File Systems for Flash Memories. Marcela Zuluaga Sebastian Isaza Dante Rodriguez
|
|
|
- Adelia Hodge
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 File Systems for Flash Memories Marcela Zuluaga Sebastian Isaza Dante Rodriguez
2 Outline Introduction to Flash Memories Introduction to File Systems File Systems for Flash Memories YAFFS (Yet Another Flash File System)
3 Introduction to Flash Memories Memories technology classification
4 Introduction to Flash Memories Flash Memories: main features Non-volatile: : it does not need power to maintain the information stored in the chip. Fast read access times (though not as fast as volatile DRAM) ) and better shock resistance than hard disks. Hence, suitable for data storage in embedded devices.
5 Introduction to Flash Memories features Unlike EEPROM,, it is erased and programmed in blocks consisting of multiple locations Costs far less than EEPROM Examples of applications include USB Flash drives, digital audio players, digital cameras and mobile phones
6 Introduction to Flash Memories Two types NOR Flash Random, direct access interface for readings Fast random reads Slow erase and write Suitable for code storage NAND Flash Random access is not supported, only sequential Lower cost (than NOR) Smaller size erase blocks Better performance for erase and write More endurance Mainly for data storage
7 Introduction to Flash Memories Disadvantages Random access for rewrite or erase not supported Finite number or erase/write cycles Higher cost per bit compared to hard disks drives
8 Introduction to File Systems Subsytem of an OS, whose purpose is to provide long- term storage Set of abstract data types ADT (set of data and operations) Storage hierarchical organization, manipulation, navigation, access, and retrieval of data Make use of an underlying data storage device Access to an array of fixed-size blocks (sectors, generally 512 bytes) File system software is responsible for organizing these sectors into files and directories,, and keeping track of which sectors belong to which file.
9 Introduction to File Systems Types of File Systems Disk file systems Storage of files on a data storage device (disk drive). Exp: FAT, NTFS, HFS, ext2, ISO 9660, ODS-5,, and UDF. Database file systems Non hierarchical structured management Identification by their characteristics, like type of file, topic, author. metadata
10 Introduction to File Systems PC File Systems FATFS File Allocation Table File System - Developed by Microsoft for MS-DOS - Supported by virtually all existing operating systems - Main drawback is fragmentation. HPFS High Performance File System - Efficient placements of the allocation tables and root directories - Filenames can be up to 254 chars long NTFS New Technology File System - Several improvements over FAT such as improved support for metadata - Advanced data structures to improve performance, reliability and disk space utilization Ext2 second extended file system - Native filesystem for Linux - Maximum data size of 4 terabytes - Maximum filename length of 255 characters
11 Introduction to File Systems FAT s File Systems FAT12 FAT16 FAT32 Developer Full Name Introduced Microsoft File Allocation Table (12-bit version) (16-bit version) (32-bit version) 1977 (Microsoft Disk BASIC) July 1988 (MS-DOS 4.0) August 1996 (Win 95 OSR2) 0x0B, 0x0C (MBR) Partition identifier 0x01 (MBR) 0x04, 0x06, 0x0E (MBR) EBD0A0A2-B9E5 B9E Max file size 32 MiB 2 GiB -87C0-68B6B72699C7 4 GiB Max number of files 4,077 65, ,435,437 Max filename size 8.3 or 255 characters when using LFNs Max volume size 32 MiB 2 GiB 4 GiB with some implementations 2 TiB
12 Introduction to File Systems Storage Level of abstraction for the HW responsible for storing and retrieving Specified blocks of data. Abstraction given by block device drivers.
13 Each file contents: File contents (data) Introduction to File Systems File Contents File attributes (metadata) File size Owner, access control lists Creation time, last access time, last modification time, File name
14 Introduction to File Systems Data Scattering File system: A mapping problem <filename, data, metadata> <a set of blocks>
15 Introduction to File Systems Ext2 file system File System Example - A disk-based file system for Linux - Similar to UNIX Fast File System (FFS) - Evolved to Ext3 File system (with journaling) - Directory: pathname metadata (i-node) - Direct/indirect block pointers: i-node i data blocks
16 Introduction to File Systems Unix File System Superblock Size description of the FS Inode Metadata, pointers Datablock Allocation for the FS
17 File Systems for Flash Memories Due to the particular characteristics of Flash memories, special file systems are needed to spread writes over the media (wear-levelling levelling) and deal with the long erase times of NOR flash blocks. Two approaches for FFS (Flash File System): Layered approach Native (or cross-layer) layer) approach
18 File Systems for Flash Memories Layered Approach Uses the Fast Translation Layer (FTL) to fully emulate a magnetic disk and includes: Sector mapping Garbage collection Power-off off recovery Bad block management Wear-leveling leveling Error correction code (ECC) Power management
19 File Systems for Flash Memories Layered Approach (2) Benefits Easy to deploy because no modification is required for upper layers Some commercial Flash memories already come with FTL. Limitations Most FTLs are patented Kernel is not aware of the presence of flash memory.
20 File Systems for Flash Memories Native Approach Cross-layer optimization Kernel manages raw flash memory directly More opportunities to optimize the performance Kernel is involved in some FTL functionalities Sector mapping, garbage collection, wear-leveling, leveling, power-off off recovery, etc Example: Flash-aware aware file systems: JFFS/JFFS2, YAFFS Limitations Need to change the host operating system Only applicable Flash-embedded devices
21 YAFFS Yet Another Flash File System
22 YAFFS History Toby Churchill Ltd (TCL) needed a flash filing system for their devices reliable with fast boot time. First option: adding NAND support to the existing flash file systems, JFFS, JFFS2 boot time and ram consumption were problem adding NAND support wasn't trivial The company Aleph One decided to design a different filing system explicitly for NAND
23 YAFFS - History..Progress Decided to create YAFFS - Dec 2001 Working on RAM emulation - March 2002 Working on real NAND (Linux) - May 2002 WinCE version - Aug 2002 uclinux use - Sept 2002 Linux rootfs - Nov 2002 psos version - Feb 2003 Shipping commercially - Early 2003
24 YAFFS Why NAND flash? Embedded and mobile systems are increasingly using NAND flash for storage because it has various advantages over other storage technologies NOR flash is not very dense (i.e. not much storage per chip), is costly and is slow to write NAND flash is low cost, dense, and writes fast; but it has other limitations It is needed a journaling file system that is able to work around the limitations of NAND and exploit it for best performance. Has a fast erase time as compared with NOR flash. The NAND physical interface is very simple The small size and low current requirements make it very suitable for embedded systems
25 YAFFS Other NAND characteristics NAND is not random access, but page oriented. Thus, we do all reads & writes in pages NAND writes will only change 1 bits to 0. The only way to get 1s again is to erase the entire block. Errors are far more likely in NAND devices. Blocks of memory can be bad when the device is shipped and further blocks can become unusable over time. Therefore error detection and correction is highly desirable. YAFFS handles bad blocks and uses formats which are resistant to corruption.
26 YAFFS YAFFS Characteristics The first NAND-specific flash file system Special reference to embedded systems primarily for internal NAND rather than removable NAND (SM cards) reliability is more important than compatibility. Exploits low-cost NAND chips and is both fast and robust Highly portable to other operating systems Open source project
27 YAFFS YAFFS Characteristics It is design based in JFFS although NOR and NAND flash have very different properties A flash file system that works with NOR incorporates various mechanisms that are not required for NAND, and NAND needs extra mechanisms not required for NOR The design was greatly simplified by not including compression Robustness through journaling strategies. Significantly reduce the RAM overheads and boot times associated with JFFS. YAFFS uses a physical flash format similar to SmartMedia.
28 YAFFS File System Design File data stored in chunks, same size as flash pages (512 bytes) Block - Erasable set of pages (usually 32) Each file has an id - equivalent to inode. Chunks numbered 1,2,3,4 etc - 0 is header. Each flash page is marked with file id and chunk number These tags are stored in the OOB - 64bits: including file id, chunk number, write, serial number, tag ECC and bytes-in in-page-used
29 YAFFS File System Design On overwriting the relevant chunks are replaced by writing new pages with new data but same tags - the old page is marked discarded File headers (mode, id, length etc) get a page of their own (chunk0) Pages also have a 2-bit 2 serial number - incremented on write Allows crash-recovery recovery when two pages have same tags (because old page has not yet been marked discarded ). A block containing only discarded pages (termed a dirty block) ) is an obvious candidate for garbage collection. YAFFS maintains a tree structure in RAM memory of the physical location of these chunks.
30 YAFFS Page allocation Pages are allocated sequentially from the currently selected block. When all the pages in the block are filled, another clean block is selected for allocation. If there are insufficient clean blocks available, then a dirty block is erased to free it up as a clean block. If no dirty blocks are available, then the dirtiest block is selected for garbage collection.
31 YAFFS Garbage collection Garbage collection is performed by copying the valid data pages into new data pages thus marking all the pages in this block dirty and freeing it up for erasure. Another idea: selecting a block at random some small percentage of the time - thus reducing the chance of wear differences. Relative to NOR, NAND writes and erases very fast. Therefore garbage collection might be performed on- demand (during a write)
32 YAFFS YAFFS 2 The original motivation for YAFFS 2 was to add support for the new NAND with 2kB pages instead of 512-byte byte pages and strictly sequential page writing order. To achieve this, a new design is used which also presents the following benefits: zero page rewrites means faster operation. (YAFFS1 uses a single rewrite in the spare area to delete a page). ability to exploit simultaneous page programming on some chips. improves performance relative to YAFFS1 speed(write:1.5x to 5x, delete: 4x, garbage collection: 2x) lower RAM footprint (approx. 25% to 50% of YAFFS1). The main philosophical difference between YAFFS and YAFFS2 is how discarded status is tracked. Since re-writing writing cannot be done, "discarded" flags are not used. Now the strategy is including more tag information.
33 YAFFS File System Limits YAFFS 2^18 files (>260,000) 2^20 max file size (512MB) 1GB max file system size YAFFS2 8GB max file system size
34 References sosp2003.pdf
Linux flash file systems JFFS2 vs UBIFS
 Linux flash file systems JFFS2 vs UBIFS Chris Simmonds 2net Limited Embedded Systems Conference UK. 2009 Copyright 2009, 2net Limited Overview Many embedded systems use raw flash chips JFFS2 has been the
Linux flash file systems JFFS2 vs UBIFS Chris Simmonds 2net Limited Embedded Systems Conference UK. 2009 Copyright 2009, 2net Limited Overview Many embedded systems use raw flash chips JFFS2 has been the
Data Storage Framework on Flash Memory using Object-based Storage Model
 2011 International Conference on Computer Science and Information Technology (ICCSIT 2011) IPCSIT vol. 51 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore DOI: 10.7763/IPCSIT.2012.V51. 118 Data Storage Framework
2011 International Conference on Computer Science and Information Technology (ICCSIT 2011) IPCSIT vol. 51 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore DOI: 10.7763/IPCSIT.2012.V51. 118 Data Storage Framework
Survey of Filesystems for Embedded Linux. Presented by Gene Sally CELF
 Survey of Filesystems for Embedded Linux Presented by Gene Sally CELF Presentation Filesystems In Summary What is a filesystem Kernel and User space filesystems Picking a root filesystem Filesystem Round-up
Survey of Filesystems for Embedded Linux Presented by Gene Sally CELF Presentation Filesystems In Summary What is a filesystem Kernel and User space filesystems Picking a root filesystem Filesystem Round-up
File Systems Management and Examples
 File Systems Management and Examples Today! Efficiency, performance, recovery! Examples Next! Distributed systems Disk space management! Once decided to store a file as sequence of blocks What s the size
File Systems Management and Examples Today! Efficiency, performance, recovery! Examples Next! Distributed systems Disk space management! Once decided to store a file as sequence of blocks What s the size
Design of a NAND Flash Memory File System to Improve System Boot Time
 International Journal of Information Processing Systems, Vol.2, No.3, December 2006 147 Design of a NAND Flash Memory File System to Improve System Boot Time Song-Hwa Park*, Tae-Hoon Lee*, and Ki-Dong
International Journal of Information Processing Systems, Vol.2, No.3, December 2006 147 Design of a NAND Flash Memory File System to Improve System Boot Time Song-Hwa Park*, Tae-Hoon Lee*, and Ki-Dong
UBIFS file system. Adrian Hunter (Адриан Хантер) Artem Bityutskiy (Битюцкий Артём)
 UBIFS file system Adrian Hunter (Адриан Хантер) Artem Bityutskiy (Битюцкий Артём) Plan Introduction (Artem) MTD and UBI (Artem) UBIFS (Adrian) 2 UBIFS scope UBIFS stands for UBI file system (argh...) UBIFS
UBIFS file system Adrian Hunter (Адриан Хантер) Artem Bityutskiy (Битюцкий Артём) Plan Introduction (Artem) MTD and UBI (Artem) UBIFS (Adrian) 2 UBIFS scope UBIFS stands for UBI file system (argh...) UBIFS
Update on filesystems for flash storage
 JM2L Update on filesystems for flash storage Michael Opdenacker. Free Electrons http://free electrons.com/ 1 Contents Introduction Available flash filesystems Our benchmarks Best choices Experimental filesystems
JM2L Update on filesystems for flash storage Michael Opdenacker. Free Electrons http://free electrons.com/ 1 Contents Introduction Available flash filesystems Our benchmarks Best choices Experimental filesystems
File System Management
 Lecture 7: Storage Management File System Management Contents Non volatile memory Tape, HDD, SSD Files & File System Interface Directories & their Organization File System Implementation Disk Space Allocation
Lecture 7: Storage Management File System Management Contents Non volatile memory Tape, HDD, SSD Files & File System Interface Directories & their Organization File System Implementation Disk Space Allocation
The Linux Virtual Filesystem
 Lecture Overview Linux filesystem Linux virtual filesystem (VFS) overview Common file model Superblock, inode, file, dentry Object-oriented Ext2 filesystem Disk data structures Superblock, block group,
Lecture Overview Linux filesystem Linux virtual filesystem (VFS) overview Common file model Superblock, inode, file, dentry Object-oriented Ext2 filesystem Disk data structures Superblock, block group,
TELE 301 Lecture 7: Linux/Unix file
 Overview Last Lecture Scripting This Lecture Linux/Unix file system Next Lecture System installation Sources Installation and Getting Started Guide Linux System Administrators Guide Chapter 6 in Principles
Overview Last Lecture Scripting This Lecture Linux/Unix file system Next Lecture System installation Sources Installation and Getting Started Guide Linux System Administrators Guide Chapter 6 in Principles
A Simple Virtual FAT File System for Wear-Leveling Onboard NAND Flash Memory
 A Simple Virtual FAT File System for Wear-Leveling Onboard NAND Flash Memory Robert Klar, Sue Baldor, Charles Howard, Randal Harmon, and Allison Bertrand Southwest Research Institute Promise of Flash Flash
A Simple Virtual FAT File System for Wear-Leveling Onboard NAND Flash Memory Robert Klar, Sue Baldor, Charles Howard, Randal Harmon, and Allison Bertrand Southwest Research Institute Promise of Flash Flash
Nasir Memon Polytechnic Institute of NYU
 Nasir Memon Polytechnic Institute of NYU SSD Drive Technology Overview SSD Drive Components NAND FLASH Microcontroller SSD Drive Forensics Challenges Overview SSD s are fairly new to the market Whereas
Nasir Memon Polytechnic Institute of NYU SSD Drive Technology Overview SSD Drive Components NAND FLASH Microcontroller SSD Drive Forensics Challenges Overview SSD s are fairly new to the market Whereas
UBI with Logging. Brijesh Singh Samsung, India [email protected]. Rohit Vijay Dongre Samsung, India [email protected].
 UBI with Logging Brijesh Singh Samsung, India [email protected] Rohit Vijay Dongre Samsung, India [email protected] Abstract Flash memory is widely adopted as a novel nonvolatile storage medium
UBI with Logging Brijesh Singh Samsung, India [email protected] Rohit Vijay Dongre Samsung, India [email protected] Abstract Flash memory is widely adopted as a novel nonvolatile storage medium
1 / 25. CS 137: File Systems. Persistent Solid-State Storage
 1 / 25 CS 137: File Systems Persistent Solid-State Storage Technology Change is Coming Introduction Disks are cheaper than any solid-state memory Likely to be true for many years But SSDs are now cheap
1 / 25 CS 137: File Systems Persistent Solid-State Storage Technology Change is Coming Introduction Disks are cheaper than any solid-state memory Likely to be true for many years But SSDs are now cheap
File System Forensics FAT and NTFS. Copyright Priscilla Oppenheimer 1
 File System Forensics FAT and NTFS 1 FAT File Systems 2 File Allocation Table (FAT) File Systems Simple and common Primary file system for DOS and Windows 9x Can be used with Windows NT, 2000, and XP New
File System Forensics FAT and NTFS 1 FAT File Systems 2 File Allocation Table (FAT) File Systems Simple and common Primary file system for DOS and Windows 9x Can be used with Windows NT, 2000, and XP New
Flash Memory. Jian-Jia Chen (Slides are based on Yuan-Hao Chang) TU Dortmund Informatik 12 Germany 2015 年 01 月 27 日. technische universität dortmund
 12 Flash Memory Jian-Jia Chen (Slides are based on Yuan-Hao Chang) TU Dortmund Informatik 12 Germany 2015 年 01 月 27 日 These slides use Microsoft clip arts Microsoft copyright restrictions apply Springer,
12 Flash Memory Jian-Jia Chen (Slides are based on Yuan-Hao Chang) TU Dortmund Informatik 12 Germany 2015 年 01 月 27 日 These slides use Microsoft clip arts Microsoft copyright restrictions apply Springer,
On Benchmarking Embedded Linux Flash File Systems
 On Benchmarking Embedded Linux Flash File Systems Pierre Olivier Université de Brest, 20 avenue Le Gorgeu, 29285 Brest cedex 3, France [email protected] Jalil Boukhobza Université de Brest, 20
On Benchmarking Embedded Linux Flash File Systems Pierre Olivier Université de Brest, 20 avenue Le Gorgeu, 29285 Brest cedex 3, France [email protected] Jalil Boukhobza Université de Brest, 20
NAND Flash & Storage Media
 ENABLING MULTIMEDIA NAND Flash & Storage Media March 31, 2004 NAND Flash Presentation NAND Flash Presentation Version 1.6 www.st.com/nand NAND Flash Memories Technology Roadmap F70 1b/c F12 1b/c 1 bit/cell
ENABLING MULTIMEDIA NAND Flash & Storage Media March 31, 2004 NAND Flash Presentation NAND Flash Presentation Version 1.6 www.st.com/nand NAND Flash Memories Technology Roadmap F70 1b/c F12 1b/c 1 bit/cell
Flash-Friendly File System (F2FS)
 Flash-Friendly File System (F2FS) Feb 22, 2013 Joo-Young Hwang ([email protected]) S/W Dev. Team, Memory Business, Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. Agenda Introduction FTL Device Characteristics
Flash-Friendly File System (F2FS) Feb 22, 2013 Joo-Young Hwang ([email protected]) S/W Dev. Team, Memory Business, Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. Agenda Introduction FTL Device Characteristics
CHAPTER 17: File Management
 CHAPTER 17: File Management The Architecture of Computer Hardware, Systems Software & Networking: An Information Technology Approach 4th Edition, Irv Englander John Wiley and Sons 2010 PowerPoint slides
CHAPTER 17: File Management The Architecture of Computer Hardware, Systems Software & Networking: An Information Technology Approach 4th Edition, Irv Englander John Wiley and Sons 2010 PowerPoint slides
File-System Implementation
 File-System Implementation 11 CHAPTER In this chapter we discuss various methods for storing information on secondary storage. The basic issues are device directory, free space management, and space allocation
File-System Implementation 11 CHAPTER In this chapter we discuss various methods for storing information on secondary storage. The basic issues are device directory, free space management, and space allocation
FAT32 vs. NTFS Jason Capriotti CS384, Section 1 Winter 1999-2000 Dr. Barnicki January 28, 2000
 FAT32 vs. NTFS Jason Capriotti CS384, Section 1 Winter 1999-2000 Dr. Barnicki January 28, 2000 Table of Contents List of Figures... iv Introduction...1 The Physical Disk...1 File System Basics...3 File
FAT32 vs. NTFS Jason Capriotti CS384, Section 1 Winter 1999-2000 Dr. Barnicki January 28, 2000 Table of Contents List of Figures... iv Introduction...1 The Physical Disk...1 File System Basics...3 File
Update on filesystems for flash storage
 Embedded Linux Conference Europe Update on filesystems for flash storage Michael Opdenacker. Free Electrons http://free electrons.com/ 1 Contents Introduction Available flash filesystems Our benchmarks
Embedded Linux Conference Europe Update on filesystems for flash storage Michael Opdenacker. Free Electrons http://free electrons.com/ 1 Contents Introduction Available flash filesystems Our benchmarks
Indexing on Solid State Drives based on Flash Memory
 Indexing on Solid State Drives based on Flash Memory Florian Keusch MASTER S THESIS Systems Group Department of Computer Science ETH Zurich http://www.systems.ethz.ch/ September 2008 - March 2009 Supervised
Indexing on Solid State Drives based on Flash Memory Florian Keusch MASTER S THESIS Systems Group Department of Computer Science ETH Zurich http://www.systems.ethz.ch/ September 2008 - March 2009 Supervised
3. USB FLASH DRIVE PREPARATION. Almost all current PC firmware permits booting from a USB drive, allowing the launch
 3. USB FLASH DRIVE PREPARATION 3.1 INTRODUCTION Almost all current PC firmware permits booting from a USB drive, allowing the launch of an operating system from a bootable flash drive. Such a configuration
3. USB FLASH DRIVE PREPARATION 3.1 INTRODUCTION Almost all current PC firmware permits booting from a USB drive, allowing the launch of an operating system from a bootable flash drive. Such a configuration
File System & Device Drive. Overview of Mass Storage Structure. Moving head Disk Mechanism. HDD Pictures 11/13/2014. CS341: Operating System
 CS341: Operating System Lect 36: 1 st Nov 2014 Dr. A. Sahu Dept of Comp. Sc. & Engg. Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati File System & Device Drive Mass Storage Disk Structure Disk Arm Scheduling RAID
CS341: Operating System Lect 36: 1 st Nov 2014 Dr. A. Sahu Dept of Comp. Sc. & Engg. Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati File System & Device Drive Mass Storage Disk Structure Disk Arm Scheduling RAID
Algorithms and Methods for Distributed Storage Networks 7 File Systems Christian Schindelhauer
 Algorithms and Methods for Distributed Storage Networks 7 File Systems Institut für Informatik Wintersemester 2007/08 Literature Storage Virtualization, Technologies for Simplifying Data Storage and Management,
Algorithms and Methods for Distributed Storage Networks 7 File Systems Institut für Informatik Wintersemester 2007/08 Literature Storage Virtualization, Technologies for Simplifying Data Storage and Management,
NAND Flash FAQ. Eureka Technology. apn5_87. NAND Flash FAQ
 What is NAND Flash? What is the major difference between NAND Flash and other Memory? Structural differences between NAND Flash and NOR Flash What does NAND Flash controller do? How to send command to
What is NAND Flash? What is the major difference between NAND Flash and other Memory? Structural differences between NAND Flash and NOR Flash What does NAND Flash controller do? How to send command to
Two Parts. Filesystem Interface. Filesystem design. Interface the user sees. Implementing the interface
 File Management Two Parts Filesystem Interface Interface the user sees Organization of the files as seen by the user Operations defined on files Properties that can be read/modified Filesystem design Implementing
File Management Two Parts Filesystem Interface Interface the user sees Organization of the files as seen by the user Operations defined on files Properties that can be read/modified Filesystem design Implementing
Object-based SCM: An Efficient Interface for Storage Class Memories
 Object-based SCM: An Efficient Interface for Storage Class Memories Yangwook Kang Jingpei Yang Ethan L. Miller Storage Systems Research Center, University of California, Santa Cruz {ywkang, yangjp, elm}@cs.ucsc.edu
Object-based SCM: An Efficient Interface for Storage Class Memories Yangwook Kang Jingpei Yang Ethan L. Miller Storage Systems Research Center, University of California, Santa Cruz {ywkang, yangjp, elm}@cs.ucsc.edu
FASS : A Flash-Aware Swap System
 FASS : A Flash-Aware Swap System Dawoon Jung, Jin-Soo Kim, Seon-Yeong Park, Jeong-Uk Kang, and Joonwon Lee Division of Computer Science Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology 373-1 Guseongdong,
FASS : A Flash-Aware Swap System Dawoon Jung, Jin-Soo Kim, Seon-Yeong Park, Jeong-Uk Kang, and Joonwon Lee Division of Computer Science Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology 373-1 Guseongdong,
COS 318: Operating Systems
 COS 318: Operating Systems File Performance and Reliability Andy Bavier Computer Science Department Princeton University http://www.cs.princeton.edu/courses/archive/fall10/cos318/ Topics File buffer cache
COS 318: Operating Systems File Performance and Reliability Andy Bavier Computer Science Department Princeton University http://www.cs.princeton.edu/courses/archive/fall10/cos318/ Topics File buffer cache
Lecture 18: Reliable Storage
 CS 422/522 Design & Implementation of Operating Systems Lecture 18: Reliable Storage Zhong Shao Dept. of Computer Science Yale University Acknowledgement: some slides are taken from previous versions of
CS 422/522 Design & Implementation of Operating Systems Lecture 18: Reliable Storage Zhong Shao Dept. of Computer Science Yale University Acknowledgement: some slides are taken from previous versions of
NAND Flash Memories. Using Linux MTD compatible mode. on ELNEC Universal Device Programmers. (Quick Guide)
 NAND Flash Memories Using Linux MTD compatible mode on ELNEC Universal Device Programmers (Quick Guide) Application Note April 2012 an_elnec_linux_mtd, version 1.04 Version 1.04/04.2012 Page 1 of 16 As
NAND Flash Memories Using Linux MTD compatible mode on ELNEC Universal Device Programmers (Quick Guide) Application Note April 2012 an_elnec_linux_mtd, version 1.04 Version 1.04/04.2012 Page 1 of 16 As
NANDFS: A Flexible Flash File System for RAM-Constrained Systems
 NANDFS: A Flexible Flash File System for RAM-Constrained Systems Aviad Zuck The Blavatnik School of Computer Science Tel-Aviv University Tel-Aviv, Israel [email protected] Ohad Barzilay The Blavatnik
NANDFS: A Flexible Flash File System for RAM-Constrained Systems Aviad Zuck The Blavatnik School of Computer Science Tel-Aviv University Tel-Aviv, Israel [email protected] Ohad Barzilay The Blavatnik
A PRAM and NAND Flash Hybrid Architecture for High-Performance Embedded Storage Subsystems
 1 A PRAM and NAND Flash Hybrid Architecture for High-Performance Embedded Storage Subsystems Chul Lee Software Laboratory Samsung Advanced Institute of Technology Samsung Electronics Outline 2 Background
1 A PRAM and NAND Flash Hybrid Architecture for High-Performance Embedded Storage Subsystems Chul Lee Software Laboratory Samsung Advanced Institute of Technology Samsung Electronics Outline 2 Background
Linux Kernel Architecture
 Linux Kernel Architecture Amir Hossein Payberah [email protected] Contents What is Kernel? Kernel Architecture Overview User Space Kernel Space Kernel Functional Overview File System Process Management
Linux Kernel Architecture Amir Hossein Payberah [email protected] Contents What is Kernel? Kernel Architecture Overview User Space Kernel Space Kernel Functional Overview File System Process Management
760 Veterans Circle, Warminster, PA 18974 215-956-1200. Technical Proposal. Submitted by: ACT/Technico 760 Veterans Circle Warminster, PA 18974.
 760 Veterans Circle, Warminster, PA 18974 215-956-1200 Technical Proposal Submitted by: ACT/Technico 760 Veterans Circle Warminster, PA 18974 for Conduction Cooled NAS Revision 4/3/07 CC/RAIDStor: Conduction
760 Veterans Circle, Warminster, PA 18974 215-956-1200 Technical Proposal Submitted by: ACT/Technico 760 Veterans Circle Warminster, PA 18974 for Conduction Cooled NAS Revision 4/3/07 CC/RAIDStor: Conduction
Windows NT File System. Outline. Hardware Basics. Ausgewählte Betriebssysteme Institut Betriebssysteme Fakultät Informatik
 Windows Ausgewählte Betriebssysteme Institut Betriebssysteme Fakultät Informatik Outline NTFS File System Formats File System Driver Architecture Advanced Features NTFS Driver On-Disk Structure (MFT,...)
Windows Ausgewählte Betriebssysteme Institut Betriebssysteme Fakultät Informatik Outline NTFS File System Formats File System Driver Architecture Advanced Features NTFS Driver On-Disk Structure (MFT,...)
Trabajo 4.5 - Memorias flash
 Memorias flash II-PEI 09/10 Trabajo 4.5 - Memorias flash Wojciech Ochalek This document explains the concept of flash memory and describes it s the most popular use. Moreover describes also Microdrive
Memorias flash II-PEI 09/10 Trabajo 4.5 - Memorias flash Wojciech Ochalek This document explains the concept of flash memory and describes it s the most popular use. Moreover describes also Microdrive
Outline. Windows NT File System. Hardware Basics. Win2K File System Formats. NTFS Cluster Sizes NTFS
 Windows Ausgewählte Betriebssysteme Institut Betriebssysteme Fakultät Informatik 2 Hardware Basics Win2K File System Formats Sector: addressable block on storage medium usually 512 bytes (x86 disks) Cluster:
Windows Ausgewählte Betriebssysteme Institut Betriebssysteme Fakultät Informatik 2 Hardware Basics Win2K File System Formats Sector: addressable block on storage medium usually 512 bytes (x86 disks) Cluster:
CSE 120 Principles of Operating Systems
 CSE 120 Principles of Operating Systems Fall 2004 Lecture 13: FFS, LFS, RAID Geoffrey M. Voelker Overview We ve looked at disks and file systems generically Now we re going to look at some example file
CSE 120 Principles of Operating Systems Fall 2004 Lecture 13: FFS, LFS, RAID Geoffrey M. Voelker Overview We ve looked at disks and file systems generically Now we re going to look at some example file
New Technologies File System (NTFS) Priscilla Oppenheimer. Copyright 2008 Priscilla Oppenheimer
 New Technologies File System (NTFS) Priscilla Oppenheimer NTFS Default file system for Windows NT, 2000, XP, and Windows Server 2003 No published spec from Microsoft that describes the on-disk layout Good
New Technologies File System (NTFS) Priscilla Oppenheimer NTFS Default file system for Windows NT, 2000, XP, and Windows Server 2003 No published spec from Microsoft that describes the on-disk layout Good
ADVANCED PROCESSOR ARCHITECTURES AND MEMORY ORGANISATION Lesson-17: Memory organisation, and types of memory
 ADVANCED PROCESSOR ARCHITECTURES AND MEMORY ORGANISATION Lesson-17: Memory organisation, and types of memory 1 1. Memory Organisation 2 Random access model A memory-, a data byte, or a word, or a double
ADVANCED PROCESSOR ARCHITECTURES AND MEMORY ORGANISATION Lesson-17: Memory organisation, and types of memory 1 1. Memory Organisation 2 Random access model A memory-, a data byte, or a word, or a double
Algorithms and Methods for Distributed Storage Networks 3. Solid State Disks Christian Schindelhauer
 Algorithms and Methods for Distributed Storage Networks 3. Solid State Disks Institut für Informatik Wintersemester 2007/08 Solid State Disks Motivation 2 10 5 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 PRODUCTION
Algorithms and Methods for Distributed Storage Networks 3. Solid State Disks Institut für Informatik Wintersemester 2007/08 Solid State Disks Motivation 2 10 5 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 PRODUCTION
Chapter Contents. Operating System Activities. Operating System Basics. Operating System Activities. Operating System Activities 25/03/2014
 Chapter Contents Operating Systems and File Management Section A: Operating System Basics Section B: Today s Operating Systems Section C: File Basics Section D: File Management Section E: Backup Security
Chapter Contents Operating Systems and File Management Section A: Operating System Basics Section B: Today s Operating Systems Section C: File Basics Section D: File Management Section E: Backup Security
Chapter 12 File Management
 Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles, 6/E William Stallings Chapter 12 File Management Dave Bremer Otago Polytechnic, N.Z. 2008, Prentice Hall Roadmap Overview File organisation and Access
Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles, 6/E William Stallings Chapter 12 File Management Dave Bremer Otago Polytechnic, N.Z. 2008, Prentice Hall Roadmap Overview File organisation and Access
Chapter 12 File Management. Roadmap
 Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles, 6/E William Stallings Chapter 12 File Management Dave Bremer Otago Polytechnic, N.Z. 2008, Prentice Hall Overview Roadmap File organisation and Access
Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles, 6/E William Stallings Chapter 12 File Management Dave Bremer Otago Polytechnic, N.Z. 2008, Prentice Hall Overview Roadmap File organisation and Access
Two Flash Technologies Compared: NOR vs NAND
 White Paper Two Flash Technologies Compared: NOR vs NAND Written by: Arie Tal OCTOBER 02 91-SR-012-04-8L REV. 1.0 Introduction Two main technologies dominate the non-volatile flash memory market today:
White Paper Two Flash Technologies Compared: NOR vs NAND Written by: Arie Tal OCTOBER 02 91-SR-012-04-8L REV. 1.0 Introduction Two main technologies dominate the non-volatile flash memory market today:
Implementation of Buffer Cache Simulator for Hybrid Main Memory and Flash Memory Storages
 Implementation of Buffer Cache Simulator for Hybrid Main Memory and Flash Memory Storages Soohyun Yang and Yeonseung Ryu Department of Computer Engineering, Myongji University Yongin, Gyeonggi-do, Korea
Implementation of Buffer Cache Simulator for Hybrid Main Memory and Flash Memory Storages Soohyun Yang and Yeonseung Ryu Department of Computer Engineering, Myongji University Yongin, Gyeonggi-do, Korea
Chapter 11: File System Implementation. Operating System Concepts 8 th Edition
 Chapter 11: File System Implementation Operating System Concepts 8 th Edition Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2009 Chapter 11: File System Implementation File-System Structure File-System Implementation
Chapter 11: File System Implementation Operating System Concepts 8 th Edition Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2009 Chapter 11: File System Implementation File-System Structure File-System Implementation
Chapter 13 File and Database Systems
 Chapter 13 File and Database Systems Outline 13.1 Introduction 13.2 Data Hierarchy 13.3 Files 13.4 File Systems 13.4.1 Directories 13.4. Metadata 13.4. Mounting 13.5 File Organization 13.6 File Allocation
Chapter 13 File and Database Systems Outline 13.1 Introduction 13.2 Data Hierarchy 13.3 Files 13.4 File Systems 13.4.1 Directories 13.4. Metadata 13.4. Mounting 13.5 File Organization 13.6 File Allocation
Chapter 13 File and Database Systems
 Chapter 13 File and Database Systems Outline 13.1 Introduction 13.2 Data Hierarchy 13.3 Files 13.4 File Systems 13.4.1 Directories 13.4. Metadata 13.4. Mounting 13.5 File Organization 13.6 File Allocation
Chapter 13 File and Database Systems Outline 13.1 Introduction 13.2 Data Hierarchy 13.3 Files 13.4 File Systems 13.4.1 Directories 13.4. Metadata 13.4. Mounting 13.5 File Organization 13.6 File Allocation
There are various types of NAND Flash available. Bare NAND chips, SmartMediaCards, DiskOnChip.
 NAND FLASH NAND vs. NOR Beside the different silicon cell design, the most important difference between NAND and NOR Flash is the bus interface. NOR Flash is connected to a address / data bus direct like
NAND FLASH NAND vs. NOR Beside the different silicon cell design, the most important difference between NAND and NOR Flash is the bus interface. NOR Flash is connected to a address / data bus direct like
Storage in Database Systems. CMPSCI 445 Fall 2010
 Storage in Database Systems CMPSCI 445 Fall 2010 1 Storage Topics Architecture and Overview Disks Buffer management Files of records 2 DBMS Architecture Query Parser Query Rewriter Query Optimizer Query
Storage in Database Systems CMPSCI 445 Fall 2010 1 Storage Topics Architecture and Overview Disks Buffer management Files of records 2 DBMS Architecture Query Parser Query Rewriter Query Optimizer Query
Chapter 12 File Management
 Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles Chapter 12 File Management Eighth Edition By William Stallings Files Data collections created by users The File System is one of the most important parts
Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles Chapter 12 File Management Eighth Edition By William Stallings Files Data collections created by users The File System is one of the most important parts
Topics in Computer System Performance and Reliability: Storage Systems!
 CSC 2233: Topics in Computer System Performance and Reliability: Storage Systems! Note: some of the slides in today s lecture are borrowed from a course taught by Greg Ganger and Garth Gibson at Carnegie
CSC 2233: Topics in Computer System Performance and Reliability: Storage Systems! Note: some of the slides in today s lecture are borrowed from a course taught by Greg Ganger and Garth Gibson at Carnegie
AN10860_1. Contact information. NXP Semiconductors. LPC313x NAND flash data and bad block management
 Rev. 01 11 August 2009 Application note Document information Info Keywords Abstract Content LPC3130 LPC3131 LPC313x LPC313X LPC3153 LPC3154 LPC3141 LPC3142 LPC31XX LPC31xx Linux kernel Apex boot loader
Rev. 01 11 August 2009 Application note Document information Info Keywords Abstract Content LPC3130 LPC3131 LPC313x LPC313X LPC3153 LPC3154 LPC3141 LPC3142 LPC31XX LPC31xx Linux kernel Apex boot loader
TUXERA NTFS for Mac USER GUIDE 2/13. Index
 2/13 Index 1. Introduction to Tuxera NTFS for Mac... 3 1.1 What is a file system driver?... 3 1.2 How does it work?... 3 2. Installation... 5 2.1 Installing Tuxera NTFS for Mac... 5 2.2 Uninstalling Tuxera
2/13 Index 1. Introduction to Tuxera NTFS for Mac... 3 1.1 What is a file system driver?... 3 1.2 How does it work?... 3 2. Installation... 5 2.1 Installing Tuxera NTFS for Mac... 5 2.2 Uninstalling Tuxera
SATA II 3Gb/s SSD. SSD630 Benefits. Enhanced Performance. Applications
 SATA II 3Gb/s SSD SSD630 Benefits Super slim thickness of 7mm Fully compatible with devices and OS that support the SATA II 3Gb/s standard Non-volatile Flash Memory for outstanding data retention Built-in
SATA II 3Gb/s SSD SSD630 Benefits Super slim thickness of 7mm Fully compatible with devices and OS that support the SATA II 3Gb/s standard Non-volatile Flash Memory for outstanding data retention Built-in
COS 318: Operating Systems. Storage Devices. Kai Li Computer Science Department Princeton University. (http://www.cs.princeton.edu/courses/cos318/)
 COS 318: Operating Systems Storage Devices Kai Li Computer Science Department Princeton University (http://www.cs.princeton.edu/courses/cos318/) Today s Topics Magnetic disks Magnetic disk performance
COS 318: Operating Systems Storage Devices Kai Li Computer Science Department Princeton University (http://www.cs.princeton.edu/courses/cos318/) Today s Topics Magnetic disks Magnetic disk performance
DFS: A File System for Virtualized Flash Storage
 DFS: A File System for Virtualized Flash Storage William K. Josephson [email protected] Lars A. Bongo [email protected] Kai Li [email protected] David Flynn [email protected] Abstract This paper
DFS: A File System for Virtualized Flash Storage William K. Josephson [email protected] Lars A. Bongo [email protected] Kai Li [email protected] David Flynn [email protected] Abstract This paper
Windows OS File Systems
 Windows OS File Systems MS-DOS and Windows 95/98/NT/2000/XP allow use of FAT-16 or FAT-32. Windows NT/2000/XP uses NTFS (NT File System) File Allocation Table (FAT) Not used so much, but look at as a contrast
Windows OS File Systems MS-DOS and Windows 95/98/NT/2000/XP allow use of FAT-16 or FAT-32. Windows NT/2000/XP uses NTFS (NT File System) File Allocation Table (FAT) Not used so much, but look at as a contrast
McGraw-Hill Technology Education McGraw-Hill Technology Education
 McGraw-Hill Technology Education McGraw-Hill Technology Education Copyright 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Copyright 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
McGraw-Hill Technology Education McGraw-Hill Technology Education Copyright 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Copyright 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
hybridfs: Integrating NAND Flash-Based SSD and HDD for Hybrid File System
 hybridfs: Integrating NAND Flash-Based SSD and HDD for Hybrid File System Jinsun Suk and Jaechun No College of Electronics and Information Engineering Sejong University 98 Gunja-dong, Gwangjin-gu, Seoul
hybridfs: Integrating NAND Flash-Based SSD and HDD for Hybrid File System Jinsun Suk and Jaechun No College of Electronics and Information Engineering Sejong University 98 Gunja-dong, Gwangjin-gu, Seoul
Lecture 25 Symbian OS
 CS 423 Operating Systems Design Lecture 25 Symbian OS Klara Nahrstedt Fall 2011 Based on slides from Andrew S. Tanenbaum textbook and other web-material (see acknowledgements) cs423 Fall 2011 1 Overview
CS 423 Operating Systems Design Lecture 25 Symbian OS Klara Nahrstedt Fall 2011 Based on slides from Andrew S. Tanenbaum textbook and other web-material (see acknowledgements) cs423 Fall 2011 1 Overview
Industrial Flash Storage Trends in Software and Security
 January 22, 2013 Industrial Flash Storage Trends in Software and Security Many flash storage devices in embedded applications are used to save data but also function as disks for the OS. Most users are
January 22, 2013 Industrial Flash Storage Trends in Software and Security Many flash storage devices in embedded applications are used to save data but also function as disks for the OS. Most users are
Learning Objectives. Chapter 1: Networking with Microsoft Windows 2000 Server. Basic Network Concepts. Learning Objectives (continued)
 Chapter 1: Networking with Microsoft Learning Objectives Plan what network model to apply to your network Compare the differences between Windows 2000 Professional, Server, Advanced Server, and Datacenter
Chapter 1: Networking with Microsoft Learning Objectives Plan what network model to apply to your network Compare the differences between Windows 2000 Professional, Server, Advanced Server, and Datacenter
On Benchmarking Popular File Systems
 On Benchmarking Popular File Systems Matti Vanninen James Z. Wang Department of Computer Science Clemson University, Clemson, SC 2963 Emails: {mvannin, jzwang}@cs.clemson.edu Abstract In recent years,
On Benchmarking Popular File Systems Matti Vanninen James Z. Wang Department of Computer Science Clemson University, Clemson, SC 2963 Emails: {mvannin, jzwang}@cs.clemson.edu Abstract In recent years,
A Data De-duplication Access Framework for Solid State Drives
 JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING 28, 941-954 (2012) A Data De-duplication Access Framework for Solid State Drives Department of Electronic Engineering National Taiwan University of Science
JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING 28, 941-954 (2012) A Data De-duplication Access Framework for Solid State Drives Department of Electronic Engineering National Taiwan University of Science
Installing a Second Operating System
 Installing a Second Operating System Click a link below to view one of the following sections: Overview Key Terms and Information Operating Systems and File Systems Managing Multiple Operating Systems
Installing a Second Operating System Click a link below to view one of the following sections: Overview Key Terms and Information Operating Systems and File Systems Managing Multiple Operating Systems
An Exploration of Hybrid Hard Disk Designs Using an Extensible Simulator
 An Exploration of Hybrid Hard Disk Designs Using an Extensible Simulator Pavan Konanki Thesis submitted to the Faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University in partial fulfillment
An Exploration of Hybrid Hard Disk Designs Using an Extensible Simulator Pavan Konanki Thesis submitted to the Faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University in partial fulfillment
Introduction to BitLocker FVE
 Introduction to BitLocker FVE (Understanding the Steps Required to enable BitLocker) Exploration of Windows 7 Advanced Forensic Topics Day 3 What is BitLocker? BitLocker Drive Encryption is a full disk
Introduction to BitLocker FVE (Understanding the Steps Required to enable BitLocker) Exploration of Windows 7 Advanced Forensic Topics Day 3 What is BitLocker? BitLocker Drive Encryption is a full disk
Linux Driver Devices. Why, When, Which, How?
 Bertrand Mermet Sylvain Ract Linux Driver Devices. Why, When, Which, How? Since its creation in the early 1990 s Linux has been installed on millions of computers or embedded systems. These systems may
Bertrand Mermet Sylvain Ract Linux Driver Devices. Why, When, Which, How? Since its creation in the early 1990 s Linux has been installed on millions of computers or embedded systems. These systems may
Storage and File Systems. Chester Rebeiro IIT Madras
 Storage and File Systems Chester Rebeiro IIT Madras 1 Two views of a file system system calls protection rwx attributes Application View Look & Feel File system Hardware view 2 Magnetic Disks Chester Rebeiro
Storage and File Systems Chester Rebeiro IIT Madras 1 Two views of a file system system calls protection rwx attributes Application View Look & Feel File system Hardware view 2 Magnetic Disks Chester Rebeiro
FUJIFILM Recording Media U.S.A., Inc. LTO Ultrium Technology
 FUJIFILM Recording Media U.S.A., Inc. LTO Ultrium Technology 1 What is LTO Ultrium Technology? LTO stands for Linear Tape Open, since it is linear data tape, and targeted to open systems environments in
FUJIFILM Recording Media U.S.A., Inc. LTO Ultrium Technology 1 What is LTO Ultrium Technology? LTO stands for Linear Tape Open, since it is linear data tape, and targeted to open systems environments in
A Survey on Android vs. Linux
 A Survey on Android vs. Linux Frank Maker 1 and Yu-Hsuan Chan 2 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of California, Davis 1 Department of Computer Science, University of California,
A Survey on Android vs. Linux Frank Maker 1 and Yu-Hsuan Chan 2 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of California, Davis 1 Department of Computer Science, University of California,
CSCA0201 FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTING. Chapter 5 Storage Devices
 CSCA0201 FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTING Chapter 5 Storage Devices 1 1. Computer Data Storage 2. Types of Storage 3. Storage Device Features 4. Other Examples of Storage Device 2 Storage Devices A storage device
CSCA0201 FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTING Chapter 5 Storage Devices 1 1. Computer Data Storage 2. Types of Storage 3. Storage Device Features 4. Other Examples of Storage Device 2 Storage Devices A storage device
Solid State Drive (SSD) FAQ
 Solid State Drive (SSD) FAQ Santosh Kumar Rajesh Vijayaraghavan O c t o b e r 2 0 1 1 List of Questions Why SSD? Why Dell SSD? What are the types of SSDs? What are the best Use cases & applications for
Solid State Drive (SSD) FAQ Santosh Kumar Rajesh Vijayaraghavan O c t o b e r 2 0 1 1 List of Questions Why SSD? Why Dell SSD? What are the types of SSDs? What are the best Use cases & applications for
QUICK RECOVERY FOR RAID
 Quick Recovery for RAID Features File Systems Supported Who suffers most Recovery Modes De-Stripper File Recovery Frequently Asked Questions QUICK RECOVERY FOR RAID Quick Recovery for RAID 0, RAID 5. Quick
Quick Recovery for RAID Features File Systems Supported Who suffers most Recovery Modes De-Stripper File Recovery Frequently Asked Questions QUICK RECOVERY FOR RAID Quick Recovery for RAID 0, RAID 5. Quick
JAM: Justifiable Allocation of Memory with Efficient Mounting and Fast Crash Recovery for NAND Flash Memory File Systems
 The International Arab Journal of Information Technology, Vol. 7, No. 4, October 2010 395 JAM: Justifiable Allocation of Memory with Efficient Mounting and Fast Crash Recovery for NAND Flash Memory File
The International Arab Journal of Information Technology, Vol. 7, No. 4, October 2010 395 JAM: Justifiable Allocation of Memory with Efficient Mounting and Fast Crash Recovery for NAND Flash Memory File
File Management Chapters 10, 11, 12
 File Management Chapters 10, 11, 12 Requirements For long-term storage: possible to store large amount of info. info must survive termination of processes multiple processes must be able to access concurrently
File Management Chapters 10, 11, 12 Requirements For long-term storage: possible to store large amount of info. info must survive termination of processes multiple processes must be able to access concurrently
1. Introduction to the UNIX File System: logical vision
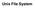 Unix File System 1. Introduction to the UNIX File System: logical vision Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2005 Operating System Concepts 7 th Edition, Feb 6, 2005 Logical structure in each FS (System V):
Unix File System 1. Introduction to the UNIX File System: logical vision Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2005 Operating System Concepts 7 th Edition, Feb 6, 2005 Logical structure in each FS (System V):
ReconFS: A Reconstructable File System on Flash Storage
 ReconFS: A Reconstructable File System on Flash Storage Youyou Lu, Jiwu Shu, and Wei Wang, Tsinghua University https://www.usenix.org/conference/fast14/technical-sessions/presentation/lu This paper is
ReconFS: A Reconstructable File System on Flash Storage Youyou Lu, Jiwu Shu, and Wei Wang, Tsinghua University https://www.usenix.org/conference/fast14/technical-sessions/presentation/lu This paper is
Operating Systems CSE 410, Spring 2004. File Management. Stephen Wagner Michigan State University
 Operating Systems CSE 410, Spring 2004 File Management Stephen Wagner Michigan State University File Management File management system has traditionally been considered part of the operating system. Applications
Operating Systems CSE 410, Spring 2004 File Management Stephen Wagner Michigan State University File Management File management system has traditionally been considered part of the operating system. Applications
Distributed File Systems
 Distributed File Systems Paul Krzyzanowski Rutgers University October 28, 2012 1 Introduction The classic network file systems we examined, NFS, CIFS, AFS, Coda, were designed as client-server applications.
Distributed File Systems Paul Krzyzanowski Rutgers University October 28, 2012 1 Introduction The classic network file systems we examined, NFS, CIFS, AFS, Coda, were designed as client-server applications.
Embedded Operating Systems in a Point of Sale Environment. White Paper
 Embedded Operating Systems in a Point of Sale Environment White Paper December 2008 Contents Embedded Operating Systems in a POS Environment... 3 Overview... 3 POS Operating Systems... 3 Operating Systems
Embedded Operating Systems in a Point of Sale Environment White Paper December 2008 Contents Embedded Operating Systems in a POS Environment... 3 Overview... 3 POS Operating Systems... 3 Operating Systems
Filing Systems. Filing Systems
 Filing Systems At the outset we identified long-term storage as desirable characteristic of an OS. EG: On-line storage for an MIS. Convenience of not having to re-write programs. Sharing of data in an
Filing Systems At the outset we identified long-term storage as desirable characteristic of an OS. EG: On-line storage for an MIS. Convenience of not having to re-write programs. Sharing of data in an
FAQ for USB Flash Drive
 FAQ for USB Flash Drive 1. What is a USB Flash Drive? A USB Flash Drive consists of a flash memory data storage device integrated with a USB interface. USB Flash Drives are typically removable and rewritable.
FAQ for USB Flash Drive 1. What is a USB Flash Drive? A USB Flash Drive consists of a flash memory data storage device integrated with a USB interface. USB Flash Drives are typically removable and rewritable.
Programming NAND devices
 Technical Guide Programming NAND devices Kelly Hirsch, Director of Advanced Technology, Data I/O Corporation Recent Design Trends In the past, embedded system designs have used NAND devices for storing
Technical Guide Programming NAND devices Kelly Hirsch, Director of Advanced Technology, Data I/O Corporation Recent Design Trends In the past, embedded system designs have used NAND devices for storing
CS 153 Design of Operating Systems Spring 2015
 CS 153 Design of Operating Systems Spring 2015 Lecture 22: File system optimizations Physical Disk Structure Disk components Platters Surfaces Tracks Arm Track Sector Surface Sectors Cylinders Arm Heads
CS 153 Design of Operating Systems Spring 2015 Lecture 22: File system optimizations Physical Disk Structure Disk components Platters Surfaces Tracks Arm Track Sector Surface Sectors Cylinders Arm Heads
SOLID STATE DRIVES AND PARALLEL STORAGE
 SOLID STATE DRIVES AND PARALLEL STORAGE White paper JANUARY 2013 1.888.PANASAS www.panasas.com Overview Solid State Drives (SSDs) have been touted for some time as a disruptive technology in the storage
SOLID STATE DRIVES AND PARALLEL STORAGE White paper JANUARY 2013 1.888.PANASAS www.panasas.com Overview Solid State Drives (SSDs) have been touted for some time as a disruptive technology in the storage
A+ Guide to Software: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e. Chapter 3 Installing Windows
 : Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e Chapter 3 Installing Windows Objectives How to plan a Windows installation How to install Windows Vista How to install Windows XP How to install Windows
: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e Chapter 3 Installing Windows Objectives How to plan a Windows installation How to install Windows Vista How to install Windows XP How to install Windows
Main Points. File layout Directory layout
 File Systems Main Points File layout Directory layout File System Design Constraints For small files: Small blocks for storage efficiency Files used together should be stored together For large files:
File Systems Main Points File layout Directory layout File System Design Constraints For small files: Small blocks for storage efficiency Files used together should be stored together For large files:
AN1819 APPLICATION NOTE Bad Block Management in Single Level Cell NAND Flash Memories
 APPLICATION NOTE Bad Block Management in Single Level Cell NAND Flash Memories This Application Note explains how to recognize factory generated Bad Blocks, and to manage Bad Blocks that develop during
APPLICATION NOTE Bad Block Management in Single Level Cell NAND Flash Memories This Application Note explains how to recognize factory generated Bad Blocks, and to manage Bad Blocks that develop during
