Public Health Medicine PUBLIC HEALTH AND Health Development Agency PRIMARY CARE GROUP STATEMENT ON MANAGED PUBLIC HEALTH NETWORKS Public health programmes within a public health service supported
Transforming the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health January 2008
 Transforming the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health January 2008 A Compelling Case for Transformation Throughout most of the modern era of medicine there has been a lack of integration
Transforming the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health January 2008 A Compelling Case for Transformation Throughout most of the modern era of medicine there has been a lack of integration
Message from the Chief Executive of the RCM
 Message from the Chief Executive of the RCM The Midwifery Leadership Competency Framework has been derived from both the NHS Leadership Qualities Framework and the Clinical Leadership Competency Framework.
Message from the Chief Executive of the RCM The Midwifery Leadership Competency Framework has been derived from both the NHS Leadership Qualities Framework and the Clinical Leadership Competency Framework.
European University Association Contribution to the Public Consultation: Science 2.0 : Science in Transition 1. September 2014
 European University Association Contribution to the Public Consultation: Science 2.0 : Science in Transition 1 September 2014 With 850 members across 47 countries, the European University Association (EUA)
European University Association Contribution to the Public Consultation: Science 2.0 : Science in Transition 1 September 2014 With 850 members across 47 countries, the European University Association (EUA)
IFMSA Policy Statement Human Resources for Health
 IFMSA Policy Statement Human Resources for Health Location: Taipei, Taiwan. Date of Adoption: August 9 th 2014. Date of Expiry: August 9 th 2017. Summary We, the International Federation of Medical Students
IFMSA Policy Statement Human Resources for Health Location: Taipei, Taiwan. Date of Adoption: August 9 th 2014. Date of Expiry: August 9 th 2017. Summary We, the International Federation of Medical Students
How To Improve Safety In The Nhs
 PS035 Original research completed in 2010 Briefing Paper Introduction: Principal Investigator: Professor John Clarkson Should the NHS adopt a new system for predicting possible risks to patient safety?
PS035 Original research completed in 2010 Briefing Paper Introduction: Principal Investigator: Professor John Clarkson Should the NHS adopt a new system for predicting possible risks to patient safety?
Public Health Research - A Case Study in Innovation
 Global trends in health research and innovation policy Jonathan Grant Oslo, January 2014 RAND Europe is an independent not-forprofit public policy research institute Not a university or management consultancy
Global trends in health research and innovation policy Jonathan Grant Oslo, January 2014 RAND Europe is an independent not-forprofit public policy research institute Not a university or management consultancy
The NHS Knowledge and Skills Framework (NHS KSF) and the Development Review Process
 The NHS Knowledge and Skills Framework (NHS KSF) and the Development Review Process [This is the final draft of the NHS KSF Handbook that will be used for national roll-out if implementation of Agenda
The NHS Knowledge and Skills Framework (NHS KSF) and the Development Review Process [This is the final draft of the NHS KSF Handbook that will be used for national roll-out if implementation of Agenda
NATIONAL NURSING RESEARCH STRATEGY FOR SOUTH AFRICA
 Trends in Nursing Vol. 1, Issue 1, 2012 http://fundisa.journals.ac.za http://dx.doi.org/10.14804/1-1-30 NATIONAL NURSING RESEARCH STRATEGY FOR SOUTH AFRICA Professor Dalena van Rooyen: Nelson Mandela Metropolitan
Trends in Nursing Vol. 1, Issue 1, 2012 http://fundisa.journals.ac.za http://dx.doi.org/10.14804/1-1-30 NATIONAL NURSING RESEARCH STRATEGY FOR SOUTH AFRICA Professor Dalena van Rooyen: Nelson Mandela Metropolitan
Vacancy Notice No: PAHO/15/FT414. Date: 4 August 2015
 Vacancy Notice No: PAHO/15/FT414 Date: 4 August 2015 Title: Center Director, Latin American and Caribbean Center on Health Sciences Information (BIREME) Grade: P5 Contract type: Fixed-term Appointment
Vacancy Notice No: PAHO/15/FT414 Date: 4 August 2015 Title: Center Director, Latin American and Caribbean Center on Health Sciences Information (BIREME) Grade: P5 Contract type: Fixed-term Appointment
EUROPLAT European Network for Psychology Learning & Teaching
 EUROPLAT European Network for Psychology Learning & Teaching Progress Report Public Part 155981-LLP-1-2009-UK-ERASMUS-ENWA Project information Project acronym: Project title: Project number: Sub-programme
EUROPLAT European Network for Psychology Learning & Teaching Progress Report Public Part 155981-LLP-1-2009-UK-ERASMUS-ENWA Project information Project acronym: Project title: Project number: Sub-programme
APPENDIX H Revolutionizing Fisheries Management Training: Putting Workshop Ideas Into Action
 APPENDIX H Revolutionizing Fisheries Management Training: Putting Workshop Ideas Into Action Prepared by Michael Harte, Falkland Islands Government, Falkland Islands Participants in the Training Managers
APPENDIX H Revolutionizing Fisheries Management Training: Putting Workshop Ideas Into Action Prepared by Michael Harte, Falkland Islands Government, Falkland Islands Participants in the Training Managers
HEALTH SYSTEM. Introduction. The. jurisdictions and we. Health Protection. Health Improvement. Health Services. Academic Public
 FUNCTIONS OF THE LOCAL PUBLIC HEALTH SYSTEM Introduction This document sets out the local PH function in England. It was originally drafted by a working group led by Maggie Rae, FPH Local Board Member
FUNCTIONS OF THE LOCAL PUBLIC HEALTH SYSTEM Introduction This document sets out the local PH function in England. It was originally drafted by a working group led by Maggie Rae, FPH Local Board Member
Case Study: Institution-Based Information Systems, Egypt National Agricultural Research Information Management System (NARIMS)
 Case Study: Institution-Based Information Systems, Egypt National Agricultural Research Information Management System (NARIMS) EXECUTIVE SUMMARY The National Agriculture Research Information Management
Case Study: Institution-Based Information Systems, Egypt National Agricultural Research Information Management System (NARIMS) EXECUTIVE SUMMARY The National Agriculture Research Information Management
14 Education of Personnel: the Key to Successful Community Based Rehabilitation
 Education of Personnel 1 14 Education of Personnel: the Key to Successful Community Based Rehabilitation Community-Based Rehabilitation (CBR) is a relatively new strategy which is increasingly being adopted
Education of Personnel 1 14 Education of Personnel: the Key to Successful Community Based Rehabilitation Community-Based Rehabilitation (CBR) is a relatively new strategy which is increasingly being adopted
Submission to the Ministry of Health. On the Mental Health and Addiction Service Development Plan. Prepared by the New Zealand Psychological Society
 Submission to the Ministry of Health On the Mental Health and Addiction Service Development Plan Prepared by the New Zealand Psychological Society August 30, 2011 30 August 2011 The Project Team Mental
Submission to the Ministry of Health On the Mental Health and Addiction Service Development Plan Prepared by the New Zealand Psychological Society August 30, 2011 30 August 2011 The Project Team Mental
Attribute 1: COMMUNICATION
 The positive are intended for use as a guide only and are not exhaustive. Not ALL will be applicable to ALL roles within a grade and in some cases may be appropriate to a Attribute 1: COMMUNICATION Level
The positive are intended for use as a guide only and are not exhaustive. Not ALL will be applicable to ALL roles within a grade and in some cases may be appropriate to a Attribute 1: COMMUNICATION Level
August 2012. Action for Global Health call for International Development Select Committee Inquiry into health systems strengthening
 August 2012 Action for Global Health call for International Development Select Committee Inquiry into health systems strengthening Introduction In recent years DFID has prioritised health and nutrition
August 2012 Action for Global Health call for International Development Select Committee Inquiry into health systems strengthening Introduction In recent years DFID has prioritised health and nutrition
3. What is Incubation?
 In reality both approaches have their place and need to be balanced in identifying the impacts achieved by public policy initiatives and learning how to improve them. This theme will surface again in the
In reality both approaches have their place and need to be balanced in identifying the impacts achieved by public policy initiatives and learning how to improve them. This theme will surface again in the
Edital Faperj n.º 38/2014 RCUK CONFAP RESEARCH PARTNERSHIPS CALL FOR PROJECTS
 Edital Faperj n.º 38/2014 RCUK CONFAP RESEARCH PARTNERSHIPS CALL FOR PROJECTS Research Councils UK (RCUK) (http://www.rcuk.ac.uk/) and the Brazilian Council of State Funding Agencies (CONFAP) (www.confap.org.br;
Edital Faperj n.º 38/2014 RCUK CONFAP RESEARCH PARTNERSHIPS CALL FOR PROJECTS Research Councils UK (RCUK) (http://www.rcuk.ac.uk/) and the Brazilian Council of State Funding Agencies (CONFAP) (www.confap.org.br;
Bachelor of Health Sciences Course outline. Health. Education
 Bachelor of Health Sciences Course outline Health. Education BHSc 3 Published September 2 by the College of Education, University of Canterbury, Private Bag 4800, Christchurch 8140, New Zealand. Information
Bachelor of Health Sciences Course outline Health. Education BHSc 3 Published September 2 by the College of Education, University of Canterbury, Private Bag 4800, Christchurch 8140, New Zealand. Information
PROMOTING ACCESS AND MEDICAL INNOVATION: INTERSECTIONS BETWEEN PUBLIC HEALTH, INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AND TRADE
 PROMOTING ACCESS AND MEDICAL INNOVATION: INTERSECTIONS BETWEEN PUBLIC HEALTH, INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AND TRADE Joint study by the WHO, WIPO and WTO Secretariats Outline and overview The WHO, WIPO and the
PROMOTING ACCESS AND MEDICAL INNOVATION: INTERSECTIONS BETWEEN PUBLIC HEALTH, INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AND TRADE Joint study by the WHO, WIPO and WTO Secretariats Outline and overview The WHO, WIPO and the
UNAIDS ISSUES BRIEF 2011 A NEW INVESTMENT FRAMEWORK FOR THE GLOBAL HIV RESPONSE
 UNAIDS ISSUES BRIEF 2011 A NEW INVESTMENT FRAMEWORK FOR THE GLOBAL HIV RESPONSE Copyright 2011 Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) All rights reserved The designations employed and the
UNAIDS ISSUES BRIEF 2011 A NEW INVESTMENT FRAMEWORK FOR THE GLOBAL HIV RESPONSE Copyright 2011 Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) All rights reserved The designations employed and the
ehealth: Information and Communication Technology in Health August 29-31, 2016
 ehealth: Information and Communication Technology in Health August 29-31, 2016 1. Profile of facilitators Name and title: 1. Martin Raab 2. Prof. Antoine Geissbuhler 3. Gonçalo Castro Current position
ehealth: Information and Communication Technology in Health August 29-31, 2016 1. Profile of facilitators Name and title: 1. Martin Raab 2. Prof. Antoine Geissbuhler 3. Gonçalo Castro Current position
Current access to health information in Zambia: a survey of selected health institutions
 DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-1842.2007.00728.x Current access to health information in Zambia: a survey Blackwell Oxford, HIR Health 1471-1834 Journal XXX 2007 Information The compilation UK Publishing Authors&
DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-1842.2007.00728.x Current access to health information in Zambia: a survey Blackwell Oxford, HIR Health 1471-1834 Journal XXX 2007 Information The compilation UK Publishing Authors&
Specialist Competencies in Nutrition Science: Public Health Nutrition
 Specialist Competencies in Nutrition Science: Public Health Nutrition A summary of the specific competencies for registration as a Public Health Nutritionist as deemed essential by the NSA and originally
Specialist Competencies in Nutrition Science: Public Health Nutrition A summary of the specific competencies for registration as a Public Health Nutritionist as deemed essential by the NSA and originally
Current reporting in published research
 Current reporting in published research Doug Altman Centre for Statistics in Medicine, Oxford, UK and EQUATOR Network Research article A published research article is a permanent record that will be used
Current reporting in published research Doug Altman Centre for Statistics in Medicine, Oxford, UK and EQUATOR Network Research article A published research article is a permanent record that will be used
2 nd EUA Funding Forum: Strategies for efficient funding of universities
 2 nd EUA Funding Forum: Strategies for efficient funding of universities Bergamo, 9-10 October 2014 Forum report Liviu Matei, General rapporteur Table of contents I. Executive Summary 3 II. What is the
2 nd EUA Funding Forum: Strategies for efficient funding of universities Bergamo, 9-10 October 2014 Forum report Liviu Matei, General rapporteur Table of contents I. Executive Summary 3 II. What is the
Introducing standards to improve healthcare delivery in resource-restricted countries
 Introducing standards to improve healthcare delivery in resource-restricted countries The Need for Standards Many resource-restricted countries struggle to meet their citizens healthcare needs and provide
Introducing standards to improve healthcare delivery in resource-restricted countries The Need for Standards Many resource-restricted countries struggle to meet their citizens healthcare needs and provide
Knowledge Management policy for Health - Service, Education and Research
 Knowledge Management policy for Health - Service, Education and Research (Final Draft Document) 1 Knowledge Management policy for Health - Service, Education and Research Department of Health Research
Knowledge Management policy for Health - Service, Education and Research (Final Draft Document) 1 Knowledge Management policy for Health - Service, Education and Research Department of Health Research
The Ethiopian national ehealth strategy and its alignment with the health informatics curriculum
 9 th Health Informatics in Africa Conference (HELINA 2014) Peer-reviewed and selected under the responsibility of the Scientific Programme Committee The Ethiopian national ehealth strategy and its alignment
9 th Health Informatics in Africa Conference (HELINA 2014) Peer-reviewed and selected under the responsibility of the Scientific Programme Committee The Ethiopian national ehealth strategy and its alignment
Submission to the Medicare Benefits Schedule Review Taskforce Consultation. 9 November 2015. 1 P age
 Submission to the Medicare Benefits Schedule Review Taskforce Consultation 9 November 2015 1 P age Introduction The George Institute for Global Health is working to improve the health of millions of people
Submission to the Medicare Benefits Schedule Review Taskforce Consultation 9 November 2015 1 P age Introduction The George Institute for Global Health is working to improve the health of millions of people
A developmental framework for pharmacists progressing to advanced levels of practice
 ACLF Advanced to Consultant level Framework A developmental framework for pharmacists progressing to advanced levels of practice Version 2009(a) CoDEG www.codeg.org ADVANCED AND CONSULTANT LEVEL COMPETENCY
ACLF Advanced to Consultant level Framework A developmental framework for pharmacists progressing to advanced levels of practice Version 2009(a) CoDEG www.codeg.org ADVANCED AND CONSULTANT LEVEL COMPETENCY
VALUE CHAIN DEVELOPMENT Training activities & Tools
 VALUE CHAIN DEVELOPMENT Training activities & Tools VALUE CHAIN DEVELOPMENT Overview The question is thus not if, but how to integrate in value chains in a way that allows for incorporation of a growing
VALUE CHAIN DEVELOPMENT Training activities & Tools VALUE CHAIN DEVELOPMENT Overview The question is thus not if, but how to integrate in value chains in a way that allows for incorporation of a growing
Effective Debt Management. Improving Debt Management Practices Worldwide
 Effective Debt Management Improving Debt Management Practices Worldwide Effective debt management is essential for economic development. As countries develop they confront increasing challenges in managing
Effective Debt Management Improving Debt Management Practices Worldwide Effective debt management is essential for economic development. As countries develop they confront increasing challenges in managing
Progress report: Artisanal and Small-scale Mining over the last 10 years. Presented by Assheton Stewart Carter SVP Global Engagement Pact
 Progress report: Artisanal and Small-scale Mining over the last 10 years Presented by Assheton Stewart Carter SVP Global Engagement Pact Objectives To give a sense of where progress has been made in the
Progress report: Artisanal and Small-scale Mining over the last 10 years Presented by Assheton Stewart Carter SVP Global Engagement Pact Objectives To give a sense of where progress has been made in the
UKCPA - A Review of the Current Pharmaceutical Facility
 Modernising Pharmacy Careers Review of Post-Registration Career Development Discussion Paper PRO FORMA FOR CAPTURING RESPONSES TO STAKEHOLDER QUESTIONS Please complete and return to: MPCProgramme@dh.gsi.gov.uk
Modernising Pharmacy Careers Review of Post-Registration Career Development Discussion Paper PRO FORMA FOR CAPTURING RESPONSES TO STAKEHOLDER QUESTIONS Please complete and return to: MPCProgramme@dh.gsi.gov.uk
HUMANITARIAN INNOVATION FUND Final Report
 HUMANITARIAN INNOVATION FUND Final Report Organisation Name Save the Children UK Project Title Problem Addressed / Thematic Focus Location Transforming decision making on emergency feeding programmes using
HUMANITARIAN INNOVATION FUND Final Report Organisation Name Save the Children UK Project Title Problem Addressed / Thematic Focus Location Transforming decision making on emergency feeding programmes using
1. Title: Support for International Development Research
 Ministry of Foreign Affairs TAS File no.: 104.C.110.b. Internal Grant Committee Meeting 2 April 2014 Agenda Item no.: 2 1. Title: Support for International Development Research 2. Partners: African Economic
Ministry of Foreign Affairs TAS File no.: 104.C.110.b. Internal Grant Committee Meeting 2 April 2014 Agenda Item no.: 2 1. Title: Support for International Development Research 2. Partners: African Economic
Having undertaken a general discussion on the basis of Report IV, Small and medium-sized enterprises and decent and productive employment creation,
 International Labour Conference Provisional Record 104th Session, Geneva, June 2015 11-1 Fourth item on the agenda: Small and medium-sized enterprises and decent and productive employment creation Reports
International Labour Conference Provisional Record 104th Session, Geneva, June 2015 11-1 Fourth item on the agenda: Small and medium-sized enterprises and decent and productive employment creation Reports
Industry Charter. Introduction. Context
 Industry Charter Introduction This short document is aimed at all industry that has an interest in working with the NHS. It sets out how Imperial College Health Partners, the Academic Health Science Network
Industry Charter Introduction This short document is aimed at all industry that has an interest in working with the NHS. It sets out how Imperial College Health Partners, the Academic Health Science Network
Strategic Plan 2013-2017
 Strategic Plan 2013-2017 2 P age Presidents Welcome It is my great pleasure to present the European Federation of Periodontology s strategy for 2013-2017. This is the European Federation of Periodontology
Strategic Plan 2013-2017 2 P age Presidents Welcome It is my great pleasure to present the European Federation of Periodontology s strategy for 2013-2017. This is the European Federation of Periodontology
Organisational Change Management
 Organisational Change Management The only thing that is constant is change in your business, your market, your competitors, and your technology. Remaining competitive and responsive to your customers and
Organisational Change Management The only thing that is constant is change in your business, your market, your competitors, and your technology. Remaining competitive and responsive to your customers and
Key Messages. Health Economics & Management
 Key Messages Health Economics & Management General World Health Summit 2011: Today s Science Tomorrow s Agenda The World Health Summit is the annual conference held by the M8 Alliance of the Academic Health
Key Messages Health Economics & Management General World Health Summit 2011: Today s Science Tomorrow s Agenda The World Health Summit is the annual conference held by the M8 Alliance of the Academic Health
Executive summary. Today s researchers require skills beyond their core competencies
 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY 9 Executive summary Today s researchers require skills beyond their core competencies The formation and careers of researchers are important policy issues and training for transferable
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY 9 Executive summary Today s researchers require skills beyond their core competencies The formation and careers of researchers are important policy issues and training for transferable
PRIMARY HEALTH CARE POLICY
 PRIMARY HEALTH CARE POLICY The Public Health Association of Australia recognises that: 1. Universal access to primary health care based on need and not on the ability to pay, is a fundamental human right.
PRIMARY HEALTH CARE POLICY The Public Health Association of Australia recognises that: 1. Universal access to primary health care based on need and not on the ability to pay, is a fundamental human right.
Continuing Medical Education in Eritrea : Need for a System
 Original Articles Continuing Medical Education in Eritrea : Need for a System Abdullahi M. Ahmed 1, Besrat Hagos 2 1. International Centre for Health Management, Istituto Superiore di Sanita, ` Rome, Italy
Original Articles Continuing Medical Education in Eritrea : Need for a System Abdullahi M. Ahmed 1, Besrat Hagos 2 1. International Centre for Health Management, Istituto Superiore di Sanita, ` Rome, Italy
Clinical Academic Careers for Nursing, Midwifery and the Allied Health Professions Council of Deans of Health Position Statement
 Clinical Academic Careers for Nursing, Midwifery and the Allied Health Professions Council of Deans of Health Position Statement Summary Clinical academics in Nursing, Midwifery and Allied Health Professions
Clinical Academic Careers for Nursing, Midwifery and the Allied Health Professions Council of Deans of Health Position Statement Summary Clinical academics in Nursing, Midwifery and Allied Health Professions
HUMAN RESOURCES FOR HEALTH A KEY PRIORITY FOR THE MINISTRY OF HEALTH
 HUMAN RESOURCES FOR HEALTH A KEY PRIORITY FOR THE MINISTRY OF HEALTH BACKGROUND In line with a global awakening of the imminent crisis in human resources for health, the WHO country office has reflected
HUMAN RESOURCES FOR HEALTH A KEY PRIORITY FOR THE MINISTRY OF HEALTH BACKGROUND In line with a global awakening of the imminent crisis in human resources for health, the WHO country office has reflected
Research Strategy. 31 st January 2011 NOTE
 Research Strategy 31 st January 2011 OTE This strategy is intended to be a dynamic, living document, and will be revised during the course of the Research Output s activities and learning. The next revision
Research Strategy 31 st January 2011 OTE This strategy is intended to be a dynamic, living document, and will be revised during the course of the Research Output s activities and learning. The next revision
Swiss Centre for International Health Improving Health Systems Worldwide
 Swiss Centre for International Health Improving Health Systems Worldwide Swiss Tropical and Public Health Institute Socinstrasse 57, P.O. Box, 4002 Basel, Switzerland, Telephone +41 61 284 81 11, www.swisstph.ch
Swiss Centre for International Health Improving Health Systems Worldwide Swiss Tropical and Public Health Institute Socinstrasse 57, P.O. Box, 4002 Basel, Switzerland, Telephone +41 61 284 81 11, www.swisstph.ch
GLOBAL ACCESS LICENSING FRAMEWORK
 GLOBAL ACCESS LICENSING FRAMEWORK Every university-developed technology with potential for further development into a drug, vaccine, or medical diagnostic should be licensed with a concrete and transparent
GLOBAL ACCESS LICENSING FRAMEWORK Every university-developed technology with potential for further development into a drug, vaccine, or medical diagnostic should be licensed with a concrete and transparent
A First Look at Attitudes Surrounding Telehealth:
 A First Look at Attitudes Surrounding Telehealth: Findings from a national survey taking a first look at attitudes, usage, and beliefs of family physicians in the U.S. towards telehealth. OVERVIEW Telehealth
A First Look at Attitudes Surrounding Telehealth: Findings from a national survey taking a first look at attitudes, usage, and beliefs of family physicians in the U.S. towards telehealth. OVERVIEW Telehealth
Brief Report of PLoS/HIFA2015 Webinar, 28th March 2012
 Brief Report of PLoS/HIFA2015 Webinar, 28th March 2012 INTRODUCTION We are delighted to report that we had a very successful Webinar on 28th March, supported by PLoS, the leading open access publisher
Brief Report of PLoS/HIFA2015 Webinar, 28th March 2012 INTRODUCTION We are delighted to report that we had a very successful Webinar on 28th March, supported by PLoS, the leading open access publisher
IFE Strategic Plan 2014 2018
 IFE Strategic Plan 2014 2018 The Institution of Fire Engineers IFE Strategic Plan 2014 2018 View online at www.ife.org.uk/ife-strategic-plan 1 The Institution of Fire Engineers A charity managed for fire
IFE Strategic Plan 2014 2018 The Institution of Fire Engineers IFE Strategic Plan 2014 2018 View online at www.ife.org.uk/ife-strategic-plan 1 The Institution of Fire Engineers A charity managed for fire
The professional development of physicians is a lifelong. Continuing Medical Education: A New Vision of the Professional Development of Physicians
 A R T I C L E Continuing Medical Education: A New Vision of the Professional Development of Physicians Nancy L. Bennett, PhD, Dave A. Davis, MD, William E. Easterling, Jr., MD, Paul Friedmann, MD, Joseph
A R T I C L E Continuing Medical Education: A New Vision of the Professional Development of Physicians Nancy L. Bennett, PhD, Dave A. Davis, MD, William E. Easterling, Jr., MD, Paul Friedmann, MD, Joseph
