Manage Your. Diabetes. Healthy Life. for a
|
|
|
- Bertha Horton
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Manage Your Diabetes for a Healthy Life
2 Know your ABCs! trying to control your A1C (blood sugar), Blood pressure, Cholesterol and stopping Smoking can help you to lower your chances of having a heart attack, stroke, and other diabetes problems. A = A1C CHeCk 2 to 4 times Per YeAr B A1C is a blood test that tells you your average blood sugar level over the last 3 months. An A1C of less than 7 is the goal. Date tested Current A1C My A1C goal for next visit is = Blood Pressure (BP) Try for a goal of less than 130/80. CHeCk each ViSit My BP is My BP goal for next visit is C = Cholesterol CHeCk each YeAr Your total cholesterol should be less than 200 and LDL (bad cholesterol) should be less than 100. For women, HDL (good cholesterol) should be more than 50; for men it should be more than 40. Date tested Current cholesterol: My goals: total total LDL LDL HDL HDL Developed by the New York Diabetes Coalition, in collaboration with the New York State Department of Health Diabetes Prevention and Control Program. Based on the American Diabetes Association Clinical Practice Recommendations. S = Stop Smoking If you need help, call the New York State Smokers Quitline ( ) or visit nysmokefree.com My quit date is 1
3 How To Take Good Care of Yourself! i Ask your doctor or health care professional about how you are doing with your diabetes. i Work with your health care team to set goals that are right for you. i take it easy! Make only a few small changes at a time and don t give up! You CAN do this!! it s also important to... exercise regularly. If you find something you like to do, like walking, just do a little more of it. Work up to at least 30 minutes a day, most days of the week. My goal is to: eat healthfully. Your doctor, dietitian, nutritionist or Certified Diabetes Educator can help you choose a meal plan with healthy foods you like. My goal is to eat more My goal is to eat less take your MeDiCiNe as instructed. Ask your doctor if you should take other medicines like an aspirin or an ACE inhibitor. Get to a HeALtHY WeiGHt. Your doctor or health care professional can help you set a weight goal that s right for you. My goal is to lose lbs. by next visit. CHeCk YoUr Feet everyday. Ask your doctor to check your feet each visit. You may not feel cuts, sores, blisters or calluses on your feet because diabetes can cause you to lose feeling in your feet. Call your doctor right away if you think there s a problem. Get a KIDNEY TEST each year. Too much sugar in the blood makes kidneys overwork, which may cause them to fail or stop working. Date tested Get a DiLAteD eye exam each year. Diabetes can lead to serious vision problems or even blindness. Visit date See a DeNtiSt every 6 months. Gum disease can make diabetes harder to control. Visit date Visit date Get a FLU SHot every year and ask if you need a pneumonia shot. Date ASk For HeLP! if dealing with your diabetes becomes too difficult, talk to your doctor or health care professional help is available. Ask for support from family and friends. Your doctor may suggest you go to a diabetes support group or visit a dietitian, nutritionist or Certified Diabetes educator. Check and log your BLooD SUGAr. Ask your doctor or health care professional about how and when to test your blood sugar. A good blood sugar range is between 90 and 130 before meals and less than 180 one to two hours after you begin eating. Keep a log of your blood sugar readings. 2 3
4 Important Contacts Primary Care or Diabetes Doctor (endocrinologist) Diabetes Educator Eye Care Doctor (ophthalmologist or optometrist) Did you know Diabetes can cause many health problems, also called complications. You may not know these problems are happening until it s too late. You can stop or slow these problems by taking good care of yourself. See your doctor or health care professional to learn how! i People with diabetes are at greater risk for heart disease and stroke. i Diabetes is the most common cause of blindness in the United States. i Diabetes is the cause of most lower leg amputations (loss of all or partial loss of foot/leg) in the United States. i Diabetes is the most common cause of kidney disease. i Diabetes is the 6th most common cause of death in the United States. Foot Care Doctor (podiatrist) Other Health Care Professional Other Health Care Professional Medical Alert Card or Bracelet Carry a medical alert card or wear a medical alert bracelet that says you have diabetes. In an emergency, others will know that you need special care. 4 5
5 For More Diabetes Information Contact: American Diabetes Association American Association of Diabetes Educators National Diabetes Education Program National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse New York Diabetes Coalition New York State Department of Health Centers for Disease Control and Prevention State of New York Department of Health /08
To help stay on schedule, keep your own written record of when you get the tests and exams. Include your goals and test results.
 Oregon Diabetes Resource Bank Handouts to help people with diabetes 1 KNOW which tests, exams, and other care you should be getting. According to national standards for quality care for diabetes, there
Oregon Diabetes Resource Bank Handouts to help people with diabetes 1 KNOW which tests, exams, and other care you should be getting. According to national standards for quality care for diabetes, there
4 Steps to Control Your Diabetes for Life
 4 Steps to Control Your Diabetes for Life Contents Step 1: Learn about diabetes... 6 Step 2: Know your diabetes ABCs... 12 Step 3: Manage your diabetes... 16 Step 4: Get routine care... 22 Notes... 26
4 Steps to Control Your Diabetes for Life Contents Step 1: Learn about diabetes... 6 Step 2: Know your diabetes ABCs... 12 Step 3: Manage your diabetes... 16 Step 4: Get routine care... 22 Notes... 26
4 Steps to Manage Your Diabetes for Life
 4 Steps to Manage Your Diabetes for Life ENGLISH A program of the National Institutes of Health and the Centers for Disease Control and Preventioni This booklet gives four key steps to help you manage
4 Steps to Manage Your Diabetes for Life ENGLISH A program of the National Institutes of Health and the Centers for Disease Control and Preventioni This booklet gives four key steps to help you manage
Learn about Diabetes. Your Guide to Diabetes: Type 1 and Type 2. You can learn how to take care of your diabetes.
 Learn about Diabetes You can learn how to take care of your diabetes and prevent some of the serious problems diabetes can cause. The more you know, the better you can manage your diabetes. Share this
Learn about Diabetes You can learn how to take care of your diabetes and prevent some of the serious problems diabetes can cause. The more you know, the better you can manage your diabetes. Share this
4 Steps. For Life. to Control Your Diabetes. National Diabetes Education Program 1-888-693-NDEP (1-888-693-6337) www.yourdiabetesinfo.
 4 Steps to Control Your Diabetes. For Life. National Diabetes Education Program 1-888-693-NDEP (1-888-693-6337) www.yourdiabetesinfo.org Contents Introduction 1 Step 1: Learn about diabetes. 3 Step 2:
4 Steps to Control Your Diabetes. For Life. National Diabetes Education Program 1-888-693-NDEP (1-888-693-6337) www.yourdiabetesinfo.org Contents Introduction 1 Step 1: Learn about diabetes. 3 Step 2:
An Overview and Guide to Healthy Living with Type 2 Diabetes
 MEETING YOUR GOALS An Overview and Guide to Healthy Living with Type 2 Diabetes MEETING YOUR GOALS This brochure was designed to help you understand the health goals to live a healthy lifestyle with type
MEETING YOUR GOALS An Overview and Guide to Healthy Living with Type 2 Diabetes MEETING YOUR GOALS This brochure was designed to help you understand the health goals to live a healthy lifestyle with type
MY TYPE 2 DIABETES NUMBERS
 BLOOD SUGAR MANAGEMENT GUIDE MY TYPE 2 DIABETES NUMBERS Understanding and Tracking the ABCs of Type 2 Diabetes 1 BLOOD MY TYPE SUGAR 2 DIABETES MANAGEMENT ABC NUMBERS GUIDE When you have type 2 diabetes,
BLOOD SUGAR MANAGEMENT GUIDE MY TYPE 2 DIABETES NUMBERS Understanding and Tracking the ABCs of Type 2 Diabetes 1 BLOOD MY TYPE SUGAR 2 DIABETES MANAGEMENT ABC NUMBERS GUIDE When you have type 2 diabetes,
DIABETES CARE. Advice. Blood Pressure. Cholesterol. Diabetes control. Eyes. Feet. Guardian Drugs
 DIABETES CARE What happens if you follow the Alphabet Strategy? As patients reach their targets, the chances of developing serious complications of diabetes will be reduced! 1 Stroke Eye disease Heart
DIABETES CARE What happens if you follow the Alphabet Strategy? As patients reach their targets, the chances of developing serious complications of diabetes will be reduced! 1 Stroke Eye disease Heart
D I D Y O U K N O W? D I A B E T E S R E S O U R C E G U I D E. Blindness Heart Disease Strokes Kidney Failure Amputation
 D I D Y O U K N O W? D I A B E T E S R E S O U R C E G U I D E Diabetes is a serious disease that can lead to Blindness Heart Disease Strokes Kidney Failure Amputation Diabetes kills almost 210,000 people
D I D Y O U K N O W? D I A B E T E S R E S O U R C E G U I D E Diabetes is a serious disease that can lead to Blindness Heart Disease Strokes Kidney Failure Amputation Diabetes kills almost 210,000 people
TYPE 2 DIABETES IN THE AFRICAN AMERICAN COMMUNITY. Understanding the Complications That May Happen Without Proper Care
 TYPE 2 DIABETES IN THE AFRICAN AMERICAN COMMUNITY Understanding the Complications That May Happen Without Proper Care STAYING HEALTHY THE IMPORTANCE OF PROPER MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES Diabetes is
TYPE 2 DIABETES IN THE AFRICAN AMERICAN COMMUNITY Understanding the Complications That May Happen Without Proper Care STAYING HEALTHY THE IMPORTANCE OF PROPER MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES Diabetes is
Type 2 diabetes Definition
 Type 2 diabetes Definition Type 2 diabetes is a lifelong (chronic) disease in which there are high levels of sugar (glucose) in the blood. Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes. Causes Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes Definition Type 2 diabetes is a lifelong (chronic) disease in which there are high levels of sugar (glucose) in the blood. Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes. Causes Diabetes
There are three major forms of this disease.
 For more information about diabetes and it s risk factors, visit our website at: doh.sd.gov/diabetes or visit the South Dakota Diabetes Association at: www.sddiabetescoalition.org/ Your body needs insulin
For more information about diabetes and it s risk factors, visit our website at: doh.sd.gov/diabetes or visit the South Dakota Diabetes Association at: www.sddiabetescoalition.org/ Your body needs insulin
Myth vs. Reality: Diabetes Related
 Myth: Only medication can control my diabetes. Reality: Lifestyle changes such as good nutrition, increased physical activity, weight loss and limiting alcohol/cigarette consumption can have a positive
Myth: Only medication can control my diabetes. Reality: Lifestyle changes such as good nutrition, increased physical activity, weight loss and limiting alcohol/cigarette consumption can have a positive
Type 2 Diabetes. Type 1 Diabetes. What is Diabetes? Diabetes during Pregnancy Very Thirsty Very Tired
 FCD2-006 BINGO GAME To Prepare bingo game:!copy Picture Cards with pictures on one side and corresponding words on the other.!cut Bingo Cards apart, duplicate if you have more than ten players.!cut apart
FCD2-006 BINGO GAME To Prepare bingo game:!copy Picture Cards with pictures on one side and corresponding words on the other.!cut Bingo Cards apart, duplicate if you have more than ten players.!cut apart
Diabetes, Type 2. RelayClinical Patient Education Sample Topic Diabetes, Type 2. What is type 2 diabetes? How does it occur?
 What is type 2 diabetes? Type 2 diabetes is a disorder that happens when your body does not make enough insulin or is unable to use its own insulin properly. The inability to use insulin is called insulin
What is type 2 diabetes? Type 2 diabetes is a disorder that happens when your body does not make enough insulin or is unable to use its own insulin properly. The inability to use insulin is called insulin
Keep your diabetes under control
 Prevent diabetes problems Keep your diabetes under control Number 1 in a Series of 7 NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services
Prevent diabetes problems Keep your diabetes under control Number 1 in a Series of 7 NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services
Preventing & Managing Complications of Diabetes
 Preventing & Managing Complications of Diabetes Target Audience: Persons with diabetes and family members Objectives: Participants will be able to: 1. identify the complications associated with diabetes
Preventing & Managing Complications of Diabetes Target Audience: Persons with diabetes and family members Objectives: Participants will be able to: 1. identify the complications associated with diabetes
Diabetes Mellitus Type 2
 Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 What is it? Diabetes is a common health problem in the U.S. and the world. In diabetes, the body does not use the food it digests well. It is hard for the body to use carbohydrates
Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 What is it? Diabetes is a common health problem in the U.S. and the world. In diabetes, the body does not use the food it digests well. It is hard for the body to use carbohydrates
Take Charge of Your Diabetes
 Take Charge of Your Diabetes A Reinforcement Booklet for People With Diabetes Purpose and Acknowledgments This simplified and shortened overview of CDC s 1997 publication, Take Charge of Your Diabetes,
Take Charge of Your Diabetes A Reinforcement Booklet for People With Diabetes Purpose and Acknowledgments This simplified and shortened overview of CDC s 1997 publication, Take Charge of Your Diabetes,
Markham Stouffville Hospital
 Markham Stouffville Hospital Adult Diabetes Education Frequently Asked Questions What is diabetes? Diabetes is a disease in which blood glucose levels are above normal. Most of the food we eat is turned
Markham Stouffville Hospital Adult Diabetes Education Frequently Asked Questions What is diabetes? Diabetes is a disease in which blood glucose levels are above normal. Most of the food we eat is turned
Keep your diabetes under control
 Prevent diabetes problems Keep your diabetes under control NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse Prevent diabetes problems: Keep your diabetes under control NATIONAL
Prevent diabetes problems Keep your diabetes under control NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse Prevent diabetes problems: Keep your diabetes under control NATIONAL
Type 2 Diabetes. Increase of diabetic complications as HAIC increases
 Type 2 Diabetes Diabetes is a disease of too much sugar (glucose) in the blood. Type 2 diabetes is caused by insulin resistance of the cells and abnormal insulin production by the pancreas. Insulin is
Type 2 Diabetes Diabetes is a disease of too much sugar (glucose) in the blood. Type 2 diabetes is caused by insulin resistance of the cells and abnormal insulin production by the pancreas. Insulin is
Healthy at Heart FEELING GOOD. Reduce Your CV Risk. It s Not Just Your Body. It s Your Outlook, Too. Issue 3
 Issue 3 Healthy at Heart Reduce Your CV Risk FEELING GOOD It s Not Just Your Body. It s Your Outlook, Too. Inside: Tips for staying active and feeling good all over Speak to your healthcare provider before
Issue 3 Healthy at Heart Reduce Your CV Risk FEELING GOOD It s Not Just Your Body. It s Your Outlook, Too. Inside: Tips for staying active and feeling good all over Speak to your healthcare provider before
Diabetes. Living with. Better Health Guide. Anywhere, TN 11111. 1008 Main Street. Janet James. BCBSNEMEMWKBCD.XML - 1768150 - VersionID: 1
 BCBSNEMEMWKBCD.XML - 1768150 - VersionID: 1 Living with Diabetes Better Health Guide Janet James 1008 Main Street Anywhere, TN 11111 65109016-999-000000006 13810 Southeast Eastgate Way, Suite 200 Bellevue,
BCBSNEMEMWKBCD.XML - 1768150 - VersionID: 1 Living with Diabetes Better Health Guide Janet James 1008 Main Street Anywhere, TN 11111 65109016-999-000000006 13810 Southeast Eastgate Way, Suite 200 Bellevue,
Am I at Risk for type 2 Diabetes? Taking Steps to Lower the Risk of Getting Diabetes NATIONAL DIABETES INFORMATION CLEARINGHOUSE
 NATIONAL DIABETES INFORMATION CLEARINGHOUSE Am I at Risk for type 2 Diabetes? Taking Steps to Lower the Risk of Getting Diabetes U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health
NATIONAL DIABETES INFORMATION CLEARINGHOUSE Am I at Risk for type 2 Diabetes? Taking Steps to Lower the Risk of Getting Diabetes U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health
I have diabetes. In case of emergency, please call: Healthcare Provider s Name. Name. Telephone. Address. Hospital. City. Pharmacy.
 Self-Care Diary Name Address City Healthcare Provider s Name Hospital State ZIP I have diabetes. In case of emergency, please call: Name Pharmacy Diabetes Educator s Name Address 1 Small Steps to Managing
Self-Care Diary Name Address City Healthcare Provider s Name Hospital State ZIP I have diabetes. In case of emergency, please call: Name Pharmacy Diabetes Educator s Name Address 1 Small Steps to Managing
Diabetes Brief. Pre diabetes occurs when glucose levels are elevated in the blood, but are not as high as someone who has diabetes.
 Diabetes Brief What is Diabetes? Diabetes mellitus is a disease of abnormal carbohydrate metabolism in which the level of blood glucose, or blood sugar, is above normal. The disease occurs when the body
Diabetes Brief What is Diabetes? Diabetes mellitus is a disease of abnormal carbohydrate metabolism in which the level of blood glucose, or blood sugar, is above normal. The disease occurs when the body
Managing the Diabetes Patient. Dan Kremer, RN, BSN Diabetes Nurse Educator
 Managing the Diabetes Patient Dan Kremer, RN, BSN Diabetes Nurse Educator Objectives Referring & assessing the inpatient Address the needed diabetes education for the patients survival skills Problem solving
Managing the Diabetes Patient Dan Kremer, RN, BSN Diabetes Nurse Educator Objectives Referring & assessing the inpatient Address the needed diabetes education for the patients survival skills Problem solving
High Blood Sugar. Printable Materials
 Printable Materials Activity Card #1 Symptoms of High Blood Sugar or Pre-Diabetes Symptoms People often don t know they have high blood sugar or pre-diabetes. There are no symptoms and pre-diabetes can
Printable Materials Activity Card #1 Symptoms of High Blood Sugar or Pre-Diabetes Symptoms People often don t know they have high blood sugar or pre-diabetes. There are no symptoms and pre-diabetes can
Preventing Type 2 Diabetes and Its Complications
 What is Diabetes? Preventing Type 2 Diabetes and Its Complications Diabetes is a chronic medical condition resulting in high blood sugar (glucose) levels in the blood. High blood sugar over years may cause
What is Diabetes? Preventing Type 2 Diabetes and Its Complications Diabetes is a chronic medical condition resulting in high blood sugar (glucose) levels in the blood. High blood sugar over years may cause
The Family Library. Understanding Diabetes
 The Family Library Understanding Diabetes What is Diabetes? Diabetes is caused when the body has a problem in making or using insulin. Insulin is a hormone secreted by the pancreas and is needed for the
The Family Library Understanding Diabetes What is Diabetes? Diabetes is caused when the body has a problem in making or using insulin. Insulin is a hormone secreted by the pancreas and is needed for the
Diabetes The Basics. What is Diabetes? How does sugar get into your cells? Type 1 diabetes. Type 2 diabetes. Why control Diabetes?
 Diabetes The Basics What is Diabetes? Diabetes is when there is too much sugar in your blood. Sugar from food you eat and drink stays in your blood instead of going into the cells in your body. The cells
Diabetes The Basics What is Diabetes? Diabetes is when there is too much sugar in your blood. Sugar from food you eat and drink stays in your blood instead of going into the cells in your body. The cells
DIABETES. Eyes, Heart, Nerves, Feet, and Kidneys. www.kidney.org
 DIABETES Eyes, Heart, Nerves, Feet, and Kidneys www.kidney.org About the Information in this Booklet Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation (NKF) offers guidelines and commentaries that help
DIABETES Eyes, Heart, Nerves, Feet, and Kidneys www.kidney.org About the Information in this Booklet Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation (NKF) offers guidelines and commentaries that help
Understanding Diabetes
 Understanding Diabetes Diabetes is a disease in which a person s blood glucose (blood sugar) is too high. When you eat, some of the food is broken down into a type of sugar called glucose, which is the
Understanding Diabetes Diabetes is a disease in which a person s blood glucose (blood sugar) is too high. When you eat, some of the food is broken down into a type of sugar called glucose, which is the
Facts About Peripheral Arterial Disease (P.A.D.)
 Facts About Peripheral Arterial Disease (P.A.D.) One in every 20 Americans over the age of 50 has P.A.D., a condition that raises the risk for heart attack and stroke. Peripheral arterial disease, or P.A.D.,
Facts About Peripheral Arterial Disease (P.A.D.) One in every 20 Americans over the age of 50 has P.A.D., a condition that raises the risk for heart attack and stroke. Peripheral arterial disease, or P.A.D.,
Diabetes 101: A Brief Overview of Diabetes and the American Diabetes Association What Happens When We Eat?
 Diabetes 101: A Brief Overview of Diabetes and the American Diabetes Association What Happens When We Eat? After eating, most food is turned into glucose, the body s main source of energy. 1 Normal Blood
Diabetes 101: A Brief Overview of Diabetes and the American Diabetes Association What Happens When We Eat? After eating, most food is turned into glucose, the body s main source of energy. 1 Normal Blood
Know Your Resistance A Guide to Better Health
 Know Your Resistance A Guide to Better Health This material is copyrighted by Bayer HealthCare LLC and is intended solely for use in the Know Your Series educational programs supported by Bayer HealthCare
Know Your Resistance A Guide to Better Health This material is copyrighted by Bayer HealthCare LLC and is intended solely for use in the Know Your Series educational programs supported by Bayer HealthCare
How To Manage Diabetes
 How To Manage Diabetes HHC Health & Home Care Serving New Yorkers For Over 45 Years 1-866-NYC-HOME www.homecarenyc.org Contents Your Blood Sugar Goals 4 Testing Your Blood Sugar 5 Blood Sugar Control
How To Manage Diabetes HHC Health & Home Care Serving New Yorkers For Over 45 Years 1-866-NYC-HOME www.homecarenyc.org Contents Your Blood Sugar Goals 4 Testing Your Blood Sugar 5 Blood Sugar Control
Know Your Numbers. The Five-Point Plan
 The Five-Point Plan Know Your Numbers 2 My husband didn t even know he had diabetes until he had a heart attack. Lupe Ontiveros Actress on Desperate Housewives 13 What does it mean to Know Your Numbers?
The Five-Point Plan Know Your Numbers 2 My husband didn t even know he had diabetes until he had a heart attack. Lupe Ontiveros Actress on Desperate Housewives 13 What does it mean to Know Your Numbers?
Type 1 diabetes Definition
 Type 1 diabetes Definition Type 1 diabetes is a chronic (lifelong) disease that occurs when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin to properly control blood sugar levels. Causes There are several
Type 1 diabetes Definition Type 1 diabetes is a chronic (lifelong) disease that occurs when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin to properly control blood sugar levels. Causes There are several
Know your Numbers The D5 Goals for Diabetes Care. Shelly Hanson RN, CNS, CDE Cuyuna Regional Medical Center November 6, 2014
 Know your Numbers The D5 Goals for Diabetes Care Shelly Hanson RN, CNS, CDE Cuyuna Regional Medical Center November 6, 2014 The D5 What is it 5 different treatment goals identified for optimal diabetes
Know your Numbers The D5 Goals for Diabetes Care Shelly Hanson RN, CNS, CDE Cuyuna Regional Medical Center November 6, 2014 The D5 What is it 5 different treatment goals identified for optimal diabetes
Diabetes: The #1 Cause of Kidney Failure
 American Kidney Fund reaching out giving hope improving lives Diabetes and Your Kidneys Large Print Edition reaching out giving hope improving lives Diabetes: The #1 Cause of Kidney Failure Your doctor
American Kidney Fund reaching out giving hope improving lives Diabetes and Your Kidneys Large Print Edition reaching out giving hope improving lives Diabetes: The #1 Cause of Kidney Failure Your doctor
Type 2 Diabetes. Type 2 Diabetes 69
 Type 2 Diabetes About 9.7 million women in the United States have diabetes. Most women and men diagnosed with diabetes have type 2 diabetes. Type 2 diabetes used to be called adult-onset diabetes. But
Type 2 Diabetes About 9.7 million women in the United States have diabetes. Most women and men diagnosed with diabetes have type 2 diabetes. Type 2 diabetes used to be called adult-onset diabetes. But
Welcome to Diabetes Education! Why Should I Take Control of My Diabetes?
 Welcome to Diabetes Education! Why Should I Take Control of My Diabetes? NEEDS and BENEFITS of SELF-MANAGEMENT You make choices about your life and health Controlling diabetes needs every day decisions
Welcome to Diabetes Education! Why Should I Take Control of My Diabetes? NEEDS and BENEFITS of SELF-MANAGEMENT You make choices about your life and health Controlling diabetes needs every day decisions
Methods for Delivering Insulin and Monitoring Blood Sugar. A Review of the Research for Children, Teens, and Adults With Diabetes
 Methods for Delivering Insulin and Monitoring Blood Sugar A Review of the Research for Children, Teens, and Adults With Diabetes Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, if: Your doctor* has told you that
Methods for Delivering Insulin and Monitoring Blood Sugar A Review of the Research for Children, Teens, and Adults With Diabetes Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, if: Your doctor* has told you that
Practice Guidelines for the
 1 Treatment goals: Practice Guidelines for the The goal of treatment is to keep blood sugar at normal or near-normal levels. This reduces the risk of complications associated with diabetes. A normal fasting
1 Treatment goals: Practice Guidelines for the The goal of treatment is to keep blood sugar at normal or near-normal levels. This reduces the risk of complications associated with diabetes. A normal fasting
Diabetes and Stroke. Understanding the connection between diabetes and the increased risk of stroke
 Diabetes and Stroke Understanding the connection between diabetes and the increased risk of stroke Make the Connection Almost 26 million people in the U.S. roughly 8 percent of the population have diabetes.
Diabetes and Stroke Understanding the connection between diabetes and the increased risk of stroke Make the Connection Almost 26 million people in the U.S. roughly 8 percent of the population have diabetes.
TakeCHARGE. Diabetes. Community Health Reports. Personal actions for better health
 TakeCHARGE Community Health Reports Personal actions for better health Diabetes A nonprofit independent licensee of the BlueCross BlueShield Association Are we taking charge of our own health? Most of
TakeCHARGE Community Health Reports Personal actions for better health Diabetes A nonprofit independent licensee of the BlueCross BlueShield Association Are we taking charge of our own health? Most of
Diabetes. Rochester Recreation Club for the Deaf January 21, 2010
 Diabetes Rochester Recreation Club for the Deaf January 21, 2010 Supporters Deaf Health Community Committee Members Cathie Armstrong Michael McKee Mistie Cramer Matt Starr Patrick Sullivan University of
Diabetes Rochester Recreation Club for the Deaf January 21, 2010 Supporters Deaf Health Community Committee Members Cathie Armstrong Michael McKee Mistie Cramer Matt Starr Patrick Sullivan University of
Diabetes Mellitus: Type 1
 Diabetes Mellitus: Type 1 What is type 1 diabetes mellitus? Type 1 diabetes is a disorder that happens when your body produces little or no insulin. The lack of insulin causes the level of sugar in your
Diabetes Mellitus: Type 1 What is type 1 diabetes mellitus? Type 1 diabetes is a disorder that happens when your body produces little or no insulin. The lack of insulin causes the level of sugar in your
High Blood Sugar: What You Need to Know
 High Blood Sugar: What You Need to Know This brochure can help you learn more about high blood sugar. It doesn t replace regular medical check-ups or your health care provider s advice. Talk with your
High Blood Sugar: What You Need to Know This brochure can help you learn more about high blood sugar. It doesn t replace regular medical check-ups or your health care provider s advice. Talk with your
Diabetes. Patient Education. What you need to know. Diabetes Facts. Improving Health Through Education. What is Diabetes?
 Diabetes What you need to know Diabetes Facts More than 3 million Canadians have diabetes (Canadian Diabetes Association, 2009). It is the 4th leading cause of death in the world (CDA, 2009). Patient Education
Diabetes What you need to know Diabetes Facts More than 3 million Canadians have diabetes (Canadian Diabetes Association, 2009). It is the 4th leading cause of death in the world (CDA, 2009). Patient Education
type 2 diabetes and you Live Well with Diabetes
 type 2 diabetes and you Live Well with Diabetes Basic Guidelines for Good Diabetes Care Check your blood sugar regularly At every doctor visit: Review your blood sugar records Blood pressure Weight Foot
type 2 diabetes and you Live Well with Diabetes Basic Guidelines for Good Diabetes Care Check your blood sugar regularly At every doctor visit: Review your blood sugar records Blood pressure Weight Foot
Post-Transplant Diabetes: What Every Patient Needs to Know
 Post-Transplant Diabetes: What Every Patient Needs to Know International Transplant Nurses Society What is Diabetes? Diabetes is an illness that effects how your body makes and uses a hormone called insulin.
Post-Transplant Diabetes: What Every Patient Needs to Know International Transplant Nurses Society What is Diabetes? Diabetes is an illness that effects how your body makes and uses a hormone called insulin.
Cardiac Rehabilitation
 Cardiac Rehabilitation Introduction Experiencing heart disease should be the beginning of a new, healthier lifestyle. Cardiac rehabilitation helps you in two ways. First, it helps your heart recover through
Cardiac Rehabilitation Introduction Experiencing heart disease should be the beginning of a new, healthier lifestyle. Cardiac rehabilitation helps you in two ways. First, it helps your heart recover through
Daily Diabetes Management Book
 01 Daily Diabetes Management Book This book belongs to Name Address Your Diabetes Health Care Team Telephone Numbers Primary Doctor Diabetes Educator Specialist Dietitian/Nutritionist Pharmacy Insurance
01 Daily Diabetes Management Book This book belongs to Name Address Your Diabetes Health Care Team Telephone Numbers Primary Doctor Diabetes Educator Specialist Dietitian/Nutritionist Pharmacy Insurance
My life with Type 2-diabetes. English
 My life with Type 2-diabetes English 1 What is type 2 diabetes Diabetes is a disease where you have increased sugar content in the blood. If you have type 2-diabetes, you lack the ability of exploiting
My life with Type 2-diabetes English 1 What is type 2 diabetes Diabetes is a disease where you have increased sugar content in the blood. If you have type 2-diabetes, you lack the ability of exploiting
UMA Diabetes Self-Care Log Book
 BRING THIS WITH YOU ON EVERY VISIT UMA Diabetes Self-Care Log Book Name MY INSTRUCTIONS FOR TESTNG MY BLOOD GLUCOSE My Doctor s name My Nurse s name Check your blood glucose: before breakfast before lunch
BRING THIS WITH YOU ON EVERY VISIT UMA Diabetes Self-Care Log Book Name MY INSTRUCTIONS FOR TESTNG MY BLOOD GLUCOSE My Doctor s name My Nurse s name Check your blood glucose: before breakfast before lunch
Diabetes Health Plan Member Guide
 Diabetes Health Plan Member Guide Welcome UnitedHealthcare Diabetes Health Plan Welcome to the Diabetes Health Plan. Our goal is to ensure you are getting the most out of your program. Please use this
Diabetes Health Plan Member Guide Welcome UnitedHealthcare Diabetes Health Plan Welcome to the Diabetes Health Plan. Our goal is to ensure you are getting the most out of your program. Please use this
Diabetes. 2. Types. Permafold Topics. What You Need To Know. One test used to diagnose diabetes is a fasting blood glucose test.
 1. What Is Diabetes? Diabetes is often called having too much sugar. It is too much sugar (glucose) in the blood and not enough in the body s cells. Glucose needs to get into the cells to be used for energy.
1. What Is Diabetes? Diabetes is often called having too much sugar. It is too much sugar (glucose) in the blood and not enough in the body s cells. Glucose needs to get into the cells to be used for energy.
Your Guide to Diabetes: Type 1 and Type 2. National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse
 Your Guide to Diabetes: Type 1 and Type 2 National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse Your Guide to Diabetes: Type 1 and Type 2 Contents Learn about Diabetes... 1 What is diabetes?... 2 What is prediabetes?...
Your Guide to Diabetes: Type 1 and Type 2 National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse Your Guide to Diabetes: Type 1 and Type 2 Contents Learn about Diabetes... 1 What is diabetes?... 2 What is prediabetes?...
Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors
 Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors Risk factors are traits and life-style habits that increase a person's chances of having coronary artery and vascular disease. Some risk factors cannot be changed or
Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors Risk factors are traits and life-style habits that increase a person's chances of having coronary artery and vascular disease. Some risk factors cannot be changed or
Diabetes and Your Kidneys
 American Kidney Fund reaching out giving hope improving lives Diabetes and Your Kidneys reaching out giving hope improving lives Diabetes: The #1 Cause of Kidney Failure Your doctor told you that you have
American Kidney Fund reaching out giving hope improving lives Diabetes and Your Kidneys reaching out giving hope improving lives Diabetes: The #1 Cause of Kidney Failure Your doctor told you that you have
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused by too little insulin, resistance to insulin, or both.
 Diabetes Definition Diabetes is a chronic (lifelong) disease marked by high levels of sugar in the blood. Causes Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused
Diabetes Definition Diabetes is a chronic (lifelong) disease marked by high levels of sugar in the blood. Causes Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused
An Overview of Medicare Covered Diabetes Supplies and Services
 News Flash - Understanding the Remittance Advice: A Guide for Medicare Providers, Physicians, Suppliers, and Billers serves as a resource on how to read and understand a Remittance Advice (RA). Inside
News Flash - Understanding the Remittance Advice: A Guide for Medicare Providers, Physicians, Suppliers, and Billers serves as a resource on how to read and understand a Remittance Advice (RA). Inside
Healthy Meals for Diabetes
 managingdiabetes TM SELECTHEALTH WINTER 2015 Healthy Meals for Diabetes Your doctor can help you make a meal plan that fits your needs. Your meal plan tells you when to eat meals and snacks, how much to
managingdiabetes TM SELECTHEALTH WINTER 2015 Healthy Meals for Diabetes Your doctor can help you make a meal plan that fits your needs. Your meal plan tells you when to eat meals and snacks, how much to
DCCT and EDIC: The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial and Follow-up Study
 DCCT and EDIC: The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial and Follow-up Study National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What
DCCT and EDIC: The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial and Follow-up Study National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What
Burden of Obesity, Diabetes and Heart Disease in New Hampshire, 2013 Update
 Burden of Obesity, Diabetes and Heart Disease in New Hampshire, 2013 Update Background Overweight and obesity have greatly increased among all age groups and regardless of income and education. Contributing
Burden of Obesity, Diabetes and Heart Disease in New Hampshire, 2013 Update Background Overweight and obesity have greatly increased among all age groups and regardless of income and education. Contributing
X-Plain Diabetes - Introduction Reference Summary
 X-Plain Diabetes - Introduction Reference Summary Introduction Diabetes is a disease that affects millions of Americans every year. Your doctor may have informed you that you have diabetes. Although there
X-Plain Diabetes - Introduction Reference Summary Introduction Diabetes is a disease that affects millions of Americans every year. Your doctor may have informed you that you have diabetes. Although there
Antipsychotic Medications and the Risk of Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease
 Antipsychotic Medications and the Risk of Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease Patient Tool #1 Understanding Diabetes and Psychiatric Illness: A Guide for Individuals, Families, and Caregivers Type 2 Diabetes,
Antipsychotic Medications and the Risk of Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease Patient Tool #1 Understanding Diabetes and Psychiatric Illness: A Guide for Individuals, Families, and Caregivers Type 2 Diabetes,
Connecticut Diabetes Statistics
 Connecticut Diabetes Statistics What is Diabetes? State Public Health Actions (1305, SHAPE) Grant March 2015 Page 1 of 16 Diabetes is a disease in which blood glucose levels are above normal. Blood glucose
Connecticut Diabetes Statistics What is Diabetes? State Public Health Actions (1305, SHAPE) Grant March 2015 Page 1 of 16 Diabetes is a disease in which blood glucose levels are above normal. Blood glucose
Type 1 and Type 2. Your Guide to Diabetes: NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH. National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse
 Your Guide to Diabetes: Type 1 and Type 2 U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse Your Guide to Diabetes: Type 1 and Type
Your Guide to Diabetes: Type 1 and Type 2 U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse Your Guide to Diabetes: Type 1 and Type
Diabetes and Heart Disease
 Diabetes and Heart Disease Diabetes and Heart Disease According to the American Heart Association, diabetes is one of the six major risk factors of cardiovascular disease. Affecting more than 7% of the
Diabetes and Heart Disease Diabetes and Heart Disease According to the American Heart Association, diabetes is one of the six major risk factors of cardiovascular disease. Affecting more than 7% of the
Pills for Type 2 Diabetes. A Guide for Adults
 Pills for Type 2 Diabetes A Guide for Adults December 2007 Fast Facts on Diabetes Pills n Different kinds of diabetes pills work in different ways to control blood sugar (blood glucose). n All the diabetes
Pills for Type 2 Diabetes A Guide for Adults December 2007 Fast Facts on Diabetes Pills n Different kinds of diabetes pills work in different ways to control blood sugar (blood glucose). n All the diabetes
is for A1c (blood sugar level) What causes unhealthy levels of blood sugar?
 diabetes matters Summer 2016 Do you have diabetes? Or do you have prediabetes and want to know more about it? Diabetes Matters is just for you, to help you learn how to live well with diabetes and prevent
diabetes matters Summer 2016 Do you have diabetes? Or do you have prediabetes and want to know more about it? Diabetes Matters is just for you, to help you learn how to live well with diabetes and prevent
QUALITY OF LIFE WITH DIABETES AND CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE
 QUALITY OF LIFE WITH DIABETES AND CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation's Kidney
QUALITY OF LIFE WITH DIABETES AND CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation's Kidney
Causes, incidence, and risk factors
 Causes, incidence, and risk factors Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused by too little insulin, resistance to insulin, or both. To understand diabetes,
Causes, incidence, and risk factors Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control blood sugar. Diabetes can be caused by too little insulin, resistance to insulin, or both. To understand diabetes,
Statistics of Type 2 Diabetes
 Statistics of Type 2 Diabetes Of the 17 million Americans with diabetes, 90 percent to 95 percent have type 2 diabetes. Of these, half are unaware they have the disease. People with type 2 diabetes often
Statistics of Type 2 Diabetes Of the 17 million Americans with diabetes, 90 percent to 95 percent have type 2 diabetes. Of these, half are unaware they have the disease. People with type 2 diabetes often
PowerPoint Lecture Outlines prepared by Dr. Lana Zinger, QCC CUNY. 12a. FOCUS ON Your Risk for Diabetes. Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
 PowerPoint Lecture Outlines prepared by Dr. Lana Zinger, QCC CUNY 12a FOCUS ON Your Risk for Diabetes Your Risk for Diabetes! Since 1980,Diabetes has increased by 50 %. Diabetes has increased by 70 percent
PowerPoint Lecture Outlines prepared by Dr. Lana Zinger, QCC CUNY 12a FOCUS ON Your Risk for Diabetes Your Risk for Diabetes! Since 1980,Diabetes has increased by 50 %. Diabetes has increased by 70 percent
Diabetes: Staying Healthy
 Diabetes: Staying Healthy Learn from the experts at Joslin Diabetes Center and Walgreens about: Eating well & being active Understanding your medicines Reducing your risks And more -! 4RUSTED 4EAM FOR
Diabetes: Staying Healthy Learn from the experts at Joslin Diabetes Center and Walgreens about: Eating well & being active Understanding your medicines Reducing your risks And more -! 4RUSTED 4EAM FOR
Baskets of Care Diabetes Subcommittee
 Baskets of Care Diabetes Subcommittee Disclaimer: This background information is not intended to be a comprehensive scientific discussion of the topic, but rather an attempt to provide a baseline level
Baskets of Care Diabetes Subcommittee Disclaimer: This background information is not intended to be a comprehensive scientific discussion of the topic, but rather an attempt to provide a baseline level
You may continue to use your old manuals by writing in the detailed changes below:
 STANFORD PATIENT EDUCATION RESEARCH CENTER: CHANGES TO THE DSMP LEADER MANUAL (2012 version to the 2015 version) Stanford has corrected the DSMP manuals with the new ADA guidelines. Call- out icons and
STANFORD PATIENT EDUCATION RESEARCH CENTER: CHANGES TO THE DSMP LEADER MANUAL (2012 version to the 2015 version) Stanford has corrected the DSMP manuals with the new ADA guidelines. Call- out icons and
WHY SHOULD I BE CAREFUL ABOUT DRINKING ALCOHOL?
 WHY SHOULD I BE CAREFUL ABOUT DRINKING ALCOHOL? If you have diabetes and take pills or insulin to control your blood sugar, you should be careful when you drink alcohol. Alcohol can cause blood sugar to
WHY SHOULD I BE CAREFUL ABOUT DRINKING ALCOHOL? If you have diabetes and take pills or insulin to control your blood sugar, you should be careful when you drink alcohol. Alcohol can cause blood sugar to
Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 What You Should Know
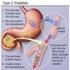 Please refer to the glossary for a definition of terms. What is Diabetes? Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 What You Should Know Erin K.P. Meyerhoff RN Instructor of Medicine Family Nurse Practitioner Certified
Please refer to the glossary for a definition of terms. What is Diabetes? Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 What You Should Know Erin K.P. Meyerhoff RN Instructor of Medicine Family Nurse Practitioner Certified
LiveHealthy! Health questions are not easy to answer alone. See inside! 24/7 Nurse Advice Line for Health Choice Members. Speak with registered nurses
 LiveHealthy! Spring 2014 24/7 Nurse Advice Line for Health Choice Members Health questions are not easy to answer alone. Get the help you need to make the right choices. Speak with registered nurses Toll-free,
LiveHealthy! Spring 2014 24/7 Nurse Advice Line for Health Choice Members Health questions are not easy to answer alone. Get the help you need to make the right choices. Speak with registered nurses Toll-free,
Diabetes and stroke. What is diabetes? What are the symptoms of diabetes? Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk
 Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Diabetes and stroke Diabetes is a condition caused by too much sugar in your blood. There are over three million people in the UK who have diabetes.
Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Diabetes and stroke Diabetes is a condition caused by too much sugar in your blood. There are over three million people in the UK who have diabetes.
Improving Diabetes Care for All New Yorkers
 Improving Diabetes Care for All New Yorkers Lynn D. Silver, MD, MPH Assistant Commissioner Bureau of Chronic Disease Prevention and Control Diana K. Berger, MD, MSc Medical Director Diabetes Prevention
Improving Diabetes Care for All New Yorkers Lynn D. Silver, MD, MPH Assistant Commissioner Bureau of Chronic Disease Prevention and Control Diana K. Berger, MD, MSc Medical Director Diabetes Prevention
Healthy Solutions for Life
 Healthy Solutions for Life 2015 Presentation Overview About Healthy Solutions for Life Disease Management Health Coaching Model DM Programs TeleCare Monitoring 2013 Nurtur Health, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Healthy Solutions for Life 2015 Presentation Overview About Healthy Solutions for Life Disease Management Health Coaching Model DM Programs TeleCare Monitoring 2013 Nurtur Health, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Diabetes means you have too much sugar in
 WHAT IS DIABETES? Diabetes means you have too much sugar in your blood. The medical word for sugar in the blood or blood sugar is glucose, but most people just say sugar. Your body changes most of the
WHAT IS DIABETES? Diabetes means you have too much sugar in your blood. The medical word for sugar in the blood or blood sugar is glucose, but most people just say sugar. Your body changes most of the
YOUR GUIDE TO. Managing and Understanding Your Cholesterol Levels
 YOUR GUIDE TO Managing and Understanding Your Cholesterol Levels Our goal at the Mercy Health Heart Institute is to help you be well. Our experienced team includes cardiologists, cardiovascular surgeons,
YOUR GUIDE TO Managing and Understanding Your Cholesterol Levels Our goal at the Mercy Health Heart Institute is to help you be well. Our experienced team includes cardiologists, cardiovascular surgeons,
How does Diabetes Effect the Feet
 How does Diabetes Effect the Feet What Skin Changes May Occur? Diabetes can cause changes in the skin of your foot. At times your foot may become very dry. The skin may peel and crack. The problem is that
How does Diabetes Effect the Feet What Skin Changes May Occur? Diabetes can cause changes in the skin of your foot. At times your foot may become very dry. The skin may peel and crack. The problem is that
Understanding Diabetes
 Understanding Diabetes What is diabetes? Diabetes is a condition where there is too much glucose (a type of sugar) in your blood. Your blood glucose level is regulated with the help of insulin, a hormone
Understanding Diabetes What is diabetes? Diabetes is a condition where there is too much glucose (a type of sugar) in your blood. Your blood glucose level is regulated with the help of insulin, a hormone
This information explains the advice about type 2 diabetes in adults that is set out in NICE guideline NG28.
 Information for the public Published: 2 December 2015 nice.org.uk About this information NICE guidelines provide advice on the care and support that should be offered to people who use health and care
Information for the public Published: 2 December 2015 nice.org.uk About this information NICE guidelines provide advice on the care and support that should be offered to people who use health and care
Understandingdiabetes
 Caring for Yourself or a Family Member Understandingdiabetes www.mainehealth.org Great changes may not happen right away, but with effort even the difficult may become easy. Bill Blackman WHAT S IN THIS
Caring for Yourself or a Family Member Understandingdiabetes www.mainehealth.org Great changes may not happen right away, but with effort even the difficult may become easy. Bill Blackman WHAT S IN THIS
Trends in Part C & D Star Rating Measure Cut Points
 Trends in Part C & D Star Rating Measure Cut Points Updated 11/18/2014 Document Change Log Previous Version Description of Change Revision Date - Initial release of the 2015 Trends in Part C & D Star Rating
Trends in Part C & D Star Rating Measure Cut Points Updated 11/18/2014 Document Change Log Previous Version Description of Change Revision Date - Initial release of the 2015 Trends in Part C & D Star Rating
DIABETIC EDUCATION MODULE ONE GENERAL OVERVIEW OF TREATMENT AND SAFETY
 DIABETIC EDUCATION MODULE ONE GENERAL OVERVIEW OF TREATMENT AND SAFETY First Edition September 17, 1997 Kevin King R.N., B.S., C.C.R.N. Gregg Kunder R.N., B.S.N., C.C.T.C. 77-120 CHS UCLA Medical Center
DIABETIC EDUCATION MODULE ONE GENERAL OVERVIEW OF TREATMENT AND SAFETY First Edition September 17, 1997 Kevin King R.N., B.S., C.C.R.N. Gregg Kunder R.N., B.S.N., C.C.T.C. 77-120 CHS UCLA Medical Center
Medicines for Type 2 Diabetes A Review of the Research for Adults
 Medicines for Type 2 Diabetes A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, if: Your doctor or health care provider has told you that you have type 2 diabetes and have high
Medicines for Type 2 Diabetes A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, if: Your doctor or health care provider has told you that you have type 2 diabetes and have high
Background (cont) World Health Organisation (WHO) and IDF predict that this number will increase to more than 1,3 million in the next 25 years.
 Diabetes Overview Background What is diabetes Non-modifiable risk factors Modifiable risk factors Common symptoms of diabetes Early diagnosis and management of diabetes Non-medical management of diabetes
Diabetes Overview Background What is diabetes Non-modifiable risk factors Modifiable risk factors Common symptoms of diabetes Early diagnosis and management of diabetes Non-medical management of diabetes
Medicare s Coverage of Diabetes Supplies & Services
 Medicare s Coverage of Diabetes Supplies & Services C E N T E R S F O R M E D I C A R E & M E D I C A I D S E R V I C E S What s covered This official government guide has important information about:
Medicare s Coverage of Diabetes Supplies & Services C E N T E R S F O R M E D I C A R E & M E D I C A I D S E R V I C E S What s covered This official government guide has important information about:
Chronic Kidney Disease and Diabetes
 Anyone with diabetes can get kidney disease. Diabetes and high blood pressure are the most common causes of kidney disease, and people often have both. Chronic (long term) kidney disease (CKD) caused by
Anyone with diabetes can get kidney disease. Diabetes and high blood pressure are the most common causes of kidney disease, and people often have both. Chronic (long term) kidney disease (CKD) caused by
