Magneto-optical microscopy (incl. time-resolved)
|
|
|
- Shanon Moody
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Magneto-optical microscopy (incl. time-resolved) J. McCord (abstract in cooperation with R. Schäfer) IFW Dresden - Institute for Metallic Materials Helmholtzstr Dresden j.mccord@ifw-dresden.de 1. Introduction Important for the understanding of the origin of magnetic properties and technological application of magnetic materials is the ability to observe the magnetic domain structure. One method, practiced since decades, is magneto-optical microscopy using conventional imaging optics. Magneto-optical microscopy is one of the most versatile techniques to image magnetic domains and magnetization processes. The method is based on the magneto-optical Faraday or Kerr effect, i.e. the rotation of linearly polarized light in dependence of the magnetization direction on transmission or reflection from a non-transparent sample, respectively. In this presentation the principles of magneto-optical microscopy, mostly Kerr microscopy and magnetic imaging based on magneto-optical indicator films, will be reviewed. A special emphasis will be on time-resolved imaging techniques. 2. Fundamentals of magneto-optical microscopy The interaction of a plane-polarized electromagnetic light wave with a magnetic material can be illustrated in an image based on the effect of the Lorentz force on the electrons set in motion by the electrical vector E of the wave. This influence is represented in Fig. 1 for the longitudinal Kerr effect. The Lorentz movement generates a magnetic contribution to the reflected light amplitude, the so-called Kerr amplitude K, which is polarized perpendicularly to the normally reflected amplitude N and causes rotation of the light through interference with N. In the simplest case, for domains with opposite magnetization, a maximum domain contrast is produced if e.g. an analyzer blocks most of the reflected light of one domain type. The domain contrast in the image is directly sensitive to the magnitude and direction of magnetization. Additional magneto-optic effects will be discussed. Fig. 1 (a) Illustration of the longitudinal Kerr effect (taken from [1]) Magneto-optical microscopy (incl. time-resolved) III.1-1 J. McCord
2 Arbitrary magnetic fields can be applied during observation so that domain nucleation and magnetization processes can be observed easily. Possibly the utmost advantage over other domain observation methods is the speed and time-resolution in which images can be acquired. A magneto-optical microscope is essentially a polarization microscope, with which maximum lateral resolution of around 300 nm can be achieved using oil immersion objectives with a high numerical aperture. The main components of a wide-field microscope are represented schematically in Fig. 2. As the magneto-optical contrast is rather weak, a highly intensive light source is used, usually a high-pressure xenon or mercury lamp. Lasers can be used for wide-field illumination in principle, but some effort is required to obtain the necessary incoherent light source from the coherent laser light. For scanning microscopy, the use of low noise lasers is used on regular basis. As the magneto-optical contrast might be very weak, significant enhancement is possible by video microscopy and digital image processing in the case of wide-field microscopy. A possible background image subtraction process is best carried out in real time at video frequency, making it possible to view magnetization processes in real-time. For laser based scanning microscopes, usually lock-in techniques are used for contrast enhancement and reduction of signal-to-noise ratio. Fig. 3 (a) Schematic representation of the main components of a Kerr microscope. The inset shows the beam path of an optical reflected light microscope. The aperture iris is displaced from the optical axis to generate oblique incidence of light (adapted from [1]). 3. Practical Aspects The optical technique has many advantages. The magnetization can be observed directly without ambiguity. The samples are not destroyed or damaged during observation and the process of observation does not influence the magnetization. The shape and size of the sample are largely arbitrary. Imaging through transparent or semi-transparent covering layers can be achieved. Free sample manipulation is easily possible during observation. High or low tem- Magneto-optical microscopy (incl. time-resolved) III.1-2 J. McCord
3 perature, mechanical stress or, most importantly, arbitrary magnetic fields may be applied, allowing to study magnetization processes easily. The same effects that are used for imaging may also be used for the magnetic characterization of the material, i.e. local hysteresis curves may be obtained by just plotting the average intensity of the Kerr images as a function of applied field. Examples for all of the above will be presented. Due to its linearity and direct sensitivity to the magnetization vector m, the Kerr effect can be used for a quantitative determination of the magnetization direction [2]. However, besides these advantages there are also a number of obstacles. Often samples have to be prepared so that they are reasonably flat and smooth on a scale exceeding the chosen lateral resolution. The resolution is limited to magnetic domains larger than about 0.2 µm, corresponding to an optical resolution of about 0.3 µm. On metals, only the surface magnetization in a layer of the penetration depth of some 10 nm can be seen. In bulk samples it restricts the possibilities of domain studies to surface domains (which in most cases are different from underlying volume domains). For thin film studies this is not necessarily a disadvantage. Using a rotatable compensator, the phase of the Kerr amplitude, generated in a certain depth, can be adjusted relative to the regularly reflected light amplitude. In this way light from selected depth zones can be made invisible if their Kerr amplitude is adjusted out of phase with respect to the regular light, layer-selective magneto-optical microscopy is possible then. 4. Time-resolved imaging Time-resolved observation of periodic magnetization processes is e.g. possible by stroboscopic imaging, using either by a triggered video camera or a pulsed light source [2]. This can be done by laser scanning techniques or by wide-field techniques. Triggering the light or camera pulses with precise timing relative to a field pulse and sweeping the delay time of probing yields a series of corresponding pictures of periodic or quasi-periodic processes. An experimental setup of such a stroboscope, as we recently installed it at IFW-Dresden, is shown in Fig. 4. Fig. 4 Schematics of an experiment for stroboscopic domain imaging, implemented in a regular wide-field Kerr microscope. The time resolution is obtained by illumination with a pulsed laser. The laser-based stroboscope allows a time resolution of below 20 ps. Magneto-optical microscopy (incl. time-resolved) III.1-3 J. McCord
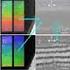
4 As the Kerr signals on small time scales are usually too weak to obtain single-shot images (depends also on chosen time-resolution), an averaging over a number of images at each time delay is necessary to obtain reasonable contrast. Prerequisite is that the fast magnetization processes are reproducible. The use of wide-field Kerr microscopy for dynamic imaging has the advantage, that also the domain ground states and quasi-static processes (i.e. in slowly changing fields) can be studied for comparison. One simple example is discussed here. The magnetization processes initiated by highfrequency fields or by field pulses are very different from those in slowly varying fields. As the switching, e.g. of a soft magnetic film element, in pulsed fields occurs in the nanosecond regime, one has to consider that the magnetization (or the domains) will not be able to instantaneously follow the magnetic field. To reach the new magnetization direction, it will have to spin about the field axis, a process called precessional motion that is gradually opposed by damping. Therefore remagnetization processes in pulsed fields may not be seen as a simple switch of magnetization direction. An example of such an experiment on a Permalloy film element is shown in Fig. 5. Fig. 5 Magnetization process of a Permalloy square element of 50 nm thickness, initiated by a diagonal, lowamplitude field pulse around the Landau ground state. In a slowly varying field (bottom row) the center vortex is shifted reversibly around its equilibrium position. In a pulsed field (upper three rows of images) the domain walls and the vortex cannot follow the field pulse. Rather rotational processes occur, until the walls are restored after about 5 ns. 5. Conclusions Magneto-optical microscopy is a versatile method for the experimental analysis of magnetic microstructures, only limited by resolution down to a few tenths of a micrometer. The dynamic capability and the compatibility with arbitrary applied fields make Kerr microscopy Magneto-optical microscopy (incl. time-resolved) III.1-4 J. McCord
5 ideally suited for the investigation of fast and slow magnetization processes. Due to the direct sensitivity and linear dependence on the magnetic polarization, the method allows the quantitative determination of magnetization vector fields at the surface of soft magnets. Bibliography (Reviews) [1] A. Hubert and R. Schäfer: Magnetic Domains. The Analysis of Magnetic Microstructures. Springer Verlag, Berlin (1998) [2] M. Freeman and W. K. Hiebert, in Spin Dynamics in Confined Magnetic Structures I, ed. by B. Hillebrands and K. Ounadjela, Springer Berlin (2002) Magneto-optical microscopy (incl. time-resolved) III.1-5 J. McCord
Ultrasonic Wave Propagation Review
 Ultrasonic Wave Propagation Review Presented by: Sami El-Ali 1 1. Introduction Ultrasonic refers to any study or application of sound waves that are higher frequency than the human audible range. Ultrasonic
Ultrasonic Wave Propagation Review Presented by: Sami El-Ali 1 1. Introduction Ultrasonic refers to any study or application of sound waves that are higher frequency than the human audible range. Ultrasonic
Magneto-Optic Kerr Eect Microscopy
 Magneto-Optic Kerr Eect Microscopy Tyler A. Hennen Electrical and Computer Engineering Department, University of Californa, San Diego 9500 Gilman Dr, La Jolla, CA 92093, USA (Dated: December 9, 2014) Magnetic
Magneto-Optic Kerr Eect Microscopy Tyler A. Hennen Electrical and Computer Engineering Department, University of Californa, San Diego 9500 Gilman Dr, La Jolla, CA 92093, USA (Dated: December 9, 2014) Magnetic
High Frequency Behaviour of Magnetic Thin Film Elements for. Microelectronics
 Dissertation High Frequency Behaviour of Magnetic Thin Film Elements for Microelectronics Chumakov Dmytro Tag der Einreichung: 20.02.2006 Table of contents Introduction 1 1. Theoretical background and
Dissertation High Frequency Behaviour of Magnetic Thin Film Elements for Microelectronics Chumakov Dmytro Tag der Einreichung: 20.02.2006 Table of contents Introduction 1 1. Theoretical background and
Scanning Near Field Optical Microscopy: Principle, Instrumentation and Applications
 Scanning Near Field Optical Microscopy: Principle, Instrumentation and Applications Saulius Marcinkevičius Optics, ICT, KTH 1 Outline Optical near field. Principle of scanning near field optical microscope
Scanning Near Field Optical Microscopy: Principle, Instrumentation and Applications Saulius Marcinkevičius Optics, ICT, KTH 1 Outline Optical near field. Principle of scanning near field optical microscope
X-Rays and Magnetism From Fundamentals to Nanoscale Dynamics
 X-Rays and Magnetism From Fundamentals to Nanoscale Dynamics Joachim Stöhr Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Laboratory X-rays have come a long way 1895 1993 10 cm 10 µm 100 nm Collaborators: SSRL Stanford:
X-Rays and Magnetism From Fundamentals to Nanoscale Dynamics Joachim Stöhr Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Laboratory X-rays have come a long way 1895 1993 10 cm 10 µm 100 nm Collaborators: SSRL Stanford:
Imaging of Spin Dynamics in Closure Domain and Vortex Structures. J. P. Park, P. Eames, D. M. Engebretson, J. Berezovsky, and P. A.
 Imaging of Spin Dynamics in Closure Domain and Vortex Structures J. P. Park, P. Eames, D. M. Engebretson, J. Berezovsky, and P. A. Crowell School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Minnesota, 116
Imaging of Spin Dynamics in Closure Domain and Vortex Structures J. P. Park, P. Eames, D. M. Engebretson, J. Berezovsky, and P. A. Crowell School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Minnesota, 116
Various Technics of Liquids and Solids Level Measurements. (Part 3)
 (Part 3) In part one of this series of articles, level measurement using a floating system was discusses and the instruments were recommended for each application. In the second part of these articles,
(Part 3) In part one of this series of articles, level measurement using a floating system was discusses and the instruments were recommended for each application. In the second part of these articles,
Near-field scanning optical microscopy (SNOM)
 Adviser: dr. Maja Remškar Institut Jožef Stefan January 2010 1 2 3 4 5 6 Fluorescence Raman and surface enhanced Raman 7 Conventional optical microscopy-limited resolution Two broad classes of techniques
Adviser: dr. Maja Remškar Institut Jožef Stefan January 2010 1 2 3 4 5 6 Fluorescence Raman and surface enhanced Raman 7 Conventional optical microscopy-limited resolution Two broad classes of techniques
- particle with kinetic energy E strikes a barrier with height U 0 > E and width L. - classically the particle cannot overcome the barrier
 Tunnel Effect: - particle with kinetic energy E strikes a barrier with height U 0 > E and width L - classically the particle cannot overcome the barrier - quantum mechanically the particle can penetrated
Tunnel Effect: - particle with kinetic energy E strikes a barrier with height U 0 > E and width L - classically the particle cannot overcome the barrier - quantum mechanically the particle can penetrated
Modern Classical Optics
 Modern Classical Optics GEOFFREY BROOKER Department of Physics University of Oxford OXPORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents 1 Electromagnetism and basic optics 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 The Maxwell equations 1
Modern Classical Optics GEOFFREY BROOKER Department of Physics University of Oxford OXPORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents 1 Electromagnetism and basic optics 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 The Maxwell equations 1
Measuring index of refraction
 Grzegorz F. Wojewoda Zespół Szkół Ogólnokształcących nr 1 Bydgoszcz, Poland Logo designed by Armella Leung, www.armella.fr.to Translation: Małgorzata Czart Measuring index of refraction The advent of low-cost
Grzegorz F. Wojewoda Zespół Szkół Ogólnokształcących nr 1 Bydgoszcz, Poland Logo designed by Armella Leung, www.armella.fr.to Translation: Małgorzata Czart Measuring index of refraction The advent of low-cost
E190Q Lecture 5 Autonomous Robot Navigation
 E190Q Lecture 5 Autonomous Robot Navigation Instructor: Chris Clark Semester: Spring 2014 1 Figures courtesy of Siegwart & Nourbakhsh Control Structures Planning Based Control Prior Knowledge Operator
E190Q Lecture 5 Autonomous Robot Navigation Instructor: Chris Clark Semester: Spring 2014 1 Figures courtesy of Siegwart & Nourbakhsh Control Structures Planning Based Control Prior Knowledge Operator
DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF PROBE WITH THREE DEGREE- OF-FREEDOM FOR NON-DESTRUCTIVE TEST USING THREE- DIMENSIONAL FINITE ELEMENT METHOD
 DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF PROBE WITH THREE DEGREE- OF-FREEDOM FOR NON-DESTRUCTIVE TEST USING THREE- DIMENSIONAL FINITE ELEMENT METHOD Masafumi Aoyanagi Graduate School of Systems and Information Engineering,
DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF PROBE WITH THREE DEGREE- OF-FREEDOM FOR NON-DESTRUCTIVE TEST USING THREE- DIMENSIONAL FINITE ELEMENT METHOD Masafumi Aoyanagi Graduate School of Systems and Information Engineering,
Polarization of Light
 Polarization of Light References Halliday/Resnick/Walker Fundamentals of Physics, Chapter 33, 7 th ed. Wiley 005 PASCO EX997A and EX999 guide sheets (written by Ann Hanks) weight Exercises and weights
Polarization of Light References Halliday/Resnick/Walker Fundamentals of Physics, Chapter 33, 7 th ed. Wiley 005 PASCO EX997A and EX999 guide sheets (written by Ann Hanks) weight Exercises and weights
The Basics of Scanning Electron Microscopy
 The Basics of Scanning Electron Microscopy The small scanning electron microscope is easy to use because almost every variable is pre-set: the acceleration voltage is always 15kV, it has only a single
The Basics of Scanning Electron Microscopy The small scanning electron microscope is easy to use because almost every variable is pre-set: the acceleration voltage is always 15kV, it has only a single
Acoustic GHz-Microscopy: Potential, Challenges and Applications
 Acoustic GHz-Microscopy: Potential, Challenges and Applications A Joint Development of PVA TePLa Analytical Systems GmbH and Fraunhofer IWM-Halle Dr. Sebastian Brand (Ph.D.) Fraunhofer CAM Fraunhofer Institute
Acoustic GHz-Microscopy: Potential, Challenges and Applications A Joint Development of PVA TePLa Analytical Systems GmbH and Fraunhofer IWM-Halle Dr. Sebastian Brand (Ph.D.) Fraunhofer CAM Fraunhofer Institute
Acousto-optic modulator
 1 of 3 Acousto-optic modulator F An acousto-optic modulator (AOM), also called a Bragg cell, uses the acousto-optic effect to diffract and shift the frequency of light using sound waves (usually at radio-frequency).
1 of 3 Acousto-optic modulator F An acousto-optic modulator (AOM), also called a Bragg cell, uses the acousto-optic effect to diffract and shift the frequency of light using sound waves (usually at radio-frequency).
A wave lab inside a coaxial cable
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Eur. J. Phys. 25 (2004) 581 591 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PHYSICS PII: S0143-0807(04)76273-X A wave lab inside a coaxial cable JoãoMSerra,MiguelCBrito,JMaiaAlves and A M Vallera
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Eur. J. Phys. 25 (2004) 581 591 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PHYSICS PII: S0143-0807(04)76273-X A wave lab inside a coaxial cable JoãoMSerra,MiguelCBrito,JMaiaAlves and A M Vallera
Atomic Force Microscopy Observation and Characterization of a CD Stamper, Lycopodium Spores, and Step-Height Standard Diffraction Grating
 Atomic Force Microscopy Observation and Characterization of a CD Stamper, Lycopodium Spores, and Step-Height Standard Diffraction Grating Michael McMearty and Frit Miot Special Thanks to Brendan Cross
Atomic Force Microscopy Observation and Characterization of a CD Stamper, Lycopodium Spores, and Step-Height Standard Diffraction Grating Michael McMearty and Frit Miot Special Thanks to Brendan Cross
SEMIAUTOMATIC SURFACE REFLECTANCE MEASUREMENT FOR MONITORING OF MATERIAL WEATHERING
 SEMIAUTOMATIC SURFACE REFLECTANCE MEASUREMENT FOR MONITORING OF MATERIAL WEATHERING V. Kocour 1, J. Valach 2 1 Motivation Summary: We present a device for measurement of surface reflectance in dependence
SEMIAUTOMATIC SURFACE REFLECTANCE MEASUREMENT FOR MONITORING OF MATERIAL WEATHERING V. Kocour 1, J. Valach 2 1 Motivation Summary: We present a device for measurement of surface reflectance in dependence
5. Scanning Near-Field Optical Microscopy 5.1. Resolution of conventional optical microscopy
 5. Scanning Near-Field Optical Microscopy 5.1. Resolution of conventional optical microscopy Resolution of optical microscope is limited by diffraction. Light going through an aperture makes diffraction
5. Scanning Near-Field Optical Microscopy 5.1. Resolution of conventional optical microscopy Resolution of optical microscope is limited by diffraction. Light going through an aperture makes diffraction
Encoders for Linear Motors in the Electronics Industry
 Technical Information Encoders for Linear Motors in the Electronics Industry The semiconductor industry and automation technology increasingly require more precise and faster machines in order to satisfy
Technical Information Encoders for Linear Motors in the Electronics Industry The semiconductor industry and automation technology increasingly require more precise and faster machines in order to satisfy
E. K. A. ADVANCED PHYSICS LABORATORY PHYSICS 3081, 4051 NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE
 E. K. A. ADVANCED PHYSICS LABORATORY PHYSICS 3081, 4051 NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE References for Nuclear Magnetic Resonance 1. Slichter, Principles of Magnetic Resonance, Harper and Row, 1963. chapter
E. K. A. ADVANCED PHYSICS LABORATORY PHYSICS 3081, 4051 NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE References for Nuclear Magnetic Resonance 1. Slichter, Principles of Magnetic Resonance, Harper and Row, 1963. chapter
Using light scattering method to find The surface tension of water
 Experiment (8) Using light scattering method to find The surface tension of water The aim of work: The goals of this experiment are to confirm the relationship between angular frequency and wave vector
Experiment (8) Using light scattering method to find The surface tension of water The aim of work: The goals of this experiment are to confirm the relationship between angular frequency and wave vector
Optical Metrology. Third Edition. Kjell J. Gasvik Spectra Vision AS, Trondheim, Norway JOHN WILEY & SONS, LTD
 2008 AGI-Information Management Consultants May be used for personal purporses only or by libraries associated to dandelon.com network. Optical Metrology Third Edition Kjell J. Gasvik Spectra Vision AS,
2008 AGI-Information Management Consultants May be used for personal purporses only or by libraries associated to dandelon.com network. Optical Metrology Third Edition Kjell J. Gasvik Spectra Vision AS,
Automotive Applications of 3D Laser Scanning Introduction
 Automotive Applications of 3D Laser Scanning Kyle Johnston, Ph.D., Metron Systems, Inc. 34935 SE Douglas Street, Suite 110, Snoqualmie, WA 98065 425-396-5577, www.metronsys.com 2002 Metron Systems, Inc
Automotive Applications of 3D Laser Scanning Kyle Johnston, Ph.D., Metron Systems, Inc. 34935 SE Douglas Street, Suite 110, Snoqualmie, WA 98065 425-396-5577, www.metronsys.com 2002 Metron Systems, Inc
Longwave IR focal-plane binary optics
 Longwave IR focal-plane binary optics Z. Sikorski, H. Polakowski Institute of Optoelectronics, Military University of Technology, 2 Kaliskiego Str., -98 Warsaw, e-mail: zsikorsk@wat.waw.pl Abstract In
Longwave IR focal-plane binary optics Z. Sikorski, H. Polakowski Institute of Optoelectronics, Military University of Technology, 2 Kaliskiego Str., -98 Warsaw, e-mail: zsikorsk@wat.waw.pl Abstract In
Lecture 4 Scanning Probe Microscopy (SPM)
 Lecture 4 Scanning Probe Microscopy (SPM) General components of SPM; Tip --- the probe; Cantilever --- the indicator of the tip; Tip-sample interaction --- the feedback system; Scanner --- piezoelectric
Lecture 4 Scanning Probe Microscopy (SPM) General components of SPM; Tip --- the probe; Cantilever --- the indicator of the tip; Tip-sample interaction --- the feedback system; Scanner --- piezoelectric
CREOL, College of Optics & Photonics, University of Central Florida
 OSE6650 - Optical Properties of Nanostructured Materials Optical Properties of Nanostructured Materials Fall 2013 Class 3 slide 1 Challenge: excite and detect the near field Thus far: Nanostructured materials
OSE6650 - Optical Properties of Nanostructured Materials Optical Properties of Nanostructured Materials Fall 2013 Class 3 slide 1 Challenge: excite and detect the near field Thus far: Nanostructured materials
EXPERIMENT O-6. Michelson Interferometer. Abstract. References. Pre-Lab
 EXPERIMENT O-6 Michelson Interferometer Abstract A Michelson interferometer, constructed by the student, is used to measure the wavelength of He-Ne laser light and the index of refraction of a flat transparent
EXPERIMENT O-6 Michelson Interferometer Abstract A Michelson interferometer, constructed by the student, is used to measure the wavelength of He-Ne laser light and the index of refraction of a flat transparent
Optical Fibres. Introduction. Safety precautions. For your safety. For the safety of the apparatus
 Please do not remove this manual from from the lab. It is available at www.cm.ph.bham.ac.uk/y2lab Optics Introduction Optical fibres are widely used for transmitting data at high speeds. In this experiment,
Please do not remove this manual from from the lab. It is available at www.cm.ph.bham.ac.uk/y2lab Optics Introduction Optical fibres are widely used for transmitting data at high speeds. In this experiment,
Fundamentals of modern UV-visible spectroscopy. Presentation Materials
 Fundamentals of modern UV-visible spectroscopy Presentation Materials The Electromagnetic Spectrum E = hν ν = c / λ 1 Electronic Transitions in Formaldehyde 2 Electronic Transitions and Spectra of Atoms
Fundamentals of modern UV-visible spectroscopy Presentation Materials The Electromagnetic Spectrum E = hν ν = c / λ 1 Electronic Transitions in Formaldehyde 2 Electronic Transitions and Spectra of Atoms
Robot Perception Continued
 Robot Perception Continued 1 Visual Perception Visual Odometry Reconstruction Recognition CS 685 11 Range Sensing strategies Active range sensors Ultrasound Laser range sensor Slides adopted from Siegwart
Robot Perception Continued 1 Visual Perception Visual Odometry Reconstruction Recognition CS 685 11 Range Sensing strategies Active range sensors Ultrasound Laser range sensor Slides adopted from Siegwart
Phased-Array ROWA-SPA: High-performance testing machine for combined, 100-percent automated testing of square and round bars
 11th European Conference on Non-Destructive Testing (ECNDT 2014), October 6-10, 2014, Prague, Czech Republic Phased-Array ROWA-SPA: High-performance testing machine for combined, 100-percent automated
11th European Conference on Non-Destructive Testing (ECNDT 2014), October 6-10, 2014, Prague, Czech Republic Phased-Array ROWA-SPA: High-performance testing machine for combined, 100-percent automated
Femtosecond laser-induced silicon surface morphology in water confinement
 Microsyst Technol (2009) 15:1045 1049 DOI 10.1007/s00542-009-0880-8 TECHNICAL PAPER Femtosecond laser-induced silicon surface morphology in water confinement Yukun Han Æ Cheng-Hsiang Lin Æ Hai Xiao Æ Hai-Lung
Microsyst Technol (2009) 15:1045 1049 DOI 10.1007/s00542-009-0880-8 TECHNICAL PAPER Femtosecond laser-induced silicon surface morphology in water confinement Yukun Han Æ Cheng-Hsiang Lin Æ Hai Xiao Æ Hai-Lung
Advancements in High Frequency, High Resolution Acoustic Micro Imaging for Thin Silicon Applications
 Advancements in High Frequency, High Resolution Acoustic Micro Imaging for Thin Silicon Applications Janet E. Semmens Sonoscan, Inc. 2149 E. Pratt Boulevard Elk Grove Village, IL 60007 USA Phone: (847)
Advancements in High Frequency, High Resolution Acoustic Micro Imaging for Thin Silicon Applications Janet E. Semmens Sonoscan, Inc. 2149 E. Pratt Boulevard Elk Grove Village, IL 60007 USA Phone: (847)
ENGINEERING METROLOGY
 ENGINEERING METROLOGY ACADEMIC YEAR 92-93, SEMESTER ONE COORDINATE MEASURING MACHINES OPTICAL MEASUREMENT SYSTEMS; DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ISFAHAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY Coordinate Measuring
ENGINEERING METROLOGY ACADEMIC YEAR 92-93, SEMESTER ONE COORDINATE MEASURING MACHINES OPTICAL MEASUREMENT SYSTEMS; DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ISFAHAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY Coordinate Measuring
International Year of Light 2015 Tech-Talks BREGENZ: Mehmet Arik Well-Being in Office Applications Light Measurement & Quality Parameters
 www.led-professional.com ISSN 1993-890X Trends & Technologies for Future Lighting Solutions ReviewJan/Feb 2015 Issue LpR 47 International Year of Light 2015 Tech-Talks BREGENZ: Mehmet Arik Well-Being in
www.led-professional.com ISSN 1993-890X Trends & Technologies for Future Lighting Solutions ReviewJan/Feb 2015 Issue LpR 47 International Year of Light 2015 Tech-Talks BREGENZ: Mehmet Arik Well-Being in
Experiment 5. Lasers and laser mode structure
 Northeastern University, PHYS5318 Spring 2014, 1 1. Introduction Experiment 5. Lasers and laser mode structure The laser is a very important optical tool that has found widespread use in science and industry,
Northeastern University, PHYS5318 Spring 2014, 1 1. Introduction Experiment 5. Lasers and laser mode structure The laser is a very important optical tool that has found widespread use in science and industry,
Lecture 20: Scanning Confocal Microscopy (SCM) Rationale for SCM. Principles and major components of SCM. Advantages and major applications of SCM.
 Lecture 20: Scanning Confocal Microscopy (SCM) Rationale for SCM. Principles and major components of SCM. Advantages and major applications of SCM. Some limitations (disadvantages) of NSOM A trade-off
Lecture 20: Scanning Confocal Microscopy (SCM) Rationale for SCM. Principles and major components of SCM. Advantages and major applications of SCM. Some limitations (disadvantages) of NSOM A trade-off
Application Note AN1
 TAKING INVENTIVE STEPS IN INFRARED. MINIATURE INFRARED GAS SENSORS GOLD SERIES UK Patent App. No. 799A USA Patent App. No. 9/78,7 World Patents Pending SENSOR OVERVIEW Application Note AN The Dynament
TAKING INVENTIVE STEPS IN INFRARED. MINIATURE INFRARED GAS SENSORS GOLD SERIES UK Patent App. No. 799A USA Patent App. No. 9/78,7 World Patents Pending SENSOR OVERVIEW Application Note AN The Dynament
1 Introduction. 1.1 Historical Perspective
 j1 1 Introduction 1.1 Historical Perspective The invention of scanning probe microscopy is considered one of the major advances in materials science since 1950 [1, 2]. Scanning probe microscopy includes
j1 1 Introduction 1.1 Historical Perspective The invention of scanning probe microscopy is considered one of the major advances in materials science since 1950 [1, 2]. Scanning probe microscopy includes
DETECTION OF SUBSURFACE DAMAGE IN OPTICAL TRANSPARENT MATERIALSS USING SHORT COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY. Rainer Boerret, Dominik Wiedemann, Andreas Kelm
 URN (Paper): urn:nbn:de:gbv:ilm1-2014iwk-199:0 58 th ILMENAU SCIENTIFIC COLLOQUIUM Technische Universität Ilmenau, 08 12 September 2014 URN: urn:nbn:de:gbv:ilm1-2014iwk:3 DETECTION OF SUBSURFACE DAMAGE
URN (Paper): urn:nbn:de:gbv:ilm1-2014iwk-199:0 58 th ILMENAU SCIENTIFIC COLLOQUIUM Technische Universität Ilmenau, 08 12 September 2014 URN: urn:nbn:de:gbv:ilm1-2014iwk:3 DETECTION OF SUBSURFACE DAMAGE
Magnetic Media Measurements with a VSM
 Magnetic Media Measurements with a VSM B. C. Dodrill Lake Shore Cryotronics, Inc. 575 McCorkle Blvd Westerville, Ohio 43082 The last 50 years have seen the development of methods for the digital storage
Magnetic Media Measurements with a VSM B. C. Dodrill Lake Shore Cryotronics, Inc. 575 McCorkle Blvd Westerville, Ohio 43082 The last 50 years have seen the development of methods for the digital storage
Synthetic Sensing: Proximity / Distance Sensors
 Synthetic Sensing: Proximity / Distance Sensors MediaRobotics Lab, February 2010 Proximity detection is dependent on the object of interest. One size does not fit all For non-contact distance measurement,
Synthetic Sensing: Proximity / Distance Sensors MediaRobotics Lab, February 2010 Proximity detection is dependent on the object of interest. One size does not fit all For non-contact distance measurement,
FTIR Instrumentation
 FTIR Instrumentation Adopted from the FTIR lab instruction by H.-N. Hsieh, New Jersey Institute of Technology: http://www-ec.njit.edu/~hsieh/ene669/ftir.html 1. IR Instrumentation Two types of instrumentation
FTIR Instrumentation Adopted from the FTIR lab instruction by H.-N. Hsieh, New Jersey Institute of Technology: http://www-ec.njit.edu/~hsieh/ene669/ftir.html 1. IR Instrumentation Two types of instrumentation
A METHOD OF PRECISE CALIBRATION FOR PIEZOELECTRICAL ACTUATORS
 Uludağ Üniversitesi Mühendislik-Mimarlık Fakültesi Dergisi, Cilt 9, Sayı, 24 A METHOD OF PRECISE CALIBRATION FOR PIEZOELECTRICAL ACTUATORS Timur CANEL * Yüksel BEKTÖRE ** Abstract: Piezoelectrical actuators
Uludağ Üniversitesi Mühendislik-Mimarlık Fakültesi Dergisi, Cilt 9, Sayı, 24 A METHOD OF PRECISE CALIBRATION FOR PIEZOELECTRICAL ACTUATORS Timur CANEL * Yüksel BEKTÖRE ** Abstract: Piezoelectrical actuators
P R E A M B L E. Facilitated workshop problems for class discussion (1.5 hours)
 INSURANCE SCAM OPTICS - LABORATORY INVESTIGATION P R E A M B L E The original form of the problem is an Experimental Group Research Project, undertaken by students organised into small groups working as
INSURANCE SCAM OPTICS - LABORATORY INVESTIGATION P R E A M B L E The original form of the problem is an Experimental Group Research Project, undertaken by students organised into small groups working as
Physics 441/2: Transmission Electron Microscope
 Physics 441/2: Transmission Electron Microscope Introduction In this experiment we will explore the use of transmission electron microscopy (TEM) to take us into the world of ultrasmall structures. This
Physics 441/2: Transmission Electron Microscope Introduction In this experiment we will explore the use of transmission electron microscopy (TEM) to take us into the world of ultrasmall structures. This
v = fλ PROGRESSIVE WAVES 1 Candidates should be able to :
 PROGRESSIVE WAVES 1 Candidates should be able to : Describe and distinguish between progressive longitudinal and transverse waves. With the exception of electromagnetic waves, which do not need a material
PROGRESSIVE WAVES 1 Candidates should be able to : Describe and distinguish between progressive longitudinal and transverse waves. With the exception of electromagnetic waves, which do not need a material
PIPELINE INSPECTION UTILIZING ULTRASOUND TECHNOLOGY: ON THE ISSUE OF RESOLUTION By, M. Beller, NDT Systems & Services AG, Stutensee, Germany
 ABSTRACT: PIPELINE INSPECTION UTILIZING ULTRASOUND TECHNOLOGY: ON THE ISSUE OF RESOLUTION By, M. Beller, NDT Systems & Services AG, Stutensee, Germany Today, in-line inspection tools are used routinely
ABSTRACT: PIPELINE INSPECTION UTILIZING ULTRASOUND TECHNOLOGY: ON THE ISSUE OF RESOLUTION By, M. Beller, NDT Systems & Services AG, Stutensee, Germany Today, in-line inspection tools are used routinely
Diffraction and Young s Single Slit Experiment
 Diffraction and Young s Single Slit Experiment Developers AB Overby Objectives Preparation Background The objectives of this experiment are to observe Fraunhofer, or far-field, diffraction through a single
Diffraction and Young s Single Slit Experiment Developers AB Overby Objectives Preparation Background The objectives of this experiment are to observe Fraunhofer, or far-field, diffraction through a single
Lenses and Apertures of A TEM
 Instructor: Dr. C.Wang EMA 6518 Course Presentation Lenses and Apertures of A TEM Group Member: Anup Kr. Keshri Srikanth Korla Sushma Amruthaluri Venkata Pasumarthi Xudong Chen Outline Electron Optics
Instructor: Dr. C.Wang EMA 6518 Course Presentation Lenses and Apertures of A TEM Group Member: Anup Kr. Keshri Srikanth Korla Sushma Amruthaluri Venkata Pasumarthi Xudong Chen Outline Electron Optics
Microscopy. MICROSCOPY Light Electron Tunnelling Atomic Force RESOLVE: => INCREASE CONTRAST BIODIVERSITY I BIOL1051 MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF MICROSCOPES
 BIODIVERSITY I BIOL1051 Microscopy Professor Marc C. Lavoie marc.lavoie@cavehill.uwi.edu MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF MICROSCOPES MAGNIFY RESOLVE: => INCREASE CONTRAST Microscopy 1. Eyepieces 2. Diopter adjustment
BIODIVERSITY I BIOL1051 Microscopy Professor Marc C. Lavoie marc.lavoie@cavehill.uwi.edu MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF MICROSCOPES MAGNIFY RESOLVE: => INCREASE CONTRAST Microscopy 1. Eyepieces 2. Diopter adjustment
Laboratory #3 Guide: Optical and Electrical Properties of Transparent Conductors -- September 23, 2014
 Laboratory #3 Guide: Optical and Electrical Properties of Transparent Conductors -- September 23, 2014 Introduction Following our previous lab exercises, you now have the skills and understanding to control
Laboratory #3 Guide: Optical and Electrical Properties of Transparent Conductors -- September 23, 2014 Introduction Following our previous lab exercises, you now have the skills and understanding to control
Chapter 8. Low energy ion scattering study of Fe 4 N on Cu(100)
 Low energy ion scattering study of 4 on Cu(1) Chapter 8. Low energy ion scattering study of 4 on Cu(1) 8.1. Introduction For a better understanding of the reconstructed 4 surfaces one would like to know
Low energy ion scattering study of 4 on Cu(1) Chapter 8. Low energy ion scattering study of 4 on Cu(1) 8.1. Introduction For a better understanding of the reconstructed 4 surfaces one would like to know
The Olympus stereology system. The Computer Assisted Stereological Toolbox
 The Olympus stereology system The Computer Assisted Stereological Toolbox CAST is a Computer Assisted Stereological Toolbox for PCs running Microsoft Windows TM. CAST is an interactive, user-friendly,
The Olympus stereology system The Computer Assisted Stereological Toolbox CAST is a Computer Assisted Stereological Toolbox for PCs running Microsoft Windows TM. CAST is an interactive, user-friendly,
It has long been a goal to achieve higher spatial resolution in optical imaging and
 Nano-optical Imaging using Scattering Scanning Near-field Optical Microscopy Fehmi Yasin, Advisor: Dr. Markus Raschke, Post-doc: Dr. Gregory Andreev, Graduate Student: Benjamin Pollard Department of Physics,
Nano-optical Imaging using Scattering Scanning Near-field Optical Microscopy Fehmi Yasin, Advisor: Dr. Markus Raschke, Post-doc: Dr. Gregory Andreev, Graduate Student: Benjamin Pollard Department of Physics,
Non-Contact Vibration Measurement of Micro-Structures
 Non-Contact Vibration Measurement of Micro-Structures Using Laser Doppler Vibrometry (LDV) and Planar Motion Analysis (PMA) to examine and assess the vibration characteristics of micro- and macro-structures.
Non-Contact Vibration Measurement of Micro-Structures Using Laser Doppler Vibrometry (LDV) and Planar Motion Analysis (PMA) to examine and assess the vibration characteristics of micro- and macro-structures.
Determination of source parameters from seismic spectra
 Topic Determination of source parameters from seismic spectra Authors Michael Baumbach, and Peter Bormann (formerly GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam, Telegrafenberg, D-14473 Potsdam, Germany); E-mail: pb65@gmx.net
Topic Determination of source parameters from seismic spectra Authors Michael Baumbach, and Peter Bormann (formerly GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam, Telegrafenberg, D-14473 Potsdam, Germany); E-mail: pb65@gmx.net
NON-DESTRUCTIVE METHODS. CE 165: Concrete Materials and Concrete Construction
 NON-DESTRUCTIVE METHODS NON-DESTRUCTIVE METHODS Purpose: quick assessment of the structure Non-Destructive Techniques Many industrialized nations currently dedicate a considerable portion of the construction
NON-DESTRUCTIVE METHODS NON-DESTRUCTIVE METHODS Purpose: quick assessment of the structure Non-Destructive Techniques Many industrialized nations currently dedicate a considerable portion of the construction
Physics 9e/Cutnell. correlated to the. College Board AP Physics 1 Course Objectives
 Physics 9e/Cutnell correlated to the College Board AP Physics 1 Course Objectives Big Idea 1: Objects and systems have properties such as mass and charge. Systems may have internal structure. Enduring
Physics 9e/Cutnell correlated to the College Board AP Physics 1 Course Objectives Big Idea 1: Objects and systems have properties such as mass and charge. Systems may have internal structure. Enduring
Confocal Microscopy and Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) A very brief primer...
 Confocal Microscopy and Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) of biofilms A very brief primer... Fundamentals of Confocal Microscopy Based on a conventional fluorescence microscope Fluorescent Microscope Confocal
Confocal Microscopy and Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) of biofilms A very brief primer... Fundamentals of Confocal Microscopy Based on a conventional fluorescence microscope Fluorescent Microscope Confocal
PHYSICAL METHODS, INSTRUMENTS AND MEASUREMENTS Vol. IV Femtosecond Measurements Combined With Near-Field Optical Microscopy - Artyom A.
 FEMTOSECOND MEASUREMENTS COMBINED WITH NEAR FIELD OPTICAL MICROSCOPY Artyom A. Astafiev, Semyonov Institute of Chemical Physics, Moscow, Russian Federation. Keywords: diffraction limit nearfield scanning
FEMTOSECOND MEASUREMENTS COMBINED WITH NEAR FIELD OPTICAL MICROSCOPY Artyom A. Astafiev, Semyonov Institute of Chemical Physics, Moscow, Russian Federation. Keywords: diffraction limit nearfield scanning
Coating Technology: Evaporation Vs Sputtering
 Satisloh Italy S.r.l. Coating Technology: Evaporation Vs Sputtering Gianni Monaco, PhD R&D project manager, Satisloh Italy 04.04.2016 V1 The aim of this document is to provide basic technical information
Satisloh Italy S.r.l. Coating Technology: Evaporation Vs Sputtering Gianni Monaco, PhD R&D project manager, Satisloh Italy 04.04.2016 V1 The aim of this document is to provide basic technical information
Introduction to Optics
 Second Edition Introduction to Optics FRANK L. PEDROTTI, S.J. Marquette University Milwaukee, Wisconsin Vatican Radio, Rome LENO S. PEDROTTI Center for Occupational Research and Development Waco, Texas
Second Edition Introduction to Optics FRANK L. PEDROTTI, S.J. Marquette University Milwaukee, Wisconsin Vatican Radio, Rome LENO S. PEDROTTI Center for Occupational Research and Development Waco, Texas
AP1 Waves. (A) frequency (B) wavelength (C) speed (D) intensity. Answer: (A) and (D) frequency and intensity.
 1. A fire truck is moving at a fairly high speed, with its siren emitting sound at a specific pitch. As the fire truck recedes from you which of the following characteristics of the sound wave from the
1. A fire truck is moving at a fairly high speed, with its siren emitting sound at a specific pitch. As the fire truck recedes from you which of the following characteristics of the sound wave from the
S. Hartmann, C. Seiler, R. Dörner and P. Grimm
 &DVH6WXG\9LVXDOL]DWLRQRI0HFKDQLFDO3URSHUWLHVDQG 'HIRUPDWLRQVRI/LYLQJ&HOOV S. Hartmann, C. Seiler, R. Dörner and P. Grimm Fraunhofer Anwendungszentrum für Computergraphik in Chemie und Pharmazie Varrentrappstraße
&DVH6WXG\9LVXDOL]DWLRQRI0HFKDQLFDO3URSHUWLHVDQG 'HIRUPDWLRQVRI/LYLQJ&HOOV S. Hartmann, C. Seiler, R. Dörner and P. Grimm Fraunhofer Anwendungszentrum für Computergraphik in Chemie und Pharmazie Varrentrappstraße
Scanning Near-Field Optical Microscopy for Measuring Materials Properties at the Nanoscale
 Scanning Near-Field Optical Microscopy for Measuring Materials Properties at the Nanoscale Outline Background Research Design Detection of Near-Field Signal Submonolayer Chemical Sensitivity Conclusions
Scanning Near-Field Optical Microscopy for Measuring Materials Properties at the Nanoscale Outline Background Research Design Detection of Near-Field Signal Submonolayer Chemical Sensitivity Conclusions
Laser-induced surface phonons and their excitation of nanostructures
 CHINESE JOURNAL OF PHYSICS VOL. 49, NO. 1 FEBRUARY 2011 Laser-induced surface phonons and their excitation of nanostructures Markus Schmotz, 1, Dominik Gollmer, 1 Florian Habel, 1 Stephen Riedel, 1 and
CHINESE JOURNAL OF PHYSICS VOL. 49, NO. 1 FEBRUARY 2011 Laser-induced surface phonons and their excitation of nanostructures Markus Schmotz, 1, Dominik Gollmer, 1 Florian Habel, 1 Stephen Riedel, 1 and
A Guide to Acousto-Optic Modulators
 A Guide to Acousto-Optic Modulators D. J. McCarron December 7, 2007 1 Introduction Acousto-optic modulators (AOMs) are useful devices which allow the frequency, intensity and direction of a laser beam
A Guide to Acousto-Optic Modulators D. J. McCarron December 7, 2007 1 Introduction Acousto-optic modulators (AOMs) are useful devices which allow the frequency, intensity and direction of a laser beam
Automatic and Objective Measurement of Residual Stress and Cord in Glass
 Automatic and Objective Measurement of Residual Stress and Cord in Glass GlassTrend - ICG TC15/21 Seminar SENSORS AND PROCESS CONTROL 13-14 October 2015, Eindhoven Henning Katte, ilis gmbh copyright ilis
Automatic and Objective Measurement of Residual Stress and Cord in Glass GlassTrend - ICG TC15/21 Seminar SENSORS AND PROCESS CONTROL 13-14 October 2015, Eindhoven Henning Katte, ilis gmbh copyright ilis
UNIT I: INTRFERENCE & DIFFRACTION Div. B Div. D Div. F INTRFERENCE
 107002: EngineeringPhysics Teaching Scheme: Lectures: 4 Hrs/week Practicals-2 Hrs./week T.W.-25 marks Examination Scheme: Paper-50 marks (2 hrs) Online -50marks Prerequisite: Basics till 12 th Standard
107002: EngineeringPhysics Teaching Scheme: Lectures: 4 Hrs/week Practicals-2 Hrs./week T.W.-25 marks Examination Scheme: Paper-50 marks (2 hrs) Online -50marks Prerequisite: Basics till 12 th Standard
Optical Storage Technology. Optical Disc Storage
 Optical Storage Technology Optical Disc Storage Introduction Since the early 1940s, magnetic recording has been the mainstay of electronic information storage worldwide. Magnetic tape has been used extensively
Optical Storage Technology Optical Disc Storage Introduction Since the early 1940s, magnetic recording has been the mainstay of electronic information storage worldwide. Magnetic tape has been used extensively
Lecture 14. Point Spread Function (PSF)
 Lecture 14 Point Spread Function (PSF), Modulation Transfer Function (MTF), Signal-to-noise Ratio (SNR), Contrast-to-noise Ratio (CNR), and Receiver Operating Curves (ROC) Point Spread Function (PSF) Recollect
Lecture 14 Point Spread Function (PSF), Modulation Transfer Function (MTF), Signal-to-noise Ratio (SNR), Contrast-to-noise Ratio (CNR), and Receiver Operating Curves (ROC) Point Spread Function (PSF) Recollect
Scanning Acoustic Microscopy Training
 Scanning Acoustic Microscopy Training This presentation and images are copyrighted by Sonix, Inc. They may not be copied, reproduced, modified, published, uploaded, posted, transmitted, or distributed
Scanning Acoustic Microscopy Training This presentation and images are copyrighted by Sonix, Inc. They may not be copied, reproduced, modified, published, uploaded, posted, transmitted, or distributed
A PHOTOGRAMMETRIC APPRAOCH FOR AUTOMATIC TRAFFIC ASSESSMENT USING CONVENTIONAL CCTV CAMERA
 A PHOTOGRAMMETRIC APPRAOCH FOR AUTOMATIC TRAFFIC ASSESSMENT USING CONVENTIONAL CCTV CAMERA N. Zarrinpanjeh a, F. Dadrassjavan b, H. Fattahi c * a Islamic Azad University of Qazvin - nzarrin@qiau.ac.ir
A PHOTOGRAMMETRIC APPRAOCH FOR AUTOMATIC TRAFFIC ASSESSMENT USING CONVENTIONAL CCTV CAMERA N. Zarrinpanjeh a, F. Dadrassjavan b, H. Fattahi c * a Islamic Azad University of Qazvin - nzarrin@qiau.ac.ir
The promise of ultrasonic phased arrays and the role of modeling in specifying systems
 1 modeling in specifying systems ABSTRACT Guillaume Neau and Deborah Hopkins This article illustrates the advantages of phased-array systems and the value of modeling through several examples taken from
1 modeling in specifying systems ABSTRACT Guillaume Neau and Deborah Hopkins This article illustrates the advantages of phased-array systems and the value of modeling through several examples taken from
Components for Infrared Spectroscopy. Dispersive IR Spectroscopy
 Components for Infrared Spectroscopy Mid-IR light: 00-000 cm - (5.5 m wavelength) Sources: Blackbody emitters Globar metal oxides Nernst Glower: Silicon Carbide Detectors: Not enough energy for photoelectric
Components for Infrared Spectroscopy Mid-IR light: 00-000 cm - (5.5 m wavelength) Sources: Blackbody emitters Globar metal oxides Nernst Glower: Silicon Carbide Detectors: Not enough energy for photoelectric
8.2 Elastic Strain Energy
 Section 8. 8. Elastic Strain Energy The strain energy stored in an elastic material upon deformation is calculated below for a number of different geometries and loading conditions. These expressions for
Section 8. 8. Elastic Strain Energy The strain energy stored in an elastic material upon deformation is calculated below for a number of different geometries and loading conditions. These expressions for
COMP175: Computer Graphics. Lecture 1 Introduction and Display Technologies
 COMP175: Computer Graphics Lecture 1 Introduction and Display Technologies Course mechanics Number: COMP 175-01, Fall 2009 Meetings: TR 1:30-2:45pm Instructor: Sara Su (sarasu@cs.tufts.edu) TA: Matt Menke
COMP175: Computer Graphics Lecture 1 Introduction and Display Technologies Course mechanics Number: COMP 175-01, Fall 2009 Meetings: TR 1:30-2:45pm Instructor: Sara Su (sarasu@cs.tufts.edu) TA: Matt Menke
AP1 Oscillations. 1. Which of the following statements about a spring-block oscillator in simple harmonic motion about its equilibrium point is false?
 1. Which of the following statements about a spring-block oscillator in simple harmonic motion about its equilibrium point is false? (A) The displacement is directly related to the acceleration. (B) The
1. Which of the following statements about a spring-block oscillator in simple harmonic motion about its equilibrium point is false? (A) The displacement is directly related to the acceleration. (B) The
Choosing a digital camera for your microscope John C. Russ, Materials Science and Engineering Dept., North Carolina State Univ.
 Choosing a digital camera for your microscope John C. Russ, Materials Science and Engineering Dept., North Carolina State Univ., Raleigh, NC One vital step is to choose a transfer lens matched to your
Choosing a digital camera for your microscope John C. Russ, Materials Science and Engineering Dept., North Carolina State Univ., Raleigh, NC One vital step is to choose a transfer lens matched to your
New Approach to Analysis of the Switching Current Data in Ferroelectric Thin Films
 Ferroelectrics, 291: 27 35, 2003 Copyright c Taylor & Francis Inc. ISSN: 0015-0193 print / 1563-5112 online DOI: 10.1080/00150190390222510 New Approach to Analysis of the Switching Current Data in Ferroelectric
Ferroelectrics, 291: 27 35, 2003 Copyright c Taylor & Francis Inc. ISSN: 0015-0193 print / 1563-5112 online DOI: 10.1080/00150190390222510 New Approach to Analysis of the Switching Current Data in Ferroelectric
SPM 150 Aarhus with KolibriSensor
 Customied Systems and Solutions Nanostructures and Thin Film Deposition Surface Analysis and Preparation Components Surface Science Applications SPM 150 Aarhus with KolibriSensor Atomic resolution NC-AFM
Customied Systems and Solutions Nanostructures and Thin Film Deposition Surface Analysis and Preparation Components Surface Science Applications SPM 150 Aarhus with KolibriSensor Atomic resolution NC-AFM
NEAR FIELD OPTICAL MICROSCOPY AND SPECTROSCOPY WITH STM AND AFM PROBES
 Vol. 93 (1997) A CTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 2 Proceedings of the 1st International Symposium on Scanning Probe Spectroscopy and Related Methods, Poznań 1997 NEAR FIELD OPTICAL MICROSCOPY AND SPECTROSCOPY
Vol. 93 (1997) A CTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 2 Proceedings of the 1st International Symposium on Scanning Probe Spectroscopy and Related Methods, Poznań 1997 NEAR FIELD OPTICAL MICROSCOPY AND SPECTROSCOPY
X-Ray Study of Soft and Hard Magnetic Thin Films
 Copyright (C) JCPDS-International Centre for Diffraction Data 1999 13 X-Ray Study of Soft and Hard Magnetic Thin Films Po-Wen Wang, 390 Reed St., Stormedia, Inc., Santa Clara CA. 95050 Abstract : This
Copyright (C) JCPDS-International Centre for Diffraction Data 1999 13 X-Ray Study of Soft and Hard Magnetic Thin Films Po-Wen Wang, 390 Reed St., Stormedia, Inc., Santa Clara CA. 95050 Abstract : This
Application of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance in Petroleum Exploration
 Application of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance in Petroleum Exploration Introduction Darko Tufekcic, consultant email: darkotufekcic@hotmail.com Electro-magnetic resonance method (GEO-EMR) is emerging as the
Application of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance in Petroleum Exploration Introduction Darko Tufekcic, consultant email: darkotufekcic@hotmail.com Electro-magnetic resonance method (GEO-EMR) is emerging as the
Calibration of AFM with virtual standards; robust, versatile and accurate. Richard Koops VSL Dutch Metrology Institute Delft
 Calibration of AFM with virtual standards; robust, versatile and accurate Richard Koops VSL Dutch Metrology Institute Delft 19-11-2015 VSL Dutch Metrology Institute VSL is the national metrology institute
Calibration of AFM with virtual standards; robust, versatile and accurate Richard Koops VSL Dutch Metrology Institute Delft 19-11-2015 VSL Dutch Metrology Institute VSL is the national metrology institute
Anomalous Hall Effect Magnetometry A Method for Studying Magnetic Processes of Thin Magnetic Films
 Anomalous Hall Effect Magnetometry A Method for Studying Magnetic Processes of Thin Magnetic Films J. R. Lindemuth a, B. C. Dodrill a and N. C. Oldham b a Lake Shore Cryotronics, Inc. 575 McCorkle Blvd,
Anomalous Hall Effect Magnetometry A Method for Studying Magnetic Processes of Thin Magnetic Films J. R. Lindemuth a, B. C. Dodrill a and N. C. Oldham b a Lake Shore Cryotronics, Inc. 575 McCorkle Blvd,
Fluid structure interaction of a vibrating circular plate in a bounded fluid volume: simulation and experiment
 Fluid Structure Interaction VI 3 Fluid structure interaction of a vibrating circular plate in a bounded fluid volume: simulation and experiment J. Hengstler & J. Dual Department of Mechanical and Process
Fluid Structure Interaction VI 3 Fluid structure interaction of a vibrating circular plate in a bounded fluid volume: simulation and experiment J. Hengstler & J. Dual Department of Mechanical and Process
Experiment 3 Lenses and Images
 Experiment 3 Lenses and Images Who shall teach thee, unless it be thine own eyes? Euripides (480?-406? BC) OBJECTIVES To examine the nature and location of images formed by es. THEORY Lenses are frequently
Experiment 3 Lenses and Images Who shall teach thee, unless it be thine own eyes? Euripides (480?-406? BC) OBJECTIVES To examine the nature and location of images formed by es. THEORY Lenses are frequently
Experimental results for the focal waveform and beam width in the focusing lens with a 100 ps filter
 EM Implosion Memos Memo 51 July, 2010 Experimental results for the focal waveform and beam width in the focusing lens with a 100 ps filter Prashanth Kumar, Carl E. Baum, Serhat Altunc, Christos G. Christodoulou
EM Implosion Memos Memo 51 July, 2010 Experimental results for the focal waveform and beam width in the focusing lens with a 100 ps filter Prashanth Kumar, Carl E. Baum, Serhat Altunc, Christos G. Christodoulou
Measurement of Resistive Wall Mode Stability in Rotating High Beta Plasmas
 Measurement of Resistive Wall Mode Stability in Rotating High Beta Plasmas H.Reimerdes, 1 J.Bialek, 1 M.S.Chance, 2 M.S.Chu, 3 A.M.Garofalo, 1 P.Gohil, 3 G.L.Jackson, 3 R.J.Jayakumar, 4 T.H.Jensen, 3#
Measurement of Resistive Wall Mode Stability in Rotating High Beta Plasmas H.Reimerdes, 1 J.Bialek, 1 M.S.Chance, 2 M.S.Chu, 3 A.M.Garofalo, 1 P.Gohil, 3 G.L.Jackson, 3 R.J.Jayakumar, 4 T.H.Jensen, 3#
LAB 7 MOSFET CHARACTERISTICS AND APPLICATIONS
 LAB 7 MOSFET CHARACTERISTICS AND APPLICATIONS Objective In this experiment you will study the i-v characteristics of an MOS transistor. You will use the MOSFET as a variable resistor and as a switch. BACKGROUND
LAB 7 MOSFET CHARACTERISTICS AND APPLICATIONS Objective In this experiment you will study the i-v characteristics of an MOS transistor. You will use the MOSFET as a variable resistor and as a switch. BACKGROUND
OPTICAL FIBERS INTRODUCTION
 OPTICAL FIBERS References: J. Hecht: Understanding Fiber Optics, Ch. 1-3, Prentice Hall N.J. 1999 D. R. Goff: Fiber Optic Reference Guide (2 nd ed.) Focal Press 1999 Projects in Fiber Optics (Applications
OPTICAL FIBERS References: J. Hecht: Understanding Fiber Optics, Ch. 1-3, Prentice Hall N.J. 1999 D. R. Goff: Fiber Optic Reference Guide (2 nd ed.) Focal Press 1999 Projects in Fiber Optics (Applications
Lab 9: The Acousto-Optic Effect
 Lab 9: The Acousto-Optic Effect Incoming Laser Beam Travelling Acoustic Wave (longitudinal wave) O A 1st order diffracted laser beam A 1 Introduction qb d O 2qb rarefractions compressions Refer to Appendix
Lab 9: The Acousto-Optic Effect Incoming Laser Beam Travelling Acoustic Wave (longitudinal wave) O A 1st order diffracted laser beam A 1 Introduction qb d O 2qb rarefractions compressions Refer to Appendix
AMPLIFIED HIGH SPEED FIBER PHOTODETECTOR USER S GUIDE
 AMPLIFIED HIGH SPEED FIBER PHOTODETECTOR USER S GUIDE Thank you for purchasing your Amplified High Speed Fiber Photodetector. This user s guide will help answer any questions you may have regarding the
AMPLIFIED HIGH SPEED FIBER PHOTODETECTOR USER S GUIDE Thank you for purchasing your Amplified High Speed Fiber Photodetector. This user s guide will help answer any questions you may have regarding the
Interferometers. OBJECTIVES To examine the operation of several kinds of interferometers. d sin = n (1)
 Interferometers The true worth of an experimenter consists in his pursuing not only what he seeks in his experiment, but also what he did not seek. Claude Bernard (1813-1878) OBJECTIVES To examine the
Interferometers The true worth of an experimenter consists in his pursuing not only what he seeks in his experiment, but also what he did not seek. Claude Bernard (1813-1878) OBJECTIVES To examine the
A More Efficient Way to De-shelve 137 Ba +
 A More Efficient Way to De-shelve 137 Ba + Abstract: Andrea Katz Trinity University UW REU 2010 In order to increase the efficiency and reliability of de-shelving barium ions, an infrared laser beam was
A More Efficient Way to De-shelve 137 Ba + Abstract: Andrea Katz Trinity University UW REU 2010 In order to increase the efficiency and reliability of de-shelving barium ions, an infrared laser beam was
