BIRMINGHAM HIP Resurfacing (BHR ) System PATIENT INFORMATION
|
|
|
- Theresa Walker
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BIRMINGHAM HIP Resurfacing (BHR ) System PATIENT INFORMATION Table of Contents 1.0 What is the BHR Device? 2.0 What is the Purpose of the BHR Device? 3.0 When Should the BHR Device Not Be Used? (Contraindications) 4.0 What Are Some of the Potential Benefits of the BHR Device? 5.0 What Are Some of the Potential Risks of the BHR Device? 6.0 What Do the Clinical Studies Show? 7.0 What Can You Do Before Your Surgery? 8.0 What Can You Expect After Your BHR Hip Resurfacing Operation? 9.0 What Problems May Occur After Your Operation? 10.0 What Are Some Warnings to Keep in Mind After Surgery? 11.0 Are There Instructions When You Leave Home or Travel? 12.0 Where Else Can You Get User Assistance Information? Glossary of Terms Artificial: Man-made. Hip Joint: A bone joint made up of a ball head (femoral head) and socket (acetabulum) Hip Dislocation: A hip problem resulting from a separation of the ball from the socket in an artificial hip replacement device. Migration: A hip complication resulting from a movement of the device out of its original position. Degenerative joint disease: A condition that causes the loss of cartilage and bone in a hip joint that eventually leads to increased hip joint pain and reduced hip joint function. Names of some types of degenerative joint diseases include; o Hip Dysplasia: An unusually-shaped hip socket. o Osteoarthritis: A condition that results in loss of bone and cartilage in the hip joint and/or formation of bone and cartilage in the joint where it normally does not occur (osteophytes). o Traumatic arthritis: A condition that results in loss of bone and cartilage in the hip joint after a physical injury to the hip joint has occurred. o Avascular Necrosis: Death of the bone in the femoral head due to loss of blood circulation within the bone caused by disease or damage to the hip bone. o Rheumatoid arthritis: A condition where the connective tissue (collagen) of the hip joint is slowly destroyed due to the body attacking its own tissue (auto-immune response). Femoral Neck Fracture: Breakage of the bone below the hip ball head. Femoral Head Collapse: Breakage of the bone within the hip ball head. Osteoporosis: A condition resulting in loss of bone that causes bone to become brittle and weak. Rehabilitation: After hip surgery, doctor prescribed exercises that help improve hip movement and healing
2 Revision: Replacement of an artificial hip device with a new artificial hip device. Revision can be required due to several reasons such as a broken device or infection or incorrect artificial hip device position in the bone. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): A medical imaging technique commonly used in radiology to visualize the internal structure and function of the body. 1.0 What Is the BHR Device? Your hip is a socket and ball joint where the thighbone and pelvis come together. As your leg moves, the ball of your thighbone (called the femoral head) moves and rotates against the socket portion of your pelvic bone (called the acetabulum). If your hip joint is diseased due to certain kinds of arthritis, or previous damage, it will become less functional and more painful over time. When your hip pain increases to the point that it can not be helped by usual measures such as pain medicine and exercises (physical therapy) and your ability to move your hip decreases, affecting your ability to do your daily activities, it may become necessary to surgically replace the hip joint. The BIRMINGHAM HIP Resurfacing (BHR) device consists of a socket in the shape of a shallow cup (acetabular component), and a cap in the form of a ball head (femoral resurfacing component). See Figures 1a and 1b. The cup replaces the damaged surface of your hip socket (acetabulum). The cap covers the ball-shaped bone at the top of your thigh (femoral head), and the cap has a small stem that is inserted into the top of your thighbone. The cap moves within the cup. The surfaces that rub against each other (the bearing couple) are made from highly-polished metal. This type of bearing couple is called a metal-on-metal bearing couple. The cup (acetabular component) is available in two styles: a one-piece cup (See Figure 1a) or a two-piece cup (See Figure 1b). The one-piece cup is a single component. The two-piece cup has a metal outer shell and a separate metal liner that locks into the shell.
3 Figure 1a: BIRMINGHAM HIP RESURFACING (BHR) device with one-piece cup Figure 1b: BIRMINGHAM HIP RESURFACING (BHR) device with two-piece cup
4 Figure 2: Total Hip Replacement (THR) device 2.0 What Is the Purpose of the BHR Device? The BHR System relieves hip pain and improves hip function by replacing the parts of your hip that have been severely damaged by degenerative joint diseases. The names of such diseases include osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, traumatic arthritis, dysplasia, or avascular necrosis. The BHR System is intended for patients who, due to their relatively younger age or increased activity level, may not be suitable for traditional total hip replacement due to an increased possibility of requiring future hip joint revision. 3.0 When Should the BHR Device Not Be Used? (Contraindications) You should not receive the BHR device if: You have an infection of the body or blood. Your bones are not yet fully grown. You have any blood vessel-related disease, muscle-related disease, or nerve-and-musclerelated disease that will prevent the artificial hip joint device from remaining stable or that may prevent you from following instructions during the recovery period. Your bones are not strong enough or healthy enough because: o You have severe bone loss (osteoporosis) or have a family history of severe bone loss, o You have bone loss (such as avascular necrosis) affecting more than half of your femoral head, o You have multiple fluid-filled cavities (cysts) greater than 1 centimeter of your femoral head, o A test (such as DEXA scan) may be needed to determine your level of bone loss.
5 You are a female of child-bearing age. It is unknown whether metal ions released by the device could harm an unborn child. Your kidneys are not working very well (function is significantly impaired). You will need testing (creatinine, GFR, BUN) before and/or after surgery to test your kidneys. You have a suppressed immune system due to diseases such as AIDS or are receiving high doses of corticosteroids. You are severely overweight. If you have had reactions to wearing metal jewelry, you may have what is called metal sensitivity. Your doctor will need complete information about your overall health to determine whether the BHR device is right for you. So, tell your doctor about any health problems you have, even if it is not related to your hip, because some medicines as well as diseases (such as diabetes) can affect your kidney or bone strength in the future. 4.0 What Are Some of the Potential Benefits of the BHR Device? Your surgeon has decided that you will benefit from hip replacement surgery. When thinking about the benefits of the BHR device, you should compare the possible risks and benefits of the device to the risks and benefits of other types of artificial hip replacement devices: Hip resurfacing versus a total hip replacement: With a hip resurfacing device, the surgeon covers your hip socket with a metal cup, and covers your femoral head with a metal cap (See Figures 1a and 1b). The BHR System is a hip resurfacing device. With a total hip replacement device, the surgeon covers your hip socket with a cup and replaces your femoral head with a metal ball attached to a long metal stem. The metal stem is inserted into your thighbone. (See Figure 2). Metal-on-metal versus metal-on-plastic or ceramic-on-ceramic: With metal-on-metal systems, the cap (ball) and the socket components are made from highlypolished metal. The BHR System is a metal-on-metal system. Other hip systems can have a metal ball with a plastic-lined socket (metal-on-plastic), or a ceramic ball with a ceramic-lined socket (ceramic-on-ceramic). Each of the device types discussed above can significantly improve hip pain and function. However, specific potential benefits of the BHR System include: The BHR s metal cup will not chip or crack as ceramic components can. The BHR does not cause thighbone (femoral shaft) fractures as total hip replacement systems can. The BHR may make future revision surgery easier because hip resurfacing surgery leaves your femoral head in place and there is no large metal stem placed in the thighbone. Revision surgery of a total hip replacement where your femoral head has already been removed and a large stem is already in place can be a more difficult operation. Dislocation of the ball head from the socket is less common with the BHR device than with total hip replacement devices. In the clinical study, 9 of 2,385 (0.3%) BHR hips experienced dislocation, compared with between 3 of 333 hips (1%) and 7 of 165 hips (4.2%) of total hip replacement patients from comparison studies. (See section 6.0.) One-piece acetabular component versus two-piece acetabular component designs:
6 o The BHR acetabular component is provided in a one- and two-piece design. o The potential benefits of the two-piece design for the patient include an option for additional fixation using bone screws, and an easier revision to a total hip replacement system if such replacement becomes necessary in the future. With the two-piece design, if the metal outer shell is well fixed, the surgeon has the option at a future revision surgery of leaving the metal outer shell in place without further disturbing the hip socket bone and replacing the metal liner with a plastic liner that can mate with a new total hip replacement system head and femoral stem. o The potential benefit of a one-piece design is that there is no risk of unintentional component disassembly. 5.0 What Are Some of the Potential Risks of the BHR Device? The potential risks of any hip joint replacement include: Damage to blood vessels, or temporary or permanent nerve damage during surgery, Sudden drop in blood pressure during surgery due to the use of bone cement Blood circulation problems because of surgery or during recovery including blood clots in the legs or lungs or heart attack. Allergic reactions to the device material or to medications you are given, Surgical wounds that take a long time to heal due to many reasons such as poor skin condition, infection, poor blood circulation, bad hygiene, etc. Infection related to surgery and wound healing. Infections may occur months to years after surgery and these infections are difficult to treat and may require reoperation with removal surgery and later replacement at another time, Dislocation of the hip, device loosening/shifting, or device wear/breakage due to muscle and fibrous tissue lack of firmness (laxity). Device placement in the wrong position in the bone, poor attachment of the device to the bone, too much weight or activity put on the device, or accidents affecting the hip joint like falls (trauma), Damage to the bones and tissue (tissue necrosis) near the hip joint, including loss of the surrounding bone (osteolysis) or staining of the hip joint fluid (metallosis) due to wearing away of the metal parts over time. Change in the length of the leg in which the device is placed, Device breakage due to weakening of the metal over time (fatigue fracture), Bone breakage due to osteoporosis or accidents (trauma), Bone loss or too much bone formation near the implants in response to the surgery or to the presence of the device in the bone. Increased hip pain and/or reduced function. Temporary or permanent device related noise such as clicking or squeaking. Inflammatory tissue response to high levels of wear debris resulting in peri-prosthetic aseptic lymphocyte dominated vasculitis associated lesions (ALVAL), fluid collections, or soft tissue masses (Pseudotumors). These potential adverse effects may require medical attention or additional surgery. Rarely do complications lead to death.
7 The potential risks of the BHR device as compared with a total hip replacement system include: The risk of femoral neck scratching (notching) during surgery that can lead to femoral neck fracture after surgery. This occurred in 10 of 2,385 (less than 1%) BHR hips in the clinical study. The risk of femoral head collapse. This occurred in 15 of 2,385 (less than 1%) BHR hips in the clinical study. The risk of avascular necrosis. This occurred in 35 of 2,385 (1%) BHR hips in the clinical study. If the ball cap part of the BHR device must be removed (revised), your surgeon will likely put a total hip replacement metal stem in your thighbone (see Figure 2). There is currently not a metal femoral head and stem for use with a BHR resurfacing cup (one- or two-piece acetabular component design). Therefore, if you have a one-piece BHR acetabular component, your surgeon will have to remove the socket part of the BHR device even if it is not a part of the problem. However, if you have a two-piece BHR acetabular component, then your surgeon can replace the metal liner of the acetabular cup with a new plastic liner that will mate with the new total hip replacement system head and femoral stem. The surgeon can leave your existing metal shell in place, if it is well fixed, without further disturbing your socket bone. If the two-piece BHR acetabular component is used, there is a risk of the potential disassembly of the two components. Patients who have a greater risk of revision than other patients include those who are female; who require a smaller component size ( 44mm); have a mal-positioned device; are obese; or, who have a diagnosis of avascular necrosis. The more risk factors a patient has, the greater the risk of procedure failure requiring a revision to the hip. The complications described above may require surgery to change from the BHR device to a total hip replacement device. You should compare these risks to the potential benefits of a BHR system, as described above. See also What Problems May Occur After Your Operation?, Section What Do the Clinical Studies Show? A clinical study was performed using a BHR femoral head resurfacing component and a onepiece acetabular cup design to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of the BHR device. The use of the BHR femoral head resurfacing component with the two-piece acetabular cup design has not been studied clinically. Complication (safety) information was collected from the entire group of 2,385 study hips. Effectiveness information was collected from the first 1,626 of the 2,385 hips because these 1,626 hips have the longest follow-up. There is 5 year follow-up information for 546 of these 1,626 hips. Safety Data The overall complication rate and the types of complications in the BHR study group were generally similar to the complications reported for other hip replacement systems. The few differences between different types of complications are discussed under Section 5 - What Are Some Potential Risks of the BHR Device? and Section 4 - What Are Some Potential Benefits of the BHR Device? Complications led to revision surgery in 27 out of 2,385 hips. See Table 1 for a summary of reasons for the revision. The 1.13% (27/2,385) revision rate at 5-years after surgery from all complications was comparable to the revision rates reported for total hip replacement devices.
8 There were no deaths related directly to use of the device in the study. All deaths were from other medical problems. Table 1: Reasons for Revision Surgeries in BHR Study (N=2,385 Hips) Reason for Revision Number of Revisions Average time to revision in years Femoral neck fracture Infection Collapsed femoral head Avascular necrosis Dislocation TOTAL 27 Effectiveness Data Effectiveness was determined by looking at: Survivorship: The cumulative percentage of patients that did not need revision of the BHR by 5 years after surgery. Oswestry Hip (OSHIP) Score: The OSHIP score asks patients questions about their hip pain, hip function, and hip movement. Based on the patient response to the questions a total score is calculated. The total score ranges from 0 (worst) to 100 (best). A score of 80 or better is generally considered a good clinical result. Patient Satisfaction: Patients in the study were asked to rate their satisfaction with the result of the BHR surgery on a scale of 0 (worst) to 4 (best). The results are shown in Table 2. Table 2: Effectiveness Measures at 5 years After Surgery Effectiveness Measure * 5 years After Surgery Survivorship: cases with device in place (not revised) 2,358 of 2,385 (98.5%) OSHIP score: of patients with a good result (80 or better) 509 of 546 (93.2%) Patient Satisfaction: patients who responded Pleased or Extremely Pleased with their results 543 of 546 (99.5%) * Survivorship data was for the safety cohort of 2,385 hips. OSHIP and Patient Satisfaction data were for a subgroup of 1,626 hips. In a unilateral hip analysis, 334 of 360 patients (92.7%) had a good OSHIP score result (80 or better), and 357 of 360 patients (99.2%) were Pleased or Extremely Pleased with their result. 7.0 What Can You Do Before Your Surgery? Your doctor may want you to meet with a Physical Therapist (PT) even before the surgery. The PT may give you some tips on preparing your house for rehabilitation, and on how you should sleep, get out of bed, sit, get up, and walk following surgery. Some things you can do before surgery to prepare for the rehabilitation period are:
9 Add extra cushions to couches and chairs. The extra height will make it easier for you to lower and raise yourself from the chair. Have armchairs available. During rehabilitation, you may be told only to sit in armchairs, as you will need the arms to help you sit down and get up. Arrange to have an elevated toilet seat and/or support bars fitted in your bathroom. Move items you may need to reach to shelves or tables above waist level. Remove all throw rugs and anything else on the floor that might cause you to slip or trip and fall. 8.0 What Can You Expect After Your BHR Hip Resurfacing Operation? Most patients are in the hospital from 4 to 6 days. The surgery usually takes 2 to 4 hours to perform. You will use walking support (canes, crutches) for about six weeks after surgery while your hip muscles are healing. You may be told not to bend your hip or waist to more than a 90- degree angle during the healing time (rehabilitation). Before you go home, your Physical Therapist (PT) will teach you to climb stairs and how to move from a bed, chair, and car. Your PT may also give you a list of exercises to do at home every day. These exercises will help you become as independent as possible in your personal care and daily activities after you return home. Physical therapy will also help prepare you for more difficult exercises, movement, and activity. Most of your therapy and healing (rehabilitation) will occur once you have checked out of the hospital. Your PT will design an exercise program to increase motion and strength of your hip, and will teach you the exercises, making sure you know proper way to do the exercises before you begin. The success of your rehabilitation is very dependent on how dedicated you are to the physical therapy program. 9.0 What Problems May Occur After Your Operation? Early Infection Contact your doctor if you experience any of the following signs of infection: Drainage and/or foul smell from surgical cut (incision). Fever/temperature above F (or 38 C) for two days. Redness or swelling or increased pain at or near the surgical cut. Late Infection To protect your hip joint from infection after your surgery, you will need antibiotics before the following procedures: Internal examinations of the bladder (cystoscopy), colon (colonoscopy) or rectum (proctoscopy). Dental work including teeth cleaning. Surgery of any kind. Placement of a tube into the ureter to drain urine from the body (urinary catheterization). Infections can travel from other parts of your body to your new hip. If you have any infection in any part of your body, contact your doctor. Late Pain or Instability Some pain is normal and expected during your rehabilitation period, and the pain should slowly decrease in the weeks following surgery. If you experience any serious, immediate, constant hip pain or pressure or feeling of unsteadiness, or if you are suddenly unable to put weight on your hip after the early post-operative pain has gone away, you should contact your doctor. These
10 signs (symptoms) may be a signal of a serious problem (such as bone breakage, dislocation, infection, device loosening, movement, or breakage). Any of these problems may require medical attention including additional surgery. Continuing Evaluation Follow your doctor s schedule for routine examinations after surgery. Routine examinations will include regular X-ray exams to look for any problems such as hip bone or device breakage, position changes, or anything abnormal. X-rays will also check the progress of bone healing around the implant What Are Some Warnings to Keep in Mind After Surgery? Take care to protect your joint replacement from too much stress and follow your surgeon s instructions regarding activity level and rehabilitation. Do not perform high impact activities such as running and jumping during the first postoperative year while the bone is healing. Early device failure (breakage or loosening) may occur if you do not follow your surgeon s limitations on activity level. Early failure can happen if you do not guard your hip joint from overloading due to activity level, failure to control body weight, or accidents such as falls. Loosening of the hip joint device may cause too much wear of the metal parts and result in very small metal particles being created. This can result in bone loss around the implant causing more loosening. Early device failure or bone loss may require additional surgery to remove the device (revision surgery). Artificial hip joints can wear out over time and may require replacement. If a physician prescribes an MRI scan for you, inform the physician that the Birmingham Hip Resurfacing (BHR) System has not been evaluated for safety and compatibility in the MR environment. The Birmingham Hip Resurfacing (BHR) System has not been tested for heating or migration in the MR environment Are there Instructions When You Leave Home or Travel? Your new hip device may activate metal detector alarms. Tell the security attendant about your artificial hip when passing through security checkpoints in airports, stores, and public buildings Where Else Can You Get User Assistance Information? Please discuss any questions regarding your hip surgery with your surgeon. For further information regarding the BHR System components, you may also contact the device manufacturer: Smith & Nephew, Inc. Orthopaedics Division 1450 Brooks Road Memphis, Tennessee USA Tel: (within the USA) , Rev. B Trademark of Smith & Nephew, Inc. Print Date: 10/10
Y O U R S U R G E O N S. choice of. implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y
 Y O U R S U R G E O N S choice of implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y Y O U R S U R G E O N S choice of implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y Your Surgeon Has Chosen the C 2 a-taper Acetabular System The
Y O U R S U R G E O N S choice of implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y Y O U R S U R G E O N S choice of implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y Your Surgeon Has Chosen the C 2 a-taper Acetabular System The
Cormet Hip Resurfacing System
 Cormet Hip Resurfacing System Patient Product Information 325 Corporate Drive Mahwah, NJ 07430 t: 1-888-STRYKER www.aboutstryker.com The information presented in this brochure is for educational purposes
Cormet Hip Resurfacing System Patient Product Information 325 Corporate Drive Mahwah, NJ 07430 t: 1-888-STRYKER www.aboutstryker.com The information presented in this brochure is for educational purposes
Patient Labeling Information System Description
 Patient Labeling Information System Description The Trident Ceramic Acetabular System is an artificial hip replacement device that features a new, state-of-the-art ceramic-on-ceramic bearing couple. The
Patient Labeling Information System Description The Trident Ceramic Acetabular System is an artificial hip replacement device that features a new, state-of-the-art ceramic-on-ceramic bearing couple. The
Anterior Hip Replacement
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Orthopaedic health. All decisions about the management of hip replacement and arthritis management must be made in
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Orthopaedic health. All decisions about the management of hip replacement and arthritis management must be made in
Your Practice Online
 P R E S E N T S Your Practice Online Disclaimer This information is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on Revision Hip Replacement or arthritis management. All decisions
P R E S E N T S Your Practice Online Disclaimer This information is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on Revision Hip Replacement or arthritis management. All decisions
Total Hip Replacement
 Please contactmethroughthegoldcoasthospitaswityouhaveanyproblemsafteryoursurgery. Dr. Benjamin Hewitt Orthopaedic Surgeon Total Hip Replacement The hip joint is a ball and socket joint that connects the
Please contactmethroughthegoldcoasthospitaswityouhaveanyproblemsafteryoursurgery. Dr. Benjamin Hewitt Orthopaedic Surgeon Total Hip Replacement The hip joint is a ball and socket joint that connects the
Hip Replacement Surgery Understanding the Risks
 Hip Replacement Surgery Understanding the Risks Understanding the Risks of Hip Replacement Surgery Introduction This booklet is designed to help your doctor talk to you about the most common risks you
Hip Replacement Surgery Understanding the Risks Understanding the Risks of Hip Replacement Surgery Introduction This booklet is designed to help your doctor talk to you about the most common risks you
X-Plain Hip Replacement Surgery - Preventing Post Op Complications Reference Summary
 X-Plain Hip Replacement Surgery - Preventing Post Op Complications Reference Summary Introduction Severe arthritis in the hip can lead to severe pain and inability to walk. To relieve the pain and improve
X-Plain Hip Replacement Surgery - Preventing Post Op Complications Reference Summary Introduction Severe arthritis in the hip can lead to severe pain and inability to walk. To relieve the pain and improve
HEADER TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT SURGERY FROM PREPARATION TO RECOVERY
 HEADER TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT SURGERY FROM PREPARATION TO RECOVERY ABOUT THE HIP JOINT The hip joint is a ball and socket joint that connects the body to the legs. The leg bone is called the femur. The
HEADER TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT SURGERY FROM PREPARATION TO RECOVERY ABOUT THE HIP JOINT The hip joint is a ball and socket joint that connects the body to the legs. The leg bone is called the femur. The
YOUR GUIDE TO TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT
 A Partnership for Better Healthcare A Partnership for Better Healthcare YOUR GUIDE TO TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT PEI Limited M50 Business Park Ballymount Road Upper Ballymount Dublin 12 Tel: 01-419 6900 Fax:
A Partnership for Better Healthcare A Partnership for Better Healthcare YOUR GUIDE TO TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT PEI Limited M50 Business Park Ballymount Road Upper Ballymount Dublin 12 Tel: 01-419 6900 Fax:
Randal S. Ford. ATTORNEY AT LAW (205) 752-4440 [email protected]. DePuy ASR Hip Implant Recall Fact Sheet
 DePuy ASR Hip Implant Recall Fact Sheet Recalled Devices: ASR XL Acetabular System on the market since 2004, and sold worldwide. Dates of Implant: July 2003 to 2010 ASR Hip Resurfacing System on the market
DePuy ASR Hip Implant Recall Fact Sheet Recalled Devices: ASR XL Acetabular System on the market since 2004, and sold worldwide. Dates of Implant: July 2003 to 2010 ASR Hip Resurfacing System on the market
Arthritis of the hip. Normal hip In an x-ray of a normal hip, the articular cartilage (the area labeled normal joint space ) is clearly visible.
 Arthritis of the hip Arthritis of the hip is a condition in which the smooth gliding surfaces of your hip joint (articular cartilage) have become damaged. This usually results in pain, stiffness, and reduced
Arthritis of the hip Arthritis of the hip is a condition in which the smooth gliding surfaces of your hip joint (articular cartilage) have become damaged. This usually results in pain, stiffness, and reduced
TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT
 TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT 2 Causes of Hip Pain Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States, and the most frequent cause of discomfort and chronic hip pain. In fact, it s estimated that
TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT 2 Causes of Hip Pain Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States, and the most frequent cause of discomfort and chronic hip pain. In fact, it s estimated that
Metal-on-Metal Hip Systems
 Meeting of the Orthopaedic and Rehabilitation Devices Advisory Panel June 27-28, 2012 Metal-on-Metal Hip Systems Center for Devices and Radiological Health U.S. Food and Drug Administration Meeting of
Meeting of the Orthopaedic and Rehabilitation Devices Advisory Panel June 27-28, 2012 Metal-on-Metal Hip Systems Center for Devices and Radiological Health U.S. Food and Drug Administration Meeting of
Appendix B: FDA Safety Communication (Website) for MoM Hip Systems
 Appendix B: FDA Safety Communication (Website) for MoM Hip Systems. 1 Metal on Metal Hip Implant Systems Home Page The Hip Joint Hip Implant Systems Metal-on-Metal Hip Implant Systems Total Hip Replacement
Appendix B: FDA Safety Communication (Website) for MoM Hip Systems. 1 Metal on Metal Hip Implant Systems Home Page The Hip Joint Hip Implant Systems Metal-on-Metal Hip Implant Systems Total Hip Replacement
Total Hip Joint Replacement. A Patient s Guide
 Total Hip Joint Replacement A Patient s Guide Don t Let Hip Pain Slow You Down What is a Hip Joint? Your joints are involved in almost every activity you do. Simple movements such as walking, bending,
Total Hip Joint Replacement A Patient s Guide Don t Let Hip Pain Slow You Down What is a Hip Joint? Your joints are involved in almost every activity you do. Simple movements such as walking, bending,
Procedure Information Guide
 Procedure Information Guide Total hip replacement Brought to you in association with EIDO and endorsed by the The Royal College of Surgeons of England Discovery has made every effort to ensure that the
Procedure Information Guide Total hip replacement Brought to you in association with EIDO and endorsed by the The Royal College of Surgeons of England Discovery has made every effort to ensure that the
ARTHROSCOPIC HIP SURGERY
 ARTHROSCOPIC HIP SURGERY Hip Arthroscopy is a relatively simple procedure whereby common disorders of the hip can be diagnosed and treated using keyhole surgery. Some conditions, which previously were
ARTHROSCOPIC HIP SURGERY Hip Arthroscopy is a relatively simple procedure whereby common disorders of the hip can be diagnosed and treated using keyhole surgery. Some conditions, which previously were
Hip Replacement. Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Tel: 01473 702107
 Information for Patients Hip Replacement Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Tel: 01473 702107 DMI ref: 0134-08.indd(RP) Issue 3: February 2008 The Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust, 2005-2008. All rights reserved.
Information for Patients Hip Replacement Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Tel: 01473 702107 DMI ref: 0134-08.indd(RP) Issue 3: February 2008 The Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust, 2005-2008. All rights reserved.
it s time for rubber to meet the road
 your total knee replacement surgery Steps to returning to a Lifestyle You Deserve it s time for rubber to meet the road AGAIN The knee is the largest joint in the body. The knee is made up of the lower
your total knee replacement surgery Steps to returning to a Lifestyle You Deserve it s time for rubber to meet the road AGAIN The knee is the largest joint in the body. The knee is made up of the lower
Why an Exactech Hip is Right for You
 Why an Exactech Hip is Right for You Why do I need a total hip replacement? Which surgical approach is best for me? How long will it last? Which implant is right for me? Founded in 1985 by an orthopaedic
Why an Exactech Hip is Right for You Why do I need a total hip replacement? Which surgical approach is best for me? How long will it last? Which implant is right for me? Founded in 1985 by an orthopaedic
Answers to commonly asked questions from patients with metal-on-metal hip replacements / resurfacings. Contents
 Answers to commonly asked questions from patients with metal-on-metal hip replacements / resurfacings John Skinner 1 and Alister Hart 2, Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeons and Directors of the London Implant
Answers to commonly asked questions from patients with metal-on-metal hip replacements / resurfacings John Skinner 1 and Alister Hart 2, Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeons and Directors of the London Implant
HIP JOINT REPLACEMENT
 HIP JOINT REPLACEMENT Information for Patients WHAT IS HIP JOINT REPLACEMENT? The hip joint is a ball-and-socket joint formed by the upper part of the thigh bone (femoral head) and a part of the pelvis
HIP JOINT REPLACEMENT Information for Patients WHAT IS HIP JOINT REPLACEMENT? The hip joint is a ball-and-socket joint formed by the upper part of the thigh bone (femoral head) and a part of the pelvis
Total hip replacement
 Patient Information to be retained by patient What is a total hip replacement? In a total hip replacement both the ball (femoral or thigh bone) side of the hip joint and the socket (acetabular or pelvic
Patient Information to be retained by patient What is a total hip replacement? In a total hip replacement both the ball (femoral or thigh bone) side of the hip joint and the socket (acetabular or pelvic
Wrist and Hand. Patient Information Guide to Bone Fracture, Bone Reconstruction and Bone Fusion: Fractures of the Wrist and Hand: Carpal bones
 Patient Information Guide to Bone Fracture, Bone Reconstruction and Bone Fusion: Wrist and Hand Fractures of the Wrist and Hand: Fractures of the wrist The wrist joint is made up of the two bones in your
Patient Information Guide to Bone Fracture, Bone Reconstruction and Bone Fusion: Wrist and Hand Fractures of the Wrist and Hand: Fractures of the wrist The wrist joint is made up of the two bones in your
Further information You can get more information and share your experience at www.aboutmyhealth.org
 OS01 Total Hip Replacement Further information You can get more information and share your experience at www.aboutmyhealth.org Local information You can get information locally from: Taunton and Somerset
OS01 Total Hip Replacement Further information You can get more information and share your experience at www.aboutmyhealth.org Local information You can get information locally from: Taunton and Somerset
P REPLACEMENT SURGERY
 P REPLACEMENT SURGERY DIRECT ANTERIOR APPROACH M I N I M I Z I N G R E C O V E R Y. M A X I M I Z I N G R E S U L T S. CENTER FOR MINIMAL INVASIVE JOINT SURGERY 2301 25TH STREET SOUTH FARGO ND 58103 701-241-9300
P REPLACEMENT SURGERY DIRECT ANTERIOR APPROACH M I N I M I Z I N G R E C O V E R Y. M A X I M I Z I N G R E S U L T S. CENTER FOR MINIMAL INVASIVE JOINT SURGERY 2301 25TH STREET SOUTH FARGO ND 58103 701-241-9300
 Total Hip Replacement Hip replacement surgery, or arthroplasty, uses implants to resurface and replace the bones in the joint, re-creating the smooth gliding surfaces that were once intact. Hip replacement
Total Hip Replacement Hip replacement surgery, or arthroplasty, uses implants to resurface and replace the bones in the joint, re-creating the smooth gliding surfaces that were once intact. Hip replacement
Total Knee Replacement Surgery
 Total Knee Replacement Surgery On this page: Overview Reasons for Surgery Evaluation Preparing for Surgery Your Surgery Risks Expectations after Surgery Convalescence Also: Partial Knee Replacement Overview
Total Knee Replacement Surgery On this page: Overview Reasons for Surgery Evaluation Preparing for Surgery Your Surgery Risks Expectations after Surgery Convalescence Also: Partial Knee Replacement Overview
Shoulder Joint Replacement
 Shoulder Joint Replacement Many people know someone with an artificial knee or hip joint. Shoulder replacement is less common, but it is just as successful in relieving joint pain. Shoulder replacement
Shoulder Joint Replacement Many people know someone with an artificial knee or hip joint. Shoulder replacement is less common, but it is just as successful in relieving joint pain. Shoulder replacement
Robotic-Arm Assisted Surgery
 Mako TM Robotic-Arm Assisted Surgery for Total Hip Replacement A Patient s Guide Causes of Your Hip Pain Your joints are involved in almost every activity you do. Movements such as walking, bending and
Mako TM Robotic-Arm Assisted Surgery for Total Hip Replacement A Patient s Guide Causes of Your Hip Pain Your joints are involved in almost every activity you do. Movements such as walking, bending and
This is my information booklet: Introduction
 Hip arthroscopy is a relatively new procedure which allows the surgeon to diagnose and treat hip disorders by providing a clear view of the inside of the hip with very small incisions. This is a more complicated
Hip arthroscopy is a relatively new procedure which allows the surgeon to diagnose and treat hip disorders by providing a clear view of the inside of the hip with very small incisions. This is a more complicated
The Total Ankle Replacement
 The Total Ankle Replacement Patient Information Patient Information This patient education brochure is presented by Small Bone Innovations, Inc. Patient results may vary. Please consult your physician
The Total Ankle Replacement Patient Information Patient Information This patient education brochure is presented by Small Bone Innovations, Inc. Patient results may vary. Please consult your physician
No two knees are alike. That s why we personalize your surgery just for you. Zimmer Patient Specific Instruments. For Knee Replacement Surgery
 No two knees are alike. That s why we personalize your surgery just for you. Zimmer Patient Specific Instruments For Knee Replacement Surgery Table of Contents Here s how it works....2 Why does my knee
No two knees are alike. That s why we personalize your surgery just for you. Zimmer Patient Specific Instruments For Knee Replacement Surgery Table of Contents Here s how it works....2 Why does my knee
Arthritis of the Shoulder
 Arthritis of the Shoulder In 2011, more than 50 million people in the United States reported that they had been diagnosed with some form of arthritis, according to the National Health Interview Survey.
Arthritis of the Shoulder In 2011, more than 50 million people in the United States reported that they had been diagnosed with some form of arthritis, according to the National Health Interview Survey.
Hip arthroscopy Frequently Asked Questions
 Hip arthroscopy Frequently Asked Questions What is a hip arthroscopy? Hip arthroscopy is key hole surgery. Usually 2-3 small incisions (about 1 cm long) are made on the side of your hip. Through these
Hip arthroscopy Frequently Asked Questions What is a hip arthroscopy? Hip arthroscopy is key hole surgery. Usually 2-3 small incisions (about 1 cm long) are made on the side of your hip. Through these
Level 1, 131-135 Summer Street ORANGE NSW 2800 Ph: 02 63631688 Fax: 02 63631865
 Write questions or notes here: Level 1, 131-135 Summer Street ORANGE NSW 2800 Ph: 02 63631688 Fax: 02 63631865 Document Title: Revision Total Hip Replacement Further Information and Feedback: Tell us how
Write questions or notes here: Level 1, 131-135 Summer Street ORANGE NSW 2800 Ph: 02 63631688 Fax: 02 63631865 Document Title: Revision Total Hip Replacement Further Information and Feedback: Tell us how
.org. Arthritis of the Hand. Description
 Arthritis of the Hand Page ( 1 ) The hand and wrist have multiple small joints that work together to produce motion, including the fine motion needed to thread a needle or tie a shoelace. When the joints
Arthritis of the Hand Page ( 1 ) The hand and wrist have multiple small joints that work together to produce motion, including the fine motion needed to thread a needle or tie a shoelace. When the joints
Level 1, 131-135 Summer Street ORANGE NSW 2800 Ph: 02 63631688 Fax: 02 63631865
 Write questions or notes here: Level 1, 131-135 Summer Street ORANGE NSW 2800 Ph: 02 63631688 Fax: 02 63631865 Document Title: Total Knee Replacement Further Information and Feedback: Tell us how useful
Write questions or notes here: Level 1, 131-135 Summer Street ORANGE NSW 2800 Ph: 02 63631688 Fax: 02 63631865 Document Title: Total Knee Replacement Further Information and Feedback: Tell us how useful
Total Hip Replacement
 NOTES Total Hip Replacement QUESTIONS DATES PHONE NOS. Compiled by Mr John F Nolan FRCS for The British Hip Society 2009. A patient s information booklet 16 1 Introduction This booklet has been produced
NOTES Total Hip Replacement QUESTIONS DATES PHONE NOS. Compiled by Mr John F Nolan FRCS for The British Hip Society 2009. A patient s information booklet 16 1 Introduction This booklet has been produced
Anterior Approach. to Hip Replacement Surgery
 Anterior Approach to Hip Replacement Surgery Introduction When debilitating pain and stiffness in your hip limits your daily activities, you may need a total hip replacement. The development of total hip
Anterior Approach to Hip Replacement Surgery Introduction When debilitating pain and stiffness in your hip limits your daily activities, you may need a total hip replacement. The development of total hip
Surgery for cervical disc prolapse or cervical osteophyte
 Mr Paul S. D Urso MBBS(Hons), PhD, FRACS Neurosurgeon Provider Nº: 081161DY Epworth Centre Suite 6.1 32 Erin Street Richmond 3121 Tel: 03 9421 5844 Fax: 03 9421 4186 AH: 03 9483 4040 email: [email protected]
Mr Paul S. D Urso MBBS(Hons), PhD, FRACS Neurosurgeon Provider Nº: 081161DY Epworth Centre Suite 6.1 32 Erin Street Richmond 3121 Tel: 03 9421 5844 Fax: 03 9421 4186 AH: 03 9483 4040 email: [email protected]
Understanding Total Hip Replacement
 Understanding Total Hip Replacement Brian J. White MD Orthopaedic Specialist in Disorders of the Hip Assistant Team Physician Denver Nuggets Western Orthopaedics Denver, Colorado Introduction This is designed
Understanding Total Hip Replacement Brian J. White MD Orthopaedic Specialist in Disorders of the Hip Assistant Team Physician Denver Nuggets Western Orthopaedics Denver, Colorado Introduction This is designed
VERILAST Technology for Hip Replacement Implants
 VERILAST Technology for Hip Replacement Implants Surgeon Name Clinic Name Clinic Address Clinic i Address Phone Number Web Address Total Hip Replacement What Is VERILAST Hip Technology? OXINIUM Oxidized
VERILAST Technology for Hip Replacement Implants Surgeon Name Clinic Name Clinic Address Clinic i Address Phone Number Web Address Total Hip Replacement What Is VERILAST Hip Technology? OXINIUM Oxidized
.org. Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder Problems. Anatomy. Cause
 Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder Problems Page ( 1 ) What most people call the shoulder is really several joints that combine with tendons and muscles to allow a wide range of motion in the arm from scratching
Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder Problems Page ( 1 ) What most people call the shoulder is really several joints that combine with tendons and muscles to allow a wide range of motion in the arm from scratching
Elbow Injuries and Disorders
 Elbow Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your elbow joint is made up of bone, cartilage, ligaments and fluid. Muscles and tendons help the elbow joint move. There are many injuries and disorders that
Elbow Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your elbow joint is made up of bone, cartilage, ligaments and fluid. Muscles and tendons help the elbow joint move. There are many injuries and disorders that
BRYAN. Cervical Disc System. Patient Information
 BRYAN Cervical Disc System Patient Information 3 BRYAN Cervical Disc System PATIENT INFORMATION BRYAN Cervical Disc System PATIENT INFORMATION 1 BRYAN Cervical Disc System This patient information brochure
BRYAN Cervical Disc System Patient Information 3 BRYAN Cervical Disc System PATIENT INFORMATION BRYAN Cervical Disc System PATIENT INFORMATION 1 BRYAN Cervical Disc System This patient information brochure
Preventing & Treating Low Back Pain
 Preventing & Treating Low Back Pain An Introduction to Low Back Pain Low back pain is the number two reason that Americans see a health care practitioner second only to colds and flu. While most people
Preventing & Treating Low Back Pain An Introduction to Low Back Pain Low back pain is the number two reason that Americans see a health care practitioner second only to colds and flu. While most people
.org. Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Anatomy
 Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Page ( 1 ) A broken ankle is also known as an ankle fracture. This means that one or more of the bones that make up the ankle joint are broken. A fractured ankle can range
Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Page ( 1 ) A broken ankle is also known as an ankle fracture. This means that one or more of the bones that make up the ankle joint are broken. A fractured ankle can range
.org. Shoulder Joint Replacement. Anatomy
 Shoulder Joint Replacement Page ( 1 ) Although shoulder joint replacement is less common than knee or hip replacement, it is just as successful in relieving joint pain. Shoulder replacement surgery was
Shoulder Joint Replacement Page ( 1 ) Although shoulder joint replacement is less common than knee or hip replacement, it is just as successful in relieving joint pain. Shoulder replacement surgery was
world-class orthopedic care right in your own backyard.
 world-class orthopedic care right in your own backyard. Patient Promise: At Adventist Hinsdale Hospital, our Patient Promise means we strive for continued excellence in everything we do. This means you
world-class orthopedic care right in your own backyard. Patient Promise: At Adventist Hinsdale Hospital, our Patient Promise means we strive for continued excellence in everything we do. This means you
Orthopaedic Spine Center. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs
 Orthopaedic Spine Center Graham Calvert MD James Woodall MD PhD Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs The cervical spine consists of the bony vertebrae, discs, nerves and other structures.
Orthopaedic Spine Center Graham Calvert MD James Woodall MD PhD Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs The cervical spine consists of the bony vertebrae, discs, nerves and other structures.
Integra. MCP Joint Replacement PATIENT INFORMATION
 Integra MCP Joint Replacement PATIENT INFORMATION Integra MCP Patient Information This brochure summarizes information about the use, risks, and benefits of the Integra MCP finger implant. Be sure to discuss
Integra MCP Joint Replacement PATIENT INFORMATION Integra MCP Patient Information This brochure summarizes information about the use, risks, and benefits of the Integra MCP finger implant. Be sure to discuss
1 of 6 1/22/2015 10:06 AM
 1 of 6 1/22/2015 10:06 AM 2 of 6 1/22/2015 10:06 AM This cross-section view of the shoulder socket shows a typical SLAP tear. Injuries to the superior labrum can be caused by acute trauma or by repetitive
1 of 6 1/22/2015 10:06 AM 2 of 6 1/22/2015 10:06 AM This cross-section view of the shoulder socket shows a typical SLAP tear. Injuries to the superior labrum can be caused by acute trauma or by repetitive
Total Hip Arthroplasty (Hip Replacement) PROCEDURAL CONSENT FORM. A. Interpreter / cultural needs. B. Condition and treatment
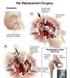 The State of Queensland (Queensland Health), 2011 Permission to reproduce should be sought from [email protected] DO NOT WRITE IN THIS BINDING MARGIN v4.00-04/2011 SW9336 Facility: Total Hip
The State of Queensland (Queensland Health), 2011 Permission to reproduce should be sought from [email protected] DO NOT WRITE IN THIS BINDING MARGIN v4.00-04/2011 SW9336 Facility: Total Hip
When is Hip Arthroscopy recommended?
 HIP ARTHROSCOPY Hip arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that uses a camera inserted through very small incisions to examine and treat problems in the hip joint. The camera displays pictures
HIP ARTHROSCOPY Hip arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that uses a camera inserted through very small incisions to examine and treat problems in the hip joint. The camera displays pictures
Your Practice Online
 P R E S E N T S Your Practice Online Disclaimer This information is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on Knee replacement or arthritis management. All decisions about
P R E S E N T S Your Practice Online Disclaimer This information is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on Knee replacement or arthritis management. All decisions about
Adult Forearm Fractures
 Adult Forearm Fractures Your forearm is made up of two bones, the radius and ulna. In most cases of adult forearm fractures, both bones are broken. Fractures of the forearm can occur near the wrist at
Adult Forearm Fractures Your forearm is made up of two bones, the radius and ulna. In most cases of adult forearm fractures, both bones are broken. Fractures of the forearm can occur near the wrist at
Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures
 Copyright 2010 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures Fractures of the heel bone, or calcaneus, can be disabling injuries. They most often occur during high-energy collisions
Copyright 2010 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures Fractures of the heel bone, or calcaneus, can be disabling injuries. They most often occur during high-energy collisions
Total knee replacement
 Patient Information to be retained by patient What is a total knee replacement? In a total knee replacement the cartilage surfaces of the thigh bone (femur) and leg bone (tibia) are replaced. The cartilage
Patient Information to be retained by patient What is a total knee replacement? In a total knee replacement the cartilage surfaces of the thigh bone (femur) and leg bone (tibia) are replaced. The cartilage
What to Expect from your Hip Arthroscopy Surgery A Guide for Patients
 What to Expect from your Hip Arthroscopy Surgery A Guide for Patients Sources of Information: http://orthoinfo.aaos.org http://dev.aana.org/portals/0/popups/animatedsurgery.htm http://www.isha.net/ http://
What to Expect from your Hip Arthroscopy Surgery A Guide for Patients Sources of Information: http://orthoinfo.aaos.org http://dev.aana.org/portals/0/popups/animatedsurgery.htm http://www.isha.net/ http://
Lumbar Laminectomy and Interspinous Process Fusion
 Lumbar Laminectomy and Interspinous Process Fusion Introduction Low back and leg pain caused by pinched nerves in the back is a common condition that limits your ability to move, walk, and work. This condition
Lumbar Laminectomy and Interspinous Process Fusion Introduction Low back and leg pain caused by pinched nerves in the back is a common condition that limits your ability to move, walk, and work. This condition
Patient Guide. Sacroiliac Joint Pain
 Patient Guide Sacroiliac Joint Pain Anatomy Where is the Sacroiliac Joint? The sacroiliac joint (SIJ) is located at the bottom end of your spine, where the "tailbone" (sacrum) joins the pelvis (ilium).
Patient Guide Sacroiliac Joint Pain Anatomy Where is the Sacroiliac Joint? The sacroiliac joint (SIJ) is located at the bottom end of your spine, where the "tailbone" (sacrum) joins the pelvis (ilium).
Shoulder Arthroscopy
 Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Shoulder Arthroscopy Arthroscopy is a procedure that orthopaedic surgeons use to inspect, diagnose, and repair problems inside a joint. The word
Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Shoulder Arthroscopy Arthroscopy is a procedure that orthopaedic surgeons use to inspect, diagnose, and repair problems inside a joint. The word
Neck Injuries and Disorders
 Neck Injuries and Disorders Introduction Any part of your neck can be affected by neck problems. These affect the muscles, bones, joints, tendons, ligaments or nerves in the neck. There are many common
Neck Injuries and Disorders Introduction Any part of your neck can be affected by neck problems. These affect the muscles, bones, joints, tendons, ligaments or nerves in the neck. There are many common
.org. Distal Radius Fracture (Broken Wrist) Description. Cause
 Distal Radius Fracture (Broken Wrist) Page ( 1 ) The radius is the larger of the two bones of the forearm. The end toward the wrist is called the distal end. A fracture of the distal radius occurs when
Distal Radius Fracture (Broken Wrist) Page ( 1 ) The radius is the larger of the two bones of the forearm. The end toward the wrist is called the distal end. A fracture of the distal radius occurs when
Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck)
 Copyright 2009 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Neck pain is extremely common. It can be caused by many things, and is most often related to getting
Copyright 2009 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Neck pain is extremely common. It can be caused by many things, and is most often related to getting
SPINAL STENOSIS Information for Patients WHAT IS SPINAL STENOSIS?
 SPINAL STENOSIS Information for Patients WHAT IS SPINAL STENOSIS? The spinal canal is best imagined as a bony tube through which nerve fibres pass. The tube is interrupted between each pair of adjacent
SPINAL STENOSIS Information for Patients WHAT IS SPINAL STENOSIS? The spinal canal is best imagined as a bony tube through which nerve fibres pass. The tube is interrupted between each pair of adjacent
Total Hip Replacement Surgery Home Care Instructions
 Total Hip Replacement Surgery Home Care Instructions Surgery: Date: Doctor: This handout will review the care you need to follow once you are home. If you have any questions or concerns, please ask your
Total Hip Replacement Surgery Home Care Instructions Surgery: Date: Doctor: This handout will review the care you need to follow once you are home. If you have any questions or concerns, please ask your
Information for the Patient About Surgical
 Information for the Patient About Surgical Decompression and Stabilization of the Spine Aging and the Spine Daily wear and tear, along with disc degeneration due to aging and injury, are common causes
Information for the Patient About Surgical Decompression and Stabilization of the Spine Aging and the Spine Daily wear and tear, along with disc degeneration due to aging and injury, are common causes
Temple Physical Therapy
 Temple Physical Therapy A General Overview of Common Neck Injuries For current information on Temple Physical Therapy related news and for a healthy and safe return to work, sport and recreation Like Us
Temple Physical Therapy A General Overview of Common Neck Injuries For current information on Temple Physical Therapy related news and for a healthy and safe return to work, sport and recreation Like Us
Total Abdominal Hysterectomy
 What is a total abdominal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through an abdominal incision (either an up and down or bikini cut). Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient.
What is a total abdominal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through an abdominal incision (either an up and down or bikini cut). Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient.
Posterior Cervical Decompression
 Posterior Cervical Decompression Spinal Unit Tel: 01473 702032 or 702097 Issue 2: January 2009 Following your recent MRI scan and consultation with your spinal surgeon, you have been diagnosed with a
Posterior Cervical Decompression Spinal Unit Tel: 01473 702032 or 702097 Issue 2: January 2009 Following your recent MRI scan and consultation with your spinal surgeon, you have been diagnosed with a
OPERATION:... Proximal tibial osteotomy Distal femoral osteotomy
 AFFIX PATIENT DETAIL STICKER HERE Forename.. Surname NHS Organisation. Responsible surgeon. Job Title Hospital Number... D.O.B.././ No special requirements OPERATION:..... Proximal tibial osteotomy Distal
AFFIX PATIENT DETAIL STICKER HERE Forename.. Surname NHS Organisation. Responsible surgeon. Job Title Hospital Number... D.O.B.././ No special requirements OPERATION:..... Proximal tibial osteotomy Distal
Total Shoulder Arthroplasty
 Specialists in Joint Replacement, Spinal Surgery, Orthopaedics and Sport Injuries Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Ms. Ruth Delaney Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon www.sportssurgeryclinic.com Introduction Arthritis
Specialists in Joint Replacement, Spinal Surgery, Orthopaedics and Sport Injuries Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Ms. Ruth Delaney Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon www.sportssurgeryclinic.com Introduction Arthritis
INFUSE Bone Graft. Patient Information Brochure
 INFUSE Bone Graft Patient Information Brochure This Patient Guide is designed to help you decide whether or not to have surgery using INFUSE Bone Graft to treat your broken tibia (lower leg). There are
INFUSE Bone Graft Patient Information Brochure This Patient Guide is designed to help you decide whether or not to have surgery using INFUSE Bone Graft to treat your broken tibia (lower leg). There are
Scaphoid Fracture of the Wrist
 Page 1 of 6 Scaphoid Fracture of the Wrist Doctors commonly diagnose a sprained wrist after a patient falls on an outstretched hand. However, if pain and swelling don't go away, doctors become suspicious
Page 1 of 6 Scaphoid Fracture of the Wrist Doctors commonly diagnose a sprained wrist after a patient falls on an outstretched hand. However, if pain and swelling don't go away, doctors become suspicious
.org. Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine. Cause. Description
 Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Page ( 1 ) Spinal fractures can vary widely in severity. While some fractures are very serious injuries that require emergency treatment, other fractures can
Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Page ( 1 ) Spinal fractures can vary widely in severity. While some fractures are very serious injuries that require emergency treatment, other fractures can
THE REVERSE SHOULDER REPLACEMENT
 THE REVERSE SHOULDER REPLACEMENT The Reverse Shoulder Replacement is a newly approved implant that has been used successfully for over ten years in Europe. It was approved by the FDA for use in the U.S.A.
THE REVERSE SHOULDER REPLACEMENT The Reverse Shoulder Replacement is a newly approved implant that has been used successfully for over ten years in Europe. It was approved by the FDA for use in the U.S.A.
LOSS OF BLADDER CONTROL IS TREATABLE TAKE CONTROL AND RESTORE YOUR LIFESTYLE
 LOSS OF BLADDER CONTROL IS TREATABLE TAKE CONTROL AND RESTORE YOUR LIFESTYLE TALKING ABOUT STRESS INCONTINENCE (SUI) Millions of women suffer from stress incontinence (SUI). This condition results in accidental
LOSS OF BLADDER CONTROL IS TREATABLE TAKE CONTROL AND RESTORE YOUR LIFESTYLE TALKING ABOUT STRESS INCONTINENCE (SUI) Millions of women suffer from stress incontinence (SUI). This condition results in accidental
Shared Decision Making
 Deciding what to do about osteoarthritis of the knee This short decision aid is to help you decide what to do about your knee osteoarthritis. You can use it on your own, or with your doctor, to help you
Deciding what to do about osteoarthritis of the knee This short decision aid is to help you decide what to do about your knee osteoarthritis. You can use it on your own, or with your doctor, to help you
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE. Health Technology Appraisal
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Health Technology Appraisal Total hip replacement and resurfacing arthroplasty for the treatment of pain or disability resulting from end stage arthritis
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Health Technology Appraisal Total hip replacement and resurfacing arthroplasty for the treatment of pain or disability resulting from end stage arthritis
Understanding Dental Implants
 Understanding Dental Implants Comfort and Confidence Again A new smile It s no fun when you re missing teeth. You may not feel comfortable eating or speaking. You might even avoid smiling in public. Fortunately,
Understanding Dental Implants Comfort and Confidence Again A new smile It s no fun when you re missing teeth. You may not feel comfortable eating or speaking. You might even avoid smiling in public. Fortunately,
Total elbow joint replacement for rheumatoid arthritis: A Patient s Guide
 www.orthop.washington.edu TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Overview 2 Review of the condition 3 Considering surgery 5 Preparing for surgery 6 About the procedure 8 Recovering from surgery 9 Convalescence and Rehabilitation
www.orthop.washington.edu TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Overview 2 Review of the condition 3 Considering surgery 5 Preparing for surgery 6 About the procedure 8 Recovering from surgery 9 Convalescence and Rehabilitation
Minimally Invasive Hip Replacement through the Direct Lateral Approach
 Surgical Technique INNOVATIONS IN MINIMALLY INVASIVE JOINT SURGERY Minimally Invasive Hip Replacement through the Direct Lateral Approach *smith&nephew Introduction Prosthetic replacement of the hip joint
Surgical Technique INNOVATIONS IN MINIMALLY INVASIVE JOINT SURGERY Minimally Invasive Hip Replacement through the Direct Lateral Approach *smith&nephew Introduction Prosthetic replacement of the hip joint
Multiple Myeloma. This reference summary will help you understand multiple myeloma and its treatment options.
 Multiple Myeloma Introduction Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells. Each year, thousands of people find out that they have multiple myeloma. This reference summary will help
Multiple Myeloma Introduction Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells. Each year, thousands of people find out that they have multiple myeloma. This reference summary will help
Other Noninfectious Diseases. Chapter 31 Lesson 3
 Other Noninfectious Diseases Chapter 31 Lesson 3 Diabetes Diabetes- a chronic disease that affects the way body cells convert food into energy. Diabetes is the seventh leading cause of death by disease
Other Noninfectious Diseases Chapter 31 Lesson 3 Diabetes Diabetes- a chronic disease that affects the way body cells convert food into energy. Diabetes is the seventh leading cause of death by disease
Before Surgery You will likely be asked to see your family physician or an internal medicine doctor for a thorough medical evaluation.
 Anterior Hip Replacement - Before and After Surgery Your Hip Evaluation An orthopaedic surgeon specializes in problems affecting bones and joints. The surgeon will ask you many questions about your hip
Anterior Hip Replacement - Before and After Surgery Your Hip Evaluation An orthopaedic surgeon specializes in problems affecting bones and joints. The surgeon will ask you many questions about your hip
X-Plain Inguinal Hernia Repair Reference Summary
 X-Plain Inguinal Hernia Repair Reference Summary Introduction Hernias are common conditions that affect men and women of all ages. Your doctor may recommend a hernia operation. The decision whether or
X-Plain Inguinal Hernia Repair Reference Summary Introduction Hernias are common conditions that affect men and women of all ages. Your doctor may recommend a hernia operation. The decision whether or
ARTHRITIS INTRODUCTION
 ARTHRITIS INTRODUCTION Arthritis is the most common disease affecting the joints. There are various forms of arthritis but the two that are the most common are osteoarthritis (OA), and rheumatoid arthritis
ARTHRITIS INTRODUCTION Arthritis is the most common disease affecting the joints. There are various forms of arthritis but the two that are the most common are osteoarthritis (OA), and rheumatoid arthritis
Total Knee Arthroplasty (Knee Replacement) PROCEDURAL CONSENT FORM. A. Interpreter / cultural needs. B. Condition and treatment
 The State of Queensland (Queensland Health), 2011 Permission to reproduce should be sought from [email protected] DO NOT WRITE IN THIS BINDING MARGIN v4.00-04/2011 SW9337 Total Knee Arthroplasty
The State of Queensland (Queensland Health), 2011 Permission to reproduce should be sought from [email protected] DO NOT WRITE IN THIS BINDING MARGIN v4.00-04/2011 SW9337 Total Knee Arthroplasty
TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT
 TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 9 What is a hip replacement? A hip replacement is an operation in which the damaged surfaces of the hip joint are removed
TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 9 What is a hip replacement? A hip replacement is an operation in which the damaged surfaces of the hip joint are removed
