RECOMMENDATION FOR THE USE OF ANTIBIOTICS FOR THE TREATMENT OF INFECTION
|
|
|
- Alison Owen
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 RECOMMENDATION FOR THE USE OF ANTIBIOTICS FOR THE TREATMENT OF INFECTION Aims to provide a simple, best guess approach to the treatment of common infections, based on known sensitivity and resistance patterns in Cumbria to promote the safe, effective and economic use of antibiotics to minimise the emergence of bacterial resistance in the community Principles of Treatment 1. This guidance is based on the best available evidence but its application must be modified by professional judgement in the light of co-existing diseases and other drug therapy. 2. Prescribe an antibiotic only when there is likely to be a clear clinical benefit.. Limit prescribing over the telephone to exceptional cases. 4. Use simple generic antibiotics first whenever possible.. The use of new and me expensive antibiotics (e.g., quinolones and cephalospins) is inappropriate when standard and less expensive antibiotics remain effective. Antibiotics are listed in der of preference. 6. Avoid widespread use of topical antibiotics (especially those agents also available as systemic preparations).. In pregnancy AVOID tetracyclines, aminoglycosides, quinolones, high dose metronidazole. Sht-term use of trimethoprim (theetical risk in first trimester in patients with po diet, as folate antagonist) nitrofurantoin (at term, theetical risk of neonatal haemolysis) is unlikely to cause problems to the foetus. 8. Doses quoted are intended f otherwise fit adults. Doses may need to be changed in children and those with renal impairment. The duration of therapy will vary by individual patient, disease severity and speed of resolution. 9. Where a best guess therapy has failed special circumstances exist, microbiological advice can be obtained from the Consultant Microbiologists at: West Cumberland Hospital Cumberland Infirmary Furness General Hospital This guidance has been produced in consultation with the consultant microbiologists and the Cumbria Medicines Management team. Published: December 2012, Review date: November 20 Condition UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT/ENT Delayed prescriptions are a useful strategy as most upper respiraty tract infections are viral, self-limiting and improve without antibiotics. Regular use of analgesics such as paracetamol and ibuprofen should be encouraged. Influenza Tonsillitis/pharyngitis/se throat Annual vaccination is essential f all those at risk of influenza. F otherwise healthy adults antivirals not recommended. Treat at risk patients, ONLY within 48 hours of onset and when influenza is circulating in the community in a care home where influenza is likely. At risk: pregnant 6 years over chronic respiraty disease (including COPD and asthma) significant cardiovascular disease (not hypertension) immunocompromised diabetes mellitus chronic neurological renal liver disease AVOID ANTIBIOTICS as 90% resolve in days without and pain only reduced by 16 hours. If Cent sce to 4: lymphadenopathy histy of fever tonsillar exudate no cough consider 2 -day delayed antibiotics immediate antibiotics. OSELTAMIVIR mg BD, if there is resistance to oseltamivir ZANAMIVIR 10mg BD (2 inhalations by diskhaler) F prophylaxis, see NICE. (NICE Influenza). Patients under 1 years see HPA Influenza link. PHENOXYMETHYLPENICILLIN 00mg QDS (severe), CLARITHROMYCIN 20-00mg BD 10 Acute rhinosinusitis Antibiotics to prevent quinsy, NNT >4000 Antibiotics to prevent otitis media, NNT 200 AVOID ANTIBIOTICS as 80% resolve in days without, and they only offer marginal benefit after days (NNT 1) Use adequate analgesia Consider -day delayed immediate antibiotic when purulent nasal discharge (NNT 8) In persistent infection use an agent with anti-anaerobic activity e.g., co-amoxiclav AMOXICILLIN 00mg TDS, 100mg daily, CLARITHROMYCIN 20mg BD 2 nd line CO-AMOXICLAV 62mg TDS
2 Otitis externa (acute) Otitis media (acute) child doses First use aural toilet and analgesia. Cure rates similar f topical acetic acid antibiotic steroid Antibiotics do not reduce pain in first 24 hours, subsequent attacks deafness. Use paracetamol NSAID. Otitis media resolves in 60% of patients in 24 hours without antibiotics. Antibiotics reduce pain at 2 days (NNT 1) Consider antibiotics (2 to days) if: <2 years AND bilateral otitis media (NNT 4) marked otoscopic signs and symptoms All ages with otrhea (NNT ) Immediate prescribing may be appropriate f the following groups: otrhoea <2 years with bilateral acute otitis media ACETIC ACID spray (EarCalm ) 1 spray TDS, PREDNISOLONE + NEOMYCIN ear drops drops TDS AMOXICILLIN 40-90mg/kg/day in divided doses up to 1 gram TDS, CLARITHROMYCIN <8kg -.mg/kg BD 8-11kg 62.mg BD 12-19kg 12mg BD 20-29kg 18.mg BD 0-40kg 20mg BD 2 nd line - CO-AMOXICLAV 1-6yrs - 16mg TDS 6-12yrs - 12mg TDS LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Lower respiraty tract infection (including acute bronchitis) in otherwise healthy individuals Exacerbations of COPD Community acquired pneumonia Bronchiectasis EYES Bacterial conjunctivitis Ocular Herpes simplex infection Haemophilus is an extracellular pathogen so macrolides (e.g., erythromycin), which concentrate intracellularly, are less effective therapy. Antibiotics are not routinely indicated. Consider prescribing an antibiotic if the person has a significantly impaired ability to fight infection (e.g., immunocompromised status, cancer, physical frailty) if acute bronchitis is likely to significantly wsen a pre-existing condition (e.g. heart failure, angina, diabetes). Alternative antibiotics may be used on the basis of sputum results. Treat exacerbations promptly with antibiotics if: purulent sputum and increased shtness of breath and/ increased sputum volume Risk facts f antibiotic resistant ganisms include co-mbid disease, severe COPD, frequent exacerbations, antibiotics in last months Assess the person's need f admission by determining CRB6 sce: Confusion (AMT<8) Respiraty rate > 0/minute Age >6 years BP systolic <90 diastolic 60 Sce 0, suitable f home treatment Sce 1-2, hospital assessment admission Sce -4, urgent hospital admission Give immediate Benzylpenicillin 1.2 grams IM Amoxicillin 1 gram al if delayed admission life-threatening Antibiotics should be given f exacerbations that present with an acute deteriation with wsening symptoms (cough, increased sputum volume change in viscosity, increased sputum purulence with without increasing wheeze, breathlessness, haemoptysis) and/ systemic upset. Sputum samples should be taken to guide therapy. Need long course of 10 to days. Treat if severe, as most are viral self-limiting. Bacterial conjunctivitis is unilateral and also selflimiting. It is characterised by red eye with mucopurulent, not watery discharge. 6% resolve on placebo by day. STD: unilateral inclusion conjunctivitis usually with urethritis (causative agent: C. trachomatis). Urgent ophthalmic referral necessary. In recurrent infection treatment may be initiated but this must be done in consultation with ophthalmologist. Avoid topical steroids and remove contacts lenses. If antibiotics are required, AMOXICILLIN 00mg TDS, 100mg daily AMOXICILLIN 00mg TDS, 100mg daily, CLARITHROMYCIN 00mg BD If CRB6=0 AMOXICILLIN 00mg TDS, 100mg daily, CLARITHROMYCIN 00mg BD If CRB6=1 & AT HOME AMOXICILLIN 00mg TDS AND CLARITHROMYCIN 00mg BD, 100mg daily Antibiotic choice should be based on previous culture results. Consider need f anti-pseudomonal cover if not responding, Pseudomonas growth from the sputum. If culture negative send sample f Aspergillus CHLORAMPHENICOL eye drops 1 drop every 2 hours f 2 days, then 4 hourly (whilst awake) f up to 1 week; eye ointment at night If pregnant histy of blood dyscrasia use FUSIDIC ACID BD Chlamydial: DOXYCYCLINE 100mg BD, AZITHROMYCIN 1 gram stat (treat the sex partner as well) Commence ACICLOVIR eye ointment, applied times a day
3 Cneal abrasions ORAL Mucosal ulceration and inflammation Dental abscess Oral thrush If cneal ulcer - Urgent ophthalmic referral is necessary. Tempary pain and swelling relief can be attained with saline mouthwash(½tsp in glass of warm water) Advise urgent dental consultation, as repeated courses of antibiotics f abscess are not appropriate. Antibiotics are only recommended if there are: signs of severe infection systemic symptoms high risk of complications Otherwise, regular analgesia should be first option until a dentist can be seen. CHLORAMPHENICOL eye ointment BD CHLORHEXIDINE 0.2% mouthwash, rinse mouth f 1 minute BD with ml diluted with equal volume of water, HYDROGEN PEROXIDE 6%, 1mls in ½ glass of warm water TDS AMOXICILLIN 00mg TDS, PHENOXYMETHYLPENICILLIN 00mg-1 gram QDS If penicillin allergic, in severe infection METRONIDAZOLE 200mg TDS NYSTATIN 100,000 units QDS, MICONAZOLE gel, ml QDS (miconazole interacts with statins and anticoagulants) Until lesion resolves of less pain allows al hygiene Acute necrotising ulcerative Refer to dentist f scaling and al hygiene advice, gingivitis after starting antibiotic Periconitis Refer to dentist f irrigation and debridement. If persistent swelling systemic symptoms, use metronidazole GASTRO-INTESTINAL INFECTIONS H.pyli infection Tetracycline 00mg four times a day may be used instead of amoxicillin in penicillin-allergic patients. Resistance to clarithromycin to metronidazole is much me common than to amoxicillin and can develop during treatment. Do not use clarithromycin metronidazole if used f any infection in the past year. Giardiasis Recurrence is high even with optimal treatment, therefe follow-up with a stool sample is advised. Threadwms Acute gastroenteritis Travellers diarrhoea C.difficile infection Treat all household contacts at the same time PLUS advise hygiene measures f 2 weeks (hand hygiene, pants at night, mning shower) PLUS wash sleepwear, bed linen, dust and vacuum on day one. Antibiotics not usually indicated. Discuss any intended treatment with microbiologist. Limit prescription of antibacterial to be carried abroad and taken if illness develops (ciprofloxacin 00mg single dose, unlicensed indication) to people travelling to remote areas in whom an episode of infective diarrhoea could be dangerous. Stop unnecessary antibiotics and/ PPIs. 0% respond to metronidazole in days, 92% in days. Admit if severe: Temperature >8. C WCC >1 Rising creatinine Signs/symptoms of severe colitis If immunosuppressed, consider fluconazole 0-100mg OD f to days METRONIDAZOLE 200mg TDS METRONIDAZOLE 200mg TDS Triple-therapy: LANSOPRAZOLE 0mg BD plus AMOXICILLIN 1 gram BD plus either CLARITHROMYCIN 00mg BD, METRONIDAZOLE 400mg BD METRONIDAZOLE 200mg TDS f days is the most tolerable and effective doses; 400mg TDS f days 2 grams daily f days MEBENDAZOLE 100mg (mebendazole is not licensed f children under 2 years, use piperazine instead) Antibiotic treatment not routinely recommended Fluid replacement essential METRONIDAZOLE 400mg TDS f 1 st and 2 nd episodes VANCOMYCIN 12mg QDS f rd episode/severe type 02 - depending on the doses One dose repeat in two weeks URINARY TRACT Amoxicillin resistance is common, therefe ONLY use if culture confirms susceptibility. In the elderly (>6 years), do not treat asymptomatic bacteriuria: it occurs in 2% of women and 10% of men and is not associated with increased mbidity. In the presence of a catheter, antibiotics will not eradicate bacteriuria; only treat if systemically unwell pyelonephritis likely. Co-amoxiclav is alternative in patients with low GFR. Nitrofurantoin should not be used if GFR is <60mL/min/1.m 2 trimethoprim if GFR is <1mL/min/1.m 2. Cystitis in women UTI in men Routine urine culture unnecessary f simple cystitis in adult women. Further diagnosis should be made on basis of symptoms and dipstick analysis (see HPA guidance). TRIMETHOPRIM 200mg BD, NITROFURANTOIN MR 100mg BD (Note that trimethoprim may cause a rise in serum creatinine especially in pre-existing renal impairment due to competition f renal excretion) Co-amoxiclav is alternative in patients with low GFR (see above) TRIMETHOPRIM 200mg BD, NITROFURANTOIN MR 100mg BD Co-amoxiclav is alternative in patients with low GFR (see above)
4 UTI confirmed asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnant women UTI in children Screening requires a urine sample to be sent to microbiology f microscopy and culture, dip stick testing alone is not adequate < months, immediate paediatric referral > months with acute pyelonephritis/upper UTI, consider referral to paediatric specialist, treat with antibiotics > months with cystitis/lower UTI, treat. If still unwell after 24 to 48 hours, child should be reassessed AMOXICILLIN 00mg TDS, NITROFURANTOIN MR 100mg BD, CEFALEXIN 00mg TDS f days, TRIMETHOPRIM 200mg BD f days (unless folate deficient taking folate antagonist [e.g. antiepileptic proguanil]) TRIMETHOPRIM 4mg/kg BD (max 200mg), CEFALEXIN 1 month-1 year - 12mg BD 1 years - 12mg TDS - 12years - 20mg TDS Pyelonephritis Culture required. CO-AMOXICLAV 62mg TDS, CIPROFLOXACIN 00mg BD Epididymo-chitis Screen f chlamydia. DOXYCYCLINE 100mg BD (lower) -10 if upper UTI GENITAL SYSTEM Vaginal candidiasis Bacterial vaginosis Chlamydia Clotrimazole and fluconazole are available over-thecounter. day course recommended during pregnancy. Fluconazole is contra-indicated in pregnancy. Usually associated with anaerobes, recurrence is frequent, but is not a sexually transmissible infection (STI). Do not retest if symptoms resolve. In pregnancy days of clindamycin gel recommended. In pregnancy testing should be repeated after 1 month to ensure cure achieved. Advise sexual abstinence until the infected woman and her partner(s) have both completed the course of treatment. If treatment with single-dose azithromycin is given, then sexual abstinence f the following days is advised. (Azithromycin has been used f 20 years, during which time a number of studies have shown that there is no increased risk of adverse effects associated with using the drug during pregnancy. It is significantly me effective and better tolerated than the alternative agents (erythromycin and amoxicillin), but its use is me limited). Pregnant woman must be retested after weeks after completing therapy (6 weeks if azithromycin used). Refer to GUM clinic f contact tracing. Add IM CEFTRIAXONE 00mg stat if there likelihood of sexually transmitted pathogen CLOTRIMAZOLE pessaries 00mg, 200mg FLUCONAZOLE 10mg METRONIDAZOLE 400mg BD, 2 grams stat, METRONIDAZOLE vaginal gel, 0.% daily apply at night CLINDAMYCIN vaginal gel, 2% daily apply at night DOXYCYCLINE 100mg BD, AZITHROMYCIN 1 gram (not licensed f use in pregnancy, see comments) Trichomoniasis Refer to GUM may be associated with other STDs. METRONIDAZOLE 400mg BD Gonrhoea - uncomplicated Increasing resistance Refer to GUM clinic f contact CEFTRIAXONE IM 00mg stat and stat tracing and screening f other sexually transmitted diseases. AZITHROMYCIN 1 gram stat Pelvic inflammaty disease Refer to GUM. Tests essential f gonococcus and chlamydia. CEFTRIAXONE IM 00mg stat followed by DOXYCYCLINE 100mg BD and METRONIDAZOLE 400mg BD OFLOXACIN 400mg BD and METRONIDAZOLE 400mg BD Acute prostatitis Send MSU f culture and start antibiotics. 2 week course may prevent chronic prostatitis. CIPROFLOXACIN 00mg BD, TRIMETHOPRIM 200mg BD Genital herpes Screening f low risk patients may be done in practice. ACICLOVIR 200mg five times a day Higher risk should be referred to GUM. Bartholins gland infection May be associated with STD consider screening. Antibiotics not indicated f uncomplicated disease Genital warts Screening f co-existent STD indicated. Podophyllotoxin is contra-indicated in pregnancy. PODOPHYLLOTOXIN applied twice daily f three consecutive days, repeated at weekly intervals if necessary f a total of 4 to courses Liquid nitrogen if small number of low volume warts keratinized WOUND AND SKIN INFECTION Cellulitis - limb If afebrile and well other than cellulitis al therapy is adequate. If febrile and unwell admit arrange f IV antibiotics (flucloxacillin clarithromycin, as approved under PCT Cellulitis pathway). FLUCLOXACILLIN 00mg QDS, CLARITHROMYCIN 00mg BD If river seawater exposure discuss with microbiologist. - facial Early referral necessary if not responding to treatment. CO-AMOXICLAV 62mg TDS 1 Stat dose stat
5 Surgical wounds, abscesses, mastitis, wound infection Leg ulcers and pressure ses Herpes zoster Animal and human bites Tick bite Abscesses should be drained. If wound could be contaminated with soil, faeces bodily fluids if infection area has po vascular supply. FLUCLOXACILLIN 00mg QDS, CLARITHROMYCIN 00mg BD CO-AMOXICLAV 62mg TDS, CLARITHROMYCIN 00mg BD and METRONIDAZOLE 400mg TDS, CLINDAMYCIN 00mg QDS Bacteria will always be present. Antibiotics do not improve healing, unless active infection. Culture swabs and antibiotics are only indicated if diabetic there is evidence of clinical infection such as inflammation/redness/cellulitis, increased pain, purulent exudate, rapid deteriation of ulcer pyrexia. ACICLOVIR 800mg five times a day, started within 2 hours of onset of rash Human bites should generally be treated with antibiotics if the skin is broken, and consideration given to tetanus, hepatitis B and HIV prophylaxis. If the skin is broken following an animal bite, consider antibiotics if puncture wound, bite to hand, foot, face, joint, tendon, ligament immunocompromised, diabetic, asplenic cirrhotic. Cat bites carry a high risk of infection and should be treated. Consider tetanus, and, if the bite occurred abroad, rabies. Lyme disease prophylaxis is indicated if tick is likely to have been attached f >24 hours, it is obviously engged. Prophylaxis not indicated if the bite occurred me than 2 hours ago, if the patient is continually exposed to ticks. CO-AMOXICLAV 62mg TDS 2 nd line Cat, dog and human bites - DOXYCYCLINE 100mg BD and METRONIDAZOLE 400mg TDS Human bites - CLARITHROMYCIN 20-00mg BD and METRONIDAZOLE 400mg TDS DOXYCYCLINE 200mg single dose Impetigo Fungal nail infections Treatment of localised erythema migrans: Treatment of later stages of Lyme disease - discuss with Microbiologist. F extensive, severe bullous impetigo, use al antibiotics DOXYCYCLINE 100mg BD, AMOXICILLIN 00mg TDS; children <8 years Amoxicillin 0mg/kg/day in divided doses f 2 weeks Erythromycin FLUCLOXACILLIN 00mg QDS, CLARITHROMYCIN 20mg to 00mg BD Reserve topical antibiotics f very localised lesions to FUSIDIC ACID, topical TDS reduce the risk of resistance. Reserve mupirocin (local) f MRSA infections. MUPIROCIN, topical TDS Take nail clippings. TERBINAFINE 20mg daily; Treatment must only be commenced after mycological fingernails, confirmation of infection. Topical amolfine should only be used where infection is confined to the distal edge of the nail in the very early stages of distal and lateral subungual onychomycosis in superficial white onychomycosis. toenails, ITRACONAZOLE 200mg BD fingernails, (2 courses) 6 to 12 weeks; to 6 months days monthly toenails, ( courses) Fungal skin infections Terbinafine not licensed in children but listed in BNFc. - dermatophyte (ringwm) Clotrimazole is an alternative. TERBINAFINE cream twice a day candida CLOTRIMAZOLE cream BD/TDS, Continue 1-2 weeks after affected area has healed Varicella zoster/chickenpox Pregnant/immunocompromised/neonate, seek urgent specialist advice Chicken pox: If started < 24 hours of rash and > ACICLOVIR 800mg five times day years severe pain dense/al rash 2 household case smoker Shingles: treat if > 0 years and within 2 hours of rash if active ophthalmic Ramsey Hunt eczema. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Meningitis stat Urgent hospital transfer is primary consideration. Only contra-indication to benzylpenicillin if true penicillin anaphylaxis; use of alternate antibiotics is not recommended. BENZYLPENICILLIN, preferably IV, but IM if access difficult Over 10 years, 1.2 grams 1 to 9 years, 600mg Under 1 year, 00mg
Treatment of sexually transmitted and other genital infections
 www.bpac.org.nz keyword: sti Treatment of sexually transmitted and other genital infections Key reviewer: Dr Murray Reid, Sexual Health Physician, Auckland Sexual Health Service General points: If one
www.bpac.org.nz keyword: sti Treatment of sexually transmitted and other genital infections Key reviewer: Dr Murray Reid, Sexual Health Physician, Auckland Sexual Health Service General points: If one
NHS FORTH VALLEY Primary Care Management of Infection Guidance
 NHS FORTH VALLEY Primary Care Management of Infection Guidance Date of First Issue January 2012 Approved February 2012 Current Issue Date September 2013 Review Date September 2015 Version 3 EQIA Yes September
NHS FORTH VALLEY Primary Care Management of Infection Guidance Date of First Issue January 2012 Approved February 2012 Current Issue Date September 2013 Review Date September 2015 Version 3 EQIA Yes September
Antibiotic Guidelines: Ear Nose and Throat (ENT) Infections. Contents
 Antibiotic Guidelines: Ear Nose and Throat (ENT) Infections. Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Antibiotic Steering Committee Additional author(s): Authors Division: DCSS & Tertiary Medicine
Antibiotic Guidelines: Ear Nose and Throat (ENT) Infections. Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Antibiotic Steering Committee Additional author(s): Authors Division: DCSS & Tertiary Medicine
Title: Antibiotic Guideline for Acute Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
 Title: Antibiotic Guideline for Acute Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Version 3 Date ratified December 2007 Review date December 2009 Ratified by NUH Antimicrobial Guidelines Committee Gynaecology Directorate
Title: Antibiotic Guideline for Acute Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Version 3 Date ratified December 2007 Review date December 2009 Ratified by NUH Antimicrobial Guidelines Committee Gynaecology Directorate
Guidelines for Treatment of Infections in Primary Care in Hull and East Riding
 Hull and East Riding Prescribing Committee Guidelines for Treatment of Infections in Primary Care in Hull and East Riding This document is based on the Public Health England advice which can be found at
Hull and East Riding Prescribing Committee Guidelines for Treatment of Infections in Primary Care in Hull and East Riding This document is based on the Public Health England advice which can be found at
POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE
 POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE Acute Pylonephritis DIAGNOSIS COMPLICATED PYELONEPHRITIS EXCLUSION CRITERIA: Male Known or suspected renal impairment (egfr < 60) Abnormality of renal tract Known or suspected renal
POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE Acute Pylonephritis DIAGNOSIS COMPLICATED PYELONEPHRITIS EXCLUSION CRITERIA: Male Known or suspected renal impairment (egfr < 60) Abnormality of renal tract Known or suspected renal
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STI) One Day Update
 Sexually Transmitted Infections (STI) One Day Update February 2015 Overview STI Guideline Changes National STI Services Results Reporting High Transmission Areas: Key Populations STI Guideline Changes
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STI) One Day Update February 2015 Overview STI Guideline Changes National STI Services Results Reporting High Transmission Areas: Key Populations STI Guideline Changes
STD Treatment Chart Nancy Harris, N.P. Women s Health Coordinator August 2003 Disease Treatment Alternative treatment
 STD Treatment Chart Nancy Harris, N.P. Women s Health Coordinator August 2003 Disease Treatment Alternative Pregnancy Chlamydia Chancroid Epdidymitis Gonorrhea: Uncomplicated (cx, urethra, and rectum):
STD Treatment Chart Nancy Harris, N.P. Women s Health Coordinator August 2003 Disease Treatment Alternative Pregnancy Chlamydia Chancroid Epdidymitis Gonorrhea: Uncomplicated (cx, urethra, and rectum):
THE KIDNEY. Bulb of penis Abdominal aorta Scrotum Adrenal gland Inferior vena cava Urethra Corona glandis. Kidney. Glans penis Testicular vein
 29 THE KIDNEY 9. Recurrent urinary tract infections Recurrent urinary tract infections The urinary tract consists of the urethra, the bladder, the ureters, the kidneys and in men the prostate gland. An
29 THE KIDNEY 9. Recurrent urinary tract infections Recurrent urinary tract infections The urinary tract consists of the urethra, the bladder, the ureters, the kidneys and in men the prostate gland. An
UTI in children. Quick reference guide. Issue date: August 2007. Urinary tract infection in children: diagnosis, treatment and long-term management
 Issue date: August 2007 UTI in children Urinary tract infection in children: diagnosis, treatment and long-term management Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Women s and Children s Health
Issue date: August 2007 UTI in children Urinary tract infection in children: diagnosis, treatment and long-term management Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Women s and Children s Health
GLOBAL OVERVIEW OF ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE STD AGENTS
 GLOBAL OVERVIEW OF ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE STD AGENTS IN Dr.P.Bhalla Director Professor and Head Dept. of Microbiology Maulana Azad Medical College New Delhi, INDIA STDs & RTIs l HIV l Gonococcal infections/
GLOBAL OVERVIEW OF ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE STD AGENTS IN Dr.P.Bhalla Director Professor and Head Dept. of Microbiology Maulana Azad Medical College New Delhi, INDIA STDs & RTIs l HIV l Gonococcal infections/
SYNDROMIC CASE MANAGEMENT OF RTIs Advantages, Limitations, Optimization
 WHO COLLABORATING CENTRE FOR RESEARCH IN HUMAN REPRODUCTION Hôpitaux Universitaires de Genève SYNDROMIC CASE MANAGEMENT OF RTIs Advantages, Limitations, Optimization Dr SALONEY NAZEER Department of Gynaecology
WHO COLLABORATING CENTRE FOR RESEARCH IN HUMAN REPRODUCTION Hôpitaux Universitaires de Genève SYNDROMIC CASE MANAGEMENT OF RTIs Advantages, Limitations, Optimization Dr SALONEY NAZEER Department of Gynaecology
signs suggesting chlamydia:
 Chlamydia - uncomplicated genital - Management View full scenario When should I suspect and test for chlamydia? Women: o Test for chlamydia if they are sexually active with symptoms and signs suggesting
Chlamydia - uncomplicated genital - Management View full scenario When should I suspect and test for chlamydia? Women: o Test for chlamydia if they are sexually active with symptoms and signs suggesting
Antimicrobial Prescribing Guidelines for Primary Care 2015
 Antimicrobial Prescribing Guidelines for Primary Care 2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS PRINCIPLES OF TREATMENT 3 SUMMARY OF UPDATES TO GUIDELINES 4 UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS Influenza 6 Pharyngitis / Sore
Antimicrobial Prescribing Guidelines for Primary Care 2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS PRINCIPLES OF TREATMENT 3 SUMMARY OF UPDATES TO GUIDELINES 4 UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS Influenza 6 Pharyngitis / Sore
VARICELLA ZOSTER (VZ) VIRUS, CHICKENPOX & SHINGLES GUIDANCE
 VARICELLA ZOSTER (VZ) VIRUS, CHICKENPOX & SHINGLES GUIDANCE Summary This guidance provides background information on varicella zoster (VZ), chickenpox and shingles and sets out the infection control measures
VARICELLA ZOSTER (VZ) VIRUS, CHICKENPOX & SHINGLES GUIDANCE Summary This guidance provides background information on varicella zoster (VZ), chickenpox and shingles and sets out the infection control measures
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Overview A urine culture must ALWAYS be interpreted in the context of the urinalysis and patient symptoms. If a patient has no signs of infection on urinalysis, no symptoms of
Urinary Tract Infections Overview A urine culture must ALWAYS be interpreted in the context of the urinalysis and patient symptoms. If a patient has no signs of infection on urinalysis, no symptoms of
California Guidelines for STD Screening and Treatment in Pregnancy
 California Guidelines for STD Screening and Treatment in Pregnancy These guidelines were developed by the California Department of Public Health (CDPH) Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD) Control Branch
California Guidelines for STD Screening and Treatment in Pregnancy These guidelines were developed by the California Department of Public Health (CDPH) Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD) Control Branch
Guidelines for Hand Foot and Mouth Disease HFMD
 Guidelines for Hand Foot and Mouth Disease HFMD Hand, foot, and mouth disease, or HFMD, is a contagious illness caused by different viruses. Infants and children younger than 5 years are more likely to
Guidelines for Hand Foot and Mouth Disease HFMD Hand, foot, and mouth disease, or HFMD, is a contagious illness caused by different viruses. Infants and children younger than 5 years are more likely to
WHO Guidelines for Pharmacological Management of Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 Influenza and other Influenza Viruses
 WHO Guidelines for Pharmacological Management of Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 Influenza and other Influenza Viruses 20 August 2009 Table of contents EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... i Other recommendations...iii 1. INTRODUCTION...
WHO Guidelines for Pharmacological Management of Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 Influenza and other Influenza Viruses 20 August 2009 Table of contents EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... i Other recommendations...iii 1. INTRODUCTION...
Diseases that can be spread during sex
 Diseases that can be spread during sex Did you know... over 65 million people in the United States have a chronic, incurable sexually transmitted disease (STD)? and that every year another 19 million persons
Diseases that can be spread during sex Did you know... over 65 million people in the United States have a chronic, incurable sexually transmitted disease (STD)? and that every year another 19 million persons
Nursing college, Second stage Microbiology Dr.Nada Khazal K. Hendi L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection
 L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection Definition A hospital acquired infection, also called a nosocomial infection, is an infection that first appears between 48 hours and four days after
L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection Definition A hospital acquired infection, also called a nosocomial infection, is an infection that first appears between 48 hours and four days after
National Chlamydia Screening Programme September 2012 PATIENT GROUP DIRECTION FOR THE ADMINISTRATION OF AZITHROMYCIN FOR CHLAMYDIA TRACHOMATIS
 PATIENT GROUP DIRECTION FOR THE ADMINISTRATION OF AZITHROMYCIN FOR CHLAMYDIA TRACHOMATIS Below is a template that can be used to produce a local patient group direction (PGD) for the administration of
PATIENT GROUP DIRECTION FOR THE ADMINISTRATION OF AZITHROMYCIN FOR CHLAMYDIA TRACHOMATIS Below is a template that can be used to produce a local patient group direction (PGD) for the administration of
Rhode Island Department of Health Division of Infectious Diseases and Epidemiology
 Rhode Island Department of Health Division of Infectious Diseases and Epidemiology STD (Sexually Transmitted Disease) PROGRAM Expedited Partner Therapy (EPT) for STDs Guidance for Medical Providers in
Rhode Island Department of Health Division of Infectious Diseases and Epidemiology STD (Sexually Transmitted Disease) PROGRAM Expedited Partner Therapy (EPT) for STDs Guidance for Medical Providers in
Patient with: 3 or more UTI in 6 months 4 or more UTI in 12 months
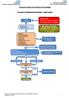 Recurrent UTI Management Pathway adult females Initial assessment Assessment questionnaire questionnaire bladder scan dipstick dipstick of of urine urine pregnancy neurological disease long - term catheters
Recurrent UTI Management Pathway adult females Initial assessment Assessment questionnaire questionnaire bladder scan dipstick dipstick of of urine urine pregnancy neurological disease long - term catheters
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN YOUNG WOMEN
 URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN YOUNG WOMEN Reviewed by Finnish Centre for Health Promotion Publisher: Ylioppilaiden terveydenhoitosäätiö Töölönkatu 37 A 00260 Helsinki Orders: julkaisutilaukset@yths.fi Author:
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN YOUNG WOMEN Reviewed by Finnish Centre for Health Promotion Publisher: Ylioppilaiden terveydenhoitosäätiö Töölönkatu 37 A 00260 Helsinki Orders: julkaisutilaukset@yths.fi Author:
INFECTION CONTROL MANUAL
 Page 1 of 19 Key Words: staff, communicable diseases, diseases, infectious diseases Policy Applies to: All staff employed by Mercy Hospital, Credentialed Specialists and Allied Health Professionals involved
Page 1 of 19 Key Words: staff, communicable diseases, diseases, infectious diseases Policy Applies to: All staff employed by Mercy Hospital, Credentialed Specialists and Allied Health Professionals involved
Treatment of Fever and Infection in Children with Transfusion Dependent Thalassaemia
 Treatment of Fever and Infection in Children with Transfusion Dependent Thalassaemia Document Information Version: 2 Date: June 2014 Authors (incl. job title): Professor David Rees, Sue Height (consultant
Treatment of Fever and Infection in Children with Transfusion Dependent Thalassaemia Document Information Version: 2 Date: June 2014 Authors (incl. job title): Professor David Rees, Sue Height (consultant
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA MINISTRY OF HEALTH AND SOCIAL WELFARE
 THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA Treat for Lymphogranuloma venereum MINISTRY OF HEALTH AND SOCIAL WELFARE Appoint to return after Patient complains of Use Discharge from Continue to 2nd Refer to surgeon
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA Treat for Lymphogranuloma venereum MINISTRY OF HEALTH AND SOCIAL WELFARE Appoint to return after Patient complains of Use Discharge from Continue to 2nd Refer to surgeon
2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY
 Measure #65 (NQF 0069): Appropriate Treatment for Children with Upper Respiratory Infection (URI) National Quality Strategy Domain: Efficiency and Cost Reduction 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES:
Measure #65 (NQF 0069): Appropriate Treatment for Children with Upper Respiratory Infection (URI) National Quality Strategy Domain: Efficiency and Cost Reduction 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES:
Have a shower, rather than a bath to avoid exposing your genitals to the chemicals in your cleaning products for too long. Always empty your bladder
 Cystitis, Avenue Medical Practice Neat Guideline Introduction Cystitis means 'inflammation of the bladder'. It causes: an urgent and frequent need to urinate, and Pain, or stinging, when passing urine.
Cystitis, Avenue Medical Practice Neat Guideline Introduction Cystitis means 'inflammation of the bladder'. It causes: an urgent and frequent need to urinate, and Pain, or stinging, when passing urine.
A guide for people with genital herpes
 A guide for people with genital herpes Contents Getting the facts 4 The key facts 6 What is genital herpes? 8 Genital herpes symptoms 10 Getting tested 12 The first outbreak 14 Recurrent outbreaks 16 Common
A guide for people with genital herpes Contents Getting the facts 4 The key facts 6 What is genital herpes? 8 Genital herpes symptoms 10 Getting tested 12 The first outbreak 14 Recurrent outbreaks 16 Common
Leader's Resource. Note: Both men and women can have an STD without physical symptoms.
 Leader's Resource Information on Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Signs and Symptoms of STDs Note: Both men and women can have an STD without physical symptoms. Any of the following can indicate to
Leader's Resource Information on Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Signs and Symptoms of STDs Note: Both men and women can have an STD without physical symptoms. Any of the following can indicate to
SHINGLES (Herpes zoster infection)
 SHINGLES (Herpes zoster infection) What are the aims of this leaflet? This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about shingles. It will tell you what it is, what causes it, what can be
SHINGLES (Herpes zoster infection) What are the aims of this leaflet? This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about shingles. It will tell you what it is, what causes it, what can be
Appropriate Treatment for Children with Upper Respiratory Infection
 BCBS ACO Measure Appropriate Treatment for Children with Upper Respiratory Infection HEDIS Measure CPT II coding required: YES Click here to go to Table of Contents BCBS Measure: Page 50 of 234 Dated:
BCBS ACO Measure Appropriate Treatment for Children with Upper Respiratory Infection HEDIS Measure CPT II coding required: YES Click here to go to Table of Contents BCBS Measure: Page 50 of 234 Dated:
Facts About Chickenpox and Shingles for Adults
 Facts About Chickenpox and Shingles for Adults What is chickenpox? Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a very contagious disease caused by the varicella-zoster virus. It is spread easily through the
Facts About Chickenpox and Shingles for Adults What is chickenpox? Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a very contagious disease caused by the varicella-zoster virus. It is spread easily through the
Expedited Partner Therapy (EPT) for Sexually Transmitted Diseases Protocol for Health Care Providers in Oregon
 Expedited Partner Therapy (EPT) for Sexually Transmitted Diseases Protocol for Health Care Providers in Oregon Oregon Health Authority Center for Public Health Practice HIV/STD/TB Section Principles of
Expedited Partner Therapy (EPT) for Sexually Transmitted Diseases Protocol for Health Care Providers in Oregon Oregon Health Authority Center for Public Health Practice HIV/STD/TB Section Principles of
Chlamydia THE FACTS. How do people get Chlamydia?
 What is Chlamydia? Chlamydia is a common bacterial infection that is sexually transmitted and often causes no symptoms. If not treated, chlamydia can damage reproductive organs and make it difficult for
What is Chlamydia? Chlamydia is a common bacterial infection that is sexually transmitted and often causes no symptoms. If not treated, chlamydia can damage reproductive organs and make it difficult for
Eastern Health MS Service. Tysabri Therapy. Information for People with MS and their Families
 Eastern Health MS Service Tysabri Therapy Information for People with MS and their Families The Eastern Health MS Service has developed this information for you as a guide through what will happen to you
Eastern Health MS Service Tysabri Therapy Information for People with MS and their Families The Eastern Health MS Service has developed this information for you as a guide through what will happen to you
Ear Infections Chickenpox chickenpox
 Ear Chickenpox Infections chickenpox Chickenpox Chickenpox is a common, very contagious viral infection that over 90% of people get during childhood unless they have been immunised. After an infection,
Ear Chickenpox Infections chickenpox Chickenpox Chickenpox is a common, very contagious viral infection that over 90% of people get during childhood unless they have been immunised. After an infection,
Yes, I know I have genital herpes:
 Counseling Messages for Herpes Simplex Type II (HSV-II) Genital herpes Always take the time to attend to the participant s feelings and emotional state; for some people, this is the most devastating news
Counseling Messages for Herpes Simplex Type II (HSV-II) Genital herpes Always take the time to attend to the participant s feelings and emotional state; for some people, this is the most devastating news
THIS IS AN OFFICIAL NH DHHS HEALTH ALERT
 THIS IS AN OFFICIAL NH DHHS HEALTH ALERT Distributed by the NH Health Alert Network Health.Alert@nh.gov August 13, 2015 1400 EDT (2:00 PM EDT) NH-HAN 20150813 Updated Centers for Disease Control (CDC)
THIS IS AN OFFICIAL NH DHHS HEALTH ALERT Distributed by the NH Health Alert Network Health.Alert@nh.gov August 13, 2015 1400 EDT (2:00 PM EDT) NH-HAN 20150813 Updated Centers for Disease Control (CDC)
Teriflunomide (Aubagio) 14mg once daily tablet
 Teriflunomide (Aubagio) 14mg once daily tablet Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Your Consultant Neurologist has suggested that you may benefit from treatment with Teriflunomide. The decision
Teriflunomide (Aubagio) 14mg once daily tablet Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Your Consultant Neurologist has suggested that you may benefit from treatment with Teriflunomide. The decision
2014 CDC Treatment Guidelines for STDs What s New, What s Important, What s Essential. STD Treatment Guidelines. How are the guidelines prepared?
 2014 CDC Treatment Guidelines for STDs What s New, What s Important, What s Essential Bradley Stoner, MD, PhD Associate Professor, Washington University School of Medicine Medical Director, St. Louis STD/HIV
2014 CDC Treatment Guidelines for STDs What s New, What s Important, What s Essential Bradley Stoner, MD, PhD Associate Professor, Washington University School of Medicine Medical Director, St. Louis STD/HIV
Antibiotic Guidelines for Primary Care
 Antibiotic Guidelines for Primary Care West Coast District Health Board 2015 PREPARED BY: WCDHB Infection Control Committee 2009 REVIEWED AND UPDATED BY: WCDHB Infection Control Committee October 2015
Antibiotic Guidelines for Primary Care West Coast District Health Board 2015 PREPARED BY: WCDHB Infection Control Committee 2009 REVIEWED AND UPDATED BY: WCDHB Infection Control Committee October 2015
Management of exacerbations in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Primary Care
 Management of exacerbations in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Primary Care Acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are associated with significant morbidity and mortality.
Management of exacerbations in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Primary Care Acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are associated with significant morbidity and mortality.
GONORRHOEA. Use of lidocaine as a diluent when using ceftriaxone (see Appendix 1)
 Key practice notes: 1 st line therapy GONORRHOEA Decreasing sensitivity of gonorrhoea to cephalosporins is now a real threat: CEFTRIAXONE 500mg IM stat first-line for all gonococcal infections AZITHROMYCIN
Key practice notes: 1 st line therapy GONORRHOEA Decreasing sensitivity of gonorrhoea to cephalosporins is now a real threat: CEFTRIAXONE 500mg IM stat first-line for all gonococcal infections AZITHROMYCIN
Patient Information Leaflet
 Patient Information Leaflet METHOTREXATE We hope this fact sheet will provide you with some information about Methotrexate and answer some of the questions you may have. Methotrexate is available in tablet
Patient Information Leaflet METHOTREXATE We hope this fact sheet will provide you with some information about Methotrexate and answer some of the questions you may have. Methotrexate is available in tablet
2010 QARR QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE Adults
 2010 QARR QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE Adults ADULT MEASURES (19 through 64 years) GUIDELINE HEDIS COMPLIANT CPT/ICD9 CODES DOCUMENTATION TIPS Well Care Access to Ambulatory Care Ensure a preventive or other
2010 QARR QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE Adults ADULT MEASURES (19 through 64 years) GUIDELINE HEDIS COMPLIANT CPT/ICD9 CODES DOCUMENTATION TIPS Well Care Access to Ambulatory Care Ensure a preventive or other
Plan early - get your vaccinations in time for full protection. To prepare for your trip, schedule an appointment: (910) 347-2154, option #2.
 The Onslow County Health Department Travel Clinic offers a complete line of immunizations and prescriptions to protect you while traveling abroad. The most appropriate immunizations and travel medications
The Onslow County Health Department Travel Clinic offers a complete line of immunizations and prescriptions to protect you while traveling abroad. The most appropriate immunizations and travel medications
STANDARD PROTOCOL STD AND HIV SCREENING AND EPIDEMIOLOGIC STD TREATMENT
 STANDARD PROTOCOL STD AND HIV SCREENING AND EPIDEMIOLOGIC STD TREATMENT RELEASE DATE: REVIEW INTERVAL: YEARLY REVIEW DATE: SITE/SERVICE UNIT: IMPLEMENTATION DATE: REVIEWED BY: CONTACT: APPROVED BY: CONTENTS
STANDARD PROTOCOL STD AND HIV SCREENING AND EPIDEMIOLOGIC STD TREATMENT RELEASE DATE: REVIEW INTERVAL: YEARLY REVIEW DATE: SITE/SERVICE UNIT: IMPLEMENTATION DATE: REVIEWED BY: CONTACT: APPROVED BY: CONTENTS
BASIC INFORMATION ABOUT HIV, HEPATITIS B and C, and TUBERCULOSIS Adapted from the CDC
 BASIC INFORMATION ABOUT HIV, HEPATITIS B and C, and TUBERCULOSIS Adapted from the CDC HIV What are HIV and AIDS? HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus. This is the virus that causes AIDS. HIV is
BASIC INFORMATION ABOUT HIV, HEPATITIS B and C, and TUBERCULOSIS Adapted from the CDC HIV What are HIV and AIDS? HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus. This is the virus that causes AIDS. HIV is
Balanitis (change on the helmet of the penis) This is a change in the skin on the glans (helmet) of the penis. It is often caused by either:-
 INFECTIONS Bacterial Vaginosis Women with Bacterial Vaginosis (BV) often complain of an increase in vaginal discharge that is "smelly" or they feel "unclean" despite regular washing. This is more noticeable
INFECTIONS Bacterial Vaginosis Women with Bacterial Vaginosis (BV) often complain of an increase in vaginal discharge that is "smelly" or they feel "unclean" despite regular washing. This is more noticeable
Pertussis Information for GPs and other Health Care Providers on Clinical and Public Health Management. March 2010
 Pertussis Information for GPs and other Health Care Providers on Clinical and Public Health Management March 2010 Infectious Agent Bordetella pertussis (a bacterium) Clinical Features Infants and Young
Pertussis Information for GPs and other Health Care Providers on Clinical and Public Health Management March 2010 Infectious Agent Bordetella pertussis (a bacterium) Clinical Features Infants and Young
COMMON BACTERIAL SKIN INFECTIONS IN GENERAL PRACTICE
 COMMON BACTERIAL SKIN INFECTIONS IN GENERAL PRACTICE The two most common bacteria to cause skin infections are staphylococcus aureus (staph aureus ) and streptococcus pyogenes ( strep) (see Table 1). Staphylococcus
COMMON BACTERIAL SKIN INFECTIONS IN GENERAL PRACTICE The two most common bacteria to cause skin infections are staphylococcus aureus (staph aureus ) and streptococcus pyogenes ( strep) (see Table 1). Staphylococcus
Accent on Health Obgyn, PC HERPES Frequently Asked Questions
 1. What is herpes? 2. How common is herpes? 3. Is there a cure for herpes? 4. What is oral herpes (cold sores)? 5. How is oral herpes spread? 6. What is genital herpes? 7. How is genital herpes spread?
1. What is herpes? 2. How common is herpes? 3. Is there a cure for herpes? 4. What is oral herpes (cold sores)? 5. How is oral herpes spread? 6. What is genital herpes? 7. How is genital herpes spread?
Additional details >>> HERE <<<
 Additional details >>> HERE http://dbvir.com/ringworm12/pdx/comw23/ Tags:
Additional details >>> HERE http://dbvir.com/ringworm12/pdx/comw23/ Tags:
Nurse Initiated Medications Procedure
 1. Purpose This Procedure is performed as a means of ensuring the safe administration of therapeutic medication to patients in accordance with all legislative and regulatory requirements. 2. Application
1. Purpose This Procedure is performed as a means of ensuring the safe administration of therapeutic medication to patients in accordance with all legislative and regulatory requirements. 2. Application
SECTION 6 THERAPEUTIC DRUG MONITORING
 SECTION 6 THERAPEUTIC DRUG MONITORING Kieran Hand Consultant Pharmacist Anti-infectives The objectives of this section are: To test your ability to monitor serum levels for drugs with a narrow therapeutic
SECTION 6 THERAPEUTIC DRUG MONITORING Kieran Hand Consultant Pharmacist Anti-infectives The objectives of this section are: To test your ability to monitor serum levels for drugs with a narrow therapeutic
POINCIANA INTERNAL MEDICINE PA. Patient Name: Social Security Number: Date of Birth: / / Sex: M/F (Circle One) Married/Single/Divorced/Widow Address:
 Patient Name: Social Security Number: Date of Birth: / / Sex: M/F (Circle One) Married/Single/Divorced/Widow Address: (Street) (City/State/Zip) Home Phone: ( ) E Mail Address: Would you be interested in
Patient Name: Social Security Number: Date of Birth: / / Sex: M/F (Circle One) Married/Single/Divorced/Widow Address: (Street) (City/State/Zip) Home Phone: ( ) E Mail Address: Would you be interested in
METHICILLIN-RESISTANT STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS (MRSA) COMMUNITY ACQUIRED vs. HEALTHCARE ASSOCIATED
 METHICILLIN-RESISTANT STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS (MRSA) COMMUNITY ACQUIRED vs. HEALTHCARE ASSOCIATED Recently, there have been a number of reports about methicillin-resistant Staph aureus (MRSA) infections
METHICILLIN-RESISTANT STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS (MRSA) COMMUNITY ACQUIRED vs. HEALTHCARE ASSOCIATED Recently, there have been a number of reports about methicillin-resistant Staph aureus (MRSA) infections
C-Difficile Infection Control and Prevention Strategies
 C-Difficile Infection Control and Prevention Strategies Adrienne Mims, MD MPH VP, Chief Medical Officer Adrienne.Mims@AlliantQuality.org 1/18/2016 1 Disclosure This educational activity does not have commercial
C-Difficile Infection Control and Prevention Strategies Adrienne Mims, MD MPH VP, Chief Medical Officer Adrienne.Mims@AlliantQuality.org 1/18/2016 1 Disclosure This educational activity does not have commercial
PLAN OF ACTION FOR. Physician Name Signature License Date
 PLAN OF ACTION FOR Patient s copy (patient s name) I Feel Well Lignes I feel short directrices of breath: I cough up sputum daily. No Yes, colour: I cough regularly. No Yes I Feel Worse I have changes
PLAN OF ACTION FOR Patient s copy (patient s name) I Feel Well Lignes I feel short directrices of breath: I cough up sputum daily. No Yes, colour: I cough regularly. No Yes I Feel Worse I have changes
Transient Hypogammaglobulinemia of Infancy. Chapter 7
 Transient Hypogammaglobulinemia of Infancy Chapter 7 An unborn baby makes no IgG (antibody) and only slowly starts producing it after birth. However, starting at about the sixth month of pregnancy, the
Transient Hypogammaglobulinemia of Infancy Chapter 7 An unborn baby makes no IgG (antibody) and only slowly starts producing it after birth. However, starting at about the sixth month of pregnancy, the
PACKAGE LEAFLET. CLINDAMYCIN capsules Clidamycin. One capsule of 75 mg contains 75 mg Clindamycin (as hydrochloride).
 PACKAGE LEAFLET CLINDAMYCIN capsules Clidamycin COMPOSITION One capsule of 75 mg contains 75 mg Clindamycin (as hydrochloride). One capsule of 150 mg contains 150 mg Clindamycin (as hydrochloride). PROPERTIES
PACKAGE LEAFLET CLINDAMYCIN capsules Clidamycin COMPOSITION One capsule of 75 mg contains 75 mg Clindamycin (as hydrochloride). One capsule of 150 mg contains 150 mg Clindamycin (as hydrochloride). PROPERTIES
Changes in the 2010 STD Treatment Guidelines: What Adolescent Health Care Providers Should Know February 2011
 Changes in the 2010 STD Treatment Guidelines: What Adolescent Health Care Providers Should Know February 2011 Gale Burstein, MD, MPH, FAAP, FSAHM 1 Amanda Jacobs, MD, FAAP, 2 Dmitry Kissin, MD, MPH, 3
Changes in the 2010 STD Treatment Guidelines: What Adolescent Health Care Providers Should Know February 2011 Gale Burstein, MD, MPH, FAAP, FSAHM 1 Amanda Jacobs, MD, FAAP, 2 Dmitry Kissin, MD, MPH, 3
Protocol for the treatment of oral candida at E.M.H.
 Protocol for the treatment of oral candida at E.M.H. Introduction Candidosis and Xerostomia [a dry mouth] are the two most common oral problems found in palliative care. Cancer patients are very susceptible
Protocol for the treatment of oral candida at E.M.H. Introduction Candidosis and Xerostomia [a dry mouth] are the two most common oral problems found in palliative care. Cancer patients are very susceptible
TB CARE EARLY DETECTION AND PREVENTION OF TUBERCULOSIS (TB) IN CHILDREN. Risk factors in children acquiring TB:
 EARLY DETECTION AND PREVENTION OF TUBERCULOSIS (TB) IN CHILDREN Risk factors in children acquiring TB: Children living in the same household as a lung TB patient (especially children under 5) Children
EARLY DETECTION AND PREVENTION OF TUBERCULOSIS (TB) IN CHILDREN Risk factors in children acquiring TB: Children living in the same household as a lung TB patient (especially children under 5) Children
Streptococcal Infections
 Streptococcal Infections Introduction Streptococcal, or strep, infections cause a variety of health problems. These infections can cause a mild skin infection or sore throat. But they can also cause severe,
Streptococcal Infections Introduction Streptococcal, or strep, infections cause a variety of health problems. These infections can cause a mild skin infection or sore throat. But they can also cause severe,
Urinary Tract Infections
 1 Infections in the urinary tract are relatively common. These infections are often referred to as bladder infections. They are also known as UTI s or urinary tract infections. When an infection is confined
1 Infections in the urinary tract are relatively common. These infections are often referred to as bladder infections. They are also known as UTI s or urinary tract infections. When an infection is confined
Alameda Alliance for Heath ICD-9 to ICD-10 TRANSLATION CODES E10.10
 DIABETES ICD-9 CM ICD-9 CM Volume 1 - Diagnosis Description ICD-10 CM - Diagnosis Code ICD-10 CM - Diagnosis Description 250.00 Diabetes mellitus without mention of complication, type II or unspecified
DIABETES ICD-9 CM ICD-9 CM Volume 1 - Diagnosis Description ICD-10 CM - Diagnosis Code ICD-10 CM - Diagnosis Description 250.00 Diabetes mellitus without mention of complication, type II or unspecified
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS ABOUT PERTUSSIS (WHOOPING COUGH)
 FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS ABOUT PERTUSSIS (WHOOPING COUGH) What is pertussis? General Questions About Pertussis Pertussis, or whooping cough, is a contagious illness that is spread when an infected person
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS ABOUT PERTUSSIS (WHOOPING COUGH) What is pertussis? General Questions About Pertussis Pertussis, or whooping cough, is a contagious illness that is spread when an infected person
FAQs on Influenza A (H1N1-2009) Vaccine
 FAQs on Influenza A (H1N1-2009) Vaccine 1) What is Influenza A (H1N1-2009) (swine flu) 1? Influenza A (H1N1-2009), previously known as "swine flu", is a new strain of influenza virus that spreads from
FAQs on Influenza A (H1N1-2009) Vaccine 1) What is Influenza A (H1N1-2009) (swine flu) 1? Influenza A (H1N1-2009), previously known as "swine flu", is a new strain of influenza virus that spreads from
Clinical Reasoning Handout: URI Symptoms Sore Throat. 1) Pearls
 Clinical Reasoning Handout: URI Symptoms Sore Throat 1) Pearls Background: Sore throat is one the most common symptoms evaluated in primary care Almost 5% of patient report sore throat as the primary reason
Clinical Reasoning Handout: URI Symptoms Sore Throat 1) Pearls Background: Sore throat is one the most common symptoms evaluated in primary care Almost 5% of patient report sore throat as the primary reason
Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Tritanrix HB [Diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (whole cell) and hepatitis B (rdna) vaccine (adsorbed)]
![Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Tritanrix HB [Diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (whole cell) and hepatitis B (rdna) vaccine (adsorbed)] Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Tritanrix HB [Diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (whole cell) and hepatitis B (rdna) vaccine (adsorbed)]](/thumbs/27/12172665.jpg) EMA/14365/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Tritanrix HB [Diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (whole cell) and hepatitis B (rdna) vaccine (adsorbed)] Overview of disease epidemiology Diphtheria
EMA/14365/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Tritanrix HB [Diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (whole cell) and hepatitis B (rdna) vaccine (adsorbed)] Overview of disease epidemiology Diphtheria
Gilenya. Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered
 Gilenya Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Your Consultant Neurologist has suggested that you may benefit from treatment with Gilenya. The decision to start this form of treatment can be difficult.
Gilenya Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Your Consultant Neurologist has suggested that you may benefit from treatment with Gilenya. The decision to start this form of treatment can be difficult.
Yoon Nofsinger, M.D. Tampa ENT Associates, 3450 East Fletcher Avenue, Tampa, FL 33613 Phone (813) 972-3353, Fax (813) 978 3667
 Yoon Nofsinger, M.D. Tampa ENT Associates, 3450 East Fletcher Avenue, Tampa, FL 33613 Phone (813) 972-3353, Fax (813) 978 3667 General Information: Allergies and Injection Therapy 1. General: You have
Yoon Nofsinger, M.D. Tampa ENT Associates, 3450 East Fletcher Avenue, Tampa, FL 33613 Phone (813) 972-3353, Fax (813) 978 3667 General Information: Allergies and Injection Therapy 1. General: You have
CDC 2015 STD Treatment Guidelines: Update for IHS Providers Sharon Adler M.D., M.P.H.
 CDC 2015 STD Treatment Guidelines: Update for IHS Providers Sharon Adler M.D., M.P.H. Clinical Faculty, CA Prevention Training Center Disclosure Information Sharon Adler MD, MPH I have no financial relationships
CDC 2015 STD Treatment Guidelines: Update for IHS Providers Sharon Adler M.D., M.P.H. Clinical Faculty, CA Prevention Training Center Disclosure Information Sharon Adler MD, MPH I have no financial relationships
Antimicrobial Guide and Management of Common Infections in Primary Care
 2015/16 Antimicrobial Guide and Management of Common Infections in Primary Care Strategies to Optimise Prescribing of Antimicrobials in Primary Care Review 2017 Version: 6.2 Review: 2017 (or earlier if
2015/16 Antimicrobial Guide and Management of Common Infections in Primary Care Strategies to Optimise Prescribing of Antimicrobials in Primary Care Review 2017 Version: 6.2 Review: 2017 (or earlier if
41 Viral rashes and skin infections
 41 Viral rashes and skin infections Clinical There are several kinds of skin infections caused by viruses, and these are best considered in the four categories that group together similar symptoms for
41 Viral rashes and skin infections Clinical There are several kinds of skin infections caused by viruses, and these are best considered in the four categories that group together similar symptoms for
A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment of Infection in the Outpatient Setting Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections
 A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment of Infection in the Outpatient Setting Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections By Gary R. Skankey, MD, FACP, Infectious Disease, Las Vegas, NV Sponsored
A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment of Infection in the Outpatient Setting Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections By Gary R. Skankey, MD, FACP, Infectious Disease, Las Vegas, NV Sponsored
Factsheet September 2012. Pertussis immunisation for pregnant women. Introduction
 Factsheet September 2012 Pertussis immunisation for pregnant women Introduction The routine childhood immunisation programme has been very effective in reducing the overall numbers of cases of pertussis.
Factsheet September 2012 Pertussis immunisation for pregnant women Introduction The routine childhood immunisation programme has been very effective in reducing the overall numbers of cases of pertussis.
Primary Care management of Overactive Bladder (OAB)
 DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) Primary Care management of Overactive Bladder (OAB) Prescribing Tips All medicines for OAB have similar dose-related efficacy. More than one agent (up
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) Primary Care management of Overactive Bladder (OAB) Prescribing Tips All medicines for OAB have similar dose-related efficacy. More than one agent (up
Alberta Health and Wellness Public Health Notifiable Disease Management Guidelines August 2011
 August 2011 Pertussis Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) August 2011 August 2011 December 2005 Case Definition
August 2011 Pertussis Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) August 2011 August 2011 December 2005 Case Definition
Riesa Gusewelle, MNSc, RN, APRN, GNP-BC. OBJECTIVES Identify early warning signs of urinary tract
 Detection, Early Management & Prevention, of Urinary Tract Infections in Older Adults Riesa Gusewelle, MNSc, RN, APRN, GNP-BC OBJECTIVES Identify early warning signs of urinary tract infections (UTIs)
Detection, Early Management & Prevention, of Urinary Tract Infections in Older Adults Riesa Gusewelle, MNSc, RN, APRN, GNP-BC OBJECTIVES Identify early warning signs of urinary tract infections (UTIs)
Solid Organ Transplantation
 Solid Organ Transplantation Infection Prevention And Control Transplant Atlantic 2011 October 13/2011 Kathy Hart Introduction In the past several years, the drugs that we use, the surgeries themselves,
Solid Organ Transplantation Infection Prevention And Control Transplant Atlantic 2011 October 13/2011 Kathy Hart Introduction In the past several years, the drugs that we use, the surgeries themselves,
BE SURE. BE SAFE. VACCINATE.
 DON T GET OR GIVE THE FLU THIS YEAR THANK YOU Vaccination is the only protection. www.immunisation.ie BE SURE. BE SAFE. VACCINATE. FLU VACCINE 2013-2014 Healthcare workers prevent the spread of flu and
DON T GET OR GIVE THE FLU THIS YEAR THANK YOU Vaccination is the only protection. www.immunisation.ie BE SURE. BE SAFE. VACCINATE. FLU VACCINE 2013-2014 Healthcare workers prevent the spread of flu and
Sepsis Awareness Month
 Aon Kenya Insurance Brokers Ltd Aon Hewitt Healthcare Division Sepsis Awareness Month Issue 11 September 2015 In this Issue 2 Getting to understand Sepsis 3 Stages in Sepsis Advancement 4 Diagnosis & Treatment
Aon Kenya Insurance Brokers Ltd Aon Hewitt Healthcare Division Sepsis Awareness Month Issue 11 September 2015 In this Issue 2 Getting to understand Sepsis 3 Stages in Sepsis Advancement 4 Diagnosis & Treatment
OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH, DISABILITY AND LEAVE SECTOR MEASURES TO MINIMIZE EXPOSURE TO BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS AND POST-EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS POLICY
 UNIVERSITY OF OTTAWA OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH, DISABILITY AND LEAVE SECTOR MEASURES TO MINIMIZE EXPOSURE TO BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS AND POST-EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS POLICY Prepared by the Occupational Health, Disability
UNIVERSITY OF OTTAWA OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH, DISABILITY AND LEAVE SECTOR MEASURES TO MINIMIZE EXPOSURE TO BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS AND POST-EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS POLICY Prepared by the Occupational Health, Disability
2. Characteristics of staff Qualifications required. Additional requirements. Continued education & training requirements
 Patient Group Direction The supply of Azithromycin 1g as a single dose by accredited Community Pharmacists to patients in receipt of a positive test result to Chlamydia trachomatis, and treatment of their
Patient Group Direction The supply of Azithromycin 1g as a single dose by accredited Community Pharmacists to patients in receipt of a positive test result to Chlamydia trachomatis, and treatment of their
HIV/AIDS. HIV- Human Immunodeficiency Virus. AIDS immume system severely damaged
 HIV/AIDS HIV- Human Immunodeficiency Virus Person is infected with virus. May have no s/s (but may transmit virus) More common to have brief flu-like illness 2-6 wks after becoming infected (swollen lymph
HIV/AIDS HIV- Human Immunodeficiency Virus Person is infected with virus. May have no s/s (but may transmit virus) More common to have brief flu-like illness 2-6 wks after becoming infected (swollen lymph
Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea, Clostridium difficile- Associated Diarrhea and Colitis
 Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea, Clostridium difficile- Associated Diarrhea and Colitis ANTIBIOTIC-ASSOCIATED DIARRHEA Disturbance of the normal colonic microflora Leading to alterations in bacterial degradation
Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea, Clostridium difficile- Associated Diarrhea and Colitis ANTIBIOTIC-ASSOCIATED DIARRHEA Disturbance of the normal colonic microflora Leading to alterations in bacterial degradation
Exposure. What Healthcare Personnel Need to Know
 Information from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Infectious Diseases Divison of Healthcare Quality Promotion and Division of Viral Hepatitis For additional brochures
Information from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Infectious Diseases Divison of Healthcare Quality Promotion and Division of Viral Hepatitis For additional brochures
Rheumatoid Arthritis. GP workshop 15 January 2011
 Rheumatoid Arthritis GP workshop 15 January 2011 Case 1 A 72 year old Malay woman with RA comes for routine follow up. She feels generally unwell in the last 5 days. Appetite is fair. Her joints are fine.
Rheumatoid Arthritis GP workshop 15 January 2011 Case 1 A 72 year old Malay woman with RA comes for routine follow up. She feels generally unwell in the last 5 days. Appetite is fair. Her joints are fine.
A Summary of the Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of. Urinary Tract Infections in Long Term Care
 A Summary of the Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Urinary Tract Infections in Long Term Care Exclusions Community acquired UTIs UTIs in acute care Prevention Limit use of catheters Ensure
A Summary of the Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Urinary Tract Infections in Long Term Care Exclusions Community acquired UTIs UTIs in acute care Prevention Limit use of catheters Ensure
Adult Vaccination Frequently Asked Questions: The Basics
 The Basics Why should I get vaccinated? Vaccination is the best way to protect against infections that can make you sick and be passed on to those around you. 1 What kinds of side effects will I get from
The Basics Why should I get vaccinated? Vaccination is the best way to protect against infections that can make you sick and be passed on to those around you. 1 What kinds of side effects will I get from
Guideline for the Management of Acute Peripheral Facial nerve palsy. Bells Palsy in Children
 Guideline for the Management of Acute Peripheral Facial nerve palsy Definition Bells Palsy in Children Bell palsy is an acute, idiopathic unilateral lower motor neurone facial nerve palsy that is not associated
Guideline for the Management of Acute Peripheral Facial nerve palsy Definition Bells Palsy in Children Bell palsy is an acute, idiopathic unilateral lower motor neurone facial nerve palsy that is not associated
Pertussis Whooping Cough Update
 May 3, 1 Dear Kitsap County Providers, This is an update about our current status of pertussis cases here in Kitsap County. We currently have 35 cases as outlined below. See the epidemiology curve (Figure
May 3, 1 Dear Kitsap County Providers, This is an update about our current status of pertussis cases here in Kitsap County. We currently have 35 cases as outlined below. See the epidemiology curve (Figure
Why Do Some Antibiotics Fail?
 Why Do Some Antibiotics Fail? Patty W. Wright, M.D. April 2010 Objective To outline common reasons why antibiotic therapy is not successful and how this can be avoided. And to teach you a little bit about
Why Do Some Antibiotics Fail? Patty W. Wright, M.D. April 2010 Objective To outline common reasons why antibiotic therapy is not successful and how this can be avoided. And to teach you a little bit about
Patient Sticker Multiple Sclerosis Ambulatory Emergency Care Pathway
 Multiple Sclerosis Ambulatory Emergency Care Pathway 1 Consultant: Dr M Oldfield Consultant: Dr D Harris Lead Nurse: Catie Paterson Ambulatory Emergency Care (AEC) Unit Patient From ED (Emergency Department)
Multiple Sclerosis Ambulatory Emergency Care Pathway 1 Consultant: Dr M Oldfield Consultant: Dr D Harris Lead Nurse: Catie Paterson Ambulatory Emergency Care (AEC) Unit Patient From ED (Emergency Department)
