CEU Update. A semi annual publication of the National Association for Health Professionals. Whooping Cough
|
|
|
- Hubert Eaton
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CEU Update A semi annual publication of the National Association for Health Professionals January 2010 Issue #0110 Whooping Cough Whooping cough is an infectious bacterial illness that affects the respiratory passages. First described in the 1640s, whooping cough is so named because spasms of coughing are punctuated by a characteristic "whoop" when the person inhales. Whooping cough is the most common vaccine preventable disease among children younger than 5 years in the United States. It is also known as pertussis the "P" in the familiar DTaP combination inoculation routinely given to children and the "p" in Tdap given to adolescents and adults. Despite the widespread use of vaccines, whooping cough has made a comeback in recent years. According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), prior to the introduction of the pertussis vaccine, there was an average of 175,000 cases of whooping cough each year. This dropped off to fewer than 3,000 cases per year in the 1980s; however, in the U.S. alone, a total of 25,827 cases of pertussis were reported in This was a huge increase compared to the only 8,296 cases reported in The World Health Organization estimates there were over 17.6 million cases of whooping cough and 297,000 deaths worldwide in 2004, making this easy to prevent disease one of the leading causes of illness and death. The WHO estimates that global vaccination prevented about 38.3 million cases and 607,000 deaths. What causes whooping cough Whooping cough is caused by the bacteria Bordetella pertussis. Humans are the only known reservoir of these bacteria. Whooping cough is spread by contact with droplets coughed out by someone with the disease or by contact with recently contaminated hard surfaces upon which the droplets landed. The bacteria thrive in the respiratory passages where they produce toxins that damage the tiny hairs (cilia) that are needed to remove particulate matter and cellular debris that are normally introduced into the airways with each breath. This results in an increased inflammation of the respiratory passages, and the typical cough which is the hallmark of the infection. Whooping cough is contagious from seven days after exposure to the bacteria and up to three weeks after the onset of coughing spasms. The most contagious time is during the first stage of the illness. Initially thought to be a disease of childhood, recent studies have shown that adults are susceptible to whooping cough and account for up to 25% of cases. The disease, however, tends to be milder in adults and adolescents a persistent cough much like an upper respiratory infection or cold. Because of this fine distinction, the diagnosis of whooping cough is frequently missed in that population and thus allows the bacteria to spread to more susceptible infants and children. Whooping cough is highly contagious. Between 75% 100% of unimmunized household contacts of a person with pertussis will develop the disease. Even among fully immunized and naturally immunized people living in the same household, there have been reports of undetectable infection following ex 1
2 treme exposure. Symptoms of whooping cough The course of whooping cough is divided into three stages. The first stage of whooping cough is the catarrhal stage. This phase typically lasts for one to two weeks. Symptoms during this phase resemble that of an upper respiratory illness: runny nose, nasal congestion, sneezing, and occasional cough. A low grade fever may be present in some cases. The second stage of whooping cough is the paroxysmal stage. The duration of this phase is highly variable, lasting between one to six weeks, or up to 10 weeks. It is characterized by intense and drawn out bouts of coughing. The attacks tend to be more frequent at night, with an average of 15 attacks in a 24 hour period. Often a "whoop" can be heard caused by the gasping person inhaling between coughs. Infants, in particular, may appear to stop breathing and perhaps turn blue during the coughing spasms. Vomiting is also common during this stage as well. The third stage of whooping cough is the convalescent stage. This can last for weeks or months and is characterized by a chronic cough that becomes less paroxysmal (fewer sudden outbursts of coughing) in nature. Seeking medical care When to call the doctor: If you suspect you or your child has whooping cough, has been exposed to someone with whooping cough, regardless of whether the child has received immunization shots, turns blue during a coughing spell, has a fever that cannot be controlled with over the counter medication, or is unable to keep solids and liquids down (vomits). When to go to the hospital: If breathing stops, call 911 emergency services and begin CPR. Go to a hospital's emergency department if someone with whooping cough shows these symptoms: inability to tolerate liquids (vomiting), uncontrolled fever even with antifever medications, signs of respiratory distress including rapid breathing and turning blue, or signs of dehydration, including weight loss, dry mucous membranes, decreased urine output. Tests and exams for whooping cough The best way to diagnose whooping cough is by confirming the presence of the specific diseasecausing bacteria Bordetella pertussis in mucus taken from the nose and throat. Because the growth of the bacteria is inhibited by cotton, either calcium alginate or Dacron swabs must be used in obtaining the sample. Studies have shown that cultures are more likely to be positive if the sample is collected during the first stage of the illness or early in the second. The likelihood for isolating the organism (and confirming the diagnosis) declines with any delay in specimen collection beyond the first three weeks of illness. A culture negative for Bordetella pertussis is usually seen after five days of treatment with antibiotics. Other laboratory methods used to diagnosis pertussis infection such as serologic testing and PCR are available in certain labs. However, neither method has been shown to be more specific than culture isolation of the organism. A complete blood count may be performed. 2
3 Treatments for whooping cough Self Care at Home Because younger children are at higher risk to develop a severe case of whooping cough than adults, most are admitted to the hospital. For children and adults who do not require hospitalization, here are some tips to manage the disease at home after a doctor has diagnosed whooping cough. Isolate the person (separate bedroom) until he or she has received five days of antibiotics. During this time, everyone who comes into contact with the sick person should wear a surgical mask to cover their face. Practice good hand washing. Whooping cough bacteria can be transmitted through contact with contaminated inanimate objects such as dishes. Drink plenty of fluids, including water, juices, soups, and eat fruits to prevent dehydration. Eat small, frequent meals to decrease the amount of vomiting. Do not give cough medications unless otherwise instructed by your doctor. Use a cool mist vaporizer to help loosen secretions and soothe the cough. Keep the home environment free from irritants that can trigger coughing, such as smoke, aerosols, and fumes. Monitor a sick child for signs of dehydration, such as dry lips and tongue, dry skin, decrease in the amount of urine or wet diapers, and crying without producing tears. Report any signs of dehydration to your doctor immediately. Medical Treatment Antibiotics are used to lessen the severity of whooping cough and make the person taking them noncontagious. Antibiotics are most effective if given early in the first phase of the illness. The 2005 Sanford Guide to Antimicrobial Therapy recommends the following antibiotic treatments: a five day course of azithromycin, a seven day course of clarithromycin, or a 14 day course of either erythromycin or trimethoprim/sulfamethoxozale (TMP/SMX). Some strains of whooping cough are resistant to certain antibiotics. Symptoms worsen if this is the case. In addition to treating the adult or child who has whooping cough, everyone in the household should be treated with antibiotics. All close contacts younger than 7 years who have not completed their primary vaccinations (including the DTaP to prevent pertussis) should complete this series with the minimum time between shots. Close contacts younger than 7 years who have completed their primary series but have not received a booster of DTaP within three years of exposure should be given the booster dose. Exposed adults should be vaccinated with Tdap. Anyone with whooping cough should be isolated for five days after starting antibiotics or until three weeks after the onset of the coughing spasms if the person has not received antibiotic treatment. Follow up care Schools and daycare facilities should be notified of whooping cough illnesses. Children who later develop cough should be evaluated by their doctors. Children younger than 7 years who attend the school or daycare and are behind in their vaccinations should receive them. School wide treatment with antibiotics is not currently recommended. Children with mild cases of whooping cough may return to school or daycare after receiving antibiotics for at least five days. 3
4 Prevention Both frequent hand washing and the use of masks will help lessen the likelihood that the bacteria will spread to other members of a household where someone has whooping cough. Also avoid touching your nose or mouth, and thus introducing the bacteria you may have picked up, during outbreaks. For children, follow the recommended schedule for the DTaP (diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis) inoculations. Shots are given at the ages of 2 months, 4 months, 6 months, months, and 4 6 years for full immunity, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics. In 2005, the U.S. government approved Tdap, the first pertussis booster shot for children 10 to 18 years of age. The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) of the Centers for Disease Control recommends one dose of Tdap in place of one Td booster. For adults years, the ACIP recommends a single dose of Tdap; If you have never received a dose of Tdap, one dose of Tdap should replace one dose of Td for booster immunization if the most recent tetanus toxoid containing vaccine was received at least 10 years earlier. Adults in close contact with infants aged 12 months or younger who have not previously received Tdap should receive a dose of Tdap; an interval as short as two years since the most recent Td is suggested. Health care personnel in settings with direct patient contact who have not previously received Tdap should receive a dose of Tdap; an interval as short as two years since the most recent Td is recommended. Whooping cough outlook Complications of whooping cough are most commonly seen in children younger than 1 year, with an increased risk of severe whooping cough in premature infants. Between , 17,000 cases of whooping cough in children under two years of age required hospitalization. Among all pertussis hospitalizations during in children under age 2 years, 92% occurred in infants under 6 months of age. In , 16% of whooping cough cases in children and adults required hospitalization. From , 66 deaths due to whooping cough were reported to the CDC. Bacterial pneumonia is the most common complication of whooping cough. It is also the most common cause of pertussis related deaths. Between the years , 4.9% of all people with whooping cough developed a bacterial pneumonia 17% were infants younger than 6 months. Other complications include bluish skin from lack of oxygen, collapse of a lung, sinusitis, otitis media (ear infection), dehydration, nosebleed, bruising, hernias, retinal detachment, rectal prolapse, seizures, diseases of the brain, and failure to thrive. Bacterial Pneumonia Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs. People with pneumonia usually complain of coughing, fever, shortness of breath, and chest pain. Your body's immune system usually keeps bacteria from infecting your lungs. In bacterial pneumonia, bacteria reproduce in your lungs, while your body tries to fight off the infection. This response to bacterial invaders is called inflammation. When the inflammation occurs in the alveoli (microscopic air sacs in the lungs), they fill with fluid. Your lungs become less elastic and cannot take oxygen into the blood or remove carbon dioxide from the blood as efficiently as usual. 4
5 When the alveoli don't work efficiently, your lungs have to work harder to satisfy your body's need for oxygen. This causes the feeling of being short of breath, which is one of the most common symptoms of pneumonia. Inflammation causes many of the other symptoms, including fever and chest pain. Pneumonia can be very serious, because it directly interferes with your body's ability to exchange carbon dioxide and oxygen. Pneumonia is different in this way from acute bronchitis, which is another disease that can cause fever, cough, chest pain, and shortness of breath. Bronchitis is caused by inflammation in the air passages (called bronchi) leading to the alveoli, not the alveoli themselves. Sometimes it is very difficult, even for a doctor, to tell pneumonia and bronchitis apart. The symptoms and physical examination can be identical. Sometimes a chest x ray is the only way to tell pneumonia and bronchitis apart. Causes of bacterial pneumonia Most pneumonia is caused by bacteria or a virus. Pneumonia from any cause can occur at any age, but people in certain age groups are at higher risk for certain types of pneumonia. The most common cause of bacterial pneumonia is a type of bacteria known as Streptococcus pneumoniae. Haemophilus influenzae, Chlamydia trachomatis, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, and Legionella pneumophila are some other major bacteria that cause pneumonia. If you inhale toxic materials, you can injure your lungs and cause chemical pneumonia. Fungi can also cause pneumonia. In certain areas of the United States, specific fungi are well known. Coccidioidomycosis is a type of fungal infection that causes a pneumonia called "San Joaquin fever" or "Valley fever." Histoplasmosis and blastomycosis are other fungal diseases that cause pneumonias. The most common way you catch pneumonia is to breathe infected air droplets from someone who has pneumonia. Another cause is an improperly cleaned air conditioner. Yet another source of infection in your lungs is spread of an infection from somewhere else in your body, such as the kidney. Your risk of catching pneumonia is determined by the specific bacteria, virus, or fungus, the number of organisms you inhale, and your body's ability to fight infections. You do not catch pneumonia by not dressing properly for cold weather or by being caught in the rain. Bacterial Pneumonia Symptoms Doctors often refer to typical and atypical pneumonias, based on the signs and symptoms of the condition. This can help to predict the type of bacteria causing the pneumonia, the duration of the illness, and the optimal treatment method. Typical pneumonia comes on very quickly, usually results in a high fever and shaking chills, usually leads to the production of yellow or brown sputum when coughing, and can cause shortness of breath, especially if you have any chronic lung conditions such as asthma or emphysema. There may be chest pain, which is usually worse with breathing or coughing. The chest also may be sore when you touch or press it. Because chest pain also can be a sign of other serious medical conditions, do not try to diagnose yourself. Older people can have confusion or a change in their mental abilities as a sign of pneumonia or other infection. Atypical pneumonia has a gradual onset. It is called "walking pneumonia." Sometimes it follows another illness in the days to weeks before the pneumonia. 5
6 The fever is usually lower, and shaking chills are less likely. There may be headache, body aches, and joint pain. Coughing may be dry or produce only a little sputum. You may not have any chest pain. Abdominal pain may be present. There may be other symptoms, such as feeling tired or weak. Seeking medical care When to call the doctor If you have a fever and cough up yellow, green, or brown sputum, make an appointment with your doctor. If you have shortness of breath, chest pain, or confusion, you should seek emergency care. If you are healthy, you can safely make an appointment to see your doctor. A day or two of waiting should not make a big difference, unless you are experiencing significant shortness of breath or if any signs of confusion are present. When to go to the hospital If you have shortness of breath, you should always seek emergency care. Shortness of breath is not simply the feeling that you can't take a full breath. Shortness of breath means that you cannot take in enough air to meet your body's needs. It is a potentially serious symptom and always requires a visit to an emergency department, no matter how healthy you are. If you have chest pain or confusion, you should seek emergency care. You are at higher risk of developing pneumonia if you have the following: a chronic health problem, such as diabetes, a poor immune system because of HIV, AIDS, steroid use, or immune suppressant medications (people with organ transplants take these medications), diseased or damaged lungs, such as with asthma or emphysema, or are very young or very old. Exams and tests Pneumonia can be diagnosed simply by a doctor listening to your lungs. Certain sounds heard through a stethoscope may indicate infection. One of the easiest tests to perform is pulse oximetry, sometimes called "pulse ox." A probe that looks like a clothespin is gently attached to your finger, toe, or ear. A special light shines through your skin to estimate how much oxygen you have in your bloodstream. If your oxygen level is lower than expected, it may mean you have pneumonia. An x ray of your chest can help identify which part of your lung is infected. An x ray also can show abnormal fluid collections which also can help diagnose pneumonia. You may have blood drawn. Laboratory tests can show that your immune system is working properly to fight off your infection. They also show whether you have enough red blood cells to carry oxygen or whether the bacteria have gotten into your bloodstream. Occasionally your doctor may need to sample blood from one of your arteries (usually in your wrist) in order to get an exact measurement of how well you are exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide. This test, called an arterial blood gas ("ABG" or "blood gas"), is very important, takes only a minute, and is done with a very small needle and syringe. This test cannot be run on the other blood that is sampled from your veins. Sometimes your doctor will collect some of your sputum and look at it under a microscope. Certain stains, or dyes, help your doctor tell which specific bacterium is causing your pneumonia. Sputum cultures may also be performed. In these tests, your sputum is put on a plate to help it grow so a laboratory 6
7 specialist can identify the specific bacteria. If you are admitted to the hospital, your doctor will draw blood and send it to the laboratory so that it may also be cultured to determine whether bacteria are present in the bloodstream. Bacterial Pneumonia Treatment If you suspect pneumonia based on the signs or symptoms, see your doctor as soon as possible. There is no home treatment for pneumonia. Although cough suppressants, expectorants, or fever lowering drugs may be helpful, they should not be started without discussing their use with your doctor. Medical Treatment If you have a bacterial pneumonia, you will need to take an antibiotic. The antibiotic choice depends on your age, your chronic medical conditions, whether or not you smoke or drink alcohol, and other medications you are taking. Tell your doctor about allergies or bad reactions to any medicines you have taken before and bring a list of your current medicines with you. Drink plenty of nonalcoholic fluids to stay hydrated. This helps your body fight the pneumonia. Feverreducing medicines such as acetaminophen (Tylenol) or ibuprofen (Advil) may also help you feel better. Because coughing helps clear infection out of your lungs, your doctor may recommend that you not use a cough suppressant. You must avoid cigarette or other tobacco smoke while you recover from pneumonia. Smoking hurts your body's ability to fight infection and makes the healing process take a lot longer. If you are severely short of breath or if you have significantly lowered oxygen levels in your bloodstream, you may need to be admitted to the hospital. You will get extra oxygen to help you breathe, and you may get your antibiotic by an IV catheter through your veins. If your pneumonia is very severe, you may need a breathing tube in your windpipe so that a machine can do the work of breathing for you. Prevention Vaccines are available that prevent certain types of pneumonia. Yet there are so many bacteria that cause pneumonia, you are not guaranteed to avoid it even with an immunization. Pneumovax and Pnu Immune are vaccines to prevent Streptococcus pneumoniae infection. According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), people in the following groups should ask their doctor about receiving the pneumococcus immunization: people age 65 and older, people with serious long term health problems such as heart failure, liver failure (cirrhosis of the liver), diabetes, or lung disease (other than asthma), people with lowered immunity due to cancer, chemotherapy, diseases or removal of the spleen, chronic kidney problems, or have had an organ or bone marrow transplant, or people who are Alaskan Native Americas or certain other Native American populations. In 2000, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) licensed a new vaccine, Prevnar, for the prevention of pneumococcal disease in children. This vaccine is recommended for healthy infants under the age of 2 and for children between the ages of 2 and 5 who have not previously been vaccinated and who are at highest risk for developing pneumococcal disease, such as those with HIV/AIDS, have certain chronic diseases, and have decreased immune function. 7
8 Issue #0110 Class A CEU CEU QUESTIONNAIRE Complete the questions below to receive 10 continuing education credits. All questions must be answered completely to receive credit. 1. What does whooping cough affect? 2. What is another name for whooping cough? 3. What is the name of the bacteria that causes whooping cough? 4. What is the WHO? 5. How is whooping cough spread? 6. What is the hallmark of the infection?. 7. How many stages is whooping cough divided into? 8. Name the stages. 9. Define paroxysmal. 10. Name 3 reasons to call the doctor. 11. When does the likelihood for isolating the organism begin to decline? 12. What are the signs of dehydration? 13. List the 3 antibiotic treatments recommended by the Sanford Guide to Antimicrobial Therapy? 14. What vaccine prevents pertussis? 15. What does DTaP vaccinate against? 8
9 16. At what ages do children receive these vaccinations? 17. What is the government approved Tdap? 18. What is the most common complication of whooping cough? 19. List 5 other complications of whooping cough. 20. What organ of the body does pneumonia affect? 21. Define inflammation. 22. What is the most common symptom of pneumonia? 23. Name 3 major bacteria that can cause pneumonia? 24. What causes chemical pneumonia? 25. What is the most common way to catch pneumonia? 26. What are Symptoms of typical pneumonia? 27. What is another name for Atypical pneumonia? 28. Emergency care should always be sought out when? 29. What is the name of the test using blood drawn from an artery? 30. What is the home treatment for pneumonia? 31. Why would cough suppressants not be recommended? 32. Why are immunizations for pneumonia not guaranteed to work? 33. What does the abbreviation CDC stand for? 9
10 34. What new vaccine did the FDA license and what does it prevent? 35. What is the FDA? Please mail this CEU back to the NAHP. DO NOT FAX IT IN. Any CEUs received via fax will be discarded without credit being awarded. Return to: NAHP P.O. Box 459 Gardner, KS Name Address City State Zip Social Security Number or Member ID Today s Date 10
11 National Association for Health Professionals P.O. Box 459 Gardner, KS
Whooping Cough. The Lungs Whooping cough is an infection of the lungs and breathing tubes, both of which are parts of the respiratory system.
 Whooping Cough Introduction Whooping cough is a serious bacterial infection of the lungs and breathing tubes. It is also called pertussis. About 16 million cases of whooping cough happen worldwide each
Whooping Cough Introduction Whooping cough is a serious bacterial infection of the lungs and breathing tubes. It is also called pertussis. About 16 million cases of whooping cough happen worldwide each
Pneumonia Education and Discharge Instructions
 Pneumonia Education and Discharge Instructions Pneumonia Education and Discharge Instructions Definition: Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs. Many different organisms can cause it, including bacteria,
Pneumonia Education and Discharge Instructions Pneumonia Education and Discharge Instructions Definition: Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs. Many different organisms can cause it, including bacteria,
What is whooping cough. (pertussis)? Information and Prevention. Ocument dn
 What is whooping cough Ocument dn (pertussis)? Information and Prevention IMPORTANT Pertussis (or whooping cough) is a highly contagious infection that can cause uncontrollable, violent coughing. If you
What is whooping cough Ocument dn (pertussis)? Information and Prevention IMPORTANT Pertussis (or whooping cough) is a highly contagious infection that can cause uncontrollable, violent coughing. If you
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS ABOUT PERTUSSIS (WHOOPING COUGH)
 FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS ABOUT PERTUSSIS (WHOOPING COUGH) What is pertussis? General Questions About Pertussis Pertussis, or whooping cough, is a contagious illness that is spread when an infected person
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS ABOUT PERTUSSIS (WHOOPING COUGH) What is pertussis? General Questions About Pertussis Pertussis, or whooping cough, is a contagious illness that is spread when an infected person
I am reaching out to you with some preventative information that you might be interested in sharing with your school community.
 Reported cases of pertussis (whooping cough) are on the rise in Colorado and El Paso County. As of October 23, more than 1,000 cases of pertussis have been reported across the state. El Paso County cases
Reported cases of pertussis (whooping cough) are on the rise in Colorado and El Paso County. As of October 23, more than 1,000 cases of pertussis have been reported across the state. El Paso County cases
Key Facts about Influenza (Flu) & Flu Vaccine
 Key Facts about Influenza (Flu) & Flu Vaccine mouths or noses of people who are nearby. Less often, a person might also get flu by touching a surface or object that has flu virus on it and then touching
Key Facts about Influenza (Flu) & Flu Vaccine mouths or noses of people who are nearby. Less often, a person might also get flu by touching a surface or object that has flu virus on it and then touching
INFLUENZA (FLU) Flu and You
 Influenza (Flu) What is the flu? The flu is an illness caused by flu viruses. The flu may make people cough and have a sore throat and fever. They may also have a runny or stuffy nose, feel tired, have
Influenza (Flu) What is the flu? The flu is an illness caused by flu viruses. The flu may make people cough and have a sore throat and fever. They may also have a runny or stuffy nose, feel tired, have
Remove this cover sheet before redistributing and replace it with your own. Please ensure that DPHHS is included on your HAN distribution list.
 State of Montana Health Alert Network DPHHS HAN ADVISORY Cover Sheet DATE: May 15, 2012 SUBJECT: Pertussis INSTRUCTIONS: DISTRIBUTE to your local HAN contacts. This HAN is intended for general sharing
State of Montana Health Alert Network DPHHS HAN ADVISORY Cover Sheet DATE: May 15, 2012 SUBJECT: Pertussis INSTRUCTIONS: DISTRIBUTE to your local HAN contacts. This HAN is intended for general sharing
safest place for your baby is in your arms...
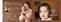 Help protect your baby by helping to protect yourself. Photo: John Bentham Imagine a cough barreling through your infant s body at up to 100 mph. Help protect yourself and your family by getting an adult
Help protect your baby by helping to protect yourself. Photo: John Bentham Imagine a cough barreling through your infant s body at up to 100 mph. Help protect yourself and your family by getting an adult
The Reality Pertussis can be a serious illness, part icularly for babies and young children.
 Sounds of Pertussis Pertussis, also known as whooping cough, is a poten tially deadly infection that can strike at any age, but is particularly dangerous for babies. The sounds of pertussis are like no
Sounds of Pertussis Pertussis, also known as whooping cough, is a poten tially deadly infection that can strike at any age, but is particularly dangerous for babies. The sounds of pertussis are like no
Frequently asked questions about whooping cough (pertussis)
 Frequently asked questions about whooping cough (pertussis) About whooping cough What is whooping cough? Whooping cough is a highly contagious illness caused by bacteria. It mainly affects the respiratory
Frequently asked questions about whooping cough (pertussis) About whooping cough What is whooping cough? Whooping cough is a highly contagious illness caused by bacteria. It mainly affects the respiratory
2 P age. Babies from Birth to Age 2
 Contents Babies from Birth to Age 2... 2 Vaccines give parents the power... 2 Vaccines are recommended throughout our lives... 3 Talk to your doctor... 3 Vaccines are very safe... 3 Whooping Cough (Pertussis)...
Contents Babies from Birth to Age 2... 2 Vaccines give parents the power... 2 Vaccines are recommended throughout our lives... 3 Talk to your doctor... 3 Vaccines are very safe... 3 Whooping Cough (Pertussis)...
New Jersey Department of Health Vaccine Preventable Disease Program Pertussis FAQs. Date: January 10, 2013
 New Jersey Department of Health Vaccine Preventable Disease Program Pertussis FAQs Date: January 10, 2013 KEY MESSAGES: 1. Pertussis is a very contagious vaccine-preventable disease that can cause serious
New Jersey Department of Health Vaccine Preventable Disease Program Pertussis FAQs Date: January 10, 2013 KEY MESSAGES: 1. Pertussis is a very contagious vaccine-preventable disease that can cause serious
Tuberculosis and You A Guide to Tuberculosis Treatment and Services
 Tuberculosis and You A Guide to Tuberculosis Treatment and Services Tuberculosis (TB) is a serious disease that can damage the lungs or other parts of the body like the brain, kidneys or spine. There are
Tuberculosis and You A Guide to Tuberculosis Treatment and Services Tuberculosis (TB) is a serious disease that can damage the lungs or other parts of the body like the brain, kidneys or spine. There are
Swine Flu and Common Infections to Prepare For. Rochester Recreation Club for the Deaf October 15, 2009
 Swine Flu and Common Infections to Prepare For Rochester Recreation Club for the Deaf October 15, 2009 Supporters Deaf Health Community Committee Members Julia Aggas Cathie Armstrong Michael McKee Mistie
Swine Flu and Common Infections to Prepare For Rochester Recreation Club for the Deaf October 15, 2009 Supporters Deaf Health Community Committee Members Julia Aggas Cathie Armstrong Michael McKee Mistie
Adult Vaccination Frequently Asked Questions: The Basics
 The Basics Why should I get vaccinated? Vaccination is the best way to protect against infections that can make you sick and be passed on to those around you. 1 What kinds of side effects will I get from
The Basics Why should I get vaccinated? Vaccination is the best way to protect against infections that can make you sick and be passed on to those around you. 1 What kinds of side effects will I get from
BASIC INFORMATION ABOUT HIV, HEPATITIS B and C, and TUBERCULOSIS Adapted from the CDC
 BASIC INFORMATION ABOUT HIV, HEPATITIS B and C, and TUBERCULOSIS Adapted from the CDC HIV What are HIV and AIDS? HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus. This is the virus that causes AIDS. HIV is
BASIC INFORMATION ABOUT HIV, HEPATITIS B and C, and TUBERCULOSIS Adapted from the CDC HIV What are HIV and AIDS? HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus. This is the virus that causes AIDS. HIV is
Pertussis Toolkit for Schools
 Pertussis Toolkit for Schools Cerro Gordo County experienced a significant pertussis outbreak in 2012. To lessen the effects of future outbreaks, several community partners worked together to improve our
Pertussis Toolkit for Schools Cerro Gordo County experienced a significant pertussis outbreak in 2012. To lessen the effects of future outbreaks, several community partners worked together to improve our
PERTUSSIS SURVEILLANCE AND RESPONSE PROTOCOL
 PERTUSSIS SURVEILLANCE AND RESPONSE PROTOCOL Public Health Action 1. Educate the public, particularly parents of infants, about the dangers of whooping cough and the advantages of initiating immunization
PERTUSSIS SURVEILLANCE AND RESPONSE PROTOCOL Public Health Action 1. Educate the public, particularly parents of infants, about the dangers of whooping cough and the advantages of initiating immunization
CATHOLIC CHARITIES MAINE FAMILY CHILD CARE
 CATHOLIC CHARITIES MAINE FAMILY CHILD CARE October 2012 In accordance with Federal law and U.S. Department of Agriculture policy, this institution is prohibited from discriminating on the basis of race,
CATHOLIC CHARITIES MAINE FAMILY CHILD CARE October 2012 In accordance with Federal law and U.S. Department of Agriculture policy, this institution is prohibited from discriminating on the basis of race,
You. guide to tuberculosis treatment and services
 Adapted from TB and You: A Guide to Tuberculosis Treatment and Services with permission from Division of Public Health TB Control Program State of North Carolina Department of Health and Human Services
Adapted from TB and You: A Guide to Tuberculosis Treatment and Services with permission from Division of Public Health TB Control Program State of North Carolina Department of Health and Human Services
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV)
 Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) What is? is a common virus that infects the linings of the airways - the nose, throat, windpipe, bronchi and bronchioles (the air passages of the lungs). RSV is found
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) What is? is a common virus that infects the linings of the airways - the nose, throat, windpipe, bronchi and bronchioles (the air passages of the lungs). RSV is found
Pneumonia. Pneumonia is an infection that makes the tiny air sacs in your lungs inflamed (swollen and sore). They then fill with liquid.
 Pneumonia Pneumonia is an infection that makes the tiny air sacs in your lungs inflamed (swollen and sore). They then fill with liquid. People with mild (not so bad) pneumonia can usually be treated at
Pneumonia Pneumonia is an infection that makes the tiny air sacs in your lungs inflamed (swollen and sore). They then fill with liquid. People with mild (not so bad) pneumonia can usually be treated at
Why you and your Family Should Get the Flu Shot
 Why you and your Family Should Get the Flu Shot Why Get VaCCinated against influenza? Influenza (flu) is a virus that can lead to serious complications, hospitalization, or even death. Even healthy children
Why you and your Family Should Get the Flu Shot Why Get VaCCinated against influenza? Influenza (flu) is a virus that can lead to serious complications, hospitalization, or even death. Even healthy children
How can you protect yourself from infections?
 How can you protect yourself from infections? Your Infection Prevention Guide www.esrdncc.org Table of Contents Preventing an infection is an important part of your kidney care...3 Things you can do...4
How can you protect yourself from infections? Your Infection Prevention Guide www.esrdncc.org Table of Contents Preventing an infection is an important part of your kidney care...3 Things you can do...4
PENNSYLVANIA DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH 2015 PAHAN 307 04-02-ADV Pertussis in Centre County
 PENNSYLVANIA DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH 2015 PAHAN 307 04-02-ADV Pertussis in Centre County DATE: 04/02/2015 TO: Health Alert Network FROM: Karen M. Murphy, PhD, RN, Acting Secretary of Health SUBJECT: DISTRIBUTION:
PENNSYLVANIA DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH 2015 PAHAN 307 04-02-ADV Pertussis in Centre County DATE: 04/02/2015 TO: Health Alert Network FROM: Karen M. Murphy, PhD, RN, Acting Secretary of Health SUBJECT: DISTRIBUTION:
What You Should Know About ASTHMA
 What You Should Know About ASTHMA 200 Hospital Drive Galax, VA 24333 (276) 236-8181 www.tcrh.org WHAT IS ASTHMA? It s a lung condition that makes breathing difficult. The cause of asthma is not known.
What You Should Know About ASTHMA 200 Hospital Drive Galax, VA 24333 (276) 236-8181 www.tcrh.org WHAT IS ASTHMA? It s a lung condition that makes breathing difficult. The cause of asthma is not known.
Information on Measles and Whooping Cough: Vaccination and Disease
 Information on Measles and Whooping Cough: Vaccination and Disease Vaccine s Mechanism of Action Vaccines expose the recipient to a small amount of an weakened organism. Through this exposure, the body
Information on Measles and Whooping Cough: Vaccination and Disease Vaccine s Mechanism of Action Vaccines expose the recipient to a small amount of an weakened organism. Through this exposure, the body
Streptococcal Infections
 Streptococcal Infections Introduction Streptococcal, or strep, infections cause a variety of health problems. These infections can cause a mild skin infection or sore throat. But they can also cause severe,
Streptococcal Infections Introduction Streptococcal, or strep, infections cause a variety of health problems. These infections can cause a mild skin infection or sore throat. But they can also cause severe,
READ THIS LEAFLET VERY CAREFULLY, AND KEEP IT IN A SAFE PLACE. FLU IS SPREADING IN IRELAND, AND THIS INFORMATION IS IMPORTANT FOR YOU AND YOUR FAMILY.
 READ THIS LEAFLET VERY CAREFULLY, AND KEEP IT IN A SAFE PLACE. FLU IS SPREADING IN IRELAND, AND THIS INFORMATION IS IMPORTANT FOR YOU AND YOUR FAMILY. Information and medical advice for the public on Pandemic
READ THIS LEAFLET VERY CAREFULLY, AND KEEP IT IN A SAFE PLACE. FLU IS SPREADING IN IRELAND, AND THIS INFORMATION IS IMPORTANT FOR YOU AND YOUR FAMILY. Information and medical advice for the public on Pandemic
Pertussis (Whooping Cough) http://www.cdc.gov/pertussis/index.html. Causes and Transmission. Causes. Transmission
 Pertussis (Whooping Cough) http://www.cdc.gov/pertussis/index.html Pertussis, also known as whooping cough, is a highly contagious respiratory disease. It is caused by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis.
Pertussis (Whooping Cough) http://www.cdc.gov/pertussis/index.html Pertussis, also known as whooping cough, is a highly contagious respiratory disease. It is caused by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis.
Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Tritanrix HB [Diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (whole cell) and hepatitis B (rdna) vaccine (adsorbed)]
![Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Tritanrix HB [Diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (whole cell) and hepatitis B (rdna) vaccine (adsorbed)] Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Tritanrix HB [Diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (whole cell) and hepatitis B (rdna) vaccine (adsorbed)]](/thumbs/27/12172665.jpg) EMA/14365/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Tritanrix HB [Diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (whole cell) and hepatitis B (rdna) vaccine (adsorbed)] Overview of disease epidemiology Diphtheria
EMA/14365/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Tritanrix HB [Diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (whole cell) and hepatitis B (rdna) vaccine (adsorbed)] Overview of disease epidemiology Diphtheria
Plan early - get your vaccinations in time for full protection. To prepare for your trip, schedule an appointment: (910) 347-2154, option #2.
 The Onslow County Health Department Travel Clinic offers a complete line of immunizations and prescriptions to protect you while traveling abroad. The most appropriate immunizations and travel medications
The Onslow County Health Department Travel Clinic offers a complete line of immunizations and prescriptions to protect you while traveling abroad. The most appropriate immunizations and travel medications
Whooping Cough Vaccine for Pregnant Women
 Whooping Cough Vaccine for Pregnant Women What is whooping cough (pertussis)? Whooping cough (also known as pertussis) is a highly contagious illness that can be life threatening. The disease is most serious
Whooping Cough Vaccine for Pregnant Women What is whooping cough (pertussis)? Whooping cough (also known as pertussis) is a highly contagious illness that can be life threatening. The disease is most serious
Pertussis Information for GPs and other Health Care Providers on Clinical and Public Health Management. March 2010
 Pertussis Information for GPs and other Health Care Providers on Clinical and Public Health Management March 2010 Infectious Agent Bordetella pertussis (a bacterium) Clinical Features Infants and Young
Pertussis Information for GPs and other Health Care Providers on Clinical and Public Health Management March 2010 Infectious Agent Bordetella pertussis (a bacterium) Clinical Features Infants and Young
X-Plain Pediatric Tuberculosis Reference Summary
 X-Plain Pediatric Tuberculosis Reference Summary Introduction Tuberculosis, or TB, is a bacterial infection that causes more deaths in the world than any other infectious disease. When a child gets TB,
X-Plain Pediatric Tuberculosis Reference Summary Introduction Tuberculosis, or TB, is a bacterial infection that causes more deaths in the world than any other infectious disease. When a child gets TB,
Emphysema. Introduction Emphysema is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD. COPD affects about 64 million people worldwide.
 Emphysema Introduction Emphysema is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD. COPD affects about 64 million people worldwide. Emphysema involves damage to the air sacs in the lungs. This
Emphysema Introduction Emphysema is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD. COPD affects about 64 million people worldwide. Emphysema involves damage to the air sacs in the lungs. This
Why Pertussis matters..
 Why Pertussis matters.. Pertussis (Whooping cough) outbreaks continue to impact children & adults, both locally and across the US. Cases have been on the rise since the 1980 s. However, recent data on
Why Pertussis matters.. Pertussis (Whooping cough) outbreaks continue to impact children & adults, both locally and across the US. Cases have been on the rise since the 1980 s. However, recent data on
Sore Throat. Definition. Causes. (Pharyngitis; Tonsillopharyngitis; Throat Infection) Pronounced: Fare-en-JY-tis /TAHN-sill-oh-fare-en-JY-tis
 Sore Throat (Pharyngitis; Tonsillopharyngitis; Throat Infection) Pronounced: Fare-en-JY-tis /TAHN-sill-oh-fare-en-JY-tis by Jennifer Lewy, MSW En Español (Spanish Version) Definition A sore throat is the
Sore Throat (Pharyngitis; Tonsillopharyngitis; Throat Infection) Pronounced: Fare-en-JY-tis /TAHN-sill-oh-fare-en-JY-tis by Jennifer Lewy, MSW En Español (Spanish Version) Definition A sore throat is the
The flu vaccination WINTER 2016/17. Who should have it and why. Flu mmunisation 2016/17
 The flu vaccination WINTER 2016/17 Who should have it and why Flu mmunisation 2016/17 The flu vaccination 1 Winter 2016/17 Helping to protect everyone, every winter This leaflet explains how you can help
The flu vaccination WINTER 2016/17 Who should have it and why Flu mmunisation 2016/17 The flu vaccination 1 Winter 2016/17 Helping to protect everyone, every winter This leaflet explains how you can help
BE SURE. BE SAFE. VACCINATE.
 DON T GET OR GIVE THE FLU THIS YEAR THANK YOU Vaccination is the only protection. www.immunisation.ie BE SURE. BE SAFE. VACCINATE. FLU VACCINE 2013-2014 Healthcare workers prevent the spread of flu and
DON T GET OR GIVE THE FLU THIS YEAR THANK YOU Vaccination is the only protection. www.immunisation.ie BE SURE. BE SAFE. VACCINATE. FLU VACCINE 2013-2014 Healthcare workers prevent the spread of flu and
Factsheet September 2012. Pertussis immunisation for pregnant women. Introduction
 Factsheet September 2012 Pertussis immunisation for pregnant women Introduction The routine childhood immunisation programme has been very effective in reducing the overall numbers of cases of pertussis.
Factsheet September 2012 Pertussis immunisation for pregnant women Introduction The routine childhood immunisation programme has been very effective in reducing the overall numbers of cases of pertussis.
Quick Reference H1N1 Flu (swine flu)
 Quick Reference H1N1 Flu (swine flu) The United States declared a public health emergency in response to the recent reports of swine flu. UMR wants to help you understand some important facts about H1N1
Quick Reference H1N1 Flu (swine flu) The United States declared a public health emergency in response to the recent reports of swine flu. UMR wants to help you understand some important facts about H1N1
The Immunization Office, located in the Student Health Center, is open year round to administer needed immunizations at a nominal fee.
 Student Health Services 2815 Cates Avenue Raleigh, NC 27695-7304 919-515-2563 healthcenter.ncsu.edu The Immunization Record Form is designed to collect information about your current immunization status.
Student Health Services 2815 Cates Avenue Raleigh, NC 27695-7304 919-515-2563 healthcenter.ncsu.edu The Immunization Record Form is designed to collect information about your current immunization status.
Better Breathing with COPD
 Better Breathing with COPD People with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) often benefit from learning different breathing techniques. Pursed Lip Breathing Pursed Lip Breathing (PLB) can be very
Better Breathing with COPD People with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) often benefit from learning different breathing techniques. Pursed Lip Breathing Pursed Lip Breathing (PLB) can be very
RSV infection. Information about RSV and how you can reduce the risk of your infant developing a severe infection.
 RSV infection Information about RSV and how you can reduce the risk of your infant developing a severe infection. What is RSV? RSV is one of the most common respiratory viruses and is spread easily. By
RSV infection Information about RSV and how you can reduce the risk of your infant developing a severe infection. What is RSV? RSV is one of the most common respiratory viruses and is spread easily. By
The Hepatitis B virus (HBV)
 The Hepatitis B virus (HBV) There are 400 million people in the world who live with chronic hepatitis B, including France. Most people don t even know they are infected. But there are several important
The Hepatitis B virus (HBV) There are 400 million people in the world who live with chronic hepatitis B, including France. Most people don t even know they are infected. But there are several important
Know the Symptoms. Call Your Doctor, Treat Whooping Gough Early. Whooping Cough Signs and Symptoms. Whooping Cough Shots Prevent the Disease
 What ls Whooping Cough? Whooping cough disease (also called pertussis) causes coughing fits that make it hard to breathe. It spreads easily when someone with the disease coughs or sneezes. It can kill
What ls Whooping Cough? Whooping cough disease (also called pertussis) causes coughing fits that make it hard to breathe. It spreads easily when someone with the disease coughs or sneezes. It can kill
Childhood Diseases and potential risks during pregnancy: (All information available on the March of Dimes Web Site.) http://www.modimes.
 Childhood Diseases and potential risks during pregnancy: (All information available on the March of Dimes Web Site.) http://www.modimes.org/ Fifth disease (erythema infectiosum) is a common, mild, childhood
Childhood Diseases and potential risks during pregnancy: (All information available on the March of Dimes Web Site.) http://www.modimes.org/ Fifth disease (erythema infectiosum) is a common, mild, childhood
2 months Diptheria; Tetanus; Whooping Cough; Hib & Polio 1st dose Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccination
 IMMUNISATIONS You may want to know if your child should have routine immunisations and whether there could be an increased risk of complications because of the heart condition. We have sought the opinions
IMMUNISATIONS You may want to know if your child should have routine immunisations and whether there could be an increased risk of complications because of the heart condition. We have sought the opinions
Whooping cough (Pertussis) Information for you
 Whooping cough (Pertussis) Information for you Visit our website: www.nhsaaa.net All our publications are available in other formats ...Information for you...information for you...information for you.
Whooping cough (Pertussis) Information for you Visit our website: www.nhsaaa.net All our publications are available in other formats ...Information for you...information for you...information for you.
COPD What Is It? Why is it so hard to catch my breath? What does COPD feel like? What causes COPD? What is an exacerbation (ig-zas-er-bay-shun)?
 Attitudes and Beliefs 4 COPD What Is It? Why is it so hard to catch my breath? COPD is a disease that damages the lungs. In a healthy lung, the airways are open and the air sacs fill up with air. Then
Attitudes and Beliefs 4 COPD What Is It? Why is it so hard to catch my breath? COPD is a disease that damages the lungs. In a healthy lung, the airways are open and the air sacs fill up with air. Then
Multiple Myeloma. This reference summary will help you understand multiple myeloma and its treatment options.
 Multiple Myeloma Introduction Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells. Each year, thousands of people find out that they have multiple myeloma. This reference summary will help
Multiple Myeloma Introduction Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells. Each year, thousands of people find out that they have multiple myeloma. This reference summary will help
FOR INFORMATION CONTACT:
 NEWS RELEASE FOR INFORMATION CONTACT: Caroline Calderone Baisley Deborah C. Travers Director of Health Director of Family Health Tel [203] 622-7836 Tel [203] 622-7854 September 10, 2014 For Immediate Release
NEWS RELEASE FOR INFORMATION CONTACT: Caroline Calderone Baisley Deborah C. Travers Director of Health Director of Family Health Tel [203] 622-7836 Tel [203] 622-7854 September 10, 2014 For Immediate Release
Seasonal Allergies. 1995-2012 The Patient Education Institute, Inc. www.x-plain.com im010101 Last reviewed: 05/30/2012 1
 Seasonal Allergies Introduction Seasonal allergies are allergies that develop during certain times of the year. Seasonal allergies are usually a response to pollen from trees, grasses, and weeds. Constant
Seasonal Allergies Introduction Seasonal allergies are allergies that develop during certain times of the year. Seasonal allergies are usually a response to pollen from trees, grasses, and weeds. Constant
Pertussis and Pregnancy
 Pertussis and Pregnancy Protect Your Patients From Pertussis (Whooping Cough) 1 Pertussis Video https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=f1g5woy5qce#a ction=share 2 1 Class Objectives By the end of this class the
Pertussis and Pregnancy Protect Your Patients From Pertussis (Whooping Cough) 1 Pertussis Video https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=f1g5woy5qce#a ction=share 2 1 Class Objectives By the end of this class the
Is your family at risk for pertussis?
 Is your family at risk for pertussis? Help protect your family against a serious disease and talk to your health-care professional about adult and adolescent immunization with Adacel vaccine. Please click
Is your family at risk for pertussis? Help protect your family against a serious disease and talk to your health-care professional about adult and adolescent immunization with Adacel vaccine. Please click
Lesson 7: Respiratory and Skeletal Systems and Tuberculosis
 Glossary 1. asthma: when the airways of the lungs narrow, making breathing difficult 2. bacteria: tiny living creatures that can only be seen with a microscope; some bacteria help the human body, and other
Glossary 1. asthma: when the airways of the lungs narrow, making breathing difficult 2. bacteria: tiny living creatures that can only be seen with a microscope; some bacteria help the human body, and other
FAQs on Influenza A (H1N1-2009) Vaccine
 FAQs on Influenza A (H1N1-2009) Vaccine 1) What is Influenza A (H1N1-2009) (swine flu) 1? Influenza A (H1N1-2009), previously known as "swine flu", is a new strain of influenza virus that spreads from
FAQs on Influenza A (H1N1-2009) Vaccine 1) What is Influenza A (H1N1-2009) (swine flu) 1? Influenza A (H1N1-2009), previously known as "swine flu", is a new strain of influenza virus that spreads from
Guidelines for Hand Foot and Mouth Disease HFMD
 Guidelines for Hand Foot and Mouth Disease HFMD Hand, foot, and mouth disease, or HFMD, is a contagious illness caused by different viruses. Infants and children younger than 5 years are more likely to
Guidelines for Hand Foot and Mouth Disease HFMD Hand, foot, and mouth disease, or HFMD, is a contagious illness caused by different viruses. Infants and children younger than 5 years are more likely to
What Is. Norovirus? Learning how to control the spread of norovirus. Web Sites
 Web Sites Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) http://www.cdc.gov/norovirus/index.html Your Local Health Department http://www.azdhs.gov/diro/lhliaison/countymap.htm What Is Ocument dn Norovirus?
Web Sites Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) http://www.cdc.gov/norovirus/index.html Your Local Health Department http://www.azdhs.gov/diro/lhliaison/countymap.htm What Is Ocument dn Norovirus?
Explanation of Immunization Requirements
 Explanation of Immunization Requirements CONTENTS Hepatitis A... 2 Hepatitis B... 3 Influenza... 4 Measles (Rubella), Mumps, and Rubella (MMR)... 5 Pertussis (Tdap)... 6 Tuberculosis (TB) Test... 7 Varicella/Chicken
Explanation of Immunization Requirements CONTENTS Hepatitis A... 2 Hepatitis B... 3 Influenza... 4 Measles (Rubella), Mumps, and Rubella (MMR)... 5 Pertussis (Tdap)... 6 Tuberculosis (TB) Test... 7 Varicella/Chicken
Influenza Vaccine Frequently Asked Questions. Influenza Control Program
 Influenza Vaccine Frequently Asked Questions Influenza Control Program Influenza or the flu can be a serious contagious disease, which is spread by droplet transmission through close contact with an infected
Influenza Vaccine Frequently Asked Questions Influenza Control Program Influenza or the flu can be a serious contagious disease, which is spread by droplet transmission through close contact with an infected
Lung Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand lung cancer and the treatment options that are available.
 Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
written by Harvard Medical School COPD It Can Take Your Breath Away www.patientedu.org/copd
 written by Harvard Medical School COPD It Can Take Your Breath Away www.patientedu.org/copd What Is COPD? COPD stands for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. There are two major diseases included in
written by Harvard Medical School COPD It Can Take Your Breath Away www.patientedu.org/copd What Is COPD? COPD stands for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. There are two major diseases included in
Ear Infections Chickenpox chickenpox
 Ear Chickenpox Infections chickenpox Chickenpox Chickenpox is a common, very contagious viral infection that over 90% of people get during childhood unless they have been immunised. After an infection,
Ear Chickenpox Infections chickenpox Chickenpox Chickenpox is a common, very contagious viral infection that over 90% of people get during childhood unless they have been immunised. After an infection,
Alberta Health and Wellness Public Health Notifiable Disease Management Guidelines August 2011
 August 2011 Pertussis Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) August 2011 August 2011 December 2005 Case Definition
August 2011 Pertussis Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) August 2011 August 2011 December 2005 Case Definition
Pertussis (whooping cough) immunisation for pregnant women the safest way to protect yourself and your baby
 Factsheet September 2012 Pertussis (whooping cough) immunisation for pregnant women the safest way to protect yourself and your baby The routine childhood immunisation programme has been very effective
Factsheet September 2012 Pertussis (whooping cough) immunisation for pregnant women the safest way to protect yourself and your baby The routine childhood immunisation programme has been very effective
Immunization Healthcare Branch. Meningococcal Vaccination Program Questions and Answers. Prepared by
 Immunization Healthcare Branch Meningococcal Vaccination Program Questions and Answers Prepared by Immunization Healthcare Branch (IHB), Defense Health Agency Last Updated: 27 Mar 06 www.vaccines.mil 877-GET-VACC
Immunization Healthcare Branch Meningococcal Vaccination Program Questions and Answers Prepared by Immunization Healthcare Branch (IHB), Defense Health Agency Last Updated: 27 Mar 06 www.vaccines.mil 877-GET-VACC
Nursing college, Second stage Microbiology Dr.Nada Khazal K. Hendi L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection
 L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection Definition A hospital acquired infection, also called a nosocomial infection, is an infection that first appears between 48 hours and four days after
L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection Definition A hospital acquired infection, also called a nosocomial infection, is an infection that first appears between 48 hours and four days after
Laboratory confirmation requires isolation of Bordetella pertussis or detection of B. pertussis nucleic acid, preferably from a nasopharyngeal swab.
 Pertussis Epidemiology in New Zealand New Zealand has continued to experience outbreaks of pertussis in recent decades. This is in part due to historically low immunisation rates and in part because immunity
Pertussis Epidemiology in New Zealand New Zealand has continued to experience outbreaks of pertussis in recent decades. This is in part due to historically low immunisation rates and in part because immunity
Asthma Care. Of course, your coach is there to answer any questions you have about your asthma, such as:
 Asthma Care All Health Coaches in the Asthma Care Management program are registered or certified respiratory therapists. Your coach will listen to your story of living with asthma. This will help your
Asthma Care All Health Coaches in the Asthma Care Management program are registered or certified respiratory therapists. Your coach will listen to your story of living with asthma. This will help your
Tuberculosis: FAQs. What is the difference between latent TB infection and TB disease?
 Tuberculosis: FAQs What is TB disease? Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease caused by bacteria (germs) that are spread from person to person through the air. TB usually affects the lungs, but it can also affect
Tuberculosis: FAQs What is TB disease? Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease caused by bacteria (germs) that are spread from person to person through the air. TB usually affects the lungs, but it can also affect
PNEUMONIA Debra Mercer BSN, RN, RRT
 PNEUMONIA Debra Mercer BSN, RN, RRT 1 Objectives Following this presentation the participant will demonstrate understanding of pneumonia by successful completion of the Pneumonia I.Q. Quiz (7 or more correct
PNEUMONIA Debra Mercer BSN, RN, RRT 1 Objectives Following this presentation the participant will demonstrate understanding of pneumonia by successful completion of the Pneumonia I.Q. Quiz (7 or more correct
Lung cancer (non-small-cell)
 Patient information from the BMJ Group Lung cancer (non-small-cell) It can be devastating to find out that you or someone close to you has lung cancer. You will have to make some important decisions about
Patient information from the BMJ Group Lung cancer (non-small-cell) It can be devastating to find out that you or someone close to you has lung cancer. You will have to make some important decisions about
Parents and Grandparents
 Parents and Grandparents Vaccination for parents and grandparents is vital to help protect newborn babies against whooping cough. Protect your baby by being immunised too. To find out more about Boostrix
Parents and Grandparents Vaccination for parents and grandparents is vital to help protect newborn babies against whooping cough. Protect your baby by being immunised too. To find out more about Boostrix
Vaccinations and Spina Bifida and Hydrocephalus
 shinecharity.org.uk info@shinecharity.org.uk 42 Park Road Peterborough PE1 2UQ 01733 555988 Vaccinations and Spina Bifida and Hydrocephalus Vaccines are made from parts of bacteria or viruses that cause
shinecharity.org.uk info@shinecharity.org.uk 42 Park Road Peterborough PE1 2UQ 01733 555988 Vaccinations and Spina Bifida and Hydrocephalus Vaccines are made from parts of bacteria or viruses that cause
Pertussis (whooping cough) immunisation for pregnant women
 Factsheet September 2012 Pertussis (whooping cough) immunisation for pregnant women Immunisation DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH Rheynn Slaynt The routine childhood immunisation programme has been very effective
Factsheet September 2012 Pertussis (whooping cough) immunisation for pregnant women Immunisation DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH Rheynn Slaynt The routine childhood immunisation programme has been very effective
Get the Facts About. Disease
 Get the Facts About TB TUBERCULOSIS Disease What s Inside: 3 PAGE Get the facts, then get the cure 4 PAGE 9 PAGE 12 PAGE Learn how TB is spread Treatment for TB disease Talking to family and friends about
Get the Facts About TB TUBERCULOSIS Disease What s Inside: 3 PAGE Get the facts, then get the cure 4 PAGE 9 PAGE 12 PAGE Learn how TB is spread Treatment for TB disease Talking to family and friends about
HEALTH EFFECTS. Inhalation
 Health Effects HEALTH EFFECTS Asbestos can kill you. You must take extra precautions when you work with asbestos. Just because you do not notice any problems while you are working with asbestos, it still
Health Effects HEALTH EFFECTS Asbestos can kill you. You must take extra precautions when you work with asbestos. Just because you do not notice any problems while you are working with asbestos, it still
& WHEN SHOULD I WORRY?
 WHEN SHOULD I WORRY? - Your guide to Coughs, Colds, Earache & Sore Throats Information For:- Who is this booklet for? Having an ill child can be a very scary experience for parents. If you understand more
WHEN SHOULD I WORRY? - Your guide to Coughs, Colds, Earache & Sore Throats Information For:- Who is this booklet for? Having an ill child can be a very scary experience for parents. If you understand more
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patient Guidebook
 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patient Guidebook The Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of the lungs and air passages. The lungs are the part of the body where gases are exchanged
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patient Guidebook The Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of the lungs and air passages. The lungs are the part of the body where gases are exchanged
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE Release #2014-04
 FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE Release #2014-04 CONTACT for this Release: Krista Dommer Office Phone: (209) 468-3571 Email: kdommer@sjcphs.org Alvaro Garza, MD, MPH. Public Health Officer MEASLES OUTBREAKS PROMPT
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE Release #2014-04 CONTACT for this Release: Krista Dommer Office Phone: (209) 468-3571 Email: kdommer@sjcphs.org Alvaro Garza, MD, MPH. Public Health Officer MEASLES OUTBREAKS PROMPT
Cocaine. Like heroin, cocaine is a drug that is illegal in some areas of the world. Cocaine is a commonly abused drug.
 Cocaine Introduction Cocaine is a powerful drug that stimulates the brain. People who use it can form a strong addiction. Addiction is when a drug user can t stop taking a drug, even when he or she wants
Cocaine Introduction Cocaine is a powerful drug that stimulates the brain. People who use it can form a strong addiction. Addiction is when a drug user can t stop taking a drug, even when he or she wants
Tdap and MenC booster vaccines. Information for parents of children in First Year of second level school
 Tdap and MenC booster vaccines Information for parents of children in First Year of second level school Tdap and MenC booster vaccines Information for parents of children in First Year of second level
Tdap and MenC booster vaccines Information for parents of children in First Year of second level school Tdap and MenC booster vaccines Information for parents of children in First Year of second level
Recognizing and Treating Fevers in Children with Complex Medical Issues by Susan Agrawal
 www.complexchild.com Recognizing and Treating Fevers in Children with Complex Medical Issues by Susan Agrawal Fevers can be some of the scariest symptoms we see in our children, but they are also some
www.complexchild.com Recognizing and Treating Fevers in Children with Complex Medical Issues by Susan Agrawal Fevers can be some of the scariest symptoms we see in our children, but they are also some
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Xofigo Therapy. For metastatic prostate cancer. What is Xofigo? How does it work?
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Xofigo Therapy For metastatic prostate cancer This handout explains how the drug Xofigo is used to treat metastatic prostate cancer. What is Xofigo? Xofigo is a radioactive
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Xofigo Therapy For metastatic prostate cancer This handout explains how the drug Xofigo is used to treat metastatic prostate cancer. What is Xofigo? Xofigo is a radioactive
APPENDIX I-A: INFORMED CONSENT BB IND 11184 Protocol CDC IRB #4167
 APPENDIX I-A: INFORMED CONSENT BB IND 11184 Protocol CDC IRB #4167 INFORMED CONSENT FOR USE OF DIPHTHERIA ANTITOXIN (DAT) FOR SUSPECTED DIPHTHERIA CASES Investigational New Drug (IND) BB 11184 Protocol
APPENDIX I-A: INFORMED CONSENT BB IND 11184 Protocol CDC IRB #4167 INFORMED CONSENT FOR USE OF DIPHTHERIA ANTITOXIN (DAT) FOR SUSPECTED DIPHTHERIA CASES Investigational New Drug (IND) BB 11184 Protocol
Canine Influenza. What do I need to know?
 Canine Influenza What do I need to know? What is canine influenza? Canine influenza is a newly emerging infectious disease caused by a flu virus. In dogs, a highly contagious strain of the influenza A
Canine Influenza What do I need to know? What is canine influenza? Canine influenza is a newly emerging infectious disease caused by a flu virus. In dogs, a highly contagious strain of the influenza A
Sinusitis. Health Promotion and Education Program. Rev. 2014 MP-HEP-PPT-766-01-050514-E
 Sinusitis Health Promotion and Education Program Rev. 2014 2014, MMM Healthcare, Inc. - PMC Medicare Choice, Inc. Reproduction of this material is prohibited. MP-HEP-PPT-766-01-050514-E M&P-PRD-TEM-030-032511-S
Sinusitis Health Promotion and Education Program Rev. 2014 2014, MMM Healthcare, Inc. - PMC Medicare Choice, Inc. Reproduction of this material is prohibited. MP-HEP-PPT-766-01-050514-E M&P-PRD-TEM-030-032511-S
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is the name for a group of lung diseases including chronic bronchitis, emphysema and chronic obstructive airways
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is the name for a group of lung diseases including chronic bronchitis, emphysema and chronic obstructive airways
WHEN COPD* SYMPTOMS GET WORSE
 WHEN COPD* SYMPTOMS GET WORSE *Includes chronic bronchitis, emphysema, or both. Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. has no ownership interest in any other organization that advertises or markets
WHEN COPD* SYMPTOMS GET WORSE *Includes chronic bronchitis, emphysema, or both. Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. has no ownership interest in any other organization that advertises or markets
For the Patient: Paclitaxel injection Other names: TAXOL
 For the Patient: Paclitaxel injection Other names: TAXOL Paclitaxel (pak'' li tax' el) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a clear liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell your
For the Patient: Paclitaxel injection Other names: TAXOL Paclitaxel (pak'' li tax' el) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a clear liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell your
Common Childhood Infections
 Common Childhood Infections Most infections are caused by germs called viruses and bacteria. While you may be able to keep germs from spreading, you can t always keep your child from getting sick. It is
Common Childhood Infections Most infections are caused by germs called viruses and bacteria. While you may be able to keep germs from spreading, you can t always keep your child from getting sick. It is
Acute Myeloid Leukemia
 Acute Myeloid Leukemia Introduction Leukemia is cancer of the white blood cells. The increased number of these cells leads to overcrowding of healthy blood cells. As a result, the healthy cells are not
Acute Myeloid Leukemia Introduction Leukemia is cancer of the white blood cells. The increased number of these cells leads to overcrowding of healthy blood cells. As a result, the healthy cells are not
Pandemic Influenza: A Guide for Individuals and Families
 Pandemic Influenza: A Guide for Individuals and Families GET INFORMED. BE PREPARED. This guide is designed to help you understand the threat of a pandemic influenza outbreak in our community. It describes
Pandemic Influenza: A Guide for Individuals and Families GET INFORMED. BE PREPARED. This guide is designed to help you understand the threat of a pandemic influenza outbreak in our community. It describes
For the Patient: Dasatinib Other names: SPRYCEL
 For the Patient: Dasatinib Other names: SPRYCEL Dasatinib (da sa' ti nib) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. Tell your doctor if you have ever
For the Patient: Dasatinib Other names: SPRYCEL Dasatinib (da sa' ti nib) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. Tell your doctor if you have ever
Community Health Administration
 Community Health Administration 300 North San Antonio Road Santa Barbara, CA 93110-1332 805/681-5439 FAX 805/681-5200 Takashi M. Wada, MD, MPH Director/Health Officer Anne M. Fearon Deputy Director Suzanne
Community Health Administration 300 North San Antonio Road Santa Barbara, CA 93110-1332 805/681-5439 FAX 805/681-5200 Takashi M. Wada, MD, MPH Director/Health Officer Anne M. Fearon Deputy Director Suzanne
Presence and extent of fatty liver or other metabolic liver diseases
 UC San Diego Health System Patient Information Sheet: Liver Biopsy What is a Liver Biopsy? A liver biopsy is a procedure where a qualified doctor (typically a hepatologist, radiologist or gastroenterologist)
UC San Diego Health System Patient Information Sheet: Liver Biopsy What is a Liver Biopsy? A liver biopsy is a procedure where a qualified doctor (typically a hepatologist, radiologist or gastroenterologist)
Paclitaxel and Carboplatin
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu What is Paclitaxel (pak-li-tax-el) and how does it work? Paclitaxel is a chemotherapy drug known as an anti-microtubule inhibitor. Another name for this drug
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu What is Paclitaxel (pak-li-tax-el) and how does it work? Paclitaxel is a chemotherapy drug known as an anti-microtubule inhibitor. Another name for this drug
