Project V3 Lava PROJECT V3 LAVA
|
|
|
- Buck Parsons
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Project V3 Lava PROJECT V3 LAVA 177
2 178
3 Project V3 Lava Coordinators: Project V3 - LAVA Realization of the lava flow hazard map at Mount Etna and set up of a method for its dynamic update Ciro Del Negro, Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia, Sezione di Catania, Piazza Roma 2, Catania, Italy, delnegro@ct.ingv.it Stefano Gresta, Dipartimento di Scienze Geologiche, Università di Catania, Corso Italia 57, Catania, Italy, gresta@unict.it Objectives Mt. Etna is one of the most active and investigated volcanoes in the world. Its eruptions are often characterized by lava flows which spread along its flanks. Such eruptions can potentially reach the villages located to medium-low elevations. Even the area where city of Catania is settled was reached in the past by the flows outpoured from eruptive fractures opened at lower elevations. In the last century, the village of Mascali was destroyed by lava flows in 1928, while the villages of Fornazzo in 1979 and Randazzo in 1981 were threatened by lava flows. More recently, several tourist facilities have been repeatedly destroyed, with serious damage to the local economy. Some results of the previous INGV-DPC ( ) Project V3_6 Etna, concerning: (i) the updated catalogue of eruptions, (ii) the better knowledge of the internal structure of the volcano, (iii) the capability to model in the near-real-time the data from the monitoring networks with the goal of identifying the most probable areas of opening of an eruptive fissure, and (iv) the considerable progress in the simulation of lava flows; allow us to define the objective of the present project. It consists in the production of hazard maps from invasion of lava flow for medium and short term. The short term maps will be dynamic instruments, which could be semi-automatically modified by considering the signals collected by the monitoring networks, the evolution of the eruption, and the weighted opinion of experts. The research in the project will include the followings steps: a. Definition and realization of databases and digital maps in GIS architecture, integrating the geological geophysical, and geochemical information. b. Definition of the principles and paradigms for the realization of the dynamic hazard map. c. Definition of the vent opening probability at medium and short term, on the basis of data from the terrestrial and satellite observation systems. d. Application of mathematical models for the prediction of lava flow paths. e. Realization of the hazard map. f. Development of methodologies for the dynamic update of the hazard map on the basis of the data from the observation systems, and comparison with test cases from recent eruptions. g. Study of the methodologies for the operational functioning of the new technologies at point f above, and of the interface modalities with the Functional Center of DPC. LAVA will provide practical forecasts of the future course of lava flows to enable quantitative hazard assessments and operational guidelines for, potentially, mitigatory 179
4 actions to be undertaken. We plan to achieve these forecasts by use of numerical computer simulation of the flow paths over the surface of the volcano, these simulations will be constrained by knowledge from former eruptions and from near real-time field and remote observations of the state of lava flow advance. 180 Espected products Data employed in the project, organized in a database. Guidelines for the realization of the lava flow hazard map and its dynamic update. Eruptive fracture/vent opening probability map at medium and short term, including the dynamic update methodologies at point f above. Lava flow hazard map at Mount Etna, including the dynamic update methodologies at point f above. Applications of the dynamic hazard maps at the two points above to test cases from recent eruptions at Mount Etna. Feasibility study for the realization of an interface at the Functional Center of DPC, to be agreed upon with the same DPC, for the products at the last three point above. State of the Art of the ongoing researches related to the present objectives It is not possible to prevent a volcano from erupting, but it is now becoming possible to forecast generally where a volcano is likely to direct a lava flow and when such a flow is underway to forecast its course and rate of advance. Timely predictions of the areas likely to be invaded by lava flows are of major interest to hazard managers during a volcanic eruption. Although most volcanic lava flows do not result in loss of human life, they can potentially cause enormous damage to property. Lava flows can bury homes and agricultural land under several meters of hardened rock. Typical examples of lava flows are from the Etna volcano, where its frequent effusive eruptions can pose hazard to several villages. In order to estimate the amount of damage that can be caused by a lava flow, it is useful to be able to predict the size and extent of such flows. Numerical simulation is a good tool to examine such events. With such simulations, one can explore various eruption scenarios and these can specifically be used to estimate the extent of the invasion area, the time required for the flow to reach a particular point and resulting morphological changes. However, it is not easy to develop a robust tool for forecasting lava flow pathways, because the temperature, rheological properties and effusion rates are not linearly dependent and they are variables on space-time domain. The INGV-DPC ( ) Project V3_6 Etna improved the hazard assessment at Etna through the development of accurate and robust physical-mathematical models able to forecast the spatial and temporal evolution of lava flows. In particular, the new MAGFLOW model [RU Del Negro] based on cellular automatons for the simulation of lava flows was applied to the recent eruptions of 2001, 2004 and 2006 Etna volcano. The evolution function of this model is a steady state solution of the Navier-Stokes equation in the case of a horizontal plan. The effect of rheology and cooling are included in the model. Total flow volumes of 2004 Etna eruption were obtained by integrating the effusion rates estimated using satellite thermal data over the entire duration of the eruption. MAGFLOW represents the central part of an extensive methodology for the compilation of hazard maps related to lava invasion at Mt Etna. Preliminary hazard map was realized by simulating a number of lava flows from a set of initial data and with different parameters of the volcanic system in a meaningful range of variation.
5 Project V3 Lava The already existing SCIARA model [RU Crisci] was integrated with a Genetic Algorithm (GA) in order to estimate the values of the parameters of the model. This procedure was necessary because SCIARA works with not physical parameters which must be determined before every simulation. The application of the GA to SCIARA model was validated simulating the eruptions of the 2001 and of Etna. Once that the SCIARA model was well calibrated and validated, an application for the new kind compilation of maps showing the hazard related to lava invasion limited to the North Eastern flank of Mount Etna was achieved. The simulations of the lava flows were also obtained with DOWNFLOW code, based on the steepest slope [RU Favalli]. Probability maps of invasion by lava flows constructed for the Mt. Etna using DOWNFLOW were based on: (i) the probability distribution of the future vents and (ii) the probability distribution of the length of future lava flows. The (E3) emulator [RU Fortuna] based on cellular nonlinear network (CNN) for the simulation of lava flows was also introduced. Two different applications were performed: the former was based on autowaves model, while in the latter the base equations of the emulator are replaced with the equation of the motion of a fluid. In framework of the previous INGV-DPC Etna Project, the treatment of the satellite imagery in order to recognize thermal anomalies (hot-spot detection) and to estimate the lava flow rate was also investigated [RUs Tramutoli and Lombardo]. In particular, it was developed an automatic system for the preprocessing and the computation of lava effusion rate using infrared satellite data [RU Del Negro]. The relationships between the thermal and dynamical aspects of lava flows, with the particular objective of understanding the formation, characteristics and evolution of lava tubes were also studied [RU Tallarico]: (i) the flow in a cylindrical tube with elliptic section, (ii) the temperature field and heat flow around elliptical tubes, (iii) the thermo elastic deformation associated to a lava tube, and (iv) the mechanism of formation of the crust, observing that it generates from the center of the channel, where the shear rate is low, to the lateral. The updating of the DEM (Digital Elevation Model) of the Mt. Etna in areas affected by the volcanic unrest was achieved through the elaboration of the aero-photogrammetric relieves and photogrammetric elaboration of historical data for the production of DEM pre and post eruption relative to the events , 1999 Bocca Nuova, Crateri Sommitali, 2001 flow from 2100 m a.s.l., flows on the S and NE flanks, Valle del Bove [RU Marsella]. At last, it was drawn the complete procedure for the reconstruction of the geometric and physical data (included associated errors), necessary for the validation of the lava flow simulations, developed for the 2001 Etna eruption - flow from 2100 m a.s.l. [RU Coltelli]. On the other side, results of the previous INGV-DPC Etna Project concern a better knowledge of the shallow plumbing system and structure of the volcano, through the location and properties of some shallow magma bodies. It is noteworthy also the identification of significant anomalies for earthquake and geochemical parameters, as well as the definition of the critical levels that define the transition between different stages of activity of the volcano, that was successfully by considering the volcanic tremor [RU Gresta]. This last result, actually allow us to track the migration of the tremor source(s) into the shallow part of the volcano body. Description of the activities Etna will undoubtedly erupt again. When it does, the first critical question that must be answered is: which areas are threatened with lava invasion? Once the threatened areas are established, we can address the second critical question: what people, property, and facilities are at risk? These questions can be answered by estimating the areas most likely 181
6 to be affected by eruptions on various parts of the volcano. On the base of our experience in both monitoring and modelling of the lava flow emplacement during past Etna eruptions, we plan to develop a methodology for computing such estimates on Etna based on the knowledge of eruptive vents and areas covered by past lava flow eruptions. We will divide the volcano into potential lava inundation zones and prepare detailed maps of these zones, which should be presented as layers of a GIS environment. The application of physical-mathematical models for simulating the lava flow paths will represent the central part of an extensive methodology for the hazard assessment at Etna. Hazard assessment will be performed by simulating a number of lava flows from a set of input data (from the record of past eruptions) in a meaningful range of variation and by adopting a high-resolution updated Digital Elevation Model (DEM). The effort to obtain a probabilistic lava flow hazard map of Etna will consist of following steps: a multivariate statistical analysis of the historical and pre-historical eruptions will provide: the likelihood of a lava vent at every position on Etna, the likelihood that vent will produce a specific type of lava flow; 2. random vent location by re-sampling of the vent density surface (Monte Carlo method), assignment of the most probable flow type, and generation of the required vent number; 3. parameterization of lava flow: creation of a library of parameter settings, corresponding to reasonable fits for each of the eruption used, by a series of trials using the numerical simulations to match the observed spatial distribution of lava; 4. simulation of the new eruptions by adopting the parameter settings that best simulate the nearest historical lava flows; 5. evaluation of the probability at any given point to be inundated by lava flows as the ratio between the number of times that point was overridden by lava and the total number of simulations. The simulation approach, to assess lava flow hazard, results in more robust and locally accurate analysis than a simple probabilistic approach and accounts for the influence of the actual topography on the path of future lava flows. Generating multiple simulations will allow us to evaluate the probability of lava inundating anywhere on the surface of the volcano. This probability will be captured as a hazard map, showing the relative frequency of lava flows that could potentially inundate specific areas. Such probability maps indicate the likely areas that could be affected but not which area will be covered by a specific eruption. The quantitative description of hazard in terms of vent opening probability will be also pursued. During recent years, new insights on the behaviour of Mt. Etna have been gained regarding the understanding of past eruptive activity, the dynamics of the volcano, the magma transfer processes, and the geophysical and geochemical monitoring. A number of expertises are now available in many fields of investigation. An effort for an effective integration of this knowledge, basically to consider information coming from monitoring activity (i.e. earthquake location, flank inflation/deflation, anomalies in other parameters) to be interpreted in terms of possible magma upraise/migration, activation of structures, etc., evolving to the occurrence of the vent opening in a given area of the volcano. The opinion of a team of experts has been already used in a Bayesian statistical procedure that accounts for any kind of available information both on real unrest of a volcano, and on
7 Project V3 Lava simulation of the Vesuvius unrest. The quality of both data and expertise by researchers will induce to test a retrospective BET application at Mt. Etna for the production of short term dynamic hazard map when critical levels of the volcano activity are reached. The problem of building scenarios through the straightforward simulation of lava flows during ongoing eruptions requires the development, validation and application of accurate and robust physical-mathematical models able to calculate their spatial and temporal evolution. Methods for modeling lava flows attempt to simulate how the complex interaction between flow dynamics and physical properties of lava lead to the final flow dimensions and morphology observed in the field. Existing and new models based on different physical formulations and approaches will be developed and applied to real cases in order to make model inter-comparisons and more robust forecasts of the phenomena. Models will also use, as much as possible, data deriving from the field observations, for model validation, and experimental data, for constitutive equations. We will focus on the integration of robust satellite techniques and advanced numerical models to develop an automatic monitoring system capable of timely identifying hot volcanic features in near real time, providing reliable estimation of the effusion rates and accurate simulation of lava flow space-time evolution in near real-time. To promptly detect volcanic hot spots, high temporal resolution satellite data will be used, implementing an innovative multi-temporal approach which has shown to be capable of strongly reducing false alarm occurrence. This approach, being potentially suitable to identify also anomalous thermal signals that may sometime precede impending eruptions, will offer a high contribute for early warning purposes. Satellite thermal anomaly maps will be used to provide early and accurate effusion rate estimations by means of standard and/or original algorithms. Effusion Rate products, together with precise and updated DEM, previously derived by using also the more recent high spatial resolution satellite stereo images, will be used as input parameters of advanced numerical modelling schemes in order to accurately simulate lava flow paths and to predict their space-time evolution in a timely manner. Finally, we will explore the possibility of slowing and diverting the lava flow by using artificial barriers to guide their course. Simulations of the lava flow paths after the designed intervention will be performed to predict the benefits of the action the related rewards and disadvantages respect to the natural path. The barriers will be modelled by modifying the pre-eruption topography to be used as input parameter of the simulations. Graphical presentation of the work packages and their interdependencies. 183
8 List of Research Units (RU): RU Scientific Responsible Organization Acronym RU-01* Ciro Del Negro INGV Sezione di Catania INGV-CT RU-02 Stefano Gresta University of Catania DSG UNICT-DSG RU-03 Gino Mirocle Crisci University of Calabria DST UNICAL-DST RU-04 Massimiliano Favalli INGV Sezione di Pisa INGV-PI RU-05 Luigi Fortuna University of Catania DIEES UNICT-DIEES RU-06 Valerio Lombardo INGV Centro Nazionale Terremoti INGV-CNT RU-07 Maria Marsella University of Roma La Sapienza DITS UNIRM-DITS RU-08 Giovanni Russo University of Catania DMI UNICT-DMI RU-09 Andrea Tallarico University of Bari DGG UNIBA-DGG RU-10 Valerio Tramutoli University of Basilicata- DIFA UNIBAS-DIFA *List of Teams (TM) of Research Unit 01: TEAM Scientific Responsible Organization Acronym TM-01A Mauro Coltelli INGV - Sezione di Catania INGV-CT TM-01B Fabrizio Ferrucci University of Calabria DST UNICAL-DST TM-01C Marco Neri INGV Sezione di Catania INGV-CT TM-01D Harry Pinkerton University of Lancaster (UK) UNILAN-UK TM-01E Danilo Reitano INGV Sezione di Catania INGV-CT TM-01F Alexis Herault INGV - Sezione di Catania INGV-CT TM-01G Annamaria Vicari INGV - Sezione di Catania INGV-CT 184
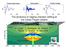
9 Project V3 Lava Description of Tasks LAVA relies upon the integration of advanced numerical models with robust satellite techniques for dynamic hazard assessment and mitigation. The project will develop along five Tasks: Task 1. Guide Line and Protocols Data Base and digital maps in GIS architecture to integrate geological, geophysical and geochemical data. Development of protocols and scenarios to manage lava flow hazard. Feasibility study to transfer results at Centro Funzionale of Department of Civil Protection (DPC). Task 2. Numerical Simulations and Satellite Techniques Development of physicalmathematical models for lava flow simulations. Development of techniques based on satellite data for collecting parameters to be input into lava flow simulators. Task 3. Lava Flow Invasion Hazard Map Definition of guidelines to develop lava flow invasion hazard maps and their dynamic update. Eruption history and features of the lava flow as a constraint on hazard simulation. Lava flow invasion hazard maps. Task 4. Vent Opening Probability Map Mid and short term probability map of eruptive fracture opening using terrestrial and satellite data. Methodologies for the dynamic updating of hazard maps based on observable data. Tests on recent eruptive events. Task 5. Scenario Forecast and Hazard Mitigation Lava flow simulations driven by infrared satellite data from active lava flows. Protocols for the real-time prediction of lava flow paths for planning emergency response. Barrier design for volcano hazard mitigation. For each Task several Working Packages (WP) have been identified to answer to the request of the project. A sketch description of each Task will be presented in the next pages together with a list of expected deliverables (according to the activities planned by each Research Unit) and the inter-connections between them. A detailed description of the scientific activities is left to the forms compiled by the Research Units. To assume an efficient management of this consortium and to build a good communication network, all Tasks will be directly managed by two coordinators. Project work breakdown structure. 185
10 TASK 1. GUIDELINES AND PROTOCOLS RU and TM Partecipating RU Del Negro, TM Coltelli, TM Ferrucci, TM Neri, TM Pinkerton, TM Reitano, TM Herault, TM Vicari, RU Gresta, RU Crisci, RU Favalli, RU Fortuna, RU Lombardo, RU Marsella, RU Russo, RU Tallarico, RU Tramutoli Objectives Definition of guidelines to develop lava flow invasion hazard maps and their dynamic update. Description of the activity From our experience in the volcano-specific work we will synthesize new methodologies, protocols, procedures and scenarios to evaluate and manage lava flow hazards. The improvement of protocols for forecasting volcanic threat and planning damage reduction efforts will be used to prepare a guide on prevention and mitigation of volcanic crisis, to be provided to local governments and civil protection authorities. Work-Packages WP Development of internal and public Web portal An internal and public Web portal will be created by the coordinators at the beginning of the project. All general information concerning the projects will be posted in this site. The lava flow hazard maps of Etna volcano, developed on an open source platform, will be transferred as tools for territorial planning and hazard mapping to end users. Role of participants Coordinators: creation of the Web portal uploaded of all general information. The other Participants: contribution with ideas, information and data. WP 1.2 Guide lines for the hazard map and methods for its dynamic update Elaboration of guidelines on how the hazard map may be organized to be more effective, including elaboration of methods for its dynamic update by considering time variations of observations and expert opinions. Role of participants Coordinators and the other Participants: transferring of new methodologies, hazard criteria, protocols, procedures and scenarios to evaluate and manage volcanic hazard to end users. WP 1.3 Feasibility study to realize a DPC interface Definition of procedures and protocols to transfer results coming from Task 3, Task 4, and Task 5 to DPC about: lateral vents opening probability for different sectors of the volcanoes, localization of the eruptive vents, lava effusion rate measurements, possible lava flow paths evaluation, lava movement speed evaluation, definition of the most exposed villages, time the lava flow needs to reach settled areas, time and kind of intervention. Role of participants Coordinators and the other Participants: transferring of new methodologies, hazard criteria, protocols, procedures and scenarios to evaluate and manage volcanic hazard to end users. 186
11 Project V3 Lava Deliverables D1.1a Web site (month 3, update monthly). D1.1b Lava flow hazard map on an open source GIS. D1.2a Report on lava flow risk evaluation criteria. D1.2b Guidelines on prevision, prevention and mitigation of volcanic hazard. D1.3a Report on procedures to manage lava flow hazard. D1.3b Protocols on hazard management for the end-users. TASK 2. NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS AND SATELLITE TECHNIQUES RU and TM Partecipating RU Del Negro, TM Ferrucci, TM Pinkerton, TM Reitano, TM Herault, TM Vicari, RU Crisci, RU Favalli, RU Fortuna, RU Lombardo, RU Russo, RU Tallarico, RU Tramutoli Objectives Development of physical-mathematical models for forecasting lava flow paths and improvement of satellite techniques to drive flow simulations. Description of the activity We will develop innovative computer codes able to include much of the physical parameterization of lava flows in terms of viscosity, yield strength, and density and bring the goal of robust forecasting closer. The code performance will be assessed by a sensitivity analysis on the input parameters, carried out by simulating actual lava flows having a well known eruptive history. Moreover, techniques capable of measuring effusion rates during an eruption are of particular value since accurate effusion rate estimates are important in hazard prediction, warning, and mitigation. To this end, we will develop techniques that use thermal infrared satellite data to estimate the instantaneous lava flow output by a vent throughout eruptions. These time-varying effusion rates will be used to drive lava flow simulations calculated by physical-mathematical models that can take into account the way in which effusion rate changes during an eruption and how this influences the spread of lava as a function of time. Work-Packages: WP 2.1 Physical and chemical parameterization of flow behavior Collection of the available physical and chemical data for all the lava flow eruptions taken into account. Conversion of laboratory-derived petrological data into admissible rheological parameter fields. Evaluation of the input parameters to be used for accurate simulations of the observed final flow extent. Role of participants TM Coltelli: collection of the available physical and chemical data for lava flow eruptions of Etna volcano; input parameter evaluation and library of simulator parameters creation. RU Tallarico and TM Pinkerton: laboratory- and field-derived lava rheology analysis and rheological modelling; input parameter evaluation and library of simulator parameters creation. WP 2.2 Development of thermal and fluid-dynamical models of lava flows Quantitative studies on the dynamics of lava flows in order to provide the physical constrains necessary to develop a method to predict the lava flows path. Improvement of the reliability of the dynamical models of lava flows considering non-linear rheologies. 187
12 The latest multicomponent models for lava viscosity will be included in the numerical codes. Role of participants RU Tallarico and TM Pinkerton: experimental data concerning thermal properties of lava. RU Russo and RU Tallarico: Dynamical models with non linear rheology. Models for crust formation. WP 2.3 Development of techniques for hot-spot detection Development and validation up to a pre-operative level of robust satellite techniques for real-time detection and monitoring of hot spots related to volcanic eruptions. Role of participants RU Tramutoli, RU Fortuna, TM Vicari, and RU Lombardo: improved algorithms for hot spots detection based on MODIS and AVHRR sensors TM Ferrucci, TM Vicari, and RU Del Negro: improved algorithms for hot spots detection based on SEVIRI and MODIS sensors. WP Development of techniques for lava effusion rate measurements Development and validation up to a pre-operative level of robust satellite techniques for near real-time effusion rate lava flow estimations. Role of participants RU Tramutoli, RU Del Negro, RU Tallarico, RU Fortuna and RU Lombardo: improved algorithms for measurements of effusion rate based on MODIS and AVHRR sensors RU Ferrucci and RU Del Negro: improved algorithms for hot spots detection based on SEVIRI and MODIS sensors. WP 2.5 Development of techniques for intra-event rapid DEM mapping Definition of an innovative approach for rapid generation Digital Elevation Model over area where volcano unrest is occurring. Role of participants RU Lombardo, RU Del Negro: Study of a methodology for post-event DEM correction starting from a pre-event DEM and jointly using all the different sensors data available over the area WP 2.6 Development of numerical models for lava flow simulations Existing and new models based on different physical formulations and approaches will be developed and applied to real cases in order to make model inter-comparisons and more robust forecasts of the phenomena. Models will also use, as much as possible, data deriving from the field observations, for model validation, and experimental data, for constitutive equations. Role of participants RU Del Negro, RU Russo, RU Fortuna, TM Herault, and TM Vicari: development of computer coded, code performance and sensitivity analyses. RU Del Negro, TM Vicari, TM Herault, and TM Coltelli: testing different ways to assimilate field observations into the simulation code. RU Del Negro, RU Fortuna, RU Russo, TM Herault, TM Vicari: sensitivity analyses on topographic data. 188
13 Project V3 Lava Deliverables D2.1 - Database of chemical and physical parameters to fit the observed geometrical features of selected eruptions. D2.2 Report on thermal and fluid-dynamical models of lava flows. D2.3 Report on techniques for hot-spot detection. D2.4 Report on techniques for lava effusion rate measurements. D2.5 Report on techniques for intra-event rapid DEM mapping. D2.6a Report on the numerical simulation techniques adopted for forecast and probabilistic hazard assessment. D2.6b Report on sensitivity analysis of the code to the input parameters. D2.6c Report on how best to assimilate observational data into simulations. TASK 3. LAVA FLOW INVASION HAZARD MAP RU and TM Partecipating RU Del Negro, TM Coltelli, TM Neri, TM Pinkerton, TM Reitano, TM Herault, TM Vicari, RU Crisci, RU Favalli, RU Fortuna, RU Russo Objectives Realization of lava flow invasion hazard maps. Lava flow hazard map for Etna volcano will be implemented on GIS environment by means of a statistical analysis of the simulated lava-flow eruptions obtained by numerical modelling of long- and short-term forecasts of the evolution of volcanic phenomena. Description of the activity The probabilistic long-term hazard assessment will be based on the positioning of a fixed number of vents, through a multivariate statistical analysis on past eruptions. Eruption history and features of the lava flow past will be a constraint on hazard simulation. The probabilistic short-term hazard assessment will be based on the evaluation of the most probable eruption expected in next period (years tens of years). The library of input chemical and physical parameters will allow to set the eruption characteristics to be assigned to the selected vents. Monte Carlo-derived ensemble simulations will be used to evaluate long-term lava flow hazard as the probability of invasion of every point that is the ratio between the number of overruns and the total number of simulations. This probability map will define the relative lava flow hazards over the whole volcano. Work-Packages WP 3.1 Eruption history as a constraint on hazard simulation Geo-Database of the features of the lava flow eruption of the last 4 century. Use of well known lava flow eruptions for Etna volcano from literature and non-published data available at the INGV-CT to constrain general volcano behaviour: duration, volume, effusion rate trend, rheological quality of the lava flow eruptions. Role of participants TM Coltelli and TM Neri: space-temporal statistical analysis of the lava flow eruptions to generate classes and probability distribution functions that will act as specific constraints to the probabilistic generation of simulation ensembles. 189
14 WP 3.2 Topographic data quality Collection of the available topographic data for all the studied volcanic areas. Analysis of the topographic data quality (precision and accuracy). Analysis of the effect of that quality on the lava flow simulations. Role of participants TM Coltelli: collection of the available Etna topographic data, analysis of their influence on lava flow simulations. RU Marsella and Favalli: topographic data requirement and quality assessment for numerical simulations; analysis of their influence on lava flow simulations. WP 3.3 GIS database developing for hazard map The already available GIS of the geological map of Etna will be extended to include the physical and chemical information of the historical lava flow eruptions revised by both recent studies and the new historical catalogue of the eruptions performed by INGV-CT. Geometrical data obtained by topographic techniques will also be included. In order to anticipate areas that could be overrun by lava from different source regions, a layer of the new GIS will be realized to report the identified lava flow inundation zones on the base of both new high-resolution geological data and the simulated lava-flow eruptions obtained by numerical modelling of long- and short-term forecasts of the evolution of volcanic phenomena. The areas with highest probability of lava invasion around several villages in the Etnean region will be identified. Role of participants RU Del Negro, TM Coltelli, and TM Reitano: updating of the GIS of Etna geological map to include physical, chemical and geometrical parameters of the historical lava flows; introducing new layers for lava inundation zoning. WP 3.4: Probabilistic lava flow simulations for long-term volcanic hazard assessment The probabilistic long-term hazard assessment will be based on the catalogue of past eruptions and on the positioning of a fixed number of vents, through a multivariate statistical analysis. The database and the considerations reported will allow to set up the eruption characteristics to be assigned to the selected vents. Role of participants RU Del Negro, RU Crisci and RU Favalli: running of a great number of lava flow simulations, whose characteristics will be selected by a statistical analysis of past events, to asses long-term hazard. RU Del Negro, TM Herault, TM Vicari, TM Coltelli, and RU Russo: statistical analysis of past events to select the characteristics of simulated lava flows. WP 3.5: Probabilistic lava flow simulations for short-term volcanic hazard assessment The probabilistic short-term hazard assessment will be based on the evaluation of the most probable eruption expected in next period (years tens of years) and on the positioning of a fixed number of vents, through a multivariate statistical analysis. Role of participants RU Del Negro, RU Crisci and RU Favalli: short-term hazard assessment running a number of lava flow simulations close to the most probable eruption expected in next period. RU Del Negro TM Herault, TM Vicari, TM Coltelli, and TM Fortuna: statistical analysis of recent events to select the characteristics of simulated lava flows. 190
15 Project V3 Lava WP 3.6 Statistic analysis of the simulation results and implementation of the hazard map The long-term hazard map will show the probability of invasion of every point, defined as the ratio between the number of overruns and the total number of simulations. This map will define the total area that could potentially be affected but not which area will be covered by a specific eruption. Role of participants RU Del Negro, RU Russo, RU Fortuna, TM Herault, TM Vicari and TM Coltelli: analysis of simulation results to provide the long- and short-term hazard map. RU Del Negro, TM Coltelli and TM Reitano: implementation of the GIS database of Etna hazard map. Deliverables: D3.1 Past eruptions features, including geological, physical chemical and geometrical data, structured as GIS layers. D3.2a Collection of all the available topographic data on Etna volcano which satisfy the accuracy requirements for the simulations. D3.2b Report on topographic data collected including quality assessment. D3.3 Generation of classes and probability distribution functions, by a space-temporal statistical analysis of the eruptions, to constrain the probabilistic generation of simulation ensembles. D3.4 Report on the result of the long-term volcanic hazard assessment. D3.5 Report on the result of the short-term volcanic hazard assessment. D3.6 GIS database of Etna lava flow hazard map. TASK 4. VENT OPENING PROBABILITY MAP RU and TM Partecipating RU Gresta, TM Neri, TM Reitano, RU Del Negro, RU Russo Objectives Definition of a medium term hazard map of the vent opening probability. Development of new methodologies to update in time the short term probability hazard map. Description of the activity Realization of a probabilistic assessment of vent location mainly based on seismological (earthquakes and tremor) and volcanological data, integrated with other geophysical and geochemical data, in co-operation with expert researchers by INGV (Roma, Bologna, Catania and Palermo). Work-Packages WP 4.1 Database in GIS architecture (in co-operation with Project V4-Flank) A huge amount of data and information need to be analyzed and combined in order to better investigate the direct and derived volcanic hazards. All data available in the project together with lava flow simulations and satellite images will be transformed and unified in a coherent way to allow integration into a geographic information system (GIS). A completely new, interactive, and user-friendly software tool will be developed as a webbased multimedia platform. Collection of geophysical, volcanological and geochemical 191
16 data acquired at Etna from 1996 to The database will be implemented with the aim of ensure the maximum compatibility with the WOVOdat standard. Role of participants TM Reitano and RU Del Negro: organization of the database, collection of validated data from surveys and previous monitoring systems operating on the volcano. RU Gresta and TM Neri: providing seismological, geophysical, volcanological, geochemical data in hard and/or elaborated versions. WP 4.2 Medium term probability map for the opening of eruptive fractures. Definition of the features of structural trends; distribution of vents, fractures and fissure. Analysis of the eruptive history of the volcano. Test for the stability and choice of the reference medium term hazard map. Role of participants RU Gresta and TM Neri: analysis and interpretation of geo-structural and volcanological data in order to produce the reference medium term hazard map. WP 4.3 Time update of the probability map for the opening of eruptive fractures. Analysis of data coming from WP4.1. Choice of the significant benchmarks for the retrospective analysis of the state of the volcano. Application of BET. Procedures to test the weight of the single input parameters. Test for the stability of results by changing input parameters and weight of the expert opinion. Choice of the reference medium term hazard map. Role of participants RU Gresta, TM Neri, and RU Russo: analysis of seismological, geophysical, volcanological, geochemical data referring to several pre-eruptive periods (basically during the time span ). Application of BET to update the probability map. Deliverables D4.1 Data base D4.2a Reference hazard map for vent opening probability D4.2b Test for the stability D4.3a Dynamic maps of the hazard of opening vents. D4.3b Test on the different weights for parameters and expert opinions D4.3c Validation of BET. TASK 5. SCENARIO FORECAST AND HAZARD MITIGATION RU and TM Partecipating RU Del Negro, TM Coltelli, TM Ferrucci, TM Herault, TM Vicari, RU Crisci, RU Favalli, RU Fortuna, RU Lombardo, RU Marsella, RU Tramutoli Objectives Lava flow simulations driven by infrared satellite data of an ongoing effusive eruption. Protocols for the real-time prediction of lava flow paths for planning emergency response. Barrier design for volcano hazard mitigation. 192
17 Project V3 Lava Description of the activity The simulation of an ongoing effusive eruption must be based on the estimation of all the observable data (position of flow source, area, thickness, channel speed, extrusion rate, front advance and temperature) using ground-based and satellite-borne techniques. This data can then be used to both initialize flow simulations and to attempt near real-time correction of these simulations via assimilation of new observations. The simulation of flow emplacement will start from the reproduction of the actual lava extent, and then it will be carried on through the implementation of a number of possible evolution scenarios. Such simulations could foresee inhabited areas or structures to be threatened by a lava flow and they may be adopted to check the results of mitigatory actions, such as building up of earth barriers or excavation of artificial channels. These operations can be easily modelled after an opportune modification of the volcano topography. Work-Packages WP 5.1 Hot-spot detection in near real-time Near real-time detection and monitoring of thermal anomalies related to volcanic eruptions from thermal infrared satellite imagery. Completely automated generation of satellite data based products. Role of participants RU Del Negro, TM Ferrucci, TM Vicari, RU Lombardo, RU Tramutoli: Implementation and test of automated processing chain for satellite product generation. RU Del Negro, TM Ferrucci, TM Vicari, RU Lombardo, RU Tramutoli: Design, implementation and test of interfaces for the integration of satellite based products into the DPC operational system. WP 5.2 Near real-time data collection of critical lava-flow emplacement parameters Observations of flow source, area, thickness, channel speed, front advance and temperature using ground-based, air-borne and satellite-borne techniques. Conversion of these specific observations in an assimilation scheme that will use them to modify/implement the forward flow simulations. Role of participants TM Coltelli: study of what observations are available and best suited for assimilation into the simulations; measurements of syn-eruptive data during an Etna eruption; conversion of specific observations in an assimilation scheme to implement the forward flow simulations. RU Marsella: measurements of syn-eruptive data during an Etna eruption by topographic techniques. RU Tallarico and TM Pinkerton: conversion of rheological observations in input data for lava flow simulation. WP 5.3 Effusion rates from thermal infrared satellite imagery Near real-time satellite-based measurements of effusion rate during on-going eruptions. Automated system for the acquisition/ processing/post-processing/delivery of satellite data. Role of participants RU Del Negro, TM Ferrucci, TM Vicari, RU Lombardo, RU Tramutoli: Implementation and test of automated processing chain for satellite product generation. RU Del Negro, TM Ferrucci, TM Vicari, RU Lombardo, RU Tramutoli: Design, implementation and test of interfaces for the integration of satellite based products into the DPC operational system. 193
18 WP 5.4 Lava flow paths forecasting during an eruption Lava flow emplacement during an ongoing eruption will be forecasted by simulations starting from the actual lava extent. A number of possible evolution scenarios should be implemented for assessing its progress. Role of participants RU Del Negro, TM Herault, TM Vicari, RU Crisci, RU Favalli: definition of possible eruption scenarios and simulation of the ongoing eruption. RU Del Negro: definition of possible environment scenarios. WP 5.5 Lava flow simulations including diversion barriers during an eruption The simulations carried out during an ongoing eruption could foresee inhabited areas or structures to be threatened by a lava flow. In such cases simulations may check the results of mitigatory actions such as building up of earth barriers or excavation of artificial channels. Such operation can be easily simulated after an opportune modification of the volcano topography. Planning the protection of some selected sensitive objectives that were really threatened during recent Etna eruptions. Role of participants TM Coltelli, TM Herault, TM Vicari: definition of mitigatory actions on the ongoing eruption and their simulation. RU Marsella: make opportune modifications of the volcano topography for planning of mitigatory actions on the ongoing eruption. RU Del Negro: management of mitigatory actions on the ongoing eruption. Deliverables D5.1a - Hot-spot detection in near real time from satellite data. D5.2a - Report on suitable observational data sources, types and quality. D5.2b - Database of all the available syn-eruptive data of an ongoing eruption (depending on the eruption). D5.3 Effusion rate measurements in near real time from satellite data. D5.4 - Report on the simulation of different scenarios of an ongoing eruption (depending on the eruption). D5.5a - Report on the simulation of different scenarios of an ongoing eruption by taking into account mitigatory actions (depending on the eruption). D5.5b - Planning, simulating and analysis of test cases of the protection of selected sensitive objectives at Etna. 194
19 Project V3 Lava Flow chart of project achievements and products 195
20 List of deliverables General 1. Data used in the project, organized in a database. 2. Guidelines for the realization of lava flow invasion hazard maps and their dynamic update. 3. Probability map of opening of new fractures and eruptive vents on a short and medium period, realized by dynamic update methodologies. 4. Hazard map for invasion of lava flows, realized using dynamic update methodology. 5. Tests of some selected eruptions for the vent opening probability maps, for the lava flow invasion hazard maps, and for the methodology for the dynamic update. 6. Feasibility study to transfer results at Centro Funzionale of Dept. of Civil Protection (DPC). Task 1. Guide Line and Protocols D1.1a Web site (month 3, update monthly). D1.1b Lava flow hazard map on an open source GIS. D1.2a Report on lava flow risk evaluation criteria. D1.2b Guidelines on prevision, prevention and mitigation of volcanic hazard. D1.3a Report on procedures to manage lava flow hazard. D1.3b Protocols on hazard management for the end-users. Task 2. Numerical Simulations and Satellite Techniques D2.1 - Database of chemical and physical parameters of selected eruptions. D2.2 Report on thermal and fluid-dynamical models of lava flows. D2.3 Report on techniques for hot-spot detection. D2.4 Report on techniques for lava effusion rate measurements. D2.5 Report on techniques for intra-event rapid DEM mapping. D2.6a Report on numerical simulation techniques adopted for forecast and probabilistic hazard assessment. D2.6b Report on sensitivity analysis of the code to the input parameters. D2.6c Report on how best to assimilate observational data into simulations. Task 3. Lava Flow Invasion Hazard Map D3.1 Past eruptions features, including geological, physical chemical and geometrical data, structured as GIS layers. D3.2a Collection of all the available topographic data on Etna volcano which satisfy the accuracy requirements for the simulations. D3.2b Report on topographic data collected including quality assessment. D3.3 Generation of classes and probability distribution functions, by a space-temporal statistical analysis of the eruptions, to constrain the probabilistic generation of simulation ensembles. D3.4 Report on the result of the long-term volcanic hazard assessment. D3.5 Report on the result of the short-term volcanic hazard assessment. D3.6 GIS database of Etna lava flow hazard map. Task 4. Vent Opening Probability Map D4.1 Data base D4.2a Reference hazard map for vent opening probability D4.2b Test for the stability D4.3a Dynamic maps of the hazard of opening vents. 196
Viscosity experiments: physical controls and implications for volcanic hazards. Ben Edwards Dept of Geology, Dickinson College
 Viscosity experiments: physical controls and implications for volcanic hazards Student Name: Ben Edwards Dept of Geology, Dickinson College OBJECTIVES OF LAB Learn about the rheological property called
Viscosity experiments: physical controls and implications for volcanic hazards Student Name: Ben Edwards Dept of Geology, Dickinson College OBJECTIVES OF LAB Learn about the rheological property called
2053-24. Advanced Workshop on Evaluating, Monitoring and Communicating Volcanic and Seismic Hazards in East Africa.
 2053-24 Advanced Workshop on Evaluating, Monitoring and Communicating Volcanic and Seismic Hazards in East Africa 17-28 August 2009 Emergency management in volcanic crisis: Italian cases Vittorio Bosi
2053-24 Advanced Workshop on Evaluating, Monitoring and Communicating Volcanic and Seismic Hazards in East Africa 17-28 August 2009 Emergency management in volcanic crisis: Italian cases Vittorio Bosi
REDUCTION OF THE ECONOMIC-FINANCIAL EXPOSURE OF THE STATE AND PROTECTION OF HUMAN LIVES
 REDUCTION OF THE ECONOMIC-FINANCIAL EXPOSURE OF THE STATE AND PROTECTION OF HUMAN LIVES Models for the prevention and mitigation of damages to people and properties through an insurance coverage PRESENTATION
REDUCTION OF THE ECONOMIC-FINANCIAL EXPOSURE OF THE STATE AND PROTECTION OF HUMAN LIVES Models for the prevention and mitigation of damages to people and properties through an insurance coverage PRESENTATION
Academic Year 2014/15. School of Industrial and Information Engineering. Degree Programme of:
 Academic Year 2014/15 School of Industrial and Information Engineering Degree Programme of: Telecommunication Engineering Laurea Magistrale (Equivalent To Master Of Science) Milano Leonardo Campus 1. General
Academic Year 2014/15 School of Industrial and Information Engineering Degree Programme of: Telecommunication Engineering Laurea Magistrale (Equivalent To Master Of Science) Milano Leonardo Campus 1. General
Integration between spaceand ground-based data sets: application on ground deformations measurements
 Integration between spaceand ground-based data sets: application on ground deformations measurements Giuseppe Puglisi Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia Sezione di Catania Osservatorio Etneo
Integration between spaceand ground-based data sets: application on ground deformations measurements Giuseppe Puglisi Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia Sezione di Catania Osservatorio Etneo
 1 2 A very short description of the functional center network: regarding the Hydraulic and Hydrogeological risk, the national alert system is ensured by the National Civil Protection Department (DPCN),
1 2 A very short description of the functional center network: regarding the Hydraulic and Hydrogeological risk, the national alert system is ensured by the National Civil Protection Department (DPCN),
DESURBS Deliverable 3.1: Specification of mapping and visualization
 DESURBS Deliverable 3.1: Specification of mapping and visualization Project full title: Designing Safer Urban Spaces Grant agreement no.: 261652 Lead beneficiary for Deliverable 3.1: Centre Internacional
DESURBS Deliverable 3.1: Specification of mapping and visualization Project full title: Designing Safer Urban Spaces Grant agreement no.: 261652 Lead beneficiary for Deliverable 3.1: Centre Internacional
Master in Earth Sciences
 Master in Earth Sciences DERDW EARTH SCIENCES MASTER IN EARTH SCIENCES The Department of Earth Sciences at ETH Zurich has been repeatedly ranked as one of the world s leading Earth Science schools. The
Master in Earth Sciences DERDW EARTH SCIENCES MASTER IN EARTH SCIENCES The Department of Earth Sciences at ETH Zurich has been repeatedly ranked as one of the world s leading Earth Science schools. The
A remote sensing instrument collects information about an object or phenomenon within the
 Satellite Remote Sensing GE 4150- Natural Hazards Some slides taken from Ann Maclean: Introduction to Digital Image Processing Remote Sensing the art, science, and technology of obtaining reliable information
Satellite Remote Sensing GE 4150- Natural Hazards Some slides taken from Ann Maclean: Introduction to Digital Image Processing Remote Sensing the art, science, and technology of obtaining reliable information
Emergency Management Service. early warning FLOOD AND FIRE ALERTS. Space
 Emergency Management Service early warning FLOOD AND FIRE ALERTS Space 1 Copernicus at a Glance Copernicus is the European Union s Earth Observation programme: a user-driven space programme under civil
Emergency Management Service early warning FLOOD AND FIRE ALERTS Space 1 Copernicus at a Glance Copernicus is the European Union s Earth Observation programme: a user-driven space programme under civil
MIDLAND ISD ADVANCED PLACEMENT CURRICULUM STANDARDS AP ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE
 Science Practices Standard SP.1: Scientific Questions and Predictions Asking scientific questions that can be tested empirically and structuring these questions in the form of testable predictions SP.1.1
Science Practices Standard SP.1: Scientific Questions and Predictions Asking scientific questions that can be tested empirically and structuring these questions in the form of testable predictions SP.1.1
Volcano Observatory Best Practices workshops: First results and future possibilities. John Eichelberger, USGS and Paolo Papale, INGV
 Volcano Observatory Best Practices workshops: First results and future possibilities John Eichelberger, USGS and Paolo Papale, INGV Volcano observatories Whether a building or a virtual entity, are the
Volcano Observatory Best Practices workshops: First results and future possibilities John Eichelberger, USGS and Paolo Papale, INGV Volcano observatories Whether a building or a virtual entity, are the
ERMES. Monitoring of radon in geogas at the Gran Sasso National Laboratory
 ERMES. Monitoring of radon in geogas at the Gran Sasso National Laboratory G. De Luca a and W. Plastino b a Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia (INGV) Centro Nazionale Terremoti (CNT), Via di
ERMES. Monitoring of radon in geogas at the Gran Sasso National Laboratory G. De Luca a and W. Plastino b a Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia (INGV) Centro Nazionale Terremoti (CNT), Via di
Geological hazards and monitoring activities at the Azores archipelago
 Geological hazards and monitoring activities at the Azores archipelago Teresa Ferreira (1,2), João Gaspar (1,2), Gabriela Queiroz (1,2) (1) CVARG (Centre for Volcanology and Geological Risks Assessment)
Geological hazards and monitoring activities at the Azores archipelago Teresa Ferreira (1,2), João Gaspar (1,2), Gabriela Queiroz (1,2) (1) CVARG (Centre for Volcanology and Geological Risks Assessment)
3D MODELING OF LARGE AND COMPLEX SITE USING MULTI-SENSOR INTEGRATION AND MULTI-RESOLUTION DATA
 3D MODELING OF LARGE AND COMPLEX SITE USING MULTI-SENSOR INTEGRATION AND MULTI-RESOLUTION DATA G. Guidi 1, F. Remondino 2, 3, M. Russo 1, F. Menna 4, A. Rizzi 3 1 Dept.INDACO, Politecnico of Milano, Italy
3D MODELING OF LARGE AND COMPLEX SITE USING MULTI-SENSOR INTEGRATION AND MULTI-RESOLUTION DATA G. Guidi 1, F. Remondino 2, 3, M. Russo 1, F. Menna 4, A. Rizzi 3 1 Dept.INDACO, Politecnico of Milano, Italy
Sensing, monitoring and actuating on the UNderwater world through a federated Research InfraStructure Extending the Future Internet SUNRISE
 Sensing, monitoring and actuating on the UNderwater world through a federated Research InfraStructure Extending the Future Internet SUNRISE Grant Agreement number 611449 Announcement of the Second Competitive
Sensing, monitoring and actuating on the UNderwater world through a federated Research InfraStructure Extending the Future Internet SUNRISE Grant Agreement number 611449 Announcement of the Second Competitive
Example of an end-to-end operational. from heat waves
 Example of an end-to-end operational service in support to civil protection from heat waves Paolo Manunta pkt006-11-1.0 1.0_WEBGIS Athens, 8 June 2007 OUTLINE Heat Island definition and causes Heat Island
Example of an end-to-end operational service in support to civil protection from heat waves Paolo Manunta pkt006-11-1.0 1.0_WEBGIS Athens, 8 June 2007 OUTLINE Heat Island definition and causes Heat Island
The Status of Geospatial Information Management in China
 The Status of Geospatial Information Management in China Submitted by the National Administration of Surveying, Mapping and Geoinformation of China 1. Administration System The National Administration
The Status of Geospatial Information Management in China Submitted by the National Administration of Surveying, Mapping and Geoinformation of China 1. Administration System The National Administration
Satellite Remote Sensing of Volcanic Ash
 Marco Fulle www.stromboli.net Satellite Remote Sensing of Volcanic Ash Michael Pavolonis NOAA/NESDIS/STAR SCOPE Nowcasting 1 Meeting November 19 22, 2013 1 Outline Getty Images Volcanic ash satellite remote
Marco Fulle www.stromboli.net Satellite Remote Sensing of Volcanic Ash Michael Pavolonis NOAA/NESDIS/STAR SCOPE Nowcasting 1 Meeting November 19 22, 2013 1 Outline Getty Images Volcanic ash satellite remote
The dynamics of magma chamber refilling at
 Vertical deformation Seismogram Gravity change The dynamics of magma chamber refilling at the Campi Flegrei caldera A. Longo 1, C. Montagna 1, M. Vassalli 2, P. Papale 1, D. Giudice 1, G. Saccorotti 1
Vertical deformation Seismogram Gravity change The dynamics of magma chamber refilling at the Campi Flegrei caldera A. Longo 1, C. Montagna 1, M. Vassalli 2, P. Papale 1, D. Giudice 1, G. Saccorotti 1
The USGS Landsat Big Data Challenge
 The USGS Landsat Big Data Challenge Brian Sauer Engineering and Development USGS EROS bsauer@usgs.gov U.S. Department of the Interior U.S. Geological Survey USGS EROS and Landsat 2 Data Utility and Exploitation
The USGS Landsat Big Data Challenge Brian Sauer Engineering and Development USGS EROS bsauer@usgs.gov U.S. Department of the Interior U.S. Geological Survey USGS EROS and Landsat 2 Data Utility and Exploitation
HAZARD MAPPING, RISK ASSESSMENT, AND INSURANCE COVERAGE OF NATURAL CATASTROPHE RISK
 SESSION III HAZARD MAPPING, RISK ASSESSMENT, AND INSURANCE COVERAGE OF NATURAL CATASTROPHE RISK Mr. Sumarjono Insurance Bureau of The Ministry of Finance of the Republic of Indonesia Geological Position
SESSION III HAZARD MAPPING, RISK ASSESSMENT, AND INSURANCE COVERAGE OF NATURAL CATASTROPHE RISK Mr. Sumarjono Insurance Bureau of The Ministry of Finance of the Republic of Indonesia Geological Position
A Study on Software Metrics and Phase based Defect Removal Pattern Technique for Project Management
 International Journal of Soft Computing and Engineering (IJSCE) A Study on Software Metrics and Phase based Defect Removal Pattern Technique for Project Management Jayanthi.R, M Lilly Florence Abstract:
International Journal of Soft Computing and Engineering (IJSCE) A Study on Software Metrics and Phase based Defect Removal Pattern Technique for Project Management Jayanthi.R, M Lilly Florence Abstract:
Using D2K Data Mining Platform for Understanding the Dynamic Evolution of Land-Surface Variables
 Using D2K Data Mining Platform for Understanding the Dynamic Evolution of Land-Surface Variables Praveen Kumar 1, Peter Bajcsy 2, David Tcheng 2, David Clutter 2, Vikas Mehra 1, Wei-Wen Feng 2, Pratyush
Using D2K Data Mining Platform for Understanding the Dynamic Evolution of Land-Surface Variables Praveen Kumar 1, Peter Bajcsy 2, David Tcheng 2, David Clutter 2, Vikas Mehra 1, Wei-Wen Feng 2, Pratyush
Volcano in the lab: a wax volcano in action: teacher s notes
 Volcano in the lab: a wax volcano in action: teacher s notes Level This activity is designed for students aged 11-14, as a simple demonstration of igneous activity. English National Curriculum reference
Volcano in the lab: a wax volcano in action: teacher s notes Level This activity is designed for students aged 11-14, as a simple demonstration of igneous activity. English National Curriculum reference
How Did These Ocean Features and Continental Margins Form?
 298 10.14 INVESTIGATION How Did These Ocean Features and Continental Margins Form? The terrain below contains various features on the seafloor, as well as parts of three continents. Some general observations
298 10.14 INVESTIGATION How Did These Ocean Features and Continental Margins Form? The terrain below contains various features on the seafloor, as well as parts of three continents. Some general observations
INGV-DPC Projects 2007 2009 VOLCANOLOGY
 INGV-DPC Projects 2007 2009 VOLCANOLOGY INGV DPC Projects 2007 2009 Volcanology Cover pictures: top: Etna, 2001 eruption. Ash plume and fallout seen from the Nicolosi Rifugio Sapienza road. Photo by P.
INGV-DPC Projects 2007 2009 VOLCANOLOGY INGV DPC Projects 2007 2009 Volcanology Cover pictures: top: Etna, 2001 eruption. Ash plume and fallout seen from the Nicolosi Rifugio Sapienza road. Photo by P.
INTRUSION PREVENTION AND EXPERT SYSTEMS
 INTRUSION PREVENTION AND EXPERT SYSTEMS By Avi Chesla avic@v-secure.com Introduction Over the past few years, the market has developed new expectations from the security industry, especially from the intrusion
INTRUSION PREVENTION AND EXPERT SYSTEMS By Avi Chesla avic@v-secure.com Introduction Over the past few years, the market has developed new expectations from the security industry, especially from the intrusion
Overview of the involvement of local Research. Organisations, Enterprises, Universities in. national and international projects on Earth
 Overview of the involvement of local Research Organisations, Enterprises, Universities in national and international projects on Earth Observation applications and services. ( Earth Observation, Satellite
Overview of the involvement of local Research Organisations, Enterprises, Universities in national and international projects on Earth Observation applications and services. ( Earth Observation, Satellite
DEPARTMENT OF PETROLEUM ENGINEERING Graduate Program (Version 2002)
 DEPARTMENT OF PETROLEUM ENGINEERING Graduate Program (Version 2002) COURSE DESCRIPTION PETE 512 Advanced Drilling Engineering I (3-0-3) This course provides the student with a thorough understanding of
DEPARTMENT OF PETROLEUM ENGINEERING Graduate Program (Version 2002) COURSE DESCRIPTION PETE 512 Advanced Drilling Engineering I (3-0-3) This course provides the student with a thorough understanding of
3D VISUALIZATION OF GEOTHERMAL WELLS DIRECTIONAL SURVEYS AND INTEGRATION WITH DIGITAL ELEVATION MODEL (DEM)
 Presented at Short Course VII on Exploration for Geothermal Resources, organized by UNU-GTP, GDC and KenGen, at Lake Bogoria and Lake Naivasha, Kenya, Oct. 27 Nov. 18, 2012. GEOTHERMAL TRAINING PROGRAMME
Presented at Short Course VII on Exploration for Geothermal Resources, organized by UNU-GTP, GDC and KenGen, at Lake Bogoria and Lake Naivasha, Kenya, Oct. 27 Nov. 18, 2012. GEOTHERMAL TRAINING PROGRAMME
Geographical Information Systems with Remote Sensing
 SCHOOL OF SCIENCE Geographical Information Systems with Remote Sensing PGDip/MSc Medway Campus www.gre.ac.uk/science Why study this programme? Geographical Information Systems (GIS) and Remote Sensing
SCHOOL OF SCIENCE Geographical Information Systems with Remote Sensing PGDip/MSc Medway Campus www.gre.ac.uk/science Why study this programme? Geographical Information Systems (GIS) and Remote Sensing
Course Outline MS Global Environmental Change candidates are required to complete the core module, as well as three compulsory modules:
 ISA Master s Degrees in Sustainability Degree Title Master of Science in Global Environmental Change University King s College University Overview King's College London, ranked among the top 25 universities
ISA Master s Degrees in Sustainability Degree Title Master of Science in Global Environmental Change University King s College University Overview King's College London, ranked among the top 25 universities
Project V4 Flank PROJECT V4 FLANK
 Project V4 Flank PROJECT V4 FLANK 259 260 Project V4 Flank Coordinators: Project V4 - FLANK Hazards related to the flank dynamics at Mt. Etna Giuseppe Puglisi, Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia,
Project V4 Flank PROJECT V4 FLANK 259 260 Project V4 Flank Coordinators: Project V4 - FLANK Hazards related to the flank dynamics at Mt. Etna Giuseppe Puglisi, Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia,
FRANCESCO BELLOCCHIO S CURRICULUM VITAE ET STUDIORUM
 FRANCESCO BELLOCCHIO S CURRICULUM VITAE ET STUDIORUM April 2011 Index Personal details and education 1 Research activities 2 Teaching and tutorial activities 3 Conference organization and review activities
FRANCESCO BELLOCCHIO S CURRICULUM VITAE ET STUDIORUM April 2011 Index Personal details and education 1 Research activities 2 Teaching and tutorial activities 3 Conference organization and review activities
CHAPTER 6 THE TERRESTRIAL PLANETS
 CHAPTER 6 THE TERRESTRIAL PLANETS MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following is NOT one of the four stages in the development of a terrestrial planet? 2. That Earth, evidence that Earth differentiated.
CHAPTER 6 THE TERRESTRIAL PLANETS MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following is NOT one of the four stages in the development of a terrestrial planet? 2. That Earth, evidence that Earth differentiated.
New challenges of water resources management: Title the future role of CHy
 New challenges of water resources management: Title the future role of CHy by Bruce Stewart* Karl Hofius in his article in this issue of the Bulletin entitled Evolving role of WMO in hydrology and water
New challenges of water resources management: Title the future role of CHy by Bruce Stewart* Karl Hofius in his article in this issue of the Bulletin entitled Evolving role of WMO in hydrology and water
California Standards Grades 9 12 Boardworks 2009 Science Contents Standards Mapping
 California Standards Grades 912 Boardworks 2009 Science Contents Standards Mapping Earth Sciences Earth s Place in the Universe 1. Astronomy and planetary exploration reveal the solar system s structure,
California Standards Grades 912 Boardworks 2009 Science Contents Standards Mapping Earth Sciences Earth s Place in the Universe 1. Astronomy and planetary exploration reveal the solar system s structure,
2015 Global Risk Assessment. Sahar Safaie Program Officer, UNISDR Risk Knowledge Section
 2015 Global Risk Assessment Sahar Safaie Program Officer, UNISDR Risk Knowledge Section Outline Global Assessment Report (GAR) evolution Global Risk Assessment for GAR15 Objective Scope Audience/Users
2015 Global Risk Assessment Sahar Safaie Program Officer, UNISDR Risk Knowledge Section Outline Global Assessment Report (GAR) evolution Global Risk Assessment for GAR15 Objective Scope Audience/Users
Laboratory scale electrical resistivity measurements to monitor the heat propagation within porous media for low enthalpy geothermal applications
 32 CONVEGNO NAZIONALE 19-21 Novembre 2013 TRIESTE Laboratory scale electrical resistivity measurements to monitor the heat propagation within porous media for low enthalpy geothermal applications N. Giordano
32 CONVEGNO NAZIONALE 19-21 Novembre 2013 TRIESTE Laboratory scale electrical resistivity measurements to monitor the heat propagation within porous media for low enthalpy geothermal applications N. Giordano
Principles and Practices of Data Integration
 Data Integration Data integration is the process of combining data of different themes, content, scale or spatial extent, projections, acquisition methods, formats, schema, or even levels of uncertainty,
Data Integration Data integration is the process of combining data of different themes, content, scale or spatial extent, projections, acquisition methods, formats, schema, or even levels of uncertainty,
Chapter Overview. Bathymetry. Measuring Bathymetry. Echo Sounding Record. Measuring Bathymetry. CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces
 Chapter Overview CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces The study of bathymetry charts ocean depths and ocean floor topography. Echo sounding and satellites are efficient bathymetric tools. Most ocean floor features
Chapter Overview CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces The study of bathymetry charts ocean depths and ocean floor topography. Echo sounding and satellites are efficient bathymetric tools. Most ocean floor features
IAG/AIG-WG-TG Summer School 2016 on Alps vs Apennines: Tectonic Geomorphology of Mountains
 IAG/AIG-WG-TG Summer School 2016 on Alps vs Apennines: Tectonic Geomorphology of Mountains Italy: Western Alps (Peveragno, CN) Central Apennines (Assergi, AQ) July 2-9, 2016 Aim and scope The IAG-WG-TG
IAG/AIG-WG-TG Summer School 2016 on Alps vs Apennines: Tectonic Geomorphology of Mountains Italy: Western Alps (Peveragno, CN) Central Apennines (Assergi, AQ) July 2-9, 2016 Aim and scope The IAG-WG-TG
Flood Zone Investigation by using Satellite and Aerial Imagery
 Flood Zone Investigation by using Satellite and Aerial Imagery Younes Daneshbod Islamic Azad University-Arsanjan branch Daneshgah Boulevard, Islamid Azad University, Arsnjan, Iran Email: daneshbod@gmail.com
Flood Zone Investigation by using Satellite and Aerial Imagery Younes Daneshbod Islamic Azad University-Arsanjan branch Daneshgah Boulevard, Islamid Azad University, Arsnjan, Iran Email: daneshbod@gmail.com
EARTHQUAKE DISASTER GIS AND SPATIAL-TEMPORAL PATTERN OF EARTHQUAKE DISASTERS IN CHINA1
 EARTHQUAKE DISASTER GIS AND SPATIAL-TEMPORAL PATTERN OF EARTHQUAKE DISASTERS IN CHINA1 Mao Feng 1 and Ma Jin feng 2 and Zhou Wen sheng 3 1 Professor,School of Architecture,Tsinghua University, BeiJing.
EARTHQUAKE DISASTER GIS AND SPATIAL-TEMPORAL PATTERN OF EARTHQUAKE DISASTERS IN CHINA1 Mao Feng 1 and Ma Jin feng 2 and Zhou Wen sheng 3 1 Professor,School of Architecture,Tsinghua University, BeiJing.
The Live Land Project ARTES Applications Workshop 19 th April 2013
 The Live Land Project ARTES Applications Workshop 19 th April 2013 Contents 1. Overview of project, expected outputs and benefits 2. ESA, Industry Partners and Clients involvement 3. Outline of programme
The Live Land Project ARTES Applications Workshop 19 th April 2013 Contents 1. Overview of project, expected outputs and benefits 2. ESA, Industry Partners and Clients involvement 3. Outline of programme
TECTONICS ASSESSMENT
 Tectonics Assessment / 1 TECTONICS ASSESSMENT 1. Movement along plate boundaries produces A. tides. B. fronts. C. hurricanes. D. earthquakes. 2. Which of the following is TRUE about the movement of continents?
Tectonics Assessment / 1 TECTONICS ASSESSMENT 1. Movement along plate boundaries produces A. tides. B. fronts. C. hurricanes. D. earthquakes. 2. Which of the following is TRUE about the movement of continents?
Post-graduate education on Climate Change at Ca Foscari University of Venice. Carlo Giupponi
 Post-graduate education on Climate Change at Ca Foscari University of Venice Carlo Giupponi Where we are Ca Foscari University of Venice Established on August 6 th 1868 as a Royal Business College, Ca
Post-graduate education on Climate Change at Ca Foscari University of Venice Carlo Giupponi Where we are Ca Foscari University of Venice Established on August 6 th 1868 as a Royal Business College, Ca
FROM DRAWING ANTICLINE AXES TO 3D MODELLING OF SEISMOGENIC SOURCES: EVOLUTION OF SEISMOTECTONIC MAPPING IN THE PO PLAIN
 FROM DRAWING ANTICLINE AXES TO 3D MODELLING OF SEISMOGENIC SOURCES: EVOLUTION OF SEISMOTECTONIC MAPPING IN THE PO PLAIN Burrato P.*, Maesano F. E. *, D Ambrogi C.**, Toscani G., Valensise G.* (*) INGV,
FROM DRAWING ANTICLINE AXES TO 3D MODELLING OF SEISMOGENIC SOURCES: EVOLUTION OF SEISMOTECTONIC MAPPING IN THE PO PLAIN Burrato P.*, Maesano F. E. *, D Ambrogi C.**, Toscani G., Valensise G.* (*) INGV,
Project abstracts (not edited) of winners of Phase 1 of the SBRI call on Adaptive Autonomous Ocean Sampling Networks
 Project abstracts (not edited) of winners of Phase 1 of the SBRI call on Adaptive Autonomous Ocean Sampling Networks NOC-DSTL-Innovate UK SBRI team Version 1: 01.04.2015 SBRI NOC-AAOSN-205 - Extending
Project abstracts (not edited) of winners of Phase 1 of the SBRI call on Adaptive Autonomous Ocean Sampling Networks NOC-DSTL-Innovate UK SBRI team Version 1: 01.04.2015 SBRI NOC-AAOSN-205 - Extending
1) Chemical Engg. PEOs & POs Programme Educational Objectives
 1) Chemical Engg. PEOs & POs Programme Educational Objectives The Programme has the following educational objectives: To prepare students for successful practice in diverse fields of chemical engineering
1) Chemical Engg. PEOs & POs Programme Educational Objectives The Programme has the following educational objectives: To prepare students for successful practice in diverse fields of chemical engineering
The Use of Geographic Information Systems in Risk Assessment
 The Use of Geographic Information Systems in Risk Assessment With Specific Focus on the RiVAMP Methodology Presented by Nadine Brown August 27, 2012 Climate Studies Group Mona Climate Change Workshop Presentation
The Use of Geographic Information Systems in Risk Assessment With Specific Focus on the RiVAMP Methodology Presented by Nadine Brown August 27, 2012 Climate Studies Group Mona Climate Change Workshop Presentation
CO 2 storage science development and application in Italy
 CO 2 storage science development and application in Italy Salvatore Lombardi Carbon Sequestration Leadership Forum, 16-19 April 2013 Rome, Italy Objectives Site selection and characterization Acquisition
CO 2 storage science development and application in Italy Salvatore Lombardi Carbon Sequestration Leadership Forum, 16-19 April 2013 Rome, Italy Objectives Site selection and characterization Acquisition
VOLCANO-RELATED HAZARDS AND RISKS IN SOUTHERN ITALY
 63 EFG Council Meeting Workshop Managing Natural Hazards Tenerife (May 10-11, 2012) VOLCANO-RELATED HAZARDS AND RISKS IN SOUTHERN ITALY Graziano G.V., Calcaterra D. & Cencetti C. National Council of Geologists,
63 EFG Council Meeting Workshop Managing Natural Hazards Tenerife (May 10-11, 2012) VOLCANO-RELATED HAZARDS AND RISKS IN SOUTHERN ITALY Graziano G.V., Calcaterra D. & Cencetti C. National Council of Geologists,
RISK AND RESILIENCE $58,000,000 +$38,000,000 / 190.0%
 RISK AND RESILIENCE $58,000,000 +$38,000,000 / 190.0% Overview The economic competiveness and societal well-being of the United States depend on the affordability, availability, quality, and reliability
RISK AND RESILIENCE $58,000,000 +$38,000,000 / 190.0% Overview The economic competiveness and societal well-being of the United States depend on the affordability, availability, quality, and reliability
Solar Tracking Application
 Solar Tracking Application A Rockwell Automation White Paper Solar trackers are devices used to orient photovoltaic panels, reflectors, lenses or other optical devices toward the sun. Since the sun s position
Solar Tracking Application A Rockwell Automation White Paper Solar trackers are devices used to orient photovoltaic panels, reflectors, lenses or other optical devices toward the sun. Since the sun s position
3. Quantitative Risk Assessment of Combined Exposure to Food Contaminants and Natural Toxins
 3. Quantitative Risk Assessment of Combined Exposure to Food Contaminants and Natural Toxins Objectives: To perform probabilistic risk modelling (exposure as well as effects) of food contaminants and natural
3. Quantitative Risk Assessment of Combined Exposure to Food Contaminants and Natural Toxins Objectives: To perform probabilistic risk modelling (exposure as well as effects) of food contaminants and natural
The CO2 Geological Storage: how it works
 The CO2 Geological Storage: how it works Salvatore Lombardi Carbonia, Centro Ricerche Sotacarbo, 27 novembre 2014 Contents of the presentation Notes on CO2 Geological Storage (CGS) How it works How we
The CO2 Geological Storage: how it works Salvatore Lombardi Carbonia, Centro Ricerche Sotacarbo, 27 novembre 2014 Contents of the presentation Notes on CO2 Geological Storage (CGS) How it works How we
A disaster occurs at the point of contact between social activities and a natural phenomenon of unusual scale.
 Hazard Mapping and Vulnerability Assessment Mr. Toshiaki Udono Senior Project Manager, Kansai Division, PASCO Corporation, Japan Mr. Awadh Kishor Sah Project Manager, Project Implementation Department,
Hazard Mapping and Vulnerability Assessment Mr. Toshiaki Udono Senior Project Manager, Kansai Division, PASCO Corporation, Japan Mr. Awadh Kishor Sah Project Manager, Project Implementation Department,
Geothermal. . To reduce the CO 2 emissions a lot of effort is put in the development of large scale application of sustainable energy.
 Geothermal Energy With increasing fossil fuel prices, geothermal energy is an attractive alternative energy source for district heating and industrial heating. In recent years the use of geothermal energy
Geothermal Energy With increasing fossil fuel prices, geothermal energy is an attractive alternative energy source for district heating and industrial heating. In recent years the use of geothermal energy
Doctor of Philosophy in Computer Science
 Doctor of Philosophy in Computer Science Background/Rationale The program aims to develop computer scientists who are armed with methods, tools and techniques from both theoretical and systems aspects
Doctor of Philosophy in Computer Science Background/Rationale The program aims to develop computer scientists who are armed with methods, tools and techniques from both theoretical and systems aspects
FIRST GRADE VOLCANOES 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 FIRST GRADE VOLCANOES 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FIRST GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Learning the shapes of volcanoes. LAB: Experimenting with "lava." POST: Comparing
FIRST GRADE VOLCANOES 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FIRST GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Learning the shapes of volcanoes. LAB: Experimenting with "lava." POST: Comparing
Embedding a geographic information system in a decision support system for landslide hazard monitoring
 Excerpt from: Marco Lazzari, Paolo Salvaneschi, "Embedding a Geographic Information Embedding a geographic information system in a decision support system for landslide hazard monitoring Marco Lazzari,
Excerpt from: Marco Lazzari, Paolo Salvaneschi, "Embedding a Geographic Information Embedding a geographic information system in a decision support system for landslide hazard monitoring Marco Lazzari,
Public Works Engineering Technician: Speciality Civil Constructions
 Public Works Engineering Technician: Speciality Civil Constructions FIRST YEAR PHYSICAL BASES OF ENGINEERING 3207001 Core 1st 1st semester 6 7.2 Rational mechanics. Wave phenomena. Electricity. Thermodynamics.
Public Works Engineering Technician: Speciality Civil Constructions FIRST YEAR PHYSICAL BASES OF ENGINEERING 3207001 Core 1st 1st semester 6 7.2 Rational mechanics. Wave phenomena. Electricity. Thermodynamics.
CAPRA Software Gabriel Bernal ITEC SAS - ERN-AL Consortium
 CAPRA Software Gabriel Bernal ITEC SAS - ERN-AL Consortium ERN CAPRA software CAPRA platform Data management FileCAT Hazard module Exposure module Vulnerability module Risk module CRISIS 2007 ERN-NH rainfall
CAPRA Software Gabriel Bernal ITEC SAS - ERN-AL Consortium ERN CAPRA software CAPRA platform Data management FileCAT Hazard module Exposure module Vulnerability module Risk module CRISIS 2007 ERN-NH rainfall
INDIVIDUAL COURSE DETAILS
 INDIVIDUAL COURSE DETAILS A. Name of Institution NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNICAL TEACHERS TRAINING AND RESEARCH TARAMANI CHENNAI 600 113 [An Autonomous Institute under Ministry of Human Resource Development,
INDIVIDUAL COURSE DETAILS A. Name of Institution NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNICAL TEACHERS TRAINING AND RESEARCH TARAMANI CHENNAI 600 113 [An Autonomous Institute under Ministry of Human Resource Development,
APPENDIX D RISK ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGY
 APPENDIX D RISK ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGY There are numerous human-health and ecological issues associated with the construction and operation of any large coal-fueled electric power generation facility.
APPENDIX D RISK ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGY There are numerous human-health and ecological issues associated with the construction and operation of any large coal-fueled electric power generation facility.
PROHITECH WP3 (Leader A. IBEN BRAHIM) A short Note on the Seismic Hazard in Israel
 PROHITECH WP3 (Leader A. IBEN BRAHIM) A short Note on the Seismic Hazard in Israel Avigdor Rutenberg and Robert Levy Technion - Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa 32000, Israel Avi Shapira International
PROHITECH WP3 (Leader A. IBEN BRAHIM) A short Note on the Seismic Hazard in Israel Avigdor Rutenberg and Robert Levy Technion - Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa 32000, Israel Avi Shapira International
Appendix B. Introduction to Landslide Evaluation Tools Mapping, Remote Sensing, and Monitoring of Landslides
 Appendix B. Introduction to Landslide Evaluation Tools Mapping, Remote Sensing, and Monitoring of Landslides 66 The Landslide Handbook A Guide to Understanding Landslides Part 1. Mapping Maps are a useful
Appendix B. Introduction to Landslide Evaluation Tools Mapping, Remote Sensing, and Monitoring of Landslides 66 The Landslide Handbook A Guide to Understanding Landslides Part 1. Mapping Maps are a useful
Information technology infrastructures and services for creating a library's unified information system
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs Proceedings of the IATUL Conferences 1999 IATUL Proceedings Information technology infrastructures and services for creating a library's unified information system Attilio
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs Proceedings of the IATUL Conferences 1999 IATUL Proceedings Information technology infrastructures and services for creating a library's unified information system Attilio
Predictive Dynamix Inc Turning Business Experience Into Better Decisions
 Overview Geospatial Data Mining for Market Intelligence By Paul Duke, Predictive Dynamix, Inc. Copyright 2000-2001. All rights reserved. Today, there is a huge amount of information readily available describing
Overview Geospatial Data Mining for Market Intelligence By Paul Duke, Predictive Dynamix, Inc. Copyright 2000-2001. All rights reserved. Today, there is a huge amount of information readily available describing
THE STRATEGIC PLAN OF THE HYDROMETEOROLOGICAL PREDICTION CENTER
 THE STRATEGIC PLAN OF THE HYDROMETEOROLOGICAL PREDICTION CENTER FISCAL YEARS 2012 2016 INTRODUCTION Over the next ten years, the National Weather Service (NWS) of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
THE STRATEGIC PLAN OF THE HYDROMETEOROLOGICAL PREDICTION CENTER FISCAL YEARS 2012 2016 INTRODUCTION Over the next ten years, the National Weather Service (NWS) of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
Cisco Network Optimization Service
 Service Data Sheet Cisco Network Optimization Service Optimize your network for borderless business evolution and innovation using Cisco expertise and leading practices. New Expanded Smart Analytics Offerings
Service Data Sheet Cisco Network Optimization Service Optimize your network for borderless business evolution and innovation using Cisco expertise and leading practices. New Expanded Smart Analytics Offerings
Wildfires pose an on-going. Integrating LiDAR with Wildfire Risk Analysis for Electric Utilities. By Jason Amadori & David Buckley
 Figure 1. Vegetation Encroachments Highlighted in Blue and Orange in Classified LiDAR Point Cloud Integrating LiDAR with Wildfire Risk Analysis for Electric Utilities Wildfires pose an on-going hazard
Figure 1. Vegetation Encroachments Highlighted in Blue and Orange in Classified LiDAR Point Cloud Integrating LiDAR with Wildfire Risk Analysis for Electric Utilities Wildfires pose an on-going hazard
ENVIRONMENTAL MONITORING Vol. I - Remote Sensing (Satellite) System Technologies - Michael A. Okoye and Greg T. Koeln
 REMOTE SENSING (SATELLITE) SYSTEM TECHNOLOGIES Michael A. Okoye and Greg T. Earth Satellite Corporation, Rockville Maryland, USA Keywords: active microwave, advantages of satellite remote sensing, atmospheric
REMOTE SENSING (SATELLITE) SYSTEM TECHNOLOGIES Michael A. Okoye and Greg T. Earth Satellite Corporation, Rockville Maryland, USA Keywords: active microwave, advantages of satellite remote sensing, atmospheric
Applied mathematics and mathematical statistics
 Applied mathematics and mathematical statistics The graduate school is organised within the Department of Mathematical Sciences.. Deputy head of department: Aila Särkkä Director of Graduate Studies: Marija
Applied mathematics and mathematical statistics The graduate school is organised within the Department of Mathematical Sciences.. Deputy head of department: Aila Särkkä Director of Graduate Studies: Marija
Propsim enabled Mobile Ad-hoc Network Testing
 www.anite.com Propsim enabled Mobile Ad-hoc Network Testing Anite is now part of Keysight Technologies Lab-based, end-to-end performance testing of systems using Propsim MANET channel emulation A Mobile
www.anite.com Propsim enabled Mobile Ad-hoc Network Testing Anite is now part of Keysight Technologies Lab-based, end-to-end performance testing of systems using Propsim MANET channel emulation A Mobile
CASE STUDY LANDSLIDE MONITORING
 Introduction Monitoring of terrain movements (unstable slopes, landslides, glaciers, ) is an increasingly important task for today s geotechnical people asked to prevent or forecast natural disaster that
Introduction Monitoring of terrain movements (unstable slopes, landslides, glaciers, ) is an increasingly important task for today s geotechnical people asked to prevent or forecast natural disaster that
Geospatial Software Solutions for the Environment and Natural Resources
 Geospatial Software Solutions for the Environment and Natural Resources Manage and Preserve the Environment and its Natural Resources Our environment and the natural resources it provides play a growing
Geospatial Software Solutions for the Environment and Natural Resources Manage and Preserve the Environment and its Natural Resources Our environment and the natural resources it provides play a growing
Digital Remote Sensing Data Processing Digital Remote Sensing Data Processing and Analysis: An Introduction and Analysis: An Introduction
 Digital Remote Sensing Data Processing Digital Remote Sensing Data Processing and Analysis: An Introduction and Analysis: An Introduction Content Remote sensing data Spatial, spectral, radiometric and
Digital Remote Sensing Data Processing Digital Remote Sensing Data Processing and Analysis: An Introduction and Analysis: An Introduction Content Remote sensing data Spatial, spectral, radiometric and
The CO2 Geological Storage: how it works Salvatore Lombardi
 The CO2 Geological Storage: how it works Salvatore Lombardi Carbonia, Centro Ricerche Sotacarbo, 27 novembre 2014 Contents of the presentation Notes on CO2 Geological Storage (CGS) How it works How we
The CO2 Geological Storage: how it works Salvatore Lombardi Carbonia, Centro Ricerche Sotacarbo, 27 novembre 2014 Contents of the presentation Notes on CO2 Geological Storage (CGS) How it works How we
Maximization versus environmental compliance
 Maximization versus environmental compliance Increase use of alternative fuels with no risk for quality and environment Reprint from World Cement March 2005 Dr. Eduardo Gallestey, ABB, Switzerland, discusses
Maximization versus environmental compliance Increase use of alternative fuels with no risk for quality and environment Reprint from World Cement March 2005 Dr. Eduardo Gallestey, ABB, Switzerland, discusses
Scientific Progress and Recommendations from the International Volcanic Ash Task Force
 Scientific Progress and Recommendations from the International Volcanic Ash Task Force Marianne Guffanti, USGS Larry Mastin, USGS Andrew Tupper, Australian Bureau of Meteorology Raul Romero, ICAO Peter
Scientific Progress and Recommendations from the International Volcanic Ash Task Force Marianne Guffanti, USGS Larry Mastin, USGS Andrew Tupper, Australian Bureau of Meteorology Raul Romero, ICAO Peter
Please Note: Temporary Graduate 485 skills assessments applicants should only apply for ANZSCO codes listed in the Skilled Occupation List above.
 ANZSCO Descriptions This ANZSCO description document has been created to assist applicants in nominating an occupation for an ICT skill assessment application. The document lists all the ANZSCO codes that
ANZSCO Descriptions This ANZSCO description document has been created to assist applicants in nominating an occupation for an ICT skill assessment application. The document lists all the ANZSCO codes that
High Resolution Information from Seven Years of ASTER Data
 High Resolution Information from Seven Years of ASTER Data Anna Colvin Michigan Technological University Department of Geological and Mining Engineering and Sciences Outline Part I ASTER mission Terra
High Resolution Information from Seven Years of ASTER Data Anna Colvin Michigan Technological University Department of Geological and Mining Engineering and Sciences Outline Part I ASTER mission Terra
PREDICTIVE AND OPERATIONAL ANALYTICS, WHAT IS IT REALLY ALL ABOUT?
 PREDICTIVE AND OPERATIONAL ANALYTICS, WHAT IS IT REALLY ALL ABOUT? Derek Vogelsang 1, Alana Duncker 1, Steve McMichael 2 1. MWH Global, Adelaide, SA 2. South Australia Water Corporation, Adelaide, SA ABSTRACT
PREDICTIVE AND OPERATIONAL ANALYTICS, WHAT IS IT REALLY ALL ABOUT? Derek Vogelsang 1, Alana Duncker 1, Steve McMichael 2 1. MWH Global, Adelaide, SA 2. South Australia Water Corporation, Adelaide, SA ABSTRACT
Description of Simandou Archaeological Potential Model. 13A.1 Overview
 13A Description of Simandou Archaeological Potential Model 13A.1 Overview The most accurate and reliable way of establishing archaeological baseline conditions in an area is by conventional methods of
13A Description of Simandou Archaeological Potential Model 13A.1 Overview The most accurate and reliable way of establishing archaeological baseline conditions in an area is by conventional methods of
Transform Boundaries
 Lecture 7 Plates and Mantle Plumes Transform Boundaries Transform boundaries occur where one segment of rigid lithosphere slides horizontally past another in response to stresses in the lithosphere. The
Lecture 7 Plates and Mantle Plumes Transform Boundaries Transform boundaries occur where one segment of rigid lithosphere slides horizontally past another in response to stresses in the lithosphere. The
GEOENGINE MSc in Geomatics Engineering (Master Thesis) Anamelechi, Falasy Ebere
 Master s Thesis: ANAMELECHI, FALASY EBERE Analysis of a Raster DEM Creation for a Farm Management Information System based on GNSS and Total Station Coordinates Duration of the Thesis: 6 Months Completion
Master s Thesis: ANAMELECHI, FALASY EBERE Analysis of a Raster DEM Creation for a Farm Management Information System based on GNSS and Total Station Coordinates Duration of the Thesis: 6 Months Completion
Geosciences - Programme subject in programme for Specialization in General Studies
 Geosciences - Programme subject in programme for Specialization in General Studies Dette er en oversettelse av den fastsatte læreplanteksten. Læreplanen er fastsatt på Bokmål Laid down as a regulation
Geosciences - Programme subject in programme for Specialization in General Studies Dette er en oversettelse av den fastsatte læreplanteksten. Læreplanen er fastsatt på Bokmål Laid down as a regulation
CPO Science and the NGSS
 CPO Science and the NGSS It is no coincidence that the performance expectations in the Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) are all action-based. The NGSS champion the idea that science content cannot
CPO Science and the NGSS It is no coincidence that the performance expectations in the Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) are all action-based. The NGSS champion the idea that science content cannot
FOURTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 FOURTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different structures of volcanoes. LAB: Modeling three types
FOURTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different structures of volcanoes. LAB: Modeling three types
From reconfigurable transceivers to reconfigurable networks, part II: Cognitive radio networks. Loreto Pescosolido
 From reconfigurable transceivers to reconfigurable networks, part II: Cognitive radio networks Loreto Pescosolido Spectrum occupancy with current technologies Current wireless networks, operating in either
From reconfigurable transceivers to reconfigurable networks, part II: Cognitive radio networks Loreto Pescosolido Spectrum occupancy with current technologies Current wireless networks, operating in either
Viscosity and Volcano Types
 20 LESSON Viscosity and Volcano Types This photo, taken in 1943 in Paricutin, Mexico, shows an eruption of the Paricutin volcano at night. Glowing hot, broken rocks outline the shape of the volcano, called
20 LESSON Viscosity and Volcano Types This photo, taken in 1943 in Paricutin, Mexico, shows an eruption of the Paricutin volcano at night. Glowing hot, broken rocks outline the shape of the volcano, called
MSc Project Management - E501
 MSc Project Management - E501 1. Aim and Objectives The aim of this Programme is to provide the private and public sectors with effective Project Leaders and Managers. Successful Project Managers will
MSc Project Management - E501 1. Aim and Objectives The aim of this Programme is to provide the private and public sectors with effective Project Leaders and Managers. Successful Project Managers will
Notable near-global DEMs include
 Visualisation Developing a very high resolution DEM of South Africa by Adriaan van Niekerk, Stellenbosch University DEMs are used in many applications, including hydrology [1, 2], terrain analysis [3],
Visualisation Developing a very high resolution DEM of South Africa by Adriaan van Niekerk, Stellenbosch University DEMs are used in many applications, including hydrology [1, 2], terrain analysis [3],
Disaster Risk Mitigation in Palestine Nablus, February 26 th 2013. Dr. Paola Ceresa
 Disaster Risk Mitigation in Palestine Nablus, February 26 th 2013 Seismic Risk Assessment of Roadway Network in Italy Dr. Paola Ceresa IUSS Pavia - Eucentre The majority of the Italian RC bridges and road
Disaster Risk Mitigation in Palestine Nablus, February 26 th 2013 Seismic Risk Assessment of Roadway Network in Italy Dr. Paola Ceresa IUSS Pavia - Eucentre The majority of the Italian RC bridges and road
VCS REDD Methodology Module. Methods for monitoring forest cover changes in REDD project activities
 1 VCS REDD Methodology Module Methods for monitoring forest cover changes in REDD project activities Version 1.0 May 2009 I. SCOPE, APPLICABILITY, DATA REQUIREMENT AND OUTPUT PARAMETERS Scope This module
1 VCS REDD Methodology Module Methods for monitoring forest cover changes in REDD project activities Version 1.0 May 2009 I. SCOPE, APPLICABILITY, DATA REQUIREMENT AND OUTPUT PARAMETERS Scope This module
SatelliteRemoteSensing for Precision Agriculture
 SatelliteRemoteSensing for Precision Agriculture Managing Director WasatSp. z o.o. Copernicus the road to economic development Warsaw, 26-27 February 2015 Activitiesof WasatSp. z o.o. The company provides
SatelliteRemoteSensing for Precision Agriculture Managing Director WasatSp. z o.o. Copernicus the road to economic development Warsaw, 26-27 February 2015 Activitiesof WasatSp. z o.o. The company provides
The role of demand-responsive energy management systems for smart cities
 The role of demand-responsive energy management systems for smart cities Carlos Henggeler Antunes Dept. of Electrical Eng. and Computers, University of Coimbra and R&D Unit INESC Coimbra COST Exploratory
The role of demand-responsive energy management systems for smart cities Carlos Henggeler Antunes Dept. of Electrical Eng. and Computers, University of Coimbra and R&D Unit INESC Coimbra COST Exploratory
