NEPHROLITHIASIS Diagnosis & Treatment
|
|
|
- Blaze Briggs
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Learning Objectives NEPHROLITHIASIS Diagnosis & Treatment Jai Radhakrishnan, MD, MS Professor of Clinical Medicine Columbia University Management of the first episode of renal colic: Optimal Imaging Treatment issues Pain Intervention Discharge Managing Recurrent stones Biochemical workup Treatment according to type of stone Pathogenesis Stone Facts Urine is normally super - saturated NIDUS Stone promoters Stone inhibitors Prevalence 12 percent of the population will have a urinary stone during their lifetime White men> white women> black women> and black men Estimated cost: 2 billion dollars/year 1,825,000 office visits in Prevalence: White Males Growth of the U.S. Kidney Stone Belt in Response to Projected Climate Change STONE BELT PNAS 2008;105: Curhan GC et al. J Urol 1994 Apr;151(4): by The National Academy of Sciences of the USA
2 Composition Case 1: The first stone A 25 year old male with no past medical history presents with acute L flank pain ( like I pulled a muscle ) Family history is notable for kidney stones in his maternal uncle Physical exam, chemistries, and blood counts are normal. Urinalysis: Trace protein and heme, 0-2 RBC s QUESTION: What is the next step? 1. Discharge from ED-urine is normal 2. KUB and intravenous urogram 3. CT urogram (without contrast) 4. Renal ultrasound Clinical Presentation Acute, colicky flank pain radiating to the groin Exam: CVA tenderness may be present Hematuria Seen in 90% Absence does not rule out stones Presence in a pt with flank pain is not diagnostic of stone Radiological Diagnosis of Stones Helical non-contrast CT USG + KUB Intravenous Urogram Renal Colic: Differential Diagnosis Radiological Diagnosis of Stones Helical non-contrast CT: the study of choice Faster and more sensitive than IVP Does not require contrast Can visualize uric acid stones Diagnosis of urinary tract abnormalities which predispose to stones R/o conditions which may masquerade as renal colic.
3 Role of Plain Abdominal Xray (KUB) Role of Renal USG To see if stone is radioopaque Radiolucent: Uric acid, indinavir. High specificity (>90 percent), Sensitivity 11 to 24 percent Usually 1 st step in pregnant patients with colic (MR can also be used) For the follow up of stones to monitor growth Case 1: The first stone ANSWER: What is the next step? 1. Discharge from ED-urine is normal 2. KUB and intravenous urogram 3. CT urogram (without contrast) 4. Renal ultrasound CT urogram shows a 9 mm radio-opaque stone in the R ureteropelvic junction. QUESTION 2: How would you treat the patient? 1. Aggressive IV fluids and narcotics 2. Aggressive IV Fluids and NSAIDS 3. NSAIDs and tamsulosin 4. Call Urology Management of Renal Colic: IV Fluids No difference in pain scales when no fluids vs. 3 liters IVF for 6 hours Scandinavian Journal of Urology & Nephrology 1983;17(2): No difference in pain/rate of passage when 3L NS vs. 20ml/hour J Endourol Oct;20(10):713-6 Management of Renal Colic Ketorolac vs. meperidine? Am J Emerg Med Jan;17(1):6-10.
4 Expulsive Therapy: α-antagonists Expulsive Therapy: Calcium Channel Blocker-Nifedipine Ann Emerg Med Nov;50(5):552-6 Ann Emerg Med Nov;50(5):552-6 Likelihood of Passage of Ureteral Stones 5 mm 68% (95% CI: 46% to 85%) >5 mm and 10 mm 47% (95% CI: 36% to 59%) Repeat imaging to confirm stone passage Urologic Intervention? INDICATIONS Stone size >10 mm/persistent Obstruction Infection Uncontrolled pain, nausea/vomiting TECHNIQUES Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy Ureteroscopic removal Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy [Open surgery] 2007 Guideline for the Management of Ureteral Calculi. J Urol Dec;178(6): ESWL: Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy Proximal stones < 2cms Contraindications Bleeding tendencies Pregnancy Uncontrolled HTN UTI Morbid obesity Long Term Risks??Renal Insufficiency?HTN Ureteroscopic removal Fragmentation of stone by laser, electrohydraulic, or ultrasound. Most stones can be treated.
5 Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy Large proximal stones CT urogram shows a 9 mm radio-opaque stone in the R ureteropelvic junction. QUESTION 2: How would you treat the patient? 1. Aggressive IV fluids and narcotics 2. Aggressive IV Fluids and NSAIDS 3. NSAIDs and tamsulosin 4. Call Urology Case 1: The first stone The stone is endourologically removed. Management After First Stone Episode -Laboratory evaluation Creatinine, HCO3, calcium and phosphate. Urine analysis, urine culture 24-hour collections are not generally needed Except in children (cystine, hyperoxaluria) What workup do you need to do? 1. No workup hour urine for stone risk analysis 3. Urine culture, basic metabolic profile, phosphate 4. Let the stone clinic handle this. Management After First Stone Episode - Evaluation of risk factors Occupation/Environment Management After First Stone Episode -Referral to Stone Clinic Children Solitary kidney Family history Diet: protein, purines, Na, fluid, Ca, oxalate Medications: Triamterene Indinavir, Sulfonamides Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Triamterene Struvite stones Abnormal renal function RTA` Indinavir
6 Case 1: The first stone What workup do you need to do? 1. No workup hour urine for stone risk analysis 3. Urine culture, basic metabolic profile, phosphate 4. Let the stone clinic handle this. Urine culture is negative BMP, Phosphate are normal. Stone analysis: Calcium oxalate. What diet advice do you give the patient? 1. 2 liters water, no special diet 2. 2 liters water, low salt, low protein, normal calcium 3. 2 liters water, low calcium 4. Drink lots of beer (+pretzels to avoid hyponatremia) Water >2.2 Liters Liters Which Beverage? Decreased Risk Coffee Tea Beer Wine Increased Risk Grapefruit juice J Urol Mar;155(3): Curhan GC et al. Am J Epidemiol 1996 Feb 1;143(3): Comparison of Two Diets for the Prevention of Recurrent Stones in Idiopathic Hypercalciuria Risk of Stones with Calcium+D Supplementation HR 1.17 [CI 1.02 to 1.34] Borghi L., N Engl J Med 2002; 346: N Engl J Med Feb 16;354(7):669-83
7 Timing of Calcium Supplement and Urinary Oxalate Effect of Low-carbohydrate High-protein Diets Kidney Int May;65(5): Reddy ST Am J Kidney Dis Aug;40(2): Management After First Stone Episode -Therapeutic Recommendations for Calcium Stones Increase urine volume to 2-2.5L/day Diet: Na <2g/day Protein <8oz/day Oxalate as low as possible Do not restrict dietary calcium Calcium supplements may increase risk Management After First Stone Episode -Recurrence Rate after the First Episode What diet advice do you give the patient? 1. 2 liter water, no special diet 2. 2 liters water, low salt, low protein, normal calcium 3. 2 liters water, low calcium 4. Drink lots of beer (+pretzels to avoid hyponatremia)
8 Case Review Emergency management Indications for referral to stone clinic Preventive strategies to start Case 2: Recurrent Stones The patient followed your instruction to adequately hydrate himself and reduce salt and protein intake. However, he experienced 3 further episodes of colic and analysis of one stone revealed calcium oxalate. How would you work up this patient? What specific treatment can you recommend based on your investigations? Workup of Recurrent Stone Formers Urine (24 hour) collections for Calcium Oxalate Citrate Uric acid ph Cystine at least once Urine culture if struvite/staghorn. The Report Calcium Stones: Pathogenesis & Treatment All patients: Urine volume >2L/day Dietary restriction: Na, Protein, oxalate Hypercalciuria Thiazides Hypocitraturia K- or Mg-K-citrate Hyperoxaluria Dietary restriction of oxalate Hyperuricosuria Dietary restriction of purine Allopurinol Primary hyperparathyroidism Parathyroidectomy Distal RTA NaHCO3 therapy Uric Acid Stones A 50-year-old male presents with the third episode of renal colic. The stone is 100% uric acid. 24 hour urine shows ph 5.5, normal levels of uric acid, calcium citrate and oxalate. The most important component of treatment is: 1. Raising urine ph 2. Reducing urinary uric acid levels with allopurinol 3. Increasing urine volume 4. Low purine diet Ann Intern Med Apr 2;158(7):535-43
9 Uric Acid Stones Pathogenesis Low urine ph Hyperuricosuria Radiolucent stones Treatment of Uric Acid Stones All patients Restrict animal protein and salt Alkalinize urine K-citrate K-Mg-citrate Urine volume not critical Hyperuricosuria Allopurinol Struvite Stones The most important component of treatment is: 1. Raising urine ph 2. Reducing urinary uric acid levels with allopurinol 3. Increasing urine volume 4. Low purine diet Urease-producing organisms (Proteus) MgNH 4 PO 4 Surgical treatment and antibiotics Guess the stone A 24-year-old male new to your practice has a history of stones since age 6. He does not have his records. Urinalysis is shown on the right. What kind of stones is he likely to have?: 1. Struvite 2. Cystine 3. Calcium phosphate 4. Uric Acid Cystine Stones Hereditary disorder(recessive) of dibasic amino acids May present with staghorn calculi Hexagonal crystals in the urine Treatment High Fluid Intake Alkalinize urine ph>7.5 Penicillamine Mercaptopropinylglycine
10 Conclusions Kidney stones are common. For renal colic, non-contrast CT urogram is the optimal imaging technique. After the first stone, lifestyle changes should be instituted A biochemical workup and specific treatment plan should be performed for recurrent stone formers. E N D Footer text is edited under "view/header and footer" menu May 22, 2013 Page 56
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones. Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke
 Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
Recurrent Kidney Stones
 Recurrent Kidney Stones Sean A. Pierre, MD; and Darren T. Beiko, MD, FRCSC As presented at the College of Canadian Family Physicians Annual Family Medicine Forum, Toronto, Ontario. Family physicians are
Recurrent Kidney Stones Sean A. Pierre, MD; and Darren T. Beiko, MD, FRCSC As presented at the College of Canadian Family Physicians Annual Family Medicine Forum, Toronto, Ontario. Family physicians are
Kidney Stones. This reference summary will help you understand kidney stones and how to treat and prevent them. Kidney
 Introduction A kidney stone is a solid piece of material that forms in the kidney from substances in the urine. Kidney stones are fairly common. Although kidney stones can be painful, they are treatable.
Introduction A kidney stone is a solid piece of material that forms in the kidney from substances in the urine. Kidney stones are fairly common. Although kidney stones can be painful, they are treatable.
Primary Care Management of Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms. Matthew B.K. Shaw Consultant Urological Surgeon
 Primary Care Management of Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Matthew B.K. Shaw Consultant Urological Surgeon NICE LUTS Guidelines Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) in men. NICE Clinical Guideline 97
Primary Care Management of Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Matthew B.K. Shaw Consultant Urological Surgeon NICE LUTS Guidelines Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) in men. NICE Clinical Guideline 97
MODULE 6: KIDNEY STONES
 MODULE 6: KIDNEY STONES KEYWORDS: Nephrolithiasis, urinary stones, kidney, calciuria, oxaluria LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this clerkship, the medical student will be able to: 1. List risk factors
MODULE 6: KIDNEY STONES KEYWORDS: Nephrolithiasis, urinary stones, kidney, calciuria, oxaluria LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this clerkship, the medical student will be able to: 1. List risk factors
X-Plain Kidney Stones Reference Summary
 X-Plain Kidney Stones Reference Summary Introduction Kidney stones are fairly common. Although they can be very painful, they are treatable, and in many cases preventable. This reference summary will help
X-Plain Kidney Stones Reference Summary Introduction Kidney stones are fairly common. Although they can be very painful, they are treatable, and in many cases preventable. This reference summary will help
Nephrology (Renal Medicine)
 Nephrology (Renal Medicine) Dr Shabbir Moochhala Consultant Nephrologist, Royal Free Hospital, London Cystinuria Patient Day 1 st Feb 2014 Nephrologist Urologist The Kidney designed for the job The body
Nephrology (Renal Medicine) Dr Shabbir Moochhala Consultant Nephrologist, Royal Free Hospital, London Cystinuria Patient Day 1 st Feb 2014 Nephrologist Urologist The Kidney designed for the job The body
URINARY (RENAL) STONE (NEPHROLITHOISIS) An Overview
 URINARY (RENAL) STONE (NEPHROLITHOISIS) An Overview UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PLB MBBS
URINARY (RENAL) STONE (NEPHROLITHOISIS) An Overview UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PLB MBBS
Diet for Kidney Stone Prevention
 Diet for Kidney Stone Prevention National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH How does diet affect the risk
Diet for Kidney Stone Prevention National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH How does diet affect the risk
Preventing Catheter Blockages: A Guide for Health Professionals
 Introduction Preventing Catheter Blockages: A Guide for Health Professionals and Long term catheterisation is common for someone with a spinal cord injury (SCI). However, it poses a concern as this method
Introduction Preventing Catheter Blockages: A Guide for Health Professionals and Long term catheterisation is common for someone with a spinal cord injury (SCI). However, it poses a concern as this method
Evaluation and medical management of the kidney stone patient
 CUA guideline Evaluation and medical management of the kidney stone patient Ryan Paterson, MD, FRCSC; * Alfonso Fernandez, MD; Hassan Razvi, MD, FRCSC; Roger Sutton, DM, FRCP, FRCPC Can Urol Assoc J 2010;4(6):375-9
CUA guideline Evaluation and medical management of the kidney stone patient Ryan Paterson, MD, FRCSC; * Alfonso Fernandez, MD; Hassan Razvi, MD, FRCSC; Roger Sutton, DM, FRCP, FRCPC Can Urol Assoc J 2010;4(6):375-9
Kidney Stones removal Without surgery
 Patient Education Service Lithotripsy - The world s latest treatment for Kidney Stones removal Without surgery With COMPUTERISED high tech DIREX LITHOTRIPTER Experience counts PIONEERS in North INDIA -
Patient Education Service Lithotripsy - The world s latest treatment for Kidney Stones removal Without surgery With COMPUTERISED high tech DIREX LITHOTRIPTER Experience counts PIONEERS in North INDIA -
Ureteroscopy with Laser Lithotripsy
 Ureteroscopy with Laser Lithotripsy Introduction Kidney stones are fairly common. Although kidney stones can be very painful, they are treatable, and in many cases preventable. Your doctor may recommend
Ureteroscopy with Laser Lithotripsy Introduction Kidney stones are fairly common. Although kidney stones can be very painful, they are treatable, and in many cases preventable. Your doctor may recommend
Kidney Disease WHAT IS KIDNEY DISEASE? TESTS TO DETECT OR DIAGNOSE KIDNEY DISEASE TREATMENT STRATEGIES FOR KIDNEY DISEASE
 Kidney Disease WHAT IS KIDNEY DISEASE? Kidney disease is when your kidneys are damaged and not functioning as they should. When kidney disease is not going away it is called chronic kidney disease or CKD.
Kidney Disease WHAT IS KIDNEY DISEASE? Kidney disease is when your kidneys are damaged and not functioning as they should. When kidney disease is not going away it is called chronic kidney disease or CKD.
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg. Automation: Introduction. Urine Automation. published by Bayer. Unit 3. Chemical Examination of Urine
 Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 3 Chemical Examination of Urine Part 7, Automation, Function Tests, and Calculi Automation: Introduction Advantages Saves time Allows for standardization of procedures
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 3 Chemical Examination of Urine Part 7, Automation, Function Tests, and Calculi Automation: Introduction Advantages Saves time Allows for standardization of procedures
1.1. Physiochemical factors involved in stone formation7 1.1.1. Supersaturation 1.1.2. Deficiencies in protective factors
 1 1. INTRODUCTION The medicinal and culinary values of various herbs have been recognized and appreciated by the people of almost every culture and every part of the globe since time immemorial. In the
1 1. INTRODUCTION The medicinal and culinary values of various herbs have been recognized and appreciated by the people of almost every culture and every part of the globe since time immemorial. In the
Published on: 07/04/2015 Page 1 of 5
 Bladder Stones A DNA test for Hyperunicosuria (HUU) to find the gene which is implicated in the development of URATE stones has been developed which work with Bulldogs and many other breeds including Black
Bladder Stones A DNA test for Hyperunicosuria (HUU) to find the gene which is implicated in the development of URATE stones has been developed which work with Bulldogs and many other breeds including Black
surg urin Surgery: Urinary System 1
 Surgery: Urinary System 1 This section contains information to assist providers in billing for surgical procedures related to the urinary system. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy Medi-Cal covers Extracorporeal
Surgery: Urinary System 1 This section contains information to assist providers in billing for surgical procedures related to the urinary system. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy Medi-Cal covers Extracorporeal
Triple phosphates (Magnesium ammonium phosphates) (Struvite)
 Amorphous phosphates Amorphous phosphates are the name given to a granular precipitate containing calcium and phosphate in an alkaline urine. Calcium phosphate crystals, regrouped under the term apatite,
Amorphous phosphates Amorphous phosphates are the name given to a granular precipitate containing calcium and phosphate in an alkaline urine. Calcium phosphate crystals, regrouped under the term apatite,
University College Hospital at Westmoreland Street. Lithotripsy. Urology Directorate
 University College Hospital at Westmoreland Street Lithotripsy Urology Directorate 2 3 If you require a large print, audio or translated version of this leaflet, please contact us on 020 3447 9179. We
University College Hospital at Westmoreland Street Lithotripsy Urology Directorate 2 3 If you require a large print, audio or translated version of this leaflet, please contact us on 020 3447 9179. We
The Interrelated Relationship Between Dysmithia and Kidrugacy
 Original Article Int J Nephrol Urol, 2009; 1(2):137-142 Non-Calculus Signs and Symptoms of Hyperoxaluria and Hyperuricosuria in Children: A Single Experience Fatemeh Beiraghdar 1, Yunes Panahi 2*, Abbas
Original Article Int J Nephrol Urol, 2009; 1(2):137-142 Non-Calculus Signs and Symptoms of Hyperoxaluria and Hyperuricosuria in Children: A Single Experience Fatemeh Beiraghdar 1, Yunes Panahi 2*, Abbas
Kidney Stones and Diet
 Kidney Stones and Diet What are kidney stones? Urine is made up of water and substances such as calcium, oxalate and uric acid. Crystals begin to form first in the kidney when: there are higher than normal
Kidney Stones and Diet What are kidney stones? Urine is made up of water and substances such as calcium, oxalate and uric acid. Crystals begin to form first in the kidney when: there are higher than normal
Feline Cystitis (Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease)
 Feline Cystitis (Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease) The term "cystitis" literally means inflammation of the urinary bladder. Although this term is rather general, there is a common form of cystitis that
Feline Cystitis (Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease) The term "cystitis" literally means inflammation of the urinary bladder. Although this term is rather general, there is a common form of cystitis that
The acute treatment of kidney stones (urolithiasis) addresses
 Renal Calculi: Emergency Department Diagnosis And Treatment Abstract The acute treatment of kidney stones (urolithiasis) addresses pain management and focuses on the effects of the morbidity associated
Renal Calculi: Emergency Department Diagnosis And Treatment Abstract The acute treatment of kidney stones (urolithiasis) addresses pain management and focuses on the effects of the morbidity associated
Acid-Base Disorders. Jai Radhakrishnan, MD, MS. Objectives. Diagnostic Considerations. Step 1: Primary Disorder. Formulae. Step 2: Compensation
 Objectives Diagnostic approach to acid base disorders Common clinical examples of acidoses and alkaloses Acid-Base Disorders Jai Radhakrishnan 1 2 Diagnostic Considerations Data points required: ABG: ph,
Objectives Diagnostic approach to acid base disorders Common clinical examples of acidoses and alkaloses Acid-Base Disorders Jai Radhakrishnan 1 2 Diagnostic Considerations Data points required: ABG: ph,
GENTLY DOES IT. Stonemanagement
 GENTLY DOES IT Kidney and ureteral stone retrieval by Sur-catch NT Basket from Olympus Stonemanagement content Content... 2 Introduction... 3 The Disease... 4-5 Causes... 5 Prevention... 6 Symptoms...
GENTLY DOES IT Kidney and ureteral stone retrieval by Sur-catch NT Basket from Olympus Stonemanagement content Content... 2 Introduction... 3 The Disease... 4-5 Causes... 5 Prevention... 6 Symptoms...
Lectures Hands On Simula on Roundtable Discussions Panel Discussion August 14, 2015
 presents Kidney Stones: Medical, Surgical and Dietary Approaches Lectures Hands On Simula on Roundtable Discussions Panel Discussion August 14, 2015 This ac vity has been approved for AMA PRA Category
presents Kidney Stones: Medical, Surgical and Dietary Approaches Lectures Hands On Simula on Roundtable Discussions Panel Discussion August 14, 2015 This ac vity has been approved for AMA PRA Category
POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE
 POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE Acute Pylonephritis DIAGNOSIS COMPLICATED PYELONEPHRITIS EXCLUSION CRITERIA: Male Known or suspected renal impairment (egfr < 60) Abnormality of renal tract Known or suspected renal
POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE Acute Pylonephritis DIAGNOSIS COMPLICATED PYELONEPHRITIS EXCLUSION CRITERIA: Male Known or suspected renal impairment (egfr < 60) Abnormality of renal tract Known or suspected renal
Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease (FLUTD)
 Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease (FLUTD) VETERINARY GUIDE 2 What is FLUTD? FLUTD describes a collection of common conditions that affect the bladder and/or urethra the narrow tube that carries urine
Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease (FLUTD) VETERINARY GUIDE 2 What is FLUTD? FLUTD describes a collection of common conditions that affect the bladder and/or urethra the narrow tube that carries urine
THE KIDNEY. Bulb of penis Abdominal aorta Scrotum Adrenal gland Inferior vena cava Urethra Corona glandis. Kidney. Glans penis Testicular vein
 29 THE KIDNEY 9. Recurrent urinary tract infections Recurrent urinary tract infections The urinary tract consists of the urethra, the bladder, the ureters, the kidneys and in men the prostate gland. An
29 THE KIDNEY 9. Recurrent urinary tract infections Recurrent urinary tract infections The urinary tract consists of the urethra, the bladder, the ureters, the kidneys and in men the prostate gland. An
Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection
 Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is pyelonephritis? Pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is pyelonephritis? Pyelonephritis
Struvite and Calcium Oxalate Jessica Clemans, DVM, ISU VMC
 Struvite and Calcium Oxalate Jessica Clemans, DVM, ISU VMC Lith= stone Organized concretions Organic Matrix: proteins, Gag s DSB Inorganic Mineral (crystals) lattice Casts, epi cells, heterogenous, suture
Struvite and Calcium Oxalate Jessica Clemans, DVM, ISU VMC Lith= stone Organized concretions Organic Matrix: proteins, Gag s DSB Inorganic Mineral (crystals) lattice Casts, epi cells, heterogenous, suture
Urolithiasis/Endourology
 Urolithiasis/Endourology Use of Ureteral Stent in Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy for Upper Urinary Calculi: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Shen Pengfei, Jiang Min, Yang Jie, Li Xiong, Li
Urolithiasis/Endourology Use of Ureteral Stent in Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy for Upper Urinary Calculi: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Shen Pengfei, Jiang Min, Yang Jie, Li Xiong, Li
Guidelines on Urolithiasis
 Guidelines on Urolithiasis C. Türk (Chair), T. Knoll (Vice-chair), A. Petrik, K. Sarica, A. Skolarikos, M. Straub, C. Seitz European Association of Urology 2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE 1. INTRODUCTION 6
Guidelines on Urolithiasis C. Türk (Chair), T. Knoll (Vice-chair), A. Petrik, K. Sarica, A. Skolarikos, M. Straub, C. Seitz European Association of Urology 2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE 1. INTRODUCTION 6
Acute Pancreatitis. Questionnaire. if yes: amount (cigarettes/day): since when (year): Drug consumption: yes / no if yes: type of drug:. amount:.
 The physical examination has to be done AT ADMISSION! The blood for laboratory parameters has to be drawn AT ADMISSION! This form has to be filled AT ADMISSION! Questionnaire Country: 1. Patient personal
The physical examination has to be done AT ADMISSION! The blood for laboratory parameters has to be drawn AT ADMISSION! This form has to be filled AT ADMISSION! Questionnaire Country: 1. Patient personal
Angela Doherty Senior Specialist Renal Dietitian Guy s Hospital
 Angela Doherty Senior Specialist Renal Dietitian Guy s Hospital Introduction Dietary Advice Fluid Intake Salt Animal Protein Alkalinisation of the Urine Achieving a Healthy Weight Anthropometry Dietary
Angela Doherty Senior Specialist Renal Dietitian Guy s Hospital Introduction Dietary Advice Fluid Intake Salt Animal Protein Alkalinisation of the Urine Achieving a Healthy Weight Anthropometry Dietary
URETEROSCOPY (AND TREATMENT OF KIDNEY STONES)
 URETEROSCOPY (AND TREATMENT OF KIDNEY STONES) AN INFORMATION LEAFLET Written by: Department of Urology May 2011 Stockport: 0161 419 5698 Website: w w w. s t o c k p o r t. n h s. u k Tameside: 0161 922
URETEROSCOPY (AND TREATMENT OF KIDNEY STONES) AN INFORMATION LEAFLET Written by: Department of Urology May 2011 Stockport: 0161 419 5698 Website: w w w. s t o c k p o r t. n h s. u k Tameside: 0161 922
Medical Malpractice in Endourology: Analysis of Closed Cases From the State of New York
 Medical Malpractice in Endourology: Analysis of Closed Cases From the State of New York Brian Duty,* Zhamshid Okhunov, Zeph Okeke and Arthur Smith From the Department of Urology, North Shore-Long Island
Medical Malpractice in Endourology: Analysis of Closed Cases From the State of New York Brian Duty,* Zhamshid Okhunov, Zeph Okeke and Arthur Smith From the Department of Urology, North Shore-Long Island
ADULT HYPERTENSION PROTOCOL STANFORD COORDINATED CARE
 I. PURPOSE To establish guidelines for the monitoring of antihypertensive therapy in adult patients and to define the roles and responsibilities of the collaborating clinical pharmacist and pharmacy resident.
I. PURPOSE To establish guidelines for the monitoring of antihypertensive therapy in adult patients and to define the roles and responsibilities of the collaborating clinical pharmacist and pharmacy resident.
Urinary Incontinence in Women. Susan Hingle, M.D. Department of Medicine
 Urinary Incontinence in Women Susan Hingle, M.D. Department of Medicine Background Estimated 13 million Americans with urinary incontinence Women are affected twice as frequently as men Only 25% will seek
Urinary Incontinence in Women Susan Hingle, M.D. Department of Medicine Background Estimated 13 million Americans with urinary incontinence Women are affected twice as frequently as men Only 25% will seek
Urologic Diseases. in America
 Urologic Diseases in America Interim Compendium April 2004 Copyright Information All material appearing in this report is in the public domain and may be reproduced or copied without permission: citation
Urologic Diseases in America Interim Compendium April 2004 Copyright Information All material appearing in this report is in the public domain and may be reproduced or copied without permission: citation
Emergencies in Post- Bariatric Surgery Patients
 Emergencies in Post- Patients Disclosures Dr. Birnbaumer has no financial disclosures Diane M. Birnbaumer, M.D., FACEP Professor of Medicine University of California, Los Angeles Senior Clinical Educator
Emergencies in Post- Patients Disclosures Dr. Birnbaumer has no financial disclosures Diane M. Birnbaumer, M.D., FACEP Professor of Medicine University of California, Los Angeles Senior Clinical Educator
Female Urinary Incontinence
 Female Urinary Incontinence Molly Heublein, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Medicine UCSF Women s Health Primary Care Disclosures I have nothing to disclose. 1 Objectives Review the problem Feel confident
Female Urinary Incontinence Molly Heublein, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Medicine UCSF Women s Health Primary Care Disclosures I have nothing to disclose. 1 Objectives Review the problem Feel confident
6/3/2011. High Prevalence and Incidence. Low back pain is 5 th most common reason for all physician office visits in the U.S.
 High Prevalence and Incidence Prevalence 85% of Americans will experience low back pain at some time in their life. Incidence 5% annual Timothy C. Shen, M.D. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Sub-specialty
High Prevalence and Incidence Prevalence 85% of Americans will experience low back pain at some time in their life. Incidence 5% annual Timothy C. Shen, M.D. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Sub-specialty
Urinary Tract Infection in Stone Patients and in Patients with Indwelling Urethral Catheters
 Urinary Tract Infection in Stone Patients and in Patients with Indwelling Urethral Catheters Pages with reference to book, From 254 To 258 Farakh A. Khan, Salman H. Siddiqui, Nasreen Akhtar ( Department
Urinary Tract Infection in Stone Patients and in Patients with Indwelling Urethral Catheters Pages with reference to book, From 254 To 258 Farakh A. Khan, Salman H. Siddiqui, Nasreen Akhtar ( Department
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections www.kidney.org Did you know that... n Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are responsible for nearly 10 million doctor visits each year. n One in five women will have at least one
Urinary Tract Infections www.kidney.org Did you know that... n Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are responsible for nearly 10 million doctor visits each year. n One in five women will have at least one
Diclofenac versus Tramadol in the Treatment of Renal Colic: A Prospective, Randomized Trial
 The Open Emergency Medicine Journal, 2011, 4, 9-13 9 Open Access Diclofenac versus Tramadol in the Treatment of Renal Colic: A Prospective, Randomized Trial Shaden Salameh*,1, Nurit Hiller 2, Meir Antopolsky
The Open Emergency Medicine Journal, 2011, 4, 9-13 9 Open Access Diclofenac versus Tramadol in the Treatment of Renal Colic: A Prospective, Randomized Trial Shaden Salameh*,1, Nurit Hiller 2, Meir Antopolsky
Guideline for Microalbuminuria Screening
 East Lancashire Diabetes Network Guideline for Microalbuminuria Screening Produced by: Task and Finish Group, Clinical Standards Group Produced: August 2006 Approved by: East Lancashire Diabetes Network
East Lancashire Diabetes Network Guideline for Microalbuminuria Screening Produced by: Task and Finish Group, Clinical Standards Group Produced: August 2006 Approved by: East Lancashire Diabetes Network
Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy. Jai Radhakrishnan, MD, MS
 Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy Jai Radhakrishnan, MD, MS History of the CRRT program 1988 Open heart program Active transplant program Deep dissatisfaction with peritoneal dialysis in hemodynamically
Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy Jai Radhakrishnan, MD, MS History of the CRRT program 1988 Open heart program Active transplant program Deep dissatisfaction with peritoneal dialysis in hemodynamically
Diagnosis and Imaging of Nephrolithiasis in the Emergency Department
 November Diagnosis and Imaging of Nephrolithiasis in the Emergency Department Mark Bisanzo, Harvard Medical School Year- III MD Agenda I. Epidemiology and risk factors II. Pathophysiology III. The Radiologist
November Diagnosis and Imaging of Nephrolithiasis in the Emergency Department Mark Bisanzo, Harvard Medical School Year- III MD Agenda I. Epidemiology and risk factors II. Pathophysiology III. The Radiologist
Diabetic Ketoacidosis: When Sugar Isn t Sweet!!!
 Diabetic Ketoacidosis: When Sugar Isn t Sweet!!! W Ricks Hanna Jr MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics University of Tennessee Health Science Center LeBonheur Children s Hospital Introduction Diabetes
Diabetic Ketoacidosis: When Sugar Isn t Sweet!!! W Ricks Hanna Jr MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics University of Tennessee Health Science Center LeBonheur Children s Hospital Introduction Diabetes
Things You Don t Want to Miss in Multiple Myeloma
 Things You Don t Want to Miss in Multiple Myeloma Sreenivasa Chandana, MD, PhD Attending Hematologist and Medical Oncologist West Michigan Cancer Center Assistant Professor, Western Michigan University
Things You Don t Want to Miss in Multiple Myeloma Sreenivasa Chandana, MD, PhD Attending Hematologist and Medical Oncologist West Michigan Cancer Center Assistant Professor, Western Michigan University
Bladder Health Promotion
 Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation Content contributions provided by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence (NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence
Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation Content contributions provided by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence (NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence
Acid-Base Disorders. Jai Radhakrishnan, MD, MS
 Acid-Base Disorders Jai Radhakrishnan, MD, MS 1 Diagnostic Considerations Data points required: ABG: ph, pco 2, HCO 3 Chem-7 panel: anion gap Step 1: Acidemia/alkalemia (Primary disorder) Step 2: Compensation
Acid-Base Disorders Jai Radhakrishnan, MD, MS 1 Diagnostic Considerations Data points required: ABG: ph, pco 2, HCO 3 Chem-7 panel: anion gap Step 1: Acidemia/alkalemia (Primary disorder) Step 2: Compensation
Chronic Kidney Disease and the Electronic Health Record. Duaine Murphree, MD Sarah M. Thelen, MD
 Chronic Kidney Disease and the Electronic Health Record Duaine Murphree, MD Sarah M. Thelen, MD Definition of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Defined by the National Kidney Foundation Either a decline in
Chronic Kidney Disease and the Electronic Health Record Duaine Murphree, MD Sarah M. Thelen, MD Definition of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Defined by the National Kidney Foundation Either a decline in
Urinary Tract Infection Update Kim Gibson, MD Joseph Toscano, MD
 82 Urinary Tract Infection Update Kim Gibson, MD Joseph Toscano, MD Abstract Urinary tract infections are commonly treated in urgent care practice. Clinicians need to be aware of the advantages and limitations
82 Urinary Tract Infection Update Kim Gibson, MD Joseph Toscano, MD Abstract Urinary tract infections are commonly treated in urgent care practice. Clinicians need to be aware of the advantages and limitations
Georgia Northwestern Technical College Practical Nursing Program CLINICAL DAILY ASSESSMENT WORKSHEET FOR MODULES I-IV STUDENT: CLINICAL INSTRUCTOR:
 Georgia Northwestern Technical College Practical Nursing Program CLINICAL DAILY ASSESSMENT WORKSHEET FOR MODULES I-IV STUDENT: CLINICAL INSTRUCTOR: CLINICAL UNIT: ASSIGNMENT DATES: PATIENT (last initial):
Georgia Northwestern Technical College Practical Nursing Program CLINICAL DAILY ASSESSMENT WORKSHEET FOR MODULES I-IV STUDENT: CLINICAL INSTRUCTOR: CLINICAL UNIT: ASSIGNMENT DATES: PATIENT (last initial):
Interpretation of Laboratory Values
 Interpretation of Laboratory Values Konrad J. Dias PT, DPT, CCS Overview Electrolyte imbalances Renal Function Tests Complete Blood Count Coagulation Profile Fluid imbalance Sodium Electrolyte Imbalances
Interpretation of Laboratory Values Konrad J. Dias PT, DPT, CCS Overview Electrolyte imbalances Renal Function Tests Complete Blood Count Coagulation Profile Fluid imbalance Sodium Electrolyte Imbalances
Analysis One Code Desc. Transaction Amount. Fiscal Period
 Analysis One Code Desc Transaction Amount Fiscal Period 57.63 Oct-12 12.13 Oct-12-38.90 Oct-12-773.00 Oct-12-800.00 Oct-12-187.00 Oct-12-82.00 Oct-12-82.00 Oct-12-110.00 Oct-12-1115.25 Oct-12-71.00 Oct-12-41.00
Analysis One Code Desc Transaction Amount Fiscal Period 57.63 Oct-12 12.13 Oct-12-38.90 Oct-12-773.00 Oct-12-800.00 Oct-12-187.00 Oct-12-82.00 Oct-12-82.00 Oct-12-110.00 Oct-12-1115.25 Oct-12-71.00 Oct-12-41.00
NORD Guides for Physicians #1. Physician s Guide to. Tyrosinemia. Type 1
 NORD Guides for Physicians #1 The National Organization for Rare Disorders Physician s Guide to Tyrosinemia Type 1 The original version of this booklet was made possible by donations in honor of Danielle
NORD Guides for Physicians #1 The National Organization for Rare Disorders Physician s Guide to Tyrosinemia Type 1 The original version of this booklet was made possible by donations in honor of Danielle
Daily Habits and Urinary Incontinence
 Effects of Daily Habits on the Bladder Many aspects of our daily life influence bladder and bowel function. Sometimes our daily habits may not be in the best interest of the bladder. A number of surprisingly
Effects of Daily Habits on the Bladder Many aspects of our daily life influence bladder and bowel function. Sometimes our daily habits may not be in the best interest of the bladder. A number of surprisingly
Blood in the urine (hematuria)
 Blood in the urine (hematuria) Hematuria refers to the presence of blood in the urine. It is important to investigate the cause of hematuria because rarely, it is caused by a serious condition, such as
Blood in the urine (hematuria) Hematuria refers to the presence of blood in the urine. It is important to investigate the cause of hematuria because rarely, it is caused by a serious condition, such as
RENAL ANGIOMYOLIPOMA EMBOLIZATION
 RENAL ANGIOMYOLIPOMA EMBOLIZATION The information about renal angiomyolipomas on the next several pages includes questions commonly asked about the embolization procedure. Please take a few moments to
RENAL ANGIOMYOLIPOMA EMBOLIZATION The information about renal angiomyolipomas on the next several pages includes questions commonly asked about the embolization procedure. Please take a few moments to
Definition, Prevalence, Pathophysiology and Complications of CKD. JM Krzesinski CHU Liège-ULg Core curriculum Nephrology September 28 th 2013
 Definition, Prevalence, Pathophysiology and Complications of CKD JM Krzesinski CHU Liège-ULg Core curriculum Nephrology September 28 th 2013 KI supplements January 2013 Objectives of the course on CKD:
Definition, Prevalence, Pathophysiology and Complications of CKD JM Krzesinski CHU Liège-ULg Core curriculum Nephrology September 28 th 2013 KI supplements January 2013 Objectives of the course on CKD:
Riesa Gusewelle, MNSc, RN, APRN, GNP-BC. OBJECTIVES Identify early warning signs of urinary tract
 Detection, Early Management & Prevention, of Urinary Tract Infections in Older Adults Riesa Gusewelle, MNSc, RN, APRN, GNP-BC OBJECTIVES Identify early warning signs of urinary tract infections (UTIs)
Detection, Early Management & Prevention, of Urinary Tract Infections in Older Adults Riesa Gusewelle, MNSc, RN, APRN, GNP-BC OBJECTIVES Identify early warning signs of urinary tract infections (UTIs)
Appendicitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
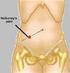 Appendicitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH The appendix is a small, tube-like structure
Appendicitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH The appendix is a small, tube-like structure
Diabetic nephropathy is detected clinically by the presence of persistent microalbuminuria or proteinuria.
 Kidney Complications Diabetic Nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy is detected clinically by the presence of persistent microalbuminuria or proteinuria. The peak incidence of nephropathy is usually 15-25 years
Kidney Complications Diabetic Nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy is detected clinically by the presence of persistent microalbuminuria or proteinuria. The peak incidence of nephropathy is usually 15-25 years
Bladder Health Promotion
 Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation endorsed by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence( NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence This presentation
Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation endorsed by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence( NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence This presentation
Understanding and Preventing Bladder Infections in Women
 Understanding and Preventing Bladder Infections in Women Understanding and Preventing Bladder Infections in Women Recurrent bladder or urinary tract infections (UTI s) are a very common diagnosis. In fact,
Understanding and Preventing Bladder Infections in Women Understanding and Preventing Bladder Infections in Women Recurrent bladder or urinary tract infections (UTI s) are a very common diagnosis. In fact,
Diabetes and the Kidneys
 Diabetes and the Kidneys Aim(s) and objective(s) This guideline focuses on the detection, prevention, and management of kidney disease in people with diabetes. The management of end-stage renal disease
Diabetes and the Kidneys Aim(s) and objective(s) This guideline focuses on the detection, prevention, and management of kidney disease in people with diabetes. The management of end-stage renal disease
Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA
 Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA 4671 S. Congress Avenue, Lake Worth, FL 33461 561.434.0111 4631 N. Congress Avenue, Suite 102, West Palm Beach, FL 33407 Urinary Tract Infection About one of every
Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA 4671 S. Congress Avenue, Lake Worth, FL 33461 561.434.0111 4631 N. Congress Avenue, Suite 102, West Palm Beach, FL 33407 Urinary Tract Infection About one of every
Prevention and Recognition of Obstetric Fistula Training Package. Module 8: Pre-repair Care and Referral for Women with Obstetric Fistula
 Prevention and Recognition of Obstetric Fistula Training Package Module 8: Pre-repair Care and Referral for Women with Obstetric Fistula Early detection and treatment If a woman has recently survived a
Prevention and Recognition of Obstetric Fistula Training Package Module 8: Pre-repair Care and Referral for Women with Obstetric Fistula Early detection and treatment If a woman has recently survived a
Diabetic Nephropathy
 Diabetic Nephropathy Kidney disease is common in people affected by diabetes mellitus Definition Urinary albumin excretion of more than 300mg in a 24 hour collection or macroalbuminuria Abnormal renal
Diabetic Nephropathy Kidney disease is common in people affected by diabetes mellitus Definition Urinary albumin excretion of more than 300mg in a 24 hour collection or macroalbuminuria Abnormal renal
Value of Ultrasound-guided Irrigation and Drainage of
 Value of Ultrasound-guided Irrigation and Drainage of Refractory Pyocysts in ADPKD 1. Daryoush Saedi M.D., Department of Radiology, Hasheminejad Kidney Center, School of Medicine, Iran University of Medical
Value of Ultrasound-guided Irrigation and Drainage of Refractory Pyocysts in ADPKD 1. Daryoush Saedi M.D., Department of Radiology, Hasheminejad Kidney Center, School of Medicine, Iran University of Medical
Positron Emission Tomography - For Patients
 Positron Emission Tomography - For Patients A physician s written order is required for any PET-CT tests. How should I prepare for my PET-CT? PET-CT is more complicated than most other tests you may be
Positron Emission Tomography - For Patients A physician s written order is required for any PET-CT tests. How should I prepare for my PET-CT? PET-CT is more complicated than most other tests you may be
Managing Changes in Your Bladder Function After Cancer Treatment
 Managing Changes in Your Bladder Function After Cancer Treatment Information for cancer survivors UHN Read this resource to learn: What a urinary problem is What causes it What you can do to improve your
Managing Changes in Your Bladder Function After Cancer Treatment Information for cancer survivors UHN Read this resource to learn: What a urinary problem is What causes it What you can do to improve your
Identifying and treating long-term kidney problems (chronic kidney disease)
 Understanding NICE guidance Information for people who use NHS services Identifying and treating long-term kidney problems (chronic kidney disease) NICE clinical guidelines advise the NHS on caring for
Understanding NICE guidance Information for people who use NHS services Identifying and treating long-term kidney problems (chronic kidney disease) NICE clinical guidelines advise the NHS on caring for
Chapter 23. Composition and Properties of Urine
 Chapter 23 Composition and Properties of Urine Composition and Properties of Urine urinalysis the examination of the physical and chemical properties of urine appearance - clear, almost colorless to deep
Chapter 23 Composition and Properties of Urine Composition and Properties of Urine urinalysis the examination of the physical and chemical properties of urine appearance - clear, almost colorless to deep
1. What is the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test?
 1. What is the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test? Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) is a protein produced by the cells of the prostate gland. The PSA test measures the level of PSA in the blood. The doctor
1. What is the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test? Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) is a protein produced by the cells of the prostate gland. The PSA test measures the level of PSA in the blood. The doctor
Hematuria in Primary Care: The Bloody Truth
 Hematuria in Primary Care: The Bloody Truth Ashlyn Bruning, MMS, PA-C NCAPA Summer Conference Disclosure: I Have No Financial or Non-financial Relationships or Conflicts of Interest to Disclose OBJECTIVES
Hematuria in Primary Care: The Bloody Truth Ashlyn Bruning, MMS, PA-C NCAPA Summer Conference Disclosure: I Have No Financial or Non-financial Relationships or Conflicts of Interest to Disclose OBJECTIVES
Calcium (serum, plasma, blood)
 Calcium (serum, plasma, blood) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Calcium (total in serum, plasma, ionised in blood (see 2.1 (2)). 1.2 Alternative names None 1.3 NMLC code 1.4 Description
Calcium (serum, plasma, blood) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Calcium (total in serum, plasma, ionised in blood (see 2.1 (2)). 1.2 Alternative names None 1.3 NMLC code 1.4 Description
Urinary Tract Infections
 1 Infections in the urinary tract are relatively common. These infections are often referred to as bladder infections. They are also known as UTI s or urinary tract infections. When an infection is confined
1 Infections in the urinary tract are relatively common. These infections are often referred to as bladder infections. They are also known as UTI s or urinary tract infections. When an infection is confined
Diagnostics: Page 2 of 5
 Proteinuria Proteinuria is a condition in which there are increased amounts of protein in the urine. There are a number of different diseases which can result in proteinuria. In the early stages of the
Proteinuria Proteinuria is a condition in which there are increased amounts of protein in the urine. There are a number of different diseases which can result in proteinuria. In the early stages of the
Section IV Diagnostic Coding and Reporting for Outpatient Services
 Section IV Diagnostic Coding and Reporting for Outpatient Services Section IV, here we come! Keep that book cracked open and let s go through Diagnostic Coding and Reporting Guidelines for Outpatient Services.
Section IV Diagnostic Coding and Reporting for Outpatient Services Section IV, here we come! Keep that book cracked open and let s go through Diagnostic Coding and Reporting Guidelines for Outpatient Services.
IM 655 Nephrology Clerkship. Selective/Elective Clerkship Rotation Syllabus
 IM 655 Nephrology Clerkship Selective/Elective Clerkship Rotation Syllabus Osteopathic Medical Specialties Mary Hughes DO Chairperson, Instructor of Record Mary Hughes DO [email protected] (100% for CLIFMS
IM 655 Nephrology Clerkship Selective/Elective Clerkship Rotation Syllabus Osteopathic Medical Specialties Mary Hughes DO Chairperson, Instructor of Record Mary Hughes DO [email protected] (100% for CLIFMS
Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW
 Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW Kidney cancer is the third most common genitourinary cancer in adults. There are approximately 54,000 new cancer cases each year in the United States, and the incidence of kidney
Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW Kidney cancer is the third most common genitourinary cancer in adults. There are approximately 54,000 new cancer cases each year in the United States, and the incidence of kidney
A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page
 A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page IX0200: Prevention & Control of Catheter Associated
A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page IX0200: Prevention & Control of Catheter Associated
Nutrition for Kidney Stones
 Nutrition for Kidney Stones 1129 Northern Blvd. Suite 101 Manhasset, NY 11030 516. 365. 5570 Created by Dr. Simon Prince, FACP, FASN and Rachel Berman RD, CSR Overview Kidney stones are more common than
Nutrition for Kidney Stones 1129 Northern Blvd. Suite 101 Manhasset, NY 11030 516. 365. 5570 Created by Dr. Simon Prince, FACP, FASN and Rachel Berman RD, CSR Overview Kidney stones are more common than
Percutaneous Abscess Drainage
 Scan for mobile link. Percutaneous Abscess Drainage An abscess is an infected fluid collection within the body. Percutaneous abscess drainage uses imaging guidance to place a thin needle through the skin
Scan for mobile link. Percutaneous Abscess Drainage An abscess is an infected fluid collection within the body. Percutaneous abscess drainage uses imaging guidance to place a thin needle through the skin
Preventive Care Recommendations THE BASIC FACTS
 Preventive Care Recommendations THE BASIC FACTS MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS Carlos Healey, diagnosed in 2001 The Three Most Common Eye Disorders in Multiple Sclerosis Blood Pressure & Pulse Height & Weight Complete
Preventive Care Recommendations THE BASIC FACTS MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS Carlos Healey, diagnosed in 2001 The Three Most Common Eye Disorders in Multiple Sclerosis Blood Pressure & Pulse Height & Weight Complete
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Under normal circumstances, a woman's uterus sheds a limited amount of blood during each menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs between
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Under normal circumstances, a woman's uterus sheds a limited amount of blood during each menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs between
A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment of Infection in the Outpatient Setting Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections
 A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment of Infection in the Outpatient Setting Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections By Gary R. Skankey, MD, FACP, Infectious Disease, Las Vegas, NV Sponsored
A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment of Infection in the Outpatient Setting Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections By Gary R. Skankey, MD, FACP, Infectious Disease, Las Vegas, NV Sponsored
AT&T Global Network Client for Windows Product Support Matrix January 29, 2015
 AT&T Global Network Client for Windows Product Support Matrix January 29, 2015 Product Support Matrix Following is the Product Support Matrix for the AT&T Global Network Client. See the AT&T Global Network
AT&T Global Network Client for Windows Product Support Matrix January 29, 2015 Product Support Matrix Following is the Product Support Matrix for the AT&T Global Network Client. See the AT&T Global Network
Learning Resource Guide. Understanding Incontinence. 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved
 Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved ElderCare Online s Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence Table of Contents Introduction
Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved ElderCare Online s Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence Table of Contents Introduction
