Estimating Cash Flows
|
|
|
- Priscilla McDonald
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Estimating Cash Flows DCF Valuation 1
2 Steps in Cash Flow Estimation Estimate the current earnings of the firm If looking at cash flows to equity, look at earnings after interest expenses - i.e. net income If looking at cash flows to the firm, look at operating earnings after taxes Consider how much the firm invested to create future growth If the investment is not expensed, it will be categorized as capital expenditures. To the extent that depreciation provides a cash flow, it will cover some of these expenditures. Increasing working capital needs are also investments for future growth If looking at cash flows to equity, consider the cash flows from net debt issues (debt issued - debt repaid) 2
3 Measuring Cash Flows 3
4 Measuring Cash Flow to the Firm EBIT ( 1 - tax rate) - (Capital Expenditures - Depreciation) - Change in Working Capital = Cash flow to the firm Where are the tax savings from interest payments in this cash flow? 4
5 From Reported to Actual Earnings 5
6 I. Update Earnings When valuing companies, we often depend upon financial statements for inputs on earnings and assets. Annual reports are often outdated and can be updated by using- Trailing 12-month data, constructed from quarterly earnings reports. Informal and unofficial news reports, if quarterly reports are unavailable. Updating makes the most difference for smaller and more volatile firms, as well as for firms that have undergone significant restructuring. Time saver: To get a trailing 12-month number, all you need is one 10K and one 10Q (example third quarter). Use the Year to date numbers from the 10Q: Trailing 12-month Revenue = Revenues (in last 10K) - Revenues from first 3 quarters of last year + Revenues from first 3 quarters of this year. 6
7 II. Correcting Accounting Earnings Make sure that there are no financial expenses mixed in with operating expenses Financial expense: Any commitment that is tax deductible that you have to meet no matter what your operating results: Failure to meet it leads to loss of control of the business. Example: Operating Leases: While accounting convention treats operating leases as operating expenses, they are really financial expenses and need to be reclassified as such. This has no effect on equity earnings but does change the operating earnings Make sure that there are no capital expenses mixed in with the operating expenses Capital expense: Any expense that is expected to generate benefits over multiple periods. R & D Adjustment: Since R&D is a capital expenditure (rather than an operating expense), the operating income has to be adjusted to reflect its treatment. 7
8 The Magnitude of Operating Leases Market Apparel Stores Furniture Stores Restaurants 8
9 Dealing with Operating Lease Expenses Operating Lease Expenses are treated as operating expenses in computing operating income. In reality, operating lease expenses should be treated as financing expenses, with the following adjustments to earnings and capital: Debt Value of Operating Leases = Present value of Operating Lease Commitments at the pre-tax cost of debt When you convert operating leases into debt, you also create an asset to counter it of exactly the same value. Adjusted Operating Earnings Adjusted Operating Earnings = Operating Earnings + Operating Lease Expenses - Depreciation on Leased Asset As an approximation, this works: Adjusted Operating Earnings = Operating Earnings + Pre-tax cost of Debt * PV of Operating Leases. 9
10 Operating Leases at The Gap in 2003 The Gap has conventional debt of about $ 1.97 billion on its balance sheet and its pre-tax cost of debt is about 6%. Its operating lease payments in the 2003 were $978 million and its commitments for the future are below: YearCommitment (millions) Present Value (at 6%) 1 $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ &7 $ each year $1, Debt Value of leases = $4, (Also value of leased asset) Debt outstanding at The Gap = $1,970 m + $4,397 m = $6,367 m Adjusted Operating Income = Stated OI + OL exp this year - Deprec n = $1,012 m m m /7 = $1,362 million (7 year life for assets) Approximate OI = $1,012 m + $ 4397 m (.06) = $1,276 m 10
11 The Collateral Effects of Treating Operating Leases as Debt 11
12 The Magnitude of R&D Expenses Market Petroleum Computers 12
13 R&D Expenses: Operating or Capital Expenses Accounting standards require us to consider R&D as an operating expense even though it is designed to generate future growth. It is more logical to treat it as capital expenditures. To capitalize R&D, Specify an amortizable life for R&D (2-10 years) Collect past R&D expenses for as long as the amortizable life Sum up the unamortized R&D over the period. (Thus, if the amortizable life is 5 years, the research asset can be obtained by adding up 1/5th of the R&D expense from five years ago, 2/5th of the R&D expense from four years ago...: 13
14 Capitalizing R&D Expenses: SAP in 2004 R & D was assumed to have a 5-year life. Year R&D Expense Unamortized portion Amortization this year Current Value of research asset = 2,914 million Amortization of research asset in 2004 = 903 million Increase in Operating Income = = 117 million 14
15 The Effect of Capitalizing R&D: SAP Conventional Accounting Income Statement EBIT& R&D = R&D = 1020 EBIT = 2025 EBIT (1-t) = 1285 m Balance Sheet Off balance sheet asset. Book value of equity at 3,768 million Euros is understated because biggest asset is off the books. Capital Expenditures Conventional net cap ex of 2 million Euros Cash Flows EBIT (1-t) = Net Cap Ex = 2 FCFF = 1283 Return on capital = 1285/( ) = 29.90% R&D treated as capital expenditure Income Statement EBIT& R&D = Amort: R&D = 903 EBIT = 2142 (Increase of 117 m) EBIT (1-t) = 1359 m Ignored tax benefit = ( )(.3654) = 43 Adjusted EBIT (1-t) = = 1402 m (Increase of 117 million) Net Income will also increase by 117 million Balance Sheet Asset Liability R&D Asset 2914 Book Equity Total Book Equity = = 6782 mil Capital Expenditures Net Cap ex = = 119 mil Cash Flows EBIT (1-t) = Net Cap Ex = 119 FCFF = 1283 m Return on capital = 1402/( ) = 19.93% 15
16 III. One-Time and Non-recurring Charges Assume that you are valuing a firm that is reporting a loss of $ 500 million, due to a one-time charge of $ 1 billion. What is the earnings you would use in your valuation? A loss of $ 500 million A profit of $ 500 million Would your answer be any different if the firm had reported one-time losses like these once every five years? Yes No 16
17 IV. Accounting Malfeasance. Though all firms may be governed by the same accounting standards, the fidelity that they show to these standards can vary. More aggressive firms will show higher earnings than more conservative firms. While you will not be able to catch outright fraud, you should look for warning signals in financial statements and correct for them: Income from unspecified sources - holdings in other businesses that are not revealed or from special purpose entities. Income from asset sales or financial transactions (for a non-financial firm) Sudden changes in standard expense items - a big drop in S,G &A or R&D expenses as a percent of revenues, for instance. Frequent accounting restatements 17
18 V. Dealing with Negative or Abnormally Low Earnings 18
19 What tax rate? The tax rate that you should use in computing the after-tax operating income should be The effective tax rate in the financial statements (taxes paid/taxable income) The tax rate based upon taxes paid and EBIT (taxes paid/ebit) The marginal tax rate for the country in which the company operates The weighted average marginal tax rate across the countries in which the company operates None of the above Any of the above, as long as you compute your after-tax cost of debt using the same tax rate 19
20 The Right Tax Rate to Use The choice really is between the effective and the marginal tax rate. In doing projections, it is far safer to use the marginal tax rate since the effective tax rate is really a reflection of the difference between the accounting and the tax books. By using the marginal tax rate, we tend to understate the after-tax operating income in the earlier years, but the after-tax tax operating income is more accurate in later years If you choose to use the effective tax rate, adjust the tax rate towards the marginal tax rate over time. While an argument can be made for using a weighted average marginal tax rate, it is safest to use the marginal tax rate of the country 20
21 A Tax Rate for a Money Losing Firm Assume that you are trying to estimate the after-tax operating income for a firm with $ 1 billion in net operating losses carried forward. This firm is expected to have operating income of $ 500 million each year for the next 3 years, and the marginal tax rate on income for all firms that make money is 40%. Estimate the after-tax operating income each year for the next 3 years. Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 EBIT Taxes EBIT (1-t) Tax rate 21
22 Net Capital Expenditures Net capital expenditures represent the difference between capital expenditures and depreciation. Depreciation is a cash inflow that pays for some or a lot (or sometimes all of) the capital expenditures. In general, the net capital expenditures will be a function of how fast a firm is growing or expecting to grow. High growth firms will have much higher net capital expenditures than low growth firms. Assumptions about net capital expenditures can therefore never be made independently of assumptions about growth in the future. 22
23 Capital expenditures should include Research and development expenses, once they have been re-categorized as capital expenses. The adjusted net cap ex will be Adjusted Net Capital Expenditures = Net Capital Expenditures + Current year s R&D expenses - Amortization of Research Asset Acquisitions of other firms, since these are like capital expenditures. The adjusted net cap ex will be Adjusted Net Cap Ex = Net Capital Expenditures + Acquisitions of other firms - Amortization of such acquisitions Two caveats: 1. Most firms do not do acquisitions every year. Hence, a normalized measure of acquisitions (looking at an average over time) should be used 2. The best place to find acquisitions is in the statement of cash flows, usually categorized under other investment activities 23
24 Cisco s Acquisitions: 1999 Acquired Method of Acquisition Price Paid GeoTel Pooling $1,344 Fibex Pooling $318 Sentient Pooling $103 American Internent Purchase $58 Summa Four Purchase $129 Clarity Wireless Purchase $153 Selsius Systems Purchase $134 PipeLinks Purchase $118 Amteva Tech Purchase $159 $2,516 24
25 Cisco s Net Capital Expenditures in 1999 Cap Expenditures (from statement of CF) = $ 584 mil - Depreciation (from statement of CF) = $ 486 mil Net Cap Ex (from statement of CF) = $ 98 mil + R & D expense (capitalized) = $ 1,594 mil - Amortization of R&D = $ 485 mil + Acquisitions = $ 2,516 mil Adjusted Net Capital Expenditures = $3,723 mil (Amortization was included in the depreciation number) 25
26 Working Capital Investments In accounting terms, the working capital is the difference between current assets (inventory, cash and accounts receivable) and current liabilities (accounts payables, short term debt and debt due within the next year) A cleaner definition of working capital from a cash flow perspective is the difference between non-cash current assets (inventory and accounts receivable) and non-debt current liabilities (accounts payable) Any investment in this measure of working capital ties up cash. Therefore, any increases (decreases) in working capital will reduce (increase) cash flows in that period. When forecasting future growth, it is important to forecast the effects of such growth on working capital needs, and building these effects into the cash flows. 26
27 Working Capital: General Propositions Changes in non-cash working capital from year to year tend to be volatile. A far better estimate of non-cash working capital needs, looking forward, can be estimated by looking at non-cash working capital as a proportion of revenues Some firms have negative non-cash working capital. Assuming that this will continue into the future will generate positive cash flows for the firm. While this is indeed feasible for a period of time, it is not forever. Thus, it is better that non-cash working capital needs be set to zero, when it is negative. 27
28 Volatile Working Capital? Amazon Cisco Motorola Revenues $ 1,640 $12,154 $30,931 Non-cash WC % of Revenues % -3.32% 8.23% Change from last year $ (309) ($700) ($829) Average: last 3 years % -3.16% 8.91% Average: industry 8.71% -2.71% 7.04% Assumption in Valuation WC as % of Revenue 3.00% 0.00% 8.23% 28
29 Dividends and Cash Flows to Equity In the strictest sense, the only cash flow that an investor will receive from an equity investment in a publicly traded firm is the dividend that will be paid on the stock. Actual dividends, however, are set by the managers of the firm and may be much lower than the potential dividends (that could have been paid out) managers are conservative and try to smooth out dividends managers like to hold on to cash to meet unforeseen future contingencies and investment opportunities When actual dividends are less than potential dividends, using a model that focuses only on dividends will under state the true value of the equity in a firm. 29
30 Measuring Potential Dividends Some analysts assume that the earnings of a firm represent its potential dividends. This cannot be true for several reasons: Earnings are not cash flows, since there are both non-cash revenues and expenses in the earnings calculation Even if earnings were cash flows, a firm that paid its earnings out as dividends would not be investing in new assets and thus could not grow Valuation models, where earnings are discounted back to the present, will over estimate the value of the equity in the firm The potential dividends of a firm are the cash flows left over after the firm has made any investments it needs to make to create future growth and net debt repayments (debt repayments - new debt issues) The common categorization of capital expenditures into discretionary and nondiscretionary loses its basis when there is future growth built into the valuation. 30
31 Estimating Cash Flows: FCFE Cash flows to Equity for a Levered Firm Net Income - (Capital Expenditures - Depreciation) - Changes in non-cash Working Capital - (Principal Repayments - New Debt Issues) = Free Cash flow to Equity I have ignored preferred dividends. If preferred stock exist, preferred dividends will also need to be netted out 31
32 Estimating FCFE when Leverage is Stable Net Income - (1- δ) (Capital Expenditures - Depreciation) - (1- δ) Working Capital Needs = Free Cash flow to Equity δ = Debt/Capital Ratio For this firm, Proceeds from new debt issues = Principal Repayments + δ (Capital Expenditures - Depreciation + Working Capital Needs) In computing FCFE, the book value debt to capital ratio should be used when looking back in time but can be replaced with the market value debt to capital ratio, looking forward. 32
33 Estimating FCFE: Disney Net Income=$ 1533 Million Capital spending = $ 1,746 Million Depreciation per Share = $ 1,134 Million Increase in non-cash working capital = $ 477 Million Debt to Capital Ratio = 23.83% Estimating FCFE (1997): Net Income $1,533 Mil - (Cap. Exp - Depr)*(1-DR) $ [( )( )] Chg. Working Capital*(1-DR) $ [477( )] = Free CF to Equity $ 704 Million Dividends Paid $ 345 Million 33
34 FCFE and Leverage: Is this a free lunch? 34
35 FCFE and Leverage: The Other Shoe Drops 35
36 Leverage, FCFE and Value In a discounted cash flow model, increasing the debt/equity ratio will generally increase the expected free cash flows to equity investors over future time periods and also the cost of equity applied in discounting these cash flows. Which of the following statements relating leverage to value would you subscribe to? Increasing leverage will increase value because the cash flow effects will dominate the discount rate effects Increasing leverage will decrease value because the risk effect will be greater than the cash flow effects Increasing leverage will not affect value because the risk effect will exactly offset the cash flow effect Any of the above, depending upon what company you are looking at and where it is in terms of current leverage 36
II. Estimating Cash Flows
 II. Estimating Cash Flows DCF Valuation Aswath Damodaran 61 Steps in Cash Flow Estimation Estimate the current earnings of the firm If looking at cash flows to equity, look at earnings after interest expenses
II. Estimating Cash Flows DCF Valuation Aswath Damodaran 61 Steps in Cash Flow Estimation Estimate the current earnings of the firm If looking at cash flows to equity, look at earnings after interest expenses
From Reported to Actual Earnings
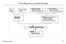 From Reported to Actual Earnings Firmʼs history Comparable Firms Operating leases - Convert into debt - Adjust operating income R&D Expenses - Convert into asset - Adjust operating income Normalize Earnings
From Reported to Actual Earnings Firmʼs history Comparable Firms Operating leases - Convert into debt - Adjust operating income R&D Expenses - Convert into asset - Adjust operating income Normalize Earnings
Net Capital Expenditures
 Net Capital Expenditures Net capital expenditures represent the difference between capital expenditures and depreciation. Depreciation is a cash inflow that pays for some or a lot (or sometimes all of)
Net Capital Expenditures Net capital expenditures represent the difference between capital expenditures and depreciation. Depreciation is a cash inflow that pays for some or a lot (or sometimes all of)
Today s Agenda. DFR1 and Quiz 3 recap. Net Capital Expenditures. Working Capital. Dividends. Estimating Cash Flows
 Today s Agenda DFR1 and Quiz 3 recap Net Capital Expenditures Working Capital Dividends Estimating Cash Flows Net Capital expenditures Net capital expenditures = capital expenditures - depreciation Depreciation
Today s Agenda DFR1 and Quiz 3 recap Net Capital Expenditures Working Capital Dividends Estimating Cash Flows Net Capital expenditures Net capital expenditures = capital expenditures - depreciation Depreciation
Financial Statement Analysis!
 Financial Statement Analysis! The raw data for investing Aswath Damodaran! 1! Questions we would like answered! Assets Liabilities What are the assets in place? How valuable are these assets? How risky
Financial Statement Analysis! The raw data for investing Aswath Damodaran! 1! Questions we would like answered! Assets Liabilities What are the assets in place? How valuable are these assets? How risky
Dealing with Operating Leases in Valuation. Aswath Damodaran. Stern School of Business. 44 West Fourth Street. New York, NY 10012
 Dealing with Operating Leases in Valuation Aswath Damodaran Stern School of Business 44 West Fourth Street New York, NY 10012 [email protected] Abstract Most firm valuation models start with the after-tax
Dealing with Operating Leases in Valuation Aswath Damodaran Stern School of Business 44 West Fourth Street New York, NY 10012 [email protected] Abstract Most firm valuation models start with the after-tax
Lecture 6. Forecasting Cash Flow Statement
 Lecture 6 Forecasting Cash Flow Statement Takeaways from income statement and balance sheet forecasting Elias Rantapuska / Aalto BIZ Finance 2 Note on our discussion today Discussion today: Rather high-level
Lecture 6 Forecasting Cash Flow Statement Takeaways from income statement and balance sheet forecasting Elias Rantapuska / Aalto BIZ Finance 2 Note on our discussion today Discussion today: Rather high-level
Research and Development Expenses: Implications for Profitability Measurement and Valuation. Aswath Damodaran. Stern School of Business
 Research and Development Expenses: Implications for Profitability Measurement and Valuation Aswath Damodaran Stern School of Business 44 West Fourth Street New York, NY 10012 [email protected] Abstract
Research and Development Expenses: Implications for Profitability Measurement and Valuation Aswath Damodaran Stern School of Business 44 West Fourth Street New York, NY 10012 [email protected] Abstract
Discounted Cash Flow Valuation: Basics
 Discounted Cash Flow Valuation: Basics Aswath Damodaran Aswath Damodaran 1 Discounted Cashflow Valuation: Basis for Approach Value = t=n CF t t =1(1+r) t where CF t is the cash flow in period t, r is the
Discounted Cash Flow Valuation: Basics Aswath Damodaran Aswath Damodaran 1 Discounted Cashflow Valuation: Basis for Approach Value = t=n CF t t =1(1+r) t where CF t is the cash flow in period t, r is the
Valuation. Aswath Damodaran Home Page: http://www.stern.nyu.edu/~adamodar Email: [email protected] This presentation is under seminars.
 Valuation Aswath Damodaran Home Page: http://www.stern.nyu.edu/~adamodar Email: [email protected] This presentation is under seminars. Aswath Damodaran 1 Some Initial Thoughts " One hundred thousand
Valuation Aswath Damodaran Home Page: http://www.stern.nyu.edu/~adamodar Email: [email protected] This presentation is under seminars. Aswath Damodaran 1 Some Initial Thoughts " One hundred thousand
I m going to cover 7 key points about FCF here:
 Free Cash Flow Overview When you re valuing a company with a DCF analysis, you need to calculate their Free Cash Flow (FCF) to figure out what they re worth. While Free Cash Flow is simple in theory, in
Free Cash Flow Overview When you re valuing a company with a DCF analysis, you need to calculate their Free Cash Flow (FCF) to figure out what they re worth. While Free Cash Flow is simple in theory, in
TYPES OF FINANCIAL RATIOS
 TYPES OF FINANCIAL RATIOS In the previous articles we discussed how to invest in the stock market and unit trusts. When investing in the stock market an investor should have a clear understanding about
TYPES OF FINANCIAL RATIOS In the previous articles we discussed how to invest in the stock market and unit trusts. When investing in the stock market an investor should have a clear understanding about
Fair Value: Fact or Opinion
 Fair Value: Fact or Opinion Aswath Damodaran Aswath Damodaran 1 Fair value is in the eyes of the beholder Don t measure fair value by precision: As uncertainty about an asset s cash flows increase, the
Fair Value: Fact or Opinion Aswath Damodaran Aswath Damodaran 1 Fair value is in the eyes of the beholder Don t measure fair value by precision: As uncertainty about an asset s cash flows increase, the
CHAPTER 15 FIRM VALUATION: COST OF CAPITAL AND APV APPROACHES
 0 CHAPTER 15 FIRM VALUATION: COST OF CAPITAL AND APV APPROACHES In the last two chapters, we examined two approaches to valuing the equity in the firm -- the dividend discount model and the FCFE valuation
0 CHAPTER 15 FIRM VALUATION: COST OF CAPITAL AND APV APPROACHES In the last two chapters, we examined two approaches to valuing the equity in the firm -- the dividend discount model and the FCFE valuation
Homework Solutions - Lecture 4
 Homework Solutions - Lecture 4 1. Estimate fundamental growth in EBIT for Nike based on the firm s reinvestment rate and ROC in the most recent year. Be sure to incorporate any necessary adjustments made
Homework Solutions - Lecture 4 1. Estimate fundamental growth in EBIT for Nike based on the firm s reinvestment rate and ROC in the most recent year. Be sure to incorporate any necessary adjustments made
Chapter 7. . 1. component of the convertible can be estimated as 1100-796.15 = 303.85.
 Chapter 7 7-1 Income bonds do share some characteristics with preferred stock. The primary difference is that interest paid on income bonds is tax deductible while preferred dividends are not. Income bondholders
Chapter 7 7-1 Income bonds do share some characteristics with preferred stock. The primary difference is that interest paid on income bonds is tax deductible while preferred dividends are not. Income bondholders
CHAPTER 14 COST OF CAPITAL
 CHAPTER 14 COST OF CAPITAL Answers to Concepts Review and Critical Thinking Questions 1. It is the minimum rate of return the firm must earn overall on its existing assets. If it earns more than this,
CHAPTER 14 COST OF CAPITAL Answers to Concepts Review and Critical Thinking Questions 1. It is the minimum rate of return the firm must earn overall on its existing assets. If it earns more than this,
Using Bloomberg to get the Data you need
 Using Bloomberg to get the Data you need 1 Contents of Package 1. Getting information on your company Pages 3-30 2. Getting information on comparable companies Pages 31-34 3. Getting macro economic information
Using Bloomberg to get the Data you need 1 Contents of Package 1. Getting information on your company Pages 3-30 2. Getting information on comparable companies Pages 31-34 3. Getting macro economic information
FSA Note: Summary of Financial Ratio Calculations
 FSA Note: Summary of Financial Ratio Calculations This note contains a summary of the more common financial statement ratios. A few points should be noted: Calculations vary in practice; consistency and
FSA Note: Summary of Financial Ratio Calculations This note contains a summary of the more common financial statement ratios. A few points should be noted: Calculations vary in practice; consistency and
CFAspace. CFA Level II. Provided by APF. Academy of Professional Finance 专 业 金 融 学 院
 CFAspace Provided by APF CFA Level II Equity Investments Free Cash Flow Valuation Part I CFA Lecturer: Hillary Wang Content Free cash flow to the firm, free cash flow to equity Ownership perspective implicit
CFAspace Provided by APF CFA Level II Equity Investments Free Cash Flow Valuation Part I CFA Lecturer: Hillary Wang Content Free cash flow to the firm, free cash flow to equity Ownership perspective implicit
Using the Bloomberg terminal for data
 Using the Bloomberg terminal for data Contents of Package 1.Getting information on your company Pages 2-31 2.Getting information on comparable companies Pages 32-39 3.Getting macro economic information
Using the Bloomberg terminal for data Contents of Package 1.Getting information on your company Pages 2-31 2.Getting information on comparable companies Pages 32-39 3.Getting macro economic information
Value of Equity and Per Share Value when there are options and warrants outstanding. Aswath Damodaran
 Value of Equity and Per Share Value when there are options and warrants outstanding Aswath Damodaran 1 Equity Value and Per Share Value: A Test Assume that you have done an equity valuation of Microsoft.
Value of Equity and Per Share Value when there are options and warrants outstanding Aswath Damodaran 1 Equity Value and Per Share Value: A Test Assume that you have done an equity valuation of Microsoft.
Value Enhancement: EVA and CFROI. Aswath Damodaran 1
 Value Enhancement: EVA and CFROI Aswath Damodaran 1 Alternative Approaches to Value Enhancement Maximize a variable that is correlated with the value of the firm. There are several choices for such a variable.
Value Enhancement: EVA and CFROI Aswath Damodaran 1 Alternative Approaches to Value Enhancement Maximize a variable that is correlated with the value of the firm. There are several choices for such a variable.
EMERSON AND SUBSIDIARIES CONSOLIDATED OPERATING RESULTS (AMOUNTS IN MILLIONS EXCEPT PER SHARE, UNAUDITED)
 CONSOLIDATED OPERATING RESULTS (AMOUNTS IN MILLIONS EXCEPT PER SHARE, UNAUDITED) TABLE 1 Quarter Ended March 31, Percent Change Net Sales $ 5,854 $ 5,919 1% Costs and expenses: Cost of sales 3,548 3,583
CONSOLIDATED OPERATING RESULTS (AMOUNTS IN MILLIONS EXCEPT PER SHARE, UNAUDITED) TABLE 1 Quarter Ended March 31, Percent Change Net Sales $ 5,854 $ 5,919 1% Costs and expenses: Cost of sales 3,548 3,583
How To Calculate Financial Leverage Ratio
 What Do Short-Term Liquidity Ratios Measure? What Is Working Capital? HOCK international - 2004 1 HOCK international - 2004 2 How Is the Current Ratio Calculated? How Is the Quick Ratio Calculated? HOCK
What Do Short-Term Liquidity Ratios Measure? What Is Working Capital? HOCK international - 2004 1 HOCK international - 2004 2 How Is the Current Ratio Calculated? How Is the Quick Ratio Calculated? HOCK
Corporate Finance: Final Exam
 Corporate Finance: Final Exam Answer all questions and show necessary work. Please be brief. This is an open books, open notes exam. For partial credit, when discounting, please show the discount rate
Corporate Finance: Final Exam Answer all questions and show necessary work. Please be brief. This is an open books, open notes exam. For partial credit, when discounting, please show the discount rate
Consolidated Statement of Profit or Loss (in million Euro)
 Consolidated Statement of Profit or Loss (in million Euro) Q3 2013 Q3 2014 % change 9m 2013 9m 2014 % change Revenue 689 636-7.7% 2,126 1,909-10.2% Cost of sales (497) (440) -11.5% (1,520) (1,324) -12.9%
Consolidated Statement of Profit or Loss (in million Euro) Q3 2013 Q3 2014 % change 9m 2013 9m 2014 % change Revenue 689 636-7.7% 2,126 1,909-10.2% Cost of sales (497) (440) -11.5% (1,520) (1,324) -12.9%
Discounted Cash Flow Valuation: The Inputs. Aswath Damodaran
 Discounted Cash Flow Valuation: The Inputs Aswath Damodaran 1 The Key Inputs in DCF Valuation Discount Rate Cost of Equity, in valuing equity Cost of Capital, in valuing the firm Cash Flows Cash Flows
Discounted Cash Flow Valuation: The Inputs Aswath Damodaran 1 The Key Inputs in DCF Valuation Discount Rate Cost of Equity, in valuing equity Cost of Capital, in valuing the firm Cash Flows Cash Flows
VALUATIONS I Financial Metrics, Ratios, & Comparables Analysis. Fall 2015 Comp Week 6
 VALUATIONS I Financial Metrics, Ratios, & Comparables Analysis Fall 2015 Comp Week 6 CODE: COMPS Timeline Date Topic 9/10/15 Introduction to Finance 9/17/15 Qualitative Analysis: SWOT and Porter s Five
VALUATIONS I Financial Metrics, Ratios, & Comparables Analysis Fall 2015 Comp Week 6 CODE: COMPS Timeline Date Topic 9/10/15 Introduction to Finance 9/17/15 Qualitative Analysis: SWOT and Porter s Five
LOS 42.a: Define and interpret free cash flow to the firm (FCFF) and free cash flow to equity (FCFE).
 The following is a review of the Equity Investments principles designed to address the learning outcome statements set forth by CFA Institute. This topic is also covered in: Free Cash Flow Valuation This
The following is a review of the Equity Investments principles designed to address the learning outcome statements set forth by CFA Institute. This topic is also covered in: Free Cash Flow Valuation This
The Adjusted Present Value Approach to Valuing Leveraged Buyouts 1
 Chapter 17 Valuation and Capital Budgeting for the Levered Firm 17A-1 Appendix 17A The Adjusted Present Value Approach to Valuing Leveraged Buyouts 1 Introduction A leveraged buyout (LBO) is the acquisition
Chapter 17 Valuation and Capital Budgeting for the Levered Firm 17A-1 Appendix 17A The Adjusted Present Value Approach to Valuing Leveraged Buyouts 1 Introduction A leveraged buyout (LBO) is the acquisition
The Adjusted Present Value Approach to Valuing Leveraged Buyouts 1 Introduction
 Chapter 18 Valuation and Capital Budgeting for the Levered Firm 18A-1 Appendix 18A The Adjusted Present Value Approach to Valuing Leveraged Buyouts 1 Introduction A leveraged buyout (LBO) is the acquisition
Chapter 18 Valuation and Capital Budgeting for the Levered Firm 18A-1 Appendix 18A The Adjusted Present Value Approach to Valuing Leveraged Buyouts 1 Introduction A leveraged buyout (LBO) is the acquisition
Consolidated Statement of Profit or Loss (in million Euro)
 Consolidated Statement of Profit or Loss (in million Euro) Q3 2014 Q3 2015 % change 9m 2014 9m 2015 % change Revenue 636 661 3.9% 1,909 1,974 3.4% Cost of sales (440) (453) 3.0% (1,324) (1,340) 1.2% Gross
Consolidated Statement of Profit or Loss (in million Euro) Q3 2014 Q3 2015 % change 9m 2014 9m 2015 % change Revenue 636 661 3.9% 1,909 1,974 3.4% Cost of sales (440) (453) 3.0% (1,324) (1,340) 1.2% Gross
Statement of Cash Flow
 Management Accounting 337 Statement of Cash Flow Cash is obviously an important asset to all, both individually and in business. A shortage or lack of cash may mean an inability to purchase needed inventory
Management Accounting 337 Statement of Cash Flow Cash is obviously an important asset to all, both individually and in business. A shortage or lack of cash may mean an inability to purchase needed inventory
Understanding A Firm s Financial Statements
 CHAPTER OUTLINE Spotlight: J&S Construction Company (http://www.jsconstruction.com) 1 The Lemonade Kids Financial statement (accounting statements) reports of a firm s financial performance and resources,
CHAPTER OUTLINE Spotlight: J&S Construction Company (http://www.jsconstruction.com) 1 The Lemonade Kids Financial statement (accounting statements) reports of a firm s financial performance and resources,
1. Operating, Investment and Financial Cash Flows
 1. Operating, Investment and Financial Cash Flows Solutions Problem 1 During 2005, Myears Oil Co. had gross sales of $1 000,000, cost of goods sold of $400,000, and general and selling expenses of $300,000.
1. Operating, Investment and Financial Cash Flows Solutions Problem 1 During 2005, Myears Oil Co. had gross sales of $1 000,000, cost of goods sold of $400,000, and general and selling expenses of $300,000.
FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
 100 Arbor Drive, Suite 108 Christiansburg, VA 24073 Voice: 540-381-9333 FAX: 540-381-8319 www.becpas.com Providing Professional Business Advisory & Consulting Services Douglas L. Johnston, II [email protected]
100 Arbor Drive, Suite 108 Christiansburg, VA 24073 Voice: 540-381-9333 FAX: 540-381-8319 www.becpas.com Providing Professional Business Advisory & Consulting Services Douglas L. Johnston, II [email protected]
Comprehensive exam Feb.11
 Comprehensive exam Feb.11 1 Objectives of the examination Apply the financial management concept to evaluate the company s performance. Relate the results of the analysis to make financial decisions or
Comprehensive exam Feb.11 1 Objectives of the examination Apply the financial management concept to evaluate the company s performance. Relate the results of the analysis to make financial decisions or
Consolidated Statement of Profit or Loss (in million Euro)
 Consolidated Statement of Profit or Loss (in million Euro) Q2 2012 Q2 2013 % H1 2012 H1 2013 % Restated * change Restated * change Revenue 779 732-6.0% 1,513 1,437-5.0% Cost of sales (553) (521) -5.8%
Consolidated Statement of Profit or Loss (in million Euro) Q2 2012 Q2 2013 % H1 2012 H1 2013 % Restated * change Restated * change Revenue 779 732-6.0% 1,513 1,437-5.0% Cost of sales (553) (521) -5.8%
Chapter 13. b. Firm Valuation at different Working Capital Ratios. WC as % of Expected FCFF Cost of Firm Value
 Chapter 13 13-1 a. Net Working Capital equals 91524-50596 = 40928. b. Non-cash working capital equals 40928-19927 + 36240 = $57241. c. Ford's working capital is high because it has a high amount of receivables.
Chapter 13 13-1 a. Net Working Capital equals 91524-50596 = 40928. b. Non-cash working capital equals 40928-19927 + 36240 = $57241. c. Ford's working capital is high because it has a high amount of receivables.
Equity Analysis and Capital Structure. A New Venture s Perspective
 Equity Analysis and Capital Structure A New Venture s Perspective 1 Venture s Capital Structure ASSETS Short- term Assets Cash A/R Inventories Long- term Assets Plant and Equipment Intellectual Property
Equity Analysis and Capital Structure A New Venture s Perspective 1 Venture s Capital Structure ASSETS Short- term Assets Cash A/R Inventories Long- term Assets Plant and Equipment Intellectual Property
CHAPTER 11 Questions and Problems
 1 CHAPTER 11 Questions and Problems (In the problems below, you can use a risk premium of 5.5% and a tax rate of 40% if either is not specified) 1. Stock buybacks really do not return cash to stockholders,
1 CHAPTER 11 Questions and Problems (In the problems below, you can use a risk premium of 5.5% and a tax rate of 40% if either is not specified) 1. Stock buybacks really do not return cash to stockholders,
MBA Financial Management and Markets Exam 1 Spring 2009
 MBA Financial Management and Markets Exam 1 Spring 2009 The following questions are designed to test your knowledge of the fundamental concepts of financial management structure [chapter 1], financial
MBA Financial Management and Markets Exam 1 Spring 2009 The following questions are designed to test your knowledge of the fundamental concepts of financial management structure [chapter 1], financial
Cash Flow Analysis Venture Business Perspective
 Cash Flow Analysis Venture Business Perspective Cash Flow (CF) Analysis What is CF and how is determined? CF Free CF Managing CF Cash Conversion Cyclical CF Break-even Valuing venture businesses based
Cash Flow Analysis Venture Business Perspective Cash Flow (CF) Analysis What is CF and how is determined? CF Free CF Managing CF Cash Conversion Cyclical CF Break-even Valuing venture businesses based
The Adjusted-Present-Value Approach to Valuing Leveraged Buyouts 1)
 IE Aufgabe 4 The Adjusted-Present-Value Approach to Valuing Leveraged Buyouts 1) Introduction A leveraged buyout (LBO) is the acquisition by a small group of equity investors of a public or private company
IE Aufgabe 4 The Adjusted-Present-Value Approach to Valuing Leveraged Buyouts 1) Introduction A leveraged buyout (LBO) is the acquisition by a small group of equity investors of a public or private company
Module 2: Preparing for Capital Venture Financing Financial Forecasting Methods TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Module 2: Preparing for Capital Venture Financing Financial Forecasting Methods Module 2: Preparing for Capital Venture Financing Financial Forecasting Methods 1.0 FINANCIAL FORECASTING METHODS 1.01 Introduction
Module 2: Preparing for Capital Venture Financing Financial Forecasting Methods Module 2: Preparing for Capital Venture Financing Financial Forecasting Methods 1.0 FINANCIAL FORECASTING METHODS 1.01 Introduction
Corporate Credit Analysis. Arnold Ziegel Mountain Mentors Associates
 Corporate Credit Analysis Arnold Ziegel Mountain Mentors Associates I. Introduction The Goals and Nature of Credit Analysis II. Capital Structure and the Suppliers of Capital January, 2008 2008 Arnold
Corporate Credit Analysis Arnold Ziegel Mountain Mentors Associates I. Introduction The Goals and Nature of Credit Analysis II. Capital Structure and the Suppliers of Capital January, 2008 2008 Arnold
CASH FLOW STATEMENT. On the statement, cash flows are segregated based on source:
 CASH FLOW STATEMENT On the statement, cash flows are segregated based on source: Operating activities: involve the cash effects of transactions that enter into the determination of net income. Investing
CASH FLOW STATEMENT On the statement, cash flows are segregated based on source: Operating activities: involve the cash effects of transactions that enter into the determination of net income. Investing
Company Financial Plan
 Financial Modeling Templates http://spreadsheetml.com/finance/companyfinancialplan.shtml Copyright (c) 2009-2014, ConnectCode All Rights Reserved. ConnectCode accepts no responsibility for any adverse
Financial Modeling Templates http://spreadsheetml.com/finance/companyfinancialplan.shtml Copyright (c) 2009-2014, ConnectCode All Rights Reserved. ConnectCode accepts no responsibility for any adverse
Homework Solutions - Lecture 2
 Homework Solutions - Lecture 2 1. The value of the S&P 500 index is 1286.12 and the treasury rate is 3.43%. In a typical year, stock repurchases increase the average payout ratio on S&P 500 stocks to over
Homework Solutions - Lecture 2 1. The value of the S&P 500 index is 1286.12 and the treasury rate is 3.43%. In a typical year, stock repurchases increase the average payout ratio on S&P 500 stocks to over
TIME WARNER CABLE INC. CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEET (Unaudited)
 CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEET June 30, December 31, 2011 2010 (in millions) ASSETS Current assets: Cash and equivalents...$ 3,510 $ 3,047 Receivables, less allowances of $86 million and $74 million as of
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEET June 30, December 31, 2011 2010 (in millions) ASSETS Current assets: Cash and equivalents...$ 3,510 $ 3,047 Receivables, less allowances of $86 million and $74 million as of
617-444-3913 617-274-7130 AKAMAI REPORTS SECOND QUARTER 2015 FINANCIAL RESULTS
 FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE Contacts: Jeff Young Tom Barth Media Relations Investor Relations Akamai Technologies Akamai Technologies 617-444-3913 617-274-7130 [email protected] [email protected] AKAMAI REPORTS
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE Contacts: Jeff Young Tom Barth Media Relations Investor Relations Akamai Technologies Akamai Technologies 617-444-3913 617-274-7130 [email protected] [email protected] AKAMAI REPORTS
Basics of Discounted Cash Flow Valuation. Aswath Damodaran
 Basics of Discounted Cash Flow Valuation Aswath Damodaran 1 Discounted Cashflow Valuation: Basis for Approach t = n CF Value = t t =1(1+ r) t where, n = Life of the asset CF t = Cashflow in period t r
Basics of Discounted Cash Flow Valuation Aswath Damodaran 1 Discounted Cashflow Valuation: Basis for Approach t = n CF Value = t t =1(1+ r) t where, n = Life of the asset CF t = Cashflow in period t r
Credit Analysis 10-1
 Credit Analysis 10-1 10-2 Liquidity and Working Capital Basics Liquidity - Ability to convert assets into cash or to obtain cash to meet short-term obligations. Short-term - Conventionally viewed as a
Credit Analysis 10-1 10-2 Liquidity and Working Capital Basics Liquidity - Ability to convert assets into cash or to obtain cash to meet short-term obligations. Short-term - Conventionally viewed as a
S Corp. vs. C Corp. Valuation (Revised 12-20-02)
 Web: www.businessvaluexpress.com Mike Adhikari Email: [email protected] Adhikari International, Inc. Phone: 847-438-1657 175 Olde Half Day Rd., Suite 100 Fax: 847-438-1835 Lincolnshire IL 60069
Web: www.businessvaluexpress.com Mike Adhikari Email: [email protected] Adhikari International, Inc. Phone: 847-438-1657 175 Olde Half Day Rd., Suite 100 Fax: 847-438-1835 Lincolnshire IL 60069
Working Capital Concept & Animation
 Working Capital Concept & Animation Meaning A measure of both a company's efficiency and its short-term financial health. The working capital is calculated as: Working Capital = Current Assets Current
Working Capital Concept & Animation Meaning A measure of both a company's efficiency and its short-term financial health. The working capital is calculated as: Working Capital = Current Assets Current
SEAGATE TECHNOLOGY PLC CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
 CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS (In millions) June 28, ASSETS Current assets: Cash and cash equivalents $ 2,259 $ 1,708 Short-term investments 47 480 Restricted cash and investments 4 101 Accounts
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS (In millions) June 28, ASSETS Current assets: Cash and cash equivalents $ 2,259 $ 1,708 Short-term investments 47 480 Restricted cash and investments 4 101 Accounts
Liquidity analysis: Length of cash cycle
 2. Liquidity analysis: Length of cash cycle Operating cycle of a merchandising firm: number of days it takes to sell inventory + number of days until the resulting receivables are converted to cash Acquisition
2. Liquidity analysis: Length of cash cycle Operating cycle of a merchandising firm: number of days it takes to sell inventory + number of days until the resulting receivables are converted to cash Acquisition
Glossary and Formulas
 A-B Accounts Payable Includes, but is not limited to, Trade Accounts Payable and Trade Acceptances, that is, amounts owed to vendors for goods and services purchased from outside suppliers and due within
A-B Accounts Payable Includes, but is not limited to, Trade Accounts Payable and Trade Acceptances, that is, amounts owed to vendors for goods and services purchased from outside suppliers and due within
Analyzing the Statement of Cash Flows
 Analyzing the Statement of Cash Flows Operating Activities NACM Upstate New York Credit Conference 2015 By Ron Sereika, CCE,CEW NACM 1 Objectives of this Educational Session u Show how the statement of
Analyzing the Statement of Cash Flows Operating Activities NACM Upstate New York Credit Conference 2015 By Ron Sereika, CCE,CEW NACM 1 Objectives of this Educational Session u Show how the statement of
Return on Equity has three ratio components. The three ratios that make up Return on Equity are:
 Evaluating Financial Performance Chapter 1 Return on Equity Why Use Ratios? It has been said that you must measure what you expect to manage and accomplish. Without measurement, you have no reference to
Evaluating Financial Performance Chapter 1 Return on Equity Why Use Ratios? It has been said that you must measure what you expect to manage and accomplish. Without measurement, you have no reference to
HEALTHCARE FINANCE: AN INTRODUCTION TO ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT. Online Appendix A Financial Ratios
 HEALTHCARE FINANCE: AN INTRODUCTION TO ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT Online Appendix A Financial Ratios INTRODUCTION In Chapter 17, we indicated that ratio analysis is a technique commonly used to
HEALTHCARE FINANCE: AN INTRODUCTION TO ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT Online Appendix A Financial Ratios INTRODUCTION In Chapter 17, we indicated that ratio analysis is a technique commonly used to
Financial Formulas. 5/2000 Chapter 3 Financial Formulas i
 Financial Formulas 3 Financial Formulas i In this chapter 1 Formulas Used in Financial Calculations 1 Statements of Changes in Financial Position (Total $) 1 Cash Flow ($ millions) 1 Statements of Changes
Financial Formulas 3 Financial Formulas i In this chapter 1 Formulas Used in Financial Calculations 1 Statements of Changes in Financial Position (Total $) 1 Cash Flow ($ millions) 1 Statements of Changes
Understanding Financial Management: A Practical Guide Guideline Answers to the Concept Check Questions
 Understanding Financial Management: A Practical Guide Guideline Answers to the Concept Check Questions Chapter 3 Interpreting Financial Ratios Concept Check 3.1 1. What are the different motivations that
Understanding Financial Management: A Practical Guide Guideline Answers to the Concept Check Questions Chapter 3 Interpreting Financial Ratios Concept Check 3.1 1. What are the different motivations that
Learning Objectives: Quick answer key: Question # Multiple Choice True/False. 14.1 Describe the important of accounting and financial information.
 0 Learning Objectives: 14.1 Describe the important of accounting and financial information. 14.2 Differentiate between managerial and financial accounting. 14.3 Identify the six steps of the accounting
0 Learning Objectives: 14.1 Describe the important of accounting and financial information. 14.2 Differentiate between managerial and financial accounting. 14.3 Identify the six steps of the accounting
1 (a) Calculation of net present value (NPV) Year 1 2 3 4 5 6 $000 $000 $000 $000 $000 $000 Sales revenue 1,600 1,600 1,600 1,600 1,600
 Answers Fundamentals Level Skills Module, Paper F9 Financial Management December 2011 Answers 1 (a) Calculation of net present value (NPV) Year 1 2 3 4 5 6 $000 $000 $000 $000 $000 $000 Sales revenue 1,600
Answers Fundamentals Level Skills Module, Paper F9 Financial Management December 2011 Answers 1 (a) Calculation of net present value (NPV) Year 1 2 3 4 5 6 $000 $000 $000 $000 $000 $000 Sales revenue 1,600
Employee Options, Restricted Stock and Value. Aswath Damodaran 1
 Employee Options, Restricted Stock and Value 1 Basic Proposition on Options Any options issued by a firm, whether to management or employees or to investors (convertibles and warrants) create claims on
Employee Options, Restricted Stock and Value 1 Basic Proposition on Options Any options issued by a firm, whether to management or employees or to investors (convertibles and warrants) create claims on
Corporate Credit Analysis. Arnold Ziegel Mountain Mentors Associates. Lesson 5 - Fundamentals of Credit and Credit Analysis (Part3)
 Corporate Credit Analysis Arnold Ziegel Mountain Mentors Associates Lesson 5 - Fundamentals of Credit and Credit Analysis (Part3) Debt Capacity, Cash Flow Forecasting, and the Lending Decision I. Debt
Corporate Credit Analysis Arnold Ziegel Mountain Mentors Associates Lesson 5 - Fundamentals of Credit and Credit Analysis (Part3) Debt Capacity, Cash Flow Forecasting, and the Lending Decision I. Debt
CHAPTER 12 RISK, COST OF CAPITAL, AND CAPITAL BUDGETING
 CHAPTER 12 RISK, COST OF CAPITAL, AND CAPITAL BUDGETING Answers to Concepts Review and Critical Thinking Questions 1. No. The cost of capital depends on the risk of the project, not the source of the money.
CHAPTER 12 RISK, COST OF CAPITAL, AND CAPITAL BUDGETING Answers to Concepts Review and Critical Thinking Questions 1. No. The cost of capital depends on the risk of the project, not the source of the money.
JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. UNAUDITED SUMMARY OF OPERATIONS FOR THE FIRST QUARTER ENDED JULY 31, 2011 AND 2010 (in thousands, except per share amounts)
 UNAUDITED SUMMARY OF OPERATIONS FOR THE FIRST QUARTER ENDED JULY 31, 2011 AND 2010 (in thousands, except per share amounts) US GAAP First Quarter Ended Revenue $ 430,069 407,938 5% Costs and Expenses Cost
UNAUDITED SUMMARY OF OPERATIONS FOR THE FIRST QUARTER ENDED JULY 31, 2011 AND 2010 (in thousands, except per share amounts) US GAAP First Quarter Ended Revenue $ 430,069 407,938 5% Costs and Expenses Cost
TIP If you do not understand something,
 Valuing common stocks Application of the DCF approach TIP If you do not understand something, ask me! The plan of the lecture Review what we have accomplished in the last lecture Some terms about stocks
Valuing common stocks Application of the DCF approach TIP If you do not understand something, ask me! The plan of the lecture Review what we have accomplished in the last lecture Some terms about stocks
FUNDAMENTALS OF HEALTHCARE FINANCE. Online Appendix B Financial Analysis Ratios
 3/27/09 FUNDAMENTALS OF HEALTHCARE FINANCE Online Appendix B Financial Analysis Ratios Introduction In Chapter 13 of Fundamentals of Healthcare Finance, we indicated that financial ratio analysis is a
3/27/09 FUNDAMENTALS OF HEALTHCARE FINANCE Online Appendix B Financial Analysis Ratios Introduction In Chapter 13 of Fundamentals of Healthcare Finance, we indicated that financial ratio analysis is a
Types of Debt & Debt Lingo Quick Reference. http://breakingintowallstreet.com. Here s the 10-second version of everything you need to know about debt:
 Here s the 10-second version of everything you need to know about debt: Debt Type Revolver Term Loan A Term Loan B Senior Notes Subordinated Notes Mezzanine Interest Rate: Lowest Low Higher Higher Higher
Here s the 10-second version of everything you need to know about debt: Debt Type Revolver Term Loan A Term Loan B Senior Notes Subordinated Notes Mezzanine Interest Rate: Lowest Low Higher Higher Higher
Finance Master. Winter 2015/16. Jprof. Narly Dwarkasing University of Bonn, IFS
 Finance Master Winter 2015/16 Jprof. Narly Dwarkasing University of Bonn, IFS Chapter 2 Outline 2.1 Firms Disclosure of Financial Information 2.2 The Balance Sheet 2.3 The Income Statement 2.4 The Statement
Finance Master Winter 2015/16 Jprof. Narly Dwarkasing University of Bonn, IFS Chapter 2 Outline 2.1 Firms Disclosure of Financial Information 2.2 The Balance Sheet 2.3 The Income Statement 2.4 The Statement
Company Share Price Valuation using Free Cash Flow To Equity
 Financial Modeling Templates Company Share Price Valuation using Free Cash Flow To Equity http://spreadsheetml.com/finance/valuation_freecashflowtoequity.shtml Copyright (c) 2009-2014, ConnectCode All
Financial Modeling Templates Company Share Price Valuation using Free Cash Flow To Equity http://spreadsheetml.com/finance/valuation_freecashflowtoequity.shtml Copyright (c) 2009-2014, ConnectCode All
Do s & Don ts of Cash Flow/Balance Sheet Forecasting
 Do s & Don ts of Cash Flow/Balance Sheet Forecasting ASA s 23 rd Advanced Business Valuation Conference San Antonio, TX - October 7, 2004 Scott A. Nammacher, ASA, CFA Managing Director Empire Valuation
Do s & Don ts of Cash Flow/Balance Sheet Forecasting ASA s 23 rd Advanced Business Valuation Conference San Antonio, TX - October 7, 2004 Scott A. Nammacher, ASA, CFA Managing Director Empire Valuation
CHAPTER 14 MARK TO MARKET: FINANCIAL SERVICE COMPANIES
 1 CHAPTER 14 MARK TO MARKET: FINANCIAL SERVICE COMPANIES Banks, insurance companies and other financial service firms pose special challenges for an analyst attempting to value them, for three reasons.
1 CHAPTER 14 MARK TO MARKET: FINANCIAL SERVICE COMPANIES Banks, insurance companies and other financial service firms pose special challenges for an analyst attempting to value them, for three reasons.
Valuation approaches to Mergers & Acquisitions
 Valuation approaches to Mergers & Acquisitions Sagar Gokani, Chief Manager M&A & IR, Piramal Healthcare Limited 7 th July 2012 Contents Approaches to Valuation Discounted Cash Flow Relative Valuation Valuing
Valuation approaches to Mergers & Acquisitions Sagar Gokani, Chief Manager M&A & IR, Piramal Healthcare Limited 7 th July 2012 Contents Approaches to Valuation Discounted Cash Flow Relative Valuation Valuing
Acquisition Valuation
 Acquisition Valuation Aswath Damodaran Aswath Damodaran 1 Issues in Acquisition Valuation Acquisition valuations are complex, because the valuation often involved issues like synergy and control, which
Acquisition Valuation Aswath Damodaran Aswath Damodaran 1 Issues in Acquisition Valuation Acquisition valuations are complex, because the valuation often involved issues like synergy and control, which
Problem 1 Problem 2 Problem 3
 Problem 1 (1) Book Value Debt/Equity Ratio = 2500/2500 = 100% Market Value of Equity = 50 million * $ 80 = $4,000 Market Value of Debt =.80 * 2500 = $2,000 Debt/Equity Ratio in market value terms = 2000/4000
Problem 1 (1) Book Value Debt/Equity Ratio = 2500/2500 = 100% Market Value of Equity = 50 million * $ 80 = $4,000 Market Value of Debt =.80 * 2500 = $2,000 Debt/Equity Ratio in market value terms = 2000/4000
For a balance sheet item, an asset increase is a Debit a liability increase is a Credit
 1 CASH FLOW ANALYSIS 1.1 Introduction For a further discussion on cash flow, please refer to the guide to financial statements in the Learning Centre. The key to cashflow analysis is recognition of cashflow,
1 CASH FLOW ANALYSIS 1.1 Introduction For a further discussion on cash flow, please refer to the guide to financial statements in the Learning Centre. The key to cashflow analysis is recognition of cashflow,
Performance Food Group Company Reports First-Quarter Fiscal 2016 Earnings
 NEWS RELEASE For Immediate Release November 4, 2015 Investors: Michael D. Neese VP, Investor Relations (804) 287-8126 [email protected] Media: Joe Vagi Manager, Corporate Communications (804) 484-7737
NEWS RELEASE For Immediate Release November 4, 2015 Investors: Michael D. Neese VP, Investor Relations (804) 287-8126 [email protected] Media: Joe Vagi Manager, Corporate Communications (804) 484-7737
Cost of Capital and Project Valuation
 Cost of Capital and Project Valuation 1 Background Firm organization There are four types: sole proprietorships partnerships limited liability companies corporations Each organizational form has different
Cost of Capital and Project Valuation 1 Background Firm organization There are four types: sole proprietorships partnerships limited liability companies corporations Each organizational form has different
STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS AND WORKING CAPITAL ANALYSIS
 C H A P T E R 1 0 STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS AND WORKING CAPITAL ANALYSIS I N T R O D U C T I O N Historically, profit-oriented businesses have used the accrual basis of accounting in which the income statement,
C H A P T E R 1 0 STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS AND WORKING CAPITAL ANALYSIS I N T R O D U C T I O N Historically, profit-oriented businesses have used the accrual basis of accounting in which the income statement,
Moody s Approach to Global Standard Adjustments in the Analysis of Financial Statements for Non-Financial Corporations Part I
 Rating Methodology February 2006 Contact Phone REGIONAL OFFICES North America Pamela Stumpp 1.212.553.1311 Europe / Middle East / Africa Eric de Bodard 331.5330.1040 Asia Pacific Clara Lau 852.2916.1133
Rating Methodology February 2006 Contact Phone REGIONAL OFFICES North America Pamela Stumpp 1.212.553.1311 Europe / Middle East / Africa Eric de Bodard 331.5330.1040 Asia Pacific Clara Lau 852.2916.1133
WESTERN DIGITAL CORPORATION CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS. (in millions; unaudited) ASSETS
 CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS (in millions; unaudited) ASSETS Apr. 1, July 3, 2016 2015 Current assets: Cash and cash equivalents $ 5,887 $ 5,024 Short-term investments 146 262 Accounts receivable,
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS (in millions; unaudited) ASSETS Apr. 1, July 3, 2016 2015 Current assets: Cash and cash equivalents $ 5,887 $ 5,024 Short-term investments 146 262 Accounts receivable,
APPENDIX 1 The Statement of Financial Position
 APPENDIX 1 The Statement of Financial Position 1. Assets: the resources of the organization which are used to provide service and generate value 2. Current assets: assets which can be converted to cash
APPENDIX 1 The Statement of Financial Position 1. Assets: the resources of the organization which are used to provide service and generate value 2. Current assets: assets which can be converted to cash
Non-GAAP Financial Measures. Second Quarter and First Half of Fiscal 2014. siemens.com. Energy efficiency. Intelligent infrastructure solutions
 Energy efficiency Next-generation healthcare Industrial productivity Intelligent infrastructure solutions Non-GAAP Financial Measures Second Quarter and First Half of Fiscal 2014 siemens.com second QUARTER
Energy efficiency Next-generation healthcare Industrial productivity Intelligent infrastructure solutions Non-GAAP Financial Measures Second Quarter and First Half of Fiscal 2014 siemens.com second QUARTER
Financial Statement and Cash Flow Analysis
 Chapter 2 Financial Statement and Cash Flow Analysis Answers to Concept Review Questions 1. What role do the FASB and SEC play with regard to GAAP? The FASB is a nongovernmental, professional standards
Chapter 2 Financial Statement and Cash Flow Analysis Answers to Concept Review Questions 1. What role do the FASB and SEC play with regard to GAAP? The FASB is a nongovernmental, professional standards
NOTICE: For details of the project history please look under the Work Plan section of this website.
 NOTICE: This Exposure Draft is available to show the historic evolution of the project. It does not include changes made by the Board following the consultation process and therefore should not be relied
NOTICE: This Exposure Draft is available to show the historic evolution of the project. It does not include changes made by the Board following the consultation process and therefore should not be relied
CHAPTER 15 Capital Structure: Basic Concepts
 Multiple Choice Questions: CHAPTER 15 Capital Structure: Basic Concepts I. DEFINITIONS HOMEMADE LEVERAGE a 1. The use of personal borrowing to change the overall amount of financial leverage to which an
Multiple Choice Questions: CHAPTER 15 Capital Structure: Basic Concepts I. DEFINITIONS HOMEMADE LEVERAGE a 1. The use of personal borrowing to change the overall amount of financial leverage to which an
In this chapter, we build on the basic knowledge of how businesses
 03-Seidman.qxd 5/15/04 11:52 AM Page 41 3 An Introduction to Business Financial Statements In this chapter, we build on the basic knowledge of how businesses are financed by looking at how firms organize
03-Seidman.qxd 5/15/04 11:52 AM Page 41 3 An Introduction to Business Financial Statements In this chapter, we build on the basic knowledge of how businesses are financed by looking at how firms organize
Chapter 15: Debt Policy
 FIN 302 Class Notes Chapter 15: Debt Policy Two Cases: Case one: NO TAX All Equity Half Debt Number of shares 100,000 50,000 Price per share $10 $10 Equity Value $1,000,000 $500,000 Debt Value $0 $500,000
FIN 302 Class Notes Chapter 15: Debt Policy Two Cases: Case one: NO TAX All Equity Half Debt Number of shares 100,000 50,000 Price per share $10 $10 Equity Value $1,000,000 $500,000 Debt Value $0 $500,000
Valuing Financial Service Firms
 1 Valuing Financial Service Firms Aswath Damodaran April 2009 Valuing banks, insurance companies and investment banks has always been difficult, but the market crisis of 2008 has elevated the concern to
1 Valuing Financial Service Firms Aswath Damodaran April 2009 Valuing banks, insurance companies and investment banks has always been difficult, but the market crisis of 2008 has elevated the concern to
EXERCISES. The cash from operating activities detail is provided as follows for class discussion:
 EXERCISES Ex. 14 1 There were net additions, such as depreciation and amortization of intangible assets of $389 million, to the net loss reported on the income statement to convert the net loss from the
EXERCISES Ex. 14 1 There were net additions, such as depreciation and amortization of intangible assets of $389 million, to the net loss reported on the income statement to convert the net loss from the
Measuring Investment Returns
 Measuring Investment Returns Aswath Damodaran Stern School of Business Aswath Damodaran 156 First Principles Invest in projects that yield a return greater than the minimum acceptable hurdle rate. The
Measuring Investment Returns Aswath Damodaran Stern School of Business Aswath Damodaran 156 First Principles Invest in projects that yield a return greater than the minimum acceptable hurdle rate. The
A Simple Model. Cash Flow Statement
 An introduction to the cash flow statement in the context of building a financial model. This series introduces the financial statements in the context of a financial model. Cash Flow Statement NOTES TO
An introduction to the cash flow statement in the context of building a financial model. This series introduces the financial statements in the context of a financial model. Cash Flow Statement NOTES TO
