Ultrasound screening for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with advanced liver fibrosis. An overview.
|
|
|
- Jeffrey Carter
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Review Med Ultrason 2014, Vol. 16, no. 2, DOI: /mu md1is2 Ultrasound screening for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with advanced liver fibrosis. An overview. Mirela Dănilă, Ioan Sporea Gastroenterology and Hepatology Department, University of Medicine and Pharmacy Victor Babeș, WFUMB Center of Excellence, Timișoara, Romania Abstract Liver cirrhosis is the major risk factor for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). All etiologic forms of liver cirrhosis may be complicated by HCC but the risk is higher in patients with hepatitis B or C viral infection. Patients at high risk for developing HCC should be included in surveillance programs. Groups at high risk are: all cirrhotic patients; non-cirrhotic patients with chronic hepatitis C and advanced liver fibrosis (F3), non-cirrhotic HBV carriers with active hepatitis. Current guidelines issued by AASLD and EASL recommend surveillance among high-risk patients by ultrasound (with or without alpha-fetoprotein) every 6 months. The aim of ultrasound screening and surveillance is to detect HCC at an early stage, when it is amenable to curative therapy, to reduce mortality. For good results, ultrasound examination must be done by highly experienced personnel, with extensive experience in the field of hepatic ultrasound. Keywords: liver cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, ultrasound, screening. Received Accepted Med Ultrason 2014, Vol. 16, No 2, Corresponding author: Mirela Dănilă 73/9 Martir Petru Domăşneanu street Timişoara, Romania mireladanila@gmail.com Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most frequent primary liver cancer occurring frequently in patients with liver cirrhosis and in patients with chronic liver disease and advanced fibrosis. The incidence of HCC is rising in many countries (especially in developing countries), being responsible for more than 500,000 deaths per year. In Romania, according to data provided by GLOBOCAN, in 2008 the incidence of liver cancer for both genders was 5.3/100,000 (8.1/100,000 in men and 3/100,000 in female patients) [1]. Cohort studies indicated that HCC is currently the major cause of liver-related death in patients with compensated cirrhosis. Hepatitis C virus (HCV) and hepatitis B infection (HBV) are associated with the highest HCC incidence in persons with cirrhosis. Treatments modalities (curative treatment) in patients with HCC are frequently outdated at the time of diagnosis, due to advanced disease. Prognosis of HCC is determined by tumor stage at diagnosis and also by the stage of liver disease. Because HCC occurs most often on a background of chronic liver disease, it is important to screen this class of patients for early detection. Ultrasonography (US) is usually used for HCC screening due to its cost-effectiveness and non-invasiveness. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS), contrast enhanced computer tomography (CE- CT) or contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (CE-MRI) are the methods used to certify the diagnosis of HCC. Target populations for screening program Cirrhosis of any etiology is the major risk factor for HCC; in approximately 90% of cases, hepatocellular carcinoma occurs in patients with liver cirrhosis [2]. The risk of HCC varies, according to the etiology of liver cirrhosis, ranging between % per year in HCV related cirrhosis [3] and % per year in HBV related cirrhosis [4]. Also, the incidence of HCC in viral C liver cirrhosis has been reported differently according to the geographi-
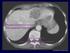
2 140 Mirela Dănilă et al Ultrasound screening for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with advanced liver fibrosis. An overview. cal region. In a retrospective cohort study, the annual HCC incidence was 1.4% in European cirrhotic HCV patients [5]. Degos et al [6] reported HCC incidence rates of 13.4%, after five years follow-up in a French cohort of patients with compensated cirrhosis. In the study performed by Lok et al [7] in the United States, the HCC incidence was higher in HCV patients with cirrhosis, than in those with bridging fibrosis (annual HCC incidence rates: 1.45% vs 0.8%, p=0.08). Infection with HBV and HCV are the major risk factors for the development of HCC. For patients with chronic hepatitis C infection, HCC surveillance is recommended in any patient who has developed cirrhosis. Some experts also recommend screening for HCC in HCV-infected patients who have advanced fibrosis, but no cirrhosis (METAVIR stage 3). HCC screening is not recommended in HCV-infected patients with no advanced fibrosis or cirrhosis. The risk for HCC decreases substantially in patients with cirrhosis who obtain a sustained virologic response (SVR) with therapy for hepatitis C, but this risk is not totally eliminated. This category of patients must also be included in the screening program for early detection of HCC. Chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is estimated to be the cause of 55-60% of HCCs in the world, up to 40% of HBV-related HCC occurring in persons who do not have cirrhosis [8]. Many studies have reported relatively a high incidence of HCC in HBV carriers [9]. In a Taiwanese study, the annual incidence rate of HCC was 0.5% [10], but another study from North America indicated that HCC incidence in HBV carriers varies considerably, with annual HCC incidence rates ranging between 0.06% and 0.46% [11,12]. In hepatitis B viral infection, high transaminases, HBeAg positive status, and high serum HBV DNA levels were risk factors for developing HCC [13]. On the other hand, any patient with liver cirrhosis can develop HCC, including patients with cirrhosis from non-viral causes, such as alcoholic cirrhosis, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), autoimmune hepatitis, and other rare causes of cirrhosis like hemochromatosis, Wilson s disease or alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency. In the later years, liver cirrhosis due to NAFLD is recognized as an important risk factor for HCC. The incidence of NAFLD/NASH (non-alcoholic steatohepatitis) is rising in many countries, in conjunction with obesity, diabetes or dyslipidemia. In a systematic review performed by Wite et al [14], an association between NAFLD/NASH and an increased risk for HCC has been found, but only in patients with cirrhosis. All HCC Guidelines (from the American Association for the Study of Liver Disease AASLD and the European Association for the Study of the Liver EASL) [15,16] recommend the screening for patients at high risk for developing HCC. These categories of patients are: 1. Cirrhotic patients, Child-Pugh stage A and B; 2. Cirrhotic patients, Child-Pugh stage C awaiting liver transplantation; 3. Non-cirrhotic HBV carriers, with active hepatitis or a family history of HCC; 4. Non-cirrhotic patients with chronic hepatitis C and advanced liver fibrosis F3. For patients with liver cirrhosis Child Pugh stage C, who are not candidates for liver transplantation, surveillance is not recommended, since life expectancy is due to the stage of the liver disease. US for HCC surveillance Current guidelines from AASLD and EASL recommend surveillance among high-risk patients by ultrasound [with or without alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)] every 6 months. The aim of US screening and surveillance is to detect HCC at an early stage, when it is amenable to curative therapy in order to reduce mortality. For a good result, US should be performed by experienced personnel. US is a noninvasive method, without any risk for the patients, well accepted by them and also inexpensive, thus making US a repetitive examination in patients with liver cirrhosis. But US detection of HCC on a cirrhotic background is a challenging issue. Liver cirrhosis is characterized by fibrous septa and regenerative nodules. These hepatic features make the evaluation of liver texture sometimes difficult. The sensitivity of US for HCC detection is also significantly associated with patients characteristics difficult in obese patients, with poor hepatic window. Fig 1. Hyperechoic hepatocellular carcinoma aspect in standard US
3 Med Ultrason 2014; 16(2): Fig 2. Hypoechoic hepatocellular carcinoma aspect in standard US Fig 3. Inhomogeneous hepatocellular carcinoma aspect in standard US Fig 4. CEUS examination in a patient with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): a) - HCC aspect in standard ultrasound; b) CEUS examination - arterial phase with hyperenhancement pattern; c) - CEUS examination late phase with wash out Other factors that influence the accuracy of US in the evaluation of liver structure are: technical performance of the US machine (US resolution has been much improved in the latest years), and also the experience of the examiner. Examination of a cirrhotic liver for detection of HCC must be done by highly experienced ultrasonographists, level 2 or 3 according to the EFSUMB and SRUMB classification of Level of Practice for US ( or ro). The US appearance of HCC varies: it may be hyperechoic or hypoechoic (fig 1, fig 2), or it may appear as a target lesion. Sometimes, a small hyperechoic HCC may be confused with hemangioma. Large HCCs are more frequent inhomogeneous (fig 3) and sometimes associated with portal vein thrombosis. Because of the increased risk of developing cancer, a liver mass in a cirrhotic patient strongly suggests the possibility of a HCC, but the final diagnosis of HCC is based on imaging methods with contrast media. In the later years, CEUS performed immediately after standard US examination allows the diagnosis of HCC in the same session [17-19] (fig 4). Sensitivity and specificity of US for early detection of HCC was evaluated in numerous studies, as well as the superiority of screening versus non-screening strategies in patients with risk for HCC. The optimal interval for ultrasonographic surveillance for early detection of HCC is not known. Based on the median doubling time of HCC [20] (range between 80 and 117 days), the recommended interval between HCC surveillance tests is 6 months. In one placebo-controlled randomized study [21], which included 19,000 HBV-infected patients, it was shown that HCC surveillance with both abdominal ultrasound and serum AFP repeated at 6 month intervals,
4 142 Mirela Dănilă et al Ultrasound screening for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with advanced liver fibrosis. An overview. Fig 5. Ultrasound in portal vein thrombosis (PVT): a) - PVT - aspect in standard ultrasound; b) - PVT - CEUS aspect with arterial enhancement in malign PVT. resulted in a 37% reduction in HCC-related mortality. According to the meta-analysis by Singal et al [22], US sensitivities for detecting early-hcc may be improved by US at 6 month intervals, compared to surveillance intervals between 6-12 month (sensitivities: 70% vs 50%, p=0.001). A recent randomized control trial [23] investigated whether a 3-mo interval of US surveillance was more effective than a 6-mo interval and no differences in detection rates of small HCC, eligible for curative treatment, were observed between the two randomized groups. A recent meta-analysis [24] has shown that US can identify subclinical HCCs with a sensitivity of 94% and 90% specificity, but US was less effective for detecting early HCC (Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage A), with a sensitivity of 63%. In the same study, combination of US and serum AFP assessment slightly increased (6%) the sensitivity of surveillance, but almost doubled the cost for each small HCC detected, due to a high number of false positives results. In a study [25] that evaluated the effectiveness of a surveillance program using ultrasound and AFP every 6 to 12 months among patients with cirrhosis, in a realworld clinical setting, the sensitivity of ultrasound alone for early-stage tumors was only 32%. The sensitivity was significantly increased to 63% (p=0.008), when used in combination with AFP. Until now, there are no official recommendations regarding the use of CE-CT or CE-MRI for HCC screening (due to the high cost), but when US visualization of the liver is inadequate, mostly in patients with liver cirrhosis, CE-CT or CE-MRI are frequently used in clinical practice for HCC screening. All studies demonstrated that survival was significantly improved among patients diagnosed with HCC, who had undergone prior screening. This was primarily due to curative therapy in patients with earlier stage HCC and less severe liver disease. AFP for screening in HCC Worldwide, AFP is the most frequently used biomarker for HCC, but not all HCC cells secrete AFP into the circulation. Also, serum AFP levels may be elevated in patients with chronic liver disease in the absence of HCC. In one systematic review, using the usual cut-off point of 20 ng/ml, sensitivities and specificities for detecting all stages of HCC were 41%-65% and 80%-94%, respectively [26] The use of serum AFP as a surveillance test has a poor sensitivity for early HCC, since only a small proportion (10-20%) of early cancers, are associated with elevated AFP serum levels [27,28]. A recent cost-effectiveness analysis found that the combination of ultrasound and AFP was the preferred strategy, when the sensitivity of ultrasound fell below 65% [25]. Thus, in clinical practice, US will be used for screening for HCC in specific categories of patients. For good results, only trained physicians, with extensive experience in the field of hepatic US, must perform this procedure (level 2 or 3 according to the EFSUMB and SRUMB classification). Also mandatory is the use of high tech US machines, preferable able to perform CEUS. In patients with a good acoustic window, this method is usually highly accurate for the diagnosis of HCC (and also for staging the tumor, concerning a possible portal thrombo-
5 sis fig 5) [29]. In cases that are not suitable for ultrasound examination, CE-CT or CE-MRI are the alternatives for screening. Conclusions All patients with advanced liver fibrosis and risk for HCC must undergo ultrasound evaluation every 6 months. Extensive US experience and good US machines are essential for a correct diagnosis. Conflict of interest: none of the authors had any conflict of interest. References 1. Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. GLOBOCAN 2008 v1.2, Cancer Incidence and Mortality Worldwide: IARC CancerBase No. 10, IARC, Lyon, 2010, Accessed on 07/04/ El-Serag HB. Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med 2011;365: Fattovich G, Stroffolini T, Zagni I, Donato F. Hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: incidence and risk factor. Gastroenterology 2004; 127: S35 S Gomez EV, Rodriguez YS, Bertot LC, et al. The natural history of compensated HCV-related cirrhosis: a prospective long-term study. J Hepatol 2013; 58: Fattovich G, Pantalena M, Zagni I, Realdi G, Schalm SW, Christensen E; European Concerted Action on Viral Hepatitis (EUROHEP). Effect of hepatitis B and C virus infections on the natural history of compensated cirrhosis: a cohort study of 297 patients. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002; 97: Degos F, Christidis C, Ganne-Carrie N, et al. Hepatitis C virus related cirrhosis: time to occurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma and death. Gut 2000; 47: Lok AS, Seeff LB, Morgan TR, et al; HALT-C Trial Group. Incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma and associated risk factors in hepatitis C-related advanced liver disease. Gastroenterolog 2009; 136: Lok AS. Hepatitis B: liver fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterol Clin Biol 2009; 33: De Franchis R, Meucci G, Vecchi M, et al. The natural history of asymptomatic hepatitis B surface antigen carriers. Ann Intern Med 1993; 118: Beasley RP, Hwang LY, Lin CC, Chien CS. Hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatitis B virus. A prospective study of men in Taiwan. Lancet 1981; 2: McMahon BJ, Alberts SR, Wainwright RB, Bulkow L, Lanier AP. Hepatitis B-related sequelae. Prospective study in 1400 hepatitis B surface antigen-positive Alaska native carriers. Arch Intern Med 1990; 150: Med Ultrason 2014; 16(2): Sherman M, Peltekian KM, Lee C. Screening for hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic carriers of hepatitis B virus: incidence and prevalence of hepatocellular carcinoma in a North American urban population. Hepatology 1995; 22: Chen CJ, Yang HI, Su J, et al; REVEAL-HBV Study Group. Risk of hepatocellular carcinoma across a biological gradient of serum hepatitis B virus DNA level. JAMA 2006; 295: White DL, Kanwal F, El-Serag HB. Association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and risk for hepatocellular cancer, based on systematic review. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2012; 10: e Bruix J, Sherman M; American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: an update. Hepatology 2011; 53: European Association for the Study of the Liver, European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer. EASL- EORTC clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 2012; 56: Martie A, Sporea I, Șirli R, Popescu A, Dănilă M. How often hepatocellular carcinoma has a typical pattern in contrast enhanced ultrasound? Maedica (Buchar) 2012; 7: Sporea I, Badea R, Popescu A, et al. Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound (CEUS) for the evaluation of focal liver lesions a prospective multicenter study of its usefulness in clinical practice. Ultraschall Med 2014 Feb Sporea I, Martie A, Bota S, Șirli R, Popescu A, Dănilă M. Characterization of focal liver lesions using contrast enhanced ultrasound as a first line method: a large monocentric experience. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis 2014; 23: Kubota K, Ina H, Okada Y, Irie T. Growth rate of primary single hepatocellular carcinoma: determining optimal screening interval with contrast enhanced computed tomography. Dig Dis Sci 2003; 48: Zhang BH, Yang BH, Tang ZY. Randomized controlled trial of screening for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2004; 130: Sigal A, Volk ML, Waljee A, et al. Meta-analysis: surveillance with ultrasound for early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2009; 30: Trinchet JC, Chaffaut C, Bourcier V, et al; Groupe d Etude et de Traitement du Carcinome Hépatocellulaire (GRETCH). Ultrasonographic surveillance of hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: a randomized trial comparing 3- and 6-month periodicities. Hepatology 2011; 54: Singal AG, Conjeevaram HS, Volk ML, et al. Effectiveness of hepatocellular carcinoma surveillance in patients with cirrhosis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2012; 21: Andersson KL, Salomon JA, Goldie SJ, Chung RT. Cost effectiveness of alternative surveillance strategies for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2008; 6:
6 144 Mirela Dănilă et al Ultrasound screening for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with advanced liver fibrosis. An overview. 26. Gupta S, Bent S, Kohlwes J. Test characteristics of alphafetoprotein for detecting hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with hepatitis C. A systematic review and critical analysis. Ann Intern Med 2003; 139: Sherman M. Current status of alpha-fetoprotein testing. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y) 2011; 7: Giannini EG, Marenco S, Borgonovo G, et al; Italian Liver Cancer (ITA.LI.CA) group. Alpha-fetoprotein has no prognostic role in small hepatocellular carcinoma identified during surveillance in compensated cirrhosis. Hepatology 2012; 56: Dănilă M, Sporea I, Popescu A, Sirli R, Sendroiu M. The value of contrast enhanced ultrasound in the evaluation of the nature of portal vein thrombosis. Med Ultrason 2011; 13:
Surveillance for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
 Surveillance for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Marion G. Peters, MD John V. Carbone, MD, Endowed Chair Professor of Medicine Chief of Hepatology Research University of California San Francisco Recorded on April
Surveillance for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Marion G. Peters, MD John V. Carbone, MD, Endowed Chair Professor of Medicine Chief of Hepatology Research University of California San Francisco Recorded on April
After the Cure: Long-Term Management of HCV Liver Disease Norah A. Terrault, MD, MPH
 After the Cure: Long-Term Management of HCV Liver Disease Norah A. Terrault, MD, MPH Professor of Medicine Department of Gastroenterology Director, Viral Hepatitis Center University of California San Francisco
After the Cure: Long-Term Management of HCV Liver Disease Norah A. Terrault, MD, MPH Professor of Medicine Department of Gastroenterology Director, Viral Hepatitis Center University of California San Francisco
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES
 PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GASTROINTESTINAL HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA GI Site Group Hepatocellular Carcinoma Authors: Dr. Jennifer Knox, Dr. Mairead McNamara 1. INTRODUCTION
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GASTROINTESTINAL HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA GI Site Group Hepatocellular Carcinoma Authors: Dr. Jennifer Knox, Dr. Mairead McNamara 1. INTRODUCTION
Screening for hepatocellular carcinoma: survival benefit and cost-effectiveness
 Review Annals of Oncology 14: 1463 1467, 2003 DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdg400 Screening for hepatocellular carcinoma: survival benefit and cost-effectiveness M.-F. Yuen & C.-L. Lai* Department of Medicine,
Review Annals of Oncology 14: 1463 1467, 2003 DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdg400 Screening for hepatocellular carcinoma: survival benefit and cost-effectiveness M.-F. Yuen & C.-L. Lai* Department of Medicine,
PREVENTION OF HCC BY HEPATITIS C TREATMENT. Morris Sherman University of Toronto
 PREVENTION OF HCC BY HEPATITIS C TREATMENT Morris Sherman University of Toronto Pathogenesis of HCC in chronic hepatitis C Injury cirrhosis HCC Injury cirrhosis HCC Time The Ideal Study Prospective randomized
PREVENTION OF HCC BY HEPATITIS C TREATMENT Morris Sherman University of Toronto Pathogenesis of HCC in chronic hepatitis C Injury cirrhosis HCC Injury cirrhosis HCC Time The Ideal Study Prospective randomized
Liver Transplantation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. John P. Roberts, MD Chief, Division of Transplant Service University of California, San Francisco
 Liver Transplantation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma John P. Roberts, MD Chief, Division of Transplant Service University of California, San Francisco Hepatocellular Carcinoma HCC is the 5th most common
Liver Transplantation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma John P. Roberts, MD Chief, Division of Transplant Service University of California, San Francisco Hepatocellular Carcinoma HCC is the 5th most common
DENOMINATOR: All patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of chronic hepatitis C cirrhosis
 Measure #401: Hepatitis C: Screening for Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) in Patients with Cirrhosis National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY
Measure #401: Hepatitis C: Screening for Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) in Patients with Cirrhosis National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY
LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS
 LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS Healthy Liver Cirrhotic Liver Tumour What causes liver cancer? Many factors may play a role in the development of cancer. Because the liver filters blood
LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS Healthy Liver Cirrhotic Liver Tumour What causes liver cancer? Many factors may play a role in the development of cancer. Because the liver filters blood
Cirrhosis and HCV. Jonathan Israel M.D.
 Cirrhosis and HCV Jonathan Israel M.D. Outline Relationship of fibrosis and cirrhosisprevalence and epidemiology. Sequelae of cirrhosis Diagnosis of cirrhosis Effect of cirrhosis on efficacy of treatment
Cirrhosis and HCV Jonathan Israel M.D. Outline Relationship of fibrosis and cirrhosisprevalence and epidemiology. Sequelae of cirrhosis Diagnosis of cirrhosis Effect of cirrhosis on efficacy of treatment
Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Guide to Screening and Diagnosis
 February 2012 Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Guide to Screening and Diagnosis Reid Merryman, Harvard Medical School Year III Agenda Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) introduction Index patient: clinical presentation
February 2012 Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Guide to Screening and Diagnosis Reid Merryman, Harvard Medical School Year III Agenda Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) introduction Index patient: clinical presentation
Lamivudine for Patients with hronic Hepatitis B and Advanced Liver Disease. From : New England Journal of Medicine
 Lamivudine for Patients with hronic Hepatitis B and Advanced Liver Disease From : New England Journal of Medicine Volume 351:1521-1531, Number 15, Oct 7, 2004 馬 偕 紀 念 醫 院 一 般 內 科, 肝 膽 腸 胃 科 新 竹 分 院 陳 重
Lamivudine for Patients with hronic Hepatitis B and Advanced Liver Disease From : New England Journal of Medicine Volume 351:1521-1531, Number 15, Oct 7, 2004 馬 偕 紀 念 醫 院 一 般 內 科, 肝 膽 腸 胃 科 新 竹 分 院 陳 重
BACKGROUND MEDIA INFORMATION Fast facts about liver disease
 BACKGROUND MEDIA INFORMATION Fast facts about liver disease Liver, or hepatic, disease comprises a wide range of complex conditions that affect the liver. Liver diseases are extremely costly in terms of
BACKGROUND MEDIA INFORMATION Fast facts about liver disease Liver, or hepatic, disease comprises a wide range of complex conditions that affect the liver. Liver diseases are extremely costly in terms of
AASLD PRACTICE GUIDELINE Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
 AASLD PRACTICE GUIDELINE Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Jordi Bruix 1 and Morris Sherman 2 Preamble These recommendations provide a data-supported approach to the diagnosis, staging and treatment
AASLD PRACTICE GUIDELINE Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Jordi Bruix 1 and Morris Sherman 2 Preamble These recommendations provide a data-supported approach to the diagnosis, staging and treatment
Hepatocellular Carcinoma: What the hepatologist wants to know
 Hepatocellular Carcinoma: What the hepatologist wants to know Hélène Castel, MD Liver Unit Hôpital St-Luc CHUM? CAR Annual Scientific Meeting Saturday, April 27 th 2013 Disclosure statement I do not have
Hepatocellular Carcinoma: What the hepatologist wants to know Hélène Castel, MD Liver Unit Hôpital St-Luc CHUM? CAR Annual Scientific Meeting Saturday, April 27 th 2013 Disclosure statement I do not have
NP/PA Clinical Hepatology Fellowship Summary of Year-Long Curriculum
 OVERVIEW OF THE FELLOWSHIP The goal of the AASLD NP/PA Fellowship is to provide a 1-year postgraduate hepatology training program for nurse practitioners and physician assistants in a clinical outpatient
OVERVIEW OF THE FELLOWSHIP The goal of the AASLD NP/PA Fellowship is to provide a 1-year postgraduate hepatology training program for nurse practitioners and physician assistants in a clinical outpatient
BURDEN OF LIVER DISEASE IN BRAZIL
 BURDEN OF LIVER DISEASE IN BRAZIL Burden of Liver Disease in Europe Blachier et al. J Hepatol 58:593, 2013 Review of 260 epidemiologic studies of the 5 previous years Cirrhosis is responsible for 170.000
BURDEN OF LIVER DISEASE IN BRAZIL Burden of Liver Disease in Europe Blachier et al. J Hepatol 58:593, 2013 Review of 260 epidemiologic studies of the 5 previous years Cirrhosis is responsible for 170.000
The Natural History of Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection
 The Natural History of Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection Brian J. McMahon, M.D. 1 ABSTRACT Three stages of chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection are recognized: the immune tolerant phase, the chronic
The Natural History of Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection Brian J. McMahon, M.D. 1 ABSTRACT Three stages of chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection are recognized: the immune tolerant phase, the chronic
Recommendations for the Identification of Chronic Hepatitis C virus infection Among Persons Born During 1945-1965
 Recommendations for the Identification of Chronic Hepatitis C virus infection Among Persons Born During 1945-1965 MMWR August 17, 2012 Prepared by : The National Viral Hepatitis Technical Assistance Center
Recommendations for the Identification of Chronic Hepatitis C virus infection Among Persons Born During 1945-1965 MMWR August 17, 2012 Prepared by : The National Viral Hepatitis Technical Assistance Center
Management of Chronic Hepatitis B: 2012 Update
 Management of Chronic Hepatitis B: 2012 Update Brian J McMahon MD, Liver Disease and Hepatitis Program Alaska Native Medical Center and Arctic Investigations Program, CDC Conflicts of Interest The Liver
Management of Chronic Hepatitis B: 2012 Update Brian J McMahon MD, Liver Disease and Hepatitis Program Alaska Native Medical Center and Arctic Investigations Program, CDC Conflicts of Interest The Liver
SBRT (Elekta), 45 Gy in fractions of 3 Gy 3x/week for 5 weeks (N=22) vs.
 Uitgangsvraag 6: Wat is de plaats van stereotactische radiotherapiebehandeling (SBRT) bij HCC patiënten? Primaire studies I Study ID II Method III Patient characteristics IV Intervention(s) V Results primary
Uitgangsvraag 6: Wat is de plaats van stereotactische radiotherapiebehandeling (SBRT) bij HCC patiënten? Primaire studies I Study ID II Method III Patient characteristics IV Intervention(s) V Results primary
Non-invasive evaluation of liver fibrosis: current clinical use and next perspectives (chronic hepatitis C)
 Non-invasive evaluation of liver fibrosis: current clinical use and next perspectives (chronic hepatitis C) Paul Calès Liver and Gastroenterology department, University hospital & HIFIH laboratory, Angers
Non-invasive evaluation of liver fibrosis: current clinical use and next perspectives (chronic hepatitis C) Paul Calès Liver and Gastroenterology department, University hospital & HIFIH laboratory, Angers
EASL EORTC Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma
 Clinical Practice Guidelines EASL EORTC Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma European Association for the Study of the Liver, European Organisation for Research and Treatment
Clinical Practice Guidelines EASL EORTC Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma European Association for the Study of the Liver, European Organisation for Research and Treatment
National Health Burden of CLD in Italy
 National Health Burden of CLD in Italy 11,000 deaths due to liver cirrhosis or HCC in 2006 Direct costs for the National Health System for treating CLD patients: 420 M / year for hospital care 164 M /
National Health Burden of CLD in Italy 11,000 deaths due to liver cirrhosis or HCC in 2006 Direct costs for the National Health System for treating CLD patients: 420 M / year for hospital care 164 M /
Hepatitis C Treatment Criteria Commercial & Minnesota Health Care Programs
 Last update: February 23, 2015 Hepatitis C Treatment Criteria Commercial & Minnesota Health Care Programs Please see healthpartners.com for Medicare coverage criteria. Table of Contents 1. Harvoni 2. Sovaldi
Last update: February 23, 2015 Hepatitis C Treatment Criteria Commercial & Minnesota Health Care Programs Please see healthpartners.com for Medicare coverage criteria. Table of Contents 1. Harvoni 2. Sovaldi
EASL EORTC Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma
 Clinical Practice Guidelines EASL EORTC Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma European Association for the Study of the Liver, European Organisation for Research and Treatment
Clinical Practice Guidelines EASL EORTC Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma European Association for the Study of the Liver, European Organisation for Research and Treatment
What to Do with the Patient With Abnormal Liver Enzymes? Nizar N. Zein, M.D. The Cleveland Clinic
 What to Do with the Patient With Abnormal Liver Enzymes? Nizar N. Zein, M.D. The Cleveland Clinic Introduction Elevated liver enzymes is often not a clinical problem by itself. However it is a warning
What to Do with the Patient With Abnormal Liver Enzymes? Nizar N. Zein, M.D. The Cleveland Clinic Introduction Elevated liver enzymes is often not a clinical problem by itself. However it is a warning
Optimal imaging surveillance schedules after liver directed therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma
 Optimal imaging surveillance schedules after liver directed therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma F. Edward Boas, MD, PhD; Bao Do, MD; John D. Louie, MD; Nishita Kothary, MD; Gloria L. Hwang, MD; William
Optimal imaging surveillance schedules after liver directed therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma F. Edward Boas, MD, PhD; Bao Do, MD; John D. Louie, MD; Nishita Kothary, MD; Gloria L. Hwang, MD; William
Clinical Application of HBs quantification
 Clinical Application of HBs quantification Hepatology on the Nile 2 Advances in Liver Disease 2014, "World Expert Review» Wednesday, September 24, 2014 Pr Tarik Asselah MD, PhD; Service d Hépatologie &
Clinical Application of HBs quantification Hepatology on the Nile 2 Advances in Liver Disease 2014, "World Expert Review» Wednesday, September 24, 2014 Pr Tarik Asselah MD, PhD; Service d Hépatologie &
Recommendations 8/14/2014. Hepatitis C Clinical Approach Primary Care. Purpose of Presentation. HCV Prevalence Year of Birth
 Hepatitis C Clinical Approach Primary Care Dr. Vicki L. MIt McIntyre, FNP Tucson Gastroenterology Specialists Tucson, Arizona University of Phoenix Lead Faculty, Department of Nursing Tucson, Arizona Purpose
Hepatitis C Clinical Approach Primary Care Dr. Vicki L. MIt McIntyre, FNP Tucson Gastroenterology Specialists Tucson, Arizona University of Phoenix Lead Faculty, Department of Nursing Tucson, Arizona Purpose
J Clin Oncol 26:177-182. 2008 by American Society of Clinical Oncology INTRODUCTION
 VOLUME 26 NUMBER 2 JANUARY 10 2008 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY O R I G I N A L R E P O R T High Viral Load and Hepatitis B Virus Subgenotype Ce Are Associated With Increased Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
VOLUME 26 NUMBER 2 JANUARY 10 2008 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY O R I G I N A L R E P O R T High Viral Load and Hepatitis B Virus Subgenotype Ce Are Associated With Increased Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA (HCC) RESECTION VERSUS TRANSPLANTATION. Francis Yao, M.D.
 UCSF TRANSPLANT CONFERENCE - 9/28/2012 HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA (HCC) RESECTION VERSUS TRANSPLANTATION Francis Yao, M.D. Professor of Clinical Medicine and Surgery Medical Director, Liver Transplantation
UCSF TRANSPLANT CONFERENCE - 9/28/2012 HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA (HCC) RESECTION VERSUS TRANSPLANTATION Francis Yao, M.D. Professor of Clinical Medicine and Surgery Medical Director, Liver Transplantation
Latin American Association for the Study of the Liver (LAASL) Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
 s4 May, Vol. 13 Supl. 1, 2014: s4-s40 Latin American Association for the Study of the Liver (LAASL) Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma On behalf of LAASL Nahum Méndez-Sánchez,
s4 May, Vol. 13 Supl. 1, 2014: s4-s40 Latin American Association for the Study of the Liver (LAASL) Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma On behalf of LAASL Nahum Méndez-Sánchez,
Peg-IFN and ribavirin: what sustained virologic response can be achieved by using HCV genotyping and viral kinetics?
 Peg-IFN and ribavirin: what sustained virologic response can be achieved by using HCV genotyping and viral kinetics? Prof. I. Bakulin Gastroenterology Department Key Questions Background Worldwide prevalence
Peg-IFN and ribavirin: what sustained virologic response can be achieved by using HCV genotyping and viral kinetics? Prof. I. Bakulin Gastroenterology Department Key Questions Background Worldwide prevalence
Consensus on Hepatobiliary Imaging Practice Guidelines
 Consensus on Hepatobiliary Imaging Practice Guidelines 1 Practice Guidelines on Hepatobiliary Imaging: A Malaysian Perspective College of Radiology, Consensus Document Eecutive Summary i This is a consensus
Consensus on Hepatobiliary Imaging Practice Guidelines 1 Practice Guidelines on Hepatobiliary Imaging: A Malaysian Perspective College of Radiology, Consensus Document Eecutive Summary i This is a consensus
Evaluation and Prognosis of Patients with Cirrhosis
 Evaluation and Prognosis of Patients with Cirrhosis Marion G. Peters, MD John V. Carbone, MD, Endowed Chair Professor of Medicine Chief of Hepatology Research University of California San Francisco Recorded
Evaluation and Prognosis of Patients with Cirrhosis Marion G. Peters, MD John V. Carbone, MD, Endowed Chair Professor of Medicine Chief of Hepatology Research University of California San Francisco Recorded
Hepatitis C Infections in Oregon September 2014
 Public Health Division Hepatitis C Infections in Oregon September 214 Chronic HCV in Oregon Since 25, when positive laboratory results for HCV infection became reportable in Oregon, 47,252 persons with
Public Health Division Hepatitis C Infections in Oregon September 214 Chronic HCV in Oregon Since 25, when positive laboratory results for HCV infection became reportable in Oregon, 47,252 persons with
Transmission of HCV in the United States (CDC estimate)
 Transmission of HCV in the United States (CDC estimate) Past and Future US Incidence and Prevalence of HCV Infection Decline among IDUs Overall incidence Overall prevalence Infected 20+ years Armstrong
Transmission of HCV in the United States (CDC estimate) Past and Future US Incidence and Prevalence of HCV Infection Decline among IDUs Overall incidence Overall prevalence Infected 20+ years Armstrong
Acute on Chronic Liver Failure: Current Concepts. Disclosures
 Acute on Chronic Liver Failure: Current Concepts Vandana Khungar, MD MSc Assistant Professor of Medicine University of Pennsylvania, Perelman School of Medicine September 20, 2015 None to declare Disclosures
Acute on Chronic Liver Failure: Current Concepts Vandana Khungar, MD MSc Assistant Professor of Medicine University of Pennsylvania, Perelman School of Medicine September 20, 2015 None to declare Disclosures
New IDSA/AASLD Guidelines for Hepatitis C
 NORTHWEST AIDS EDUCATION AND TRAINING CENTER New IDSA/AASLD Guidelines for Hepatitis C John Scott, MD, MSc Associate Professor, UW SoM Asst Director, Liver Clinic, Harborview Medical Center Presentation
NORTHWEST AIDS EDUCATION AND TRAINING CENTER New IDSA/AASLD Guidelines for Hepatitis C John Scott, MD, MSc Associate Professor, UW SoM Asst Director, Liver Clinic, Harborview Medical Center Presentation
AASLD PRACTICE GUIDELINE. Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An Update. Surveillance and Diagnosis. Staging and Treatment of HCC
 AASLD PRACTICE GUIDELINE Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An Update Jordi Bruix, 1 and Morris Sherman 2 Since the publication of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD)
AASLD PRACTICE GUIDELINE Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An Update Jordi Bruix, 1 and Morris Sherman 2 Since the publication of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD)
Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis
 Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis Professor Matthew Cramp South West Liver Unit and Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry, Plymouth Summary liver function / liver function
Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis Professor Matthew Cramp South West Liver Unit and Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry, Plymouth Summary liver function / liver function
Placing Nation on the Path Toward the Elimination of Hepatitis C
 Placing Nation on the Path Toward the Elimination of Hepatitis C John W. Ward, M.D. Division of Viral Hepatitis Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Division of Viral Hepatitis National Center for
Placing Nation on the Path Toward the Elimination of Hepatitis C John W. Ward, M.D. Division of Viral Hepatitis Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Division of Viral Hepatitis National Center for
Hepatitis C virus related cirrhosis: time to occurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma and death
 Gut ;47:3 36 3 Hepatitis C virus related cirrhosis: time to occurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma and death F Degos, C Christidis, N Ganne-Carrie, J-P Farmachidi, C Degott, C Guettier, J-C Trinchet, M
Gut ;47:3 36 3 Hepatitis C virus related cirrhosis: time to occurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma and death F Degos, C Christidis, N Ganne-Carrie, J-P Farmachidi, C Degott, C Guettier, J-C Trinchet, M
Abnormal Liver Function. Dr William Alazawi MA(Cantab) PhD MRCP Senior Lecturer and Consultant in Hepatology Queen Mary, University of London
 Abnormal Liver Function Dr William Alazawi MA(Cantab) PhD MRCP Senior Lecturer and Consultant in Hepatology Queen Mary, University of London Does Liver Disease Matter? Mortality in England & Wales Liver-related
Abnormal Liver Function Dr William Alazawi MA(Cantab) PhD MRCP Senior Lecturer and Consultant in Hepatology Queen Mary, University of London Does Liver Disease Matter? Mortality in England & Wales Liver-related
Efficacy of Prophylactic Entecavir for Hepatitis B Virus- Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma Receiving Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization
 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2015.16.18.8659 Efficacy of Prophylactic Entecavir for Hepatitis B Virus Related HCC Receiving Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization RESEARCH ARTICLE Efficacy of
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2015.16.18.8659 Efficacy of Prophylactic Entecavir for Hepatitis B Virus Related HCC Receiving Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization RESEARCH ARTICLE Efficacy of
Approach to Patients with Elevated AFP without Liver Mass. Cesar Yaghi MD Hotel Dieu de France Université Saint Joseph cesar.yaghi@usj.edu.
 Approach to Patients with Elevated AFP without Liver Mass Cesar Yaghi MD Hotel Dieu de France Université Saint Joseph cesar.yaghi@usj.edu.lb Alpha Fetoprotein in HCC Levels greater than 500 mcg/l (normal
Approach to Patients with Elevated AFP without Liver Mass Cesar Yaghi MD Hotel Dieu de France Université Saint Joseph cesar.yaghi@usj.edu.lb Alpha Fetoprotein in HCC Levels greater than 500 mcg/l (normal
Leading the Way to Treat Liver Cancer
 Leading the Way to Treat Liver Cancer Guest Expert: Sukru, MD Professor of Transplant Surgery Mario Strazzabosco, MD Professor of Internal Medicine www.wnpr.org www.yalecancercenter.org Welcome to Yale
Leading the Way to Treat Liver Cancer Guest Expert: Sukru, MD Professor of Transplant Surgery Mario Strazzabosco, MD Professor of Internal Medicine www.wnpr.org www.yalecancercenter.org Welcome to Yale
Management of hepatitis C: pre- and post-liver transplantation. Piyawat Komolmit Bangkok
 Management of hepatitis C: pre- and post-liver transplantation Piyawat Komolmit Bangkok Liver transplantation and CHC Cirrhosis secondary to HCV is the leading cause of liver transplantation in the US
Management of hepatitis C: pre- and post-liver transplantation Piyawat Komolmit Bangkok Liver transplantation and CHC Cirrhosis secondary to HCV is the leading cause of liver transplantation in the US
Surviving Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the San Joaquin Valley
 Original article Annals of Gastroenterology (2012) 2, 1-9 Survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma in the San Joaquin Valley: a comparison with California Cancer Registry data Pradeep R. Atla
Original article Annals of Gastroenterology (2012) 2, 1-9 Survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma in the San Joaquin Valley: a comparison with California Cancer Registry data Pradeep R. Atla
Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treatment Decision Tree
 Treatment Decision Tree Derek DuBay, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery Liver Transplant and Hepatobiliary Surgery UAB Department of Surgery 1 UAB Liver Tumor Clinic Referrals: 205 996 5970 (phone) 205
Treatment Decision Tree Derek DuBay, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery Liver Transplant and Hepatobiliary Surgery UAB Department of Surgery 1 UAB Liver Tumor Clinic Referrals: 205 996 5970 (phone) 205
Medical publications on HBV and HCV Coinfection
 Recent advances of HBV and HCV co-infection 台 中 榮 總 內 科 部 胃 腸 肝 膽 科 呂 宜 達 醫 師 2013.03.28 Outline Epidemiology of HBV and HCV coinfection Clinical significance of HBV and HCV coinfection Interplay between
Recent advances of HBV and HCV co-infection 台 中 榮 總 內 科 部 胃 腸 肝 膽 科 呂 宜 達 醫 師 2013.03.28 Outline Epidemiology of HBV and HCV coinfection Clinical significance of HBV and HCV coinfection Interplay between
New Data Supporting Modified RECIST (mrecist) for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Running Title: Modified RECIST (mrecist) for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
 New Data Supporting Modified RECIST (mrecist) for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Running Title: Modified RECIST (mrecist) for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Riccardo Lencioni Author s Affiliation: Division of Diagnostic
New Data Supporting Modified RECIST (mrecist) for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Running Title: Modified RECIST (mrecist) for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Riccardo Lencioni Author s Affiliation: Division of Diagnostic
Case Finding for Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C
 Case Finding for Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C John W. Ward, M.D. Division of Viral Hepatitis Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Atlanta, Georgia, USA Division of Viral Hepatitis National Center
Case Finding for Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C John W. Ward, M.D. Division of Viral Hepatitis Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Atlanta, Georgia, USA Division of Viral Hepatitis National Center
Hepatitis C. Eliot Godofsky, MD University Hepatitis Center Bradenton, FL
 Hepatitis C Eliot Godofsky, MD University Hepatitis Center Bradenton, FL Recent Advances in Hepatitis C Appreciation that many patients are undiagnosed Improved screening to identify infected persons Assessment
Hepatitis C Eliot Godofsky, MD University Hepatitis Center Bradenton, FL Recent Advances in Hepatitis C Appreciation that many patients are undiagnosed Improved screening to identify infected persons Assessment
2015 Outpatient Chronic Hepatitis B Management
 2015 Outpatient Chronic Hepatitis B Management Hepatitis B Hepatitis B Info 70% of acute infections are subclinical More severe symptoms when in addition to other liver disease Fulminant Hepatitis
2015 Outpatient Chronic Hepatitis B Management Hepatitis B Hepatitis B Info 70% of acute infections are subclinical More severe symptoms when in addition to other liver disease Fulminant Hepatitis
Locoregional Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cory Johnston and Sung Cho HPB Surgery Fellows Providence Portland, Oregon
 Locoregional Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cory Johnston and Sung Cho HPB Surgery Fellows Providence Portland, Oregon Hepatocellular Carcinoma The 3 rd most common cause of cancer- related death
Locoregional Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cory Johnston and Sung Cho HPB Surgery Fellows Providence Portland, Oregon Hepatocellular Carcinoma The 3 rd most common cause of cancer- related death
Boehringer Ingelheim- sponsored Satellite Symposium. HCV Beyond the Liver
 Boehringer Ingelheim- sponsored Satellite Symposium HCV Beyond the Liver HCV AS A METABOLIC MODIFIER: STEATOSIS AND INSULIN RESISTANCE Francesco Negro University Hospital of Geneva Switzerland Clinical
Boehringer Ingelheim- sponsored Satellite Symposium HCV Beyond the Liver HCV AS A METABOLIC MODIFIER: STEATOSIS AND INSULIN RESISTANCE Francesco Negro University Hospital of Geneva Switzerland Clinical
Decision to Continue the Development of Tecemotide (L-BLP25) in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer to be Announced
 September 27, 2013 ONO PHARMACEUTICAL CO., LTD. Corporate Communications Phone: +81-6-6263-5670 Decision to Continue the Development of Tecemotide (L-BLP25) in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer to be Announced
September 27, 2013 ONO PHARMACEUTICAL CO., LTD. Corporate Communications Phone: +81-6-6263-5670 Decision to Continue the Development of Tecemotide (L-BLP25) in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer to be Announced
Hepatitis B and C Co-infection. Mark Hull MHSc, FRCPC Clinical Assistant Professor Division of AIDS
 Hepatitis B and C Co-infection Mark Hull MHSc, FRCPC Clinical Assistant Professor Division of AIDS Objectives Review natural history of hepatitis coinfection Brief overview of treatment indications for
Hepatitis B and C Co-infection Mark Hull MHSc, FRCPC Clinical Assistant Professor Division of AIDS Objectives Review natural history of hepatitis coinfection Brief overview of treatment indications for
Hepatocellular carcinoma: Dutch guideline for surveillance, diagnosis and therapy
 REVIEW Hepatocellular carcinoma: Dutch guideline for surveillance, diagnosis and therapy F.A.L.M. Eskens 1 *, K.J. van Erpecum 5, K.P. de Jong 7, O.M. van Delden 8, H.J. Klumpen 9, C. Verhoef 2, P.L.M.
REVIEW Hepatocellular carcinoma: Dutch guideline for surveillance, diagnosis and therapy F.A.L.M. Eskens 1 *, K.J. van Erpecum 5, K.P. de Jong 7, O.M. van Delden 8, H.J. Klumpen 9, C. Verhoef 2, P.L.M.
Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Albania: Incidence and Risk Factors
 Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Albania: Incidence and Risk Factors Bashkim Resuli 1, Agim Sallaku 2 1 University Service of Gastrohepatology, Faculty of Medicine, Tirana, Albania 2 University Service of Oncology,
Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Albania: Incidence and Risk Factors Bashkim Resuli 1, Agim Sallaku 2 1 University Service of Gastrohepatology, Faculty of Medicine, Tirana, Albania 2 University Service of Oncology,
Liver means Life. Why this manifesto? We are eager to ensure. that we can contribute. to society as much. as possible, and we. are equally keen to
 Manifesto by the European Liver Patients Association (ELPA) on policy measures against chronic liver disease 2014 to 2019 Why this manifesto? Every five years European voters get the opportunity to have
Manifesto by the European Liver Patients Association (ELPA) on policy measures against chronic liver disease 2014 to 2019 Why this manifesto? Every five years European voters get the opportunity to have
NASH: It is not JUST a Fatty Liver. Karen F. Murray, M.D. Director of Hepatobiliary Program Children s Hospital and Regional Medical Center
 NASH: It is not JUST a Fatty Liver Karen F. Murray, M.D. Director of Hepatobiliary Program Children s Hospital and Regional Medical Center Stages of Fatty Liver Disorders Fatty Liver 16-35% of Western
NASH: It is not JUST a Fatty Liver Karen F. Murray, M.D. Director of Hepatobiliary Program Children s Hospital and Regional Medical Center Stages of Fatty Liver Disorders Fatty Liver 16-35% of Western
How To Decide If You Should Get A Mammogram
 American Medical Women s Association Position Paper on Principals of Breast Cancer Screening Breast cancer affects one woman in eight in the United States and is the most common cancer diagnosed in women
American Medical Women s Association Position Paper on Principals of Breast Cancer Screening Breast cancer affects one woman in eight in the United States and is the most common cancer diagnosed in women
Economic Impact of Treatment Options for Hepatic Encephalopathy
 Economic Impact of Treatment Options for Hepatic Encephalopathy Carroll B. Leevy, M.D. 1 ABSTRACT Complications of chronic liver disease, such as hepatic encephalopathy (HE), can have a substantial impact
Economic Impact of Treatment Options for Hepatic Encephalopathy Carroll B. Leevy, M.D. 1 ABSTRACT Complications of chronic liver disease, such as hepatic encephalopathy (HE), can have a substantial impact
EVALUATION OF LIVER FIBROSIS BY FIBROSCAN
 EVALUATION OF LIVER FIBROSIS BY FIBROSCAN M. Beaugrand Service d Hépatologied Hopital J. Verdier BONDY 93143 et Université Paris XIII DRESDEN 13.10.2007 ASSESSMENT OF FIBROSIS : WHY? Management of individual
EVALUATION OF LIVER FIBROSIS BY FIBROSCAN M. Beaugrand Service d Hépatologied Hopital J. Verdier BONDY 93143 et Université Paris XIII DRESDEN 13.10.2007 ASSESSMENT OF FIBROSIS : WHY? Management of individual
Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound (CEUS)
 Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound (CEUS) Odd Helge Gilja, MD, PhD Professor Department of Medicine Haukeland University Hospital Bergen, Norway The Micro-Bubble Contrast Agents - World View IEEE Transactions
Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound (CEUS) Odd Helge Gilja, MD, PhD Professor Department of Medicine Haukeland University Hospital Bergen, Norway The Micro-Bubble Contrast Agents - World View IEEE Transactions
Hepatocellular Carcinoma Management Guidelines
 Hepatocellular Carcinoma Management Guidelines By Ashraf Omar M.D, Prof. of Hepatology & Tropical Medicine Cairo University Staging Strategy and Treatment for Patients With HCC HCC PST 0, Child-Pugh A
Hepatocellular Carcinoma Management Guidelines By Ashraf Omar M.D, Prof. of Hepatology & Tropical Medicine Cairo University Staging Strategy and Treatment for Patients With HCC HCC PST 0, Child-Pugh A
Approach to Abnormal Liver Tests
 Approach to Abnormal Liver Tests Naga P. Chalasani, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine and Cellular & Integrative Physiology Director, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Indiana University School
Approach to Abnormal Liver Tests Naga P. Chalasani, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine and Cellular & Integrative Physiology Director, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Indiana University School
THE SECOND VERSION of Evidence-based Clinical
 bs_bs_banner doi: 10.1111/hepr.12464 Special Report Evidence-based Clinical Practice Guidelines for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The Japan Society of Hepatology 2013 update (3rd JSH-HCC Guidelines) Norihiro
bs_bs_banner doi: 10.1111/hepr.12464 Special Report Evidence-based Clinical Practice Guidelines for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The Japan Society of Hepatology 2013 update (3rd JSH-HCC Guidelines) Norihiro
Noninvasive Means of Diagnosing Liver Fibrosis in Hepatitis C*
 530 BJID 2007; 11 (December) Noninvasive Means of Diagnosing Liver Fibrosis in Hepatitis C* Eduardo Sellan Lopes Gonçales, Adriana Flávia Feltrim Angerami and Fernando Lopes Gonçales Junior Study Group
530 BJID 2007; 11 (December) Noninvasive Means of Diagnosing Liver Fibrosis in Hepatitis C* Eduardo Sellan Lopes Gonçales, Adriana Flávia Feltrim Angerami and Fernando Lopes Gonçales Junior Study Group
Long-term Results of Pegylated Interferon alfa-2a and Tenofovir for Hepatitis B
 Long-term Results of Pegylated Interferon alfa-2a and Tenofovir for Hepatitis B Patrick Marcellin Viral Hepatitis Research Center Hôpital Beaujon, University of Paris France OBJECTIVES OF THERAPY IN CHRONIC
Long-term Results of Pegylated Interferon alfa-2a and Tenofovir for Hepatitis B Patrick Marcellin Viral Hepatitis Research Center Hôpital Beaujon, University of Paris France OBJECTIVES OF THERAPY IN CHRONIC
Epidemiology of Hepatitis C Infection. Pablo Barreiro Service of Infectious Diseases Hospital Carlos III, Madrid
 Epidemiology of Hepatitis C Infection Pablo Barreiro Service of Infectious Diseases Hospital Carlos III, Madrid Worldwide Prevalence of Hepatitis C 10% No data available WHO.
Epidemiology of Hepatitis C Infection Pablo Barreiro Service of Infectious Diseases Hospital Carlos III, Madrid Worldwide Prevalence of Hepatitis C 10% No data available WHO.
UK Guidelines for the management of suspected hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in adults
 UK Guidelines for the management of suspected hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in adults SD Ryder DM FRCP Consultant Hepatologist Queens Medical Centre Nottingham University Hospitals NHS Trust Wolfson Digestive
UK Guidelines for the management of suspected hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in adults SD Ryder DM FRCP Consultant Hepatologist Queens Medical Centre Nottingham University Hospitals NHS Trust Wolfson Digestive
Seton Medical Center Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patterns of Care Study Rate of Treatment with Chemoembolization 2007 2012 N = 50
 General Data Seton Medical Center Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patterns of Care Study Rate of Treatment with Chemoembolization 2007 2012 N = 50 The vast majority of the patients in this study were diagnosed
General Data Seton Medical Center Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patterns of Care Study Rate of Treatment with Chemoembolization 2007 2012 N = 50 The vast majority of the patients in this study were diagnosed
New All Oral Therapy for Chronic Hepatitis C Virus (HCV): A Cost-Benefit Analysis
 New All Oral Therapy for Chronic Hepatitis C Virus (HCV): A Cost-Benefit Analysis Jennifer Orsi, MPH 4 th International Conference on Viral Hepatitis March 17, 2014 2014 Walgreen Co. All rights reserved.
New All Oral Therapy for Chronic Hepatitis C Virus (HCV): A Cost-Benefit Analysis Jennifer Orsi, MPH 4 th International Conference on Viral Hepatitis March 17, 2014 2014 Walgreen Co. All rights reserved.
Indications in Hepatology and Liver Diseases
 exclusively working in Health Care sananet GmbH Tilo Stolzke Breite Str. 6-8 23562 Lübeck Germany Telefon : +49 451 400 8301 Telefax : +49 451 400 8302 E-Mail : stolzke@sananet.com Internet : www.sananet.com
exclusively working in Health Care sananet GmbH Tilo Stolzke Breite Str. 6-8 23562 Lübeck Germany Telefon : +49 451 400 8301 Telefax : +49 451 400 8302 E-Mail : stolzke@sananet.com Internet : www.sananet.com
Machine learning of patient similarity: a case study on predicting survival in cancer patient after locoregional chemotherapy.
 Title Machine learning of patient similarity: a case study on predicting survival in cancer patient after locoregional chemotherapy Author(s) Chan, LWC; Chan, T; Cheng, LF; Mak, WS Citation The 2010 IEEE
Title Machine learning of patient similarity: a case study on predicting survival in cancer patient after locoregional chemotherapy Author(s) Chan, LWC; Chan, T; Cheng, LF; Mak, WS Citation The 2010 IEEE
LIVER FUNCTION TESTS AND STATINS
 LIVER FUNCTION TESTS AND STATINS Philippe J. Zamor and Mark W. Russo Current Opinion in Cardiology 2011,26:338 341 SUMMARY Purpose of review: To discuss recent data on statins in patients with elevated
LIVER FUNCTION TESTS AND STATINS Philippe J. Zamor and Mark W. Russo Current Opinion in Cardiology 2011,26:338 341 SUMMARY Purpose of review: To discuss recent data on statins in patients with elevated
Disclosure of Conflicts of Interest Learner Assurance Statement:
 Raj Reddy, MD Ruimy Family President's Distinguished Professor of Medicine Professor of Medicine in Surgery Director of Hepatology Director, Viral Hepatitis Center Medical Director, Liver Transplantation
Raj Reddy, MD Ruimy Family President's Distinguished Professor of Medicine Professor of Medicine in Surgery Director of Hepatology Director, Viral Hepatitis Center Medical Director, Liver Transplantation
190.25 - Alpha-fetoprotein
 Other Names/Abbreviations AFP 190.25 - Alpha-fetoprotein Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is a polysaccharide found in some carcinomas. It is effective as a biochemical marker for monitoring the response of certain
Other Names/Abbreviations AFP 190.25 - Alpha-fetoprotein Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is a polysaccharide found in some carcinomas. It is effective as a biochemical marker for monitoring the response of certain
7. Prostate cancer in PSA relapse
 7. Prostate cancer in PSA relapse A patient with prostate cancer in PSA relapse is one who, having received a primary treatment with intent to cure, has a raised PSA (prostate-specific antigen) level defined
7. Prostate cancer in PSA relapse A patient with prostate cancer in PSA relapse is one who, having received a primary treatment with intent to cure, has a raised PSA (prostate-specific antigen) level defined
SHAHID AZIZ DO, FACOI.
 SHAHID AZIZ DO, FACOI. ASSOCIATE CLINICAL PROFESSOR OF GI AND LIVER DISEASE. UT SOUTHWESTERN HEALTH SCIENCE CENTER, DALLAS ADJUNCT CLINICAL ASSISTANT PROFESSOR DEPT OF MEDICINE UNT HEALTH SCIENCE CENTER
SHAHID AZIZ DO, FACOI. ASSOCIATE CLINICAL PROFESSOR OF GI AND LIVER DISEASE. UT SOUTHWESTERN HEALTH SCIENCE CENTER, DALLAS ADJUNCT CLINICAL ASSISTANT PROFESSOR DEPT OF MEDICINE UNT HEALTH SCIENCE CENTER
Therapy of decompensated cirrhosis Pre-transplant for HBV and HCV
 Therapy of decompensated cirrhosis Pre-transplant for HBV and HCV Universitätsklinikum Leipzig Thomas Berg Sektion Hepatologie Klinik und Poliklinik für Gastroenterologie und Rheumatologie Leber- und Studienzentrum
Therapy of decompensated cirrhosis Pre-transplant for HBV and HCV Universitätsklinikum Leipzig Thomas Berg Sektion Hepatologie Klinik und Poliklinik für Gastroenterologie und Rheumatologie Leber- und Studienzentrum
Screening and Treatment for Hepatitis C in HIV Co-Infected Patients in Primary Care
 Screening and Treatment for Hepatitis C in HIV Co-Infected Patients in Primary Care Amanda Hutton Parrott, DPT, NP Carol Dawson Rose, PhD, RN, FAAN Roland Zepf, MS, RN, ACRN Patricia Ambrose, MS, RN Background
Screening and Treatment for Hepatitis C in HIV Co-Infected Patients in Primary Care Amanda Hutton Parrott, DPT, NP Carol Dawson Rose, PhD, RN, FAAN Roland Zepf, MS, RN, ACRN Patricia Ambrose, MS, RN Background
2.5 Cancer of the liver
 ALCOHOL CONSUMPTION 399 2.4.7 Effect modification The combined effects of smoking and alcoholic beverage consumption on the development of cancer of the oesophagus have been examined in several studies
ALCOHOL CONSUMPTION 399 2.4.7 Effect modification The combined effects of smoking and alcoholic beverage consumption on the development of cancer of the oesophagus have been examined in several studies
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Prognosis and Treatment
 Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Prognosis and Treatment Zachary Henry, M.D. Assistant Professor UVA Gastroenterology & Hepatology October 28, 2015 Overview Case Presentation Prognosis Effects of fibrosis
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Prognosis and Treatment Zachary Henry, M.D. Assistant Professor UVA Gastroenterology & Hepatology October 28, 2015 Overview Case Presentation Prognosis Effects of fibrosis
Co-infected health-care workers
 Co-infected health-care workers Y.Yazdanpanah Service Universitaire des Maladies Infectieuses et du Voyageur C.H. Tourcoing, Faculté de Médecine de Lille CNRS U362, Lille, France Co-infected health-care
Co-infected health-care workers Y.Yazdanpanah Service Universitaire des Maladies Infectieuses et du Voyageur C.H. Tourcoing, Faculté de Médecine de Lille CNRS U362, Lille, France Co-infected health-care
Hepatitis C Glossary of Terms
 Acute Hepatitis C A short-term illness that usually occurs within the first six months after someone is exposed to the hepatitis C virus (HCV). 1 Antibodies Proteins produced as part of the body s immune
Acute Hepatitis C A short-term illness that usually occurs within the first six months after someone is exposed to the hepatitis C virus (HCV). 1 Antibodies Proteins produced as part of the body s immune
Update on Hepatitis C. Sally Williams MD
 Update on Hepatitis C Sally Williams MD Hep C is Everywhere! Hepatitis C Magnitude of the Infection Probably 8 to 10 million people in the U.S. are infected with Hep C 30,000 new cases are diagnosed annually;
Update on Hepatitis C Sally Williams MD Hep C is Everywhere! Hepatitis C Magnitude of the Infection Probably 8 to 10 million people in the U.S. are infected with Hep C 30,000 new cases are diagnosed annually;
Results Demographic profile of these children is shown in Table I.
 Prevalence of Antibody to Hepatitis C Virus in Pakistani Thalassaemics by Particle Agglutination Test Utilizing C 200 and C 22-3 Viral Antigen Coated Particles Pages with reference to book, From 269 To
Prevalence of Antibody to Hepatitis C Virus in Pakistani Thalassaemics by Particle Agglutination Test Utilizing C 200 and C 22-3 Viral Antigen Coated Particles Pages with reference to book, From 269 To
Management of Hepatocellular
 Clinician s Guide version 08-05-09 Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs Veterans Health Administration VA Hepatitis C Resource Center Program & VA National Clinical
Clinician s Guide version 08-05-09 Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs Veterans Health Administration VA Hepatitis C Resource Center Program & VA National Clinical
Update on hepatitis C: treatment and care and future directions
 Update on hepatitis C: treatment and care and future directions Professor Greg Dore Viral Hepatitis Clinical Research Program, National Centre in HIV Epidemiology and Clinical Research, University of New
Update on hepatitis C: treatment and care and future directions Professor Greg Dore Viral Hepatitis Clinical Research Program, National Centre in HIV Epidemiology and Clinical Research, University of New
HCV in 2020: Any cases left? Rafael Esteban Hospital General Universitario Valle Hebron Barcelona. Spain
 HCV in 2020: Any cases left? Rafael Esteban Hospital General Universitario Valle Hebron Barcelona. Spain Yes, still too many Measures to eradicate an Infectious Disease Prevention: Vaccination Screening
HCV in 2020: Any cases left? Rafael Esteban Hospital General Universitario Valle Hebron Barcelona. Spain Yes, still too many Measures to eradicate an Infectious Disease Prevention: Vaccination Screening
HEPATITIS C TREATMENT GUIDELINES
 HEPATITIS C TREATMENT GUIDELINES Updated May 21, 2014 INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Review the posted Hepatitis C Treatment Guidelines document to validate that your patient meets the criteria for treatment. 2. Complete
HEPATITIS C TREATMENT GUIDELINES Updated May 21, 2014 INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Review the posted Hepatitis C Treatment Guidelines document to validate that your patient meets the criteria for treatment. 2. Complete
Alanine aminotransferase (serum, plasma)
 Alanine aminotransferase (serum, plasma) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) 1.2 Alternative names Systematic name L alanine:2 oxoglutarate aminotransferase
Alanine aminotransferase (serum, plasma) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) 1.2 Alternative names Systematic name L alanine:2 oxoglutarate aminotransferase
Racial and Insurance Disparities in the Receipt of Transplant Among Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma
 Racial and Insurance Disparities in the Receipt of Transplant Among Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma Jeanette C. Yu, MD, MPH 1 ; Alfred I. Neugut, MD, PhD 1,2 ; Shuang Wang, PhD 3 ; Judith S. Jacobson,
Racial and Insurance Disparities in the Receipt of Transplant Among Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma Jeanette C. Yu, MD, MPH 1 ; Alfred I. Neugut, MD, PhD 1,2 ; Shuang Wang, PhD 3 ; Judith S. Jacobson,
KY Hepatitis Connections
 KY Hepatitis Connections Greetings partners and colleagues! March is here and spring is right around the corner. I have settled into my new role and have received input from many of you related to the
KY Hepatitis Connections Greetings partners and colleagues! March is here and spring is right around the corner. I have settled into my new role and have received input from many of you related to the
CASL Symposium Hepatitis B Co-chairs: Carla Coffin and Mang Ma
 CASL Symposium Hepatitis B Co-chairs: Carla Coffin and Mang Ma Occult HBV Infection: Assessment and Clinical Significance D. Lorne Tyrrell Director, Li Ka Shing Institute of Virology University of Alberta
CASL Symposium Hepatitis B Co-chairs: Carla Coffin and Mang Ma Occult HBV Infection: Assessment and Clinical Significance D. Lorne Tyrrell Director, Li Ka Shing Institute of Virology University of Alberta
