Suggested Solutions to Assignment 3 (Optional)
|
|
|
- Dwight Woods
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EC313 Taxation Instructor: Sharif F. Khan Department of Economics Wilfrid Laurier University Fall 2012 Suggested Solutions to Assignment 3 (Optional) Total Marks: 50 Read each part of the question very carefully. Show all the steps of your calculations to get full marks. 1. [10 Marks] The nation of Fishkasar has a tax rate of 10% on the first 20,000 walops (the national currency) of taxable income, then 25% on the next 30,000 walops, then 50% on all taxable income above 50,000 walops. Fishkasar provides a 4,000-walop exemption per family member. a. Jamil s family has three members and earns 50,000 walops per year. Calculate the family s marginal and average tax rates. The first step is to compute Jamil s family s taxable income: before exemptions, its income is 50,000. It gets a 4,000-walop exemption for each of the three family members, for a total of 12,000 in exemptions. Hence, taxable income is 50,000 12,000 = 38,000. Since this is between 20,000 and 50,000, the family faces a 25% marginal tax rate. To compute the average tax rate, first compute the total tax liability. The first 20,000 of taxable income is taxed at 10%. The next 18,000 is taxed at 25%. The total tax is thus.1 20, ,000 = 2, ,500 = 6,500. The average tax rate is thus 100% 6,500/50,000 = 13%. b. Boba s family has five members and earns 85,000 walops per year. Calculate the family s marginal and average tax rates. Boba s family s taxable income is 85, ,000 = 65,000. This is greater than 50,000, so the family is in the 50% marginal tax bracket. The family s total tax liability is.1 20, , ,000 = 17,000. Its average tax rate is thus 100% 17,000/85,000 = 20%. Page 1 of 6 Pages
2 c. Suppose that Fishkasar changed its tax code to a flat tax of 30% with an 8,000-walop per family member exemption. Would this change in the tax system make the system more progressive, more regressive, or neither? The flattening of the marginal rate schedule tends to make this change less progressive. Indeed, the flat 30% marginal rate structure is not progressive at all: any two families with positive taxable income will face the same marginal tax rate, regardless of their income. On the other hand, the increase in the per-family-member exemption tends to make the average rates more progressive. For simplicity, consider two single-member households with incomes of 8,000 and 12,000 walops, respectively. Under the old system, the first would have an average tax rate of 400/8,000 = 5% and the second would have an average tax rate of 800/12, %, so the tax is system was slightly progressive in this income range. Under the new system, the first would have no tax liability and hence a 0% average tax rate; the second would have an average tax rate of 30% 4000/12,000 = 10%. So the new system is more progressive in this income range. 2. Suppose that the U.S. personal income tax system became a flat tax system, in which all taxpayers paid a certain percentage of their incomes in tax, and in which there are no exemptions or deductions. In which way(s) could this flat tax be more regressive than the present U.S. system? In which ways could it be more progressive than the present system? [5 marks] On its face, this tax is more regressive than the current system because poorer taxpayers would pay exactly the same marginal tax rate as wealthier taxpayers. This system might be more progressive than it looks, however, given the elimination of exemptions and deductions. Wealthier taxpayers would lose their home interest deductions, tax-preferred savings mechanisms, and other benefits; wealthy entrepreneurs would lose their business expense deductions. The antiprogressive nature of tax deductions the fact that deductions are more valuable to high-bracket taxpayers would end. As a result, some wealthier taxpayers may be more harmed by this change than the less wealthy. 3. Why should casualty losses or large medical expenditures be fully tax-deductible only under certain circumstances? [5 marks] The justification for allowing deductions for casualty losses or large medical expenditures is based on the idea that people should pay taxes based on their ability to afford them. According to the Haig-Simons definition of income, only income that increases a person s ability to consume should be taxed. Catastrophic losses reduce a person s ability to consume and so, out of fairness, should reduce their tax liability. In some cases, however, expenditures on medical care might represent utility-increasing consumption. A person who obtains nonessential medical care, such as cosmetic procedures, has actually increased consumption. In some cases, casualty losses should not be fully deductible under the Haig- Simons measure either. Some casualty losses are not random but rather are part of the Page 2 of 6 Pages
3 expected cost of living in a particular location. Parts of Florida are prone to hurricane damage; parts of California are susceptible to earthquake damage. Those are known risks and so tend to reduce the price of property in those locations. Thus, property owners in these areas have already had their consumption increased because their housing costs are lower than the costs of identical housing in low-risk locations. Realization of the known risk simply offsets the increased ability to consume. Expenditures for medical care or casualty loss should be fully tax-deductible only when they are unexpected, not voluntary or controlled by the recipient, and do not increase consumption. 4. Professor Slither attended the Antarctic Economic Association meetings. She is able to fully deduct from her taxes the hotel expenses that she incurred, but can deduct only half of the meals expenses that she incurred. Why does the U.S. tax code make this distinction? Does this tax policy make sense, from a Haig-Simons perspective? [5 marks] Business deductions for meals were the target of a lot of negative publicity, resulting in a political response to limit them. The perception was that people were wining and dining at the taxpayers expense. A Haig-Simons perspective would consider business expenditures to be legitimate deductions from taxable income to the extent that they reduce the taxpayer s ability to voluntarily consume. Given this view, allowing full deductibility for hotel expenses but not meals makes some sense. A person does not reduce his or her housing expenses by staying in a hotel on a business trip. The mortgage or the rent at home must still be paid, so this business expense is in addition to the individual s base consumption of housing and thus reduces his or her ability to consume. In addition, for many people, staying in a fancy hotel on a business trip can be a treat, increasing utility. To the extent that the hotel provides greater utility for the traveler than staying home would, perhaps it should be included. This, of course, would be impossible to calculate. Meals, on the other hand, replace consumption that people would have had to provide if they were not on a trip. Because they would have had to eat regardless of the trip, this expense does not reduce other consumption dollar-for-dollar. Page 3 of 6 Pages
4 5. [5 marks] Your roommate and you had identical high school grade point averages and SAT scores. In many respects, one would expect that you would be equally successful. But because you chose economics as a major and your roommate chose geology, you will be paying a larger amount of tax in the future than your roommate will because your income will be higher. Is this attribute of the tax code vertically equitable? Is it horizontally equitable? Vertical equity requires that the person with the higher income pay the higher tax. If the economics major earns more than the geology major, then according to this principle the economics major should pay the higher tax. Horizontal equity requires that people with similar ability to pay should pay the same tax. In this case, measuring ability to pay solely by salary, they should pay different tax amounts. The difference in salaries, though, was generated solely by the choices the roommates made, presumably with information about the expected return to different majors. An argument could be made that any difference in their salaries is attributable to compensating wage differentials: the lower-wage major receives nonmonetary satisfaction from his or her job sufficient to offset the monetary wage difference. In other words, total compensation to the two majors (monetary plus nonmonetary) must, by definition, be equal. Any difference in monetary wage is made up in nonmonetary amenities. That argument supports the claim that this difference in tax liability is inequitable, as taxes are levied only against monetary wages. 6. [5 marks] The government of Utopia plans to offer a transportation tax credit in which families receive a share of their expenditures on transportation to and from work or school as a reduction in their tax bill. Utopia is considering two forms of this tax credit, one that is fully refundable and one in which the tax credit is limited to the amount of taxes the family pays. Which form of the tax credit is more progressive? Explain. It is more progressive to allow for a refundable tax credit than to limit the credit to taxes actually paid. Unless a tax credit is fully refundable, families whose incomes are so low that they do not owe any income taxes do not receive the credit. Critics of refundable tax credits might claim that it isn t a tax refund if you haven t paid taxes in the first place, but this is not quite correct. Everyone pays some taxes, whether in the form of sales taxes when they purchase goods or in the form of increased prices when taxes are passed through to the consumer. Thus, a fully refundable tax credit sent to families who have not paid income taxes will offset other taxes they have paid. Page 4 of 6 Pages
5 7. Suppose that the government adopts a Haig-Simons comprehensive income definition. Will this make employers more likely or less likely to offer employerprovided pension plans or health insurance coverage? Why? Adoption of the Haig-Simons definition would require inclusion of employerprovided benefits in taxable income because these benefits increase employees ability to consume. Taxation of these benefits would make them less attractive to workers, so employers would not be able to substitute benefits for wages as easily as they do now. As a result, employers would be less likely to offer the benefits. On the other hand, even if the benefits were taxed, employers may be able to provide them more efficiently and thus, more cheaply than employees could obtain them in private markets. If it were cheaper to obtain group health insurance through an employer than it would be to purchase private insurance in the market, even when the benefit is taxed, then workers might remain willing to trade off higher wages for more benefits. And the total cost of hiring a worker may be less for the firm offering the benefits, in which case some employers would still provide the benefits. 8. [5 marks] Oregon has an income tax but no state sales tax, while Washington has no state income tax but does have a state sales tax. Oregon residents can deduct the state taxes they pay (the income tax payments) from their federal income taxes, while Washington residents cannot deduct the state taxes they pay (the sales tax payments). What are the equity implications of this difference? Consider two people with the same earnings and spending patterns, one of whom lives in Washington and one of whom lives in Oregon. The income taxes paid in Oregon are deductible from federal income taxes, but the sales taxes paid in Washington are not. Oregonians will therefore pay less federal tax, all else equal, than will Washingtonians. This is not horizontally equitable. Partly offsetting this horizontal equity concern is the fact that people choose whether to live in Oregon or Washington, so the equity issues are less pressing than if taxes were inequitable based on some factor over which people have no choice. Furthermore, markets adjust for these differences. People know or could know this essential difference between the two states and the implications for federal tax deductibility when choosing where to live. Housing prices and other cost-of-living components may have been adjusted to account for this apparent inequity already. For example, if the absence of sales tax has made Oregon a more desirable state of residence, then that difference should already be reflected in higher housing prices in Oregon. If this is the case, then being able to deduct income taxes in Oregon may simply offset the difference in the cost of living there. Page 5 of 6 Pages
6 9. [5 marks] The largest tax break for most Americans is the mortgage interest tax deduction, which allows home owners to deduct from their taxable income the amount of money they pay in interest to finance their homes. This tax break is intended to encourage home ownership. Compare this tax deduction to a uniform tax credit for home ownership on equity and efficiency grounds. The more expensive the home, the larger the mortgage; the larger the mortgage, the bigger the deduction. Compounding this effect is the tendency for wealthier people to live in larger, more expensive homes and face a higher marginal tax rate. Therefore, both the size and the marginal value of the mortgage deduction are higher for wealthier taxpayers. This is in direct contradiction to vertical equity. Deductions favor high tax bracket taxpayers because they reduce the base on which taxes are calculated. Sometimes a deduction can drop the base to a lower tax bracket. Even if it doesn t reduce the taxpayer s marginal rate, it reduces the number of dollars to which that taxpayer s highest bracket applies. In contrast, tax credits benefit all taxpayers equally by reducing the taxpayers tax liability dollar for dollar. As a result, tax credits do not disproportionately benefit high tax bracket payers. In addition, making the credit uniform avoids the problem of providing the largest subsidies to those living in the fanciest homes. On equity grounds, the tax credit appears to be preferred. Offsetting this benefit is the fact that housing prices vary significantly by geographic region. A credit that is generous in some parts of the country would be very small relative to housing prices in other areas. The tax credit would seem to be better on efficiency grounds as well. The mortgage deduction as it is now implemented distorts consumption behavior in favor of more expensive homes. A uniform credit would continue to encourage home ownership at some basic level (which may be justified based on the positive externalities involved) but would not subsidize McMansions. Page 6 of 6 Pages
National Small Business Network
 National Small Business Network WRITTEN STATEMENT FOR THE RECORD US SENATE COMMITTEE ON FINANCE U.S. HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES COMMITTEE ON WAYS AND MEANS JOINT HEARING ON TAX REFORM AND THE TAX TREATMENT
National Small Business Network WRITTEN STATEMENT FOR THE RECORD US SENATE COMMITTEE ON FINANCE U.S. HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES COMMITTEE ON WAYS AND MEANS JOINT HEARING ON TAX REFORM AND THE TAX TREATMENT
Tax Subsidies for Health Insurance An Issue Brief
 Tax Subsidies for Health Insurance An Issue Brief Prepared by the Kaiser Family Foundation July 2008 Tax Subsidies for Health Insurance Most workers pay both federal and state taxes for wages paid to them
Tax Subsidies for Health Insurance An Issue Brief Prepared by the Kaiser Family Foundation July 2008 Tax Subsidies for Health Insurance Most workers pay both federal and state taxes for wages paid to them
Financial Planning. Introduction. Learning Objectives
 Financial Planning Introduction Financial Planning Learning Objectives Lesson 1 Budgeting: How to Live on Your Own and Not Move Home in a Week Prepare a budget and determine disposable income. Identify
Financial Planning Introduction Financial Planning Learning Objectives Lesson 1 Budgeting: How to Live on Your Own and Not Move Home in a Week Prepare a budget and determine disposable income. Identify
Things could easily be improved without needing a rewrite of the whole tax system. Some of the major issues with income tax are
 Simple Tax is Better Tax Submission to Re:think Better tax system, better Australia By Lorraine May 2015 Executive Summary The current tax system is needlessly complex. To some degree tax needs to be complex
Simple Tax is Better Tax Submission to Re:think Better tax system, better Australia By Lorraine May 2015 Executive Summary The current tax system is needlessly complex. To some degree tax needs to be complex
HANDOUTS Property Taxation Review Committee
 HANDOUTS Property Taxation Review Committee Legislative Services Agency September 1, 2004 Criteria For Good Proposals for Property Tax Reform Dr. Thomas Pogue, University of Iowa DISCLAIMER The Iowa General
HANDOUTS Property Taxation Review Committee Legislative Services Agency September 1, 2004 Criteria For Good Proposals for Property Tax Reform Dr. Thomas Pogue, University of Iowa DISCLAIMER The Iowa General
NAR Frequently Asked Questions Health Insurance Reform
 NEW MEDICARE TAX ON UNEARNED NET INVESTMENT INCOME Q-1: Who will be subject to the new taxes imposed in the health legislation? A: A new 3.8% tax will apply to the unearned income of High Income taxpayers.
NEW MEDICARE TAX ON UNEARNED NET INVESTMENT INCOME Q-1: Who will be subject to the new taxes imposed in the health legislation? A: A new 3.8% tax will apply to the unearned income of High Income taxpayers.
1 The Terrace, PO Box 3724, Wellington 6140 Tel: (04) 472-2733 Email: [email protected]
 1 The Terrace, PO Box 3724, Wellington 6140 Tel: (04) 472-2733 Email: [email protected] Document: Aligning the Tax Rates on PIEs and Other Investments Author: [Inland Revenue] Date:
1 The Terrace, PO Box 3724, Wellington 6140 Tel: (04) 472-2733 Email: [email protected] Document: Aligning the Tax Rates on PIEs and Other Investments Author: [Inland Revenue] Date:
The Tax Benefits and Revenue Costs of Tax Deferral
 The Tax Benefits and Revenue Costs of Tax Deferral Copyright 2012 by the Investment Company Institute. All rights reserved. Suggested citation: Brady, Peter. 2012. The Tax Benefits and Revenue Costs of
The Tax Benefits and Revenue Costs of Tax Deferral Copyright 2012 by the Investment Company Institute. All rights reserved. Suggested citation: Brady, Peter. 2012. The Tax Benefits and Revenue Costs of
The Treatment of Tax Credits in the National Accounts
 The Treatment of Tax Credits in the National Accounts Summary The recording of tax credits in the system of national accounts is an issue of increasing importance. There is no guidance in the existing
The Treatment of Tax Credits in the National Accounts Summary The recording of tax credits in the system of national accounts is an issue of increasing importance. There is no guidance in the existing
Retirement incomes. Aisur. Submission to the Tax White Paper Task Force. July 2015
 Retirement incomes Submission to the Tax White Paper Task Force July 2015 Executive summary 2015 1 Background The Australian retirement income system comprises three pillars: a publicly funded means tested
Retirement incomes Submission to the Tax White Paper Task Force July 2015 Executive summary 2015 1 Background The Australian retirement income system comprises three pillars: a publicly funded means tested
Domestic Relocation U.S. Based Early Experience Program
 Domestic Relocation U.S. Based Early Experience Program Updated: October 1, 2010 1. ELIGIBILITY 2. MISCELLANEOUS LUMP SUM ALLOWANCE 3. HOMEFINDING TRIPS TO THE NEW LOCATION 4. TEMPORARY LIVING ARRANGEMENTS
Domestic Relocation U.S. Based Early Experience Program Updated: October 1, 2010 1. ELIGIBILITY 2. MISCELLANEOUS LUMP SUM ALLOWANCE 3. HOMEFINDING TRIPS TO THE NEW LOCATION 4. TEMPORARY LIVING ARRANGEMENTS
A 5.5% solidarity surcharge is imposed on the income tax liability of all taxpayers.
 Worldwide personal tax guide 2013 2014 Germany Local information Tax Authority Website Tax Year Tax Return due date 31 May 2013 Is joint filing possible Are tax return extensions possible 2013 income tax
Worldwide personal tax guide 2013 2014 Germany Local information Tax Authority Website Tax Year Tax Return due date 31 May 2013 Is joint filing possible Are tax return extensions possible 2013 income tax
Lesson Description. Grade Level. Concepts. Objectives. Content Standards
 Lesson Description The lead article in the spring 2010 issue of Inside the Vault discusses the redistribution of wealth through taxation. In this lesson, students use different household scenarios to examine
Lesson Description The lead article in the spring 2010 issue of Inside the Vault discusses the redistribution of wealth through taxation. In this lesson, students use different household scenarios to examine
Chapter 4: Key Conclusions from the Evaluation of the Current Washington Tax Structure
 Chapter 4: Key Conclusions from the Evaluation of the Current Washington Tax Structure Introduction This chapter presents the key conclusions and the Committee s view based on the evaluation of the current
Chapter 4: Key Conclusions from the Evaluation of the Current Washington Tax Structure Introduction This chapter presents the key conclusions and the Committee s view based on the evaluation of the current
Eliminating Double Taxation through Corporate Integration
 FISCAL FACT Feb. 2015 No. 453 Eliminating Double Taxation through Corporate Integration By Kyle Pomerleau Economist Key Findings The United States tax code places a double-tax on corporate income with
FISCAL FACT Feb. 2015 No. 453 Eliminating Double Taxation through Corporate Integration By Kyle Pomerleau Economist Key Findings The United States tax code places a double-tax on corporate income with
Notes on indifference curve analysis of the choice between leisure and labor, and the deadweight loss of taxation. Jon Bakija
 Notes on indifference curve analysis of the choice between leisure and labor, and the deadweight loss of taxation Jon Bakija This example shows how to use a budget constraint and indifference curve diagram
Notes on indifference curve analysis of the choice between leisure and labor, and the deadweight loss of taxation Jon Bakija This example shows how to use a budget constraint and indifference curve diagram
business owner issues and depreciation deductions
 business owner issues and depreciation deductions Individuals who are owners of a business, whether as sole proprietors or through a partnership, limited liability company or S corporation, have specific
business owner issues and depreciation deductions Individuals who are owners of a business, whether as sole proprietors or through a partnership, limited liability company or S corporation, have specific
READING 11: TAXES AND PRIVATE WEALTH MANAGEMENT IN A GLOBAL CONTEXT
 READING 11: TAXES AND PRIVATE WEALTH MANAGEMENT IN A GLOBAL CONTEXT Introduction Taxes have a significant impact on net performance and affect an adviser s understanding of risk for the taxable investor.
READING 11: TAXES AND PRIVATE WEALTH MANAGEMENT IN A GLOBAL CONTEXT Introduction Taxes have a significant impact on net performance and affect an adviser s understanding of risk for the taxable investor.
Medical Spending Accounts and the Loss of Tax Benefits
 Flexible Spending Accounts POLICY GUIDE Flexible spending accounts are arrangements that allow employees to pay for qualified health care or dependent care expenses on a pre-tax basis. Employers may offer
Flexible Spending Accounts POLICY GUIDE Flexible spending accounts are arrangements that allow employees to pay for qualified health care or dependent care expenses on a pre-tax basis. Employers may offer
April 8,2005 JEFFREY KUPFER, EXECUTIVE DIRECTOR PRESIDENT S ADVISORY PANEL ON FEDERAL TAX REFORM
 DEPARTMENT OF THE TREASURY WASHINGTON, D.C. 20220 April 8,2005 MEMORANDUM FOR FROM SUBJECT JEFFREY KUPFER, EXECUTIVE DIRECTOR PRESIDENT S ADVISORY PANEL ON FEDERAL TAX REFORM ROBERT CAmoLi& DEPUTY ASSISTANT
DEPARTMENT OF THE TREASURY WASHINGTON, D.C. 20220 April 8,2005 MEMORANDUM FOR FROM SUBJECT JEFFREY KUPFER, EXECUTIVE DIRECTOR PRESIDENT S ADVISORY PANEL ON FEDERAL TAX REFORM ROBERT CAmoLi& DEPUTY ASSISTANT
Chapter 2 THE NATURE OF THE VALUE-ADDED
 - 5 - Chapter 2 THE NATURE OF THE VALUE-ADDED TAX I. Introduction A value-added tax is a multistage sales tax that is collected at each stage or point in the production and distribution process. ~n a typical
- 5 - Chapter 2 THE NATURE OF THE VALUE-ADDED TAX I. Introduction A value-added tax is a multistage sales tax that is collected at each stage or point in the production and distribution process. ~n a typical
How To Calculate Tax In The United States
 TAXATION OF U.S. EXPATRIATES gtn.com C O N T E N T S 1. Introduction 1 2. Case Study Facts 2 3. U.S. Income Taxation Overview 4 Federal Income Tax Calculation 5 Foreign Earned Income and Housing Exclusions
TAXATION OF U.S. EXPATRIATES gtn.com C O N T E N T S 1. Introduction 1 2. Case Study Facts 2 3. U.S. Income Taxation Overview 4 Federal Income Tax Calculation 5 Foreign Earned Income and Housing Exclusions
Income in the Netherlands is categorised into boxes. The above table relates to Box 1 income.
 Worldwide personal tax guide 2013 2014 The Netherlands Local information Tax Authority Website Tax Year Tax Return due date Is joint filing possible Are tax return extensions possible Belastingdienst www.belastingdienst.nl
Worldwide personal tax guide 2013 2014 The Netherlands Local information Tax Authority Website Tax Year Tax Return due date Is joint filing possible Are tax return extensions possible Belastingdienst www.belastingdienst.nl
How To Know If A Health Insurance Tax Is Progressive
 Citizens for Tax Justice December 11, 2009 Would the Senate Democrats proposed excise tax on highcost employer-paid health insurance benefits be progressive? Summary Senate Democrats have proposed a new,
Citizens for Tax Justice December 11, 2009 Would the Senate Democrats proposed excise tax on highcost employer-paid health insurance benefits be progressive? Summary Senate Democrats have proposed a new,
Deciding How Much Financial Assistance to Use to Lower Your Monthly Premiums
 What You Need to Know about Health Insurance Getting Financial Assistance Deciding How Much Financial Assistance About this fact sheet You decide how much of your financial assistance the marketplace will
What You Need to Know about Health Insurance Getting Financial Assistance Deciding How Much Financial Assistance About this fact sheet You decide how much of your financial assistance the marketplace will
Income tax for individuals is computed on a monthly basis by applying the above progressive tax rates to employment income.
 Worldwide personal tax guide 2013 2014 China Local information Tax Authority Website Tax Year Tax Return due date Is joint filing possible Are tax return extensions possible State Administration of Taxation
Worldwide personal tax guide 2013 2014 China Local information Tax Authority Website Tax Year Tax Return due date Is joint filing possible Are tax return extensions possible State Administration of Taxation
INTERACTION OF AUTOMATIC IRAS AND THE RETIREMENT SAVINGS CONTRIBUTIONS CREDIT (SAVER S CREDIT)
 INTERACTION OF AUTOMATIC IRAS AND THE RETIREMENT SAVINGS CONTRIBUTIONS CREDIT (SAVER S CREDIT) A Report Prepared for AARP By: Optimal Benefit Strategies, LLC Judy Xanthopoulos, PhD Mary M. Schmitt, Esq.
INTERACTION OF AUTOMATIC IRAS AND THE RETIREMENT SAVINGS CONTRIBUTIONS CREDIT (SAVER S CREDIT) A Report Prepared for AARP By: Optimal Benefit Strategies, LLC Judy Xanthopoulos, PhD Mary M. Schmitt, Esq.
Accounts payable Money which you owe to an individual or business for goods or services that have been received but not yet paid for.
 A Account A record of a business transaction. A contract arrangement, written or unwritten, to purchase and take delivery with payment to be made later as arranged. Accounts payable Money which you owe
A Account A record of a business transaction. A contract arrangement, written or unwritten, to purchase and take delivery with payment to be made later as arranged. Accounts payable Money which you owe
Tax: Are we paying our fair share?
 Australian Council of Social Service Tax: Are we paying our fair share? The effects of the current tax mix on contributions to the tax system ACOSS Tax Talk No 1 January 2015 1 Who we are ACOSS is the
Australian Council of Social Service Tax: Are we paying our fair share? The effects of the current tax mix on contributions to the tax system ACOSS Tax Talk No 1 January 2015 1 Who we are ACOSS is the
Health Reform in a Nutshell: What Small Businesses Need to Know Now.
 Health Reform in a Nutshell: What Small Businesses Need to Know Now. With the passage of the most significant reform of America s modern-day health care system, many small business owners and human resources
Health Reform in a Nutshell: What Small Businesses Need to Know Now. With the passage of the most significant reform of America s modern-day health care system, many small business owners and human resources
Executive Summary. 204 N. First St., Suite C PO Box 7 Silverton, OR 97381 www.ocpp.org 503-873-1201 fax 503-873-1947
 Executive Summary 204 N. First St., Suite C PO Box 7 Silverton, OR 97381 www.ocpp.org 503-873-1201 fax 503-873-1947 On Whose Backs? Tax Distribution, Income Inequality, and Plans for Raising Revenue By
Executive Summary 204 N. First St., Suite C PO Box 7 Silverton, OR 97381 www.ocpp.org 503-873-1201 fax 503-873-1947 On Whose Backs? Tax Distribution, Income Inequality, and Plans for Raising Revenue By
Econ 101: Principles of Microeconomics
 Econ 101: Principles of Microeconomics Chapter 7: Taxes Fall 2010 Herriges (ISU) Ch. 7: Taxes Fall 2010 1 / 25 Outline 1 The Excise Tax 2 The Benefits and Costs of Taxation 3 Tax Fairness versus Tax Efficiency
Econ 101: Principles of Microeconomics Chapter 7: Taxes Fall 2010 Herriges (ISU) Ch. 7: Taxes Fall 2010 1 / 25 Outline 1 The Excise Tax 2 The Benefits and Costs of Taxation 3 Tax Fairness versus Tax Efficiency
A Comparison of Income and Consumption Taxes
 A Comparison of Income and Consumption Taxes A Presentation to The President's Advisory Panel on Federal Tax Reform by William G. Gale Brookings Institution and Tax Policy Center February 16, 2005 Elements
A Comparison of Income and Consumption Taxes A Presentation to The President's Advisory Panel on Federal Tax Reform by William G. Gale Brookings Institution and Tax Policy Center February 16, 2005 Elements
Tax Planning Opportunities Involving Professional Corporations
 Tax Planning Opportunities Involving Professional Corporations A Discussion Paper Prepared by: Alan Koop, CA Prepared for: The Saskatchewan Provincial Court Judges Association Table of Contents Executive
Tax Planning Opportunities Involving Professional Corporations A Discussion Paper Prepared by: Alan Koop, CA Prepared for: The Saskatchewan Provincial Court Judges Association Table of Contents Executive
Account a service provided by a bank allowing a customer s money to be handled and tracks money coming in and going out of the account.
 Account a service provided by a bank allowing a customer s money to be handled and tracks money coming in and going out of the account. Account fee the amount charged by a financial institution for the
Account a service provided by a bank allowing a customer s money to be handled and tracks money coming in and going out of the account. Account fee the amount charged by a financial institution for the
Mandatory Private Health Insurance as Supplementary Financing
 Chapter 12 SUPPLEMENTARY FINANCING OPTION (5) MANDATORY PRIVATE HEALTH INSURANCE Mandatory Private Health Insurance as Supplementary Financing 12.1 Mandatory private health insurance is where private health
Chapter 12 SUPPLEMENTARY FINANCING OPTION (5) MANDATORY PRIVATE HEALTH INSURANCE Mandatory Private Health Insurance as Supplementary Financing 12.1 Mandatory private health insurance is where private health
Part A. Excluded Sources of Income--Fringe Benefits
 Current Law CHAPTER 3 FAIR AND NEUTRAL TAXATION Part A. Excluded Sources of Income--Fringe Benefits An employee is generally required to include in gross income all compensation received during the year
Current Law CHAPTER 3 FAIR AND NEUTRAL TAXATION Part A. Excluded Sources of Income--Fringe Benefits An employee is generally required to include in gross income all compensation received during the year
Tax Relief in 2001 through 2011
 in 2001 through 2011 Department of the Treasury May 2008 in 2001 through 2011 The tax relief enacted during the President s term in office, principally in the Economic Growth and Relief Reconciliation
in 2001 through 2011 Department of the Treasury May 2008 in 2001 through 2011 The tax relief enacted during the President s term in office, principally in the Economic Growth and Relief Reconciliation
SEMA MEMBERS WANT TO KNOW
 SEMA MEMBERS WANT TO KNOW WHEN DID OBAMACARE TAKE EFFECT? It is being phased-in over 10 years beginning in 2010, with new requirements and benefits being added each year. The most consequential change
SEMA MEMBERS WANT TO KNOW WHEN DID OBAMACARE TAKE EFFECT? It is being phased-in over 10 years beginning in 2010, with new requirements and benefits being added each year. The most consequential change
PREVIEW. California Tax Facts. An Overview of the Golden State s Tax Structure
 PREVIEW California Tax Facts An Overview of the Golden State s Tax Structure 1 PREVIEW California Tax Facts An Overview of the Golden State s Tax Structure 3 ABOUT THE CALIFORNIA TAX FOUNDATION The California
PREVIEW California Tax Facts An Overview of the Golden State s Tax Structure 1 PREVIEW California Tax Facts An Overview of the Golden State s Tax Structure 3 ABOUT THE CALIFORNIA TAX FOUNDATION The California
Under current tax law, health insurance premiums are largely taxexempt
 The Cost Of Tax-Exempt Health Benefits In 2004 Tax policies for health insurance will cost the federal government $188.5 billion in lost revenue in 2004, and most of the benefit goes to those with the
The Cost Of Tax-Exempt Health Benefits In 2004 Tax policies for health insurance will cost the federal government $188.5 billion in lost revenue in 2004, and most of the benefit goes to those with the
tax planning strategies
 tax planning strategies In addition to saving income taxes for the current and future years, effective tax planning can reduce eventual estate taxes, maximize the amount of funds you will have available
tax planning strategies In addition to saving income taxes for the current and future years, effective tax planning can reduce eventual estate taxes, maximize the amount of funds you will have available
Living and Working in Austria. 1 l Income tax in Austria 2 l Social Security in Austria 3 l Residence And Work Permits in Austria
 Tax l Accounting l Audit l Advisory Living and Working in Austria 1 l Income tax in Austria 2 l Social Security in Austria 3 l Residence And Work Permits in Austria We are pleased to present you in our
Tax l Accounting l Audit l Advisory Living and Working in Austria 1 l Income tax in Austria 2 l Social Security in Austria 3 l Residence And Work Permits in Austria We are pleased to present you in our
How do the 2016 Presidential Tax Plans Compare So Far?
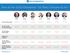 How do the 2016 Presidential Tax Plans Compare So Far? 10-Year GDP Growth 10.0% 16.0% -1.0% 13.9% 15.0% -9.5% 11.5% 10-Year Capital Investment Growth 28.8% 46.6% -2.8% 43.9% 48.9% -18.6% 29% 10-Year Wage
How do the 2016 Presidential Tax Plans Compare So Far? 10-Year GDP Growth 10.0% 16.0% -1.0% 13.9% 15.0% -9.5% 11.5% 10-Year Capital Investment Growth 28.8% 46.6% -2.8% 43.9% 48.9% -18.6% 29% 10-Year Wage
Since 1960's, U.S. personal savings rate (fraction of income saved) averaged 7%, lower than 15% OECD average. Why? Why do we care?
 Taxation and Personal Saving, G 22 Since 1960's, U.S. personal savings rate (fraction of income saved) averaged 7%, lower than 15% OECD average. Why? Why do we care? Efficiency issues 1. Negative consumption
Taxation and Personal Saving, G 22 Since 1960's, U.S. personal savings rate (fraction of income saved) averaged 7%, lower than 15% OECD average. Why? Why do we care? Efficiency issues 1. Negative consumption
Tax Subsidies for Private Health Insurance
 Tax Subsidies for Private Health Insurance Matthew Rae, Gary Claxton, Nirmita Panchal, Larry Levitt The federal and state tax systems provide significant financial benefits for people with private health
Tax Subsidies for Private Health Insurance Matthew Rae, Gary Claxton, Nirmita Panchal, Larry Levitt The federal and state tax systems provide significant financial benefits for people with private health
Hurley, Chapter 7 (see also review in chapter 3)
 Hurley, Chapter 7 (see also review in chapter 3) Chris Auld Economics 318 February 20, 2014 Why is health care different? Is health care different from other commodities? Yes, but not because it s really
Hurley, Chapter 7 (see also review in chapter 3) Chris Auld Economics 318 February 20, 2014 Why is health care different? Is health care different from other commodities? Yes, but not because it s really
SNURE LAW OFFICE, PSC
 SNURE LAW OFFICE, PSC A Professional Services Corporation Clark B. Snure Retired Of counsel Thomas G. Burke Joseph F. Quinn Brian K. Snure [email protected] MEMORANDUM To: Washington Fire Protection Districts
SNURE LAW OFFICE, PSC A Professional Services Corporation Clark B. Snure Retired Of counsel Thomas G. Burke Joseph F. Quinn Brian K. Snure [email protected] MEMORANDUM To: Washington Fire Protection Districts
CALIFORNIA WITHHOLDING SCHEDULES FOR 2015
 California provides two methods for determining the amount of wages and salaries to be withheld for state personal income tax: METHOD A - WAGE BRACKET TABLE METHOD (Limited to wages/salaries less than
California provides two methods for determining the amount of wages and salaries to be withheld for state personal income tax: METHOD A - WAGE BRACKET TABLE METHOD (Limited to wages/salaries less than
A super waste of money
 A super waste of money Redesigning super tax concessions April 2015 ISSN 1836-9014 Matt Grudnoff Policy Brief About TAI The Australia Institute is an independent public policy think tank based in Canberra.
A super waste of money Redesigning super tax concessions April 2015 ISSN 1836-9014 Matt Grudnoff Policy Brief About TAI The Australia Institute is an independent public policy think tank based in Canberra.
Farmer Savings Accounts
 Farmer Savings Accounts Mark A. Edelman, Iowa State University James D. Monke, Economic Research Service, USDA Ron Durst, Economic Research Service, USDA Introduction Various incentives can be used to
Farmer Savings Accounts Mark A. Edelman, Iowa State University James D. Monke, Economic Research Service, USDA Ron Durst, Economic Research Service, USDA Introduction Various incentives can be used to
The Opportunity Cost of Study Abroad Programs: An Economics-Based Analysis
 Frontiers: The Interdisciplinary Journal of Study Abroad The Opportunity Cost of Study Abroad Programs: An Economics-Based Analysis George Heitmann Muhlenberg College I. Introduction Most colleges and
Frontiers: The Interdisciplinary Journal of Study Abroad The Opportunity Cost of Study Abroad Programs: An Economics-Based Analysis George Heitmann Muhlenberg College I. Introduction Most colleges and
Impact of the Health Insurance Annual Fee Tax
 Impact of the Health Insurance Annual Fee Tax Robert A. Book, Ph.D. February 20, 2014 Executive Summary The Affordable Care Act's "annual fee on health insurance is a unique tax levied on health insurance
Impact of the Health Insurance Annual Fee Tax Robert A. Book, Ph.D. February 20, 2014 Executive Summary The Affordable Care Act's "annual fee on health insurance is a unique tax levied on health insurance
Charitable giving techniques
 Charitable giving techniques Helping achieve your charitable and estate-planning goals Trust tip A trust can be thought of as having two parts an income interest and a remainder interest. The income interest
Charitable giving techniques Helping achieve your charitable and estate-planning goals Trust tip A trust can be thought of as having two parts an income interest and a remainder interest. The income interest
THE GRADUATED PERSONAL INCOME TAX ASSESSMENT: FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
 LEGISLATIVE REVENUE OFFICE State Capitol Building 900 Court St. NE, Room H-197 Salem, Oregon 97301 Research Brief (503) 986-1266 FAX (503) 986-1770 http://www.leg.state.or.us/comm/lro/home.htm Number 3-03
LEGISLATIVE REVENUE OFFICE State Capitol Building 900 Court St. NE, Room H-197 Salem, Oregon 97301 Research Brief (503) 986-1266 FAX (503) 986-1770 http://www.leg.state.or.us/comm/lro/home.htm Number 3-03
25*$1,6$7,21)25(&2120,&&223(5$7,21$1''(9(/230(17
 25*$1,6$7,21)25(&2120,&&223(5$7,21$1''(9(/230(17 7D[3ROLF\5HIRUPVLQ,WDO\ &(175()257$;32/,&
25*$1,6$7,21)25(&2120,&&223(5$7,21$1''(9(/230(17 7D[3ROLF\5HIRUPVLQ,WDO\ &(175()257$;32/,&
Ohio State University Extension, 2120 Fyffe Road, Columbus, OH 43210
 FACT SHEET Ohio State University Extension, 2120 Fyffe Road, Columbus, OH 43210 Shale Oil and Gas Development Fact Sheet Series Income Tax Management of Oil and Gas Lease Payments Introduction Chris Zoller
FACT SHEET Ohio State University Extension, 2120 Fyffe Road, Columbus, OH 43210 Shale Oil and Gas Development Fact Sheet Series Income Tax Management of Oil and Gas Lease Payments Introduction Chris Zoller
INCOME TAXES. Government (public) spending, federal income taxes, state income taxes, marginal vs. average tax rates, tax planning
 Grades 9-12 Lesson 9 INCOME TAXES Key concepts: Government (public) spending, federal income taxes, state income taxes, marginal vs. average tax rates, tax planning Summary: This lesson introduces students
Grades 9-12 Lesson 9 INCOME TAXES Key concepts: Government (public) spending, federal income taxes, state income taxes, marginal vs. average tax rates, tax planning Summary: This lesson introduces students
Staying Healthy, Wealthy & Wise: The Aftermath of the Fiscal Cliff. Heather Kovalsky, CPA
 Staying Healthy, Wealthy & Wise: The Aftermath of the Fiscal Cliff Heather Kovalsky, CPA 2013 Tax Changes The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act American Tax Relief Act of 2012 The Patient Protection
Staying Healthy, Wealthy & Wise: The Aftermath of the Fiscal Cliff Heather Kovalsky, CPA 2013 Tax Changes The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act American Tax Relief Act of 2012 The Patient Protection
Section 79 Permanent Benefit Plans. Producer Guide. Your future. Made easier. LIFE INSURANCE
 Section 79 Permanent Benefit Plans Producer Guide These materials are not intended to and cannot be used to avoid tax penalties and they were prepared to support the promotion or marketing of the matters
Section 79 Permanent Benefit Plans Producer Guide These materials are not intended to and cannot be used to avoid tax penalties and they were prepared to support the promotion or marketing of the matters
Paying your way. Tax issues for the self employed
 Paying your way Tax issues for the self employed May 2012 Tax issues for the self employed This is a brief overview of tax issues that affect the self employed. Understanding your tax responsibilities
Paying your way Tax issues for the self employed May 2012 Tax issues for the self employed This is a brief overview of tax issues that affect the self employed. Understanding your tax responsibilities
TAX CONSIDERATIONS BUSINESSES. Marty Verdick
 TAX CONSIDERATIONS FOR SMALL BUSINESSES Marty Verdick RSM McGladrey, Inc. Overview of Topics General federal tax issues Federal tax incentives Entity selection tax issues State tax issues Sales & use tax
TAX CONSIDERATIONS FOR SMALL BUSINESSES Marty Verdick RSM McGladrey, Inc. Overview of Topics General federal tax issues Federal tax incentives Entity selection tax issues State tax issues Sales & use tax
President Bush s Health Care Tax Deduction Proposal: Coverage, Cost and Distributional Impacts. John Sheils and Randy Haught
 www.lewin.com President Bush s Health Care Tax Deduction Proposal: Coverage, Cost and Distributional Impacts John Sheils and Randy Haught President Bush proposes to replace the existing tax exemption for
www.lewin.com President Bush s Health Care Tax Deduction Proposal: Coverage, Cost and Distributional Impacts John Sheils and Randy Haught President Bush proposes to replace the existing tax exemption for
Tax Benefits for Parents of Children At Sylvan
 Tax Benefits for Parents of Children At Sylvan If you have a child with a learning delay or is enrolled in partime tutoring services or a preschool or school age child, you may qualify for valuable tax
Tax Benefits for Parents of Children At Sylvan If you have a child with a learning delay or is enrolled in partime tutoring services or a preschool or school age child, you may qualify for valuable tax
GIIRS Emerging Market Assessment Resource Guide: Worker Benefits
 GIIRS Emerging Market Assessment Resource Guide: What s in this Guide? I. What are Employee Benefits? II. Types of Employee Benefits III. Importance of Benefits IV. Implementation V. Additional Resources
GIIRS Emerging Market Assessment Resource Guide: What s in this Guide? I. What are Employee Benefits? II. Types of Employee Benefits III. Importance of Benefits IV. Implementation V. Additional Resources
Details and Analysis of Dr. Ben Carson s Tax Plan
 FISCAL FACT Jan. 2016 No. 493 Details and Analysis of Dr. Ben Carson s Tax Plan By Kyle Pomerleau Director of Federal Projects Key Findings Dr. Ben Carson s tax plan would replace the federal income tax
FISCAL FACT Jan. 2016 No. 493 Details and Analysis of Dr. Ben Carson s Tax Plan By Kyle Pomerleau Director of Federal Projects Key Findings Dr. Ben Carson s tax plan would replace the federal income tax
THE FEDERAL LOW-INCOME HOUSING TAX CREDIT AND HISTORIC REHABILITATION TAX CREDIT
 THE FEDERAL LOW-INCOME HOUSING TAX CREDIT AND HISTORIC REHABILITATION TAX CREDIT This outline provides an overview of the federal low-income housing tax credit and historic rehabilitation tax credit. I.
THE FEDERAL LOW-INCOME HOUSING TAX CREDIT AND HISTORIC REHABILITATION TAX CREDIT This outline provides an overview of the federal low-income housing tax credit and historic rehabilitation tax credit. I.
United States General Accounting Office. Testimony Before the Committee on Finance, United States Senate
 GAO United States General Accounting Office Testimony Before the Committee on Finance, United States Senate For Release on Delivery Expected at 10:00 a.m. EST on Thursday March 8, 2001 ALTERNATIVE MINIMUM
GAO United States General Accounting Office Testimony Before the Committee on Finance, United States Senate For Release on Delivery Expected at 10:00 a.m. EST on Thursday March 8, 2001 ALTERNATIVE MINIMUM
Worldwide personal tax guide 2013 2014. Japan. Local information. 2013 National Income Tax Rates Taxable Income Band National Income Tax Rates
 Worldwide personal tax guide 2013 2014 Japan Local information Tax Authority Ministry of Finance Website www.mof.go.jp Tax Year 1 January to 31 December Tax Return due date 15 March Is joint filing possible
Worldwide personal tax guide 2013 2014 Japan Local information Tax Authority Ministry of Finance Website www.mof.go.jp Tax Year 1 January to 31 December Tax Return due date 15 March Is joint filing possible
