Preventing Type 2 Diabetes and Its Complications
|
|
|
- Aubrie Malone
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
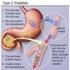
1 What is Diabetes? Preventing Type 2 Diabetes and Its Complications Diabetes is a chronic medical condition resulting in high blood sugar (glucose) levels in the blood. High blood sugar over years may cause damage to nearly every organ in the body. Blood sugar is controlled by insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas. Insulin allows cells to absorb the sugar from your blood. Diabetes is not contagious, but it does run in families. Different types of diabetes exist. The most common type of diabetes is called Type 2 diabetes. Type 2 diabetes begins when the body is unable to react appropriately to insulin. Type 1 diabetes occurs when the pancreas stops producing enough insulin and usually begins in childhood. Diabetes can also occur during pregnancy and is called gestational diabetes. Although this is temporary, mothers who have gestational diabetes are more likely to develop Type 2 diabetes later in life. Who gets Type 2 Diabetes? Type 2 diabetes is very common. It can occur at any age but most often affects people over age 40. Type 2 diabetes is occurring more frequently in the United States than in the past, especially among adolescents and children. While anyone can develop diabetes, certain groups have an increased risk of developing the disease. These groups include overweight people, American Indians, Blacks, Hispanics, Asians, blood relatives of people with Type 2 diabetes and women who had diabetes during pregnancy. How do I prevent diabetes? Maintain a healthy weight and stay active! Controlling your weight with an appropriate diet and physical activity routine is the best way to lower your risk of developing diabetes. Your health care provider (physician, nurse practitioner, or physician assistant), a dietician, and/or a trainer may be helpful in creating an appropriate diet and exercise regimen. Regardless of your weight, most health care providers recommend at least 30 minutes of moderate physical activity (brisk walking or a similar/more strenuous activity) at least 5 days per week. How do I know if I have diabetes? You may not know. Some people with diabetes do not have any symptoms. Others may experience excessive thirst, frequent urination and hunger. Symptoms of lightheadedness, blurred vision, tiredness and weight changes may also occur. Detecting diabetes requires a blood test to measure blood sugar level. It is still uncertain whether routine testing for early diabetes is necessary for all people. However, experts recommend testing people who have high blood pressure or high cholesterol. Certain at risk individuals such as those who are overweight, older than 40 years of age and/or ethnically at risk may be 1
2 considered for routine testing. If you develop any of the symptoms listed above, you should immediately visit a health care provider to be tested. What are the common long-term complications of diabetes? 1. Heart Disease and Stroke Heart disease and strokes are the leading causes of the death in the United States. People with Type 2 diabetes have two to four times the risk of dying from heart disease or strokes. How does diabetes affect the heart and cause strokes? Research is being conducted to better understand why people with diabetes have more heart disease and strokes than those without diabetes. A significant factor is the damage that occurs to the blood vessels that supply the heart and brain. How do you know if you have heart disease or have had a stroke? Most people with heart disease are not aware of it. Physical exam, electrocardiogram (EKG), and exercise testing are some ways that heart disease is diagnosed. Unfortunately, for many people the first sign that they have heart disease is a heart attack. Heart attacks generally feel like crushing chest pressure and may cause shortness of breath or pain in the left arm. In people with diabetes, chest pain may be minimal or not felt at all due to nerve damage from diabetes. The symptoms of a stroke can vary. Often individuals may notice an area of their body that suddenly becomes weak or numb. Slurred speech, blurred vision or loss of consciousness may also occur. If I have heart disease or if I have a stroke what should I do? If you believe you may be suffering from a heart attack or stroke, you should call 911 and get to an emergency room right away. When in doubt, GO! The quicker you seek medical care, the better your chances of recovery. If you have signs or indication of old heart damage, your health care provider will likely order other tests or consult a cardiologist to determine the nature and extent of the damage. 2. Kidney Disease The kidneys help clean your blood of unneeded chemicals and salts. These substances are removed from the body in urine. 2
3 Diabetes can cause damage to the kidneys and is the most common cause of a serious condition called End Stage Renal (Kidney) Disease (ESRD). People with ESRD need to have their blood artificially cleaned (dialysis) or may even require a kidney transplant. How does diabetes affect the kidneys? High sugar levels in diabetes damage the small blood vessels in the kidneys. As these blood vessels are damaged, the kidneys begin to malfunction. The kidneys become ineffective at cleaning the blood stream and excreting the appropriate chemicals and salts in your urine. Having high blood pressure in addition to diabetes can worsen the kidney damage. How do you know if your kidneys are being affected by diabetes? Most people with diabetes who have kidney damage have no symptoms. A urine test should be done every year to look for a protein called albumin. Albumin in the urine usually is a sign of kidney damage. If the urine test for kidney disease is not normal, what should happen? This depends. If your blood pressure and blood sugar are not optimal then the goal should be to optimize them. If the blood pressure is elevated, two types of medications can be helpful in both reducing blood pressure and slowing the progression of kidney damage. These medications are called Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors and Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs). If your blood pressure is optimal, these medications may still be useful to protect the kidneys. Your health care provider can help you decide what option is best for you. Lastly, if there is significant damage to the kidneys, then a low protein diet may be useful. This should be discussed with your diabetes care provider and dietician as to what foods are appropriate to eat. 3. Eye Complications After having Type 2 diabetes for 20 years, more than 60% of people will have some degree of eye damage (called retinopathy). Diabetes causes more cases of blindness among adults than any other disease. How does diabetes affect the eyes? Diabetes damages the small blood vessels that supply the back of the eye (retina) with needed nutrients. These vessels begin to leak and become blocked with plaque buildup. In more severe forms of damage, new blood vessels can form on the back of the eye which can bleed and cause detachment of the retina. How do I know if I have eye damage? 3
4 Eye damage can occur very gradually and you may not even know it is happening until it is too late. Therefore, it is important for all people with type 2 diabetes to have a dilated eye exam by an optometrist or ophthalmologist shortly after being diagnosed and every year afterwards. If retinopathy does develop, it will be detected early and further damage can be avoided. If I have eye damage already what should I do? Maintaining good control of your blood sugar and blood pressure is critical to prevent further damage. Laser surgery can be beneficial for those with eye disease due to diabetes. The type of surgery depends on the extent of the disease. There is a risk of vision loss with some forms of surgery so this should be discussed with an ophthalmologist. Surgery normally does not reverse loss of vision but can prevent further loss or slow the progression. 4. Nerve Damage Over 50% of people with diabetes will suffer from nerve damage. This is referred to as diabetic neuropathy. Diabetic neuropathy can affect every part of the body but most commonly affects the feet/legs. How does diabetes affect the nerves? There are many factors that contribute to diabetic neuropathy. Reduced blood supply to the nerves from damaged blood vessels can lead to nerve death. Nerve damage may also occur from toxins generated in the blood of people with diabetes. How do I know if I have nerve damage? It usually takes many years of poor sugar control to develop a neuropathy. The first symptoms tend to appear in the hands and/or feet. At first, you may notice a slight numbness or tingling. Occasionally, pain may be felt. Your care provider may notice a decreased sensation during the physical exam. While damage to nerves of the hands and feet is the most common neuropathy of diabetes, nearly all nerves in the body may be affected. Both men and women may notice sexual problems resulting from nerve damage. Men may have difficulty achieving and maintaining an erection while women may notice vaginal dryness. If I have nerve damage already, what should I do? You need to pay special attention to the condition of your feet. Because of nerve damage, injuries such as cuts and blisters may go unnoticed. These injuries also take longer to heal in diabetes. If left untreated, small cuts and blisters can progress and cause permanent damage to the skin, bones and muscles and may require amputation. 4
5 Daily foot care is an important routine and includes inspection for open sores, redness or blisters, washing with soap and water, drying, and using clean socks. Never go barefoot! You should pay particular attention to areas around calluses where ulcers are most likely to develop. Overweight individuals should begin diet and exercise to lose weight and reduce unnecessary pressure on the feet. If an open wound is found, you should visit your provider. If dry skin is noted, hydrating lotion should be applied to the feet. However, lotion should never be applied between the toes. Toenails should be kept short and routinely trimmed. Itchy, red feet may be the first sign of an infection and your provider should be notified. Your provider will examine your feet on a regular basis. What are the short-term consequences of having high blood sugar? For people with type 2 diabetes, having a consistently high blood sugar can trigger a Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Nonketotic (HONK) state or Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA). In these states people often become confused and tired. If the sugars remain high, seizures and, rarely, coma can occur. If I have diabetes, how do I prevent complications? It is important to understand that specific complications of diabetes have many causes and following just one strategy cannot prevent the complications. For this reason, it is important to follow all five of the preventive strategies discussed below. Following the recommendations may not eliminate all complications of diabetes, but it will significantly decrease your odds of developing them. 1. Sugar Control When you are diagnosed with diabetes, it is important to monitor your blood sugar level. This can be done with a glucometer, an instrument that determines the sugar level in a sample of blood. Glucometers require a small drop of blood that can be obtained by pricking your finger with a lancet. Ideal levels are mg/dl before meals and less than two hours after meals. Some individuals are able to control their blood sugars with exercise and diet alone, while others require medications. There are different medications that your doctor may prescribe. Many medications such as sulfonylureas (glipizide/glyburide), metformin and glitazones (pioglitazone/rosiglitazone) are pills that can be taken orally. Insulin is currently available only as an injectable medication. Each of these medications can be used alone or in combination. Your health care provider will help determine which, if any, medication is right for you. Your health care provider may also test your blood to determine the average control of your diabetes. This test is called A1C or glycosylated hemoglobin. A measurement of less than 7% indicates very good control. 5
6 2. Weight Control and Diet Being overweight makes insulin less effective in delivering sugar (an energy source) to your body's cells. To control your weight, diet and exercise are critical. A healthy diet consists of fat, protein, and carbohydrates. Dietary fat should be low in saturated/trans fats found in fatty meats, high-fat dairy products, fried foods and highly processed snacks. Good sources of protein include fish, beans, poultry and lean meats. Carbohydrates come in many forms including sugars, starches, and fibers. While the amount consumed rather than the type affects blood sugar levels the most, carbohydrates such as whole grains (found in some breads and cereals), vegetables, fruits and foods high in fiber (beans, nuts) are better sources than highly refined sugars found in many snack foods. Discuss your food selection and portion size with your provider and/or dietician to individualize a program that is most appropriate for you. Participating in regular physical activity is equally important for weight control. 3. Physical Activity Physical activity helps the body s cells respond better to insulin and lowers blood glucose levels. The recommendation for physical activity is no different for people with diabetes than those without diabetes. Moderate activity such as brisk walking, biking, running, aerobics or swimming for at least 30 minutes five times per week is recommended. You should always check with you health care provider before beginning physical activity. Exercise will decrease your blood sugar levels and your medication may need adjustment to ensure your blood sugar does not go too low. 4. Blood Pressure Control Exercise, weight loss and diet can help lower blood pressure. However, blood pressure control may require use of a medication. ACE inhibitors and ARBs are particularly useful medications for people with diabetes because they not only lower blood pressure, but also protect the kidneys from damage. 5. Cholesterol Control There are many types of cholesterol and all are fatty particles that circulate in the blood. LDL is typically called the bad cholesterol. Reducing cholesterol can be done in three ways exercise, nutrition and medication. Often, exercise and nutrition are sufficient to lower your cholesterol. However, you may require the addition of a cholesterol lowering medication to reach the target level. Your diabetes care provider can help you coordinate a plan in order to reach these goals. 6. Aspirin Therapy Aspirin has been found to be effective in preventing heart disease and stroke. It prevents the blockage of blood vessels. However, aspirin can cause stomach irritation and bleeding, so discuss with your providers whether aspirin therapy is right for you. 6
7 7. Smoking Cessation Quitting smoking is extremely important in preventing heart disease and stroke. There are a number of smoking cessation strategies that are effective and your provider can help you quit. How often should I go to my diabetes care provider? This depends on how well your blood sugar is controlled. Most people in the initial stages of diabetes require frequent visits to their provider and may need to be seen weekly until blood sugar levels are controlled. Once control is established, you should be seen every 3-6 months. The frequency of your visits can be discussed with your provider. At these visits you can expect your feet to be examined, your blood pressure measured and lab work done. Once per year you will need a dilated eye exam and a urine test. Below is a list of procedures that should be done and their frequency. Your diabetes care provider will perform and coordinate these tests and exams. PROCEDURE FREQUENCY DESCRIPTION Blood A1C 3-6 months Average of sugar control over 2-3 month period (goal: < 7%) Blood Cholesterol LDL HDL Triglycerides Yearly Measurement of fatty particles contributing to heart and blood vessel damage. (goal: fasting LDL < 100 mg/dl) Urine Microalbumin Yearly Determines if kidneys are properly filtering. (goal: spot urine < 30 ug/mg creatinine) Eye Exam Yearly Dilated exam by optometrist or ophthalmologist to look at the retina (back of eye). Foot Exam Every visit to your provider Allows for early detection of nerve and blood vessel damage. Blood Pressure Every visit to your provider High BP is a risk for heart, blood vessel, kidney and eye disease. (goal: < 130/80 mm Hg) Summary Diabetes is a common disease leading to significant complications of many organ systems. Current studies suggest that exercise and proper nutrition can prevent Type 2 diabetes from occurring. However, if you already have diabetes, there are strategies that help prevent or reduce the risk of complications. These strategies include being physically active, eating a healthy diet, taking your medications and regularly visiting your health care provider. 7
8 Prepared by Stephen Benoit, MD, MPH and Dan Zisook, MD, MPH on behalf of the American College of Preventive Medicine. May
X-Plain Diabetes - Introduction Reference Summary
 X-Plain Diabetes - Introduction Reference Summary Introduction Diabetes is a disease that affects millions of Americans every year. Your doctor may have informed you that you have diabetes. Although there
X-Plain Diabetes - Introduction Reference Summary Introduction Diabetes is a disease that affects millions of Americans every year. Your doctor may have informed you that you have diabetes. Although there
There are three major forms of this disease.
 For more information about diabetes and it s risk factors, visit our website at: doh.sd.gov/diabetes or visit the South Dakota Diabetes Association at: www.sddiabetescoalition.org/ Your body needs insulin
For more information about diabetes and it s risk factors, visit our website at: doh.sd.gov/diabetes or visit the South Dakota Diabetes Association at: www.sddiabetescoalition.org/ Your body needs insulin
The Family Library. Understanding Diabetes
 The Family Library Understanding Diabetes What is Diabetes? Diabetes is caused when the body has a problem in making or using insulin. Insulin is a hormone secreted by the pancreas and is needed for the
The Family Library Understanding Diabetes What is Diabetes? Diabetes is caused when the body has a problem in making or using insulin. Insulin is a hormone secreted by the pancreas and is needed for the
Type 2 diabetes Definition
 Type 2 diabetes Definition Type 2 diabetes is a lifelong (chronic) disease in which there are high levels of sugar (glucose) in the blood. Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes. Causes Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes Definition Type 2 diabetes is a lifelong (chronic) disease in which there are high levels of sugar (glucose) in the blood. Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes. Causes Diabetes
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused by too little insulin, resistance to insulin, or both.
 Diabetes Definition Diabetes is a chronic (lifelong) disease marked by high levels of sugar in the blood. Causes Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused
Diabetes Definition Diabetes is a chronic (lifelong) disease marked by high levels of sugar in the blood. Causes Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused
Understanding Diabetes
 Understanding Diabetes What is diabetes? Diabetes is a condition where there is too much glucose (a type of sugar) in your blood. Your blood glucose level is regulated with the help of insulin, a hormone
Understanding Diabetes What is diabetes? Diabetes is a condition where there is too much glucose (a type of sugar) in your blood. Your blood glucose level is regulated with the help of insulin, a hormone
Nutrition. Type 2 Diabetes: A Growing Challenge in the Healthcare Setting NAME OF STUDENT
 1 Nutrition Type 2 Diabetes: A Growing Challenge in the Healthcare Setting NAME OF STUDENT 2 Type 2 Diabetes: A Growing Challenge in the Healthcare Setting Introduction and background of type 2 diabetes:
1 Nutrition Type 2 Diabetes: A Growing Challenge in the Healthcare Setting NAME OF STUDENT 2 Type 2 Diabetes: A Growing Challenge in the Healthcare Setting Introduction and background of type 2 diabetes:
Diabetes. Patient Education. What you need to know. Diabetes Facts. Improving Health Through Education. What is Diabetes?
 Diabetes What you need to know Diabetes Facts More than 3 million Canadians have diabetes (Canadian Diabetes Association, 2009). It is the 4th leading cause of death in the world (CDA, 2009). Patient Education
Diabetes What you need to know Diabetes Facts More than 3 million Canadians have diabetes (Canadian Diabetes Association, 2009). It is the 4th leading cause of death in the world (CDA, 2009). Patient Education
Take Charge of Your Diabetes
 Take Charge of Your Diabetes A Reinforcement Booklet for People With Diabetes Purpose and Acknowledgments This simplified and shortened overview of CDC s 1997 publication, Take Charge of Your Diabetes,
Take Charge of Your Diabetes A Reinforcement Booklet for People With Diabetes Purpose and Acknowledgments This simplified and shortened overview of CDC s 1997 publication, Take Charge of Your Diabetes,
Diabetes Mellitus Type 2
 Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 What is it? Diabetes is a common health problem in the U.S. and the world. In diabetes, the body does not use the food it digests well. It is hard for the body to use carbohydrates
Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 What is it? Diabetes is a common health problem in the U.S. and the world. In diabetes, the body does not use the food it digests well. It is hard for the body to use carbohydrates
Background (cont) World Health Organisation (WHO) and IDF predict that this number will increase to more than 1,3 million in the next 25 years.
 Diabetes Overview Background What is diabetes Non-modifiable risk factors Modifiable risk factors Common symptoms of diabetes Early diagnosis and management of diabetes Non-medical management of diabetes
Diabetes Overview Background What is diabetes Non-modifiable risk factors Modifiable risk factors Common symptoms of diabetes Early diagnosis and management of diabetes Non-medical management of diabetes
Type 2 Diabetes. Type 1 Diabetes. What is Diabetes? Diabetes during Pregnancy Very Thirsty Very Tired
 FCD2-006 BINGO GAME To Prepare bingo game:!copy Picture Cards with pictures on one side and corresponding words on the other.!cut Bingo Cards apart, duplicate if you have more than ten players.!cut apart
FCD2-006 BINGO GAME To Prepare bingo game:!copy Picture Cards with pictures on one side and corresponding words on the other.!cut Bingo Cards apart, duplicate if you have more than ten players.!cut apart
Type 2 Diabetes. Increase of diabetic complications as HAIC increases
 Type 2 Diabetes Diabetes is a disease of too much sugar (glucose) in the blood. Type 2 diabetes is caused by insulin resistance of the cells and abnormal insulin production by the pancreas. Insulin is
Type 2 Diabetes Diabetes is a disease of too much sugar (glucose) in the blood. Type 2 diabetes is caused by insulin resistance of the cells and abnormal insulin production by the pancreas. Insulin is
DIABETES A chronic, debilitating and often deadly disease A global epidemic Diabetes in Africa
 DIABETES A chronic, debilitating and often deadly disease Diabetes is a chronic condition that arises when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin, or when the body cannot effectively use the insulin
DIABETES A chronic, debilitating and often deadly disease Diabetes is a chronic condition that arises when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin, or when the body cannot effectively use the insulin
4 Steps to Control Your Diabetes for Life
 4 Steps to Control Your Diabetes for Life Contents Step 1: Learn about diabetes... 6 Step 2: Know your diabetes ABCs... 12 Step 3: Manage your diabetes... 16 Step 4: Get routine care... 22 Notes... 26
4 Steps to Control Your Diabetes for Life Contents Step 1: Learn about diabetes... 6 Step 2: Know your diabetes ABCs... 12 Step 3: Manage your diabetes... 16 Step 4: Get routine care... 22 Notes... 26
Understanding Diabetes
 Understanding Diabetes Diabetes is a disease in which a person s blood glucose (blood sugar) is too high. When you eat, some of the food is broken down into a type of sugar called glucose, which is the
Understanding Diabetes Diabetes is a disease in which a person s blood glucose (blood sugar) is too high. When you eat, some of the food is broken down into a type of sugar called glucose, which is the
Markham Stouffville Hospital
 Markham Stouffville Hospital Adult Diabetes Education Frequently Asked Questions What is diabetes? Diabetes is a disease in which blood glucose levels are above normal. Most of the food we eat is turned
Markham Stouffville Hospital Adult Diabetes Education Frequently Asked Questions What is diabetes? Diabetes is a disease in which blood glucose levels are above normal. Most of the food we eat is turned
High Blood Sugar. Printable Materials
 Printable Materials Activity Card #1 Symptoms of High Blood Sugar or Pre-Diabetes Symptoms People often don t know they have high blood sugar or pre-diabetes. There are no symptoms and pre-diabetes can
Printable Materials Activity Card #1 Symptoms of High Blood Sugar or Pre-Diabetes Symptoms People often don t know they have high blood sugar or pre-diabetes. There are no symptoms and pre-diabetes can
Post-Transplant Diabetes: What Every Patient Needs to Know
 Post-Transplant Diabetes: What Every Patient Needs to Know International Transplant Nurses Society What is Diabetes? Diabetes is an illness that effects how your body makes and uses a hormone called insulin.
Post-Transplant Diabetes: What Every Patient Needs to Know International Transplant Nurses Society What is Diabetes? Diabetes is an illness that effects how your body makes and uses a hormone called insulin.
TERMS FOR UNDERSTANDING YOUR TYPE 2 DIABETES. Definitions for Common Terms Related to Type 2 Diabetes
 TERMS FOR UNDERSTANDING YOUR TYPE 2 DIABETES Definitions for Common Terms Related to Type 2 Diabetes TYPE 2 DIABETES AND BLOOD SUGAR 1-3 This list of terms may help you beter understand type 2 diabetes,
TERMS FOR UNDERSTANDING YOUR TYPE 2 DIABETES Definitions for Common Terms Related to Type 2 Diabetes TYPE 2 DIABETES AND BLOOD SUGAR 1-3 This list of terms may help you beter understand type 2 diabetes,
Causes, incidence, and risk factors
 Causes, incidence, and risk factors Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused by too little insulin, resistance to insulin, or both. To understand diabetes,
Causes, incidence, and risk factors Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused by too little insulin, resistance to insulin, or both. To understand diabetes,
Statistics of Type 2 Diabetes
 Statistics of Type 2 Diabetes Of the 17 million Americans with diabetes, 90 percent to 95 percent have type 2 diabetes. Of these, half are unaware they have the disease. People with type 2 diabetes often
Statistics of Type 2 Diabetes Of the 17 million Americans with diabetes, 90 percent to 95 percent have type 2 diabetes. Of these, half are unaware they have the disease. People with type 2 diabetes often
PowerPoint Lecture Outlines prepared by Dr. Lana Zinger, QCC CUNY. 12a. FOCUS ON Your Risk for Diabetes. Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
 PowerPoint Lecture Outlines prepared by Dr. Lana Zinger, QCC CUNY 12a FOCUS ON Your Risk for Diabetes Your Risk for Diabetes! Since 1980,Diabetes has increased by 50 %. Diabetes has increased by 70 percent
PowerPoint Lecture Outlines prepared by Dr. Lana Zinger, QCC CUNY 12a FOCUS ON Your Risk for Diabetes Your Risk for Diabetes! Since 1980,Diabetes has increased by 50 %. Diabetes has increased by 70 percent
Learn about Diabetes. Your Guide to Diabetes: Type 1 and Type 2. You can learn how to take care of your diabetes.
 Learn about Diabetes You can learn how to take care of your diabetes and prevent some of the serious problems diabetes can cause. The more you know, the better you can manage your diabetes. Share this
Learn about Diabetes You can learn how to take care of your diabetes and prevent some of the serious problems diabetes can cause. The more you know, the better you can manage your diabetes. Share this
Diabetes, Type 2. RelayClinical Patient Education Sample Topic Diabetes, Type 2. What is type 2 diabetes? How does it occur?
 What is type 2 diabetes? Type 2 diabetes is a disorder that happens when your body does not make enough insulin or is unable to use its own insulin properly. The inability to use insulin is called insulin
What is type 2 diabetes? Type 2 diabetes is a disorder that happens when your body does not make enough insulin or is unable to use its own insulin properly. The inability to use insulin is called insulin
Welcome to Diabetes Education! Why Should I Take Control of My Diabetes?
 Welcome to Diabetes Education! Why Should I Take Control of My Diabetes? NEEDS and BENEFITS of SELF-MANAGEMENT You make choices about your life and health Controlling diabetes needs every day decisions
Welcome to Diabetes Education! Why Should I Take Control of My Diabetes? NEEDS and BENEFITS of SELF-MANAGEMENT You make choices about your life and health Controlling diabetes needs every day decisions
Diabetes and Your Kidneys
 American Kidney Fund reaching out giving hope improving lives Diabetes and Your Kidneys reaching out giving hope improving lives Diabetes: The #1 Cause of Kidney Failure Your doctor told you that you have
American Kidney Fund reaching out giving hope improving lives Diabetes and Your Kidneys reaching out giving hope improving lives Diabetes: The #1 Cause of Kidney Failure Your doctor told you that you have
DIABETES CARE. Advice. Blood Pressure. Cholesterol. Diabetes control. Eyes. Feet. Guardian Drugs
 DIABETES CARE What happens if you follow the Alphabet Strategy? As patients reach their targets, the chances of developing serious complications of diabetes will be reduced! 1 Stroke Eye disease Heart
DIABETES CARE What happens if you follow the Alphabet Strategy? As patients reach their targets, the chances of developing serious complications of diabetes will be reduced! 1 Stroke Eye disease Heart
Diabetes. 2. Types. Permafold Topics. What You Need To Know. One test used to diagnose diabetes is a fasting blood glucose test.
 1. What Is Diabetes? Diabetes is often called having too much sugar. It is too much sugar (glucose) in the blood and not enough in the body s cells. Glucose needs to get into the cells to be used for energy.
1. What Is Diabetes? Diabetes is often called having too much sugar. It is too much sugar (glucose) in the blood and not enough in the body s cells. Glucose needs to get into the cells to be used for energy.
HOW TO CARE FOR A PATIENT WITH DIABETES
 HOW TO CARE FOR A PATIENT WITH DIABETES INTRODUCTION Diabetes is one of the most common diseases in the United States, and diabetes is a disease that affects the way the body handles blood sugar. Approximately
HOW TO CARE FOR A PATIENT WITH DIABETES INTRODUCTION Diabetes is one of the most common diseases in the United States, and diabetes is a disease that affects the way the body handles blood sugar. Approximately
Chronic Kidney Disease and Diabetes
 Anyone with diabetes can get kidney disease. Diabetes and high blood pressure are the most common causes of kidney disease, and people often have both. Chronic (long term) kidney disease (CKD) caused by
Anyone with diabetes can get kidney disease. Diabetes and high blood pressure are the most common causes of kidney disease, and people often have both. Chronic (long term) kidney disease (CKD) caused by
Type 1 diabetes Definition
 Type 1 diabetes Definition Type 1 diabetes is a chronic (lifelong) disease that occurs when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin to properly control blood sugar levels. Causes There are several
Type 1 diabetes Definition Type 1 diabetes is a chronic (lifelong) disease that occurs when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin to properly control blood sugar levels. Causes There are several
DIABETES MELLITUS. By Tracey Steenkamp Biokineticist at the Institute for Sport Research, University of Pretoria
 DIABETES MELLITUS By Tracey Steenkamp Biokineticist at the Institute for Sport Research, University of Pretoria What is Diabetes Diabetes Mellitus (commonly referred to as diabetes ) is a chronic medical
DIABETES MELLITUS By Tracey Steenkamp Biokineticist at the Institute for Sport Research, University of Pretoria What is Diabetes Diabetes Mellitus (commonly referred to as diabetes ) is a chronic medical
Am I at Risk for type 2 Diabetes? Taking Steps to Lower the Risk of Getting Diabetes NATIONAL DIABETES INFORMATION CLEARINGHOUSE
 NATIONAL DIABETES INFORMATION CLEARINGHOUSE Am I at Risk for type 2 Diabetes? Taking Steps to Lower the Risk of Getting Diabetes U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health
NATIONAL DIABETES INFORMATION CLEARINGHOUSE Am I at Risk for type 2 Diabetes? Taking Steps to Lower the Risk of Getting Diabetes U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health
This information explains the advice about type 2 diabetes in adults that is set out in NICE guideline NG28.
 Information for the public Published: 2 December 2015 nice.org.uk About this information NICE guidelines provide advice on the care and support that should be offered to people who use health and care
Information for the public Published: 2 December 2015 nice.org.uk About this information NICE guidelines provide advice on the care and support that should be offered to people who use health and care
DIABETES. Eyes, Heart, Nerves, Feet, and Kidneys. www.kidney.org
 DIABETES Eyes, Heart, Nerves, Feet, and Kidneys www.kidney.org About the Information in this Booklet Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation (NKF) offers guidelines and commentaries that help
DIABETES Eyes, Heart, Nerves, Feet, and Kidneys www.kidney.org About the Information in this Booklet Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation (NKF) offers guidelines and commentaries that help
TYPE 2 DIABETES IN THE AFRICAN AMERICAN COMMUNITY. Understanding the Complications That May Happen Without Proper Care
 TYPE 2 DIABETES IN THE AFRICAN AMERICAN COMMUNITY Understanding the Complications That May Happen Without Proper Care STAYING HEALTHY THE IMPORTANCE OF PROPER MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES Diabetes is
TYPE 2 DIABETES IN THE AFRICAN AMERICAN COMMUNITY Understanding the Complications That May Happen Without Proper Care STAYING HEALTHY THE IMPORTANCE OF PROPER MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES Diabetes is
Type 2 Diabetes. What is diabetes? Understanding blood glucose and insulin. What is Type 2 diabetes? Page 1 of 5
 Page 1 of 5 Type 2 Diabetes Type 2 diabetes occurs mainly in people aged over 40. The 'first-line' treatment is diet, weight control and physical activity. If the blood glucose level remains high despite
Page 1 of 5 Type 2 Diabetes Type 2 diabetes occurs mainly in people aged over 40. The 'first-line' treatment is diet, weight control and physical activity. If the blood glucose level remains high despite
Manage Your. Diabetes. Healthy Life. for a
 Manage Your Diabetes for a Healthy Life Know your ABCs! trying to control your A1C (blood sugar), Blood pressure, Cholesterol and stopping Smoking can help you to lower your chances of having a heart attack,
Manage Your Diabetes for a Healthy Life Know your ABCs! trying to control your A1C (blood sugar), Blood pressure, Cholesterol and stopping Smoking can help you to lower your chances of having a heart attack,
High blood sugars caused by steroids
 High blood sugars caused by steroids Your blood sugars are high because you are taking a medication called steroids. Steroids are used to: decrease swelling decrease the natural response of your immune
High blood sugars caused by steroids Your blood sugars are high because you are taking a medication called steroids. Steroids are used to: decrease swelling decrease the natural response of your immune
Cardiac Rehabilitation
 Cardiac Rehabilitation Introduction Experiencing heart disease should be the beginning of a new, healthier lifestyle. Cardiac rehabilitation helps you in two ways. First, it helps your heart recover through
Cardiac Rehabilitation Introduction Experiencing heart disease should be the beginning of a new, healthier lifestyle. Cardiac rehabilitation helps you in two ways. First, it helps your heart recover through
DIABETES YOUR GUIDE TO
 YOUR GUIDE TO DIABETES b What is diabetes? b Type 2 diabetes prevention b Prevention checklist b Living with diabetes b Complications b Terms to know b Resources To promote and protect the health of Canadians
YOUR GUIDE TO DIABETES b What is diabetes? b Type 2 diabetes prevention b Prevention checklist b Living with diabetes b Complications b Terms to know b Resources To promote and protect the health of Canadians
Diabetes Brief. Pre diabetes occurs when glucose levels are elevated in the blood, but are not as high as someone who has diabetes.
 Diabetes Brief What is Diabetes? Diabetes mellitus is a disease of abnormal carbohydrate metabolism in which the level of blood glucose, or blood sugar, is above normal. The disease occurs when the body
Diabetes Brief What is Diabetes? Diabetes mellitus is a disease of abnormal carbohydrate metabolism in which the level of blood glucose, or blood sugar, is above normal. The disease occurs when the body
Diabetes. Rochester Recreation Club for the Deaf January 21, 2010
 Diabetes Rochester Recreation Club for the Deaf January 21, 2010 Supporters Deaf Health Community Committee Members Cathie Armstrong Michael McKee Mistie Cramer Matt Starr Patrick Sullivan University of
Diabetes Rochester Recreation Club for the Deaf January 21, 2010 Supporters Deaf Health Community Committee Members Cathie Armstrong Michael McKee Mistie Cramer Matt Starr Patrick Sullivan University of
Diabetes Fundamentals
 Diabetes Fundamentals Prevalence of Diabetes in the U.S. Undiagnosed 10.7% of all people 20+ 23.1% of all people 60+ (12.2 million) Slide provided by Roche Diagnostics Sources: ADA, WHO statistics Prevalence
Diabetes Fundamentals Prevalence of Diabetes in the U.S. Undiagnosed 10.7% of all people 20+ 23.1% of all people 60+ (12.2 million) Slide provided by Roche Diagnostics Sources: ADA, WHO statistics Prevalence
What is Type 2 Diabetes?
 Type 2 Diabetes What is Type 2 Diabetes? Diabetes is a condition where there is too much glucose in the blood. Our pancreas produces a hormone called insulin. Insulin works to regulate our blood glucose
Type 2 Diabetes What is Type 2 Diabetes? Diabetes is a condition where there is too much glucose in the blood. Our pancreas produces a hormone called insulin. Insulin works to regulate our blood glucose
Practice Guidelines for the
 1 Treatment goals: Practice Guidelines for the The goal of treatment is to keep blood sugar at normal or near-normal levels. This reduces the risk of complications associated with diabetes. A normal fasting
1 Treatment goals: Practice Guidelines for the The goal of treatment is to keep blood sugar at normal or near-normal levels. This reduces the risk of complications associated with diabetes. A normal fasting
Diabetes: The #1 Cause of Kidney Failure
 American Kidney Fund reaching out giving hope improving lives Diabetes and Your Kidneys Large Print Edition reaching out giving hope improving lives Diabetes: The #1 Cause of Kidney Failure Your doctor
American Kidney Fund reaching out giving hope improving lives Diabetes and Your Kidneys Large Print Edition reaching out giving hope improving lives Diabetes: The #1 Cause of Kidney Failure Your doctor
4 Steps to Manage Your Diabetes for Life
 4 Steps to Manage Your Diabetes for Life ENGLISH A program of the National Institutes of Health and the Centers for Disease Control and Preventioni This booklet gives four key steps to help you manage
4 Steps to Manage Your Diabetes for Life ENGLISH A program of the National Institutes of Health and the Centers for Disease Control and Preventioni This booklet gives four key steps to help you manage
Know Your Numbers. The Five-Point Plan
 The Five-Point Plan Know Your Numbers 2 My husband didn t even know he had diabetes until he had a heart attack. Lupe Ontiveros Actress on Desperate Housewives 13 What does it mean to Know Your Numbers?
The Five-Point Plan Know Your Numbers 2 My husband didn t even know he had diabetes until he had a heart attack. Lupe Ontiveros Actress on Desperate Housewives 13 What does it mean to Know Your Numbers?
Healthy at Heart FEELING GOOD. Reduce Your CV Risk. It s Not Just Your Body. It s Your Outlook, Too. Issue 3
 Issue 3 Healthy at Heart Reduce Your CV Risk FEELING GOOD It s Not Just Your Body. It s Your Outlook, Too. Inside: Tips for staying active and feeling good all over Speak to your healthcare provider before
Issue 3 Healthy at Heart Reduce Your CV Risk FEELING GOOD It s Not Just Your Body. It s Your Outlook, Too. Inside: Tips for staying active and feeling good all over Speak to your healthcare provider before
Type 2 Diabetes Type 2 Diabetes
 Pennington Nutrition Series Healthier lives through education in nutrition and preventive medicine Pub No. 33 Type 2 is the most common form of diabetes. In this form, the body does not produce enough
Pennington Nutrition Series Healthier lives through education in nutrition and preventive medicine Pub No. 33 Type 2 is the most common form of diabetes. In this form, the body does not produce enough
Diabetes Mellitus: Type 1
 Diabetes Mellitus: Type 1 What is type 1 diabetes mellitus? Type 1 diabetes is a disorder that happens when your body produces little or no insulin. The lack of insulin causes the level of sugar in your
Diabetes Mellitus: Type 1 What is type 1 diabetes mellitus? Type 1 diabetes is a disorder that happens when your body produces little or no insulin. The lack of insulin causes the level of sugar in your
4 Steps. For Life. to Control Your Diabetes. National Diabetes Education Program 1-888-693-NDEP (1-888-693-6337) www.yourdiabetesinfo.
 4 Steps to Control Your Diabetes. For Life. National Diabetes Education Program 1-888-693-NDEP (1-888-693-6337) www.yourdiabetesinfo.org Contents Introduction 1 Step 1: Learn about diabetes. 3 Step 2:
4 Steps to Control Your Diabetes. For Life. National Diabetes Education Program 1-888-693-NDEP (1-888-693-6337) www.yourdiabetesinfo.org Contents Introduction 1 Step 1: Learn about diabetes. 3 Step 2:
Facts About Peripheral Arterial Disease (P.A.D.)
 Facts About Peripheral Arterial Disease (P.A.D.) One in every 20 Americans over the age of 50 has P.A.D., a condition that raises the risk for heart attack and stroke. Peripheral arterial disease, or P.A.D.,
Facts About Peripheral Arterial Disease (P.A.D.) One in every 20 Americans over the age of 50 has P.A.D., a condition that raises the risk for heart attack and stroke. Peripheral arterial disease, or P.A.D.,
How To Manage Diabetes
 How To Manage Diabetes HHC Health & Home Care Serving New Yorkers For Over 45 Years 1-866-NYC-HOME www.homecarenyc.org Contents Your Blood Sugar Goals 4 Testing Your Blood Sugar 5 Blood Sugar Control
How To Manage Diabetes HHC Health & Home Care Serving New Yorkers For Over 45 Years 1-866-NYC-HOME www.homecarenyc.org Contents Your Blood Sugar Goals 4 Testing Your Blood Sugar 5 Blood Sugar Control
Diabetes and Stroke. Understanding the connection between diabetes and the increased risk of stroke
 Diabetes and Stroke Understanding the connection between diabetes and the increased risk of stroke Make the Connection Almost 26 million people in the U.S. roughly 8 percent of the population have diabetes.
Diabetes and Stroke Understanding the connection between diabetes and the increased risk of stroke Make the Connection Almost 26 million people in the U.S. roughly 8 percent of the population have diabetes.
It s time to TALK Targets A guide to taking control of your type 2 diabetes
 It s time to TALK Targets A guide to taking control of your type 2 diabetes The TALK Targets campaign was initiated and fully funded by Novo Nordisk. By supporting you and your healthcare team, TALK Targets
It s time to TALK Targets A guide to taking control of your type 2 diabetes The TALK Targets campaign was initiated and fully funded by Novo Nordisk. By supporting you and your healthcare team, TALK Targets
Diabetes. Living with. Better Health Guide. Anywhere, TN 11111. 1008 Main Street. Janet James. BCBSNEMEMWKBCD.XML - 1768150 - VersionID: 1
 BCBSNEMEMWKBCD.XML - 1768150 - VersionID: 1 Living with Diabetes Better Health Guide Janet James 1008 Main Street Anywhere, TN 11111 65109016-999-000000006 13810 Southeast Eastgate Way, Suite 200 Bellevue,
BCBSNEMEMWKBCD.XML - 1768150 - VersionID: 1 Living with Diabetes Better Health Guide Janet James 1008 Main Street Anywhere, TN 11111 65109016-999-000000006 13810 Southeast Eastgate Way, Suite 200 Bellevue,
High Blood Sugar: What You Need to Know
 High Blood Sugar: What You Need to Know This brochure can help you learn more about high blood sugar. It doesn t replace regular medical check-ups or your health care provider s advice. Talk with your
High Blood Sugar: What You Need to Know This brochure can help you learn more about high blood sugar. It doesn t replace regular medical check-ups or your health care provider s advice. Talk with your
High Blood Pressure and Chronic Kidney Disease
 High Blood Pressure and Chronic Kidney Disease For People with CKD Stages 1 4 www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney
High Blood Pressure and Chronic Kidney Disease For People with CKD Stages 1 4 www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney
Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 What You Should Know
 Please refer to the glossary for a definition of terms. What is Diabetes? Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 What You Should Know Erin K.P. Meyerhoff RN Instructor of Medicine Family Nurse Practitioner Certified
Please refer to the glossary for a definition of terms. What is Diabetes? Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 What You Should Know Erin K.P. Meyerhoff RN Instructor of Medicine Family Nurse Practitioner Certified
Medical Assistant s Diabetes Survey
 Medical Assistant s Diabetes Survey Instructions: Circle one answer for each question. Thank-you. Basic Knowledge 1. Risk factors for developing Type 2 diabetes include: a. Family members with diabetes
Medical Assistant s Diabetes Survey Instructions: Circle one answer for each question. Thank-you. Basic Knowledge 1. Risk factors for developing Type 2 diabetes include: a. Family members with diabetes
DIABETIC EDUCATION MODULE ONE GENERAL OVERVIEW OF TREATMENT AND SAFETY
 DIABETIC EDUCATION MODULE ONE GENERAL OVERVIEW OF TREATMENT AND SAFETY First Edition September 17, 1997 Kevin King R.N., B.S., C.C.R.N. Gregg Kunder R.N., B.S.N., C.C.T.C. 77-120 CHS UCLA Medical Center
DIABETIC EDUCATION MODULE ONE GENERAL OVERVIEW OF TREATMENT AND SAFETY First Edition September 17, 1997 Kevin King R.N., B.S., C.C.R.N. Gregg Kunder R.N., B.S.N., C.C.T.C. 77-120 CHS UCLA Medical Center
Treatment of diabetes In order to survive, people with type 1 diabetes must have insulin delivered by a pump or injections.
 National Diabetes Statistics What is diabetes? Diabetes mellitus is a group of diseases characterized by high levels of blood glucose resulting from defects in insulin production, insulin action, or both.
National Diabetes Statistics What is diabetes? Diabetes mellitus is a group of diseases characterized by high levels of blood glucose resulting from defects in insulin production, insulin action, or both.
High Blood pressure and chronic kidney disease
 High Blood pressure and chronic kidney disease For People with CKD Stages 1 4 www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney
High Blood pressure and chronic kidney disease For People with CKD Stages 1 4 www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney
Baskets of Care Diabetes Subcommittee
 Baskets of Care Diabetes Subcommittee Disclaimer: This background information is not intended to be a comprehensive scientific discussion of the topic, but rather an attempt to provide a baseline level
Baskets of Care Diabetes Subcommittee Disclaimer: This background information is not intended to be a comprehensive scientific discussion of the topic, but rather an attempt to provide a baseline level
Diabetes 101: A Brief Overview of Diabetes and the American Diabetes Association What Happens When We Eat?
 Diabetes 101: A Brief Overview of Diabetes and the American Diabetes Association What Happens When We Eat? After eating, most food is turned into glucose, the body s main source of energy. 1 Normal Blood
Diabetes 101: A Brief Overview of Diabetes and the American Diabetes Association What Happens When We Eat? After eating, most food is turned into glucose, the body s main source of energy. 1 Normal Blood
Other Noninfectious Diseases. Chapter 31 Lesson 3
 Other Noninfectious Diseases Chapter 31 Lesson 3 Diabetes Diabetes- a chronic disease that affects the way body cells convert food into energy. Diabetes is the seventh leading cause of death by disease
Other Noninfectious Diseases Chapter 31 Lesson 3 Diabetes Diabetes- a chronic disease that affects the way body cells convert food into energy. Diabetes is the seventh leading cause of death by disease
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition that occurs as a result of problems with the production and/or action of insulin in the body.
 International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Background Information Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition that occurs as a result of problems with the production and/or action of insulin in the body.
International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Background Information Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition that occurs as a result of problems with the production and/or action of insulin in the body.
What is diabetes? Diabetes is a condition which occurs as a result of problems with the production and supply of insulin in the body.
 What is diabetes? Diabetes is a condition which occurs as a result of problems with the production and supply of insulin in the body. Most of the food we eat is turned into glucose, a form of sugar. We
What is diabetes? Diabetes is a condition which occurs as a result of problems with the production and supply of insulin in the body. Most of the food we eat is turned into glucose, a form of sugar. We
Type 1 Diabetes ( Juvenile Diabetes)
 Type 1 Diabetes W ( Juvenile Diabetes) hat is Type 1 Diabetes? Type 1 diabetes, also known as juvenile-onset diabetes, is one of the three main forms of diabetes affecting millions of people worldwide.
Type 1 Diabetes W ( Juvenile Diabetes) hat is Type 1 Diabetes? Type 1 diabetes, also known as juvenile-onset diabetes, is one of the three main forms of diabetes affecting millions of people worldwide.
Myth vs. Reality: Diabetes Related
 Myth: Only medication can control my diabetes. Reality: Lifestyle changes such as good nutrition, increased physical activity, weight loss and limiting alcohol/cigarette consumption can have a positive
Myth: Only medication can control my diabetes. Reality: Lifestyle changes such as good nutrition, increased physical activity, weight loss and limiting alcohol/cigarette consumption can have a positive
Is Insulin Effecting Your Weight Loss and Your Health?
 Is Insulin Effecting Your Weight Loss and Your Health? Teressa Alexander, M.D., FACOG Women s Healthcare Associates www.rushcopley.com/whca 630-978-6886 Obesity is Epidemic in the US 2/3rds of U.S. adults
Is Insulin Effecting Your Weight Loss and Your Health? Teressa Alexander, M.D., FACOG Women s Healthcare Associates www.rushcopley.com/whca 630-978-6886 Obesity is Epidemic in the US 2/3rds of U.S. adults
An Overview and Guide to Healthy Living with Type 2 Diabetes
 MEETING YOUR GOALS An Overview and Guide to Healthy Living with Type 2 Diabetes MEETING YOUR GOALS This brochure was designed to help you understand the health goals to live a healthy lifestyle with type
MEETING YOUR GOALS An Overview and Guide to Healthy Living with Type 2 Diabetes MEETING YOUR GOALS This brochure was designed to help you understand the health goals to live a healthy lifestyle with type
Preventing & Managing Complications of Diabetes
 Preventing & Managing Complications of Diabetes Target Audience: Persons with diabetes and family members Objectives: Participants will be able to: 1. identify the complications associated with diabetes
Preventing & Managing Complications of Diabetes Target Audience: Persons with diabetes and family members Objectives: Participants will be able to: 1. identify the complications associated with diabetes
Diabetes and Heart Disease
 Diabetes and Heart Disease Diabetes and Heart Disease According to the American Heart Association, diabetes is one of the six major risk factors of cardiovascular disease. Affecting more than 7% of the
Diabetes and Heart Disease Diabetes and Heart Disease According to the American Heart Association, diabetes is one of the six major risk factors of cardiovascular disease. Affecting more than 7% of the
If diabetes is not treated it can cause long-term health problems because the high glucose levels in the blood damage the blood vessels.
 INFORMATION FOR PEOPLE WITH DIABETES Diabetes Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition caused by too much glucose (sugar) in your blood. Your blood sugar level can be too high if your body does not make
INFORMATION FOR PEOPLE WITH DIABETES Diabetes Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition caused by too much glucose (sugar) in your blood. Your blood sugar level can be too high if your body does not make
Eating Well with Diabetes. Cassie Vanderwall UW Health Nutrition Registered Dietitian Certified Personal Trainer Certified Diabetes Educator
 Eating Well with Diabetes Cassie Vanderwall UW Health Nutrition Registered Dietitian Certified Personal Trainer Certified Diabetes Educator Outline What is Diabetes? Diabetes Self-Management Eating Well
Eating Well with Diabetes Cassie Vanderwall UW Health Nutrition Registered Dietitian Certified Personal Trainer Certified Diabetes Educator Outline What is Diabetes? Diabetes Self-Management Eating Well
Diabetes and stroke. What is diabetes? What are the symptoms of diabetes? Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk
 Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Diabetes and stroke Diabetes is a condition caused by too much sugar in your blood. There are over three million people in the UK who have diabetes.
Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Diabetes and stroke Diabetes is a condition caused by too much sugar in your blood. There are over three million people in the UK who have diabetes.
is for A1c (blood sugar level) What causes unhealthy levels of blood sugar?
 diabetes matters Summer 2016 Do you have diabetes? Or do you have prediabetes and want to know more about it? Diabetes Matters is just for you, to help you learn how to live well with diabetes and prevent
diabetes matters Summer 2016 Do you have diabetes? Or do you have prediabetes and want to know more about it? Diabetes Matters is just for you, to help you learn how to live well with diabetes and prevent
Diabetes for CNAs. This course has been awarded two (2.0) contact hours. This course expires on January 31, 2017.
 Diabetes for CNAs This course has been awarded two (2.0) contact hours. This course expires on January 31, 2017. Copyright 2005 by RN.com. All Rights Reserved. Reproduction and distribution of these materials
Diabetes for CNAs This course has been awarded two (2.0) contact hours. This course expires on January 31, 2017. Copyright 2005 by RN.com. All Rights Reserved. Reproduction and distribution of these materials
High Blood Pressure (Essential Hypertension)
 Sacramento Heart & Vascular Medical Associates February 18, 2012 500 University Ave. Sacramento, CA 95825 Page 1 916-830-2000 Fax: 916-830-2001 What is essential hypertension? Blood pressure is the force
Sacramento Heart & Vascular Medical Associates February 18, 2012 500 University Ave. Sacramento, CA 95825 Page 1 916-830-2000 Fax: 916-830-2001 What is essential hypertension? Blood pressure is the force
High Blood Pressure and Chronic Kidney Disease. For People With CKD Stages 1 4
 High Blood Pressure and Chronic Kidney Disease For People With CKD Stages 1 4 National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative (NKF-KDOQI ) The National Kidney Foundation s Kidney
High Blood Pressure and Chronic Kidney Disease For People With CKD Stages 1 4 National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative (NKF-KDOQI ) The National Kidney Foundation s Kidney
InDependent Diabetes Trust
 InDependent Diabetes Trust Kidneys and Diabetes Updated July 2015 Registered Company Number 3148360 Registered Charity No 1058284 Contents Introduction Healthy Kidneys Kidney disease and diabetes The use
InDependent Diabetes Trust Kidneys and Diabetes Updated July 2015 Registered Company Number 3148360 Registered Charity No 1058284 Contents Introduction Healthy Kidneys Kidney disease and diabetes The use
what is diabetes? What actually goes wrong? Talking diabetes No.42
 Talking diabetes No.42 what is diabetes? Diabetes is the name given to a group of different conditions in which there is too much glucose in the blood. The pancreas either cannot make insulin or the insulin
Talking diabetes No.42 what is diabetes? Diabetes is the name given to a group of different conditions in which there is too much glucose in the blood. The pancreas either cannot make insulin or the insulin
Health Maintenance: Controlling Cholesterol
 Sacramento Heart & Vascular Medical Associates February 18, 2012 500 University Ave. Sacramento, CA 95825 Page 1 What is cholesterol? Cholesterol is a fatty substance. It has both good and bad effects
Sacramento Heart & Vascular Medical Associates February 18, 2012 500 University Ave. Sacramento, CA 95825 Page 1 What is cholesterol? Cholesterol is a fatty substance. It has both good and bad effects
GFR (Glomerular Filtration Rate) A Key to Understanding How Well Your Kidneys Are Working
 GFR (Glomerular Filtration Rate) A Key to Understanding How Well Your Kidneys Are Working www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National
GFR (Glomerular Filtration Rate) A Key to Understanding How Well Your Kidneys Are Working www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National
Do You Know the Health Risks of Being Overweight?
 Do You Know the Health Risks of Being Overweight? U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH WIN Weight-control Information Network What are the risks to my health from
Do You Know the Health Risks of Being Overweight? U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH WIN Weight-control Information Network What are the risks to my health from
Diabetes and kidney disease. The foundation of kidney care.
 Diabetes and kidney disease The foundation of kidney care. T H E K I D N E Y F O U N D A T I O N O F C A N A D A 1 Diabetes and kidney disease What is diabetes? Diabetes is a disease that is caused by
Diabetes and kidney disease The foundation of kidney care. T H E K I D N E Y F O U N D A T I O N O F C A N A D A 1 Diabetes and kidney disease What is diabetes? Diabetes is a disease that is caused by
Management of Diabetes
 Management of Diabetes Blood Glucose Monitoring MANAGEMENT OF DIABETES Once someone is told they have diabetes, they are usually asked to check their blood glucose at home with a home blood glucose meter
Management of Diabetes Blood Glucose Monitoring MANAGEMENT OF DIABETES Once someone is told they have diabetes, they are usually asked to check their blood glucose at home with a home blood glucose meter
DCCT and EDIC: The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial and Follow-up Study
 DCCT and EDIC: The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial and Follow-up Study National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What
DCCT and EDIC: The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial and Follow-up Study National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What
N E B R A S K A JAIL BULLETIN NUMBER 102 OCTOBER 1993
 N E B R A S K A JAIL BULLETIN NUMBER 102 OCTOBER 1993 The Jail Bulletin is a monthly feature of the Crime Commission Update. The Bulletin may be used as a supplement to your jail in-service training program
N E B R A S K A JAIL BULLETIN NUMBER 102 OCTOBER 1993 The Jail Bulletin is a monthly feature of the Crime Commission Update. The Bulletin may be used as a supplement to your jail in-service training program
IDDM generally occurs in children and adolescents, though it can appear at any age.
 Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Insulin-dependent diabetes (IDDM) is a chronic disease that usually begins in childhood. It is not the most common form of diabetes--iddm accounts for only 5 percent or less
Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Insulin-dependent diabetes (IDDM) is a chronic disease that usually begins in childhood. It is not the most common form of diabetes--iddm accounts for only 5 percent or less
Managing Diabetes in the Athletic Population
 Managing Diabetes in the Athletic Population Michael Prybicien, LA, ATC, CSCS, CES, PES Athletic Trainer, Passaic High School Overlook Medical Center & Adjunct Faculty, William Paterson University Dedicated
Managing Diabetes in the Athletic Population Michael Prybicien, LA, ATC, CSCS, CES, PES Athletic Trainer, Passaic High School Overlook Medical Center & Adjunct Faculty, William Paterson University Dedicated
Understanding Diabetes
 Patient Education Understanding Diabetes This handout describes diabetes, the complications related to the disease, and how you can prevent these complications. Blood Sugar Control Diabetes is a disease
Patient Education Understanding Diabetes This handout describes diabetes, the complications related to the disease, and how you can prevent these complications. Blood Sugar Control Diabetes is a disease
Avastin (Bevacizumab) Intravitreal Injection
 Avastin (Bevacizumab) Intravitreal Injection This handout describes how Avastin may be used to treat wet age related macular degeneration (AMD) or macular edema due to retinal vascular disease such as
Avastin (Bevacizumab) Intravitreal Injection This handout describes how Avastin may be used to treat wet age related macular degeneration (AMD) or macular edema due to retinal vascular disease such as
Participant Guide Adopt a healthy lifestyle: prevent or better manage type 2 diabetes
 HealthSelectSM Lose and Win Session 13 of Texas Pre-diabetes & type II diabetes Participant Guide Adopt a healthy lifestyle: prevent or better manage type 2 diabetes Chances are that you know someone that
HealthSelectSM Lose and Win Session 13 of Texas Pre-diabetes & type II diabetes Participant Guide Adopt a healthy lifestyle: prevent or better manage type 2 diabetes Chances are that you know someone that
Diabetes: Staying Healthy
 Diabetes: Staying Healthy Learn from the experts at Joslin Diabetes Center and Walgreens about: Eating well & being active Understanding your medicines Reducing your risks And more -! 4RUSTED 4EAM FOR
Diabetes: Staying Healthy Learn from the experts at Joslin Diabetes Center and Walgreens about: Eating well & being active Understanding your medicines Reducing your risks And more -! 4RUSTED 4EAM FOR
Gestational diabetes. Information to help you stay healthy during your pregnancy. What is gestational diabetes?
 Gestational diabetes Information to help you stay healthy during your pregnancy What is gestational diabetes? How gestational diabetes can affect my baby How to take care of myself and my baby during pregnancy
Gestational diabetes Information to help you stay healthy during your pregnancy What is gestational diabetes? How gestational diabetes can affect my baby How to take care of myself and my baby during pregnancy
