FOCUS DRIVER ZOOM DRIVER IRIS METER. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (30) (51) 24 SYNCHRONOUS
|
|
|
- Randell Allison
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 US A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (30) (51) IMAGE CAPTURING APPARATUS, EXPOSURE CONTROL METHOD, AND COMPUTER-READABLE RECORDING MEDIUM Applicant: Kohji KUWATA, Kanagawa (JP) Inventor: Appl. No.: 14/196,041 Mar. 4, 2013 Kohji KUWATA, Kanagawa (JP) Filed: Mar. 4, 2014 Foreign Application Priority Data (JP) Publication Classi?cation Int. Cl. H04N 5/235 ( ) (52) U.S.Cl. CPC..... H04N5/2352( ) USPC /241 (57) ABSTRACT An image capturing apparatus includes an image capturing module and a controller that controls exposure of the image capturing module by dividing a captured image by the image capturing module into a plurality of image areas, weighting brightness of a predetermined pixel in each of the image areas, and being based on the weighted brightness of the predetermined pixel in each image area. The controller per forms a weighting correction process that increases weight ing to the brightness of the predetermined pixel in each image area when the size of the image area after a correction process in which distortion aberration of the captured image is cor rected is larger than the size of the before-corrected image area, and decreases the weighting to the brightness of the predetermined pixel in each image area when the size of the after-corrected image area is smaller than the size of the before-corrected image area. 1 H 512 IMAGING ELEMENT 7 ANALOG AID DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING ID CONVERTER 2') PROCESSING C'RCU'T CIRCUIT A It M A A A A IRIS METER FOCUS DRIVER ZOOM DRIVER 24 SYNCHRONOUS SIGNAL GENERATOR CAMERA MICROCOMPUTER : INTEGRATING CIRCUIT A V g26 MODE MICROCOMPUTER OPERATING MODULE
2 Patent Application Publication Sep. 4, 2014 Sheet 1 0f 7 US 2014/ A1 FIG L12 <13 <14 15 ANALOG DIGITAL IMAGING ~ AID SIGNAL LENS :> ELEMENT PROCESS'NGZD CONVERTER :>PROCESSING CIRCUIT CIRCUIT IK lk lk lk IK IK 1k 523 DRIVER 5 0: LL] E 2 g 4 E a: [I E w 3 SYNCHRONOUS _ a O % o <II'I2 &TI% '~ = GENERATOR LL N A CAMERA MICROCOMPUTER 18 ;17 - INTEGRATING CIRCUIT s26 ' 4 L MODE MICROCOMPUTER 1k 25 OPERATING MODULE
3 Patent Application Publication Sep. 4, 2014 Sheet 2 0f 7 US 2014/ A1 FIG.2 DIVIDE CAPTURED IMAGE INTO PLURALITY OF IMAGE AREAS AND CALCULATE BRIGHTNESS REPRESENTING EACH IMAGE AREA $201 WEIGHT BRIGHTNESS REPRESENTING EACH IMAGE AREA 8202 CORRECT DISTORTION ABERRATION \~8204 CORRECT WEIGHTING TO BRIGHTNESS 8205 REPRESENTING EACH AREA CONTROL EXPOSURE OF IMAGE CAPTURING APPARATUS 8206
4 Patent Application Publication Sep. 4, 2014 Sheet 3 0f 7 US 2014/ A1 FIG-.3 (a) A OB 00 OB 0A O8 09 on OE F A A 0A A A A 05 OD 1O 16 1C 1F 1C OD C 2B ZB 1C C ZB ZB 1C C 1F 1C (C) 03 O4 O7 OB DE 10 OE OD O7 O B 21 1B 14 O OE E O OE E O4 O B 21 1B 14 O4 O3 O4 O7 OB OE 1O OE OD O7 (d) O6 O8 09 O OB 0C OB O6 09 OE OE 09 0C 10 1F 32 4E 32 1F 10 0C OD OD OC 1O C 03 OE C OE O3
5 Patent Application Publication Sep. 4, 2014 Sheet 4 0f 7 US 2014/ A1 FIG.4 CAPTURED IMAGE BEFORE CORRECTING DISTORTION ABERRATION o a=== ===== a a I CAPTURED IMAGE AFTER CORRECTING DISTORTION ABERRATION
6 Patent Application Publication Sep. 4, 2014 Sheet 5 0f 7 US 2014/ A1 CAPTURED IMAGE BEFORE CORRECTING DISTORTION ABERRATION CAPTURED IMAGE AFTER CORRECTING DISTORTION ABERRATION 0 10% OF IMAGE AFlg,1" l?fc'g?gr'il PORTION AREA IN CENTRAL PORTION EXPAND PORTION SURROUNDING CENTRAL PORTION
7
8 Patent Application Publication Sep. 4, 2014 Sheet 7 0f 7 US 2014/ A1 CAPTURED IMAGE BEFORE CORRECTING DISTORTION ABERRATION CENTRAL PORTION CAPTURED IMAGE AFTER CORRECTING DISTORTION ABERRATION CENTRAL PORTION I
9 US 2014/ A1 Sep. 4, 2014 IMAGE CAPTURING APPARATUS, EXPOSURE CONTROL METHOD, AND COMPUTER-READABLE RECORDING MEDIUM CROSS-REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATIONS [0001] The present application claims priority to and incor porates by reference the entire contents of Japanese Patent Application No ?led in Japan on Mar. 4, BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION [0002] 1. Field of the Invention [0003] The present invention relates to an image capturing apparatus, an exposure control method, and a computer-read able recording medium. [0004] 2. Description of the Related Art [0005] Conventional technologies for controlling exposure in an image capturing apparatus such as a digital camera include a multi-zone metering method that divides a captured image captured and acquired by the image capturing appara tus into a plurality of photometric areas (one example of an image area) and controls the exposure based on the photo metric results of the respective photometric areas, a center weighted metering method that controls the exposure by weighting the brightness of a central portion of the captured image (one example of an image area), a partial metering method that performs photometry on several tens of percent of the captured image in a central portion (one example of an image area) and controls the exposure based on the photo metric result thereof, and a spot metering method that per forms photometry on several percent of the captured image in a central portion (one example of an image area) and controls the exposure based on the photometric result thereof. [0006] As for the image capturing apparatus used in a tele vision conference system (also referred to as a teleconference system and a video conference system) or the like, an image capturing apparatus equipped with a wide-angle lens is used to capture a wide range so as to capture the images of all of the participants in a conference or to convey a realistic feeling of the conference venue. The captured image captured and acquired by the image capturing apparatus having a wide angle lens results in a distorted captured image due to the characteristics of the wide-angle lens, and thus the captured image is not transmitted to a destination as it is, but transmit ted to the destination in a state of the distortion being sup pressed by adding a geometrical deformation to the captured image. When the geometrical distortion is added to the cap tured image, however, the size of the captured image varies, and thus when the exposure is controlled based on the bright ness of the captured image before adding the geometrical deformation without considering the variation, optimal expo sure control may not be made. [0007] In view of the foregoing, there is a need to provide an image capturing apparatus, an exposure control method, and a computer-readable recording medium having a computer program that permit optimal exposure control to be achieved when distortion aberration of a captured image captured and acquired by an image capturing module is corrected. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION [0008] It is an object of the present invention to at least partially solve the problems in the conventional technology. [0009] According to the present invention, there is provided an image capturing apparatus comprising: an image capturing module; and a controller con?gured to control expo sure of the image capturing module by dividing a captured image cap tured and acquired by the image capturing module into a plurality of image areas, weighting brightness of a predeter mined pixel in each of the image areas, and being based on the weighted brightness of the predetermined pixel in each image area, wherein the controller performs a weighting correction process that increases weighting to the brightness of the pre determined pixel in each image area, when a size of the image area after a correction process in which distortion aberration of the captured image is corrected is larger than the size of the image area before the correction process, and the controller performs a weight correction process that decreases the weighting to the brightness of the predetermined pixel in each image area, when the size of the image area after the correc tion process is smaller than the size of the image area before the correction process. [0010] The present invention also provides an exposure control method performed by an image capturing apparatus, the exposure control method comprising: controlling expo sure of the image capturing apparatus by a controller dividing a captured image captured and acquired by the image captur ing apparatus into a plurality of image areas, weighting brightness of a predetermined pixel in each of the image areas, and being based on the weighted brightness of the predetermined pixel in each image area, wherein the control ler performs a weighting correction process that increases weighting to the brightness of the predetermined pixel in each image area, when a size of the image area after a correction process in which distortion aberration of the captured image is corrected is larger than the size of the image area before the correction process, and the controller performs a weighting correction process that decreases the weighting to the bright ness of the predetermined pixel in each image area, when the size of the image area after the correction process is smaller than the size of the image area before the correction process. [0011] The present invention also provides a non-transitory computer-readable recording medium that contains a com puter program that causes a computer to function as: a con troller con?gured to control exposure of an image capturing module by dividing a captured image captured and acquired by the image capturing module into a plurality of image areas, weighting brightness of a predetermined pixel in each of the image areas, and being based on the weighted brightness of the predetermined pixel in each image area, wherein the con troller performs a weighting correction process that increases weighting to the brightness of the predetermined pixel in each image area, when a size of the image area after a correction process in which distortion aberration of the captured image is corrected is larger than the size of the image area before the correction process, and the controller performs a weighting correction process that decreases the weighting to the bright ness of the predetermined pixel in each image area, when the size of the image area after the correction process is smaller than the size of the image area before the correction process. [0012] The above and other objects, features, advantages and technical and industrial signi?cance of this invention will be better understood by reading the following detailed description of presently preferred embodiments of the inven tion, when considered in connection with the accompanying drawings.
10 US 2014/ A1 Sep. 4, 2014 BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS [0013] FIG. 1 is a block diagram illustrating a con?guration of an image capturing apparatus according to an embodiment of the present invention; [0014] FIG. 2 is a?owchart illustrating a sequence of a process performed to control exposure in the image capturing apparatus in the embodiment; [0015] FIGS. 3(a) to 3(d) are tables for explaining weight ing to the brightness representing each image area performed in the image capturing apparatus in the embodiment; [0016] FIG. 4 is a diagram for explaining a process of correcting distortion aberration performed in the image cap turing apparatus in the embodiment; [0017] FIG. 5 is a diagram for explaining the process of correcting distortion aberration performed in the image cap turing apparatus in the embodiment; [0018] FIG. 6 is a diagram for explaining a weighting cor rection process performed in the image capturing apparatus in the embodiment; and [0019] FIG. 7 is a diagram for explaining exposure control performed in the image capturing apparatus in the embodi ment. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENT [0020] With reference to the accompanying drawings, an exemplary embodiment of an image capturing apparatus, an exposure control method, and a computer-readable recording medium having a computer program according to the present invention Will be described in detail hereinafter. [0021] FIG. 1 is a block diagram illustrating a con?guration of an image capturing apparatus according to the embodi ment. An image capturing apparatus 1 according to the embodiment includes a lens 11, an imaging element 12, an analog processing circuit 13, an A/D converter 14, a digital signal processing circuit 15, an integrating circuit 17, a cam era microcomputer 18, an iris meter 19, a focus driver 20, a zoom driver 21, a timing circuit 22, a driver 23, a synchronous signal generator 24, an operating module 25, and a mode microcomputer 26. [0022] The lens 11 forms an image of a subject on the imaging element 12. The imaging element 12 is a charge coupled device (CCD) image sensor, a complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) image sensor, or the like on Which the image of the subject (a captured image) is formed by the lens 11, and outputs an analog signal of the captured image formed (hereinafter referred to as an image capturing signal). In the embodiment, the imaging element 12 outputs the image capturing signal of the captured image formed. In the embodiment, the lens 11 and the imaging element 12 together serve as an image capturing module that captures the image of a subject. [0023] The analog processing circuit 13 performs a sample and-hold process that reduces noise in the image capturing signal output from the imaging element 12, and performs gain adjustment of the image capturing signal output from the imaging element 12. In the embodiment, the analog process ing circuit 13 performs correlated double sampling (CDS) to reduce the noise in the image capturing signal output from the imaging element 12. In the embodiment, the analog process ing circuit 13 further performs automatic gain control (AGC) to adjust the gain of the image capturing signal output from the imaging element 12. [0024] The analog/digital (A/D) converter 14 converts the image capturing signal in an analog form output from the imaging element 12 into an image capturing signal in a digital form. [0025] The digital signal processing circuit 15 converts the digital image capturing signal converted by the A/ D converter 14 into a video signal. The digital signal processing circuit 15 then outputs the converted video signal to a display device (for example, a view?nder and an external television receiver) that displays an image (captured image) derived from the video signal, to a storage module that stores therein the video signal, and to others. In the embodiment, the digital signal processing circuit 15 outputs the video signal by con verting into an analog signal by a D/A converter. Further more, in the embodiment, the digital signal processing circuit 15, being controlled by the camera microcomputer 18, adjusts White balance of the image derived from the converted video signal. [0026] The integrating circuit 17 acquires the brightness of the image derived from the video signal (captured image) output from the digital signal processing circuit 15 as control information used for exposure control (AE: automatic expo sure) of the image capturing apparatus 1. In the embodiment, the integrating circuit 17 further acquires control information used for automatic focus (AF: autofocus) that automatically adjusts the focus of the image capturing apparatus 1 and for White balance adjustment (AWB: automatic White balance) using the video signal output from the digital signal process ing circuit 15. The integrating circuit 17 then outputs the acquired control information to the camera microcomputer 18. [0027] The iris meter 19 adjusts the diaphragms of the lens 11 according to an iris operation signal used for the iris adjustment of the lens 11. The focus driver 20 adjusts the focus of the image capturing apparatus 1 according to a focus operation signal used for the focus adjustment of the image capturing apparatus 1. The zoom driver 21 adjusts the focal length of the lens 11 according to a zoom operation signal used for the adjustment of the focal length of the lens 11. [0028] The driver 23 activates an electronic shutter of the imaging element 12. The synchronous signal generator 24 outputs a synchronous signal to convert the image capturing signal in a digital form into the video signal in synchroniza tion With the timing of the image being formed on the imaging element 12. [0029] The timing circuit 22 controls the timing of opening the electronic shutter of the imaging element 12 (timing of forming the image on the imaging element 12), and the timing of converting the image capturing signal in a digital form into the video signal. [0030] The operating module 25 can input various settings for the image capturing apparatus 1. As the various settings, there are included: a setting to switch on or off the exposure control of the image capturing apparatus 1; a setting to select a determining method (for example, a multi-zone metering method, a center-weighted metering method, a partial meter ing method, and a spot metering method) of exposure (a shutter speed, an exposure time, and others) When the expo sure control (AE) of the image capturing apparatus 1 is set to on; a setting to switch on or off the White balance adjustment (AWB); a setting to switch on or off the autofocus of the image capturing apparatus 1; a setting to switch on or off the adjustment of the diaphragms of the lens 11; a setting to switch on or off the adjustment of the focal length of the lens
11 US 2014/ A1 Sep. 4, ; and so on. The mode microcomputer 26 sets the various settings received from the operating module 25 to the image capturing apparatus 1. [0031] The camera microcomputer 18 controls the various modules of the image capturing apparatus 1. More speci? cally, the camera microcomputer 18 controls the timing cir cuit 22 according to the control information output from the integrating circuit 17 to control the exposure of the image capturing apparatus 1. The camera microcomputer 18 further controls the digital signal processing circuit 15 according to the control information output from the integrating circuit 17 to control the adjustment of the white balance of the image derived from the video signal. [0032] Furthermore, the camera microcomputer 18 outputs the focus operation signal to the focus driver 20 according to the control signal output from the integrating circuit 17 and the focus detected by a focus-lens position sensor so as to control the focusing of the image capturing apparatus 1. The camera microcomputer 18 further outputs the iris operation signal to the iris meter 19 according to an aperture value of the lens 11 detected by an iris opening sensor (a hall element) to control the adjustment of the diaphragms of the lens 11. Moreover, the camera microcomputer 18 outputs the zoom operation signal to the zoom driver 21 according to the focal length of the lens 11 detected by a zoom-lens position sensor to control the adjustment of the focal length of the lens 11. [0033] A process performed to control the exposure of the image capturing apparatus 1 in the embodiment will now be described in detail. FIG. 2 is a?owchart illustrating a sequence of the process to control the exposure performed in the image capturing apparatus in the embodiment. [0034] When the exposure control of the image capturing apparatus 1 is set to be on by the mode microcomputer 26, the integrating circuit 17 acquires the video signal output from the digital signal processing circuit 15, divides a captured image derived from the video signal acquired (in other words, the captured image displayed on the display device) into a plurality of image areas, and calculates the brightness that represents each of the image areas (Step S201). [0035] In the embodiment, the integrating circuit 17 divides the captured image derived from the acquired video signal into a plurality of image areas (for example, 63 image areas). The integrating circuit 17 then calculates, for each image area, an integrated value of the brightness of a plurality of pixels included in an image area as the brightness represent ing the image area. While the integrating circuit 17 calculates the integrated value of the brightness of the pixels included in the image area as the brightness representing the image area in the embodiment, it is not restricted to this. For example, the integrating circuit 17 may calculate the average of the bright ness of the pixels included in an image area as the brightness representing the image area. That is, the brightness represent ing an image area may be being used as is the brightness of pixels included in the image area, being calculated using a predetermined expression, or being in other ways. Further more, the brightness representing an image area may be the brightness of a single pixel or a plurality of pixels included in the image area (more speci?cally, a predetermined pixel in the image area). [0036] In the embodiment, when the brightness represent ing each of the image areas is calculated, the integrating circuit 17 further calculates the integrated value of the bright ness representing each of the image areas calculated (in other words, the brightness of the whole captured image) as the brightness representing the captured image. [0037] When the integrating circuit 17 calculates the brightness representing each image area, the camera micro computer 18 weights the brightness representing each image area (Step S202). In the embodiment, the camera microcom puter 18 weights the brightness representing each image area by multiplying the brightness representing the image area thereof by a weighting coe?icient. [0038] While the camera microcomputer 18 weights the brightness representing each image area by multiplying the brightness representing the image area thereof by the weight ing coef?cient in the embodiment, it is not restricted to this. For example, the camera microcomputer 18 may add a cor rection value preset to each of the image areas to the bright ness representing the image area, thereby the camera micro computer 18 weights the brightness representing each image area. [0039] Now, with reference to FIG. 3, weighting to the brightness representing image areas is described. FIGS. 3(a) to 3(d) are tables for explaining the weighting to the bright ness representing each of the image areas performed in the image capturing apparatus in the embodiment. In the embodi ment, the camera microcomputer 18 differentiates, for each of the image areas, a correction value to be added to the bright ness representing an image area, according to the determining method of exposure set by the mode microcomputer 26. For example, when the determining method of exposure set by the mode microcomputer 26 is a bottom-weighted metering method that optimizes the exposure for a lower portion of the captured image, the camera microcomputer 18 increases the correction value to be added to the brightness representing the image areas in the lower portion of the captured image. Con sequently, as illustrated in FIG. 3(a), the camera microcom puter 18 can optimize the exposure for the image areas in the lower portion of the captured image. [0040] Furthermore, when the determining method of exposure set by the mode microcomputer 26 is a center weighted metering method that optimizes the exposure for a central portion of the captured image, the camera microcom puter 18 increases the correction values to be added to the brightness representing the image areas in the central portion of the captured image. Consequently, as illustrated in FIGS. 3(1)), 3(0) and 3(d), the camera microcomputer 18 can opti mize the exposure for the image areas in the central portion of the captured image. [0041] Referring back to FIG. 2, the camera microcom puter 18 determines whether or not the lens 11 is a wide-angle lens based on the focal length of the lens 11 detected by the zoom-lens position sensor (Step S203). In the embodiment, the camera microcomputer 18 is assumed to determine that the lens 11 is a wide-angle lens when the focal length of the lens 11 detected by the zoom-lens position sensor is shorter than a predetermined focal length. While the camera micro computer 18 uses the focal length of the lens 11 detected by the zoom-lens position sensor to determine whether the lens 11 is a wide-angle lens in the embodiment, it is not restricted to this. For example, the camera microcomputer 18 may determine whether the lens 11 is a wide-angle lens by using the focal length of the lens 11 received from the outside of the image capturing apparatus 1 or a parameter acquirable from the lens 11. [0042] When the lens 11 is determined to be a wide-angle lens as the focal length of the lens detected is shorter than the
12 US 2014/ A1 Sep. 4, 2014 predetermined focal length (Yes at Step S203), the camera microcomputer 18 performs a correction process to correct distortion aberration of the captured image derived from the video signal output from the digital signal processing circuit 15 (Step S204). In the embodiment, the camera microcom puter 18 included in the image capturing apparatus 1 per forms the correction process to correct the distortion aberra tion of the captured image. However it is not restricted to this. A device external to the image capturing apparatus 1 (for example, a display device that displays the captured image) may perform the correction process to correct the distortion aberration of the captured image. [0043] FIGS. 4 and 5 are diagrams for explaining the pro cess of correcting distortion aberration performed in the image capturing apparatus in the embodiment. In the embodi ment, when the camera microcomputer 18 corrects the dis tortion in which the central portion of the captured image before the correction is distorted to bulge outward (what is called barrel distortion) as illustrated in FIG. 4, the camera microcomputer 18 performs at least one of reducing the image areas in the central portion of the captured image and expanding the image areas surrounding the central portion of the captured image. Consequently, the camera microcom puter 18 corrects the distortion aberration of the captured image derived from the video signal output from the digital signal processing circuit 15. [0044] In the embodiment, the camera microcomputer 18 changes the correction method to correct the distortion aber ration of the captured image in response to the determining method of exposure set by the mode microcomputer 26. For example, when the determining method of exposure in the image capturing apparatus 1 is a center-weighted metering method that increases the weighting to the brightness repre senting the image areas in the central portion of the captured image, as illustrated in FIG. 5, the camera microcomputer 18 does not perform the reduction on the central portion of the captured image (for example, 10% of the central portion of the captured image) out of a plurality of image areas into which the captured image is divided, but performs the expan sion on the image areas surrounding the central portion of the captured image to correct the distortion aberration of the captured image. [0045] While the camera microcomputer 18 corrects the distortion aberration of the captured image without correcting the image areas in the central portion of the captured image in the embodiment, the amount of correction for the central portion of the captured image rendered by the process of correcting distortion aberration for the captured image only needs to be smaller than the amount of correction for the image areas surrounding the central portion of the captured image. Consequently, when the exposure is controlled based on the central portion of the captured image, the amount of variation in weighting to the brightness of the central portion of the captured image in response to the correction of distor tion aberration can be made small, and thus the exposure can be controlled based on the brightness close to the brightness of the central portion of the captured image before the distor tion aberration is corrected. [0046] Referring back to FIG. 2, the camera microcom puter 18 corrects the weighting to the brightness representing each of the image areas included in the captured image, based on the size of the image area included in the captured image before the process of correcting distortion aberration and the size of the image area included in the captured image after the process of correcting distortion aberration (Step S205). More speci?cally, the camera microcomputer 18 performs the pro cess of increasing the weighting to the brightness represent ing each image area, when the size of the image area after the process of correcting distortion aberration is larger than the size of the image area before the process of correcting distor tion aberration. And, the camera microcomputer 18 performs the process of decreasing the weighting to the brightness representing each image area, when the size of the image area after the process of correcting distortion aberration is smaller than the size of the image area before the process of correcting distortion aberration (hereinafter referred to as a weighting correction process). Consequently, even when the sizes of each image area included in the captured image before and after the process of correcting distortion aberration differ by the correction of the distortion aberration of the captured image, the degree of brightness representing each image area re?ected on the exposure control can be made as a value corresponding to the size of the image area, and thus optimal exposure control can be made. More speci?cally, when the size of the image area is increased by the process of correcting distortion aberration, increasing the weighting to the image area can increase the degree of brightness of the increased image area re?ected on the exposure control, permitting the optimal exposure control to be made. Furthermore, when the size of the image area is decreased by the process of correct ing distortion aberration, decreasing the weighting to the image area can decrease the degree of brightness of the decreased image area re?ected on the exposure control, per mitting the optimal exposure control to be made. [0047] In the embodiment, the camera microcomputer 18 calculates, for each of the image areas included in the cap tured image, an area ratio obtained by dividing the size of the image area after the process of correcting distortion aberra tion by the size of the image area before the process of correcting distortion aberration. The camera microcomputer 18 then multiplies a weighting coe?icient, by which the brightness representing each image area is multiplied, by the area ratio calculated for each image area to perform the weighting correction process in which the weighting to the brightness representing each image area is corrected. [0048] FIG. 6 is a diagram for explaining the weighting correction process performed in the image capturing appara tus in the embodiment. For example, as illustrated in FIG. 6, when the correction is made by reducing the image areas in a central portion of the captured image out of a plurality of image areas xl to x65 included in a captured image, and by expanding the image areas surrounding the central portion of the captured image, the camera microcomputer 18 divides the size of the image area x33 after the process of correcting distortion aberration by the size of the image area x33 before the process of correcting distortion aberration, thereby the area ratio (for example, 1/3) is calculated. The camera micro computer 18 then multiplies the area ratio of 1/3 calculated for the image area x33 by the weighting coe?icient, by which the brightness representing the image area x33 is multiplied, to perform the weighting correction process in which the weighting to the brightness representing the image area x33 is corrected. The camera microcomputer 18 further performs the weighting correction process on the other image areas included in the captured image in the same manner. [0049] Referring back to FIG. 2, the camera microcom puter 18 controls the exposure of the image capturing appa ratus 1 based on the brightness representing each image area
13 US 2014/ Al Sep. 4, 2014 on which the weighting correction process was performed (Step S206). Meanwhile, when the lens 11 is not determined to be a wide-angle lens (No at Step S203), the camera micro computer 18 controls the exposure of the image capturing apparatus 1 based on the weighted brightness representing each image area (more speci?cally, the brightness represent ing each image area on which the weighting correction pro cess was not performed) (Step S206). [0050] In the embodiment, the camera microcomputer 18 controls the timing circuit 22 to adjust the exposure time of the imaging element 12 so as to control the exposure of the image capturing apparatus 1. For example, when the deter mining method of exposure set by the mode microcomputer 26 is a center-weighted metering method, the camera micro computer 18 calculates an average value of the brightness representing a plurality of image areas on which the weight ing correction process has been performed, and adjusts the exposure time based on the average value calculated. In the embodiment, the camera microcomputer 18 and the integrat ing circuit 17 together serve as a controller. [0051] FIG. 7 is a diagram for explaining the exposure control performed in the image capturing apparatus in the embodiment. When the determining method of exposure set by the mode microcomputer 26 is a partial metering method (or a spot metering method) and the size of the image areas in a central portion (focused portion) of the captured image is reduced to correct distortion aberration as illustrated in FIG. 7, the camera microcomputer 18 controls the exposure of the image capturing apparatus 1 based only on the brightness representing the image areas in the central portion of the captured image for which the distortion aberration has been corrected (for example, 10% of the central portion of the captured image for which the distortion aberration was cor rected), out of a plurality of image areas on which the weight ing correction process has been performed. As a conse quence, the brightness of the image areas surrounding the central portion of the captured image is not re?ected on the exposure control, and thus the exposure for the central portion of the captured image can be an optimum exposure. [0052] As in the foregoing, the image capturing apparatus 1 according to the embodiment performs the weighting correc tion process in which the weighting to the brightness repre senting each image area is increased, when the size of the image area after the process of correcting distortion aberra tion for the captured image is larger than the size of the image area before the correction process, and when the size of each image area after the correction process is smaller than the size of the image area before the correction process, the weighting to the brightness representing the image area is decreased. This permits the degree of brightness representing each image area re?ected on the exposure control to be made as a value corresponding to the size of the respective image areas even when the sizes of the image area included in the captured image before and after the process of correcting distortion aberration differ by the correction of distortion aberration of the captured image, and thus when the distortion aberration of the captured image is corrected, the optimal exposure control can be made. [0053] The program executed in the image capturing appa ratus 1 in the embodiment is embedded in advance and pro vided in a read only memory (ROM) or the like. [0054] The program executed in the image capturing appa ratus 1 in the embodiment may be recorded and provided in a computer readable recording medium such as a compact disc read only memory (CD-ROM), a?exible disk (FD), a com pact disc recordable (CD-R), and a digital versatile disc (DVD), as an installable or executable?le. [0055] The program executed in the image capturing appa ratus 1 in the embodiment may be stored in a computer connected to a network such as the Internet and provided being downloaded via the network. Furthermore, the program executed in the image capturing apparatus 1 in the embodi ment may be provided or distributed via a network such as the Internet. [0056] The program executed by the image capturing appa ratus in the embodiment is modularly con?gured including the controller, and as the actual hardware, a central processing unit (CPU) reads out the program from the ROM and executes the program to load and generate the controller on a main storage device. [0057] The present invention has an advantageous effect of permitting optimal exposure control to be achieved when the distortion aberration of a captured image captured and acquired by an image capturing module is corrected. [0058] Although the invention has been described with respect to speci?c embodiments for a complete and clear disclosure, the appended claims are not to be thus limited but are to be construed as embodying all modi?cations and alter native constructions that may occur to one skilled in the art that fairly fall within the basic teaching herein set forth. What is claimed is: 1. An image capturing apparatus comprising: an image capturing module; and a controller con?gured to control exposure of the image capturing module by dividing a captured image captured by the image capturing module into a plurality of image areas, weighting brightness of a predetermined pixel in each of the image areas, and being based on the weighted brightness of the predetermined pixel in each image area, wherein the controller performs a weighting correction process that increases weighting to the brightness of the predeter mined pixel in each image area, when a size of the image area after a correction process in which distortion aber ration of the captured image is corrected is larger than the size of the image area before the correction process, and the controller performs a weight correction process that decreases the weighting to the brightness of the prede termined pixel in each image area, when the size of the image area after the correction process is smaller than the size of the image area before the correction process. 2. The image capturing apparatus according to claim 1, wherein the controller weights the brightness of a predetermined pixel in each image area by multiplying the brightness of the predetermined pixel in each image area by a weight ing coe?icient, and the weighting correction process multiplies the weighting coe?icient by an area ratio obtained by dividing the size of the image area after the correction process by the size of the image area before the correction process. 3. The image capturing apparatus according to claim 1, wherein the controller performs the weighting correction process, when a lens included in the image capturing module is a wide-angle lens having a focal length shorter than a predetermined focal length.
14 US 2014/ A1 Sep. 4, The image capturing apparatus according to claim 1, wherein the controller makes an amount of correction by the cor rection process for a central portion of the captured image smaller than the amount of correction by the correction process for a portion surrounding the central portion of the captured image, when it is used a center weighted metering method that increases the weighting to the brightness of a predetermined pixel in the image area in the central portion of the captured image. 5. The image capturing apparatus according to claim 1, wherein the controller controls the exposure of the image capturing module based only on the brightness of a predetermined pixel in the image areas in a central portion of the cap tured image after the correction process. 6. An exposure control method performed by an image capturing apparatus, the exposure control method compris ing: controlling exposure of the image capturing apparatus by a controller dividing a captured image captured by the image capturing apparatus into a plurality of image areas, weighting brightness of a predetermined pixel in each of the image areas, and being based on the weighted brightness of the predetermined pixel in each image area, wherein the controller performs a weighting correction process that increases weighting to the brightness of the predeter mined pixel in each image area, when a size of the image area after a correction process in which distortion aber ration of the captured image is corrected is larger than the size of the image area before the correction process, and the controller performs a weighting correction process that decreases the weighting to the brightness of the prede termined pixel in each image area, when the size of the image area after the correction process is smaller than the size of the image area before the correction process. 7. A non-transitory computer-readable recording medium that contains a computer program that causes a computer to function as: a controller con?gured to control exposure of an image capturing module by dividing a captured image captured by the image capturing module into a plurality of image areas, weighting brightness of a predetermined pixel in each of the image areas, and being based on the weighted brightness of the predetermined pixel in each image area, wherein the controller performs a weighting correction process that increases weighting to the brightness of the predeter mined pixel in each image area, when a size of the image area after a correction process in which distortion aber ration of the captured image is corrected is larger than the size of the image area before the correction process, and the controller performs a weighting correction process that decreases the weighting to the brightness of the prede termined pixel in each image area, when the size of the image area after the correction process is smaller than the size of the image area before the correction process. * * * * *
\ \ \ connection connection connection interface interface interface
 US 20140122910A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 20140122910 A1 Chiu et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 1, 2014 (54) RACK SERVER SYSTEM AND OPERATION Publication Classi?cation
US 20140122910A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 20140122910 A1 Chiu et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 1, 2014 (54) RACK SERVER SYSTEM AND OPERATION Publication Classi?cation
US 20140046812A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0046812 A1 FAN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb.
 US 20140046812A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0046812 A1 FAN et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) EXPENSE REPORTS FOR PAYMENTS MADE (52) US. Cl. WITH A MOBILE DEVICE
US 20140046812A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0046812 A1 FAN et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) EXPENSE REPORTS FOR PAYMENTS MADE (52) US. Cl. WITH A MOBILE DEVICE
US 20070139188A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0139188 A1 Ollis et al. HOME PROCESSOR /\ J\ NETWORK
 US 20070139188A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0139188 A1 Ollis et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 21, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR COMMUNICATING
US 20070139188A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0139188 A1 Ollis et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 21, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR COMMUNICATING
llllllllllllllillllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllll
 llllllllllllllillllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllll USOO5535162A United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,535,162 Uenoyama [45] Date of Patent: Jul. 9, 1996 [54] ELECTRICALLY
llllllllllllllillllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllll USOO5535162A United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,535,162 Uenoyama [45] Date of Patent: Jul. 9, 1996 [54] ELECTRICALLY
US 20020072350A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0072350 A1 Fukuzato (43) Pub. Date: Jun.
 US 20020072350A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 20020072350 A1 Fukuzato (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 13, 2002 (54) BACKUP METHOD OF APPLICATIONS OF PORTABLE CELLULAR PHONE
US 20020072350A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 20020072350 A1 Fukuzato (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 13, 2002 (54) BACKUP METHOD OF APPLICATIONS OF PORTABLE CELLULAR PHONE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0035525 A1 Wu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 20, 2003
 (19) United States US 20030035525A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0035525 A1 Wu et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (76) (21) (22) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR DISTINGUISHING TELEPHONE NUMBER
(19) United States US 20030035525A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0035525 A1 Wu et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (76) (21) (22) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR DISTINGUISHING TELEPHONE NUMBER
51 7 522 Ml CRO- MICRO PLEASE
 US005951462A Ulllted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,951,462 Yamanaka [45] Date of Patent: Sep. 14, 1999 [54] ELECTRONIC ENDOSCOPE SYSTEM FOR 5,402,769 4/1995 Tsuji..... 600/109 DISPLAYING UNCONNECTED
US005951462A Ulllted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,951,462 Yamanaka [45] Date of Patent: Sep. 14, 1999 [54] ELECTRONIC ENDOSCOPE SYSTEM FOR 5,402,769 4/1995 Tsuji..... 600/109 DISPLAYING UNCONNECTED
US 201203 03424Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2012/0303424 A1 Lundstrom (43) Pub. Date: NOV.
 US 201203 03424Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2012/0303424 A1 Lundstrom (43) Pub. Date: NOV. 29, 2012 (54) METHOD AND SOFTWARE FOR Publication Classi?cation
US 201203 03424Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2012/0303424 A1 Lundstrom (43) Pub. Date: NOV. 29, 2012 (54) METHOD AND SOFTWARE FOR Publication Classi?cation
US 20090157756Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0157756 A1 Sanvido (43) Pub. Date: Jun.
 US 20090157756Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0157756 A1 Sanvido (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 18, 2009 (54) FILE SYSTEM FOR STORING FILES IN Publication Classi?cation
US 20090157756Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0157756 A1 Sanvido (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 18, 2009 (54) FILE SYSTEM FOR STORING FILES IN Publication Classi?cation
205 Controller / 205
 US 20130089195A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2013/0089195 A1 KIMBLE (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 1 1, 2013 (54) NEXT GENERATION AUTO-DIALER (52) US. Cl. CPC..... H04M3/42
US 20130089195A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2013/0089195 A1 KIMBLE (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 1 1, 2013 (54) NEXT GENERATION AUTO-DIALER (52) US. Cl. CPC..... H04M3/42
60 REDIRECTING THE PRINT PATH MANAGER 1
 US006788429B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,788,429 B1 Clough et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 7, 2004 (54) REMOTE PRINT QUEUE MANAGEMENT FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors: James
US006788429B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,788,429 B1 Clough et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 7, 2004 (54) REMOTE PRINT QUEUE MANAGEMENT FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors: James
(71) Applicant: SPEAKWRITE, LLC,Austin, TX (US)
 US 20130304465Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0304465 A1 Henry et al. (43) Pub. Date: NOV. 14, 2013 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR AUDIO-VIDEO (52) US. Cl.
US 20130304465Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0304465 A1 Henry et al. (43) Pub. Date: NOV. 14, 2013 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR AUDIO-VIDEO (52) US. Cl.
software, and perform automatic dialing according to the /*~102
 US 20140105199A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0105199 A1 Tian (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR AUTOMATIC DIALING ACCESS POINTS (71) Applicant:
US 20140105199A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0105199 A1 Tian (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR AUTOMATIC DIALING ACCESS POINTS (71) Applicant:
US 20070016324A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0016324 A1. Operating System. 106 q f 108.
 US 20070016324A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0016324 A1 Oddiraj u et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 18, 2007 (54) SYSTEM BOOT OPTMZER (75) nventors: Chandar
US 20070016324A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0016324 A1 Oddiraj u et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 18, 2007 (54) SYSTEM BOOT OPTMZER (75) nventors: Chandar
Lookup CNAM / other database for calllng
 (19) United States US 20140003589Al (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0003589 A1 Martino et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 2, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) PROVIDING AUDIO
(19) United States US 20140003589Al (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0003589 A1 Martino et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 2, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) PROVIDING AUDIO
7714 Evaluation 7 logic
 US 20140229045A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0229045 A1 Borchers et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 14, 2014 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) METHOD FOR OPERATING
US 20140229045A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0229045 A1 Borchers et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 14, 2014 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) METHOD FOR OPERATING
Hay (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 17, 2002
 US 20020152322A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0152322 A1 Hay (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 17, 2002 (54) (76) (21) (22) (51) (52) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR FACILITATING
US 20020152322A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0152322 A1 Hay (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 17, 2002 (54) (76) (21) (22) (51) (52) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR FACILITATING
US 20130254326Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0254326 A1 Weng et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep.
 1 l US 20130254326Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0254326 A1 Weng et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 26, 2013 (54) ELECTRONIC DEVICE, CLOUD STORAGE Publication
1 l US 20130254326Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0254326 A1 Weng et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 26, 2013 (54) ELECTRONIC DEVICE, CLOUD STORAGE Publication
US 20050027827A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0027827 A1 Owhadi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb.
 US 20050027827A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0027827 A1 Owhadi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 3, 2005 (54) SYSTEM FOR PROVIDING SUPPORT FOR AN ELECTRONIC
US 20050027827A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0027827 A1 Owhadi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 3, 2005 (54) SYSTEM FOR PROVIDING SUPPORT FOR AN ELECTRONIC
(54) LOTTERY METHOD Publication Classi?cation
 US 20130231987A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0231987 A1 Veverka et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 5, 2013 (54) LOTTERY METHOD Publication Classi?cation (71)
US 20130231987A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0231987 A1 Veverka et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 5, 2013 (54) LOTTERY METHOD Publication Classi?cation (71)
Back up information data by blocks, and generate backup data of each block
 US 20140046903A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0046903 A1 Ylll (43) Pub. Date: (54) DATA BACKUP AND RECOVERY METHOD Publication Classi?cation FOR MOBILE
US 20140046903A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0046903 A1 Ylll (43) Pub. Date: (54) DATA BACKUP AND RECOVERY METHOD Publication Classi?cation FOR MOBILE
US 20020116467A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0116467 A1 Boyer et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug.
 US 20020116467A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0116467 A1 Boyer et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 22, 2002 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classi?cation
US 20020116467A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0116467 A1 Boyer et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 22, 2002 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classi?cation
(54) RETARGETING RELATED TECHNIQUES (52) US. Cl... 705/1453 AND OFFERINGS. (75) Inventors: Ayrnan Farahat, San Francisco, (57) ABSTRACT
 US 20120271714Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2012/0271714 A1 Farahat et a]. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 25, 2012 (54) RETARGETING RELATED TECHNIQUES (52) US. Cl......
US 20120271714Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2012/0271714 A1 Farahat et a]. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 25, 2012 (54) RETARGETING RELATED TECHNIQUES (52) US. Cl......
Patent Application Publication Sep. 30, 2004 Sheet 1 0f 2. Hierarchical Query. Contact Ow FIG. 1
 US 20040193595A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0193595 A1 Kaminsky et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2004 (54) NEAREST KNOWN PERSON DIRECTORY FUNCTION (75)
US 20040193595A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0193595 A1 Kaminsky et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2004 (54) NEAREST KNOWN PERSON DIRECTORY FUNCTION (75)
(Us) (73) Assignee: Avaya Technology Corp. Je?' McElroy, Columbia, SC (US); (21) Appl. No.: 10/413,024. (22) Filed: Apr. 14, 2003 (57) ABSTRACT
 US 20040202300A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0202300 A1 Cooper et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 14, 2004 (54) CALL HANDLING USING NON-SPEECH CUES VIA A PERSONAL
US 20040202300A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0202300 A1 Cooper et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 14, 2004 (54) CALL HANDLING USING NON-SPEECH CUES VIA A PERSONAL
US 20070019798Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0019798 A1 Voight et al. SUBSCRIBER DATABASE.
 US 20070019798Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0019798 A1 Voight et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 25, 2007 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR PROVIDING CUSTOMIZED
US 20070019798Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0019798 A1 Voight et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 25, 2007 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR PROVIDING CUSTOMIZED
US 20130007621A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0007621 A1 Warren (43) Pub. Date: Jan.
 US 20130007621A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0007621 A1 Warren (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2013 (54) (76) (21) (22) (51) (52) SYSTEM FOR LEARNING NAMES OF
US 20130007621A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0007621 A1 Warren (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2013 (54) (76) (21) (22) (51) (52) SYSTEM FOR LEARNING NAMES OF
US 20130097447A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0097447 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr.
 US 20130097447A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0097447 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 18, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR CONTROLLING SLEEP MODE
US 20130097447A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0097447 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 18, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR CONTROLLING SLEEP MODE
(54) (71) (72) Vedelago (TV) (IT) (73) (21) (22) (30) Chirignago (VE) (IT); Alberto Al?er, Foreign Application Priority Data
 US 20130094227Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0094227 A1 Scordino et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 18, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) MOUNTING DEVICE
US 20130094227Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0094227 A1 Scordino et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 18, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) MOUNTING DEVICE
Ulllted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,943,406
![Ulllted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,943,406 Ulllted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,943,406](/thumbs/30/14188909.jpg) US005943406A Ulllted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,943,406 Leta et al. [45] Date of Patent: Aug. 24, 1999 [54] TELEPHONE CALL TRACKING AND 4,813,065 3/1989 Segala..... 379/112 BILLING SYSTEM
US005943406A Ulllted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,943,406 Leta et al. [45] Date of Patent: Aug. 24, 1999 [54] TELEPHONE CALL TRACKING AND 4,813,065 3/1989 Segala..... 379/112 BILLING SYSTEM
US 20130138449A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2013/0138449 A1 Pi0t (43) Pub. Date: May 30, 2013
 US 20130138449A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2013/0138449 A1 Pi0t (43) Pub. Date: May 30, 2013 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR SCHEDULING (52) us. c1. HoME VISITS
US 20130138449A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2013/0138449 A1 Pi0t (43) Pub. Date: May 30, 2013 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR SCHEDULING (52) us. c1. HoME VISITS
(12) United States Patent (16) Patent N6.= US 6,198,814 B1 Gill (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2001
 US006198814B1 (12) United States Patent (16) Patent N6.= Gill (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2001 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR ENTERING 5,621,790 * 4/1997 Grossman 6161...... 379/266 CALL OUTCOME RECORDS IN
US006198814B1 (12) United States Patent (16) Patent N6.= Gill (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2001 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR ENTERING 5,621,790 * 4/1997 Grossman 6161...... 379/266 CALL OUTCOME RECORDS IN
Telephone Dressing Systems - Advantages and Disadvantages
 I US 20030185352A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0185352 A1 Savage et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) AUTOMATED MESSAGE BROADCAST SYSTEM WITH DUAL MESSAGE SOURCES
I US 20030185352A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0185352 A1 Savage et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) AUTOMATED MESSAGE BROADCAST SYSTEM WITH DUAL MESSAGE SOURCES
check is encoded for causing it to b; oplerable with a, predetermined metering device. In t e a ternative em
 12/23/82 Unlted States XF? LHBI'I'QOES Patent [19] [11] 4,317,028 Simjian [] Feb. 23, 1982 [54] SUBSCRIBER CHECK ACCEPTING AND check adapted to operate a metering device comprises ISSUING APPARATUS means
12/23/82 Unlted States XF? LHBI'I'QOES Patent [19] [11] 4,317,028 Simjian [] Feb. 23, 1982 [54] SUBSCRIBER CHECK ACCEPTING AND check adapted to operate a metering device comprises ISSUING APPARATUS means
(54) RAPID NOTIFICATION SYSTEM (52) US. Cl... 709/206. (57) ABSTRACT (75) Inventors: Anand Rajasekar, San Jose, CA
 US 20120303720A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2012/0303720 A1 Rajasekar et a]. (43) Pub. Date: NOV. 29, 2012 (54) RAPID NOTIFICATION SYSTEM (52) US. Cl......
US 20120303720A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2012/0303720 A1 Rajasekar et a]. (43) Pub. Date: NOV. 29, 2012 (54) RAPID NOTIFICATION SYSTEM (52) US. Cl......
Filetto et al. [45] Date of Patent: Feb. 15, 2000
![Filetto et al. [45] Date of Patent: Feb. 15, 2000 Filetto et al. [45] Date of Patent: Feb. 15, 2000](/thumbs/39/20301551.jpg) US006025842A United. States Patent [19] [11] P a t en tn um b er: 6, 025, 842 Filetto et al. [45] Date of Patent: Feb. 15, 2000 [54] SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR WINDOW 5,046,001 9/1991 Barker et al...... 364/200
US006025842A United. States Patent [19] [11] P a t en tn um b er: 6, 025, 842 Filetto et al. [45] Date of Patent: Feb. 15, 2000 [54] SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR WINDOW 5,046,001 9/1991 Barker et al...... 364/200
United States Patent [191
 United States Patent [191 Fancy [54] REDUNDANT SIGNAL CIRCUIT [75] Inventor: Thomas A. Fancy, Westminster, Mass. [73] Assignee: General Electric Company, Schenectady, NY. [211 Appl. No.: 854,973 [22] Filed:
United States Patent [191 Fancy [54] REDUNDANT SIGNAL CIRCUIT [75] Inventor: Thomas A. Fancy, Westminster, Mass. [73] Assignee: General Electric Company, Schenectady, NY. [211 Appl. No.: 854,973 [22] Filed:
222252 211222 1111;111:131... ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 2221522 [73] Assigneez Rockwell Semiconductor Systems 5,754,639 5/1998 Flockhart et al...
![222252 211222 1111;111:131... ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 2221522 [73] Assigneez Rockwell Semiconductor Systems 5,754,639 5/1998 Flockhart et al... 222252 211222 1111;111:131... ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 2221522 [73] Assigneez Rockwell Semiconductor Systems 5,754,639 5/1998 Flockhart et al...](/thumbs/31/14952948.jpg) I I US0059012A Ulllted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: Dez0nn0 [] Date of Patent: * May 4, 1999 [54] APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,526,416 6/1996 DeZonno et al...... 379/266 IDENTIFYING RECORDS ()1?
I I US0059012A Ulllted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: Dez0nn0 [] Date of Patent: * May 4, 1999 [54] APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,526,416 6/1996 DeZonno et al...... 379/266 IDENTIFYING RECORDS ()1?
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 7,068,424 B1 Jennings et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 27, 2006
 US007068424B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 7,068,424 B1 Jennings et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 27, 2006 (54) MULTIPLE PULSE GENERATION 6,141,127 A * 10/2000 Boivin et a1...... 398/92
US007068424B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 7,068,424 B1 Jennings et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 27, 2006 (54) MULTIPLE PULSE GENERATION 6,141,127 A * 10/2000 Boivin et a1...... 398/92
(12) United States Patent Takada
 US008218645B2 (12) United States Patent Takada (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,218,645 B2 Jul. 10, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR ENCODING AND DECODING BY WAVELET TRANSFORM (75) Inventor:
US008218645B2 (12) United States Patent Takada (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,218,645 B2 Jul. 10, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR ENCODING AND DECODING BY WAVELET TRANSFORM (75) Inventor:
How To Make A Programmable Logic Network From A Program To A Program
 Àug.19,19694 c. CHEMLA :TAL ' 3,462,738. _ POLYPHASE PRIORITY DETERMINING SYSTEM Filed May 19, 1966 s sheets-*sheet x l I I I ` ` i i tu t1 t2 t3 t1. t5 te t7 te ts îlo tu t1: ha tu. BY mventors. clauos
Àug.19,19694 c. CHEMLA :TAL ' 3,462,738. _ POLYPHASE PRIORITY DETERMINING SYSTEM Filed May 19, 1966 s sheets-*sheet x l I I I ` ` i i tu t1 t2 t3 t1. t5 te t7 te ts îlo tu t1: ha tu. BY mventors. clauos
(12) Ulllted States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,028,070 B2 Boyd et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 27, 2011
 US008028070B2 (12) Ulllted States Patent (10) Patent N0.: Boyd et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 27, 2011 (54) SYNCHRONIZING TASKS BETWEEN 2002/0065926 A1 * 5/2002 Hackney et al...... 709/231 SERVERS 2004/0221323
US008028070B2 (12) Ulllted States Patent (10) Patent N0.: Boyd et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 27, 2011 (54) SYNCHRONIZING TASKS BETWEEN 2002/0065926 A1 * 5/2002 Hackney et al...... 709/231 SERVERS 2004/0221323
(12) United States Patent Edelen
 US008285799B2 (12) United States Patent Edelen (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 9, 2012 (54) QUOTA-BASED ARCHIVING (75) Inventor: James Edelen, Renton, WA (U S) (73) Assignee: Microsoft Corporation,
US008285799B2 (12) United States Patent Edelen (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 9, 2012 (54) QUOTA-BASED ARCHIVING (75) Inventor: James Edelen, Renton, WA (U S) (73) Assignee: Microsoft Corporation,
US 20020141557A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0141557 A1 STRANDBERG (43) Pub. Date: Oct.
 ---- US 20020141557A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0141557 A1 STRANDBERG (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR PROVIDING AN AUTOMATIC TELEPHONE CALL
---- US 20020141557A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0141557 A1 STRANDBERG (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR PROVIDING AN AUTOMATIC TELEPHONE CALL
. tlllll,1! 1% 11:11 I.,W/ "-111 // out AIHI/ ) I \\ M10. 1 I! (1' 1L- 1!!! I VEHICLE} I] r20 (TRAFFIC COMPUTER 10 RECEIVING UNIT 41 I \ ")SENSOR
![. tlllll,1! 1% 11:11 I.,W/ -111 // out AIHI/ ) I \\ M10. 1 I! (1' 1L- 1!!! I VEHICLE} I] r20 (TRAFFIC COMPUTER 10 RECEIVING UNIT 41 I \ )SENSOR . tlllll,1! 1% 11:11 I.,W/ -111 // out AIHI/ ) I \\ M10. 1 I! (1' 1L- 1!!! I VEHICLE} I] r20 (TRAFFIC COMPUTER 10 RECEIVING UNIT 41 I \ )SENSOR](/thumbs/32/15591097.jpg) United States Patent [19] Albrecht et al. US005812069A [11] Patent Number: [] Date of Patent: Sep. 22, 1998 [54] METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR FORECASTING TRAFFIC FLOWS [75] Inventors: UWe Albrecht, Miinchen;
United States Patent [19] Albrecht et al. US005812069A [11] Patent Number: [] Date of Patent: Sep. 22, 1998 [54] METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR FORECASTING TRAFFIC FLOWS [75] Inventors: UWe Albrecht, Miinchen;
US 20120222106Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0222106 A1 Kuehl (43) Pub. Date: Aug.
 US 20120222106Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0222106 A1 Kuehl (43) Pub. Date: (54) AUTOMATED HYBRID CONNECTIONS (52) US. Cl...... 726/11 BETWEEN MULTIPLE
US 20120222106Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0222106 A1 Kuehl (43) Pub. Date: (54) AUTOMATED HYBRID CONNECTIONS (52) US. Cl...... 726/11 BETWEEN MULTIPLE
(12) United States Patent Hiramoto et a].
![(12) United States Patent Hiramoto et a]. (12) United States Patent Hiramoto et a].](/thumbs/40/20551369.jpg) US008767114B2 (12) United States Patent Hiramoto et a]. (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,767,114 B2 Jul. 1, 2014 (54) SOLID-STATE IMAGING ELEMENT AND IMAGING DEVICE (75) Inventors: Masao Hiramoto,
US008767114B2 (12) United States Patent Hiramoto et a]. (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,767,114 B2 Jul. 1, 2014 (54) SOLID-STATE IMAGING ELEMENT AND IMAGING DEVICE (75) Inventors: Masao Hiramoto,
Access List: my-fw-rule
 US 200701573 02Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0157302 A1 Ottamalika et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2007 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR Publication Classi?cation
US 200701573 02Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0157302 A1 Ottamalika et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2007 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR Publication Classi?cation
US 201403 80094A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0380094 A1 Kota et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec.
 US 201403 80094A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0380094 A1 Kota et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) AVOIDING RESTART ON ERROR IN DATA (52) US. Cl. INTEGRATION CPC.....
US 201403 80094A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0380094 A1 Kota et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) AVOIDING RESTART ON ERROR IN DATA (52) US. Cl. INTEGRATION CPC.....
(54) (75) (2006.01) (73) (21) (22) (63) Peschel, Schoengeising (DE); (30) Foreign Application Priority Data. Robert Trimpe, Wessling (DE)
 US 20120073912Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0073912 A1 CAMILO-MARTINEZ et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 29, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) PNEUMATICALLY
US 20120073912Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0073912 A1 CAMILO-MARTINEZ et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 29, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) PNEUMATICALLY
US 20130169877A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2013/0169877 A1 DANG (43) Pub. Date: Jul.
 US 20130169877A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2013/0169877 A1 DANG (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 4, 2013 (54) SUPPLEMENTAL AUDIO AND VISUAL (52) US. Cl. SYSTEM FORA VIDEO
US 20130169877A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2013/0169877 A1 DANG (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 4, 2013 (54) SUPPLEMENTAL AUDIO AND VISUAL (52) US. Cl. SYSTEM FORA VIDEO
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,253,226 B2 Oguri (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 28, 2012
 US008253226B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,253,226 B2 Oguri (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 28, 2012 (54) ELECTRONIC PARTS, AND METHOD FOR (56) References Cited ARRANGING SHIELDING CASE AND
US008253226B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,253,226 B2 Oguri (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 28, 2012 (54) ELECTRONIC PARTS, AND METHOD FOR (56) References Cited ARRANGING SHIELDING CASE AND
(IP Connection) Miami (54) (76) (21) (22) (51) (52) Application
 US 20070016777Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0016777 A1 Henderson et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 18, 2007 (54) (76) (21) (22) (51) (52) METHOD OF AND SYSTEM
US 20070016777Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0016777 A1 Henderson et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 18, 2007 (54) (76) (21) (22) (51) (52) METHOD OF AND SYSTEM
(12> Ulllted States Patent (16) Patent N6.= US 6,320,621 B1 Fu (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 20, 2001
 US006320621B1 (12> Ulllted States Patent (16) Patent N6.= Fu (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 20, 2001 (54) METHOD OF SELECTINGADIGITAL 5,818,935 * 10/1998 Maa..... 380/20 ING SERVICE 5.900.908 * 5/1999 Kirkland
US006320621B1 (12> Ulllted States Patent (16) Patent N6.= Fu (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 20, 2001 (54) METHOD OF SELECTINGADIGITAL 5,818,935 * 10/1998 Maa..... 380/20 ING SERVICE 5.900.908 * 5/1999 Kirkland
(43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008
 US 20080022336A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0022336 A1 Howcroft et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) SET-TOP BOX NETWORK DIAGNOSTICS (75) (73) (21)
US 20080022336A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0022336 A1 Howcroft et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) SET-TOP BOX NETWORK DIAGNOSTICS (75) (73) (21)
(72) Inventors: Juergen RIEDL, Koenigsbrunn (DE); USPC ( 267/285)
 US 20130087957A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0087957 A1 RIEDL et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 11, 2013 (54) DEVICE FOR DAMPING THE VIBRATIONS Publication Classi?cation
US 20130087957A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0087957 A1 RIEDL et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 11, 2013 (54) DEVICE FOR DAMPING THE VIBRATIONS Publication Classi?cation
United States Patent [191 Brugliera et al.
 United States Patent [191 Brugliera et al. [11] [45] Patent Number: 4,910,767 Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 1990 [54] [75] [73] [21] [22] [51] [52] [58] [56] ANI AUTO DIALER WITH CARRIER CURRENT INTERFACE Inventors:
United States Patent [191 Brugliera et al. [11] [45] Patent Number: 4,910,767 Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 1990 [54] [75] [73] [21] [22] [51] [52] [58] [56] ANI AUTO DIALER WITH CARRIER CURRENT INTERFACE Inventors:
US 20130325834A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2013/0325834 A1 Simburg (43) Pub. Date: Dec.
 US 20130325834A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2013/0325834 A1 Simburg (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 5, 2013 (54) LINK ALLOCATION FOR SEARCH ENGINE (52) US. Cl. OPTIMIZATION
US 20130325834A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2013/0325834 A1 Simburg (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 5, 2013 (54) LINK ALLOCATION FOR SEARCH ENGINE (52) US. Cl. OPTIMIZATION
(12) Ulllted States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,532,017 B2 Ojala et a]. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 10, 2013
![(12) Ulllted States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,532,017 B2 Ojala et a]. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 10, 2013 (12) Ulllted States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,532,017 B2 Ojala et a]. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 10, 2013](/thumbs/40/20548245.jpg) US008532017B2 (12) Ulllted States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,532,017 B2 Ojala et a]. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 10, 2013 (54) TPC COMMAND SIGNALING IN DL (58) Field of Classi?cation Search CONTROL CHANNEL
US008532017B2 (12) Ulllted States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,532,017 B2 Ojala et a]. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 10, 2013 (54) TPC COMMAND SIGNALING IN DL (58) Field of Classi?cation Search CONTROL CHANNEL
US 20020174380A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2002/0174380 A1. Mannarsamy (43) Pub. Date: NOV.
 US 20020174380A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2002/0174380 A1 Mannarsamy (43) Pub. Date: NOV. 21, 2002 (54) HELPDESK SYSTEM AND METHOD (52) US. Cl...... 714/25
US 20020174380A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2002/0174380 A1 Mannarsamy (43) Pub. Date: NOV. 21, 2002 (54) HELPDESK SYSTEM AND METHOD (52) US. Cl...... 714/25
(54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR OBTAINING Publication Classi?cation AND EXECUTING INSTRUCTIONS FROM A (51) Int Cl PRIVATE NETWORK G06F 15/16 (2006.
 US 20120215827A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0215827 A1 Rachitsky et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 23, 2012 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR OBTAINING Publication
US 20120215827A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0215827 A1 Rachitsky et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 23, 2012 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR OBTAINING Publication
(10) Patent N0.: US 6,570,581 B1 Smith (45) Date of Patent: May 27, 2003
 US006570581B1 (12) United States Patent () Patent N0.: Smith (45) Date of Patent: May 27, 2003 (54) ON-LOCATION VIDEO ASSISTANCE 5,960,074 A * 9/1999 Clark..... 370/3 SYSTEM WITH COMPUTER GENERATEI) 6,166,744
US006570581B1 (12) United States Patent () Patent N0.: Smith (45) Date of Patent: May 27, 2003 (54) ON-LOCATION VIDEO ASSISTANCE 5,960,074 A * 9/1999 Clark..... 370/3 SYSTEM WITH COMPUTER GENERATEI) 6,166,744
wanagamem transformation and management
 US 20120150919Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0150919 A1 Brown et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 14, 2012 (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) (51) AGENCY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
US 20120150919Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0150919 A1 Brown et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 14, 2012 (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) (51) AGENCY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
i 1 4 115 5330355 122 123 X USE HOST USB B105 121R CONTROLLER 111a 40 11a 1 21
 US007519756B2 (12) Ulllted States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 7,519,756 B2 Yamamoto et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Apr. 14, 2009 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (52) US. Cl...... 710/302; 710/10; 710/14; CONTROLLING
US007519756B2 (12) Ulllted States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 7,519,756 B2 Yamamoto et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Apr. 14, 2009 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (52) US. Cl...... 710/302; 710/10; 710/14; CONTROLLING
US 20120215907A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0215907 A1 Chung (43) Pub. Date: Aug.
 US 20120215907A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0215907 A1 Chung (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR (52) US. Cl...... 709/224 SELF-ADJUSTING LOGGING
US 20120215907A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0215907 A1 Chung (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR (52) US. Cl...... 709/224 SELF-ADJUSTING LOGGING
(54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR FINDING Publication Classi?cation CONNECTIONS AMONG SUBSCRIBERS TO AN EMAIL CAMPAIGN (51) Int- Cl
 US 201403 79420A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0379420 A1 Chestnut et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2014 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR FINDING Publication
US 201403 79420A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0379420 A1 Chestnut et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2014 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR FINDING Publication
/ \33 40 \ / \\ \ \ M / 32. 28f 1. (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication Lawser et al. NETWORK \ 36. SERVlCE 'NTERNET SERVICE
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication Lawser et al. US 20130336314A1 (10) Pub. N0.: US 2013/0336314 A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 19, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) METHOD FOR COMPLETING
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication Lawser et al. US 20130336314A1 (10) Pub. N0.: US 2013/0336314 A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 19, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) METHOD FOR COMPLETING
ADD UPLOADED DATA TO CLOUD DATA REPOSITORY
 US 20120311081A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0311081 A1 Robbin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 6, 2012 (54) MANAGEMENT OF NETWORK-BASED DIGITAL DATA REPOSITORY
US 20120311081A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0311081 A1 Robbin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 6, 2012 (54) MANAGEMENT OF NETWORK-BASED DIGITAL DATA REPOSITORY
How an electronic shutter works in a CMOS camera. First, let s review how shutters work in film cameras.
 How an electronic shutter works in a CMOS camera I have been asked many times how an electronic shutter works in a CMOS camera and how it affects the camera s performance. Here s a description of the way
How an electronic shutter works in a CMOS camera I have been asked many times how an electronic shutter works in a CMOS camera and how it affects the camera s performance. Here s a description of the way
(54) Applicant: (71) (72) Assignee: (73) (21) (22) (60)
 US 20140373140A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0373140 A1 Waters, JR. et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 18, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) DATA CENTER
US 20140373140A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0373140 A1 Waters, JR. et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 18, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) DATA CENTER
(43) Pub. Date: Feb. 16, 2012
 US 20120041897A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0041897 A1 Teague et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) MARKET INDICATOR PROCESS AND METHOD
US 20120041897A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0041897 A1 Teague et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) MARKET INDICATOR PROCESS AND METHOD
(30) Foreign Application Priority Data
 US 20040015727A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0015727 A1 Lahti et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 22, 2004 (54) SYNCHRONIZATION METHOD (76) Inventors: Jerry Lahti,
US 20040015727A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0015727 A1 Lahti et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 22, 2004 (54) SYNCHRONIZATION METHOD (76) Inventors: Jerry Lahti,
US 20090055802A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0055802 A1 CROSBY (43) Pub. Date: Feb.
 US 20090055802A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0055802 A1 CROSBY (43) Pub. Date: (54) SELECTIVE MONITORING OF SOFTWARE Publication Classi?cation APPLICATIONS
US 20090055802A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0055802 A1 CROSBY (43) Pub. Date: (54) SELECTIVE MONITORING OF SOFTWARE Publication Classi?cation APPLICATIONS
US 20060100919A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0100919 A1 Levine (43) Pub. Date: May 11, 2006
 US 20060100919A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0100919 A1 Levine (43) Pub. Date: May 11, 2006 (54) EMPLOYEE RECRUITING SYSTEMS AND METHODS (76) Inventor:
US 20060100919A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0100919 A1 Levine (43) Pub. Date: May 11, 2006 (54) EMPLOYEE RECRUITING SYSTEMS AND METHODS (76) Inventor:
remote backup central communications and storage facility
 US 20040122914A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0122914 A1 Williams (43) Pub. Date: (54) SECURE DATA BACKUP (52) US. Cl...... 709/217; 711/162 COMMUNICATIONS
US 20040122914A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0122914 A1 Williams (43) Pub. Date: (54) SECURE DATA BACKUP (52) US. Cl...... 709/217; 711/162 COMMUNICATIONS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0325512 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 5, 2013
 (19) United States US 20130325512Al (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0325512 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 5, 2013 (54) ELECTRONIC MEDICAL RECORD SYSTEM Publication Classi?cation
(19) United States US 20130325512Al (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0325512 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 5, 2013 (54) ELECTRONIC MEDICAL RECORD SYSTEM Publication Classi?cation
Support systems messaging via email
 > _. US 20110231500A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0231500 A1 Zhu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 22, 201 1 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR INTEGRATING Publication
> _. US 20110231500A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0231500 A1 Zhu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 22, 201 1 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR INTEGRATING Publication
US005847562A United States Patent [19] [ill Patent Number: 5,847,562 Fulton et al. [45] Date of Patent: Dec. 8, 1998. 1-0- Experimental data
![US005847562A United States Patent [19] [ill Patent Number: 5,847,562 Fulton et al. [45] Date of Patent: Dec. 8, 1998. 1-0- Experimental data US005847562A United States Patent [19] [ill Patent Number: 5,847,562 Fulton et al. [45] Date of Patent: Dec. 8, 1998. 1-0- Experimental data](/thumbs/39/20158028.jpg) 1 I11111 1l1 Il11Il11I I 111111 I I 1l US005847562A United States Patent [19] [ill Patent Number: 5,847,562 Fulton et al. [45] Date of Patent: Dec. 8, 1998 [54] THICKNESS GAUGING OF SINGLE-LAYER CONDUCTIVE
1 I11111 1l1 Il11Il11I I 111111 I I 1l US005847562A United States Patent [19] [ill Patent Number: 5,847,562 Fulton et al. [45] Date of Patent: Dec. 8, 1998 [54] THICKNESS GAUGING OF SINGLE-LAYER CONDUCTIVE
US 20120066004A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0066004 A1 Lee (43) Pub. Date: Mar.
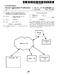 US 212664A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (1) Pub. o.: US 212/664 A1 Lee (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 15, 212 (54) (76) (21) (22) (6) METHOD AD SYSTEM FOR PERSOAL ISURACE COMPARISO AD
US 212664A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (1) Pub. o.: US 212/664 A1 Lee (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 15, 212 (54) (76) (21) (22) (6) METHOD AD SYSTEM FOR PERSOAL ISURACE COMPARISO AD
Naylor, Lake OsWego, OR (US) (51) Int_ CL
 US 20100023688A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0023688 A1 Crowther et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYMMETRICAL STORAGE ACCESS ON (86) PCT No.: PCT/US2007/001542
US 20100023688A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0023688 A1 Crowther et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYMMETRICAL STORAGE ACCESS ON (86) PCT No.: PCT/US2007/001542
GATEWAY ' 8 8 8 o o o
 US 20130102274A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0102274 A1 Lauwaert (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 25, 2013 (54) SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR MOBILE Publication Classi?cation
US 20130102274A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0102274 A1 Lauwaert (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 25, 2013 (54) SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR MOBILE Publication Classi?cation
US 20130117218A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0117218 A1 Fan et al.
 US 20130117218A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0117218 A1 Fan et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 9, 2013 (54) CROSS-STORE ELECTRONIC DISCOVERY (75) Inventors: John
US 20130117218A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0117218 A1 Fan et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 9, 2013 (54) CROSS-STORE ELECTRONIC DISCOVERY (75) Inventors: John
Ulllted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 6,141,545
![Ulllted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 6,141,545 Ulllted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 6,141,545](/thumbs/27/11642488.jpg) US0061445A Ulllted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: Begeja et al. [45] Date of Patent: *Oct. 31, 2000 [54] METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR REMOTE 5,440,614 8/1995 Sonberg et a1...... 455/414 CALL FORWARDING
US0061445A Ulllted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: Begeja et al. [45] Date of Patent: *Oct. 31, 2000 [54] METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR REMOTE 5,440,614 8/1995 Sonberg et a1...... 455/414 CALL FORWARDING
(12) United States Patent
 US007983978B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: Brusso et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 19, 2011 (54) FOREIGN CURRENCY INDEX OTHER PUBLICATIONS New Summary Measures of the Foreign Exchange Value
US007983978B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: Brusso et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 19, 2011 (54) FOREIGN CURRENCY INDEX OTHER PUBLICATIONS New Summary Measures of the Foreign Exchange Value
E70 Rear-view Camera (RFK)
 Table of Contents (RFK) Subject Page Introduction..................................................3 Rear-view Camera..............................................3 Input/Output...................................................4
Table of Contents (RFK) Subject Page Introduction..................................................3 Rear-view Camera..............................................3 Input/Output...................................................4
: 2R5 ML OR 2. United States Patent [191. Fig-A3 [111 3,909,553. [451 Sept. 30, 1975 C54 ( T : Marshall. Laboratories Incorporated, Northlake, Ill.
 United States Patent [191 Marshall [111 3,909,553 [451 Sept. 30, 1975 I54] LINE CARD FOR KEY TELEPHONE SYSTEMS ADAPTED TO PROVIDE MUSIC DURING HOLD CONDITION [75] Inventor: Richard A. Marshall, Bensenville.
United States Patent [191 Marshall [111 3,909,553 [451 Sept. 30, 1975 I54] LINE CARD FOR KEY TELEPHONE SYSTEMS ADAPTED TO PROVIDE MUSIC DURING HOLD CONDITION [75] Inventor: Richard A. Marshall, Bensenville.
TEPZZ 96 A_T EP 2 961 111 A1 (19) (11) EP 2 961 111 A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ 96 A_T (11) EP 2 961 111 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication:.12.1 Bulletin 1/3 (21) Application number: 147426.7 (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ 96 A_T (11) EP 2 961 111 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication:.12.1 Bulletin 1/3 (21) Application number: 147426.7 (22) Date
(12) United States Patent Wen et a].
![(12) United States Patent Wen et a]. (12) United States Patent Wen et a].](/thumbs/27/10120921.jpg) ' US008719918B2 (12) United States Patent Wen et a]. (10) Patent N0.: () Date of Patent: May 6, 14 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (87) () () (51) (52) (58) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR DISTRIBUTED SECURITY CONTROL
' US008719918B2 (12) United States Patent Wen et a]. (10) Patent N0.: () Date of Patent: May 6, 14 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (87) () () (51) (52) (58) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR DISTRIBUTED SECURITY CONTROL
Ff'if ~ _ INVISIWALL. Shively (43) Pub. Date: NOV. 28, 2002 . LOCAL ONSITE. (Us) (21) Appl. No.: 09/865,377
 US 20020178378A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0178378 A1 Shively (43) Pub. Date: NOV. 28, 2002 (54) SECURE NTRUSON DETECTON SYSTEM (76) nventor: Geo?'rey
US 20020178378A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0178378 A1 Shively (43) Pub. Date: NOV. 28, 2002 (54) SECURE NTRUSON DETECTON SYSTEM (76) nventor: Geo?'rey
22X DSP COLOR ZOOM CAMERA AUTO FOCUS ZOOM CAMERA
 Instruction Manual 22X DSP COLOR ZOOM CAMERA AUTO FOCUS ZOOM CAMERA OPERATION / INSTALLATION MANUAL Thank you for using this product. Please read this manual carefully before use, Please keep this instruction
Instruction Manual 22X DSP COLOR ZOOM CAMERA AUTO FOCUS ZOOM CAMERA OPERATION / INSTALLATION MANUAL Thank you for using this product. Please read this manual carefully before use, Please keep this instruction
Levy Processing System 1_Q
 US 20130332350A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0332350 A1 Polk (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 12, 2013 (54) SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR (52) US. Cl. PROCESSINIG LEIES
US 20130332350A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0332350 A1 Polk (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 12, 2013 (54) SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR (52) US. Cl. PROCESSINIG LEIES
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,721,047 B2 Sakurai et a]. (45) Date of Patent: May 13, 2014
![(12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,721,047 B2 Sakurai et a]. (45) Date of Patent: May 13, 2014 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,721,047 B2 Sakurai et a]. (45) Date of Patent: May 13, 2014](/thumbs/39/20155291.jpg) USOO8721047B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,721,047 B2 Sakurai et a]. (45) Date of Patent: May 13, 2014 (54) LIQUID EJECTION HEAD AND INK JET (56) References Cited PRINTING APPARATUS
USOO8721047B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,721,047 B2 Sakurai et a]. (45) Date of Patent: May 13, 2014 (54) LIQUID EJECTION HEAD AND INK JET (56) References Cited PRINTING APPARATUS
US 20050026694A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0026694 A1 Kelly et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb.
 US 20050026694A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 20050026694 A1 Kelly et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 3, 2005 (54) PRIZE REDEMPTION SYSTEM FOR GAMES EXECUTED OVER A
US 20050026694A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 20050026694 A1 Kelly et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 3, 2005 (54) PRIZE REDEMPTION SYSTEM FOR GAMES EXECUTED OVER A
United States. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0268350 A1 Koonce et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 10, 2013 (19) (54) (71) (72)
 (19) United States US 20130268350A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0268350 A1 Koonce et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 10, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (63) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR
(19) United States US 20130268350A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0268350 A1 Koonce et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 10, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (63) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR
US 20070041365A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0041365 A1 Nej ah (43) Pub. Date: Feb.
 US 20070041365A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0041365 A1 Nej ah (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 22, 2007 (54) EBAY AND GOOGLE VOIP TELEPHONE (75) Inventor: Allen Nejah,
US 20070041365A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0041365 A1 Nej ah (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 22, 2007 (54) EBAY AND GOOGLE VOIP TELEPHONE (75) Inventor: Allen Nejah,
subscription event billing event Dispatch selection to user
 US 20050289047A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0289047 A1 Oliver et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) VIRTUAL MARKETPLACE FOR WIRELESS DEVICE APPLICATIONS
US 20050289047A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0289047 A1 Oliver et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) VIRTUAL MARKETPLACE FOR WIRELESS DEVICE APPLICATIONS
US 20110043191A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0043191 A1 Gutierrez (43) Pub. Date: Feb.
 US 20110043191A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0043191 A1 Gutierrez (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 24, 2011 (54) PHOENIX PROBE X VOLTAGE TESTER Publication Classi?cation
US 20110043191A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0043191 A1 Gutierrez (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 24, 2011 (54) PHOENIX PROBE X VOLTAGE TESTER Publication Classi?cation
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,671,016 B2 Little (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 11, 2014
 US008671016B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,671,016 B2 Little (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 11, 2014 (54) METHODS AND APPARATUS FOR 2003/0023481 A1 * 1/2003 Calvert et a1...... 705/14 ADVERTISING
US008671016B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,671,016 B2 Little (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 11, 2014 (54) METHODS AND APPARATUS FOR 2003/0023481 A1 * 1/2003 Calvert et a1...... 705/14 ADVERTISING
(54) METHOD FOR AUTOMATED HANDLING OF Publication Classi?cation OUTBOUND CONTACTS REQUIRING ASSURED CONNECTION TO A LIVE AGENT (51) Int- Cl
 US 20140044256A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0044256 A1 Zgardovski et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD FOR AUTOMATED HANDLING OF Publication Classi?cation
US 20140044256A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0044256 A1 Zgardovski et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD FOR AUTOMATED HANDLING OF Publication Classi?cation
NETWORK BOUNDARY PRIVATE NETWORK PUBLIC _1 NETWORK
 US 20050177647A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0177647 A1 Anantha et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) MOBILE IP EXTENSION TO SUPPORT PRIVATE
US 20050177647A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0177647 A1 Anantha et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) MOBILE IP EXTENSION TO SUPPORT PRIVATE
