Exponents and Polynomials
|
|
|
- Brendan Harrell
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHAPTER 6 Exponents and Polynomials Solutions Key are you ready?. F 2. B. C 4. D 5. E ( -0) 4 9. x 0. k = = = -(2 2) = = = 2 7. ( -) 6 = (-)(-)(-)(-)(-)(-) = 4. 5 = = = = , p p = p + 9p = p 22. 8y - 4x + 2y + 7x - x = 8y + 2y - 4x + 7x - x = 0y + 2x 2. (2 + w - 5) + 6w - - 5w = w + 6w - 5w = 4 + 4w 24. 6n n = 6n + 5n - 4 = n no 26. yes; ÇÇ 8 = Ç 9 2 = yes; ÇÇ 6 = Ç 6 2 = no 29. yes: ÇÇ 00 = ÇÇ 0 2 = 0 0. yes; Ç 4 = Ç 2 2 = 2. yes; Ç = Ç 2 = 2. no 6- integer exponents Check it out!. 5 - = 5 = = m is equal to 25 m. 2a. 0-4 = = = 0,000 _ b. ( -2) -4 = = ( -2) 4 (-2)(-2)(-2)(-2) = 6 _ c. ( -2) -5 = = ( -2) 5 (-2)(-2)(-2)(-2)(-2) = - 2 d = a. p - = 4-4 = = 64 = 4a. 2r 0 m - = 2 r 0 m - = 2 m = 2 m c. g 4 = g 4 h -6 h -6 = g 4 h 6 = g 4 h 6 = = - 2 think and discuss. -2; 0; t 2. For a negative exponent in the numerator, move the power to the denominator and change the negative exponent to a positive exponent; possible answer: 2 - =. Exercises guided practice Simplifying Expressions with Negative Exponents b. 8a -2 b 0 = 8(-2) -2 (6) 0 = 8 _ ( -2) 2 = 8 (-2)(-2) = 8 4 = 2 b. r - 7 = r - = 7 r 7 = 7r For a negative exponent in the denominator, move the power to the numerator and change the negative exponent to a positive exponent; possible answer: = 4 x 5. x _. 0-7 = = = 0,000,000 m 0-7 m is equal to 0,000,000 m = 6 2 = 6 6 = 6. 0 = = - = = = 5 5 = - 25 = Holt McDougal Algebra
2 6. -8 = = = - = = - 52 = = = = (4.2) 0 = _ 0. ( -) - = = ( -) (-)(-)(-) = = b -2 = (-) -2 = _ ( -) 2 = (-)(-) = 9 4. ( m - 4) -5 = (6-4) -5 = 2-5 = = 4 4 = = = m 0 = 4 m 0 = 4 = = 7 r -7 r -7 = 7 r 7 = 7r x 0 y -4 = 2 x 0 y -4 = 2 y 4 = 2 y c 4 = c 4 d - d - = c 4 d = c 4 d. (2t) -4 = (2(2)) -4 = = = 256 = 5. 2x 0 y - = 2(7) 0 ( -4) - = 2 _ ( -4) = 2 (-4)(-4)(-4) = 2-64 = k -4 = k -4 = k 4 = k 4 9. x 0 = x 0 d - d - = x 0 d = x 0 d 2. f -4 = f -4 g -6 g -6 = g 6 f 4 = g 6 f 4 2. p 7 q - = p 7 q - = p 7 q = p 7 q practice and problem solving = = = 2 - oz is equal to 2 oz = = 4 = = 625 = = = - = = = - = = = = = 49. ( = = 2 = 69. ( -) - = _ = ( -) (-) = - 4. ( -4) 2 = (-4)(-4) = 6 5. ( 2) -2 = ( _ = 2) 2 _ _ = _ = ) 0 = = - = x -4 = 4-4 = 4 4 = 8. ( 2 v ) - = ( 2 (9) ) - = 6-6 = = 26 = = (0 - d) 0 = (0 - ) 0 = (-) 0 = 40. 0m - n -5 = 0(0) - ( -2) -5 = 0 _ 0 ( -2) 5 = 0 0 (-2)(-2)(-2)(-2)(-2) = Holt McDougal Algebra
3 4. (ab) -2 = ( ( -2 2 ) ) (8) = 2-2 = 2 2 = 2 2 = w v x v = 4() 0 ( -5) 0 = 4 = 4 4. k -4 = 44. 2z -8 = 2 z -8 k _ = 2b - 2 b - = 2 b = b x - = -5 x - = -5 5 x = - x 49. _ 2f 0 = 2 7g -0 7 f 0 g -0 = 2 7 g 0 = 2g s 5 = s 5 t -2 t -2 = s 5 t 2 = s 5 t 2 5. b 0 c 0 = b 0 c 0 = = _ = q -2 r q -2 r 0 s a -7 b 2 c d -4 = q 2 = q 2 s 0 = a -7 b 2 = a 7 = b 2 d 4 a 7 c b 2 = 2 z 8 = 2 z c -2 d = c -2 d = d c d 2 = c x -6 y -2 = 4 x -6 y -2 = 4 x 6 y 2 = 4 x 6 y r -5 = r -5 s - s - = s r 5 _ = s r w -5 = w -5 x -6 x -6 = x 6 w c d -4 d 4 c = x 6 w 5 m - n 5 = 2 = 2 m - n 5 m n 5 = 2n 5 m 57. _ h k - = 6m 2 6 h k - m 2 = 6 h k m 2 = _ h 6m 2 k 58. z -5 = = = 2 = 60. ( yz) 0 = ((-)(2)) 0 = (-2) 0 = 62. ( xy - ) -2 = (()(-) - ) -2 = (-6) -2 = _ ( -6) 2 = (-6)(-6) = ( yz) -x = ((-)(2)) - = (-2) - = _ ( -2) = (-2)(-2)(-2) = ( x + y) -4 = ( + (-)) -4 = = = 6 = 6. ( xyz) - = (()(-)(2)) - = (-6) - = (-6) = x -y = -(-) = = 65. xy -4 = ()(-) -4 = _ ( -) 4 = (-)(-)(-)(-) = = 66. Equation A is incorrect because 5 was incorrectly moved to the denominator. The negative exponent applies only to the base x. 67. a b -2 = a b -2 = a b 2 = a b v 0 w 2 y - = v 0 w 2 y - = w 2 y = w 2 y 68. c -4 d = c -4 d = d c 4 = d c ( a 2 b -7 ) 0 = 97 Holt McDougal Algebra
4 7. -5y -6 = -5 y -6 = -5 y 6 5 = - y a = 2 a b - b - = 2 a b = 2a b 75. x -8 = y 2 x -8 y 2 = x 8 y 2 = x 8 y p - = q - 5 p - q - = -4 p q = - 4q p _ 72. 2a -5 = 2 a -5 b -6 b -6 = 2 b 6 a 5 = 2b 6 a m 2 = m 2 n - n - = m 2 n = m 2 n 77. Red blood cell: 25,000 - = 25,000 White blood cell: (500) -2 = = = = 250,000 = 250,000 Platelet: (000) -2 = = _ = = _,000,000 = _,000, always 79. never 80. sometimes 8. sometimes 82. never 8. sometimes = 2 2 = (2 2 2) = 8 8 = a n a -n = 2-2 = 2 2 = ( ) = 9 9 = 85. Possible answer: Look at the pattern below. As the exponent goes down by, the value is half of what it was before. 2 = 8, 2 2 = 4, 2 = 2, 2 0 =, 2 - = 2, 2-2 = 4, 2 - = 8 = = 2 2 = = 2-2 ; = = 9 9 = ; = 8 8 = = 8-2 ; = = ; = = = ; = = = 0 - ; = 4 2 = 4 4 = 6 = ; = ; - 94a. fw = v b. fw = v fw = v f f test prep w = v f w = v f w = v f - w = vf - c. s = s D; Since 0.04 = 25 = 5 5 = = 5-2, A, B, and 5 2 C are all equal and do not equal J 6-2 = 6 2 = A 98., or.25 _ a b -2 = a b -2 4 c - c - = a c b 2 = a c b (6 + 2) 0 = = = = =, or a n ; a -n = a n and b 0 = if b 0. So you have a n, or simply a n. 98 Holt McDougal Algebra
5 challenge and extend 00. x y = 2 x y Possible answer: y increases more rapidly as x increases. 0. n n ( -) n n = ; (-) n = - if n is odd, and (-) n = if n is even. 6-2 rational exponents check it out! a. 8 4 = 4 ÇÇ 8 = b = ÇÇ ÇÇ 256 = + 4 = 5 2a. 6 4 = 6 = ( 6 4 4) = ( 4 ÇÇ 6 ) = 2 = 8 c = 27 = ( 27 4 ) 4 = ( ÇÇ 27 ) 4 = 4 = 8 x b. 2 5 = = ( 5 2 5) 2 = ( 5 Ç ) 2 =. C = 72m 4 = 72(8) 4 = 72 ( 4 ÇÇ 8 ) 4 = 72 ( Ç 4 ) = 72 () = = 944 The panda needs 944 Calories per day. 4a. 4 ÇÇÇ x 4 y 2 = (x 4 y 2 ) 4 = ( x 4 ) 4 (y 2 ) 4 = ( x 4 4 ) ( y 2 4 ) = ( x ) (y ) = x y think and discuss ( b. xy 2) 2 5 x Ç 5 ( = xy 2) 2 x = ( x 2 ) ( y 2 2 ) ( x - ) = ( x 2 ) y ( x - ) = ( x 2 ) ( x - ) y = x 2 + (-) y = xy. Rewrite the expression as 25 to the power, all 0 raised to the power 5. Then simplify the exponent. Finally take the square root. 2. to _ 2 Fractional Exponent _ b n _ m b n exercises guided practice. 5 Definition _ n A number raised to the power of is equal to the nth root of that number. A number raised to the power of _ m n is equal to the nth root of that number raised to the mth power. _ 2 6 Numerical Example = 6 = 6 _ 2 6 = 6 = 6 = 26 ( ) 2. 8 = Ç 8 = = ÇÇ 6 = = 6 Ç 0 = = ÇÇ 27 = = ÇÇ 8 = = ÇÇ 26 = = 9 Ç = = 4 ÇÇ 625 = = ÇÇ 6 + Ç = 6 + = = 4 ÇÇ 8 + Ç 8 = + 2 = = ( 8 4) = ( 4 ÇÇ 8 ) = = = ( 25 ) 2 = ( ÇÇ 25 ) 2 = 5 2 = = Ç 8 + ÇÇ 64 = = = ÇÇ 25-4 Ç = 5 - = = ( 8 ) 5 = ( Ç 8 ) 5 = 2 5 = = ( 25 2) = ( ÇÇ 25 ) = 5 = Holt McDougal Algebra
6 = ( 6 2) = ( ÇÇ 6 ) = 6 = = 4 Ç = 4 Ç = 22. P = 4a 2 = 4(64) 2 = 4( ÇÇ 64 ) = 4(8) = 2 The perimeter is 2 m. 2. ÇÇ x 4 y 2 = (x 4 y 2 ) 2 = ( x 4 2 ) ( y 2 2 ) = x 2 y = x 2 y 25. ÇÇ x 6 y 6 = (x 6 y 6 ) 2 = ( x 6 2 ) ( y 6 2 ) = x y = x y 27. ( a 2) 2 Ç a 2 = ( a 2 2 ) ( a 2 ) 2 = ( a ) ( a 2 2 ) = a a = a + = a 2 ( 29. z ) _ Ç z 2 = z _ ( z 2 ) 2 _ z 2 2 = z = z = z = ( 64 ) 4 = ( ÇÇ 64 ) 4 = 4 4 = = Ç 0 2 = 4 Ç 0 = Ç z 4 = ( z 4 ) 4 = z 4 4 = z = z 26. ÇÇÇ a 2 b 6 = ( a 2 b 6 ) = ( a 2 ) ( b 6 ) 28. ( x practice and problem solving = a 4 b 2 = a 4 b 2 6 ) 4 Ç y 4 = ( x ) 6 (y 4 ) 4 = ( x 2 4 ) ( y 4) = x 2 y = x 2 y 0. ÇÇ x 6 y 9 x 2 = (x 6 y 9 ) x 2 ( = 6 x _ ) 9 ( y ) x 2 = x 2 y = y x = ÇÇ 00 = = 5 Ç =. 52 = ÇÇ 52 = = ÇÇ 729 = = 5 ÇÇ 2 = = ÇÇ 96 = = 8 ÇÇ 256 = _ 2 = ÇÇ 400 = = ÇÇ 25 + ÇÇ 8 = 25 ÇÇ ÇÇ = = 4 = 5 - = = ÇÇ 2-5 ÇÇ 24 = - = = ( Ç 4 ) = 2 = = ( 4 ÇÇ 256 ) = 4 = = ( ÇÇ 00 ) = 0 = = ( Ç 9 ) 5 5. B = 8 = 8 = 5 = 24 2 m 2 (64) = 4 ÇÇ Ç 0 = = = ( ÇÇ 27 ) 2 = = = ( 6 ÇÇ 64 ) 5 = 2 5 = = ( Ç ) 5 = 5 = = ( 5 ÇÇ 24 ) 2 = 8 ( ÇÇ 64 ) 2 = 8 (4) 2 = 8 (6) = 2 The mass of the mouse s brain is 2g. 52. ÇÇ a 6 c 9 = ( a 6 c 9 ) = ( a 6 ) ( c 9 ) = a 2 c = a 2 c ÇÇÇ x 6 y 4 = (x 6 y 4 ) 4 = ( x 6 4 ) ( y 4 4 ) 56. ( x = x 4 y = x 4 y 2 = 2 = 9 5. ÇÇ 8m = ( 8m ) = ( 8 ) ( m ) = ( Ç 8 ) m = 2m 55. ÇÇ 27x 6 = ( 27x 6 ) = ( 27 ) ( x 6 ) = ( ÇÇ 27 ) x 2 = x 2 2y ) Ç x ( a 2 b 4 ) 2 Ç b 6 = ( x 2 ) 2 (y 2 ) x 2 = ( a 2 4 ) ( b 2) ( b 6 ) = x y 6 x = ( a ) ( b 2 6 ) ( b ) = x + y 6 = x 2 y 6 = x 2 y 6 = a b 2 b 2 = a b = a b 4 = ab Holt McDougal Algebra
7 58. x ÇÇ 6 y 6 yx 2 = (x 6 y 6 ) yx 2 = ( x 6 ) ( y 6 ) y - x -2 = ( x 2 ) (y 2 ) (y - ) ( x -2 ) = x 2-2 y 2 - = x 0 y = y ( 59. a 2 b 2) 4 Ç b 2 = ( a 2 4 ) ( b b 2 4 ) = ( a 8 ) ( b 2 ) ( b - ) = a 8 b 2 - = a 8 b = a 8 b x 4 = 4 ( 4 ÇÇ 256 ) x = 4 4 x = 4 x = x= 5 ( 225 x) x = 5 x 225 = 5 x 5 2 = 5 x x = x = 6 ( ÇÇ 64 ) x = 6 4 x = 6 x = x = 8 ( 27 4 x ) x 4 = 8 x ( 8 27 = ( 4 ÇÇ 8 ) x 27 = x x = 69 ) 2 = ÇÇ 8 69 ÇÇ = _ 8 ÇÇ 69 = 9 8 ) 4 = 4 ÇÇ ( 256 _ = 4 ÇÇ ÇÇ = 4 6. x 5 = ( x 5) 5 = 5 x = 6. x 6 = 0 ( x 6) 6 = 0 6 x = x 4 = 25 ( x 4 ) 4 = 25 4 x = ( ÇÇ 25 ) 4 x = 5 4 x = x 2 = 26 ( ÇÇ 6 ) x = 26 6 x = 26 x = 27) = ÇÇ 8 27 = Ç 8 ÇÇ 27 = 2 6) 2 = ÇÇ ( 8 7. ( = Ç ÇÇ 6 = 4 6) 72. ( ( ( ( 27 2 = ( ÇÇ 9 6 ) = ( Ç 9 ÇÇ 6 ) = ( 4) = ) 4 = ( 4 ÇÇ 6 8 ) = ( 4 ÇÇ 6 4 ÇÇ 8 ) = ( 2 ) = ) 2 = ( ÇÇ 4 25 ) = ( Ç 4 ÇÇ 25 ) 5 ) = ) = ÇÇ = ( 2 2 = ( ÇÇ ÇÇ ) = ( 4 ) 2 = ) 7. ( ( 4 49 ) 77. ( = ( ÇÇ ) = ( Ç ÇÇ ) = ( 2 ) 2 = 4 9 _ 2 = ( ÇÇ 4 49 ) = ( _ Ç 4 ÇÇ 49 ) = ( 2 7 ) = ) 4 = ( 4 ÇÇ 8 ) 4 25 ) 79. ( 8 = ( 4 Ç = ( 4 8 ÇÇ ) ) = 27 = ( ÇÇ ) _ = ( Ç 8 = ( 2 4 ÇÇ 25 ) 5) 4 = Lion: Wolf: L = 2m 5 L = 2m 5 = 2(24) 5 = 2(2) 5 = 2( 5 ÇÇ 24 ) = 2( 5 ÇÇ 2 ) = 2() = 6 = 2(2) = 24 The lion s lifespan is 6-24 = 2 years longer than the wolf s. 8. r = 0.62V = 0.62(27) = 0.62( ÇÇ 27 ) = 0.62() =.86 The radius is.86 in. 82. ( _ b ) = b _ = b = b. Also, by definition ( Ç b ) = b. Therefore b _ = b Ç. 8. n 2 will be less than n because 2 <. n 2 will be greater than n because 2 >. 84. A is incorrect; the first line should be 64 _ 2 = ( ÇÇ 64 ). 20 Holt McDougal Algebra
8 B) 85a. d = ( 0.8 L 2 _ = ( 0.8 ( ) ) = (0.8(25)) 2 = (00) 2 2 = ÇÇ 00 = 0 Distance to light source is 0 in. B) 2 b. d = ( 0.8 L = ( 0.8 ( ) ) = (0.8(500)) 2 = (400) 2 2 = ÇÇ 400 = 20 Distance doubles to 20 in = 4 2 = ( 4 ) 2 = 64 2 = = 4 2 = ( 4 2) = 2 = 8 It is often easier to take the square root first so that the remaining numbers in the calculation are smaller. 87. B; = 9 Ç + 8 Ç = + 2 = C; ÇÇ a 9 b = ( a 9 b ) = ( a 9 ) ( b ) = a b = a b challenge and extend 9. ( a ) ( a ) ( a ) = a ( + + ) = a = a 92. ( x 2) 5 ( x 2) = ( 5 x 2) ( x 2) = x ( ) = x 8 2 = x F; 4 2 = ( Ç 4 ) = 2 = H; ÇÇ 6 2 = ( Ç 2 4 ) 2 = ( ) = = 2 8 which is not an integer 9. ( x ) 4 ( x 5 ) = ( 4 x ) ( 5 x ) = x ( ) = x 9 = x 94. y 5 = 2 (y 5 ) 5 = 2 5 y 5 5 = 5 ÇÇ 2 y = 2 y = = 8 x (8) = (8) 8 x 8 = x 8 = ( x ) Ç 8 = x 2 = x 2 = x 97. S = (4π) (V) 2 = (4π) ((6π)) 2 = (4π) (08π) 2 = 4 π 08 2 π 2 = π + 2 = ( 2 2 ) 08 2 π = π = (2 08) 2 π = 26 2 π = ( ÇÇ 26 ) 2 π = 6 2 π = 6π cm x = x 27 = x = 27 ( x ) = 27 x = ÇÇ 27 x = x = Both volume and surface area are described by 6π (although the units are different). ready to go on? Section A Quiz. t -6 = 2-6 = 2 6 = = n - = (-5) - = _ ( -5) = (-5)(-5)(-5) = _ -25 = Holt McDougal Algebra
9 . r 0 s -2 = = 0 2 = 0 0 = x 4 = x 4 y -6 y -6 = x 4 y 6 = x 4 y 6 7. a - = a - b -2 b -2 = b 2 a = b 2 a 4. 5k - = 5 k - = 5 5 k = k 6. 8f -4 g 0 = 8 f -4 g 0 _ = 8 8 f 4 = f = = = 000 = = = = = = 0 0 = 0. 0 = = 0 0 = 00 0 = = = ÇÇ 8 = = ÇÇ 25 = = Ç 4 = 64 ÇÇ = = 0. ÇÇ x 8 y 4 = (x 8 y 4 ) 2 = ( x 8 ) 2 (y 4 ) 2 = ( x 8 2 ) ( y 4 2 ) = ( x 4 ) (y 2 ) = x 4 y 2 4. Ç r 9 = ( r 9 ) = r 9 = r 5. 6 z ÇÇ 2 = ( z 2 ) 6 = z 2 6 = z 2 6. ÇÇÇ p q 2 = (p q 2 ) = (p ) (q 2 ) = ( p ) ( q 2 ) = (p )(q 4 ) = pq 4 6- polynomials Check it out! a. The degree is. b. The degree is. c. The degree is. 2a. 5x: degree -6: degree 0 The degree of the polynomial is. b. x y 2 : degree 5 x 2 y : degree 5 -x 4 : degree 4 2: degree 0 The degree of the polynomial is 5. a. 6-4x 2 + x 5 + 9x x 5 + 9x - 4x The leading coefficient is. b. 8y 5 - y 8 + 4y -y 8 + 8y 5 + 4y The leading coefficient is -. 4a. Degree: Terms: 4 x + x 2 -x + 2 is a cubic polynomial. b. Degree: 0 Terms: 6 is a constant monomial. c. Degree: 8 Terms: -y 8 + 8y 5 + 4y is an 8th-degree trinomial t t + 6 = -6(5) (5) + 6 = -6(25) + 400(5) + 6 = = 606 When the firework explodes, it will be 606 ft above the ground. think and discuss. Possible answer: 2x 2 + x - contains an a expression with a negative exponent. - b contains a variable within a denominator. 2. Monomials x 2 exercises Polynomials Trinomials 2x 2 + 6x - 7 guided practice Binomials x + 2. d 2. c. a 4. The degree is The degree is. 6. The degree is The degree is Holt McDougal Algebra
10 8. x 2 : degree 2-2x: degree : degree 0 The degree of the polynomial is a 2 b: degree 2a b 5 : degree 8 The degree of the polynomial is y: degree -84y : degree 00: degree 0 -y 2 : degree 2 The degree of the polynomial is.. r : degree r 2 : degree 2-5: degree 0 The degree of the polynomial is. 2. a : degree a 2 : degree 2-2a: degree The degree of the polynomial is.. k 4 : degree 4 k : degree -2k 2 : degree 2 k: degree The degree of the polynomial is b b 2 b 2-2b + 5 The leading coefficient is. 5. 9a 8-8a 9-8a 9 + 9a 8 The leading coefficient is s 2 - s + - s 7 -s 7 + 5s 2 - s + The leading coefficient is x + x 2 - x 2 + 2x - The leading coefficient is. 8. 5g g 2 g 2 + 5g - 7 The leading coefficient is. 9. c 2 + 5c 4 + 5c - 4 5c 4 + 5c + c 2-4 The leading coefficient is Degree: 2 Terms: x 2 + 2x + is a quadratic trinomial. 2. Degree: Terms: 2 x - 7 is a linear binomial. 22. Degree: 4 Terms: 8 + k + 5k 4 is a quartic trinomial. 2. Degree: 4 Terms: 4 q q + q 4 is a quartic polynomial. 24. Degree: Terms: 2 5k 2 + 7k is a cubic binomial. 25. Degree: 4 Terms: 2a + 4a 2 - a 4 is a quartic trinomial r 2 +.4rl =.4(6) 2 +.4(6)(0) =.4(6) +.4(6)(0) = = 0.44 The surface area of the cone is approximately 0.44 cm 2. practice and problem solving 27. The degree is The degree is. 29. The degree is The degree is 0.. The degree is The degree is 5.. The degree is. 4. The degree is a 2 : degree 2 a 4 : degree 4-6a: degree The degree of the polynomial is b: degree -5: degree 0 The degree of the polynomial is. 7..5y 2 : degree 2-4.y: degree -6: degree 0 The degree of the polynomial is f 4 : degree 4 2f 6 : degree 6 0f 8 : degree 8 The degree of the polynomial is n : degree -2n: degree The degree of the polynomial is r : degree 4r 6 : degree 6 The degree of the polynomial is t - 4t 2 + t 4.9t - 4t 2 + t The leading coefficient is a - 0a a 2 + 8a + 2 The leading coefficient is x 7 - x + x - x 5 + x 0 x 0 + x 7 - x 5 + x - x The leading coefficient is m m 2 -m 2 - m + 7 The leading coefficient is x 2 + 5x x 5x + x 2 + 5x - 4 The leading coefficient is n + - n 2 -n 2-2n + The leading coefficient is d + d 2 - d + 5 -d + d 2 + 4d + 5 The leading coefficient is s 2 + 2s + 6 2s + s The leading coefficient is x 2 - x 5 - x + -x 5 - x + 4x 2 + The leading coefficient is Degree: 0 Terms: 2 is a constant monomial. 5. Degree: Terms: 6k is a linear monomial. 52. Degree: Terms:.5x - 4.x - 6 is a cubic trinomial. 5. Degree: 2 Terms: 4g + 2g 2 - is a quadratic trinomial. 54. Degree: 2 Terms: 2 2x 2-6x is a quadratic binomial. 55. Degree: 4 Terms: 6 - s - s 4 is a quartic trinomial. 204 Holt McDougal Algebra
11 56. Degree: Terms: c c is a cubic trinomial. 57. Degree: 2 Terms: -y 2 is a quadratic monomial v v 2 =.675(0) (0) 2 =.675(0) (900) = = The stopping distance of a car traveling at 0 mi/h is ft. 59. always 60. sometimes 6. never 62. sometimes 6a. 4c - 9c c = 4() - 9() () = 4() - 9() + 9.5() = = 58.5 The volume of the box when c = in. is 58.5 in. b. 4c - 9c c = 4(.5) - 9(.5) (.5) = 4(.75) - 9(2.25) + 9.5(.5) = = 66 The volume of the box when c =.5 in. is 66 in. c. 4c - 9c c = 4(4.25) - 9(4.25) (4.25) = 4(76.765) - 9(8.06) + 9.5(4.25) = = 0 The volume of the box when c = 4.25 in. is 0 in. d. Yes; the width of the cardboard is 8.5 in., so 4.25 in. cuts will meet, leaving nothing to fold up. Polynomial x = -2 x = 0 x = x x 5 + x + 4x x Possible answer: x 2 + x Possible answer: 5x Possible answer: Possible answer: 6x 7. Possible answer: x Possible answer: 2x 2 - x Possible answer: First identify the degree of each term. From left to right, the degrees are, 0, 2, 4, and. Arrange the terms in order of decreasing degree, and move the plus or minus sign in front of each term with it: -2x 4 + 4x + 5x 2 - x -. 74a. 2x: degree 6: degree 0 The degree of the polynomial is. 74b. 8x 2 : degree 2 2x: degree The degree of the polynomial is A is incorrect. The student incorrectly multiplied - by -2 before evaluating the power. test prep 76. C; A has degree 8, B has degree, C has degree 0, and D has degree 2. So C has the greatest degree. 77. J -x + 4x 2-5x + 7 = -(-) + 4(-) 2-5(-) + 7 = -(-) + 4() - 5(-) + 7 = = Time (s) Height (ft) The rocket will be the highest after 2 s. Challenge and Extend 79a. 0.06m m m = 0.06(2) (2) (2) = 0.06(8) (4) (2) = m m m = 0.06(5) (5) (5) = 0.06(25) (25) (5) = The average length of a two-month-old baby boy is 58 cm and the average length of a five-month-old baby boy is 65 cm. b. 0.06m m m = 0.06(0) (0) (0) = 0.06(0) (0) (0) = = 50.0 The average length of a newborn baby boy is 50.0 cm. c. The first three terms of the polynomial will equal 0, so just look at the constant. 80a. 4x 5 + x 6-4 b. yes; 0 < x < ; raising a number between 0 and to a higher power results in a lesser number. So if x is between 0 and, the bionomial with the least degree will have the greatest value. adding and subtracting polynomials Check it out! a. 2s 2 + s 2 + s = 5s 2 + s b. 4z z = 4z 4 + 6z = 20z Holt McDougal Algebra
12 c. 2x 8 + 7y 8 - x 8 - y 8 = 2x 8 - x 8 + 7y 8 - y 8 = x 8 + 6y 8 d. 9b c 2 + 5b c 2 - b c 2 = b c 2 2. (5a + a 2-6a + 2a 2 ) + ( 7a - 0a ) = (5a + 7a ) + (a 2 + 2a 2 ) + (-6a - 0a) = 2a + 5a 2-6a. (2x 2 - x 2 + ) - (x 2 + x + ) = (2x 2 - x 2 + ) + ( -x 2 - x - ) = ( 2x 2 - x 2 - x 2 ) + (-x) + ( - ) = -2x 2 - x 4. (-0.0x x - 500) + (-0.02x 2 + 2x - 700) -0.05x x think and discuss. -2x 2 and -9x 2 ; -4.7y and y; 5 x 2 y and 5x 2 y 2. Take the opposite of each term: -9t 2 + 5t Adding: (8 a 2 b + 9 a 2 + b ) + (7 a 2 b + 6 a b ) = 25 a 2 b + 5 a 2 + b exercises guided practice. 7a 2-0a 2 + 9a = -a 2 + 9a Polynomials Subtracting: (6 m 5 n - 8 m + 2) - (2 m 5 n + m - ) = (6 m 5 n - 8 m + 2) + (- 2 m 5 n - m + ) = 4 m 5 n - 9 m + 2. x 2 + 9y 2-6x 2 = x 2-6x 2 + 9y 2 = 7x 2 + 9y r r + 0.9r 4 = 0.07r r r = 0.26r r 4. 4 p + 2 p 5. 5b c + b c - b c = 2 p = b c 6. -8m m = -8m + m = m - 7. (5n + n + 6) + (8n + 9) = (5n + 8n ) + n + (6 + 9) = 2n + n (.7q 2-8q +.7) + (4.q 2-2.9q +.6) = (.7q q 2 ) + (-8q - 2.9q) + (.7 +.6) = 8q 2-0.9q (-x + 2) + (9x 2 + 2x - 8) = 9x 2 + (-x + 2x) + (2-8) = 9x 2 - x (9x 4 + x ) + (2x 4 + 6x - 8x 4 + x ) = (9x 4 + 2x 4-8x 4 ) + (x + 6x + x ) = x 4 + 8x. (6c 4 + 8c + 6) - ( 2c 4 ) = (6c 4 + 8c + 6) + ( -2c 4 ) = ( 6c 4-2c 4 ) + 8c + 6 = 4c 4 + 8c (6y 2-8y + 9) - (6y 2-2y + 7y) = (6y 2-8y + 9) + (-6y 2 + 2y - 7y) = (6y 2-6y 2 ) + (-8y + 2y - 7y) + 9 = 0y 2 - y + 9. (2r + 5) - (5r - 6) = (2r + 5) + (-5r + 6) = (2r - 5r) + (5 + 6) = -r + 4. (-7k 2 + ) - (2k 2 + 5k - ) = (-7k 2 + ) + (-2k 2-5k + ) = ( -7k 2-2k 2 ) + (-5k) + ( + ) = -9k 2-5k m ABD = (8a 2-2a + 5) + (7a + 4) = 8a 2 + (-2a + 7a) + (5 + 4) = 8a 2 + 5a + 9 practice and problem solving 6. 4k + 6k 2 + 9k = 4k + 9k + 6k 2 = k + 6k m + 2n 2 + 6n - 8m = 5m - 8m + 2n 2 + 6n = 2n 2 + 6n - m a 4-8.b 4 -.6b 4 = 2.5a 4 -.7b xy - 4x 2 y - 2xy = 7xy - 2xy - 4x 2 y = -4x 2 y + 5xy 2. -6x + 5x + 2x + 4x = -6x + 2x + 4x + 5x = 5x 22. x 2 + x + x + 2x 2 = x 2 + 2x 2 + x + x = x 2 + 4x 9. 2d d 5 = 2d 5 - d 5 + = d x x - = x - x = 2x Holt McDougal Algebra
13 24. b - 2b - - b - b = b - b - 2b - b - = 2b - b ( 2t 2-8t ) + (8t 2 + 9t) = (2t 2 + 8t 2 ) + (-8t + 9t) = 0t 2 + t 26. (-7x 2-2x + ) + ( 4x 2-9x ) = (-7x 2 + 4x 2 ) + (-2x - 9x) + = -x 2 - x ( x 5 - x ) + (x 4 + x) = (x 5 + x 4 ) + (-x + x) = x 5 + x (-2z + z + 2z + z)+ ( z - 5z 2 ) = (-2z + 2z + z ) + ( -5z 2 ) + (z + z) = z - 5z 2 + 2z 29. (t + 8t 2 ) - ( t ) = (t + 8t 2 ) + ( -t ) = ( t - t ) + 8t 2 = -2t + 8t 2 0. ( x 2 - x ) - (x 2 + x - x) = ( x 2 - x ) + (-x 2 - x + x) = ( x 2 - x 2 ) + (-x - x + x) = 2x 2 - x. (5m + ) - ( 6m - 2m 2 ) = (5m + ) + (-6m + 2m 2 ) = -6m + 2m 2 + 5m + 2. (s 2 + 4s)- (-0s 2 + 6s) = (s 2 + 4s)+ ( 0s 2-6s ) = (s 2 + 0s 2 ) + (4s - 6s) = s 2-2s. width = (6w 2 + 8) - 2(w 2 - w + 2) = (6w 2 + 8) + (-2( w 2 ) - 2(-w) - 2(2)) = (6w 2 + 8) + (-2w 2 + 6w - 4) = ( 6w 2-2w 2 ) + 6w + (8-4) = 4w 2 + 6w P = 2l + 2w = 2(4a + b) + 2(7a - 2b) = 2(4a) + 2(b) + 2(7a) + 2(-2b) = 8a + 6b + 4a - 4b = 8a + 4a + 6b - 4b = 22a + 2b 5. (2t - 7) + (-t + 2) = (2t - t) + (-7 + 2) = t (4m 2 + m)+ ( -2m 2 ) = ( 4m 2-2m 2 ) + m = 2m 2 + m 7. (4n - 2) - 2n = (4n - 2) + (-2n) = (4n - 2n) + (-2) = 2n (4x 2 + x - 6) + (2x 2-4x + 5) 8. (-v - 7) - (-2v) = (-v - 7) + (2v) = (-v + 2v) + (-7) = v - 7 = (4x 2 + 2x 2 ) + (x - 4x) + (-6 + 5) = 6x 2 - x ( 2z 2 - z - ) + ( 2z 2-7z - ) = (2z 2 + 2z 2 ) + (-z - 7z) + (- - ) = 4z 2-0z (5u 2 + u + 7) - (u + 2u 2 + ) = (5u 2 + u + 7) + ( -u - 2u 2 - ) = ( -u ) + ( 5u 2-2u 2 ) + u + (7 - ) = -u + u 2 + u (-7h 2-4h + 7) - (7h 2-4h + ) = (-7h 2-4h + 7) + (-7h 2 + 4h - ) = ( -7h 2-7h 2 ) + (-4h + 4h) + (7 - ) = -4h P = 2l + 2w 5 = 2(2x + ) + 2(x + 7) 5 = 2(2x) + 2() + 2(x) + 2(7) 5 = 4x x = 4x + 6x = 0x = 0x 5 0 = 0x 0 = x, or x = Yes; the simplified form of both expressions is 5m 2 + 2m - 0. No; the simplified form of the original expression is -9m 2-2m + 0 and the simplified form of the new expression is -9m 2 + 2m B is incorrect. The student incorrectly tried to combine 6n and -n 2, which are not like terms, and tried to combine 4n 2 and 9n, which are not like terms. Polynomial Polynomial 2 Sum 46. x 2-6 x 2-0x + 2 4x 2-0x x + 5 x + 6 5x x 4 - x 2-9 5x x 4 - x x - 6x - 6x + 4 7x x + 5x 2 7x - 5x 2 + 9x x 2 + x - 5 x + x x 2 + 2x No; polynomial addition simply involves combining like terms. No matter what order the terms are combined in, the sum will be the same. Yes; in polynomial subtraction, the subtraction sign is distributed among all terms in the second polynomial, changing all the signs to their opposites. 207 Holt McDougal Algebra
14 5a. x + 4 x Possible answer: 2m + m, m + m + m + m 6. Possible answer: 4m + m b. P = 2l + 2w = 2(x + 4) + 2(x - ) = 2(x) + 2(4) + 2(x) + 2(-) = 2x x - 6 = 2x + 2x = 4x + 2 c. P = 4x + 2 = 4(5) + 2 = = 62 He will need 62 ft of fencing. test prep 54. C; Since -4y 2 + 9y 2 + 2y 2 = -y 2, and - 2 =, the term must be in the form ay. So -2y + ay - 6y = -5y gives -2 + a - 6 = -5 or a =. So the missing term is y. 55. G; Since 2t - 4t - (-7t - t) = 2t + 6t -5t - t, G is correct. 56a. P = 2l + 2w - = 2(2x - ) + 2(x + 4) - = 2(2x) + 2(-) + 2(x) + 2(4) - = 4x x = 4x + 2x = 6x + b. 6x + = 50 _ - - 6x = 47 6x 6 = 47 6 x 7.8 7; If x = 7, Tammy will need 6(7) + = 45 feet of wallpaper border. However, if x = 8, Tammy will need 6(8) + = 5 feet of wallpaper border, which is more than the store has. c. (2x - ) ft (x + 4) ft = (2(7) - )ft (7 + 4) ft = ft ft CHALLENGE AND EXTEND 57. P = b + 2s - 2s - 2s P - 2s = b b = (2x + x 2 + 8) - 2(x + 5) = (2x + x 2 + 8) + (-2x - 2(5)) = (2x + x 2 + 8) + ( -2x - 0 ) = ( 2x - 2x ) + x 2 + (8-0) = x Possible answer: 2m + 2m, 2m + m 59. Possible answer: 5m + 2m, m - m 62. Possible answer: 2m + m 2 + m, m + m 2 + m, m - 2m 2 + m 6-5 multiplying POlynomials Check it out! a. ( x ) ( 6x 2 ) = ( 6)( x x 2 ) = 8x 5 b. ( 2r 2 t ) ( 5t ) c. ( x 2 y ) ( 2x z 2 ) (y 4 z 5 ) = ( 2 ) ( x 2 x ) (y y 4 )( z 2 z 5 ) = 4x 5 y 5 z 7 2a. 2(4x 2 + x + ) = 2( 4x 2 ) + 2(x) + 2() = 8x 2 + 2x + 6 b. ab(5a 2 + b) = ab( 5a 2 ) + ab(b) = ( 5)( a a 2 ) ( b) + ()(a)(b b) = 5a b + ab 2 c. 5r 2 s 2 ( r - s) = 5r 2 s 2 ( r) + 5r 2 s 2 ( -s) = (2 5)( r 2 ) ( t t ) = 0r 2 t 4 = (5)( r 2 r ) ( s 2 ) + (5 (-)) ( r 2 ) ( s 2 s ) = 5r s 2-5r 2 s a. (a + )(a - 4) = a(a) + a(-4) + (a) + (-4) = a 2-4a + a - 2 = a 2 - a - 2 b. ( x - ) 2 = (x - )(x - ) = x(x) + x(-) - (x) - (-) = x 2 - x - x + 9 = x 2-6x + 9 c. ( 2a - b 2 ) (a + 4b 2 ) = 2a(a) + 2a( 4b 2 ) - b 2 ( a) - b 2 ( 4b 2 ) = 2a 2 + 8ab 2 - ab 2-4b 4 = 2a 2 + 7ab 2-4b 4 4a. (x + )(x 2-4x + 6) = x(x 2-4x + 6) + (x 2-4x + 6) = x( x 2 ) + x(-4x) + x(6) + ( x 2 ) + (-4x) + (6) = x - 4x 2 + 6x + x 2-2x + 8 = x - x 2-6x Holt McDougal Algebra
15 b. (x + 2)(x 2-2x + 5) = x(x 2-2x + 5) + 2(x 2-2x + 5) = x( x 2 ) + x(-2x) + x(5) + 2 ( x 2 ) + 2( -2x) + 2(5) = x - 6x 2 + 5x + 2x 2-4x + 0 = x - 4x 2 + x + 0 5a. Let x represent the width of the rectangle. A = lw = (x - 4)(x) = x(x) - 4(x) = x 2-4x The area is represented by x 2-4x. b. A = x 2-4x = (6) 2-4(6) = 6-24 = 2 The area is 2 m 2. think and discuss. Possible answer: Both numbers and polynomials are set up in two rows and require you to multiply each item in the top row by an item in the bottom row. In the end, you add vertically to get the answer. When you are multiplying polynomials, the items are monomial terms. When your are multiplying numbers, the items are digits. 2. Distributive Property: 5x (x + 2) = 5x 2 + 0x Rectangle model: (x + 2)(x 2 + 2x + ) x + 2 x 2 x + 2x + 2 x 2 4x 2 x 2 x 2 x + 4x 2 + 5x + 2 exercises guided practice. ( 2x 2 ) ( 7x 4 ) = (2 7)( x 2 x 4 ) = 4x 6 Multiplying Polynomials 2. ( -5mn ) ( 4m 2 n 2 ) FOIL method: (x + )(x + 2) = x 2 + 2x + x + 2 = x 2 + x + 2 Vertical method: (x + 2)(x 2 + x + 2) x 2 + x + 2 x x x x + x x x + 5 x x + 4 = (-5 4)( m m 2 ) ( n n 2 ) = -20m n 5. ( 6rs 2 ) ( s t 2 ) ( 2 r 4 t ) = ( 6 2 ) ( r r 4 ) ( s 2 s ) ( t 2 t ) = r 5 s 5 t 5 4. ( a 5 ) (2a) = ( 2 ) ( a 5 a ) = 4a 6 5. (-x 4 y 2 )(-7x y) = (- (-7))( x 4 x ) (y 2 y) = 2x 7 y 6. (-2pq )(5p 2 q 2 )(-q 4 ) = (-2 5 (-))(p p 2 )(q q 2 q 4 ) = 0p q (x 2 + 2x + ) = 4( x 2 ) + 4(2x) + 4() = 4x 2 + 8x ab(2a 2 + b ) = ab( 2a 2 ) + ab ( b ) = ( 2)( a a 2 ) ( b) + ( )(a) ( b b ) = 6a b + 9ab a b(a 2 b + ab 2 ) = 2a b( a 2 b ) + 2a b ( ab 2 ) = (2 )( a a 2 ) ( b b) + (2) ( a a ) ( b b 2 ) = 6a 5 b 2 + 2a 4 b 0. -x(x 2-4x + 6) = -x( x 2 ) - x(-4x) - x(6) = -x + 2x 2-8x. 5x 2 y(2xy - y) = 5x 2 y(2xy ) + 5x 2 y(-y) = (5 2)( x 2 x ) (y y ) + (5 (-))( x 2 ) ( y y) = 0x y 4-5x 2 y m 2 n mn 2 (4m - n) = (5)( m 2 m ) ( n n 2 ) (4m - n) = 5m n 5 (4m - n) = 5m n 5 (4m) + 5m n 5 ( -n) = (5 4)( m m ) ( n 5 ) + (5 (-)) ( m ) ( n 5 n ) = 20m 4 n 5-5m n 6. (x + )(x - 2) = x(x) + x(-2) + (x) + (-2) = x 2-2x + x - 2 = x 2 - x ( x + ) 2 = (x + )(x + ) = x(x) + x() + (x) + () = x 2 + x + x + = x 2 + 2x Holt McDougal Algebra
16 5. ( x - 2) 2 = (x - 2)(x - 2) = x(x) + x(-2) - 2(x) - 2(-2) = x 2-2x - 2x + 4 = x 2-4x (y - )(y - 5) = y(y) + y(-5) - (y) - (-5) = y 2-5y - y + 5 = y 2-8y ( 4a - 2b ) ( a - b 2 ) = 4a ( a) + 4a ( -b 2 ) - 2b(a) - 2b ( -b 2 ) = 4a 4-2ab - 2a b 2 + 6b 8. ( m 2-2mn ) (mn + n 2 ) = m 2 (mn) + m 2 ( n 2 ) - 2mn(mn) - 2mn ( n 2 ) = m n + m 2 n 2-6m 2 n 2-2mn = m n - 5m 2 n 2-2mn 9. (x + 5)(x 2-2x + ) = x(x 2-2x + ) + 5(x 2-2x + ) = x( x 2 ) + x(-2x) + x() + 5 ( x 2 ) + 5(-2x) + 5() = x - 2x 2 + x + 5x 2-0x + 5 = x + x 2-7x (x + 4)(x 2-5x + 2) = x(x 2-5x + 2) + 4(x 2-5x + 2) = x( x 2 ) + x(-5x) + x(2) + 4 ( x 2 ) + 4(-5x) + 4(2) = x - 5x 2 + 6x + 4x 2-20x + 8 = x - x 2-4x (2x - 4)(-x + 2x - 5) = 2x(-x + 2x - 5) - 4(-x + 2x - 5) = 2x( -x ) + 2x(2x) + 2x(-5) - 4 ( -x ) - 4(2x) - 4(-5) = -6x 4 + 4x 2-0x + 2x - 8x + 20 = -6x 4 + 2x + 4x 2-8x (-4x + 6)(2x - x 2 + ) = -4x(2x - x 2 + ) + 6(2x - x 2 + ) = -4x( 2x ) -4x ( -x 2 ) -4x() + 6 ( 2x ) + 6 ( -x 2 ) + 6() = -8x 4 + 4x - 4x + 2x - 6x = -8x 4 + 6x - 6x 2-4x (x - 5)(x 2 + x + ) = x(x 2 + x + ) - 5(x 2 + x + ) = x( x 2 ) + x(x) + x() -5 ( x 2 ) - 5(x) - 5() = x + x 2 + x - 5x 2-5x - 5 = x - 4x 2-4x (a + b)(a - b)(b - a) = (a(a) + a(-b) + b(a) + b(-b))( b- a) = (a 2 - ab + ab - b 2 )( b - a) = ( a 2 - b 2 ) ( b - a) = a 2 ( b) + a 2 ( -a) - b 2 ( b) - b 2 ( -a) = a 2 b - a - b + ab 2 = -a + a 2 b + ab 2 - b 25a. A = lw = (2x - )(x) = 2x(x) - (x) = 2x 2 - x The area is represented by 2x 2 - x. b. A = 2x 2 - x = 2(4) 2 - (4) = 2(6) - (4) = 2-2 = 20 The area is 20 in 2. practice and problem solving 26. ( x 2 ) ( 8x 5 ) = ( 8)( x 2 x 5 ) = 24x ( -2r s 4 ) ( 6r 2 s ) = (-2 6)( r r 2 ) ( s 4 s ) = -2r 5 s (5xy 2 ) ( x 2 z ) (y z 4 ) = ( 5 ) ( x x 2 ) (y 2 y )( z z 4 ) = 5x y 5 z ( -2a ) ( -5a) = (-2 (-5))( a a ) = 0a 4 0. (6x y 2 )(-2x 2 y) = (6 (-2))( x x 2 ) (y 2 y) = -2x 5 y. ( -a 2 b ) ( -2b ) ( -a b 2 ) = (- (-2) (-))( a 2 a ) ( b b b 2 ) = -6a 5 b 6 2. ( 7x 2 ) (xy 5 )(2x y 2 ) = (7 2)( x 2 x x ) (y 5 y 2 ) = 4x 6 y 7. ( -4a bc 2 ) ( a b 2 c) ( ab 4 c 5 ) = (-4 )( a a a ) ( b b 2 b 4 ) ( c 2 c c 5 ) = -2a 7 b 7 c 8 4. ( 2mn 2 ) ( 2m 2 n ) (mn) = (2 2)( m m 2 m ) ( n 2 n n ) = 24m 4 n 4 20 Holt McDougal Algebra
17 5. 9s(s + 6) = 9s(s) + 9s(6) = 9s s 7. x( 9x 2-4x ) = x( 9x 2 ) + x(-4x) = 27x - 2x s 2 t ( 2s - t 2 ) = 5s 2 t (2s) + 5s 2 t ( -t 2 ) 6. 9( 2x 2-5x ) = 9( 2x 2 ) + 9(-5x) = 8x 2-45x 8. (2x 2 + 5x + 4) = ( 2x 2 ) + (5x) + (4) = 6x 2 + 5x + 2 = (5 2)( s 2 s ) ( t ) + (5 (-)) ( s 2 ) ( t t 2 ) = 0s t - 5s 2 t x 2 y 5x 2 y(6x + y 2 ) = (5)( x 2 x 2 ) (y y)(6x + y 2 ) = 5x 4 y 4 (6x + y 2 ) = 5x 4 y 4 (6x) + 5x 4 y 4 (y 2 ) = (5 6)( x 4 x ) (y 4 ) + (5)( x 4 ) (y 4 y 2 ) = 0x 5 y 4 + 5x 4 y x( 2x 2 - x - ) = -5x( 2x 2 ) - 5x(-x) - 5x(-) = -0x + 5x 2 + 5x a 2 b ( ab 2 - a 2 b ) = -2a 2 b ( ab 2 ) - 2a 2 b ( -a 2 b ) = (-2 )( a 2 a ) ( b b 2 ) - (2 -) ( a 2 a 2 ) ( b b ) = -6a b 5 + 2a 4 b x y x 2 y 2 (2x - y) = (-7)( x x 2 ) (y y 2 )(2x - y) = -7x 5 y (2x - y) = -7x 5 y (2x) - 7x 5 y ( -y) = (-7 2)( x 5 x ) (y ) + (-7 (-))( x 5 ) (y y) = -4x 6 y + 7x 5 y (x + 5)(x - ) = x(x) + x(-) + 5(x) + 5(-) = x 2 - x + 5x - 5 = x 2 + 2x ( x + 4) 2 = (x + 4)(x + 4) = x(x) + x(4) + 4(x) + 4(4) = x 2 + 4x + 4x + 6 = x 2 + 8x ( m - 5) 2 = (m - 5)(m - 5) = m(m) + m(-5) - 5(m) - 5(-5) = m 2-5m - 5m + 25 = m 2-0m (5x - 2)(x + ) = 5x(x) + 5x() - 2(x) - 2() = 5x 2 + 5x - 2x - 6 = 5x 2 + x (x - 4) 2 = (x - 4)(x - 4) = x(x) + x(-4) - 4(x) - 4(-4) = 9x 2-2x -2x + 6 = 9x 2-24x (5x + 2)(2x - ) = 5x(2x)+ 5x(-) + 2(2x)+ 2(-) = 0x 2-5x + 4x - 2 = 0x 2 - x (x - )(x - 2) = x(x) + x(-2) - (x) - (-2) = x 2-2x - x + 2 = x 2 - x (x - 8)(7x + 4) = x(7x) + x(4) - 8(7x) - 8(4) = 7x 2 + 4x - 56x - 2 = 7x 2-52x (2x + 7)(x + 7) = 2x(x) + 2x(7) + 7(x) + 7(7) = 6x 2 + 4x + 2x + 49 = 6x 2 + 5x (x + 2)(x 2 - x + 5) = x(x 2 - x + 5) + 2(x 2 - x + 5) = x( x 2 ) + x(-x) + x(5) + 2 ( x 2 ) + 2(-x) + 2(5) = x - x 2 + 5x + 2x 2-6x + 0 = x - x 2 - x (2x + 5)(x 2-4x + ) = 2x(x 2-4x + ) + 5(x 2-4x + ) = 2x( x 2 ) + 2x(-4x) + 2x() + 5 ( x 2 ) + 5(-4x) + 5() = 2x - 8x 2 + 6x + 5x 2-20x + 5 = 2x - x 2-4x (5x - )(-2x + 4x - ) = 5x(-2x + 4x - ) - (-2x + 4x - ) = 5x( -2x ) + 5x(4x) + 5x(-) - ( -2x ) - (4x) - (-) = -0x x 2-5x + 2x - 4x + = -0x 4 + 2x + 20x 2-9x (x - )(x 2-5x + 6) = x(x 2-5x + 6) - (x 2-5x + 6) = x( x 2 ) + x(-5x) + x(6) - ( x 2 ) - (-5x) - (6) = x - 5x 2 + 6x - x 2 + 5x - 8 = x - 8x 2 + 2x ( 2x 2 - ) (4x - x 2 + 7) = 2x 2 (4x - x 2 + 7) - (4x - x 2 + 7) = 2x 2 ( 4x ) + 2x 2 ( -x 2 ) + 2x 2 (7) - ( 4x ) - ( -x 2 ) - (7) = 8x 5-2x 4 + 4x 2-2x + x 2-2 = 8x 5-2x 4-2x + 7x Holt McDougal Algebra
18 58. ( x - 4) = (x - 4)(x - 4)(x - 4) = (x(x) + x(-4) - 4(x) - 4(-4))( x - 4) = (x 2-4x - 4x + 6)( x - 4) = (x 2-8x + 6)( x - 4) = (x - 4)(x 2-8x + 6) = x(x 2-8x + 6) - 4(x 2-8x + 6) = x( x 2 ) + x(-8x) + x(6) - 4 ( x 2 ) - 4(-8x) - 4(6) = x - 8x 2 + 6x - 4x 2 + 2x - 64 = x - 2x x (x - 2)(x 2 + 2x + ) = x(x 2 + 2x + ) - 2(x 2 + 2x + ) = x( x 2 ) + x(2x) + x() - 2 ( x 2 ) - 2(2x) - 2() = x + 2x 2 + x - 2x 2-4x - 2 = x - x (2x + 0)(4 - x + 6x ) = 2x(4 - x + 6x ) + 0(4 - x + 6x ) = 2x(4) + 2x(-x) + 2x( 6x ) + 0(4) + 0(-x) + 0( 6x ) = 8x - 2x 2 + 2x x + 60x = 2x x - 2x 2-2x ( - x) = ( - x)( - x)( - x) = (() + (-x) - x() - x(-x))( - x) = ( - x - x + x 2 )( - x) = ( - 2x + x 2 )( - x) = ( - x)( - 2x + x 2 ) = ( - 2x + x 2 ) - x( - 2x + x 2 ) = - 2x + x 2 -x() - x(-2x) -x( x 2 ) = - 2x + x 2 - x + 2x 2 - x = -x + x 2 - x + 62a. A = lw = (x + )(x) = x(x) + (x) = x 2 + x The area is represented by x 2 + x. b. A = x 2 + x = (5) 2 + (5) = = 40 The area is 40 ft A = s 2 = (4x - 6) 2 = (4x - 6)(4x - 6) = 4x(4x) + 4x(-6) - 6(4x) - 6(-6) = 6x 2-24x - 24x + 6 = 6x 2-48x + 6 The area is represented by 6x 2-48x a. x + 4 x + b. A = lw = (x + 4)(x + ) = x(x) + x() + 4(x) + 4() = x 2 + x + 4x + 4 = x 2 + 5x + 4 The area is represented by x 2 + 5x + 4. c. A = x 2 + 5x + 4 = (4) 2 + 5(4) + 4 = = 40 The area is 40 ft 2. A Degree of A B Degree of B A B Degree of A B 2x 2 2 x 5 5 6x a. 5x 2x x 5 + 5x 5 b. x x 2 - x 2 x 4 - x + 4 2x 2-2x c. x - x - 2x 2 + x 4-5x + 6x 2 + x - 4 d. m + n 66. A = lw = (2x + )(4x) = 2x(4x) + (4x) = 8x 2 + 2x The area is represented by 8x 2 + 2x. 67. A = lw = (2x + )(2x + ) = [(2x) + ()](2x + ) = (6x + )(2x + ) = 6x(2x) + 6x() + (2x) + () = 2x 2 + 6x + 6x + = 2x 2 + 2x + The area is represented by 2x 2 + 2x A = lw = (x - 5)(x - 5) = x(x) + x(-5) - 5(x) - 5(-5) = x 2-5x - 5x + 25 = x 2-0x + 25 The area is represented by x 2-0x a. A = lw = (2x)(x) = 2x 2 The area is represented by 2x 2. b. A = 2x 2 = 2(20) 2 = 2(400) = 800 The area is 800 m Holt McDougal Algebra
19 70. (.5a ) ( 4a 6 ) = (.5 4)( a a 6 ) = 6a 9 7. (2x + 5)(x - 6) = 2x(x) + 2x(-6) + 5(x) + 5(-6) = 2x 2-2x + 5x - 0 = 2x 2-7x (g - )(g + 5) = g(g) + g(5) - (g) - (5) = g 2 + 5g - g - 5 = g 2 + 4g (4x - 2y)(2x - y) = 4x(2x) + 4x(-y) - 2y(2x) - 2y(-y) = 8x 2-2xy - 4xy + 6y 2 = 8x 2-6xy + 6y (x + )(x - ) = x(x) + x(-) + (x) + (-) = x 2 - x + x - 9 = x (.5x - )(4x + 2) =.5x(4x) +.5x(2) - (4x) - (2) = 6x 2 + x - 2x - 6 = 6x 2-9x (x - 0)(x + 4) = x(x) + x(4) - 0(x) - 0(4) = x 2 + 4x - 0x - 40 = x 2-6x x 2 ( x + ) = x 2 ( x) + x 2 () = x + x (x + )(x 2 + 2x) = x( x 2 ) + x(2x) + ( x 2 ) + (2x) = x + 2x 2 + x 2 + 2x = x + x 2 + 2x 79. (x - 4)(2x 2 + x - 6) = x(2x 2 + x - 6) - 4(2x 2 + x - 6) = x( 2x 2 ) + x(x) + x(-6) - 4 ( 2x 2 ) - 4(x) - 4(-6) = 2x + x 2-6x - 8x 2-4x + 24 = 2x - 7x 2-0x (a + b)(a - b) 2 = (a + b)(a - b)(a - b) = (a(a) + a(-b) + b(a) + b(-b))( a - b) = (a 2 - ab + ab - b 2 )( a - b) = ( a 2 - b 2 ) ( a - b) = a 2 ( a) + a 2 ( -b) - b 2 ( a) - b 2 ( -b) = a - a 2 b - ab 2 + b 8. (2p - q) = (2p - q)(2p - q)(2p - q) = (2p(2p) + 2p(-q) - q(2p) - q(-q))( 2p - q) 82a. = (4p 2-6pq - 6pq + 9q 2 )( 2 p - q) = (4p 2-2pq + 9q 2 )(2p - q) = (2p - q)(4p 2-2pq + 9q 2 ) = 2p(4p 2-2pq + 9q 2 ) - q(4p 2-2pq + 9q 2 ) = 2p(4p 2 ) + 2p(-2pq) + 2p(9q 2 ) - q(4p 2 ) - q(-2pq) - q(9q 2 ) = 8p - 24p 2 q + 8pq 2-2p 2 q + 6pq 2-27q = 8p - 6p 2 q + 54pq 2-27q x x 25 b. The length is 25 + x + x = 2x The width is 0 + x + x = 2x + 0. c. A = lw = (2x + 25)(2x + 0) = 2x(2x) + 2x(0) + 25(2x) + 25(0) = 4x x + 50x = 4x x Possible answer: Each letter in FOIL represents a pair of terms in a certain position within the factors. The letters must account for every pairing of terms while describing first, outside, inside, and last positions. This is only possible with two binomials. 84. A = lwh = (x + 5)(x)(x + 2) = (x(x) + 5(x))( x + 2) = (x 2 + 5x)(x + 2) = x 2 ( x) + x 2 (2) + 5x(x) + 5x(2) = x + 2x 2 + 5x 2 + 0x = x + 7x 2 + 0x The area is represented by x + 7x 2 + 0x. 85. Yes; x = Let x represent the width of the rectangle. A = lw = (x + )(x) = x(x) + (x) = x 2 + x Since (4.5) = , the width of the rectangle is about 4.5 ft. test prep 87. C (a + )(a - 6) = a(a) + a(-6) + (a) + (-6) = a 2-6a + a - 6 = a 2-5a Holt McDougal Algebra
20 88. H 2a( a 2 - ) = 2a( a 2 ) + 2a(-) = 2a - 2a 89. D x y 2 z x 2 yz = ()( x x 2 ) (y 2 y)(z z) = x 5 y z 2 This has degree = 0. challenge and extend 90. 6x 2-2(x 2-2x + 4) = 6x 2-2( x 2 ) - 2(-2x) - 2(4) = 6x 2-6x 2 + 4x - 8 = 4x x 2-2x(x + ) = x 2-2x(x) - 2x() = x 2-2x 2-6x = -x 2-6x 92. x(4x - 2) + x(x + ) = x(4x) + x(-2) + x(x) + x() = 4x 2-2x + x 2 + x = 7x 2 + x 9a. A = lw = (x + )(x - ) = x(x) + x(-) + (x) + (-) = x 2 - x + x - = x 2 - The area is represented by x 2 -. b. A = lw = (x + 5)(x + ) - (x + )(x - ) = x(x) + x() + 5(x) + 5() - ( x 2 - ) = x 2 + x + 5x x 2 + = 8x A = s 2 = (8 + 2x) 2 = (8 + 2x)(8 + 2x) = 8(8) + 8(2x) + 2x(8) + 2x(2x) = x + 6x + 4x 2 = 4x 2 + 2x + 64 P = 4s = 4(x ) = 4( x 2 ) + 4(48) = 4x A = P 4x 2 + 2x + 64 = 4x x 2-4x 2 2x + 64 = x = 28 2x 2 = 28 2 x = x(x + )(x + 2) = (x(x) + x())( x + 2) = (x 2 + x)(x + 2) = x 2 ( x) + x 2 (2) + x(x) + x(2) = x + 2x 2 + x 2 + 2x = x + x 2 + 2x 96. x m (x n + x n - 2 ) = x 5 + x x m ( x n ) + x m ( x n - 2 ) = x 5 + x x m + n + x m + n - 2 = x 5 + x Therefore, it must be true that: m + n = 5 m + n = 5 m + n - 2 = m + n = 5 Therefore, the system is consistent and dependent, so there is an infinite number of solutions. One is m = 2; n = x a (5x 2a - + 2x 2a + 2 ) = 0x + 4x 8 2x a ( 5x 2a - ) + 2x a ( 2x 2a + 2 ) = 0x + 4x 8 0x a - + 4x a + 2 = 0x + 4x 8 Therefore, it must be true that: a - = and a + 2 = a = 6 and a = 6 a = 6 a = 6 a = special Products of Binomials Check it out! a. ( a + b) 2 = a 2 + 2ab + b 2 ( x + 6) 2 = (x) 2 + 2(x)(6) + (6) 2 = x 2 + 2x + 6 b. ( a + b) 2 = a 2 + 2ab + b 2 (5a + b) 2 = (5a) 2 + 2(5a)(b) + (b) 2 = 25a 2 + 0ab + b 2 c. ( a + b) 2 = a 2 + 2ab + b 2 ( + c ) 2 = () 2 + 2()( c ) + ( c ) 2 = + 2c + c 6 2a. ( a - b) 2 = a 2-2ab + b 2 ( x - 7) 2 = (x) 2-2(x)(7) + (7) 2 = x 2-4x + 49 b. ( a - b) 2 = a 2-2ab + b 2 (b - 2c) 2 = (b) 2-2(b)(2c) + (2c) 2 = 9b 2-2bc + 4c 2 c. ( a - b) 2 = a 2-2ab + b 2 ( a 2-4 ) 2 = ( a 2 ) 2-2( a 2 ) (4) + (4) 2 = a 4-8a a. (a + b)(a - b) = a 2 - b 2 (x + 8)(x - 8) = (x) 2 - (8) 2 = x Holt McDougal Algebra
21 b. (a + b)(a - b) = a 2 - b 2 ( + 2y 2 )( - 2y 2 ) = () 2 - (2y 2 ) 2 = 9-4y 4 c. (a + b)(a - b) = a 2 - b 2 (9 + r)(9 - r) = (9) 2 - (r) 2 = 8 - r 2 4. Area of : (5 + x)(5 - x) = (5) 2 - (x) 2 = 25 - x 2 Area of : x 2 Total area = area of + area of = ( 25 - x 2 ) + x 2 = 25 + (-x 2 + x 2 ) = 25 The area of the pool is 25. think and discuss. (a + b)(a - b) = a 2 - ab + ab - b 2 = a 2 - b 2 2. product. Special Products of Binomials Perfect-Square Trinomials ( a + b ) 2 = a ab + b 2 ( x + 4) 2 = x x + 6 Exercises guided practice ( a - b ) 2 = a 2-2 ab + b 2 ( x - 4) 2 = x 2-8 x + 6 Difference of Two Squares ( a + b)( a - b) = a 2 - b 2 ( x + 4)( x - 4) = x 2-6. Possible answer: a trinomial that is the result of squaring a binomial. 2. ( a + b) 2 = a 2 + 2ab + b 2 ( x + 7) 2 = (x) 2 + 2(x)(7) + (7) 2 = x 2 + 4x ( a + b) 2 = a 2 + 2ab + b 2 (2 + x) 2 = (2) 2 + 2(2)(x) + (x) 2 = 4 + 4x + x 2 4. ( a + b) 2 = a 2 + 2ab + b 2 ( x + ) 2 = (x) 2 + 2(x)() + () 2 = x 2 + 2x + 5. ( a + b) 2 = a 2 + 2ab + b 2 (2x + 6) 2 = (2x) 2 + 2(2x)(6) + (6) 2 = 4x x ( a + b) 2 = a 2 + 2ab + b 2 (5x + 9) 2 = (5x) 2 + 2(5x)(9) + (9) 2 = 25x x ( a + b) 2 = a 2 + 2ab + b 2 (2a + 7b) 2 = (2a) 2 + 2(2a)(7b) + (7b) 2 = 4a ab + 49b 2 8. ( a - b) 2 = a 2-2ab + b 2 ( x - 6) 2 = (x) 2-2(x)(6) + (6) 2 = x 2-2x ( a - b) 2 = a 2-2ab + b 2 ( x - 2) 2 = (x) 2-2(x)(2) + (2) 2 = x 2-4x ( a - b) 2 = a 2-2ab + b 2 (2x - ) 2 = (2x) 2-2(2x)() + () 2 = 4x 2-4x +. ( a - b) 2 = a 2-2ab + b 2 (8 - x) 2 = (8) 2-2(8)(x) + (x) 2 = 64-6x + x 2 2. ( a - b) 2 = a 2-2ab + b 2 (6p - q) 2 = (6p) 2-2(6p)(q) + (q) 2 = 6p 2-2pq + q 2. ( a - b) 2 = a 2-2ab + b 2 (7a - 2b) 2 = (7a) 2-2(7a)(2b) + (2b) 2 = 49a 2-28ab + 4b 2 4. (a + b)(a - b) = a 2 - b 2 (x + 5)(x - 5) = (x) 2 - (5) 2 = x (a + b)(a - b) = a 2 - b 2 (x + 6)(x - 6) = (x) 2 - (6) 2 = x (a + b)(a - b) = a 2 - b 2 (5x + )(5x - ) = (5x) 2 - () 2 = 25x 2-7. (a + b)(a - b) = a 2 - b 2 (2x 2 + )( 2x 2 - ) = ( 2x 2 ) 2 - () 2 = 4x (a - b)(a + b) = a 2 - b 2 ( 9 - x ) (9 + x ) = (9) 2 - ( x ) 2 = 8 - x 6 9. (a - b)(a + b) = a 2 - b 2 (2x - 5y)(2x + 5y) = (2x) 2 - (5y) 2 = 4x 2-25y Area of big : (x + ) 2 = (x) 2 + 2(x)() + () 2 = x 2 + 6x + 9 Area of small : (x + ) 2 = (x) 2 + 2(x)() + () 2 = x 2 + 2x + Total area = area of big + area of small = (x 2 + 6x + 9) + (x 2 + 2x + ) = (x 2 + x 2 ) + (6x + 2x) + (9 + ) = 2x 2 + 8x + 0 The area of the figure is 2x 2 + 8x + 0. practice and problem solving 2. ( a + b) 2 = a 2 + 2ab + b 2 ( x + ) 2 = (x) 2 + 2(x)() + () 2 = x 2 + 6x Holt McDougal Algebra
22 22. ( a + b) 2 = a 2 + 2ab + b 2 (4 + z) 2 = (4) 2 + 2(4)(z) + (z) 2 = 6 + 8z + z 2 2. ( a + b) 2 = a 2 + 2ab + b 2 (x 2 + y 2 ) 2 = ( x 2 ) 2 + 2( x 2 ) (y 2 ) + (y 2 ) 2 = x 4 + 2x 2 y 2 + y ( a + b) 2 = a 2 + 2ab + b 2 (p + 2q ) 2 = (p) 2 + 2(p)(2q ) + (2q ) 2 = p 2 + 4pq + 4q ( a + b) 2 = a 2 + 2ab + b 2 (2 + x) 2 = (2) 2 + 2(2)(x) + (x) 2 = 4 + 2x + 9x ( a + b) 2 = a 2 + 2ab + b 2 (r 2 + 5t) 2 = ( r 2 ) 2 + 2( r 2 ) (5t) + (5t) 2 = r 4 + 0r 2 t + 25t ( a - b) 2 = a 2-2ab + b 2 ( s 2-7 ) 2 = ( s 2 ) 2-2( s 2 ) (7) + (7) 2 = s 4-4s ( a - b) 2 = a 2-2ab + b 2 ( 2c - d ) 2 = (2c) 2-2(2c)( d ) + ( d ) 2 = 4c 2-4cd + d ( a - b) 2 = a 2-2ab + b 2 ( a - 8) 2 = (a) 2-2(a)(8) + (8) 2 = a 2-6a ( a - b) 2 = a 2-2ab + b 2 (5 - w) 2 = (5) 2-2(5)(w) + (w) 2 = 25-0w + w 2. ( a - b) 2 = a 2-2ab + b 2 (x - 4) 2 = (x) 2-2(x)(4) + (4) 2 = 9x 2-24x ( a - b) 2 = a 2-2ab + b 2 ( - x 2 ) 2 = () 2-2()( x 2 ) + ( x 2 ) 2 = - 2x 2 + x 4. (a - b)(a + b) = a 2 - b 2 (a - 0)(a + 0) = (a) 2 - (0) 2 = a (a + b)(a - b) = a 2 - b 2 (y + 4)(y - 4) = (y) 2 - (4) 2 = y (a + b)(a - b) = a 2 - b 2 (7x + )(7x - ) = (7x) 2 - () 2 = 49x (a - b)(a + b) = a 2 - b 2 ( x 2-2 ) (x 2 + 2) = ( x 2 ) 2 - (2) 2 = x (a + b)(a - b) = a 2 - b 2 (5a 2 + 9)( 5a 2-9 ) = ( 5a 2 ) 2 - (9) 2 = 25a (a + b)(a - b) = a 2 - b 2 (x + y 2 )(x 2 - y 2 ) = ( x ) 2 - (y 2 ) 2 9. A = πr 2 = π(x + 4) 2 = x 6 - y 4 = π((x) 2 + 2(x)(4) + (4) 2 ) = π(x 2 + 8x + 6) = π( x 2 ) + π(8x) + π(6) = πx 2 + 8πx + 6π The area of the puzzle is πx 2 + 8πx + 6π. 40a. x > 2; values less than or equal to 2 cause the width of the rectangle to be zero or negative, which does not make sense. b. Area of : (x - ) 2 = (x) 2-2(x)() + () 2 = x 2-2x + Area of : x(x - 2) = x(x) + x(-2) = x 2-2x Since x 2-2x + > x 2-2x, the square has the greater area. c. Difference = area of - area of = (x 2-2x + ) - ( x 2-2x ) = (x 2-2x + ) + (-x 2 + 2x) = ( x 2 - x 2 ) + (-2x + 2x) + = The difference in area is square unit. 4. ( a + b) 2 = a 2 + 2ab + b 2 ( x + y) 2 = (x) 2 + 2(x)(y) + (y) 2 = x 2 + 2xy + y ( a - b) 2 = a 2-2ab + b 2 ( x - y) 2 = (x) 2-2(x)(y) + (y) 2 = x 2-2xy + y 2 4. (a + b)(a - b) = a 2 - b 2 (x 2 + 4)( x 2-4 ) = ( x 2 ) 2 - (4) 2 = x ( a + b) 2 = a 2 + 2ab + b 2 (x 2 + 4) 2 = ( x 2 ) 2 + 2( x 2 ) (4) + (4) 2 = x 4 + 8x ( a - b) 2 = a 2-2ab + b 2 ( x 2-4 ) 2 = ( x 2 ) 2-2( x 2 ) (4) + (4) 2 = x 4-8x ( a - b) 2 = a 2-2ab + b 2 ( - x) 2 = () 2-2()(x) + (x) 2 = - 2x + x 2 26 Holt McDougal Algebra
23 47. ( a + b) 2 = a 2 + 2ab + b 2 ( + x) 2 = () 2 + 2()(x) + (x) 2 = + 2x + x 2 6. Possible answer: The square of a difference is not the same as a difference of squares; a 2-2ab + b 2. 64a. 48. (a - b)(a + b) = a 2 - b 2 ( - x)( + x) = () 2 - (x) 2 = - x 2 x + x (a - b)(a - b) = a 2-2ab + b 2 ( x - a ) ( x - a ) = ( x ) 2-2( x ) ( a ) + ( a ) 2 = x 6-2x a + a ( a + b)(a + b) = a 2 + 2ab + b 2 (5 + n)(5 + n) = (5) 2 + 2(5)(n) + (n) 2 = n + n 2 5. (a - b)(a + b) = a 2 - b 2 (6a - 5b)(6a + 5b) = (6a) 2 - (5b) 2 = 6a 2-25b (a - b)(a - b) = a 2-2ab + b 2 ( r - 4t 4 ) ( r - 4t 4 ) = (r) 2-2(r) ( 4t 4 ) + ( 4t 4 ) 2 = r 2-8rt 4 + 6t 8 a b ( a - b) 2 a 2-2ab + b 2 4 ( - 4) 2 = 9 () 2-2()(4) + (4) 2 = (2-4) 2 = 4 (2) 2-2(2)(4) + (4) 2 = ( - 2) 2 = () 2-2()(2) + (2) 2 = a b ( a + b) 2 a 2 + 2ab + b ( + 4) 2 = 25 () 2 + 2()(4) + (4) 2 = (2 + 5) 2 = 49 (2) 2 + 2(2)(5) + (5) 2 = ( + 0) 2 = 9 () 2 + 2()(0) + (0) 2 = 9 a b (a + b)(a - b) a 2 - b ( + 4)( - 4) = -5 () 2 - (4) 2 = (2 + )(2 - ) = -5 (2) 2 - () 2 = ( + 2)( - 2) = 5 () 2 - (2) 2 = 5 6. a b = ( a + b) 2 - (a - b) = (5 + 24)2 - (5-24) 2 4 = (59)2 - () = 4 = _ 60 4 = Notice that: ( a - b) 2 = a 2-2ab - b 2 = 6x 2-24x + c Therefore, a 2 = 6x 2 = (4x) 2. So a = ±4x. Therefore, -24x = -2ab = -2(±4x)b = 8xb. -24x = 8xb _ -24x = 8xb _ 8x 8x ± = b So c = b 2 = (±) 2 = 9. b. A = lw = (x + )(x - ) = (x) 2 - () 2 = x 2-9 The area is represented by x 2-9. c. P = 2l + 2w 48 = 2(x + ) + 2(x - ) 48 = 2(x) + 2() + 2(x) + 2(-) 48 = 2x x = 2x + 2x = 4x 48 4 = 4x 4 2 = x A = x 2-9 = (2) 2-9 = 44-9 = 5 The area of the region is 5 ft For ax 2-49 to be a perfect square, ax 2 needs to be a perfect square. Therefore, a must be a perfect square. So all the possible values of a are all the perfect squares from to 00;, 4, 9, 6, 25, 6, 49, 64, 8, When one binomial is in the form a + b and the other is in the form a - b; (x + 2)(x - 2) = x 2-4. test prep 67. B (a - b)(a - b) = a 2-2ab + b 2 (5x - 6y)(5x - 6y) = (5x) 2-2(5x)(6y) + (6y) 2 = 25x 2-60xy + 6y J; The 25x 2 region means ±5x is squared. The 4 region means ±2 is squared. The two 0x regions mean that the product of ±5x and ±2 is positive, so the terms have the same sign. Therefore, it must be J. 69. D; If a = 0, then b = 2 from the first equation. Notice that (0) 2 - (2) 2 = 00-4 = 96, so a = 0, b = 2 is a solution to both equations. Therefore, a = H; Notice that (r + s) 2 = r 2 + 2rs + s 2 = 64. Since rs = 5, r 2 + 2(5) + s 2 = 64, or r 2 + s 2 = Holt McDougal Algebra
24 challenge and extend 7. (x + 4)(x + 4)(x - 4) = (( x) 2 + 2(x)(4) + (4) 2 )( x - 4) = (x 2 + 8x + 6)( x - 4) = (x - 4)(x 2 + 8x + 6) = x(x 2 + 8x + 6) - 4(x 2 + 8x + 6) = x( x 2 ) + x(8x) + x(6) - 4 ( x 2 ) - 4(8x) - 4(6) = x + 8x 2 + 6x - 4x 2-2x - 64 = x + 4x 2-6x (x + 4)(x - 4)(x - 4) = (( x) 2 - (4) 2 )( x - 4) = ( x 2-6 ) ( x - 4) = x 2 ( x) + x 2 ( -4) - 6(x) - 6(-4) = x - 4x 2-6x Let x 2 + bx + c = x 2 + bx + (± Ç c ) 2 since c = (± Ç c ) 2. x 2 + bx + (± Ç c ) 2 = (x± Ç c )(x± Ç c ) because the trinomial is a perfect square. (x± c Ç )(x± Ç c ) = x 2 ± 2 Ç c x + (± Ç c ) 2 by multiplication. Make the coefficients of x: b = ±2 Ç c. 74. Rewrite 27 as and 9 as = (2 + 4)(2-4) = (2) 2 - (4) 2 = = 5 ready to go on? Section B Quiz. 4r 2 + 2r 6 - r 2r 6 + 4r 2 - r The leading coefficient is y y + 2y -8y + y 2 + 2y + 7 The leading coefficient is t - 4t + t 4 t 4-2t - 4t The leading coefficient is. 4. n + + n 2 n 2 + n + The leading coefficient is x x + 2 The leading coefficient is. 6. -a a 7 + a a 7 - a 2 + a + 6 The leading coefficient is. 7. Degree: Terms: 2x + 5x - 4 is a cubic trinomial. 8. Degree: 2 Terms: 5b 2 is a quadratic monomial. 9. Degree: 4 Terms: 4 6p 2 + p - p 4 + 2p is a quartic polynomial. 0. Degree: 2 Terms: x x is a quadratic trinomial.. Degree: 7 Terms: 4-2x x - 2x 7 is a 7th-degree polynomial. 2. Degree: 4 Terms: 4 5-6b 2 + b - 4b 4 is a quartic polynomial.. C(x) = x - 5x + 4 C(900) = (900) - 5(900) + 4 = 729,000,000 -, = 728,986,54 The cost to manufacture 900 units is $728,986, (0m + 4m 2 ) + (7m 2 + m) = 0m + (4m 2 + 7m 2 ) + m = 0m + m 2 + m 5. ( t 2-2t ) + (9t 2 + 4t - 6) = (t 2 + 9t 2 ) + (-2t + 4t) + (-6) = 2t 2 + 2t ( 2d 6 - d 2 ) + (2d 4 + ) = 2d 6 + 2d 4 - d (6y + 4y 2 ) - (2y 2 + y) = (6y + 4y 2 ) + (-2y 2 - y) = 6y + (4y 2-2y 2 ) + (-y) = 6y + 2y 2 - y 8. ( 7n 2 - n ) - (5n 2 + 5n) = ( 7n 2 - n ) + ( -5n 2-5n ) = ( 7n 2-5n 2 ) + (-n - 5n) = 2n 2-8n 9. ( b 2-0 ) - (-5b + 4b) = ( b 2-0 ) + ( 5b - 4b ) = 5b + b 2-4b P = (2s + 4) + (4s 2 + ) + (5s) = 2s + 4s 2 + 5s + (4 + ) = 2s + 4s 2 + 5s h 5h 5 = (2 5)( h h 5 ) = 0h ab(5a + a 2 b) = 2ab( 5a ) + 2ab ( a 2 b ) 22. ( s 8 t 4 ) ( -6st ) = (-6)( s 8 s ) ( t 4 t ) = -6s 9 t 7 = (2 5)( a a ) ( b) + (2 ) ( a a 2 ) ( b b) = 0a 4 b + 6a b (k + 5) 2 = (k + 5)(k + 5) = k(k) + k(5) + 5(k) + 5(5) = 9k 2 + 5k + 5k + 25 = 9k 2 + 0k (2x + y)(4x 2 + y) = 2x ( 4x 2 ) + 2x ( y) + y ( 4x 2 ) + y(y) = 8x 5 + 2x y + 2x 2 y + y 2 28 Holt McDougal Algebra
Definitions 1. A factor of integer is an integer that will divide the given integer evenly (with no remainder).
 Math 50, Chapter 8 (Page 1 of 20) 8.1 Common Factors Definitions 1. A factor of integer is an integer that will divide the given integer evenly (with no remainder). Find all the factors of a. 44 b. 32
Math 50, Chapter 8 (Page 1 of 20) 8.1 Common Factors Definitions 1. A factor of integer is an integer that will divide the given integer evenly (with no remainder). Find all the factors of a. 44 b. 32
1.3 Polynomials and Factoring
 1.3 Polynomials and Factoring Polynomials Constant: a number, such as 5 or 27 Variable: a letter or symbol that represents a value. Term: a constant, variable, or the product or a constant and variable.
1.3 Polynomials and Factoring Polynomials Constant: a number, such as 5 or 27 Variable: a letter or symbol that represents a value. Term: a constant, variable, or the product or a constant and variable.
Polynomials. Key Terms. quadratic equation parabola conjugates trinomial. polynomial coefficient degree monomial binomial GCF
 Polynomials 5 5.1 Addition and Subtraction of Polynomials and Polynomial Functions 5.2 Multiplication of Polynomials 5.3 Division of Polynomials Problem Recognition Exercises Operations on Polynomials
Polynomials 5 5.1 Addition and Subtraction of Polynomials and Polynomial Functions 5.2 Multiplication of Polynomials 5.3 Division of Polynomials Problem Recognition Exercises Operations on Polynomials
Factoring Polynomials
 UNIT 11 Factoring Polynomials You can use polynomials to describe framing for art. 396 Unit 11 factoring polynomials A polynomial is an expression that has variables that represent numbers. A number can
UNIT 11 Factoring Polynomials You can use polynomials to describe framing for art. 396 Unit 11 factoring polynomials A polynomial is an expression that has variables that represent numbers. A number can
1.3 Algebraic Expressions
 1.3 Algebraic Expressions A polynomial is an expression of the form: a n x n + a n 1 x n 1 +... + a 2 x 2 + a 1 x + a 0 The numbers a 1, a 2,..., a n are called coefficients. Each of the separate parts,
1.3 Algebraic Expressions A polynomial is an expression of the form: a n x n + a n 1 x n 1 +... + a 2 x 2 + a 1 x + a 0 The numbers a 1, a 2,..., a n are called coefficients. Each of the separate parts,
How To Factor By Gcf In Algebra 1.5
 7-2 Factoring by GCF Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 1 Warm Up Simplify. 1. 2(w + 1) 2. 3x(x 2 4) 2w + 2 3x 3 12x Find the GCF of each pair of monomials. 3. 4h 2 and 6h 2h 4. 13p and 26p
7-2 Factoring by GCF Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 1 Warm Up Simplify. 1. 2(w + 1) 2. 3x(x 2 4) 2w + 2 3x 3 12x Find the GCF of each pair of monomials. 3. 4h 2 and 6h 2h 4. 13p and 26p
expression is written horizontally. The Last terms ((2)( 4)) because they are the last terms of the two polynomials. This is called the FOIL method.
 A polynomial of degree n (in one variable, with real coefficients) is an expression of the form: a n x n + a n 1 x n 1 + a n 2 x n 2 + + a 2 x 2 + a 1 x + a 0 where a n, a n 1, a n 2, a 2, a 1, a 0 are
A polynomial of degree n (in one variable, with real coefficients) is an expression of the form: a n x n + a n 1 x n 1 + a n 2 x n 2 + + a 2 x 2 + a 1 x + a 0 where a n, a n 1, a n 2, a 2, a 1, a 0 are
Operations with Algebraic Expressions: Multiplication of Polynomials
 Operations with Algebraic Expressions: Multiplication of Polynomials The product of a monomial x monomial To multiply a monomial times a monomial, multiply the coefficients and add the on powers with the
Operations with Algebraic Expressions: Multiplication of Polynomials The product of a monomial x monomial To multiply a monomial times a monomial, multiply the coefficients and add the on powers with the
Name Intro to Algebra 2. Unit 1: Polynomials and Factoring
 Name Intro to Algebra 2 Unit 1: Polynomials and Factoring Date Page Topic Homework 9/3 2 Polynomial Vocabulary No Homework 9/4 x In Class assignment None 9/5 3 Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Pg. 332
Name Intro to Algebra 2 Unit 1: Polynomials and Factoring Date Page Topic Homework 9/3 2 Polynomial Vocabulary No Homework 9/4 x In Class assignment None 9/5 3 Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Pg. 332
FACTORING POLYNOMIALS
 296 (5-40) Chapter 5 Exponents and Polynomials where a 2 is the area of the square base, b 2 is the area of the square top, and H is the distance from the base to the top. Find the volume of a truncated
296 (5-40) Chapter 5 Exponents and Polynomials where a 2 is the area of the square base, b 2 is the area of the square top, and H is the distance from the base to the top. Find the volume of a truncated
Alum Rock Elementary Union School District Algebra I Study Guide for Benchmark III
 Alum Rock Elementary Union School District Algebra I Study Guide for Benchmark III Name Date Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Algebra Standard 10.0 A polynomial is a sum of one ore more monomials. Polynomial
Alum Rock Elementary Union School District Algebra I Study Guide for Benchmark III Name Date Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Algebra Standard 10.0 A polynomial is a sum of one ore more monomials. Polynomial
Using the ac Method to Factor
 4.6 Using the ac Method to Factor 4.6 OBJECTIVES 1. Use the ac test to determine factorability 2. Use the results of the ac test 3. Completely factor a trinomial In Sections 4.2 and 4.3 we used the trial-and-error
4.6 Using the ac Method to Factor 4.6 OBJECTIVES 1. Use the ac test to determine factorability 2. Use the results of the ac test 3. Completely factor a trinomial In Sections 4.2 and 4.3 we used the trial-and-error
6.1 Add & Subtract Polynomial Expression & Functions
 6.1 Add & Subtract Polynomial Expression & Functions Objectives 1. Know the meaning of the words term, monomial, binomial, trinomial, polynomial, degree, coefficient, like terms, polynomial funciton, quardrtic
6.1 Add & Subtract Polynomial Expression & Functions Objectives 1. Know the meaning of the words term, monomial, binomial, trinomial, polynomial, degree, coefficient, like terms, polynomial funciton, quardrtic
FACTORING ax 2 bx c. Factoring Trinomials with Leading Coefficient 1
 5.7 Factoring ax 2 bx c (5-49) 305 5.7 FACTORING ax 2 bx c In this section In Section 5.5 you learned to factor certain special polynomials. In this section you will learn to factor general quadratic polynomials.
5.7 Factoring ax 2 bx c (5-49) 305 5.7 FACTORING ax 2 bx c In this section In Section 5.5 you learned to factor certain special polynomials. In this section you will learn to factor general quadratic polynomials.
15.1 Factoring Polynomials
 LESSON 15.1 Factoring Polynomials Use the structure of an expression to identify ways to rewrite it. Also A.SSE.3? ESSENTIAL QUESTION How can you use the greatest common factor to factor polynomials? EXPLORE
LESSON 15.1 Factoring Polynomials Use the structure of an expression to identify ways to rewrite it. Also A.SSE.3? ESSENTIAL QUESTION How can you use the greatest common factor to factor polynomials? EXPLORE
How To Solve Factoring Problems
 05-W4801-AM1.qxd 8/19/08 8:45 PM Page 241 Factoring, Solving Equations, and Problem Solving 5 5.1 Factoring by Using the Distributive Property 5.2 Factoring the Difference of Two Squares 5.3 Factoring
05-W4801-AM1.qxd 8/19/08 8:45 PM Page 241 Factoring, Solving Equations, and Problem Solving 5 5.1 Factoring by Using the Distributive Property 5.2 Factoring the Difference of Two Squares 5.3 Factoring
NSM100 Introduction to Algebra Chapter 5 Notes Factoring
 Section 5.1 Greatest Common Factor (GCF) and Factoring by Grouping Greatest Common Factor for a polynomial is the largest monomial that divides (is a factor of) each term of the polynomial. GCF is the
Section 5.1 Greatest Common Factor (GCF) and Factoring by Grouping Greatest Common Factor for a polynomial is the largest monomial that divides (is a factor of) each term of the polynomial. GCF is the
Factoring Quadratic Expressions
 Factoring the trinomial ax 2 + bx + c when a = 1 A trinomial in the form x 2 + bx + c can be factored to equal (x + m)(x + n) when the product of m x n equals c and the sum of m + n equals b. (Note: the
Factoring the trinomial ax 2 + bx + c when a = 1 A trinomial in the form x 2 + bx + c can be factored to equal (x + m)(x + n) when the product of m x n equals c and the sum of m + n equals b. (Note: the
By reversing the rules for multiplication of binomials from Section 4.6, we get rules for factoring polynomials in certain forms.
 SECTION 5.4 Special Factoring Techniques 317 5.4 Special Factoring Techniques OBJECTIVES 1 Factor a difference of squares. 2 Factor a perfect square trinomial. 3 Factor a difference of cubes. 4 Factor
SECTION 5.4 Special Factoring Techniques 317 5.4 Special Factoring Techniques OBJECTIVES 1 Factor a difference of squares. 2 Factor a perfect square trinomial. 3 Factor a difference of cubes. 4 Factor
Mathematics Placement
 Mathematics Placement The ACT COMPASS math test is a self-adaptive test, which potentially tests students within four different levels of math including pre-algebra, algebra, college algebra, and trigonometry.
Mathematics Placement The ACT COMPASS math test is a self-adaptive test, which potentially tests students within four different levels of math including pre-algebra, algebra, college algebra, and trigonometry.
Copy in your notebook: Add an example of each term with the symbols used in algebra 2 if there are any.
 Algebra 2 - Chapter Prerequisites Vocabulary Copy in your notebook: Add an example of each term with the symbols used in algebra 2 if there are any. P1 p. 1 1. counting(natural) numbers - {1,2,3,4,...}
Algebra 2 - Chapter Prerequisites Vocabulary Copy in your notebook: Add an example of each term with the symbols used in algebra 2 if there are any. P1 p. 1 1. counting(natural) numbers - {1,2,3,4,...}
( ) FACTORING. x In this polynomial the only variable in common to all is x.
 FACTORING Factoring is similar to breaking up a number into its multiples. For example, 10=5*. The multiples are 5 and. In a polynomial it is the same way, however, the procedure is somewhat more complicated
FACTORING Factoring is similar to breaking up a number into its multiples. For example, 10=5*. The multiples are 5 and. In a polynomial it is the same way, however, the procedure is somewhat more complicated
SPECIAL PRODUCTS AND FACTORS
 CHAPTER 442 11 CHAPTER TABLE OF CONTENTS 11-1 Factors and Factoring 11-2 Common Monomial Factors 11-3 The Square of a Monomial 11-4 Multiplying the Sum and the Difference of Two Terms 11-5 Factoring the
CHAPTER 442 11 CHAPTER TABLE OF CONTENTS 11-1 Factors and Factoring 11-2 Common Monomial Factors 11-3 The Square of a Monomial 11-4 Multiplying the Sum and the Difference of Two Terms 11-5 Factoring the
6.3 FACTORING ax 2 bx c WITH a 1
 290 (6 14) Chapter 6 Factoring e) What is the approximate maximum revenue? f) Use the accompanying graph to estimate the price at which the revenue is zero. y Revenue (thousands of dollars) 300 200 100
290 (6 14) Chapter 6 Factoring e) What is the approximate maximum revenue? f) Use the accompanying graph to estimate the price at which the revenue is zero. y Revenue (thousands of dollars) 300 200 100
Veterans Upward Bound Algebra I Concepts - Honors
 Veterans Upward Bound Algebra I Concepts - Honors Brenda Meery Kaitlyn Spong Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) www.ck12.org Chapter 6. Factoring CHAPTER
Veterans Upward Bound Algebra I Concepts - Honors Brenda Meery Kaitlyn Spong Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) www.ck12.org Chapter 6. Factoring CHAPTER
Tool 1. Greatest Common Factor (GCF)
 Chapter 4: Factoring Review Tool 1 Greatest Common Factor (GCF) This is a very important tool. You must try to factor out the GCF first in every problem. Some problems do not have a GCF but many do. When
Chapter 4: Factoring Review Tool 1 Greatest Common Factor (GCF) This is a very important tool. You must try to factor out the GCF first in every problem. Some problems do not have a GCF but many do. When
Factoring and Applications
 Factoring and Applications What is a factor? The Greatest Common Factor (GCF) To factor a number means to write it as a product (multiplication). Therefore, in the problem 48 3, 4 and 8 are called the
Factoring and Applications What is a factor? The Greatest Common Factor (GCF) To factor a number means to write it as a product (multiplication). Therefore, in the problem 48 3, 4 and 8 are called the
POLYNOMIALS and FACTORING
 POLYNOMIALS and FACTORING Exponents ( days); 1. Evaluate exponential expressions. Use the product rule for exponents, 1. How do you remember the rules for exponents?. How do you decide which rule to use
POLYNOMIALS and FACTORING Exponents ( days); 1. Evaluate exponential expressions. Use the product rule for exponents, 1. How do you remember the rules for exponents?. How do you decide which rule to use
Factor Polynomials Completely
 9.8 Factor Polynomials Completely Before You factored polynomials. Now You will factor polynomials completely. Why? So you can model the height of a projectile, as in Ex. 71. Key Vocabulary factor by grouping
9.8 Factor Polynomials Completely Before You factored polynomials. Now You will factor polynomials completely. Why? So you can model the height of a projectile, as in Ex. 71. Key Vocabulary factor by grouping
Factoring a Difference of Two Squares. Factoring a Difference of Two Squares
 284 (6 8) Chapter 6 Factoring 87. Tomato soup. The amount of metal S (in square inches) that it takes to make a can for tomato soup is a function of the radius r and height h: S 2 r 2 2 rh a) Rewrite this
284 (6 8) Chapter 6 Factoring 87. Tomato soup. The amount of metal S (in square inches) that it takes to make a can for tomato soup is a function of the radius r and height h: S 2 r 2 2 rh a) Rewrite this
Florida Math 0028. Correlation of the ALEKS course Florida Math 0028 to the Florida Mathematics Competencies - Upper
 Florida Math 0028 Correlation of the ALEKS course Florida Math 0028 to the Florida Mathematics Competencies - Upper Exponents & Polynomials MDECU1: Applies the order of operations to evaluate algebraic
Florida Math 0028 Correlation of the ALEKS course Florida Math 0028 to the Florida Mathematics Competencies - Upper Exponents & Polynomials MDECU1: Applies the order of operations to evaluate algebraic
Factoring Trinomials: The ac Method
 6.7 Factoring Trinomials: The ac Method 6.7 OBJECTIVES 1. Use the ac test to determine whether a trinomial is factorable over the integers 2. Use the results of the ac test to factor a trinomial 3. For
6.7 Factoring Trinomials: The ac Method 6.7 OBJECTIVES 1. Use the ac test to determine whether a trinomial is factorable over the integers 2. Use the results of the ac test to factor a trinomial 3. For
CM2202: Scientific Computing and Multimedia Applications General Maths: 2. Algebra - Factorisation
 CM2202: Scientific Computing and Multimedia Applications General Maths: 2. Algebra - Factorisation Prof. David Marshall School of Computer Science & Informatics Factorisation Factorisation is a way of
CM2202: Scientific Computing and Multimedia Applications General Maths: 2. Algebra - Factorisation Prof. David Marshall School of Computer Science & Informatics Factorisation Factorisation is a way of
Algebra 1 Chapter 08 review
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Algebra 1 Chapter 08 review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Simplify the difference. 1. (4w 2 4w 8) (2w 2 + 3w 6)
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Algebra 1 Chapter 08 review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Simplify the difference. 1. (4w 2 4w 8) (2w 2 + 3w 6)
MTH 092 College Algebra Essex County College Division of Mathematics Sample Review Questions 1 Created January 17, 2006
 MTH 092 College Algebra Essex County College Division of Mathematics Sample Review Questions Created January 7, 2006 Math 092, Elementary Algebra, covers the mathematical content listed below. In order
MTH 092 College Algebra Essex County College Division of Mathematics Sample Review Questions Created January 7, 2006 Math 092, Elementary Algebra, covers the mathematical content listed below. In order
Greatest Common Factor (GCF) Factoring
 Section 4 4: Greatest Common Factor (GCF) Factoring The last chapter introduced the distributive process. The distributive process takes a product of a monomial and a polynomial and changes the multiplication
Section 4 4: Greatest Common Factor (GCF) Factoring The last chapter introduced the distributive process. The distributive process takes a product of a monomial and a polynomial and changes the multiplication
MATH 90 CHAPTER 6 Name:.
 MATH 90 CHAPTER 6 Name:. 6.1 GCF and Factoring by Groups Need To Know Definitions How to factor by GCF How to factor by groups The Greatest Common Factor Factoring means to write a number as product. a
MATH 90 CHAPTER 6 Name:. 6.1 GCF and Factoring by Groups Need To Know Definitions How to factor by GCF How to factor by groups The Greatest Common Factor Factoring means to write a number as product. a
MATH 60 NOTEBOOK CERTIFICATIONS
 MATH 60 NOTEBOOK CERTIFICATIONS Chapter #1: Integers and Real Numbers 1.1a 1.1b 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.8 Chapter #2: Algebraic Expressions, Linear Equations, and Applications 2.1a 2.1b 2.1c 2.2 2.3a 2.3b 2.4 2.5
MATH 60 NOTEBOOK CERTIFICATIONS Chapter #1: Integers and Real Numbers 1.1a 1.1b 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.8 Chapter #2: Algebraic Expressions, Linear Equations, and Applications 2.1a 2.1b 2.1c 2.2 2.3a 2.3b 2.4 2.5
BEGINNING ALGEBRA ACKNOWLEDMENTS
 BEGINNING ALGEBRA The Nursing Department of Labouré College requested the Department of Academic Planning and Support Services to help with mathematics preparatory materials for its Bachelor of Science
BEGINNING ALGEBRA The Nursing Department of Labouré College requested the Department of Academic Planning and Support Services to help with mathematics preparatory materials for its Bachelor of Science
Polynomials and Factoring
 7.6 Polynomials and Factoring Basic Terminology A term, or monomial, is defined to be a number, a variable, or a product of numbers and variables. A polynomial is a term or a finite sum or difference of
7.6 Polynomials and Factoring Basic Terminology A term, or monomial, is defined to be a number, a variable, or a product of numbers and variables. A polynomial is a term or a finite sum or difference of
The Greatest Common Factor; Factoring by Grouping
 296 CHAPTER 5 Factoring and Applications 5.1 The Greatest Common Factor; Factoring by Grouping OBJECTIVES 1 Find the greatest common factor of a list of terms. 2 Factor out the greatest common factor.
296 CHAPTER 5 Factoring and Applications 5.1 The Greatest Common Factor; Factoring by Grouping OBJECTIVES 1 Find the greatest common factor of a list of terms. 2 Factor out the greatest common factor.
Math 10C. Course: Polynomial Products and Factors. Unit of Study: Step 1: Identify the Outcomes to Address. Guiding Questions:
 Course: Unit of Study: Math 10C Polynomial Products and Factors Step 1: Identify the Outcomes to Address Guiding Questions: What do I want my students to learn? What can they currently understand and do?
Course: Unit of Study: Math 10C Polynomial Products and Factors Step 1: Identify the Outcomes to Address Guiding Questions: What do I want my students to learn? What can they currently understand and do?
CAHSEE on Target UC Davis, School and University Partnerships
 UC Davis, School and University Partnerships CAHSEE on Target Mathematics Curriculum Published by The University of California, Davis, School/University Partnerships Program 006 Director Sarah R. Martinez,
UC Davis, School and University Partnerships CAHSEE on Target Mathematics Curriculum Published by The University of California, Davis, School/University Partnerships Program 006 Director Sarah R. Martinez,
FACTORING OUT COMMON FACTORS
 278 (6 2) Chapter 6 Factoring 6.1 FACTORING OUT COMMON FACTORS In this section Prime Factorization of Integers Greatest Common Factor Finding the Greatest Common Factor for Monomials Factoring Out the
278 (6 2) Chapter 6 Factoring 6.1 FACTORING OUT COMMON FACTORS In this section Prime Factorization of Integers Greatest Common Factor Finding the Greatest Common Factor for Monomials Factoring Out the
Factoring (pp. 1 of 4)
 Factoring (pp. 1 of 4) Algebra Review Try these items from middle school math. A) What numbers are the factors of 4? B) Write down the prime factorization of 7. C) 6 Simplify 48 using the greatest common
Factoring (pp. 1 of 4) Algebra Review Try these items from middle school math. A) What numbers are the factors of 4? B) Write down the prime factorization of 7. C) 6 Simplify 48 using the greatest common
MATH 10034 Fundamental Mathematics IV
 MATH 0034 Fundamental Mathematics IV http://www.math.kent.edu/ebooks/0034/funmath4.pdf Department of Mathematical Sciences Kent State University January 2, 2009 ii Contents To the Instructor v Polynomials.
MATH 0034 Fundamental Mathematics IV http://www.math.kent.edu/ebooks/0034/funmath4.pdf Department of Mathematical Sciences Kent State University January 2, 2009 ii Contents To the Instructor v Polynomials.
Algebra I Vocabulary Cards
 Algebra I Vocabulary Cards Table of Contents Expressions and Operations Natural Numbers Whole Numbers Integers Rational Numbers Irrational Numbers Real Numbers Absolute Value Order of Operations Expression
Algebra I Vocabulary Cards Table of Contents Expressions and Operations Natural Numbers Whole Numbers Integers Rational Numbers Irrational Numbers Real Numbers Absolute Value Order of Operations Expression
Higher Education Math Placement
 Higher Education Math Placement Placement Assessment Problem Types 1. Whole Numbers, Fractions, and Decimals 1.1 Operations with Whole Numbers Addition with carry Subtraction with borrowing Multiplication
Higher Education Math Placement Placement Assessment Problem Types 1. Whole Numbers, Fractions, and Decimals 1.1 Operations with Whole Numbers Addition with carry Subtraction with borrowing Multiplication
Math 0980 Chapter Objectives. Chapter 1: Introduction to Algebra: The Integers.
 Math 0980 Chapter Objectives Chapter 1: Introduction to Algebra: The Integers. 1. Identify the place value of a digit. 2. Write a number in words or digits. 3. Write positive and negative numbers used
Math 0980 Chapter Objectives Chapter 1: Introduction to Algebra: The Integers. 1. Identify the place value of a digit. 2. Write a number in words or digits. 3. Write positive and negative numbers used
Algebra Cheat Sheets
 Sheets Algebra Cheat Sheets provide you with a tool for teaching your students note-taking, problem-solving, and organizational skills in the context of algebra lessons. These sheets teach the concepts
Sheets Algebra Cheat Sheets provide you with a tool for teaching your students note-taking, problem-solving, and organizational skills in the context of algebra lessons. These sheets teach the concepts
Chapter R.4 Factoring Polynomials
 Chapter R.4 Factoring Polynomials Introduction to Factoring To factor an expression means to write the expression as a product of two or more factors. Sample Problem: Factor each expression. a. 15 b. x
Chapter R.4 Factoring Polynomials Introduction to Factoring To factor an expression means to write the expression as a product of two or more factors. Sample Problem: Factor each expression. a. 15 b. x
This is Factoring and Solving by Factoring, chapter 6 from the book Beginning Algebra (index.html) (v. 1.0).
 This is Factoring and Solving by Factoring, chapter 6 from the book Beginning Algebra (index.html) (v. 1.0). This book is licensed under a Creative Commons by-nc-sa 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/
This is Factoring and Solving by Factoring, chapter 6 from the book Beginning Algebra (index.html) (v. 1.0). This book is licensed under a Creative Commons by-nc-sa 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/
Factoring Trinomials of the Form x 2 bx c
 4.2 Factoring Trinomials of the Form x 2 bx c 4.2 OBJECTIVES 1. Factor a trinomial of the form x 2 bx c 2. Factor a trinomial containing a common factor NOTE The process used to factor here is frequently
4.2 Factoring Trinomials of the Form x 2 bx c 4.2 OBJECTIVES 1. Factor a trinomial of the form x 2 bx c 2. Factor a trinomial containing a common factor NOTE The process used to factor here is frequently
Factoring Special Polynomials
 6.6 Factoring Special Polynomials 6.6 OBJECTIVES 1. Factor the difference of two squares 2. Factor the sum or difference of two cubes In this section, we will look at several special polynomials. These
6.6 Factoring Special Polynomials 6.6 OBJECTIVES 1. Factor the difference of two squares 2. Factor the sum or difference of two cubes In this section, we will look at several special polynomials. These
The majority of college students hold credit cards. According to the Nellie May
 CHAPTER 6 Factoring Polynomials 6.1 The Greatest Common Factor and Factoring by Grouping 6. Factoring Trinomials of the Form b c 6.3 Factoring Trinomials of the Form a b c and Perfect Square Trinomials
CHAPTER 6 Factoring Polynomials 6.1 The Greatest Common Factor and Factoring by Grouping 6. Factoring Trinomials of the Form b c 6.3 Factoring Trinomials of the Form a b c and Perfect Square Trinomials
Simplifying Algebraic Fractions
 5. Simplifying Algebraic Fractions 5. OBJECTIVES. Find the GCF for two monomials and simplify a fraction 2. Find the GCF for two polynomials and simplify a fraction Much of our work with algebraic fractions
5. Simplifying Algebraic Fractions 5. OBJECTIVES. Find the GCF for two monomials and simplify a fraction 2. Find the GCF for two polynomials and simplify a fraction Much of our work with algebraic fractions
A Systematic Approach to Factoring
 A Systematic Approach to Factoring Step 1 Count the number of terms. (Remember****Knowing the number of terms will allow you to eliminate unnecessary tools.) Step 2 Is there a greatest common factor? Tool
A Systematic Approach to Factoring Step 1 Count the number of terms. (Remember****Knowing the number of terms will allow you to eliminate unnecessary tools.) Step 2 Is there a greatest common factor? Tool
Polynomial Equations and Factoring
 7 Polynomial Equations and Factoring 7.1 Adding and Subtracting Polynomials 7.2 Multiplying Polynomials 7.3 Special Products of Polynomials 7.4 Dividing Polynomials 7.5 Solving Polynomial Equations in
7 Polynomial Equations and Factoring 7.1 Adding and Subtracting Polynomials 7.2 Multiplying Polynomials 7.3 Special Products of Polynomials 7.4 Dividing Polynomials 7.5 Solving Polynomial Equations in
Answers to Basic Algebra Review
 Answers to Basic Algebra Review 1. -1.1 Follow the sign rules when adding and subtracting: If the numbers have the same sign, add them together and keep the sign. If the numbers have different signs, subtract
Answers to Basic Algebra Review 1. -1.1 Follow the sign rules when adding and subtracting: If the numbers have the same sign, add them together and keep the sign. If the numbers have different signs, subtract
5.1 FACTORING OUT COMMON FACTORS
 C H A P T E R 5 Factoring he sport of skydiving was born in the 1930s soon after the military began using parachutes as a means of deploying troops. T Today, skydiving is a popular sport around the world.
C H A P T E R 5 Factoring he sport of skydiving was born in the 1930s soon after the military began using parachutes as a means of deploying troops. T Today, skydiving is a popular sport around the world.
SUNY ECC. ACCUPLACER Preparation Workshop. Algebra Skills
 SUNY ECC ACCUPLACER Preparation Workshop Algebra Skills Gail A. Butler Ph.D. Evaluating Algebraic Epressions Substitute the value (#) in place of the letter (variable). Follow order of operations!!! E)
SUNY ECC ACCUPLACER Preparation Workshop Algebra Skills Gail A. Butler Ph.D. Evaluating Algebraic Epressions Substitute the value (#) in place of the letter (variable). Follow order of operations!!! E)
Factoring Flow Chart
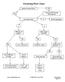 Factoring Flow Chart greatest common factor? YES NO factor out GCF leaving GCF(quotient) how many terms? 4+ factor by grouping 2 3 difference of squares? perfect square trinomial? YES YES NO NO a 2 -b
Factoring Flow Chart greatest common factor? YES NO factor out GCF leaving GCF(quotient) how many terms? 4+ factor by grouping 2 3 difference of squares? perfect square trinomial? YES YES NO NO a 2 -b
POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS
 POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS Polynomial Division.. 314 The Rational Zero Test.....317 Descarte s Rule of Signs... 319 The Remainder Theorem.....31 Finding all Zeros of a Polynomial Function.......33 Writing a
POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS Polynomial Division.. 314 The Rational Zero Test.....317 Descarte s Rule of Signs... 319 The Remainder Theorem.....31 Finding all Zeros of a Polynomial Function.......33 Writing a
Radicals - Multiply and Divide Radicals
 8. Radicals - Multiply and Divide Radicals Objective: Multiply and divide radicals using the product and quotient rules of radicals. Multiplying radicals is very simple if the index on all the radicals
8. Radicals - Multiply and Divide Radicals Objective: Multiply and divide radicals using the product and quotient rules of radicals. Multiplying radicals is very simple if the index on all the radicals
Algebra 2 PreAP. Name Period
 Algebra 2 PreAP Name Period IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS FOR STUDENTS!!! We understand that students come to Algebra II with different strengths and needs. For this reason, students have options for completing
Algebra 2 PreAP Name Period IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS FOR STUDENTS!!! We understand that students come to Algebra II with different strengths and needs. For this reason, students have options for completing
Factoring. Factoring Monomials Monomials can often be factored in more than one way.
 Factoring Factoring is the reverse of multiplying. When we multiplied monomials or polynomials together, we got a new monomial or a string of monomials that were added (or subtracted) together. For example,
Factoring Factoring is the reverse of multiplying. When we multiplied monomials or polynomials together, we got a new monomial or a string of monomials that were added (or subtracted) together. For example,
Big Bend Community College. Beginning Algebra MPC 095. Lab Notebook
 Big Bend Community College Beginning Algebra MPC 095 Lab Notebook Beginning Algebra Lab Notebook by Tyler Wallace is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License. Permissions beyond
Big Bend Community College Beginning Algebra MPC 095 Lab Notebook Beginning Algebra Lab Notebook by Tyler Wallace is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License. Permissions beyond
SECTION 0.6: POLYNOMIAL, RATIONAL, AND ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS
 (Section 0.6: Polynomial, Rational, and Algebraic Expressions) 0.6.1 SECTION 0.6: POLYNOMIAL, RATIONAL, AND ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES Be able to identify polynomial, rational, and algebraic
(Section 0.6: Polynomial, Rational, and Algebraic Expressions) 0.6.1 SECTION 0.6: POLYNOMIAL, RATIONAL, AND ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES Be able to identify polynomial, rational, and algebraic
Section 1. Finding Common Terms
 Worksheet 2.1 Factors of Algebraic Expressions Section 1 Finding Common Terms In worksheet 1.2 we talked about factors of whole numbers. Remember, if a b = ab then a is a factor of ab and b is a factor
Worksheet 2.1 Factors of Algebraic Expressions Section 1 Finding Common Terms In worksheet 1.2 we talked about factors of whole numbers. Remember, if a b = ab then a is a factor of ab and b is a factor
Answer Key for California State Standards: Algebra I
 Algebra I: Symbolic reasoning and calculations with symbols are central in algebra. Through the study of algebra, a student develops an understanding of the symbolic language of mathematics and the sciences.
Algebra I: Symbolic reasoning and calculations with symbols are central in algebra. Through the study of algebra, a student develops an understanding of the symbolic language of mathematics and the sciences.
Factors and Products
 CHAPTER 3 Factors and Products What You ll Learn use different strategies to find factors and multiples of whole numbers identify prime factors and write the prime factorization of a number find square
CHAPTER 3 Factors and Products What You ll Learn use different strategies to find factors and multiples of whole numbers identify prime factors and write the prime factorization of a number find square
Sect 6.7 - Solving Equations Using the Zero Product Rule
 Sect 6.7 - Solving Equations Using the Zero Product Rule 116 Concept #1: Definition of a Quadratic Equation A quadratic equation is an equation that can be written in the form ax 2 + bx + c = 0 (referred
Sect 6.7 - Solving Equations Using the Zero Product Rule 116 Concept #1: Definition of a Quadratic Equation A quadratic equation is an equation that can be written in the form ax 2 + bx + c = 0 (referred
10.1. Solving Quadratic Equations. Investigation: Rocket Science CONDENSED
 CONDENSED L E S S O N 10.1 Solving Quadratic Equations In this lesson you will look at quadratic functions that model projectile motion use tables and graphs to approimate solutions to quadratic equations
CONDENSED L E S S O N 10.1 Solving Quadratic Equations In this lesson you will look at quadratic functions that model projectile motion use tables and graphs to approimate solutions to quadratic equations
Factoring Polynomials and Solving Quadratic Equations
 Factoring Polynomials and Solving Quadratic Equations Math Tutorial Lab Special Topic Factoring Factoring Binomials Remember that a binomial is just a polynomial with two terms. Some examples include 2x+3
Factoring Polynomials and Solving Quadratic Equations Math Tutorial Lab Special Topic Factoring Factoring Binomials Remember that a binomial is just a polynomial with two terms. Some examples include 2x+3
Factoring Algebra- Chapter 8B Assignment Sheet
 Name: Factoring Algebra- Chapter 8B Assignment Sheet Date Section Learning Targets Assignment Tues 2/17 Find the prime factorization of an integer Find the greatest common factor (GCF) for a set of monomials.
Name: Factoring Algebra- Chapter 8B Assignment Sheet Date Section Learning Targets Assignment Tues 2/17 Find the prime factorization of an integer Find the greatest common factor (GCF) for a set of monomials.
In the above, the number 19 is an example of a number because its only positive factors are one and itself.
 Math 100 Greatest Common Factor and Factoring by Grouping (Review) Factoring Definition: A factor is a number, variable, monomial, or polynomial which is multiplied by another number, variable, monomial,
Math 100 Greatest Common Factor and Factoring by Grouping (Review) Factoring Definition: A factor is a number, variable, monomial, or polynomial which is multiplied by another number, variable, monomial,
Factoring - Greatest Common Factor
 6.1 Factoring - Greatest Common Factor Objective: Find the greatest common factor of a polynomial and factor it out of the expression. The opposite of multiplying polynomials together is factoring polynomials.
6.1 Factoring - Greatest Common Factor Objective: Find the greatest common factor of a polynomial and factor it out of the expression. The opposite of multiplying polynomials together is factoring polynomials.
Polynomials and Factoring; More on Probability
 Polynomials and Factoring; More on Probability Melissa Kramer, (MelissaK) Anne Gloag, (AnneG) Andrew Gloag, (AndrewG) Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required)
Polynomials and Factoring; More on Probability Melissa Kramer, (MelissaK) Anne Gloag, (AnneG) Andrew Gloag, (AndrewG) Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required)
Factoring Polynomials
 Factoring Polynomials 8A Factoring Methods 8-1 Factors and Greatest Common Factors Lab Model Factoring 8-2 Factoring by GCF Lab Model Factorization of Trinomials 8-3 Factoring x 2 + bx + c 8-4 Factoring
Factoring Polynomials 8A Factoring Methods 8-1 Factors and Greatest Common Factors Lab Model Factoring 8-2 Factoring by GCF Lab Model Factorization of Trinomials 8-3 Factoring x 2 + bx + c 8-4 Factoring
SIMPLIFYING SQUARE ROOTS
 40 (8-8) Chapter 8 Powers and Roots 8. SIMPLIFYING SQUARE ROOTS In this section Using the Product Rule Rationalizing the Denominator Simplified Form of a Square Root In Section 8. you learned to simplify
40 (8-8) Chapter 8 Powers and Roots 8. SIMPLIFYING SQUARE ROOTS In this section Using the Product Rule Rationalizing the Denominator Simplified Form of a Square Root In Section 8. you learned to simplify
Negative Integer Exponents
 7.7 Negative Integer Exponents 7.7 OBJECTIVES. Define the zero exponent 2. Use the definition of a negative exponent to simplify an expression 3. Use the properties of exponents to simplify expressions
7.7 Negative Integer Exponents 7.7 OBJECTIVES. Define the zero exponent 2. Use the definition of a negative exponent to simplify an expression 3. Use the properties of exponents to simplify expressions
Radicals - Rationalize Denominators
 8. Radicals - Rationalize Denominators Objective: Rationalize the denominators of radical expressions. It is considered bad practice to have a radical in the denominator of a fraction. When this happens
8. Radicals - Rationalize Denominators Objective: Rationalize the denominators of radical expressions. It is considered bad practice to have a radical in the denominator of a fraction. When this happens
Factoring Polynomials
 Factoring Polynomials 4-1-2014 The opposite of multiplying polynomials is factoring. Why would you want to factor a polynomial? Let p(x) be a polynomial. p(c) = 0 is equivalent to x c dividing p(x). Recall
Factoring Polynomials 4-1-2014 The opposite of multiplying polynomials is factoring. Why would you want to factor a polynomial? Let p(x) be a polynomial. p(c) = 0 is equivalent to x c dividing p(x). Recall
6706_PM10SB_C4_CO_pp192-193.qxd 5/8/09 9:53 AM Page 192 192 NEL
 92 NEL Chapter 4 Factoring Algebraic Epressions GOALS You will be able to Determine the greatest common factor in an algebraic epression and use it to write the epression as a product Recognize different
92 NEL Chapter 4 Factoring Algebraic Epressions GOALS You will be able to Determine the greatest common factor in an algebraic epression and use it to write the epression as a product Recognize different
SOL Warm-Up Graphing Calculator Active
 A.2a (a) Using laws of exponents to simplify monomial expressions and ratios of monomial expressions 1. Which expression is equivalent to (5x 2 )(4x 5 )? A 9x 7 B 9x 10 C 20x 7 D 20x 10 2. Which expression
A.2a (a) Using laws of exponents to simplify monomial expressions and ratios of monomial expressions 1. Which expression is equivalent to (5x 2 )(4x 5 )? A 9x 7 B 9x 10 C 20x 7 D 20x 10 2. Which expression
7-6. Choosing a Factoring Model. Extension: Factoring Polynomials with More Than One Variable IN T RO DUC E T EACH. Standards for Mathematical Content
 7-6 Choosing a Factoring Model Extension: Factoring Polynomials with More Than One Variable Essential question: How can you factor polynomials with more than one variable? What is the connection between
7-6 Choosing a Factoring Model Extension: Factoring Polynomials with More Than One Variable Essential question: How can you factor polynomials with more than one variable? What is the connection between
Exponents and Radicals
 Exponents and Radicals (a + b) 10 Exponents are a very important part of algebra. An exponent is just a convenient way of writing repeated multiplications of the same number. Radicals involve the use of
Exponents and Radicals (a + b) 10 Exponents are a very important part of algebra. An exponent is just a convenient way of writing repeated multiplications of the same number. Radicals involve the use of
AIP Factoring Practice/Help
 The following pages include many problems to practice factoring skills. There are also several activities with examples to help you with factoring if you feel like you are not proficient with it. There
The following pages include many problems to practice factoring skills. There are also several activities with examples to help you with factoring if you feel like you are not proficient with it. There
1.1 Practice Worksheet
 Math 1 MPS Instructor: Cheryl Jaeger Balm 1 1.1 Practice Worksheet 1. Write each English phrase as a mathematical expression. (a) Three less than twice a number (b) Four more than half of a number (c)
Math 1 MPS Instructor: Cheryl Jaeger Balm 1 1.1 Practice Worksheet 1. Write each English phrase as a mathematical expression. (a) Three less than twice a number (b) Four more than half of a number (c)
Factoring Guidelines. Greatest Common Factor Two Terms Three Terms Four Terms. 2008 Shirley Radai
 Factoring Guidelines Greatest Common Factor Two Terms Three Terms Four Terms 008 Shirley Radai Greatest Common Factor 008 Shirley Radai Factoring by Finding the Greatest Common Factor Always check for
Factoring Guidelines Greatest Common Factor Two Terms Three Terms Four Terms 008 Shirley Radai Greatest Common Factor 008 Shirley Radai Factoring by Finding the Greatest Common Factor Always check for
Factoring. 472 Chapter 9 Factoring
 Factoring Lesson 9- Find the prime factorizations of integers and monomials. Lesson 9- Find the greatest common factors (GCF) for sets of integers and monomials. Lessons 9-2 through 9-6 Factor polynomials.
Factoring Lesson 9- Find the prime factorizations of integers and monomials. Lesson 9- Find the greatest common factors (GCF) for sets of integers and monomials. Lessons 9-2 through 9-6 Factor polynomials.
Vocabulary Words and Definitions for Algebra
 Name: Period: Vocabulary Words and s for Algebra Absolute Value Additive Inverse Algebraic Expression Ascending Order Associative Property Axis of Symmetry Base Binomial Coefficient Combine Like Terms
Name: Period: Vocabulary Words and s for Algebra Absolute Value Additive Inverse Algebraic Expression Ascending Order Associative Property Axis of Symmetry Base Binomial Coefficient Combine Like Terms
ALGEBRA 2: 4.1 Graph Quadratic Functions in Standard Form
 ALGEBRA 2: 4.1 Graph Quadratic Functions in Standard Form Goal Graph quadratic functions. VOCABULARY Quadratic function A function that can be written in the standard form y = ax 2 + bx+ c where a 0 Parabola
ALGEBRA 2: 4.1 Graph Quadratic Functions in Standard Form Goal Graph quadratic functions. VOCABULARY Quadratic function A function that can be written in the standard form y = ax 2 + bx+ c where a 0 Parabola
Factoring Polynomials
 Factoring Polynomials Factoring Factoring is the process of writing a polynomial as the product of two or more polynomials. The factors of 6x 2 x 2 are 2x + 1 and 3x 2. In this section, we will be factoring
Factoring Polynomials Factoring Factoring is the process of writing a polynomial as the product of two or more polynomials. The factors of 6x 2 x 2 are 2x + 1 and 3x 2. In this section, we will be factoring
Chapter 5. Rational Expressions
 5.. Simplify Rational Expressions KYOTE Standards: CR ; CA 7 Chapter 5. Rational Expressions Definition. A rational expression is the quotient P Q of two polynomials P and Q in one or more variables, where
5.. Simplify Rational Expressions KYOTE Standards: CR ; CA 7 Chapter 5. Rational Expressions Definition. A rational expression is the quotient P Q of two polynomials P and Q in one or more variables, where
Factoring Methods. Example 1: 2x + 2 2 * x + 2 * 1 2(x + 1)
 Factoring Methods When you are trying to factor a polynomial, there are three general steps you want to follow: 1. See if there is a Greatest Common Factor 2. See if you can Factor by Grouping 3. See if
Factoring Methods When you are trying to factor a polynomial, there are three general steps you want to follow: 1. See if there is a Greatest Common Factor 2. See if you can Factor by Grouping 3. See if
A Quick Algebra Review
 1. Simplifying Epressions. Solving Equations 3. Problem Solving 4. Inequalities 5. Absolute Values 6. Linear Equations 7. Systems of Equations 8. Laws of Eponents 9. Quadratics 10. Rationals 11. Radicals
1. Simplifying Epressions. Solving Equations 3. Problem Solving 4. Inequalities 5. Absolute Values 6. Linear Equations 7. Systems of Equations 8. Laws of Eponents 9. Quadratics 10. Rationals 11. Radicals
3.1. RATIONAL EXPRESSIONS
 3.1. RATIONAL EXPRESSIONS RATIONAL NUMBERS In previous courses you have learned how to operate (do addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division) on rational numbers (fractions). Rational numbers
3.1. RATIONAL EXPRESSIONS RATIONAL NUMBERS In previous courses you have learned how to operate (do addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division) on rational numbers (fractions). Rational numbers
