Condensed Molasses Solubles and Corn Steep Liquor As Protein Supplements for Range Cows
|
|
|
- Jordan Harrell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Condensed Molasses Solubles and Corn Steep Liquor As Protein Supplements for Range Cows K.S. Lusby, S.L. Armbruster and M.J. Dvorak Story in Brief Corn steep liquor (CSL) and condensed molasses solubles (CMS) were compared in two trials to cottonseed meal as protein supplements for wintering dry, pregnant Hereford cows on native range. In trial I, 48 cows were assigned to four protein treatments: negative control, positive control, CMS and CSL that furnished.30,.64,.57 and.66 Ib supplemental crude protein per head per day, respectively. Cows were group-fed 6 days per week. Weight losses for 112 days were greatest for negative control and CMS and least for positive control and CSL. Rumen ammonia-n levels at I-and 4-hr postfeeding were higher (P<.05) for CMS and CSL than for either control. In trial 2, 60 cows were individuallv fed 6 days each week four protein supplements: negative control, positive contro'l, CSM and CSL to provide 8,.51,.40 and.511b crude protein per day for 84 days, respectively. Weight losses after 56 and 84 days of supplementation and condition losses after 84 days were lower (P<.Ol) for cows fed the positive control and CSL than for the negative control and CMS. Weight losses for the negative control, positive control, CMS and CSt,. were 44.0, 11.0,44.0 and 14.0 Ib after 56 days and 57.0,11.0,51.0 and 22.0 Ib after 84 days, respectively. Condition losses were.96,.33,.90 and.28, respectively, after 84 days. Rumen ammonia levels were higher at I-and 4-hr postfeeding for cows fed both liquid supplements than for controls. The CSL supplement contained 72 percent of the crude protein as amino acids compared to 39 percent for CSL. Tungstic acid precipitable protein was much higher in CSL (35 percent) than in CMS (12 percent). Corn steep liquor appeared to be about equal to cottonseed meal for wintering dry, pregnant cows on native range. Introduction Liquid supplements contain a variety of ingredients, many of which are byproducts from the manufacture of foods, alcoholic beverages, glutamic acid and other products. The increased use of liquid by-products as feed ingredients has been caused by several factors, among which are the high cost of molasses, poor results with urea-molasses for cattle consuming low quality roughage and environmental regulations prohibiting the dumping of wastes. Little is known about the composition of many liquid feed ingredients or their usefulness as protein sources to ruminants fed low quality roughage. If these ingredients have nitrogenous fractions that are mostly ammonia, urea or ammonium compounds, they will likely perform no better than urea-molasses mixes. However, if their nitrogen fractions are high in amino acids, peptides and proteins of plant or microbial origin, some by-products could be acceptable protein sources for ruminants, 40 Oklahoma Agricultural Experiment Station
2 Two of the most common by-products in liquid suppl~ments are condensed fermented corn extractives, commonly referred to as corn steep liquor (CSL) and condensed molasses solubles (CMS). Corn steep liquor is obtained during the wet milling of corn and contains most of the soluble proteins of corn. Condensed molasses solubles is the residue from molasses that has been used in various fermentations to produce glutamic acid, citric acid, ethanol and other products. The objective of this research was to evaluate CSL and CMS as protein sources for beef cows grazing dormant native range. Materials and Methods mall. Forty-eight dry, pregnant Hereford cows were allotted by weight to four supplemental protein treatments (Table I). Treatments were: negative control,.30 Ib crude protein (CP) per day; positive control,.62 Ib CP per day; CMS,.62 Ib CP per day; and CSL,.62 Ib per day. Each treatment was replicated twice with each replicate grazing a pasture of about 80 acres. Forage consisted of native tallgrass with little bluestem, big bluestem, switchgrass and Indiangrass. All supplements were calculated to be approximately isocaloric and to provide equal amounts of phosphorus and potassium. Initially cows were offered liquid supplements ad libitum in lick tanks filled twice weekly. However, it was apparent after I week that the liquid supplements were very palatable and that all supplement was consumed within a few hours after the tanks were filled. Thereafter, supplements were fed 6 days per week with dry supplements fed in metal troughs and liquid supplements fed in lick feeders made from metal drums. Table 1. Percent composition of supplements fed in trial 1 Ingredient Negative control Treatments Condensed molasses Positive solubles control (CMS) Corn steep liquor (CSL) Cottonseedmeal Corn, ground Dicalciumphosphate Salt Potassiumchloride Tracemineral premix VitaminA (30,000 IUlg) Cane molasses CMS CSL Ammoniumpolyphosphate Phosphoricacid Analysis (as fed) Dry matter,% Crude protein, % Animal Science Research Report 41
3 Liquid supplements were mixed at a commercial facilityand stored in 55 gal steel drums until feeding. Dry supplements were manufactured at the Oklahoma State University feedmill. Cows were weighed after overnight withdrawal from feed and water at the beginning of the study and at 28-day intervals thereafter. The trial was conducted for 112days, from November 22, 1978, to March 3, One animal from each CSL replicate refused to eat supplement and was removed from the study; both cows were extremely timid and refused to approach the feeders with others present. One cow was removed from the positive control because she aborted, and one cow was removed from the negative control because she calved during the study. In mid-january cows from one replicate of each treatment were fed their supplements individually. Rumen fluid samples were withdrawn via stomach tube at I hour and 4 hours after feeding for rumen ammonia analyses. Microbial action was stopped in rumen fluid by adding 5 g of meta-phosphoric acid per 50 ml of rumen fluid. Samples were then frozen for subsequent rumen ammonia analysis. mal 2 Sixty dry, pregnant Hereford cows were allotted by weight to four supplemental protein treatments (Table 2). Treatments were: negative control (8 percent CP), positive control (24 percent CP), CMS (16 percent CP) and CSL (18 percent CP). Liquid supplements were again mixed at a commercial delivered and stored in bulk rather than drums as in trial 1. facility but were Table 2. Percent composition of supplements fed in trial 2 Treatments Condensed Com molasses steep Negative Positive solubles liquor Ingredient control control (CMS) (CSL) Cottonseedmeal 48.0 Corn, ground Dicalciumphosphate Sail Potassiumchloride Tracemineral mix VitaminA (30,000 IU/g) CMS 71 CSL 71 Water 7.7 Cane molasses Sulfuric acid.5.5 Phosphoricacid Analysis (as-fed) Dry matter,% Crude protein, % ph Oklahoma Agricultural Experiment Station
4 Cows were gathered at 8 a.m., 6 days each week and fed their suppiements individually. Cows on all treatments grazed a common pasture with ample standing tallgrass forage as described in trial 1. The trial lasted 84 days, from December 7, 1979, to February 29, Large round bales of wheat straw were offered free choice on days when snow or ice covered the grass. During the first 56 days of the study, the positive control, CMS and CSL supplements were fed in isonitrogenous amounts based on bi-weekly analysis of supplements. The negative control was fed to provide one-third the CP of the positive control. At these levels of consumption, all supplements were formulated to provide equal amounts of supplemental energy. During the last 28 days of the study, supplement levels were increased to maintain weight of the positive control cows. However, CMS was less palatable than the other supplements, so cows fed CMS were allowed to consume all they would in 45 minutes. Weights were taken, and rumen fluid was sampled from 10 cows on each treatment as described in trial 1. Cows were visually scored for condition at the beginning and end of the trial based on a rank of I '= very thin to 10 = very fat. Supplements were sampled weekly for analysis. Results and Discussion mall. Supplements were readily consumed by all cows (Table 3) except two that refused to approach the lick feeders and thus were removed from the study. The liquid supplements were palatable, evidenced by the fact that during the first week of Table 3. Weights, weight changes and rumen ammonia levels for cows in trial 1 Treatments Negative Positive Item control control CMS CSL Number of cows Replication Replication Initial cow wt Replication Replication Wt change, 112 days Replication Replication Supp consumption, kg/day Crude protein intake Rumen Ammonia-N mg/dl 1 hr postfeeding 1.78c 1.48c 22.90a 13.70b 4 hr postfeeding.46b 2.28b 8.84a 8.88a a.b,cmeans withdifferentsuperscript lettersdiffersignificantly(p<.05) Animal Science Research Report 43
5 the study cows on CSL and CMS consumed a 3-day allowance (over 12 Ib per head) within 4 hours. Apparently, ammonia toxicity is not a major problem with CSL- or CMS- based supplements. A similar intake of a urea-molasses supplement with 90 percent of the crude protein equivalent from urea would have provided about.30 gramsllb body weight of urea to a 950-lb cow and probably would have been toxic. Cows fed CSL gained weight during the II2-day trial, and their performance slightly exceeded that of positive control cows. Positive control cows tended to lose less weight than negative control cows. Weight losses of CMS cows tended to be between the positive and negative controls. Rumen ammonia-n levels at I-hour postfeeding were highest (P<.05) for the liquid supplements and lowest for control supplements. CSM produced higher (P<.05) levels than did CSL. Ammonia-!\' concentrations at 4-hour postfeeding were similar for CMS and CSL, with both liquid supplements producing more rumen ammonia (P<.05) than the control supplements. '!Hal 2. Cows grazing a single pasture were individually fed to measure supplement intake of each animal and to eliminate the pasture effects encountered in trial 1. Sulfuric.acid, a common intake limiter, was added to both liquid supplements (Table 2) at the manufacturing plant; and as a result, they were not as palatable as in trial 1. Three cows refused to eat the CMS supplement and were switched with two cows from the positive control and one cow from the negative control that would readily consume CMS. All CSL supplement and most of the CMS was readily consumed at the levels offered for the first 56 days of the trial (Table 4). When the supplement levels were increased during the final 28 days of the trial to maintain weight of the positive control cows, all but one cow on CSL consumed the increased supplement. Several cows fed CMS refused to consume a level that was isonitrogenous to the positive control. In addition to the presence of sulfuric acid, reduced supplement intake in trial 2 compared to trial 1 could be attributed to the absence of feeding competition and to the lower molasses content of the liquid supplements. The negative controls lost more (P<.OI) weight than the positive controls after 56 and 84 days. Cows fed CSL lost 8.0 Ibduring the final 28 days compared to no weight loss for the positive controls; however, one-half the weight loss in the CSL group occurred in one cow that consumed only 65 percent of her supplement during the last 28 days. Weight losses for the negative control and CMS groups were almost identical throughout the study. Condition score changes followed weight change patterns, with negative control and CMS cows losing more (P<.O 1) condition during the trial than positive control or CSL cows. Rumen ammonia-n concentrations for CMS and CSL were similar at I-hour postfeeding but were higher (P<.05) for CSL than CMS at 4 hours. Both liquid supplements produced higher (P<.05) rumen ammonia-n levels than the control supplements at both sampling times. Weight changes for cows fed CSL were similar to those of cows fed the cottonseed meal-based positive control supplements in both trials, indicating CSL is an effective protein source for cows on dormant range grass. Conversely, the performance of cows on CMS was about equal to that of cows fed the negative control supplements in both trials, suggesting CMS is a poorly utilized protein source for cows on low quality forage. A detailed analysis of the nitrogen fractions in the CMS and CSL supplements fed in trial 2 is shown in Table 5 and provides some explanation for the perform- 44 Oklahoma Agricultural Experiment Station
6 Table 4. Mean weights, weight changes and rumen ammonia levels for cows in trial2 Item Number of cows Condensed molasses Negative Positive solubles control control (CMS) Corn steep liquor (CSL) 15 Initial cow wt Wt change, 56 days b b Last 28 days Total, 84 days b b Condition score, initial Condition score change, 84 days Supplement consumption, Ib/day First 56 days Last 28 days Total 84 days Crude protein intake, Ib/day First 56 days Last 28 days Total 84 days Rumen Ammonia-N, mg/dl 1 hr postfeeding 63b 6.79b 4 hr postfeeding 3.89c 51c a.b,cmeanswithdifferentsuperscriptlettersdiffersignificantly(p<.05). ance differences. Although the analyses are of the complete supplements rather than of CSL and CMS alone, they should represent these ingredients since the CP of molasses is low, and molasses made up small and similar proportions (17.2 and 25.5 percent) of the CMS and CSL supplements, respectively. Amino acid analysis of unhydrolyzed samples of each supplement indicate the concentrations of free amino acids, while analysis after hydrolysis indicates total amino acids including those in peptides and proteins. Corn steep liquor contained 72.5 percent of the CP as amino acids compared to 39.3 percent for CMS. Subtracting free amino acids (unhydrolyzed) from total amino acids (hydrolyzed) shows that CSL contained about twice the level of amino acids in the form of peptides and proteins as CMS. TunKstic acid precipitable protein was much higher in CSL (35 percent) than in CMS (12 percent). Ammonia-N contributed 35.3 percent of the CP in CMS compared to 6.3 percent of the CP in CSL Animal Science Research Report 45
7 Table 5. Analysis of liquid supplements fed In trial 2 CMS CSL Item Hydrolyzed Unhydrolyzed Hydrolyzed Unhydrolyzed Amino acids, % of dry matter Aspartic acid Thereonine Serine Glutamic acid Proline Glycine Alanine Cystine Valine Methionine Isoleucine Leucine Tyrosine Phenylalanine Histidine Lysine Arginine Total amino acids, % of dry matter Crude protein, % of dry matter Composition (%) of crude protein, Ammonia-N Free amino acids8 Peptide and protein amino acidsb Tungstic acid precipitable protein "Calculated from unhydrolyzed sample. "Calculated from hydrolyzed sample Other research has shown that amino acids are utilized by rumen bacteria and that rumen microbial protein yield can be increased by adding amino acids to a diet containing urea as the sole nitrogen source. Amino acids are also converted to volatile fatty acids by rumen bacteria and have been shown to stimulate rumen cellulolytic activity. An Ohio study showed that corn steep liquor significantly increased crude fiber, cellulose and dry matter digestibilities in lambs when added to a 50 percent roughage ration. Results of this research indicate tht liquid supplement ingredients must be evaluated for type as well as amount of NPI\'. 46 Oklahoma Agricultural Experiment Station
FEEDING THE DAIRY COW DURING LACTATION
 Department of Animal Science FEEDING THE DAIRY COW DURING LACTATION Dairy Cattle Production 342-450A Page 1 of 8 Feeding the Dairy Cow during Lactation There are main stages in the lactation cycle of the
Department of Animal Science FEEDING THE DAIRY COW DURING LACTATION Dairy Cattle Production 342-450A Page 1 of 8 Feeding the Dairy Cow during Lactation There are main stages in the lactation cycle of the
CORN BY-PRODUCTS IN DAIRY COW RATIONS
 CORN BY-PRODUCTS IN DAIRY COW RATIONS Dennis Lunn, Ruminant Nutritionist Shur-Gain, Nutreco Canada Inc. CORN BY-PRODUCTS IN DAIRY COW RATIONS Dennis Lunn, Ruminant Nutritionist Shur-Gain, Nutreco Canada
CORN BY-PRODUCTS IN DAIRY COW RATIONS Dennis Lunn, Ruminant Nutritionist Shur-Gain, Nutreco Canada Inc. CORN BY-PRODUCTS IN DAIRY COW RATIONS Dennis Lunn, Ruminant Nutritionist Shur-Gain, Nutreco Canada
PRODUCING WHEY SILAGE FOR GROWING
 PRODUCING WHEY SILAGE FOR GROWING AND FINISHING CATTLE D.R. ZoBell and W. C. Burrell October 2002 AG 514 INTRODUCTION Roughage is the principal component of most cattle diets and as such can greatly influence
PRODUCING WHEY SILAGE FOR GROWING AND FINISHING CATTLE D.R. ZoBell and W. C. Burrell October 2002 AG 514 INTRODUCTION Roughage is the principal component of most cattle diets and as such can greatly influence
NUTRIENT SPECIFICATIONS OF TURKEY WASTE MATERIAL
 UTILIZATION OF TURKEY WASTE MATERIAL IN BEEF CATTLE DIETS Dale R. ZoBell, PhD, Beef Cattle Specialist Gary Anderson, Sanpete County Agent Clell Bagley, DVM, Extension Veterinarian July 1999 AG504 INTRODUCTION
UTILIZATION OF TURKEY WASTE MATERIAL IN BEEF CATTLE DIETS Dale R. ZoBell, PhD, Beef Cattle Specialist Gary Anderson, Sanpete County Agent Clell Bagley, DVM, Extension Veterinarian July 1999 AG504 INTRODUCTION
Introduction. Introduction Nutritional Requirements. Six Major Classes of Nutrients. Water 12/1/2011. Regional Hay School -- Bolivar, MO 1
 Cattle and Horse Nutrition Dona Goede Livestock Specialist Introduction Many health, reproductive and production problems can be prevented with good nutrition. Poor nutrition results in: Poor conception
Cattle and Horse Nutrition Dona Goede Livestock Specialist Introduction Many health, reproductive and production problems can be prevented with good nutrition. Poor nutrition results in: Poor conception
Summary. Keywords: methanol, glycerin, intake, beef cattle. Introduction
 Effect of Methanol Infusion on Intake and Digestion of a Grain-based Diet by Beef Cattle K.N. Winsco, N.M. Kenney, R.O. Dittmar, III, J.A. Coverdale, J.E. Sawyer, and T.A. Wickersham Texas A & M University,
Effect of Methanol Infusion on Intake and Digestion of a Grain-based Diet by Beef Cattle K.N. Winsco, N.M. Kenney, R.O. Dittmar, III, J.A. Coverdale, J.E. Sawyer, and T.A. Wickersham Texas A & M University,
CREEP FEEDING BEEF CALVES
 CREEP FEEDING BEEF CALVES CIRCULAR E-848 OKLAHOMA COOPERATIVE EXTENSION SERVICE DIVISION OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES AND NATURAL RESOURCES OKLAHOMA STATE UNIVERSITY 1 CREEP FEEDING BEEF CALVES Keith S. Lusby
CREEP FEEDING BEEF CALVES CIRCULAR E-848 OKLAHOMA COOPERATIVE EXTENSION SERVICE DIVISION OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES AND NATURAL RESOURCES OKLAHOMA STATE UNIVERSITY 1 CREEP FEEDING BEEF CALVES Keith S. Lusby
Effect of Flaxseed Inclusion on Ruminal Fermentation, Digestion and Microbial Protein Synthesis in Growing and Finishing Diets for Beef Cattle
 Effect of Flaxseed Inclusion on Ruminal Fermentation, Digestion and Microbial Protein Synthesis in Growing and Finishing Diets for Beef Cattle T.C. Gilbery, G.P. Lardy, D.S. Hagberg and M.L. Bauer NDSU
Effect of Flaxseed Inclusion on Ruminal Fermentation, Digestion and Microbial Protein Synthesis in Growing and Finishing Diets for Beef Cattle T.C. Gilbery, G.P. Lardy, D.S. Hagberg and M.L. Bauer NDSU
Protein and Energy Supplementation to Beef Cows Grazing New Mexico Rangelands
 Protein and Energy Supplementation to Beef Cows Grazing New Mexico Rangelands Cooperative Extension Service Circular 564 College of Agriculture and Home Economics CONTENTS General ruminant nutrition...
Protein and Energy Supplementation to Beef Cows Grazing New Mexico Rangelands Cooperative Extension Service Circular 564 College of Agriculture and Home Economics CONTENTS General ruminant nutrition...
Forage Crises? Extending Forages and Use of Non-forage Fiber Sources. Introduction
 Forage Crises? Extending Forages and Use of Non-forage Fiber Sources Mike Allen and Jennifer Voelker Michigan State University Dept. of Animal Science Introduction Forage availability is sometimes limited
Forage Crises? Extending Forages and Use of Non-forage Fiber Sources Mike Allen and Jennifer Voelker Michigan State University Dept. of Animal Science Introduction Forage availability is sometimes limited
Understanding Feed Analysis Terminology
 Understanding Feed Analysis Terminology One of the most important steps in developing a ration suitable for dairy animals is feed testing. It is essential to have a starting point in order to formulate
Understanding Feed Analysis Terminology One of the most important steps in developing a ration suitable for dairy animals is feed testing. It is essential to have a starting point in order to formulate
Feeding Corn to Beef Cows
 ExEx 2048 September 2005 Animal & Range Sciences COLLEGE OF AGRICULTURE & BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES / SOUTH DAKOTA STATE UNIVERSITY / USDA Feeding Corn to Beef Cows Cody Wright, Extension beef specialist In
ExEx 2048 September 2005 Animal & Range Sciences COLLEGE OF AGRICULTURE & BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES / SOUTH DAKOTA STATE UNIVERSITY / USDA Feeding Corn to Beef Cows Cody Wright, Extension beef specialist In
Distillers Grains for Beef Cattle
 Distillers Grains for Beef Cattle Terry Klopfenstein Distillers byproducts are excellent feed resources for feedlot cattle. Distillers byproducts are normally available for use in feedlot finishing diets
Distillers Grains for Beef Cattle Terry Klopfenstein Distillers byproducts are excellent feed resources for feedlot cattle. Distillers byproducts are normally available for use in feedlot finishing diets
ROLLED VERSUS WHOLE CORN: EFFECTS ON RUMINAL FERMENTATION OF FEEDLOT STEERS
 ROLLED VERSUS WHOLE CORN: EFFECTS ON RUMINAL FERMENTATION OF FEEDLOT STEERS D. S. Secrist 1, F. N. Owens 2, W. J. Hill 1 and S. D. Welty 3 Story in Brief The differences between rolled (2 particle sizes)
ROLLED VERSUS WHOLE CORN: EFFECTS ON RUMINAL FERMENTATION OF FEEDLOT STEERS D. S. Secrist 1, F. N. Owens 2, W. J. Hill 1 and S. D. Welty 3 Story in Brief The differences between rolled (2 particle sizes)
How To Feed Cows In The Winter
 A l a s k a L i v e s t o c k S e r i e s Winter Feeding Programs For Beef Cattle and Calves LPM-00741 Before making management and feeding decisions about beef cattle and calves, consider the following
A l a s k a L i v e s t o c k S e r i e s Winter Feeding Programs For Beef Cattle and Calves LPM-00741 Before making management and feeding decisions about beef cattle and calves, consider the following
Land O Lakes Feed DDGS. Nutrients Concentrate: United States Ethanol Outlook. A Growing Opportunity
 DDGS A Growing Opportunity Dr. Harold Tilstra Region Manager Land O Lakes Feed hdtilstra@landolakes.com 4/9/2004 Land O' Lakes Feed; Tilstra 2 Land O Lakes Feed Vision: To To be the leading animal nutrition
DDGS A Growing Opportunity Dr. Harold Tilstra Region Manager Land O Lakes Feed hdtilstra@landolakes.com 4/9/2004 Land O' Lakes Feed; Tilstra 2 Land O Lakes Feed Vision: To To be the leading animal nutrition
Understanding CNCPS and CPM: Biology, Modeling, and Best Cost Applications for Balancing the Nutrient Requirements in Dairy Diets
 Understanding CNCPS and CPM: Biology, Modeling, and Best Cost Applications for Balancing the Nutrient Requirements in Dairy Diets T. R. Overton, M. E. Van Amburgh, and L. E. Chase Department of Animal
Understanding CNCPS and CPM: Biology, Modeling, and Best Cost Applications for Balancing the Nutrient Requirements in Dairy Diets T. R. Overton, M. E. Van Amburgh, and L. E. Chase Department of Animal
The Production and Use of High-Valued Canola Protein Concentrates
 The Production and Use of High-Valued Canola Protein Concentrates David D. Maenz Chief Scientific Officer MCN BioProducts Inc. Conventional Canola Processing Whole seed Solvent extraction or double press
The Production and Use of High-Valued Canola Protein Concentrates David D. Maenz Chief Scientific Officer MCN BioProducts Inc. Conventional Canola Processing Whole seed Solvent extraction or double press
Alternative Feeds for Beef Cattle
 DIVISION OF AGRICULTURE RESEARCH & EXTENSION University of Arkansas System Agriculture and Natural Resources Alternative Feeds for Beef Cattle FSA3047 Shane Gadberry Associate Professor - Animal Science
DIVISION OF AGRICULTURE RESEARCH & EXTENSION University of Arkansas System Agriculture and Natural Resources Alternative Feeds for Beef Cattle FSA3047 Shane Gadberry Associate Professor - Animal Science
Grouping to Increase Milk Yield and Decrease Feed Costs
 61 Grouping to Increase Milk Yield and Decrease Feed Costs Michael S. Allen 1 Department of Animal Science Michigan State University Abstract There are many advantages of grouping cows to optimize their
61 Grouping to Increase Milk Yield and Decrease Feed Costs Michael S. Allen 1 Department of Animal Science Michigan State University Abstract There are many advantages of grouping cows to optimize their
Feedlot Lamb Nutrition
 Feedlot Lamb Nutrition Joseph S. Rook, D.V.M. MSU Extension & Ag Experiment Station College of Veterinary Medicine Due to the relatively small number of sizable lamb feeder operations in MI, practitioners
Feedlot Lamb Nutrition Joseph S. Rook, D.V.M. MSU Extension & Ag Experiment Station College of Veterinary Medicine Due to the relatively small number of sizable lamb feeder operations in MI, practitioners
Creep Feeding Beef Calves Dan E. Eversole, Extension Animal Scientist, Virginia Tech
 publication 400-003 Creep Feeding Beef Calves Dan E. Eversole, Extension Animal Scientist, Virginia Tech OVERVIEW Creep feeding is the managerial practice of supplying supplemental feed (usually concentrates)
publication 400-003 Creep Feeding Beef Calves Dan E. Eversole, Extension Animal Scientist, Virginia Tech OVERVIEW Creep feeding is the managerial practice of supplying supplemental feed (usually concentrates)
6/29/2009 6.8 5.3 TDN
 Common Sense Meat Goat-Nutrition Brian Freking OSU LeFlore Co. Extension Nutrition Feeding goats is the single largest expense behind the purchase cost of the animals. Can be as high as 60% of the total
Common Sense Meat Goat-Nutrition Brian Freking OSU LeFlore Co. Extension Nutrition Feeding goats is the single largest expense behind the purchase cost of the animals. Can be as high as 60% of the total
Full hand feeding of beef cattle quantities
 JANUARY 2007 PRIMEFACT 295 (REPLACES AGNOTE DAI-172) Full hand feeding of beef cattle quantities Bill McKiernan Research Leader Animal Production, Production Research, Orange Assessing the situation The
JANUARY 2007 PRIMEFACT 295 (REPLACES AGNOTE DAI-172) Full hand feeding of beef cattle quantities Bill McKiernan Research Leader Animal Production, Production Research, Orange Assessing the situation The
Managing Bermudagrass Pasture to Reduce Winter Hay Feeding in Beef Cattle Operations
 Oklahoma Cooperative Extension Service ANSI-3035 Managing Bermudagrass Pasture to Reduce Winter Hay Feeding in Beef Cattle Operations David Lalman Extension Beef Cattle Specialist, Animal Science Bob Woods
Oklahoma Cooperative Extension Service ANSI-3035 Managing Bermudagrass Pasture to Reduce Winter Hay Feeding in Beef Cattle Operations David Lalman Extension Beef Cattle Specialist, Animal Science Bob Woods
Response of Dairy Cows to Supplements of Energy and Protein in Early and Mid Lactation
 Response of Dairy Cows to Supplements of Energy and Protein in Early and Mid Lactation Ryan Law, Fiona Young and Conrad Ferris Innovative and practical management approaches to reduce nitrogen excretion
Response of Dairy Cows to Supplements of Energy and Protein in Early and Mid Lactation Ryan Law, Fiona Young and Conrad Ferris Innovative and practical management approaches to reduce nitrogen excretion
BEC Feed Solutions. Steve Blake BEC Feed Solutions
 BEC Feed Solutions Presenter: Steve Blake BEC Feed Solutions Nutritional Role of Phosphorus Phosphorus (P) is present in all cells in the body Essential for many digestive and metabolic processes, including
BEC Feed Solutions Presenter: Steve Blake BEC Feed Solutions Nutritional Role of Phosphorus Phosphorus (P) is present in all cells in the body Essential for many digestive and metabolic processes, including
EXTENSION CIRCULAR 422 FROM FEED TO MILK: UNDERSTANDING RUMEN FUNCTION
 EXTENSION CIRCULAR 422 FROM FEED TO MILK: UNDERSTANDING RUMEN FUNCTION CONTENTS Part I: Background in Basic Nutrition of Dairy Cattle... 1 Rumen physiology...1 Rumination and saliva production... 3 Function
EXTENSION CIRCULAR 422 FROM FEED TO MILK: UNDERSTANDING RUMEN FUNCTION CONTENTS Part I: Background in Basic Nutrition of Dairy Cattle... 1 Rumen physiology...1 Rumination and saliva production... 3 Function
DIGESTION is the physical and
 Digestion DIGESTION is the physical and chemical breakdown of feeds as they pass through the gastrointestinal tract. The structures of the gastrointestinal tract include the mouth, the esophagus, the stomach,
Digestion DIGESTION is the physical and chemical breakdown of feeds as they pass through the gastrointestinal tract. The structures of the gastrointestinal tract include the mouth, the esophagus, the stomach,
Animal Science Research Centre - Beef Unit Trial Results 2005 (a) Evaluation of head-cut whole crop wheat and barley for beef cattle
 Animal Science Research Centre - Beef Unit Trial Results 2005 (a) Evaluation of head-cut whole crop wheat and barley for beef cattle Introduction: A preliminary investigation at Harper Adams University
Animal Science Research Centre - Beef Unit Trial Results 2005 (a) Evaluation of head-cut whole crop wheat and barley for beef cattle Introduction: A preliminary investigation at Harper Adams University
AN EVALUATION OF DEXTROSE, LACTOSE, AND WHEY SOURCES IN PHASE 2 STARTER DIETS FOR WEANLING PIGS 1
 Swine Day 2007 AN EVALUATION OF DEXTROSE, LACTOSE, AND WHEY SOURCES IN PHASE 2 STARTER DIETS FOR WEANLING PIGS 1 J. R. Bergstrom, C. N. Groesbeck, J. M. Benz, M. D. Tokach, J. L. Nelssen, S. S. Dritz 2,
Swine Day 2007 AN EVALUATION OF DEXTROSE, LACTOSE, AND WHEY SOURCES IN PHASE 2 STARTER DIETS FOR WEANLING PIGS 1 J. R. Bergstrom, C. N. Groesbeck, J. M. Benz, M. D. Tokach, J. L. Nelssen, S. S. Dritz 2,
Ruminant Digestive System
 Ruminant Digestive System Complex structure with four compartments Source: Animal Feeding and Nutrition (Jurgens) Ruminant Characteristics Primarily herbivores Cattle, sheep, goats, deer, elk Camelids
Ruminant Digestive System Complex structure with four compartments Source: Animal Feeding and Nutrition (Jurgens) Ruminant Characteristics Primarily herbivores Cattle, sheep, goats, deer, elk Camelids
Effective Fiber for Dairy Cows
 Feed Management A Key Ingredient in Livestock and Poultry Nutrient Management Effective Fiber for Dairy Cows R. D. Shaver Professor and Extension Dairy Nutritionist Department of Dairy Science College
Feed Management A Key Ingredient in Livestock and Poultry Nutrient Management Effective Fiber for Dairy Cows R. D. Shaver Professor and Extension Dairy Nutritionist Department of Dairy Science College
Energy in the New Dairy NRC. Maurice L. Eastridge 1 Department of Animal Sciences The Ohio State University
 Energy in the New Dairy NRC Maurice L. Eastridge 1 Department of Animal Sciences The Ohio State University Introduction Energy is vital to the function of all cells, and thus physiologically, it is vital
Energy in the New Dairy NRC Maurice L. Eastridge 1 Department of Animal Sciences The Ohio State University Introduction Energy is vital to the function of all cells, and thus physiologically, it is vital
Payback News. Beef Cows-The Cheapest Mineral Isn t
 November, 2015 Volume 2, Issue 4 CHS Nutrition Payback News In this issue of Payback News: Beef Cows-The Cheapest Mineral Isn t Bull Wintering Tips Inside this issue: Beef Cows-The Cheapest Mineral Isn
November, 2015 Volume 2, Issue 4 CHS Nutrition Payback News In this issue of Payback News: Beef Cows-The Cheapest Mineral Isn t Bull Wintering Tips Inside this issue: Beef Cows-The Cheapest Mineral Isn
Copyright 2000-2003 Mark Brandt, Ph.D. 35
 Amino acid breakdown Amino acids comprise one of the three major energy sources for animals. They are an especially important energy source for carnivorous animals, and for all animals during early starvation
Amino acid breakdown Amino acids comprise one of the three major energy sources for animals. They are an especially important energy source for carnivorous animals, and for all animals during early starvation
THE EVALUATION OF DISTILLERS CO-PRODUCTS IN DAIRY BEEF PRODUCTION
 THE EVALUATION OF DISTILLERS CO-PRODUCTS IN DAIRY BEEF PRODUCTION Allen Trenkle Iowa State University Feeding dairy beef, predominantly Holstein steers, has evolved into a highly specialized segment of
THE EVALUATION OF DISTILLERS CO-PRODUCTS IN DAIRY BEEF PRODUCTION Allen Trenkle Iowa State University Feeding dairy beef, predominantly Holstein steers, has evolved into a highly specialized segment of
Selenium and Selenium Yeast Use in Feed. Division of Regulatory Services University of Kentucky April 25, 2005
 Selenium and Selenium Yeast Use in Feed Division of Regulatory Services University of Kentucky April 25, 2005 REVISED JULY 19, 2007 Meagan Davis, Feed Registration Specialist Selenium, long known for its
Selenium and Selenium Yeast Use in Feed Division of Regulatory Services University of Kentucky April 25, 2005 REVISED JULY 19, 2007 Meagan Davis, Feed Registration Specialist Selenium, long known for its
PROFICIENCY TESTING PROGRAMS FEED
 PROFICIENCY TESTING PROGRAMS FEED A13 Feed 14 Forages 22 A26a A42 A67 A67a Silages Amino acids Premix Pet food (10 rounds per year) Pet food (5 rounds per year) A = PTS accredited by COFRAC A = Circuit
PROFICIENCY TESTING PROGRAMS FEED A13 Feed 14 Forages 22 A26a A42 A67 A67a Silages Amino acids Premix Pet food (10 rounds per year) Pet food (5 rounds per year) A = PTS accredited by COFRAC A = Circuit
Separation of Amino Acids by Paper Chromatography
 Separation of Amino Acids by Paper Chromatography Chromatography is a common technique for separating chemical substances. The prefix chroma, which suggests color, comes from the fact that some of the
Separation of Amino Acids by Paper Chromatography Chromatography is a common technique for separating chemical substances. The prefix chroma, which suggests color, comes from the fact that some of the
Sheep Nutrition. Sheep Nutrition. Nutrient Needs. Sheep Nutrition Water. Products Produced. Use of Pasture\Range and Forages.
 Products Produced Muscle (Meat) Milk Fiber (wool, mohair, cashmere) Use of Pasture\Range and Forages Able to produce acceptable product on forage Nutrient Needs Water Energy (TDN, ME, or NE) Protein (CP
Products Produced Muscle (Meat) Milk Fiber (wool, mohair, cashmere) Use of Pasture\Range and Forages Able to produce acceptable product on forage Nutrient Needs Water Energy (TDN, ME, or NE) Protein (CP
The Effect of Citric Acid, Phytase, and Their Interaction on Gastric ph, and Ca, P, and Dry Matter Digestibilities
 The Effect of Citric Acid, Phytase, and Their Interaction on Gastric ph, and Ca, P, and Dry Matter Digestibilities J. P. Rice 1, R. S. Pleasant 2, and J. S. Radcliffe 1 1 Department of Animal Sciences
The Effect of Citric Acid, Phytase, and Their Interaction on Gastric ph, and Ca, P, and Dry Matter Digestibilities J. P. Rice 1, R. S. Pleasant 2, and J. S. Radcliffe 1 1 Department of Animal Sciences
AN ACCELERATED FEEDING STUDY
 AN ACCELERATED FEEDING STUDY FOR DAIRY BEEF STEERS D. R. ZoBell, Allen Young and Bruce Godfrey Utah State University September 2001 AG 512 INTRODUCTION A large number of Holstein bull (steer) calves are
AN ACCELERATED FEEDING STUDY FOR DAIRY BEEF STEERS D. R. ZoBell, Allen Young and Bruce Godfrey Utah State University September 2001 AG 512 INTRODUCTION A large number of Holstein bull (steer) calves are
Heat of combustion (gross energy)
 J.D. Pagan 71 MEASURING THE DIGESTIBLE ENERGY CONTENT OF HORSE FEEDS JOE D. PAGAN Kentucky Equine Research, Inc., Versailles, Kentucky, USA One of the most important measures of a horse feed s value is
J.D. Pagan 71 MEASURING THE DIGESTIBLE ENERGY CONTENT OF HORSE FEEDS JOE D. PAGAN Kentucky Equine Research, Inc., Versailles, Kentucky, USA One of the most important measures of a horse feed s value is
As grain prices fluctuate
 MICHIGAN STATE U N I V E R S I T Y EXTENSION Extension Bulletin E-3074 New December 2009 Incorporating Distiller s Grain in Beef Cattle Diets As grain prices fluctuate over time, beef cattle producers
MICHIGAN STATE U N I V E R S I T Y EXTENSION Extension Bulletin E-3074 New December 2009 Incorporating Distiller s Grain in Beef Cattle Diets As grain prices fluctuate over time, beef cattle producers
Effects of Supplemental Vitamin E with Different Oil Sources on Growth, Health, and Carcass Parameters of Preconditioned Beef Calves 1
 Oregon State University BEEF25 Beef Research Report Beef Cattle Sciences Effects of Supplemental Vitamin E with Different Oil Sources on Growth, Health, and Carcass Parameters of Preconditioned Beef Calves
Oregon State University BEEF25 Beef Research Report Beef Cattle Sciences Effects of Supplemental Vitamin E with Different Oil Sources on Growth, Health, and Carcass Parameters of Preconditioned Beef Calves
NITRATES IN LIVESTOCK FEED
 NITRATES IN LIVESTOCK FEED Dan B. Faulkner and Mike F. Hutjens University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign Drought conditions often result in poor pastures and reduced forage yields. Often producers wish
NITRATES IN LIVESTOCK FEED Dan B. Faulkner and Mike F. Hutjens University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign Drought conditions often result in poor pastures and reduced forage yields. Often producers wish
ALFALFA FOR BEEF COWS
 Fact Sheet 93-23 ALFALFA FOR BEEF COWS John Balliette, Eureka County Extension Educator Ron Torell, Northeast Area Livestock Specialist Introduction Protein and energy supplements do not necessarily need
Fact Sheet 93-23 ALFALFA FOR BEEF COWS John Balliette, Eureka County Extension Educator Ron Torell, Northeast Area Livestock Specialist Introduction Protein and energy supplements do not necessarily need
Uses and Abuses of NIR for Feed Analysis
 Uses and Abuses of NIR for Feed Analysis Dan Undersander 1 University of Wisconsin Madison, WI Introduction Dairymen use feed and forage testing to reduce feed costs and maximize production. As such, accuracy
Uses and Abuses of NIR for Feed Analysis Dan Undersander 1 University of Wisconsin Madison, WI Introduction Dairymen use feed and forage testing to reduce feed costs and maximize production. As such, accuracy
Protein. Protein. Why is protein important?
 Protein Protein Though protein is often perceived as an area of concern for vegans, it is actually very easily accessible on a vegan diet, particularly if a variety of plant foods are consumed regularly.
Protein Protein Though protein is often perceived as an area of concern for vegans, it is actually very easily accessible on a vegan diet, particularly if a variety of plant foods are consumed regularly.
Human Tubal Fluid (HTF) Media & Modifi ed Human Tubal Fluid (mhtf) Medium with Gentamicin
 Human Tubal Fluid (HTF) Media & Modifi ed Human Tubal Fluid (mhtf) Medium with Gentamicin HTF Media are intended for use in assisted reproductive procedures which include gamete and embryo manipulation
Human Tubal Fluid (HTF) Media & Modifi ed Human Tubal Fluid (mhtf) Medium with Gentamicin HTF Media are intended for use in assisted reproductive procedures which include gamete and embryo manipulation
What is Nitrite Toxicity? Georgia Cattleman, June 2002 John Andrae, Forage Extension Specialist
 What is Nitrite Toxicity? Georgia Cattleman, June 2002 John Andrae, Forage Extension Specialist Many beef producers are familiar with high nitrates in forages and their toxic effects in cattle. Probably
What is Nitrite Toxicity? Georgia Cattleman, June 2002 John Andrae, Forage Extension Specialist Many beef producers are familiar with high nitrates in forages and their toxic effects in cattle. Probably
Creep Feeding Beef Calves
 Creep Feeding Beef Calves Creep Feeding Basics Preweaning supplementing, or creep feeding, is the nutrient supplementation of nursing beef calves. Supplements can include creep feeding with concentrated
Creep Feeding Beef Calves Creep Feeding Basics Preweaning supplementing, or creep feeding, is the nutrient supplementation of nursing beef calves. Supplements can include creep feeding with concentrated
BURNETT CENTER INTERNET PROGRESS REPORT. No. 12 April, 2001. Summary of the 2000 Texas Tech University Consulting Nutritionist Survey
 BURNETT CENTER INTERNET PROGRESS REPORT No. 12 April, 2001 Summary of the 2000 Texas Tech University Consulting Nutritionist Survey M. L. Galyean and J. F. Gleghorn Department of Animal Science and Food
BURNETT CENTER INTERNET PROGRESS REPORT No. 12 April, 2001 Summary of the 2000 Texas Tech University Consulting Nutritionist Survey M. L. Galyean and J. F. Gleghorn Department of Animal Science and Food
Digestion of feeds in the milk-fed calf
 3 Digestion of feeds in the milk-fed calf This chapter describes the various processes of digestion in the milk-fed calf. The main points in this chapter The adult animal requires a fully functioning rumen
3 Digestion of feeds in the milk-fed calf This chapter describes the various processes of digestion in the milk-fed calf. The main points in this chapter The adult animal requires a fully functioning rumen
MANAGEMENT OF MEADOW FESCUE PASTURE FOR HIGH-PRODUCING DAIRY COWS IN NORTHERN JAPAN
 ID #22-25 MANAGEMENT OF MEADOW FESCUE PASTURE FOR HIGH-PRODUCING DAIRY COWS IN NORTHERN JAPAN K. Sudo 1, K. Ochiai 2 and T. Ikeda 3 1 Hokkaido National Agricultural Experiment Station, Hitsujigaoka, Toyohira,
ID #22-25 MANAGEMENT OF MEADOW FESCUE PASTURE FOR HIGH-PRODUCING DAIRY COWS IN NORTHERN JAPAN K. Sudo 1, K. Ochiai 2 and T. Ikeda 3 1 Hokkaido National Agricultural Experiment Station, Hitsujigaoka, Toyohira,
Summary of Distillers Grains Feeding Recommendations for Beef
 Summary of Distillers Grains Feeding Recommendations for Beef WDGS can be added to corn-based rations for finishing cattle at levels ranging from 10 to 40% of total ration dry matter. When added at levels
Summary of Distillers Grains Feeding Recommendations for Beef WDGS can be added to corn-based rations for finishing cattle at levels ranging from 10 to 40% of total ration dry matter. When added at levels
Accelerated Replacement Heifer Feeding Programs
 Accelerated Replacement Heifer Feeding Programs Michael F. Hutjens Department of Animal Sciences, University of Illinois, 232 ASL, 1207 W. Gregory Drive, Urbana, Illinois 61801 Email: hutjensm@uiuc.edu
Accelerated Replacement Heifer Feeding Programs Michael F. Hutjens Department of Animal Sciences, University of Illinois, 232 ASL, 1207 W. Gregory Drive, Urbana, Illinois 61801 Email: hutjensm@uiuc.edu
Beef Cattle Handbook
 Beef Cattle Handbook BCH-5610 Product of Extension Beef Cattle Resource Committee Nitrates in Livestock Feed Dan B. Faulkner, Extension Beef Specialist, University of Illinois Mike F. Hutjens, Extension
Beef Cattle Handbook BCH-5610 Product of Extension Beef Cattle Resource Committee Nitrates in Livestock Feed Dan B. Faulkner, Extension Beef Specialist, University of Illinois Mike F. Hutjens, Extension
N-P-K FERTILIZERS. by M.L. Vitosh Extension Specialist, Crop and Soil Sciences
 Michigan State University Extension! Extension Bulletin E-896! Reprint July 1996 N-P-K FERTILIZERS by M.L. Vitosh Extension Specialist, Crop and Soil Sciences T here are many grades and analyses of nitrogen
Michigan State University Extension! Extension Bulletin E-896! Reprint July 1996 N-P-K FERTILIZERS by M.L. Vitosh Extension Specialist, Crop and Soil Sciences T here are many grades and analyses of nitrogen
Nutrient and Fertilizer Value of Dairy Manure
 Agriculture and Natural Resources FSA4017 Nutrient and Fertilizer Value of Dairy Manure Jodie A. Pennington Professor - Dairy and Goats Karl VanDevender Professor - Waste Management John A. Jennings Professor
Agriculture and Natural Resources FSA4017 Nutrient and Fertilizer Value of Dairy Manure Jodie A. Pennington Professor - Dairy and Goats Karl VanDevender Professor - Waste Management John A. Jennings Professor
Marmara Üniversitesi Fen-Edebiyat Fakültesi Kimya Bölümü / Biyokimya Anabilim Dalı
 EXPERIMENT IX Marmara Üniversitesi DETERMINATION OF N-TERMINAL AMINO ACID RESIDUE OF PROTEINS BY THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY Functions of the proteins depend upon its amino acid sequence. Because amino acid
EXPERIMENT IX Marmara Üniversitesi DETERMINATION OF N-TERMINAL AMINO ACID RESIDUE OF PROTEINS BY THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY Functions of the proteins depend upon its amino acid sequence. Because amino acid
Feeding Flood-Damaged or Sprouted Crops to Livestock
 Feeding Flood-Damaged or Sprouted Crops to Livestock High moisture conditions often lead to crop damage and losses. Some losses are from grain sprouting in the head before harvest. These sprouted grains
Feeding Flood-Damaged or Sprouted Crops to Livestock High moisture conditions often lead to crop damage and losses. Some losses are from grain sprouting in the head before harvest. These sprouted grains
Most limiting amino acid concept...
 Review... Proteins are composed of amino acids Amino acids are the essential nutrients The dietary provision of amino acids in correct amount and provisions determines the adequacy of the protein in the
Review... Proteins are composed of amino acids Amino acids are the essential nutrients The dietary provision of amino acids in correct amount and provisions determines the adequacy of the protein in the
Corn Stalks and Drought-Damaged Corn Hay as Emergency Feeds for Beef Cattle
 Contacts: Matt Poore, Science, 919.515.7798 Jim Turner, Science, 828.246.4466 North Carolina Cooperative Extension College of Agriculture and Life Sciences North Carolina State University or contact your
Contacts: Matt Poore, Science, 919.515.7798 Jim Turner, Science, 828.246.4466 North Carolina Cooperative Extension College of Agriculture and Life Sciences North Carolina State University or contact your
Increasing Profitability Through an Accelerated Heifer Replacement Program
 Increasing Profitability Through an Accelerated Heifer Replacement Program Robert B. Corbett, D.V.M Dairy Health Consultation Accelerating heifer growth has been a very controversial subject in recent
Increasing Profitability Through an Accelerated Heifer Replacement Program Robert B. Corbett, D.V.M Dairy Health Consultation Accelerating heifer growth has been a very controversial subject in recent
Mammalian digestive tracts
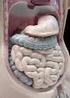 Mammalian digestive tracts Mouth: mastication, some digestive enzymes Esophagus: simple transport tube Stomach: most initial digestion, some physical processing Small intestine: digestion continues, some
Mammalian digestive tracts Mouth: mastication, some digestive enzymes Esophagus: simple transport tube Stomach: most initial digestion, some physical processing Small intestine: digestion continues, some
PROCESSING OF WHEAT FOR GROWING-FINISHING SWINE
 PROCESSING OF WHEAT FOR GROWING-FINISHING SWINE W.G. Luce 1, A.C. Clutter 2, C.V. Maxwell 3, S.R. McPeake 4 and R. Vencl 5 Story in Brief A trial involving 470 crossbred pigs was conducted to evaluate
PROCESSING OF WHEAT FOR GROWING-FINISHING SWINE W.G. Luce 1, A.C. Clutter 2, C.V. Maxwell 3, S.R. McPeake 4 and R. Vencl 5 Story in Brief A trial involving 470 crossbred pigs was conducted to evaluate
What a re r Lipids? What a re r Fatty y Ac A ids?
 2010 - Beef Cattle In-Service Training Inclusion of Lipids into Beef Cattle Diets Reinaldo F. Cooke, Ph. D. Oregon State University EOARC, Burns What are Lipids? Organic compounds Plant and animal compounds
2010 - Beef Cattle In-Service Training Inclusion of Lipids into Beef Cattle Diets Reinaldo F. Cooke, Ph. D. Oregon State University EOARC, Burns What are Lipids? Organic compounds Plant and animal compounds
PUTTING FORAGES TOGETHER FOR YEAR ROUND GRAZING
 PUTTING FORAGES TOGETHER FOR YEAR ROUND GRAZING Jimmy C. Henning A good rotational grazing system begins with a forage system that allows the maximum number of grazing days per year with forages that are
PUTTING FORAGES TOGETHER FOR YEAR ROUND GRAZING Jimmy C. Henning A good rotational grazing system begins with a forage system that allows the maximum number of grazing days per year with forages that are
EFFECT OF AGRADO ON THE HEALTH AND PERFORMANCE OF TRANSPORT-STRESSED HEIFER CALVES. Authors:
 EFFECT OF AGRADO ON THE HEALTH AND PERFORMANCE OF TRANSPORT-STRESSED HEIFER CALVES 1999 Animal Science Research Report Authors: Story in Brief Pages 176-181 T.C. Stovall, D.R. Gill, H. Han, J.T. Wagner
EFFECT OF AGRADO ON THE HEALTH AND PERFORMANCE OF TRANSPORT-STRESSED HEIFER CALVES 1999 Animal Science Research Report Authors: Story in Brief Pages 176-181 T.C. Stovall, D.R. Gill, H. Han, J.T. Wagner
NUTRITION MANAGEMENT OF PREGNANT AND LACTATING MARES
 University of Nebraska Cooperative Extension EC 95-272-B NUTRITION MANAGEMENT OF PREGNANT AND LACTATING MARES Kathy Anderson, Ph.D. Extension Horse Specialist University of Nebraska Issued in furtherance
University of Nebraska Cooperative Extension EC 95-272-B NUTRITION MANAGEMENT OF PREGNANT AND LACTATING MARES Kathy Anderson, Ph.D. Extension Horse Specialist University of Nebraska Issued in furtherance
Grain Finishing Beef: Alternative Rations, Cattle Performance and Feeding Costs for Small Feeders
 January 2014 AG/AppliedEconomics/2014-01pr Grain Finishing Beef: Alternative Rations, Cattle Performance and Feeding Costs for Small Feeders Dillon M. Feuz and Jesse Russell Introduction Even though many
January 2014 AG/AppliedEconomics/2014-01pr Grain Finishing Beef: Alternative Rations, Cattle Performance and Feeding Costs for Small Feeders Dillon M. Feuz and Jesse Russell Introduction Even though many
Practical Beef Cattle Nutrition
 Practical Beef Cattle Nutrition About HCC Hybu Cig Cymru/Meat Promotion Wales (HCC) is the strategic body for the promotion and development of red meat in Wales and the development of the Welsh red meat
Practical Beef Cattle Nutrition About HCC Hybu Cig Cymru/Meat Promotion Wales (HCC) is the strategic body for the promotion and development of red meat in Wales and the development of the Welsh red meat
Digestive System of the Horse and Feeding Management
 Agriculture and Natural Resources FSA3038 Digestive System of the Horse and Feeding Management Steven M. Jones Associate Professor Animal Science Animals have different types of digestive systems based
Agriculture and Natural Resources FSA3038 Digestive System of the Horse and Feeding Management Steven M. Jones Associate Professor Animal Science Animals have different types of digestive systems based
Biochemistry - I. Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture-11 Enzyme Mechanisms II
 Biochemistry - I Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture-11 Enzyme Mechanisms II In the last class we studied the enzyme mechanisms of ribonuclease A
Biochemistry - I Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture-11 Enzyme Mechanisms II In the last class we studied the enzyme mechanisms of ribonuclease A
Dr Erhard Briendenhann
 Dr Erhard Briendenhann Protein Research Foundation Soya processing nutritional and financial benefits Sponsored by: Protein Research Foundation SOYBEAN PROCESSING Nutritional and financial benefits Dr
Dr Erhard Briendenhann Protein Research Foundation Soya processing nutritional and financial benefits Sponsored by: Protein Research Foundation SOYBEAN PROCESSING Nutritional and financial benefits Dr
Source Amino Acids as Used in Cosmetics
 Scientific Literature Review Source Amino Acids as Used in Cosmetics May 23, 2012 The 2012 Cosmetic Ingredient Review Expert Panel members are: Chairman, Wilma F. Bergfeld, M.D., F.A.C.P.; Donald V. Belsito,
Scientific Literature Review Source Amino Acids as Used in Cosmetics May 23, 2012 The 2012 Cosmetic Ingredient Review Expert Panel members are: Chairman, Wilma F. Bergfeld, M.D., F.A.C.P.; Donald V. Belsito,
Strategies for Diet Formulation with High Corn Prices
 87 Strategies for Diet Formulation with High Corn Prices Joanne Knapp J.D. Heiskell & Co. Abstract Due to unprecedented changes in grain prices during the past year, the dairy industry is reexamining how
87 Strategies for Diet Formulation with High Corn Prices Joanne Knapp J.D. Heiskell & Co. Abstract Due to unprecedented changes in grain prices during the past year, the dairy industry is reexamining how
In many areas of the country, the Holstein
 A3659 Managing Holstein Steers for Beef Production Michael G. Siemens In many areas of the country, the Holstein steer is gaining popularity because it offers profit opportunities for alert, innovative
A3659 Managing Holstein Steers for Beef Production Michael G. Siemens In many areas of the country, the Holstein steer is gaining popularity because it offers profit opportunities for alert, innovative
H H N - C - C 2 R. Three possible forms (not counting R group) depending on ph
 Amino acids - 0 common amino acids there are others found naturally but much less frequently - Common structure for amino acid - C, -N, and functional groups all attached to the alpha carbon N - C - C
Amino acids - 0 common amino acids there are others found naturally but much less frequently - Common structure for amino acid - C, -N, and functional groups all attached to the alpha carbon N - C - C
The A to Z of Meat Goat Production
 The A to Z of Meat Goat Production Russell Ramsey, Regional Agriculture Business Management Specialist, University of Missouri Extension SARE National Conference-August 15-17, 17, 2006 Oconomowoc, Wisconsin
The A to Z of Meat Goat Production Russell Ramsey, Regional Agriculture Business Management Specialist, University of Missouri Extension SARE National Conference-August 15-17, 17, 2006 Oconomowoc, Wisconsin
Comparison of Software Applications for Formulating Dairy Rations
 Comparison of Software Applications for Formulating Dairy Rations Dan N. Waldner Extension Dairy Specialist Oklahoma State University Introduction A variety of software programs are available in the marketplace
Comparison of Software Applications for Formulating Dairy Rations Dan N. Waldner Extension Dairy Specialist Oklahoma State University Introduction A variety of software programs are available in the marketplace
Creep-Feeding Beef Calves
 EC 935 Reprinted June 1993 Creep-Feeding Beef Calves 75 F. Rulofson and W.A. Zollinger Gross income in the cow-calf phase of the beef industry depends on the production of calves with high weaning weights.
EC 935 Reprinted June 1993 Creep-Feeding Beef Calves 75 F. Rulofson and W.A. Zollinger Gross income in the cow-calf phase of the beef industry depends on the production of calves with high weaning weights.
Balancing chemical reaction equations (stoichiometry)
 Balancing chemical reaction equations (stoichiometry) This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit
Balancing chemical reaction equations (stoichiometry) This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit
Swine Feeding and Fitting Guidelines. Ryan Harrell Dec. 2008
 Swine Feeding and Fitting Guidelines Ryan Harrell Dec. 2008 Know What You Are Feeding For?! Barrows should be fed differently from Gilts.! Market Gilts should be fed differently from Breeding Gilts! Market
Swine Feeding and Fitting Guidelines Ryan Harrell Dec. 2008 Know What You Are Feeding For?! Barrows should be fed differently from Gilts.! Market Gilts should be fed differently from Breeding Gilts! Market
COLD STRESS IN COWS. Brian Tarr, Ruminant Nutritionist Shur Gain, Nutreco Canada Inc.
 COLD STRESS IN COWS Brian Tarr, Ruminant Nutritionist Shur Gain, Nutreco Canada Inc. Cold Stress in Cows Brian Tarr, Ruminant Nutritionist Shur Gain, Nutreco Canada Inc. Getting cows through the winter
COLD STRESS IN COWS Brian Tarr, Ruminant Nutritionist Shur Gain, Nutreco Canada Inc. Cold Stress in Cows Brian Tarr, Ruminant Nutritionist Shur Gain, Nutreco Canada Inc. Getting cows through the winter
BOC334 (Proteomics) Practical 1. Calculating the charge of proteins
 BC334 (Proteomics) Practical 1 Calculating the charge of proteins Aliphatic amino acids (VAGLIP) N H 2 H Glycine, Gly, G no charge Hydrophobicity = 0.67 MW 57Da pk a CH = 2.35 pk a NH 2 = 9.6 pi=5.97 CH
BC334 (Proteomics) Practical 1 Calculating the charge of proteins Aliphatic amino acids (VAGLIP) N H 2 H Glycine, Gly, G no charge Hydrophobicity = 0.67 MW 57Da pk a CH = 2.35 pk a NH 2 = 9.6 pi=5.97 CH
The Organic Chemistry of Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
 Essential rganic Chemistry Chapter 16 The rganic Chemistry of Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins Amino Acids a-amino carboxylic acids. The building blocks from which proteins are made. H 2 N C 2 H Note:
Essential rganic Chemistry Chapter 16 The rganic Chemistry of Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins Amino Acids a-amino carboxylic acids. The building blocks from which proteins are made. H 2 N C 2 H Note:
Pipe Cleaner Proteins. Essential question: How does the structure of proteins relate to their function in the cell?
 Pipe Cleaner Proteins GPS: SB1 Students will analyze the nature of the relationships between structures and functions in living cells. Essential question: How does the structure of proteins relate to their
Pipe Cleaner Proteins GPS: SB1 Students will analyze the nature of the relationships between structures and functions in living cells. Essential question: How does the structure of proteins relate to their
Eco Gest YS, Whole Plant Yucca schidigera, benefits in cattle
 Eco Gest YS, Whole Plant Yucca schidigera, benefits in cattle Even though Eco Gest YS is classified as natural feed flavoring agents, beef and dairy cattle performance improvements result from more than
Eco Gest YS, Whole Plant Yucca schidigera, benefits in cattle Even though Eco Gest YS is classified as natural feed flavoring agents, beef and dairy cattle performance improvements result from more than
The role of palm oil in a sustainable dairy industry
 Richard Kirkland September 2011 The role of palm oil in a sustainable dairy industry This is the final article in the series looking at issues relating to the sustainability and use of palm oil in the
Richard Kirkland September 2011 The role of palm oil in a sustainable dairy industry This is the final article in the series looking at issues relating to the sustainability and use of palm oil in the
A diet fit for a pig: seven basic rules
 A diet fit for a pig: seven basic rules June 2013 Primefact 1292 1 st edition Jayce Morgan, Livestock Officer Pigs, Tamworth NSW Introduction When a pig is fed a proper diet there are benefits to the pig
A diet fit for a pig: seven basic rules June 2013 Primefact 1292 1 st edition Jayce Morgan, Livestock Officer Pigs, Tamworth NSW Introduction When a pig is fed a proper diet there are benefits to the pig
USING HUMIC COMPOUNDS TO IMPROVE EFFICIENCY OF FERTILISER NITROGEN
 USING HUMIC COMPOUNDS TO IMPROVE EFFICIENCY OF FERTILISER NITROGEN Phillip Schofield 1, Nicky Watt 2 and Max Schofield 3 1 Abron Farm Consultant, 3/129 Maraekakaho Rd Hastings Phillip.schofield@abron.co.nz
USING HUMIC COMPOUNDS TO IMPROVE EFFICIENCY OF FERTILISER NITROGEN Phillip Schofield 1, Nicky Watt 2 and Max Schofield 3 1 Abron Farm Consultant, 3/129 Maraekakaho Rd Hastings Phillip.schofield@abron.co.nz
Full hand feeding of beef cattle management
 JANUARY 2007 PRIMEFACT 339 (REPLACES AGNOTE DAI-173) Full hand feeding of beef cattle management Ian Blackwood Livestock Officer, Extensive Industries Development, Paterson (Tocal) Ed Clayton Former Livestock
JANUARY 2007 PRIMEFACT 339 (REPLACES AGNOTE DAI-173) Full hand feeding of beef cattle management Ian Blackwood Livestock Officer, Extensive Industries Development, Paterson (Tocal) Ed Clayton Former Livestock
Managing of Annual Winter Forages in Southwest Texas
 r r r rr EDUCATION RESEARCH EXTENSION The Texas A&M University System Soil & Crop Sciences Managing of Annual Winter Forages in Southwest Texas Mr Charles Stichler Assocaite Professor and Extension Agronomist
r r r rr EDUCATION RESEARCH EXTENSION The Texas A&M University System Soil & Crop Sciences Managing of Annual Winter Forages in Southwest Texas Mr Charles Stichler Assocaite Professor and Extension Agronomist
UTI CAT FOOD COMPARISON CHART
 UTI CAT FOOD COMPARISON CHART believes that urinary tract infections, crystals and kidney problems in today s cat are due mainly to excessive minerals consumed by our cats as they age. Once you cat reaches
UTI CAT FOOD COMPARISON CHART believes that urinary tract infections, crystals and kidney problems in today s cat are due mainly to excessive minerals consumed by our cats as they age. Once you cat reaches
MEASURING PHYSICALLY EFFECTIVE FIBER ON-FARM TO PREDICT COW RESPONSE
 MEASURING PHYSICALLY EFFECTIVE FIBER ON-FARM TO PREDICT COW RESPONSE K. W. Cotanch and R. J. Grant W. H. Miner Agricultural Research Institute Chazy, NY INTRODUCTION This paper is a follow-up to our 2005
MEASURING PHYSICALLY EFFECTIVE FIBER ON-FARM TO PREDICT COW RESPONSE K. W. Cotanch and R. J. Grant W. H. Miner Agricultural Research Institute Chazy, NY INTRODUCTION This paper is a follow-up to our 2005
CAPRICORN: A Windows Program for Formulating and Evaluating Rations for Goats
 CAPRICORN: A Windows Program for Formulating and Evaluating Rations for Goats A. Ahmadi 1, P.H. Robinson 1 1 Animal Science, University of California, Davis, California, USA, phrobinson@ucdavis.edu Abstract
CAPRICORN: A Windows Program for Formulating and Evaluating Rations for Goats A. Ahmadi 1, P.H. Robinson 1 1 Animal Science, University of California, Davis, California, USA, phrobinson@ucdavis.edu Abstract
Subject: Comments on the Conservation Reserve Program Interim Rule
 September 27, 2010 Director Conservation and Environmental Programs Division USDA FSA CREPD Mail Stop 0513 1400 Independence Ave, SW Washington, DC 20250-0513 Subject: Comments on the Conservation Reserve
September 27, 2010 Director Conservation and Environmental Programs Division USDA FSA CREPD Mail Stop 0513 1400 Independence Ave, SW Washington, DC 20250-0513 Subject: Comments on the Conservation Reserve
