World Humanities. Background Reading:The Beginnings of Civilization, 10, B.C.E. I CAN...
|
|
|
- Hector Bailey
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 World Humanities Background Reading:The Beginnings of Civilization, 10, B.C.E. I CAN... Explain the link between the Neolithic food-producing revolution and the emergence of civilizations. Identify the causes that transformed early communities in southwest Asia into the first cities, kingdoms, and empires. Describe how civilization took shape along the Nile River in Egypt. Discuss the impact of food production and metallurgy on the first human populations of Europe. KEY IDEAS The development of food production through agriculture and the domestication of animals led to the development of large settlements and the emergence of powerful elites. In southwest Asia and Egypt, civilizations arose that were based on cities, and devoted their resources to irrigation, warfare, and worship. Long-distance trade was an important feature of these early civilizations, as was the development of writing. As the case of Europe in this era illustrates, the development of civilization did not happen everywhere at the same time. I. DEFINING CIVILIZATION, DEFINING WESTERN CIVILIZATION Culture is used by anthropologists to refer to all the different ways in which humans collectively adjust to their environment, and transmit experiences and knowledge to their descendants. Culture is best understood as a web of interconnected meanings that allows a particular group of people to understand themselves and their place in the world, and each culture is distinctive. Culture, then, is distinct from civilization, which is defined as a city-based society in which there are differing occupations and levels of wealth wherein elites exercise economic, political, and religious power. A. Making Civilization Possible: The Food-Producing Revolution The first modern humans supported themselves by gathering wild foods. After the Ice Age ended, humans slowly discovered how to increase their food supply by planting crops and domesticating animals. As a result, the human population increased, and food surpluses allowed for economic specialization and exchange, and fostered the growth of social, political, and religious hierarchies. B. The First Food-Producing Communities Archaeological excavations of Neolithic sites in three areas of southwest Asia give evidence of the development of agriculture beginning around 8000 B.C.E. As a result, there developed in these areas increasingly complex forms of political organization and religious observance, as well as longdistance trade.
2 C. Transformations in Europe Europe lagged in developing a Neolithic culture, widespread only by about 2500 B.C.E. Metallurgy, using copper, reached the Balkans by about 4500 B.C.E. and the use of the plow by about 2600 B.C.E. Monumental building in Europe resulted in megaliths that marked burial sites, from about 4000 B.C.E. Stonehenge is the best example. By 1600 B.C.E., Europe had achieved some, but not all of the requirements for civilization. II. MESOPOTAMIA: KINGDOMS, EMPIRES, AND CONQUESTS Southwest Asia played a special role in history by standing at the crossroads of Africa, Asia and Europe, and as being considered the birthplace of civilization. A. The Sumerian Kingdoms About 5300 B.C.E., a dynamic civilization that would last for 3,000 years began to emerge from the villages, and later cities, of Sumer (or southern Mesopotamia). In learning to control the waters of the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers to irrigate crops, the Sumerians developed the foundation of civilization: the city. By 2500 B.C.E., 12 cities dominated Sumer. Providing markets and encouraging craft specialists, Sumerian cities were important economic centers, in which centralized authorities directed labor and economic activity: a redistributive economy. In the earliest period, temple priests held central authority, acting for the god or goddess that owned all of the city-state s lands and resources. Later, kings dominated, possibly coming to power through their role as war leaders in periods of expansion. Long-distance trade and a fostered diplomacy helped to maintain a coherent Sumerian culture as well as to increase Sumerians knowledge of foreign peoples. B. The Akkadian Empire of Sargon the Great With their conquest by the Akkadian king Sargon, the Sumerian cities found themselves part of a new kind of political entity: the empire. Controlling a large empire presented new challenges, including new organizational methods. Akkadian kings tried to ensure loyalty by portraying themselves as semi-divine figures, and met the problem of financing an empire through various means, one of the most important of which was taxing trade. Thus, long-distance trade held great importance for these kings, and the cities of Mesopotamia prospered. Two military innovations helped create and maintain the Akkadian empire: the composite bow and the chariot. Nonetheless, Akkadian rule collapsed around 2250 B.C.E. C. The Ur III Dynasty and the Rise of Assyria After the fall of the Akkadian Empire, the Sumerian city-states regained their autonomy. Around 2100 B.C.E., they were again subjects of an empire. The empire of Sargon was replaced by a powerful dynasty centered in the city of Ur. Ur s kings centralized both government and economic production, but their most important innovation came in the area of law, by establishing the custom of collecting and writing down laws. Ur, however, collapsed about 2000 B.C.E., with the Amorite invasion. D. Assyria and Babylonia Another period ensued, in which city-states squabbled for domination. In this period, strong central control of the economy lapsed, and some individuals traded for themselves. As an example, Assyrian merchants traded throughout Anatolia. Profits and risks were both high, and the Assyria flourished. Further south, the kingdom of Babylon expanded under Hammurabi. Dominating Mesopotamia, Hammurabi issued a law code that covered every aspect of economic life. Taxation was high, and Hammurabi s death was followed by a revolt. His empire was lost by 1650.
3 E. Cultural Continuities: The Transmission of Mesopotamian Cultures 1. THE MESOPOTAMIAN WORLD VIEW: RELIGION The deification of unreliable natural forces was central to Mesopotamian beliefs. In their polytheistic religion, Enlil, Enki, Marduk and Inanna were the most important deities. The priests, as intermediaries, had a key role, presiding over the temples of the ziggurats. An example is the ziggurat of Ur, built by Ur-Nammu for the city-states chief deity. 1. THE MESOPOTAMIAN WORLDVIEW: SCIENCE? Divination was widely used, reading the natural world for messages from the unseen world. The use of divination in Mesopotamia can be termed a proto-science for it was systematic, and deductive. In astronomy and mathematics, this proto-scientific mentality led to such ideas as square and cube roots, exponents, the 360-degree circle, and the base-ten system. 2. THE DEVELOPMENT OF WRITING The need to keep accurate records led to the earliest writing by about 4000 B.C.E. in Uruk, and the cuneiform system by about 3200 B.C.E. Scribes were important to leaders, and the use of cuneiform spread. 3. THE EPIC OF GILGAMESH The story of the historical king of Uruk, Gilgamesh, was worked into a popular legend. The Epic of Gilgamesh comes to us in Akkadian, but it pre-dates the Akkadian Empire, and had a wide influence in the Middle East. 4. LAW AND ORDER Sumerian law codes the most famous being that of Hammurabi are dated to at least 2350 B.C.E. Though they are tricky to use as historical sources, they do reveal the preoccupations of their times. For example Hammurabi s code makes class distinctions clear. The code also discusses family matters in detail, and reveals the patriarchy of Babylonian society. The harshness of some of the punishments called for sometimes distracts us from the fact that such codes established the precedent for the Western tradition of a punishment that should fit the crime. III. EGYPT: THE EMPIRE OF THE NILE Egyptian civilization was built on the narrow strip of fertile land along the Nile River. Largely isolated from other areas by deserts, Egypt enjoyed stability. Its history is divided into Predynastic, Early Dynastic and three Old Kingdom periods, separated by intermediate periods of destabilization. A. Egypt s Rise to Empire Like Mesopotamian civilization, that of Egypt moved from hunter-gatherer societies, through a period of small villages, then small towns, by 3500 B.C.E. A common culture developed by 3000 B.C.E., unified by communications along the Nile River, and organized politically into Upper and Lower Egypt. 1. THE KINGS AND THE GODS IN THE OLD KINGDOM Egyptian kings established themselves as religious, social, and political focal points. The story of the struggle between Seth and Osiris embodied the centrality of the Nile, the basis for monarchy, and the Egyptian concept of world order. The king only later pharaoh was the incarnation of the god Horus, who restored order after the destruction of Osiris. The ruler thus
4 established ma at a term which means right order, truth, justice and was responsible for maintaining the cosmic order. Egyptian religion was polytheistic, but imbued with a greater sense of order. For Egyptians, religion might be practiced at home, to household gods, or on the state level, where the worship of such gods (such as the sun god Re) were part of a stable, cyclical nature in their world. 2. THE PYRAMIDS The first pyramids were massive royal temples, part of the Egyptian focus on the afterlife. Later pyramids, such as the Great Pyramid of Giza, dated to around 2600 B.C.E., were also tombs. The process of building the pyramids could be a long-running project, involving tens of thousands of workers. 3. THE SOCIAL AND POLITICAL ORDER IN THE OLD KINGDOM The king and his family, though at the summit of Egyptian society, were constrained by the need to preserve ma at, through precise rituals. The Egyptian nobility were important in the kingdom s redistributive economy. The need to keep exact records led to the development of hieroglyphic writing. The rest of society was divided into artisans, peasants, and slaves. Egyptian women could buy and sell property, and were considered equal to their husbands in marriage. 4. WHERE IS MA AT? THE COLLAPSE OF THE OLD KINGDOM The Old Kingdom was brought down around 2200 B.C.E., presumably because of drought and resulting famine. In the First Intermediate Period that followed, Egyptian culture experienced a heightened sense of uncertainty, and the afterlife became more important. 5. THE MIDDLE KINGDOM, CA B.C.E. The Middle Kingdom was begun by Mentuhotep II ( B.C.E.), and was centered on Thebes. In this period, the king was less omnipotent, and the nobility gained in power. For most, assuring their place in eternity became a troubling preoccupation, to be helped by the use of scarabs. 6. ENCOUNTERS WITH OTHER CIVILIZATIONS Egypt wanted to protect its international trade and was willing to use force if necessary, but preferred to use diplomacy and friendship when possible. Trade with Nubia now Sudan was particularly important, and was protected by a system of forts that protected the flow of gold and ivory into Egypt. Peoples from surrounding lands moved into Egypt, merging with and invigorating Egyptian culture. Near the end of the Middle Kingdom, political order in Canaan broke down, and the Canaanites became more aggressive towards neighboring lands. The Second Intermediate Period resulted in Egypt. The Hyksos one of these Canaanite groups established rule over Egypt by about 1650 B.C.E. Largely assimilated into Egyptian culture, they nevertheless brought innovation as well. Most importantly, the Hyksos introduced the use of bronze and the light chariot. The use of the chariot fostered the growth of empires in Egypt and throughout the
5 region. The Late Bronze Age, from about 1500 B.C.E., was a period of greater international contact and instability. B. The New Kingdom: The Egyptian Empire in the Late Bronze Age With the expulsion of the Hyksos around 1550 B.C.E., King Ahmose I began the New Kingdom. This period saw the expansion of Egypt far into Asia, and the first use of the title pharaoh. 1. BUILDING AN EMPIRE: MILITARY CONQUEST AND THE TERRITORIAL EXPANSION A conscription of one in ten villagers created a large standing army. The idea that only in Egypt did order reign provided an ideological basis for conquest. Thutmose I conquered southern Palestine. Thutmose III conquered the entire coastline, controlling Cannan, which was valued for its natural resources and its trading connections. To the south, Egypt again controlled Nubia, reinforcing its hold by encouraging colonization. 2. KEEPING AN EMPIRE: ADMINISTRATIVE AND DIPLOMATIC INNOVATION Sophisticated bureaucratic methods helped to maintain the empire won by force. The vizier and regional administrators ran the kingdom. Using the lure of trading privileges, the pharaohs used diplomacy to maintain their empire. 3. CONTINUITY IN THE NEW KINGDOM As in the earlier periods, a redistributive economy was overseen by the government and temples. Monumental building continued: most notably the Great Temple of Abu Simbel, built by Ramesses II. The status of women was maintained, with some women holding priesthoods. 4. CHANGE IN THE NEW KINGDOM Although female rulers had not been unknown in Egyptian history, the reign of Hatshepsut was unusual. She ruled as a male pharaoh, even to the extent of generally being depicted as a man. Her son, Thutmose III, had evidence of her reign erased, perhaps in an attempt to reassert ma at. Later in the New Kingdom, Amenhotep IV took the name Akhenaten, and declared the deified sun disc the only god. The Amarna Period was initiated by Akhenaten when the capital was moved to a new site, Amarna, to signal a more complete break. Historians disagree whether this was true monotheism, or an attempt to return to Old Kingdom worship. After Akhenaten s death, the court returned to Memphis, and the successor, Tutankhamun, returned to traditional worship. In the twelfth century B.C.E., Egypt again experienced a period of disruption, which was shared by the entire Middle East. IV. CONCLUSION: CIVILIZATION AND THE WEST By 3000 B.C.E., civilization had not yet developed in Europe, but had developed in Mesopotamia and Egypt. Europe the West would eventually claim these Near Eastern civilizations as remote ancestors, from whom the West inherited such crucial components as systems of writing and the idea of law codes based on abstract principles.
Mesopotamia is the first known civilization. Mesopotamia means land between two rivers. This civilization began on the plains between the Tigris and
 Mesopotamia Review Mesopotamia is the first known civilization. Mesopotamia means land between two rivers. This civilization began on the plains between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers. This curving strip
Mesopotamia Review Mesopotamia is the first known civilization. Mesopotamia means land between two rivers. This civilization began on the plains between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers. This curving strip
Four Early River Valley Civilizations. Egyptian Civilization - Nile River
 Four Early River Valley Civilizations Egyptian Civilization - Nile River Early River Valley Civilizations Egyptian Civilization - Nile River I. GEOGRAPHY A. The Nile Egypt on the Nile 1. Egypt s settlements
Four Early River Valley Civilizations Egyptian Civilization - Nile River Early River Valley Civilizations Egyptian Civilization - Nile River I. GEOGRAPHY A. The Nile Egypt on the Nile 1. Egypt s settlements
Egyptian History 101 By Vickie Chao
 Egyptian History 101 By Vickie Chao 1 A long time ago, before Egypt was a united country, there were two kingdoms -- Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt. Upper Egypt was in the south. It controlled the areas along
Egyptian History 101 By Vickie Chao 1 A long time ago, before Egypt was a united country, there were two kingdoms -- Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt. Upper Egypt was in the south. It controlled the areas along
Period #1: Technological and Environmental Transformations, c. 8,000 B.C.E. - 600 B.C.E. Study Guide by Key Concepts
 Note: the question numbers are my own customization, and do NOT reflect official College Board designation. Ask yourself the question in the left column. Your answer should come close to the middle column.
Note: the question numbers are my own customization, and do NOT reflect official College Board designation. Ask yourself the question in the left column. Your answer should come close to the middle column.
AP World History Class Notes, Bentley Brief Edition Ch 1 The Foundations of Complex Societies September 14, 2010
 This first chapter of Traditions and Encounters sets the stage for the drama of world history by tracing the development of humans from their earliest appearance on earth through the rise of important
This first chapter of Traditions and Encounters sets the stage for the drama of world history by tracing the development of humans from their earliest appearance on earth through the rise of important
Year 2 History: Ancient Egypt Resource Pack
 Year 2 History: Ancient Egypt Resource Pack This pack includes the following lessons: Locating Egypt The River Nile Archeology Hieroglyphics Pharaohs Every effort has been made to seek permission for the
Year 2 History: Ancient Egypt Resource Pack This pack includes the following lessons: Locating Egypt The River Nile Archeology Hieroglyphics Pharaohs Every effort has been made to seek permission for the
7 WHERE AND WHY DID THE FIRST CITIES APPEAR?
 7 WHERE AND WHY DID THE FIRST CITIES APPEAR? In this three-part video David Christian explains how the rise of agriculture led to the formation of the world s first large-scale civilizations. Fueled by
7 WHERE AND WHY DID THE FIRST CITIES APPEAR? In this three-part video David Christian explains how the rise of agriculture led to the formation of the world s first large-scale civilizations. Fueled by
The Rise of Civilizations
 Page 1 of 6 The Rise of Civilizations Thousands of years ago, several societies in different parts of the world changed from hunting and gathering to farming. Some began to produce surpluses of food. Those
Page 1 of 6 The Rise of Civilizations Thousands of years ago, several societies in different parts of the world changed from hunting and gathering to farming. Some began to produce surpluses of food. Those
Egypt. The Old Kingdom
 Egypt The Old Kingdom Vocabulary: Narmer (Menes)- King that united Upper and Lower Egypt Old Kingdom Began around 2600BC, rise of Egyptian cities as centers for religion and government Artisans- someone
Egypt The Old Kingdom Vocabulary: Narmer (Menes)- King that united Upper and Lower Egypt Old Kingdom Began around 2600BC, rise of Egyptian cities as centers for religion and government Artisans- someone
Timeline of Egyptian History. Ancient Egypt (Languages: Egyptian written in hieroglyphics and Hieratic script)
 Timeline of Egyptian History 1 Ancient Egypt (Languages: Egyptian written in hieroglyphics and Hieratic script) Timeline of Egyptian History 2 Early Dynastic Period 3100 2686 BCE 1 st & 2 nd Dynasty Narmer
Timeline of Egyptian History 1 Ancient Egypt (Languages: Egyptian written in hieroglyphics and Hieratic script) Timeline of Egyptian History 2 Early Dynastic Period 3100 2686 BCE 1 st & 2 nd Dynasty Narmer
Lesson 2 Life in Ancient Egypt
 Lesson 2 Life in Ancient Egypt MAIN IDEAS Economics Egyptians developed a complex society with many different jobs and social roles. Science and Technology Egyptians made advances in calendars, geometry,
Lesson 2 Life in Ancient Egypt MAIN IDEAS Economics Egyptians developed a complex society with many different jobs and social roles. Science and Technology Egyptians made advances in calendars, geometry,
In this chapter, you will learn about the African kingdom of Kush. Kush was located on the Nile River, to the south of Egypt.
 Name: Date: Period: Lesson 10 - The Kingdom of Kush Section 1 - Introduction In this chapter, you will learn about the African kingdom of Kush. Kush was located on the Nile River, to the south of Egypt.
Name: Date: Period: Lesson 10 - The Kingdom of Kush Section 1 - Introduction In this chapter, you will learn about the African kingdom of Kush. Kush was located on the Nile River, to the south of Egypt.
EARLIEST CIVILIZATIONS. Egypt and the Kingdom of Kush
 PART I Chapter 2 EARLIEST CIVILIZATIONS Egypt and the Kingdom of Kush I. The First and Second Dynasties (3100 2686 B.C.) II. 1. The natural barriers of deserts and sea insulated Egypt from invading armies
PART I Chapter 2 EARLIEST CIVILIZATIONS Egypt and the Kingdom of Kush I. The First and Second Dynasties (3100 2686 B.C.) II. 1. The natural barriers of deserts and sea insulated Egypt from invading armies
Sources for the War of Reunification at the end of the Second Intermediate Period
 Sources for the War of Reunification at the end of the Second Intermediate Period Archaeological: body of Seqenenre-Taa campaign palace (?) at Deir el Ballas remarkably little else destruction layers at
Sources for the War of Reunification at the end of the Second Intermediate Period Archaeological: body of Seqenenre-Taa campaign palace (?) at Deir el Ballas remarkably little else destruction layers at
PYRAMID CFE 3284V. OPEN CAPTIONED PBS VIDEO 1988 Grade Levels: 9-13+ 57 minutes 1 Instructional Graphic Enclosed
 PYRAMID CFE 3284V OPEN CAPTIONED PBS VIDEO 1988 Grade Levels: 9-13+ 57 minutes 1 Instructional Graphic Enclosed DESCRIPTION Burial practices and beliefs, such as the building of pyramids, mummification,
PYRAMID CFE 3284V OPEN CAPTIONED PBS VIDEO 1988 Grade Levels: 9-13+ 57 minutes 1 Instructional Graphic Enclosed DESCRIPTION Burial practices and beliefs, such as the building of pyramids, mummification,
SOCIAL STUDIES UNIT OUTLINES - SIXTH GRADE
 SOCIAL STUDIES UNIT OUTLINES - SIXTH GRADE In sixth grade, students are ready to deepen their understanding of the Earth and its peoples through the study of history, geography, politics, culture, and
SOCIAL STUDIES UNIT OUTLINES - SIXTH GRADE In sixth grade, students are ready to deepen their understanding of the Earth and its peoples through the study of history, geography, politics, culture, and
Woolooware High School YEAR 7 EGYPT HOMEWORK NAME: CLASS: TEACHER: HOMEWORK #
 Woolooware High School YEAR 7 EGYPT HOMEWORK NAME: CLASS: TEACHER: HOMEWORK # H0MEWORK # I THE RIVER NILE The river Nile is one of the world's great rivers. It begins its long journey in Africa, as two
Woolooware High School YEAR 7 EGYPT HOMEWORK NAME: CLASS: TEACHER: HOMEWORK # H0MEWORK # I THE RIVER NILE The river Nile is one of the world's great rivers. It begins its long journey in Africa, as two
CH10 Practice Test 2015
 Name Date Mastering the Content Circle the letter next to the best answer. CH10 Practice Test 2015 1. An important way historians learn about ancient Kush is through A. Syrian trade agreements. B. Sumerian
Name Date Mastering the Content Circle the letter next to the best answer. CH10 Practice Test 2015 1. An important way historians learn about ancient Kush is through A. Syrian trade agreements. B. Sumerian
Ancient Egypt and Kush. Topic 3 Presentation
 Ancient Egypt and Kush Topic 3 Presentation Egyptian Civilization: The Gift of the Nile The Egyptian Nile surpasses all the rivers of the world in sweetness of taste, in length of course and usefulness.
Ancient Egypt and Kush Topic 3 Presentation Egyptian Civilization: The Gift of the Nile The Egyptian Nile surpasses all the rivers of the world in sweetness of taste, in length of course and usefulness.
Unit 4 Lesson 8 The Qin and Han Dynasties
 Unit 4 Lesson 8 The Qin and Han Dynasties Directions Read the False statements below. Replace each underlined word with one from the word bank that makes each sentence True. Word Bank Ying Zheng army copper
Unit 4 Lesson 8 The Qin and Han Dynasties Directions Read the False statements below. Replace each underlined word with one from the word bank that makes each sentence True. Word Bank Ying Zheng army copper
Ancient Egypt Handouts
 Ancient Egypt Handouts Map of Egypt Lower Egypt Upper Egypt Ancient Egypt 1 Map of Egypt-Answer Sheet 30ºE 40ºE 50ºN Mediterranean Sea 40ºN Africa Alexandria Rosetta Giza Memphis Sinai Pen. Middle East
Ancient Egypt Handouts Map of Egypt Lower Egypt Upper Egypt Ancient Egypt 1 Map of Egypt-Answer Sheet 30ºE 40ºE 50ºN Mediterranean Sea 40ºN Africa Alexandria Rosetta Giza Memphis Sinai Pen. Middle East
The history of Egypt is divided into dynasties of rulers. What is a dynasty? A succession of rulers from the same family or line is called a Dynasty.
 1 The history of Egypt is divided into dynasties of rulers What is a dynasty? A succession of rulers from the same family or line is called a Dynasty. 2 3 Predynasty: c.3100 2649 BC Major Events: Unification
1 The history of Egypt is divided into dynasties of rulers What is a dynasty? A succession of rulers from the same family or line is called a Dynasty. 2 3 Predynasty: c.3100 2649 BC Major Events: Unification
Government of Ancient Egypt Question Packet
 Government of Ancient Egypt Question Packet Your group will research Ancient Egyptian culture focusing on the Government of Ancient Egypt. Assign jobs to group members. Everyone must have a job. Research
Government of Ancient Egypt Question Packet Your group will research Ancient Egyptian culture focusing on the Government of Ancient Egypt. Assign jobs to group members. Everyone must have a job. Research
AFRICAN KINGDOMS. Ghana. Around AD 800 the rulers of many farming villages united to create the kingdom of Ghana.
 AFRICAN KINGDOMS In Africa, towns soon became part of an important trade network. Gold and salt were the most important products traded. People needed salt in their diets to prevent dehydration. There
AFRICAN KINGDOMS In Africa, towns soon became part of an important trade network. Gold and salt were the most important products traded. People needed salt in their diets to prevent dehydration. There
SSWH3 THE STUDENT WILL EXAMINE THE POLITICAL, PHILOSOPHICAL, AND CULTURAL INTERACTION OF CLASSICAL MEDITERRANEAN SOCIETIES FROM 700 BCE TO 400 CE.
 SSWH3 THE STUDENT WILL EXAMINE THE POLITICAL, PHILOSOPHICAL, AND CULTURAL INTERACTION OF CLASSICAL MEDITERRANEAN SOCIETIES FROM 700 BCE TO 400 CE. A. COMPARE THE ORIGINS AND STRUCTURE OF THE GREEK POLIS,
SSWH3 THE STUDENT WILL EXAMINE THE POLITICAL, PHILOSOPHICAL, AND CULTURAL INTERACTION OF CLASSICAL MEDITERRANEAN SOCIETIES FROM 700 BCE TO 400 CE. A. COMPARE THE ORIGINS AND STRUCTURE OF THE GREEK POLIS,
Human Heritage A World History 2006
 Academic Content Standards Social Studies Minnesota Arizona Human Heritage A World History 2006 STANDARDS Strand 2: World History Concept 1: Research Skills for History PO 1. Construct charts, graphs,
Academic Content Standards Social Studies Minnesota Arizona Human Heritage A World History 2006 STANDARDS Strand 2: World History Concept 1: Research Skills for History PO 1. Construct charts, graphs,
READING 1. Family and Household in Ancient Egypt. Patriarchy
 READING 1 Candice Goucher, Charles LeGuin, and Linda Walton, Ordering the World: Family and Household, in In the Balance: Themes in Global History (Boston: McGraw-Hill, 1998), 301 5. Abstract: This essay
READING 1 Candice Goucher, Charles LeGuin, and Linda Walton, Ordering the World: Family and Household, in In the Balance: Themes in Global History (Boston: McGraw-Hill, 1998), 301 5. Abstract: This essay
AP World History 2015-2016 Essay #1 (Ancient Civilizations) Textbook
 AP World History 2015-2016 Essay #1 (Ancient Civilizations) Textbook Mesopotamia left column Egypt right column Mesopotamian Geography An arc of land curves from the Persian Gulf to the eastern Mediterranean
AP World History 2015-2016 Essay #1 (Ancient Civilizations) Textbook Mesopotamia left column Egypt right column Mesopotamian Geography An arc of land curves from the Persian Gulf to the eastern Mediterranean
Exploring Four Empires of Mesopotamia
 Exploring Four Empires of Mesopotamia This timeline shows four empires that ruled Mesopotamia during a period of almost 1800 years. This timeline shows four empires that ruled Mesopotamia during a period
Exploring Four Empires of Mesopotamia This timeline shows four empires that ruled Mesopotamia during a period of almost 1800 years. This timeline shows four empires that ruled Mesopotamia during a period
The Neolithic Revolution
 The Neolithic Revolution The archaeologist took out his small brush and carefully removed the remaining dirt from the fragment of human skull. To help him reconstruct the life of the ancient human, he
The Neolithic Revolution The archaeologist took out his small brush and carefully removed the remaining dirt from the fragment of human skull. To help him reconstruct the life of the ancient human, he
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS. Christine H. Salcito, Director of Curriculum and Instruction Tiffany Lynch, Program Supervisor of Literacy.
 CURRICULUM FOR SOCIAL STUDIES GRADE 6 This curriculum is part of the Educational Program of Studies of the Rahway Public Schools. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS Christine H. Salcito, Director of Curriculum and Instruction
CURRICULUM FOR SOCIAL STUDIES GRADE 6 This curriculum is part of the Educational Program of Studies of the Rahway Public Schools. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS Christine H. Salcito, Director of Curriculum and Instruction
WHI.03: Early River Valley Civilizations
 WHI.03: Early River Valley Civilizations In this space, you will create a visual representation of what you have learned in the notes that follow on pages 18-32. You will be graded on your use of space,
WHI.03: Early River Valley Civilizations In this space, you will create a visual representation of what you have learned in the notes that follow on pages 18-32. You will be graded on your use of space,
Natural Advantages 2/21/2012. Lecture 9: Pre-Dynastic Egypt
 Lecture 9: Pre-Dynastic Egypt HIST 213 Spring 2012 750 miles long Natural Advantages Transportation (both ways) rich soil (450/sq. mi.) annual flooding (silt) simple irrigation systems relatively unified
Lecture 9: Pre-Dynastic Egypt HIST 213 Spring 2012 750 miles long Natural Advantages Transportation (both ways) rich soil (450/sq. mi.) annual flooding (silt) simple irrigation systems relatively unified
In this chapter, you will visit ancient Egypt. You will meet four leaders, called pharaohs.
 Name: Date: Period: Lesson 8 - The Ancient Egyptian Pharaohs Section 1 - Introduction In this chapter, you will visit ancient Egypt. You will meet four leaders, called pharaohs. In 1922, archaeologists
Name: Date: Period: Lesson 8 - The Ancient Egyptian Pharaohs Section 1 - Introduction In this chapter, you will visit ancient Egypt. You will meet four leaders, called pharaohs. In 1922, archaeologists
Egypt Unit Project Topics (Newspaper Articles & Visual Presentations)
 Egypt Projects 1 Egypt Unit Project Topics (Newspaper Articles & Visual Presentations) Your project topic is meant to be used for a newspaper article. Every student will write 1 newspaper article. Each
Egypt Projects 1 Egypt Unit Project Topics (Newspaper Articles & Visual Presentations) Your project topic is meant to be used for a newspaper article. Every student will write 1 newspaper article. Each
THE WEST Encounters and Transformations
 INSTRUCTOR S MANUAL to accompany Levack/Muir/Veldman/Maas THE WEST Encounters and Transformations Second Edition Sharon Arnoult Midwestern State University New York Boston San Francisco London Toronto
INSTRUCTOR S MANUAL to accompany Levack/Muir/Veldman/Maas THE WEST Encounters and Transformations Second Edition Sharon Arnoult Midwestern State University New York Boston San Francisco London Toronto
Teacher s Masters California Education and the Environment Initiative. History-Social Science Standards 6.2.6. and 6.2.8. Egypt and Kush: A Tale of
 6 Teacher s Masters California Education and the Environment Initiative History-Social Science Standards 6.2.6. and 6.2.8. Egypt and Kush: A Tale of Two Kingdoms California Education and the Environment
6 Teacher s Masters California Education and the Environment Initiative History-Social Science Standards 6.2.6. and 6.2.8. Egypt and Kush: A Tale of Two Kingdoms California Education and the Environment
What the Ancients Knew The Egyptians Teacher s Guide
 What the Ancients Knew The Egyptians Grade Level: 6 8 Curriculum Focus: Social Studies Lesson Duration: 5 class periods Program Description What the Ancients Knew: The Egyptians The earliest Egyptians
What the Ancients Knew The Egyptians Grade Level: 6 8 Curriculum Focus: Social Studies Lesson Duration: 5 class periods Program Description What the Ancients Knew: The Egyptians The earliest Egyptians
Jainism Jainism also began in India; religion teaches ahimsa nonviolence - Jains believe all living things have souls and should not be hurt
 Lesson 3 Buddhism and India s Golden Age MAIN IDEAS Belief System A teacher called the Buddha developed a new religion that focused on helping people to escape suffering. Government The Maurya rulers united
Lesson 3 Buddhism and India s Golden Age MAIN IDEAS Belief System A teacher called the Buddha developed a new religion that focused on helping people to escape suffering. Government The Maurya rulers united
Africa Before the Slave Trade
 Africa Before the Slave Trade Overview of African Kingdoms Ghana and Songhai Ghana (Wagadu) is the earliest known empire of the western Sudan, came into the history books around the eighth century but
Africa Before the Slave Trade Overview of African Kingdoms Ghana and Songhai Ghana (Wagadu) is the earliest known empire of the western Sudan, came into the history books around the eighth century but
WORKSHEET PHARAOHS, PYRAMIDS AND THE WORLD OF THE GODS
 WORKSHEET PHARAOHS, PYRAMIDS AND THE WORLD OF THE GODS 2 1. THE PHARAOH The word pharaoh comes from Egyptian and means great house. The term was used along with the five royal names of the king. The pharaohs
WORKSHEET PHARAOHS, PYRAMIDS AND THE WORLD OF THE GODS 2 1. THE PHARAOH The word pharaoh comes from Egyptian and means great house. The term was used along with the five royal names of the king. The pharaohs
7 URUK CIVILIZATION 950L
 7 URUK CIVILIZATION 950L URUK THE WORLD S FIRST BIG CITY By Cynthia Stokes Brown, adapted by Newsela Between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, the soil was rich and easy to farm. It is there that the world
7 URUK CIVILIZATION 950L URUK THE WORLD S FIRST BIG CITY By Cynthia Stokes Brown, adapted by Newsela Between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, the soil was rich and easy to farm. It is there that the world
Emergence of Civilizations / Anthro 341: Notes 17 Egypt: Naqada III and Early Dynastic Copyright Bruce Owen 2009
 Emergence of Civilizations / Anthro 341: Notes 17 Egypt: Naqada III and Early Dynastic Copyright Bruce Owen 2009 Naqada III (roughly 3200-3050 BC): the last century of the Predynastic period Contemporary
Emergence of Civilizations / Anthro 341: Notes 17 Egypt: Naqada III and Early Dynastic Copyright Bruce Owen 2009 Naqada III (roughly 3200-3050 BC): the last century of the Predynastic period Contemporary
Chorus OUR DEAR QUEEN IT IS HER DESTINY TO RULE THIS POWERFUL KINGDON
 1 You can download the songs and song sheet by going to: www.southlandsings.org/rendon Rendon Characters: - Nadia Her Husband Thutmose II- Chance Nephew- Fernando Slaves/servants Guards/military Advisors
1 You can download the songs and song sheet by going to: www.southlandsings.org/rendon Rendon Characters: - Nadia Her Husband Thutmose II- Chance Nephew- Fernando Slaves/servants Guards/military Advisors
Chapter 3. Ancient Egypt & Nubia
 Chapter 3 Ancient Egypt & Nubia Section 1 The Geography of the Nile The longest river in the world is - The Nile River - Flows north East Africa to Mediterranean Sea - Over 4,000 miles long (more than
Chapter 3 Ancient Egypt & Nubia Section 1 The Geography of the Nile The longest river in the world is - The Nile River - Flows north East Africa to Mediterranean Sea - Over 4,000 miles long (more than
An Overview of Western Civilization
 The Six Major Periods of Western Civilization (BCE = BC; CE = AD) 1. Mesopotamia, Egypt, & Hebrews (3000-500 BCE) 2. Ancient Greece (1200-200 BCE) 3. Ancient Rome (753 BCE - 476 CE) -----------------------------------------------------------------
The Six Major Periods of Western Civilization (BCE = BC; CE = AD) 1. Mesopotamia, Egypt, & Hebrews (3000-500 BCE) 2. Ancient Greece (1200-200 BCE) 3. Ancient Rome (753 BCE - 476 CE) -----------------------------------------------------------------
The Role of Women in Ancient Egypt
 Princess with offerings The role, contribution and influence women played in ancient Egyptian society extended well beyond their daily life and into the afterlife, with letters to the dead imploring help
Princess with offerings The role, contribution and influence women played in ancient Egyptian society extended well beyond their daily life and into the afterlife, with letters to the dead imploring help
DRAW CONCLUSIONS As you read, draw conclusions about the importance of the Nile River to life in Egypt. Focus Skill
 Lesson 1 PAGES 116 121 OBJECTIVES Evaluate the impact of the Nile River on life in ancient Egypt. Analyze the relationship between nature and the religion of the ancient Egyptians. Examine how the peoples
Lesson 1 PAGES 116 121 OBJECTIVES Evaluate the impact of the Nile River on life in ancient Egypt. Analyze the relationship between nature and the religion of the ancient Egyptians. Examine how the peoples
EARLY CIVILIZATIONS IN THE EASTERN HEMISPHERE. Reading study guide
 EARLY CIVILIZATIONS IN THE EASTERN HEMISPHERE Reading study guide Table of contents introduction to EARLY CIVILIZATIONS IN THE EASTERN HEMISPHERE.. 3 CHAPTER 1. ANCIENT Mesopotamia. 4 CHAPTER 2. ANCIENT
EARLY CIVILIZATIONS IN THE EASTERN HEMISPHERE Reading study guide Table of contents introduction to EARLY CIVILIZATIONS IN THE EASTERN HEMISPHERE.. 3 CHAPTER 1. ANCIENT Mesopotamia. 4 CHAPTER 2. ANCIENT
Unit 01 - Study Questions 1. In what ways did geography and climate affect the development of human society? 2. What were the economic and social
 Unit 01 - Study Questions 1. In what ways did geography and climate affect the development of human society? 2. What were the economic and social results of the agricultural revolution? 3. What are the
Unit 01 - Study Questions 1. In what ways did geography and climate affect the development of human society? 2. What were the economic and social results of the agricultural revolution? 3. What are the
GRADE. World History: Societies of the Past 2 CLUSTER. Early Societies of Mesopotamia, Egypt, or the Indus Valley
 Wld Histy: Societies of the Past Early Societies of Mesopotamia, Egypt, the Indus Valley Early Societies of Mesopotamia, Egypt, the Indus Valley Cluster Learning Experiences: Overview..1 Overview of Early
Wld Histy: Societies of the Past Early Societies of Mesopotamia, Egypt, the Indus Valley Early Societies of Mesopotamia, Egypt, the Indus Valley Cluster Learning Experiences: Overview..1 Overview of Early
Ancestral Africa and the African Diaspora. James Robinson, MA
 Ancestral Africa and the African Diaspora James Robinson, MA Modern Africa Africa is a vast place, over three times the size of the USA, with climates ranging from desert to temperate to equatorial. Master
Ancestral Africa and the African Diaspora James Robinson, MA Modern Africa Africa is a vast place, over three times the size of the USA, with climates ranging from desert to temperate to equatorial. Master
WORLD HISTORY AND GEOGRAPHY: ANCIENT CIVILIZATIONS
 WORLD HISTORY AND GEOGRAPHY: ANCIENT CIVILIZATIONS Students in grade six expand their understanding of history by studying the people and events that ushered in the dawn of the major Western and non- Western
WORLD HISTORY AND GEOGRAPHY: ANCIENT CIVILIZATIONS Students in grade six expand their understanding of history by studying the people and events that ushered in the dawn of the major Western and non- Western
West Africa: Bantu Migration and the Stainless Society
 West Africa: Bantu Migration and the Stainless Society Bantu Migration Around 1500 BCE farmers of the Niger and Benue River valleys in West Africa began migrating south and east, bringing with them their
West Africa: Bantu Migration and the Stainless Society Bantu Migration Around 1500 BCE farmers of the Niger and Benue River valleys in West Africa began migrating south and east, bringing with them their
CHINA OVERVIEW: A BRIEF HISTORY OF CHINESE DYNASTIES. Student Handouts, Inc.
 CHINA OVERVIEW: A BRIEF HISTORY OF CHINESE DYNASTIES Student Handouts, Inc. GEOGRAPHY OF CHINA Larger than the United States Climate varies North Temperate and cold South Subtropical Erosion Floods and
CHINA OVERVIEW: A BRIEF HISTORY OF CHINESE DYNASTIES Student Handouts, Inc. GEOGRAPHY OF CHINA Larger than the United States Climate varies North Temperate and cold South Subtropical Erosion Floods and
Ancient China. Military Stamp/Seal. The Qin and Han Dynasties
 Ancient China The Qin and Han Dynasties Military Stamp/Seal http://history.cultural-china.com/chinawh/images/exbig_images/c03bc44c62df55844b6ebc96427e0f5f.jpg Qin Shi Huangdi 246BCE - Warring States Period
Ancient China The Qin and Han Dynasties Military Stamp/Seal http://history.cultural-china.com/chinawh/images/exbig_images/c03bc44c62df55844b6ebc96427e0f5f.jpg Qin Shi Huangdi 246BCE - Warring States Period
Ancient Egypt and Kush
 CHAPTER 4 4500 BC AD 400 Ancient Egypt and Kush Essential Question How was the success of the Egyptian civilization tied to the Nile River? What You Will Learn... In this chapter you will learn about two
CHAPTER 4 4500 BC AD 400 Ancient Egypt and Kush Essential Question How was the success of the Egyptian civilization tied to the Nile River? What You Will Learn... In this chapter you will learn about two
Bible and Spade 15.2 (2002) 35-38 [text only] Copyright 2002 by Bible and Spade. Cited with permission. Joseph in Egypt Second of Six Parts
![Bible and Spade 15.2 (2002) 35-38 [text only] Copyright 2002 by Bible and Spade. Cited with permission. Joseph in Egypt Second of Six Parts Bible and Spade 15.2 (2002) 35-38 [text only] Copyright 2002 by Bible and Spade. Cited with permission. Joseph in Egypt Second of Six Parts](/thumbs/40/21010519.jpg) Bible and Spade 15.2 (2002) 35-38 [text only] Copyright 2002 by Bible and Spade. Cited with permission. Joseph in Egypt Second of Six Parts 1 By Charles Aling Joseph began life in Egypt as a slave (Gn
Bible and Spade 15.2 (2002) 35-38 [text only] Copyright 2002 by Bible and Spade. Cited with permission. Joseph in Egypt Second of Six Parts 1 By Charles Aling Joseph began life in Egypt as a slave (Gn
Ancient China: The Qin and Han Dynasties**
 Name Period Date Ancient China: The Qin and Han Dynasties** 246BCE - Warring States Period Zhou Dynasty has almost no power in China Qin Shi Huangdi comes to power in 246BCE as king of state of Qin Conquers
Name Period Date Ancient China: The Qin and Han Dynasties** 246BCE - Warring States Period Zhou Dynasty has almost no power in China Qin Shi Huangdi comes to power in 246BCE as king of state of Qin Conquers
Ghana: A West African Trading Empire
 Ghana: A West African Trading Empire The kingdom of Ghana lasted from 500 C.E. to the 11 th century C.E. The kingdom arose from the Sahel of Africa and spread to the valley between the Senegal and Niger
Ghana: A West African Trading Empire The kingdom of Ghana lasted from 500 C.E. to the 11 th century C.E. The kingdom arose from the Sahel of Africa and spread to the valley between the Senegal and Niger
Students will: Explain how ancient Egypt was united. Analyze the workings of government and the importance of religion in Egypt.
 Ancient Egypt Unit Name: Lisa Nash Grade Level: 6 Lesson Topic: The Kingdoms of Egypt Day 02, 03, & 04 of 14 Teacher s Initials: Date: November 10, 11, & 12, 2003 Instructional Goals Students will: Explain
Ancient Egypt Unit Name: Lisa Nash Grade Level: 6 Lesson Topic: The Kingdoms of Egypt Day 02, 03, & 04 of 14 Teacher s Initials: Date: November 10, 11, & 12, 2003 Instructional Goals Students will: Explain
Ninth Grade History & Social Science World History I
 SEPTEMBER WHI.1 Historical Research and Geographical Analysis *(ongoing throughout year) identify, analyze, and interpret primary and secondary sources use maps, globes, artifacts, pictures identify major
SEPTEMBER WHI.1 Historical Research and Geographical Analysis *(ongoing throughout year) identify, analyze, and interpret primary and secondary sources use maps, globes, artifacts, pictures identify major
The Sudanic African Empires: Ghana / Mali / Songhay & The Swahili City States of East Africa
 The Sudanic African Empires: Ghana / Mali / Songhay & The Swahili City States of East Africa AP World History Mr. Blankenship Ghana Mali Songhay Swahili States The Kingdom of Ghana emerged c. 5 th century
The Sudanic African Empires: Ghana / Mali / Songhay & The Swahili City States of East Africa AP World History Mr. Blankenship Ghana Mali Songhay Swahili States The Kingdom of Ghana emerged c. 5 th century
2015.16 Seventh Grade, Social Studies, Quarter 1
 2015.16 Seventh Grade, Social Studies, Quarter 1 The Fall and Legacy of Rome and the Early Modern World Civilizations of Africa, China, and the Islamic World: Students analyze the legacy of the Roman Empire
2015.16 Seventh Grade, Social Studies, Quarter 1 The Fall and Legacy of Rome and the Early Modern World Civilizations of Africa, China, and the Islamic World: Students analyze the legacy of the Roman Empire
Y OHANNIS ANCIENT EGYPT. Pharaohs and Dynasties
 Y OHANNIS ANCIENT EGYPT Pharaohs and Dynasties Predynastic Dynasty Zozer Mastaba: 2600 Hieroglyphics: 2680 3000 Archaic 3000-2700 1-2 Old Kingdom 2700-2119 2500 3-10 First Intermediate Middle Kingdom 2119-1550
Y OHANNIS ANCIENT EGYPT Pharaohs and Dynasties Predynastic Dynasty Zozer Mastaba: 2600 Hieroglyphics: 2680 3000 Archaic 3000-2700 1-2 Old Kingdom 2700-2119 2500 3-10 First Intermediate Middle Kingdom 2119-1550
The Origins and Impacts of the Persian Empire
 The Origins and Impacts of the Persian Empire The origin of the Persian Empire can be attributed to the leadership of one man Cyrus the Great. A brilliant and powerful Persian king, Cyrus strategy for
The Origins and Impacts of the Persian Empire The origin of the Persian Empire can be attributed to the leadership of one man Cyrus the Great. A brilliant and powerful Persian king, Cyrus strategy for
ARCHAEO-PRO SAMPLE QUESTION SHEET
 ARCHAEO-PRO SAMPLE QUESTION SHEET 1. Case 11 The Royal Graves of Ur What animal is mounted on the top of the rein ring? How old are the Royal Cemetery burials? Why do you think the excavator believed these
ARCHAEO-PRO SAMPLE QUESTION SHEET 1. Case 11 The Royal Graves of Ur What animal is mounted on the top of the rein ring? How old are the Royal Cemetery burials? Why do you think the excavator believed these
GLOBAL REGENTS REVIEW PACKET NUMBER THREE - PAGE 1 of 19 THIS IS GLOBAL REGENTS REVIEW PACKET NUMBER THREE CHARACTERISTICS (ELEMENTS) OF CIVILIZATIONS
 GLOBAL REGENTS REVIEW PACKET NUMBER THREE - PAGE 1 of 19 THIS IS GLOBAL REGENTS REVIEW PACKET NUMBER THREE THE TOPICS OF STUDY IN THIS PACKET ARE: THE NEOLITHIC REVOLUTION CHARACTERISTICS (ELEMENTS) OF
GLOBAL REGENTS REVIEW PACKET NUMBER THREE - PAGE 1 of 19 THIS IS GLOBAL REGENTS REVIEW PACKET NUMBER THREE THE TOPICS OF STUDY IN THIS PACKET ARE: THE NEOLITHIC REVOLUTION CHARACTERISTICS (ELEMENTS) OF
Subject Area: World History Standard: Understands major global trends from 1000 to 1500 CE
 #3567 THE AZTECS Grade Levels: 9-12 25 minutes AMBROSE VIDEO PUBLISHING 1998 1 Student Activity Sheet DESCRIPTION Aztec civilization flourished in Mexico for three centuries before Cortez and his Spanish
#3567 THE AZTECS Grade Levels: 9-12 25 minutes AMBROSE VIDEO PUBLISHING 1998 1 Student Activity Sheet DESCRIPTION Aztec civilization flourished in Mexico for three centuries before Cortez and his Spanish
Egyptian Pyramids Lesson Plan. Central Historical Question: Did slaves build the Great Pyramid at Giza?
 Egyptian Pyramids Lesson Plan Central Historical Question: Did slaves build the Great Pyramid at Giza? Materials: Introductory PowerPoint Copies of Documents A-E Guiding Questions Graphic Organizer Plan
Egyptian Pyramids Lesson Plan Central Historical Question: Did slaves build the Great Pyramid at Giza? Materials: Introductory PowerPoint Copies of Documents A-E Guiding Questions Graphic Organizer Plan
Ancient Egypt. LEVELED BOOK L Ancient Egypt. www.readinga-z.com. Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials.
 Ancient Egypt A Reading A Z Level L Leveled Book Word Count: 482 LEVELED BOOK L Ancient Egypt Written by Kira Freed Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials. www.readinga-z.com Ancient
Ancient Egypt A Reading A Z Level L Leveled Book Word Count: 482 LEVELED BOOK L Ancient Egypt Written by Kira Freed Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials. www.readinga-z.com Ancient
History programmes of study: key stage 3
 History programmes of study: key stage 3 National curriculum in England Purpose of study A high-quality history education will help pupils gain a coherent knowledge and understanding of Britain s past
History programmes of study: key stage 3 National curriculum in England Purpose of study A high-quality history education will help pupils gain a coherent knowledge and understanding of Britain s past
KINGS AND EVENTS OF THE BABYLONIAN, PERSIAN, AND GREEK DYNASTIES
 KINGS AND EVENTS OF THE BABYLONIAN, PERSIAN, AND GREEK DYNASTIES 612 B.C. Nineveh falls to neo-babylonian army (Nebuchadnezzar) 608 Pharaoh Necho II marched to Carchemesh to halt expansion of neo-babylonian
KINGS AND EVENTS OF THE BABYLONIAN, PERSIAN, AND GREEK DYNASTIES 612 B.C. Nineveh falls to neo-babylonian army (Nebuchadnezzar) 608 Pharaoh Necho II marched to Carchemesh to halt expansion of neo-babylonian
Name Class Date. Ancient China Section 4
 Name Class Date Ancient China Section 4 MAIN IDEAS 1. Han dynasty government was based on the ideas of Confucius. 2. Family life was supported and strengthened in Han China. 3. The Han made many achievements
Name Class Date Ancient China Section 4 MAIN IDEAS 1. Han dynasty government was based on the ideas of Confucius. 2. Family life was supported and strengthened in Han China. 3. The Han made many achievements
Bentley Chapter 13 Study Guide: The Expansive Realm of Islam
 Name Date Period Bentley Chapter 13 Study Guide: The Expansive Realm of Islam Eyewitness: Season of the Mecca Pilgrimage (259-268) 1. What is the dar al-islam? A Prophet and His World (260) 2. Who were
Name Date Period Bentley Chapter 13 Study Guide: The Expansive Realm of Islam Eyewitness: Season of the Mecca Pilgrimage (259-268) 1. What is the dar al-islam? A Prophet and His World (260) 2. Who were
The Xenophile Historian
 The Xenophile Historian Map Gallery Map 1: The spread of civilization in thousand-year steps. The purple areas became civilized by 3000 B.C. Civilization spread to the green areas by 2000 B.C., yellow
The Xenophile Historian Map Gallery Map 1: The spread of civilization in thousand-year steps. The purple areas became civilized by 3000 B.C. Civilization spread to the green areas by 2000 B.C., yellow
Jamestown Settlement Family Gallery Guide From Africa to Virginia
 Jamestown Settlement Family Gallery Guide From Africa to Virginia Not long after the English settled Jamestown in 1607, the first Africans were brought to Virginia. They arrived in 1619 from the Kongo/Angola
Jamestown Settlement Family Gallery Guide From Africa to Virginia Not long after the English settled Jamestown in 1607, the first Africans were brought to Virginia. They arrived in 1619 from the Kongo/Angola
Kingship in the Hebrew Bible By Cian Power
 Kingship in the Hebrew Bible By Cian Power Understanding kingship is essential when reading the Hebrew Bible/Old Testament. Most of its authors knew no other political system and it influenced their work
Kingship in the Hebrew Bible By Cian Power Understanding kingship is essential when reading the Hebrew Bible/Old Testament. Most of its authors knew no other political system and it influenced their work
Empires of Early Africa
 Empires of Early Africa Teacher s Guide Grade Level: 9-12 Curriculum Focus: World History Lesson Duration: Two class periods Program Description The Nile: Where Egypt Began (5 min.) Examines the Nile s
Empires of Early Africa Teacher s Guide Grade Level: 9-12 Curriculum Focus: World History Lesson Duration: Two class periods Program Description The Nile: Where Egypt Began (5 min.) Examines the Nile s
Advanced Placement (AP ) Social Studies Courses
 Advanced Placement (AP ) Social Studies Courses The AP social studies courses are intended to provide a rigorous college level introduction to the social sciences for high school students. While no official
Advanced Placement (AP ) Social Studies Courses The AP social studies courses are intended to provide a rigorous college level introduction to the social sciences for high school students. While no official
Sumerian Civilization
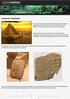 Sumerian Civilization In the south eastern region of Mesopotamia between the mighty Euphrates and Tigris Rivers lay the ruins of the Sumerian City- States. The history of the Sumerians is shrouded in mystery.
Sumerian Civilization In the south eastern region of Mesopotamia between the mighty Euphrates and Tigris Rivers lay the ruins of the Sumerian City- States. The history of the Sumerians is shrouded in mystery.
Great Egyptians: Akhenaten: The Rebel Pharaoh and the Mystery of Tutankhamen: Teacher s Guide
 Great Egyptians: Akhenaten: The Rebel Pharaoh and the Mystery of Tutankhamen: Teacher s Guide Grade Level: 6-8 Curriculum Focus: World History Lesson Duration: Two class periods Program Description Akhenaten
Great Egyptians: Akhenaten: The Rebel Pharaoh and the Mystery of Tutankhamen: Teacher s Guide Grade Level: 6-8 Curriculum Focus: World History Lesson Duration: Two class periods Program Description Akhenaten
eb.com/>. eastern Africa, history of. Encyclopaedia Britannica Online. May 27,
 Daily Life in Aksum Aksum was a powerful and wealthy ancient kingdom. Located in East Africa, it was very influential between A.D. 50 and 600. During this time, goods from all over the ancient world were
Daily Life in Aksum Aksum was a powerful and wealthy ancient kingdom. Located in East Africa, it was very influential between A.D. 50 and 600. During this time, goods from all over the ancient world were
Foundations of Technology, Third Edition / Technology, Engineering, and Design
 Presentation 2.2.1 The Big Idea Technology is in a constant state of change as humans continue to improve and innovate old technologies for new applications. Need to Know When did technology begin? What
Presentation 2.2.1 The Big Idea Technology is in a constant state of change as humans continue to improve and innovate old technologies for new applications. Need to Know When did technology begin? What
- 7. Oracle bones were used a. to practice written Chinese. b. to try to predict the future. p Ch 14 Ancient China section 1
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A p Ch 14 Ancient China section 1 Multiple Choice Identzh the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. - I. Before the Shang kingdom arose, Chinese civilization
Name: Class: Date: ID: A p Ch 14 Ancient China section 1 Multiple Choice Identzh the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. - I. Before the Shang kingdom arose, Chinese civilization
The First Civilizations
 The First Civilizations Guide to Reading Section Preview Early civilizations introduced key belief systems through law codes and religious beliefs that have influenced Western thought. In ancient Mesopotamia,
The First Civilizations Guide to Reading Section Preview Early civilizations introduced key belief systems through law codes and religious beliefs that have influenced Western thought. In ancient Mesopotamia,
World History: Essential Questions
 World History: Essential Questions Content Standard 1.0: Culture encompasses similarities and differences among people including their beliefs, knowledge, changes, values, and traditions. Students will
World History: Essential Questions Content Standard 1.0: Culture encompasses similarities and differences among people including their beliefs, knowledge, changes, values, and traditions. Students will
Social Studies World History Unit 01 Early Civilizations (8000 BC 500 BC) 2013 2014
 Social Studies World History Unit 01 Early Civilizations (8000 BC 500 BC) 2013 2014 1 Which geographic factor likely contributed to the beginning of the Neolithic Revolution? A changing sea levels forced
Social Studies World History Unit 01 Early Civilizations (8000 BC 500 BC) 2013 2014 1 Which geographic factor likely contributed to the beginning of the Neolithic Revolution? A changing sea levels forced
Views of God Created 8/11/2005 Revised on 12/29/10 Page 1 of 6. The God of Israel. An Ancient People s Growing Understanding
 Views of God Created 8/11/2005 Revised on 12/29/10 Page 1 of 6 The God of Israel An Ancient People s Growing Understanding That Israel s understanding of God changed over time is not a controversial claim.
Views of God Created 8/11/2005 Revised on 12/29/10 Page 1 of 6 The God of Israel An Ancient People s Growing Understanding That Israel s understanding of God changed over time is not a controversial claim.
5- Why did the Shogun rule Japan?
 Global History and Geography I The Rise of Feudalism in Japan Name: The emperor was an important political and religious figure in Japan. However, by the 1100s, the emperor s power was so weakened that
Global History and Geography I The Rise of Feudalism in Japan Name: The emperor was an important political and religious figure in Japan. However, by the 1100s, the emperor s power was so weakened that
CHAPTER ONE: A CONTINENT OF VILLAGES, TO 1500
 CHAPTER ONE: A CONTINENT OF VILLAGES, TO 1500 SETTLING THE CONTINENT Who Are the Indian People? Migration from Asia Clovis: The First American Technology NEW WAYS OF LIVING ON THE LAND Hunting Traditions
CHAPTER ONE: A CONTINENT OF VILLAGES, TO 1500 SETTLING THE CONTINENT Who Are the Indian People? Migration from Asia Clovis: The First American Technology NEW WAYS OF LIVING ON THE LAND Hunting Traditions
Prentice Hall World Studies 2005, 8 Book Series Correlated to: Millard Public School District (Nebraska) Social Studies Standards (Grades 6-7)
 Millard Public School District (Nebraska) Social Studies Standards (Grades 6-7) Note: This is a sample correlation based on four available titles of the new 2005 series in development. Titles include:,
Millard Public School District (Nebraska) Social Studies Standards (Grades 6-7) Note: This is a sample correlation based on four available titles of the new 2005 series in development. Titles include:,
Ancient Civilizations: Prehistory to Egypt
 Chapter 1 Ancient Civilizations: Prehistory to Egypt 1 1-4 Stonehenge, c. 2000 b.c.e., Salisbury Plain, Wiltshire, England learning objectives Understand the distinctive artistic, literary, and cultural
Chapter 1 Ancient Civilizations: Prehistory to Egypt 1 1-4 Stonehenge, c. 2000 b.c.e., Salisbury Plain, Wiltshire, England learning objectives Understand the distinctive artistic, literary, and cultural
World History and Geography: Early Civilizations through the Decline of the Roman Empire (5 th century C.E.)
 Sixth Grade World History and Geography: Early Civilizations through the Decline of the Roman Empire (5 th century C.E.) Course Description: Sixth grade students will study the beginning of early civilizations
Sixth Grade World History and Geography: Early Civilizations through the Decline of the Roman Empire (5 th century C.E.) Course Description: Sixth grade students will study the beginning of early civilizations
Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Chapter 15 Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The first Aztecs were a. fishers from the west coast of Mexico. b. shepherds from the mountains
Chapter 15 Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The first Aztecs were a. fishers from the west coast of Mexico. b. shepherds from the mountains
HOW TO WRITE A DYNAMITE COMPARE AND CONTRAST AP ESSAY Remember :
 HOW TO WRITE A DYNAMITE COMPARE AND CONTRAST AP ESSAY Remember : 1. Introduction should be no longer than 2-3 sentences. 2. Thesis must be clear, analytical (i.e.,complex - arguable, tenable and comprehensive
HOW TO WRITE A DYNAMITE COMPARE AND CONTRAST AP ESSAY Remember : 1. Introduction should be no longer than 2-3 sentences. 2. Thesis must be clear, analytical (i.e.,complex - arguable, tenable and comprehensive
Section 1- Geography and the Early Greeks
 Name: Class: Date: 6 th Grade World History Chapter 8 Study Guide: Ancient Greece Section 1- Geography and the Early Greeks 1) Complete the chart below to show how geography shaped the lives of early Greeks.
Name: Class: Date: 6 th Grade World History Chapter 8 Study Guide: Ancient Greece Section 1- Geography and the Early Greeks 1) Complete the chart below to show how geography shaped the lives of early Greeks.
Social Studies Standard Articulated by Grade Level Sixth Grade
 History Strands emphasize World history from its earliest cultures through the Enlightenment, including the early cultures of the Americas. Concept 1: Research Skills for History PO 1. Construct charts,
History Strands emphasize World history from its earliest cultures through the Enlightenment, including the early cultures of the Americas. Concept 1: Research Skills for History PO 1. Construct charts,
HISTORY AND SOCIAL SCIENCE STANDARDS OF LEARNING ENHANCED SCOPE AND SEQUENCE
 HISTORY AND SOCIAL SCIENCE STANDARDS OF LEARNING ENHANCED SCOPE AND SEQUENCE World History and Geography to 1500 A.D. (C.E.) Commonwealth of Virginia Department of Education Copyright 2010 by the Virginia
HISTORY AND SOCIAL SCIENCE STANDARDS OF LEARNING ENHANCED SCOPE AND SEQUENCE World History and Geography to 1500 A.D. (C.E.) Commonwealth of Virginia Department of Education Copyright 2010 by the Virginia
