Costing statement: Generalised anxiety disorder and panic disorder (with or without agoraphobia) in adults
|
|
|
- Alexandra Poole
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Costing statement: Generalised anxiety disorder and panic disorder (with or without agoraphobia) in adults Introduction The partial update of the guideline on Generalised anxiety disorder and panic disorder (with or without agoraphobia) in adults (NICE clinical guideline 113) is unlikely to have a significant impact on the use of NHS resources at a national level. The guideline partially updates and replaces NICE clinical guideline 22 (published 2004; amended 2007). We have focused on areas where the recommendations have changed. Because of variations in practice across the country, organisations may incur costs or savings depending on their circumstances. For example where organisations have fully implemented previous guidance, there may be the opportunity to realise savings due to the use of low intensity psychological interventions. Conversely, where organisations have not fully implemented previous guidance they may incur additional costs in implementing the recommendations. Therefore, we encourage organisations to assess their compliance with the recommendations and any costs or savings locally. To help this process a local costing template has been developed. Background Generalised anxiety disorder (GAD) is one of a range of anxiety disorders that includes panic disorder (with and without agoraphobia), post-traumatic stress disorder, obsessive compulsive disorder, social phobia, specific phobias (for example, of spiders) and acute stress disorder. Anxiety disorders can exist in isolation but more commonly occur with other anxiety and depressive disorders. adults 1 of 9
2 NICE clinical guideline 22 looked at the management of panic disorder, with or without agoraphobia, and generalised anxiety disorder. The present guideline updates the recommendations on the management of generalised anxiety disorder. It does not update the recommendations on the management of panic disorder. Other anxiety disorders for which there are NICE guidelines are post-traumatic stress disorder and obsessive compulsive disorder (NICE 2005a, 2005b). The guideline does not address the management of GAD in children and adolescents. The guideline introduces a stepped-care model for people with GAD as set out in table 1. Table 1 The stepped-care model Focus of the intervention STEP 4: Complex treatmentrefractory GAD and very marked functional impairment, such as selfneglect or a high risk of self-harm STEP 3: GAD with an inadequate response to step 2 interventions or marked functional impairment STEP 2: Diagnosed GAD that has not improved after education and active monitoring in primary care STEP 1: All known and suspected presentations of GAD Nature of the intervention Highly specialist treatment, such as complex drug and/or psychological treatment regimens; input from multi-agency teams, crisis services, day hospitals or inpatient care Choice of a high-intensity psychological intervention (cognitive behavioural therapy/applied relaxation) or a drug treatment Low-intensity psychological interventions: pure self-help*, guided self-help and psychoeducational groups Identification and assessment; education about GAD and treatment options; active monitoring *Pure self-help is defined as a self-administered intervention intended to treat GAD and involves self-help materials (usually a book or workbook). It is similar to guided self-help but without any contact with a healthcare professional. adults 2 of 9
3 Stepped care (Scogin et al. 2003) is a framework that is increasingly being used in the UK to specify best-practice clinical pathways to care. Stepped care is designed to increase the efficiency of service provision with an overall benefit to patient populations. The basic principle is that people presenting with a common mental health disorder will step through progressive levels of treatment as necessary, with the expectation that many of these people will recover during the less intensive phases. Recommendation 1.2.1, Follow the stepped-care model, offering the least intrusive, most effective intervention first is anticipated to have the most significant change on the use of resources when compared with the previous guidance (NICE clinical guideline 22). Epidemiology The estimated proportion of people in England with GAD was 4.4% in the most recent Adult Psychiatric Morbidity Survey (APMS) (McManus et al. 2009), a figure that has varied little across the three survey years 1993, 1997 and Prevalence rates have generally been found to be between 1.5 and 2.5 times higher in women than men. In the APMS cited above, the rates were 3.4% for men and 5.3% for women. The APMS in England also suggested only 34% of people with GAD were receiving any kind of treatment for their condition at the time of the survey. Of these, 53% were receiving medication, 21% counselling or other psychological therapy, and 26% a combination of drugs and psychological treatment. There is a NICE guideline on common mental health disorders expected in 2011, which may help to improve diagnosis of GAD. Cost impact Each organisation is requested to review its own position in respect of the guidance. The estimated cost and the details of interventions changed as a result of the guidance update are summarised in table 2. adults 3 of 9
4 Table 2 Estimated cost of each step Intervention Cost of intervention Identification and assessment Minimal Low-intensity psychological 540 for 6 sessions or 45 per person interventions (LIPI) based on a group of 12 Drug treatment From 189 to 449 High-intensity psychological 1125 per person for 15 sessions interventions (HIPI) As shown for drug treatment & HIPI but Highly specialist treatment combined. Inpatient episode 6496 Identification and assessment There are unlikely to be any significant costs in this intervention it is about existing services indentifying early and communicating the diagnosis of GAD. Following on from this, the next step is to provide education about the nature of GAD and the options for treatment, along with appropriate monitoring. Recommendation states: Education and monitoring may improve less severe presentations and avoid the need for further interventions. Low-intensity psychological Interventions This consists of the following first-line treatment: non-facilitated self-help guided self-help psychoeducational groups. It is only the latter psychoeducational groups that are an addition to NICE clinical guideline 22 and therefore it is those costs that are quoted in table 2. A typical group will have a ratio of 12 participants to 1 therapist and consist of six weekly sessions, each lasting 2 hours. The estimated cost of 6 sessions is 540 or 45 per person. It is assumed this is delivered by a Band 5 mental health worker at cost of 45 per hour for face-to-face contact (Curtis 2009). adults 4 of 9
5 It is recognised that organisations may wish to use other low intensity psychological interventions recommended in the original clinical guideline. The cost of these other low-intensity psychological interventions is given in the costing template, as a note to Step 2. Should organisations wish to use the costs of the other low-intensity psychological interventions the costing template provided should be amended accordingly. Drug treatment The guideline recommends that if a person with GAD chooses drug treatment, offer a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI). Consider offering sertraline first because it is the most cost-effective drug, but note that at the time of publication (January 2011) sertraline did not have UK marketing authorisation for this indication. Informed consent should be obtained and documented. Monitor the person carefully for adverse reactions The guideline recommends that if sertraline is ineffective offer an alternative SSRI or a serotonin noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) should be offered. It also recommends that pregabalin be considered if the person cannot tolerate SSRIs. The drug treatment cost is calculated, based on Guideline Development Group (GDG) expert opinion, as one initiation visit, two visits over the first 8 weeks of treatment and one during the maintenance period.a total of four GP visits at a cost of 35 per visit (Curtis 2009).The treatment period, based upon GDG expert opinion, is 8 weeks of initial treatment and 6 months of maintenance treatment. The respective drug costs are shown in table 3 below: adults 5 of 9
6 Table 3 Drug costs Drug Drug cost for GP Average Daily Total cost of drug treatment visits Dosage treatment period 2 cost Milligrams Duloxetine Escitalopram Paroxetine Pregabalin Sertraline Venlafaxine At the time of publication (January 2011), sertraline did not have UK marketing authorisation for this indication. Informed consent should be obtained and documented. 2. The average treatment period is 8 weeks of initial treatment and 6 months of maintenance treatment. Drug costs are taken from the British national formulary 60 (BNF 60) (September 2010) The guideline also recommends that benzodiazepine should not be offered for the treatment of GAD in primary or secondary care except as a short-term measure during crises. As this is stated in the BNF 60 it is assumed that this is current practice and no further savings will occur from not using this drug. High-intensity psychological Interventions This consists of cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) or applied relaxation. CBT and applied relaxation consist of sessions, each lasting 1 hour. The estimated cost is 1125 per 15 sessions. This is based on a unit cost for clinical psychologists of 75 per hour of client contact (Curtis 2009). Highly specialist treatment This could involve offering a combination of psychological interventions and drug treatment, a multidisciplinary team assessment and an inpatient episode of care. The cost of an inpatient episode of care based on an average length of stay of 22.4 days at a daily rate of 290 for a stay in a mental health unit is Currently 4% of adults 6 of 9
7 people with GAD are estimated to have an inpatient episode of care. (Full guideline table 16.) Annual costs of health and social care incurred by people with GAD The GDG by combining the data in APMS with GDG expert opinion estimated the annual cost for health and social care for people with GAD at per person. (Full guideline table 16) Other considerations Due to the low diagnosis rate of GAD by GPs, commissioners should promote this guideline to ensure that patients with GAD are offered treatment. This should avoid future health and social care costs for people who would have previously gone untreated. CG 22 did not use the stepped care approach to GAD which may have resulted in higher cost interventions being used first. Commissioners should review the local position to ensure that the stepped care model is now being used. Furthermore the lack of availability of psychological interventions also makes it more likely that medication would be used for treatment of GAD. The improving access to psychological therapies (IAPT) initiatives has increased the availability of recommended psychological interventions for the treatment of GAD. Organisations should review their own position in respect of these initiatives. Commissioners avoiding drug treatment should be aware that the cost of a GP visit will not be cash releasing, however it will create additional capacity if the diagnosis rates increase for GAD. Conclusion NICE clinical guideline 113 partially updates and replaces NICE clinical guideline 22.. It introduces the stepped-care model as recommended practice for the management of GAD. This allows less intensive low-cost psychological interventions adults 7 of 9
8 to be used first and if GAD does not improve then to step up to SSRI medication or more expensive highly intensive psychological interventions. Following the model allows the service to be delivered in an efficient and effective way. The guideline also recognises the low diagnosis rate for GAD and the opportunity for health and social care costs to be avoided should diagnosis rates improve. Commissioners are requested to review their local position in order to make sure they are using resources effectively in the treatment of GAD. To support this process a local costing template has been developed. adults 8 of 9
9 References McManus, S., Meltzer, H., Brugha, T., et al. (2009) Adult psychiatric morbidity in England, 2007: Results of a household survey. Leeds: The NHS Information Centre for Health and Social Care. Scogin, F., Hanson, A., & Welsh, D. (2003) Self-administered treatment in stepped-care models of depression treatment. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 59, Curtis, L. (2009) Unit Costs of Health and Social Care Canterbury: University of Kent adults 9 of 9
Common mental health disorders
 Issue date: May 2011 Common mental health disorders Identification and pathways to care NICE clinical guideline 123 Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Mental Health NICE clinical guideline
Issue date: May 2011 Common mental health disorders Identification and pathways to care NICE clinical guideline 123 Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Mental Health NICE clinical guideline
Costing statement: Depression: the treatment and management of depression in adults. (update) and
 Costing statement: Depression: the treatment and management of depression in adults (update) and Depression in adults with a chronic physical health problem: treatment and management Summary It has not
Costing statement: Depression: the treatment and management of depression in adults (update) and Depression in adults with a chronic physical health problem: treatment and management Summary It has not
`çããçå=jéåí~ä= aáëçêçéêëw=^åñáéíó=~åç= aééêéëëáçå. aêk=`=f=lâçåü~ jéçáå~ä=aáêéåíçê lñäé~ë=kep=cçìåç~íáçå=qêìëí=
 `çããçå=jéåí~ä= aáëçêçéêëw=^åñáéíó=~åç= aééêéëëáçå aêk=`=f=lâçåü~ jéçáå~ä=aáêéåíçê lñäé~ë=kep=cçìåç~íáçå=qêìëí= Overview: Common Mental What are they? Disorders Why are they important? How do they affect
`çããçå=jéåí~ä= aáëçêçéêëw=^åñáéíó=~åç= aééêéëëáçå aêk=`=f=lâçåü~ jéçáå~ä=aáêéåíçê lñäé~ë=kep=cçìåç~íáçå=qêìëí= Overview: Common Mental What are they? Disorders Why are they important? How do they affect
Step 4: Complex and severe depression in adults
 Step 4: Complex and severe depression in adults A NICE pathway brings together all NICE guidance, quality standards and materials to support implementation on a specific topic area. The pathways are interactive
Step 4: Complex and severe depression in adults A NICE pathway brings together all NICE guidance, quality standards and materials to support implementation on a specific topic area. The pathways are interactive
Depression in adults with a chronic physical health problem
 Depression in adults with a chronic physical health problem Treatment and management Issued: October 2009 NICE clinical guideline 91 guidance.nice.org.uk/cg91 NICE has accredited the process used by the
Depression in adults with a chronic physical health problem Treatment and management Issued: October 2009 NICE clinical guideline 91 guidance.nice.org.uk/cg91 NICE has accredited the process used by the
Depression in children and young people. Identification and management in primary, community and secondary care
 NICE guideline May 2005 Issue date: September 2005 Depression in children and young people Identification and management in primary, community and secondary care Clinical Guideline 28 Developed by the
NICE guideline May 2005 Issue date: September 2005 Depression in children and young people Identification and management in primary, community and secondary care Clinical Guideline 28 Developed by the
Depression in Adults
 Depression in Adults A chapter of Croydon s mental health Joint Strategic Needs Assessment 2012/13 Health and Wellbeing Board 5 December 2012 Bernadette Alves, Locum Consultant in Public Health Croydon
Depression in Adults A chapter of Croydon s mental health Joint Strategic Needs Assessment 2012/13 Health and Wellbeing Board 5 December 2012 Bernadette Alves, Locum Consultant in Public Health Croydon
Step 2: Recognised depression in adults persistent subthreshold depressive symptoms or mild to moderate depression
 Step 2: Recognised depression in adults persistent subthreshold depressive symptoms or mild to moderate depression A NICE pathway brings together all NICE guidance, quality standards and materials to support
Step 2: Recognised depression in adults persistent subthreshold depressive symptoms or mild to moderate depression A NICE pathway brings together all NICE guidance, quality standards and materials to support
NICE clinical guideline 90
 Depression in adults The treatment and management of depression in adults Issued: October 2009 NICE clinical guideline 90 guidance.nice.org.uk/cg90 NHS Evidence has accredited the process used by the Centre
Depression in adults The treatment and management of depression in adults Issued: October 2009 NICE clinical guideline 90 guidance.nice.org.uk/cg90 NHS Evidence has accredited the process used by the Centre
Depression. The treatment and management of depression in adults. This is a partial update of NICE clinical guideline 23
 Issue date: October 2009 Depression The treatment and management of depression in adults This is a partial update of NICE clinical guideline 23 NICE clinical guideline 90 Developed by the National Collaborating
Issue date: October 2009 Depression The treatment and management of depression in adults This is a partial update of NICE clinical guideline 23 NICE clinical guideline 90 Developed by the National Collaborating
Alcohol-use disorders: alcohol dependence. Costing report. Implementing NICE guidance
 Alcohol-use disorders: alcohol dependence Costing report Implementing NICE guidance February 2011 (February 2011) 1 of 37 NICE clinical guideline 115 This costing report accompanies the clinical guideline:
Alcohol-use disorders: alcohol dependence Costing report Implementing NICE guidance February 2011 (February 2011) 1 of 37 NICE clinical guideline 115 This costing report accompanies the clinical guideline:
Mental Health Needs Assessment Personality Disorder Prevalence and models of care
 Mental Health Needs Assessment Personality Disorder Prevalence and models of care Introduction and definitions Personality disorders are a complex group of conditions identified through how an individual
Mental Health Needs Assessment Personality Disorder Prevalence and models of care Introduction and definitions Personality disorders are a complex group of conditions identified through how an individual
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Schizophrenia: core interventions in the treatment and management of schizophrenia in primary and secondary care (update) 1.1
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Schizophrenia: core interventions in the treatment and management of schizophrenia in primary and secondary care (update) 1.1
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD): the treatment of PTSD in adults and children
 Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD): the treatment of PTSD in adults and children Understanding NICE guidance information for people with PTSD, their advocates and carers, and the public March 2005 Information
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD): the treatment of PTSD in adults and children Understanding NICE guidance information for people with PTSD, their advocates and carers, and the public March 2005 Information
NICE Pathways bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic.
 bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published.
bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published.
Costing report. Drug misuse: psychosocial interventions and opioid detoxification. Implementing NICE guidance. July 2007
 Drug misuse: psychosocial interventions and opioid detoxification Costing report Implementing NICE guidance July 2007 NICE clinical guidelines 51 and 52 National costing report: Drug misuse guidelines
Drug misuse: psychosocial interventions and opioid detoxification Costing report Implementing NICE guidance July 2007 NICE clinical guidelines 51 and 52 National costing report: Drug misuse guidelines
Clinical guideline Published: 28 October 2009 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg90
 Depression in adults: recognition and management Clinical guideline Published: 28 October 2009 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg90 NICE 2009. All rights reserved. Last updated April 2016 Your responsibility The
Depression in adults: recognition and management Clinical guideline Published: 28 October 2009 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg90 NICE 2009. All rights reserved. Last updated April 2016 Your responsibility The
Post-traumatic stress disorder overview
 Post-traumatic stress disorder overview A NICE pathway brings together all NICE guidance, quality standards and materials to support implementation on a specific topic area. The pathways are interactive
Post-traumatic stress disorder overview A NICE pathway brings together all NICE guidance, quality standards and materials to support implementation on a specific topic area. The pathways are interactive
Psychological Wellbeing Practitioner - Best Practice Guide
 Psychological Wellbeing Practitioner - Best Practice Guide 1 Introduction The Improving Access to Psychological Therapies (IAPT) programme was established in 2008 to enable people with common mental health
Psychological Wellbeing Practitioner - Best Practice Guide 1 Introduction The Improving Access to Psychological Therapies (IAPT) programme was established in 2008 to enable people with common mental health
IAPT OUTLINE SERVICE SPECIFICATION
 IAPT OUTLINE SERVICE SPECIFICATION Improving Access to Psychological Therapies Programme (IAPT) The IAPT Programme is a Department of Health initiative to improve access to psychological therapies. It
IAPT OUTLINE SERVICE SPECIFICATION Improving Access to Psychological Therapies Programme (IAPT) The IAPT Programme is a Department of Health initiative to improve access to psychological therapies. It
Depression in children and young people. Quick reference guide. Issue date: September 2005
 Quick reference guide Issue date: September 2005 Depression in children and young people Identification and management in primary, community and secondary care Clinical Guideline 28 Developed by the National
Quick reference guide Issue date: September 2005 Depression in children and young people Identification and management in primary, community and secondary care Clinical Guideline 28 Developed by the National
Sunderland Psychological Wellbeing Service
 Sunderland Psychological Wellbeing Service Information for Referrers Offering a range of psychological therapies across Sunderland. To make a referral call 0191 566 5454 A partnership between Northumberland,
Sunderland Psychological Wellbeing Service Information for Referrers Offering a range of psychological therapies across Sunderland. To make a referral call 0191 566 5454 A partnership between Northumberland,
Amendments to recommendations concerning venlafaxine
 Amendments to recommendations concerning venlafaxine On 31 May 2006 the MHRA issued revised prescribing advice for venlafaxine*. This amendment brings the guideline into line with the new advice but does
Amendments to recommendations concerning venlafaxine On 31 May 2006 the MHRA issued revised prescribing advice for venlafaxine*. This amendment brings the guideline into line with the new advice but does
Clinical guideline Published: 29 November 2005 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg31
 Obsessive-compulsive e disorder and body dysmorphic disorder: treatment Clinical guideline Published: 29 November 2005 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg31 NICE 2005. All rights reserved. Contents Introduction...
Obsessive-compulsive e disorder and body dysmorphic disorder: treatment Clinical guideline Published: 29 November 2005 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg31 NICE 2005. All rights reserved. Contents Introduction...
Behaviour Research and Therapy (in press)
 Behaviour Research and Therapy (in press) Improving Access to Psychological Therapy: Initial Evaluation of Two UK Demonstration Sites David M Clark NIHR Biomedical Research Centre for Mental Health, South
Behaviour Research and Therapy (in press) Improving Access to Psychological Therapy: Initial Evaluation of Two UK Demonstration Sites David M Clark NIHR Biomedical Research Centre for Mental Health, South
Treatment and management of depression in adults, including adults with a chronic physical health problem
 Issue date: October 2009 Depression Treatment and management of depression in adults, including adults with a chronic physical health problem This is an update of NICE clinical guideline 23 Developed by
Issue date: October 2009 Depression Treatment and management of depression in adults, including adults with a chronic physical health problem This is an update of NICE clinical guideline 23 Developed by
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder and Body Dysmorphic Disorder
 South West London and St George s Mental Health NHS Trust A National Service for Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder and Body Dysmorphic Disorder Springfield University Hospital A Referrer s Guide 1 Who we are
South West London and St George s Mental Health NHS Trust A National Service for Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder and Body Dysmorphic Disorder Springfield University Hospital A Referrer s Guide 1 Who we are
SPECIALIST ARTICLE A BRIEF GUIDE TO PSYCHOLOGICAL THERAPIES
 SPECIALIST ARTICLE A BRIEF GUIDE TO PSYCHOLOGICAL THERAPIES Psychological therapies are increasingly viewed as an important part of both mental and physical healthcare, and there is a growing demand for
SPECIALIST ARTICLE A BRIEF GUIDE TO PSYCHOLOGICAL THERAPIES Psychological therapies are increasingly viewed as an important part of both mental and physical healthcare, and there is a growing demand for
Depression: management of depression in primary and secondary care
 Issue date: December 2004 Quick reference guide Depression: management of depression in primary and secondary care Clinical Guideline 23 Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Mental Health
Issue date: December 2004 Quick reference guide Depression: management of depression in primary and secondary care Clinical Guideline 23 Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Mental Health
Borderline personality disorder
 Borderline personality disorder Treatment and management Issued: January 2009 NICE clinical guideline 78 guidance.nice.org.uk/cg78 NICE 2009 Contents Introduction... 3 Person-centred care... 5 Key priorities
Borderline personality disorder Treatment and management Issued: January 2009 NICE clinical guideline 78 guidance.nice.org.uk/cg78 NICE 2009 Contents Introduction... 3 Person-centred care... 5 Key priorities
Retrospective case record audit: service users who ended therapy
 Retrospective case record audit: service users who ended therapy How to submit your data to NAPT: Your service lead has agreed with the NAPT Team how your service's audit data will be submitted. Please
Retrospective case record audit: service users who ended therapy How to submit your data to NAPT: Your service lead has agreed with the NAPT Team how your service's audit data will be submitted. Please
IMR ISSUES, DECISIONS AND RATIONALES The Final Determination was based on decisions for the disputed items/services set forth below:
 Case Number: CM13-0018009 Date Assigned: 10/11/2013 Date of Injury: 06/11/2004 Decision Date: 01/13/2014 UR Denial Date: 08/16/2013 Priority: Standard Application Received: 08/29/2013 HOW THE IMR FINAL
Case Number: CM13-0018009 Date Assigned: 10/11/2013 Date of Injury: 06/11/2004 Decision Date: 01/13/2014 UR Denial Date: 08/16/2013 Priority: Standard Application Received: 08/29/2013 HOW THE IMR FINAL
Enhancing Recovery Rates in IAPT Services: Lessons from analysis of the Year One data.
 P a g e 0 Restricted Enhancing Recovery Rates in IAPT Services: Lessons from analysis of the Year One data. Alex Gyani 1, Roz Shafran 1, Richard Layard 2 & David M Clark 3 1 University of Reading, 2 London
P a g e 0 Restricted Enhancing Recovery Rates in IAPT Services: Lessons from analysis of the Year One data. Alex Gyani 1, Roz Shafran 1, Richard Layard 2 & David M Clark 3 1 University of Reading, 2 London
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder and Body Dysmorphic Disorder
 South West London and St George s Mental Health NHS Trust Trustwide Service for Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder and Body Dysmorphic Disorder Springfield University Hospital A Referrer s Guide 1 Who we are
South West London and St George s Mental Health NHS Trust Trustwide Service for Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder and Body Dysmorphic Disorder Springfield University Hospital A Referrer s Guide 1 Who we are
SOMERSET DUAL DIAGNOSIS PROTOCOL OCTOBER 2011
 SOMERSET DUAL DIAGNOSIS PROTOCOL OCTOBER 2011 This document is intended to be used with the Somerset Dual Diagnosis Operational Working guide. This document provides principles governing joint working
SOMERSET DUAL DIAGNOSIS PROTOCOL OCTOBER 2011 This document is intended to be used with the Somerset Dual Diagnosis Operational Working guide. This document provides principles governing joint working
NICE Pathways bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic.
 bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published.
bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published.
Antidepressant treatment in adults
 Antidepressant treatment in adults A NICE pathway brings together all NICE guidance, quality standards and materials to support implementation on a specific topic area. The pathways are interactive and
Antidepressant treatment in adults A NICE pathway brings together all NICE guidance, quality standards and materials to support implementation on a specific topic area. The pathways are interactive and
and body dysmorphic disorder (BDD) in adults, children and young people Issue date: November 2005
 Issue date: November 2005 Treating obsessivecompulsive disorder (OCD) and body dysmorphic disorder (BDD) in adults, children and young people Understanding NICE guidance information for people with OCD
Issue date: November 2005 Treating obsessivecompulsive disorder (OCD) and body dysmorphic disorder (BDD) in adults, children and young people Understanding NICE guidance information for people with OCD
Falling Between Two Stools. Dual Diagnosis: The need for multidisciplinary awareness and cooperation. Eoin Stephens
 Falling Between Two Stools Dual Diagnosis: The need for multidisciplinary awareness and cooperation Eoin Stephens PCI College Dual Diagnosis Ireland www.pcicollege.ie www.dualdiagnosis.ie Dual Diagnosis
Falling Between Two Stools Dual Diagnosis: The need for multidisciplinary awareness and cooperation Eoin Stephens PCI College Dual Diagnosis Ireland www.pcicollege.ie www.dualdiagnosis.ie Dual Diagnosis
Asthma, anxiety & depression
 Anxiety and are common in people with asthma. The good news is that there are effective treatments both for asthma and for anxiety and. With careful management, the symptoms of anxiety and can be treated
Anxiety and are common in people with asthma. The good news is that there are effective treatments both for asthma and for anxiety and. With careful management, the symptoms of anxiety and can be treated
Understanding obsessivecompulsive. disorder. Obsessive-compulsive
 Understanding obsessivecompulsive disorder Obsessive-compulsive disorder Understanding obsessivecompulsive disorder Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is described as an anxiety disorder. An obsession
Understanding obsessivecompulsive disorder Obsessive-compulsive disorder Understanding obsessivecompulsive disorder Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is described as an anxiety disorder. An obsession
How to Identify and Diagnose Depression
 Depression Spirella Building, Letchworth, SG6 4ET 01462 476700 www.mstrust.org.uk reg charity no. 1088353 Depression and MS Date of issue: March 2010 Review date: March 2011 Contents Introduction 2 1.
Depression Spirella Building, Letchworth, SG6 4ET 01462 476700 www.mstrust.org.uk reg charity no. 1088353 Depression and MS Date of issue: March 2010 Review date: March 2011 Contents Introduction 2 1.
Making sense of cognitive behaviour therapy (CBT)
 Making sense of cognitive behaviour therapy (CBT) Making sense of cognitive behaviour therapy What is cognitive behaviour therapy? 4 How does negative thinking start? 6 What type of problems can CBT help
Making sense of cognitive behaviour therapy (CBT) Making sense of cognitive behaviour therapy What is cognitive behaviour therapy? 4 How does negative thinking start? 6 What type of problems can CBT help
in young people Management of depression in primary care Key recommendations: 1 Management
 Management of depression in young people in primary care Key recommendations: 1 Management A young person with mild or moderate depression should typically be managed within primary care services A strength-based
Management of depression in young people in primary care Key recommendations: 1 Management A young person with mild or moderate depression should typically be managed within primary care services A strength-based
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
 Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) Post traumatic stress disorder is a condition where you have recurring distressing memories, flashbacks, and other symptoms after suffering a traumatic event. Treatment
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) Post traumatic stress disorder is a condition where you have recurring distressing memories, flashbacks, and other symptoms after suffering a traumatic event. Treatment
Case study: implementing the recommendations of the Tier 4 review. Rachel Bryant-Waugh
 Case study: implementing the recommendations of the Tier 4 review Rachel Bryant-Waugh 22 nd October 2015 Eating Disorders (CYP) Taking conclusions and recommendations of Tier 4 review forwards Autumn statement:
Case study: implementing the recommendations of the Tier 4 review Rachel Bryant-Waugh 22 nd October 2015 Eating Disorders (CYP) Taking conclusions and recommendations of Tier 4 review forwards Autumn statement:
Psychological Wellbeing Practitioners
 Psychological Wellbeing Practitioners Playing a key role in maintaining the nation s wellbeing Best Practice Guide 1 Forewords The publication of this good practice guide is a fantastic opportunity to
Psychological Wellbeing Practitioners Playing a key role in maintaining the nation s wellbeing Best Practice Guide 1 Forewords The publication of this good practice guide is a fantastic opportunity to
Borderline personality disorder
 Understanding NICE guidance Information for people who use NHS services Borderline personality disorder NICE clinical guidelines advise the NHS on caring for people with specific conditions or diseases
Understanding NICE guidance Information for people who use NHS services Borderline personality disorder NICE clinical guidelines advise the NHS on caring for people with specific conditions or diseases
Borderline personality disorder
 Issue date: January 2009 Borderline personality disorder Borderline personality disorder: treatment and management NICE clinical guideline 78 Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Mental Health
Issue date: January 2009 Borderline personality disorder Borderline personality disorder: treatment and management NICE clinical guideline 78 Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Mental Health
General Hospital Information
 Inpatient Programs General Hospital Information General Information The Melbourne Clinic is a purpose built psychiatric hospital established in 1975, intially privately owned by a group of psychiatrists
Inpatient Programs General Hospital Information General Information The Melbourne Clinic is a purpose built psychiatric hospital established in 1975, intially privately owned by a group of psychiatrists
Implementing NICE guidelines for the psychological treatment of depression and anxiety disorders: The IAPT experience
 International Review of Psychiatry, August 2011; 23: 375 384 Implementing NICE guidelines for the psychological treatment of depression and anxiety disorders: The IAPT experience DAVID M. CLARK University
International Review of Psychiatry, August 2011; 23: 375 384 Implementing NICE guidelines for the psychological treatment of depression and anxiety disorders: The IAPT experience DAVID M. CLARK University
GMMMG Interface Prescribing Subgroup. Shared Care Template
 GMMMG Interface Prescribing Subgroup Shared Care Template Shared Care Guideline for Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) for the treatment of Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD) and Body Dysmorphic
GMMMG Interface Prescribing Subgroup Shared Care Template Shared Care Guideline for Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) for the treatment of Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD) and Body Dysmorphic
NICE Clinical guideline 23
 NICE Clinical guideline 23 Depression Management of depression in primary and secondary care Consultation on amendments to recommendations concerning venlafaxine On 31 May 2006 the MHRA issued revised
NICE Clinical guideline 23 Depression Management of depression in primary and secondary care Consultation on amendments to recommendations concerning venlafaxine On 31 May 2006 the MHRA issued revised
Rehabilitation after critical illness
 Quick reference guide Issue date: March 2009 Rehabilitation after critical illness NICE clinical guideline 83 Developed by the Centre for Clinical Practice at NICE Patient-centred care This is a quick
Quick reference guide Issue date: March 2009 Rehabilitation after critical illness NICE clinical guideline 83 Developed by the Centre for Clinical Practice at NICE Patient-centred care This is a quick
Antidepressants and suicidal thoughts and behaviour. Pharmacovigilance Working Party. January 2008
 Antidepressants and suicidal thoughts and behaviour Pharmacovigilance Working Party January 2008 PhVWP PAR January 2008 Page 1/15 1. Introduction The Pharmacovigilance Working Party has on a number of
Antidepressants and suicidal thoughts and behaviour Pharmacovigilance Working Party January 2008 PhVWP PAR January 2008 Page 1/15 1. Introduction The Pharmacovigilance Working Party has on a number of
The NICE Guideline For OCD - Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
 Autumn 2015 Contents Welcome...1 What we are calling for...2 Background information...3 Better understanding...4 Clear treatment pathways...5 Appropriate diagnosis and reporting...6 Summary of actions
Autumn 2015 Contents Welcome...1 What we are calling for...2 Background information...3 Better understanding...4 Clear treatment pathways...5 Appropriate diagnosis and reporting...6 Summary of actions
How To Get Help From Inspireira
 INSPIRA HEALTH NETWORK Behavioral Health and Wellness Providing Quality Care Across the Region Comprehensive Programs Tailored for Your Needs Inspira offers a range of behavioral health and wellness services
INSPIRA HEALTH NETWORK Behavioral Health and Wellness Providing Quality Care Across the Region Comprehensive Programs Tailored for Your Needs Inspira offers a range of behavioral health and wellness services
MOH CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES 6/2011 DEPRESSION
 MOH CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES 6/2011 DEPRESSION Executive summary of recommendations Details of recommendations can be found in the main text at the pages indicated. Clinical evaluation D The basic
MOH CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES 6/2011 DEPRESSION Executive summary of recommendations Details of recommendations can be found in the main text at the pages indicated. Clinical evaluation D The basic
POST-TRAUMATIC STRESS DISORDER PTSD Diagnostic Criteria PTSD Detection and Diagnosis PC-PTSD Screen PCL-C Screen PTSD Treatment Treatment Algorithm
 E-Resource March, 2014 POST-TRAUMATIC STRESS DISORDER PTSD Diagnostic Criteria PTSD Detection and Diagnosis PC-PTSD Screen PCL-C Screen PTSD Treatment Treatment Algorithm Post-traumatic Stress Disorder
E-Resource March, 2014 POST-TRAUMATIC STRESS DISORDER PTSD Diagnostic Criteria PTSD Detection and Diagnosis PC-PTSD Screen PCL-C Screen PTSD Treatment Treatment Algorithm Post-traumatic Stress Disorder
TITLE: Cannabinoids for the Treatment of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder: A Review of the Clinical Effectiveness and Guidelines
 TITLE: Cannabinoids for the Treatment of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder: A Review of the Clinical Effectiveness and Guidelines DATE: 01 December 2009 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES: Post-traumatic stress disorder
TITLE: Cannabinoids for the Treatment of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder: A Review of the Clinical Effectiveness and Guidelines DATE: 01 December 2009 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES: Post-traumatic stress disorder
Alcohol-use disorders
 Issue date: February 2011 Alcohol-use disorders Diagnosis, assessment and management of harmful drinking and alcohol dependence Alcohol dependence: NICE guideline FINAL DRAFT (February 2011) 1 NICE clinical
Issue date: February 2011 Alcohol-use disorders Diagnosis, assessment and management of harmful drinking and alcohol dependence Alcohol dependence: NICE guideline FINAL DRAFT (February 2011) 1 NICE clinical
mpv`elildf`^i=qob^qjbkqp=ñçê= ^åñáéíó=~åç=aééêéëëáçå h~íó=dê~òéäêççâ `äáåáå~ä=ié~çi=dêééåïáåü=qáãé=qç=q~äâ `çåëìäí~åí=`äáåáå~ä=mëóåüçäçöáëí
 mpv`elildf`^i=qob^qjbkqp=ñçê= ^åñáéíó=~åç=aééêéëëáçå h~íó=dê~òéäêççâ `äáåáå~ä=ié~çi=dêééåïáåü=qáãé=qç=q~äâ `çåëìäí~åí=`äáåáå~ä=mëóåüçäçöáëí Plan of the presentation Summary of NICE recommended psychological
mpv`elildf`^i=qob^qjbkqp=ñçê= ^åñáéíó=~åç=aééêéëëáçå h~íó=dê~òéäêççâ `äáåáå~ä=ié~çi=dêééåïáåü=qáãé=qç=q~äâ `çåëìäí~åí=`äáåáå~ä=mëóåüçäçöáëí Plan of the presentation Summary of NICE recommended psychological
Primary care based guided self-help for depression provided by a nurse practitioner: a pilot evaluation.
 Primary Care Mental Health 2007;4:00 00 # 2007 Radcliffe Publishing International research Primary care based guided self-help for depression provided by a nurse practitioner: a pilot evaluation. F Philp
Primary Care Mental Health 2007;4:00 00 # 2007 Radcliffe Publishing International research Primary care based guided self-help for depression provided by a nurse practitioner: a pilot evaluation. F Philp
The Mind guide to who's who in mental health. guide to. who s who in mental health
 The Mind guide to who's who in mental health guide to who s who in mental health The Mind guide to who's who in mental health This online booklet is for anyone who wants to find out more about the different
The Mind guide to who's who in mental health guide to who s who in mental health The Mind guide to who's who in mental health This online booklet is for anyone who wants to find out more about the different
NICE Pathways bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic.
 bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published.
bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published.
Joint Commissioning Panel for Mental Health
 Joint Commissioning Panel for Mental Health Guidance for commissioners of perinatal mental health services 1 www.jcpmh.info Guidance for commissioners of perinatal mental health services Volume Two: Practical
Joint Commissioning Panel for Mental Health Guidance for commissioners of perinatal mental health services 1 www.jcpmh.info Guidance for commissioners of perinatal mental health services Volume Two: Practical
Overview of Mental Health Medication Trends
 America s State of Mind Report is a Medco Health Solutions, Inc. analysis examining trends in the utilization of mental health related medications among the insured population. The research reviewed prescription
America s State of Mind Report is a Medco Health Solutions, Inc. analysis examining trends in the utilization of mental health related medications among the insured population. The research reviewed prescription
Low back pain. Quick reference guide. Issue date: May 2009. Early management of persistent non-specific low back pain
 Issue date: May 2009 Low back pain Early management of persistent non-specific low back pain Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Primary Care About this booklet This is a quick reference
Issue date: May 2009 Low back pain Early management of persistent non-specific low back pain Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Primary Care About this booklet This is a quick reference
Alcohol-use disorders
 Issue date: February 2011 Alcohol-use disorders Diagnosis, assessment and management of harmful drinking and alcohol dependence Alcohol dependence: NICE guideline FINAL DRAFT (February 2011) 1 NICE clinical
Issue date: February 2011 Alcohol-use disorders Diagnosis, assessment and management of harmful drinking and alcohol dependence Alcohol dependence: NICE guideline FINAL DRAFT (February 2011) 1 NICE clinical
Learning Disabilities
 Learning Disabilities Positive Practice Guide January 2009 Relieving distress, transforming lives Learning Disabilities Positive Practice Guide January 2009 Contents 1. Background and policy framework
Learning Disabilities Positive Practice Guide January 2009 Relieving distress, transforming lives Learning Disabilities Positive Practice Guide January 2009 Contents 1. Background and policy framework
Depression Pathway. Patient Education Box 4. Guided self help Box 18. pg 11
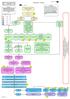 LCFT localised Map pathway June 2009 Depression Pathway Instructions: Throughout this pathway if you click on the Bookmarks tab to the left of the screen and then click on the various documents you will
LCFT localised Map pathway June 2009 Depression Pathway Instructions: Throughout this pathway if you click on the Bookmarks tab to the left of the screen and then click on the various documents you will
Stroke rehabilitation
 Costing report Stroke rehabilitation Published: June 2013 http://guidance.nice.org.uk/cg162 This costing report accompanies the clinical guideline: Stroke rehabilitation (available online at http://guidance.nice.org.uk/cg162).
Costing report Stroke rehabilitation Published: June 2013 http://guidance.nice.org.uk/cg162 This costing report accompanies the clinical guideline: Stroke rehabilitation (available online at http://guidance.nice.org.uk/cg162).
Mental Health Services Follow-up
 Mental Health Services Follow-up REGIONAL SUMMARY Performance Review Unit Department of Health, Social Services and Public Safety CONTENTS page BACKGROUND... 3 STRATEGIC DIRECTION... 6 PROVISION OF SERVICES...
Mental Health Services Follow-up REGIONAL SUMMARY Performance Review Unit Department of Health, Social Services and Public Safety CONTENTS page BACKGROUND... 3 STRATEGIC DIRECTION... 6 PROVISION OF SERVICES...
There are four groups of medications most likely to be used for depression: Antidepressants Antipsychotics Mood stabilisers Augmenting agents.
 What this fact sheet covers: Physical treatments (medication, ECT and TMS) Psychological treatments Self-help & alternative therapies Key points to remember Where to get more information. Introduction
What this fact sheet covers: Physical treatments (medication, ECT and TMS) Psychological treatments Self-help & alternative therapies Key points to remember Where to get more information. Introduction
Anxiety Care Pathway Panic Disorder and Generalised Anxiety Disorder
 Anxiety Care Pathway Panic Disorder and Generalised Anxiety Disorder December 2009 Instructions: Throughout this pathway if you click on the Bookmarks tab to the left of the screen and then click on the
Anxiety Care Pathway Panic Disorder and Generalised Anxiety Disorder December 2009 Instructions: Throughout this pathway if you click on the Bookmarks tab to the left of the screen and then click on the
Alcohol-use disorders: diagnosis, assessment and management of harmful drinking and alcohol dependence
 Alcohol-use disorders: diagnosis, assessment and management of harmful drinking and alcohol dependence Issued: February 2011 guidance.nice.org.uk/cg115 NICE has accredited the process used by the Centre
Alcohol-use disorders: diagnosis, assessment and management of harmful drinking and alcohol dependence Issued: February 2011 guidance.nice.org.uk/cg115 NICE has accredited the process used by the Centre
Clinical guideline Published: 28 January 2009 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg78
 Borderline personality disorder: recognition and management Clinical guideline Published: 28 January 2009 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg78 NICE 2009. All rights reserved. Your responsibility The recommendations
Borderline personality disorder: recognition and management Clinical guideline Published: 28 January 2009 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg78 NICE 2009. All rights reserved. Your responsibility The recommendations
Assessment of depression in adults in primary care
 Assessment of depression in adults in primary care Adapted from: Identification of Common Mental Disorders and Management of Depression in Primary care. New Zealand Guidelines Group 1 The questions and
Assessment of depression in adults in primary care Adapted from: Identification of Common Mental Disorders and Management of Depression in Primary care. New Zealand Guidelines Group 1 The questions and
Disclosures Christer Allgulander
 How Patients With Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) Are Treated in Specialized Care: A Pharmacoepidemiological Case Register Study in Sweden Christer Allgulander MD, Karolinska Institutet, Sweden Jan
How Patients With Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) Are Treated in Specialized Care: A Pharmacoepidemiological Case Register Study in Sweden Christer Allgulander MD, Karolinska Institutet, Sweden Jan
Family members and significant others affected by the drug or alcohol use of another person
 Family members and significant others affected by the drug or alcohol use of another person Having a member of your family, a relative or friend with problematic drug or alcohol use can be very distressing.
Family members and significant others affected by the drug or alcohol use of another person Having a member of your family, a relative or friend with problematic drug or alcohol use can be very distressing.
TREATMENT-RESISTANT DEPRESSION AND ANXIETY
 University of Washington 2012 TREATMENT-RESISTANT DEPRESSION AND ANXIETY Catherine Howe, MD, PhD University of Washington School of Medicine Definition of treatment resistance Failure to remit after 2
University of Washington 2012 TREATMENT-RESISTANT DEPRESSION AND ANXIETY Catherine Howe, MD, PhD University of Washington School of Medicine Definition of treatment resistance Failure to remit after 2
SLEEP DISTURBANCE AND PSYCHIATRIC DISORDERS
 E-Resource December, 2013 SLEEP DISTURBANCE AND PSYCHIATRIC DISORDERS Between 10-18% of adults in the general population and up to 50% of adults in the primary care setting have difficulty sleeping. Sleep
E-Resource December, 2013 SLEEP DISTURBANCE AND PSYCHIATRIC DISORDERS Between 10-18% of adults in the general population and up to 50% of adults in the primary care setting have difficulty sleeping. Sleep
ROUTES TO RECOVERY: PSYCHOSOCIAL INTERVENTIONS FOR DRUG MISUSE. A framework and toolkit for implementing NICErecommended.
 A framework and toolkit for implementing NICErecommended treatment interventions ROUTES TO RECOVERY: PSYCHOSOCIAL INTERVENTIONS FOR DRUG MISUSE EFFECTIVE TREATMENT CHANGING LIVES www.nta.nhs.uk PSYCHOSOCIAL
A framework and toolkit for implementing NICErecommended treatment interventions ROUTES TO RECOVERY: PSYCHOSOCIAL INTERVENTIONS FOR DRUG MISUSE EFFECTIVE TREATMENT CHANGING LIVES www.nta.nhs.uk PSYCHOSOCIAL
CPD sample profile. 1.1 Full name: Counselling Psychologist early career 1.2 Profession: Counselling Psychologist 1.3 Registration number: PYLxxxxx
 CPD sample profile 1.1 Full name: Counselling Psychologist early career 1.2 Profession: Counselling Psychologist 1.3 Registration number: PYLxxxxx 2. Summary of recent work experience/practice. I have
CPD sample profile 1.1 Full name: Counselling Psychologist early career 1.2 Profession: Counselling Psychologist 1.3 Registration number: PYLxxxxx 2. Summary of recent work experience/practice. I have
Organising and planning services for people with a personality disorder
 Organising and planning services for people with a personality disorder A NICE pathway brings together all NICE guidance, quality standards and materials to support implementation on a specific topic area.
Organising and planning services for people with a personality disorder A NICE pathway brings together all NICE guidance, quality standards and materials to support implementation on a specific topic area.
Anxiety, Panic and Other Disorders
 Methodist Assistance Program Anxiety, Panic and Other Disorders Anxiety, panic and other disorders such as agoraphobia, social phobia, compulsive disorder and posttraumatic stress disorder are all very
Methodist Assistance Program Anxiety, Panic and Other Disorders Anxiety, panic and other disorders such as agoraphobia, social phobia, compulsive disorder and posttraumatic stress disorder are all very
Generalised anxiety disorder in adults
 www.bpac.org.nz keyword: anxiety Generalised anxiety disorder in adults diagnosis and management Key concepts: Anxiety disorders are the most frequently seen mental disorders in primary care Generalised
www.bpac.org.nz keyword: anxiety Generalised anxiety disorder in adults diagnosis and management Key concepts: Anxiety disorders are the most frequently seen mental disorders in primary care Generalised
Bipolar disorder. The management of bipolar disorder in adults, children and adolescents, in primary and secondary care
 Issue date: July 2006 Bipolar disorder The management of bipolar disorder in adults, children and adolescents, in primary and secondary care NICE clinical guideline 38 Developed by the National Collaborating
Issue date: July 2006 Bipolar disorder The management of bipolar disorder in adults, children and adolescents, in primary and secondary care NICE clinical guideline 38 Developed by the National Collaborating
Alcohol use disorders: sample chlordiazepoxide dosing regimens for use in managing alcohol withdrawal
 Alcohol use disorders: sample chlordiazepoxide dosing regimens for use in managing alcohol withdrawal February 2010 NICE clinical guidelines 100 and 115 1 These sample chlordiazepoxide dosing regimens
Alcohol use disorders: sample chlordiazepoxide dosing regimens for use in managing alcohol withdrawal February 2010 NICE clinical guidelines 100 and 115 1 These sample chlordiazepoxide dosing regimens
Author: ADPH, SLOUGH June 2014 adapted from RBWM template 1
 CHILD AND ADOLESCENT MENTAL HEALTH SERVICES, Tier 1, 2, 3 & 4, available to SLOUGH Children, Young People Schools. Areas of Need* Tier 1 Tier1/2 Tier 2 Tier3/4** *Taken from: Guidance for commissioners
CHILD AND ADOLESCENT MENTAL HEALTH SERVICES, Tier 1, 2, 3 & 4, available to SLOUGH Children, Young People Schools. Areas of Need* Tier 1 Tier1/2 Tier 2 Tier3/4** *Taken from: Guidance for commissioners
OCD & Anxiety: Helen Blair Simpson, M.D., Ph.D.
 OCD & Anxiety: Symptoms, Treatment, & How to Cope Helen Blair Simpson, M.D., Ph.D. Professor of Clinical Psychiatry, Columbia University Director of the Anxiety Disorders Clinic, New York State Psychiatric
OCD & Anxiety: Symptoms, Treatment, & How to Cope Helen Blair Simpson, M.D., Ph.D. Professor of Clinical Psychiatry, Columbia University Director of the Anxiety Disorders Clinic, New York State Psychiatric
Needs Assessment for people with Borderline Personality Disorder and Antisocial Personality Disorder in Derbyshire County and Derby City
 Needs Assessment for people with Borderline Personality Disorder and Antisocial Personality Disorder in Derbyshire County and Derby City Dr Elizabeth Orton, Specialist Trainee in Public Health 1 Introduction
Needs Assessment for people with Borderline Personality Disorder and Antisocial Personality Disorder in Derbyshire County and Derby City Dr Elizabeth Orton, Specialist Trainee in Public Health 1 Introduction
Services for Children and Young People with Mental Health Needs. Lancashire s Local Offer. Lancashire s Health Services
 Services for Children and Young People with Mental Health Needs Lancashire s Local Offer Lancashire s Health Services 1. Name of the service and what the service provides Lancashire Care NHS Foundation
Services for Children and Young People with Mental Health Needs Lancashire s Local Offer Lancashire s Health Services 1. Name of the service and what the service provides Lancashire Care NHS Foundation
2008-2009 Annual Report of Trustwide Service for OCD/BDD and other severe neurotic conditions (BCPU)
 1 2008-2009 Annual Report of Trustwide Service for OCD/BDD and other severe neurotic conditions (BCPU) 1 2 Page Introduction and Background 3 What was Commissioned 3 Problems in Third Year 3 Special Achievements
1 2008-2009 Annual Report of Trustwide Service for OCD/BDD and other severe neurotic conditions (BCPU) 1 2 Page Introduction and Background 3 What was Commissioned 3 Problems in Third Year 3 Special Achievements
Social Phobia. Fact sheet 39. What is Social Phobia? Signs and symptoms. How common is Social Phobia and who experiences it?
 Social Phobia Fact sheet 39 What is Social Phobia? It is normal to feel nervous in situations in which we could possibly come under the scrutiny of others, whether they are strangers or people we know.
Social Phobia Fact sheet 39 What is Social Phobia? It is normal to feel nervous in situations in which we could possibly come under the scrutiny of others, whether they are strangers or people we know.
How To Deliver A Substance Use Treatment
 DMHAS ASAM SERVICE DESCRIPTIONS Please carefully review the Service Descriptions that are included in the DMHAS FFS Initiatives in this Annex A1 contract section. Initial the boxes below to identify the
DMHAS ASAM SERVICE DESCRIPTIONS Please carefully review the Service Descriptions that are included in the DMHAS FFS Initiatives in this Annex A1 contract section. Initial the boxes below to identify the
Modernising Mental Health Services in Bristol. 23 rd February Care Forum- Vassall centre
 Modernising Mental Health Services in Bristol 23 rd February Care Forum- Vassall centre Maya Bimson- Programme Director, Modernising mental health services in Bristol project. Mark Hayman- Associate Director
Modernising Mental Health Services in Bristol 23 rd February Care Forum- Vassall centre Maya Bimson- Programme Director, Modernising mental health services in Bristol project. Mark Hayman- Associate Director
Educational and Clinical Psychological Services in County Clare. An integrated approach to supporting the students in your school
 Useful contact and referral inmation To communicate with NEPS in relation to children s learning, social, emotional and behavioural difficulties in school, contact: Your school s NEPS Psychologist. Phone:
Useful contact and referral inmation To communicate with NEPS in relation to children s learning, social, emotional and behavioural difficulties in school, contact: Your school s NEPS Psychologist. Phone:
Better Access to Mental Health Care initiative
 Better Access to Mental Health Care initiative Orientation manual for clinical psychologists, psychologists, social workers and occupational therapists The Australian Psychological Society Ltd 11/257 Collins
Better Access to Mental Health Care initiative Orientation manual for clinical psychologists, psychologists, social workers and occupational therapists The Australian Psychological Society Ltd 11/257 Collins
Talking therapies: A four-year plan of action
 Talking therapies: A four-year plan of action A supporting document to No health without mental health: A crossgovernment mental health outcomes strategy for people of all ages Contents Foreword by the
Talking therapies: A four-year plan of action A supporting document to No health without mental health: A crossgovernment mental health outcomes strategy for people of all ages Contents Foreword by the
