Cardiac Syncope. spot it, stop it! Syncope is Tranient Loss of Consciousness (T- LOC) due to: transient global cerebral hypoperfusion
|
|
|
- Terence Williams
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Definition Cardiac Syncope spot it, stop it! David Gareth Jones Heart Rhythm Centre Royal Brompton & Harefield NHS Foundation Trust Syncope is Tranient Loss of Consciousness (T- LOC) due to: transient global cerebral hypoperfusion characterized by: Rapid onset Short duration Spontaneous complete recovery Transient Loss of Consciousness Classification of Transient Loss of Consciousness (TLOC) Real or Apparent TLOC Syncope Neurally-mediated reflex syndromes Orthostatic hypotension Cardiac arrhythmias Structural cardiovascular disease Disorders Mimicking Syncope With loss of consciousness, i.e., seizure disorders, concussion Without loss of consciousness, i.e., psychogenic pseudosyncope Syncope A Symptom, Not a Diagnosis Syncope in context Self-limited loss of consciousness and postural tone Relatively rapid onset Variable warning symptoms Spontaneous, complete, and usually prompt recovery without medical or surgical intervention Underlying mechanism is transient global cerebral hypoperfusion.
2 SchematicDrawing Neurally-Mediated Reflex Syncope Pathophysiology Vasovagal Syncope (VVS) Carotid Sinus Syndrome (CSS) Situational syncope Post-micturition Cough Swallow Defecation Blood drawing, etc. Autonomic Nervous System Brignole M, et al. Europace, 2004;6: Benditt D, et al. Neurally mediated syncope: Pathophysiology, investigations and treatment. Blanc JJ, et al. eds. Futura
3 VVS Clinical Pathophysiology Syncope Due to Structural Cardiovascular Disease: Principle Mechanisms Neurally-mediated physiologic reflex mechanism with two components: 1. Cardioinhibitory ( HR) 2. Vasodepressor ( BP) despite heart beats, no significant BP generated Both components are usually present 2 1 Acute MI/Ischemia 2 neural reflex bradycardia+ vasodilatation, arrhythmias, low output (rare) Previous MI/scar VF/VT! Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy Limited output during exertion (increased obstruction, greater demand), arrhythmias, neural reflex Pulmonary embolus/ pulmonary hypertension Neural reflex, inadequate flow with exertion Valvular abnormalities Aortic stenosis limited output, neural reflex dilation in periphery Mitral stenosis, atrial myxoma Obstruction to adequate flow Acute aortic dissection Neural reflex mechanism, pericardial tamponade Wieling W, et al. In: Benditt D, et al. The Evaluation and Treatment of Syncope. Futura. 2003; Syncope Due to Cardiac Arrhythmias Cardiac syncope can be a harbinger of sudden death Bradyarrhythmias Sinus arrest, exit block High grade or acute complete AV block Can be accompanied by vasodilatation (VVS, CSH) Tachyarrhythmias Atrial fibrillation/flutter with rapid ventricular rate (eg, pre-excitation syndrome) Paroxysmal SVT or VT Torsade de pointes Survival with and without syncope 6-month mortality rate of greater than 10% Cardiac syncope doubled the risk of death Includes cardiac arrhythmias and SHD Probability of Survival No Syncope Vasovagal and Other Causes Cardiac Cause Follow-Up (yr) Soteriades ES, et al. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:878. Initial Evaluation key questions Is it syncope? 1.Is it a syncopal episode or not? Was LOC complete? 2.Has the aetiological diagnosis been determined? 3.Are there data suggestive of a high risk of cardiovascular events or death? Was LOC transient with rapid onset and short duration? Did the patient recover spontaneously, completely and without sequelae? Did the patient lose postural tone?
4 Aetiology - questions Aetiology - questions Circumstances Position, activites, precipitators Onset Nausea, vomiting, sweating, aura, pain, blurred vision Eyewitness account(s) Nature of fall, colour, duration LOC (often overestimated!) Movements (tonic, clonic, tonic-clonic, myoclonus, automatism) Onset of movements (at start, or delayed), duration Symptoms at end of attack Nausea, vomiting, feeling cold, muscle ache, injury, chest pain, palpitations, confusion, incontinence Background Family history (SCD!), past cardiac Hx, medications Neurological history inc. Parkinsonism, epilepsy Metabolic disorders (DM), alcohol Syncope history Frequency of episodes, individual histories for each when possible Risk stratification Risk stratification in hospital evaluation Abnormal ECG* Cardiac disease (history or exam) Family history of sudden cardiac death Severe injury/accident * SA/AV disease, BBB, acute MI/NSTEMI, Q waves, WPW, LVH/HCM, long QT, short QT, Brugada etc. etc! Heart Monitoring Options Implantable Loop Recorder (ILR) e.g. Reveal OPTION 12-Lead 10 Seconds Holter Monitor 2 Days Event Recorders (non-lead and loop) 7-30 Days ILR TIME (Months) CASE: 83 year-old woman with syncope due to bradycardia: Pacemaker implanted. CASE: 28 year-old man presents to A&E multiple times after falls resulting in trauma. VT: Ablated Brignole M, et al. Europace, 2004;6:
5 Cardiac Rhythms During Unexplained Syncope Composite: N=133 to 7109 Arrhythmia 22% (13-32%) Bradycardia 16% (11-21%) Tachycardia 6% (2-11%) Other 11% No Recurrence 36% (31-48%) Normal Sinus Rhythm 31% (17-44%) Seidl K. Europace. 2000;2(3): Krahn AD. PACE. 2002;25: Medtronic ILR Replacement Data. FY03, 04. On file. Treatment of Syncope Due to Bradyarrhythmia Treatment of Syncope Due to Tachyarrhythmia Class I indication for pacing using dual chamber system wherever possible 08:23:21 0.4nV Atrial tachyarrhythmias AVRT due to accessory pathway ablation of pathway Preexcited AF down accessory pathway ablation!! Ventricular pacing in atrial fibrillation with slow ventricular response :21 8:23:29 :22 :23 :24 :25 :26 :27 :28 : AVNRT ablation of AV nodal slow pathway Atrial fib consider pacing; ablation for paroxysmal AF (also?sss) Atrial flutter ablation if typical (right atrial) flutter Ventricular tachyarrhythmias :29 08:23:37 :30 :31 :32 :33 :34 :35 :36 : Ventricular tachycardia ICD (most, esp. if low EF), ablation in some Torsade de pointes withdraw offending drug or implant ICD (long QT/Brugada/short QT) :37 :38 :39 :40 :41 :42 :43 :44 : Drug therapy may be an alternative in some cases Treatment of neurally mediated syncope Brugada syndrome Lifestyle Avoidance of triggers when possible Maintain hydration and salt intake Physical counter-pressure manoeuvres hand grip, arm tensing, leg crossing Tilt training Difficult need to be motivated! Pharmacological measures Avoid/minimise hypotensive agents when possible Alpha agonists may be helpful (OH vs. VVS) midodrine Beta-blockers not helpful Pacing? controversial - syncope recurrence still >20% (40% unpaced) even if well-selected (cardioinhibitory) Best guided by ILR (evidence of asystole or symptomatic bradycardia)
6 Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy WPW WPW Preexcited AF Long QT Syndromes Mechanism Abnormalities of sodium and/or potassium channels Susceptibility to polymorphic VT (Torsade de pointes) Prevalence Drug-induced forms Common Genetic forms Relatively rare, but increasingly being recognized Concealed forms: Syncope: Torsade de Pointes From the files of DG Benditt, MD. U of M Cardiac Arrhythmia Center May be common Provide basis for drug-induced torsade Long QT Syndromes: 12-Lead ECG
7 Drug-Induced QT Prolongation (some) Treatment of Long QT Antiarrhythmics Class IA...Quinidine, Procainamide, Disopyramide Class III Sotalol, Amiodarone, Dronedarone Psychoactive Agents Phenothiazines, Amitriptyline, Imipramine, Ziprasidone Antibiotics Erythromycin, Pentamidine, Fluconazole, Ciprofloxacin and other quinolones Nonsedating antihistamines Terfenadine, Astemizole Others Cisapride, Droperidol, Haloperidol Suspicion and recognition are critical Emergency treatment (for recurrent/incessant Torsades de Pointes) Avoid amiodarone Intravenous magnesium Pacing to overcome bradycardia or pauses Isoproterenol to increase heart rate and shorten repolarization If drug induced: Reverse bradycardia Withdraw drug Avoid ALL long-qt provoking agents If genetic: Avoid ALL long-qt provoking agents For more information visit Conclusion Syncope is a common symptom with many causes Thorough history, examination and investigation can facilitate appropriate treatment Cardiac syncope is frequently associated with an adverse prognosis and typically warrants urgent and/or in-patient investigation Seek cardiology opinion if cardiac syncope strongly suspected ESC guidelines (current 2009) offer guidance on best practice Appendix ESC treatment guidelines syncope 2009
8
9
Syncope. Approach Diagnosis and Treatment. Robert Satran MD
 Syncope Approach Diagnosis and Treatment Robert Satran MD Transient Loss of Consciousness (TLOC) Transient Loss of Consciousness (TLOC ) Classification Underlying Mechanism Is Transient Global Cerebral
Syncope Approach Diagnosis and Treatment Robert Satran MD Transient Loss of Consciousness (TLOC) Transient Loss of Consciousness (TLOC ) Classification Underlying Mechanism Is Transient Global Cerebral
Assessment, diagnosis and specialist referral of adults (>16 years) with an episode of transient loss of consciousness (TLoC) or a blackout.
 Assessment, diagnosis and specialist referral of adults (>16 years) with an episode of transient loss of consciousness (TLoC) or a blackout. TLoC is common huge variation in management range of clinicians
Assessment, diagnosis and specialist referral of adults (>16 years) with an episode of transient loss of consciousness (TLoC) or a blackout. TLoC is common huge variation in management range of clinicians
Approach to the Patient with Syncope
 Syncope Case Study 38-year-old female with recurrent syncope occasionally occurring during emotional stressful times. Her physical examination and 12 lead EKG are normal. Approach to the Patient with Syncope
Syncope Case Study 38-year-old female with recurrent syncope occasionally occurring during emotional stressful times. Her physical examination and 12 lead EKG are normal. Approach to the Patient with Syncope
Professor Rose Anne Kenny, St James Hospital &Trinity College, Dublin
 Syncope Presentation and Investigation in the Acute Setting Professor Rose Anne Kenny, St James Hospital &Trinity College, Dublin Definition- Presentation Syncope is a syndrome consisting of a relatively
Syncope Presentation and Investigation in the Acute Setting Professor Rose Anne Kenny, St James Hospital &Trinity College, Dublin Definition- Presentation Syncope is a syndrome consisting of a relatively
Syncope 2015: Evaluation and Treatment. Steve Greer, MD FHRS BHHI Primary Care Symposium February 27, 2015
 Syncope 2015: Evaluation and Treatment Steve Greer, MD FHRS BHHI Primary Care Symposium February 27, 2015 Financial disclosures Research Support National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Boston Scientific
Syncope 2015: Evaluation and Treatment Steve Greer, MD FHRS BHHI Primary Care Symposium February 27, 2015 Financial disclosures Research Support National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Boston Scientific
Introduction. What is syncope?
 Syncope Introduction What is syncope? Syncope (SING-kuh-pee) is a medical term for fainting. When you faint, your brain is not receiving enough blood and oxygen, so you lose consciousness temporarily.
Syncope Introduction What is syncope? Syncope (SING-kuh-pee) is a medical term for fainting. When you faint, your brain is not receiving enough blood and oxygen, so you lose consciousness temporarily.
Defining and classifying syncope. Clinical Autonomic Research 2004;14 (Suppl 1): 4 8
 Defining and classifying syncope Roland D. Thijs, 1 Wouter Wieling, 2 Horacio Kaufmann, 3 J. Gert van Dijk 1 Clinical Autonomic Research 2004;14 (Suppl 1): 4 8 [1] Department of Neurology and Clinical
Defining and classifying syncope Roland D. Thijs, 1 Wouter Wieling, 2 Horacio Kaufmann, 3 J. Gert van Dijk 1 Clinical Autonomic Research 2004;14 (Suppl 1): 4 8 [1] Department of Neurology and Clinical
Recurrent AF: Choosing the Right Medication.
 In the name of God Shiraz E-Medical Journal Vol. 11, No. 3, July 2010 http://semj.sums.ac.ir/vol11/jul2010/89015.htm Recurrent AF: Choosing the Right Medication. Basamad Z. * Assistant Professor, Department
In the name of God Shiraz E-Medical Journal Vol. 11, No. 3, July 2010 http://semj.sums.ac.ir/vol11/jul2010/89015.htm Recurrent AF: Choosing the Right Medication. Basamad Z. * Assistant Professor, Department
Syncope. enough to include disorders such as epileptic seizures and concussion. January 14-15, 2011 SCA Conference 1
 Syncope and Atypical Seizures Ravi Mandapati, M.D., FACC.; FHRS Director, Specialized Program for Arrhythmias in Congenital Heart Disease UCLA Cardiac Arrhythmia Center David Geffen School of Medicine
Syncope and Atypical Seizures Ravi Mandapati, M.D., FACC.; FHRS Director, Specialized Program for Arrhythmias in Congenital Heart Disease UCLA Cardiac Arrhythmia Center David Geffen School of Medicine
Atrial Fibrillation: Drugs, Ablation, or Benign Neglect. Robert Kennedy, MD October 10, 2015
 Atrial Fibrillation: Drugs, Ablation, or Benign Neglect Robert Kennedy, MD October 10, 2015 Definitions 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS Guideline for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: Executive Summary.
Atrial Fibrillation: Drugs, Ablation, or Benign Neglect Robert Kennedy, MD October 10, 2015 Definitions 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS Guideline for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: Executive Summary.
Diana Heiman, MD Associate Professor, Family Medicine Residency Director East Tennessee State University
 Diana Heiman, MD Associate Professor, Family Medicine Residency Director East Tennessee State University Objectives Define exercise associated collapse (EAC) and exercise-associated postural hypotension
Diana Heiman, MD Associate Professor, Family Medicine Residency Director East Tennessee State University Objectives Define exercise associated collapse (EAC) and exercise-associated postural hypotension
Conflicts of interest: None
 Syncope in Athletes Thomas G. Allison, PhD, MPH Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN USA 13 th Annual Review Course in Clinical Cardiology Zurich 14 April, 2015 CP972908-1 Conflicts of interest: None Syncope: Definition
Syncope in Athletes Thomas G. Allison, PhD, MPH Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN USA 13 th Annual Review Course in Clinical Cardiology Zurich 14 April, 2015 CP972908-1 Conflicts of interest: None Syncope: Definition
Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms)
 Patient information factsheet Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Patient information factsheet Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (RATE VS RHYTHM CONTROL)
 ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (RATE VS RHYTHM CONTROL) By Prof. Dr. Helmy A. Bakr Mansoura Universirty 2014 AF Classification: Mechanisms of AF : Selected Risk Factors and Biomarkers for AF: WHY AF? 1. Atrial fibrillation
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (RATE VS RHYTHM CONTROL) By Prof. Dr. Helmy A. Bakr Mansoura Universirty 2014 AF Classification: Mechanisms of AF : Selected Risk Factors and Biomarkers for AF: WHY AF? 1. Atrial fibrillation
Acquired, Drug-Induced Long QT Syndrome
 Acquired, Drug-Induced Long QT Syndrome A Guide for Patients and Health Care Providers Sudden Arrhythmia Death Syndromes (SADS) Foundation 508 E. South Temple, Suite 202 Salt Lake City, Utah 84102 800-STOP
Acquired, Drug-Induced Long QT Syndrome A Guide for Patients and Health Care Providers Sudden Arrhythmia Death Syndromes (SADS) Foundation 508 E. South Temple, Suite 202 Salt Lake City, Utah 84102 800-STOP
trust clinical guideline
 CG23 VERSION 1.0 1/7 Guideline ID CG23 Version 1.0 Title Approved by Transient Loss of Consciousness Clinical Effectiveness Group Date Issued 01/01/2013 Review Date 31/12/2016 Directorate Authorised Staff
CG23 VERSION 1.0 1/7 Guideline ID CG23 Version 1.0 Title Approved by Transient Loss of Consciousness Clinical Effectiveness Group Date Issued 01/01/2013 Review Date 31/12/2016 Directorate Authorised Staff
Clinical characteristics and prodrome of Vasovagal syncope(vvs) in young and old.
 Clinical characteristics and prodrome of Vasovagal syncope(vvs) in young and old. Clodagh O Dwyer, Ciara rice, Dymphna Hade, Lisa Byrne, Michelle Burke, CW Fan, RA Kenny Falls & Blackout Unit, St. James
Clinical characteristics and prodrome of Vasovagal syncope(vvs) in young and old. Clodagh O Dwyer, Ciara rice, Dymphna Hade, Lisa Byrne, Michelle Burke, CW Fan, RA Kenny Falls & Blackout Unit, St. James
Fainting - Syncope. This reference summary explains fainting. It discusses the causes and treatment options for the condition.
 Fainting - Syncope Introduction Fainting, also known as syncope, is a temporary loss of consciousness. It is caused by a drop in blood flow to the brain. You may feel dizzy, lightheaded or nauseous before
Fainting - Syncope Introduction Fainting, also known as syncope, is a temporary loss of consciousness. It is caused by a drop in blood flow to the brain. You may feel dizzy, lightheaded or nauseous before
Syncope in the Elderly Assessment and Treatment. Professor Rose Anne Kenny Trinity College Dublin Newcastle University
 Syncope in the Elderly Assessment and Treatment Professor Rose Anne Kenny Trinity College Dublin Newcastle University Definition Syncope is a syndrome consisting of a relatively short period of temporary
Syncope in the Elderly Assessment and Treatment Professor Rose Anne Kenny Trinity College Dublin Newcastle University Definition Syncope is a syndrome consisting of a relatively short period of temporary
Ngaire has Palpitations
 Ngaire has Palpitations David Heaven Cardiac Electrophysiologist/Heart Rhythm Specialist Middlemore, Auckland City and Mercy Hospitals Auckland Heart Group MCQ Ms A is 45, and a healthy marathon runner.
Ngaire has Palpitations David Heaven Cardiac Electrophysiologist/Heart Rhythm Specialist Middlemore, Auckland City and Mercy Hospitals Auckland Heart Group MCQ Ms A is 45, and a healthy marathon runner.
5/1/2015. When should I worry? Presyncope is the feeling that one is about to pass out but remains conscious with a transient loss of postural tone.
 When should I worry? Robert Vogt-Lowell, MD, FAAP, FAAC, MAAC Pediatric Cardiologist Pediatrix Cardiology of Miami DEFINITIONS Syncope is a transient loss of consciousness and muscle tone that results
When should I worry? Robert Vogt-Lowell, MD, FAAP, FAAC, MAAC Pediatric Cardiologist Pediatrix Cardiology of Miami DEFINITIONS Syncope is a transient loss of consciousness and muscle tone that results
8 Peri-arrest arrhythmias
 8 Peri-arrest arrhythmias Introduction Cardiac arrhythmias are relatively common in the peri-arrest period. They are common in the setting of acute myocardial infarction and may precipitate ventricular
8 Peri-arrest arrhythmias Introduction Cardiac arrhythmias are relatively common in the peri-arrest period. They are common in the setting of acute myocardial infarction and may precipitate ventricular
Presenter Disclosure Information
 2:15 3 pm Managing Arrhythmias in Primary Care Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Raul Mitrani, MD, FACC, FHRS: Speakers Bureau for Medtronic.
2:15 3 pm Managing Arrhythmias in Primary Care Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Raul Mitrani, MD, FACC, FHRS: Speakers Bureau for Medtronic.
GUIDELINE 11.9 MANAGING ACUTE DYSRHYTHMIAS. (To be read in conjunction with Guideline 11.7 Post-Resuscitation Therapy in Adult Advanced Life Support)
 AUSTRALIAN RESUSCITATION COUNCIL GUIDELINE 11.9 MANAGING ACUTE DYSRHYTHMIAS (To be read in conjunction with Guideline 11.7 Post-Resuscitation Therapy in Adult Advanced Life Support) The term cardiac arrhythmia
AUSTRALIAN RESUSCITATION COUNCIL GUIDELINE 11.9 MANAGING ACUTE DYSRHYTHMIAS (To be read in conjunction with Guideline 11.7 Post-Resuscitation Therapy in Adult Advanced Life Support) The term cardiac arrhythmia
Treating AF: The Newest Recommendations. CardioCase presentation. Ethel s Case. Wayne Warnica, MD, FACC, FACP, FRCPC
 Treating AF: The Newest Recommendations Wayne Warnica, MD, FACC, FACP, FRCPC CardioCase presentation Ethel s Case Ethel, 73, presents with rapid heart beating and mild chest discomfort. In the ED, ECG
Treating AF: The Newest Recommendations Wayne Warnica, MD, FACC, FACP, FRCPC CardioCase presentation Ethel s Case Ethel, 73, presents with rapid heart beating and mild chest discomfort. In the ED, ECG
Guidelines on management (diagnosis and treatment) of syncope*
 European Heart Journal (2001) 22, 1256 1306 doi:10.1053/euhj.2001.2739, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Task Force Report Guidelines on management (diagnosis and treatment) of syncope*
European Heart Journal (2001) 22, 1256 1306 doi:10.1053/euhj.2001.2739, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Task Force Report Guidelines on management (diagnosis and treatment) of syncope*
Clinical Glidepath TM Tools Syncope Frail Life expectancy less than five years or significant functional impairment
 Robust Elderly greater ALL GROUPS 1 SYMPTOMS a) wth, nausea b) postural symptoms c) chest pain, dyspnea, post-exercise, dizziness, history of heart disease, palpitations, family history (prolonged QT)
Robust Elderly greater ALL GROUPS 1 SYMPTOMS a) wth, nausea b) postural symptoms c) chest pain, dyspnea, post-exercise, dizziness, history of heart disease, palpitations, family history (prolonged QT)
Palpitations & AF. Richard Grocott Mason Consultant Cardiologist THH NHS Foundation Trust & Royal Brompton & Harefield NHS Foundation Trust
 Palpitations & AF Richard Grocott Mason Consultant Cardiologist THH NHS Foundation Trust & Royal Brompton & Harefield NHS Foundation Trust Palpitations Frequent symptom Less than 50% associated with arrhythmia
Palpitations & AF Richard Grocott Mason Consultant Cardiologist THH NHS Foundation Trust & Royal Brompton & Harefield NHS Foundation Trust Palpitations Frequent symptom Less than 50% associated with arrhythmia
Neurocardiogenic Syncope
 Neurocardiogenic Syncope Christopher Bonnet, M.D. Director, Clinical Electrophysiology Definition of Syncope Abrupt and transient loss of consciousness Loss of postural tone Spontaneous and rapid recovery
Neurocardiogenic Syncope Christopher Bonnet, M.D. Director, Clinical Electrophysiology Definition of Syncope Abrupt and transient loss of consciousness Loss of postural tone Spontaneous and rapid recovery
Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : ICD-9-CM to ICD-10-CM Cardiac Rhythm and Heart Failure Diagnoses
 Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : to 402.01 Hypertensive heart disease, malignant, with heart failure 402.11 Hypertensive heart disease, benign, with heart failure 402.91 Hypertensive heart disease, unspecified,
Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : to 402.01 Hypertensive heart disease, malignant, with heart failure 402.11 Hypertensive heart disease, benign, with heart failure 402.91 Hypertensive heart disease, unspecified,
Wyatt Decker, M.D., FACEP Mayo Clinic College of Medicine, 200 First Street SW, Rochester, MN 55905
 WHICH PATIENTS WITH SYNCOPE NEED TO BE ADMITTED TO THE HOSPITAL Wyatt Decker, M.D., FACEP Mayo Clinic College of Medicine, 200 First Street SW, Rochester, MN 55905 Case Unresponsive 82 y.o. male - found
WHICH PATIENTS WITH SYNCOPE NEED TO BE ADMITTED TO THE HOSPITAL Wyatt Decker, M.D., FACEP Mayo Clinic College of Medicine, 200 First Street SW, Rochester, MN 55905 Case Unresponsive 82 y.o. male - found
Life Threatening EKG s In The Office. Joseph A Manfredi, MD, FACC, FHRS GHS Cardiovascular Symposium
 Life Threatening EKG s In The Office Joseph A Manfredi, MD, FACC, FHRS GHS Cardiovascular Symposium January 24 th, 2015 Disclosures Speaker Honorariums: STJM, Boston Scientific Advisory role: Medtronic
Life Threatening EKG s In The Office Joseph A Manfredi, MD, FACC, FHRS GHS Cardiovascular Symposium January 24 th, 2015 Disclosures Speaker Honorariums: STJM, Boston Scientific Advisory role: Medtronic
Potential Causes of Sudden Cardiac Arrest in Children
 Potential Causes of Sudden Cardiac Arrest in Children Project S.A.V.E. When sudden death occurs in children, adolescents and younger adults, heart abnormalities are likely causes. These conditions are
Potential Causes of Sudden Cardiac Arrest in Children Project S.A.V.E. When sudden death occurs in children, adolescents and younger adults, heart abnormalities are likely causes. These conditions are
Syncope: David G Benditt an overview of diagnosis and treatment
 ARTÍCULO DE REVISIÓN REV URUG CARDIOL 2011; 26: 55-70 Syncope: David G Benditt an overview of diagnosis and treatment Syncope: an overview of diagnosis and treatment DAVID G BENDITT. MD, FACC, FHRS, FESC,
ARTÍCULO DE REVISIÓN REV URUG CARDIOL 2011; 26: 55-70 Syncope: David G Benditt an overview of diagnosis and treatment Syncope: an overview of diagnosis and treatment DAVID G BENDITT. MD, FACC, FHRS, FESC,
Atrial Fibrillation and Cardiac Device Therapy RAKESH LATCHAMSETTY, MD DIVISION OF ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN HOSPITAL ANN ARBOR, MI
 Atrial Fibrillation and Cardiac Device Therapy RAKESH LATCHAMSETTY, MD DIVISION OF ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN HOSPITAL ANN ARBOR, MI Outline Atrial Fibrillation What is it? What are the associated
Atrial Fibrillation and Cardiac Device Therapy RAKESH LATCHAMSETTY, MD DIVISION OF ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN HOSPITAL ANN ARBOR, MI Outline Atrial Fibrillation What is it? What are the associated
PRACTICAL APPROACH TO SVT. Graham C. Wong MD MPH Division of Cardiology Vancouver General Hospital University of British Columbia
 PRACTICAL APPROACH TO SVT Graham C. Wong MD MPH Division of Cardiology Vancouver General Hospital University of British Columbia CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF THE HEART SA node His bundle Left bundle AV node Right
PRACTICAL APPROACH TO SVT Graham C. Wong MD MPH Division of Cardiology Vancouver General Hospital University of British Columbia CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF THE HEART SA node His bundle Left bundle AV node Right
The Emerging Atrial Fibrillation Epidemic: Treat It, Leave It or Burn It?
 The Emerging Atrial Fibrillation Epidemic: Treat It, Leave It or Burn It? Indiana Chapter-ACC 17 th Annual Meeting Indianapolis, Indiana October 19, 2013 Deepak Bhakta MD FACC FACP FAHA FHRS CCDS Associate
The Emerging Atrial Fibrillation Epidemic: Treat It, Leave It or Burn It? Indiana Chapter-ACC 17 th Annual Meeting Indianapolis, Indiana October 19, 2013 Deepak Bhakta MD FACC FACP FAHA FHRS CCDS Associate
Current Management of Atrial Fibrillation DISCLOSURES. Heart Beat Anatomy. I have no financial conflicts to disclose
 Current Management of Atrial Fibrillation Mary Macklin, MSN, APRN Concord Hospital Cardiac Associates DISCLOSURES I have no financial conflicts to disclose Book Women: Fit at Fifty. A Guide to Living Long.
Current Management of Atrial Fibrillation Mary Macklin, MSN, APRN Concord Hospital Cardiac Associates DISCLOSURES I have no financial conflicts to disclose Book Women: Fit at Fifty. A Guide to Living Long.
Guidelines on Management (Diagnosis and Treatment) of Syncope Update 2004 q Executive Summary
 European Heart Journal (2004) 25, 2054 2072 ESC Guidelines Guidelines on Management (Diagnosis and Treatment) of Syncope Update 2004 q Executive Summary The Task Force on Syncope, European Society of Cardiology
European Heart Journal (2004) 25, 2054 2072 ESC Guidelines Guidelines on Management (Diagnosis and Treatment) of Syncope Update 2004 q Executive Summary The Task Force on Syncope, European Society of Cardiology
Atrial Fibrillation Peter Santucci, MD Revised May, 2008
 Atrial Fibrillation Peter Santucci, MD Revised May, 2008 Atrial fibrillation (AF) is an irregular, disorganized rhythm characterized by a lack of organized mechanical atrial activity. The atrial rate is
Atrial Fibrillation Peter Santucci, MD Revised May, 2008 Atrial fibrillation (AF) is an irregular, disorganized rhythm characterized by a lack of organized mechanical atrial activity. The atrial rate is
HTEC 91. Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms. NSR with PAC. Nonconducted PAC. Nonconducted PAC. Premature Atrial Contractions (PACs)
 HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 4 Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms PACs: Premature Atrial Contractions PAT: Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia AF: Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter Premature Atrial
HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 4 Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms PACs: Premature Atrial Contractions PAT: Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia AF: Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter Premature Atrial
Syncopal Attacks Imitating Epileptic Seizures
 Syncopal Attacks Imitating Epileptic Seizures 2 Syncopes are among the most common non-epileptic attacks misdiagnosed as 1, 25-39 epileptic seizures, including GTCSs. A syncope is de fi ned as a paroxysmal
Syncopal Attacks Imitating Epileptic Seizures 2 Syncopes are among the most common non-epileptic attacks misdiagnosed as 1, 25-39 epileptic seizures, including GTCSs. A syncope is de fi ned as a paroxysmal
Atrial Fibrillation The Basics
 Atrial Fibrillation The Basics Family Practice Symposium Tim McAveney, M.D. 10/23/09 Objectives Review the fundamentals of managing afib Discuss the risks for stroke and the indications for anticoagulation
Atrial Fibrillation The Basics Family Practice Symposium Tim McAveney, M.D. 10/23/09 Objectives Review the fundamentals of managing afib Discuss the risks for stroke and the indications for anticoagulation
ACLS PHARMACOLOGY 2011 Guidelines
 ACLS PHARMACOLOGY 2011 Guidelines ADENOSINE Narrow complex tachycardias or wide complex tachycardias that may be supraventricular in nature. It is effective in treating 90% of the reentry arrhythmias.
ACLS PHARMACOLOGY 2011 Guidelines ADENOSINE Narrow complex tachycardias or wide complex tachycardias that may be supraventricular in nature. It is effective in treating 90% of the reentry arrhythmias.
2320-6691 2015; 3(3B):1132-1136 ISSN 2347-954X
 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2015; 3(3B):1132-1136 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2015; 3(3B):1132-1136 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Arrhythmia from a GP Perspective. Dr Jonathan Shribman GPSI Cardiology Northamptonshire
 Arrhythmia from a GP Perspective Dr Jonathan Shribman GPSI Cardiology Northamptonshire Arrhythmia from a GP Perspective Common presentation in General Practice Associated with considerable morbidity But
Arrhythmia from a GP Perspective Dr Jonathan Shribman GPSI Cardiology Northamptonshire Arrhythmia from a GP Perspective Common presentation in General Practice Associated with considerable morbidity But
Atrial Fibrillation Management Across the Spectrum of Illness
 Disclosures Atrial Fibrillation Management Across the Spectrum of Illness NONE Barbara Birriel, MSN, ACNP-BC, FCCM The Pennsylvania State University Objectives AF Discuss the pathophysiology, diagnosis,
Disclosures Atrial Fibrillation Management Across the Spectrum of Illness NONE Barbara Birriel, MSN, ACNP-BC, FCCM The Pennsylvania State University Objectives AF Discuss the pathophysiology, diagnosis,
Atrial Fibrillation An update on diagnosis and management
 Dr Arvind Vasudeva Consultant Cardiologist Atrial Fibrillation An update on diagnosis and management Atrial fibrillation (AF) remains the commonest disturbance of cardiac rhythm seen in clinical practice.
Dr Arvind Vasudeva Consultant Cardiologist Atrial Fibrillation An update on diagnosis and management Atrial fibrillation (AF) remains the commonest disturbance of cardiac rhythm seen in clinical practice.
The causes of collapse can be broadly categorised into : syncope, weakness and seizures.
 VICAS Winter Conference 2010 Cork, Ireland Mike Martin COLLAPSE & ARRHYTMIAS Mike Martin MVB, DVC, MRCVS. Specialist in Vet Cardiology Veterinary Cardiorespiratory Centre, Thera House, Kenilworth, Warwickshire.
VICAS Winter Conference 2010 Cork, Ireland Mike Martin COLLAPSE & ARRHYTMIAS Mike Martin MVB, DVC, MRCVS. Specialist in Vet Cardiology Veterinary Cardiorespiratory Centre, Thera House, Kenilworth, Warwickshire.
RATE VERSUS RHYTHM CONTROL OF ATRIAL FIBRILLATION: SPECIAL CONSIDERATION IN ELDERLY. Charles Jazra
 RATE VERSUS RHYTHM CONTROL OF ATRIAL FIBRILLATION: SPECIAL CONSIDERATION IN ELDERLY Charles Jazra NO CONFLICT OF INTEREST TO DECLARE Relationship Between Atrial Fibrillation and Age Prevalence, percent
RATE VERSUS RHYTHM CONTROL OF ATRIAL FIBRILLATION: SPECIAL CONSIDERATION IN ELDERLY Charles Jazra NO CONFLICT OF INTEREST TO DECLARE Relationship Between Atrial Fibrillation and Age Prevalence, percent
An Introduction to Tachyarrhythmias R. A. Seyon MN, NP, CCN(C) & Dr. R. G. Williams
 Arrhythmias 1 An Introduction to Tachyarrhythmias R. A. Seyon MN, NP, CCN(C) & Dr. R. G. Williams Things to keep in mind when analyzing arrhythmias: Electrical activity recorded in 12 and 15 leads Examine
Arrhythmias 1 An Introduction to Tachyarrhythmias R. A. Seyon MN, NP, CCN(C) & Dr. R. G. Williams Things to keep in mind when analyzing arrhythmias: Electrical activity recorded in 12 and 15 leads Examine
Atrial fibrillation. Quick reference guide. Issue date: June 2006. The management of atrial fibrillation
 Quick reference guide Issue date: June 2006 Atrial fibrillation The management of atrial fibrillation Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Chronic Conditions Contents Contents Patient-centred
Quick reference guide Issue date: June 2006 Atrial fibrillation The management of atrial fibrillation Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Chronic Conditions Contents Contents Patient-centred
Novartis Gilenya FDO Program Clinical Protocol and Highlights from Prescribing Information (PI)
 Novartis Gilenya FDO Program Clinical Protocol and Highlights from Prescribing Information (PI) Highlights from Prescribing Information - the link to the full text PI is as follows: http://www.pharma.us.novartis.com/product/pi/pdf/gilenya.pdf
Novartis Gilenya FDO Program Clinical Protocol and Highlights from Prescribing Information (PI) Highlights from Prescribing Information - the link to the full text PI is as follows: http://www.pharma.us.novartis.com/product/pi/pdf/gilenya.pdf
ANNE ARUNDEL MEDICAL CENTER CRITICAL CARE MEDICATION MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF NURSING AND PHARMACY. Guidelines for Use of Intravenous Isoproterenol
 ANNE ARUNDEL MEDICAL CENTER CRITICAL CARE MEDICATION MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF NURSING AND PHARMACY Guidelines for Use of Intravenous Isoproterenol Major Indications Status Asthmaticus As a last resort for
ANNE ARUNDEL MEDICAL CENTER CRITICAL CARE MEDICATION MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF NURSING AND PHARMACY Guidelines for Use of Intravenous Isoproterenol Major Indications Status Asthmaticus As a last resort for
Guidelines on Management (Diagnosis and Treatment) of Syncope e Update 2004 *
 Europace (2004) 6, 467e537 ESC GUIDELINES Guidelines on Management (Diagnosis and Treatment) of Syncope e Update 2004 * The Task Force on Syncope, European Society of Cardiology ** Task Force members:
Europace (2004) 6, 467e537 ESC GUIDELINES Guidelines on Management (Diagnosis and Treatment) of Syncope e Update 2004 * The Task Force on Syncope, European Society of Cardiology ** Task Force members:
Equine Cardiovascular Disease
 Equine Cardiovascular Disease 3 rd most common cause of poor performance in athletic horses (after musculoskeletal and respiratory) Cardiac abnormalities are rare Clinical Signs: Poor performance/exercise
Equine Cardiovascular Disease 3 rd most common cause of poor performance in athletic horses (after musculoskeletal and respiratory) Cardiac abnormalities are rare Clinical Signs: Poor performance/exercise
Autonomic Stress Test
 Autonomic Stress Test (The expanded head-up tilt test) Artur Fedorowski Syncope Unit Skåne University Hospital, Malmö, Sweden NordSync 2011, Malmö Disclosure None The expanded head-up tilt test When? Why?
Autonomic Stress Test (The expanded head-up tilt test) Artur Fedorowski Syncope Unit Skåne University Hospital, Malmö, Sweden NordSync 2011, Malmö Disclosure None The expanded head-up tilt test When? Why?
Atrial Fibrillation Based on ESC Guidelines. Moshe Swissa MD Kaplan Medical Center
 Atrial Fibrillation Based on ESC Guidelines Moshe Swissa MD Kaplan Medical Center Epidemiology AF affects 1 2% of the population, and this figure is likely to increase in the next 50 years. AF may long
Atrial Fibrillation Based on ESC Guidelines Moshe Swissa MD Kaplan Medical Center Epidemiology AF affects 1 2% of the population, and this figure is likely to increase in the next 50 years. AF may long
Episode 20 Atrial fibrillation Prepared by Dr. Lucas Chartier
 Episode 20 Atrial fibrillation Prepared by Dr. Lucas Chartier Most common dysrhythmia seen in ED, and incidence increasing with ageing population Presentation Common presentations: younger patients often
Episode 20 Atrial fibrillation Prepared by Dr. Lucas Chartier Most common dysrhythmia seen in ED, and incidence increasing with ageing population Presentation Common presentations: younger patients often
Managing the Patient with Atrial Fibrillation
 Pocket Guide Managing the Patient with Atrial Fibrillation Updated April 2012 Editor Stephen R. Shorofsky, MD, Ph.D. Assistant Editors Anastasios Saliaris, MD Shawn Robinson, MD www.hrsonline.org DEFINITION
Pocket Guide Managing the Patient with Atrial Fibrillation Updated April 2012 Editor Stephen R. Shorofsky, MD, Ph.D. Assistant Editors Anastasios Saliaris, MD Shawn Robinson, MD www.hrsonline.org DEFINITION
COVERAGE GUIDANCE: ABLATION FOR ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 COVERAGE GUIDANCE: ABLATION FOR ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Question: How should the EGBS Coverage Guidance regarding ablation for atrial fibrillation be applied to the Prioritized List? Question source: Evidence
COVERAGE GUIDANCE: ABLATION FOR ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Question: How should the EGBS Coverage Guidance regarding ablation for atrial fibrillation be applied to the Prioritized List? Question source: Evidence
ACLS RHYTHM TEST. 2. A 74-year-old woman with chest pain. Blood pressure 192/90 and rates her pain 9/10.
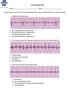 ACLS RHYTHM TEST Name Date Choose the best answer for each of the following questions. Each of the following strips is 6 seconds in length. 1. Identify the following rhythm a. Sinus bradycardia with 2
ACLS RHYTHM TEST Name Date Choose the best answer for each of the following questions. Each of the following strips is 6 seconds in length. 1. Identify the following rhythm a. Sinus bradycardia with 2
Electrophysiology Heart Study - EPS -
 Electrophysiology Heart Study - EPS - What is an EPS? EPS is short for ElectroPhysiology heart Study. This procedure looks at the electrical system of your heart. An EPS will show if you have a heart rhythm
Electrophysiology Heart Study - EPS - What is an EPS? EPS is short for ElectroPhysiology heart Study. This procedure looks at the electrical system of your heart. An EPS will show if you have a heart rhythm
Introduction to Electrophysiology. Wm. W. Barrington, MD, FACC University of Pittsburgh Medical Center
 Introduction to Electrophysiology Wm. W. Barrington, MD, FACC University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Objectives Indications for EP Study How do we do the study Normal recordings Abnormal Recordings Limitations
Introduction to Electrophysiology Wm. W. Barrington, MD, FACC University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Objectives Indications for EP Study How do we do the study Normal recordings Abnormal Recordings Limitations
Addendum to the Guideline on antiarrhythmics on atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter
 22 July 2010 EMA/CHMP/EWP/213056/2010 Addendum to the Guideline on antiarrhythmics on atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter Draft Agreed by Efficacy Working Party July 2008 Adoption by CHMP for release
22 July 2010 EMA/CHMP/EWP/213056/2010 Addendum to the Guideline on antiarrhythmics on atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter Draft Agreed by Efficacy Working Party July 2008 Adoption by CHMP for release
Chest Pain in Young Athletes. Christopher Davis, MD, PhD Pediatric Cardiology Rady Children s Hospital San Diego cdavis@rchsd.
 Chest Pain in Young Athletes Christopher Davis, MD, PhD Pediatric Cardiology Rady Children s Hospital San Diego cdavis@rchsd.org 858-966-5855 None Disclosures Chest Pain: the good news and the bad news:
Chest Pain in Young Athletes Christopher Davis, MD, PhD Pediatric Cardiology Rady Children s Hospital San Diego cdavis@rchsd.org 858-966-5855 None Disclosures Chest Pain: the good news and the bad news:
Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of syncope (version 2009)
 European Heart Journal doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehp298 ESC GUIDELINES Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of syncope (version 2009) The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Management of Syncope of the
European Heart Journal doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehp298 ESC GUIDELINES Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of syncope (version 2009) The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Management of Syncope of the
CLINICAL MEDICINE. Syncope. Pushpa Yadav*, Arvind Sethi**, AK Agarwal***, Arun Jain*
 CLINICAL MEDICINE JIACM 2003; 4(24): 286-91 Syncope Pushpa Yadav*, Arvind Sethi**, AK Agarwal***, Arun Jain* Syncope is a term applicable to sudden and transient loss of consciousness alongwith postural
CLINICAL MEDICINE JIACM 2003; 4(24): 286-91 Syncope Pushpa Yadav*, Arvind Sethi**, AK Agarwal***, Arun Jain* Syncope is a term applicable to sudden and transient loss of consciousness alongwith postural
TABLE 1 Clinical Classification of AF. New onset AF (first detected) Paroxysmal (<7 days, mostly < 24 hours)
 Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation Deborah Ritchie RN, MN, Robert S Sheldon MD, PhD Cardiovascular Research Group, University of Calgary, Alberta Partly
Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation Deborah Ritchie RN, MN, Robert S Sheldon MD, PhD Cardiovascular Research Group, University of Calgary, Alberta Partly
Atrial Fibrillation 2014 How to Treat How to Anticoagulate. Allan Anderson, MD, FACC, FAHA Division of Cardiology
 Atrial Fibrillation 2014 How to Treat How to Anticoagulate Allan Anderson, MD, FACC, FAHA Division of Cardiology Projection for Prevalence of Atrial Fibrillation: 5.6 Million by 2050 Projected number of
Atrial Fibrillation 2014 How to Treat How to Anticoagulate Allan Anderson, MD, FACC, FAHA Division of Cardiology Projection for Prevalence of Atrial Fibrillation: 5.6 Million by 2050 Projected number of
Setting up a Blackout Service
 Setting up a Blackout Service Jayne Mudd, Nurse Consultant, Cardiac Rhythm Management James Cook University Hospital, Middlesbrough South Tees NHS Foundation Trust NECVN: Population of approximately 2.8
Setting up a Blackout Service Jayne Mudd, Nurse Consultant, Cardiac Rhythm Management James Cook University Hospital, Middlesbrough South Tees NHS Foundation Trust NECVN: Population of approximately 2.8
Atrial Fibrillation: Do We Have A Cure? Raymond Kawasaki, MD AMG Electrophysiology February 21, 2015
 Atrial Fibrillation: Do We Have A Cure? Raymond Kawasaki, MD AMG Electrophysiology February 21, 2015 Disclaimer I have no relationships to disclose Do we have a cure for Atrial Fibrillation? The short
Atrial Fibrillation: Do We Have A Cure? Raymond Kawasaki, MD AMG Electrophysiology February 21, 2015 Disclaimer I have no relationships to disclose Do we have a cure for Atrial Fibrillation? The short
Syncope: Overview and approach to management
 1 CHAPTER 1 Syncope: Overview and approach to management Brian Olshansky, MD Introduction Syncope is a common, important medical problem caused by many conditions, ranging from benign and self-limiting
1 CHAPTER 1 Syncope: Overview and approach to management Brian Olshansky, MD Introduction Syncope is a common, important medical problem caused by many conditions, ranging from benign and self-limiting
SYNCOPE a symptom, not a diagnosis
 SYNCOPE a symptom, not a diagnosis Dr Jaycen Cruickshank Ballarat Emergency Education Grampians Emergency Medicine Training Hub Syncope Learning objectives Learning objectives To name the common and important
SYNCOPE a symptom, not a diagnosis Dr Jaycen Cruickshank Ballarat Emergency Education Grampians Emergency Medicine Training Hub Syncope Learning objectives Learning objectives To name the common and important
Medtronic Cardiac Rhythm and Heart Failure ICD-10 Coding for Physicians
 Medtronic Cardiac Rhythm and Heart Failure ICD-10 Coding for Physicians May 19, 2015 Disclaimer This presentation is intended for educational use. Any duplication is prohibited without written consent
Medtronic Cardiac Rhythm and Heart Failure ICD-10 Coding for Physicians May 19, 2015 Disclaimer This presentation is intended for educational use. Any duplication is prohibited without written consent
Official Online ACLS Exam
 \ Official Online ACLS Exam Please fill out this form before you take the exam. Name : Email : Phone : 1. Hypovolemia initially produces which arrhythmia? A. PEA B. Sinus tachycardia C. Symptomatic bradyarrhythmia
\ Official Online ACLS Exam Please fill out this form before you take the exam. Name : Email : Phone : 1. Hypovolemia initially produces which arrhythmia? A. PEA B. Sinus tachycardia C. Symptomatic bradyarrhythmia
Patient Information Sheet Electrophysiological study
 Patient Information Sheet Electrophysiological study Your doctor has recommended performing an electrophysiological study (also called EPS). EPS is a diagnostic procedure designed to test and evaluate
Patient Information Sheet Electrophysiological study Your doctor has recommended performing an electrophysiological study (also called EPS). EPS is a diagnostic procedure designed to test and evaluate
Unrestricted grant Boehringer Ingelheim
 ED Management of Recent Onset tat Atrial Fibrillation and Flutter (RAFF) Canadian Cardiovascular Society Guidelines 2010 CAEP St John s 2011 Ian Stiell MD MSc FRCPC Professor and Chair, Dept of Emergency
ED Management of Recent Onset tat Atrial Fibrillation and Flutter (RAFF) Canadian Cardiovascular Society Guidelines 2010 CAEP St John s 2011 Ian Stiell MD MSc FRCPC Professor and Chair, Dept of Emergency
Review of Important ECG Findings in Patients with Syncope Joseph Toscano, MD
 92 Review of Important ECG Findings in Patients with Syncope Joseph Toscano, MD Abstract Guidelines recommend 12-lead ECG as an important test to perform in patients with syncope. Though the incidence
92 Review of Important ECG Findings in Patients with Syncope Joseph Toscano, MD Abstract Guidelines recommend 12-lead ECG as an important test to perform in patients with syncope. Though the incidence
Catheter Ablation. A Guided Approach for Treating Atrial Arrhythmias
 Catheter Ablation A Guided Approach for Treating Atrial Arrhythmias A P A T I E N T H A N D B O O K This brochure will provide an overview of atrial arrhythmias (heart rhythm problems affecting the upper
Catheter Ablation A Guided Approach for Treating Atrial Arrhythmias A P A T I E N T H A N D B O O K This brochure will provide an overview of atrial arrhythmias (heart rhythm problems affecting the upper
Medical management of CHF: A New Class of Medication. Al Timothy, M.D. Cardiovascular Institute of the South
 Medical management of CHF: A New Class of Medication Al Timothy, M.D. Cardiovascular Institute of the South Disclosures Speakers Bureau for Amgen Background Chronic systolic congestive heart failure remains
Medical management of CHF: A New Class of Medication Al Timothy, M.D. Cardiovascular Institute of the South Disclosures Speakers Bureau for Amgen Background Chronic systolic congestive heart failure remains
Syncope in Children and Adolescents: What Are the Peculiar Features?
 Syncope in Children and Adolescents: What Are the Peculiar Features? W. WIELING 1,N.VAN DIJK 1, K.S. GANZEBOOM 1,J.P.SAUL 2 Epidemiology Syncope can be defined as a temporary loss of consciousness and
Syncope in Children and Adolescents: What Are the Peculiar Features? W. WIELING 1,N.VAN DIJK 1, K.S. GANZEBOOM 1,J.P.SAUL 2 Epidemiology Syncope can be defined as a temporary loss of consciousness and
How to control atrial fibrillation in 2013 The ideal patient for a rate control strategy
 How to control atrial fibrillation in 2013 The ideal patient for a rate control strategy L. Pison, MD Advances in Cardiac Arrhythmias and Great Innovations in Cardiology - Torino, September 28 th 2013
How to control atrial fibrillation in 2013 The ideal patient for a rate control strategy L. Pison, MD Advances in Cardiac Arrhythmias and Great Innovations in Cardiology - Torino, September 28 th 2013
Atrial fibrillation (AF) care pathways. for the primary care physicians
 Atrial fibrillation (AF) care pathways for the primary care physicians by University of Minnesota Physicians Heart, October, 2011 Evaluation by the primary care physician: 1. Comprehensive history and
Atrial fibrillation (AF) care pathways for the primary care physicians by University of Minnesota Physicians Heart, October, 2011 Evaluation by the primary care physician: 1. Comprehensive history and
Management of ATRIAL FIBRILLATION. in general practice. 22 BPJ Issue 39
 Management of ATRIAL FIBRILLATION in general practice 22 BPJ Issue 39 What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common cardiac arrhythmia encountered in primary care. It is often
Management of ATRIAL FIBRILLATION in general practice 22 BPJ Issue 39 What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common cardiac arrhythmia encountered in primary care. It is often
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) MANAGEMENT of Atrial Fibrillation (AF)
 DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) MANAGEMENT of Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Key priorities Identification and diagnosis Treatment for persistent AF Treatment for permanent AF Antithrombotic
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) MANAGEMENT of Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Key priorities Identification and diagnosis Treatment for persistent AF Treatment for permanent AF Antithrombotic
Automatic External Defibrillators
 Last Review Date: May 27, 2016 Number: MG.MM.DM.10dC2 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or primary care provider must submit to EmblemHealth
Last Review Date: May 27, 2016 Number: MG.MM.DM.10dC2 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or primary care provider must submit to EmblemHealth
Living with Low Blood Pressure
 Living with Low Blood Pressure Understand the medical jargon and tips on how to cope with low Blood Pressure (BP) What is low blood pressure? Blood pressure (BP) is measured in millimetres of mercury (mm
Living with Low Blood Pressure Understand the medical jargon and tips on how to cope with low Blood Pressure (BP) What is low blood pressure? Blood pressure (BP) is measured in millimetres of mercury (mm
Consensus statement for the diagnosis and management of syncope. Argentine Society of Cardiology
 CONSENSUS Consensus statement for the diagnosis and management of syncope. Argentine Society of Cardiology Director Dr. Claudio Militello MTSAC Committee of Editorial Staff Dr. Rafael Acunzo MTSAC Dr.
CONSENSUS Consensus statement for the diagnosis and management of syncope. Argentine Society of Cardiology Director Dr. Claudio Militello MTSAC Committee of Editorial Staff Dr. Rafael Acunzo MTSAC Dr.
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION: Scope of the Problem. October 2015
 ATRIAL FIBRILLATION: Scope of the Problem October 2015 Purpose of the Presentation Review the worldwide incidence and prognosis associated with atrial fibrillation (AF) Identify the types of AF, clinical
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION: Scope of the Problem October 2015 Purpose of the Presentation Review the worldwide incidence and prognosis associated with atrial fibrillation (AF) Identify the types of AF, clinical
Cardioversion for. Atrial Fibrillation. Your Heart s Electrical System Cardioversion Living with Atrial Fibrillation
 Cardioversion for Atrial Fibrillation Your Heart s Electrical System Cardioversion Living with Atrial Fibrillation When You Have Atrial Fibrillation You ve been told you have a heart condition called atrial
Cardioversion for Atrial Fibrillation Your Heart s Electrical System Cardioversion Living with Atrial Fibrillation When You Have Atrial Fibrillation You ve been told you have a heart condition called atrial
NAME OF THE HOSPITAL: 1. Coronary Balloon Angioplasty: M7F1.1/ Angioplasty with Stent(PTCA with Stent): M7F1.3
 1. Coronary Balloon Angioplasty: M7F1.1/ Angioplasty with Stent(PTCA with Stent): M7F1.3 1. Name of the Procedure: Coronary Balloon Angioplasty 2. Select the Indication from the drop down of various indications
1. Coronary Balloon Angioplasty: M7F1.1/ Angioplasty with Stent(PTCA with Stent): M7F1.3 1. Name of the Procedure: Coronary Balloon Angioplasty 2. Select the Indication from the drop down of various indications
What Can I Do about Atrial Fibrillation (AF)?
 Additional Device Information 9529 Reveal XT Insertable Cardiac Monitor The Reveal XT Insertable Cardiac Monitor is an implantable patientactivated and automatically activated monitoring system that records
Additional Device Information 9529 Reveal XT Insertable Cardiac Monitor The Reveal XT Insertable Cardiac Monitor is an implantable patientactivated and automatically activated monitoring system that records
TILT TESTING INFORMATION AND PROTOCOLS
 TILT TESTING INFORMATION AND PROTOCOLS For technicians and doctors June 2008 Dr Nicola Cooper Consultant in Acute Medicine & Geriatrics TILT TESTING This information has been compiled for technicians and
TILT TESTING INFORMATION AND PROTOCOLS For technicians and doctors June 2008 Dr Nicola Cooper Consultant in Acute Medicine & Geriatrics TILT TESTING This information has been compiled for technicians and
ACLS Cardiac Arrest Algorithm Neumar, R. W. et al. Circulation 2010;122:S729-S767
 ACLS Cardiac Arrest Algorithm Neumar, R. W. et al. Circulation 2010;122:S729-S767 Copyright 2010 American Heart Association ACLS Cardiac Arrest Circular Algorithm Neumar, R. W. et al. Circulation 2010;122:S729-S767
ACLS Cardiac Arrest Algorithm Neumar, R. W. et al. Circulation 2010;122:S729-S767 Copyright 2010 American Heart Association ACLS Cardiac Arrest Circular Algorithm Neumar, R. W. et al. Circulation 2010;122:S729-S767
Basics of Pacing. Ruth Hickling, RN-BSN Tasha Conley, RN-BSN
 Basics of Pacing Ruth Hickling, RN-BSN Tasha Conley, RN-BSN The Cardiac Conduction System Cardiac Conduction System Review Normal Conduction Conduction QRS QRS Complex Complex RR PP ST ST segment segment
Basics of Pacing Ruth Hickling, RN-BSN Tasha Conley, RN-BSN The Cardiac Conduction System Cardiac Conduction System Review Normal Conduction Conduction QRS QRS Complex Complex RR PP ST ST segment segment
Syncope in the Primary Care Setting. Ibrahim Hanna MD
 Syncope in the Primary Care Setting Ibrahim Hanna MD Definitions SYNCOPE: Abrupt but transient loss of consciousness associated with the absence of postural tone, followed by a rapid and usually complete
Syncope in the Primary Care Setting Ibrahim Hanna MD Definitions SYNCOPE: Abrupt but transient loss of consciousness associated with the absence of postural tone, followed by a rapid and usually complete
Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Explained
 James Paget University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Explained Patient Information Contents What are the symptoms of atrial fibrillation (AF)? 3 Normal heartbeat 4 How common
James Paget University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Explained Patient Information Contents What are the symptoms of atrial fibrillation (AF)? 3 Normal heartbeat 4 How common
Evaluation of Syncope
 Evaluation of Syncope W. Richard Bukata, MD Clinical Professor Emergency Medicine at the Los Angeles County / University of Southern Calilomia Medical Center; Medical Director of the Emergency Department
Evaluation of Syncope W. Richard Bukata, MD Clinical Professor Emergency Medicine at the Los Angeles County / University of Southern Calilomia Medical Center; Medical Director of the Emergency Department
Cardiology ICD-10-CM Coding Tip Sheet Overview of Key Chapter Updates for Cardiology
 Cardiology ICD-10-CM Coding Tip Sheet Overview of Key Chapter Updates for Cardiology Chapter 4: Endocrine, Nutritional, and Metabolic Diseases (E00-E89) The diabetes mellitus codes are combination codes
Cardiology ICD-10-CM Coding Tip Sheet Overview of Key Chapter Updates for Cardiology Chapter 4: Endocrine, Nutritional, and Metabolic Diseases (E00-E89) The diabetes mellitus codes are combination codes
