Principles of Antimicrobial Therapy. Principles of Antimicrobial Therapy. Principles of Antimicrobial Therapy. Principles of Antimicrobial Therapy
|
|
|
- Gertrude Roberts
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Disclosures and Special Request 8/12/13 Systemic Antibiotic Management of Infection and Ocular Disease Blair Lonsberry, MS, OD, MEd., FAAO Diplomate, American Board of Optometry Clinic Director and Professor of Optometry Pacific University College of Optometry Paid consultant for: Alcon Pharmaceuticals, Bausch and Lomb, Carl Zeiss Meditec, Merck Pharmaceuticals, NiCox, SARCode Special Request: Interactive remotes don t work on your TV, so please don t take them home! J Commitment to change: - write down three things that you learned from this presentation that you can incorporate into your practice to improve patient care - revisit these points a month from now, again in 3 months and 6 months and see if you have adopted them - make a commitment to change how you care for patients! Principles of Antimicrobial Therapy Structural and biochemical differences exist between humans and microorganisms. Antimicrobial therapy takes advantage of these differences, e.g. Bacterial cell wall Bacterial ribosomes Principles of Antimicrobial Therapy Selection of an appropriate antimicrobial requires: knowledge of the organisms identity, its susceptibility, site of infection, patient factors, safety of agent and cost of therapy. Often, the organism is not conclusively identified, and the treatment is empirical. the choice of agents in the absence of confirmatory testing maybe guided by known association of a particular organism with an infection in a given clinical setting Principles of Antimicrobial Therapy Bacteriostatic vs. Bactericidal drugs: bacteriostatic drugs arrest the growth and replication of bacteria thus limiting the spread of infection while the body attacks. bactericidal drugs kill bacteria at serum concentration levels Principles of Antimicrobial Therapy Adequate levels of the antibiotic must reach the site of infection. different tissues have variable permeability to the drugs. natural barriers to drug delivery exist, such as prostate, CNS, brain and vitreous. Patient factors are crucial in drug selection. For example: the status of patient s immune system, kidneys, liver, circulation, age, gender, pregnancy, breast feeding, allergies, etc. 1!
2 Principles of Antimicrobial Therapy many of the antibiotics are minimally toxic such as penicillins as they interfere with a site unique to bacteria growth others are reserved for life-threatening infections because of potential for serious toxicity e.g. chloramphenicol cost of therapy also needs to be considered, ie. if similar efficacy is achieved with a generic or less expensive medication (or combo of meds) that may increase compliance. Chemotherapeutic Spectra Narrow-spectrum antibiotics: act only on a single or a limited group of microorganisms, e.g. isoniazid active only against mycobacteria. Extended-spectrum antibiotics: effective against gram + and significant number of gram - bacteria, e.g ampicillin. Broad-spectrum antibiotics: effective against wide variety of microbial species (e.g. tetracycline and chloramphenicol). their use can drastically alter the bodies normal flora (and result in superinfections) Preventing Resistance Just one organism, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), kills more Americans every year ( 19,000) than emphysema, HIV/AIDS, Parkinson's disease, and homicide combined most serious MRSA infections, an estimated 85%, are associated with a healthcare exposure, but nearly 14% of the infections are communityassociated. Almost 2 million Americans per year develop hospital-acquired infections (HAIs), resulting in 99,000 deaths the vast majority of which are due to antibiotic-resistant pathogens CDC: Get Smart: Know When Antibiotics Work teaches both the provider and the patient when antibiotics should be used. The IDSA suggests five to seven days is long enough to treat a bacterial infection without encouraging resistance in adults, though children should still get the longer course this is different than previous guidelines of treating infections from days. 8/12/13 Number of New Molecular Entity (NME) Systemic Antibiotics Approved by the US FDA Per Fiveyear Period, Through 3/11. Shortage of New Antibiotics Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) Clin Infect Dis. 2011;52:S397-S428 The Author Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please journals.permissions@oup.com. In 2010, in recognition of the need for creative, new ideas to address the antibiotic pipeline problem and a measurable goal by which to gauge progress, IDSA (Infectious Diseases Society of America) launched the initiative. 8/12/13 The initiative calls for the development of 10 novel, safe and effective, systemic antibiotics by !
3 New Class of Antibiotics Fidaxomicin (Dificid) is the first of a new class of antibiotics called macrocycles and was approved by the FDA in May 2011; Optimer Pharmaceuticals it s a narrow-spectrum drug aimed specifically at Clostridium difficile, the bacterial, toxin-producing, potentially fatal infection of the gut that occurs when broad-spectrum antibiotics have killed off the other populations of bacteria that normally live in the intestines Fidaxomicin s existing competition is vancomycin as compared against vancomycin, fidaxomicin was noninferior, in industry jargon Ocular TRUST 3: Ongoing Longitudinal Surveillance of Antimicrobial Susceptibility in Ocular Isolates Background: Ocular TRUST is an ongoing annual survey of nationwide antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of common ocular pathogens. To date, more than 1,000 isolates from ocular infections have been submitted to an independent, central laboratory for in vitro testing. Ocular TRUST, now in its third year, remains the only longitudinal nationwide susceptibility surveillance program specific to ocular isolates. 8/12/13 Ocular Trust 3 Antimicrobials tested represent six classes of drugs: fluoroquinolones (ciprofloxacin, gatifloxacin, levofloxacin, moxifloxacin); dihydrofolate reductase inhibitors (trimethoprim); macrolides (azithromycin); aminoglycosides (tobramycin); polypeptides (polymyxin B); and β-lactams (penicillin). Staphylococci were classified as methicillin-resistant (MRSA) or methicillin-susceptible (MSSA) based on susceptibility to oxacillin. Ocular Trust 3: Results most antimicrobials, except penicillin and polymyxin B, continue to be highly active against MSSA (azithromycin shows only moderate activity) with the exception of trimethoprim and tobramycin, less than one-third of MRSA strains are susceptible to ophthalmic antimicrobials susceptibility profiles remain virtually identical for the fluoroquinolones, regardless of methicillin phenotype S. aureus is more susceptible to the fluoroquinolones than to macrolides, as represented by azithromycin OPHTHALMIC MRSA INFECTIONS IN THE PARKLAND HEALTH AND HOSPITAL SYSTEM, Blomquist, Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc 2006;104: Sites of An5microbial Ac5ons 1 million patients seen in the system from , with 3460 confirmed MRSA infections!!- of the total MRSA infections, 1.3% if them were ocular! Antibiotics can be classified by their chemical structure, the organisms they are effective against or by their site of action. Ophthalmic Infection Percent of Cases Preseptal cellulitis 42% Conjunctivitis 21% Corneal ulcers 10% Endophthalmitis 8% Orbital cellulitis 2% Other: e.g. dacrocystitis 10% 3!
4 Inhibitors of Cell Wall Synthesis Inhibitors of Cell Wall Synthesis Human cells do not possess a cell wall like bacteria do it is a very selective way to interfere with bacterial growth. To be maximally effective, the inhibitors require actively proliferating bacteria they are ineffective against non-dividing bacteria. The most important members of this group are: B-lactam antibiotics and vancomycin. B- Lactam An5bio5cs This group includes: penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems and monobactams. B-lactamase inhibitors are sometimes added in combination to reduce a bacteria s ability to overcome the activity of the antibiotic E.g potassium clavulanate (clavulanic acid) Penicillins Among the most widely effective and least toxic increased resistance has limited their use they are bactericidal Interfere with the last step of bacterial wall synthesis, resulting in cell lysis. Therapeutic application in gram (+) cocci and bacilli, gram (-) cocci, anaerobic, spirochetes (syphilis). The most common side effects include hypersensitivity and diarrhea. Penicillins Penicillins: Dicloxacillin This group includes the following commonly used members: Amoxicillin (250/500 tid, 875 mg bid or extended release 775mg qd) treatment of otitis media, sinusitis, and infections caused by susceptible staph/strept involving upper and lower respiratory tract, skin and urinary tract; prophylaxis of infective endocarditis Pediatric dosing: <3 months: oral mg/kg/day divided q 12 hrs >3 months: oral mg/kg/day divided 8-12 hrs >12 yrs: extended release 775 mg daily Dicloxacillin ( mg) penicillinase resistant, used in penicillin resistant staph administer orally at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after meals Dosing: Children<40kg: mg/kg daily divided Children>40kg: mg q 6 hours Adults: 250 mg q 6 hours 4!
5 Penicillins Name Treatment for Administration Penicillin G and V All stages and forms of syphilis Via IM or IV injection Ampicillin Nafcillin Prophylactic use in dental Adults: surgery patients mg every 6 hours Active against haemophilus and salmonella Osteomyelitis, septicemia, endocarditis and CNS infections IM/IV Adults: mg every 4-6 hours Penicillins: Augmen5n Augmentin is amoxicillin with potassium clavulanate (clavulanic acid 125 mg). Clavulanate is a B-Lactamase inhibitor which reduces a bacteria s ability to negate the effect of the amoxicillin by inactivating penicillinase (enzyme that inactivates the antibiotic affect). Dicloxacillin can also be used in infections due to penicillinase-producing staph. Penicillins: Augmen5n Augmentin is very effective for skin and skin structure infections such as: dacryocystitis, internal hordeola, pre-septal cellulitis. Treatment of: otitis media, sinusitis, lower respiratory and urinary infections. Given prophylactically to dental surgery patients. Penicillins: Augmen5n It has low: GI upset, allergic reaction and anaphylaxis. Serious complications include: anemia, pseudomembranous colitis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Penicillins: Augmentin. Adults: mg tab q 8hr (tid) (also available in chewable tablets and suspension) or 875 mg q 12hr (bid) 1000 mg XR: q12 hr and not for use in children <16 Peds: <3 mos 30mg/kg/day divided q12hrs using suspension >3 mos 45-90mg/kg/day divided q12hrs (otitis media 90mg for 10 days) Sinusitis Red Eye Sinus infections (rhinosinusitis), are an inflammation of the nasal and sinus passages that can cause uncomfortable pressure on either side of the nose and last for weeks The increase in mucus creates pressure in the sinuses that leads to pain. The sinuses surround the ocular region pressure from sinuses may feel like eye pressure. swollen sinuses and nasal membranes can push against ocular nerves resulting in pain. Most develop during or after a cold or other upper respiratory infection, but allergens and environmental irritants may also trigger them 5!
6 Sinusitis Treatment The infection is likely bacterial and should be treated with antibiotics if: symptoms last for 10 days without improvement, or include fever of 102 degrees or higher, nasal discharge and facial pain lasting three to four days Because of increasing resistance to the antibiotic amoxicillin the current standard of care the ISDA recommends Augmentin Augmentin 250/500 TID for 5-7 days for adults, days for children Penicillins: Hordeola: Internal are secondary to a staph infection of the meibomian glands External are an infection of the Zeis or Moll glands Patients present with tenderness and swelling of affected area. Standard treatment includes: good lid hygiene with warm compresses and lid washes Dicloxacillin 250 mg po QID for 7-10 days. may consider topical AB ung on external hordeolum. Penicillins: Dacryocystitis infection of the lacrimal sac usually secondary to an obstruction. in pediatric patients: the obstruction usually resolves by age 9-12 months. many pediatric ophthalmologists will wait until after this age to probe the ducts to free the obstruction. Penicillins: Dacryocystitis Dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR) surgical procedure of choice. allows for the bypassing of the lacrimal duct apparatus as long as the canalicular apparatus is intact. Punctal dilation and nasolacrimal irrigation is contraindicated in the acute stage due to the increased risk of periorbital cellulitis. Penicillins: Dacrocystitis Treatment includes: Augmentin 500/125 mg (500 mg amoxicillin/125 mg clavulanic acid) TID or 875/125 mg BID for 7-10 days or Dicloxacillin 250 mg po QID. Penicillins: Preseptal Celluli5s Infection and inflammation located anterior to the orbital septum and limited to the superficial periorbital tissues and eyelids. usually follows periorbital trauma or dermal infection (suspect staph sp in trauma). eyelid swelling, redness, ptosis, pain and low grade fever. Tx: Augmentin 500/125 mg TID or 875/125 mg BID for 7-10 days or if moderate to severe IV Fortaz (ceftazidime) 1-2 g q8h. 6!
7 Cephalosporins Closely related structurally and functionally to the penicillins, have the same mode of action, affected by the same resistance mechanisms. tend to be more resistant to B-lactamases. classified as 1st, 2nd, 3rd, and 4th generation based largely on their bacterial susceptibility patterns and resistance to B- lactamases. Should be avoided or used with caution in patients who are allergic to penicillin (apprx 10% x-reaction with penicillin allergy has been reported but thought to be much closer to the 1-2%) allergic response without allergy to penicillin is 1-2%. Typically administered IV or IM, poor oral absorption. Cephalosporins 1st generation: cefadroxil (Duricef), cefazolin (Ancef), cephalexin (Keflex), and cephalothin 2nd generations: cefaclor (Ceclor), cefprozil, cefuroxime (Zinacef), cefotetan, cefoxitin 3rd generation: cefnir, cefixime, cefotaxime (Claforan), ceftazidime (Fortaz), ceftibuten, ceftizoxime, ceftriaxone (Rocephin IM/IV). 4th generation: cefepime Duricef, Keflex, Ceclor (all orally administered) are effective against most gram positive pathogens and especially good for skin and soft tissue infections. Cephalosporins Keflex (cephalexin): treatment of respiratory, GI, skin and skin structure, and bone infections as well as otitis media Adults: mg every 6 hours - typical dosing 500 every 6 hours Children: mg/kg/day divided 6-8 hours Cephalosporins: Hyperacute Conjunc5vi5s Hyperacute conjunctivitis: usually secondary to gonorrhea or chlamydia. profuse purulent discharge, pain, redness, chemosis, papillae, positive nodes Chlamydia Chlamydia is the most frequently reported bacterial sexually transmitted disease in the United States Chlamydia is known as a "silent" disease because the majority of infected people have no symptoms if symptoms do occur, they usually appear within 1 to 3 weeks after exposure women who have symptoms might have an abnormal vaginal discharge or a burning sensation when urinating men with signs or symptoms might have a discharge from their penis or a burning sensation when urinating men might also have burning and itching around the opening of the penis. Chlamydia: Treatment Recommended Treatment Regimens: Azithromycin 1 g orally in a single dose OR Doxycycline 100 mg orally twice a day for 7 days Alternative Treatment Regimens: Erythromycin base 500 mg orally four times a day for 7 days OR Erythromycin ethylsuccinate 800 mg orally four times a day for 7 days OR Levofloxacin 500 mg orally once daily for 7 days OR Ofloxacin 300 mg orally twice a day for 7 days 8/12/13 8/12/13 7!
8 Chlamydia: Treatment Azithromycin versus doxycycline: for the treatment of genital chlamydial infection treatments were equally efficacious Azithromycin should always be available to treat patients for whom compliance with multiday dosing is uncertain. Levofloxacin and ofloxacin are effective treatment alternatives but are more expensive and offer no advantage in the dosage regimen. other quinolones either are not reliably effective against chlamydial infection or have not been evaluated adequately Gonorrhea Some men with gonorrhea may have no symptoms at all signs or symptoms appear 1 to 14 days after infection signs and symptoms include a burning sensation when urinating, or a white, yellow, or green discharge from the penis sometimes men with gonorrhea get painful or swollen testicles. In women, the symptoms of gonorrhea are often mild, but most women who are infected have no symptoms. symptoms can be so non-specific as to be mistaken for a bladder or vaginal infection. initial symptoms and signs in women include a painful or burning sensation when urinating, increased vaginal discharge, or vaginal bleeding between periods. risk of developing serious complications from the infection, regardless of the presence or severity of symptoms. 8/12/13 8/12/13 Gonorrhea Treatment Adult cervical/urethral infection: Ceftriaxone (Rocephin) IM injection of 250 mg in a single dose If not an option then: Cefixime (Suprax) 400 mg oral in a single dose Alternative treatments include: Azythromycin 1 gram single dose Doxycycline 100 mg BID 7-10 days Neonatal: mg/kg, up to 125 mg IV/IM cetriaxone daily for 7 days. Syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, chancroid, HIV infection, and AIDS are reportable diseases in every state. Gonorrhea Conjunc5vi5s Treatment For patients with gonorrhea conjunctivitis: Single 250 mg IM injection Ceftriaxone (Rocehphin) or/ Cefixime (Suprax) 400 mg oral in a single dose concurrent use of ocular lavage and topical fluoroqinolone e.g. cipro/moxi/besi/ gatifloxacin q1-2 hrs Cephalosporins: Dacryocystitis Dacryocystitis Tx: Keflex mg po QID, In febrile cases: IV cefazolin (Ancef) 1g q8h or IV cefuroxime (Zinacef) 1.5g q8h. Cephalosporins: Dacryoadeni5s An inflammation or infection of the lacrimal gland. S&S include: swelling of lid, pain in area of swelling, excess tearing or discharge and swelling of lymph nodes. maybe secondary to viral or bacterial infection Tx: Keflex (cephalexin) mg po QID, for more severe cases IV cefazolin (Ancef) 200mg/kg divided into 3 doses. 8!
9 Cephalosporins: Preseptal Cellulitis infection and inflammation anterior to the orbital septum and limited to the superficial periorbital tissues and eyelids. Signs and Symptoms include: eyelid swelling, redness, ptosis, pain and low grade fever. Cephalosporins: Preseptal Cellulitis Treatment Tx: Mild: Ceclor (cefaclor) mg q8h Moderate to severe: IM Rocephin (ceftriaxone) 1-2 grams/day or IV Fortaz (ceftazidime) 1-2 g q8h. Cephalosporins: Orbital Cellulitis infection and inflammation within the orbital cavity producing orbital S&S. most commonly secondary to ethmoid sinusitis. Staph and Strept most common isolates. Signs and Symptoms include: decreased VA, pain, red eye, HA, diplopia, bulging eye, APD, EOM restriction, lid swelling and fever (generally 102 degrees F or higher) Cephalosporins: Orbital Cellulitis Treatment IV Antibiotics for 7-10 days: IV Ceftriaxone (Rocephin) 50 mg/kg/q12h/day OR IV Cefotaxime (Claphoran)50 mg/kg/q6h/day PLUS " IV clindamycin 40 mg/kg/day in 3 doses IF PATIENT HAS A PENICILLIN ALLERGY IV vancomycin 30 mg/kg/day in 3 doses infused over 90 minutes Oral treatment 2-3 weeks post IV: Amoxicillin-clavulanate 875 mg/125 mg PO q12h or Cefpodoxime 200 mg PO q12h or Cefdinir 600 mg/day PO q 12h Cephalosporin: Endophthalmi5s Endophthalmitis: intraocular infection involving anterior/ posterior segments usually secondary to postoperative infection. 95% gram +ve bacteria including staph (80%), strept (10%) with about 6% gram ve organisms. Patients present with: pain, photophobia, discharge, red eye, decreased VA, proptosis, corneal edema, injection, KP s, AC reaction, vitritis, etc. Endophthalmitis Treatment Intravitreal: vancomycin 1 mg/0.1ml and ceftazidime (Fortaz) 2.25 mg/0.1 ml (or amikacin), Subconjunctival: vancomycin 25mg and ceftazidime (Fortaz) 100mg (gentamicin) and dexamethasone 12-24mg, Topical: fortified vancomycin (Vancocin HCl 2.5% Ophthalmic) and ceftazidime (Fortaz) 50mg/ml/hr, topical steroid and cycloplegic, controversial IV systemic AB. 9!
10 Vancomycin/Bacitracin Vancomycin and bacitracin both inhibit cell wall synthesis. Vancomycin is increasingly important as it is effective against multiple drug-resistant organisms (such as MRSA/MRSE and enterococci) used in patients who have penicillin allergies often considered the drug of last resort, though overuse has brought about resistance. Bacitracin is active against a wide variety of gram (+) organisms restricted to topical use due to its potential for nephrotoxicity. Vancomycin Vancomycin is typically administered systemically as an infusion due to its poor oral absorption complications are minimized when it is administered at less than 10 mg/min topical fortified vancomycin can be compounded (25-50 mg/ml) (Vancocin HCl 2.5% Ophthalmic Drops) Complications include: anaphylaxis (hypotension, wheezing, dyspnea, urticaria, pruritis), upper body flushing, pain secondary to muscle spasm, nausea, diarrhea, headache. typically the most serious complication is nephrotoxicity but it is an infrequent complication. Vancomycin Orbital Cellulitis: Infection and inflammation within the orbital cavity producing orbital S&S. decreased VA, pain, red eye, HA, diplopia, bulging eye, APD, EOM restriction, lid swelling and fever. IV ceftriaxone (Rocephin) 50 mg/kg/ Q12h/day or IV cefotaxime (Claforan) 50 mg/kg/ Q6h/day plus IV vancomycin 30 mg/kg/day in 3 doses infused over 90 minutes (penicillin allergy) or IV clindamycin 40 mg/kg/day in 3 doses. Vancomycin Endophthalmitis: intraocular infection involving anterior/posterior segments usually secondary to postoperative infection. present with pain, photophobia, discharge, red eye, decreased VA, proptosis, corneal edema, injection, KP s, AC reaction, vitritis, etc. Intravitreal vancomycin 1 mg/0.1ml and ceftazidime 2.25 mg/0.1 ml (or amikacin), subconj vancomycin 25mg and ceftazidime 100mg (gentamicin) and dexamethasone 12-24mg, topical fortified vancomycin and ceftazidime 50mg/ml/hr, topical steroid and cycloplegic Bacitracin Due to nephrotoxicity, bacitracin not used as a systemic med. Bacitracin useful for bacterial lid disease (staph blepharitis) has a low rate of allergy and toxicity. Primarily gram + activity so usually found in combination with a gram - compound e.g. polymixin B (Polysporin). PROTEIN SYNTHESIS INHIBITORS 10!
11 Protein Synthesis Inhibitors These antibiotics work by targeting the bacterial ribosome. they are structurally different from mammalian ribosomes, in higher concentrations many of these antibiotics can cause toxic effects. This group includes: (a) tetracyclines, (b) aminoglycosides, (c) macrolides, (d) chloramphenicol, (e) clindamycin, (f) quinupristin/dalfopristin and (g) linezolid Tetracyclines Nonresistant strains concentrate this antibiotic intracellularly resulting in inhibition of protein synthesis. Broad spectrum, bacteriostatic, effective against gram (+) and (-) bacteria and against non-bacterial organisms widespread resistance has limited their use. Drug of choice for Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever, Cholera, Lyme disease, mycoplasma pneumonia, and chlamydial infections. Side effects include gastric discomfort, phototoxicity, effects on calcified tissues, vestibular problems, pseudotumor. Tetracyclines This group includes: Tetracycline (250mg mg cap BID-QID) needs to be taken 1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal. Minocycline (100 mg cap BID) Doxycycline (20mg mg cap or tab BID) Tetracyclines: Acne Rosacea Acne rosacea: affects females>males after 30 with peak incidence 4-7th decade of Celtic/Northern European descent. Males more disfigured. 4 subtypes with classic signs of flushing, papules or pustules usually in crops, telangiectasia. secondary ocular complications (85% of patients) and often precede other skin manifestations include erythema, itching and burning. Mainstay oral Tx is Oracea (40 mg in morning) or tetracycline 500 mg po BID or doxycycline 100 mg po BID or minocycline 100 mg po BID for 4-12 wks. NOTE: Oracea is subantimicrobial therapy Acne Rosacea Treatments Oral Antibiotics Topical Treatments Non-Prescription Erythromycin metronidazole (Metrogel) Rosacea-Ltd III Tetracycline Doxycycline BenzaClin (Clindamycin 1% & benzoyl peroxide 5%) BenzaMycin (Erythromycin 3% & benzoyl peroxide 5%) ZenMed Neova Therapy Minocycline tretinoin (Retin-A) Kinerase Clindamycin 1% lotion/gel Plexion Cleanser/Lotion (Sulfa 10% & sulfur 5%) Rosacare Tetracyclines: Adult Inclusion Conjunc5vi5s occurs in sexually active adults women are more susceptible than men. usually transmitted through hand-toeye spread of infected genital secretions. incubation period is one to two weeks Signs and Symptoms: ocular irritation, watering, mucopurulent discharge and positive nodes often a unilateral disease but can involve both eyes follicles inferior fornix, mixed papillary/follicular on upper lid, subepithelial infiltrates, SPK. 11!
12 Tetracyclines: Adult Inclusion Conjunc5vi5s Treatment If left untreated, resolves spontaneously in 6-18 months can be treated topically with tetracycline, erythromycin, and fluoroquinolones due to the high prevalence of concomitant genital tract infection, systemic antibiotic therapy is recommended Mainstay oral treatment is: Doxycycline 100 mg po BID for 7-10 days. Topical AB therapy is done concurrently. Recent Case 21 yo Hispanic female Chief Complaint: Red eye Quality: Painful irritation; progressing in severity Duration: Started that same morning Location: OD only Relief: OTC allergy drop provides no relief (pt believed it to be allergies) Associated symptoms: Throbbing pain, watering, no light sensitivity, no pain with blinking Severity: 7.5/10 PMHx: Asthma diagnosed 7-8 yrs prior. Inhaler PRN, usually once a month. Heart murmur diagnosed at birth, without causing any complications. Allergies: NKDA Medications: IUD for birth control Examination Aided VAs: OD 20/25 +1 OS 20/20 OU 20/20 OD SLE Lid/Lashes: slight ptosis of UL, with swelling; mild mucous discharge Palpebral Conjunctiva: 2+ follicles (inf), 1+ papillary rxn (sup + inf) Anterior Chamber: Deep and quiet IOP: OD: 18 OS: 21 Posterior pole unremarkable Assessment/Plan Pain In or Around Eye Assessment Photophobia, follicles, and papillary rxn Mild mucous discharge, inferior fornix OD Plan 1 gtt Durezol OU in-office Pt education of iritis, symptoms, and course of treatment Dispensed sample of Tobradex ST q2h OU x 2-3 days Rx Z-pak RTC 1 2 days for red eye follow-up Tetracyclines: Hordeola Internal are secondary to a staph infection of the meibomian glands, while external are an infection of the Zeis or Moll glands. Px present with tenderness and swelling of affected area. Standard treatment includes: good lid hygiene with warm compresses and lid scrubs in conjunction with doxycycline mg po BID for 2-3 weeks. may consider topical AB ung on external hordeolum. Tetracyclines: Meibomian Gland Dysfunction Meibomian gland dysfunction: also referred to as meibomitis and patients experience dry eye problems secondary to increased evaporation of the tears. signs include noticeable capping of the glands and frothing of tear film. Standard treatment includes: good lid hygiene with warm compresses and lid scrubs in conjunction with doxycycline 50 mg po BID for 2-3 months. Erythomycin ung (Ilotycin) can also be used externally. 12!
13 Tetracyclines: Recurrent Corneal Erosion RCE: repeated, spontaneous disruption of corneal epi. patient experiences foreign body sensation, photophobia, blepharospasm, decreased VA and lacrimation upon waking. History of trauma usually reported or EBMD Aminoglycosides Previously were mainstay treatment for infections due to aerobic gram (-) bacilli. due to serious associated toxicities, they have been replaced by safer antibiotics such as 3rd gen cephalosporins, fluoroquinilones, cilastin. Effective in the treatment of infections suspected of being due to aerobic gram (-) bacilli including Pseudomonas. usually combined with B-lactam or vancomycin for anaerobic bacteria. They are bacteriocidal! Can have severe adverse effects including ototoxicity, nephrotoxicity, delay in nerve conduction, and skin rash. Aminoglycosides: Ocular Indica5ons Systemic aminoglycocides not commonly indicated for ocular conditions amikacin has been used for endophthalmitis IV and intravitreal Topical preparations are widely used as single agent preparations, in combination with other antibiotics as well as in combination with steroids. Tetracyclines: Recurrent Corneal Erosion Standard treatment includes: bandage contact lens, hyperosmotics treat with doxycycline 50 mg po BID for 2-3 months include use of topical steroid bid-tid for 6-8 weeks. if recurrence still happen, consider stromal puncture of affected area. Aminoglycosides This group includes: Gentamicin Neomycin Streptomycin Tobramycin Amikacin Macrolides Erythromycin was the first of these drugs, as an alternative to penicillin. Bacteriostatic though at [higher] maybe cidal Macrolides bind to the bacterial ribosome and inhibit protein synthesis. have same spectrum of action as penicillins so are used in those patients who are allergic to that group. Resistance to erythromycin is becoming a serious clinical problem. Adverse effects include: epigastric distress, jaundice, ototoxicity and contraindicated in patients with hepatic disease. 13!
14 Macrolides This group includes: Erythromycin (125 or 250 mg cap, enteric coated) dosing 250mg q 6h or 500 q12h Clarithromycin Azithromycin (Z-pak) (500mg first day, then 250 mg for next 4 days) Telithromycin Macrolides Azithromycin (Z-pak) is active against respiratory infections due to H. influenzae and Moraxella. it is a costly medication (generic now available), now a preferred therapy for urethritis by chlamydia. excellent for soft tissue infections. use with caution in patients with impaired liver function and no controlled studies for use in pregnancy. Recent New Report A study published in a recent addition of the New England Journal of Medicine, found patients prescribed Z-Pak were more likely to die than those prescribed amoxicillin. The results were especially pronounced for those who died of heart attacks Patients on azithromycin had two and a half times the odds of dying from a cardiovascular than did patients on amoxicillin. FDA Recommendation: those patients on azythromycin should continue taking their medication Azithromycin and the Risk of Cardiovascular Death. Wayne A. Ray, Ph.D., Katherine T. Murray, M.D., Kathi Hall, 8/12/13 B.S., Patrick G. Arbogast, Ph.D., and C. Michael Stein, M.B., Ch.B. N Engl J Med 2012; 366: Macrolide: Hyperacute Conjunctivitis Hyperacute conjunctivitis: usually secondary to gonorrhea or chlamydia. profuse purulent discharge, pain, redness, chemosis, positive nodes. Tx: Azithromycin (Zithromax) 1 gram single oral dose. concurrent use of ocular lavage and topical fluoroqinolone (e.g. cipro// moxi/besi/gatifloxacin q1-2 hrs). Macrolides: Adult Inclusion Conjunctivitis Adult Inclusion Conjunctivitis: occurs in sexually active adults presenting with ocular irritation, watering, mucopurulent discharge and positive nodes. follicles inferior fornix, mixed papillary/follicular on upper lid, subepithelial infiltrates, SPK. Inclusion conjunctivitis: Azithromycin 20 mg/kg (1 gram for adult) as a single dose or 500 mg first day then 250 mg daily for 4 days, erythromycin 250 mg po QID for 14 days. Macrolides: Ocular Indica5ons Erythromycin can be used as alternative treatment in patient with: internal hordeola, pre-septal cellulitis, dacrocystitis remember high incidence of staph resistance. 14!
15 Macrolides: Ocular Indica5ons Erythromycin available in topical ointment form Ilotycin for treatment of superficial infections blepharitis and prophylaxis of ophthalmia neonatorum AzaSite Azythromycin ophthalmic solution 1% Indicated for the treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis Delivery vehicle is DuraSite which forms a gel-like matrix which enhances contact time to the ocular surface results in high drug concentration in a variety of ocular tissues drug concentration levels remain high for a sustained period of time even after dosing stopped Chloramphenicol Active against a wide range of gram (+) and (-) organisms. because of its toxicity, its use is restricted to lifethreatening infections for which no alternative exists. Bacteriocidal and bacteriostatic depending on the organism. Adverse effects include hemolytic and aplastic anemia. Chloramphenicol: Ocular Indica5ons Systemic treatment rarely used for ocular conditions. Available in solution 0.5% and ointment 1% (Chloroptic) generally not used in the US but commonly used abroad (Europe and Australia). Effective against most ocular bacterial infections but because of potentially fatal complications should only be used as a last resort. Inhibitors of Nucleic Acid Synthesis/ Function. Inhibitors of Nucleic Acid Synthesis/Function The fluoroquinolones are the main group of antibiotics that act in this fashion. they enter the bacterium via passive diffusion and once inside the cell inhibit the replication of bacterial DNA by interfering with the action of DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV during bacterial growth and reproduction. Norfloxacin was the first member of this group and has been rapidly followed by newer generations of drugs which offer greater potency, a broader spectrum and a better safety profile. unfortunately, their overuse has already led to the emergence of resistant strains. 15!
16 Inhibitors of Nucleic Acid Synthesis/ Function. Rifampin is the other major member of this group and is an inhibitor of RNA synthesis Bactericidal Is a broad spectrum antibiotic but is used mostly in the treatment of TB resistance is common Rifampin is typically used in combination with other anti-tb meds has a new role in treatment of MRSA in combination with fusidic acid. Inhibitors of Nucleic Acid Synthesis/ Function. All the fluoro are bactericidal, with activity becoming more pronounced as the serum [drug] increases. in general, they are effective against gram(-) bacteria including pseudomonas and haemophilus, and have good activity against some gram (+) organisms such as strept. Common practice to classify the fluoro into generations with nalidixic acid being 1st generation. Inhibitors of Nucleic Acid Synthesis/ Function. Ciprofloxacin is the most frequently used fluoro in the US. effective against many systemic infections, with the exception of serious infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staph aureus, the enterococci and pneumococci. it is used in treating infections caused by enterobacteria (ex. travelers diarrhea) and drug of choice for anthrax prophylaxis. has good activity against pseudomonas, and may have synergistic activity with B-lactams. Resistance has developed due to mutations in both gyrase and topoisomerase. Inhibitors of Nucleic Acid Synthesis/ Function. The fluoro are generally very well tolerated though some of the most common adverse reactions include: GI upset, CNS problems (HA and dizziness), phototoxicity, liver toxicity, nephrotoxicity, and connective tissue problems should be avoided in pregnancy, nursing mothers and children under age of 18 Ocular Indications Hyperacute conjunctivitis (chlamydia): Oral or IM fluoroquinolone (only indicated if unable to use cephalosporin) Cat Scratch Disease: ciprofloxacin mg po q 12h for days. Orbital cellulitis: IV ciprofloxacin Majority of the use of fluoroquinolones in ocular use is in the form of topical drops and ointments. Used in all forms of infections and prophylaxis in ocular surgeries. Fluoroquinolone: Hyperacute Conjunctivitis Tx: Gonorrhea: CDC in 2007 took fluoros off potential treatment due to resistance. They maybe used in cases of proven resistance to cephalosporins Chlamydia: can use as alternative therapy after azythromycin and doxycycline E.g. Ofloxacin: 300 mg orally twice a day for 7 days or Levofloxacin 500 mg orally once daily for 7 days concurrent use of ocular lavage and topical fluoroqinolone (e.g. cipro// moxi/besi/gatifloxacin q1-2 hrs). 16!
17 Fluoroquinolone: Cat-Scratch Disease Cat-scratch disease (Parinaud s): infection with Bartonella resulting in granulomatous conjunctivitis with associated preauricular lymphadenopathy, neuroretinitis, focal chorioretinitis. Tx: e.g. oral ciprofloxacin 500 mg or gatifloxacin or moxifoxacin 400mg, IV fluoroqinolone. concurrent use of ocular lavage and topical fluoroqinolone (e.g. cipro// moxi/gatifloxacin q1-2 hrs). Ocular Fluoroquinolones Commonly used in optometry for treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis and keratitis standard of care for the treatment of bacterial keratitis FDA approved are Ciloxan, Ocuflox, Iquix most practitioners utilize newer generation Vigamox, Zymar, Besivance, Iquix (levofloxacin 1.5%) (3rd gen though increased concentration from previous Quixin 0.5% levofloxacin) Ocular Fluoroquinolones Besivance (besifloxacin 0.6%) is strictly an ophthalmic preparation with no systemic counterpart thought to possibly reduce chance of resistance development has DuraSite as vehicle so forms a gel-like liquid on the eye increasing contact time animal data has shown possible increased activity for MRSA Ocular Fluoroquinolones Allergan released a concentrated form of gatifloxacin Zymar is gatifloxacin 0.3% (currently discontinued) Zymaxid is gatifloxacin 0.5% Indicated for bacterial conjunctivitis Alcon has released Moxeza which is same concentration of moxifloxacin as Vigamox but with an added ingredient to increase ocular contact time Vigamox is 0.3% moxifloxacin Inhibitors of Metabolism Inhibitors of Metabolism Folic acid is required for the synthesis of precursor molecules for RNA, DNA and other compounds necessary for cellular growth. in the absence of folic acid, cells cannot grow or divide. (a) Sulfonamides and (b) trimethoprim are folic acid antagonists and interfere with an infecting bacteria s ability to divide. Compounding the two has made a synergistic compound used for effective treatment of a variety of bacterial infections. 17!
18 Sulfonamides Sulfa drugs are seldom prescribed alone except in the developing countries, where they are used because of their low cost and efficacy in certain infections such as trachoma. With the combination with trimethoprim, co-trioxazole there was a renewed interest in the sulfa drugs. Sulfa drugs are bacteriostatic, active against selective enterobacteria in the urinary tract. resistance exists is those bacteria that don t synthesize folic acid and in any PABA producing bacteria (purulent producing bacteria). Sulfonamides Adverse effects include: hypersensitivity reactions such as rashes, angioedema, Stevens-Johnson syndrome are fairly common. may also result in nephrotoxicity, hemolytic anemia, drug potentiation Ex. increased effect of hypoglycemic effect of tolbutamide or anticoagulent of warfarin Sulfonamides: Ocular Indica5ons No common indications for systemic sulfonamides (sulfadiazine is sometimes used as adjunct therapy in toxoplasmosis Tx) though topical preparations do exist. Sulfa s have limited use due to resistance and allergic reactions used more by non-ophthalmic providers. Available in combination with steroids ex. Blephamide Trimethoprim and Pyrimethamine Similar antibacterial spectrum as sulfonamides, though has a fold more potent affect than the sulfonamides. Trimethoprim maybe used on its own to treat acute UTI s and in the treatment of bacterial prostatitis (fluor preferred though) and vaginitis been found to be an effective treatment option for MRSA Pyrimethamine is used for prophylaxis and Tx of malaria. Resistance does exist, and adverse affects include several blood anemias which can be reversed by administering folinic acid. Trimethoprim: Ocular Indica5ons Combined with sulfa (Bactrim/Septra) indicated for MRSA suspected infections Trimethoprim is found in combination with polymixin B in a topical eye drop. Trimethoprim has both gram +/- activity but not effective against pseudomonas so Polymixin B is added. Low rate of allergic and toxic reactions, and approved for children >2 months. Pyrimethamine: Ocular Indica5ons Toxoplasmosis chorioretinitis (acquired) presents with: decreased VA, photophobia, floaters, vascular sheathing, full-thickness retinal necrosis, fluffy, yellow-white retinal lesion adjacent to old scars, overlying vitreous reaction (headlights in fog), and anterior chamber reaction. 18!
19 Treatment Pyrimethamine 25 mg po 1-2 times/day (loading dose 75mg) and sulfadiazine 1 g po 6hrs and clindamycin 300 mg po 6hrs. Co- Trimoxazole (Bactrim/Septra) Combination of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole shows greater antimicrobial activity than equivalent quantities of either drug alone. Has broader spectrum of action than the sulfa s and is effective in treating: UTIs and respiratory tract infections often considered for treatment of MRSA skin infections Co- Trimoxazole (Bactrim/Septra) Resistance is more difficult because has to develop resistance to both drugs. Adverse effects include: severe potential for dermatologic reactions, GI upset, blood disorders, and drug potentiation. Co-Trimoxazole (Bactrim/Septra) Available: Bactrim/Septra tablets: contains 80 mg trimethoprim and 400 mg sulfamethoxazole dosing 2 tablets every 12 hours Bactrim DS/Septra DS (Double Strenth) contains 160 mg trimethoprim and 800 mg sulfamethoxazole Dosing 1 tablet every 12 hours Case 25 WF presents to ER with swollen and painful RUL started 2 days previously medical and ocular history unremarkable. VA normal, EOM s unrestricted, pupils normal, CVF full, CT or orbit reveals swelling anterior to orbital septum. Inhibitors of Cell Membrane Function 19!
20 V: Inhibitors of Cell Membrane Func5on Isoniazid is the most potent of the anti-tubercular drugs and interferes with the production of mycobacterial cell walls. Mycobacteria is a slow growing organism and treatment is often required from 6 months to several years. due to poor compliance, resistance has developed and therefore treatment is never given as a single agent. Multi-drug therapy is given and maybe changed on a regular basis in order to effectively treat the patient. Thank You!!! 8/12/13 20!
2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY
 Measure #65 (NQF 0069): Appropriate Treatment for Children with Upper Respiratory Infection (URI) National Quality Strategy Domain: Efficiency and Cost Reduction 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES:
Measure #65 (NQF 0069): Appropriate Treatment for Children with Upper Respiratory Infection (URI) National Quality Strategy Domain: Efficiency and Cost Reduction 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES:
Date: November 30, 2010
 Department of Health and Human Services Public Health Service Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research Date: November 30, 2010 To: Through: From: Subject: Drug Name(s): Application
Department of Health and Human Services Public Health Service Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research Date: November 30, 2010 To: Through: From: Subject: Drug Name(s): Application
Appropriate Treatment for Children with Upper Respiratory Infection
 BCBS ACO Measure Appropriate Treatment for Children with Upper Respiratory Infection HEDIS Measure CPT II coding required: YES Click here to go to Table of Contents BCBS Measure: Page 50 of 234 Dated:
BCBS ACO Measure Appropriate Treatment for Children with Upper Respiratory Infection HEDIS Measure CPT II coding required: YES Click here to go to Table of Contents BCBS Measure: Page 50 of 234 Dated:
Drug Use Review. Edward Cox, M.D. Director Office of Antimicrobial Products
 Department of Health and Human Services Public Health Service Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research Drug Use Review Date: April 5, 2012 To: Through: Edward Cox, M.D. Director
Department of Health and Human Services Public Health Service Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research Drug Use Review Date: April 5, 2012 To: Through: Edward Cox, M.D. Director
Chapter 20: Antimicrobial Drugs
 Chapter 20: Antimicrobial Drugs 1. Overview of Antimicrobial Drugs 2. Antibacterial Drugs 3. Antiviral Drugs 4. Drugs for Eukaryotic Pathogens 1. Overview of Antimicrobial Drugs Antibiotics An antibiotic
Chapter 20: Antimicrobial Drugs 1. Overview of Antimicrobial Drugs 2. Antibacterial Drugs 3. Antiviral Drugs 4. Drugs for Eukaryotic Pathogens 1. Overview of Antimicrobial Drugs Antibiotics An antibiotic
INFECTION CONTROL ISSUES IN LONG TERM CARE NURSING FACILITIES PREPARED BY: AUDRIUS V. PLIOPLYS MD, FRCPC, FAAP, CMD
 INFECTION CONTROL ISSUES MAY 1, 1996, HILLSIDE, IL IN LONG TERM CARE NURSING FACILITIES PREPARED BY: AUDRIUS V. PLIOPLYS MD, FRCPC, FAAP, CMD MEDICAL DIRECTOR OF ALDEN VILLAGE, LITTLE ANGELS, MARKLUND,
INFECTION CONTROL ISSUES MAY 1, 1996, HILLSIDE, IL IN LONG TERM CARE NURSING FACILITIES PREPARED BY: AUDRIUS V. PLIOPLYS MD, FRCPC, FAAP, CMD MEDICAL DIRECTOR OF ALDEN VILLAGE, LITTLE ANGELS, MARKLUND,
The State of Therapeutics in Eye Care (Part I)
 The State of Therapeutics in Eye Care (Part I) Ron Melton, OD, FAAO Randall Thomas, OD, MPH, FAAO www.eyeupdate.com 1 st World Congress of Optometry Medellin, Columbia August 14-16, 2015 Gilenya First
The State of Therapeutics in Eye Care (Part I) Ron Melton, OD, FAAO Randall Thomas, OD, MPH, FAAO www.eyeupdate.com 1 st World Congress of Optometry Medellin, Columbia August 14-16, 2015 Gilenya First
Blue Team Teaching Module: Periorbital/Orbital Infections
 Blue Team Teaching Module: Periorbital/Orbital Infections Format: 1. Case 2. Topic Summary 3. Questions 4. References Case: A 3-year-old boy presents with 2 days of increasing redness, swelling, and pain
Blue Team Teaching Module: Periorbital/Orbital Infections Format: 1. Case 2. Topic Summary 3. Questions 4. References Case: A 3-year-old boy presents with 2 days of increasing redness, swelling, and pain
Frequently Asked Questions
 Guidelines for Testing and Treatment of Gonorrhea in Ontario, 2013 Frequently Asked Questions Table of Contents Background... 1 Treatment Recommendations... 2 Treatment of Contacts... 4 Administration
Guidelines for Testing and Treatment of Gonorrhea in Ontario, 2013 Frequently Asked Questions Table of Contents Background... 1 Treatment Recommendations... 2 Treatment of Contacts... 4 Administration
Lecture Outline. Quinolones
 Lecture Outline Quinolones Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole Miscellaneous antimicrobials - Metronidazole Daptomycin Cases Quinolones Bactericidal broad spectrum antibiotics Increasingly used because of their
Lecture Outline Quinolones Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole Miscellaneous antimicrobials - Metronidazole Daptomycin Cases Quinolones Bactericidal broad spectrum antibiotics Increasingly used because of their
STD Treatment Chart Nancy Harris, N.P. Women s Health Coordinator August 2003 Disease Treatment Alternative treatment
 STD Treatment Chart Nancy Harris, N.P. Women s Health Coordinator August 2003 Disease Treatment Alternative Pregnancy Chlamydia Chancroid Epdidymitis Gonorrhea: Uncomplicated (cx, urethra, and rectum):
STD Treatment Chart Nancy Harris, N.P. Women s Health Coordinator August 2003 Disease Treatment Alternative Pregnancy Chlamydia Chancroid Epdidymitis Gonorrhea: Uncomplicated (cx, urethra, and rectum):
Vancomycin. Beta-lactams. Beta-lactams. Vancomycin (Glycopeptide) Rifamycins (rifampin) MID 4
 Antibiotic Classes Introduction to Antimicrobials Rachel J. Gordon, MD, MPH Assistant Professor of Clinical Medicine and Epidemiology Beta-lactams Inhibit cell wall synthesis Penicillins Cephalosporins
Antibiotic Classes Introduction to Antimicrobials Rachel J. Gordon, MD, MPH Assistant Professor of Clinical Medicine and Epidemiology Beta-lactams Inhibit cell wall synthesis Penicillins Cephalosporins
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Overview A urine culture must ALWAYS be interpreted in the context of the urinalysis and patient symptoms. If a patient has no signs of infection on urinalysis, no symptoms of
Urinary Tract Infections Overview A urine culture must ALWAYS be interpreted in the context of the urinalysis and patient symptoms. If a patient has no signs of infection on urinalysis, no symptoms of
REFRACTIVE SURGERY NIGHTMARES Dr.ATHIYA AGARWAL
 REFRACTIVE SURGERY NIGHTMARES Dr.ATHIYA AGARWAL POST LASIK INFECTION Infection occurring after photorefractive keratectomy (PRK) may be 1. Secondary to the defect in the epithelium as well as the use of
REFRACTIVE SURGERY NIGHTMARES Dr.ATHIYA AGARWAL POST LASIK INFECTION Infection occurring after photorefractive keratectomy (PRK) may be 1. Secondary to the defect in the epithelium as well as the use of
Antibiotic Guidelines: Ear Nose and Throat (ENT) Infections. Contents
 Antibiotic Guidelines: Ear Nose and Throat (ENT) Infections. Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Antibiotic Steering Committee Additional author(s): Authors Division: DCSS & Tertiary Medicine
Antibiotic Guidelines: Ear Nose and Throat (ENT) Infections. Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Antibiotic Steering Committee Additional author(s): Authors Division: DCSS & Tertiary Medicine
Managing Challenging Cases in Refractive Surgery
 Managing Challenging Cases in Refractive Surgery Missouri Optometric Association Stephen A. Wexler, MD Eric E. Polk, OD, FAAO Outline The presenters will review challenging cases they have managed in refractive
Managing Challenging Cases in Refractive Surgery Missouri Optometric Association Stephen A. Wexler, MD Eric E. Polk, OD, FAAO Outline The presenters will review challenging cases they have managed in refractive
Intra-abdominal abdominal Infections
 Intra-abdominal abdominal Infections Marnie Peterson, Pharm.D., BCPS Dept. of Pediatric Infectious Diseases Medical School University of Minnesota Intra-abdominal abdominal Infections Intra-abdominal abdominal
Intra-abdominal abdominal Infections Marnie Peterson, Pharm.D., BCPS Dept. of Pediatric Infectious Diseases Medical School University of Minnesota Intra-abdominal abdominal Infections Intra-abdominal abdominal
THIS IS AN OFFICIAL NH DHHS HEALTH ALERT
 THIS IS AN OFFICIAL NH DHHS HEALTH ALERT Distributed by the NH Health Alert Network Health.Alert@nh.gov August 13, 2015 1400 EDT (2:00 PM EDT) NH-HAN 20150813 Updated Centers for Disease Control (CDC)
THIS IS AN OFFICIAL NH DHHS HEALTH ALERT Distributed by the NH Health Alert Network Health.Alert@nh.gov August 13, 2015 1400 EDT (2:00 PM EDT) NH-HAN 20150813 Updated Centers for Disease Control (CDC)
Why Do Some Antibiotics Fail?
 Why Do Some Antibiotics Fail? Patty W. Wright, M.D. April 2010 Objective To outline common reasons why antibiotic therapy is not successful and how this can be avoided. And to teach you a little bit about
Why Do Some Antibiotics Fail? Patty W. Wright, M.D. April 2010 Objective To outline common reasons why antibiotic therapy is not successful and how this can be avoided. And to teach you a little bit about
PACKAGE LEAFLET. CLINDAMYCIN capsules Clidamycin. One capsule of 75 mg contains 75 mg Clindamycin (as hydrochloride).
 PACKAGE LEAFLET CLINDAMYCIN capsules Clidamycin COMPOSITION One capsule of 75 mg contains 75 mg Clindamycin (as hydrochloride). One capsule of 150 mg contains 150 mg Clindamycin (as hydrochloride). PROPERTIES
PACKAGE LEAFLET CLINDAMYCIN capsules Clidamycin COMPOSITION One capsule of 75 mg contains 75 mg Clindamycin (as hydrochloride). One capsule of 150 mg contains 150 mg Clindamycin (as hydrochloride). PROPERTIES
Liofilchem - Antibiotic Disk Interpretative Criteria and Quality Control - F14013 - Rev.7 / 20.02.2013
 Liofilchem Antibiotic Disk Interpretative Criteria and Quality Control F0 Rev.7 /.02. Amikacin AK Amoxicillin + Clavulanic acid AUG (+) ATCC 352 Coagulasenegative staphylococci Amoxicillin + Clavulanic
Liofilchem Antibiotic Disk Interpretative Criteria and Quality Control F0 Rev.7 /.02. Amikacin AK Amoxicillin + Clavulanic acid AUG (+) ATCC 352 Coagulasenegative staphylococci Amoxicillin + Clavulanic
SURGICAL PROPHYLAXIS: ANTIBIOTIC RECOMMENDATIONS FOR ADULT PATIENTS
 Page 1 of 8 TITLE: SURGICAL PROPHYLAXIS: ANTIBIOTIC RECOMMENDATIONS FOR ADULT PATIENTS GUIDELINE: Antibiotics are administered prior to surgical procedures to prevent surgical site infections. PURPOSE:
Page 1 of 8 TITLE: SURGICAL PROPHYLAXIS: ANTIBIOTIC RECOMMENDATIONS FOR ADULT PATIENTS GUIDELINE: Antibiotics are administered prior to surgical procedures to prevent surgical site infections. PURPOSE:
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENT CLASSES AND SUBCLASSES
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENT CLASSES AND SUBCLASSES FOR USE WITH CLSI DOCUMENTS M2 AND M7 Beta-lactams: penicillins e penicillin a penicillin beta-lactam/beta-lactamase inhibitor combinations aminopenicillin a
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENT CLASSES AND SUBCLASSES FOR USE WITH CLSI DOCUMENTS M2 AND M7 Beta-lactams: penicillins e penicillin a penicillin beta-lactam/beta-lactamase inhibitor combinations aminopenicillin a
Thyroid Eye Disease. Anatomy: There are 6 muscles that move your eye.
 Thyroid Eye Disease Your doctor thinks you have thyroid orbitopathy. This is an autoimmune condition where your body's immune system is producing factors that stimulate enlargement of the muscles that
Thyroid Eye Disease Your doctor thinks you have thyroid orbitopathy. This is an autoimmune condition where your body's immune system is producing factors that stimulate enlargement of the muscles that
Frequently Asked Questions
 Frequently Asked Questions Testing for Gonorrhea Q1: What test should be completed for accurately diagnosing gonorrhea? A1: Testing is done with either a culture or a NAAT (nucleic acid amplification test).
Frequently Asked Questions Testing for Gonorrhea Q1: What test should be completed for accurately diagnosing gonorrhea? A1: Testing is done with either a culture or a NAAT (nucleic acid amplification test).
Cefuroxime apollo +9191 46 950 950
 Cefuroxime apollo +9191 46 950 950 Cefuroxime apollo +9191 46 950 950 Cefuroxime CAS Number : 55268-75-2 Molecular Weight : 424.385 g/mol Molecular Formula : C16H16N4O8S Systematic (IUPAC) : (6R,7R)-3-
Cefuroxime apollo +9191 46 950 950 Cefuroxime apollo +9191 46 950 950 Cefuroxime CAS Number : 55268-75-2 Molecular Weight : 424.385 g/mol Molecular Formula : C16H16N4O8S Systematic (IUPAC) : (6R,7R)-3-
Expedited Partner Therapy (EPT) for Sexually Transmitted Diseases Protocol for Health Care Providers in Oregon
 Expedited Partner Therapy (EPT) for Sexually Transmitted Diseases Protocol for Health Care Providers in Oregon Oregon Health Authority Center for Public Health Practice HIV/STD/TB Section Principles of
Expedited Partner Therapy (EPT) for Sexually Transmitted Diseases Protocol for Health Care Providers in Oregon Oregon Health Authority Center for Public Health Practice HIV/STD/TB Section Principles of
Antimicrobial Stewardship for Hospital Acquired Infection Prevention: Focus on C. difficile infection
 Antimicrobial Stewardship for Hospital Acquired Infection Prevention: Focus on C. difficile infection Emi Minejima, PharmD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pharmacy USC School of Pharmacy minejima@usc.edu
Antimicrobial Stewardship for Hospital Acquired Infection Prevention: Focus on C. difficile infection Emi Minejima, PharmD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pharmacy USC School of Pharmacy minejima@usc.edu
Develop an understanding of the differential diagnosis of pseudomembranous colitis
 Update on Clostridium difficile Colitis Clostridium difficile infection has recently emerged in populations without any known risk factors. This presentation will focus on the historical background, diagnosis,
Update on Clostridium difficile Colitis Clostridium difficile infection has recently emerged in populations without any known risk factors. This presentation will focus on the historical background, diagnosis,
Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea, Clostridium difficile- Associated Diarrhea and Colitis
 Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea, Clostridium difficile- Associated Diarrhea and Colitis ANTIBIOTIC-ASSOCIATED DIARRHEA Disturbance of the normal colonic microflora Leading to alterations in bacterial degradation
Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea, Clostridium difficile- Associated Diarrhea and Colitis ANTIBIOTIC-ASSOCIATED DIARRHEA Disturbance of the normal colonic microflora Leading to alterations in bacterial degradation
Rhode Island Department of Health Division of Infectious Diseases and Epidemiology
 Rhode Island Department of Health Division of Infectious Diseases and Epidemiology STD (Sexually Transmitted Disease) PROGRAM Expedited Partner Therapy (EPT) for STDs Guidance for Medical Providers in
Rhode Island Department of Health Division of Infectious Diseases and Epidemiology STD (Sexually Transmitted Disease) PROGRAM Expedited Partner Therapy (EPT) for STDs Guidance for Medical Providers in
CDC 2015 STD Treatment Guidelines: Update for IHS Providers Sharon Adler M.D., M.P.H.
 CDC 2015 STD Treatment Guidelines: Update for IHS Providers Sharon Adler M.D., M.P.H. Clinical Faculty, CA Prevention Training Center Disclosure Information Sharon Adler MD, MPH I have no financial relationships
CDC 2015 STD Treatment Guidelines: Update for IHS Providers Sharon Adler M.D., M.P.H. Clinical Faculty, CA Prevention Training Center Disclosure Information Sharon Adler MD, MPH I have no financial relationships
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN YOUNG WOMEN
 URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN YOUNG WOMEN Reviewed by Finnish Centre for Health Promotion Publisher: Ylioppilaiden terveydenhoitosäätiö Töölönkatu 37 A 00260 Helsinki Orders: julkaisutilaukset@yths.fi Author:
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN YOUNG WOMEN Reviewed by Finnish Centre for Health Promotion Publisher: Ylioppilaiden terveydenhoitosäätiö Töölönkatu 37 A 00260 Helsinki Orders: julkaisutilaukset@yths.fi Author:
bactericidal Gram+ streptococci, enterococci, meningococci, treponema pallidum (syphilis), most anaerobes poor activity against Gram- rods
 Penicillin binds penicillin binding beta-lactamase proteins (transpeptidases, cleaves beta-lactam carboxypeptidases); ring and inactivates enzymes involved in cell drug wall (peptidoglycan) (chromosomal
Penicillin binds penicillin binding beta-lactamase proteins (transpeptidases, cleaves beta-lactam carboxypeptidases); ring and inactivates enzymes involved in cell drug wall (peptidoglycan) (chromosomal
APPENDIX B: UWHC SURGICAL ANTIMICROBIAL PROPHYLAXIS GUIDELINES
 APPENDIX B: UWHC SURGICAL ANTIMICROBIAL PROPHYLAXIS GUIDELINES Principles of prophylaxis 1) Use antimicrobials for surgical procedures where prophylactic antimicrobials have been found to be beneficial.
APPENDIX B: UWHC SURGICAL ANTIMICROBIAL PROPHYLAXIS GUIDELINES Principles of prophylaxis 1) Use antimicrobials for surgical procedures where prophylactic antimicrobials have been found to be beneficial.
Nursing college, Second stage Microbiology Dr.Nada Khazal K. Hendi L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection
 L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection Definition A hospital acquired infection, also called a nosocomial infection, is an infection that first appears between 48 hours and four days after
L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection Definition A hospital acquired infection, also called a nosocomial infection, is an infection that first appears between 48 hours and four days after
Dechra Veterinary Products Limited (A business unit of Dechra Pharmaceuticals PLC) Sansaw Business Park Hadnall, Shrewsbury Shropshire SY4 4AS
 Dechra Veterinary Products Limited (A business unit of Dechra Pharmaceuticals PLC) Sansaw Business Park Hadnall, Shrewsbury Shropshire SY4 4AS Tel: 01939 211200 Fax: 01939 211201 Email: info.uk@dechra.com
Dechra Veterinary Products Limited (A business unit of Dechra Pharmaceuticals PLC) Sansaw Business Park Hadnall, Shrewsbury Shropshire SY4 4AS Tel: 01939 211200 Fax: 01939 211201 Email: info.uk@dechra.com
Nursing 113. Pharmacology Principles
 Nursing 113 Pharmacology Principles 1. The study of how drugs enter the body, reach the site of action, and are removed from the body is called a. pharmacotherapeutics b. pharmacology c. pharmacodynamics
Nursing 113 Pharmacology Principles 1. The study of how drugs enter the body, reach the site of action, and are removed from the body is called a. pharmacotherapeutics b. pharmacology c. pharmacodynamics
Dental Work and the Risk of Bacterial Endocarditis
 Variety Children s Heart Centre Dental Work and the Risk of Bacterial Endocarditis Certain heart conditions and structural defects increase the risk of developing endocarditis (a heart valve infection)
Variety Children s Heart Centre Dental Work and the Risk of Bacterial Endocarditis Certain heart conditions and structural defects increase the risk of developing endocarditis (a heart valve infection)
Title: Antibiotic Guideline for Acute Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
 Title: Antibiotic Guideline for Acute Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Version 3 Date ratified December 2007 Review date December 2009 Ratified by NUH Antimicrobial Guidelines Committee Gynaecology Directorate
Title: Antibiotic Guideline for Acute Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Version 3 Date ratified December 2007 Review date December 2009 Ratified by NUH Antimicrobial Guidelines Committee Gynaecology Directorate
Leader's Resource. Note: Both men and women can have an STD without physical symptoms.
 Leader's Resource Information on Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Signs and Symptoms of STDs Note: Both men and women can have an STD without physical symptoms. Any of the following can indicate to
Leader's Resource Information on Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Signs and Symptoms of STDs Note: Both men and women can have an STD without physical symptoms. Any of the following can indicate to
Streptococcal Infections
 Streptococcal Infections Introduction Streptococcal, or strep, infections cause a variety of health problems. These infections can cause a mild skin infection or sore throat. But they can also cause severe,
Streptococcal Infections Introduction Streptococcal, or strep, infections cause a variety of health problems. These infections can cause a mild skin infection or sore throat. But they can also cause severe,
skin and soft tissue infections (skinfold pyoderma, impetigo, folliculitis, furunculosis, cellulitis) caused by susceptible strains of organisms.
 Part II SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCT MARBOCYL P 5 mg tablet 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Active Ingredient Marbofloxacin 5mg per tablet
Part II SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCT MARBOCYL P 5 mg tablet 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Active Ingredient Marbofloxacin 5mg per tablet
Biologic Treatments for Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Biologic Treatments Rheumatoid Arthritis (also known as cytokine inhibitors, TNF inhibitors, IL 1 inhibitor, or Biologic Response Modifiers) Description Biologics are new class of drugs that have been
Biologic Treatments Rheumatoid Arthritis (also known as cytokine inhibitors, TNF inhibitors, IL 1 inhibitor, or Biologic Response Modifiers) Description Biologics are new class of drugs that have been
THE KIDNEY. Bulb of penis Abdominal aorta Scrotum Adrenal gland Inferior vena cava Urethra Corona glandis. Kidney. Glans penis Testicular vein
 29 THE KIDNEY 9. Recurrent urinary tract infections Recurrent urinary tract infections The urinary tract consists of the urethra, the bladder, the ureters, the kidneys and in men the prostate gland. An
29 THE KIDNEY 9. Recurrent urinary tract infections Recurrent urinary tract infections The urinary tract consists of the urethra, the bladder, the ureters, the kidneys and in men the prostate gland. An
Teriflunomide (Aubagio) 14mg once daily tablet
 Teriflunomide (Aubagio) 14mg once daily tablet Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Your Consultant Neurologist has suggested that you may benefit from treatment with Teriflunomide. The decision
Teriflunomide (Aubagio) 14mg once daily tablet Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Your Consultant Neurologist has suggested that you may benefit from treatment with Teriflunomide. The decision
Eye Trauma: Incidence
 Ocular Emergencies and Trauma Stuart Fourman, MD Director, Glaucoma Center Department of Ophthalmology Stony Brook University Eye Trauma: Incidence 1.3 million eye injuries per year in the United States.
Ocular Emergencies and Trauma Stuart Fourman, MD Director, Glaucoma Center Department of Ophthalmology Stony Brook University Eye Trauma: Incidence 1.3 million eye injuries per year in the United States.
 Skin and Soft tissue Infections: new bugs, old drugs Disclosure Statement Sponsor: Goodman Photographic Presented by: Dr. Kristopher Wiebe, MD, CCFP (EM) Presented to: BC Chapter, Canadian Society of Hospital
Skin and Soft tissue Infections: new bugs, old drugs Disclosure Statement Sponsor: Goodman Photographic Presented by: Dr. Kristopher Wiebe, MD, CCFP (EM) Presented to: BC Chapter, Canadian Society of Hospital
Institute of Ophthalmology. Thyroid Eye Disease. aka Thyroid Associated Ophthalmopathy
 Institute of Ophthalmology Thyroid Eye Disease aka Thyroid Associated Ophthalmopathy Causes TED/TAO is an eye disease associated with disease of the thyroid gland Most commonly, it occurs with an overactive
Institute of Ophthalmology Thyroid Eye Disease aka Thyroid Associated Ophthalmopathy Causes TED/TAO is an eye disease associated with disease of the thyroid gland Most commonly, it occurs with an overactive
Allan J Panzer, O.D. Therapeutic Optometrist. www.houstondryeyeclinic.com
 Allan J Panzer, O.D. Therapeutic Optometrist www.houstondryeyeclinic.com What conditions are you likely to see in your office? Watery Eyes Symptom: Tearing Common causes: Scratched eye Corneal foreign
Allan J Panzer, O.D. Therapeutic Optometrist www.houstondryeyeclinic.com What conditions are you likely to see in your office? Watery Eyes Symptom: Tearing Common causes: Scratched eye Corneal foreign
MANAGEMENT OF COMMON SIDE EFFECTS of INH (Isoniazid), RIF (Rifampin), PZA (Pyrazinamide), and EMB (Ethambutol)
 MANAGEMENT OF COMMON SIDE EFFECTS of INH (Isoniazid), RIF (Rifampin), PZA (Pyrazinamide), and EMB (Ethambutol) 1. Hepatotoxicity: In Active TB Disease a. Background: 1. Among the 4 standard anti-tb drugs,
MANAGEMENT OF COMMON SIDE EFFECTS of INH (Isoniazid), RIF (Rifampin), PZA (Pyrazinamide), and EMB (Ethambutol) 1. Hepatotoxicity: In Active TB Disease a. Background: 1. Among the 4 standard anti-tb drugs,
GLOBAL OVERVIEW OF ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE STD AGENTS
 GLOBAL OVERVIEW OF ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE STD AGENTS IN Dr.P.Bhalla Director Professor and Head Dept. of Microbiology Maulana Azad Medical College New Delhi, INDIA STDs & RTIs l HIV l Gonococcal infections/
GLOBAL OVERVIEW OF ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE STD AGENTS IN Dr.P.Bhalla Director Professor and Head Dept. of Microbiology Maulana Azad Medical College New Delhi, INDIA STDs & RTIs l HIV l Gonococcal infections/
NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital Sites: Columbia University Medical Center Guideline: Medication Use Manual Page 1 of 12
 Page 1 of 12 TITLE: ANTIBIOTICS IN ADULT PATIENTS EMPIRIC USE GUIDELINES, COLUMBIA UNIVERSITY MEDICAL CENTER MEDICATION GUIDELINE PURPOSE: These are the 2011 guidelines for the empiric use of antibiotics
Page 1 of 12 TITLE: ANTIBIOTICS IN ADULT PATIENTS EMPIRIC USE GUIDELINES, COLUMBIA UNIVERSITY MEDICAL CENTER MEDICATION GUIDELINE PURPOSE: These are the 2011 guidelines for the empiric use of antibiotics
Introduction to Antimicrobial Therapy
 Introduction to Antimicrobial Therapy Christine Kubin, Pharm.D., BCPS Clinical Pharmacist, Infectious Diseases Case #1 L.G. is a 78 yo woman admitted for cardiac cath. 3-vessel disease was identified and
Introduction to Antimicrobial Therapy Christine Kubin, Pharm.D., BCPS Clinical Pharmacist, Infectious Diseases Case #1 L.G. is a 78 yo woman admitted for cardiac cath. 3-vessel disease was identified and
Dosing information in renal impairment
 No. Drug name Usual dose Adjustment for Renal failure estimated CrCl (ml/min) Aminoglycoside antibiotics 1 Amikacin 2 Gentamicin 7.5 mg /kg q 12 hr > 50-90 7.5 mg/kg q 12 hr 10-50 7.5 mg/kg q 24 hr < 10
No. Drug name Usual dose Adjustment for Renal failure estimated CrCl (ml/min) Aminoglycoside antibiotics 1 Amikacin 2 Gentamicin 7.5 mg /kg q 12 hr > 50-90 7.5 mg/kg q 12 hr 10-50 7.5 mg/kg q 24 hr < 10
Exposure. What Healthcare Personnel Need to Know
 Information from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Infectious Diseases Divison of Healthcare Quality Promotion and Division of Viral Hepatitis For additional brochures
Information from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Infectious Diseases Divison of Healthcare Quality Promotion and Division of Viral Hepatitis For additional brochures
Urinary Tract Infections
 1 Infections in the urinary tract are relatively common. These infections are often referred to as bladder infections. They are also known as UTI s or urinary tract infections. When an infection is confined
1 Infections in the urinary tract are relatively common. These infections are often referred to as bladder infections. They are also known as UTI s or urinary tract infections. When an infection is confined
The Immune System and Disease
 Chapter 40 The Immune System and Disease Section 40 1 Infectious Disease (pages 1029 1033) This section describes the causes of disease and explains how infectious diseases are transmitted Introduction
Chapter 40 The Immune System and Disease Section 40 1 Infectious Disease (pages 1029 1033) This section describes the causes of disease and explains how infectious diseases are transmitted Introduction
Keflex Online No Prescription Canada
 Keflex Online No Prescription Canada keflex tablets for dogs buying keflex amoxicillin keflex keflex and mrsa keflex canine uti keflex capsules what is it used for purchasing keflex online keflex mrsa
Keflex Online No Prescription Canada keflex tablets for dogs buying keflex amoxicillin keflex keflex and mrsa keflex canine uti keflex capsules what is it used for purchasing keflex online keflex mrsa
1) Siderophores are bacterial proteins that compete with animal A) Antibodies. B) Red blood cells. C) Transferrin. D) White blood cells. E) Receptors.
 Prof. Lester s BIOL 210 Practice Exam 4 (There is no answer key. Please do not email or ask me for answers.) Chapters 15, 16, 17, 19, HIV/AIDS, TB, Quorum Sensing 1) Siderophores are bacterial proteins
Prof. Lester s BIOL 210 Practice Exam 4 (There is no answer key. Please do not email or ask me for answers.) Chapters 15, 16, 17, 19, HIV/AIDS, TB, Quorum Sensing 1) Siderophores are bacterial proteins
Treatment of Fever and Infection in Children with Transfusion Dependent Thalassaemia
 Treatment of Fever and Infection in Children with Transfusion Dependent Thalassaemia Document Information Version: 2 Date: June 2014 Authors (incl. job title): Professor David Rees, Sue Height (consultant
Treatment of Fever and Infection in Children with Transfusion Dependent Thalassaemia Document Information Version: 2 Date: June 2014 Authors (incl. job title): Professor David Rees, Sue Height (consultant
Understanding your Tecfidera treatment
 Understanding your Tecfidera treatment Information for patients who have been prescribed treatment with Tecfidera. (dimethyl fumarate) Contents About Multiple Sclerosis (MS) What is MS? Symptoms of MS
Understanding your Tecfidera treatment Information for patients who have been prescribed treatment with Tecfidera. (dimethyl fumarate) Contents About Multiple Sclerosis (MS) What is MS? Symptoms of MS
Understanding your Tecfidera treatment
 Understanding your Tecfidera treatment Information for patients who have been prescribed treatment with Tecfidera. (dimethyl fumarate) Contents About Multiple Sclerosis (MS) What is MS? Symptoms of MS
Understanding your Tecfidera treatment Information for patients who have been prescribed treatment with Tecfidera. (dimethyl fumarate) Contents About Multiple Sclerosis (MS) What is MS? Symptoms of MS
www.biochemj.org/bj/330/0581/bj3300581.htm
 Ribosomes as Antibiotic Targets www.biochemj.org/bj/330/0581/bj3300581.htm Ware, Bioscience in the 21 st Century, 2009 PERSPECTIVE Widespread use of antibiotics after WWII improved human health globally
Ribosomes as Antibiotic Targets www.biochemj.org/bj/330/0581/bj3300581.htm Ware, Bioscience in the 21 st Century, 2009 PERSPECTIVE Widespread use of antibiotics after WWII improved human health globally
PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET. CEFALEXIN 250 mg AND 500 mg CAPSULES CEFALEXIN
 PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET CEFALEXIN 250 mg AND 500 mg CAPSULES CEFALEXIN Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine. - Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET CEFALEXIN 250 mg AND 500 mg CAPSULES CEFALEXIN Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine. - Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
Assistance. Teaching Plan. With Self-Administered Medication
 Assistance With Self-Administered Medication Teaching Plan Note to leader: Complete Page 4 of the learning guide and insert it in the learning guide before making copies of the lesson for each learner.
Assistance With Self-Administered Medication Teaching Plan Note to leader: Complete Page 4 of the learning guide and insert it in the learning guide before making copies of the lesson for each learner.
BOTOX Treatment. for Chronic Migraine. Information for patients and their families. Botulinum Toxin Type A
 BOTOX Treatment Botulinum Toxin Type A for Chronic Migraine Information for patients and their families. Is Chronic Migraine the same as Migraine? Chronic Migraine is similar to migraine as sufferers experience
BOTOX Treatment Botulinum Toxin Type A for Chronic Migraine Information for patients and their families. Is Chronic Migraine the same as Migraine? Chronic Migraine is similar to migraine as sufferers experience
Treatment of skin and soft tissue infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in adults
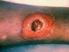 1 of 6 9/24/2010 11:16 AM Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2010 UpToDate Treatment of skin and soft tissue infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in adults Author
1 of 6 9/24/2010 11:16 AM Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2010 UpToDate Treatment of skin and soft tissue infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in adults Author
Acne (Acne Vulgaris) A common type of bacteria that lives on the skin, known as Propionibacterium acnes, sometimes
 Acne (Acne Vulgaris) Acne, clinically known as acne vulgaris, is the most common skin disease. It affects 85% of teenagers, some as young as 12, and often continues into adulthood. It is also called pimples,
Acne (Acne Vulgaris) Acne, clinically known as acne vulgaris, is the most common skin disease. It affects 85% of teenagers, some as young as 12, and often continues into adulthood. It is also called pimples,
SYNDROMIC CASE MANAGEMENT OF RTIs Advantages, Limitations, Optimization
 WHO COLLABORATING CENTRE FOR RESEARCH IN HUMAN REPRODUCTION Hôpitaux Universitaires de Genève SYNDROMIC CASE MANAGEMENT OF RTIs Advantages, Limitations, Optimization Dr SALONEY NAZEER Department of Gynaecology
WHO COLLABORATING CENTRE FOR RESEARCH IN HUMAN REPRODUCTION Hôpitaux Universitaires de Genève SYNDROMIC CASE MANAGEMENT OF RTIs Advantages, Limitations, Optimization Dr SALONEY NAZEER Department of Gynaecology
ORTHOPAEDIC INFECTION PREVENTION AND CONTROL: AN EMERGING NEW PARADIGM
 ORTHOPAEDIC INFECTION PREVENTION AND CONTROL: AN EMERGING NEW PARADIGM AMERICAN ACADEMY OF ORTHOPAEDIC SURGEONS 77th Annual Meeting March 9-12, 2010 New Orleans, Louisiana COMMITTEE ON PATIENT SAFETY PREPARED
ORTHOPAEDIC INFECTION PREVENTION AND CONTROL: AN EMERGING NEW PARADIGM AMERICAN ACADEMY OF ORTHOPAEDIC SURGEONS 77th Annual Meeting March 9-12, 2010 New Orleans, Louisiana COMMITTEE ON PATIENT SAFETY PREPARED
METHICILLIN-RESISTANT STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS (MRSA) COMMUNITY ACQUIRED vs. HEALTHCARE ASSOCIATED
 METHICILLIN-RESISTANT STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS (MRSA) COMMUNITY ACQUIRED vs. HEALTHCARE ASSOCIATED Recently, there have been a number of reports about methicillin-resistant Staph aureus (MRSA) infections
METHICILLIN-RESISTANT STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS (MRSA) COMMUNITY ACQUIRED vs. HEALTHCARE ASSOCIATED Recently, there have been a number of reports about methicillin-resistant Staph aureus (MRSA) infections
PERTUSSIS SURVEILLANCE AND RESPONSE PROTOCOL
 PERTUSSIS SURVEILLANCE AND RESPONSE PROTOCOL Public Health Action 1. Educate the public, particularly parents of infants, about the dangers of whooping cough and the advantages of initiating immunization
PERTUSSIS SURVEILLANCE AND RESPONSE PROTOCOL Public Health Action 1. Educate the public, particularly parents of infants, about the dangers of whooping cough and the advantages of initiating immunization
General Trends in Infectious Disease
 General Trends in Infectious Disease Four phenomena underline the increase in ID problems: Aging population Increasing numbers of immunocompromised patients Increased mobility of the population Newly emerging
General Trends in Infectious Disease Four phenomena underline the increase in ID problems: Aging population Increasing numbers of immunocompromised patients Increased mobility of the population Newly emerging
Antibiotic Prophylaxis for the Prevention of Infective Endocarditis and Prosthetic Joint Infections for Dentists
 PRACTICE ADVISORY SERVICE FAQ 6 Crescent Road, Toronto, ON Canada M4W 1T1 T: 416.961.6555 F: 416.961.5814 Toll Free: 1.800.565.4591 www.rcdso.org Antibiotic Prophylaxis for the Prevention of Infective
PRACTICE ADVISORY SERVICE FAQ 6 Crescent Road, Toronto, ON Canada M4W 1T1 T: 416.961.6555 F: 416.961.5814 Toll Free: 1.800.565.4591 www.rcdso.org Antibiotic Prophylaxis for the Prevention of Infective
Summary Acne vulgaris is a chronic, treatable disease but response to treatment may be delayed.
 TREATMENT OF ACNE VULGARIS Summary Acne vulgaris is a chronic, treatable disease but response to treatment may be delayed. Topical agents are useful as monotherapy for mild acne and in combination with
TREATMENT OF ACNE VULGARIS Summary Acne vulgaris is a chronic, treatable disease but response to treatment may be delayed. Topical agents are useful as monotherapy for mild acne and in combination with
INFUSE Bone Graft (rhbmp-2/acs)
 1 INFUSE Bone Graft (rhbmp-2/acs) For patients who need more bone to place dental implants Enjoy living with INFUSE Bone Graft. www.medtronic.com Medtronic Spinal and Biologics Business Worldwide Headquarters
1 INFUSE Bone Graft (rhbmp-2/acs) For patients who need more bone to place dental implants Enjoy living with INFUSE Bone Graft. www.medtronic.com Medtronic Spinal and Biologics Business Worldwide Headquarters
patient group direction
 DICLOFENAC v01 1/8 DICLOFENAC PGD Details Version 1.0 Legal category Staff grades Approved by POM Paramedic (Non-ECP) Nurse (Non-ECP) Emergency Care Practitioner (Paramedic) Emergency Care Practitioner
DICLOFENAC v01 1/8 DICLOFENAC PGD Details Version 1.0 Legal category Staff grades Approved by POM Paramedic (Non-ECP) Nurse (Non-ECP) Emergency Care Practitioner (Paramedic) Emergency Care Practitioner
IDSA GUIDELINES EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
 IDSA GUIDELINES International Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Treatment of Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis and Pyelonephritis in Women: A 2010 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and
IDSA GUIDELINES International Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Treatment of Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis and Pyelonephritis in Women: A 2010 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and
C. difficile Infections
 C. difficile Infections Introduction C. difficile is a type of bacteria that can cause diarrhea and infection of the colon. This bacterium is more likely to infect patients at hospitals and other healthcare
C. difficile Infections Introduction C. difficile is a type of bacteria that can cause diarrhea and infection of the colon. This bacterium is more likely to infect patients at hospitals and other healthcare
X-Plain Pediatric Tuberculosis Reference Summary
 X-Plain Pediatric Tuberculosis Reference Summary Introduction Tuberculosis, or TB, is a bacterial infection that causes more deaths in the world than any other infectious disease. When a child gets TB,
X-Plain Pediatric Tuberculosis Reference Summary Introduction Tuberculosis, or TB, is a bacterial infection that causes more deaths in the world than any other infectious disease. When a child gets TB,
Medicines To Treat Alcohol Use Disorder A Review of the Research for Adults
 Medicines To Treat Alcohol Use Disorder A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor* said you have alcohol use disorder
Medicines To Treat Alcohol Use Disorder A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor* said you have alcohol use disorder
growing problem By: Jena Cummins, Doctor of Pharmacy Candidate
 Clostridium difficile: A growing problem By: Jena Cummins, Doctor of Pharmacy Candidate Introduction The word difficile il is Latin for the word difficult. Clostridium difficile, affectionately known as
Clostridium difficile: A growing problem By: Jena Cummins, Doctor of Pharmacy Candidate Introduction The word difficile il is Latin for the word difficult. Clostridium difficile, affectionately known as
Immunization Healthcare Branch. Human Papillomavirus Vaccination Program Questions and Answers. Prepared by
 Immunization Healthcare Branch Human Papillomavirus Vaccination Program Questions and Answers Prepared by Immunization Healthcare Branch (IHB), Defense Health Agency Last Updated: 02 Jan 14 www.vaccines.mil
Immunization Healthcare Branch Human Papillomavirus Vaccination Program Questions and Answers Prepared by Immunization Healthcare Branch (IHB), Defense Health Agency Last Updated: 02 Jan 14 www.vaccines.mil
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STI) One Day Update
 Sexually Transmitted Infections (STI) One Day Update February 2015 Overview STI Guideline Changes National STI Services Results Reporting High Transmission Areas: Key Populations STI Guideline Changes
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STI) One Day Update February 2015 Overview STI Guideline Changes National STI Services Results Reporting High Transmission Areas: Key Populations STI Guideline Changes
Drug Utilization and Evaluation of Cephalosporin s At Tertiary Care Teaching Hospital, Bangalore
 Research Article Drug Utilization and Evaluation of Cephalosporin s At Tertiary Care Teaching Hospital, Bangalore HS. Shekar 1*, HR. Chandrashekhar 2, M. Govindaraju 3, P. Venugopalreddy 1, Chikkalingiah
Research Article Drug Utilization and Evaluation of Cephalosporin s At Tertiary Care Teaching Hospital, Bangalore HS. Shekar 1*, HR. Chandrashekhar 2, M. Govindaraju 3, P. Venugopalreddy 1, Chikkalingiah
MEDICATION GUIDE KOMBIGLYZE XR (kom-be-glyze X-R) (saxagliptin and metformin HCl extended-release) tablets
 MEDICATION GUIDE KOMBIGLYZE XR (kom-be-glyze X-R) (saxagliptin and metformin HCl extended-release) tablets Read this Medication Guide carefully before you start taking KOMBIGLYZE XR and each time you get
MEDICATION GUIDE KOMBIGLYZE XR (kom-be-glyze X-R) (saxagliptin and metformin HCl extended-release) tablets Read this Medication Guide carefully before you start taking KOMBIGLYZE XR and each time you get
California Gonorrhea Treatment Guidelines
 Califnia Gonrhea Treatment Guidelines These guidelines were developed by the Califnia Department of Public Health (CDPH) Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD) Control Branch in conjunction with the Califnia
Califnia Gonrhea Treatment Guidelines These guidelines were developed by the Califnia Department of Public Health (CDPH) Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD) Control Branch in conjunction with the Califnia
Tracy Carter PGY-4 OUCOM/Doctors Hospital Ophthalmology Columbus, OH
 A CASE OF CHRONIC CONJUNCTIVITIS Tracy Carter PGY-4 OUCOM/Doctors Hospital Ophthalmology Columbus, OH Lecture Objectives To share and review the different types of eye conditions that can cause chronic
A CASE OF CHRONIC CONJUNCTIVITIS Tracy Carter PGY-4 OUCOM/Doctors Hospital Ophthalmology Columbus, OH Lecture Objectives To share and review the different types of eye conditions that can cause chronic
C-Difficile Infection Control and Prevention Strategies
 C-Difficile Infection Control and Prevention Strategies Adrienne Mims, MD MPH VP, Chief Medical Officer Adrienne.Mims@AlliantQuality.org 1/18/2016 1 Disclosure This educational activity does not have commercial
C-Difficile Infection Control and Prevention Strategies Adrienne Mims, MD MPH VP, Chief Medical Officer Adrienne.Mims@AlliantQuality.org 1/18/2016 1 Disclosure This educational activity does not have commercial
There Are Millions of People at Risk For Dry Eye Who Is Likely to Develop This Irritating Condition?
 There Are Millions of People at Risk For Dry Eye Who Is Likely to Develop This Irritating Condition? Dry eye can be a temporary or chronic condition and occurs when the eye does not produce tears properly,
There Are Millions of People at Risk For Dry Eye Who Is Likely to Develop This Irritating Condition? Dry eye can be a temporary or chronic condition and occurs when the eye does not produce tears properly,
bioavailability of azithromycin in mice staph aureus azithromycin aminoglycosides azithromycin
 Infrequent: anorexia, constipation, dysphagia, azithromycin 250mg no script flatulence, gastroenteritis. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. For these situations, opioids are medicines
Infrequent: anorexia, constipation, dysphagia, azithromycin 250mg no script flatulence, gastroenteritis. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. For these situations, opioids are medicines
COMPOSITION: Each capsule contains clindamycin hydrochloride equivalent to 150 mg clindamycin base.
 APPROVED PACKAGE INSERT DALACIN C 150 mg CAPSULES SCHEDULING STATUS: S4 PROPRIETARY NAME (and dosage form): DALACIN C TM 150 mg (Capsules) COMPOSITION: Each capsule contains clindamycin hydrochloride equivalent
APPROVED PACKAGE INSERT DALACIN C 150 mg CAPSULES SCHEDULING STATUS: S4 PROPRIETARY NAME (and dosage form): DALACIN C TM 150 mg (Capsules) COMPOSITION: Each capsule contains clindamycin hydrochloride equivalent
TREATMENT OF STI CONTACTS
 This decision support tool is effective as of October 2014. For more information or to provide feedback on this or any other decision support tool, email certifiedpractice@crnbc.ca TREATMENT OF STI CONTACTS
This decision support tool is effective as of October 2014. For more information or to provide feedback on this or any other decision support tool, email certifiedpractice@crnbc.ca TREATMENT OF STI CONTACTS
OTITIS MEDIA AND SINUSITIS
 Page 1 OTITIS MEDIA AND SINUSITIS I. OTITIS MEDIA A. Definition: 1. Inflammatory reaction to foreign antigens in the middle ear that cannot adequately drain via the eustachian tube. 2. Three major divisions
Page 1 OTITIS MEDIA AND SINUSITIS I. OTITIS MEDIA A. Definition: 1. Inflammatory reaction to foreign antigens in the middle ear that cannot adequately drain via the eustachian tube. 2. Three major divisions
Acne Vulgaris: Basic Facts
 Acne 1 Module Instructions The following module contains hyperlinked information which serves to offer more information on topics you may or may not be familiar with. We encourage that you read all the
Acne 1 Module Instructions The following module contains hyperlinked information which serves to offer more information on topics you may or may not be familiar with. We encourage that you read all the
Treatment of sexually transmitted and other genital infections
 www.bpac.org.nz keyword: sti Treatment of sexually transmitted and other genital infections Key reviewer: Dr Murray Reid, Sexual Health Physician, Auckland Sexual Health Service General points: If one
www.bpac.org.nz keyword: sti Treatment of sexually transmitted and other genital infections Key reviewer: Dr Murray Reid, Sexual Health Physician, Auckland Sexual Health Service General points: If one
Diseases that can be spread during sex
 Diseases that can be spread during sex Did you know... over 65 million people in the United States have a chronic, incurable sexually transmitted disease (STD)? and that every year another 19 million persons
Diseases that can be spread during sex Did you know... over 65 million people in the United States have a chronic, incurable sexually transmitted disease (STD)? and that every year another 19 million persons
Results of all scientific investigations with the A.Vogel Sore Throat Spray. Issue 2 - June 2008
 Results of all scientific investigations with the A.Vogel Sore Issue 2 - June 2008 Antiviral Antibacterial Anti-inflammatory Analgetic Immunemodulatory Authors: Andy Suter, Medical Department Roland Schoop,
Results of all scientific investigations with the A.Vogel Sore Issue 2 - June 2008 Antiviral Antibacterial Anti-inflammatory Analgetic Immunemodulatory Authors: Andy Suter, Medical Department Roland Schoop,
Emergency Anaphylaxis Management: Opportunities for Improvement. Ronna Campbell, MD, PhD August 31, 2015
 Emergency Anaphylaxis Management: Opportunities for Improvement Ronna Campbell, MD, PhD August 31, 2015 disclosures Anaphylaxis Roundtable discussion held at the 2014 American College of Allergy, Asthma
Emergency Anaphylaxis Management: Opportunities for Improvement Ronna Campbell, MD, PhD August 31, 2015 disclosures Anaphylaxis Roundtable discussion held at the 2014 American College of Allergy, Asthma
