Intradiscal Electrothermal Treatment for Chronic Lower Back Pain Patients with Internal Disc Disruption
|
|
|
- Jordan Rich
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Yonsei Medical Journal Vol. 46, No. 4, pp , 2005 Intradiscal Electrothermal Treatment for Chronic Lower Back Pain Patients with Internal Disc Disruption Si-Young Park, 1 Seong-Hwan Moon, 1 Moon Soo Park, 2 Hak-Sun Kim, 1 Youn-Jin Choi, 1 and Hwan-Mo Lee 1 1 Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea; 2 Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Ulsan University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. Chronic lower back pain is one of the most common musculoskeletal problems; it is also the most expensive industrial injury. Not surprisingly, many treatments have been developed to combat this expensive and debilitating condition. One of these, intradiscal electrothermal treatment (IDET), was developed for patients with chronic discogenic lower back pain who failed to improve with any of the wide variety of non- surgical treatments. The present study sought to evaluate the efficacy of IDET for patients with chronic lower back pain. Twenty-five patients were enrolled in this prospective study; the patients received IDET between June 2001 and June MRI was used to confirm the diagnosis of internal disc disruption in all patients. The patients then underwent a pre-operative provocative test and discography. The follow-up duration was at least 1 year in all cases, and the visual analogue scale, recovery rate, and satisfaction of each patient were evaluated. The average age of the patients was 32 years (age range 18 to 49 years), and the patient group was 33% male and 67% female. Of the 25 patients, 5 underwent lumbar fusion surgery within 1 year of IDET. After IDET, 8 patients (32%) reported more pain than before, 14 patients (56%) reported less pain, and 3 patients (12%) experienced no change. Twelve patients (48%) were satisfied with IDET, 11 (44%) were dissatisfied, and 2 (8%) were undecided about the treatment. At least 1 year after IDET, nearly half the study patients were dissatisfied with their medical outcome. Consequently, 5 patients (20%) underwent fusion surgery at 1 year after IDET. Although other studies have shown good results with IDET for at least 2 years, this investigation suggests the IDET may be somewhat less effective. In order to firmly establish the efficacy of IDET for treating chronic discogenic lower back pain, additional studies with larger numbers of patients evaluated over longer time Received March 28, 2005 Accepted July 18, 2005 Reprint address: requests to Dr. Hwan-Mo Lee, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, 134 Shinchon-dong, Seodaemun-gu, Seoul , Korea. Tel: , Fax: , [email protected]. ac.kr periods are recommended. Key Words: Intradiscal electrothermal treatment (IDET), internal disc disruption, back pain INTRODUCTION Chronic lower back pain is one of the most common musculoskeletal problems and represents the most expensive industrial injury. 1-3 It has been estimated that up to 80% of the general population experiences lower back pain at some time, 4 and even despite its widespread nature, the management of chronic lower back pain remains a formidable challenge for spine specialists. Reports attribute approximately 40% of chronic lower back pain to an internal disc disruption, and these abnormal disc changes might induce back as well as thigh pain. 5 While internal disc disruption is recognized as a cause of discogenic lower back pain, there is no shortage of controversy as to its diagnosis and management. 6 Both surgical and non-surgical approaches have long been used to treat chronic lower back pain, especially in cases of internal disc disruption, but no approach has been without problems. 5,6 Whereas lumbar fusion surgery has traditionally been used to treat discogenic back pain, patients and spine specialists have recently shifted their preference to noninvasive or minimally invasive procedures in place of surgical operations, such as the long-standing lumbar fusion procedure. 7,8 This shift in opinion introduces the need for an alternative therapy for chronic lower back pain. Intradiscal electrothermal treatment (IDET) was developed as a potential alternative therapy for
2 Si-Young Park, et al. patients with chronic lower back pain resulting from an internal disc disruption who failed to improve with any of the wide variety of non-surgical treatments available. 9,10 IDET involves coagulating the anulus fibrosus of the painful disc with a flexible electrode, which is threaded into the disc percutaneously under fluoroscopic control. The procedure has been promoted by several articles that have reported both favorable and unfavorable responses The mechanism by which IDET relieves discogenic diseases is unclear, 15 and the success rate of the IDET procedure is also in question ,16 Thus, this study evaluated the efficacy of IDET for patients with chronic lower back pain diagnosed as internal disc disruption by monitoring the level of pain and satisfaction of patients at least 1 year after IDET. MATERIALS AND METHODS Twenty-five patients were enrolled in this prospective study and underwent IDET between June 2001 and June Physical examination and MRI were used to diagnose internal disc disruptions in all enrolled patients, with the MRI films of each patient classified according to the grading system reported by Thomson. 17,18 A discography was also taken and a provocative test was performed pre-operatively. All patients had a positive discogram, a diagnosis of discogenic lower back pain, and a history of failed conservative treatments. The inclusion and exclusion criteria for performing IDET were as follows: Inclusion criteria Unremitting, persistent lower back pain of continuous duration for at least 6 months Lack of satisfactory improvement with a comprehensive non-surgical treatment such as oral anti-inflammatory medication, physical therapy, epidural pain block, or activity modification Normal neurological examination Negative straight leg raising test Provocative test positive for discogenic pain MRI not demonstrating a neural compressive lesion Preserved disc height of at least 50% Exclusion criteria Inflammatory arthritis Stenosis, segmental instability Disc extrusion or sequestered disc Evidence of neural compression on MRI Previous lumbar surgery Severe loss of disc height (at least 50%) Worker insurance cases All patients underwent routine IDET. Under local anesthesia, an 18-gauge spinal needle was placed, with fluoroscopic guidance, into the center of the disc to be treated. An intradiscal catheter with a temperature-controlled thermal resistance coil was passed deeply through the needle and navigated intradiscally by fluoroscopy. The catheter was pushed as far as possible adjacent to the inner posterior anulus and then gradually heated to 90 over 12 minutes. This temperature was maintained for 4 minutes, after which 1 mg of cephazolin was injected intradiscally as a prophylactic against infection. No steroids or other medicines were injected. 9,10 Following IDET, all patients were discharged from the hospital within 3 days. Regular postoperative follow ups were performed at 3 and 6 months, 1, 1.5, and 2 years. At least 1 year after IDET, variations in the patients' symptoms, particularly in back pain, satisfaction rates, visual analog scale (VAS), and self recovery rates, were recorded and compared with the pre-operative status. RESULTS Demographic characteristics The IDET study group was composed of 25 patients (9 males and 16 females; mean age, 32 years; range, 18 to 49 years) with a pre-idet symptom duration of approximately 2 years. Most patients had more than two experiences of another treatment such as medication, physical therapy, pain block, acupuncture, herbal medication, or chiropractic treatment. The IDET targets were L3/4 in 3 patients, L4/5 in 13 patients, and L5/S1 in 9 patients. The disc degeneration grade
3 IDET for Chronic Lower Back Pain Patients with Internal Disc Disruption Table 1. Thompson s Disc Degeneration Grade (Macro) Nucleus Anulus Endplate Vertebral body Bulging gel Discrete fibrous lamellas Hyaline, uniformly thick Margins rounded White fibrous tissue Peripherally Consolidated fibrous tissue Horizontal cleft parallel to endplate Cleft extend through nucleus and anulus Mucinous material between lamella Extensive mucinous infiltration; Loss of anular-nuclear demarcation Focal disruptions Thickness irregular Focal defect in cartilage Fibrocartilage extending from subchondral bone-irregularity & focal sclerosis in subchondral bone Diffuse sclerosis Margins pointed Early chondrocyte or osteophyte at margin Osteophyte < 2 mm Osteophyte > 2 mm Table 2. MRI Grading Structure Distinction of nucleus & anulus Signal intensity Height of disc Homogeneous, bright white Clear Hyperintense isointense to CSF Normal Inhomogeneous C/S horizonatal band Clear Hyperintense, isointense to CSF Normal Inhomegeneous, gray Unclear Intermediate Normal to slight decrease Inhomogeneous, gray to black Lost Intermediate to hypointense Normal to moderate decrease Inhomogeneous, black Lost Hypointense Collapsed disc space on MRI according to Thompson's grading (Table 1 and 2) was recorded, with 9 patients in grade II and 16 patients in grade III (Table 3). Clinical results At least 1 year after the IDET procedure, 21 of the 25 study patients complained of lingering back pain despite some relief of symptoms compared to their pre-idet status. On the visual analog scale, 7.3 points were checked pre-idet and 4.9 points were checked 1 year after IDET. The recovery rate for overall back pain symptoms was approximately 40%. Regarding the number of back pain complaints, 8 patients (32%) complained of more pain after the treatment, 3 patients (12%) reported no changes, and 14 patients (56%) reported less pain compared with their pre-idet status. In terms of satisfaction rate, 12 patients (48%) were satisfied with IDET, 11 patients (44%) were dissatisfied, and 2 (8%) were undecided (Table 4). Complications Within 1 year of IDET, 5 of the 25 patients (20%) had undergone a lumbar surgery (all were fusion surgeries). One patient who received IDET at the L3/4 disc for back pain complained 5 weeks later of similar back pain as well as newly-developed radiating pain in both lower extremities. This patient was treated conservatively with medications, a back brace, and physical therapy, but his symptoms increased in severity. He also complained of chills and night fever. A second lumbar spine MRI was taken (Fig. 1) to evaluate the spine status, this time showing endplate erosion, edema, and periligamentus spreading along the posterior longitudinal ligament and infiltrating the paravertebral soft tissue. These findings were consistent with discitis. The patient underwent L3-L4 lumbar fusion surgery 2 months after IDET. In the other back operation cases for patients complaining of increased pain after IDET, 2 patients underwent
4 Si-Young Park, et al. Table 3. Demographic Characterisitics # Sex Age (yrs) Dx Sx (yrs) Level (L) Disco MRI* F/U (yrs) 1 F 28 IDD 2 4/ M 35 IDD 5 5/ F 40 IDD 8 4/ M 18 IDD 2 4/ F 32 IDD 1 5/ M 23 IDD 1 4/ F 38 IDD 1 5/ F 35 IDD 3 4/ F 39 IDD 2 5/ M 30 IDD 2 4/ F 49 IDD 2 4/ F 25 IDD 1 5/ M 27 IDD 1 3/ M 36 IDD 1 4/ F 35 IDD 1 5/ F 33 IDD 4 4/ M 36 IDD 4 5/ F 32 IDD 6 4/ F 27 IDD 2 3/ M 33 IDD 2 5/ F 31 IDD 3 5/ F 39 IDD 4 4/ F 26 IDD 1 4/ M 25 IDD 1 4/ F 30 IDD 1 3/ Level, L-lumbar; 1-1st sacrum. Disco, finding of discogram. *Thompson s degeneration of disc grade. Duration of symptoms (years). Minimum 1 year follow up (1-2 years). T1 weight image T2 weight image Gd enhance image Fig. 1. Post IDET MRI films show end plate edema and erosion of L3 and L4. These findings are compatible to iatrogenic discitis.
5 IDET for Chronic Lower Back Pain Patients with Internal Disc Disruption Table 4. Clinical Outcomes # Back pain VAS Recovery Pre* Post Rate (%) Satisfaction Complication 1 less U 2 less S 3 more D Fusion surgery 4 less S 5 less S 6 less S 7 less S 8 less U 9 more D 10 more D Fusion surgery 11 same D 12 less S 13 more D Infection 14 less S 15 less S 16 less S 17 more D 18 less S 19 same D 20 less S 21 more D Fusion surgery 22 more D 23 less S 24 same D 25 more D Fusion surgery * Pre-IDET VAS. Post-IDET VAS. S, satisfied; D, unsatisfied; U, undecided. fusion surgery by the posterior approach and 2 by the anterior approach. DISCUSSION Chronic discogenic lower back pain is a difficult condition to treat, even as methods for diagnosing the pain's source improve. A provocative discogram was developed as a less subjective method for pinpointing an internal discal disruption as the source of pain, and despite some controversy, a painful sensation during discography was used as an indication for surgery. 19,20 Whereas lumbar fusion surgery was long used to treat discogenic lower back pain, noninvasive and minimally invasive treatments have recently come into favor. 7,8 Saal et al. introduced IDET for treating discogenic lower back pain in 1997, 9 and interest in this minimally-invasive substitute for lumbar fusion surgery has only increased in the ensuing years. Consequently, several studies have sought to evaluate the efficacy and mechanics of IDET since its introduction Innervation of the anulus fibrosus and disc has been the topic of considerable research. In a normal intervertebral disc, the sensory nerve endings are confined to the outer third of the anulus
6 Si-Young Park, et al. fibrosus by the sinuvertebral nerve. 21,22 Freemont et al. demonstrated an association between nerve ingrowth, substance P expression, and discal degeneration, and suggested that the extent of what they termed neoneurolisation was greatest at the intervertebral discs responsible for pain generation. 23 Similarly, Coppes et al. noted that disc degeneration and perhaps injury were associated with centripetal ingrowth of nerve fibers into that disc. 24 These findings led to the speculation that a physiological basis for true discogenic pain existed and that the anulus fibrosus, in particular its posterior aspect, was the source of back pain. 23,24 The mechanisms by which IDET controls pain from an internal disc disruption are theorized to be functional deafferentation of the disc through ablation of the anular nociceptors. 25 Deafferentation is indeed the goal, and the use of thermal energy to produce a wider lesion directed toward the site of lower back pain, in particular toward the posterior anulus fibrosus, seems plausible. 26 Although deafferentation has the theoretical advantage of producing prompt pain relief, longterm follow up studies have not been promising. 14 An increase in anular stability via coagulation of anular collagen fiber to the disc is believed to be another mechanistic advantage of IDET, 27 yet no alteration of the anular morphology was observed when IDET-treated regions were compared with non-heated regions of the same disc in a cadaver study. 14 The same study also found no difference in stability before and after IDET. 14 In reviewing the literature published to date on IDET, no clear consensus emerges regarding its effects on neuronal deafferentation, collagen modulation, or spinal stability. The mechanisms of IDET by which discogenic pain is controlled remain uncertain. Not only are the mechanisms of IDET unknown, but the success rate of the procedure varies significantly from study to study ,15,16 Some authors have reported high success rates for relieving chronic discogenic lower back pain with IDET, while others have not. Yet other authors have reported several complications of IDET, including thermal osteonecrosis, large herniated discs, and infected discitis. 13,28,29 Despite the small cohort in the present study, 21 of the 25 patients (84%) complained of some amount of back pain after IDET. While the overall pain score was lower on the visual analog scale after IDET as compared with their pre-idet status, nearly half of the patients were dissatisfied with the procedure because of remaining back pain. Four patients also had to undergo lumbar fusion surgery due to unfavorable results of IDET, with one case requiring fusion as a consequence of infection. A significant number of patients were dissatisfied with IDET in our study, despite most reporting lessened back pain. This result was markedly different than previous studies for which positive results were reported for parameters such as the visual analog scale, SF35, and ODI. Positive findings might also be seen for these parameters in our study, but we believe that the patient selfsatisfaction rate with the procedure is a more important parameter for comparing with other treatment modalities. It should be noted that we could not identify any factors contributing to the negative effect of IDET, such as age, sex, weight, symptom duration, or disc degeneration grade. In conclusion, although other results of IDET in internal disc disruption patients might appear hopeful, potential IDET candidates should undergo a thorough evaluation before this treatment method is recommended. Also, a large prospective randomized long-term study should be carried out to confirm the efficacy of IDET for treating chronic lower back pain and internal disc disruptions. REFERENCES 1. Kelsey JL, White AA. Epidemiology and impact of low back pain. Spine 1980;5: Nachemson AL, Bigos S. The low back pain. In: Cruess RL, Rennie WRJ, editors. Adult orthopaedics. New York: Churchill-Livingstone; p Spengler DM, Bigos S, Martin NA, Zeh J, Fisher L, Nachemson A. Back injuries in industry: a retrospective study. Spine 1986;11: Anderson GBJ. Epidemiological features of chronic low back pain. Lancet 1999;354: Schwartzer AC, Aprill CN, Derby R, Fortin J, Kine G, Bogduk N. The prevalence and clinical features of internal disc disruption in patients with chronic low back pain. Spine 1995;20: Crock HV. A reappraisal of intervertebral disc lesions.
7 IDET for Chronic Lower Back Pain Patients with Internal Disc Disruption Med J Aust 1970;1: Kevin TF, Lamgston TH, James DS. Minimally invasive lumbar fusion. Spine 2003;28:S Foley KT, Lefkowitz MA. Advances in minimally invasive spine surgery. Clin Neurosurg 2002;49: Saal JA, Saal JS, Ashley J. Targeted intradiscal thermal therapy: preliminary feasibility results. Presented at the anual meeting of the international society for the study of the lumbar spine, Singapore, June 2-6, Saal JA, Saal JS. Intradiscal electrothermal treatment for chronic discogenic low back pain. Spine 2002;27: Ashok B, Andersson GBJ, Chaudhary H, An HS. Intradiscal electrothermal therapy: A treatment option in patients with internal disc disruption. Spine 2003;28:S Karasek M, Bogduk N. Twelve-month follow up of a controlled trial of intradiscal thermal anuloplasty for back pain due to internal disc disruption. Spine 2000; 25: Timothy TD, Rick BD, Parveen S, Goldstein TB. The IDET procedure for chronic discogenic low back pain. Spine 2004;29: Wetzel FD, Mcnally TA, Philips FM. Intradiscal electrothermal therapy used to manage chronic discogenic low back pain. Spine 2002;27: Kleinstueck FS, Diederich CJ, Nau WH, Puttlitz CM, Smith JA, Bradford D, et al. Acute biomechanical and histological effects of intradiscal electrothermal therapy on human lumbar discs. Spine 2001;26: Cohen SP, Larkin T, Abdi S, Chang A, Stojanovic M. Risk factors for failure and complications of intradiscal electrothermal therapy: A pilot study. Spine 2003;28: Thompson JP, Pearce RH, Schechter MT, Adams ME, Tsang IKT, Bishop PB. Preliminary evaluation of a scheme for grading the gross morphology of the human intervetebral disc. Spine 1990;15: Pfirrmann CW, Metzdorf A, Zanetti M, Holder J, Boos N. Magnetic resonance classification of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine 2001;26: Briney TJ, White JJ, Berens D. Comparison of MRI and discography in the diagnosis of lumbar degenerative disc disease. Spine 1998;23: Collins CD, Stack JP, O'Connell DJ, Walsh M, Mcmanus FP, Redmond OM, et al. The role of discography in lumbar disc disease a comparative study of MRI and discography. Clin Radiol 1990;42: Bogduk N, Tynan W, Wilson AS. The nerve supply to the human intervertebral discs. J Anat 1981;132: Groen GJ, Baljet B, Drukker J. The nerve and nerve plexuses of the human vertebral column. Am J Anat 1990;188: Freemont AJ, Peacock TE, Goupille P, Hoyland JA, OBrien J, Jayson MI. Nerve ingrowth into disease intervertebral disc in low back pain. Lancet 1997;350: Coppes MH, Marani E, Thomeer RT, Gerbrand J. Innervation of painful lumbar disc disease. Spine 1997;22: Letcher F, Goldring S. The effect of radiofrequency current and heat on peripheral nerve action potential in the cat. J Neurosurg 1968;29: Saal JA, Saal JS. Thermal characteristics of lumbar disc: Evaluation of a novel approach to targeted intradiscal thermal therapy. Presented at the 13th annual meeting of the North American Spine Society. San Francisco, California, October 28-31, Lee J, Luts GE, Campbell D, Rodeo SA, Wright T. Stability of the spine after intradiscal electrothermal therapy. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2001;82: Djurasovic M, Glassman SD, Dimar JR, Johnson JR. Vertebral osteonecrosis associated with the use of intradiscal electrothermal therapy. Spine 2002;27:E Cohen SP, Larkin T, Polly D. A giant herniated disc following intradiscal electrothermal therapy. J Spinal Disord Tech 2002;15:
Nonoperative Management of Herniated Cervical Intervertebral Disc With Radiculopathy. Spine Volume 21(16) August 15, 1996, pp 1877-1883
 Nonoperative Management of Herniated Cervical Intervertebral Disc With Radiculopathy 1 Spine Volume 21(16) August 15, 1996, pp 1877-1883 Saal, Joel S. MD; Saal, Jeffrey A. MD; Yurth, Elizabeth F. MD FROM
Nonoperative Management of Herniated Cervical Intervertebral Disc With Radiculopathy 1 Spine Volume 21(16) August 15, 1996, pp 1877-1883 Saal, Joel S. MD; Saal, Jeffrey A. MD; Yurth, Elizabeth F. MD FROM
Treating Bulging Discs & Sciatica. Alexander Ching, MD
 Treating Bulging Discs & Sciatica Alexander Ching, MD Disclosures Depuy Spine Teaching and courses K2 Spine Complex Spine Study Group Disclosures Take 2 I am a spine surgeon I like spine surgery I believe
Treating Bulging Discs & Sciatica Alexander Ching, MD Disclosures Depuy Spine Teaching and courses K2 Spine Complex Spine Study Group Disclosures Take 2 I am a spine surgeon I like spine surgery I believe
Advances In Spine Care. James D. Bruffey M.D. Scripps Clinic Division of Orthopaedic Surgery Section of Spinal Surgery
 Advances In Spine Care James D. Bruffey M.D. Scripps Clinic Division of Orthopaedic Surgery Section of Spinal Surgery Introduction The Spine - A common source of problems Back pain is the #2 presenting
Advances In Spine Care James D. Bruffey M.D. Scripps Clinic Division of Orthopaedic Surgery Section of Spinal Surgery Introduction The Spine - A common source of problems Back pain is the #2 presenting
X Stop Spinal Stenosis Decompression
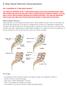 X Stop Spinal Stenosis Decompression Am I a candidate for X Stop spinal surgery? You may be a candidate for the X Stop spinal surgery if you have primarily leg pain rather than mostly back pain and your
X Stop Spinal Stenosis Decompression Am I a candidate for X Stop spinal surgery? You may be a candidate for the X Stop spinal surgery if you have primarily leg pain rather than mostly back pain and your
A Patient s Guide to Artificial Cervical Disc Replacement
 A Patient s Guide to Artificial Cervical Disc Replacement Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, an upper spine condition that can cause pain and numbness
A Patient s Guide to Artificial Cervical Disc Replacement Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, an upper spine condition that can cause pain and numbness
Options for Cervical Disc Degeneration A Guide to the Fusion Arm of the M6 -C Artificial Disc Study
 Options for Cervical Disc Degeneration A Guide to the Fusion Arm of the M6 -C Artificial Disc Study Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, an upper spine
Options for Cervical Disc Degeneration A Guide to the Fusion Arm of the M6 -C Artificial Disc Study Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, an upper spine
Effects of vertebral axial decompression on intradiscal pressure
 This article is reprinted with the permission of the authors from the Journal of Neurosurgery, Volume 81. J Neurosurg 81:350-353, 1994 Effects of vertebral axial decompression on intradiscal pressure GUSTAVO
This article is reprinted with the permission of the authors from the Journal of Neurosurgery, Volume 81. J Neurosurg 81:350-353, 1994 Effects of vertebral axial decompression on intradiscal pressure GUSTAVO
OUTLINE. Anatomy Approach to LBP Discogenic LBP. Treatment. Herniated Nucleus Pulposus Annular Tear. Non-Surgical Surgical
 DISCOGENIC PAIN OUTLINE Anatomy Approach to LBP Discogenic LBP Herniated Nucleus Pulposus Annular Tear Treatment Non-Surgical Surgical Facet Joints: bear 20% of weight Discs bear 80% of weight Neural Foramen
DISCOGENIC PAIN OUTLINE Anatomy Approach to LBP Discogenic LBP Herniated Nucleus Pulposus Annular Tear Treatment Non-Surgical Surgical Facet Joints: bear 20% of weight Discs bear 80% of weight Neural Foramen
Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, The Cervical Spine. What is the Cervical Spine?
 Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, an upper spine condition that can cause pain and numbness in the neck, shoulders, arms, and even hands. This patient
Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, an upper spine condition that can cause pain and numbness in the neck, shoulders, arms, and even hands. This patient
MANUSCRIPT PUBLICATIONS
 YUNG CHEN, MD Appointments Faculty, Assistant Professor Founder / Director of Interventional Spine Center Founder / Director of Interventional Spine Cadaver Course Director of Interventional Spine Fellowship
YUNG CHEN, MD Appointments Faculty, Assistant Professor Founder / Director of Interventional Spine Center Founder / Director of Interventional Spine Cadaver Course Director of Interventional Spine Fellowship
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF LOW BACK PAIN. Arnold J. Weil, M.D., M.B.A. Non-Surgical Orthopaedics, P.C. Atlanta, GA
 DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF LOW BACK PAIN Arnold J. Weil, M.D., M.B.A. Non-Surgical Orthopaedics, P.C. Atlanta, GA MEDICAL ALGORITHM OF REALITY LOWER BACK PAIN Yes Patient will never get better until case
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF LOW BACK PAIN Arnold J. Weil, M.D., M.B.A. Non-Surgical Orthopaedics, P.C. Atlanta, GA MEDICAL ALGORITHM OF REALITY LOWER BACK PAIN Yes Patient will never get better until case
Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
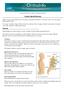 Copyright 2009 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Almost everyone will experience low back pain at some point in their lives. A common cause of low back pain is lumbar spinal
Copyright 2009 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Almost everyone will experience low back pain at some point in their lives. A common cause of low back pain is lumbar spinal
NON SURGICAL SPINAL DECOMPRESSION. Dr. Douglas A. VanderPloeg
 NON SURGICAL SPINAL DECOMPRESSION Dr. Douglas A. VanderPloeg CONTENTS I. Incidence of L.B.P. II. Anatomy Review III. IV. Disc Degeneration, Bulge, and Herniation Non-Surgical Spinal Decompression 1. History
NON SURGICAL SPINAL DECOMPRESSION Dr. Douglas A. VanderPloeg CONTENTS I. Incidence of L.B.P. II. Anatomy Review III. IV. Disc Degeneration, Bulge, and Herniation Non-Surgical Spinal Decompression 1. History
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery For Your Patients
 Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery For Your Patients Lukas P. Zebala, M.D. Assistant Professor Orthopaedic and Neurological Spine Surgery Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Washington University School of
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery For Your Patients Lukas P. Zebala, M.D. Assistant Professor Orthopaedic and Neurological Spine Surgery Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Washington University School of
SPINE ANATOMY AND PROCEDURES. Tulsa Spine & Specialty Hospital 6901 S. Olympia Avenue Tulsa, Oklahoma 74132
 SPINE ANATOMY AND PROCEDURES Tulsa Spine & Specialty Hospital 6901 S. Olympia Avenue Tulsa, Oklahoma 74132 SPINE ANATOMY The spine consists of 33 bones called vertebrae. The top 7 are cervical, or neck
SPINE ANATOMY AND PROCEDURES Tulsa Spine & Specialty Hospital 6901 S. Olympia Avenue Tulsa, Oklahoma 74132 SPINE ANATOMY The spine consists of 33 bones called vertebrae. The top 7 are cervical, or neck
Discogenic Pain: Diagnosis and Treatment
 Discogenic Pain: Diagnosis and Treatment James P. Rathmell, M.D. Professor of Anesthesiology University of Vermont College of Medicine Burlington, Vermont, USA Cottage Sunrise Westford, Vermont 2005 Learning
Discogenic Pain: Diagnosis and Treatment James P. Rathmell, M.D. Professor of Anesthesiology University of Vermont College of Medicine Burlington, Vermont, USA Cottage Sunrise Westford, Vermont 2005 Learning
Temple Physical Therapy
 Temple Physical Therapy A General Overview of Common Neck Injuries For current information on Temple Physical Therapy related news and for a healthy and safe return to work, sport and recreation Like Us
Temple Physical Therapy A General Overview of Common Neck Injuries For current information on Temple Physical Therapy related news and for a healthy and safe return to work, sport and recreation Like Us
.org. Herniated Disk in the Lower Back. Anatomy. Description
 Herniated Disk in the Lower Back Page ( 1 ) Sometimes called a slipped or ruptured disk, a herniated disk most often occurs in your lower back. It is one of the most common causes of low back pain, as
Herniated Disk in the Lower Back Page ( 1 ) Sometimes called a slipped or ruptured disk, a herniated disk most often occurs in your lower back. It is one of the most common causes of low back pain, as
Low Back Pain (LBP) Prevalence. Low Back Pain (LBP) Prevalence. Lumbar Fusion: Where is the Evidence?
 15 th Annual Cleveland Clinic Pain Management Symposium Sarasota, Florida Lumbar Fusion: Where is the Evidence? Gordon R. Bell, M.D. Director, Cleveland Clinic Low Back Pain (LBP) Prevalence Lifetime prevalence:
15 th Annual Cleveland Clinic Pain Management Symposium Sarasota, Florida Lumbar Fusion: Where is the Evidence? Gordon R. Bell, M.D. Director, Cleveland Clinic Low Back Pain (LBP) Prevalence Lifetime prevalence:
Nomenclature and Standard Reporting Terminology of Intervertebral Disk Herniation
 167 Nomenclature and Standard Reporting Terminology of Intervertebral Disk Herniation Richard F. Costello, DO a, *, Douglas P. Beall, MD a,b MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING CLINICS Magn Reson Imaging Clin N
167 Nomenclature and Standard Reporting Terminology of Intervertebral Disk Herniation Richard F. Costello, DO a, *, Douglas P. Beall, MD a,b MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING CLINICS Magn Reson Imaging Clin N
Options for Cervical Disc Degeneration A Guide to the M6-C. clinical study
 Options for Cervical Disc Degeneration A Guide to the M6-C clinical study Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, an upper spine condition that can cause
Options for Cervical Disc Degeneration A Guide to the M6-C clinical study Each year, hundreds of thousands of adults are diagnosed with Cervical Disc Degeneration, an upper spine condition that can cause
Cervical Spine Surgery. Orthopaedic Nursing Seminar. Dr Michelle Atkinson. Friday October 21 st 2011. Cervical Disc Herniation
 Cervical Spine Surgery Dr Michelle Atkinson The Sydney and Dalcross Adventist Hospitals Orthopaedic Nursing Seminar Friday October 21 st 2011 Cervical disc herniation The most frequently treated surgical
Cervical Spine Surgery Dr Michelle Atkinson The Sydney and Dalcross Adventist Hospitals Orthopaedic Nursing Seminar Friday October 21 st 2011 Cervical disc herniation The most frequently treated surgical
visualized. The correct level is then identified again. With the use of a microscope and
 SURGERY FOR SPINAL STENOSIS Laminectomy A one inch (or longer for extensive stenosis) incision is made in the middle of the back over the effected region of the spine. The muscles over the bone are moved
SURGERY FOR SPINAL STENOSIS Laminectomy A one inch (or longer for extensive stenosis) incision is made in the middle of the back over the effected region of the spine. The muscles over the bone are moved
Spinal Surgery Functional Status and Quality of Life Outcome Specifications 2015 (01/01/2013 to 12/31/2013 Dates of Procedure) September 2014
 Description Methodology For patients ages 18 years and older who undergo a lumbar discectomy/laminotomy or lumbar spinal fusion procedure during the measurement year, the following measures will be calculated:
Description Methodology For patients ages 18 years and older who undergo a lumbar discectomy/laminotomy or lumbar spinal fusion procedure during the measurement year, the following measures will be calculated:
Low Back Injury in the Industrial Athlete: An Anatomic Approach
 Low Back Injury in the Industrial Athlete: An Anatomic Approach Earl J. Craig, M.D. Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Epidemiology
Low Back Injury in the Industrial Athlete: An Anatomic Approach Earl J. Craig, M.D. Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Epidemiology
Does the pain radiating down your legs, buttocks or lower back prevent you from walking long distances?
 Does the pain radiating down your legs, buttocks or lower back prevent you from walking long distances? Do you experience weakness, tingling, numbness, stiffness, or cramping in your legs, buttocks or
Does the pain radiating down your legs, buttocks or lower back prevent you from walking long distances? Do you experience weakness, tingling, numbness, stiffness, or cramping in your legs, buttocks or
A review of spinal problems
 Dr Ulrich R Hähnle MD, FCS Orthopaedic Surgeon, Wits Facharzt für Orthopädie, Berlin Phone: +27 11 485 3236 Fax: +27 11 485 2446 Suite 102, Medical Centre, Linksfield Park Clinic P.O. Box 949, Johannesburg
Dr Ulrich R Hähnle MD, FCS Orthopaedic Surgeon, Wits Facharzt für Orthopädie, Berlin Phone: +27 11 485 3236 Fax: +27 11 485 2446 Suite 102, Medical Centre, Linksfield Park Clinic P.O. Box 949, Johannesburg
Effects of Vertebral Axial Decompression (VAX-D) On Intradiscal Pressure
 Effects of Vertebral Axial Decompression (VAX-D) On Intradiscal Pressure Gustavo Ramos, M.D., William Marin, M.D. Journal of Neursurgery 81:35-353 1994 Departments of Neurosurgery and Radiology, Rio Grande
Effects of Vertebral Axial Decompression (VAX-D) On Intradiscal Pressure Gustavo Ramos, M.D., William Marin, M.D. Journal of Neursurgery 81:35-353 1994 Departments of Neurosurgery and Radiology, Rio Grande
Spine University s Guide to Kinetic MRIs Detect Disc Herniations
 Spine University s Guide to Kinetic MRIs Detect Disc Herniations 2 Introduction Traditionally, doctors use a procedure called magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to diagnose disc injuries. Kinetic magnetic
Spine University s Guide to Kinetic MRIs Detect Disc Herniations 2 Introduction Traditionally, doctors use a procedure called magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to diagnose disc injuries. Kinetic magnetic
.org. Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Anatomy. Cause
 Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Page ( 1 ) Neck pain can be caused by many things but is most often related to getting older. Like the rest of the body, the disks and joints in the neck (cervical
Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Page ( 1 ) Neck pain can be caused by many things but is most often related to getting older. Like the rest of the body, the disks and joints in the neck (cervical
The Furcal nerve. Ronald L L Collins,MB,BS(UWI),FRCS(Edin.),FICS (Fort Lee Surgical Center, Fort Lee,NJ)
 The Furcal nerve. Ronald L L Collins,MB,BS(UWI),FRCS(Edin.),FICS (Fort Lee Surgical Center, Fort Lee,NJ) The furcal nerve is regarded as an anomalous nerve root, and has been found with significant frequency
The Furcal nerve. Ronald L L Collins,MB,BS(UWI),FRCS(Edin.),FICS (Fort Lee Surgical Center, Fort Lee,NJ) The furcal nerve is regarded as an anomalous nerve root, and has been found with significant frequency
https://www.laserspineinstitute.com/back_problems/foraminal_stenosis/e...
 Questions? Call toll free 1-866-249-1627 Contact us today. We're here for you seven days a week. MRI Review Consultation Live help Call 1-866-249-1627 Chat Live Home Laser Spine Institute Laser Spine Institute's
Questions? Call toll free 1-866-249-1627 Contact us today. We're here for you seven days a week. MRI Review Consultation Live help Call 1-866-249-1627 Chat Live Home Laser Spine Institute Laser Spine Institute's
Spinal Decompression
 Spinal Decompression Spinal decompression is just one more tool we have to treat radiculopathy. With appropriate education and exercises, this modality has been proven to assist in the resolution of symptoms
Spinal Decompression Spinal decompression is just one more tool we have to treat radiculopathy. With appropriate education and exercises, this modality has been proven to assist in the resolution of symptoms
Information on the Chiropractic Care of Lower Back Pain
 Chiropractic Care of Lower Back Pain Lower back pain is probably the most common condition seen the the Chiropractic office. Each month it is estimated that up to one third of persons experience some type
Chiropractic Care of Lower Back Pain Lower back pain is probably the most common condition seen the the Chiropractic office. Each month it is estimated that up to one third of persons experience some type
Spinal Decompression: Measurement of Treatment Outcomes. William D. Grant, EdD. Catherine E. Saxton, BS
 1 Spinal Decompression: Measurement of Treatment Outcomes. William D. Grant, EdD Catherine E. Saxton, BS Correspondence to: William D. Grant, EdD SUNY Upstate Medical University IHP 3302 750 E. Adams St.
1 Spinal Decompression: Measurement of Treatment Outcomes. William D. Grant, EdD Catherine E. Saxton, BS Correspondence to: William D. Grant, EdD SUNY Upstate Medical University IHP 3302 750 E. Adams St.
Discogenic Low Backache A clinical and MRI correlative study A DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO UNIVERSITY OF SEYCHELLES AMERICAN INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE
 Discogenic Low Backache A clinical and MRI correlative study A DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO UNIVERSITY OF SEYCHELLES AMERICAN INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REGULATIONS FOR THE AWARD
Discogenic Low Backache A clinical and MRI correlative study A DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO UNIVERSITY OF SEYCHELLES AMERICAN INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REGULATIONS FOR THE AWARD
enspire Interventional, Novel approach in Percutaneous Discectomy in Percutaneous Discectomy Samyadev Datta, MD, FRCA Center for Pain Management
 enspire Interventional, Novel approach in Percutaneous Discectomy in Percutaneous Discectomy Samyadev Datta, MD, FRCA Center for Pain Management Anatomy Intervertebral Disc: Fibrocartilaginous joint Makes
enspire Interventional, Novel approach in Percutaneous Discectomy in Percutaneous Discectomy Samyadev Datta, MD, FRCA Center for Pain Management Anatomy Intervertebral Disc: Fibrocartilaginous joint Makes
TREATMENT OF AN L5/S1 EXTRUDED DISC HERNIATION USING SPINAL DECOMPRESSION: A CASE STUDY. Jack Choate, DC
 TREATMENT OF AN L5/S1 EXTRUDED DISC HERNIATION USING SPINAL DECOMPRESSION: A CASE STUDY Jack Choate, DC ABSTRACT Objective: To discuss a case of an acute lumbar disc herniation that was successfully treated
TREATMENT OF AN L5/S1 EXTRUDED DISC HERNIATION USING SPINAL DECOMPRESSION: A CASE STUDY Jack Choate, DC ABSTRACT Objective: To discuss a case of an acute lumbar disc herniation that was successfully treated
Sample Treatment Protocol
 Sample Treatment Protocol 1 Adults with acute episode of LBP Definition: Acute episode Back pain lasting
Sample Treatment Protocol 1 Adults with acute episode of LBP Definition: Acute episode Back pain lasting
The Dehydrated Lumbar Intervertebral Disk on MR, its Anatomy, Biochemistry and Biomechanics
 NRJ Digital - The Neuroradiology Journal 1: 639-644, 2011 www.centauro.it The Dehydrated Lumbar Intervertebral Disk on MR, its Anatomy, Biochemistry and Biomechanics V. HAUgHToN Radiology Department, Wisconsin
NRJ Digital - The Neuroradiology Journal 1: 639-644, 2011 www.centauro.it The Dehydrated Lumbar Intervertebral Disk on MR, its Anatomy, Biochemistry and Biomechanics V. HAUgHToN Radiology Department, Wisconsin
Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization
 Client HMSA: PQSR 2009 Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization Strength of Recommendation Organizations
Client HMSA: PQSR 2009 Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization Strength of Recommendation Organizations
MRI AND DISCOGRAPHY OF ANNULAR TEARS AND INTERVERTEBRAL DISC DEGENERATION
 MRI AND DISCOGRAPHY OF ANNULAR TEARS AND INTERVERTEBRAL DISC DEGENERATION A PROSPECTIVE CLINICAL COMPARISON 0. L. OSTI, R. D. FRASER From the Royal Adelaide Hospital, South Australia We attempted to correlate
MRI AND DISCOGRAPHY OF ANNULAR TEARS AND INTERVERTEBRAL DISC DEGENERATION A PROSPECTIVE CLINICAL COMPARISON 0. L. OSTI, R. D. FRASER From the Royal Adelaide Hospital, South Australia We attempted to correlate
On Cervical Zygapophysial Joint Pain After Whiplash. Spine December 1, 2011; Volume 36, Number 25S, pp S194 S199
 On Cervical Zygapophysial Joint Pain After Whiplash 1 Spine December 1, 2011; Volume 36, Number 25S, pp S194 S199 Nikolai Bogduk, MD, PhD FROM ABSTRACT Objective To summarize the evidence that implicates
On Cervical Zygapophysial Joint Pain After Whiplash 1 Spine December 1, 2011; Volume 36, Number 25S, pp S194 S199 Nikolai Bogduk, MD, PhD FROM ABSTRACT Objective To summarize the evidence that implicates
Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
 Lumbar Spinal Stenosis North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Lumbar Spinal Stenosis? The vertebrae are the bones that make up the lumbar spine (low back). The spinal canal runs through
Lumbar Spinal Stenosis North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Lumbar Spinal Stenosis? The vertebrae are the bones that make up the lumbar spine (low back). The spinal canal runs through
If you or a loved one have suffered because of a negligent error during spinal surgery, you will be going through a difficult time.
 If you or a loved one have suffered because of a negligent error during spinal surgery, you will be going through a difficult time. You may be worried about your future, both in respect of finances and
If you or a loved one have suffered because of a negligent error during spinal surgery, you will be going through a difficult time. You may be worried about your future, both in respect of finances and
Information for the Patient About Surgical
 Information for the Patient About Surgical Decompression and Stabilization of the Spine Aging and the Spine Daily wear and tear, along with disc degeneration due to aging and injury, are common causes
Information for the Patient About Surgical Decompression and Stabilization of the Spine Aging and the Spine Daily wear and tear, along with disc degeneration due to aging and injury, are common causes
Lumbar Disc Herniation/Bulge Protocol
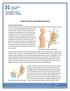 Lumbar Disc Herniation/Bulge Protocol Anatomy and Biomechanics The lumbar spine is made up of 5 load transferring bones called vertebrae. They are stacked in a column with an intervertebral disc sandwiched
Lumbar Disc Herniation/Bulge Protocol Anatomy and Biomechanics The lumbar spine is made up of 5 load transferring bones called vertebrae. They are stacked in a column with an intervertebral disc sandwiched
How To Get An Mri Of The Lumbar Spine W/O Contrast
 Date notice sent to all parties: May 27, 2014 IRO CASE #: ReviewTex, Inc. 1818 Mountjoy Drive San Antonio, TX 78232 (phone) 210-598-9381 (fax) 210-598-9382 [email protected] Notice of Independent Review
Date notice sent to all parties: May 27, 2014 IRO CASE #: ReviewTex, Inc. 1818 Mountjoy Drive San Antonio, TX 78232 (phone) 210-598-9381 (fax) 210-598-9382 [email protected] Notice of Independent Review
Open Discectomy. North American Spine Society Public Education Series
 Open Discectomy North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Open Discectomy? Open discectomy is the most common surgical treatment for ruptured or herniated discs of the lumbar spine.
Open Discectomy North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Open Discectomy? Open discectomy is the most common surgical treatment for ruptured or herniated discs of the lumbar spine.
Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck)
 Copyright 2009 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Neck pain is extremely common. It can be caused by many things, and is most often related to getting
Copyright 2009 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Neck pain is extremely common. It can be caused by many things, and is most often related to getting
Imaging degenerative disk disease in the lumbar spine. Elaine Besancon MS III Dr. Gillian Lieberman
 Imaging degenerative disk disease in the lumbar spine Elaine Besancon MS III Dr. Gillian Lieberman Learning Objectives Anatomy review Pathophysiology of degenerative disc disease Common sequelae of disk
Imaging degenerative disk disease in the lumbar spine Elaine Besancon MS III Dr. Gillian Lieberman Learning Objectives Anatomy review Pathophysiology of degenerative disc disease Common sequelae of disk
Back & Neck Pain Survival Guide
 Back & Neck Pain Survival Guide www.kleinpeterpt.com Zachary - 225-658-7751 Baton Rouge - 225-768-7676 Kleinpeter Physical Therapy - Spine Care Program Finally! A Proven Assessment & Treatment Program
Back & Neck Pain Survival Guide www.kleinpeterpt.com Zachary - 225-658-7751 Baton Rouge - 225-768-7676 Kleinpeter Physical Therapy - Spine Care Program Finally! A Proven Assessment & Treatment Program
The Petrylaw Lawsuits Settlements and Injury Settlement Report
 The Petrylaw Lawsuits Settlements and Injury Settlement Report BACK INJURIES How Minnesota Juries Decide the Value of Pain and Suffering in Back Injury Cases The Petrylaw Lawsuits Settlements and Injury
The Petrylaw Lawsuits Settlements and Injury Settlement Report BACK INJURIES How Minnesota Juries Decide the Value of Pain and Suffering in Back Injury Cases The Petrylaw Lawsuits Settlements and Injury
Herniated Cervical Disc
 Herniated Cervical Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The backbone, or spine, is composed of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The vertebrae
Herniated Cervical Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The backbone, or spine, is composed of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The vertebrae
DISCOGENIC PAIN TREATMENT
 DISCOGENIC PAIN TREATMENT CLINICAL POLICY Policy Number: OUTPATIENT 037.12 T2 Effective Date: February 1, 2016 Table of Contents BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS.. APPLICABLE LINES OF BUSINESS/PRODUCTS... NON-COVERAGE
DISCOGENIC PAIN TREATMENT CLINICAL POLICY Policy Number: OUTPATIENT 037.12 T2 Effective Date: February 1, 2016 Table of Contents BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS.. APPLICABLE LINES OF BUSINESS/PRODUCTS... NON-COVERAGE
Intradiscal Pressure Study of Percutaneous Disc Decompression With Nucleoplasty in Human Cadavers
 Intradiscal Pressure Study of Percutaneous Disc Decompression With Nucleoplasty in Human Cadavers SPINE Volume 28, Number 7, pp 661 665 2003, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Yung C. Chen, MD,* Sang-heon
Intradiscal Pressure Study of Percutaneous Disc Decompression With Nucleoplasty in Human Cadavers SPINE Volume 28, Number 7, pp 661 665 2003, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Yung C. Chen, MD,* Sang-heon
ISPI Newsletter Archive Lumbar Spine Surgery
 ISPI Newsletter Archive Lumbar Spine Surgery January 2005 Effects of Charite Artificial Disc on the Implanted and Adjacent Spinal Segments Mechanics Using a Hybrid Testing Protocol Spine. 30(24):2755-2764,
ISPI Newsletter Archive Lumbar Spine Surgery January 2005 Effects of Charite Artificial Disc on the Implanted and Adjacent Spinal Segments Mechanics Using a Hybrid Testing Protocol Spine. 30(24):2755-2764,
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
 A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
Pain Management. the primary procedure allowable reimbursement; 50% of add-on. Injection/Destruction Procedures
 Pain Management In addition to the General Guidelines, this section applies to the unique guidelines for Pain Management services. I. Reimbursement for Pain Management Services A. Pain Management Base
Pain Management In addition to the General Guidelines, this section applies to the unique guidelines for Pain Management services. I. Reimbursement for Pain Management Services A. Pain Management Base
Non Surgical Management of Back pain. Dr Pankaj Wadhwa MBBS,MD(Anaesth),DNB,Dip.Acu, FIPP, Fellowship in Pain Management.
 Non Surgical Management of Back pain. Dr Pankaj Wadhwa MBBS,MD(Anaesth),DNB,Dip.Acu, FIPP, Fellowship in Pain Management. MAGNITUDE OF THE PROBLEM It is one of the commonest experiences of humankind. It
Non Surgical Management of Back pain. Dr Pankaj Wadhwa MBBS,MD(Anaesth),DNB,Dip.Acu, FIPP, Fellowship in Pain Management. MAGNITUDE OF THE PROBLEM It is one of the commonest experiences of humankind. It
Spine DJD Nomenclature. Sonia K Ghei, MD
 Spine DJD Nomenclature Sonia K Ghei, MD Recommendations of the Combined Task Forces of the North American Spine Society, American Society of Spine Radiology, and American Society of Neuroradiology http://www.asnr.org/spine_nomenclature/
Spine DJD Nomenclature Sonia K Ghei, MD Recommendations of the Combined Task Forces of the North American Spine Society, American Society of Spine Radiology, and American Society of Neuroradiology http://www.asnr.org/spine_nomenclature/
White Paper: Reducing Utilization Concerns Regarding Spinal Fusion and Artificial Disc Implants
 White Paper: Reducing Utilization Concerns Regarding Spinal Fusion and Artificial Disc Implants For Health Plans, Medical Management Organizations and TPAs Executive Summary Back pain is one of the most
White Paper: Reducing Utilization Concerns Regarding Spinal Fusion and Artificial Disc Implants For Health Plans, Medical Management Organizations and TPAs Executive Summary Back pain is one of the most
Herniated Disk in the Lower Back
 Nader M. Hebela, MD Fellow of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons http://orthodoc.aaos.org/hebela Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Neurological Institute Al Maryah Island
Nader M. Hebela, MD Fellow of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons http://orthodoc.aaos.org/hebela Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Neurological Institute Al Maryah Island
1 REVISOR 5223.0070. (4) Pain associated with rigidity (loss of motion or postural abnormality) or
 1 REVISOR 5223.0070 5223.0070 MUSCULOSKELETAL SCHEDULE; BACK. Subpart 1. Lumbar spine. The spine rating is inclusive of leg symptoms except for gross motor weakness, bladder or bowel dysfunction, or sexual
1 REVISOR 5223.0070 5223.0070 MUSCULOSKELETAL SCHEDULE; BACK. Subpart 1. Lumbar spine. The spine rating is inclusive of leg symptoms except for gross motor weakness, bladder or bowel dysfunction, or sexual
.org. Cervical Radiculopathy (Pinched Nerve) Anatomy. Cause
 Cervical Radiculopathy (Pinched Nerve) Page ( 1 ) Cervical radiculopathy, commonly called a pinched nerve occurs when a nerve in the neck is compressed or irritated where it branches away from the spinal
Cervical Radiculopathy (Pinched Nerve) Page ( 1 ) Cervical radiculopathy, commonly called a pinched nerve occurs when a nerve in the neck is compressed or irritated where it branches away from the spinal
REVIEW DECISION. Review Reference #: R0103014 Board Decision under Review: March 3, 2009
 REVIEW DECISION Re: Review Reference #: R0103014 Board Decision under Review: March 3, 2009 Date: Review Officer: Lyall Zucko The worker requests a review of the decision of WorkSafeBC (the Board) dated
REVIEW DECISION Re: Review Reference #: R0103014 Board Decision under Review: March 3, 2009 Date: Review Officer: Lyall Zucko The worker requests a review of the decision of WorkSafeBC (the Board) dated
Lower Back Pain. Introduction. Anatomy
 Lower Back Pain Introduction Back pain is the number one problem facing the workforce in the United States today. To illustrate just how big a problem low back pain is, consider these facts: Low back pain
Lower Back Pain Introduction Back pain is the number one problem facing the workforce in the United States today. To illustrate just how big a problem low back pain is, consider these facts: Low back pain
Spinal Surgery 2. Teaching Aims. Common Spinal Pathologies. Disc Degeneration. Disc Degeneration. Causes of LBP 8/2/13. Common Spinal Conditions
 Teaching Aims Spinal Surgery 2 Mr Mushtaque A. Ishaque BSc(Hons) BChir(Cantab) DM FRCS FRCS(Ed) FRCS(Orth) Hunterian Professor at The Royal College of Surgeons of England Consultant Orthopaedic Spinal
Teaching Aims Spinal Surgery 2 Mr Mushtaque A. Ishaque BSc(Hons) BChir(Cantab) DM FRCS FRCS(Ed) FRCS(Orth) Hunterian Professor at The Royal College of Surgeons of England Consultant Orthopaedic Spinal
Neck Pain Overview Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment Options
 Neck Pain Overview Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment Options Neck pain is one of the most common forms of pain for which people seek treatment. Most individuals experience neck pain at some point during
Neck Pain Overview Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment Options Neck pain is one of the most common forms of pain for which people seek treatment. Most individuals experience neck pain at some point during
An Algorithmic Approach to Diagnosis and Management of Low Back Pain
 Manchikanti, Singh An Algorithmic Approach to Diagnosis and Management of Low Back Pain 597 An Algorithmic Approach to Diagnosis and Management of Low Back Pain Laxmaiah Manchikanti, MD Vijay Singh, MD
Manchikanti, Singh An Algorithmic Approach to Diagnosis and Management of Low Back Pain 597 An Algorithmic Approach to Diagnosis and Management of Low Back Pain Laxmaiah Manchikanti, MD Vijay Singh, MD
Case Studies Updated 10.24.11
 S O L U T I O N S Case Studies Updated 10.24.11 Hill DT Solutions Cervical Decompression Case Study An 18-year-old male involved in a motor vehicle accident in which his SUV was totaled suffering from
S O L U T I O N S Case Studies Updated 10.24.11 Hill DT Solutions Cervical Decompression Case Study An 18-year-old male involved in a motor vehicle accident in which his SUV was totaled suffering from
SPINAL STENOSIS Information for Patients WHAT IS SPINAL STENOSIS?
 SPINAL STENOSIS Information for Patients WHAT IS SPINAL STENOSIS? The spinal canal is best imagined as a bony tube through which nerve fibres pass. The tube is interrupted between each pair of adjacent
SPINAL STENOSIS Information for Patients WHAT IS SPINAL STENOSIS? The spinal canal is best imagined as a bony tube through which nerve fibres pass. The tube is interrupted between each pair of adjacent
Patient Guide to Lower Back Surgery
 The following is a sampling of products offered by Zimmer Spine for use in Open Lumbar Fusion procedures. Patient Guide to Lower Back Surgery Open Lumbar Fusion Dynesys The Dynesys Dynamic Stabilization
The following is a sampling of products offered by Zimmer Spine for use in Open Lumbar Fusion procedures. Patient Guide to Lower Back Surgery Open Lumbar Fusion Dynesys The Dynesys Dynamic Stabilization
Spine Trauma: When to Transfer. Alexander Ching, MD Director, Orthopaedic Spine Trauma OHSU
 Spine Trauma: When to Transfer Alexander Ching, MD Director, Orthopaedic Spine Trauma OHSU Disclosures Depuy Spine Consultant (teaching and courses) Department education and research funds Atlas Spine
Spine Trauma: When to Transfer Alexander Ching, MD Director, Orthopaedic Spine Trauma OHSU Disclosures Depuy Spine Consultant (teaching and courses) Department education and research funds Atlas Spine
Here is a SPECIAL REPORT on Spinal Decompression Therapy
 Here is a SPECIAL REPORT on Spinal Decompression Therapy YOU MAY BE ABLE TO AVOID SURGERY WITH SPINAL DECOMPRESSION THERAPY If you or a loved one is suffering from disc herniation(s), degenerative joint
Here is a SPECIAL REPORT on Spinal Decompression Therapy YOU MAY BE ABLE TO AVOID SURGERY WITH SPINAL DECOMPRESSION THERAPY If you or a loved one is suffering from disc herniation(s), degenerative joint
LOW BACK PAIN; MECHANICAL
 1 ORTHO 16 LOW BACK PAIN; MECHANICAL Background This case definition was developed by the Armed Forces Health Surveillance Center (AFHSC) for the purpose of epidemiological surveillance of a condition
1 ORTHO 16 LOW BACK PAIN; MECHANICAL Background This case definition was developed by the Armed Forces Health Surveillance Center (AFHSC) for the purpose of epidemiological surveillance of a condition
Management of spinal cord compression
 Management of spinal cord compression (SUMMARY) Main points a) On diagnosis, all patients should receive dexamethasone 10mg IV one dose, then 4mg every 6h. then switched to oral dose and tapered as tolerated
Management of spinal cord compression (SUMMARY) Main points a) On diagnosis, all patients should receive dexamethasone 10mg IV one dose, then 4mg every 6h. then switched to oral dose and tapered as tolerated
Title: Interspinous Process Decompression with the X-Stop Device for Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: A Retrospective Review. Authors: Jennifer R.
 Title: Interspinous Process Decompression with the X-Stop Device for Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: A Retrospective Review. Authors: Jennifer R. Madonia-Barr, MS, PA-C and David L. Kramer, MD Institution: Connecticut
Title: Interspinous Process Decompression with the X-Stop Device for Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: A Retrospective Review. Authors: Jennifer R. Madonia-Barr, MS, PA-C and David L. Kramer, MD Institution: Connecticut
Patient Information. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion Surgery (ACDF).
 Patient Information. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion Surgery (ACDF). Understanding your spine Disc Between each pair of vertebrae there is a disc that acts as a cushion to protect the vertebra,
Patient Information. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion Surgery (ACDF). Understanding your spine Disc Between each pair of vertebrae there is a disc that acts as a cushion to protect the vertebra,
Spine or Sacrum? Diagnosing S.I. Joint Pain
 Nevada Academy of Family Physicians, Winter CME Meeting Harrah s Lake Tahoe, January 28, 2016 Spine or Sacrum? Diagnosing S.I. Joint Pain To obtain an appropriate pain diagnosis. Direct the patient to
Nevada Academy of Family Physicians, Winter CME Meeting Harrah s Lake Tahoe, January 28, 2016 Spine or Sacrum? Diagnosing S.I. Joint Pain To obtain an appropriate pain diagnosis. Direct the patient to
Clinical Guideline. Low Back Pain Orthopaedics. Princess Alexandra Hospital Emergency Department. 1 Purpose. 2 Background
 Princess Alexandra Hospital Emergency Department Clinical Guideline Orthopaedics Review Officer: Katherine Isoardi Version no: 1 Approval date: 18/03/2015 Review date: 18/03/2017 Approving Officer Dr James
Princess Alexandra Hospital Emergency Department Clinical Guideline Orthopaedics Review Officer: Katherine Isoardi Version no: 1 Approval date: 18/03/2015 Review date: 18/03/2017 Approving Officer Dr James
6/3/2011. High Prevalence and Incidence. Low back pain is 5 th most common reason for all physician office visits in the U.S.
 High Prevalence and Incidence Prevalence 85% of Americans will experience low back pain at some time in their life. Incidence 5% annual Timothy C. Shen, M.D. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Sub-specialty
High Prevalence and Incidence Prevalence 85% of Americans will experience low back pain at some time in their life. Incidence 5% annual Timothy C. Shen, M.D. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Sub-specialty
Patient Information. Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Surgery (LLIF).
 Patient Information. Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Surgery (LLIF). Understanding your spine Disc Between each pair of vertebrae there is a disc that acts as a cushion to protect the vertebra, allows
Patient Information. Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Surgery (LLIF). Understanding your spine Disc Between each pair of vertebrae there is a disc that acts as a cushion to protect the vertebra, allows
Herniated Disk. This reference summary explains herniated disks. It discusses symptoms and causes of the condition, as well as treatment options.
 Herniated Disk Introduction Your backbone, or spine, has 24 moveable vertebrae made of bone. Between the bones are soft disks filled with a jelly-like substance. These disks cushion the vertebrae and keep
Herniated Disk Introduction Your backbone, or spine, has 24 moveable vertebrae made of bone. Between the bones are soft disks filled with a jelly-like substance. These disks cushion the vertebrae and keep
Case Series on Chronic Whiplash Related Neck Pain Treated with Intraarticular Zygapophysial Joint Regeneration Injection Therapy
 Pain Physician 2007; 10:313-318 ISSN 1533-3159 Case Series Case Series on Chronic Whiplash Related Neck Pain Treated with Intraarticular Zygapophysial Joint Regeneration Injection Therapy R. Allen Hooper
Pain Physician 2007; 10:313-318 ISSN 1533-3159 Case Series Case Series on Chronic Whiplash Related Neck Pain Treated with Intraarticular Zygapophysial Joint Regeneration Injection Therapy R. Allen Hooper
EPIDURAL STEROID AND FACET INJECTIONS FOR SPINAL PAIN
 MEDICAL POLICY EPIDURAL STEROID AND FACET INJECTIONS FOR SPINAL PAIN Policy Number: 2015T0004W Effective Date: December 1, 2015 Table of Contents BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS COVERAGE RATIONALE APPLICABLE CODES..
MEDICAL POLICY EPIDURAL STEROID AND FACET INJECTIONS FOR SPINAL PAIN Policy Number: 2015T0004W Effective Date: December 1, 2015 Table of Contents BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS COVERAGE RATIONALE APPLICABLE CODES..
Herniated Lumbar Disc
 Herniated Lumbar Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The spine is made up of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The disc is a combination of strong
Herniated Lumbar Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The spine is made up of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The disc is a combination of strong
Patient Guide to Neck Surgery
 The following is a sampling of products offered by Zimmer Spine for use in Anterior Cervical Fusion procedures. Patient Guide to Neck Surgery Anterior Cervical Fusion Trinica Select With the Trinica and
The following is a sampling of products offered by Zimmer Spine for use in Anterior Cervical Fusion procedures. Patient Guide to Neck Surgery Anterior Cervical Fusion Trinica Select With the Trinica and
Orthopaedic Spine Center. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs
 Orthopaedic Spine Center Graham Calvert MD James Woodall MD PhD Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs The cervical spine consists of the bony vertebrae, discs, nerves and other structures.
Orthopaedic Spine Center Graham Calvert MD James Woodall MD PhD Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs The cervical spine consists of the bony vertebrae, discs, nerves and other structures.
Minimalinvasive treatment of hip joint arthrosis
 Minimalinvasive treatment of hip joint arthrosis Maybe, you have already noticed the following cases histories in your practice: A patient came for treatment of a lumbar prolapsed intervertebral disc.
Minimalinvasive treatment of hip joint arthrosis Maybe, you have already noticed the following cases histories in your practice: A patient came for treatment of a lumbar prolapsed intervertebral disc.
Cervical Spine Radiculopathy: Convervative Treatment. Christos K. Yiannakopoulos, MD Orthopaedic Surgeon
 Cervical Spine Radiculopathy: Convervative Treatment Christos K. Yiannakopoulos, MD Orthopaedic Surgeon Laboratory for the Research of the Musculoskeletal System, University of Athens & IASO General Hospital,
Cervical Spine Radiculopathy: Convervative Treatment Christos K. Yiannakopoulos, MD Orthopaedic Surgeon Laboratory for the Research of the Musculoskeletal System, University of Athens & IASO General Hospital,
EPIDURAL STEROID AND FACET INJECTIONS FOR SPINAL PAIN
 CLINICAL POLICY EPIDURAL STEROID AND FACET INJECTIONS FOR SPINAL PAIN Policy Number: PAIN 019.16 T2 Effective Date: December 1, 2015 Table of Contents CONDITIONS OF COVERAGE... BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS..
CLINICAL POLICY EPIDURAL STEROID AND FACET INJECTIONS FOR SPINAL PAIN Policy Number: PAIN 019.16 T2 Effective Date: December 1, 2015 Table of Contents CONDITIONS OF COVERAGE... BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS..
Adult Spine Rotation Specific Evaluation Orthopaedic Surgery Training Program School of Medicine, Queen s University
 Adult Spine Rotation Specific Evaluation Orthopaedic Surgery Training Program School of Medicine, Queen s University CanMEDS Roles / Competencies Name: PGY Rotation Dates: s s Exceeds N/A Attending Staff:
Adult Spine Rotation Specific Evaluation Orthopaedic Surgery Training Program School of Medicine, Queen s University CanMEDS Roles / Competencies Name: PGY Rotation Dates: s s Exceeds N/A Attending Staff:
WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 1708/15
 WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 1708/15 BEFORE: E. Kosmidis : Vice-Chair E. Tracey : Member Representative of Employers C. Salama : Member Representative of Workers HEARING:
WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 1708/15 BEFORE: E. Kosmidis : Vice-Chair E. Tracey : Member Representative of Employers C. Salama : Member Representative of Workers HEARING:
The Newest Breakthrough In Non- Surgical Treatment of Herniated or Degenerative Discs
 The Newest Breakthrough In Non- Surgical Treatment of Herniated or Degenerative Discs The DRX 9000 is Your Answer To Persistent Back Pain To People Who Want To Be Rid Of Lower Back Pain But Think They
The Newest Breakthrough In Non- Surgical Treatment of Herniated or Degenerative Discs The DRX 9000 is Your Answer To Persistent Back Pain To People Who Want To Be Rid Of Lower Back Pain But Think They
BRYAN. Cervical Disc System. Patient Information
 BRYAN Cervical Disc System Patient Information 3 BRYAN Cervical Disc System PATIENT INFORMATION BRYAN Cervical Disc System PATIENT INFORMATION 1 BRYAN Cervical Disc System This patient information brochure
BRYAN Cervical Disc System Patient Information 3 BRYAN Cervical Disc System PATIENT INFORMATION BRYAN Cervical Disc System PATIENT INFORMATION 1 BRYAN Cervical Disc System This patient information brochure
Neck Pain Frequently Asked Questions. Moe R. Lim, MD UNC Orthopaedics (919-96B-ONES) UNC Spine Center (919-957-6789)
 Neck Pain Frequently Asked Questions Moe R. Lim, MD UNC Orthopaedics (919-96B-ONES) UNC Spine Center (919-957-6789) Neck Pain Human Spine 25 bones Cervical (7) Thoracic (12) Lumbar (5) Sacrum Human Spine
Neck Pain Frequently Asked Questions Moe R. Lim, MD UNC Orthopaedics (919-96B-ONES) UNC Spine Center (919-957-6789) Neck Pain Human Spine 25 bones Cervical (7) Thoracic (12) Lumbar (5) Sacrum Human Spine
American Journal of Pain Management Vol. 7 No. 2 April 1997
 American Journal of Pain Management Vol. 7 No. 2 April 1997 Emerging Technologies: Preliminary Findings DECOMPRESSION, REDUCTION, AND STABILIZATION OF THE LUMBAR SPINE: A COST-EFFECTIVE TREATMENT FOR LUMBOSACRAL
American Journal of Pain Management Vol. 7 No. 2 April 1997 Emerging Technologies: Preliminary Findings DECOMPRESSION, REDUCTION, AND STABILIZATION OF THE LUMBAR SPINE: A COST-EFFECTIVE TREATMENT FOR LUMBOSACRAL
