How Subnets Work in Practice. Fred Marshall Coastal Computers & Networks
|
|
|
- Brice Antony Houston
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 How Subnets Work in Practice Fred Marshall Coastal Computers & Networks Background There's lots of literature available on how the bit structure of an address can be split up using the subnet mask. Generally, any address is split up between what's referred to as a "network address" part and a "host address" part. It's assumed that all computers are either on the "network" meaning that they all have the same network address or they aren't. Here are some examples: Computer #1 IP: Subnet Mask: Computer #2 IP: Subnet Mask: Computer #3 IP: Subnet Mask: Here, computers #1 and #2 have private range IP addresses and have the same subnet address. They are said to be on network which has 254 usable addresses from to Computer #3 isn't on the same network. It is on network: which has 14 usable addresses from to All of this sort of thing you can read about all day by Googling "how does a subnet mask work?" But, after a while you might want to understand just a bit more about how the subnet mask works how it makes things happen (and not happen) in a real network. Packets All communications of interest here are accomplished by the transmission and reception of "packets" of data. Each packet has a "source address" (where it's coming from) and a "destination address" (where it's intended to end up). NOTE: there is no subnet mask included in the packet!! This means that no computer on the network "knows" what the source or destination subnet masks are. It only knows what its own subnet mask is!! The implication of this is that a computer (or router or ) only uses its subnet mask after it has received a packet. Routing
2 When a packet leaves your computer it is either sent to a "next hop" address or it's sent directly to the destination address. This is important. If a packet is destined for an address on the same "network" as defined by its own subnet mask, then the packet is just "put on the wire"; i.e. it's sent directly to the intended destination and there isn't any "next hop" really. Or, if you like, the "next hop" IS the destination. In contrast, if a packet is destined for an address that is not on the same "network" as defined by its own subnet mask, then the packet is forwarded to an interim computer or device which would be the logical "next hop". Most networks have at least one "gateway" router that is the normal "next hop" device for any packets that aren't on the source computer's network. It's the router's job to "route" the packets it receives to the proper physical port or connection and on to the next "next hop" in gettting to the destination. Note that routing of packets beyond the "next hop" is outside the control of the originating source computer. A typical small router has two "ports" to which it might send packets: - a WAN or Internet port - a LAN port or switch with multiple physical ports If neither the WAN or the LAN are appropriate launch points to a next hop, then the packet is dropped. So, there are 3 possible outcomes when a packet reaches the router: - go to a next hop from the WAN port; so perhaps on to the internet, - go to a next hop (likely the destination) from the LAN port, - disappear. Each computer and each router (just another computer) have a "routing table" that it uses to decide how packets are to be handled. If you open a command line window and type something like: route print you'll see the routing table for your computer. Let's say it's Computer #1 from above. Among the table entries you'll see: Active Routes: Network Destination Netmask Gateway Interface Metric Default Gateway: Here, as it says, the default gateway is the router with LAN address
3 Note that this doesn't tell us what the subnet mask for the router LAN might be!! Anyway, the way to read the table is this: The "interface" column says that all of these packets go out from network interface on the computer which is A network destination of pretty much means "any other address" should be routed to the gateway router. So, really there are no dropped packets here they either go on the wire directly or to the gateway router. Now, if a packet is destined for a computer that's turned off, then it's lost as there's no computer to receive it. A network destination of means any address in *my* subnet just goes out on the wire directly to the destination address. Note the difference in the routing table "gateway". In this case it's simply the network interface on the computer while for any other address it's , the router. There are plenty of better and more detailed explanations of routing tables so one can look them up OK. So now let's consider what happens when a packet arrives at the router: As above, the router has a routing table of its own. In the router, there are more choices than we see in the computer's routing table. As above, the packets can go to the WAN/internet interface, they can go to the LAN interface or they can be dropped not going to either interface. It's really beyond the intent of this paper to get into all the rules. How Subnet Settings Interact OK. So now we have some background on packets and routing. The key question we want to address here is: What happens if computers and devices using different networks and subnet masks are physically connected together? Can they communicate? Will they? Note: This has nothing to do with the operating system on any of the computers. At least it's not intended to! Let's take a couple of examples:
4 Example 1: One computer on a network that's a subset of the other computer and the router: Computer "A" Subnet Mask: Computer "B" Subnet Mask: Router LAN: Subnet Mask: Router WAN: Subnet Mask: Source Destination Next Hop Result Single hop Double hop Packet dropped in router In the first case, Computer "A" sees the address of Computer "B" as inside its own network and sends the packet directly to Computer "B". In the second case, Computer "B" sees the address of Computer "A" as outside its own network and sends the packet to the router. The router sees the packet as belonging to its LAN network and puts the packet back out on the LAN; this time it's addressed to Computer "A" while on the first hop it was addressed to the router. In the third case, Computer "A" sees the address as outside its own network and sends the packet to the router. The router doesn't have an interface configured that will accept this address as a destination and the packet is dropped. Example 2: One computer on a network that's a superset of the other computer and the router: Computer "A" Subnet Mask: Computer "B" Subnet Mask: Router LAN: Subnet Mask: Router WAN: Subnet Mask: Source Destination Next Hop Result Single hop
5 Packet dropped in router Packet dropped in router Packet put on the wire In the first case, Computer "A" sees the address of Computer "B" as inside its own network and sends the packet directly to Computer "B". In the second case, Computer "B" sees the address of Computer "A" as outside its own network and sends the packet to the router. The router doesn't have an interface configured that will accept this address as a destination and the packet is dropped. In the third case, Computer "A" sees the address as outside its own network and sends the packet to the router. The router doesn't have an interface configured that will accept this address as a destination and the packet is dropped. In the fourth case, Computer "A" sees the address of as inside its own network and sends the packet directly to that address. If the subnet mask of Computer "A" is set in error and the intent was for it to go to the router then this packet might be lost. The fourth case shows how a group of computers could communicate on a LAN without involving the router and be somewhat isolated from other computers on the same physical LAN by the choice of subnet mask on the router. Example 3: The router is on a network that's a superset of any of the computers and the router: Computer "A" Subnet Mask: Computer "B" Subnet Mask: Computer "C" Subnet Mask: (Computers "A" and "B" are on different subnets. Router LAN: Subnet Mask: Router WAN: Subnet Mask: Source Destination Next Hop Result Double hop Double hop
6 Double hop In the first case, Computer "A" sees the address of Computer "B" as outside its own network and sends the packet to the router. The router sees the address of Computer "B" as inside its own network and puts the packet back out on the LAN, addressed for Computer "B". In the second case, Computer "B" sees the address of Computer "A" as outside its own network and sends the packet to the router. The router sees the address of Computer "A" as inside its own network and puts the packet back out on the LAN, addressed for Computer "A". In the third case, Computer "A" sees the address as outside its own network and sends the packet to the router. The router sees the address of Computer "C" as inside its own network and puts the packet back out on the LAN, addressed for Computer "C". Conclusions Either packets go out directly "on the wire" or to the router. No computer will put packets out "on the wire" unless the destination address is within that computer's own network range as defined by its own address and its subnet mask. If a packet is "on the wire" then it will reach its destination if such a destination exists. If a packet goes to the router then: - If the router sees that the packet is on its LAN network (as defined by the router's own LAN subnet mask), then it will put the packet back out on the LAN. - If the router sees that the packet is not on its LAN network (and assuming that other rules allow it), it will put the packet out on the WAN. This means that subnetting doesn't necessarily yield separation between computers. There are two simple ways that a computer can be reached from a computer on a different subnet: 1) If the originating computer is on a network that includes the destination computer then it doesn't matter what the subnet of the destination computer is. And, it's only the destination computer that "knows" what its subnet is. Accordingly, this condition is completely out of the control of the destination computer. The originating computer can (and will) send packets to the destination computer. 2) If there's a router in the picture then if the originating computer is on a network that is a subset of the LAN network of the router, the router will redirect packets back to the LAN that are within the larger router network.
7 There are practical implications of this: One can set the subnet mask of a computer so that it's on a very small network compared to the other computers on a LAN. - all packets destined for this computer will arrive just fine even if the source computers are in a larger network. - return packets from this computer will be sent to its gateway / router and presumably back out on the LAN. One can set the subnet mask of a computer so that it's on a very large network compared to the other computers on a LAN. - any packets destined for computers on this larger network, but are actually on another LAN, will be lost because they aren't sent to the router. -
Lab 10.3.5a Basic Subnetting
 Lab 10.3.5a Basic Subnetting Objective How to identify reasons to use a subnet mask How to distinguish between a default subnet mask and a custom subnet mask What given requirements determine the subnet
Lab 10.3.5a Basic Subnetting Objective How to identify reasons to use a subnet mask How to distinguish between a default subnet mask and a custom subnet mask What given requirements determine the subnet
How To Load balance traffic of Mail server hosted in the Internal network and redirect traffic over preferred Interface
 How To Load balance traffic of Mail server hosted in the Internal network and redirect traffic over preferred Interface How To Configure load sharing and redirect mail server traffic over preferred Gateway
How To Load balance traffic of Mail server hosted in the Internal network and redirect traffic over preferred Interface How To Configure load sharing and redirect mail server traffic over preferred Gateway
Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1 (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or to provide
(Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or to provide
Source net: 200.1.1.0 Destination net: 200.1.2.0 Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0 Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0. Router Hub
 then to a router. Remember that with a Class C network address, the first 3 octets, or 24 bits, are assigned as the network address. So, these are two different Class C networks. This leaves one octet,
then to a router. Remember that with a Class C network address, the first 3 octets, or 24 bits, are assigned as the network address. So, these are two different Class C networks. This leaves one octet,
Module 10 Subnetting Class A, B and C addresses. Solutions to the Lab Exercises 10.3.5a, 10.3.5b, 10.3.5c and 10.3.5d
 Module 10 Subnetting Class A, B and C addresses Solutions to the Lab Exercises 10.3.5a, 10.3.5b, 10.3.5c and 10.3.5d 10.3.5a Basic Subnetting Use the following information and answer the following subnet
Module 10 Subnetting Class A, B and C addresses Solutions to the Lab Exercises 10.3.5a, 10.3.5b, 10.3.5c and 10.3.5d 10.3.5a Basic Subnetting Use the following information and answer the following subnet
Network Layer IPv4. Dr. Sanjay P. Ahuja, Ph.D. Fidelity National Financial Distinguished Professor of CIS. School of Computing, UNF
 Network Layer IPv4 Dr. Sanjay P. Ahuja, Ph.D. Fidelity National Financial Distinguished Professor of CIS School of Computing, UNF IPv4 Internet Protocol (IP) is the glue that holds the Internet together.
Network Layer IPv4 Dr. Sanjay P. Ahuja, Ph.D. Fidelity National Financial Distinguished Professor of CIS School of Computing, UNF IPv4 Internet Protocol (IP) is the glue that holds the Internet together.
Enabling NAT and Routing in DGW v2.0 June 6, 2012
 Enabling NAT and Routing in DGW v2.0 June 6, 2012 Proprietary 2012 Media5 Corporation Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Starting Services... 4 Distinguishing your WAN and LAN interfaces... 5 Configuring
Enabling NAT and Routing in DGW v2.0 June 6, 2012 Proprietary 2012 Media5 Corporation Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Starting Services... 4 Distinguishing your WAN and LAN interfaces... 5 Configuring
1 PC to WX64 direction connection with crossover cable or hub/switch
 1 PC to WX64 direction connection with crossover cable or hub/switch If a network is not available, or if it is desired to keep the WX64 and PC(s) completely separated from other computers, a simple network
1 PC to WX64 direction connection with crossover cable or hub/switch If a network is not available, or if it is desired to keep the WX64 and PC(s) completely separated from other computers, a simple network
CCNA R&S: Introduction to Networks. Chapter 9: Subnetting IP Networks
 CCNA R&S: Introduction to Networks Chapter 9: Subnetting IP Networks Frank Schneemann Chapter 9: Subnetting IP Networks Subnetting IP Networks In this chapter, you will be learning how devices can be grouped
CCNA R&S: Introduction to Networks Chapter 9: Subnetting IP Networks Frank Schneemann Chapter 9: Subnetting IP Networks Subnetting IP Networks In this chapter, you will be learning how devices can be grouped
Lab 10.4.1 IP Addressing Overview
 Lab 10.4.1 IP ing Overview Estimated time: 30 min. Objectives: Background: This lab will focus on your ability to accomplish the following tasks: Name the five different classes of IP addresses Describe
Lab 10.4.1 IP ing Overview Estimated time: 30 min. Objectives: Background: This lab will focus on your ability to accomplish the following tasks: Name the five different classes of IP addresses Describe
LAN TCP/IP and DHCP Setup
 CHAPTER 2 LAN TCP/IP and DHCP Setup 2.1 Introduction In this chapter, we will explain in more detail the LAN TCP/IP and DHCP Setup. 2.2 LAN IP Network Configuration In the Vigor 2900 router, there are
CHAPTER 2 LAN TCP/IP and DHCP Setup 2.1 Introduction In this chapter, we will explain in more detail the LAN TCP/IP and DHCP Setup. 2.2 LAN IP Network Configuration In the Vigor 2900 router, there are
Networking Basics for Automation Engineers
 Networking Basics for Automation Engineers Page 1 of 10 mac-solutions.co.uk v1.0 Oct 2014 1. What is Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)------------------------------------------------------------
Networking Basics for Automation Engineers Page 1 of 10 mac-solutions.co.uk v1.0 Oct 2014 1. What is Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)------------------------------------------------------------
Vocia MS-1 Network Considerations for VoIP. Vocia MS-1 and Network Port Configuration. VoIP Network Switch. Control Network Switch
 Vocia MS-1 Network Considerations for VoIP Vocia software rev. 1.4 or higher required Vocia MS-1 and Network Port Configuration The Vocia Message Server 1 (MS-1) has a number of roles in a Vocia Paging
Vocia MS-1 Network Considerations for VoIP Vocia software rev. 1.4 or higher required Vocia MS-1 and Network Port Configuration The Vocia Message Server 1 (MS-1) has a number of roles in a Vocia Paging
How To Understand and Configure Your Network for IntraVUE
 How To Understand and Configure Your Network for IntraVUE Summary This document attempts to standardize the methods used to configure Intrauve in situations where there is little or no understanding of
How To Understand and Configure Your Network for IntraVUE Summary This document attempts to standardize the methods used to configure Intrauve in situations where there is little or no understanding of
ICS 351: Today's plan
 ICS 351: Today's plan Quiz, on overall Internet function, linux and IOS commands, network monitoring, protocols IPv4 addresses: network part and host part address masks IP interface configuration IPv6
ICS 351: Today's plan Quiz, on overall Internet function, linux and IOS commands, network monitoring, protocols IPv4 addresses: network part and host part address masks IP interface configuration IPv6
Teldat Router. ARP Proxy
 Teldat Router ARP Proxy Doc. DM734-I Rev. 10.00 November, 2002 INDEX Chapter 1 Introduction...1 1. ARP Proxy... 2 Chapter 2 Configuration...4 1. ARP Proxy Configuration... 5 1.1. Enabling ARP Proxy...
Teldat Router ARP Proxy Doc. DM734-I Rev. 10.00 November, 2002 INDEX Chapter 1 Introduction...1 1. ARP Proxy... 2 Chapter 2 Configuration...4 1. ARP Proxy Configuration... 5 1.1. Enabling ARP Proxy...
IP Addressing and Subnetting. 2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
 IP Addressing and Subnetting 2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Objectives Upon completion, you will be able to: Discuss the Types of Network Addressing Explain the Form of an IP Address
IP Addressing and Subnetting 2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Objectives Upon completion, you will be able to: Discuss the Types of Network Addressing Explain the Form of an IP Address
1:1 NAT in ZeroShell. Requirements. Overview. Network Setup
 1:1 NAT in ZeroShell Requirements The version of ZeroShell used for writing this document is Release 1.0.beta11. This document does not describe installing ZeroShell, it is assumed that the user already
1:1 NAT in ZeroShell Requirements The version of ZeroShell used for writing this document is Release 1.0.beta11. This document does not describe installing ZeroShell, it is assumed that the user already
1.0 Basic Principles of TCP/IP Network Communications
 Section 1 Basic Principles of TCP/IP Network Communications Section 2 Introduction to Doors NetXtreme Section 3 Common Connection Issues Section 4 Common Causes Section 5 Tools Section 6 Contact Keri Systems
Section 1 Basic Principles of TCP/IP Network Communications Section 2 Introduction to Doors NetXtreme Section 3 Common Connection Issues Section 4 Common Causes Section 5 Tools Section 6 Contact Keri Systems
co Characterizing and Tracing Packet Floods Using Cisco R
 co Characterizing and Tracing Packet Floods Using Cisco R Table of Contents Characterizing and Tracing Packet Floods Using Cisco Routers...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1 Prerequisites...1
co Characterizing and Tracing Packet Floods Using Cisco R Table of Contents Characterizing and Tracing Packet Floods Using Cisco Routers...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1 Prerequisites...1
IP Filter/Firewall Setup
 IP Filter/Firewall Setup Introduction The IP Filter/Firewall function helps protect your local network against attack from outside. It also provides a method of restricting users on the local network from
IP Filter/Firewall Setup Introduction The IP Filter/Firewall function helps protect your local network against attack from outside. It also provides a method of restricting users on the local network from
Configuring Static IP for your Pace Devices
 Configuring Static IP for your Pace Devices This Section will walk you through configuring the RG for use of a Static IP block. As mentioned earlier but repeated here for convenience is an overview in
Configuring Static IP for your Pace Devices This Section will walk you through configuring the RG for use of a Static IP block. As mentioned earlier but repeated here for convenience is an overview in
DG Forwarding Algorithm
 DG Forwarding Algorithm Host or Router first check if destination on same Network Router multiple interfaces Match found deliver to that Network If not found default router for every router a default router
DG Forwarding Algorithm Host or Router first check if destination on same Network Router multiple interfaces Match found deliver to that Network If not found default router for every router a default router
Application Description
 Application Description Firewall in front of LAN Different Servers located behind Firewall Firewall to be accessible from Internet Load Balancer to be installed in a TRANSPARENT MODE between Firewall and
Application Description Firewall in front of LAN Different Servers located behind Firewall Firewall to be accessible from Internet Load Balancer to be installed in a TRANSPARENT MODE between Firewall and
Quick Note 53. Ethernet to W-WAN failover with logical Ethernet interface.
 Quick Note 53 Ethernet to W-WAN failover with logical Ethernet interface. Digi Support August 2015 1 Contents 1 Introduction... 2 1.1 Introduction... 2 1.2 Assumptions... 3 1.3 Corrections... 3 2 Version...
Quick Note 53 Ethernet to W-WAN failover with logical Ethernet interface. Digi Support August 2015 1 Contents 1 Introduction... 2 1.1 Introduction... 2 1.2 Assumptions... 3 1.3 Corrections... 3 2 Version...
PART IV. Network Layer
 PART IV Network Layer Position of network layer Network layer duties Internetworking : heterogeneous Physical Networks To look Like a single network to he upper layers The address at Network layer must
PART IV Network Layer Position of network layer Network layer duties Internetworking : heterogeneous Physical Networks To look Like a single network to he upper layers The address at Network layer must
Supporting Multiple Firewalled Subnets on SonicOS Enhanced
 SONICOS ENHANCED Supporting Multiple Firewalled Subnets on SonicOS Enhanced Introduction This tech note describes how to configure secondary subnets with static ARP which allows multiple subnets to be
SONICOS ENHANCED Supporting Multiple Firewalled Subnets on SonicOS Enhanced Introduction This tech note describes how to configure secondary subnets with static ARP which allows multiple subnets to be
Instructor Notes for Lab 3
 Instructor Notes for Lab 3 Do not distribute instructor notes to students! Lab Preparation: Make sure that enough Ethernet hubs and cables are available in the lab. The following tools will be used in
Instructor Notes for Lab 3 Do not distribute instructor notes to students! Lab Preparation: Make sure that enough Ethernet hubs and cables are available in the lab. The following tools will be used in
Part A:Background/Preparation
 Lab no 1 PC Network TCP/IP Configuration In this lab we will learn about Computer Networks Configuration Introduction to IP addressing Identify tools used for discovering a computer s network configuration
Lab no 1 PC Network TCP/IP Configuration In this lab we will learn about Computer Networks Configuration Introduction to IP addressing Identify tools used for discovering a computer s network configuration
Computer Networks I Laboratory Exercise 1
 Computer Networks I Laboratory Exercise 1 The lab is divided into two parts where the first part is a basic PC network TCP/IP configuration and connection to the Internet. The second part is building a
Computer Networks I Laboratory Exercise 1 The lab is divided into two parts where the first part is a basic PC network TCP/IP configuration and connection to the Internet. The second part is building a
Computer Networks By Bahaa Q. Al-Mussawi Subnetting Basics Reduced network traffic Optimized network performance Simplified management
 Subnetting Basics You learned previously how to define and find the valid host ranges used in a Class A, Class B, and Class C network address by turning the host bits all off and then all on. This is very
Subnetting Basics You learned previously how to define and find the valid host ranges used in a Class A, Class B, and Class C network address by turning the host bits all off and then all on. This is very
configure WAN load balancing
 How To configure WAN load balancing Introduction With the increasing use of the Internet to service core business functions comes the need for reliable WAN connectivity. A specific aspect of this requirement
How To configure WAN load balancing Introduction With the increasing use of the Internet to service core business functions comes the need for reliable WAN connectivity. A specific aspect of this requirement
Document No. FO1101 Issue Date: Work Group: FibreOP Technical Team October 31, 2013 FINAL:
 Document No. FO1101 Issue Date: Work Group: FibreOP Technical Team October 31, 2013 FINAL: Title: FibreOP Business Internet 5 Static IP Customer Configuration Version 1.1 Summary: This document provides
Document No. FO1101 Issue Date: Work Group: FibreOP Technical Team October 31, 2013 FINAL: Title: FibreOP Business Internet 5 Static IP Customer Configuration Version 1.1 Summary: This document provides
CREATING AN IKE IPSEC TUNNEL BETWEEN AN INTERNET SECURITY ROUTER AND A WINDOWS 2000/XP PC
 CREATING AN IKE IPSEC TUNNEL BETWEEN AN INTERNET SECURITY ROUTER AND A WINDOWS 2000/XP PC 1 Introduction Release date: 11/12/2003 This application note details the steps for creating an IKE IPSec VPN tunnel
CREATING AN IKE IPSEC TUNNEL BETWEEN AN INTERNET SECURITY ROUTER AND A WINDOWS 2000/XP PC 1 Introduction Release date: 11/12/2003 This application note details the steps for creating an IKE IPSec VPN tunnel
1 Data information is sent onto the network cable using which of the following? A Communication protocol B Data packet
 Review questions 1 Data information is sent onto the network cable using which of the following? A Communication protocol B Data packet C Media access method D Packages 2 To which TCP/IP architecture layer
Review questions 1 Data information is sent onto the network cable using which of the following? A Communication protocol B Data packet C Media access method D Packages 2 To which TCP/IP architecture layer
LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING
 LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING In this lab you will work with four different network topologies. The topology for Parts 1-4 is shown in Figure 3.1. These parts address router configuration on Linux PCs and a
LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING In this lab you will work with four different network topologies. The topology for Parts 1-4 is shown in Figure 3.1. These parts address router configuration on Linux PCs and a
(Refer Slide Time: 02:17)
 Internet Technology Prof. Indranil Sengupta Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No #06 IP Subnetting and Addressing (Not audible: (00:46)) Now,
Internet Technology Prof. Indranil Sengupta Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No #06 IP Subnetting and Addressing (Not audible: (00:46)) Now,
You can probably work with decimal. binary numbers needed by the. Working with binary numbers is time- consuming & error-prone.
 IP Addressing & Subnetting Made Easy Working with IP Addresses Introduction You can probably work with decimal numbers much easier than with the binary numbers needed by the computer. Working with binary
IP Addressing & Subnetting Made Easy Working with IP Addresses Introduction You can probably work with decimal numbers much easier than with the binary numbers needed by the computer. Working with binary
CS 326e F2002 Lab 1. Basic Network Setup & Ethereal Time: 2 hrs
 CS 326e F2002 Lab 1. Basic Network Setup & Ethereal Time: 2 hrs Tasks: 1 (10 min) Verify that TCP/IP is installed on each of the computers 2 (10 min) Connect the computers together via a switch 3 (10 min)
CS 326e F2002 Lab 1. Basic Network Setup & Ethereal Time: 2 hrs Tasks: 1 (10 min) Verify that TCP/IP is installed on each of the computers 2 (10 min) Connect the computers together via a switch 3 (10 min)
TCP/IP works on 3 types of services (cont.): TCP/IP protocols are divided into three categories:
 Due to the number of hardware possibilities for a network, there must be a set of rules for how data should be transmitted across the connection media. A protocol defines how the network devices and computers
Due to the number of hardware possibilities for a network, there must be a set of rules for how data should be transmitted across the connection media. A protocol defines how the network devices and computers
VLSM & IP ADDRESSING EXAMPLE QUESTIONS with answers;
 VLSM & IP ADDRESSING EXAMPLE QUESTIONS with answers; 1 Given the network address of 112.44.0.0 and the network mask of 255.255.0.0 Would the two stations with addresses 112.44.22.19/16 and 112.44.23.2/16
VLSM & IP ADDRESSING EXAMPLE QUESTIONS with answers; 1 Given the network address of 112.44.0.0 and the network mask of 255.255.0.0 Would the two stations with addresses 112.44.22.19/16 and 112.44.23.2/16
Linksys Gateway SPA2100-SU Manual
 Linksys Gateway SPA2100-SU Manual Manuel de l'utilisateur Table of Contents Looking for Basic Setup Instructions?... 3 Most Recent Version of this Manual... 3 Advanced Setup Instructions... 4 Wiring Your
Linksys Gateway SPA2100-SU Manual Manuel de l'utilisateur Table of Contents Looking for Basic Setup Instructions?... 3 Most Recent Version of this Manual... 3 Advanced Setup Instructions... 4 Wiring Your
Configuring Network Address Translation (NAT)
 8 Configuring Network Address Translation (NAT) Contents Overview...................................................... 8-3 Translating Between an Inside and an Outside Network........... 8-3 Local and
8 Configuring Network Address Translation (NAT) Contents Overview...................................................... 8-3 Translating Between an Inside and an Outside Network........... 8-3 Local and
The IP Transmission Process. V1.4: Geoff Bennett
 The IP Transmission Process V1.4: Geoff Bennett Contents Communication Between Hosts Through a MAC Bridge Through a LAN Switch Through a Router The tutorial is divided into four sections. Section 1 looks
The IP Transmission Process V1.4: Geoff Bennett Contents Communication Between Hosts Through a MAC Bridge Through a LAN Switch Through a Router The tutorial is divided into four sections. Section 1 looks
Computer Networks. Introduc)on to Naming, Addressing, and Rou)ng. Week 09. College of Information Science and Engineering Ritsumeikan University
 Computer Networks Introduc)on to Naming, Addressing, and Rou)ng Week 09 College of Information Science and Engineering Ritsumeikan University MAC Addresses l MAC address is intended to be a unique identifier
Computer Networks Introduc)on to Naming, Addressing, and Rou)ng Week 09 College of Information Science and Engineering Ritsumeikan University MAC Addresses l MAC address is intended to be a unique identifier
Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding. Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1
 Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 1 1 Objectives Identify a router as a computer with an OS and hardware designed for the routing process. Demonstrate
Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 1 1 Objectives Identify a router as a computer with an OS and hardware designed for the routing process. Demonstrate
IP Addressing A Simplified Tutorial
 Application Note IP Addressing A Simplified Tutorial July 2002 COMPAS ID 92962 Avaya Labs 1 All information in this document is subject to change without notice. Although the information is believed to
Application Note IP Addressing A Simplified Tutorial July 2002 COMPAS ID 92962 Avaya Labs 1 All information in this document is subject to change without notice. Although the information is believed to
CCNA2 Chapter 11 Practice
 CCNA2 Chapter 11 Practice Two neighbouring routers are configured for OSPF, but they have different hello and dead intervals. What will happen? They will become adjacent as long as they are configured
CCNA2 Chapter 11 Practice Two neighbouring routers are configured for OSPF, but they have different hello and dead intervals. What will happen? They will become adjacent as long as they are configured
APPENDIX B. Routers route based on the network number. The router that delivers the data packet to the correct destination host uses the host ID.
 APPENDIX B IP Subnetting IP Addressing Routers route based on the network number. The router that delivers the data packet to the correct destination host uses the host ID. IP Classes An IP address is
APPENDIX B IP Subnetting IP Addressing Routers route based on the network number. The router that delivers the data packet to the correct destination host uses the host ID. IP Classes An IP address is
First of all Let's look at how you would connect your laptop via Ethernet, as it is the easier of the two methods.
 How to get a Internet Connection on your laptop This guide will help you to get an internet connection on your laptop either via Wi-Fi (e.g. in a café or hotel) or via Ethernet (the RJ45 type connector
How to get a Internet Connection on your laptop This guide will help you to get an internet connection on your laptop either via Wi-Fi (e.g. in a café or hotel) or via Ethernet (the RJ45 type connector
Configuring a customer owned router to function as a switch with Ultra TV
 Configuring a customer owned router to function as a switch with Ultra TV This method will turn the customer router into a wireless switch and allow the Ultra Gateway to perform routing functions and allow
Configuring a customer owned router to function as a switch with Ultra TV This method will turn the customer router into a wireless switch and allow the Ultra Gateway to perform routing functions and allow
Expert Reference Series of White Papers. Basics of IP Address Subnetting
 Expert Reference Series of White Papers Basics of IP Address Subnetting 1-800-COURSES www.globalknowledge.com Basics of IP Address Subnetting Norbert Gregorio, Global Knowledge Instructor Introduction
Expert Reference Series of White Papers Basics of IP Address Subnetting 1-800-COURSES www.globalknowledge.com Basics of IP Address Subnetting Norbert Gregorio, Global Knowledge Instructor Introduction
Quick Guide of DDNS Settings
 Quick Guide of DDNS Settings Solution: With the development of surveillance systems, more and more users want to use ADSL to realize video surveillance through network. But ADSL gives dynamic IP addresses
Quick Guide of DDNS Settings Solution: With the development of surveillance systems, more and more users want to use ADSL to realize video surveillance through network. But ADSL gives dynamic IP addresses
Slave Computer 1 Slave Computer 2
 MotoTally Networking Guide Windows XP Introduction This networking guide will show you how to configure your computers on a network so you can run multiple instances of MotoTally on multiple computers,
MotoTally Networking Guide Windows XP Introduction This networking guide will show you how to configure your computers on a network so you can run multiple instances of MotoTally on multiple computers,
How to Create Subnets To create subnetworks, you take bits from the host portion of the IP address and reserve them to define the subnet address.
 SUBNET MASK To define the network and host portions of an address, the devices use a separate 32-bit pattern called a subnet mask. We express the subnet mask in the same dotted decimal format as the IPv4
SUBNET MASK To define the network and host portions of an address, the devices use a separate 32-bit pattern called a subnet mask. We express the subnet mask in the same dotted decimal format as the IPv4
Internet Protocol version 4 Part I
 Internet Protocol version 4 Part I Claudio Cicconetti International Master on Information Technology International Master on Communication Networks Engineering Table of Contents
Internet Protocol version 4 Part I Claudio Cicconetti International Master on Information Technology International Master on Communication Networks Engineering Table of Contents
IP Sub Networking Mini Howto
 Table of Contents IP Sub Networking Mini Howto...1 Robert Hart, hartr@interweft.com.au...1 1. Copyright...1 2. Introduction...1 3. The Anatomy of IP numbers...1 4. What are subnets?...1 5. Why subnetwork?...1
Table of Contents IP Sub Networking Mini Howto...1 Robert Hart, hartr@interweft.com.au...1 1. Copyright...1 2. Introduction...1 3. The Anatomy of IP numbers...1 4. What are subnets?...1 5. Why subnetwork?...1
This techno knowledge paper can help you if: You need to setup a WAN connection between a Patton Router and a NetGuardian.
 Problem: Patton / 240T WAN Setup Platform: NetGuardian 240T This TKP is a guide to setting up a PPP to T1 WAN connection between a Patton Model 2603 Router and a NetGuardian 240T. The example in this guide
Problem: Patton / 240T WAN Setup Platform: NetGuardian 240T This TKP is a guide to setting up a PPP to T1 WAN connection between a Patton Model 2603 Router and a NetGuardian 240T. The example in this guide
estadium Project Lab 8: Wireless Mesh Network Setup with DD WRT
 estadium Project Lab 8: Wireless Mesh Network Setup with DD WRT Objectives To become familiar with wireless mesh networks and show set up a wireless mesh network test bed using the DD WRT firmware. We
estadium Project Lab 8: Wireless Mesh Network Setup with DD WRT Objectives To become familiar with wireless mesh networks and show set up a wireless mesh network test bed using the DD WRT firmware. We
How to convert a wireless router to be a wireless. access point
 How to convert a wireless router to be a wireless access point Thanks for purchasing Edimax Wireless Router. This instruction can be applied if you want to keep your wired router and you need Edimax Wireless
How to convert a wireless router to be a wireless access point Thanks for purchasing Edimax Wireless Router. This instruction can be applied if you want to keep your wired router and you need Edimax Wireless
EMG Ethernet Modbus Gateway User Manual
 EMG Ethernet Modbus Gateway User Manual Rev 2.2 07/2010 CONTENTS 1. Introduction 1.1. General Features 1.2 Installing the Drivers 2. Configuration 2.1 Main Device Parameters 2.1.1 RS485 Serial Communication
EMG Ethernet Modbus Gateway User Manual Rev 2.2 07/2010 CONTENTS 1. Introduction 1.1. General Features 1.2 Installing the Drivers 2. Configuration 2.1 Main Device Parameters 2.1.1 RS485 Serial Communication
Chapter 3: IP Addressing and VLSM
 Chapter 3: IP Addressing and VLSM QUESTION 54 What is the principle reason to use a private IP address on an internal network? A. Subnet strategy for private companies. B. Manage and scale the growth of
Chapter 3: IP Addressing and VLSM QUESTION 54 What is the principle reason to use a private IP address on an internal network? A. Subnet strategy for private companies. B. Manage and scale the growth of
Debugging Network Communications. 1 Check the Network Cabling
 Debugging Network Communications Situation: you have a computer and your NetBurner device on a network, but you cannot communicate between the two. This application note provides a set of debugging steps
Debugging Network Communications Situation: you have a computer and your NetBurner device on a network, but you cannot communicate between the two. This application note provides a set of debugging steps
SUBNETTING SCENARIO S
 SUBNETTING SCENARIO S This white paper provides several in-depth scenario s dealing with a very confusing topic, subnetting. Many networking engineers need extra practice to completely understand the intricacies
SUBNETTING SCENARIO S This white paper provides several in-depth scenario s dealing with a very confusing topic, subnetting. Many networking engineers need extra practice to completely understand the intricacies
Session Title: Exploring Packet Tracer v5.3 IP Telephony & CME. Scenario
 Session Title: Exploring Packet Tracer v5.3 IP Telephony & CME Scenario With the scheduled release of Packet Tracer v5.3 in the near future, this case study is designed to provide you with an insight into
Session Title: Exploring Packet Tracer v5.3 IP Telephony & CME Scenario With the scheduled release of Packet Tracer v5.3 in the near future, this case study is designed to provide you with an insight into
Establishing a VPN tunnel to CNet CWR-854 VPN router using WinXP IPSec client
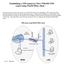 Establishing a VPN tunnel to CNet CWR-854 VPN router using WinXP IPSec client Generally speaking, remote users need to use a VPN client software for establishing a VPN connection to their home/work router
Establishing a VPN tunnel to CNet CWR-854 VPN router using WinXP IPSec client Generally speaking, remote users need to use a VPN client software for establishing a VPN connection to their home/work router
Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials.
 Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials. CHAPTER 5 OBJECTIVES Configure a router with an initial configuration. Use the
Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials. CHAPTER 5 OBJECTIVES Configure a router with an initial configuration. Use the
Technical Support Information Belkin internal use only
 The fundamentals of TCP/IP networking TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocols) is a set of networking protocols that is used for communication on the Internet and on many other networks.
The fundamentals of TCP/IP networking TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocols) is a set of networking protocols that is used for communication on the Internet and on many other networks.
Lecture 8. IP Fundamentals
 Lecture 8. Internet Network Layer: IP Fundamentals Outline Layer 3 functionalities Internet Protocol (IP) characteristics IP packet (first look) IP addresses Routing tables: how to use ARP Layer 3 functionalities
Lecture 8. Internet Network Layer: IP Fundamentals Outline Layer 3 functionalities Internet Protocol (IP) characteristics IP packet (first look) IP addresses Routing tables: how to use ARP Layer 3 functionalities
Guideline for setting up a functional VPN
 Guideline for setting up a functional VPN Why do I want a VPN? VPN by definition creates a private, trusted network across an untrusted medium. It allows you to connect offices and people from around the
Guideline for setting up a functional VPN Why do I want a VPN? VPN by definition creates a private, trusted network across an untrusted medium. It allows you to connect offices and people from around the
Chapter7 Setting the Receiving PC for Direct Upload. Setting the Receiving PC for Direct Upload... 148 For Windows... 148 For Macintosh...
 Chapter7 Setting the Receiving PC for Direct Upload Setting the Receiving PC for Direct Upload... 148 For Windows... 148 For Macintosh... 153 Setting the Receiving PC for Direct Upload This section explains
Chapter7 Setting the Receiving PC for Direct Upload Setting the Receiving PC for Direct Upload... 148 For Windows... 148 For Macintosh... 153 Setting the Receiving PC for Direct Upload This section explains
3201 Computer Networks 2014/2015 Handout: Subnetting Question
 Subnetting Questions with Answers Question1: Given the following: Network address: 192.168.10.0 Subnet mask: 255.255.255.224 1. How many subnets? Ans: 6 2. How many hosts? Ans: 30 3. What are the valid
Subnetting Questions with Answers Question1: Given the following: Network address: 192.168.10.0 Subnet mask: 255.255.255.224 1. How many subnets? Ans: 6 2. How many hosts? Ans: 30 3. What are the valid
Configuration Guide. How to Configure SSL VPN Features in DSR Series. Overview
 Configuration Guide How to Configure SSL VPN Features in DSR Series Overview This document describes how to configure D-Link DSR-500N to enable SSL VPN feature. An SSL VPN is a form of VPN that can be
Configuration Guide How to Configure SSL VPN Features in DSR Series Overview This document describes how to configure D-Link DSR-500N to enable SSL VPN feature. An SSL VPN is a form of VPN that can be
Enabling Internet Connection Sharing on Windows 2000 15. Enabling ICS On Windows XP As The Host 4 Enabling ICS On Windows XP As The Client 11
 Sharing an Internet Connection with SatDirect Plus Table of Contents Contents Section 1: Section 2: Section 3: Introduction... 1 Physical Setup......2 Enabling Internet Connection Sharing on Windows XP
Sharing an Internet Connection with SatDirect Plus Table of Contents Contents Section 1: Section 2: Section 3: Introduction... 1 Physical Setup......2 Enabling Internet Connection Sharing on Windows XP
CCNA Tutorial Series SUBNETTING
 CCNA Tutorial Series This document contains the Course Map For The Interactive flash tutorial at: http://www.semsim.com/ccna/tutorial/subnetting/subnetting.html HOME PAGE Course Objectives Pre-test By
CCNA Tutorial Series This document contains the Course Map For The Interactive flash tutorial at: http://www.semsim.com/ccna/tutorial/subnetting/subnetting.html HOME PAGE Course Objectives Pre-test By
Advanced Topics: IP Subnetting A WHITE PAPER PREPARED FOR ASPE TECHNOLOGY. www.aspetech.com toll-free: 877-800-5221
 Advanced Topics: IP Subnetting A WHITE PAPER PREPARED FOR ASPE TECHNOLOGY www.aspetech.com toll-free: 877-800-5221 Advanced Topics IP Subnetting It is almost impossible to lay out an IP network without
Advanced Topics: IP Subnetting A WHITE PAPER PREPARED FOR ASPE TECHNOLOGY www.aspetech.com toll-free: 877-800-5221 Advanced Topics IP Subnetting It is almost impossible to lay out an IP network without
Unix System Administration
 Unix System Administration Chris Schenk Lecture 08 Tuesday Feb 13 CSCI 4113, Spring 2007 ARP Review Host A 128.138.202.50 00:0B:DB:A6:76:18 Host B 128.138.202.53 00:11:43:70:45:81 Switch Host C 128.138.202.71
Unix System Administration Chris Schenk Lecture 08 Tuesday Feb 13 CSCI 4113, Spring 2007 ARP Review Host A 128.138.202.50 00:0B:DB:A6:76:18 Host B 128.138.202.53 00:11:43:70:45:81 Switch Host C 128.138.202.71
For extra services running behind your router. What to do after IP change
 For extra services running behind your router. What to do after IP change This guide is for customers who meet the following conditions: - Customers who have moved from a TPG Layer 3 plan to a TPG Layer
For extra services running behind your router. What to do after IP change This guide is for customers who meet the following conditions: - Customers who have moved from a TPG Layer 3 plan to a TPG Layer
Packet Tracer 3 Lab VLSM 2 Solution
 Packet Tracer 3 Lab VLSM 2 Solution Objective Create a simulated network topology using Packet Tracer Design an IP addressing scheme using a Class B subnetwork address and VLSM Apply IP addresses to the
Packet Tracer 3 Lab VLSM 2 Solution Objective Create a simulated network topology using Packet Tracer Design an IP addressing scheme using a Class B subnetwork address and VLSM Apply IP addresses to the
Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 2 Conceitos de protocolos de Encaminhamento Cap 2
 Static Routing Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 2 1 1 Objectives Define the general role a router plays in networks. Describe the directly connected networks, different router interfaces Examine
Static Routing Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 2 1 1 Objectives Define the general role a router plays in networks. Describe the directly connected networks, different router interfaces Examine
CS335 Sample Questions for Exam #2
 CS335 Sample Questions for Exam #2.) Compare connection-oriented with connectionless protocols. What type of protocol is IP? How about TCP and UDP? Connection-oriented protocols Require a setup time to
CS335 Sample Questions for Exam #2.) Compare connection-oriented with connectionless protocols. What type of protocol is IP? How about TCP and UDP? Connection-oriented protocols Require a setup time to
Subnetting,Supernetting, VLSM & CIDR
 Subnetting,Supernetting, VLSM & CIDR WHAT - IP Address Unique 32 or 128 bit Binary, used to identify a system on a Network or Internet. Network Portion Host Portion CLASSFULL ADDRESSING IP address space
Subnetting,Supernetting, VLSM & CIDR WHAT - IP Address Unique 32 or 128 bit Binary, used to identify a system on a Network or Internet. Network Portion Host Portion CLASSFULL ADDRESSING IP address space
Configure WAN Load Balancing
 AlliedWare TM OS How To Configure WAN Load Balancing Introduction With the increasing use of the Internet to service core business functions comes the need for reliable WAN connectivity. A specific aspect
AlliedWare TM OS How To Configure WAN Load Balancing Introduction With the increasing use of the Internet to service core business functions comes the need for reliable WAN connectivity. A specific aspect
Quick Guide of HiDDNS Settings (with UPnP)
 Quick Guide of HiDDNS Settings (with UPnP) Solution 1: With the development of surveillance systems, more and more users want to use ADSL to realize video surveillance through network. But ADSL gives dynamic
Quick Guide of HiDDNS Settings (with UPnP) Solution 1: With the development of surveillance systems, more and more users want to use ADSL to realize video surveillance through network. But ADSL gives dynamic
2. Are explicit proxy connections also affected by the ARM config?
 Achieving rapid success with WCCP and Web Security Gateway October 2011 Webinar Q/A 1. What if you are already using WCCP for Cisco waas on the same routers that you need to use WCCP for websense? Using
Achieving rapid success with WCCP and Web Security Gateway October 2011 Webinar Q/A 1. What if you are already using WCCP for Cisco waas on the same routers that you need to use WCCP for websense? Using
VLAN 802.1Q. 1. VLAN Overview. 1. VLAN Overview. 2. VLAN Trunk. 3. Why use VLANs? 4. LAN to LAN communication. 5. Management port
 1. VLAN Overview 2. VLAN Trunk 3. Why use VLANs? 4. LAN to LAN communication 5. Management port 6. Applications 6.1. Application 1 6.2. Application 2 6.3. Application 3 6.4. Application 4 6.5. Application
1. VLAN Overview 2. VLAN Trunk 3. Why use VLANs? 4. LAN to LAN communication 5. Management port 6. Applications 6.1. Application 1 6.2. Application 2 6.3. Application 3 6.4. Application 4 6.5. Application
Multi-Homing Dual WAN Firewall Router
 Multi-Homing Dual WAN Firewall Router Quick Installation Guide M73-APO09-400 Multi-Homing Dual WAN Firewall Router Overview The Multi-Homing Dual WAN Firewall Router provides three 10/100Mbit Ethernet
Multi-Homing Dual WAN Firewall Router Quick Installation Guide M73-APO09-400 Multi-Homing Dual WAN Firewall Router Overview The Multi-Homing Dual WAN Firewall Router provides three 10/100Mbit Ethernet
Firewall VPN Router. Quick Installation Guide M73-APO09-380
 Firewall VPN Router Quick Installation Guide M73-APO09-380 Firewall VPN Router Overview The Firewall VPN Router provides three 10/100Mbit Ethernet network interface ports which are the Internal/LAN, External/WAN,
Firewall VPN Router Quick Installation Guide M73-APO09-380 Firewall VPN Router Overview The Firewall VPN Router provides three 10/100Mbit Ethernet network interface ports which are the Internal/LAN, External/WAN,
ECE 358: Computer Networks. Solutions to Homework #4. Chapter 4 - The Network Layer
 ECE 358: Computer Networks Solutions to Homework #4 Chapter 4 - The Network Layer P 4. Consider the network below. a. Suppose that this network is a datagram network. Show the forwarding table in router
ECE 358: Computer Networks Solutions to Homework #4 Chapter 4 - The Network Layer P 4. Consider the network below. a. Suppose that this network is a datagram network. Show the forwarding table in router
Bandwidth-based load-balancing with failover. The easy way. We need more bandwidth.
 Bandwidth-based load-balancing with failover. The easy way. We need more bandwidth. Presenter information Tomas Kirnak Network design Security, wireless Servers, Virtualization Mikrotik Certified Trainer
Bandwidth-based load-balancing with failover. The easy way. We need more bandwidth. Presenter information Tomas Kirnak Network design Security, wireless Servers, Virtualization Mikrotik Certified Trainer
Chapter 3 LAN Configuration
 Chapter 3 LAN Configuration This chapter describes how to configure the advanced LAN features of your ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN. This chapter contains the following sections
Chapter 3 LAN Configuration This chapter describes how to configure the advanced LAN features of your ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN. This chapter contains the following sections
Application Note Configuring the UGate 3000 for use with ClipMail Pro and ClipExpress
 Application Note Configuring the UGate 3000 for use with Introduction This Application Note guides the ClipMail user through the UGate gateway configuration process by using a simple dial up connection
Application Note Configuring the UGate 3000 for use with Introduction This Application Note guides the ClipMail user through the UGate gateway configuration process by using a simple dial up connection
Multi-Homing Security Gateway
 Multi-Homing Security Gateway MH-5000 Quick Installation Guide 1 Before You Begin It s best to use a computer with an Ethernet adapter for configuring the MH-5000. The default IP address for the MH-5000
Multi-Homing Security Gateway MH-5000 Quick Installation Guide 1 Before You Begin It s best to use a computer with an Ethernet adapter for configuring the MH-5000. The default IP address for the MH-5000
CET442L Lab #2. IP Configuration and Network Traffic Analysis Lab
 CET442L Lab #2 IP Configuration and Network Traffic Analysis Lab Goals: In this lab you will plan and implement the IP configuration for the Windows server computers on your group s network. You will use
CET442L Lab #2 IP Configuration and Network Traffic Analysis Lab Goals: In this lab you will plan and implement the IP configuration for the Windows server computers on your group s network. You will use
IP Addressing. and Subnetting. Workbook Version 1.5. Student Name:
 IP Addressing and Subnetting Workbook Version.5 Student Name: IP Address Classes Class A 27 (Network 27 is reserved for loopback and internal testing) Leading bit pattern... Network. Host. Host. Host Class
IP Addressing and Subnetting Workbook Version.5 Student Name: IP Address Classes Class A 27 (Network 27 is reserved for loopback and internal testing) Leading bit pattern... Network. Host. Host. Host Class
Connecting with Computer Science, 2e. Chapter 5 The Internet
 Connecting with Computer Science, 2e Chapter 5 The Internet Objectives In this chapter you will: Learn what the Internet really is Become familiar with the architecture of the Internet Become familiar
Connecting with Computer Science, 2e Chapter 5 The Internet Objectives In this chapter you will: Learn what the Internet really is Become familiar with the architecture of the Internet Become familiar
1. How many unique network IDs are there in class A addresses? # of unique hosts?
 CS445: IPv4 Addresses In-class activity Names: Part 1: Address Classes Original three classes of IPv4 addresses: A: 0 network (7 bits) host (24 bits) B: 10 network (14 bits) host (16 bits) C: 110 network
CS445: IPv4 Addresses In-class activity Names: Part 1: Address Classes Original three classes of IPv4 addresses: A: 0 network (7 bits) host (24 bits) B: 10 network (14 bits) host (16 bits) C: 110 network
ICS 351: Today's plan. IP addresses Network Address Translation Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol Small Office / Home Office configuration
 ICS 351: Today's plan IP addresses Network Address Translation Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol Small Office / Home Office configuration IP address exhaustion IPv4 addresses are 32 bits long so there
ICS 351: Today's plan IP addresses Network Address Translation Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol Small Office / Home Office configuration IP address exhaustion IPv4 addresses are 32 bits long so there
Scalable Linux Clusters with LVS
 Scalable Linux Clusters with LVS Considerations and Implementation, Part I Eric Searcy Tag1 Consulting, Inc. emsearcy@tag1consulting.com April 2008 Abstract Whether you are perusing mailing lists or reading
Scalable Linux Clusters with LVS Considerations and Implementation, Part I Eric Searcy Tag1 Consulting, Inc. emsearcy@tag1consulting.com April 2008 Abstract Whether you are perusing mailing lists or reading
One of the most important topics in any discussion of TCP/IP is IP. IP Addressing
 IP Addressing 125 machine, called a RARP server, responds with the answer, and the identity crisis is over. RARP uses the information it does know about the machine s MAC address to learn its IP address
IP Addressing 125 machine, called a RARP server, responds with the answer, and the identity crisis is over. RARP uses the information it does know about the machine s MAC address to learn its IP address
