Physiotherapy treatment in cystic fibrosis: airway clearance techniques
|
|
|
- Evelyn Mitchell
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Physiotherapy treatment in cystic fibrosis: airway clearance techniques Factsheet March 2013
2 Physiotherapy treatment in cystic fibrosis: airway clearance techniques Introduction Looking after the chest and keeping the lungs clear is an extremely important part of the care of cystic fibrosis (CF). Over the years many different treatment techniques have been developed in order to help with this. This factsheet explains why it is important to keep the lungs clear and the various airway clearance techniques available. There are also many other important aspects of physiotherapy in cystic fibrosis and a number of other factsheets are available from the Cystic Fibrosis Trust which deal with issues such as exercise, and physiotherapy in babies and children. Written by S. Ammani Prasad, MCSP, Tamara Orska, MCSP, Kate Ferguson, MCSP, Penny Agent, MCSP and Mary Dodd, FCSP on behalf of the Association of Chartered Physiotherapists in Cystic Fibrosis. Updated by Elaine Dhouieb MCSP and Alison Gates MCSP. Last reviewed February
3 Contents How the lungs work 4 How CF can affect the lungs 5 Keeping the lungs clear 5 How much airway clearance is needed? 5 Airway clearance techniques 6 Active cycle of breathing techniques 6 Postural drainage and percussion 7 Autogenic drainage 8 High frequency chest wall oscillation 9 Positive expiratory pressure (PEP) 9 Oscillating PEP devices 9 Other important aspects of chest care in CF 10 Physical activity 10 Inhalation therapy 11 Oxygen therapy 12 Non-invasive ventilation 12 Infection control 12 Further information 12 3
4 How the lungs work The purpose of the lungs is to transfer oxygen from air we breathe into our blood. Our blood then transports the oxygen to the tissues and organs of our bodies, which need oxygen to function. The lungs start at the back of the throat with the windpipe (trachea), which then divides into two airways (tubes), one going in to each lung. In each lung, the airways branch in a tree-like manner and get smaller in diameter. Eventually, they form small air sacs called alveoli at the edge of the chest. Intertwined with the smallest airways and air sacs are lots of tiny blood vessels called capillaries. Oxygen from the air we breathe in is transferred from the air sacs into the blood in the capillaries. At the same time waste gases are transferred from the blood into the airways and expelled as we breathe out. The lining of the airways continually produce mucus, to keep the airways moist and to trap dust and debris that may enter the lungs. The airways are also lined with microscopic hairs (cilia) which move the mucus up to the throat, allowing it to be cleared. Your lungs 4
5 How cystic fibrosis can affect the lungs In cystic fibrosis the mucus produced by the lungs is stickier than normal, and CF lungs are more prone to infection. Infection in the lungs also leads to swelling of the airways and this makes the airway tubes narrower. The airways react to the swelling by producing more mucus. All of these factors can make it harder for patients with cystic fibrosis to clear mucus from their lungs. Repeated infections cause irreversible damage to the lung tissue. Thicker mucus Bacterial infection Inflammation of the airways Increased mucus produced Repeated infection Chronic lung damage Keeping the lungs clear Chest physiotherapy uses airway clearance techniques to help to clear excess thick sticky mucus from the lungs. It is important to try and clear these secretions as they increase the problems with infection / inflammation and can block the smaller airways, which can result in the lungs not being able to work effectively. In addition to chest physiotherapy, antibiotics and inhaled medicines that help to open the airways and thin the mucus (mucolytics) are also used to help keep the chest clear. How much airway clearance is needed? The amount of treatment needed depends very much on the individual. The physiotherapist will help to decide how much treatment is needed and how often. Once the lungs become productive, airway clearance treatment is usually needed on a daily basis, and may be required up to three-four times a day if there is active infection. However, when well treatment will be needed less frequently once or twice a day. The length of each treatment session will again vary according to need. Sessions may only be minutes when there are only small amounts of secretions, however longer treatments will be necessary if there is a lot of sputum to be cleared. The type of treatment will alter over time, as various techniques are more suitable for different ages and at different stages of the disease process. The physiotherapist will continue to monitor this and change treatment as necessary. It is therefore very important that everyone with cystic fibrosis is regularly reviewed by a specialist physiotherapist. 5
6 Airway clearance techniques The following section is a basic guide to the most commonly used physiotherapy techniques in the UK. Which technique is used for any one person depends on many factors and the physiotherapist will help to decide on the most suitable technique. It is very important that your airway clearance programme is monitored regularly by the physiotherapist. It is likely that you will use more than one method of treatment over time, as you get older and if there are changes to the way your lungs are affected. The techniques below are not discussed in any particular order, and no single technique has been shown to be more effective than the others. Active cycle of breathing techniques The active cycle of breathing techniques (ACBT) consists of a combination of: Breathing Control (BC) This is a period of relaxed breathing. It is a very important part of this technique as it allows pauses for rest and helps avoid any tightening of the airways, which can make it difficult to clear secretions. The upper chest should remain relaxed with most of the movement occuring in the lower chest. The length of time spent on breathing control depends on the individual. The physiotherapist will advise you on timings. Thoracic Expansion Exercises (TEE) These are also known as deep breathing exercises. They help the lungs to expand more effectively and allow air to get behind any secretions so that they can then be pushed up the airways towards the mouth. The breath in should be slow and deep. At the end of the breath in, the breath is held for a few seconds. Breathing out is relaxed and quiet. TEE are sometimes accompanied by percussion or vibrations (see below) but this may not be necessary. The Forced Expiration Technique (FET) This technique consists of huffing and must be combined with breathing control. It helps to move secretions from the smaller to the larger airways from where they can be cleared more easily. A medium sized breath in is followed by a forced, but not violent, breath out (often called a huff). It should be made by squeezing the abdominal/ tummy muscles while keeping the mouth and throat open - just as if trying to steam up a mirror with your breath. Huffing at different levels can move secretions in different parts of the lungs, your physiotherapist will teach you about this. One or two huffs are followed by a period of breathing control. Often a huff is not sufficient to clear the secretions completely and therefore it is necessary to cough afterwards. Coughing should not be very forced or go on for a long time. If secretions are not cleared after one or two coughs, then the ACBT should be resumed until they are higher up and can be cleared more easily. 6
7 The ACBT can be performed in sitting or in positions as described later. The cycle of different breathing techniques can be repeated until the chest is clear or a period of rest is needed. The physiotherapist will give advice regarding how many cycles are needed and the length of treatment. Positioning Your physiotherapist may advise using different positions or postural drainage during airway clearance. Postural drainage Gravity assisted positioning, often called postural drainage (PD), uses different body positions to help the drainage of secretions from particular areas of the lungs and also helps to increase the air movement or ventilation to different parts of the lungs. It is often used in conjunction with other techniques e.g. ACBT or percussion, and can be used in adults or children to treat more specific areas of the lung if this is necessary. In babies, your physiotherapist may suggest routine daily treatment consisting of about 5 minutes in each position, this may be one session in all 4 positions, or two sessions with two positions per session. In the presence of infection or increased secretions then more frequent and longer treatment may be required. For those babies with no chest problems, routine daily treatment may not be necessary, but treatment will always be required whenever the baby has any signs of increased cough or infection. In older children and adults more specific postural drainage positions may be used. Again, the physiotherapist will teach and advise which of these are necessary for an individual using this technique. In some cases, tipping may be advised which involves lying with the head lower than the chest in a tipped position. Some people find tipping uncomfortable as it makes them breathless, and some do not find it a particularly useful addition to their treatment. There is some concern that using a head down tipped position might increase the reflux of food from the stomach (particularly in babies). In view of this, many CF centres now use a modified type of PD where the head down tip is not used. The specialist physiotherapist at your Centre will advise you whether or not to use a head down tip for physiotherapy. If PD is being used it should always be undertaken at least one hour after food, to reduce the risk of reflux of stomach contents. Positioning Your physiotherapist may advise lying on either side, your front and back and sitting rather than specific postural drainage positions. 7
8 Percussion and vibration Percussion This technique is also known as chest clapping, and is used to help loosen secretions. It is usually combined with modified PD or PD and is sometimes also used during the Thoracic Expansion Exercise phase of the ACBT. To perform percussion a cupped hand is used to clap the chest firmly and rhythmically (over a layer of clothing or a towel). This is usually undertaken by a parent or carer although some people do it themselves. Parents are often taught this technique (combined with modified PD) when their baby is first diagnosed with cystic fibrosis. Many babies quite enjoy having percussion and it is not painful or uncomfortable. Vibrations/ Chest shaking This technique consists of several short rhythmical squeezes to the chest wall as the child/adult breathes out. Some people find this to be helpful in mobilising secretions. Like percussion, vibrations/chest shaking is sometimes used with TEE (in ACBT). Autogenic drainage Autogenic drainage (AD) is a series of breathing exercises which aims to use high flows of air to move secretions from the smaller airways, up into the larger airways so they can be cleared with as little effort as possible. AD consists of three different phases of breathing: 1. A mobilising phase 2. A collecting phase 3. A clearing phase By breathing at different levels, secretions can be moved from different parts of the airways. Secretions lower down in the airways are mobilised by breathing at a lower lung volumes (i.e. with only a small amount of air in the lungs). By then breathing at higher lung volumes (with a larger amount of air in the lungs), secretions which have mobilised higher up into the airways can then be moved and cleared. The breathing technique (whichever lung volume is being used) consists of a slow breath in followed by a pause, where the breath is then held for a few seconds. This allows air to fill the lungs more effectively improving ventilation). The breath out is active but in a sighing manner and should not be forced. As secretions move higher, crackles should be heard or felt. Once the secretions have been moved to a higher level they can be cleared with a gentle huff. The technique can then be continued until the chest feels clear or as clear as possible. This technique should be taught by a physiotherapist who has been trained in AD. AD can be used in children and adults, some physiotherapists also use an assisted form of AD in babies. 8
9 High Frequency Chest Wall Oscillation HFCWO (sometimes know as Vest therapy) has been used in the USA for many years. It is now available to purchase in the UK. The equipment consists of an electric air compressor which is connected to an inflatable jacket The compressor sends pulses of air into the jacket, which vibrates the chest wall and lungs within. These vibrations help to move sputum within the lungs. Although this equipment is now available in the UK, it is generally not widely used. Vest therapy is a useful technique in some patients, however it has not been shown to be of significantly more benefit than any other techniques. Positive Expiratory Pressure Positive expiratory pressure (PEP) is a technique that applies a back pressure to the airways during the breath out. This helps to open up airways and get air behind secretions to help move them higher up the airway. A number of PEP devices are available, some have a mask and some a mouthpiece. The PEP device gives a small degree of resistance to the breath out and this resistance splints open the airways. Treatment is usually done in sitting with the elbows supported, however with some of the devices a postural drainage position may also be incorporated. After 8-12 breaths through the PEP device, one or two huffs or a huff and a cough, with breathing control are used to clear the secretions. The PEP cycle is repeated until the chest feels clear. The PEP system needs to be reviewed regularly at clinic visits, as the amount of resistance used may need to be altered from time to time to ensure that an adequate pressure is being used. Sometimes a slightly different technique of PEP (high pressure PEP) is used where the last breath out through the device is forced and long to produce a greater back pressure. This is a specialist technique which needs careful assessment and teaching. Bubble PEP is another modification of PEP and is very useful in young children. It uses exactly the same action as PEP described above, but instead of using a mask or mouthpiece the child blows out through a length of plastic tubing placed in a bottle of water and soap to produce lots of bubbles. This is a fun way of getting small children to do PEP therapy. Oscillating positive expiratory pressure devices (Oscillating PEP) These devices combine vibration of the airways with PEP. Several different devices are available for this type of treatment and the physiotherapist will help to decide which one is most suitable for each patient. The devices include: The Flutter The Acapella The Cornet 9
10 The Flutter The Flutter is a small pipe shaped device which contains a metal ball in a cone. During the breath out the ball moves up and down in the cone. This interrupts the flow of air and gives an intermittent back pressure to the airways as well as causing them to vibrate. Flutter treatment is usually done in sitting. The angle at which the Flutter is held will change the area where the vibrations are felt and so it should be held at an angle where maximum vibrations are felt within the chest. The physiotherapist will advice on the best way to use the flutter, but usually the treatment combines cycles of normal breaths followed by one or two big and active breaths out through the device. The Cornet The Cornet consists of a curved hard plastic tube within which sits a soft flexible rubber tube. It works in a very similar way as the flutter, producing a vibration and PEP effect in the airways. The degree of PEP and vibration can be altered by changing the twist in the rubber tube. The Cornet can be used in any treatment position and like the flutter a combination of breathing techniques are used to help to move and clear secretions. The Acapella The Acapella device also works in a very similar way to the flutter. It consists of a plastic outer shell, inside which is a lever and magnets. The lever action and the attraction between the magnets during the breath out provide the vibration and PEP. The degree of PEP and vibration can be altered by a dial at the end of the device. Treatment can take place in any position and is very similar to that of the Flutter. Thorough, daily cleaning and drying is vital for all devices as unwashed devices can harbour bacteria. There will be individual cleaning instructions for different devices. Other important aspects of chest care in cystic fibrosis Physical activity Physical exercise is an essential part of the management of cystic fibrosis. As well as having beneficial effects on fitness levels, muscles, bone structure and posture it also complements airway clearance and helps to keep the chest clear. A separate factsheet that offers advice and explains the benefits of exercise is available from the Cystic Fibrosis Trust (see back page for contact details). Some children and adults use a combination of exercise and airway clearance for their physiotherapy. 10
11 Inhalation therapy A range of inhaled drugs may be prescribed as part of the daily management of cystic fibrosis. These may include bronchodilators (to open the airways), nebulised antibiotics (to help fight infection), mucolytics (to thin sputum e.g. DNase [Pulmozyme]), expectorants (to clear sputum e.g. hypertonic saline) and inhaled steroids (see the Cystic Fibrosis Trust factsheet Nebuliser therapy in cystic fibrosis). The order in which these medications are taken in is usually assessed on an individual basis and the physiotherapist will advise you about this. Bronchodilators are usually taken before airway clearance and antibiotics after airway clearance. The exact timing for taking DNase (Pulmozyme) does vary but in general, it should always be taken at least 30 minutes before physiotherapy (but preferably longer, sometimes it is taken just after the morning physiotherapy session so that it can act in the lungs for a longer period of time). However it is recommended that DNase is NOT taken within 30 minutes of an inhaled antibiotic, to prevent the medication being inactivated. It is important that any medications that are inhaled are able to get in to the airways in order to be effective. These medicines are given using either an inhaler or via a nebuliser system. Inhaler devices Various devices are available for a range of drugs. Some devices are combined with a spacer to improve delivery. The drugs commonly given via inhaler are bronchodilators and inhaled steroids. However, in future antibiotics will be available via this method. Nebuliser systems Traditional nebuliser systems consist of an air compressor with a separate nebuliser unit in which the liquid drug is placed. Different types of drug require separate nebuliser chambers. There have been many developments in nebuliser systems and there are now a wide variety of devices available. The latest of these are small, hand held, battery driven, efficient in terms of delivery time and quiet.. These devices often combine an air compressor and nebuliser system in one, resulting in a single hand-held device. Drugs commonly nebulised are bronchodilators, antibiotics, DNase and other mucolytics (to thin sputum). Whichever device is prescribed, the CF nurse or physiotherapist should teach you how to use it properly. However, some general points to remember are: The order in which medications are taken needs to be assessed individually. Babies and small children may need to use masks with devices, although mouthpieces should be introduced as early as possible. A mask may need to be used for nebulised antibiotics if there is severe sinus disease or after lung/heart-lung transplant. Thorough, daily cleaning and drying is vital for all devices as unwashed devices can harbour bacteria or the device may become blocked and not work effectively. Different nebuliser chambers may be needed for different drugs 11
12 Oxygen therapy As lung problems worsen and the lungs become less efficient at taking in enough oxygen, it may be necessary for some people to use oxygen therapy. This will happen at different times for different people, and at first oxygen may only be required during an infection, during exercise or for use at night time. Later it may be need for longer periods. Oxygen is an extremely helpful therapy and it can make a huge difference to how well you feel and how much you can do during the day. The CF team will monitor things very closely and use various tests to decide if and when oxygen needs to be started (these include exercise tests, and sleep studies). Oxygen can be given via a variety of masks or nasal cannulae. Small oxygen cylinders and other portable oxygen devices can be provided so that it is still relatively easy to get out and about. In the home, an oxygen concentrator machine may be installed to provide a regular supply of oxygen. Non-invasive ventilation With worsening lung disease, some people may need to use non-invasive ventilation (NIV) to help with their breathing. This is normally used when there is a build up of carbon dioxide (waste gas) and oxygen levels are low. Sometimes NIV is used overnight or at other times it is used to assist with airway clearance. In a very few cases, people need to breath with the assistance of NIV for the majority of the day and night. NIV can be used with a mouthpiece, nose or face-mask. Whenever it is started, a full explanation is essential and the machine settings need to be checked regularly. Even when using NIV, it is possible to talk, eat and drink although care should be taken when eating and drinking while using the machine. Infection control Every specialist CF centre and clinic will have their own Infection Control Policy to minimize the risk of cross infection between you and others with cystic fibrosis and to prevent the spread of CF organisms. Some centres and clinics segregate their outpatient clinics. This might mean that you are not moved around the clinic to see the various members of the team but are shown to one room where all the team will come to see you, or the clinic may segregate according to the organism grown in your sputum. Special attention should be paid at all times by you and your physiotherapist when handling sputum during airway clearance and exercise. These treatments will always be performed in a separate area away from other people with cystic fibrosis. Personal hygiene e.g. handwashing, covering your nose and mouth when coughing and sneezing and disposing of tissues and sputum pots in appropriate waste bins, all help to prevent cross infection. Any equipment given to you will be for your own personal use and should not be shared with others. The CF Trust also provides guidelines about the potential risks away from the hospital and these are available directly from the Trust. If you have any concerns or worries you should speak to your CF consultant, specialist nurse and physiotherapist. 12
13 Further information The Cystic Fibrosis Trust provides information about cystic fibrosis through our factsheets, leaflets and other publications. Most of our publications can be downloaded from our website ordered using our online publications order form. Visit Alternatively, to order hard copies of our publications you can telephone the CF Trust on If you would like further information about cystic fibrosis please contact: Cystic Fibrosis Trust 11 London Road Bromley Kent BR1 1BY T cysticfibrosis.org.uk enquiries@cysticfibrosis.org.uk Helpline We would welcome your feedback on this or any other of our publications. Please publications@cysticfibrosis.org.uk. More factsheets available at: cysticfibrosis.org.uk/publications Cystic Fibrosis Trust This factsheet may be copied in whole or in part, without prior permission being sought from the copyright holder, provided the purpose of copying is not for commercial gain and due acknowledgement is given. The information included in this publication is not intended to replace any advice you may receive from your doctor or CF multidisciplinary team and it is important that you seek medical advice whenever considering a change of treatment. Cystic Fibrosis Trust, registered as a charity in England and Wales ( ) and in Scotland (SC040196). A company limited by guarantee, registered in England and Wales number Registered office: 11 London Road, Bromley, Kent BR1 1BY.
Active Cycle of Breathing Technique
 Patient Information Leaflet Physiotherapy Department Active Cycle of Breathing Technique Derriford Hospital Derriford Road Plymouth PL6 8DH Tel: 0845 155 8155 www.plymouthhospitals.nhs.uk Active Cycle
Patient Information Leaflet Physiotherapy Department Active Cycle of Breathing Technique Derriford Hospital Derriford Road Plymouth PL6 8DH Tel: 0845 155 8155 www.plymouthhospitals.nhs.uk Active Cycle
Urinary incontinence
 Urinary incontinence Factsheet March 2013 Urinary incontinence Introduction Women and girls with cystic fibrosis (CF) are more likely to experience urinary incontinence (UI) than the healthy population.
Urinary incontinence Factsheet March 2013 Urinary incontinence Introduction Women and girls with cystic fibrosis (CF) are more likely to experience urinary incontinence (UI) than the healthy population.
Medication and Devices for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
 Medication and Devices for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Patients with COPD take a wide variety of medicines to manage their symptoms these include: Inhaled Short Acting Bronchodilators
Medication and Devices for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Patients with COPD take a wide variety of medicines to manage their symptoms these include: Inhaled Short Acting Bronchodilators
Better Breathing with COPD
 Better Breathing with COPD People with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) often benefit from learning different breathing techniques. Pursed Lip Breathing Pursed Lip Breathing (PLB) can be very
Better Breathing with COPD People with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) often benefit from learning different breathing techniques. Pursed Lip Breathing Pursed Lip Breathing (PLB) can be very
Breathing Exercises and Clearing Your Chest
 Information for patients Breathing Exercises and Clearing Your Chest Physiotherapy Department Tel: 01473 702073 DMI ref: 1898-08.indd(RP) Issue 1: October 2008 The Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust, 2008. All
Information for patients Breathing Exercises and Clearing Your Chest Physiotherapy Department Tel: 01473 702073 DMI ref: 1898-08.indd(RP) Issue 1: October 2008 The Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust, 2008. All
Whooping Cough. The Lungs Whooping cough is an infection of the lungs and breathing tubes, both of which are parts of the respiratory system.
 Whooping Cough Introduction Whooping cough is a serious bacterial infection of the lungs and breathing tubes. It is also called pertussis. About 16 million cases of whooping cough happen worldwide each
Whooping Cough Introduction Whooping cough is a serious bacterial infection of the lungs and breathing tubes. It is also called pertussis. About 16 million cases of whooping cough happen worldwide each
Help Yourself Breathe. Tender Loving Care for Your Lungs. Department of Physiotherapy. PD 1359 (Rev 06-2009) File: peyles
 Help Yourself Breathe Tender Loving Care for Your Lungs PD 1359 (Rev 06-2009) File: peyles Department of Physiotherapy Why are you breathless? Chronic Airflow Limitation or Obstruction is a decrease in
Help Yourself Breathe Tender Loving Care for Your Lungs PD 1359 (Rev 06-2009) File: peyles Department of Physiotherapy Why are you breathless? Chronic Airflow Limitation or Obstruction is a decrease in
About lung cancer. Contents. The lungs
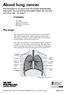 This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding lung cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 7. The lungs Contents The lungs Types of lung cancer
This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding lung cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 7. The lungs Contents The lungs Types of lung cancer
What You Should Know About ASTHMA
 What You Should Know About ASTHMA 200 Hospital Drive Galax, VA 24333 (276) 236-8181 www.tcrh.org WHAT IS ASTHMA? It s a lung condition that makes breathing difficult. The cause of asthma is not known.
What You Should Know About ASTHMA 200 Hospital Drive Galax, VA 24333 (276) 236-8181 www.tcrh.org WHAT IS ASTHMA? It s a lung condition that makes breathing difficult. The cause of asthma is not known.
How to Do Chest Physical Therapy (CPT) Babies and Toddlers
 How to Do Chest Physical Therapy (CPT) Babies and Toddlers (2001, 2004, 2009) The Emily Center, Phoenix Children s Hospital 1 2 (2001, 2004, 2009) The Emily Center, Phoenix Children s Hospital Name of
How to Do Chest Physical Therapy (CPT) Babies and Toddlers (2001, 2004, 2009) The Emily Center, Phoenix Children s Hospital 1 2 (2001, 2004, 2009) The Emily Center, Phoenix Children s Hospital Name of
Stem cell transplant, you and your rehabilitation Information for patients and their carers
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Physiotherapy department Stem cell transplant, you and your rehabilitation Information for patients and their carers Stem cell transplant exercise handout Thank you
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Physiotherapy department Stem cell transplant, you and your rehabilitation Information for patients and their carers Stem cell transplant exercise handout Thank you
Emphysema. Introduction Emphysema is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD. COPD affects about 64 million people worldwide.
 Emphysema Introduction Emphysema is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD. COPD affects about 64 million people worldwide. Emphysema involves damage to the air sacs in the lungs. This
Emphysema Introduction Emphysema is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD. COPD affects about 64 million people worldwide. Emphysema involves damage to the air sacs in the lungs. This
Lesson 7: Respiratory and Skeletal Systems and Tuberculosis
 Glossary 1. asthma: when the airways of the lungs narrow, making breathing difficult 2. bacteria: tiny living creatures that can only be seen with a microscope; some bacteria help the human body, and other
Glossary 1. asthma: when the airways of the lungs narrow, making breathing difficult 2. bacteria: tiny living creatures that can only be seen with a microscope; some bacteria help the human body, and other
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is the name for a group of lung diseases including chronic bronchitis, emphysema and chronic obstructive airways
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is the name for a group of lung diseases including chronic bronchitis, emphysema and chronic obstructive airways
Cystic fibrosis and bone health
 Cystic fibrosis and bone health Factsheet March 2013 Cystic fibrosis and bone health Introduction As we get older our bones become thinner and weaker, and may become more susceptible to fracture. However
Cystic fibrosis and bone health Factsheet March 2013 Cystic fibrosis and bone health Introduction As we get older our bones become thinner and weaker, and may become more susceptible to fracture. However
Physiotherapy for COPD. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Healthcare you can Trust. Pulmonary Rehabilitation
 Pulmonary Rehabilitation Pulmonary rehabilitation is a course of exercise and education designed to help people with COPD get fitter, cope with their symptoms and understand their condition better. Evidence
Pulmonary Rehabilitation Pulmonary rehabilitation is a course of exercise and education designed to help people with COPD get fitter, cope with their symptoms and understand their condition better. Evidence
Your Lungs and COPD. Patient Education Pulmonary Rehabilitation. A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs
 Patient Education Your Lungs and COPD A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs Your lungs are organs that process every breath you take. They provide oxygen (O 2 ) to the blood and
Patient Education Your Lungs and COPD A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs Your lungs are organs that process every breath you take. They provide oxygen (O 2 ) to the blood and
There is no cure for COPD Chronic Bronchitis Emphysema
 Live Well With COPD Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, or COPD is a lung disease. People with COPD have a hard time getting air in and out of their lungs. There is no cure for COPD. COPD is also commonly
Live Well With COPD Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, or COPD is a lung disease. People with COPD have a hard time getting air in and out of their lungs. There is no cure for COPD. COPD is also commonly
Pneumonia Education and Discharge Instructions
 Pneumonia Education and Discharge Instructions Pneumonia Education and Discharge Instructions Definition: Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs. Many different organisms can cause it, including bacteria,
Pneumonia Education and Discharge Instructions Pneumonia Education and Discharge Instructions Definition: Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs. Many different organisms can cause it, including bacteria,
Physiotherapy for Video Assisted Thoracic Surgery Patients
 Physio for VATS patients Royal Devon and Exeter NHS Foundation Trust Physiotherapy for Video Assisted Thoracic Surgery Patients July 2008 (Review date: July 2011) Physiotherapy Department...01392 402438
Physio for VATS patients Royal Devon and Exeter NHS Foundation Trust Physiotherapy for Video Assisted Thoracic Surgery Patients July 2008 (Review date: July 2011) Physiotherapy Department...01392 402438
Understanding COPD. An educational health series from
 Understanding COPD An educational health series from Our Mission since 1899 is to heal, to discover, and to educate as a preeminent healthcare institution. We serve by providing the best integrated and
Understanding COPD An educational health series from Our Mission since 1899 is to heal, to discover, and to educate as a preeminent healthcare institution. We serve by providing the best integrated and
Asthma and COPD Awareness
 Asthma and COPD Awareness Molina Breathe with Ease sm and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Molina Healthcare of Michigan Fall 2012 Importance of Controller Medicines Asthma is a disease that causes
Asthma and COPD Awareness Molina Breathe with Ease sm and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Molina Healthcare of Michigan Fall 2012 Importance of Controller Medicines Asthma is a disease that causes
Lung Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand lung cancer and the treatment options that are available.
 Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Keeping your lungs healthy
 Keeping your lungs healthy A guide for you after spinal cord injury and other neurological conditions Regional Rehabilitation Program This booklet has been written by the health care providers who provide
Keeping your lungs healthy A guide for you after spinal cord injury and other neurological conditions Regional Rehabilitation Program This booklet has been written by the health care providers who provide
These factors increase your chance of developing emphysema. Tell your doctor if you have any of these risk factors:
 Emphysema Pronounced: em-fiss-see-mah by Debra Wood, RN En Español (Spanish Version) Definition Emphysema is a chronic obstructive disease of the lungs. The lungs contain millions of tiny air sacs called
Emphysema Pronounced: em-fiss-see-mah by Debra Wood, RN En Español (Spanish Version) Definition Emphysema is a chronic obstructive disease of the lungs. The lungs contain millions of tiny air sacs called
Call Your Home Health Nurse and/or Physician. Call 911. Self Management for COPD COMMUNITY HEALTH AND COUNSELING SERVICES
 COMMUNITY HEALTH AND COUNSELING SERVICES Self Management for COPD Call Your Home Health Nurse and/or Physician Call 911 Sputum (phlegm) that increases in amount/color or becomes thicker than usual Unrelieved
COMMUNITY HEALTH AND COUNSELING SERVICES Self Management for COPD Call Your Home Health Nurse and/or Physician Call 911 Sputum (phlegm) that increases in amount/color or becomes thicker than usual Unrelieved
In case of an urgent concern or emergency, call 911 or go to the nearest emergency department right away.
 Asthma Basics Patient and Family Education This teaching sheet contains general information only. Talk with your child s doctor or a member of your child s healthcare team about specific care of your child.
Asthma Basics Patient and Family Education This teaching sheet contains general information only. Talk with your child s doctor or a member of your child s healthcare team about specific care of your child.
X-Plain Pediatric Tuberculosis Reference Summary
 X-Plain Pediatric Tuberculosis Reference Summary Introduction Tuberculosis, or TB, is a bacterial infection that causes more deaths in the world than any other infectious disease. When a child gets TB,
X-Plain Pediatric Tuberculosis Reference Summary Introduction Tuberculosis, or TB, is a bacterial infection that causes more deaths in the world than any other infectious disease. When a child gets TB,
Asthma Care. Of course, your coach is there to answer any questions you have about your asthma, such as:
 Asthma Care All Health Coaches in the Asthma Care Management program are registered or certified respiratory therapists. Your coach will listen to your story of living with asthma. This will help your
Asthma Care All Health Coaches in the Asthma Care Management program are registered or certified respiratory therapists. Your coach will listen to your story of living with asthma. This will help your
Living with a lung condition:
 Living with a lung condition: how exercise and eating well can make a difference to your life This information is for people living with a lung condition in the UK and your family and carers. It will help
Living with a lung condition: how exercise and eating well can make a difference to your life This information is for people living with a lung condition in the UK and your family and carers. It will help
Controlling symptoms of mesothelioma
 Controlling symptoms of mesothelioma This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding mesothelioma. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 9. Contents
Controlling symptoms of mesothelioma This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding mesothelioma. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 9. Contents
CT scan. Useful information. Contents. This information is about CT scans. There are sections on
 CT scan Useful information Contents This information is about CT scans. There are sections on How a CT scanner works What happens Preparation for the scan Abdominal CT scans CT scans of the head CT scans
CT scan Useful information Contents This information is about CT scans. There are sections on How a CT scanner works What happens Preparation for the scan Abdominal CT scans CT scans of the head CT scans
School and cystic fibrosis A guide for teachers and parents
 School and cystic fibrosis A guide for teachers and parents Factsheet March 2013 School and cystic fibrosis. A guide for teachers and parents Introduction This guide aims to provide information about all
School and cystic fibrosis A guide for teachers and parents Factsheet March 2013 School and cystic fibrosis. A guide for teachers and parents Introduction This guide aims to provide information about all
TB CARE EARLY DETECTION AND PREVENTION OF TUBERCULOSIS (TB) IN CHILDREN. Risk factors in children acquiring TB:
 EARLY DETECTION AND PREVENTION OF TUBERCULOSIS (TB) IN CHILDREN Risk factors in children acquiring TB: Children living in the same household as a lung TB patient (especially children under 5) Children
EARLY DETECTION AND PREVENTION OF TUBERCULOSIS (TB) IN CHILDREN Risk factors in children acquiring TB: Children living in the same household as a lung TB patient (especially children under 5) Children
online version Understanding Indwelling Urinary Catheters and Drainage Systems Useful information When to call for help
 When to call for help This will depend on the individual situation, but usually help should be sought if any of the following occurs: 1. The catheter does not start to drain, despite trying the problem
When to call for help This will depend on the individual situation, but usually help should be sought if any of the following occurs: 1. The catheter does not start to drain, despite trying the problem
Treating Mesothelioma - A Quick Guide
 Treating Mesothelioma - A Quick Guide Contents This is a brief summary of the information on Treating mesothelioma from CancerHelp UK. You will find more detailed information on the website. In this information
Treating Mesothelioma - A Quick Guide Contents This is a brief summary of the information on Treating mesothelioma from CancerHelp UK. You will find more detailed information on the website. In this information
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
stretches and exercises
 stretches and exercises The enclosed sheets contain stretches and exercises which can be used to delay and minimise the development of contractures and deformities occurring in children with Duchenne muscular
stretches and exercises The enclosed sheets contain stretches and exercises which can be used to delay and minimise the development of contractures and deformities occurring in children with Duchenne muscular
On the Go with Oxygen
 On the Go with Oxygen Oxygen is in the air we breathe and is necessary to live. When we breathe in, oxygen enters the lungs and it goes into the blood. When the lungs cannot transfer enough oxygen into
On the Go with Oxygen Oxygen is in the air we breathe and is necessary to live. When we breathe in, oxygen enters the lungs and it goes into the blood. When the lungs cannot transfer enough oxygen into
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patient Guidebook
 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patient Guidebook The Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of the lungs and air passages. The lungs are the part of the body where gases are exchanged
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patient Guidebook The Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of the lungs and air passages. The lungs are the part of the body where gases are exchanged
written by Harvard Medical School COPD It Can Take Your Breath Away www.patientedu.org/copd
 written by Harvard Medical School COPD It Can Take Your Breath Away www.patientedu.org/copd What Is COPD? COPD stands for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. There are two major diseases included in
written by Harvard Medical School COPD It Can Take Your Breath Away www.patientedu.org/copd What Is COPD? COPD stands for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. There are two major diseases included in
Pneumonia. Pneumonia is an infection that makes the tiny air sacs in your lungs inflamed (swollen and sore). They then fill with liquid.
 Pneumonia Pneumonia is an infection that makes the tiny air sacs in your lungs inflamed (swollen and sore). They then fill with liquid. People with mild (not so bad) pneumonia can usually be treated at
Pneumonia Pneumonia is an infection that makes the tiny air sacs in your lungs inflamed (swollen and sore). They then fill with liquid. People with mild (not so bad) pneumonia can usually be treated at
Royal Manchester Children s Hospital. Asthma. Information For Parents and Carers. Ward: Ward Telephone Number: Consultant:
 Royal Manchester Children s Hospital Asthma Information For Parents and Carers Ward: Ward Telephone Number: Consultant: Understanding asthma Asthma is a common condition that affects approximately 1 in
Royal Manchester Children s Hospital Asthma Information For Parents and Carers Ward: Ward Telephone Number: Consultant: Understanding asthma Asthma is a common condition that affects approximately 1 in
Surgery for oesophageal cancer
 Surgery for oesophageal cancer This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding oesophageal cancer (cancer of the gullet). You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy
Surgery for oesophageal cancer This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding oesophageal cancer (cancer of the gullet). You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy
Fourth Grade The Human Body: The Respiratory System Assessment
 Fourth Grade The Human Body: The Respiratory System Assessment 1a. The brings air in and out of the body. a. respiratory system b. circulatory system 1b. The system is the part of the body responsible
Fourth Grade The Human Body: The Respiratory System Assessment 1a. The brings air in and out of the body. a. respiratory system b. circulatory system 1b. The system is the part of the body responsible
Tunnelled indwelling pleural catheter (TIPC)
 Tunnelled indwelling pleural catheter (TIPC) A patient s guide 1 What is a tunnelled indwelling pleural catheter? A tunnelled indwelling pleural catheter is a specially designed small tube to drain fluid
Tunnelled indwelling pleural catheter (TIPC) A patient s guide 1 What is a tunnelled indwelling pleural catheter? A tunnelled indwelling pleural catheter is a specially designed small tube to drain fluid
Asbestos and your lungs
 This information describes what asbestos is and the lung conditions that are caused by exposure to it. It also includes information about what to do if you have been exposed to asbestos, and the benefits
This information describes what asbestos is and the lung conditions that are caused by exposure to it. It also includes information about what to do if you have been exposed to asbestos, and the benefits
Oxford Centre for Respiratory Medicine Bronchial-Artery Embolisation Information for patients
 Oxford Centre for Respiratory Medicine Bronchial-Artery Embolisation Information for patients This leaflet tells you about the bronchial-artery embolisation procedure. It explains what is involved and
Oxford Centre for Respiratory Medicine Bronchial-Artery Embolisation Information for patients This leaflet tells you about the bronchial-artery embolisation procedure. It explains what is involved and
HEALTH EFFECTS. Inhalation
 Health Effects HEALTH EFFECTS Asbestos can kill you. You must take extra precautions when you work with asbestos. Just because you do not notice any problems while you are working with asbestos, it still
Health Effects HEALTH EFFECTS Asbestos can kill you. You must take extra precautions when you work with asbestos. Just because you do not notice any problems while you are working with asbestos, it still
Mesothelioma and Asbestos
 CANCER INFORMATION FACTSHEET Mesothelioma and Asbestos The information in this factsheet will help you to understand more about mesothelioma. It is an agreed view on this cancer by medical experts. We
CANCER INFORMATION FACTSHEET Mesothelioma and Asbestos The information in this factsheet will help you to understand more about mesothelioma. It is an agreed view on this cancer by medical experts. We
Information for Behavioral Health Providers in Primary Care. Asthma
 What is Asthma? Information for Behavioral Health Providers in Primary Care Asthma Asthma (AZ-ma) is a chronic (long-term) lung disease that inflames and narrows the airways. Asthma causes recurring periods
What is Asthma? Information for Behavioral Health Providers in Primary Care Asthma Asthma (AZ-ma) is a chronic (long-term) lung disease that inflames and narrows the airways. Asthma causes recurring periods
Kent Oncology Centre Radiotherapy Side Effects and Management: Breast and Chest Wall Information for patients Maidstone Hospital
 Kent Oncology Centre Radiotherapy Side Effects and Management: Breast and Chest Wall Information for patients We hope this leaflet will help you understand the side effects that may occur when having external
Kent Oncology Centre Radiotherapy Side Effects and Management: Breast and Chest Wall Information for patients We hope this leaflet will help you understand the side effects that may occur when having external
The Annual Direct Care of Asthma
 The Annual Direct Care of Asthma The annual direct health care cost of asthma in the United States is approximately $11.5 billion; indirect costs (e.g. lost productivity) add another $4.6 billion for a
The Annual Direct Care of Asthma The annual direct health care cost of asthma in the United States is approximately $11.5 billion; indirect costs (e.g. lost productivity) add another $4.6 billion for a
Respiratory Disorders
 Respiratory Disorders Teaching Plan To use this lesson for self-study, the learner should read the material, do the activity, and take the test. For group study, the leader may give each learner a copy
Respiratory Disorders Teaching Plan To use this lesson for self-study, the learner should read the material, do the activity, and take the test. For group study, the leader may give each learner a copy
What You And Your Family Can Do About Asthma
 GLOBAL INITIATIVE FOR ASTHMA What You And Your Family Can Do About Asthma BASED ON THE GLOBAL STRATEGY FOR ASTHMA MANAGEMENT AND PREVENTION NHLBI/WHO WORKSHOP REPORT NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH NATIONAL
GLOBAL INITIATIVE FOR ASTHMA What You And Your Family Can Do About Asthma BASED ON THE GLOBAL STRATEGY FOR ASTHMA MANAGEMENT AND PREVENTION NHLBI/WHO WORKSHOP REPORT NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH NATIONAL
COPD What Is It? Why is it so hard to catch my breath? What does COPD feel like? What causes COPD? What is an exacerbation (ig-zas-er-bay-shun)?
 Attitudes and Beliefs 4 COPD What Is It? Why is it so hard to catch my breath? COPD is a disease that damages the lungs. In a healthy lung, the airways are open and the air sacs fill up with air. Then
Attitudes and Beliefs 4 COPD What Is It? Why is it so hard to catch my breath? COPD is a disease that damages the lungs. In a healthy lung, the airways are open and the air sacs fill up with air. Then
Anxiety and breathing difficulties
 Patient information factsheet Anxiety and breathing difficulties Breathing is something that we all automatically do and we often take this for granted. Some chronic health conditions, for example asthma
Patient information factsheet Anxiety and breathing difficulties Breathing is something that we all automatically do and we often take this for granted. Some chronic health conditions, for example asthma
What If I Have a Spot on My Lung? Do I Have Cancer? Patient Education Guide
 What If I Have a Spot on My Lung? Do I Have Cancer? Patient Education Guide A M E R I C A N C O L L E G E O F C H E S T P H Y S I C I A N S Lung cancer is one of the most common cancers. About 170,000
What If I Have a Spot on My Lung? Do I Have Cancer? Patient Education Guide A M E R I C A N C O L L E G E O F C H E S T P H Y S I C I A N S Lung cancer is one of the most common cancers. About 170,000
Patient Information and Daily Programme for Patients Having Whipple s Surgery (Pancreatico duodenectomy)
 Patient Information and Daily Programme for Patients Having Whipple s Surgery (Pancreatico duodenectomy) Date of admission Date of surgery Expected Length of Stay in hospital We will aim to discharge you
Patient Information and Daily Programme for Patients Having Whipple s Surgery (Pancreatico duodenectomy) Date of admission Date of surgery Expected Length of Stay in hospital We will aim to discharge you
ASTHMA IN INFANTS AND YOUNG CHILDREN
 ASTHMA IN INFANTS AND YOUNG CHILDREN What is Asthma? Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways. Symptoms of asthma are variable. That means that they can be mild to severe, intermittent to
ASTHMA IN INFANTS AND YOUNG CHILDREN What is Asthma? Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways. Symptoms of asthma are variable. That means that they can be mild to severe, intermittent to
Current Features SPECIAL EDITION
 Lewis H. Walker Cystic Fibrosis Center January 1, 2010 Special Edition Inside this issue: Special Edition Explanation Identifying Pulmonary Exacerbations of CF: The Akron Pulmonary Exacerbation Score PES
Lewis H. Walker Cystic Fibrosis Center January 1, 2010 Special Edition Inside this issue: Special Edition Explanation Identifying Pulmonary Exacerbations of CF: The Akron Pulmonary Exacerbation Score PES
MANAGING BREATHLESSNESS
 12 Leaflet issued by: Pulmonary Rehabilitation Service Anglian Community Enterprise (CIC) Kennedy House Kennedy Way, Clacton-on-sea Essex CO15 4AB Tel: 01255 206263 MANAGING BREATHLESSNESS On request,
12 Leaflet issued by: Pulmonary Rehabilitation Service Anglian Community Enterprise (CIC) Kennedy House Kennedy Way, Clacton-on-sea Essex CO15 4AB Tel: 01255 206263 MANAGING BREATHLESSNESS On request,
Managing my Breathlessness
 James Paget University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Managing my Breathlessness Patient Information Contents Living with breathlessness 3 Battery life 4 How can I control my breathlessness? 5 Simple breathing
James Paget University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Managing my Breathlessness Patient Information Contents Living with breathlessness 3 Battery life 4 How can I control my breathlessness? 5 Simple breathing
Physiotherapie mit oszillierenden PEP-Systemen (RC-Cornet, VRP1 ) bei COPD
 Physiotherapie mit oszillierenden PEP-Systemen (RC-Cornet, VRP1 ) bei COPD U. H. Cegla Pneumologie-Zentrum, Dernbach Pneumologie 2; 54: Seite 44-446 Translation Physiotherapy with oscillating PEP systems
Physiotherapie mit oszillierenden PEP-Systemen (RC-Cornet, VRP1 ) bei COPD U. H. Cegla Pneumologie-Zentrum, Dernbach Pneumologie 2; 54: Seite 44-446 Translation Physiotherapy with oscillating PEP systems
CLINICAL GUIDELINES FOR THE PHYSIOTHERAPY MANAGEMENT OF CYSTIC FIBROSIS
 I N F O R M A T I O N CLINICAL GUIDELINES FOR THE PHYSIOTHERAPY MANAGEMENT OF CYSTIC FIBROSIS Association of Chartered Physiotherapists in Cystic Fibrosis (ACPCF) Recommendations of a Working Group Cystic
I N F O R M A T I O N CLINICAL GUIDELINES FOR THE PHYSIOTHERAPY MANAGEMENT OF CYSTIC FIBROSIS Association of Chartered Physiotherapists in Cystic Fibrosis (ACPCF) Recommendations of a Working Group Cystic
Understanding and Living with... Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease or COPD
 Understanding and Living with... Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease or COPD Understanding and Living with... Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease or COPD Contents Introduction 5 The Lungs 6 COPD 8
Understanding and Living with... Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease or COPD Understanding and Living with... Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease or COPD Contents Introduction 5 The Lungs 6 COPD 8
Pelvic Girdle Pain (PGP) Fact Sheet
 Pelvic Girdle Pain (PGP) Fact Sheet Physiotherapy PGP describes pain that is experienced in the front (symphysis pubis joint) and/or back (sacroiliac joints) of your pelvis. This is a common problem, affecting
Pelvic Girdle Pain (PGP) Fact Sheet Physiotherapy PGP describes pain that is experienced in the front (symphysis pubis joint) and/or back (sacroiliac joints) of your pelvis. This is a common problem, affecting
Mesothelioma and Asbestos
 Cancer information factsheet Mesothelioma and Asbestos The information in this factsheet will help you to understand more about mesothelioma. It is an agreed view on this cancer by medical experts. We
Cancer information factsheet Mesothelioma and Asbestos The information in this factsheet will help you to understand more about mesothelioma. It is an agreed view on this cancer by medical experts. We
Information for people being discharged with a naso-gastric (NG) feeding tube
 Information for people being discharged with a naso-gastric (NG) feeding tube The aim of this leaflet is to provide patients with the relevant information for the use of a nasogastric tube. It will include:
Information for people being discharged with a naso-gastric (NG) feeding tube The aim of this leaflet is to provide patients with the relevant information for the use of a nasogastric tube. It will include:
Spinal Cord and Bladder Management Male: Intermittent Catheter
 Spinal Cord and Bladder Management Male: Intermittent Catheter The 5 parts of the urinary system work together to get rid of waste and make urine. Urine is made in your kidneys and travels down 2 thin
Spinal Cord and Bladder Management Male: Intermittent Catheter The 5 parts of the urinary system work together to get rid of waste and make urine. Urine is made in your kidneys and travels down 2 thin
Undergoing an Oesophageal Endoscopic Resection (ER)
 Contact Information If you have an enquiry about your appointment time/date please contact the Booking Office on 0300 422 6350. For medication enquiries please call 0300 422 8232, this is an answer machine
Contact Information If you have an enquiry about your appointment time/date please contact the Booking Office on 0300 422 6350. For medication enquiries please call 0300 422 8232, this is an answer machine
Cough, as a leading symptom, would certainly be in the top 10 of reasons for seeing a GP.
 COUGH Cough, as a leading symptom, would certainly be in the top 10 of reasons for seeing a GP. A cough in a child seems to cause more concern, even when it has not been present very long, whereas in adults
COUGH Cough, as a leading symptom, would certainly be in the top 10 of reasons for seeing a GP. A cough in a child seems to cause more concern, even when it has not been present very long, whereas in adults
Your health care provider may prescribe bronchodilators such as albuterol for emergency relief if an acute asthma attack occurs.
 Patient Information ASMANEX TWISTHALER 220 mcg (mometasone furoate inhalation powder) ASMANEX TWISTHALER 110 mcg (mometasone furoate inhalation powder) FOR ORAL INHALATION ONLY Please read this leaflet
Patient Information ASMANEX TWISTHALER 220 mcg (mometasone furoate inhalation powder) ASMANEX TWISTHALER 110 mcg (mometasone furoate inhalation powder) FOR ORAL INHALATION ONLY Please read this leaflet
Breathing techniques to help breathlessness 1
 Breathing techniques to help breathlessness 1 Breathing techniques to help breathlessness This information is from the booklet Managing breathlessness. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send
Breathing techniques to help breathlessness 1 Breathing techniques to help breathlessness This information is from the booklet Managing breathlessness. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send
TOWN OF FAIRFIELD HEALTH DEPARTMENT PUBLIC HEALTH NURSING
 TOWN OF FAIRFIELD HEALTH DEPARTMENT PUBLIC HEALTH NURSING PROGRAM: School Health APPROVED BY: Board of Health School Medical Advisor POLICY: With Portable Suction Machine DATE: March 14, 1994 POLICY DEFINITION:
TOWN OF FAIRFIELD HEALTH DEPARTMENT PUBLIC HEALTH NURSING PROGRAM: School Health APPROVED BY: Board of Health School Medical Advisor POLICY: With Portable Suction Machine DATE: March 14, 1994 POLICY DEFINITION:
Treating Sleep Apnea A Review of the Research for Adults
 Treating Sleep Apnea A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, if: A doctor said you have mild, moderate, or severe obstructive sleep apnea, or OSA. People with OSA may
Treating Sleep Apnea A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, if: A doctor said you have mild, moderate, or severe obstructive sleep apnea, or OSA. People with OSA may
COPD PATIENT SUPPORT COPD PATIENT SUPPORT
 COPD COPD Exercise Your Lungs Daily Breathing Exercises to Help You Clear Your Chest Breaking the Cycle of Breathlessness This piece has been reviewed by COPD Support Ireland. If you have been diagnosed
COPD COPD Exercise Your Lungs Daily Breathing Exercises to Help You Clear Your Chest Breaking the Cycle of Breathlessness This piece has been reviewed by COPD Support Ireland. If you have been diagnosed
Tracheostomy Care at Home
 Tracheostomy Care at Home Patient Education CARE AND TREATMENT This information will help you understand how to care for a person with a tracheostomy at home. It is a supplement to the teaching offered
Tracheostomy Care at Home Patient Education CARE AND TREATMENT This information will help you understand how to care for a person with a tracheostomy at home. It is a supplement to the teaching offered
Support for breathing problems
 8A Support for breathing problems Information for people with or affected by motor neurone disease Motor neurone disease (MND) affects people in different ways. You are unlikely to have exactly the same
8A Support for breathing problems Information for people with or affected by motor neurone disease Motor neurone disease (MND) affects people in different ways. You are unlikely to have exactly the same
Steroid treatment in cystic fibrosis
 Steroid treatment in cystic fibrosis Factsheet March 2013 Steroid treatment in cystic fibrosis Introduction This factsheet contains information on steroid treatment in cystic fibrosis, including the different
Steroid treatment in cystic fibrosis Factsheet March 2013 Steroid treatment in cystic fibrosis Introduction This factsheet contains information on steroid treatment in cystic fibrosis, including the different
Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System Basic functions of the respiratory system: as a Gas exchange supply oxygen to aerobic tissues in the body and remove carbon dioxide waste product. in-
Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System Basic functions of the respiratory system: as a Gas exchange supply oxygen to aerobic tissues in the body and remove carbon dioxide waste product. in-
Mesothelioma. 1995-2013, The Patient Education Institute, Inc. www.x-plain.com ocft0101 Last reviewed: 03/21/2013 1
 Mesothelioma Introduction Mesothelioma is a type of cancer. It starts in the tissue that lines your lungs, stomach, heart, and other organs. This tissue is called mesothelium. Most people who get this
Mesothelioma Introduction Mesothelioma is a type of cancer. It starts in the tissue that lines your lungs, stomach, heart, and other organs. This tissue is called mesothelium. Most people who get this
Surgery for breast cancer in men
 Surgery for breast cancer in men This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding breast cancer in men. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 9. Contents
Surgery for breast cancer in men This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding breast cancer in men. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 9. Contents
X-Plain Foley Catheter Male Reference Summary
 X-Plain Foley Catheter Male Reference Summary Introduction A Foley catheter is a tube that is put through the urinary opening and into your bladder to drain urine. Your doctor may have placed or may ask
X-Plain Foley Catheter Male Reference Summary Introduction A Foley catheter is a tube that is put through the urinary opening and into your bladder to drain urine. Your doctor may have placed or may ask
COPD. Information brochure for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
 COPD Information brochure for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. CONTENTS What does COPD mean?...04 What are the symptoms of COPD?...06 What causes COPD?...09 Treating COPD...10 Valve therapy in COPD...12
COPD Information brochure for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. CONTENTS What does COPD mean?...04 What are the symptoms of COPD?...06 What causes COPD?...09 Treating COPD...10 Valve therapy in COPD...12
MRSA. Living with. Acknowledgements. (Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus)
 How can I keep myself healthy? Hand washing and use of an alcohol-based hand sanitizer are the primary way to prevent acquiring or transmitting bacteria. If you get a cut or scrape, wash it well with soap
How can I keep myself healthy? Hand washing and use of an alcohol-based hand sanitizer are the primary way to prevent acquiring or transmitting bacteria. If you get a cut or scrape, wash it well with soap
Oxygenation. Chapter 21. Anatomy and Physiology of Breathing. Anatomy and Physiology of Breathing*
 Oxygenation Chapter 21 Anatomy and Physiology of Breathing Inspiration ~ breathing in Expiration ~ breathing out Ventilation ~ Movement of air in & out of the lungs Respiration ~ exchange of O2 & carbon
Oxygenation Chapter 21 Anatomy and Physiology of Breathing Inspiration ~ breathing in Expiration ~ breathing out Ventilation ~ Movement of air in & out of the lungs Respiration ~ exchange of O2 & carbon
What is Balloon Sinuplasty?
 What is Balloon Sinuplasty? The painful symptoms associated with chronic sinusitis can be overwhelming. If symptoms are difficult to control with medications alone, your primary doctor may refer you to
What is Balloon Sinuplasty? The painful symptoms associated with chronic sinusitis can be overwhelming. If symptoms are difficult to control with medications alone, your primary doctor may refer you to
Thymus Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand what thymus cancer is and what treatment options are available.
 Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
HOW TO CARE FOR YOUR CATHETER (FEMALE)
 HOW TO CARE FOR YOUR CATHETER (FEMALE) Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What is a catheter? A catheter is a narrow flexible soft tube inserted into the bladder for the purpose
HOW TO CARE FOR YOUR CATHETER (FEMALE) Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What is a catheter? A catheter is a narrow flexible soft tube inserted into the bladder for the purpose
THORACIC DIAGNOSTIC ASSESMENT PROGRAM (DAP) PATIENT INFORMATION FOR:
 central east regional cancer program in partnership with cancer care ontario THORACIC DIAGNOSTIC ASSESMENT PROGRAM (DAP) PATIENT INFORMATION FOR: Thoracic dap booklet March2012.indd 1 SCHEDULED TESTS YOUR
central east regional cancer program in partnership with cancer care ontario THORACIC DIAGNOSTIC ASSESMENT PROGRAM (DAP) PATIENT INFORMATION FOR: Thoracic dap booklet March2012.indd 1 SCHEDULED TESTS YOUR
Chemotherapy for lung cancer
 This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding lung cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 8. Contents Chemoradiation Small cell lung cancer
This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding lung cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 8. Contents Chemoradiation Small cell lung cancer
Tuberculosis: FAQs. What is the difference between latent TB infection and TB disease?
 Tuberculosis: FAQs What is TB disease? Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease caused by bacteria (germs) that are spread from person to person through the air. TB usually affects the lungs, but it can also affect
Tuberculosis: FAQs What is TB disease? Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease caused by bacteria (germs) that are spread from person to person through the air. TB usually affects the lungs, but it can also affect
Advanced Lung Cancer Treatment - Chemotherapy vs Radiotherapy
 Which treatment for advanced lung cancer This information tells you about the treatments for advanced lung cancer. Chemotherapy and radiotherapy can both be used to treat advanced lung cancer. They can
Which treatment for advanced lung cancer This information tells you about the treatments for advanced lung cancer. Chemotherapy and radiotherapy can both be used to treat advanced lung cancer. They can
Pre-lab homework Lab 6: Respiration and Gas exchange
 Lab Section: Pre-lab homework Lab 6: Respiration and Gas exchange Name: 1. Name the organs used for gas exchange in each of the following organisms: Humans Fish Insects 2. What are three features common
Lab Section: Pre-lab homework Lab 6: Respiration and Gas exchange Name: 1. Name the organs used for gas exchange in each of the following organisms: Humans Fish Insects 2. What are three features common
Respiratory Health for People with Profound and Multiple Learning Disabilities www.pamis.org.uk
 Respiratory Health for People with Profound and Multiple Learning Disabilities www.pamis.org.uk Introduction Respiratory disease is consistently shown to be the leading cause of death for people with profound
Respiratory Health for People with Profound and Multiple Learning Disabilities www.pamis.org.uk Introduction Respiratory disease is consistently shown to be the leading cause of death for people with profound
UNDERGOING OESOPHAGEAL STENT INSERTION
 UNDERGOING OESOPHAGEAL STENT INSERTION Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 5 Introduction This leaflet tells you about the procedure known as oesophageal stent insertion, explains
UNDERGOING OESOPHAGEAL STENT INSERTION Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 5 Introduction This leaflet tells you about the procedure known as oesophageal stent insertion, explains
Common Mistakes with inhaler Technique
 Common Mistakes with inhaler Technique Inhaling medication into the lungs can be very effective - but frequently it is not. The most common reasons for patients not responding to treatment are:- Being
Common Mistakes with inhaler Technique Inhaling medication into the lungs can be very effective - but frequently it is not. The most common reasons for patients not responding to treatment are:- Being
Radiotherapy for breast cancer
 Radiotherapy for breast cancer This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding breast cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 6. Contents Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy for breast cancer This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding breast cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 6. Contents Radiotherapy
Tuberculosis and You A Guide to Tuberculosis Treatment and Services
 Tuberculosis and You A Guide to Tuberculosis Treatment and Services Tuberculosis (TB) is a serious disease that can damage the lungs or other parts of the body like the brain, kidneys or spine. There are
Tuberculosis and You A Guide to Tuberculosis Treatment and Services Tuberculosis (TB) is a serious disease that can damage the lungs or other parts of the body like the brain, kidneys or spine. There are
