Vortical Swirls in Hurricane Eye Clouds
|
|
|
- Sydney Harrison
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 3144 MONTHLY WEATHER REVIEW VOLUME 130 Vortical Swirls in Hurricane Eye Clouds JAMES P. KOSSIN Cooperative Institute for Meteorological Satellite Studies, University of Wisconsin Madison, Madison, Wisconsin BRIAN D. MCNOLDY AND WAYNE H. SCHUBERT Department of Atmospheric Science, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, Colorado 11 April 2002 and 14 June 2002 ABSTRACT A collection of images depicting various swirling patterns within low-level cloud decks in hurricane eyes is presented and described. A possible causal mechanism for the presence of these cloud patterns is suggested by comparison of the observed cloud patterns with the evolution of passive tracers in a simple 2D barotropic model. The model is initialized with a barotropically unstable flow field that imitates the observed flows in hurricanes, and numerical integration of this field simulates vigorous mixing between eye and eyewall. During the mixing process, passive tracers initially embedded in the flow form swirling patterns in the eye that are strikingly similar to cloud patterns often observed in the eyes of hurricanes. 1. Observations of vortical swirls in hurricane eye clouds Mature hurricanes often have low-level stratus or stratocumulus cloud decks below the inversion level in their eyes, and it is not uncommon to find various vortical, or swirling, shapes embedded in these cloud decks. An example of this phenomenon in Atlantic Hurricane Erin at 1515 UTC 11 September 2001 is shown in Fig. 1. At that time, the low clouds in the eye of Erin appeared as convoluted cloud streets that form an oxbow northeast of the storm center and an elliptical swirl west of center. Regions between the cloud streets were relatively devoid of clouds. Also visible at that time [1115 eastern daylight time (EDT)] was a smoke and dust plume being advected southward from the collapsed World Trade Center buildings near the southern tip of Manhattan, New York. The south tower of the World Trade Center collapsed at 1405 UTC (1005 EDT), and the north tower collapsed at 1428 UTC (1028 EDT), 47 min before the time of Fig. 1. In this case, the presence of Hurricane Erin may have been beneficial, because Erin s surface flow contributed to the northerly winds that carried smoke and dust away from a highly populated area. The swirling patterns in hurricane eye clouds can take on a variety of shapes, ranging from circles centered in Corresponding author address: Dr. James P. Kossin, Cooperative Institute for Meteorological Satellite Studies, University of Wisconsin Madison, Madison, WI kossin@ssec.wisc.edu the eye to convoluted patterns containing multiple swirls at varying positions in the eye. Figure 2 displays eyecloud patterns in western Pacific Supertyphoon Ida (1958), western Pacific Supertyphoon Yuri (1991), eastern Pacific Hurricane Emilia (1994), Atlantic Hurricane Alberto (2000), western Pacific Typhoon Man-Yi (2001), Atlantic Hurricane Erin (2001), western Pacific Typhoon Nari (2001), and western Pacific Supertyphoon Podul (2001). The dominant pattern in the eye clouds of Man-Yi (Fig. 2f), Erin (Fig. 2g), and Podul (Fig. 2i) was approximately circular with its center nearly collocated with the eye center, suggesting that the vorticity structures in the eyes of these storms were approximately axisymmetric. The patterns evident in the eye clouds of Ida, Yuri, Emilia, Alberto (Figs. 2a e), and Nari (Fig. 2h) are not well described by circles centered in the eyes, and they are more complicated and variable from storm to storm. The various shapes seen in these storms suggest that coherent regions of vorticity were present in their eyes and that the spatial scales of the coherent regions of vorticity were smaller than the parent vortex (i.e., the hurricane inner core) in which they were embedded. Such small-scale regions of vorticity are known as mesovortices, and their presence in hurricane eyes and eyewalls has been widely documented (Fletcher et al. 1961; Marks and Houze 1984; Muramatsu 1986; Bluestein and Marks 1987; Marks and Black 1990; Black and Marks 1991; Willoughby and Black 1996; Hasler et al. 1997). The cloud patterns in Ida (Fig. 2b) suggest that a mesovortex was located in the lower-right part of the 2002 American Meteorological Society
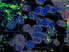
2 DECEMBER 2002 PICTURE OF THE MONTH 3145 FIG. 1. Moderate-Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) satellite image of Atlantic Hurricane Erin at 1515 UTC 11 Sep The right inset shows a magnified image of convoluted clouds in the eye. The left inset shows a smoke and dust plume being carried southward from the collapsed World Trade Center buildings, away from the populated island of Manhattan, in part by Erin s surface flow.
3 3146 MONTHLY WEATHER REVIEW VOLUME 130 FIG. 2. Montage of images showing a variety of swirling patterns in hurricane eye clouds: (a),(b) high-altitude U- 2 aircraft photographic reconnaissance (from Fletcher et al. 1961), (c),(d) photographs taken from the space shuttle, and (e) (i) MODIS images.
4 DECEMBER 2002 PICTURE OF THE MONTH 3147 eye and another mesovortex was located adjacent (above and left) to the first mesovortex. A similar mesovortex configuration was evident in Emilia (Fig. 2d), but the two mesovortices were located in the lower-left and upper-right parts of the eye. In Emilia, the mesovortex at the upper right appears to be larger than its neighbor to the lower left. The pattern in Alberto (Fig. 2e) suggests that a relatively large mesovortex was located in the upper part of the eye and at least three smaller mesovortices were located in the left, bottom, and right regions of the eye. The clouds in the eye of Nari (Fig. 2h) exhibited complexity similar to that of those in Alberto. Three distinct mesovortices appear; one in the upper part of the eye, one in the left part, and one in the lower-right part. The areas surrounding the mesovortices were relatively cloud free. It is not clear whether the cloud-free regions are a result of horizontal advective processes or of local updraft downdraft couplets associated with the mesovortices. Our interpretation of the relationship between flow patterns and stratiform cloud patterns assumes that the cloud lines are approximately parallel to local streamlines. Although there are situations in which stratiform cloud lines over general oceanic regions are aligned so as to be nearly perpendicular to local streamlines, this is not likely to be true here. Wind patterns in the neighborhood of hurricane mesovortices can be inferred to be coincident with cloud patterns by using a combination of photographs (Bluestein and Marks 1987), radar (Willoughby and Black 1996), and flight-level data (Black and Marks 1991). The relationship between cloud lines and streamlines in the hurricane eye is most likely that they are parallel in a manner analogous to the swirling features of von Kármán vortices that are sometimes evident in low-level marine stratiform clouds downwind of islands. FIG. 2.(Continued) 2. Dynamical interpretation In this section we suggest a dynamic mechanism, based on barotropic stability arguments, to explain the presence of mesovortices in the hurricane eye. The barotropic dynamics are presented using a simple nondivergent barotropic numerical model, and they show that numerical integration of barotropically unstable initial conditions leads to a breakdown of the eyewall and formation of mesovortices that migrate from the eyewall into the eye. Passive tracers, initially inserted into the flow to represent cloud particles, are convoluted by the mesovortices and form swirling patterns that are very similar to the swirling patterns observed in the eye clouds of the storms shown in Figs. 1 and 2. When a hurricane eye forms, inner-core deep convection is generally confined to the annular region of the eyewall. Such an annular convective structure confines the diabatic production of potential vorticity (PV) to the annulus and will, over time, produce a PV structure described by relatively high PV in the eyewall
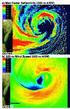
5 3148 MONTHLY WEATHER REVIEW VOLUME 130 FIG. 3. Two-dimensional maps showing the evolving distribution of passive eyewall tracers placed in the initially unstable model flow.
6 DECEMBER 2002 PICTURE OF THE MONTH 3149 flanked on both sides by relatively low PV. Such a PV structure is called a hollow tower PV structure (Möller and Smith 1994), and the reversal of the radial PV gradient sets the stage for barotropic instability. Evidence that such PV structures are typically present in developing and mature hurricanes was shown by Kossin and Eastin (2001). To demonstrate the nonlinear evolution of hollowtower, or annular, PV structures, we consider the simplified framework of a nondivergent barotropic model and employ the same pseudospectral numerical model described by Schubert et al. (1999). This model isolates the dynamics in the absence of any baroclinic effects and thus might seem inappropriate for modeling mature hurricanes, which typically have large vertical wind shear in the near core. However, recent work by Nolan and Montgomery (2002) shows that instabilities in three-dimensional hurricane-like vortices are fundamentally two-dimensional in nature and are modeled well in a nondivergent barotropic framework. Our axisymmetric initial condition, consisting of an annular vorticity structure, and all model parameters (domain size, grid spacing, time step, and kinematic viscosity) are the same as those used by Kossin and Eastin (2001). The initial profile of vorticity describes a hurricane-like vortex with maximum tangential wind of 60 m s 1 at radius r 20 km. To describe the evolution of cloud particles, concentric rings of passive tracers are placed initially into the annulus of high vorticity (i.e., the eyewall ). The tracers are initially contained along eight concentric rings with r 15,16,...,22km.The number of tracers along a concentric ring increases with increasing radius so that the number concentration of the tracers is the same along each ring. The tracer evolution is shown in Fig. 3 in the form of two-dimensional maps. At time t 4.5 h, barotropic instability of the flow around the eyewall has resulted in wave breaking and distortion of the tracers. At t 6.5 h, most of the tracers are embedded in coherent mesovortices, with the remaining tracers smeared out within filaments of vorticity that connect the mesovortices. A distinct mesovortex in the eastern quadrant of the vortex has migrated into the eye. During the subsequent 2 h, interaction of the mesovortices and convolution of the filaments result in a variety of swirling shapes within the tracer field, and at t 8.5 h the tracer field is remarkably similar to the low-level cloud fields observed in the eyes of Hurricane Alberto (Fig. 2e) and Typhoon Nari (Fig. 2h). By t 24 h (not shown), the tracers (and the vorticity field) have nearly achieved their axisymmetric end state. At this time, the vorticity is approximately monotonic and the eyewall tracers form circles centered in the eye (see Kossin and Eastin 2001; their Fig. 11). 3. Concluding remarks The observed presence of swirling shapes in the low cloud decks in hurricane eyes was first formally documented by Fletcher et al. (1961) using high-altitude U- 2 aircraft photographic reconnaissance. Nowadays, the appearance of swirling eye clouds, usually noted in satellite imagery, often inspires a flurry of informal scientific communication that is generally in the form of electronic mail containing remarkable images of hurricane eyes. This article has documented a number of these images and has offered a physical mechanism, based on simple 2D barotropic dynamics, to explain the source of flow patterns that may be responsible for the presence of vortical swirls in hurricane low-level eye clouds. Acknowledgments. This work was supported by NASA Grant NAG , NOAA Grant NA67RJ0152, and NSF Grant ATM We are grateful to Hugh Willoughby and an anonymous reviewer for their thoughtful comments on the original manuscript. REFERENCES Black, P. G., and F. D. Marks, 1991: The structure of an eyewall meso-vortex in Hurricane Hugo (1989). Preprints, 19th Conf. on Hurricanes and Tropical Meteorology, Miami, FL, Amer. Meteor. Soc., Bluestein, H. B., and F. D. Marks, 1987: On the structure of the eyewall of Hurricane Diana (1984): Comparison of radar and visual characteristics. Mon. Wea. Rev., 115, Fletcher, R. D., J. R. Smith, and R. C. Bundgaard, 1961: Superior photographic reconnaissance of tropical cyclones. Weatherwise, 14 (3), Hasler, A. F., P. G. Black, V. M. Karyampudi, M. Jentoft-Nilsen, K. Palaniappan, and D. Chesters, 1997: Synthesis of eyewall mesovortex and supercell convective structures in Hurricane Luis with GOES-8/9 stereo, concurrent 1-min GOES-9 and NOAA airborne radar observations. Preprints, 22d Conf. on Hurricanes and Tropical Meteorology, Fort Collins, CO, Amer. Meteor. Soc., Kossin, J. P., and M. D. Eastin, 2001: Two distinct regimes in the kinematic and thermodynamic structure of the hurricane eye and eyewall. J. Atmos. Sci., 58, Marks, F. D., and R. A. Houze, 1984: Airborne Doppler radar observations in Hurricane Debby. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 65, , and P. G. Black, 1990: Close encounter with an intense mesoscale vortex within Hurricane Hugo (September 15, 1989). Extended Abstracts, Fourth Conf. on Mesoscale Processes, Boulder, CO, Amer. Meteor. Soc., Möller, J. D., and R. K. Smith, 1994: The development of potential vorticity in a hurricane-like vortex. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 120, Muramatsu, T., 1986: The structure of polygonal eye of a typhoon. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 64, Nolan, D. S., and M. T. Montgomery, 2002: Nonhydrostatic, threedimensional perturbations to balanced, hurricane-like vortices. Part I: Linearized formulation, stability, and evolution. J. Atmos. Sci., 59, Schubert, W. H., M. T. Montgomery, R. K. Taft, T. A. Guinn, S. R. Fulton, J. P. Kossin, and J. P. Edwards, 1999: Polygonal eyewalls, asymmetric eye contraction, and potential vorticity mixing in hurricanes. J. Atmos. Sci., 56, Willoughby, H. E., and P. G. Black, 1996: Hurricane Andrew in Florida: Dynamics of a disaster. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 77,
Award Number: N00014-07-1-0163
 Tropical Cyclone Structure and Intensity Change Related to Eyewall Replacement Cycles and Annular Storm Formation, Utilizing Objective Interpretation of Satellite Data and Model Analyses James P. Kossin
Tropical Cyclone Structure and Intensity Change Related to Eyewall Replacement Cycles and Annular Storm Formation, Utilizing Objective Interpretation of Satellite Data and Model Analyses James P. Kossin
Frank and Charles Cohen Department of Meteorology The Pennsylvania State University University Park, PA, 16801 -U.S.A.
 376 THE SIMULATION OF TROPICAL CONVECTIVE SYSTEMS William M. Frank and Charles Cohen Department of Meteorology The Pennsylvania State University University Park, PA, 16801 -U.S.A. ABSTRACT IN NUMERICAL
376 THE SIMULATION OF TROPICAL CONVECTIVE SYSTEMS William M. Frank and Charles Cohen Department of Meteorology The Pennsylvania State University University Park, PA, 16801 -U.S.A. ABSTRACT IN NUMERICAL
USING THE GOES 3.9 µm SHORTWAVE INFRARED CHANNEL TO TRACK LOW-LEVEL CLOUD-DRIFT WINDS ABSTRACT
 USING THE GOES 3.9 µm SHORTWAVE INFRARED CHANNEL TO TRACK LOW-LEVEL CLOUD-DRIFT WINDS Jason P. Dunion 1 and Christopher S. Velden 2 1 NOAA/AOML/Hurricane Research Division, 2 UW/CIMSS ABSTRACT Low-level
USING THE GOES 3.9 µm SHORTWAVE INFRARED CHANNEL TO TRACK LOW-LEVEL CLOUD-DRIFT WINDS Jason P. Dunion 1 and Christopher S. Velden 2 1 NOAA/AOML/Hurricane Research Division, 2 UW/CIMSS ABSTRACT Low-level
Goal: Understand the conditions and causes of tropical cyclogenesis and cyclolysis
 Necessary conditions for tropical cyclone formation Leading theories of tropical cyclogenesis Sources of incipient disturbances Extratropical transition Goal: Understand the conditions and causes of tropical
Necessary conditions for tropical cyclone formation Leading theories of tropical cyclogenesis Sources of incipient disturbances Extratropical transition Goal: Understand the conditions and causes of tropical
Environmental Sensitivity of Tropical Cyclone Outflow
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Environmental Sensitivity of Tropical Cyclone Outflow Principal Investigator: Sharanya J. Majumdar Department of Atmospheric
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Environmental Sensitivity of Tropical Cyclone Outflow Principal Investigator: Sharanya J. Majumdar Department of Atmospheric
Mesoscale Interactions in Tropical Cyclone Genesis
 2643 Mesoscale Interactions in Tropical Cyclone Genesis J. SIMPSON Earth Sciences Directorate, NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland E. RITCHIE Department of Meteorology, Naval Postgraduate
2643 Mesoscale Interactions in Tropical Cyclone Genesis J. SIMPSON Earth Sciences Directorate, NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland E. RITCHIE Department of Meteorology, Naval Postgraduate
7B.2 MODELING THE EFFECT OF VERTICAL WIND SHEAR ON TROPICAL CYCLONE SIZE AND STRUCTURE
 7B.2 MODELING THE EFFECT OF VERTICAL WIND SHEAR ON TROPICAL CYCLONE SIZE AND STRUCTURE Diana R. Stovern* and Elizabeth A. Ritchie University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona 1. Introduction An ongoing problem
7B.2 MODELING THE EFFECT OF VERTICAL WIND SHEAR ON TROPICAL CYCLONE SIZE AND STRUCTURE Diana R. Stovern* and Elizabeth A. Ritchie University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona 1. Introduction An ongoing problem
NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE. Observations of a Severe Left Moving Thunderstorm
 500 WEATHER AND FORECASTING VOLUME 16 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE Observations of a Severe Left Moving Thunderstorm LEWIS D. GRASSO AND ERIC R. HILGENDORF Cooperative Institute for Research in the Atmosphere,
500 WEATHER AND FORECASTING VOLUME 16 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE Observations of a Severe Left Moving Thunderstorm LEWIS D. GRASSO AND ERIC R. HILGENDORF Cooperative Institute for Research in the Atmosphere,
MountainZebra: Real-Time Archival and 4D Visualization of Radar Volumes Over Complex Terrain
 MountainZebra: Real-Time Archival and D Visualization of Radar Volumes Over Complex Terrain Curtis James, Stacy Brodzik, Harry Edmon, Robert Houze, and Sandra Yuter Department of Atmospheric Sciences,
MountainZebra: Real-Time Archival and D Visualization of Radar Volumes Over Complex Terrain Curtis James, Stacy Brodzik, Harry Edmon, Robert Houze, and Sandra Yuter Department of Atmospheric Sciences,
Left moving thunderstorms in a high Plains, weakly-sheared environment
 Left moving thunderstorms in a high Plains, weakly-sheared environment by John F. Weaver 1 and John F. Dostalek Cooperative Institute for Research in the Atmosphere, CIRA Colorado State University Fort
Left moving thunderstorms in a high Plains, weakly-sheared environment by John F. Weaver 1 and John F. Dostalek Cooperative Institute for Research in the Atmosphere, CIRA Colorado State University Fort
6.4 THE SIERRA ROTORS PROJECT, OBSERVATIONS OF MOUNTAIN WAVES. William O. J. Brown 1 *, Stephen A. Cohn 1, Vanda Grubiši 2, and Brian Billings 2
 6.4 THE SIERRA ROTORS PROJECT, OBSERVATIONS OF MOUNTAIN WAVES William O. J. Brown 1 *, Stephen A. Cohn 1, Vanda Grubiši 2, and Brian Billings 2 1 National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, Colorado.
6.4 THE SIERRA ROTORS PROJECT, OBSERVATIONS OF MOUNTAIN WAVES William O. J. Brown 1 *, Stephen A. Cohn 1, Vanda Grubiši 2, and Brian Billings 2 1 National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, Colorado.
WEATHER RADAR VELOCITY FIELD CONFIGURATIONS ASSOCIATED WITH SEVERE WEATHER SITUATIONS THAT OCCUR IN SOUTH-EASTERN ROMANIA
 Romanian Reports in Physics, Vol. 65, No. 4, P. 1454 1468, 2013 ATMOSPHERE PHYSICS WEATHER RADAR VELOCITY FIELD CONFIGURATIONS ASSOCIATED WITH SEVERE WEATHER SITUATIONS THAT OCCUR IN SOUTH-EASTERN ROMANIA
Romanian Reports in Physics, Vol. 65, No. 4, P. 1454 1468, 2013 ATMOSPHERE PHYSICS WEATHER RADAR VELOCITY FIELD CONFIGURATIONS ASSOCIATED WITH SEVERE WEATHER SITUATIONS THAT OCCUR IN SOUTH-EASTERN ROMANIA
Cloud/Hydrometeor Initialization in the 20-km RUC Using GOES Data
 WORLD METEOROLOGICAL ORGANIZATION COMMISSION FOR BASIC SYSTEMS OPEN PROGRAMMME AREA GROUP ON INTEGRATED OBSERVING SYSTEMS EXPERT TEAM ON OBSERVATIONAL DATA REQUIREMENTS AND REDESIGN OF THE GLOBAL OBSERVING
WORLD METEOROLOGICAL ORGANIZATION COMMISSION FOR BASIC SYSTEMS OPEN PROGRAMMME AREA GROUP ON INTEGRATED OBSERVING SYSTEMS EXPERT TEAM ON OBSERVATIONAL DATA REQUIREMENTS AND REDESIGN OF THE GLOBAL OBSERVING
In a majority of ice-crystal icing engine events, convective weather occurs in a very warm, moist, tropical-like environment. aero quarterly qtr_01 10
 In a majority of ice-crystal icing engine events, convective weather occurs in a very warm, moist, tropical-like environment. 22 avoiding convective Weather linked to Ice-crystal Icing engine events understanding
In a majority of ice-crystal icing engine events, convective weather occurs in a very warm, moist, tropical-like environment. 22 avoiding convective Weather linked to Ice-crystal Icing engine events understanding
Western North Pacific Tropical Cyclone Formation and Structure Change in TCS08
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Western North Pacific Tropical Cyclone Formation and Structure Change in TCS08 Patrick A. Harr Department of Meteorology,
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Western North Pacific Tropical Cyclone Formation and Structure Change in TCS08 Patrick A. Harr Department of Meteorology,
Regional Forecast Center Timişoara 15. Gh. Adam St., Timişoara, Romania, e-mail: cristi_nichita2004@yahoo.com
 Analele UniversităŃii din Oradea Seria Geografie Tom XX, no. 2/2010 (December), pp 197-203 ISSN 1221-1273, E-ISSN 2065-3409 Article no. 202106-492 SOME DOPPLER RADAR FEATURES OF SEVERE WEATHER IN SUPERCELLS
Analele UniversităŃii din Oradea Seria Geografie Tom XX, no. 2/2010 (December), pp 197-203 ISSN 1221-1273, E-ISSN 2065-3409 Article no. 202106-492 SOME DOPPLER RADAR FEATURES OF SEVERE WEATHER IN SUPERCELLS
On the use of Synthetic Satellite Imagery to Evaluate Numerically Simulated Clouds
 On the use of Synthetic Satellite Imagery to Evaluate Numerically Simulated Clouds Lewis D. Grasso (1) Cooperative Institute for Research in the Atmosphere, Fort Collins, Colorado Don Hillger NOAA/NESDIS/STAR/RAMMB,
On the use of Synthetic Satellite Imagery to Evaluate Numerically Simulated Clouds Lewis D. Grasso (1) Cooperative Institute for Research in the Atmosphere, Fort Collins, Colorado Don Hillger NOAA/NESDIS/STAR/RAMMB,
Overview: The relative importance of intense vs. moderate convection to rapid intensification
 Overview: The relative importance of intense vs. moderate convection to rapid intensification Edward Zipser Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT, USA ed.zipser@utah.edu
Overview: The relative importance of intense vs. moderate convection to rapid intensification Edward Zipser Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT, USA ed.zipser@utah.edu
http://www.nrl.navy.mil/pao/pressrelease.php?y=2008&r=91-08r
 Page 1 of 7 NRL Press Release 91-08r 12/15/2008 nrlpao@nrl.navy.mil 202-767-2541 NRL's P-3 Aircraft Support Project to Study Tropical Cyclones Email Follow NRL RSS Feed Related Visuals The Naval Research
Page 1 of 7 NRL Press Release 91-08r 12/15/2008 nrlpao@nrl.navy.mil 202-767-2541 NRL's P-3 Aircraft Support Project to Study Tropical Cyclones Email Follow NRL RSS Feed Related Visuals The Naval Research
An Operational Local Data Integration System (LDIS) at WFO Melbourne
 1. Introduction An Operational Local Data Integration System (LDIS) at WFO Melbourne Peter F. Blottman, Scott M. Spratt, David W. Sharp, and Anthony J. Cristaldi III WFO Melbourne, FL Jonathan L. Case
1. Introduction An Operational Local Data Integration System (LDIS) at WFO Melbourne Peter F. Blottman, Scott M. Spratt, David W. Sharp, and Anthony J. Cristaldi III WFO Melbourne, FL Jonathan L. Case
A Real Case Study of Using Cloud Analysis in Grid-point Statistical Interpolation Analysis and Advanced Research WRF Forecast System
 A Real Case Study of Using Cloud Analysis in Grid-point Statistical Interpolation Analysis and Advanced Research WRF Forecast System Ming Hu 1 and Ming Xue 1, 1 Center for Analysis and Prediction of Storms,
A Real Case Study of Using Cloud Analysis in Grid-point Statistical Interpolation Analysis and Advanced Research WRF Forecast System Ming Hu 1 and Ming Xue 1, 1 Center for Analysis and Prediction of Storms,
MICROPHYSICS COMPLEXITY EFFECTS ON STORM EVOLUTION AND ELECTRIFICATION
 MICROPHYSICS COMPLEXITY EFFECTS ON STORM EVOLUTION AND ELECTRIFICATION Blake J. Allen National Weather Center Research Experience For Undergraduates, Norman, Oklahoma and Pittsburg State University, Pittsburg,
MICROPHYSICS COMPLEXITY EFFECTS ON STORM EVOLUTION AND ELECTRIFICATION Blake J. Allen National Weather Center Research Experience For Undergraduates, Norman, Oklahoma and Pittsburg State University, Pittsburg,
A Cloud-Resolving Simulation of Hurricane Bob (1991): Storm Structure and Eyewall Buoyancy
 JUNE 2002 BRAUN 1573 A Cloud-Resolving Simulation of Hurricane Bob (1991): Storm Structure and Eyewall Buoyancy SCOTT A. BRAUN Laboratory for Atmospheres, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland
JUNE 2002 BRAUN 1573 A Cloud-Resolving Simulation of Hurricane Bob (1991): Storm Structure and Eyewall Buoyancy SCOTT A. BRAUN Laboratory for Atmospheres, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland
Urban heat islands and summertime convective thunderstorms in Atlanta: three case studies
 Atmospheric Environment 34 (2000) 507}516 Urban heat islands and summertime convective thunderstorms in Atlanta: three case studies Robert Bornstein*, Qinglu Lin Department of Meteorology, San Jose State
Atmospheric Environment 34 (2000) 507}516 Urban heat islands and summertime convective thunderstorms in Atlanta: three case studies Robert Bornstein*, Qinglu Lin Department of Meteorology, San Jose State
How To Model An Ac Cloud
 Development of an Elevated Mixed Layer Model for Parameterizing Altocumulus Cloud Layers S. Liu and S. K. Krueger Department of Meteorology University of Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah Introduction Altocumulus
Development of an Elevated Mixed Layer Model for Parameterizing Altocumulus Cloud Layers S. Liu and S. K. Krueger Department of Meteorology University of Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah Introduction Altocumulus
The Influence of Airborne Doppler Radar Data Quality on Numerical Simulations of a Tropical Cyclone
 FEBRUARY 2012 Z H A N G E T A L. 231 The Influence of Airborne Doppler Radar Data Quality on Numerical Simulations of a Tropical Cyclone LEI ZHANG* AND ZHAOXIA PU Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University
FEBRUARY 2012 Z H A N G E T A L. 231 The Influence of Airborne Doppler Radar Data Quality on Numerical Simulations of a Tropical Cyclone LEI ZHANG* AND ZHAOXIA PU Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University
8B.6 A DETAILED ANALYSIS OF SPC HIGH RISK OUTLOOKS, 2003-2009
 8B.6 A DETAILED ANALYSIS OF SPC HIGH RISK OUTLOOKS, 2003-2009 Jason M. Davis*, Andrew R. Dean 2, and Jared L. Guyer 2 Valparaiso University, Valparaiso, IN 2 NOAA/NWS Storm Prediction Center, Norman, OK.
8B.6 A DETAILED ANALYSIS OF SPC HIGH RISK OUTLOOKS, 2003-2009 Jason M. Davis*, Andrew R. Dean 2, and Jared L. Guyer 2 Valparaiso University, Valparaiso, IN 2 NOAA/NWS Storm Prediction Center, Norman, OK.
Chapter 7 Stability and Cloud Development. Atmospheric Stability
 Chapter 7 Stability and Cloud Development Atmospheric Stability 1 Cloud Development - stable environment Stable air (parcel) - vertical motion is inhibited if clouds form, they will be shallow, layered
Chapter 7 Stability and Cloud Development Atmospheric Stability 1 Cloud Development - stable environment Stable air (parcel) - vertical motion is inhibited if clouds form, they will be shallow, layered
NAVAL POSTGRADUATE SCHOOL DISSERTATION
 NAVAL POSTGRADUATE SCHOOL MONTEREY, CALIFORNIA DISSERTATION THE RE-INTENSIFICATION OF TYPHOON SINLAKU (2008) by Elizabeth R. Sanabia June 2010 Dissertation Supervisor: Patrick A. Harr Approved for public
NAVAL POSTGRADUATE SCHOOL MONTEREY, CALIFORNIA DISSERTATION THE RE-INTENSIFICATION OF TYPHOON SINLAKU (2008) by Elizabeth R. Sanabia June 2010 Dissertation Supervisor: Patrick A. Harr Approved for public
P1.2 NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF LONG DISTANCE TRANSPORTATION OF VOLCANO ASH FROM PINATUBO
 P1.2 NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF LONG DISTANCE TRANSPORTATION OF VOLCANO ASH FROM PINATUBO Tan Jiqing Xu Juan (Institution of Meteorological Information and Prediction of Disaster Events, Zhejiang University,
P1.2 NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF LONG DISTANCE TRANSPORTATION OF VOLCANO ASH FROM PINATUBO Tan Jiqing Xu Juan (Institution of Meteorological Information and Prediction of Disaster Events, Zhejiang University,
Breeding and predictability in coupled Lorenz models. E. Kalnay, M. Peña, S.-C. Yang and M. Cai
 Breeding and predictability in coupled Lorenz models E. Kalnay, M. Peña, S.-C. Yang and M. Cai Department of Meteorology University of Maryland, College Park 20742 USA Abstract Bred vectors are the difference
Breeding and predictability in coupled Lorenz models E. Kalnay, M. Peña, S.-C. Yang and M. Cai Department of Meteorology University of Maryland, College Park 20742 USA Abstract Bred vectors are the difference
Parameterization of Cumulus Convective Cloud Systems in Mesoscale Forecast Models
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Parameterization of Cumulus Convective Cloud Systems in Mesoscale Forecast Models Yefim L. Kogan Cooperative Institute
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Parameterization of Cumulus Convective Cloud Systems in Mesoscale Forecast Models Yefim L. Kogan Cooperative Institute
SIXTH INTERNATIONAL WORKSHOP ON TROPICAL CYCLONES. Topic 1.1 : Environmental Effects on Tropical Cyclone Structure and Structure Change
 WMO/CAS/WWW SIXTH INTERNATIONAL WORKSHOP ON TROPICAL CYCLONES Topic 1.1 : Environmental Effects on Tropical Cyclone Structure and Structure Change Rapporteur: E. A. Ritchie Department of Atmospheric Sciences
WMO/CAS/WWW SIXTH INTERNATIONAL WORKSHOP ON TROPICAL CYCLONES Topic 1.1 : Environmental Effects on Tropical Cyclone Structure and Structure Change Rapporteur: E. A. Ritchie Department of Atmospheric Sciences
Surface Rainfall Cold Cloud Fractional Coverage Relationship in TOGA COARE: A Function of Vertical Wind Shear
 407 Surface Rainfall Cold Cloud Fractional Coverage Relationship in TOGA COARE: A Function of Vertical Wind Shear THOMAS R. SAXEN* AND STEVEN A. RUTLEDGE Department of Atmospheric Science, Colorado State
407 Surface Rainfall Cold Cloud Fractional Coverage Relationship in TOGA COARE: A Function of Vertical Wind Shear THOMAS R. SAXEN* AND STEVEN A. RUTLEDGE Department of Atmospheric Science, Colorado State
A Review on the Uses of Cloud-(System-)Resolving Models
 A Review on the Uses of Cloud-(System-)Resolving Models Jeffrey D. Duda Since their advent into the meteorological modeling world, cloud-(system)-resolving models (CRMs or CSRMs) have become very important
A Review on the Uses of Cloud-(System-)Resolving Models Jeffrey D. Duda Since their advent into the meteorological modeling world, cloud-(system)-resolving models (CRMs or CSRMs) have become very important
Meteorology: Weather and Climate
 Meteorology: Weather and Climate Large Scale Weather Systems Lecture 1 Tropical Cyclones: Location and Structure Prof. Roy Thompson Crew building Large-scale Weather Systems Tropical cyclones (1-2) Location,
Meteorology: Weather and Climate Large Scale Weather Systems Lecture 1 Tropical Cyclones: Location and Structure Prof. Roy Thompson Crew building Large-scale Weather Systems Tropical cyclones (1-2) Location,
Trimodal cloudiness and tropical stable layers in simulations of radiative convective equilibrium
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L08802, doi:10.1029/2007gl033029, 2008 Trimodal cloudiness and tropical stable layers in simulations of radiative convective equilibrium D. J. Posselt, 1 S. C. van
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L08802, doi:10.1029/2007gl033029, 2008 Trimodal cloudiness and tropical stable layers in simulations of radiative convective equilibrium D. J. Posselt, 1 S. C. van
Ongoing Development and Testing of Generalized Cloud Analysis Package within GSI for Initializing Rapid Refresh
 Preprints, 13 th Conf. on Aviation, Range and Aerospace Meteorology. January 2008, New Orleans, LA, Amer. Meteor. Soc. 7.4 Ongoing Development and Testing of Generalized Cloud Analysis Package within GSI
Preprints, 13 th Conf. on Aviation, Range and Aerospace Meteorology. January 2008, New Orleans, LA, Amer. Meteor. Soc. 7.4 Ongoing Development and Testing of Generalized Cloud Analysis Package within GSI
Follow That Hurricane!
 Discover Your World With NOAA Follow That Hurricane! What You Will Do Devastating damage expected A most Track a hurricane on the same powerful hurricane with unprecedented type of chart used at the strength
Discover Your World With NOAA Follow That Hurricane! What You Will Do Devastating damage expected A most Track a hurricane on the same powerful hurricane with unprecedented type of chart used at the strength
Altuğ Aksoy Current Affiliation: Academic Background. Current Research Interests and Activities
 Altuğ Aksoy Current Affiliation: Work Address: E-Mail: Webpage: Cooperative Institute for Marine and Atmospheric Studies (CIMAS), Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science (RSMAS), University
Altuğ Aksoy Current Affiliation: Work Address: E-Mail: Webpage: Cooperative Institute for Marine and Atmospheric Studies (CIMAS), Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science (RSMAS), University
DIURNAL CYCLE OF CLOUD SYSTEM MIGRATION OVER SUMATERA ISLAND
 DIURNAL CYCLE OF CLOUD SYSTEM MIGRATION OVER SUMATERA ISLAND NAMIKO SAKURAI 1, FUMIE MURATA 2, MANABU D. YAMANAKA 1,3, SHUICHI MORI 3, JUN-ICHI HAMADA 3, HIROYUKI HASHIGUCHI 4, YUDI IMAN TAUHID 5, TIEN
DIURNAL CYCLE OF CLOUD SYSTEM MIGRATION OVER SUMATERA ISLAND NAMIKO SAKURAI 1, FUMIE MURATA 2, MANABU D. YAMANAKA 1,3, SHUICHI MORI 3, JUN-ICHI HAMADA 3, HIROYUKI HASHIGUCHI 4, YUDI IMAN TAUHID 5, TIEN
The HRD real-time hurricane wind analysis system
 Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics 77&78 (1998) 53 64 The HRD real-time hurricane wind analysis system Mark D. Powell*, Sam H. Houston, Luis R. Amat, Nirva Morisseau-Leroy NOAA/AOML
Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics 77&78 (1998) 53 64 The HRD real-time hurricane wind analysis system Mark D. Powell*, Sam H. Houston, Luis R. Amat, Nirva Morisseau-Leroy NOAA/AOML
HIGH RESOLUTION SATELLITE IMAGERY OF THE NEW ZEALAND AREA: A VIEW OF LEE WAVES*
 Weather and Climate (1982) 2: 23-29 23 HIGH RESOLUTION SATELLITE IMAGERY OF THE NEW ZEALAND AREA: A VIEW OF LEE WAVES* C. G. Revell New Zealand Meteorological Service, Wellington ABSTRACT Examples of cloud
Weather and Climate (1982) 2: 23-29 23 HIGH RESOLUTION SATELLITE IMAGERY OF THE NEW ZEALAND AREA: A VIEW OF LEE WAVES* C. G. Revell New Zealand Meteorological Service, Wellington ABSTRACT Examples of cloud
REMOTE SENSING OF CLOUD-AEROSOL RADIATIVE EFFECTS FROM SATELLITE DATA: A CASE STUDY OVER THE SOUTH OF PORTUGAL
 REMOTE SENSING OF CLOUD-AEROSOL RADIATIVE EFFECTS FROM SATELLITE DATA: A CASE STUDY OVER THE SOUTH OF PORTUGAL D. Santos (1), M. J. Costa (1,2), D. Bortoli (1,3) and A. M. Silva (1,2) (1) Évora Geophysics
REMOTE SENSING OF CLOUD-AEROSOL RADIATIVE EFFECTS FROM SATELLITE DATA: A CASE STUDY OVER THE SOUTH OF PORTUGAL D. Santos (1), M. J. Costa (1,2), D. Bortoli (1,3) and A. M. Silva (1,2) (1) Évora Geophysics
J4.1 CENTRAL NORTH CAROLINA TORNADOES FROM THE 16 APRIL 2011 OUTBREAK. Matthew Parker* North Carolina State University, Raleigh, North Carolina
 J4.1 CENTRAL NORTH CAROLINA TORNADOES FROM THE 16 APRIL 2011 OUTBREAK Matthew Parker* North Carolina State University, Raleigh, North Carolina Jonathan Blaes NOAA/National Weather Service, Raleigh, North
J4.1 CENTRAL NORTH CAROLINA TORNADOES FROM THE 16 APRIL 2011 OUTBREAK Matthew Parker* North Carolina State University, Raleigh, North Carolina Jonathan Blaes NOAA/National Weather Service, Raleigh, North
DETAILED STORM SIMULATIONS BY A NUMERICAL CLOUD MODEL WITH ELECTRIFICATION AND LIGHTNING PARAMETERIZATIONS
 DETAILED STORM SIMULATIONS BY A NUMERICAL CLOUD MODEL WITH ELECTRIFICATION AND LIGHTNING PARAMETERIZATIONS Don MacGorman 1, Ted Mansell 1,2, Conrad Ziegler 1, Jerry Straka 3, and Eric C. Bruning 1,3 1
DETAILED STORM SIMULATIONS BY A NUMERICAL CLOUD MODEL WITH ELECTRIFICATION AND LIGHTNING PARAMETERIZATIONS Don MacGorman 1, Ted Mansell 1,2, Conrad Ziegler 1, Jerry Straka 3, and Eric C. Bruning 1,3 1
Hurricanes. Characteristics of a Hurricane
 Hurricanes Readings: A&B Ch. 12 Topics 1. Characteristics 2. Location 3. Structure 4. Development a. Tropical Disturbance b. Tropical Depression c. Tropical Storm d. Hurricane e. Influences f. Path g.
Hurricanes Readings: A&B Ch. 12 Topics 1. Characteristics 2. Location 3. Structure 4. Development a. Tropical Disturbance b. Tropical Depression c. Tropical Storm d. Hurricane e. Influences f. Path g.
Storms Short Study Guide
 Name: Class: Date: Storms Short Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A(n) thunderstorm forms because of unequal heating
Name: Class: Date: Storms Short Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A(n) thunderstorm forms because of unequal heating
Tropical Cloud Population
 Tropical Cloud Population Before Satellites Visual Observation View from and aircraft flying over the South China Sea Radiosonde Data Hot tower hypothesis Riehl & Malkus 1958 Satellite Observations Post
Tropical Cloud Population Before Satellites Visual Observation View from and aircraft flying over the South China Sea Radiosonde Data Hot tower hypothesis Riehl & Malkus 1958 Satellite Observations Post
Evaluation of VIIRS cloud top property climate data records and their potential improvement with CrIS
 Evaluation of VIIRS cloud top property climate data records and their potential improvement with CrIS Dr. Bryan A. Baum (PI) Space Science and Engineering Center University of Wisconsin-Madison Madison,
Evaluation of VIIRS cloud top property climate data records and their potential improvement with CrIS Dr. Bryan A. Baum (PI) Space Science and Engineering Center University of Wisconsin-Madison Madison,
Project Title: Quantifying Uncertainties of High-Resolution WRF Modeling on Downslope Wind Forecasts in the Las Vegas Valley
 University: Florida Institute of Technology Name of University Researcher Preparing Report: Sen Chiao NWS Office: Las Vegas Name of NWS Researcher Preparing Report: Stanley Czyzyk Type of Project (Partners
University: Florida Institute of Technology Name of University Researcher Preparing Report: Sen Chiao NWS Office: Las Vegas Name of NWS Researcher Preparing Report: Stanley Czyzyk Type of Project (Partners
Simulation of low clouds from the CAM and the regional WRF with multiple nested resolutions
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L08813, doi:10.1029/2008gl037088, 2009 Simulation of low clouds from the CAM and the regional WRF with multiple nested resolutions Wuyin
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L08813, doi:10.1029/2008gl037088, 2009 Simulation of low clouds from the CAM and the regional WRF with multiple nested resolutions Wuyin
Developing Continuous SCM/CRM Forcing Using NWP Products Constrained by ARM Observations
 Developing Continuous SCM/CRM Forcing Using NWP Products Constrained by ARM Observations S. C. Xie, R. T. Cederwall, and J. J. Yio Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Livermore, California M. H. Zhang
Developing Continuous SCM/CRM Forcing Using NWP Products Constrained by ARM Observations S. C. Xie, R. T. Cederwall, and J. J. Yio Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Livermore, California M. H. Zhang
Authors and Affiliations Kristopher Bedka 1, Cecilia Wang 1, Ryan Rogers 2, Larry Carey 2, Wayne Feltz 3, and Jan Kanak 4
 1. Title Slide Title: Analysis of the Co-Evolution of Total Lightning, Ground-Based Radar-Derived Fields, and GOES-14 1-Minute Super Rapid Scan Satellite Observations of Deep Convective Cloud Tops Authors
1. Title Slide Title: Analysis of the Co-Evolution of Total Lightning, Ground-Based Radar-Derived Fields, and GOES-14 1-Minute Super Rapid Scan Satellite Observations of Deep Convective Cloud Tops Authors
Weather Radar Basics
 Weather Radar Basics RADAR: Radio Detection And Ranging Developed during World War II as a method to detect the presence of ships and aircraft (the military considered weather targets as noise) Since WW
Weather Radar Basics RADAR: Radio Detection And Ranging Developed during World War II as a method to detect the presence of ships and aircraft (the military considered weather targets as noise) Since WW
Research Objective 4: Develop improved parameterizations of boundary-layer clouds and turbulence for use in MMFs and GCRMs
 Research Objective 4: Develop improved parameterizations of boundary-layer clouds and turbulence for use in MMFs and GCRMs Steve Krueger and Chin-Hoh Moeng CMMAP Site Review 31 May 2007 Scales of Atmospheric
Research Objective 4: Develop improved parameterizations of boundary-layer clouds and turbulence for use in MMFs and GCRMs Steve Krueger and Chin-Hoh Moeng CMMAP Site Review 31 May 2007 Scales of Atmospheric
An A-Train Water Vapor Thematic Climate Data Record Using Cloud Classification
 An A-Train Water Vapor Thematic Climate Data Record Using Cloud Classification Eric J. Fetzer, Qing Yue, Alexandre Guillaume, Van T. Dang, Calvin Liang, Brian H. Kahn, Brian D. Wilson, Bjorn H. Lambrigtsen
An A-Train Water Vapor Thematic Climate Data Record Using Cloud Classification Eric J. Fetzer, Qing Yue, Alexandre Guillaume, Van T. Dang, Calvin Liang, Brian H. Kahn, Brian D. Wilson, Bjorn H. Lambrigtsen
EDUCATION TEACHING EXPERIENCE INSTRUCTOR ADDITIONAL COURSES PREPARED TO TEACH
 Nicholas D. Metz Department of Geoscience, Lansing 101A Hobart and William Smith Colleges 300 Pulteney Street, Geneva, NY 14456 Office Phone: (315) 781-3615 Cell Phone: (716) 228-6006 Email: nmetz@hws.edu
Nicholas D. Metz Department of Geoscience, Lansing 101A Hobart and William Smith Colleges 300 Pulteney Street, Geneva, NY 14456 Office Phone: (315) 781-3615 Cell Phone: (716) 228-6006 Email: nmetz@hws.edu
MINI-SUPERCELL EVENT OF 23 OCTOBER 2004 IN THE MEMPHIS COUNTY WARNING AREA
 MINI-SUPERCELL EVENT OF 23 OCTOBER 2004 IN THE MEMPHIS COUNTY WARNING AREA Jonathan L. Howell* and Jason F. Beaman National Weather Service Forecast Office Memphis, Tennessee August 15, 2006 1. INTRODUCTION
MINI-SUPERCELL EVENT OF 23 OCTOBER 2004 IN THE MEMPHIS COUNTY WARNING AREA Jonathan L. Howell* and Jason F. Beaman National Weather Service Forecast Office Memphis, Tennessee August 15, 2006 1. INTRODUCTION
UTILIZING GOOGLE EARTH AS A GIS PLATFORM FOR WEATHER APPLICATIONS
 UTILIZING GOOGLE EARTH AS A GIS PLATFORM FOR WEATHER APPLICATIONS Travis M. Smith 1,2 and Valliappa Lakshmanan 1,2 1 U. of Oklahoma/CIMMS; 2 NOAA/NSSL 1. Introduction Google Earth (formerly known as Keyhole;
UTILIZING GOOGLE EARTH AS A GIS PLATFORM FOR WEATHER APPLICATIONS Travis M. Smith 1,2 and Valliappa Lakshmanan 1,2 1 U. of Oklahoma/CIMMS; 2 NOAA/NSSL 1. Introduction Google Earth (formerly known as Keyhole;
Exploring Florida: Teaching Resources for Science 1 of 6
 Exploring Florida: Teaching Resources for Science 1 of 6 Tropical Cyclones This document describes tropical cyclones and the dangers they pose to coastal populations. It is intended to help teachers improve
Exploring Florida: Teaching Resources for Science 1 of 6 Tropical Cyclones This document describes tropical cyclones and the dangers they pose to coastal populations. It is intended to help teachers improve
Description of zero-buoyancy entraining plume model
 Influence of entrainment on the thermal stratification in simulations of radiative-convective equilibrium Supplementary information Martin S. Singh & Paul A. O Gorman S1 CRM simulations Here we give more
Influence of entrainment on the thermal stratification in simulations of radiative-convective equilibrium Supplementary information Martin S. Singh & Paul A. O Gorman S1 CRM simulations Here we give more
The ARM-GCSS Intercomparison Study of Single-Column Models and Cloud System Models
 The ARM-GCSS Intercomparison Study of Single-Column Models and Cloud System Models R. T. Cederwall and D. J. Rodriguez Atmospheric Science Division Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Livermore, California
The ARM-GCSS Intercomparison Study of Single-Column Models and Cloud System Models R. T. Cederwall and D. J. Rodriguez Atmospheric Science Division Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Livermore, California
Can latent heat release have a negative effect on polar low intensity?
 Can latent heat release have a negative effect on polar low intensity? Ivan Føre, Jon Egill Kristjansson, Erik W. Kolstad, Thomas J. Bracegirdle and Øyvind Sætra Polar lows: are intense mesoscale cyclones
Can latent heat release have a negative effect on polar low intensity? Ivan Føre, Jon Egill Kristjansson, Erik W. Kolstad, Thomas J. Bracegirdle and Øyvind Sætra Polar lows: are intense mesoscale cyclones
Convective Clouds. Convective clouds 1
 Convective clouds 1 Convective Clouds Introduction Convective clouds are formed in vertical motions that result from the instability of the atmosphere. This instability can be caused by: a. heating at
Convective clouds 1 Convective Clouds Introduction Convective clouds are formed in vertical motions that result from the instability of the atmosphere. This instability can be caused by: a. heating at
P10.145 POTENTIAL APPLICATIONS OF A CONUS SOUNDING CLIMATOLOGY DEVELOPED AT THE STORM PREDICTION CENTER
 P10.145 POTENTIAL APPLICATIONS OF A CONUS SOUNDING CLIMATOLOGY DEVELOPED AT THE STORM PREDICTION CENTER Jaret W. Rogers*, Richard L. Thompson, and Patrick T. Marsh NOAA/NWS Storm Prediction Center Norman,
P10.145 POTENTIAL APPLICATIONS OF A CONUS SOUNDING CLIMATOLOGY DEVELOPED AT THE STORM PREDICTION CENTER Jaret W. Rogers*, Richard L. Thompson, and Patrick T. Marsh NOAA/NWS Storm Prediction Center Norman,
INTRODUCTION STORM CHRONOLOGY AND OBSERVATIONS
 THE MESOCYCLONE EVOLUTION OF THE WARREN, OKLAHOMA TORNADOES By Timothy P. Marshall and Erik N. Rasmussen (Reprinted from the 12th Conference on Severe Local Storms, American Meteorological Society, San
THE MESOCYCLONE EVOLUTION OF THE WARREN, OKLAHOMA TORNADOES By Timothy P. Marshall and Erik N. Rasmussen (Reprinted from the 12th Conference on Severe Local Storms, American Meteorological Society, San
Heavy Rainfall from Hurricane Connie August 1955 By Michael Kozar and Richard Grumm National Weather Service, State College, PA 16803
 Heavy Rainfall from Hurricane Connie August 1955 By Michael Kozar and Richard Grumm National Weather Service, State College, PA 16803 1. Introduction Hurricane Connie became the first hurricane of the
Heavy Rainfall from Hurricane Connie August 1955 By Michael Kozar and Richard Grumm National Weather Service, State College, PA 16803 1. Introduction Hurricane Connie became the first hurricane of the
Cloud detection and clearing for the MOPITT instrument
 Cloud detection and clearing for the MOPITT instrument Juying Warner, John Gille, David P. Edwards and Paul Bailey National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, Colorado ABSTRACT The Measurement Of
Cloud detection and clearing for the MOPITT instrument Juying Warner, John Gille, David P. Edwards and Paul Bailey National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, Colorado ABSTRACT The Measurement Of
OBSERVATIONS FROM THE APRIL 13 2004 WAKE LOW DAMAGING WIND EVENT IN SOUTH FLORIDA. Robert R. Handel and Pablo Santos NOAA/NWS, Miami, Florida ABSTRACT
 OBSERVATIONS FROM THE APRIL 13 2004 WAKE LOW DAMAGING WIND EVENT IN SOUTH FLORIDA Robert R. Handel and Pablo Santos NOAA/NWS, Miami, Florida ABSTRACT On Tuesday, April 13, 2004, a high wind event swept
OBSERVATIONS FROM THE APRIL 13 2004 WAKE LOW DAMAGING WIND EVENT IN SOUTH FLORIDA Robert R. Handel and Pablo Santos NOAA/NWS, Miami, Florida ABSTRACT On Tuesday, April 13, 2004, a high wind event swept
Turbulent mixing in clouds latent heat and cloud microphysics effects
 Turbulent mixing in clouds latent heat and cloud microphysics effects Szymon P. Malinowski1*, Mirosław Andrejczuk2, Wojciech W. Grabowski3, Piotr Korczyk4, Tomasz A. Kowalewski4 and Piotr K. Smolarkiewicz3
Turbulent mixing in clouds latent heat and cloud microphysics effects Szymon P. Malinowski1*, Mirosław Andrejczuk2, Wojciech W. Grabowski3, Piotr Korczyk4, Tomasz A. Kowalewski4 and Piotr K. Smolarkiewicz3
2.8 ENTRAINMENT AND THE FINE STRUCTURE OF THE STRATOCUMULUS TOPPED BOUNDARY LAYERS
 2.8 ENTRAINMENT AND THE FINE STRUCTURE OF THE STRATOCUMULUS TOPPED BOUNDARY LAYERS Q. Wang 1, M. S. Horner 1, S. Wang 2, and J.A. Kalogiros 3 1 Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey, CA 2 Naval Research
2.8 ENTRAINMENT AND THE FINE STRUCTURE OF THE STRATOCUMULUS TOPPED BOUNDARY LAYERS Q. Wang 1, M. S. Horner 1, S. Wang 2, and J.A. Kalogiros 3 1 Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey, CA 2 Naval Research
Since launch in April of 2006, CloudSat has provided
 A Multipurpose Radar Simulation Package: QuickBeam BY J. M. HAYNES, R. T. MARCHAND, Z. LUO, A. BODAS-SALCEDO, AND G. L. STEPHENS Since launch in April of 2006, CloudSat has provided the first near-global
A Multipurpose Radar Simulation Package: QuickBeam BY J. M. HAYNES, R. T. MARCHAND, Z. LUO, A. BODAS-SALCEDO, AND G. L. STEPHENS Since launch in April of 2006, CloudSat has provided the first near-global
Chapter 3: Weather Map. Weather Maps. The Station Model. Weather Map on 7/7/2005 4/29/2011
 Chapter 3: Weather Map Weather Maps Many variables are needed to described weather conditions. Local weathers are affected by weather pattern. We need to see all the numbers describing weathers at many
Chapter 3: Weather Map Weather Maps Many variables are needed to described weather conditions. Local weathers are affected by weather pattern. We need to see all the numbers describing weathers at many
This chapter discusses: 1. Definitions and causes of stable and unstable atmospheric air. 2. Processes that cause instability and cloud development
 Stability & Cloud Development This chapter discusses: 1. Definitions and causes of stable and unstable atmospheric air 2. Processes that cause instability and cloud development Stability & Movement A rock,
Stability & Cloud Development This chapter discusses: 1. Definitions and causes of stable and unstable atmospheric air 2. Processes that cause instability and cloud development Stability & Movement A rock,
Thomas Fiolleau Rémy Roca Frederico Carlos Angelis Nicolas Viltard. www.satmos.meteo.fr
 Comparison of tropical convective systems life cycle characteristics from geostationary and TRMM observations for the West African, Indian and South American regions Thomas Fiolleau Rémy Roca Frederico
Comparison of tropical convective systems life cycle characteristics from geostationary and TRMM observations for the West African, Indian and South American regions Thomas Fiolleau Rémy Roca Frederico
J3.3 AN END-TO-END QUALITY ASSURANCE SYSTEM FOR THE MODERNIZED COOP NETWORK
 J3.3 AN END-TO-END QUALITY ASSURANCE SYSTEM FOR THE MODERNIZED COOP NETWORK Christopher A. Fiebrich*, Renee A. McPherson, Clayton C. Fain, Jenifer R. Henslee, and Phillip D. Hurlbut Oklahoma Climatological
J3.3 AN END-TO-END QUALITY ASSURANCE SYSTEM FOR THE MODERNIZED COOP NETWORK Christopher A. Fiebrich*, Renee A. McPherson, Clayton C. Fain, Jenifer R. Henslee, and Phillip D. Hurlbut Oklahoma Climatological
Wind shear - poses challenges and dangers at the most critical stages of flight
 Wind shear - poses challenges and dangers at the most critical stages of flight Authored and illustrated by Sari Jay June 2009 Introduction Over 40 years ago, in the 1960s, low level wind shear was just
Wind shear - poses challenges and dangers at the most critical stages of flight Authored and illustrated by Sari Jay June 2009 Introduction Over 40 years ago, in the 1960s, low level wind shear was just
OPERATIONAL USE OF TOTAL LIGHTNING INFORMATION FOR WEATHER AND AVIATION AT DALLAS-FORT WORTH
 7.4 OPERATIONAL USE OF TOTAL LIGHTNING INFORMATION FOR WEATHER AND AVIATION AT DALLAS-FORT WORTH Martin J. Murphy*, Ronald L. Holle, and Nicholas W.S. Demetriades Vaisala Inc., Tucson, Arizona 1. INTRODUCTION
7.4 OPERATIONAL USE OF TOTAL LIGHTNING INFORMATION FOR WEATHER AND AVIATION AT DALLAS-FORT WORTH Martin J. Murphy*, Ronald L. Holle, and Nicholas W.S. Demetriades Vaisala Inc., Tucson, Arizona 1. INTRODUCTION
4.2 A VIRTUAL TORNADIC THUNDERSTORM ENABLING STUDENTS TO CONSTRUCT KNOWLEDGE ABOUT STORM DYNAMICS THROUGH DATA COLLECTION AND ANALYSIS
 4.2 A VIRTUAL TORNADIC THUNDERSTORM ENABLING STUDENTS TO CONSTRUCT KNOWLEDGE ABOUT STORM DYNAMICS THROUGH DATA COLLECTION AND ANALYSIS William A. Gallus, Jr*., Cinzia Cervato, Carolina Cruz-Neira, Galen
4.2 A VIRTUAL TORNADIC THUNDERSTORM ENABLING STUDENTS TO CONSTRUCT KNOWLEDGE ABOUT STORM DYNAMICS THROUGH DATA COLLECTION AND ANALYSIS William A. Gallus, Jr*., Cinzia Cervato, Carolina Cruz-Neira, Galen
How to analyze synoptic-scale weather patterns Table of Contents
 How to analyze synoptic-scale weather patterns Table of Contents Before You Begin... 2 1. Identify H and L pressure systems... 3 2. Locate fronts and determine frontal activity... 5 3. Determine surface
How to analyze synoptic-scale weather patterns Table of Contents Before You Begin... 2 1. Identify H and L pressure systems... 3 2. Locate fronts and determine frontal activity... 5 3. Determine surface
1 In this report, "tropical cyclone (TC)" is used as a generic term that includes "low pressure area (LPA)", "tropical depression
 Comparative Study on Organized Convective Cloud Systems detected through Early Stage Dvorak Analysis and Tropical Cyclones in Early Developing Stage in the Western North Pacific and the South China Sea
Comparative Study on Organized Convective Cloud Systems detected through Early Stage Dvorak Analysis and Tropical Cyclones in Early Developing Stage in the Western North Pacific and the South China Sea
Cloud Grid Information Objective Dvorak Analysis (CLOUD) at the RSMC Tokyo - Typhoon Center
 Cloud Grid Information Objective Dvorak Analysis (CLOUD) at the RSMC Tokyo - Typhoon Center Kenji Kishimoto, Masaru Sasaki and Masashi Kunitsugu Forecast Division, Forecast Department Japan Meteorological
Cloud Grid Information Objective Dvorak Analysis (CLOUD) at the RSMC Tokyo - Typhoon Center Kenji Kishimoto, Masaru Sasaki and Masashi Kunitsugu Forecast Division, Forecast Department Japan Meteorological
Numerical Simulation of Cyclone Sidr Using a Cloud-Resolving Model: Characteristics and Formation Process of an Outer Rainband
 MARCH 2012 A K T E R A N D T S U B O K I 789 Numerical Simulation of Cyclone Sidr Using a Cloud-Resolving Model: Characteristics and Formation Process of an Outer Rainband NASREEN AKTER Hydrospheric Atmospheric
MARCH 2012 A K T E R A N D T S U B O K I 789 Numerical Simulation of Cyclone Sidr Using a Cloud-Resolving Model: Characteristics and Formation Process of an Outer Rainband NASREEN AKTER Hydrospheric Atmospheric
SURFACE SOURCE OF ICE PARTICLES IN MOUNTAIN CLOUDS
 SURFACE SOURCE OF ICE PARTICLES IN MOUNTAIN CLOUDS Gabor Vali, Bart Geerts, David Leon and Jefferson R. Snider. Department of Atmospheric Science, University of Wyoming Laramie, WY USA.
SURFACE SOURCE OF ICE PARTICLES IN MOUNTAIN CLOUDS Gabor Vali, Bart Geerts, David Leon and Jefferson R. Snider. Department of Atmospheric Science, University of Wyoming Laramie, WY USA.
TROPICAL CYCLONES. Kerry Emanuel 1. INTRODUCTION. Key Words climate
 Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2003. 31:75 104 doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.31.100901.141259 Copyright c 2003 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved First published online as a Review in Advance on February
Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2003. 31:75 104 doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.31.100901.141259 Copyright c 2003 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved First published online as a Review in Advance on February
6A.2 The testing of NSSL multi-sensor applications and data from prototype platforms in NWS forecast operations
 6A.2 The testing of NSSL multi-sensor applications and data from prototype platforms in NWS forecast operations Kevin A. Scharfenberg* and Travis M. Smith Cooperative Institute for Mesoscale Meteorology
6A.2 The testing of NSSL multi-sensor applications and data from prototype platforms in NWS forecast operations Kevin A. Scharfenberg* and Travis M. Smith Cooperative Institute for Mesoscale Meteorology
P2.4 SIERRA ROTORS: A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF THREE MOUNTAIN WAVE AND ROTOR EVENTS
 P2.4 SIERRA ROTORS: A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF THREE MOUNTAIN WAVE AND ROTOR EVENTS Vanda Grubišić and Brian J. Billings Desert Research Institute, Reno, NV 1. INTRODUCTION The Sierra Rotors Project (SRP)
P2.4 SIERRA ROTORS: A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF THREE MOUNTAIN WAVE AND ROTOR EVENTS Vanda Grubišić and Brian J. Billings Desert Research Institute, Reno, NV 1. INTRODUCTION The Sierra Rotors Project (SRP)
Comparison of the Vertical Velocity used to Calculate the Cloud Droplet Number Concentration in a Cloud-Resolving and a Global Climate Model
 Comparison of the Vertical Velocity used to Calculate the Cloud Droplet Number Concentration in a Cloud-Resolving and a Global Climate Model H. Guo, J. E. Penner, M. Herzog, and X. Liu Department of Atmospheric,
Comparison of the Vertical Velocity used to Calculate the Cloud Droplet Number Concentration in a Cloud-Resolving and a Global Climate Model H. Guo, J. E. Penner, M. Herzog, and X. Liu Department of Atmospheric,
Real-time Ocean Forecasting Needs at NCEP National Weather Service
 Real-time Ocean Forecasting Needs at NCEP National Weather Service D.B. Rao NCEP Environmental Modeling Center December, 2005 HYCOM Annual Meeting, Miami, FL COMMERCE ENVIRONMENT STATE/LOCAL PLANNING HEALTH
Real-time Ocean Forecasting Needs at NCEP National Weather Service D.B. Rao NCEP Environmental Modeling Center December, 2005 HYCOM Annual Meeting, Miami, FL COMMERCE ENVIRONMENT STATE/LOCAL PLANNING HEALTH
History of satellites, and implications for hurricanes monitoring and forecasting
 History of satellites, and implications for hurricanes monitoring and forecasting Pat Fitzpatrick Mississippi State University With assistance from Lisa Fitzpatrick 1 Precursor to U.S. Weather Satellite
History of satellites, and implications for hurricanes monitoring and forecasting Pat Fitzpatrick Mississippi State University With assistance from Lisa Fitzpatrick 1 Precursor to U.S. Weather Satellite
3.4 HURRICANE SEA TO AIR HEAT TRANSFER
 3.4 HURRICANE SEA TO AIR HEAT TRANSFER Louis M. Michaud 1, AVEtec Energy Corporation, 1.0 INTRODUCTION Sea to air heat fluxes calculated using the interfacial heat transfer equation are much lower than
3.4 HURRICANE SEA TO AIR HEAT TRANSFER Louis M. Michaud 1, AVEtec Energy Corporation, 1.0 INTRODUCTION Sea to air heat fluxes calculated using the interfacial heat transfer equation are much lower than
Internal waves and vortices in satellite images
 Internal waves and vortices in satellite images Amelia Carolina Sparavigna Department of Applied Science and Technology Politecnico di Torino, Italy Some recent papers proposed the use of the satellite
Internal waves and vortices in satellite images Amelia Carolina Sparavigna Department of Applied Science and Technology Politecnico di Torino, Italy Some recent papers proposed the use of the satellite
A SEVERE WEATHER CLIMATOLOGY FOR THE WILMINGTON, NC WFO COUNTY WARNING AREA
 A SEVERE WEATHER CLIMATOLOGY FOR THE WILMINGTON, NC WFO COUNTY WARNING AREA Carl R. Morgan National Weather Service Wilmington, NC 1. INTRODUCTION The National Weather Service (NWS) Warning Forecast Office
A SEVERE WEATHER CLIMATOLOGY FOR THE WILMINGTON, NC WFO COUNTY WARNING AREA Carl R. Morgan National Weather Service Wilmington, NC 1. INTRODUCTION The National Weather Service (NWS) Warning Forecast Office
Using Cloud-Resolving Model Simulations of Deep Convection to Inform Cloud Parameterizations in Large-Scale Models
 Using Cloud-Resolving Model Simulations of Deep Convection to Inform Cloud Parameterizations in Large-Scale Models S. A. Klein National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Geophysical Fluid Dynamics
Using Cloud-Resolving Model Simulations of Deep Convection to Inform Cloud Parameterizations in Large-Scale Models S. A. Klein National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Geophysical Fluid Dynamics
Chapter 6: Cloud Development and Forms
 Chapter 6: Cloud Development and Forms (from The Blue Planet ) Why Clouds Form Static Stability Cloud Types Why Clouds Form? Clouds form when air rises and becomes saturated in response to adiabatic cooling.
Chapter 6: Cloud Development and Forms (from The Blue Planet ) Why Clouds Form Static Stability Cloud Types Why Clouds Form? Clouds form when air rises and becomes saturated in response to adiabatic cooling.
Chapter 3: Weather Map. Station Model and Weather Maps Pressure as a Vertical Coordinate Constant Pressure Maps Cross Sections
 Chapter 3: Weather Map Station Model and Weather Maps Pressure as a Vertical Coordinate Constant Pressure Maps Cross Sections Weather Maps Many variables are needed to described dweather conditions. Local
Chapter 3: Weather Map Station Model and Weather Maps Pressure as a Vertical Coordinate Constant Pressure Maps Cross Sections Weather Maps Many variables are needed to described dweather conditions. Local
WV IMAGES. Christo Georgiev. NIMH, Bulgaria. Satellite Image Interpretation and Applications EUMeTrain Online Course, 10 30 June 2011
 WV IMAGES Satellite Image Interpretation and Applications EUMeTrain Online Course, 10 30 June 2011 Christo Georgiev NIMH, Bulgaria INTRODICTION The radiometer SEVIRI of Meteosat Second Generation (MSG)
WV IMAGES Satellite Image Interpretation and Applications EUMeTrain Online Course, 10 30 June 2011 Christo Georgiev NIMH, Bulgaria INTRODICTION The radiometer SEVIRI of Meteosat Second Generation (MSG)
Evaluation of the Effect of Upper-Level Cirrus Clouds on Satellite Retrievals of Low-Level Cloud Droplet Effective Radius
 Evaluation of the Effect of Upper-Level Cirrus Clouds on Satellite Retrievals of Low-Level Cloud Droplet Effective Radius F.-L. Chang and Z. Li Earth System Science Interdisciplinary Center University
Evaluation of the Effect of Upper-Level Cirrus Clouds on Satellite Retrievals of Low-Level Cloud Droplet Effective Radius F.-L. Chang and Z. Li Earth System Science Interdisciplinary Center University
2. G-IV Tail Doppler Radar Experiment
 2. G-IV Tail Doppler Radar Experiment Principal Investigator(s): John Gamache, Peter Dodge, Paul Reasor, Altug Aksoy, and Vijay Tallapragada Primary IFEX Goal: 1 - Collect observations that span the TC
2. G-IV Tail Doppler Radar Experiment Principal Investigator(s): John Gamache, Peter Dodge, Paul Reasor, Altug Aksoy, and Vijay Tallapragada Primary IFEX Goal: 1 - Collect observations that span the TC
