How To Treat Osteoporosis
|
|
|
- Audra Hamilton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Treatment Guidelines for Osteoporosis in Adults. Background Osteoporosis is a condition characterised by a reduction in bone mass density increasing the risk of fracture. Fractures occur most commonly in the hip, spine and wrist. Vertebral fractures due to osteoporosis can cause loss of height, curvature of the spine and chronic back pain. One in three women and one in twelve men over 50 are affected by osteoporosis and almost half of all women experience an osteoporotic fracture by the time they reach the age of In October 2008 NICE produced TA 160 and TA161 for the primary and secondary prevention of osteoporotic fractures. This guidance is restricted to postmenopausal women with osteoporosis as defined by a bone mineral density T-score of -2.5, and does not include men with osteoporosis or individuals treated with glucocorticoids. In addition, NICE guidance for second line options demands different combinations of bone density and risk factors for different treatments which is complicated to operate in a primary care setting. Several recently introduced interventions, including ibandronic acid, zoledronic acid and more recently denosumab (separate NICE TA204) are not included in the guidance. The National Osteoporosis Guideline Group (NOGG) was launched in October 2008 to address these deficits. It is endorsed by many scientific and professional organizations including the National Osteoporosis Society and the Royal College of Physicians. Areas of agreement between NICE and NOGG include recommendations to treat elderly postmenopausal women with a fragility fracture and the use of generic alendronate as a first line option. There is also agreement that bone mineral density measurements may be useful in reaching treatment decisions in younger postmenopausal women with a fragility fracture. However, whereas NICE requires a T-score -2.5 in most women for either primary or secondary prevention, NOGG recognises the added contribution of independent clinical risk factors to fracture prediction and recommends the use of the WHO-supported fracture risk algorithm FRAX. Many cost-effectiveness studies of bone-sparing therapy use the Fracture Risk Assessment tool FRAX to identify fracture risk thresholds where drugs become cost effective. The recent short NCGC Clinical Guideline 146 (August 2012), Osteoporosis: assessing the risk of fragility fracture, aims to provide guidance on the selection and use of such risk assessment tools in the care of people who may be at risk of fragility fractures. It suggests all women over 65yrs are assessed and all men over 75yrs and concurs with the algorithm on the following page suggesting patients over the age of 50yrs should be assessed for risk in the presence of certain risk factors. FRAX combines the major risk factors of age, fracture history and BMD with parental hip fracture, rheumatoid arthritis, alcohol, smoking and chronic disease history to calculate 10-year absolute risk of major osteoporotic fracture and hip fracture. This absolute risk is deemed more appropriate than relying on single risk factors. In order to provide comprehensive and practical guidance for the management of osteoporosis in primary care setting, the following guidelines suggest a combination of NICE and NOGG that retains the main principles of NICE guidance but incorporates the greater workability of NOGG. It also incorporates NOGG guidance for men with osteoporosis, individuals treated with glucocorticoids, and the use of more recently introduced interventions. For the purpose of these guidelines, in line with NICE, intolerance of alendronate or risedronate is defined as persistent upper gastrointestinal disturbance that is sufficiently severe to warrant discontinuation of treatment, and that occurs even though the instructions for administration have been followed correctly. An unsatisfactory response following treatment for secondary prevention of osteoporosis ie after a fragility fracture is defined as occurring when a woman has another fragility fracture despite adhering fully to treatment for 1 year and there is evidence of a decline in BMD below her pre-treatment baseline. 1 National Service Framework for Older People, Department of Health,
2 Treatment Guidelines for Osteoporosis in Adults Fragility fracture No Fragility fracture Primary care Postmenopausal women >75yrs Postmenopausal women < 75yrs or men > 50yrs Osteoporosis treatment Falls assessment Lifestyle advice Calcium and Vitamin D supplement (Adcal D3 / Accrete D3 preferred products) Treatment options: Post menopausal women: Alendronic acid 70mg weekly or Risedronate 35mg weekly or Ibandronic acid 150mg monthly (note more expensive therefore reserved for patients who experience problems taking oral bisphosphonates: alendronic acid 0.90/month / risderonate 1.16 /month, ibandoronic acid 3.02/month based on prices in Feb 2014 Drug Tariff) If intolerant to initial chosen bisphosphonate trial of another listed bisphosphonate would be the next appropriate treatment of option or bisphosphonate contraindicated / intolerant to two bisphosphonates consider denosumab 60mg SC (see prescribing information sheet) Based on NICE TA160 Osteoporosis - Primary Prevention and TA Note: In line with the EMA guidance April 2014 strontium has been restricted to patients with severe osteoporosis who cannot be treated with other medicines approved for ostreoporosis (see page 5) For men and prevention/treatment of corticosteroid induced osteoporosis refer to table for summary of licensed indications Postmenopausal women OR men > 50 yrs with > 1 clinical risk factor Independent risk factors: Alcohol > 4units a day Rheumatoid arthritis Parental history of hip fracture Indicators of low bone mineral density(bmd) Low BMI < 22kg/m 2 Taking an oral glucocorticosteroid for 3mths Ankylosing spondylitis Crohn s disease Conditions resulting in prolonged immobility Untreated premature menopause Calculate 10 yr probability of fracture Using FRAX tool FRAX tool Lifestyle Advice Adequate nutrition with calcium and Vitamin D Regular weight bearing exercise Avoid smoking and excess alcohol High risk High risk Intermediate risk DEXA & Recalculate FRAX Low risk Low risk Secondary care Refer For: Patients unable to tolerate/ respond to oral bisphosphonate and / or denosumab treatment. Osteoporosis with complex medical problems Fragility fractures due to other bone disease Secondary care treatment options: The following are red drugs on the traffic light system refer to PAD Medication Dose Zoledronic acid Teriparatide Strontium 5mg annual IV infusion 20mcg daily by subcutaneous injection (max. duration 18 months, not to be repeated) 2g once daily in water 2
3 Additional local guidance: Table Summarising NHS Surrey treatment options for osteoporosis 2 Drugs Indication / dose Contra-indications Side-effects Counselling Alendronic acid tablets 10mg Alendronic acid 70mg once weekly Treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis 10mg daily or 70mg once weekly. Treatment of osteoporosis in men 10mg daily Prevention and treatment of corticosteroid- induced osteoporosis in postmenopausal women not receiving hormone replacement therapy 10mg daily Abnormalities of oesophagus, factors which delay gastric emptying hypocalcaemia. Avoid if egfr less than 35ml/minute/1.73m² Abdominal pain, dyspepsia, constipation, diarrhoea, flatulence, oesophageal ulcer, melaena, dysphagia, abdominal distension, acid regurgitation, musculoskeletal pain, headache Take on an empty stomach at least 30 minutes before breakfast or other medicines. Swallow whole with plenty of water while sitting or standing and remain upright for at least 30min after taking. Note: Alendronic Acid Oral Solution 70mg/100ml is also available - the information above applying to the solid oral dosage form also applies to the liquid formulation. Risedronate As for alendronic acid sodium tablets 5mg tablets Risedronate sodium 35mg once weekly tablets Ibandronic acid 150mg tablets once a month Zolendronic acid intravenous infusion 5mg once a year Treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis to reduce risk of vertebral or hip fractures 5mg daily or 35mg weekly Prevention of osteoporosis (including corticosteroid induced osteoporosis) in postmenopausal women 5mg daily Treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women at increased risk of fracture Treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis and osteoporosis in men (including corticosteroidinduced osteoporosis) Avoid if egfr less than 30ml/minute/1.73m² As for risedronate Hypersensitivity to the active substance, to any bisphosphonates or to any of the excipients Patients with hypocalcaemia Severe renal impairment with creatinine clearance < 35 ml/min Pregnancy and breast-feeding Constipation, dyspepsia, nausea, abdominal pain, diarrhoea, headache, musculoskeletal pain Hypocalcaemia, hypophosphataemia influenza like symptoms, bone paid, diarrhoea, nausea, vomiting, gastritis, abdominal pain, dyspepsia, headache, rash, hypersensitivity reactions, urticarial, very rarely osteonecrosis of the jaw Hypophosphataemia, anaemia, myalgia, arthralgia, GI disturbances, AF, headache, dizziness, renal impairment, Rarely osteonecrosis of the jaw Swallow whole with full glass of water on rising. Take on an empty stomach at least 30mins before first food or drink of the day. Stand or sit upright for at least 30mins.Do not take tablets at bedtime or before rising. Swallow whole with full glass of water on rising. Take on an empty stomach at least 30mins before first food or drink of the day. Stand or sit upright for at least 30mins.Do not take tablets at bedtime or before rising. Single infusion once a year administered over at least 15 minutes 2 For further detailed information please refer to BNF(latest edition) and 3
4 Denosumab 60mg SC pre filled syringe every 6 months Strontium 2g sachet Denosumab for the treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women at increased risk of fractures Treatment of severe osteoporosis in postmenopausal women / adult men at high risk of fracture, for whom treatment with other medicinal products approved for the treatment of osteoporosis is not possible due to, for example, contraindications or intolerance. Prescribers are advised to: Assess patients risk of developing CVD before starting treatment Monitor patients CVD risk on a regular basis, generally every 6-12months Stop treatment if the patient develops IHD, PAD, CVD or if hypertension is uncontrolled The decision to prescribe strontium ranelate should be based on an assessment of the individual patient's overall risks Treatment should only be initiated by a physician with experience in the treatment of osteoporosis Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients Hypocalcaemia must be corrected by adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D before initiating therapy. No dose adjustment is required in patients with renal Impairment, however, if patient creatinine clearance < 30 ml/min or receiving dialysis there is greater risk of developing hypocalcaemia. Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients Current or previous venous thromboembolic events (VTE), including deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Temporary or permanent immobilisation due to e.g. post-surgical recovery or prolonged bed rest. Established, current or past history of ischaemic heart disease, peripheral arterial disease and/or cerebrovascular disease. Uncontrolled hypertension Mild, transient decreases in serum calcium. Skin infections predominantly cellulitis. Other common undesirable effects (incidence of 1-10%) were urinary tract infection, upper respiratory tract infection, cataracts, constipation, sciatica, rash, pain in extremity. There have been no reports of anaphylaxis with the injection of denosumab to date. Nausea, diarrhoea, venous thromboembolism, headache, dermatitis, eczema, very rarely hypersensitivity reactions including rash, pruritus, urticarial and angioedema. Also reported gastrooesophageal reflux, dyspepsia, abdominal pain, vomiting, constipation, flatulence, stomatitis, peripheral oedema, bone marrow suppression, alopecia. Severe allergic reactions including drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) have been reported To report any adverse events to the doctor who administered the injection. To attend the GP surgery every 6 months for the denosumab injection. The absorption of strontium ranelate is reduced by food, milk and derivative products and therefore, strontium should be administered inbetween meals. Given the slow absorption, strontium should be taken at bedtime, preferably at least two hours after eating Teriparatide 250mcg/ml, 2.4ml prefilled syringe 20mcg daily Treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and men at increased risk of fractures Treatment of corticosteroid induced osteoporosis Pre-existing hypercalcaemia, skeletal malignancies, metabolic bone disease including Pagets and hyperparathyroidism, previous radiation to the skeleton Gastro-intestinal disorders (including nausea, reflux and haemorrhoids); palpitations, dyspnoea, headach, fatigue, depression, dizziness, vertigo, anaemia, increased sweating, muscle cramps, sciatica, myalgia, arthralgia By subcutaneous injection daily 4
5 EMA guidance (Feb 2014): Strontium Osseor/human_referral_prac_ jsp&mid=WC0b01ac05805c516f Recommended further restricting the use of the strontium to patients who cannot be treated with other medicines approved for osteoporosis. In addition these patients should continue to be evaluated regularly by their doctor (every 6 to 12 months) and treatment should be stopped if patients develop heart or circulatory problems, such as uncontrolled high blood pressure or angina. As recommended in a previous review, patients who have a history of certain heart or circulatory problems, such as stroke and heart attack, must not use the medicine. MHRA / CHM advice Bisphosphonates: Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (Oct 2007 and Nov 2009) Patients who are prescribed bisphosphonates should have a dental examination, prior to treatment, if they have poor dental health. During bisphosphonate treatment patients should maintain good oral hygiene, receive routine dental check ups, and report any oral symptoms. MHRA / CHM advice Bisphosphonates: Atypical femoral fractures (Jun 11) Atypical femoral fractures have been reported rarely with bisphosphonate therapy, mainly in patients receiving long-term treatment for osteoporosis. o Atypical femoral fractures are often bilateral; therefore the contralateral femur should be examined in bisphosphonate-treated patients who have sustained a femoral shaft fracture o Discontinuation of bisphosphonate therapy in patients suspected to have an atypical femur fracture should be considered while they are evaluated, and should be based on an assessment of the benefits and risks of treatment for the individual o During bisphosphonate treatment, patients should be advised to report any thigh, hip, or groin pain. Any patient who presents with such symptoms should be evaluated for an incomplete femur fracture o The optimum duration of bisphosphonate treatment for osteoporosis has not been established. The need for continued treatment should be re-evaluated periodically based on the benefits and potential risks of bisphosphonate therapy for individual patients, particularly after 5 or more years of use Adherence with bone protection treatments The key factors that affect adherence to treatment are adverse events, lack of understanding of the condition / disease being treated, lack of information about the treatment (including potential side effects) and lack of follow up. The following measures should be implemented to help improve adherence with treatment: Ensure patients understand what is being treated (fracture risk/osteoporosis) Give patient detailed information about the treatment (how it works,potential side effects) Follow up the patient a telephone follow up 3 to 6 months after starting treatment Encourage patients to contact GP practice if any side effects / problems 5
6 Additional local guidance: Currently there is limited national guidance surrounding a number of key questions in relation to the ongoing management of osteoporosis. The following advice is based on current available guidance and local specialist opinion. How long should treatment be continued and when to switch treatment? Year 1 & 2: Patients should continue to receive the same treatment for osteoporosis during the initial 2 years of treatment even if they experience a fragility fracture. NICE guidance recommends that an unsatisfactory response following treatment for secondary prevention of osteoporosis is defined as occurring when a woman has another fragility fracture despite adhering fully to treatment to 1 year and there is evidence of a decline in BMD below her pre-treatment baseline, however, in some cases there will be no baseline BMD for reference. Treatment should not be routinely switched and a DEXA scan is not routinely recommended. It is important that patients should always be counselled regarding compliance. Year 3, 4 & 5: if a patient has a fragility fracture after 2 years of being on the same treatment then consider changing therapy. If compliance is an issue with oral bisphosphonates then a suitable alternative could be IV bisphosphonate therapy. A DEXA scan is not routinely required at this stage. (Note if a change of therapy is considered appropriate then the patient will start at the beginning of year one of treatment again for the purpose of this guidance). At year 6: Patient taking Alendronate: advice from National Osteoporosis Society (Supported by the Royal College of General Practitioners) - In view of its long half-life it is possible to stop it for 3 years and still maintain its anti-fracture efficacy. Risedronate has a much shorter half-life and therefore should not be stopped. - The rationale for giving bisphosphonate holidays is that bone inertia develops with prolonged use and may lead to atypical fractures. However, there is no evidence that bone suppression gets more severe with time. The risks of atypical fractures appear to be higher in patients treated for longer duration with bisphosphonates but as yet there is no definitive causal relationship association between bisphosphonates and atypical fractures. - Usually most physicians stop alendronate at between 5 and 7 years for a 3 year break. - It is important to select the right patient. A DXA scan needs to be done before stopping bisphosphonates to ensure the BMD is improving and is no longer in the osteoporotic range. - Patients with severe osteoporosis e.g. multiple vertebral fractures, need to continue bisphosphonates as the benefits of osteoporotic fracture prevention outweigh the risks of atypical fractures. Atypical fractures occur rarely and are not restricted to bisphosphonate users. They are sub-trochanteric fractures, often bilateral and usually present with thigh pain. The fractures are commonly transverse and may be identified on X-rays and MRI scans. - Patients on prednisolone or patients who have had a vertebral fracture should not usually be considered for a treatment break. Patient taking other treatment: Review patient and ensure compliance with continuation of treatment If a patient has a new fracture, during their treatment break, they should be reassessed immediately. Calcium Unnecessary calcium supplementation should be avoided given the recent data which suggest that calcium supplementation might raise MI risk. Patients who are at low risk of osteoporosis, have a normal bone density or who are osteopenic should be given dietary advice and only treated with calcium if overtly dietary deficient (ref EPIC-Heidelberg study from Heart 2012,98:
7 Other medicines which can increase the risk of osteoporosis: Taking corticosteroid tablets for other medical conditions for over three months Anti epileptic drugs Breast cancer treatments such as aromatase inhibitors Prostate cancer drugs that affect either the production of the male hormone testosterone or the way it works in the body. Corticosteroid-induced osteoporosis: To reduce the risk of osteoporosis doses of oral corticosteroids should be as low as possible and courses of treatment as short as possible. The risk of osteoporosis may be related to cumulative dose of corticosteroids; even intermittent courses can therefore increase the risk. The greatest rate of bone loss occurs during the first 6 12 months of corticosteroid use and so early steps to prevent the development of osteoporosis are important. Long-term use of high-dose inhaled corticosteroids may also contribute to corticosteroid-induced osteoporosis. Patients taking (or who are likely to take) an oral corticosteroid for 3 months or longer should be assessed and where necessary given prophylactic treatment - those aged over 65 years or with a previous fragility fracture should routinely be offered bone protection as they are at greater risk. Patients over 40 but under 65 can be offered a DXA scan and should be considered for treatment if T-score < It is difficult to interpret DXA scans and apply this guidance to patients under 40. Bisphosphonates should be used with caution in patients under 40 and pre-menopausal women. It is therefore suggested that specialist advice is sought with regards to these patients. The therapeutic options for prophylaxis and treatment of corticosteroid-induced osteoporosis are the same: a bisphosphonate hormone replacement (HRT in women, testosterone in men [unlicensed indication]) teriparatide (specialist use only) Aromatase inhibitors and osteoporosis: Aromatase inhibitors reduce oestrogen levels which increase the rate of bone turnover and can cause significant and very rapid bone density loss of up to 8 per cent per year in younger women. NICE clinical guideline 80 Early and locally advanced breast cancer (Mar 09): diagnosis and treatment. Assessment and treatment of bone loss (page 66, section 5.6): Patients with early invasive breast cancer should have a baseline dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scan to assess bone mineral density if they: are starting adjuvant aromatase inhibitor treatment have treatment-induced menopause are starting ovarian ablation/suppression therapy Do not offer a DEXA scan to patients with early invasive breast cancer who are receiving tamoxifen alone, regardless of pretreatment menopausal status. Offer bisphosphonates to patients identified by algorithms 1 and 2 in Guidance for the management of breast cancer treatment-induced bone loss: a consensus position statement from a UK expert group (2008) 7
Drug treatment pathway for Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women
 Drug treatment pathway for Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women Version 1.0 Ratified by: East Sussex HEMC Date ratified: 26.01.2011 Job title of originator/author Gillian Ells, East Sussex HEMC Pharmacist
Drug treatment pathway for Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women Version 1.0 Ratified by: East Sussex HEMC Date ratified: 26.01.2011 Job title of originator/author Gillian Ells, East Sussex HEMC Pharmacist
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) OSTEOPOROSIS GUIDELINE
 DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) OSTEOPOROSIS GUIDELINE This is an updated guideline It incorporates the latest NICE guidance There are strong recommendations for calcium + vitamin D
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) OSTEOPOROSIS GUIDELINE This is an updated guideline It incorporates the latest NICE guidance There are strong recommendations for calcium + vitamin D
How To Take A Bone Marrow Transplant
 Drug treatments to protect your bones This information is an extract from the booklet, Bone health. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 5. Contents Bisphosphonates
Drug treatments to protect your bones This information is an extract from the booklet, Bone health. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 5. Contents Bisphosphonates
SUMMARY OF THE RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (by medicinal product)
 PART VI SUMMARY OF THE RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (by medicinal product) Format and content of the summary of the RMP The summary of the RMP part VI contains information based on RMP modules SI, SVIII and RMP
PART VI SUMMARY OF THE RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (by medicinal product) Format and content of the summary of the RMP The summary of the RMP part VI contains information based on RMP modules SI, SVIII and RMP
Cystic fibrosis and bone health
 Cystic fibrosis and bone health Factsheet March 2013 Cystic fibrosis and bone health Introduction As we get older our bones become thinner and weaker, and may become more susceptible to fracture. However
Cystic fibrosis and bone health Factsheet March 2013 Cystic fibrosis and bone health Introduction As we get older our bones become thinner and weaker, and may become more susceptible to fracture. However
Medications for Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis
 1 Medications for Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis Osteoporosis is a disease where the strength of bones is less than normal, making them more susceptible to fracture, or breaking, than normal
1 Medications for Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis Osteoporosis is a disease where the strength of bones is less than normal, making them more susceptible to fracture, or breaking, than normal
Drugs for osteoporosis
 Drug information Drugs for osteoporosis Drugs for osteoporosis This leaflet provides information on drugs for osteoporosis and will answer any questions you have about the treatment. Arthritis Research
Drug information Drugs for osteoporosis Drugs for osteoporosis This leaflet provides information on drugs for osteoporosis and will answer any questions you have about the treatment. Arthritis Research
Medications to Prevent and Treat Osteoporosis
 Medications to Prevent and Treat Osteoporosis National Institutes of Health Osteoporosis and Related Bone Diseases ~ National Resource Center 2 AMS Circle Bethesda, MD 20892-3676 Tel: (800) 624-BONE or
Medications to Prevent and Treat Osteoporosis National Institutes of Health Osteoporosis and Related Bone Diseases ~ National Resource Center 2 AMS Circle Bethesda, MD 20892-3676 Tel: (800) 624-BONE or
Osteoporosis Medications
 Osteoporosis Medications When does a doctor prescribe osteoporosis medications? Healthcare providers look at several pieces of information before prescribing a bone- preserving or bone- building medication.
Osteoporosis Medications When does a doctor prescribe osteoporosis medications? Healthcare providers look at several pieces of information before prescribing a bone- preserving or bone- building medication.
How To Choose A Biologic Drug
 North Carolina Rheumatology Association Position Statements I. Biologic Agents A. Appropriate delivery, handling, storage and administration of biologic agents B. Indications for biologic agents II. III.
North Carolina Rheumatology Association Position Statements I. Biologic Agents A. Appropriate delivery, handling, storage and administration of biologic agents B. Indications for biologic agents II. III.
OSTEOPOROSIS -Medical Management of Men and Women who have (or are at risk of ) Osteoporosis
 Basingstoke, Southampton and Winchester District Prescribing Committee OSTEOPOROSIS -Medical Management of Men and Women who have (or are at risk of ) Osteoporosis Frail, increased fall risk + housebound
Basingstoke, Southampton and Winchester District Prescribing Committee OSTEOPOROSIS -Medical Management of Men and Women who have (or are at risk of ) Osteoporosis Frail, increased fall risk + housebound
Drug treatments for osteoporosis
 Drug treatments for osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis occurs when the struts which make up the mesh-like structure within bones become thin causing them to become fragile and break easily,
Drug treatments for osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis occurs when the struts which make up the mesh-like structure within bones become thin causing them to become fragile and break easily,
What You Need to Know for Better Bone Health
 What You Need to Know for Better Bone Health A quick lesson about bones: Why healthy bones matter The healthier your bones The more active you can be Bone health has a major effect on your quality of life
What You Need to Know for Better Bone Health A quick lesson about bones: Why healthy bones matter The healthier your bones The more active you can be Bone health has a major effect on your quality of life
Osteoporosis. Dr Gordon MacDonald BSc MB BChir MRCP Consultant Rheumatologist. Rheumatology and Arthritis Seminar Tuesday 5 th February 2013
 Osteoporosis Dr Gordon MacDonald BSc MB BChir MRCP Consultant Rheumatologist Rheumatology and Arthritis Seminar Tuesday 5 th February 2013 Plan What is osteoporosis? Consequences of osteoporosis Risk factors
Osteoporosis Dr Gordon MacDonald BSc MB BChir MRCP Consultant Rheumatologist Rheumatology and Arthritis Seminar Tuesday 5 th February 2013 Plan What is osteoporosis? Consequences of osteoporosis Risk factors
OSTEOPOROSIS REHABILITATION PROGRAM
 OSTEOPOROSIS REHABILITATION PROGRAM Tricia Orme, R.N. BSc(N) Mary Pack Arthritis Program Victoria i Arthritis i Centre Objectives Participants will gain an understanding of what Osteoporosis is and how
OSTEOPOROSIS REHABILITATION PROGRAM Tricia Orme, R.N. BSc(N) Mary Pack Arthritis Program Victoria i Arthritis i Centre Objectives Participants will gain an understanding of what Osteoporosis is and how
Osteoporosis Treatments That Help Prevent Broken Bones. A Guide for Women After Menopause
 Osteoporosis Treatments That Help Prevent Broken Bones A Guide for Women After Menopause June 2008 fast facts Medicines for osteoporosis (OSS-tee-oh-puh-ROW-sis) can lower your chance of breaking a bone.
Osteoporosis Treatments That Help Prevent Broken Bones A Guide for Women After Menopause June 2008 fast facts Medicines for osteoporosis (OSS-tee-oh-puh-ROW-sis) can lower your chance of breaking a bone.
Patient Information Once Weekly FOSAMAX (FOSS-ah-max) (alendronate sodium) Tablets and Oral Solution
 Patient Information Once Weekly FOSAMAX (FOSS-ah-max) (alendronate sodium) Tablets and Oral Solution Read this information before you start taking FOSAMAX *. Also, read the leaflet each time you refill
Patient Information Once Weekly FOSAMAX (FOSS-ah-max) (alendronate sodium) Tablets and Oral Solution Read this information before you start taking FOSAMAX *. Also, read the leaflet each time you refill
PROTOCOL FOR PATIENTS WITH ABNORMAL LAB AND X-RAY VALUES
 PROTOCOL FOR PATIENTS WITH ABNORMAL LAB AND X-RAY VALUES Patients newly diagnosed as osteopenic or osteoporotic on a radiology report or patients receiving abnormal lab values on the following lab tests
PROTOCOL FOR PATIENTS WITH ABNORMAL LAB AND X-RAY VALUES Patients newly diagnosed as osteopenic or osteoporotic on a radiology report or patients receiving abnormal lab values on the following lab tests
HERTFORDSHIRE MEDICINES MANAGEMENT COMMITTEE (HMMC) RIVAROXABAN RECOMMENDED see specific recommendations for licensed indications below
 Name: generic (trade) Rivaroxaban (Xarelto ) HERTFORDSHIRE MEDICINES MANAGEMENT COMMITTEE (HMMC) RIVAROXABAN RECOMMENDED see specific recommendations for licensed indications below What it is Indications
Name: generic (trade) Rivaroxaban (Xarelto ) HERTFORDSHIRE MEDICINES MANAGEMENT COMMITTEE (HMMC) RIVAROXABAN RECOMMENDED see specific recommendations for licensed indications below What it is Indications
Module 5 - Speaking of Bones Osteoporosis For Health Professionals: Fracture Risk Assessment. William D. Leslie, MD MSc FRCPC
 Module 5 - Speaking of Bones Osteoporosis For Health Professionals: Fracture Risk Assessment William D. Leslie, MD MSc FRCPC Case #1 Age 53: 3 years post-menopause Has always enjoyed excellent health with
Module 5 - Speaking of Bones Osteoporosis For Health Professionals: Fracture Risk Assessment William D. Leslie, MD MSc FRCPC Case #1 Age 53: 3 years post-menopause Has always enjoyed excellent health with
Bone Basics National Osteoporosis Foundation 2013
 When you have osteoporosis, your bones become weak and are more likely to break (fracture). You can have osteoporosis without any symptoms. Because it can be prevented and treated, an early diagnosis is
When you have osteoporosis, your bones become weak and are more likely to break (fracture). You can have osteoporosis without any symptoms. Because it can be prevented and treated, an early diagnosis is
Clinical Practice Guideline for Osteoporosis Screening and Treatment
 Clinical Practice Guideline for Osteoporosis Screening and Treatment Osteoporosis is a condition of decreased bone mass, leading to bone fragility and an increased susceptibility to fractures. While osteoporosis
Clinical Practice Guideline for Osteoporosis Screening and Treatment Osteoporosis is a condition of decreased bone mass, leading to bone fragility and an increased susceptibility to fractures. While osteoporosis
Scans and tests and osteoporosis
 Scans and tests and osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis occurs when the struts which make up the mesh-like structure within bones become thin causing them to become fragile and break easily,
Scans and tests and osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis occurs when the struts which make up the mesh-like structure within bones become thin causing them to become fragile and break easily,
Enoxaparin for long term anticoagulation in patients unsuitable for oral anticoagulants
 Enoxaparin for long term anticoagulation in patients unsuitable for oral anticoagulants Traffic light classification- Amber 2 Information sheet for Primary Care Prescribers Relevant Licensed Indications
Enoxaparin for long term anticoagulation in patients unsuitable for oral anticoagulants Traffic light classification- Amber 2 Information sheet for Primary Care Prescribers Relevant Licensed Indications
SIGMA sums it up: Answers to questions about osteoporosis and denosumab therapy
 SIGMA sums it up: Answers to questions about osteoporosis and denosumab therapy Table of contents Who is SIGMA? Frequently asked questions we will address: 1. What is osteoporosis? 2. Why is it important
SIGMA sums it up: Answers to questions about osteoporosis and denosumab therapy Table of contents Who is SIGMA? Frequently asked questions we will address: 1. What is osteoporosis? 2. Why is it important
Falls and Fracture Risk assessment and management
 Falls and Fracture Risk assessment and management Disclosures: Although various guidelines and studies were reviewed, this represents my own personal bias and conclusions. What do we know? 1) Fractures
Falls and Fracture Risk assessment and management Disclosures: Although various guidelines and studies were reviewed, this represents my own personal bias and conclusions. What do we know? 1) Fractures
Patient Group Direction Hospital: Bristol Royal Infirmary Department: UHBristol Thrombosis Service University Hospitals Bristol NHS Foundation Trust.
 Patient Group Direction Hospital: Bristol Royal Infirmary Department: UHBristol Thrombosis Service University Hospitals Bristol NHS Foundation Trust. This Patient Group Direction (PGD) has been written
Patient Group Direction Hospital: Bristol Royal Infirmary Department: UHBristol Thrombosis Service University Hospitals Bristol NHS Foundation Trust. This Patient Group Direction (PGD) has been written
P AC K AG E L E AF L E T: INFORMAT I ON FO R THE USER. 500 mg, film-coated tablet Active substance: metformin hydrochloride
 P AC K AG E L E AF L E T: INFORMAT I ON FO R THE USER Siofor 500 500 mg, film-coated tablet Active substance: metformin hydrochloride For use in children above 10 years and adults Read all of this leaflet
P AC K AG E L E AF L E T: INFORMAT I ON FO R THE USER Siofor 500 500 mg, film-coated tablet Active substance: metformin hydrochloride For use in children above 10 years and adults Read all of this leaflet
BULLETIN. Slovak Republic Ministry of Health
 BULLETIN Slovak Republic Ministry of Health Part 51-53 November 13, 2009 No. 57 CONTENTS: 52. Slovak Republic Ministry of Health Guidelines for the Diagnosis of Glucocorticoidinduced Osteoporosis 52. Slovak
BULLETIN Slovak Republic Ministry of Health Part 51-53 November 13, 2009 No. 57 CONTENTS: 52. Slovak Republic Ministry of Health Guidelines for the Diagnosis of Glucocorticoidinduced Osteoporosis 52. Slovak
Osteoporosis Assessment Using DXA and Instant Vertebral Assessment. Working Together For A Healthier Community
 Osteoporosis Assessment Using DXA and Instant Vertebral Assessment Working Together For A Healthier Community Osteoporosis The Silent Thief The Facts About Osteoporosis 1 in 2 women will develop osteoporosis
Osteoporosis Assessment Using DXA and Instant Vertebral Assessment Working Together For A Healthier Community Osteoporosis The Silent Thief The Facts About Osteoporosis 1 in 2 women will develop osteoporosis
Osteoporosis has been identified by the US Surgeon General
 New Guidelines for the Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis E. Michael Lewiecki, MD, and Nelson B. Watts, MD Abstract: The World Health Organization Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX ) and the National
New Guidelines for the Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis E. Michael Lewiecki, MD, and Nelson B. Watts, MD Abstract: The World Health Organization Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX ) and the National
Initiate Atorvastatin 20mg daily
 Type 2 Diabetes Patient Objectives Stopping Smoking BMI > 25 kg m² Control BP to
Type 2 Diabetes Patient Objectives Stopping Smoking BMI > 25 kg m² Control BP to
Adjunctive psychosocial intervention. Conditions requiring dose reduction. Immediate, peak plasma concentration is reached within 1 hour.
 Shared Care Guideline for Prescription and monitoring of Naltrexone Hydrochloride in alcohol dependence Author(s)/Originator(s): (please state author name and department) Dr Daly - Consultant Psychiatrist,
Shared Care Guideline for Prescription and monitoring of Naltrexone Hydrochloride in alcohol dependence Author(s)/Originator(s): (please state author name and department) Dr Daly - Consultant Psychiatrist,
The Role of Bisphosphonates in Multiple Myeloma: 2007 Update Clinical Practice Guideline
 The Role of Bisphosphonates in Multiple Myeloma: 2007 Update Clinical Practice Guideline Introduction ASCO convened an Update Committee to review and update the 2002 recommendations for the role of bisphosphonates
The Role of Bisphosphonates in Multiple Myeloma: 2007 Update Clinical Practice Guideline Introduction ASCO convened an Update Committee to review and update the 2002 recommendations for the role of bisphosphonates
Essential Shared Care Agreement Drugs for Dementia
 Ref No. E040 Essential Shared Care Agreement Drugs for Dementia Please complete the following details: Patient s name, address, date of birth Consultant s contact details (p.3) And send One copy to: 1.
Ref No. E040 Essential Shared Care Agreement Drugs for Dementia Please complete the following details: Patient s name, address, date of birth Consultant s contact details (p.3) And send One copy to: 1.
The menopausal transition usually has three parts:
 The menopausal transition usually has three parts: Perimenopause begins several years before a woman s last menstrual period, when the ovaries gradually produce less estrogen. In the last 1-2 years of
The menopausal transition usually has three parts: Perimenopause begins several years before a woman s last menstrual period, when the ovaries gradually produce less estrogen. In the last 1-2 years of
RISK EVALUATION AND MITIGATION STRATEGY (REMS)
 Page 1 Initial REMS Approval: July 2009 Most Recent Modification: August 2013 NDA 21-318 FORTEO (teriparatide) (rdna origin) Injection RISK EVALUATION AND MITIGATION STRATEGY (REMS) Eli Lilly and Company
Page 1 Initial REMS Approval: July 2009 Most Recent Modification: August 2013 NDA 21-318 FORTEO (teriparatide) (rdna origin) Injection RISK EVALUATION AND MITIGATION STRATEGY (REMS) Eli Lilly and Company
A Treatment Algorithm for Indian Patients of Osteoporosis
 Indian Medical Gazette FEBRUARY 2012 67 Symposia Update A Treatment Algorithm for Indian Patients of Osteoporosis Shailendra Mohan Lakhotia, Senior Consultant Orthopedic Surgeon, Kolkata 700 045. Prashant
Indian Medical Gazette FEBRUARY 2012 67 Symposia Update A Treatment Algorithm for Indian Patients of Osteoporosis Shailendra Mohan Lakhotia, Senior Consultant Orthopedic Surgeon, Kolkata 700 045. Prashant
Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Page 1
 Breast Cancer Summary Breast cancers which are detected early are curable by local treatments. The initial surgery will give the most information about the cancer; such as size or whether the glands (or
Breast Cancer Summary Breast cancers which are detected early are curable by local treatments. The initial surgery will give the most information about the cancer; such as size or whether the glands (or
Steroids. What are steroids?
 Steroids What are steroids? Also known as corticosteroids and glucocorticoids, steroids are hormones that are normally produced by the adrenal glands. They are mainly used in multiple sclerosis (MS) because
Steroids What are steroids? Also known as corticosteroids and glucocorticoids, steroids are hormones that are normally produced by the adrenal glands. They are mainly used in multiple sclerosis (MS) because
patient group direction
 DICLOFENAC v01 1/8 DICLOFENAC PGD Details Version 1.0 Legal category Staff grades Approved by POM Paramedic (Non-ECP) Nurse (Non-ECP) Emergency Care Practitioner (Paramedic) Emergency Care Practitioner
DICLOFENAC v01 1/8 DICLOFENAC PGD Details Version 1.0 Legal category Staff grades Approved by POM Paramedic (Non-ECP) Nurse (Non-ECP) Emergency Care Practitioner (Paramedic) Emergency Care Practitioner
Osteoporosis Treatment Guide
 Osteoporosis Treatment Guide An estimated 10 million Americans have osteoporosis. Another 34 million have low bone mass. If left untreated, osteoporosis can be both debilitating and painful. Fortunately,
Osteoporosis Treatment Guide An estimated 10 million Americans have osteoporosis. Another 34 million have low bone mass. If left untreated, osteoporosis can be both debilitating and painful. Fortunately,
Maintenance of abstinence in alcohol dependence
 Shared Care Guideline for Prescription and monitoring of Acamprosate Calcium Author(s)/Originator(s): (please state author name and department) Dr Daly - Consultant Psychiatrist, Alcohol Services Dr Donnelly
Shared Care Guideline for Prescription and monitoring of Acamprosate Calcium Author(s)/Originator(s): (please state author name and department) Dr Daly - Consultant Psychiatrist, Alcohol Services Dr Donnelly
Prescriber Guide. 20mg. 15mg. Simply Protecting More Patients. Simply Protecting More Patients
 Prescriber Guide 20mg Simply Protecting More Patients 15mg Simply Protecting More Patients 1 Dear Doctor, This prescriber guide was produced by Bayer Israel in cooperation with the Ministry of Health as
Prescriber Guide 20mg Simply Protecting More Patients 15mg Simply Protecting More Patients 1 Dear Doctor, This prescriber guide was produced by Bayer Israel in cooperation with the Ministry of Health as
Donepezil (Aricept ), Galantamine (Reminyl XL ), Rivastigmine (Exelon ) and Memantine (Ebixa )
 Donepezil (Aricept ), Galantamine (Reminyl XL ), Rivastigmine (Exelon ) and Memantine (Ebixa ) ESCA: For the treatment of Alzheimer s disease. SECONDARY CARE SECTION TO BE COMPLETED BY INITIATING DOCTOR
Donepezil (Aricept ), Galantamine (Reminyl XL ), Rivastigmine (Exelon ) and Memantine (Ebixa ) ESCA: For the treatment of Alzheimer s disease. SECONDARY CARE SECTION TO BE COMPLETED BY INITIATING DOCTOR
Fast Facts on Osteoporosis
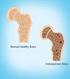 Fast Facts on Osteoporosis Definition Prevalence Osteoporosis, or porous bone, is a disease characterized by low bone mass and structural deterioration of bone tissue, leading to bone fragility and an
Fast Facts on Osteoporosis Definition Prevalence Osteoporosis, or porous bone, is a disease characterized by low bone mass and structural deterioration of bone tissue, leading to bone fragility and an
Denosumab (Prolia) for postmenopausal osteoporosis
 Denosumab (Prolia) for postmenopausal osteoporosis This Medicine Update is for women who are using, or thinking about using, denosumab. Summary Denosumab is a new medicine for women with osteoporosis.
Denosumab (Prolia) for postmenopausal osteoporosis This Medicine Update is for women who are using, or thinking about using, denosumab. Summary Denosumab is a new medicine for women with osteoporosis.
New Oral Anticoagulants. How safe are they outside the trials?
 New Oral Anticoagulants How safe are they outside the trials? Objectives The need for anticoagulant therapy Indications for anticoagulation Traditional anticoagulant therapies Properties of new oral anticoagulants
New Oral Anticoagulants How safe are they outside the trials? Objectives The need for anticoagulant therapy Indications for anticoagulation Traditional anticoagulant therapies Properties of new oral anticoagulants
Intravenous Methyl Prednisolone in Multiple Sclerosis
 Intravenous Methyl Prednisolone in Multiple Sclerosis Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Relapse management in multiple sclerosis Relapses in multiple sclerosis (MS) are common and caused by
Intravenous Methyl Prednisolone in Multiple Sclerosis Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Relapse management in multiple sclerosis Relapses in multiple sclerosis (MS) are common and caused by
INITIATING ORAL AUBAGIO (teriflunomide) THERAPY
 FOR YOUR PATIENTS WITH RELAPSING FORMS OF MS INITIATING ORAL AUBAGIO (teriflunomide) THERAPY WARNING: HEPATOTOXICITY AND RISK OF TERATOGENICITY Severe liver injury including fatal liver failure has been
FOR YOUR PATIENTS WITH RELAPSING FORMS OF MS INITIATING ORAL AUBAGIO (teriflunomide) THERAPY WARNING: HEPATOTOXICITY AND RISK OF TERATOGENICITY Severe liver injury including fatal liver failure has been
Naltrexone Shared Care Guideline for the treatment of alcohol dependence and opioid dependance
 Naltrexone Shared Care Guideline for the treatment of alcohol dependence and opioid dependance Introduction Indication/Licensing information: Naltrexone is licensed for use as an additional therapy, within
Naltrexone Shared Care Guideline for the treatment of alcohol dependence and opioid dependance Introduction Indication/Licensing information: Naltrexone is licensed for use as an additional therapy, within
Prolia 2 shots a year proven to help strengthen bones.
 Ask your doctor if Prolia (denosumab) is right for you and visit us at www.prolia.com For women with postmenopausal osteoporosis at high risk for fracture: there s Prolia. Prolia 2 shots a year proven
Ask your doctor if Prolia (denosumab) is right for you and visit us at www.prolia.com For women with postmenopausal osteoporosis at high risk for fracture: there s Prolia. Prolia 2 shots a year proven
**Form 1: - Consultant Copy** Telephone Number: Fax Number: Email: Author: Dr Bernard Udeze Pharmacist: Claire Ault Date of issue July 2011
 Effective Shared Care Agreement for the treatment of Dementia in Alzheimer s Disease Donepezil tablets / orodispersible tablets (Aricept / Aricept Evess ) These forms (1 and 2) are to be completed by both
Effective Shared Care Agreement for the treatment of Dementia in Alzheimer s Disease Donepezil tablets / orodispersible tablets (Aricept / Aricept Evess ) These forms (1 and 2) are to be completed by both
Low Molecular Weight Heparin. All Wales Medicines Strategy Group (AWMSG) Recommendations and advice
 Low Molecular Weight Heparin All Wales Medicines Strategy Group (AWMSG) Recommendations and advice Starting Point Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH): Inhibits factor Xa and factor IIa (thrombin) Small
Low Molecular Weight Heparin All Wales Medicines Strategy Group (AWMSG) Recommendations and advice Starting Point Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH): Inhibits factor Xa and factor IIa (thrombin) Small
How To Treat An Elderly Patient
 1. Introduction/ Getting to know our Seniors a. Identify common concepts and key terms used when discussing geriatrics b. Distinguish between different venues of senior residence c. Advocate the necessity
1. Introduction/ Getting to know our Seniors a. Identify common concepts and key terms used when discussing geriatrics b. Distinguish between different venues of senior residence c. Advocate the necessity
(NON-PRESCRIPTION) LEAFLET: USER INFORMATION. CALTRATE VITAMIN D3 600mg/400 IU, film-coated tablet Calcium and Cholecalciferol
 (NON-PRESCRIPTION) LEAFLET: USER INFORMATION CALTRATE VITAMIN D3 600mg/400 IU, film-coated tablet Calcium and Cholecalciferol Read all of this leaflet carefully because it contains important information
(NON-PRESCRIPTION) LEAFLET: USER INFORMATION CALTRATE VITAMIN D3 600mg/400 IU, film-coated tablet Calcium and Cholecalciferol Read all of this leaflet carefully because it contains important information
Indication: Indication: Protaxos is indicated in adults.
 Maklumat tambahan indikasi untuk upload pada laman web Year 2013 Products Approved For Additional Indication (DCA 262 28 Mac 2013) NO PRODUCT (ACTIVE INGREDIENT) 1. 1.1 EVISTA TABLET 60MG [ Raloxifene
Maklumat tambahan indikasi untuk upload pada laman web Year 2013 Products Approved For Additional Indication (DCA 262 28 Mac 2013) NO PRODUCT (ACTIVE INGREDIENT) 1. 1.1 EVISTA TABLET 60MG [ Raloxifene
Surgical Weight Loss. Mission Bariatrics
 Surgical Weight Loss Mission Bariatrics Obesity is a major health problem in the United States, with more than one in every three people suffering from this chronic condition. Obese adults are at an increased
Surgical Weight Loss Mission Bariatrics Obesity is a major health problem in the United States, with more than one in every three people suffering from this chronic condition. Obese adults are at an increased
Rivaroxaban: Amber Drug Guidance for the prevention of stroke and systemic embolism in patients with non-valvular AF
 Leeds Rivaroxaban: Amber Drug Guidance for the prevention of stroke and systemic embolism in patients with non-valvular AF Amber Drug Level 3 (amber drug with monitoring requirements) We have started your
Leeds Rivaroxaban: Amber Drug Guidance for the prevention of stroke and systemic embolism in patients with non-valvular AF Amber Drug Level 3 (amber drug with monitoring requirements) We have started your
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) SHARED CARE AGREEMENT FRAMEWORK
 DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) SHARED CARE AGREEMENT FRAMEWORK ACAMPROSATE CALCIUM (Campral EC) for alcohol abstinence ESCA: Adjunct in the treatment of chronic alcohol dependence (under
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) SHARED CARE AGREEMENT FRAMEWORK ACAMPROSATE CALCIUM (Campral EC) for alcohol abstinence ESCA: Adjunct in the treatment of chronic alcohol dependence (under
DVT/PE Management with Rivaroxaban (Xarelto)
 DVT/PE Management with Rivaroxaban (Xarelto) Rivaroxaban is FDA approved for the acute treatment of DVT and PE and reduction in risk of recurrence of DVT and PE. FDA approved indications: Non valvular
DVT/PE Management with Rivaroxaban (Xarelto) Rivaroxaban is FDA approved for the acute treatment of DVT and PE and reduction in risk of recurrence of DVT and PE. FDA approved indications: Non valvular
Teriflunomide (Aubagio) 14mg once daily tablet
 Teriflunomide (Aubagio) 14mg once daily tablet Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Your Consultant Neurologist has suggested that you may benefit from treatment with Teriflunomide. The decision
Teriflunomide (Aubagio) 14mg once daily tablet Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Your Consultant Neurologist has suggested that you may benefit from treatment with Teriflunomide. The decision
LEFLUNOMIDE (Adults)
 Shared Care Guideline DRUG: Introduction: LEFLUNOMIDE (Adults) Indication: Disease modifying drug for rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis Licensing Information: Disease modifying drug for active
Shared Care Guideline DRUG: Introduction: LEFLUNOMIDE (Adults) Indication: Disease modifying drug for rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis Licensing Information: Disease modifying drug for active
Severe rheumatoid arthritis (a disease that causes inflammation of the joints),where MabThera is given intravenously together with methotrexate.
 EMA/614203/2010 EMEA/H/C/000165 EPAR summary for the public rituximab This is a summary of the European public assessment report (EPAR) for. It explains how the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human
EMA/614203/2010 EMEA/H/C/000165 EPAR summary for the public rituximab This is a summary of the European public assessment report (EPAR) for. It explains how the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human
PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ Tablets (High dose phosphate supplement)
 1 PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ Tablets (High dose phosphate supplement) PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ Tablets are a high dose phosphate supplement containing sodium phosphate monobasic. The CAS registry number
1 PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ Tablets (High dose phosphate supplement) PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ Tablets are a high dose phosphate supplement containing sodium phosphate monobasic. The CAS registry number
Rivaroxaban: Prescribing Guidance for the treatment of provoked venous thromboembolism (VTE)
 Rivaroxaban: Prescribing Guidance for the treatment of provoked venous thromboembolism (VTE) Amber Drug Level 2 Leeds We have started your patient on rivaroxaban for the treatment of provoked VTE (deep
Rivaroxaban: Prescribing Guidance for the treatment of provoked venous thromboembolism (VTE) Amber Drug Level 2 Leeds We have started your patient on rivaroxaban for the treatment of provoked VTE (deep
West of Scotland Cancer Network Chemotherapy Protocol. Cisplatin and Pemetrexed for Malignant Mesothelioma (LUWOS 0021)
 West of Scotland Cancer Network Chemotherapy Protocol Cisplatin and Pemetrexed for Malignant Mesothelioma (LUWOS 0021) Indication Palliative chemotherapy for malignant mesothelioma of the pleura Eligibility
West of Scotland Cancer Network Chemotherapy Protocol Cisplatin and Pemetrexed for Malignant Mesothelioma (LUWOS 0021) Indication Palliative chemotherapy for malignant mesothelioma of the pleura Eligibility
Safety Information Card for Xarelto Patients
 Safety Information Card for Xarelto Patients 15mg Simply Protecting More Patients 20mg Simply Protecting More Patients Keep this card with you at all times Present this card to every physician or dentist
Safety Information Card for Xarelto Patients 15mg Simply Protecting More Patients 20mg Simply Protecting More Patients Keep this card with you at all times Present this card to every physician or dentist
White, circular, biconvex, uncoated tablets with a score line on one side, plain on the other.
 Nausicalm Cyclizine hydrochloride Ph. Eur. 50 mg Presentation White, circular, biconvex, uncoated tablets with a score line on one side, plain on the other. Uses Actions The active ingredient-cyclizine
Nausicalm Cyclizine hydrochloride Ph. Eur. 50 mg Presentation White, circular, biconvex, uncoated tablets with a score line on one side, plain on the other. Uses Actions The active ingredient-cyclizine
Osteoporosis and Arthritis: Two Common but Different Conditions
 and : Two Common but Different Conditions National Institutes of Health and Related Bone Diseases ~ National Resource Center 2 AMS Circle Bethesda, MD 20892 3676 Tel: 800 624 BONE or 202 223 0344 Fax:
and : Two Common but Different Conditions National Institutes of Health and Related Bone Diseases ~ National Resource Center 2 AMS Circle Bethesda, MD 20892 3676 Tel: 800 624 BONE or 202 223 0344 Fax:
Menopause Guidance on management and prescribing HRT for GPs based on NICE guidance 2015
 PRIMARY CARE WOMEN S HEALTH FORUM GUIDELINES Menopause Guidance on management and prescribing HRT for GPs based on NICE guidance 2015 Written by Dr Imogen Shaw This guidance is designed to support you
PRIMARY CARE WOMEN S HEALTH FORUM GUIDELINES Menopause Guidance on management and prescribing HRT for GPs based on NICE guidance 2015 Written by Dr Imogen Shaw This guidance is designed to support you
Anticoagulant therapy
 Anticoagulation: The risks Anticoagulant therapy 1990 2002: 600 incidents reported 120 resulted in death of patient 92 deaths related to warfarin usage 28 reports related to heparin usage Incidents in
Anticoagulation: The risks Anticoagulant therapy 1990 2002: 600 incidents reported 120 resulted in death of patient 92 deaths related to warfarin usage 28 reports related to heparin usage Incidents in
PATIENT CONSENT TO PROCEDURE - ROUX-EN-Y GASTRIC BYPASS
 As a patient you must be adequately informed about your condition and the recommended surgical procedure. Please read this document carefully and ask about anything you do not understand. Please initial
As a patient you must be adequately informed about your condition and the recommended surgical procedure. Please read this document carefully and ask about anything you do not understand. Please initial
Shared Care Guideline-Use of Donepezil, Galantamine, Rivastigmine and Memantine in Dementia
 Shared Care Guideline-Use of Donepezil, Galantamine, Rivastigmine and Memantine in Dementia Version: 3.0 Ratified by: Medicines Committee Date ratified: 16 th November 2011 Name of originator/author: James
Shared Care Guideline-Use of Donepezil, Galantamine, Rivastigmine and Memantine in Dementia Version: 3.0 Ratified by: Medicines Committee Date ratified: 16 th November 2011 Name of originator/author: James
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH. Risedronate Sodium (as the hemi-pentahydrate) Tablets, USP 5 mg, 30 mg, 35 mg, 75 mg and 150 mg
 PRODUCT MONOGRAPH Risedronate Sodium (as the hemi-pentahydrate) Tablets, USP 5 mg, 30 mg, 35 mg, 75 mg and 150 mg Risedronate Sodium (as the hemi-pentahydrate) Delayed-Release Tablets 35 mg Warner Chilcott
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH Risedronate Sodium (as the hemi-pentahydrate) Tablets, USP 5 mg, 30 mg, 35 mg, 75 mg and 150 mg Risedronate Sodium (as the hemi-pentahydrate) Delayed-Release Tablets 35 mg Warner Chilcott
Chapter 6 Gastrointestinal Impairment
 Chapter 6 Gastrointestinal This chapter consists of 2 parts: Part 6.1 Diseases of the digestive system Part 6.2 Abdominal wall hernias and obesity PART 6.1: DISEASES OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Diseases of
Chapter 6 Gastrointestinal This chapter consists of 2 parts: Part 6.1 Diseases of the digestive system Part 6.2 Abdominal wall hernias and obesity PART 6.1: DISEASES OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Diseases of
Dabigatran: Amber Drug Guidance for the prevention of stroke and systemic embolism in patients with non-valvular AF
 Leeds Dabigatran: Amber Drug Guidance for the prevention of stroke and systemic embolism in patients with non-valvular AF Amber Drug Level 3 (amber drug with monitoring requirements) We have started your
Leeds Dabigatran: Amber Drug Guidance for the prevention of stroke and systemic embolism in patients with non-valvular AF Amber Drug Level 3 (amber drug with monitoring requirements) We have started your
Shared Care Agreement Insulin Degludec (Tresiba )
 Licensed Indication Shared Care Agreement Insulin Degludec (Tresiba ) Insulin Degludec is licensed for the treatment of diabetes mellitus in adults. Countess of Chester prescribing guidelines Restricting
Licensed Indication Shared Care Agreement Insulin Degludec (Tresiba ) Insulin Degludec is licensed for the treatment of diabetes mellitus in adults. Countess of Chester prescribing guidelines Restricting
I B2.4. Design of the patient information leaflet for VariQuin
 (English translation of official Dutch version) I B2.4. Design of the patient information leaflet for VariQuin Information for the Patient: Read this package leaflet carefully when you have some time to
(English translation of official Dutch version) I B2.4. Design of the patient information leaflet for VariQuin Information for the Patient: Read this package leaflet carefully when you have some time to
Dallas Neurosurgical and Spine Associates, P.A Patient Health History
 Dallas Neurosurgical and Spine Associates, P.A Patient Health History DOB: Date: Reason for your visit (Chief complaint): Past Medical History Please check corresponding box if you have ever had any of
Dallas Neurosurgical and Spine Associates, P.A Patient Health History DOB: Date: Reason for your visit (Chief complaint): Past Medical History Please check corresponding box if you have ever had any of
NHS FORTH VALLEY Rivaroxaban for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation
 NHS FORTH VALLEY Rivaroxaban for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation Date of First Issue 06/06/2012 Approved 06/06/2012 Current Issue Date 29/10/2014 Review Date 29/10/2016 Version 1.4 EQIA Yes 01/06/2012
NHS FORTH VALLEY Rivaroxaban for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation Date of First Issue 06/06/2012 Approved 06/06/2012 Current Issue Date 29/10/2014 Review Date 29/10/2016 Version 1.4 EQIA Yes 01/06/2012
1MFBTF GJMM PVU GPSNT BOE GBY 'PSNT XJMM CF TJHOFE BU ZPVS BQQPJOUNFOU
 CELL PHONE: PATIENT HISTORY FORM - CONFIDENTIAL DATE: PATIENT: (LAST NAME) (FIRST NAME) (Ml) (NICKNAME) DOB: Primary Physician/ Family Doctor: Phone: Past Medical History (Click all that apply) High blood
CELL PHONE: PATIENT HISTORY FORM - CONFIDENTIAL DATE: PATIENT: (LAST NAME) (FIRST NAME) (Ml) (NICKNAME) DOB: Primary Physician/ Family Doctor: Phone: Past Medical History (Click all that apply) High blood
The Menopause and Subtotal Hysterectomy
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Women s Health The Menopause and Subtotal Hysterectomy Information for patients The menopause At the menopause the ovaries stop working. This means that the female
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Women s Health The Menopause and Subtotal Hysterectomy Information for patients The menopause At the menopause the ovaries stop working. This means that the female
Hull & East Riding Prescribing Committee
 Hull & East Riding Prescribing Committee Guideline on Prescribing of Gonadorelin (GnRH) Analogues and Progesterone Receptor Modulators in treatment of Endometriosis or prior to Endometrial Ablation, or
Hull & East Riding Prescribing Committee Guideline on Prescribing of Gonadorelin (GnRH) Analogues and Progesterone Receptor Modulators in treatment of Endometriosis or prior to Endometrial Ablation, or
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused by too little insulin, resistance to insulin, or both.
 Diabetes Definition Diabetes is a chronic (lifelong) disease marked by high levels of sugar in the blood. Causes Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused
Diabetes Definition Diabetes is a chronic (lifelong) disease marked by high levels of sugar in the blood. Causes Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused
European Medicines Agency recommends restricting use of trimetazidine-containing medicines
 22 June 2012 EMA/CHMP/417861/2012 Press Office Press release European Medicines Agency recommends restricting use of trimetazidine-containing medicines Restricted indication for patients with stable angina
22 June 2012 EMA/CHMP/417861/2012 Press Office Press release European Medicines Agency recommends restricting use of trimetazidine-containing medicines Restricted indication for patients with stable angina
Breast Pathway Group FEC 60 (Fluorouracil / Epirubicin / Cyclophosphamide) in Early Breast Cancer in Elderly / Frail
 Breast Pathway Group FEC 60 (Fluorouracil / Epirubicin / Cyclophosphamide) in Early Breast Cancer in Elderly / Frail Indication: Neoadjuvant or adjuvant therapy for elderly and frail patients with breast
Breast Pathway Group FEC 60 (Fluorouracil / Epirubicin / Cyclophosphamide) in Early Breast Cancer in Elderly / Frail Indication: Neoadjuvant or adjuvant therapy for elderly and frail patients with breast
Rivaroxaban for the treatment of Deep Vein Thrombosis in patients unsuitable for vitamin K antagonists
 Rivaroxaban for the treatment of Deep Vein Thrombosis in patients unsuitable for vitamin K antagonists Traffic light classification- Amber 2 specialist initiation Information sheet for Primary Care Prescribers
Rivaroxaban for the treatment of Deep Vein Thrombosis in patients unsuitable for vitamin K antagonists Traffic light classification- Amber 2 specialist initiation Information sheet for Primary Care Prescribers
Clinical Policy Guideline
 Clinical Policy Guideline Policy Title: Bone Density Testing Policy No: B0215A.00 Effective Date: 01/01/15 Date Reviewed: 03/25/15 I. DEFINITION/BACKGROUND Bone density testing is used to estimate the
Clinical Policy Guideline Policy Title: Bone Density Testing Policy No: B0215A.00 Effective Date: 01/01/15 Date Reviewed: 03/25/15 I. DEFINITION/BACKGROUND Bone density testing is used to estimate the
Primary Care management of Overactive Bladder (OAB)
 DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) Primary Care management of Overactive Bladder (OAB) Prescribing Tips All medicines for OAB have similar dose-related efficacy. More than one agent (up
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) Primary Care management of Overactive Bladder (OAB) Prescribing Tips All medicines for OAB have similar dose-related efficacy. More than one agent (up
CHOP Chemotherapy Regimen for Lymphoma Information for Patients
 CHOP Chemotherapy Regimen for Lymphoma Information for Patients The Regimen Contains: C: Cytoxan (cyclophosphamide) H: Adriamycin (hydroxy doxorubicin) O: vincristine (Oncovin ) P: Prednisone How Is This
CHOP Chemotherapy Regimen for Lymphoma Information for Patients The Regimen Contains: C: Cytoxan (cyclophosphamide) H: Adriamycin (hydroxy doxorubicin) O: vincristine (Oncovin ) P: Prednisone How Is This
Osteoporosis. Condition. Osteoporosis. information and answers. to your questions about this condition. and answers to your questions
 Condition Osteoporosis Osteoporosis This This booklet leaflet provides provides information and answers to your questions information and answers about this condition. to your questions about this condition.
Condition Osteoporosis Osteoporosis This This booklet leaflet provides provides information and answers to your questions information and answers about this condition. to your questions about this condition.
