The Brain Injury Handbook. sponsored by
|
|
|
- Augusta Walters
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 sponsored by The Brain Injury Handbook
2 The Brain Injury Handbook Rehab Group in the UK Head Office, Pavilion 7, Watermark Park, 325 Govan Road, Glasgow, G51 2SE Tel: Fax:
3 copyright 2010 by Rehab Group in the UK, Pavilion 7, Watermark Park, 325 Govan Road, Glasgow, G51 2SE All rights reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part by any means whatsoever without written permission of Rehab is prohibited by law. Disclaimer Advertisements in The Brain Injury Handbook are accepted on a commercial basis. By publishing an advertisement, Rehab does not indicate endorsement of the product or services provided by the advertiser. Acknowledgements The publishers are grateful to the following people who gave their valuable time, support and expertise to the production of this handbook: Dr Andrew Bateman, Bill Braithwaite QC, David Bromley, Dr John Evans, Simon Garlick, Rona Gibb of the National Society for Epilepsy, James Japp, Gary Rhodes OBE, Dr Lesley Murphy, Dr Bill McKinlay, Maria McRobbie, Patrick O Shea at the Court of Protection, Rachel Redhead, Jean Martin Savage, Robert Sturgeon, Robert Swanney, Kate Swinburn, Jim Weir BA (Hons), CQSW and Rachel Wilson. We are grateful to our advertisers and sponsors whose support allows us to provide this handbook free of charge. Rehab has made every effort to ensure the accuracy of this handbook and has tried, to the best of its ability, to reflect best practice and the most current information. However, in view of the continuous changes in the healthcare arena, and in rehabilitation in particular, Rehab urges readers to use the handbook only as a guide to help inform their discussions with professionals. It is no substitute for the professional advice and guidance given by the healthcare and rehabilitation specialists assigned to an individual case, and the information provided must be considered alongside the recommendations of the treatment team. If you read anything that confuses or concerns you, talk it over with your medical team. We hope you will find the The Brain Injury Handbook invaluable reading and a great source of help. A copy of the handbook can also be accessed online at Contents The Brain Injury Handbook header Foreword 4 Gary Rhodes OBE Introduction 7 Angela Kerins, Chief Executive, Rehab Group A word from the Editor 9 Jonathan Smallman Section 1 13 Understanding brain injury and the brain Section 2 19 The brain injury itself Section 3 23 The consequences of brain injury Section 4 51 Recovery and rehabilitation Section 5 71 Returning to work after a brain injury Section 6 89 Legal issues Section Useful contacts and resources 2 The Brain Injury Handbook 3
4 Foreword Gary Rhodes OBE Chef, Restaurateur and Author Over the last 35 years, Gary Rhodes has become one of the UK s most high profile and respected chefs, restaurateurs and food authors. Despite overcoming a brain injury in the very early days of his career, he has always found the dedication to his craft and relentless pursuit of perfection required to remain at the top of his profession. Whilst enjoying one of my first cooking jobs in Amsterdam in the late 1970s, I was knocked down by a car and required brain surgery. Though the resulting injuries initially threatened my career, I was lucky to make a full recovery and return to the kitchen less than a year later. Gary s distinguished career, tireless attention to detail and unique mastery of the Great British Classics truly sets him apart. He has won a constellation of Michelin stars and is consistently revered by his peers as truly The Chef s Chef. About Rehab s work, he says, I have known about the fantastic work that Rehab does ever since I enjoyed the opportunity of being the Starter for its 2010 annual parliamentary pancake race. Having since become familiar with The Brain Injury Handbook, I see it is a great example of just one of the ways that Rehab supports people with brain injury. It provides crucial information and help, not only to people with brain injury themselves, but also to their families, friends and carers. It is my privilege to be associated with Rehab and the vital work that it is doing. 4 The Brain Injury Handbook 5
5 Introduction Thompson & Co SOLICITORS Angela Kerins Chief Executive, Rehab Group We help people who have left hospital following a brain injury to get their lives back on track...enabling them to move forward in their lives with independence and confidence. SERIOUS HEAD INJURY Have you suffered a Serious Head Injury as a result of an Accident? You may be entitled to Compensation We offer a sympathetic, professional and friendly service All Claims are dealt with by a specialist senior solicitor Keep 100% of your Compensation NO WIN, NO FEE CALL FREE Home & Hospital Visits Available Welcome to the 2010 updated edition of The Brain Injury Handbook, in which you will find comprehensive information, advice and statistics on acquired brain injury, or ABI, in the UK. The Rehab Group provides a range of innovative acquired brain injury services in the UK. As a leading provider in this area, we understand the effects of brain injury and how it is most effectively managed. It s not always easy to tell if someone has an acquired brain injury, and for this reason it s often referred to as the hidden disability. An acquired brain injury can happen to anyone, at any time in their life. It s not just those who sustain the injury that are affected but a whole circle of people, including family, friends and colleagues, who will all need to learn about the consequences of an acquired brain injury, how to support the person affected and how to access the services available to them. This is where we can help. The Rehab Group is a leading non- Governmental organisation which works towards a world where every person has the opportunity to achieve their potential. We work in local communities to provide high quality services and opportunities to people who need them. In the UK, the Rehab Group consists of three sister organisations Momentum, TBG Learning and The Chaseley Trust, each dedicated to assisting people in moving forward with their lives. In 1992, Rehab developed its vocational brain injury service, designed to support people to return to the workforce, training and further education. Since then, our services have continued to expand and now we offer a range of brain injury services across England and Scotland, helping people to regain their independence and confidence. As medical advances continue, the number of people surviving serious brain injury increases. This positive news means that more people are leaving hospital with the hope of moving on with their lives. Acquired brain injury dramatically changes lives. Common difficulties, including memory problems, personality changes, communication problems and fatigue can make day-to-day tasks a real challenge. Returning to the same employment as before may be impossible for many people. All of these factors can make life difficult but our brain injury rehabilitation programmes focus on strategies for coping with, and overcoming, these problems. 6 The Brain Injury Handbook 7
6 A word from the Editor header Jonathan Smallman The services that we provide include comprehensive assessment, specialist training, job coaching, work placement and job retention support. This handbook contains comprehensive information and details of supports available. Whether it s you or a family member who has sustained a brain injury, or you are a professional working in the field, we trust that you will find this an informative and useful resource. It s not just those who sustain the injury that are affected but a whole circle of people, including family, friends and colleagues, who will all need to learn about the consequences of an acquired brain injury, how to support the person affected and how to access the services available to them. Welcome to the latest issue of The Brain Injury Handbook. Having first-hand experience of brain injury, I have, in my role as Editor of the handbook, used the knowledge gained from my accident and its consequences to reflect on brain injury from personal and professional perspectives. We look at the definition of brain injury and how the brain works; the injury itself; the likely consequences; the recovery, rehabilitation and return to work; related compensation and legal claims; and useful contacts and further reading. You may be reading this handbook either as a person affected by brain injury or as a concerned family member. It is likely that this situation is new ground for you. Through our brain injury rehabilitation and neurodisability centres, we are able to offer assessment, treatment and rehabilitation to adults with acquired brain injury who suffer from physical, emotional and behavioural problems. Our programmes include cognitive rehabilitation, practical living and social skills, communication therapy, health education, leisure interests including creative and recreational pursuits, behavioural programmes including challenging behaviour and physical fitness. Programmes are set up on either a one to one basis and/or in a group setting. They are individually tailored to the personal needs of every patient. The centres are part of The Huntercombe Group, which has other hospitals and units treating mental health issues, eating disorders, addictions and learning disabilities. For information, please contact or visit our website: With that in mind, the handbook has been designed to offer vital reference and advice surrounding recovery and rehabilitation both in the short- and long-term. Professionals, people with brain injuries, their families, carers and friends should all find it of interest. The information and advice provided has been drawn from a number of sources. It has come from detailed research, from Rehab s own working experience, from a number of professionals with experience of brain injury and, last but not least, from people who also have personal experience of the trauma of brain injury within the family unit and who have chosen to share their stories. We have tried to structure the handbook so that you can easily access the information most relevant to you at any particular time. The facts A brain injury can happen to anyone at any time. Each year in the UK, some 140,000 individuals and their families and friends will encounter brain injury and its consequences. Around 85 per cent of injuries will be categorised as mild to moderate. 8 The Brain Injury Handbook 9
7 Although these will leave minimal long-term consequences, they may seriously disrupt a person s life for months and, sometimes, years. A further 10 per cent will suffer a moderate and 5 per cent a severe brain injury. This is likely to result in complex long-term problems affecting their personality, their thinking, their relationships and their ability to continue to lead independent and fruitful lives. There is no doubting the level of trauma that a brain injury will impose on a person be that physically, mentally, emotionally or, as is common, all three. However, the trauma also experienced by a concerned family can be equally significant. A brain injury requires that everyone involved has to become almost immediately familiar with a whole new reality associated with the recovery and rehabilitation process. A useful guide Research has highlighted the need for the family unit, which often provides support, to have written information about brain injury available, so enabling a clear understanding of the likely consequences. Although this handbook has been designed to provide that, it can also be used as a reference book for those who have experienced a brain injury first-hand. It is not a definitive guide to the condition and it may not answer all questions; however, it should provide a useful overview. We hope you will find The Brain Injury Handbook invaluable reading and a great source of help. A copy of the handbook can also be accessed via the Rehab website, JonathanSmallman@chaseleytrust.org A brain injury requires that everyone involved has to become almost immediately familiar with a whole new reality associated with the recovery and rehabilitation process. 10 The Brain Injury Handbook 11
8 Section 1 Section header 1 Understanding brain injury and the brain Stephenson Unit is an 11-bed, purpose built, acquired brain injury rehabilitation facility located within St. Mary s Care Centre. What is acquired brain injury? Adopting a multi-disciplinary approach to care, placing an emphasis on dignity, respect and unconditional positive regard whilst maximising independent functioning, providing the highest quality service to optimise a quality of life experience through an individually designed pathway of care. As part of our homes for life philosophy, we are developing a range of supported independent living accommodation. Acquired brain injury (also known as ABI) is damage to the brain that was not present at birth but has occurred since and which is non-progressive. An acquired brain injury can result from traumatic brain injury and non-traumatic brain injury. The most common causes of traumatic brain injury are road traffic accidents, assaults and falls. Non-traumatic brain injury has a variety of causes. The most common causes are stroke and other problems within blood vessels supplying the brain, tumours, infections, poisoning through ingestion or inhalation of toxic substances, metabolic disorders such as liver and kidney disease or diabetic coma and lack of blood flow (ischemia) or oxygen (hypoxia) to the brain. Acquired brain injury therefore excludes brain injury which was present at birth (congenital brain injury) and brain conditions which are degenerative such as dementia, multiple sclerosis or Parkinson s disease. Some forms of acquired brain injury, e.g. stroke or tumour, tend to cause localised damage to the brain whereas others, e.g. hypoxia and meningitis, usually cause widespread brain damage. The effects of acquired brain injury upon the individual can therefore vary dramatically from person to person. Given the diverse nature of acquired brain injury, it is understandable that in this area of rehabilitation various terms are often used to describe the nature of the brain injury, e.g. head injury, brain injury, traumatic brain injury, acquired brain injury. To avoid confusion and for the sake of consistency, this handbook will refer to brain injury throughout to denote any form of acquired brain injury as defined here. 12 The Brain Injury Handbook 13
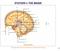
9 Understanding brain injury and the brain Section 1 What does the brain do and how does it work? The brain is the control centre for all the body s functions, such as walking, talking, swallowing, breathing, taste, smell, heart rate and so on. It also controls all our thinking functions, our emotions, how we behave and all our intellectual (cognitive) activities, such as how we attend to things, how we perceive and understand our world and its physical surroundings, how we learn and remember and so on. Everything, in fact! It follows, therefore, that damage to the brain for whatever reason can impair some or all of these functions or activities. How much impairment a person will have will depend on the type, location and severity of the injury. It will help to understand this if we have a look at the structure of the brain and the functions of the different areas within it. The structure and function of the brain The brain is a soft, jelly-like material that is completely enclosed in the skull and floats in a protective sea of cerebrospinal fluid. This fluid supports and nourishes the brain and acts as a kind of shock absorber for rapid head movements. To some extent the skull protects the brain but nature wasn t kind when designing the inner surface with its bony ridges. These can lacerate and bruise the delicate surface of the brain if it is forced violently against the inside of the skull, as can happen in a road traffic accident (also known as an RTA) or fall. The brain is also protected by three layers of membrane that lie between it and the skull. If the brain is shaken about, these membranes and blood vessels can tear and bleed. If enough blood escapes, blood clots will form and can press on the brain and cause damage. There can also be damage if the blood vessels become weakened and burst, as in the case of a brain haemorrhage. Damage will also occur if the blood supply to the brain is interrupted for any reason. The brain is made up of billions of cells, blood vessels, fluid and nerve cells called neurons. These have delicate nerve fibres that radiate from the cell body and connect to millions of other nerve cells to form highly-complex communication between different parts of the brain. It is believed that each individual neuron network connects with approximately 1,100 other neurons. Nobody really knows how many neurons there are in the brain but the favoured estimate by neuroscientists is 12 billion. Professor Susan Greenfield, an eminent neuroscientist, has suggested that we think of neurons as trees in the Amazon rainforest and the leaves on those trees as the connections between the neurons. If the brain is shaken about, these delicate nerve fibres get disrupted and damaged, resulting in a disruption of the communication pathways and the consequent disruption of certain skills and abilities. There are three main areas that play a vital part in our ability to function: 1 The cerebral cortex 2 The brain stem 3 The cerebellum Figure 1 The brain cerebral cortex brain stem spinal cord 1 The cerebral cortex The cerebral cortex (Figure 1) is the largest part of the brain and is the area that is responsible for all our thinking activities. It is divided into two connected halves the left and right cerebral hemispheres. The left hemisphere controls the right side of the body and the right hemisphere controls the left. For example, if a person sustains a brain injury, such as a stroke, to the left hemisphere in the area of the cerebral cortex that controls movement, this may result in weakness or even paralysis of the right arm and leg. In most people, the left hemisphere primarily controls verbal functions such as speech and language while the right hemisphere primarily controls visual spatial (non-verbal) functions such as those involved in drawing, rhythm or finding one s way in unfamiliar surroundings. The hemispheres are known to process material in different ways with the left cerebral hemisphere specialising in processing cerebrospinal fluid skull cerebellum material in a sequential and logical manner and the right cerebral hemisphere processing information in a holistic and intuitive way. The cerebral cortex is further divided into four areas, or lobes, each of which controls specific functions and skills. 14 The Brain Injury Handbook 15
10 Understanding brain injury and the brain Section 1 16 Figure 2 Cerebral lobes motor cortex (movement) frontal lobes The frontal lobes temporal lobe (auditory lobe) brain stem The frontal lobes (Figure 2) have been termed the executive of the brain. This is where all of our higher-level thinking goes on, allowing us to reason logically, make decisions, plan, organise and problem-solve, exercise good judgement and monitor or manage our actions. It is considered to be the home of our personality and the control centre for our emotions and behaviour. The frontal lobes allow us to apply our knowledge and adapt our behaviour so that it is appropriate to the situation we are in. The frontal lobes also contain the motor cortex, a vital part of the brain system controlling movement. The frontal lobes are extremely vulnerable to injury due to their position at the front of the skull. Studies have found that the frontal area is the most common region of injury, even following mild brain injury. Damage to this area can cause myriad cognitive problems and can dramatically change social behaviour and somatosensory cortex (sensations) spinal cord parietal lobe occipital lobe cerebellum personality. Physical problems can include the loss of fine movements, lack of strength in the arms, hands and fingers, little spontaneous facial expression or difficulty in speaking. The temporal lobe The temporal lobe (Figure 2) lies just behind our ears and contains the auditory cortex. This allows us to interpret sound. The temporal lobe stores most of our memories and is involved in aspects of language, including our ability to use language and understand what we hear. Like the frontal lobes, the temporal lobe is involved in regulating certain aspects of personality. Deep inside the temporal lobe are the structures of the hypothalamus and limbic system. The hypothalamus is involved in instinctual behaviours such as aggression, sexual arousal, appetite, thirst and temperature control. The limbic system is in control of emotional reactions. Damage to these areas can severely disrupt our emotions resulting in sudden and dramatic mood swings; and can also lead to inappropriate social behaviour such as hyper-sexuality and impulsiveness. The parietal lobe The parietal lobe (Figure 2) contains the somatosensory cortex which receives and analyses information from the skin concerning touch, pressure, temperature and some aspects of pain. The parietal lobe is vital to our spatial understanding of the world. For example, it enables us to understand where we are in relation to our surroundings and where our body parts are in relation to each other, as well as the spatial relationships between the things we perceive in our environment. Damage to the parietal lobe can impair reading, writing and mathematical abilities, drawing and constructional tasks, as well as self-care abilities such as washing and dressing. The occipital lobe The occipital lobe (Figure 2) analyses what we see and is, therefore, responsible for sight. If it is damaged, blindness or partial blindness can result. 2 The brain stem The brain stem (Figure 2) is connected to the spinal cord and from there to the whole of the central nervous system in the rest of the body. The brain stem controls movements of the throat, so damage to this area may result in impairments in speech and swallowing. It also controls consciousness, alertness and functions that are not under conscious control, such as breathing, body temperature, heart rate and blood pressure. It is therefore an extremely critical area in terms of damage to the brain stem interrupting normal nerve fibres. 3 The cerebellum The cerebellum (Figure 2) is located just behind the top part of the brain stem and controls fine muscle co-ordination, balance and posture. Damage to this area can affect our ability to move quickly and gracefully or to perform such functions as climbing up a ladder or buttoning up a jacket. In summary, damage to a particular part of the brain can produce impairment in the function that it controls. If the damage is limited to a small area, then it is likely that only a few functions will be impaired. If, however, as is more common, there is widespread damage, then this can produce a complex array of physical and psychological problems. The frontal lobes are extremely vulnerable to injury due to their position at the front of the skull. Studies have found that the frontal area is the most common region of injury, even following mild brain injury. The Brain Injury Handbook 17
Section 1 Understanding brain injury and the brain
 Section 1 Understanding brain injury and the brain Acquired brain injury (also known as ABI) is damage to the brain that was not present at birth but has occurred since, and which is non-progressive. An
Section 1 Understanding brain injury and the brain Acquired brain injury (also known as ABI) is damage to the brain that was not present at birth but has occurred since, and which is non-progressive. An
Section 1. Understanding brain injury and the brain. What is acquired brain injury? Section 1
 Section 1 Understanding brain injury and the brain Section 1 What is acquired brain injury? Acquired brain injury (also known as ABI) is damage to the brain that was not present at birth but has occurred
Section 1 Understanding brain injury and the brain Section 1 What is acquired brain injury? Acquired brain injury (also known as ABI) is damage to the brain that was not present at birth but has occurred
Basic Brain Information
 Basic Brain Information Brain facts Your brain weighs about 3lbs, or just under 1.5Kg It has the texture of blancmange Your brain is connected to your spinal cord by the brain stem Behind your brain stem
Basic Brain Information Brain facts Your brain weighs about 3lbs, or just under 1.5Kg It has the texture of blancmange Your brain is connected to your spinal cord by the brain stem Behind your brain stem
Basic brain information
 Basic brain information Brain facts Your brain weighs about 3lbs, or just under 1.5Kg It has the texture of blancmange Your brain is connected to your spinal cord by the brain stem Behind your brain stem
Basic brain information Brain facts Your brain weighs about 3lbs, or just under 1.5Kg It has the texture of blancmange Your brain is connected to your spinal cord by the brain stem Behind your brain stem
BINSA Information on Brain Injury
 Acquired Brain Injury (ABI) There are a number of ways an individual can suffer an acquired brain injury (ABI) Figure one - ABI causes Significant causes of ABI Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Traumatic Brain
Acquired Brain Injury (ABI) There are a number of ways an individual can suffer an acquired brain injury (ABI) Figure one - ABI causes Significant causes of ABI Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Traumatic Brain
Module 1: The Brain and the Central Nervous System (CNS)
 Module 1: The Brain and the Central Nervous System (CNS) By the end of this unit, the learner will be able to: Describe the anatomy of the brain and the central nervous system Identify regions of the brain
Module 1: The Brain and the Central Nervous System (CNS) By the end of this unit, the learner will be able to: Describe the anatomy of the brain and the central nervous system Identify regions of the brain
The Brain Injury Handbook. sponsored by. The Brain Injury Handbook
 The Brain Injury Handbook sponsored by The Brain Injury Handbook a Supporting brain injured people and their carers We understand the impact a brain injury can have on the whole family. Our specialist
The Brain Injury Handbook sponsored by The Brain Injury Handbook a Supporting brain injured people and their carers We understand the impact a brain injury can have on the whole family. Our specialist
Background on Brain Injury
 CHAPTER 1 Background on Brain Injury In this chapter, you will: Read about Alberta s definition of Acquired Brain Injury and how that affects which supports you will be able to access. Learn about the
CHAPTER 1 Background on Brain Injury In this chapter, you will: Read about Alberta s definition of Acquired Brain Injury and how that affects which supports you will be able to access. Learn about the
The Brain Injury Handbook. Sponsored by. The Brain Injury Handbook. sponsored by
 The Brain Injury Handbook sponsored by Sponsored by The Brain Injury Handbook a Suffered a serious head injury? We can help brighten your future. At Harris Fowler, we support you every step of the way.
The Brain Injury Handbook sponsored by Sponsored by The Brain Injury Handbook a Suffered a serious head injury? We can help brighten your future. At Harris Fowler, we support you every step of the way.
Homework Help Stroke
 The Brain & Strokes Your brain is the most complex organ in your body. It is the command centre for everything you do, think, sense and say! It has over 100 billion special nerve cells called neurons.
The Brain & Strokes Your brain is the most complex organ in your body. It is the command centre for everything you do, think, sense and say! It has over 100 billion special nerve cells called neurons.
The brain structure and function
 The brain structure and function This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding brain tumours. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 5. Contents Introduction
The brain structure and function This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding brain tumours. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 5. Contents Introduction
Traumatic Brain Injury and Incarceration. Objectives. Traumatic Brain Injury. Which came first, the injury or the behavior?
 Traumatic Brain Injury and Incarceration Which came first, the injury or the behavior? Barbara Burchell Curtis RN, MSN Objectives Upon completion of discussion, participants should be able to Describe
Traumatic Brain Injury and Incarceration Which came first, the injury or the behavior? Barbara Burchell Curtis RN, MSN Objectives Upon completion of discussion, participants should be able to Describe
Our highly specialised team has wide experience in dealing with
 Our highly specialised team has wide experience in dealing with complex claims arising from brain injury. We work in a supportive, considered & clear way, dedicated to achieving the best possible outcome
Our highly specialised team has wide experience in dealing with complex claims arising from brain injury. We work in a supportive, considered & clear way, dedicated to achieving the best possible outcome
brain injury take care of yourself. we ll take care of the rest.
 take care of yourself. we ll take care of the rest. common injuries While injuries to the head do not always result in damage to the brain, it s important to note the most common forms of head trauma that
take care of yourself. we ll take care of the rest. common injuries While injuries to the head do not always result in damage to the brain, it s important to note the most common forms of head trauma that
Parts of the Brain. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
Functions of the Brain
 Objectives 0 Participants will be able to identify 4 characteristics of a healthy brain. 0 Participants will be able to state the functions of the brain. 0 Participants will be able to identify 3 types
Objectives 0 Participants will be able to identify 4 characteristics of a healthy brain. 0 Participants will be able to state the functions of the brain. 0 Participants will be able to identify 3 types
The Brain of a Normal Human
 The Brain of a Normal Human Your Brain Evolved Over Time Human Brain Logic and reasoning Mammalian Brain More complex feelings and reactions Lizard Brain Basic functions The Brain Stem or Hindbrain (The
The Brain of a Normal Human Your Brain Evolved Over Time Human Brain Logic and reasoning Mammalian Brain More complex feelings and reactions Lizard Brain Basic functions The Brain Stem or Hindbrain (The
BIOLOGY STUDY PACKET THE BRAIN
 BIOLOGY STUDY PACKET THE BRAIN SC.912.L.14.26 AA Spring 2012 The intent of this packet is to supplement regular classroom instruction, not to replace it. This also supposes that the students have access
BIOLOGY STUDY PACKET THE BRAIN SC.912.L.14.26 AA Spring 2012 The intent of this packet is to supplement regular classroom instruction, not to replace it. This also supposes that the students have access
Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron
 Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron Generally speaking, we can divide the nervous system into different parts, according to location and function. So far we have mentioned the central nervous system
Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron Generally speaking, we can divide the nervous system into different parts, according to location and function. So far we have mentioned the central nervous system
Professor McLellan Emeritus Professor of Rehabilitation
 Brain injury can be devastating for families and carers as well as the people directly affected. These cases require specialist advice and support and that is what the Brain Injury Group provides. It is
Brain injury can be devastating for families and carers as well as the people directly affected. These cases require specialist advice and support and that is what the Brain Injury Group provides. It is
IMPROVING YOUR EXPERIENCE
 Comments trom the Aberdeen City Joint Futures Brain Injury Group The Aberdeen City Joint Futures Brain Injury Group is made up of representatives from health (acute services, rehabilitation and community),
Comments trom the Aberdeen City Joint Futures Brain Injury Group The Aberdeen City Joint Futures Brain Injury Group is made up of representatives from health (acute services, rehabilitation and community),
Human Neuroanatomy. Grades 9-12. Driving Question: How did the evolution of the human brain impact the structure and function it has today?
 Human Neuroanatomy Grades 9-12 Driving Question: How did the evolution of the human brain impact the structure and function it has today? Objectives: Students will be able to Describe the basic parts and
Human Neuroanatomy Grades 9-12 Driving Question: How did the evolution of the human brain impact the structure and function it has today? Objectives: Students will be able to Describe the basic parts and
REHABILITATION MEDICINE by PROFESSOR ANTHONY WARD
 REHABILITATION MEDICINE by PROFESSOR ANTHONY WARD What is Rehabilitation Medicine? Rehabilitation Medicine (RM) is the medical specialty with rehabilitation as its primary strategy. It provides services
REHABILITATION MEDICINE by PROFESSOR ANTHONY WARD What is Rehabilitation Medicine? Rehabilitation Medicine (RM) is the medical specialty with rehabilitation as its primary strategy. It provides services
Anosmia Following Traumatic Brain Injury. Patient Information Booklet. Talis Consulting Limited
 Anosmia Following Traumatic Brain Injury Patient Information Booklet Talis Consulting Limited What is Anosmia? Anosmia literally means no smell and refers to any condition whereby a person loses their
Anosmia Following Traumatic Brain Injury Patient Information Booklet Talis Consulting Limited What is Anosmia? Anosmia literally means no smell and refers to any condition whereby a person loses their
Brain Tumor 101. Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center
 Brain Tumor 101 Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center Objectives Identify the different parts of the brain Describe how each part of the brain works Connect each part
Brain Tumor 101 Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center Objectives Identify the different parts of the brain Describe how each part of the brain works Connect each part
B U R T & D A V I E S PERSONAL INJURY LAWYERS
 TRANSPORT ACCIDENT LAW - TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY Traumatic Brain Injury ( TBI ) is a common injury in transport accidents. TBI s are probably the most commonly undiagnosed injuries in a hospital setting.
TRANSPORT ACCIDENT LAW - TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY Traumatic Brain Injury ( TBI ) is a common injury in transport accidents. TBI s are probably the most commonly undiagnosed injuries in a hospital setting.
Brain Power. Counseling and Mental Health
 Brain Power Counseling and Mental Health TEA COPYRIGHT Copyright Texas Education Agency, 2012. These Materials are copyrighted and trademarked as the property of the Texas Education Agency (TEA) and may
Brain Power Counseling and Mental Health TEA COPYRIGHT Copyright Texas Education Agency, 2012. These Materials are copyrighted and trademarked as the property of the Texas Education Agency (TEA) and may
We have made the following changes to the Critical Illness events covered under our group critical illness policy.
 We have made the following changes to the Critical Illness events covered under our group critical illness policy. March 2015 Because everyone needs a back-up plan 7 New critical illness events added to
We have made the following changes to the Critical Illness events covered under our group critical illness policy. March 2015 Because everyone needs a back-up plan 7 New critical illness events added to
It s All in the Brain!
 It s All in the Brain! Presented by: Mari Hubig, M.Ed. 0-3 Outreach Coordinator Educational Resource Center on Deafness What is the Brain? The brain is a muscle In order to grow and flourish, the brain
It s All in the Brain! Presented by: Mari Hubig, M.Ed. 0-3 Outreach Coordinator Educational Resource Center on Deafness What is the Brain? The brain is a muscle In order to grow and flourish, the brain
Cerebral Palsy. In order to function, the brain needs a continuous supply of oxygen.
 Cerebral Palsy Introduction Cerebral palsy, or CP, can cause serious neurological symptoms in children. Up to 5000 children in the United States are diagnosed with cerebral palsy every year. This reference
Cerebral Palsy Introduction Cerebral palsy, or CP, can cause serious neurological symptoms in children. Up to 5000 children in the United States are diagnosed with cerebral palsy every year. This reference
The Cranium Connection
 Your Brain! The brain is the command center of your body. It controls just about everything you do, even when you are sleeping. Weighing about 3 pounds, the brain is made up of many parts that all work
Your Brain! The brain is the command center of your body. It controls just about everything you do, even when you are sleeping. Weighing about 3 pounds, the brain is made up of many parts that all work
Cerebral Palsy. 1995-2014, The Patient Education Institute, Inc. www.x-plain.com nr200105 Last reviewed: 06/17/2014 1
 Cerebral Palsy Introduction Cerebral palsy, or CP, can cause serious neurological symptoms in children. Thousands of children are diagnosed with cerebral palsy every year. This reference summary explains
Cerebral Palsy Introduction Cerebral palsy, or CP, can cause serious neurological symptoms in children. Thousands of children are diagnosed with cerebral palsy every year. This reference summary explains
Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain Organization
 Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain Organization Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Course Outline Lecture 1: Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain
Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain Organization Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Course Outline Lecture 1: Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain
Types of Brain Injury
 Types of Brain Injury The bones of your skull are hard and they protect your brain. Your brain is soft, like firm Jell-O. When your head moves, your brain moves inside your skull. When your head is hit
Types of Brain Injury The bones of your skull are hard and they protect your brain. Your brain is soft, like firm Jell-O. When your head moves, your brain moves inside your skull. When your head is hit
Chapter 4: Eligibility Categories
 23 Chapter 4: Eligibility Categories In this chapter you will: learn the different special education categories 24 IDEA lists different disability categories under which children may be eligible for services.
23 Chapter 4: Eligibility Categories In this chapter you will: learn the different special education categories 24 IDEA lists different disability categories under which children may be eligible for services.
Occupational therapy after stroke
 Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Occupational therapy after stroke After a stroke, you are likely to need help to regain your abilities, learn new skills and cope with any remaining
Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Occupational therapy after stroke After a stroke, you are likely to need help to regain your abilities, learn new skills and cope with any remaining
Glossary. Activities of Daily Living (ADL): routine daily self care skills, including dressing, bathing, toileting, and feeding.
 Glossary Acoustic nerve: the nerve that is responsible for hearing. Activities of Daily Living (ADL): routine daily self care skills, including dressing, bathing, toileting, and feeding. Adaptive physical
Glossary Acoustic nerve: the nerve that is responsible for hearing. Activities of Daily Living (ADL): routine daily self care skills, including dressing, bathing, toileting, and feeding. Adaptive physical
Nationwide providers of specialist care and rehabilitation
 Valuing People VP Community Care Nationwide providers of specialist care and rehabilitation 9 YEARS OF SPECIALIST CARE VP Community Care An introduction to what we do Registered with the CQC, we support
Valuing People VP Community Care Nationwide providers of specialist care and rehabilitation 9 YEARS OF SPECIALIST CARE VP Community Care An introduction to what we do Registered with the CQC, we support
The Central Nervous System
 A fact sheet for patients and carers Spinal strokes This fact sheet provides information on spinal strokes. Our fact sheets are designed as general introductions to each subject and are intended to be
A fact sheet for patients and carers Spinal strokes This fact sheet provides information on spinal strokes. Our fact sheets are designed as general introductions to each subject and are intended to be
Brain Injuries INJURY & NEGLIGENCE SPECIALISTS
 Brain Injuries INJURY & NEGLIGENCE SPECIALISTS Injury & Negligence At all times they put my interests first and gave excellent advice. Client interviewed for Chambers (Independent Legal Guide) WELCOME
Brain Injuries INJURY & NEGLIGENCE SPECIALISTS Injury & Negligence At all times they put my interests first and gave excellent advice. Client interviewed for Chambers (Independent Legal Guide) WELCOME
What is vascular dementia?
 alzheimers.org.uk What is vascular dementia? Vascular dementia is the second most common form of dementia after Alzheimer s disease. It is caused by problems in the supply of blood to the brain. This factsheet
alzheimers.org.uk What is vascular dementia? Vascular dementia is the second most common form of dementia after Alzheimer s disease. It is caused by problems in the supply of blood to the brain. This factsheet
Delirium. The signs of delirium are managed by treating the underlying cause of the medical condition causing the delirium.
 Delirium Introduction Delirium is a complex symptom where a person becomes confused and shows significant changes in behavior and mental state. Signs of delirium include problems with attention and awareness,
Delirium Introduction Delirium is a complex symptom where a person becomes confused and shows significant changes in behavior and mental state. Signs of delirium include problems with attention and awareness,
BINSA Information on Mild Traumatic Brain Injury
 Mild traumatic brain injuries (MTBI) occur through sporting, car and workplace accidents. Mild brain injury is not easily diagnosed. This fact sheet explains how it may be recognised and assessed, and
Mild traumatic brain injuries (MTBI) occur through sporting, car and workplace accidents. Mild brain injury is not easily diagnosed. This fact sheet explains how it may be recognised and assessed, and
Sheep Brain Dissection Picture Guide
 Sheep Brain Dissection Picture Guide Figure 1: Right Hemisphere of Sheep s Brain Figure 2: Underside of Sheep s Brain Figure 3: Saggital cut of Sheep s Brain to reveal subcortical structures Figure 4:
Sheep Brain Dissection Picture Guide Figure 1: Right Hemisphere of Sheep s Brain Figure 2: Underside of Sheep s Brain Figure 3: Saggital cut of Sheep s Brain to reveal subcortical structures Figure 4:
acbis Chapter 1: Overview of Brain Injury
 acbis Academy for the Certification of Brain Injury Specialists Certification Exam Preparation Course Chapter 1: Overview of Brain Injury Module Objectives Describe the incidence, prevalence and epidemiology
acbis Academy for the Certification of Brain Injury Specialists Certification Exam Preparation Course Chapter 1: Overview of Brain Injury Module Objectives Describe the incidence, prevalence and epidemiology
Specialist brain injury services. Rehabilitation Transitional medical care Community support Special education
 Specialist brain injury services Rehabilitation Transitional medical care Community support Special education I don t know where we d be without the support we ve had from the staff at The Children s Trust.
Specialist brain injury services Rehabilitation Transitional medical care Community support Special education I don t know where we d be without the support we ve had from the staff at The Children s Trust.
NHS Continuing Healthcare
 NHS Continuing Healthcare Questionnaire In association with Questionnaire 1. Full name of patient 2. Home address (prior to transfer into care home if applicable) 3. Patient s Date of Birth 4. Patient
NHS Continuing Healthcare Questionnaire In association with Questionnaire 1. Full name of patient 2. Home address (prior to transfer into care home if applicable) 3. Patient s Date of Birth 4. Patient
Manifesto for Acquired Brain Injury Rehabilitation
 Manifesto for Acquired Brain Injury Rehabilitation For further information please contact: Chloë Hayward UKABIF Executive Director PO Box 355 Plymouth PL3 4WD Tel: 01752 601318 Email: ukabif@btconnect.com
Manifesto for Acquired Brain Injury Rehabilitation For further information please contact: Chloë Hayward UKABIF Executive Director PO Box 355 Plymouth PL3 4WD Tel: 01752 601318 Email: ukabif@btconnect.com
Amazing AmMy Brain! DID YOU KNOW..
 My Amazing Brain! DID YOU KNOW... 3 Your Amazing Brain 4-5 How your Amazing Brain Works 6 7 Left Brain, Right Brain 8 Brain Facts 9 Senses 10 Look after your Brain 11 What Does a Brain Scientist Do? MY
My Amazing Brain! DID YOU KNOW... 3 Your Amazing Brain 4-5 How your Amazing Brain Works 6 7 Left Brain, Right Brain 8 Brain Facts 9 Senses 10 Look after your Brain 11 What Does a Brain Scientist Do? MY
Brain Injuries INJURY & NEGLIGENCE SPECIALISTS
 Brain Injuries INJURY & NEGLIGENCE SPECIALISTS Injury & Negligence I had total confidence in their ability to deal with my case. Adam Fitzgibbon Liverpool WELCOME TO PANNONE PART OF SLATER & GORDON On
Brain Injuries INJURY & NEGLIGENCE SPECIALISTS Injury & Negligence I had total confidence in their ability to deal with my case. Adam Fitzgibbon Liverpool WELCOME TO PANNONE PART OF SLATER & GORDON On
DRIVER REHABILITATION OVERVIEW
 DRIVER REHABILITATION OVERVIEW What is included in a Driving Evaluation? The purpose of the evaluation is to determine if the individual s medical condition, medications, functional limitations and/ or
DRIVER REHABILITATION OVERVIEW What is included in a Driving Evaluation? The purpose of the evaluation is to determine if the individual s medical condition, medications, functional limitations and/ or
The Petrylaw Lawsuits Settlements and Injury Settlement Report
 The Petrylaw Lawsuits Settlements and Injury Settlement Report TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURIES How Minnesota Juries Decide the Value of Pain and Suffering in Brain Injury Cases The Petrylaw Lawsuits Settlements
The Petrylaw Lawsuits Settlements and Injury Settlement Report TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURIES How Minnesota Juries Decide the Value of Pain and Suffering in Brain Injury Cases The Petrylaw Lawsuits Settlements
Traumatic Brain Injury
 Traumatic Brain Injury NICHCY Disability Fact Sheet #18 Updated, July 2014 Susan s Story Susan was 7 years old when she was hit by a car while riding her bike. She broke her arm and leg. She also hit her
Traumatic Brain Injury NICHCY Disability Fact Sheet #18 Updated, July 2014 Susan s Story Susan was 7 years old when she was hit by a car while riding her bike. She broke her arm and leg. She also hit her
Diuretics: You may get diuretic medicine to help decrease swelling in your brain. This may help your brain get better blood flow.
 Hemorrhagic Stroke GENERAL INFORMATION: What is a hemorrhagic stroke? A hemorrhagic stroke happens when a blood vessel in the brain bursts. This may happen if the blood vessel wall is weak, or sometimes
Hemorrhagic Stroke GENERAL INFORMATION: What is a hemorrhagic stroke? A hemorrhagic stroke happens when a blood vessel in the brain bursts. This may happen if the blood vessel wall is weak, or sometimes
What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)?
 What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair 1 What
What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair 1 What
3) Cerebral Cortex & Functions of the 4 LOBES. 5) Cranial Nerves (Nerves In the Cranium, i.e., Head)
 Lecture 5 (Oct 8 th ): ANATOMY and FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Lecture Outline 1) Basic Divisions (CNS vs. PNS, Somatic vs. Autonomic) and Directional Terms 2) The Brain (Hindbrain/ Midbrain/ Forebrain)
Lecture 5 (Oct 8 th ): ANATOMY and FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Lecture Outline 1) Basic Divisions (CNS vs. PNS, Somatic vs. Autonomic) and Directional Terms 2) The Brain (Hindbrain/ Midbrain/ Forebrain)
3. The neuron has many branch-like extensions called that receive input from other neurons. a. glia b. dendrites c. axons d.
 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer: A difficulty: 1 factual
Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer: A difficulty: 1 factual
Occupational Therapy Services
 Occupational Therapy Services The JSP occupational therapy service provides high quality intervention to children and adults whose lives have been affected by an acquired disability. Our occupational therapists
Occupational Therapy Services The JSP occupational therapy service provides high quality intervention to children and adults whose lives have been affected by an acquired disability. Our occupational therapists
Legal Support Service North West. Support for life after childhood brain and other serious injuries. www.childbraininjurytrust.org.
 Legal Support Service North West Support for life after childhood brain and other serious injuries www.childbraininjurytrust.org.uk Hello and welcome to the Legal Support Services booklet for the North
Legal Support Service North West Support for life after childhood brain and other serious injuries www.childbraininjurytrust.org.uk Hello and welcome to the Legal Support Services booklet for the North
Traumatic Brain Injury. Working with persons with traumatic brain injury (TBI) in the community.
 Traumatic Brain Injury Working with persons with traumatic brain injury (TBI) in the community. Fact or Fiction about Brain Injury 1. Traumatic brain injury is caused by a disease. 2. Children are more
Traumatic Brain Injury Working with persons with traumatic brain injury (TBI) in the community. Fact or Fiction about Brain Injury 1. Traumatic brain injury is caused by a disease. 2. Children are more
What is cerebral palsy?
 What is cerebral palsy? This booklet will help you to have a better understanding of the physical and medical aspects of cerebral palsy. We hope it will be a source of information to anyone who wishes
What is cerebral palsy? This booklet will help you to have a better understanding of the physical and medical aspects of cerebral palsy. We hope it will be a source of information to anyone who wishes
Clinical Neuropsychology. Recovery & Rehabilitation. Alan Sunderland School of Psychology
 Clinical Neuropsychology. Recovery & Rehabilitation Alan Sunderland School of Psychology 1 The Changing Role of Clinical Neuropsychology HISTORY The Origins of Clinical Neuropsychology Emergence as a profession
Clinical Neuropsychology. Recovery & Rehabilitation Alan Sunderland School of Psychology 1 The Changing Role of Clinical Neuropsychology HISTORY The Origins of Clinical Neuropsychology Emergence as a profession
Brain Cancer. This reference summary will help you understand how brain tumors are diagnosed and what options are available to treat them.
 Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
Function (& other notes)
 LAB 8. ANATOMY OF THE HUMAN BRAIN In this exercise you each will map the human brain both anatomy and function so that you can develop a more accurate picture of what s going on in your head :-) EXTERNAL
LAB 8. ANATOMY OF THE HUMAN BRAIN In this exercise you each will map the human brain both anatomy and function so that you can develop a more accurate picture of what s going on in your head :-) EXTERNAL
Traumatic Brain Injury
 Traumatic Brain Injury NICHCY Disability Fact Sheet #18 Resources updated, March 2011 Susan s Story Susan was 7 years old when she was hit by a car while riding her bike. She broke her arm and leg. She
Traumatic Brain Injury NICHCY Disability Fact Sheet #18 Resources updated, March 2011 Susan s Story Susan was 7 years old when she was hit by a car while riding her bike. She broke her arm and leg. She
Sunderland and Gateshead Community Acquired Brain Injury Service (CABIS) Patient Information Leaflet
 Sunderland and Gateshead Community Acquired Brain Injury Service (CABIS) Patient Information Leaflet Shining a light on the future Sunderland and Gateshead Community Acquired Brain Injury Service [CABIS]
Sunderland and Gateshead Community Acquired Brain Injury Service (CABIS) Patient Information Leaflet Shining a light on the future Sunderland and Gateshead Community Acquired Brain Injury Service [CABIS]
Cortical Visual Impairment An introduction
 Cortical Visual Impairment An introduction This is a general introduction to Cortical Visual Impairment intended for families and support workers who may live with or support children and adults with learning
Cortical Visual Impairment An introduction This is a general introduction to Cortical Visual Impairment intended for families and support workers who may live with or support children and adults with learning
Quality Measures for Long-stay Residents Percent of residents whose need for help with daily activities has increased.
 Quality Measures for Long-stay Residents Percent of residents whose need for help with daily activities has increased. This graph shows the percent of residents whose need for help doing basic daily tasks
Quality Measures for Long-stay Residents Percent of residents whose need for help with daily activities has increased. This graph shows the percent of residents whose need for help doing basic daily tasks
Catastrophic Injuries
 Catastrophic Injuries Lyons Davidson catastrophic injury service our clients are at the heart of our business For advice about your catastrophic injury claim please contact us on Freephone 0800 694 0233
Catastrophic Injuries Lyons Davidson catastrophic injury service our clients are at the heart of our business For advice about your catastrophic injury claim please contact us on Freephone 0800 694 0233
The Role of a Case Manager The experience of others
 The Role of a Case Manager The experience of others Independent Living Solutions Ltd Case Management and Rehabilitation Services Introduction When a person s life has been changed by injury - however caused
The Role of a Case Manager The experience of others Independent Living Solutions Ltd Case Management and Rehabilitation Services Introduction When a person s life has been changed by injury - however caused
Momentum Skills North East Services for Acquired Brain Injury and Neurological Conditions
 Momentum Skills North East Services for Acquired Brain Injury and Neurological Conditions Who is the service for? Momentum Skills North East caters for individuals who wish to re-engage with their local
Momentum Skills North East Services for Acquired Brain Injury and Neurological Conditions Who is the service for? Momentum Skills North East caters for individuals who wish to re-engage with their local
HEAD INJURY; THE REHABILITATION PATHWAY. Professor Graham Powell. Professor of Clinical and Neuropsychology
 HEAD INJURY; THE REHABILITATION PATHWAY by Professor Graham Powell Professor of Clinical and Neuropsychology The management of head injury will broadly flow along a pathway from Accident and Emergency
HEAD INJURY; THE REHABILITATION PATHWAY by Professor Graham Powell Professor of Clinical and Neuropsychology The management of head injury will broadly flow along a pathway from Accident and Emergency
Good Samaritan Inpatient Rehabilitation Program
 Good Samaritan Inpatient Rehabilitation Program Living at your full potential. Welcome When people are sick or injured, our goal is their maximum recovery. We help people live to their full potential.
Good Samaritan Inpatient Rehabilitation Program Living at your full potential. Welcome When people are sick or injured, our goal is their maximum recovery. We help people live to their full potential.
TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY (TBI) According to the IDEA, (2004), traumatic brain injury is defined by as:
 TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY (TBI) DEFINITION: According to the IDEA, (2004), traumatic brain injury is defined by as: An acquired injury to the brain caused by an external physical force, resulting in total
TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY (TBI) DEFINITION: According to the IDEA, (2004), traumatic brain injury is defined by as: An acquired injury to the brain caused by an external physical force, resulting in total
Nervous System: PNS and CNS
 Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Work After Stroke. Updated: April 2015 Review date: April 2016. Employers Guide
 Work After Stroke Updated: April 2015 Review date: April 2016 Employers Guide The Work After Stroke research project team would like to thank all Different Strokes members who took part in the 3-year project,
Work After Stroke Updated: April 2015 Review date: April 2016 Employers Guide The Work After Stroke research project team would like to thank all Different Strokes members who took part in the 3-year project,
Patient Information. Posterior Cervical Surgery. Here to help. Respond Deliver & Enable
 Here to help Our Health Information Centre (HIC) provides advice and information on a wide range of health-related topics. We also offer: Services for people with disabilities. Information in large print,
Here to help Our Health Information Centre (HIC) provides advice and information on a wide range of health-related topics. We also offer: Services for people with disabilities. Information in large print,
A Guide To Our Family Services For Disabled Children
 Caudwell Children A Guide To Our Family Services For Disabled Children Supported by caudwellchildren caudwellchildren.com caudwellkids How We Can Help You may be reading this information because a child
Caudwell Children A Guide To Our Family Services For Disabled Children Supported by caudwellchildren caudwellchildren.com caudwellkids How We Can Help You may be reading this information because a child
VP Community Care Specialist Brain Injury Services
 VP Community Care Specialist Brain Injury Services Brain Injury Services VP Community Care provides specialist support and rehabilitation for people who have an acquired brain injury, physical disability
VP Community Care Specialist Brain Injury Services Brain Injury Services VP Community Care provides specialist support and rehabilitation for people who have an acquired brain injury, physical disability
Slide 4: Forebrain Structures. Slide 5: 4 Lobes of the Cerebral Cortex. Slide 6: The Cerebral Hemispheres (L & R)
 Slide 1: [Film Clip: The Brain #2- Phineas Gage] Integrated Bodily Communications Within Brain (Hemispheres and structures) The remaining Nervous System Endocrine System (Hormonal communication) Our bodies-
Slide 1: [Film Clip: The Brain #2- Phineas Gage] Integrated Bodily Communications Within Brain (Hemispheres and structures) The remaining Nervous System Endocrine System (Hormonal communication) Our bodies-
The road to recovery. The support available to help you with your recovery after stroke
 The road to recovery The road to recovery The support available to help you with your recovery after stroke We re for life after stroke Introduction Need to talk? Call our confidential Stroke Helpline
The road to recovery The road to recovery The support available to help you with your recovery after stroke We re for life after stroke Introduction Need to talk? Call our confidential Stroke Helpline
http://images.tutorvista.com/content/control5coordination/human5brain.jpeg!! 387
 http://images.tutorvista.com/content/control5coordination/human5brain.jpeg!! 387! 388! http://my.fresnounified.org/personal/lygonza/gonzalez/neuron/neuron5synapse%20communication.png!! http://www.urbanchildinstitute.org/sites/all/files/databooks/2011/ch15fg25communication5between5neurons.jpg!!
http://images.tutorvista.com/content/control5coordination/human5brain.jpeg!! 387! 388! http://my.fresnounified.org/personal/lygonza/gonzalez/neuron/neuron5synapse%20communication.png!! http://www.urbanchildinstitute.org/sites/all/files/databooks/2011/ch15fg25communication5between5neurons.jpg!!
Posterior Cervical Decompression
 Posterior Cervical Decompression Spinal Unit Tel: 01473 702032 or 702097 Issue 2: January 2009 Following your recent MRI scan and consultation with your spinal surgeon, you have been diagnosed with a
Posterior Cervical Decompression Spinal Unit Tel: 01473 702032 or 702097 Issue 2: January 2009 Following your recent MRI scan and consultation with your spinal surgeon, you have been diagnosed with a
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz
 Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz 1. The term central nervous system refers to the: A) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems B) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz 1. The term central nervous system refers to the: A) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems B) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves
Methamphetamine. Like heroin, meth is a drug that is illegal in some areas of the world. Meth is a highly addictive drug.
 Methamphetamine Introduction Methamphetamine is a very addictive stimulant drug. People who use it can form a strong addiction. Addiction is when a drug user can t stop taking a drug, even when he or she
Methamphetamine Introduction Methamphetamine is a very addictive stimulant drug. People who use it can form a strong addiction. Addiction is when a drug user can t stop taking a drug, even when he or she
Table of contents Topic Page
 Table of contents Topic Page Introduction 1 What is an acquired brain injury? 3 What type of damage has occurred? 4 How much damage has occurred? 5 What tests will my child need? 7 What happens when the
Table of contents Topic Page Introduction 1 What is an acquired brain injury? 3 What type of damage has occurred? 4 How much damage has occurred? 5 What tests will my child need? 7 What happens when the
Inpatient, outpatient and therapy services
 Brain injury and neuro-rehabilitation services focused on recovery. Inpatient, outpatient and therapy services Milwaukee Center for Independence Nexday programs provide a continuum of care for people recovering
Brain injury and neuro-rehabilitation services focused on recovery. Inpatient, outpatient and therapy services Milwaukee Center for Independence Nexday programs provide a continuum of care for people recovering
PSK171 STRESS MANAGEMENT
 PSK171 STRESS MANAGEMENT Chapter 2 Systems that control stress arousal Controlling Stress & Tension Girdano, Dusek & Everly Ligands Ligands (amino acid molecules) Biochemicals that carry information Neurohormones
PSK171 STRESS MANAGEMENT Chapter 2 Systems that control stress arousal Controlling Stress & Tension Girdano, Dusek & Everly Ligands Ligands (amino acid molecules) Biochemicals that carry information Neurohormones
Guide to Brain Injury
 CLINICAL NEGLIGENCE BRAIN INJURY Guide to Brain Injury 2 Many victims of brain injury do experience life-long and life-changing symptoms and need rehabilitation, care and support to help re-build their
CLINICAL NEGLIGENCE BRAIN INJURY Guide to Brain Injury 2 Many victims of brain injury do experience life-long and life-changing symptoms and need rehabilitation, care and support to help re-build their
How To Manage A Catastrophic Injury
 Report #14 CATASTROPHIC INJURIES: Paralysis, Amputation, Burns Overview: A catastrophic injury or illness usually occurs suddenly and without warning. Injuries may be considered catastrophic when they
Report #14 CATASTROPHIC INJURIES: Paralysis, Amputation, Burns Overview: A catastrophic injury or illness usually occurs suddenly and without warning. Injuries may be considered catastrophic when they
Healing the Invisible Wound. Recovery and Rehabilitation from a Post Traumatic. Stress Injury. By Dr. Amy Menna
 Healing the Invisible Wound Recovery and Rehabilitation from a Post Traumatic Stress Injury By Dr. Amy Menna Post Traumatic Stress Disorder can affect anyone. It is a term used to describe a reaction to
Healing the Invisible Wound Recovery and Rehabilitation from a Post Traumatic Stress Injury By Dr. Amy Menna Post Traumatic Stress Disorder can affect anyone. It is a term used to describe a reaction to
Speech and language therapy after stroke
 Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Speech and language therapy after stroke Speech and language therapy (SLT) can help if you have communication problems or swallowing problems after
Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Speech and language therapy after stroke Speech and language therapy (SLT) can help if you have communication problems or swallowing problems after
EMOTIONAL AND BEHAVIOURAL CONSEQUENCES OF HEAD INJURY
 Traumatic brain injury EMOTIONAL AND BEHAVIOURAL CONSEQUENCES OF HEAD INJURY Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a common neurological condition that can have significant emotional and cognitive consequences.
Traumatic brain injury EMOTIONAL AND BEHAVIOURAL CONSEQUENCES OF HEAD INJURY Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a common neurological condition that can have significant emotional and cognitive consequences.
Lifetime Protection Plan from Standard Life Protecting you and your family
 Lifetime Protection Plan from Standard Life Protecting you and your family Remember when you thought you were invincible 1 of 33 2 of 33 When was the last time you felt invincible? Contents The need for
Lifetime Protection Plan from Standard Life Protecting you and your family Remember when you thought you were invincible 1 of 33 2 of 33 When was the last time you felt invincible? Contents The need for
A patient guide to mild traumatic brain injury
 A patient guide to mild traumatic brain injury Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
A patient guide to mild traumatic brain injury Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Icanho. Brain injury rehabilitation service. Stowmarket, Suffolk
 Icanho Brain injury rehabilitation service Stowmarket, Suffolk Contents Welcome to Icanho Icanho provides highly specialised, community-based rehabilitation for adults with acquired brain injury, including
Icanho Brain injury rehabilitation service Stowmarket, Suffolk Contents Welcome to Icanho Icanho provides highly specialised, community-based rehabilitation for adults with acquired brain injury, including
Requisite Skills and Abilities to Become a Registered Psychiatric Nurse in B.C.
 Requisite Skills and Abilities to Become a Registered Psychiatric Nurse in B.C. What is the purpose of Requisite Skills and Abilities? Canadians expect the health care system to provide them with safe,
Requisite Skills and Abilities to Become a Registered Psychiatric Nurse in B.C. What is the purpose of Requisite Skills and Abilities? Canadians expect the health care system to provide them with safe,
Related KidsHealth Links. Discussion Questions
 Grades 6 to 8 Human Body Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This
Grades 6 to 8 Human Body Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This
Closed Automobile Insurance Third Party Liability Bodily Injury Claim Study in Ontario
 Page 1 Closed Automobile Insurance Third Party Liability Bodily Injury Claim Study in Ontario Injury Descriptions Developed from Newfoundland claim study injury definitions No injury Death Psychological
Page 1 Closed Automobile Insurance Third Party Liability Bodily Injury Claim Study in Ontario Injury Descriptions Developed from Newfoundland claim study injury definitions No injury Death Psychological
3030. Eligibility Criteria.
 3030. Eligibility Criteria. 5 CA ADC 3030BARCLAYS OFFICIAL CALIFORNIA CODE OF REGULATIONS Barclays Official California Code of Regulations Currentness Title 5. Education Division 1. California Department
3030. Eligibility Criteria. 5 CA ADC 3030BARCLAYS OFFICIAL CALIFORNIA CODE OF REGULATIONS Barclays Official California Code of Regulations Currentness Title 5. Education Division 1. California Department
