Towards a Fault-Resilient Cloud Management Stack
|
|
|
- Lee Colin Harrell
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Towards a Fault-Resilient Cloud Management Stack Xiaoen Ju Livio Soares Kang G. Shin Kyung Dong Ryu University of Michigan IBM T.J. Watson Research Center Abstract Cloud management stacks have become a new important layer in cloud computing infrastructure, simplifying the configuration and management of cloud computing environments. As the resource manager and controller of an entire cloud, a cloud management stack has significant impact on the fault-resilience of a cloud platform. However, our preliminary study on the fault-resilience of OpenStack an open source state-of-the-art cloud management stack shows that such an emerging software stack needs to be better designed and tested in order to serve as a building block for fault-resilient cloud environments. We discuss the issues identified by our faultinjection tool and make suggestions on how to strengthen cloud management stacks. 1 Introduction Cloud computing has become an increasingly popular computing platform. With this increasing popularity comes the issue of how to efficiently manage such a new computing infrastructure. Cloud management stacks have been introduced to address this challenge, facilitating the formation and management of cloud platforms. Since cloud platforms usually consist of hundreds or thousands of commodity servers, failures are the norm instead of the exception [1, 3]. Cloud platforms, as well as applications running in the cloud, need to be designed to tolerate failures induced by software bugs, hardware defects and human errors. The scope of failures varies from one single process to an entire data center, with a timescale ranging from subseconds to days. The same requirement on fault-resilience also applies to cloud management stacks, which themselves run in the cloud environment. Unfortunately, to the best of our knowledge, the fault-resilience of cloud management stacks has not received enough attention from the cloud computing community. Despite the widespread awareness of the prevalence of failures, the community is still largely focusing on how to enhance the functionality of this emerging software stack. We argue that fault-resilience should remain one of the most important features of any software designed for the cloud environment. Lack of fault-resilience significantly weakens the usefulness of cloud-scale software. We believe that fault-resilience is so fundamental that it needs to be deeply integrated into the design of cloud-scale software instead of being treated as an optional feature or an afterthought. This holds for cloud applications and, more importantly, for cloud management stacks, due to the latter s significant impact on cloud platforms. In this paper, we explore the fault-resilience of Open- Stack, a popular open source cloud management stack that has been drawing significant attention in recent years. By reporting the issues discovered in our study as well as making associated design recommendations and suggestions, we would like to re-stress the importance of fault-resilience for cloud management stacks and call for a collaborative effort in addressing OpenStack s faultresilience issues. 2 Methodology OpenStack is a high-level cloud operating system that builds and manages cloud platforms running on top of commodity hardware. It functions via the coordination and cooperation of its various service groups, such as compute services for provisioning and managing virtual machines (VMs) inside a cloud, image services for managing template VM images, and an identity service for authentication. Two major communication mechanisms are employed in OpenStack, with the Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP) for communications within the compute service group, and the Representational State Transfer (REST) mechanism for communications among other services, as well as with external users. OpenStack also relies on many external services, such
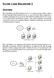
2 as local hypervisors and databases, and communicates with them using libraries that fulfill their communication specifications, such as libvirt for hypervisors and SQLAlchemy for database access. We use fault injection to study the fault-resilience of OpenStack. We define fault-resilience to be the ability to maintain correct functionalities under faults. Specifically, we study the impact of faults on OpenStack s external API interface and its persistent states. These two aspects are important because OpenStack relies on the persistent states (e.g., states in its databases) to manage a cloud platform (i.e., which VMs are currently running at which physical hosts), and OpenStack s external API is the interface for communicating with users. A welldesigned fault-resilient cloud management stack should maintain correct information in its persistent states and generate correct responses to users requests via the external API in a timely manner, despite faults. We use three fault types in our study: server crashes, transient server non-responsiveness and network partitions. These fault types, albeit simple, are common cases that lead to failure situations in a cloud environment. We inject faults into OpenStack at the locations where two services communicate. Take server crash faults as an example. In our single-fault-injection experiments, for a message sent from one service to another, we inject a crash fault to the sender service in one experiment, before the message is sent, and a crash fault to the receiver service in another experiment, before the message is received. We believe that our messageflow-driven fault injection can effectively reveal faultresilience issues, because (1) message flows indicate the execution paths inside OpenStack for request processing, (2) heinous bugs affecting the fault-resilience of cloud systems such as OpenStack are usually related to the interaction of several services, which can be characterized by their message flows, and (3) bugs and issues within a single service can be located and resolved by mature single-process debugging techniques. Faults are injected to three OpenStack services authentication, image and compute services as well as external supporting services such as database services, local hypervisor managers and AMQP brokers. We target at these services because they are indispensable for running OpenStack. We consider extending the coverage to other services (e.g., object store) our future work. Our fault-injection tool consists of three components: a logging and synchronization module, a fault-injection module and a specification checking module. The logging and synchronization module logs messages among OpenStack services and coordinates the execution of OpenStack and the fault-injection tool via logging events (e.g., packet send/receive). The fault-injection module injects faults into OpenStack along message flows cap- Logging and Synchroni zation OpenStack Fault Injection Specs expect State S 1. A is communicating with B 2. Crash B Test Plan crash receiver Fault Injection Controller 3. Resume A 4. Result: State S 5. Expect State S Spec Checking 6. Detect violations Figure 1: Fault-injection workflow example. 1: Detect fault-injection opportunity and pause execution. 2: Inject fault. 3: Resume execution. 4: Report results. 5: Check specifications. 6: Detect violations. tured by the logging module. The specification checking module verifies whether OpenStack, with injected faults, complies with specifications related to its expected persistent states and its responses to users. We focus on the fault-resilience of OpenStack during the processing of the most commonly used external requests, such as VM creation and deletion. For each request, we first execute it and record the message flows among OpenStack services. We then generate an execution graph from the message logs, which characterizes the execution path of OpenStack during the request processing. A node in the graph represents a communication event, recording the communicating entity (e.g., an API server process of the compute service) and the type of communication (e.g., an outgoing RPC message). An edge in the graph connects the sender and the receiver of a communication event. Based on the execution graph and a predefined fault-specification 1, we generate a collection of test plans, each consisting of a fault to be injected into a certain location in the execution graph. We then conduct fault-injection by initializing OpenStack into the same state as in the logging procedure, replaying the external request and injecting faults according to the test plans. After the tests complete, we collect results (both user observable responses from OpenStack and its internal persistent states) and verify them with predefined specifications. Upon verification failure, we manually examine OpenStack s implementation to identify bugs causing the invalid results. Figure 1 illustrates the fault injection process. We use a simplistic experiment setting (similar to OpenStack s default setting) in which all OpenStack and external supporting services have only one instance. Up to three nodes are used in each fault-injection test for 1 A predefined fault-specification indicates the fault type injected to an execution, e.g., a sender server crash. 2
3 Table 1: Summary of Fault-Resilience Issues Category Count Out-of-the-box fault resilience solution 1 Timeout mechanism 2 Cross-layer coordination 1 Supporting library interference 1 Periodic check 5 Miscellaneous programming bugs 3 proper fault isolation. 3 Fault-Resilience Issues in OpenStack Using the fault-injection tool described in the previous section, we identify several fault-resilience issues in OpenStack (Essex version), which, unless solved properly, lead to undesirable results in the cloud environment managed by OpenStack. Note that we only categorize and discuss the issues uncovered by our tool, which are by no means close to a complete set of fault-resilience issues in OpenStack or other cloud management stacks. Yet based on our own experience with OpenStack deployment as well as what other users have reported, we believe that the following issues, summarized in Table 1, are commonly found in real-world scenarios. It is also worth noting that, although the number of issues discussed in this study seems limited, some of them, such as the lack of timeout in REST communications (cf. Section 3.2) and the state transition deficiency (cf. Section 3.5), are repeatedly manifested with faults injected in common execution paths of OpenStack. 3.1 Out-of-the-Box Fault-Resilience To the best of our knowledge, OpenStack has not been designed to enable a straightforward out-of-the-box fault-resilience solution via a unified deployment procedure. This may arise from a plausible opinion in the OpenStack community: fault-resilience is not mandatory for all use cases. Given the critical role OpenStack plays in the cloud, however, it would be reasonable to expect that production-level OpenStack deployment requires fault-resilience, which should be easily enabled across all services in the stack. Our experience shows that OpenStack falls short in this aspect. For example, supporting services, such as the libvirt service, cannot be configured within OpenStack to restart automatically upon crashes. Similarly, the service failover feature a key ingredient of high availability systems can only be enabled outside OpenStack, via the support of services such as Pacemaker. Another example is that, when using Qpid as OpenStack s AMQP broker service, third-party modules need to be separately downloaded, compiled and configured in order for the durable queue features a default Qpid setting inside OpenStack to function properly. A unified deployment procedure delivered out of the box, aggregating all necessary configuration options relevant to fault-resilience, will significantly improve user experience. 3.2 Timeout Mechanism Timeout is a common mechanism in distributed systems to prevent the malfunctioning of one component from blocking the rest of the system. One known difficulty in employing this mechanism is the selection of a proper timeout value. A timeout value that is too short leads to unnecessary disruption of system operation due to premature activation of the recovery logic. A timeout value that is too long, on the other hand, delays failure detection, thus negatively affecting the progress of the system. Being a distributed system itself, OpenStack uses timeout values as a safety net for service coordination. For example, OpenStack associates a timeout value (60 seconds by default) for RPC calls, preventing the caller from indefinitely waiting for a reply. However, our tool shows that there are cases in common execution paths inside OpenStack where critical timeout values remain unspecified. For example, OpenStack uses the WSGI module in the Eventlet library to coordinate its services during the processing of external requests. The WSGI module in turn utilizes the httplib2 library for communication. Probably, due to backward compatibility considerations, httplib2 associates a timeout value only with connection establishment and request sending operations but not with response obtaining operations (e.g., via HTTPConnection class s getresponse function). As a result, if a network partition occurs between two communicating services, after a service sends a request to the other but before it obtains a response, then the request issuing service will remain blocked indefinitely. In this case, associating a proper timeout value for the response obtaining operation would solve the problem. As discussed at the beginning of this section, however, timeout selection is no easy task. This problem is exacerbated by the fact that OpenStack relies on many external services, which may have their own timeout settings. Without fine-tuning these external timeout settings, OpenStack may demonstrate unexpected behaviors when faults occur in the external services. For example, if configured to use MySQL as its database service, OpenStack then uses the MySQLdb library to communicate with the database service. In this setting, our tool identifies that if a network partition occurs between an OpenStack service and the MySQL database, after a connection has been established but before the Open- 3
4 Stack service can issue a SQL statement execution command, then the OpenStack service may remain blocked for about 930 seconds a common behavior among applications using the MySQLdb library. OpenStack does not provide a default timeout value specific to its services for SQL statement execution. Admittedly, such a value may be difficult to specify. But relying on the default behavior of supporting libraries may not be the optimal solution for OpenStack services, either. We recommend the design of innovative approaches to systematic configuration of timeout values scattered in management stacks themselves as well as in supporting libraries and services, thus better orchestrating cloud management stacks in their entirety. 3.3 Cross-Layer Coordination As described above, OpenStack uses many external services, such as Qpid, libvirt and MySQL, for efficiently achieving a rich set of functionalities. These services usually provide client libraries to facilitate communications between service applicants and providers. The common design pattern in OpenStack is to insert another set of layers of abstraction between OpenStack services and those external services, defining a uniform protocol for each category of services (e.g., database service category, local hypervisor management category and AMQP communication category) and abstracting away the incompatibility among lower-level supporting services (e.g., between SQLite and MySQL). The advantages related to such an encapsulation design are numerous. However, our study indicates that such additional abstraction layers, when implemented without sufficient caution, may introduce subtle bugs. Below we use a concrete example to elaborate this argument. Consider the communication between OpenStack and Qpid service. Qpid provides a client library for binding to a Qpid service (functioning as an AMQP broker). On top of this library, OpenStack implements its own wrapper library for Qpid, whose functions are in turn invoked by a higher-level AMQP abstraction layer in OpenStack. A configuration option is exposed from the lower-level Qpid library via OpenStack wrappers to system administrators in order to set the upper bound of connection retries from the client side to a Qpid broker. Upon loss of connectivity when an OpenStack service sends an RPC message to a Qpid broker, the client-side Qpid library retries to connect back to the broker until the configured upper bound is reached. The state of the connection is considered temporarily erroneous during the connection retires. Once the retry limit is reached, the Qpid library transits the state of the connection to a permanent erroneous state and stops reconnection. However, this configuration option is not honored by the indirection layers in OpenStack. Specifically, OpenStack s Qpid wrapper keeps polling the state of the connection without differentiating whether the connection resides in a temporary or permanent erroneous state. This behavior is undesirable because the connection maintained by the lower-level Qpid library, once becoming permanently erroneous, will not be set to operational even if the root cause for the loss of connectivity (e.g., a network partition between the OpenStack service using the Qpid library and the Qpid broker) is resolved. The implementation of OpenStack s Qpid wrapper unnecessarily blocks the RPC issuer service in this case. 3.4 Supporting Library Interference Issues related to the use of external libraries in Open- Stack are not confined to the OpenStack-and-externallibrary boundaries. External libraries can, in reality, interfere with each other in unexpected ways. Notably, OpenStack utilizes the Eventlet and Greenlet libraries for cooperative threading. With those libraries, user-level threads in an OpenStack service are scheduled cooperatively: one thread continues executing without preemption until it reaches a scheduling point defined by the libraries, at which point the control flow is switched to another thread (if such a thread exists). This user-level thread scheduling requires the modification of certain blocking standard Python library calls, such as sleep, in order to prevent the caller thread from blocking the entire OpenStack service. The Eventlet library provides standard library function patches to achieve the cooperative scheduling. However, those patches are not 100 percent compatible with the standard library. Their subtle nuances may negatively affect the functionality of other external libraries used in OpenStack. Consider the client library of Qpid again. Before an OpenStack service can use the connection objects provided by the Qpid client library to communicate with a Qpid broker, a connection pool needs to be instantiated. During this procedure, the Qpid client library internally uses a pipe to synchronize a waiter object which waits for the connection to a Qpid broker to be established and a connection engine object responsible for the connection establishment. The Qpid library implements this conventional consumer/producer synchronization by having the waiter issuing a select call on the read end of the pipe and, when the call returns with a file descriptor ready for reading, issuing a read call on the file descriptor. However, our tool shows that this design causes the blocking of an entire OpenStack service if, at the connection pool creation time, no Qpid broker is active. The OpenStack service in question remains blocked even if a Qpid broker becomes active after the pool creation attempt. This bug is caused by the fact that in OpenStack, 4
5 the select function call is patched by the Eventlet library, and there is an incompatibility issue related to the patched version. The standard library version of select returns a non-empty collection of file descriptors in the read file descriptor list only if they are ready for reading. The Eventlet implementation, however, returns such a non-empty collection if the file descriptors are ready for reading or if there are exceptional conditions associated with them (such as the occurrence of a POLLERR or a POLLHUP event, due to the fact that select is implemented by poll in Eventlet). This nuance makes it possible for the Qpid library to read a not-yet-ready file descriptor after the return of a preceding select call, which in turn causes the blocking. This issue, as well as the one in Section 3.3, clearly indicates that examining the fault-resilience of one module in an isolated environment is insufficient for guaranteeing the overall fault-resilience. We would thus suggest that cloud management stack developers conduct thorough testing on the overall fault-resilience of the stacks, with a focus on the compatibility of external libraries. 3.5 Periodic Check Periodic checks are widely used in OpenStack, mainly for monitoring the well-being of various services. Our study suggests that this mechanism be extended to other aspects of OpenStack as well. One such aspect is the persistent states of the cloud environment maintained by OpenStack. For example, our study shows that during the processing of a VM creation request, if the scheduler or the compute service crashes or restarts, then the created VM may remain in the transient BUILD state. This is an undesirable behavior because a created VM should enter a stable state ACTIVE if the creation is successful and ERROR otherwise in a timely manner. Having aborted the VM creation due to service crashes yet marking the VM creation as in progress would confuse users. A periodic service for checking the progress of request processing and resetting related VMs to their according stable states will prove useful in this case. Similarly, if an RPC cast message related to the deallocation of a fixed IP is lost during the deletion of a VM, the IP remains in the allocated state while its associated VM has been deleted and the lease of that IP address has expired. Such an IP address cannot be reused by other VMs, causing network resource leakage. A periodic check is needed in this case to reap orphan IPs. The Falcon spy network [2] seems a promising potential enhancement to existing periodic checking mechanisms in OpenStack. Falcon proposes the use of a hierarchical probing architecture in which heartbeat messages from one layer are monitored by the layer underneath it. In a cloud management stack, we may reuse the idea and design a layered spy network, within which the uppermost spy monitors the processing of requests in a service (e.g., the processing of a VM creation request by a given compute service), and the rest spies monitor lower abstraction layers in the management stack. 3.6 Miscellaneous Programming Bugs Our fault-injection tool has also found bugs which seem to result from occasional inadvertence. For example, one flaw in OpenStack s Qpid wrapper is that, when an exception occurs during an open-connection operation to a Qpid broker, the wrapper constantly retries open without first using close to reset certain internal states maintained by the connection, causing subsequent calls to fail. Another example is that, when a user invokes an external compute API but the authentication operation fails due to an internal error condition in the authentication service, the compute API service replies a confusing error message to the user, mistakenly attributing the failed authentication to the use of an invalid token instead of reporting the internal error. 4 Conclusions In this paper, we described our first attempt to address the fault-resilience issues related to the emerging cloud management stacks. With a preliminary fault-injection tool, we studied the fault-resilience of OpenStack, provided in-depth discussions on six categories of fault-resilience issues, and proposed suggestions on how to strengthen this software layer. Acknowledgment We thank Dilma Da Silva, David Oppenheimer (our shepherd) and the anonymous reviewers for their valuable suggestions. The work reported in this paper was supported in part by the US Air Force Office of Scientific Research under Grant No. FA References [1] AMAZON. Summary of the Amazon EC2 and Amazon RDS service disruption in the US east region. message/65648/. Retrieved in March, [2] LENERS, J. B., WU, H., HUNG, W.-L., AGUILERA, M. K., AND WALFISH, M. Detecting failures in distributed systems with the falcon spy network. In SOSP 11. [3] MICROSOFT. Summary of Windows Azure service disruption on Feb 29th, archive/2012/03/09/summary-of-windows-azureservice-disruption-on-feb-29th-2012.aspx. Retrieved in March,
IaaS Cloud Architectures: Virtualized Data Centers to Federated Cloud Infrastructures
 IaaS Cloud Architectures: Virtualized Data Centers to Federated Cloud Infrastructures Dr. Sanjay P. Ahuja, Ph.D. 2010-14 FIS Distinguished Professor of Computer Science School of Computing, UNF Introduction
IaaS Cloud Architectures: Virtualized Data Centers to Federated Cloud Infrastructures Dr. Sanjay P. Ahuja, Ph.D. 2010-14 FIS Distinguished Professor of Computer Science School of Computing, UNF Introduction
BMC Cloud Management Functional Architecture Guide TECHNICAL WHITE PAPER
 BMC Cloud Management Functional Architecture Guide TECHNICAL WHITE PAPER Table of Contents Executive Summary............................................... 1 New Functionality...............................................
BMC Cloud Management Functional Architecture Guide TECHNICAL WHITE PAPER Table of Contents Executive Summary............................................... 1 New Functionality...............................................
THE WINDOWS AZURE PROGRAMMING MODEL
 THE WINDOWS AZURE PROGRAMMING MODEL DAVID CHAPPELL OCTOBER 2010 SPONSORED BY MICROSOFT CORPORATION CONTENTS Why Create a New Programming Model?... 3 The Three Rules of the Windows Azure Programming Model...
THE WINDOWS AZURE PROGRAMMING MODEL DAVID CHAPPELL OCTOBER 2010 SPONSORED BY MICROSOFT CORPORATION CONTENTS Why Create a New Programming Model?... 3 The Three Rules of the Windows Azure Programming Model...
Overview of Luna High Availability and Load Balancing
 SafeNet HSM TECHNICAL NOTE Overview of Luna High Availability and Load Balancing Contents Introduction... 2 Overview... 2 High Availability... 3 Load Balancing... 4 Failover... 5 Recovery... 5 Standby
SafeNet HSM TECHNICAL NOTE Overview of Luna High Availability and Load Balancing Contents Introduction... 2 Overview... 2 High Availability... 3 Load Balancing... 4 Failover... 5 Recovery... 5 Standby
Software-Defined Networks Powered by VellOS
 WHITE PAPER Software-Defined Networks Powered by VellOS Agile, Flexible Networking for Distributed Applications Vello s SDN enables a low-latency, programmable solution resulting in a faster and more flexible
WHITE PAPER Software-Defined Networks Powered by VellOS Agile, Flexible Networking for Distributed Applications Vello s SDN enables a low-latency, programmable solution resulting in a faster and more flexible
Running a Workflow on a PowerCenter Grid
 Running a Workflow on a PowerCenter Grid 2010-2014 Informatica Corporation. No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form, by any means (electronic, photocopying, recording or otherwise)
Running a Workflow on a PowerCenter Grid 2010-2014 Informatica Corporation. No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form, by any means (electronic, photocopying, recording or otherwise)
ELIXIR LOAD BALANCER 2
 ELIXIR LOAD BALANCER 2 Overview Elixir Load Balancer for Elixir Repertoire Server 7.2.2 or greater provides software solution for load balancing of Elixir Repertoire Servers. As a pure Java based software
ELIXIR LOAD BALANCER 2 Overview Elixir Load Balancer for Elixir Repertoire Server 7.2.2 or greater provides software solution for load balancing of Elixir Repertoire Servers. As a pure Java based software
Solution for private cloud computing
 The CC1 system Solution for private cloud computing 1 Outline What is CC1? Features Technical details Use cases By scientist By HEP experiment System requirements and installation How to get it? 2 What
The CC1 system Solution for private cloud computing 1 Outline What is CC1? Features Technical details Use cases By scientist By HEP experiment System requirements and installation How to get it? 2 What
RCL: Design and Open Specification
 ICT FP7-609828 RCL: Design and Open Specification D3.1.1 March 2014 _D3.1.1_RCLDesignAndOpenSpecification_v1.0 Document Information Scheduled delivery Actual delivery Version Responsible Partner 31.03.2014
ICT FP7-609828 RCL: Design and Open Specification D3.1.1 March 2014 _D3.1.1_RCLDesignAndOpenSpecification_v1.0 Document Information Scheduled delivery Actual delivery Version Responsible Partner 31.03.2014
Whitepaper Continuous Availability Suite: Neverfail Solution Architecture
 Continuous Availability Suite: Neverfail s Continuous Availability Suite is at the core of every Neverfail solution. It provides a comprehensive software solution for High Availability (HA) and Disaster
Continuous Availability Suite: Neverfail s Continuous Availability Suite is at the core of every Neverfail solution. It provides a comprehensive software solution for High Availability (HA) and Disaster
1.1 SERVICE DESCRIPTION
 ADVANIA OPENCLOUD SERCVICE LEVEL AGREEMENT 1.1 SERVICE DESCRIPTION The service is designed in a way that will minimize Advania s operational involvement. Advania administrates the cloud platform and provides
ADVANIA OPENCLOUD SERCVICE LEVEL AGREEMENT 1.1 SERVICE DESCRIPTION The service is designed in a way that will minimize Advania s operational involvement. Advania administrates the cloud platform and provides
ActiveVOS Server Architecture. March 2009
 ActiveVOS Server Architecture March 2009 Topics ActiveVOS Server Architecture Core Engine, Managers, Expression Languages BPEL4People People Activity WS HT Human Tasks Other Services JMS, REST, POJO,...
ActiveVOS Server Architecture March 2009 Topics ActiveVOS Server Architecture Core Engine, Managers, Expression Languages BPEL4People People Activity WS HT Human Tasks Other Services JMS, REST, POJO,...
Lecture 02a Cloud Computing I
 Mobile Cloud Computing Lecture 02a Cloud Computing I 吳 秀 陽 Shiow-yang Wu What is Cloud Computing? Computing with cloud? Mobile Cloud Computing Cloud Computing I 2 Note 1 What is Cloud Computing? Walking
Mobile Cloud Computing Lecture 02a Cloud Computing I 吳 秀 陽 Shiow-yang Wu What is Cloud Computing? Computing with cloud? Mobile Cloud Computing Cloud Computing I 2 Note 1 What is Cloud Computing? Walking
Introduction to OpenStack
 Introduction to OpenStack Carlo Vallati PostDoc Reseracher Dpt. Information Engineering University of Pisa [email protected] Cloud Computing - Definition Cloud Computing is a term coined to refer
Introduction to OpenStack Carlo Vallati PostDoc Reseracher Dpt. Information Engineering University of Pisa [email protected] Cloud Computing - Definition Cloud Computing is a term coined to refer
The Lagopus SDN Software Switch. 3.1 SDN and OpenFlow. 3. Cloud Computing Technology
 3. The Lagopus SDN Software Switch Here we explain the capabilities of the new Lagopus software switch in detail, starting with the basics of SDN and OpenFlow. 3.1 SDN and OpenFlow Those engaged in network-related
3. The Lagopus SDN Software Switch Here we explain the capabilities of the new Lagopus software switch in detail, starting with the basics of SDN and OpenFlow. 3.1 SDN and OpenFlow Those engaged in network-related
Cisco TelePresence Management Suite Extension for Microsoft Exchange Version 4.0.3
 Cisco TelePresence Management Suite Extension for Microsoft Exchange Version 4.0.3 Software Release Notes Revised September 2014 Contents Introduction 1 Changes to interoperability 1 Product documentation
Cisco TelePresence Management Suite Extension for Microsoft Exchange Version 4.0.3 Software Release Notes Revised September 2014 Contents Introduction 1 Changes to interoperability 1 Product documentation
Peach Fuzzer Platform
 Fuzzing is a software testing technique that introduces invalid, malformed, or random data to parts of a computer system, such as files, network packets, environment variables, or memory. How the tested
Fuzzing is a software testing technique that introduces invalid, malformed, or random data to parts of a computer system, such as files, network packets, environment variables, or memory. How the tested
Appendix to; Assessing Systemic Risk to Cloud Computing Technology as Complex Interconnected Systems of Systems
 Appendix to; Assessing Systemic Risk to Cloud Computing Technology as Complex Interconnected Systems of Systems Yacov Y. Haimes and Barry M. Horowitz Zhenyu Guo, Eva Andrijcic, and Joshua Bogdanor Center
Appendix to; Assessing Systemic Risk to Cloud Computing Technology as Complex Interconnected Systems of Systems Yacov Y. Haimes and Barry M. Horowitz Zhenyu Guo, Eva Andrijcic, and Joshua Bogdanor Center
KVM, OpenStack, and the Open Cloud
 KVM, OpenStack, and the Open Cloud Adam Jollans, IBM & Mike Kadera, Intel CloudOpen Europe - October 13, 2014 13Oct14 Open VirtualizaGon Alliance 1 Agenda A Brief History of VirtualizaGon KVM Architecture
KVM, OpenStack, and the Open Cloud Adam Jollans, IBM & Mike Kadera, Intel CloudOpen Europe - October 13, 2014 13Oct14 Open VirtualizaGon Alliance 1 Agenda A Brief History of VirtualizaGon KVM Architecture
Virtualization, SDN and NFV
 Virtualization, SDN and NFV HOW DO THEY FIT TOGETHER? Traditional networks lack the flexibility to keep pace with dynamic computing and storage needs of today s data centers. In order to implement changes,
Virtualization, SDN and NFV HOW DO THEY FIT TOGETHER? Traditional networks lack the flexibility to keep pace with dynamic computing and storage needs of today s data centers. In order to implement changes,
Cloud in a box. Scalable Cloud Computing strategy.
 Cloud in a box. Scalable Cloud Computing strategy. Ing. Alfredo Sánchez Rodríguez SOFTEL, GEIC [email protected] Abstract IT infrastructures have become so complicated and vulnerable, that currently 70%
Cloud in a box. Scalable Cloud Computing strategy. Ing. Alfredo Sánchez Rodríguez SOFTEL, GEIC [email protected] Abstract IT infrastructures have become so complicated and vulnerable, that currently 70%
Application Discovery Manager User s Guide vcenter Application Discovery Manager 6.2.1
 Application Discovery Manager User s Guide vcenter Application Discovery Manager 6.2.1 This document supports the version of each product listed and supports all subsequent versions until the document
Application Discovery Manager User s Guide vcenter Application Discovery Manager 6.2.1 This document supports the version of each product listed and supports all subsequent versions until the document
Federated Application Centric Infrastructure (ACI) Fabrics for Dual Data Center Deployments
 Federated Application Centric Infrastructure (ACI) Fabrics for Dual Data Center Deployments March 13, 2015 Abstract To provide redundancy and disaster recovery, most organizations deploy multiple data
Federated Application Centric Infrastructure (ACI) Fabrics for Dual Data Center Deployments March 13, 2015 Abstract To provide redundancy and disaster recovery, most organizations deploy multiple data
Cisco Prime Data Center Network Manager Release 7.0: Fabric Management for Cisco Dynamic Fabric Automation
 Data Sheet Cisco Prime Data Center Network Manager Release 7.0: Fabric Management for Cisco Dynamic Fabric Automation Product Overview Cisco Prime Data Center Network Manager (DCNM) software is a foundation
Data Sheet Cisco Prime Data Center Network Manager Release 7.0: Fabric Management for Cisco Dynamic Fabric Automation Product Overview Cisco Prime Data Center Network Manager (DCNM) software is a foundation
Business Application Services Testing
 Business Application Services Testing Curriculum Structure Course name Duration(days) Express 2 Testing Concept and methodologies 3 Introduction to Performance Testing 3 Web Testing 2 QTP 5 SQL 5 Load
Business Application Services Testing Curriculum Structure Course name Duration(days) Express 2 Testing Concept and methodologies 3 Introduction to Performance Testing 3 Web Testing 2 QTP 5 SQL 5 Load
Wishful Thinking vs. Reality in Regards to Virtual Backup and Restore Environments
 NOVASTOR WHITE PAPER Wishful Thinking vs. Reality in Regards to Virtual Backup and Restore Environments Best practices for backing up virtual environments Published by NovaStor Table of Contents Why choose
NOVASTOR WHITE PAPER Wishful Thinking vs. Reality in Regards to Virtual Backup and Restore Environments Best practices for backing up virtual environments Published by NovaStor Table of Contents Why choose
KVM, OpenStack, and the Open Cloud
 KVM, OpenStack, and the Open Cloud Adam Jollans, IBM Southern California Linux Expo February 2015 1 Agenda A Brief History of VirtualizaJon KVM Architecture OpenStack Architecture KVM and OpenStack Case
KVM, OpenStack, and the Open Cloud Adam Jollans, IBM Southern California Linux Expo February 2015 1 Agenda A Brief History of VirtualizaJon KVM Architecture OpenStack Architecture KVM and OpenStack Case
Configuring Health Monitoring
 CHAPTER 6 This chapter describes how to configure the health monitoring on the CSM and contains these sections: Configuring Probes for Health Monitoring, page 6-1 Configuring Route Health Injection, page
CHAPTER 6 This chapter describes how to configure the health monitoring on the CSM and contains these sections: Configuring Probes for Health Monitoring, page 6-1 Configuring Route Health Injection, page
Mobile Cloud Computing T-110.5121 Open Source IaaS
 Mobile Cloud Computing T-110.5121 Open Source IaaS Tommi Mäkelä, Otaniemi Evolution Mainframe Centralized computation and storage, thin clients Dedicated hardware, software, experienced staff High capital
Mobile Cloud Computing T-110.5121 Open Source IaaS Tommi Mäkelä, Otaniemi Evolution Mainframe Centralized computation and storage, thin clients Dedicated hardware, software, experienced staff High capital
Lambda Architecture for Batch and Real- Time Processing on AWS with Spark Streaming and Spark SQL. May 2015
 Lambda Architecture for Batch and Real- Time Processing on AWS with Spark Streaming and Spark SQL May 2015 2015, Amazon Web Services, Inc. or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Notices This document
Lambda Architecture for Batch and Real- Time Processing on AWS with Spark Streaming and Spark SQL May 2015 2015, Amazon Web Services, Inc. or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Notices This document
vsphere Replication for Disaster Recovery to Cloud
 vsphere Replication for Disaster Recovery to Cloud vsphere Replication 5.8 This document supports the version of each product listed and supports all subsequent versions until the document is replaced
vsphere Replication for Disaster Recovery to Cloud vsphere Replication 5.8 This document supports the version of each product listed and supports all subsequent versions until the document is replaced
Relational Databases in the Cloud
 Contact Information: February 2011 zimory scale White Paper Relational Databases in the Cloud Target audience CIO/CTOs/Architects with medium to large IT installations looking to reduce IT costs by creating
Contact Information: February 2011 zimory scale White Paper Relational Databases in the Cloud Target audience CIO/CTOs/Architects with medium to large IT installations looking to reduce IT costs by creating
A Look at the New Converged Data Center
 Organizations around the world are choosing to move from traditional physical data centers to virtual infrastructure, affecting every layer in the data center stack. This change will not only yield a scalable
Organizations around the world are choosing to move from traditional physical data centers to virtual infrastructure, affecting every layer in the data center stack. This change will not only yield a scalable
Release Notes: SANsymphony-V System Center Operations Manager (SCOM) Management Pack 1.3
 Release Notes Cumulative Change Summary Date Original 1.0 release November 1, 2011 Added additional troubleshooting notes April 3, 2012 Clarified Management Pack Software Requirements; added known issue
Release Notes Cumulative Change Summary Date Original 1.0 release November 1, 2011 Added additional troubleshooting notes April 3, 2012 Clarified Management Pack Software Requirements; added known issue
www.novell.com/documentation Jobs Guide Identity Manager 4.0.1 February 10, 2012
 www.novell.com/documentation Jobs Guide Identity Manager 4.0.1 February 10, 2012 Legal Notices Novell, Inc. makes no representations or warranties with respect to the contents or use of this documentation,
www.novell.com/documentation Jobs Guide Identity Manager 4.0.1 February 10, 2012 Legal Notices Novell, Inc. makes no representations or warranties with respect to the contents or use of this documentation,
MANAGEMENT AND ORCHESTRATION WORKFLOW AUTOMATION FOR VBLOCK INFRASTRUCTURE PLATFORMS
 VCE Word Template Table of Contents www.vce.com MANAGEMENT AND ORCHESTRATION WORKFLOW AUTOMATION FOR VBLOCK INFRASTRUCTURE PLATFORMS January 2012 VCE Authors: Changbin Gong: Lead Solution Architect Michael
VCE Word Template Table of Contents www.vce.com MANAGEMENT AND ORCHESTRATION WORKFLOW AUTOMATION FOR VBLOCK INFRASTRUCTURE PLATFORMS January 2012 VCE Authors: Changbin Gong: Lead Solution Architect Michael
Extending the Internet of Things to IPv6 with Software Defined Networking
 Extending the Internet of Things to IPv6 with Software Defined Networking Abstract [WHITE PAPER] Pedro Martinez-Julia, Antonio F. Skarmeta {pedromj,skarmeta}@um.es The flexibility and general programmability
Extending the Internet of Things to IPv6 with Software Defined Networking Abstract [WHITE PAPER] Pedro Martinez-Julia, Antonio F. Skarmeta {pedromj,skarmeta}@um.es The flexibility and general programmability
How To Test Your Web Site On Wapt On A Pc Or Mac Or Mac (Or Mac) On A Mac Or Ipad Or Ipa (Or Ipa) On Pc Or Ipam (Or Pc Or Pc) On An Ip
 Load testing with WAPT: Quick Start Guide This document describes step by step how to create a simple typical test for a web application, execute it and interpret the results. A brief insight is provided
Load testing with WAPT: Quick Start Guide This document describes step by step how to create a simple typical test for a web application, execute it and interpret the results. A brief insight is provided
System Administration Training Guide. S100 Installation and Site Management
 System Administration Training Guide S100 Installation and Site Management Table of contents System Requirements for Acumatica ERP 4.2... 5 Learning Objects:... 5 Web Browser... 5 Server Software... 5
System Administration Training Guide S100 Installation and Site Management Table of contents System Requirements for Acumatica ERP 4.2... 5 Learning Objects:... 5 Web Browser... 5 Server Software... 5
Cloud Computing Architecture: A Survey
 Cloud Computing Architecture: A Survey Abstract Now a day s Cloud computing is a complex and very rapidly evolving and emerging area that affects IT infrastructure, network services, data management and
Cloud Computing Architecture: A Survey Abstract Now a day s Cloud computing is a complex and very rapidly evolving and emerging area that affects IT infrastructure, network services, data management and
STeP-IN SUMMIT 2013. June 18 21, 2013 at Bangalore, INDIA. Performance Testing of an IAAS Cloud Software (A CloudStack Use Case)
 10 th International Conference on Software Testing June 18 21, 2013 at Bangalore, INDIA by Sowmya Krishnan, Senior Software QA Engineer, Citrix Copyright: STeP-IN Forum and Quality Solutions for Information
10 th International Conference on Software Testing June 18 21, 2013 at Bangalore, INDIA by Sowmya Krishnan, Senior Software QA Engineer, Citrix Copyright: STeP-IN Forum and Quality Solutions for Information
2) Xen Hypervisor 3) UEC
 5. Implementation Implementation of the trust model requires first preparing a test bed. It is a cloud computing environment that is required as the first step towards the implementation. Various tools
5. Implementation Implementation of the trust model requires first preparing a test bed. It is a cloud computing environment that is required as the first step towards the implementation. Various tools
Storage XenMotion: Live Storage Migration with Citrix XenServer
 Storage XenMotion: Live Storage Migration with Citrix XenServer Enabling cost effective storage migration and management strategies for enterprise and cloud datacenters www.citrix.com Table of Contents
Storage XenMotion: Live Storage Migration with Citrix XenServer Enabling cost effective storage migration and management strategies for enterprise and cloud datacenters www.citrix.com Table of Contents
Cisco Intelligent Automation for Cloud
 Product Data Sheet Cisco Intelligent Automation for Cloud Early adopters of cloud-based service delivery were seeking additional cost savings beyond those achieved with server virtualization and abstraction.
Product Data Sheet Cisco Intelligent Automation for Cloud Early adopters of cloud-based service delivery were seeking additional cost savings beyond those achieved with server virtualization and abstraction.
Developing ASP.NET MVC 4 Web Applications MOC 20486
 Developing ASP.NET MVC 4 Web Applications MOC 20486 Course Outline Module 1: Exploring ASP.NET MVC 4 The goal of this module is to outline to the students the components of the Microsoft Web Technologies
Developing ASP.NET MVC 4 Web Applications MOC 20486 Course Outline Module 1: Exploring ASP.NET MVC 4 The goal of this module is to outline to the students the components of the Microsoft Web Technologies
How To Install An Aneka Cloud On A Windows 7 Computer (For Free)
 MANJRASOFT PTY LTD Aneka 3.0 Manjrasoft 5/13/2013 This document describes in detail the steps involved in installing and configuring an Aneka Cloud. It covers the prerequisites for the installation, the
MANJRASOFT PTY LTD Aneka 3.0 Manjrasoft 5/13/2013 This document describes in detail the steps involved in installing and configuring an Aneka Cloud. It covers the prerequisites for the installation, the
Job Reference Guide. SLAMD Distributed Load Generation Engine. Version 1.8.2
 Job Reference Guide SLAMD Distributed Load Generation Engine Version 1.8.2 June 2004 Contents 1. Introduction...3 2. The Utility Jobs...4 3. The LDAP Search Jobs...11 4. The LDAP Authentication Jobs...22
Job Reference Guide SLAMD Distributed Load Generation Engine Version 1.8.2 June 2004 Contents 1. Introduction...3 2. The Utility Jobs...4 3. The LDAP Search Jobs...11 4. The LDAP Authentication Jobs...22
Highly Available AMPS Client Programming
 Highly Available AMPS Client Programming 60East Technologies Copyright 2013 All rights reserved. 60East, AMPS, and Advanced Message Processing System are trademarks of 60East Technologies, Inc. All other
Highly Available AMPS Client Programming 60East Technologies Copyright 2013 All rights reserved. 60East, AMPS, and Advanced Message Processing System are trademarks of 60East Technologies, Inc. All other
CLOUD COMPUTING. When It's smarter to rent than to buy
 CLOUD COMPUTING When It's smarter to rent than to buy Is it new concept? Nothing new In 1990 s, WWW itself Grid Technologies- Scientific applications Online banking websites More convenience Not to visit
CLOUD COMPUTING When It's smarter to rent than to buy Is it new concept? Nothing new In 1990 s, WWW itself Grid Technologies- Scientific applications Online banking websites More convenience Not to visit
EMC RepliStor for Microsoft Windows ERROR MESSAGE AND CODE GUIDE P/N 300-002-826 REV A02
 EMC RepliStor for Microsoft Windows ERROR MESSAGE AND CODE GUIDE P/N 300-002-826 REV A02 EMC Corporation Corporate Headquarters: Hopkinton, MA 01748-9103 1-508-435-1000 www.emc.com Copyright 2003-2005
EMC RepliStor for Microsoft Windows ERROR MESSAGE AND CODE GUIDE P/N 300-002-826 REV A02 EMC Corporation Corporate Headquarters: Hopkinton, MA 01748-9103 1-508-435-1000 www.emc.com Copyright 2003-2005
ViSION Status Update. Dan Savu Stefan Stancu. D. Savu - CERN openlab
 ViSION Status Update Dan Savu Stefan Stancu D. Savu - CERN openlab 1 Overview Introduction Update on Software Defined Networking ViSION Software Stack HP SDN Controller ViSION Core Framework Load Balancer
ViSION Status Update Dan Savu Stefan Stancu D. Savu - CERN openlab 1 Overview Introduction Update on Software Defined Networking ViSION Software Stack HP SDN Controller ViSION Core Framework Load Balancer
Network Virtualization Platform (NVP) Incident Reports
 Network Virtualization Platform (NVP) s ORD Service Interruption During Scheduled Maintenance June 20th, 2013 Time of Incident: 03:45 CDT While performing a scheduled upgrade on the Software Defined Networking
Network Virtualization Platform (NVP) s ORD Service Interruption During Scheduled Maintenance June 20th, 2013 Time of Incident: 03:45 CDT While performing a scheduled upgrade on the Software Defined Networking
Security Management of Cloud-Native Applications. Presented By: Rohit Sharma MSc in Dependable Software Systems (DESEM)
 Security Management of Cloud-Native Applications Presented By: Rohit Sharma MSc in Dependable Software Systems (DESEM) 1 Outline Context State-of-the-Art Design Patterns Threats to cloud systems Security
Security Management of Cloud-Native Applications Presented By: Rohit Sharma MSc in Dependable Software Systems (DESEM) 1 Outline Context State-of-the-Art Design Patterns Threats to cloud systems Security
Service Virtualization: Managing Change in a Service-Oriented Architecture
 Service Virtualization: Managing Change in a Service-Oriented Architecture Abstract Load balancers, name servers (for example, Domain Name System [DNS]), and stock brokerage services are examples of virtual
Service Virtualization: Managing Change in a Service-Oriented Architecture Abstract Load balancers, name servers (for example, Domain Name System [DNS]), and stock brokerage services are examples of virtual
Dell Enterprise Reporter 2.5. Configuration Manager User Guide
 Dell Enterprise Reporter 2.5 2014 Dell Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. This guide contains proprietary information protected by copyright. The software described in this guide is furnished under a software license
Dell Enterprise Reporter 2.5 2014 Dell Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. This guide contains proprietary information protected by copyright. The software described in this guide is furnished under a software license
Dell High Availability Solutions Guide for Microsoft Hyper-V
 Dell High Availability Solutions Guide for Microsoft Hyper-V www.dell.com support.dell.com Notes and Cautions NOTE: A NOTE indicates important information that helps you make better use of your computer.
Dell High Availability Solutions Guide for Microsoft Hyper-V www.dell.com support.dell.com Notes and Cautions NOTE: A NOTE indicates important information that helps you make better use of your computer.
Installing Intercloud Fabric Firewall
 This chapter contains the following sections: Information About the Intercloud Fabric Firewall, page 1 Prerequisites, page 1 Guidelines and Limitations, page 2 Basic Topology, page 2 Intercloud Fabric
This chapter contains the following sections: Information About the Intercloud Fabric Firewall, page 1 Prerequisites, page 1 Guidelines and Limitations, page 2 Basic Topology, page 2 Intercloud Fabric
Private Clouds Can Be Complicated: The Challenges of Building and Operating a Microsoft Private Cloud
 Private Clouds Can Be Complicated: The Challenges of Building and Operating a Microsoft Private Cloud Tony Bradley Microsoft MVP, CISSP-ISSAP Principal Analyst, Bradley Strategy Group The connected, mobile
Private Clouds Can Be Complicated: The Challenges of Building and Operating a Microsoft Private Cloud Tony Bradley Microsoft MVP, CISSP-ISSAP Principal Analyst, Bradley Strategy Group The connected, mobile
Load testing with. WAPT Cloud. Quick Start Guide
 Load testing with WAPT Cloud Quick Start Guide This document describes step by step how to create a simple typical test for a web application, execute it and interpret the results. 2007-2015 SoftLogica
Load testing with WAPT Cloud Quick Start Guide This document describes step by step how to create a simple typical test for a web application, execute it and interpret the results. 2007-2015 SoftLogica
Windows Azure Data Services (basics) 55093A; 3 Days
 Lincoln Land Community College Capital City Training Center 130 West Mason Springfield, IL 62702 217-782-7436 www.llcc.edu/cctc Windows Azure Data Services (basics) 55093A; 3 Days Course Description This
Lincoln Land Community College Capital City Training Center 130 West Mason Springfield, IL 62702 217-782-7436 www.llcc.edu/cctc Windows Azure Data Services (basics) 55093A; 3 Days Course Description This
Migration Scenario: Migrating Backend Processing Pipeline to the AWS Cloud
 Migration Scenario: Migrating Backend Processing Pipeline to the AWS Cloud Use case Figure 1: Company C Architecture (Before Migration) Company C is an automobile insurance claim processing company with
Migration Scenario: Migrating Backend Processing Pipeline to the AWS Cloud Use case Figure 1: Company C Architecture (Before Migration) Company C is an automobile insurance claim processing company with
DHCP Failover. Necessary for a secure and stable network. DHCP Failover White Paper Page 1
 DHCP Failover Necessary for a secure and stable network DHCP Failover White Paper Page 1 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 3 2. Basic DHCP Redundancy... 3 3. VitalQIP Failover Solution... 5 4. VitalQIP
DHCP Failover Necessary for a secure and stable network DHCP Failover White Paper Page 1 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 3 2. Basic DHCP Redundancy... 3 3. VitalQIP Failover Solution... 5 4. VitalQIP
Outgoing VDI Gateways:
 ` Outgoing VDI Gateways: Creating a Unified Outgoing Virtual Desktop Infrastructure with Windows Server 2008 R2 and ObserveIT Daniel Petri January 2010 Copyright 2010 ObserveIT Ltd. 2 Table of Contents
` Outgoing VDI Gateways: Creating a Unified Outgoing Virtual Desktop Infrastructure with Windows Server 2008 R2 and ObserveIT Daniel Petri January 2010 Copyright 2010 ObserveIT Ltd. 2 Table of Contents
White Paper Take Control of Datacenter Infrastructure
 Take Control of Datacenter Infrastructure Uniting the Governance of a Single System of Record with Powerful Automation Tools Take Control of Datacenter Infrastructure A new breed of infrastructure automation
Take Control of Datacenter Infrastructure Uniting the Governance of a Single System of Record with Powerful Automation Tools Take Control of Datacenter Infrastructure A new breed of infrastructure automation
TIBCO StreamBase High Availability Deploy Mission-Critical TIBCO StreamBase Applications in a Fault Tolerant Configuration
 TIBCO StreamBase High Availability Deploy Mission-Critical TIBCO StreamBase s in a Fault Tolerant Configuration TIBCO STREAMBASE HIGH AVAILABILITY The TIBCO StreamBase event processing platform provides
TIBCO StreamBase High Availability Deploy Mission-Critical TIBCO StreamBase s in a Fault Tolerant Configuration TIBCO STREAMBASE HIGH AVAILABILITY The TIBCO StreamBase event processing platform provides
Log Analyzer Reference
 IceWarp Unified Communications Log Analyzer Reference Version 10.4 Printed on 27 February, 2012 Contents Log Analyzer 1 Quick Start... 2 Required Steps... 2 Optional Steps... 3 Advanced Configuration...
IceWarp Unified Communications Log Analyzer Reference Version 10.4 Printed on 27 February, 2012 Contents Log Analyzer 1 Quick Start... 2 Required Steps... 2 Optional Steps... 3 Advanced Configuration...
IBM Tivoli Monitoring V6.2.3, how to debug issues with Windows performance objects issues - overview and tools.
 IBM Tivoli Monitoring V6.2.3, how to debug issues with Windows performance objects issues - overview and tools. Page 1 of 13 The module developer assumes that you understand basic IBM Tivoli Monitoring
IBM Tivoli Monitoring V6.2.3, how to debug issues with Windows performance objects issues - overview and tools. Page 1 of 13 The module developer assumes that you understand basic IBM Tivoli Monitoring
The Win32 Network Management APIs
 The Win32 Network Management APIs What do we have in this session? Intro Run-Time Requirements What's New in Network Management? Windows 7 Windows Server 2003 Windows XP Network Management Function Groups
The Win32 Network Management APIs What do we have in this session? Intro Run-Time Requirements What's New in Network Management? Windows 7 Windows Server 2003 Windows XP Network Management Function Groups
Active-Active and High Availability
 Active-Active and High Availability Advanced Design and Setup Guide Perceptive Content Version: 7.0.x Written by: Product Knowledge, R&D Date: July 2015 2015 Perceptive Software. All rights reserved. Lexmark
Active-Active and High Availability Advanced Design and Setup Guide Perceptive Content Version: 7.0.x Written by: Product Knowledge, R&D Date: July 2015 2015 Perceptive Software. All rights reserved. Lexmark
Transactionality and Fault Handling in WebSphere Process Server Web Service Invocations. version 0.5 - Feb 2011
 Transactionality and Fault Handling in WebSphere Process Server Web Service Invocations version 0.5 - Feb 2011 IBM Corporation, 2011 This edition applies to Version 6.2 of WebSphere Process Server 1 /
Transactionality and Fault Handling in WebSphere Process Server Web Service Invocations version 0.5 - Feb 2011 IBM Corporation, 2011 This edition applies to Version 6.2 of WebSphere Process Server 1 /
ERserver. iseries. Work management
 ERserver iseries Work management ERserver iseries Work management Copyright International Business Machines Corporation 1998, 2002. All rights reserved. US Government Users Restricted Rights Use, duplication
ERserver iseries Work management ERserver iseries Work management Copyright International Business Machines Corporation 1998, 2002. All rights reserved. US Government Users Restricted Rights Use, duplication
PLUMgrid Toolbox: Tools to Install, Operate and Monitor Your Virtual Network Infrastructure
 Toolbox: Tools to Install, Operate and Monitor Your Virtual Network Infrastructure Introduction The concept of Virtual Networking Infrastructure (VNI) is disrupting the networking space and is enabling
Toolbox: Tools to Install, Operate and Monitor Your Virtual Network Infrastructure Introduction The concept of Virtual Networking Infrastructure (VNI) is disrupting the networking space and is enabling
Building an AWS-Compatible Hybrid Cloud with OpenStack
 Building an AWS-Compatible Hybrid Cloud with OpenStack AWS is Transforming IT Amazon Web Services (AWS) commands a significant lead in the public cloud services market, with revenue estimated to grow from
Building an AWS-Compatible Hybrid Cloud with OpenStack AWS is Transforming IT Amazon Web Services (AWS) commands a significant lead in the public cloud services market, with revenue estimated to grow from
HAWAII TECH TALK SDN. Paul Deakin Field Systems Engineer
 HAWAII TECH TALK SDN Paul Deakin Field Systems Engineer SDN What Is It? SDN stand for Software Defined Networking SDN is a fancy term for: Using a controller to tell switches where to send packets SDN
HAWAII TECH TALK SDN Paul Deakin Field Systems Engineer SDN What Is It? SDN stand for Software Defined Networking SDN is a fancy term for: Using a controller to tell switches where to send packets SDN
Ubuntu OpenStack on VMware vsphere: A reference architecture for deploying OpenStack while limiting changes to existing infrastructure
 TECHNICAL WHITE PAPER Ubuntu OpenStack on VMware vsphere: A reference architecture for deploying OpenStack while limiting changes to existing infrastructure A collaboration between Canonical and VMware
TECHNICAL WHITE PAPER Ubuntu OpenStack on VMware vsphere: A reference architecture for deploying OpenStack while limiting changes to existing infrastructure A collaboration between Canonical and VMware
Shoal: IaaS Cloud Cache Publisher
 University of Victoria Faculty of Engineering Winter 2013 Work Term Report Shoal: IaaS Cloud Cache Publisher Department of Physics University of Victoria Victoria, BC Mike Chester V00711672 Work Term 3
University of Victoria Faculty of Engineering Winter 2013 Work Term Report Shoal: IaaS Cloud Cache Publisher Department of Physics University of Victoria Victoria, BC Mike Chester V00711672 Work Term 3
Figure 1: MQSeries enabled TCL application in a heterogamous enterprise environment
 MQSeries Enabled Tcl Application Ping Tong, Senior Consultant at Intelliclaim Inc., [email protected] Daniel Lyakovetsky, CIO at Intelliclaim Inc., [email protected] Sergey Polyakov, VP Development
MQSeries Enabled Tcl Application Ping Tong, Senior Consultant at Intelliclaim Inc., [email protected] Daniel Lyakovetsky, CIO at Intelliclaim Inc., [email protected] Sergey Polyakov, VP Development
www.basho.com Technical Overview Simple, Scalable, Object Storage Software
 www.basho.com Technical Overview Simple, Scalable, Object Storage Software Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1 Introduction & Overview... 1 Architecture... 2 How it Works... 2 APIs and Interfaces...
www.basho.com Technical Overview Simple, Scalable, Object Storage Software Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1 Introduction & Overview... 1 Architecture... 2 How it Works... 2 APIs and Interfaces...
Intel Ethernet Switch Load Balancing System Design Using Advanced Features in Intel Ethernet Switch Family
 Intel Ethernet Switch Load Balancing System Design Using Advanced Features in Intel Ethernet Switch Family White Paper June, 2008 Legal INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL
Intel Ethernet Switch Load Balancing System Design Using Advanced Features in Intel Ethernet Switch Family White Paper June, 2008 Legal INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL
SharePoint Integration Framework Developers Cookbook
 Sitecore CMS 6.3 to 6.6 and SIP 3.2 SharePoint Integration Framework Developers Cookbook Rev: 2013-11-28 Sitecore CMS 6.3 to 6.6 and SIP 3.2 SharePoint Integration Framework Developers Cookbook A Guide
Sitecore CMS 6.3 to 6.6 and SIP 3.2 SharePoint Integration Framework Developers Cookbook Rev: 2013-11-28 Sitecore CMS 6.3 to 6.6 and SIP 3.2 SharePoint Integration Framework Developers Cookbook A Guide
Drawbacks to Traditional Approaches When Securing Cloud Environments
 WHITE PAPER Drawbacks to Traditional Approaches When Securing Cloud Environments Drawbacks to Traditional Approaches When Securing Cloud Environments Exec Summary Exec Summary Securing the VMware vsphere
WHITE PAPER Drawbacks to Traditional Approaches When Securing Cloud Environments Drawbacks to Traditional Approaches When Securing Cloud Environments Exec Summary Exec Summary Securing the VMware vsphere
Lesson Plans Microsoft s Managing and Maintaining a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment
 Lesson Plans Microsoft s Managing and Maintaining a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment (Exam 70-290) Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1 Course Overview... 2 Section 0-1: Introduction... 4
Lesson Plans Microsoft s Managing and Maintaining a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment (Exam 70-290) Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1 Course Overview... 2 Section 0-1: Introduction... 4
Analysis and Research of Cloud Computing System to Comparison of Several Cloud Computing Platforms
 Volume 1, Issue 1 ISSN: 2320-5288 International Journal of Engineering Technology & Management Research Journal homepage: www.ijetmr.org Analysis and Research of Cloud Computing System to Comparison of
Volume 1, Issue 1 ISSN: 2320-5288 International Journal of Engineering Technology & Management Research Journal homepage: www.ijetmr.org Analysis and Research of Cloud Computing System to Comparison of
Develop a process for applying updates to systems, including verifying properties of the update. Create File Systems
 RH413 Manage Software Updates Develop a process for applying updates to systems, including verifying properties of the update. Create File Systems Allocate an advanced file system layout, and use file
RH413 Manage Software Updates Develop a process for applying updates to systems, including verifying properties of the update. Create File Systems Allocate an advanced file system layout, and use file
Load DynamiX Storage Performance Validation: Fundamental to your Change Management Process
 Load DynamiX Storage Performance Validation: Fundamental to your Change Management Process By Claude Bouffard Director SSG-NOW Labs, Senior Analyst Deni Connor, Founding Analyst SSG-NOW February 2015 L
Load DynamiX Storage Performance Validation: Fundamental to your Change Management Process By Claude Bouffard Director SSG-NOW Labs, Senior Analyst Deni Connor, Founding Analyst SSG-NOW February 2015 L
Novell PlateSpin Orchestrate
 AUTHORIZED DOCUMENTATION Virtual Machine Management Guide Novell PlateSpin Orchestrate 2.6 March 29, 2011 www.novell.com Legal Notices Novell, Inc., makes no representations or warranties with respect
AUTHORIZED DOCUMENTATION Virtual Machine Management Guide Novell PlateSpin Orchestrate 2.6 March 29, 2011 www.novell.com Legal Notices Novell, Inc., makes no representations or warranties with respect
Overview Motivating Examples Interleaving Model Semantics of Correctness Testing, Debugging, and Verification
 Introduction Overview Motivating Examples Interleaving Model Semantics of Correctness Testing, Debugging, and Verification Advanced Topics in Software Engineering 1 Concurrent Programs Characterized by
Introduction Overview Motivating Examples Interleaving Model Semantics of Correctness Testing, Debugging, and Verification Advanced Topics in Software Engineering 1 Concurrent Programs Characterized by
Provisioning Server Service Template
 Provisioning Server Service Template Provisioning Server 7.1 Service Template Technology Preview for System Center - Virtual Machine Manager The Citrix Provisioning Server System Center - Virtual Machine
Provisioning Server Service Template Provisioning Server 7.1 Service Template Technology Preview for System Center - Virtual Machine Manager The Citrix Provisioning Server System Center - Virtual Machine
Active-Active ImageNow Server
 Active-Active ImageNow Server Getting Started Guide ImageNow Version: 6.7. x Written by: Product Documentation, R&D Date: March 2014 2014 Perceptive Software. All rights reserved CaptureNow, ImageNow,
Active-Active ImageNow Server Getting Started Guide ImageNow Version: 6.7. x Written by: Product Documentation, R&D Date: March 2014 2014 Perceptive Software. All rights reserved CaptureNow, ImageNow,
Description of Microsoft Internet Information Services (IIS) 5.0 and
 Page 1 of 10 Article ID: 318380 - Last Review: July 7, 2008 - Revision: 8.1 Description of Microsoft Internet Information Services (IIS) 5.0 and 6.0 status codes This article was previously published under
Page 1 of 10 Article ID: 318380 - Last Review: July 7, 2008 - Revision: 8.1 Description of Microsoft Internet Information Services (IIS) 5.0 and 6.0 status codes This article was previously published under
NEXT GENERATION ARCHIVE MIGRATION TOOLS
 NEXT GENERATION ARCHIVE MIGRATION TOOLS Cloud Ready, Scalable, & Highly Customizable - Migrate 6.0 Ensures Faster & Smarter Migrations EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Data migrations and the products used to perform
NEXT GENERATION ARCHIVE MIGRATION TOOLS Cloud Ready, Scalable, & Highly Customizable - Migrate 6.0 Ensures Faster & Smarter Migrations EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Data migrations and the products used to perform
IBM Cloud Security Draft for Discussion September 12, 2011. 2011 IBM Corporation
 IBM Cloud Security Draft for Discussion September 12, 2011 IBM Point of View: Cloud can be made secure for business As with most new technology paradigms, security concerns surrounding cloud computing
IBM Cloud Security Draft for Discussion September 12, 2011 IBM Point of View: Cloud can be made secure for business As with most new technology paradigms, security concerns surrounding cloud computing
High Availability Solutions for the MariaDB and MySQL Database
 High Availability Solutions for the MariaDB and MySQL Database 1 Introduction This paper introduces recommendations and some of the solutions used to create an availability or high availability environment
High Availability Solutions for the MariaDB and MySQL Database 1 Introduction This paper introduces recommendations and some of the solutions used to create an availability or high availability environment
