Shark Cart Aquarium of the Pacific
|
|
|
- Alexina Turner
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Shark Cart Aquarium of the Pacific This activity outline was developed for use in a variety of informal venues. By design, it provides the content, pedagogy and strategy necessary for implementation by both the novice and experienced informal educator. It is expected that this outline will be adapted and improved upon by the user. We welcome your feedback! Synopsis of the Activity Visitors learn about the diversity of shark feeding adaptations and diet by interacting with shark artifacts. Shark teeth are the focus of the activity, but shark senses, anatomy and conservation may also be discussed. Audience The whale cart will target visitors of all ages. Themes can be modified easily with age appropriate concepts. Suited for small groups of participants. Setting Open areas on the floor easily visible to visitors. Activity Goals Learners will examine a variety of shark artifacts and gain an understanding of shark diversity through the investigation of shark feeding adaptations. Concepts There are many different kinds of sharks and rays. Different sharks have different types of teeth. Shark teeth are adapted for eating different kinds of prey. Ocean Literacy Principles 5. The ocean supports a great diversity of life and ecosystems. d. Ocean biology provides many unique examples of life cycles, adaptations and important relationships among organisms (symbiosis, predator-prey dynamics and energy transfer) that do not occur on land. Materials All materials are housed on or within a large rolling cart: Fabricated Great White Shark Jaw Bull Shark Jaw Mako Shark Jaw Zebra Shark Jaw Ray Jaw Pictures of sharks Models of sharks (optional) Megalodon tooth (optional)
2 Preparation and Set-up Bring the cart to the activity location and place the items on top of the cart. Be sure to set the jaws apart from the photos and arrange them randomly. Guiding Questions What do you notice about these items? How do they feel? What do you think sharks eat? What do you think a shark with pointy teeth would eat? What is your evidence? What are some differences between these teeth and the others? What do you think a shark or ray with flat teeth would eat? What is your evidence? How do you think humans might be connected to sharks? How can someone like you help protect sharks? Activity Description Introduction: Invite guests to come explore the shark cart. Because the scale of some of the objects is quite impressive, using artifacts like the white shark jaw or the megalodon tooth might be of interest. Also, noting the diversity of teeth could help gain guest interest. For instance, you could say, Have you ever seen a shark tooth the size of your hand? Do you think all sharks have teeth like that? Come over and find out. Free exploration: Invite them to view and interact with the shark artifacts. Allow them to gently touch and handle the artifacts. As visitors freely explore, ask them questions about their observations of the artifacts to encourage them to think about the composition of the objects, the biology of the organism, and the use of the body part. Suggested questions: How do they feel? What do you notice about them? How are they similar to each other? How are they different from each other? What is your evidence? What is this jaw made of? How about the teeth? Are there parts of your body that are made of the same kinds of materials? What are they? How might this item help the animal survive? Key ideas to address in this conversation: Sharks are fish in the class Chondrichthyes, which also includes rays, skates, and chimeras. All members of this class have cartilaginous skeletons; cartilage is the same dense but flexible connective tissue that is found in human ears and noses. There are over 400 species of sharks alone which encompasses are large diversity of body sizes, morphologies and adaptations. Form, Function, and Feeding: Let visitors know that, similar to other animals, sharks teeth offer a lot of information about what sharks eat. Invite visitors to take a closer look at the different teeth, and challenge them to figure out what the shark might eat based on
3 the size and shape of the teeth. Remember to encourage visitors to explain and provide evidence for their ideas. Consider sharing pictures of the different sharks with visitors so that they can recognize the size of the predators in relation to the teeth. Encourage visitors to ask questions and talk with others in their group. Suggested questions: What similarities do you notice about these teeth/jaws? (size, shape, features, composition) What differences do you notice about these teeth/jaws? (size, shape, features, composition) Based on what you observe in the jaws and teeth, what do you think this shark eats? What is your evidence? How do you think this shark captures its prey? What is your evidence? How do you think this shark eats its prey? What is your evidence? Do you think other animals have similar adaptations? Do your teeth say much about what you eat? What is your evidence? (The same could be asked of other aquarium animals; guests could be directed to exhibits to make observations.) Key ideas to address in this conversation There is a large diversity of sharks with an equally large diversity in feeding adaptations. Shark teeth can be big or small, sharp or blunt, serrated or smooth. Serrated teeth can be used like knives to cut up larger prey items, like marine mammals or large fish. Pointy teeth can be used to grasp foods, but may not be appropriate for cutting up prey. Many animals with sharp pointy teeth swallow their prey whole (and are therefore limited by the size of their gape.) Flat teeth are used for crushing prey, especially those with hard shells, such as mollusks and crustaceans. One thing that all different types of teeth have in common is that they are exchangeable throughout the entire life. The teeth of a shark are attached to the skin covering the jaw, and are arranged in multiple rows. Behind each tooth there are several new ones waiting to be used. Some sharks change their teeth randomly while others change the entire row at the same time. The teeth are embedded in the gums but not attached directly to the jawbone, as in other fishes. The exchange of teeth goes on the entire life and for some species it has been estimated that they use as many as 30,000 teeth during their lifetime. The jaws are not firmly fixed to the braincase, but instead loosely connected. This loose attachment allows sharks to widen their mouth and extend the upper jaw so they can engulf large items of food and even whole animals. Most sharks only use the first one or two rows of teeth in the front, but some species use as many as eight rows at the same time. The rows that are not in use lie with the teeth bent back in the gums and wait for their turn. Each new tooth is slightly larger than the tooth it replaces.
4 This discussion of form and function in teeth is especially important to help dispel the myth that sharks are maneaters. Most shark attack incidents are a case of mistaken identity. Related Activities/Extensions/Modifications Shark Conservation: Sharks are misunderstood animals that play an important role in the balance of the ocean ecosystem. Visitors that understand shark feeding adaptations can be directed to other places in the ISEI to see sharks and to appreciate their value in ecosystem function, engineering, design, and tourism. Additional Resources Background Vocabulary Predator - any organism that exists by killing and eating other organisms Prey - an animal hunted or seized for food Cartilaginous - having a skeleton composed either entirely or mainly of cartilage, such as vertebrates of the class Chondrichthyes, which includes the sharks, rays, and skates Cartilage - a firm, elastic, flexible type of connective tissue of a translucent whitish or yellowish color Adaptation- structure or behavior that helps an organism to survive Sharks and Rays: Sharks, rays, and ratfish are referred to as cartilaginous fishes. These animals have a skeleton of cartilage, which is less dense than bone and allows them to conserve energy while swimming. While a cartilaginous skeleton makes them lighter, sharks are still more dense than the surrounding seawater and will sink if they stop swimming. Many people believe that if a shark stops swimming it will not be able to breath and will die. This is only true for a small percentage of sharks. Many sharks have adaptations that allow them to breathe while lying motionless on the ocean floor. Shark teeth: A shark s teeth are made of enamel and dentine. They are the only hard part on a shark and the only part that readily becomes a fossil. A shark s teeth are set in rows and are replaced constantly as they fall out. A shark may lose and re-grow 30,000 teeth in a lifetime. Great White: Great White sharks can grow to be 22 feet long, although they are more often less than 20 feet. White sharks have serrated, triangular teeth that act like knives. Young Great White sharks prey primarily upon fishes. Larger Great Whites eat marine mammals, turtles, sea birds, and large fishes. While these sharks have been known to bite people, attacks are largely viewed to be a case of mistaken identity. A shark may bite a surfer or a scuba diver because they resemble a seal or sea lion. Usually, after the initial bite the person is spit out and the shark swims away.
5 Bull Shark: Bull sharks have thick triangular teeth that are serrated to tear large prey into bite-sized pieces. Like most sharks, Bull sharks typically prey on other fish, but turtles, birds, marine mammals, and carrion are also on the menu. Amazingly Bull Sharks have the ability to swim into freshwater. They have been found hundreds of miles up rivers and there is even a landlocked population of Bull shark in Lake Nicaragua. Mako Shark: Mako sharks are one of the fastest fishes in the sea. They use their sharp pointy teeth not to tear, but to grasp and swallow their prey whole. They typically eat open ocean fishes like mackerels, tunas, and even other sharks. Zebra Shark: A Zebra shark is black with white bars while a juvenile and loses this coloration gradually as it grows. As an adult, zebra sharks actually have spots. The teeth of this shark are small and pointy and help them to grasp small fishes and crustaceans. Ray: Not all rays are stingrays. While some rays possess a sting many others do not. The sting is used only in self-defense and not to capture prey. Rays are dorso-ventrally flattened (i.e., like a pancake) and their mouths are located on the ventral side of their body. They typically have flattened teeth to crush and eat hard-shelled invertebrates, often eating those that live in the sediment. Teeth and jaws (from A shark tooth can be big or small, sharp or blunt, serrated or smooth. The shape of the teeth is an adaptation to what the animal eats. Flat teeth are useful to crush mollusks and crustaceans, while sharp teeth are more adapted to rip chunks of flesh out of a prey. One thing that all different types of teeth have in common is that they are exchangeable throughout the entire life. The teeth are attached to multiple rows in the jaws. Behind each tooth there are several new ones waiting to be used. Some sharks change their teeth randomly while others change the entire row at the same time. The teeth are embedded in the gums but not attached directly to the jawbone, as in other fishes. The teeth are actually enlarged and modified placoid scales and just like our teeth, they consist of an outer enamel layer and an inner pulp. Most sharks only use the first one or two rows of teeth in the front, but some species use as many as eight rows at the same time. The rows that are not in use lie with the teeth bent back in the gums and wait for their turn. Each new tooth is slightly larger than the tooth it replaces. The older the shark gets and the more it grows, the larger its teeth gets. The size of the teeth of the same individual can vary depending on where in the jaw the tooth is. However, some species have all teeth in the same size. The exchange of teeth goes on the entire life and for some species it has been estimated that they use as many as 30,000 teeth during their lifetime. The jaws are not firmly fixed to the braincase, but instead loosely connected. This loose attachment allows sharks to widen their mouth and extend the upper jaw so they can engulf large items of food and even whole animals. Ref: Hickman CP, Roberts LS and Larson A (2000), Animal Diversity, McGraw-Hill
6 Higher Education, USA -- Springer VG and Gold JP (1989), Sharks in question: the Smithsonian answer book, Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington, D.C. London Skeleton (from The skeleton of sharks is to a large extent made out of cartilage, unlike other vertebrate s skeletons, which are made out of bone. Cartilage is a type of connective tissue composed of cells called chondrocytes suspended in a matrix of protein. The parts of the skeleton that are in need of extra support, e.g. jaws, vertebrae or gill arches, are built up by calcified cartilage. The calcified cartilage is harder than normal cartilage due to deposits of calcium salt. Often, the appearance of calcified cartilage and bone is very similar, and differences are apparent only after the tissues have been specially treated and examined with a microscope. The main difference between bone and cartilage is that bone is composed of osteocytes instead of chondrocytes. The cartilaginous skeleton of the modern shark is something that probably has evolved from a bony skeleton, which means that the previous ancestor of today's sharks had a skeleton made out of bone. There is no reason to believe that having a cartilaginous skeleton is disadvantageous. On the contrary, cartilage is less dense and more elastic than bone, providing advantages of buoyancy and flexibility. Because cartilage and other soft parts decay rapidly, it is rare to find complete or even nearly complete fossil remains of sharks. This is one reason why evolutionary relationships of sharks are so difficult to trace. Often teeth, scales, spines or vertebrae are the only parts remaining in fossils, and from these parts alone, it is very hard to figure out what the entire shark looked like. Ref: Hickman CP, Roberts LS and Larson A (2000), Animal Diversity, McGraw-Hill Higher Education, USA -- Springer VG and Gold JP (1989), Sharks in question: the Smithsonian answer book, Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington, D.C. London
Supported by. A seven part series exploring the fantastic world of science.
 Supported by A seven part series exploring the fantastic world of science. Find out about the different types of teeth in your mouth. Milk Teeth As a child you have 20 milk teeth. Your first tooth appears
Supported by A seven part series exploring the fantastic world of science. Find out about the different types of teeth in your mouth. Milk Teeth As a child you have 20 milk teeth. Your first tooth appears
These pages build on Units 2B & C and introduce predator-prey relationships and food chains.
 Unit 4B Habitats Teaching Notes These pages build on Units 2B & C and introduce predator-prey relationships and food chains. Curriculum, resource and other links Sc1 & Sc2 Resources Associated with this
Unit 4B Habitats Teaching Notes These pages build on Units 2B & C and introduce predator-prey relationships and food chains. Curriculum, resource and other links Sc1 & Sc2 Resources Associated with this
Bony Fish Anatomy Worksheet
 Educational Material Bony Fish Anatomy Worksheet Teacher Information This activity is designed to be team-taught by the classroom and art teacher. Use this guide in conjunction with fish-related art to
Educational Material Bony Fish Anatomy Worksheet Teacher Information This activity is designed to be team-taught by the classroom and art teacher. Use this guide in conjunction with fish-related art to
Talking About Penguins by Guy Belleranti
 Talking About Penguins Penguins are one of the world s most interesting birds. They waddle when they walk, and have flippers instead of wings. The bones in a penguin s flippers are heavier and more solid
Talking About Penguins Penguins are one of the world s most interesting birds. They waddle when they walk, and have flippers instead of wings. The bones in a penguin s flippers are heavier and more solid
Evolutionary Evidence
 Evolutionary Evidence 7th Grade, Science and English/Language Arts: Age of Mammals Make the most of your Museum field trip by integrating it into your classroom curriculum. These lesson plans provide a
Evolutionary Evidence 7th Grade, Science and English/Language Arts: Age of Mammals Make the most of your Museum field trip by integrating it into your classroom curriculum. These lesson plans provide a
Silent, Nighttime Hunters By Guy Belleranti
 By Guy Belleranti Owls are raptors, or birds of prey. They are carnivores who quickly and silently swoop down on their prey from above. Most raptors such as eagles, hawks and falcons are day hunters. They
By Guy Belleranti Owls are raptors, or birds of prey. They are carnivores who quickly and silently swoop down on their prey from above. Most raptors such as eagles, hawks and falcons are day hunters. They
Animal skeletons. The museum holds hundreds of skeletons - of fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals.
 Animal skeletons All animals have skeletons of one sort or another. Mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians and fish have bony skeletons. These skeletons come in all shapes and sizes, but they also share
Animal skeletons All animals have skeletons of one sort or another. Mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians and fish have bony skeletons. These skeletons come in all shapes and sizes, but they also share
Unit 3L.4: Body Parts and Functions
 Unit 3L.4: Organs in the Human body Keeping Healthy The Skeleton Science skills: Classification Observing Making models Data collection By the end of this unit you should: Compare the structure of humans
Unit 3L.4: Organs in the Human body Keeping Healthy The Skeleton Science skills: Classification Observing Making models Data collection By the end of this unit you should: Compare the structure of humans
Investigating Adaptations
 Investigating Adaptations 4 th Grade Duration Pre-Visit: 40 minutes Museum Visit: 60 minutes Post Visit: 50 minutes Concepts Adaptations reveal what organisms need in their environment to survive. Location
Investigating Adaptations 4 th Grade Duration Pre-Visit: 40 minutes Museum Visit: 60 minutes Post Visit: 50 minutes Concepts Adaptations reveal what organisms need in their environment to survive. Location
Comparative Physiology Symmetry in Marine Organisms
 Series 1 Name Date Don t forget to have your worksheet stamped at the front desk when you finish! Comparative Physiology Symmetry in Marine Organisms Part One: Learning Symmetry The body plans of organisms
Series 1 Name Date Don t forget to have your worksheet stamped at the front desk when you finish! Comparative Physiology Symmetry in Marine Organisms Part One: Learning Symmetry The body plans of organisms
The Facts About Right Whales
 The Facts About Right Whales Where have all the right whales gone? Hunters killed almost all the North Atlantic right whales by the early 20th century. It has been against the law to hunt them for more
The Facts About Right Whales Where have all the right whales gone? Hunters killed almost all the North Atlantic right whales by the early 20th century. It has been against the law to hunt them for more
Introduction to Dental Anatomy
 Introduction to Dental Anatomy Vickie P. Overman, RDH, MEd Continuing Education Units: N/A This continuing education course is intended for dental students and dental hygiene students. Maintaining the
Introduction to Dental Anatomy Vickie P. Overman, RDH, MEd Continuing Education Units: N/A This continuing education course is intended for dental students and dental hygiene students. Maintaining the
This is a series of skulls and front leg fossils of organisms believed to be ancestors of the modern-day horse.
 Evidence of Evolution Background When Charles Darwin first proposed the idea that all new species descend from an ancestor, he performed an exhaustive amount of research to provide as much evidence as
Evidence of Evolution Background When Charles Darwin first proposed the idea that all new species descend from an ancestor, he performed an exhaustive amount of research to provide as much evidence as
Frog Scavenger Hunt Activity
 Frog Scavenger Hunt Activity Materials: Frog questions worksheet (pages 2-3) 18 frog fact cards (pages 4-8) Scissors and scotch tape Preparation: Print the frog fact cards and cut them apart. Make copies
Frog Scavenger Hunt Activity Materials: Frog questions worksheet (pages 2-3) 18 frog fact cards (pages 4-8) Scissors and scotch tape Preparation: Print the frog fact cards and cut them apart. Make copies
Name: DUE: May 2, 2013 Ms. Galaydick. Geologic Time Scale Era Period End date (in millions of years) Cenozoic Quaternary present
 Name: DUE: May 2, 2013 Ms. Galaydick Objective: Use the diagrams to answer the questions for each set: USING SCIENCE SKILLS PART #1 Geologic Time Scale Era Period End date (in millions of years) Cenozoic
Name: DUE: May 2, 2013 Ms. Galaydick Objective: Use the diagrams to answer the questions for each set: USING SCIENCE SKILLS PART #1 Geologic Time Scale Era Period End date (in millions of years) Cenozoic
World Oceans Day at ZSL Whipsnade Zoo
 World Oceans Day at ZSL Whipsnade Zoo Teachers notes KS 1 & KS 2 This booklet will help you to focus your self guided trail on ocean animals, looking at the adaptations of the species and focusing in on
World Oceans Day at ZSL Whipsnade Zoo Teachers notes KS 1 & KS 2 This booklet will help you to focus your self guided trail on ocean animals, looking at the adaptations of the species and focusing in on
Life processes. All animals have to carry out seven life processes. These are: 2. Respiration taking in one gas and getting rid of another
 Food chains Life processes All animals have to carry out seven life processes. These are: 1. Movement being able to move its body 2. Respiration taking in one gas and getting rid of another 3. Reproduction
Food chains Life processes All animals have to carry out seven life processes. These are: 1. Movement being able to move its body 2. Respiration taking in one gas and getting rid of another 3. Reproduction
Fishy Adaptations. Adapted from: Fashion a Fish in Project Wild Aquatic Education Activity Guide. The Council for Environmental Education, 1992
 Fishy Adaptations Adapted from: Fashion a Fish in Project Wild Aquatic Education Activity Guide. The Council for Environmental Education, 1992 Physical Structure Grade Level: Basic Duration: 45 minutes
Fishy Adaptations Adapted from: Fashion a Fish in Project Wild Aquatic Education Activity Guide. The Council for Environmental Education, 1992 Physical Structure Grade Level: Basic Duration: 45 minutes
www.irishseedsavers.ie Natural surface water on earth includes lakes, ponds, streams, rivers, estuaries, seas and oceans.
 www.irishseedsavers.ie POND LIFE FACT SHEET Natural surface water on earth includes lakes, ponds, streams, rivers, estuaries, seas and oceans. A pond is a small body of fresh water shallow enough for sunlight
www.irishseedsavers.ie POND LIFE FACT SHEET Natural surface water on earth includes lakes, ponds, streams, rivers, estuaries, seas and oceans. A pond is a small body of fresh water shallow enough for sunlight
Bone, Antler, Ivory, and Teeth
 Bone, Antler, Ivory, and Teeth Found in such items as tools, jewelry, and decorations Identification and General Information Items derived from skeletal materials are both versatile and durable. Bone,
Bone, Antler, Ivory, and Teeth Found in such items as tools, jewelry, and decorations Identification and General Information Items derived from skeletal materials are both versatile and durable. Bone,
Is That Mammal a Carnivore, Herbivore or Omnivore?
 Name: Is That Mammal a Carnivore, by Guy Belleranti A mammal can be a carnivore (meat eater), herbivore (plant eater) or omnivore (meat and plant eater). By looking at the teeth, eye position and feet
Name: Is That Mammal a Carnivore, by Guy Belleranti A mammal can be a carnivore (meat eater), herbivore (plant eater) or omnivore (meat and plant eater). By looking at the teeth, eye position and feet
Shark Traveling Trunk. Cape Lookout National Seashore
 Shark Traveling Trunk Cape Lookout National Seashore HOW TO USE THIS TRUNK: This traveling trunk is designed to be used in the classroom to introduce students to sharks. It is intended to be used for grades
Shark Traveling Trunk Cape Lookout National Seashore HOW TO USE THIS TRUNK: This traveling trunk is designed to be used in the classroom to introduce students to sharks. It is intended to be used for grades
Build Vocabulary Students will have a more successful lab experience if they understand these terms.
 Chapter 18 Lab Dichotomous Keys Open-Ended Inquiry Design Your Own Lab Problem Can you construct a dichotomous key that could be used to identify organisms? Introduction In May 2007, scientists and other
Chapter 18 Lab Dichotomous Keys Open-Ended Inquiry Design Your Own Lab Problem Can you construct a dichotomous key that could be used to identify organisms? Introduction In May 2007, scientists and other
UNIT TWO TURTLE BIOLOGY
 UNIT TWO TURTLE BIOLOGY 43 44 Science Expectations met in this unit: UNIT TWO: TURTLE BIOLOGY Activity Number: Activity Name Strand Grade 2 Growth and Changes in Animals Grade 4 Habitats and 5: Camouflage
UNIT TWO TURTLE BIOLOGY 43 44 Science Expectations met in this unit: UNIT TWO: TURTLE BIOLOGY Activity Number: Activity Name Strand Grade 2 Growth and Changes in Animals Grade 4 Habitats and 5: Camouflage
Evolution (18%) 11 Items Sample Test Prep Questions
 Evolution (18%) 11 Items Sample Test Prep Questions Grade 7 (Evolution) 3.a Students know both genetic variation and environmental factors are causes of evolution and diversity of organisms. (pg. 109 Science
Evolution (18%) 11 Items Sample Test Prep Questions Grade 7 (Evolution) 3.a Students know both genetic variation and environmental factors are causes of evolution and diversity of organisms. (pg. 109 Science
Evidence for evolution factsheet
 The theory of evolution by natural selection is supported by a great deal of evidence. Fossils Fossils are formed when organisms become buried in sediments, causing little decomposition of the organism.
The theory of evolution by natural selection is supported by a great deal of evidence. Fossils Fossils are formed when organisms become buried in sediments, causing little decomposition of the organism.
Animals and Adaptation
 Animals and Adaptation From: http://www.learninghaven.com/science/articles/animals_and_adaptation.htm In order for animals to survive, they need to be able to adapt. In this lesson we will look at the
Animals and Adaptation From: http://www.learninghaven.com/science/articles/animals_and_adaptation.htm In order for animals to survive, they need to be able to adapt. In this lesson we will look at the
Who Glows there? Bioluminescence of Fireflies, Mushrooms, and Jellyfish
 Who Glows there? Bioluminescence of Fireflies, Mushrooms, and Jellyfish Glenna Smith Anthony Todd Background: Most people think of fireflies when it comes to bioluminescent or glowin-the-dark organisms,
Who Glows there? Bioluminescence of Fireflies, Mushrooms, and Jellyfish Glenna Smith Anthony Todd Background: Most people think of fireflies when it comes to bioluminescent or glowin-the-dark organisms,
Mini Dinosaurs. Grades K 1 2. Compiled by
 Mini Dinosaurs Grades K 1 2 Compiled by Leanne M. Burrow, Extension educator, 4 H/ Youth development, Purdue University Cooperative Extension Service Henry County Resources and References Exploring 4 H,
Mini Dinosaurs Grades K 1 2 Compiled by Leanne M. Burrow, Extension educator, 4 H/ Youth development, Purdue University Cooperative Extension Service Henry County Resources and References Exploring 4 H,
Pond Vocabulary Words and Meanings
 Pond Vocabulary Words and Meanings Adapt: to adjust to a use or situation Aquatic: from or in the water Bacteria: tiny organisms, too small to be seen with the naked eye Carnivore: an animal that eats
Pond Vocabulary Words and Meanings Adapt: to adjust to a use or situation Aquatic: from or in the water Bacteria: tiny organisms, too small to be seen with the naked eye Carnivore: an animal that eats
Your Own Teeth and Gums
 Your Own Teeth and Gums CHAPTER1 Next time you look in a mirror, look at your teeth and the skin (gums) around them. Look in your children s mouths, too. Look at both gums and teeth, because the health
Your Own Teeth and Gums CHAPTER1 Next time you look in a mirror, look at your teeth and the skin (gums) around them. Look in your children s mouths, too. Look at both gums and teeth, because the health
When Is an Elephant Not an Elephant? When It's a Seal, Of Course! By Mikki Sadil
 Everyone knows that elephants have trunks. But did you know there is a kind of seal that also has a trunk? This is the elephant seal, which gets its name from the extra large proboscis, or nose, on the
Everyone knows that elephants have trunks. But did you know there is a kind of seal that also has a trunk? This is the elephant seal, which gets its name from the extra large proboscis, or nose, on the
Dinosaur Time-line. What other animals lived then? How long ago did the dinosaurs live? Did dinosaurs live at the same time as people?
 Dinosaur Time-line How long ago did the dinosaurs live? The Age of Dinosaurs began nearly 250 million years ago, but the first true dinosaurs appeared closer to 220 million years ago. Some dinosaurs evolved
Dinosaur Time-line How long ago did the dinosaurs live? The Age of Dinosaurs began nearly 250 million years ago, but the first true dinosaurs appeared closer to 220 million years ago. Some dinosaurs evolved
What activities do you think an organism would use bioluminescence for?
 Relationships for Survival: The Role of Bioluminescence overview In these activities, students will focus on ecological relationships and investigate the many ways that species might interact using bioluminescence.
Relationships for Survival: The Role of Bioluminescence overview In these activities, students will focus on ecological relationships and investigate the many ways that species might interact using bioluminescence.
Lesson 2: Save your Smile from Tooth Decay
 Lesson 2: Save your Smile from Tooth Decay OVERVIEW Objectives: By the end of the lesson, the Lay Health Worker will be able to: 1. Describe what tooth decay is and how it happens. 2. State the causes
Lesson 2: Save your Smile from Tooth Decay OVERVIEW Objectives: By the end of the lesson, the Lay Health Worker will be able to: 1. Describe what tooth decay is and how it happens. 2. State the causes
AMERICAN MUSEUM OF NATURAL HISTORY SCAVENGER HUNT
 AMERICAN MUSEUM OF NATURAL HISTORY SCAVENGER HUNT Begin on the 4 th floor. Take the stairs since they are faster than the elevators. Look but do not touch while in the museum. Keep your voices low but
AMERICAN MUSEUM OF NATURAL HISTORY SCAVENGER HUNT Begin on the 4 th floor. Take the stairs since they are faster than the elevators. Look but do not touch while in the museum. Keep your voices low but
Animal Adaptations -- Vocabulary
 Section 1 Objectives o Children will understand what animal adaptations are. o Children will be able to explain why animal adaptations are important. o Children will be able to explain different types
Section 1 Objectives o Children will understand what animal adaptations are. o Children will be able to explain why animal adaptations are important. o Children will be able to explain different types
Animal Classification K-4
 Animal Classification K-4 Introduction: The theme of this self-guided experience is classification of animals. Students will learn to use body coverings as an aid to classification. As the group tours
Animal Classification K-4 Introduction: The theme of this self-guided experience is classification of animals. Students will learn to use body coverings as an aid to classification. As the group tours
Observing Vertebrate Skeletons
 Name Class Date Chapter 33 Comparing Chordates Observing Vertebrate Skeletons Introduction One characteristic common to all vertebrates is the presence of a skeleton. The endoskeleton provides support,
Name Class Date Chapter 33 Comparing Chordates Observing Vertebrate Skeletons Introduction One characteristic common to all vertebrates is the presence of a skeleton. The endoskeleton provides support,
many diverse adaptations to life -
 Introduction to Fish Biology About 25,000 species of fish have been described this is the most numerous group of vertebrates approximately 45%-50% of all vertebrate species are fish dominant life form
Introduction to Fish Biology About 25,000 species of fish have been described this is the most numerous group of vertebrates approximately 45%-50% of all vertebrate species are fish dominant life form
nucleus cytoplasm membrane wall A cell is the smallest unit that makes up living and nonliving things.
 1 In nature there are living things and nonliving things. Living things depend on three basic life processes: nutrition, sensitivity and reproduction. Living things are made up of cells. 1. Match the two
1 In nature there are living things and nonliving things. Living things depend on three basic life processes: nutrition, sensitivity and reproduction. Living things are made up of cells. 1. Match the two
Teacher s Manual Carnivore/Herbivore Week
 Teacher s Manual Carnivore/Herbivore Week This kit contains a week s worth of Lunch and Learn type activities that is, five half-hour lessons related to the theme of Carnivores and Herbivores. It contains
Teacher s Manual Carnivore/Herbivore Week This kit contains a week s worth of Lunch and Learn type activities that is, five half-hour lessons related to the theme of Carnivores and Herbivores. It contains
GRADE 6 DENTAL HEALTH
 GRADE 6 DENTAL HEALTH DENTAL HEALTH GRADE: 6 LESSON: 1 THEME: STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION CONCEPT: THE STRUCTURE OF A TOOTH IS RELATED TO ITS FUNCTION PREPARATION: 1. Prepare an overhead transparency of Parts
GRADE 6 DENTAL HEALTH DENTAL HEALTH GRADE: 6 LESSON: 1 THEME: STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION CONCEPT: THE STRUCTURE OF A TOOTH IS RELATED TO ITS FUNCTION PREPARATION: 1. Prepare an overhead transparency of Parts
Chapter 11. What are the functions of the skeletal system? More detail on bone
 Skeletal System Chapter 11 11.1 Overview of the skeletal system What are the functions of the skeletal system? 1. Supports the body 2. Protects the soft body parts 3. Produces blood cells 4. Stores minerals
Skeletal System Chapter 11 11.1 Overview of the skeletal system What are the functions of the skeletal system? 1. Supports the body 2. Protects the soft body parts 3. Produces blood cells 4. Stores minerals
Animal Tissues. I. Epithelial Tissue
 Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
Reptiles and Amphibians by Guy Belleranti
 Name: Take a look at the four animals pictures below. Do you know which ones are reptiles and which ones are amphibians? The chameleon is an unusual lizard that can change the color of its scaly body.
Name: Take a look at the four animals pictures below. Do you know which ones are reptiles and which ones are amphibians? The chameleon is an unusual lizard that can change the color of its scaly body.
DEVELOPMENT AND GROWTH OF THE MANDIBLE
 2012-2013 ORAL BIOLOGY DEVELOPMENT AND GROWTH OF THE MANDIBLE Ass. Prof. Dr. Heba M. Elsabaa Development and Growth of the Mandible DEVELOPMENT OF THE MANDIBLE The Mandible Is the largest and strongest
2012-2013 ORAL BIOLOGY DEVELOPMENT AND GROWTH OF THE MANDIBLE Ass. Prof. Dr. Heba M. Elsabaa Development and Growth of the Mandible DEVELOPMENT OF THE MANDIBLE The Mandible Is the largest and strongest
ANGEL DENTAL CARE Implant Consent
 This information is to help you make an informed decision about having implant treatment. You should take as much time as you wish to make the decision in relation to signing the following consent form.
This information is to help you make an informed decision about having implant treatment. You should take as much time as you wish to make the decision in relation to signing the following consent form.
Sea Turtles of Maryland
 Sea Turtles of Maryland Green Sea Turtle Hawksbill Sea Turtle Kemp's Ridley Sea Turtle Leatherback Sea Turtle Loggerhead Sea Turtle Olive Ridley Sea Turtle To report a sea turtle sighting, stranding or
Sea Turtles of Maryland Green Sea Turtle Hawksbill Sea Turtle Kemp's Ridley Sea Turtle Leatherback Sea Turtle Loggerhead Sea Turtle Olive Ridley Sea Turtle To report a sea turtle sighting, stranding or
Can You Tell a 'Gator From a Croc? by Guy Belleranti
 Can You Tell a 'Gator From a Croc? Look closely at the reptiles pictured below. Can you tell which one is the crocodile and which is the alligator? Many people confuse crocodiles and alligators, and it's
Can You Tell a 'Gator From a Croc? Look closely at the reptiles pictured below. Can you tell which one is the crocodile and which is the alligator? Many people confuse crocodiles and alligators, and it's
Mammal Scavenger Hunt Activity
 Mammal Scavenger Hunt Activity Materials: Mammal questions worksheet (pages 2-3) 18 Mammal fact cards (pages 4-8) Tape and scissors Preparation: Print the fact cards on card stock or brightly-colored paper
Mammal Scavenger Hunt Activity Materials: Mammal questions worksheet (pages 2-3) 18 Mammal fact cards (pages 4-8) Tape and scissors Preparation: Print the fact cards on card stock or brightly-colored paper
Name Class Date. Adapting to the Environment Adaptations and Survival
 CHAPTER 3 4 SECTIN Adapting to the Environment Adaptations and Survival EFRE YU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What adaptations help animals survive? What
CHAPTER 3 4 SECTIN Adapting to the Environment Adaptations and Survival EFRE YU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What adaptations help animals survive? What
Section 3: Trophic Structures
 Marine Conservation Science and Policy Service learning Program Trophic Structure refers to the way in which organisms utilize food resources and hence where energy transfer occurs within an ecosystem.
Marine Conservation Science and Policy Service learning Program Trophic Structure refers to the way in which organisms utilize food resources and hence where energy transfer occurs within an ecosystem.
NOTE TO TEACHER: It is appropriate to introduce the mitochondria (where energy is made) as a major structure common to all cells.
 5.2.1 Recall the cell as the smallest unit of life and identify its major structures (including cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and vacuole). Taxonomy level: 1.1 and 1.2-A Remember Factual Knowledge
5.2.1 Recall the cell as the smallest unit of life and identify its major structures (including cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and vacuole). Taxonomy level: 1.1 and 1.2-A Remember Factual Knowledge
Behaviour. Age 6-11 years. Contents
 SEA LIFE for schools Behaviour Age 6-11 years Self-guided learning This guide provides you with information linked to key displays throughout SEA LIFE Loch Lomond which can be used to explore the key behaviour
SEA LIFE for schools Behaviour Age 6-11 years Self-guided learning This guide provides you with information linked to key displays throughout SEA LIFE Loch Lomond which can be used to explore the key behaviour
Grade Level Content Expectations addressed: Activities: Schedule of Field Trip Activities at the Detroit Zoo 8:15 am Board Bus at School
 Title: Comparing and Contrasting Ecosystem Biodiversity Submitted by: Tracy Ortiz Email: tracy.ortiz@att.net School: Coffey K-8 Educational Learning Community Date: May 12, 2010 Target Grade: 6 Duration:
Title: Comparing and Contrasting Ecosystem Biodiversity Submitted by: Tracy Ortiz Email: tracy.ortiz@att.net School: Coffey K-8 Educational Learning Community Date: May 12, 2010 Target Grade: 6 Duration:
Coral Reefs Lecture Notes
 Coral Reefs Lecture Notes (Topic 10D) page 1 Coral Reefs Lecture Notes Corals Polyps & Zooxanthellae Coral Polyps Are coral polyps algae or animals? Description (What do coral polyps look like? Make a
Coral Reefs Lecture Notes (Topic 10D) page 1 Coral Reefs Lecture Notes Corals Polyps & Zooxanthellae Coral Polyps Are coral polyps algae or animals? Description (What do coral polyps look like? Make a
The Take-Apart Human Body
 The Take-Apart Human Body As any teacher knows, children are naturally curious about their bodies. Their questions are endless, and present a tremendous educational opportunity: How do my ears work? Where
The Take-Apart Human Body As any teacher knows, children are naturally curious about their bodies. Their questions are endless, and present a tremendous educational opportunity: How do my ears work? Where
X-Plain Perforated Ear Drum Reference Summary
 X-Plain Perforated Ear Drum Reference Summary Introduction Perforated eardrum is a common condition. The eardrum is a thin layer of tissue at the end of the ear canal inside the ear. Eardrum perforations
X-Plain Perforated Ear Drum Reference Summary Introduction Perforated eardrum is a common condition. The eardrum is a thin layer of tissue at the end of the ear canal inside the ear. Eardrum perforations
Crabs. Focus Question
 Topics Crabs, Adaptations Crabs Grades PreK-2 Site Indoors Duration 30 minutes (minimum) Materials Crab Cards Clay or foil Pipe cleaners Egg carton sections, small boxes, jars, lids, food cups, yogurt
Topics Crabs, Adaptations Crabs Grades PreK-2 Site Indoors Duration 30 minutes (minimum) Materials Crab Cards Clay or foil Pipe cleaners Egg carton sections, small boxes, jars, lids, food cups, yogurt
Lesson 6: Fisheries Management in the Open Ocean. Open Ocean
 !!! Open Ocean Concepts How does fishing equipment affect the amount of fish and bycatch caught in a fishery? How can we change the way we fish to use the ocean better? Standards Addressed HCPS 5. & 5.2
!!! Open Ocean Concepts How does fishing equipment affect the amount of fish and bycatch caught in a fishery? How can we change the way we fish to use the ocean better? Standards Addressed HCPS 5. & 5.2
2. What kind of energy is stored in food? A. chemical energy B. heat energy C. kinetic energy D. light energy
 Assessment Bank Matter and Energy in Living Things SC.8.L.18.4 1. What is energy? A. anything that takes up space B. anything that has mass C. the ability to conduct current D. the ability to do work 2.
Assessment Bank Matter and Energy in Living Things SC.8.L.18.4 1. What is energy? A. anything that takes up space B. anything that has mass C. the ability to conduct current D. the ability to do work 2.
Dental Implants - the tooth replacement solution
 Dental Implants - the tooth replacement solution Are missing teeth causing you to miss out on life? Missing teeth and loose dentures make too many people sit on the sidelines and let life pass them by.
Dental Implants - the tooth replacement solution Are missing teeth causing you to miss out on life? Missing teeth and loose dentures make too many people sit on the sidelines and let life pass them by.
Activity: Can You Identify the Age?
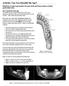 Activity: Can You Identify the Age? Skeletons are good age markers because teeth and bones mature at fairly predictable rates. How Teeth Reveal Age For toddler to age 21, teeth are the most accurate age
Activity: Can You Identify the Age? Skeletons are good age markers because teeth and bones mature at fairly predictable rates. How Teeth Reveal Age For toddler to age 21, teeth are the most accurate age
SECOND GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 SECOND GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SECOND GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Investigating the parts of a volcano. LAB: Comparing the parts of a
SECOND GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SECOND GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Investigating the parts of a volcano. LAB: Comparing the parts of a
Tooth Decay. What Is Tooth Decay? Tooth decay happens when you have an infection of your teeth.
 Tooth Decay What Is Tooth Decay? Tooth decay happens when you have an infection of your teeth. When you eat food and drink, it is broken down into acid. This acid helps to make plaque (a sticky substance).
Tooth Decay What Is Tooth Decay? Tooth decay happens when you have an infection of your teeth. When you eat food and drink, it is broken down into acid. This acid helps to make plaque (a sticky substance).
TLC Online Curriculum
 TLC Online Curriculum Lesson Title: Reptile Adaptations Grade level: 4-5 Subject Area: Animals Duration: Two or three class periods Objectives: Students will understand the following: 1. Adaptation describes
TLC Online Curriculum Lesson Title: Reptile Adaptations Grade level: 4-5 Subject Area: Animals Duration: Two or three class periods Objectives: Students will understand the following: 1. Adaptation describes
Chordates -> Vertebrates. From basal Deuterostomes
 Chordates -> Vertebrates From basal Deuterostomes Outline Origins of Deuterostomes & Chordates Characteristics of Deuterostomes & Chordates Themes in Chordate evolution? Vertebrate adaptations? How are
Chordates -> Vertebrates From basal Deuterostomes Outline Origins of Deuterostomes & Chordates Characteristics of Deuterostomes & Chordates Themes in Chordate evolution? Vertebrate adaptations? How are
Scientific Method Worksheet
 Scientific Method Worksheet Anyone who has ever read a mystery novel or seen a whodunit on TV, has seen the scientific method in action. Anyone who has ever tried to figure out what happens to the refrigerator
Scientific Method Worksheet Anyone who has ever read a mystery novel or seen a whodunit on TV, has seen the scientific method in action. Anyone who has ever tried to figure out what happens to the refrigerator
Ecology 1 Star. 1. Missing from the diagram of this ecosystem are the
 Name: ate: 1. Missing from the diagram of this ecosystem are the 5. ase your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology.. biotic factors and decomposers.
Name: ate: 1. Missing from the diagram of this ecosystem are the 5. ase your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology.. biotic factors and decomposers.
Dinosaur Vocabulary List & Definitions
 Name Dinosaur Vocabulary List & Definitions dinosaur extinct fossil herbivore paleontology predator prehistoric skeleton prey carnivore one of various extinct reptiles that lived approximately l00 million
Name Dinosaur Vocabulary List & Definitions dinosaur extinct fossil herbivore paleontology predator prehistoric skeleton prey carnivore one of various extinct reptiles that lived approximately l00 million
Lab #10 Invertebrates 2 and Vertebrates 1 (Exercises 39, 40)
 Name Bio 182-General Biology Lab #10 Invertebrates 2 and Vertebrates 1 (Exercises 39, 40) Answer the questions in the space provided. You need to turn this sheet at the end of the lab. In general know
Name Bio 182-General Biology Lab #10 Invertebrates 2 and Vertebrates 1 (Exercises 39, 40) Answer the questions in the space provided. You need to turn this sheet at the end of the lab. In general know
Part 1: Physiology. Below is a cut-through view of a human head:
 The Frenzel Technique, Step-by-Step by Eric Fattah, Copyright 2001 efattah@interchange.ubc.ca This document should be in electronic form at: http://www.ericfattah.com/equalizing.html Feel free to distribute
The Frenzel Technique, Step-by-Step by Eric Fattah, Copyright 2001 efattah@interchange.ubc.ca This document should be in electronic form at: http://www.ericfattah.com/equalizing.html Feel free to distribute
2. You are going to be reading about one type of dinosaur called Tyrannosaurus rex or T. rex for short. What do you know about this dinosaur?
 Building Context 1. You are going to be reading about a dinosaur. Write down some things that you know about dinosaurs. 2. You are going to be reading about one type of dinosaur called Tyrannosaurus rex
Building Context 1. You are going to be reading about a dinosaur. Write down some things that you know about dinosaurs. 2. You are going to be reading about one type of dinosaur called Tyrannosaurus rex
Practice Questions 1: Evolution
 Practice Questions 1: Evolution 1. Which concept is best illustrated in the flowchart below? A. natural selection B. genetic manipulation C. dynamic equilibrium D. material cycles 2. The diagram below
Practice Questions 1: Evolution 1. Which concept is best illustrated in the flowchart below? A. natural selection B. genetic manipulation C. dynamic equilibrium D. material cycles 2. The diagram below
giganotosaurus Michael P. Goecke
 giganotosaurus Michael P. Goecke Giganotosaurus A Buddy Book by Michael P. Goecke VISIT US AT www.abdopublishing.com Published by ABDO Publishing Company, 4940 Viking Drive, Edina, Minnesota 55435. Copyright
giganotosaurus Michael P. Goecke Giganotosaurus A Buddy Book by Michael P. Goecke VISIT US AT www.abdopublishing.com Published by ABDO Publishing Company, 4940 Viking Drive, Edina, Minnesota 55435. Copyright
Dino Data Adapted from Dino Data Activity www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/education/lessons/dinodata/dino_data.html
 Dino Data Adapted from Dino Data Activity www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/education/lessons/dinodata/dino_data.html Grade Level: Grades 6-8 Preparation Time: less than 5 minutes Activity Duration: up to five classroom
Dino Data Adapted from Dino Data Activity www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/education/lessons/dinodata/dino_data.html Grade Level: Grades 6-8 Preparation Time: less than 5 minutes Activity Duration: up to five classroom
Figure 4. Clown fish and anemone. Figure 5. Sea spider. Page 2 of 6. Saylor URL: www.saylor.org/bio102
 Symbiosis The phrase symbiotic relationship simply refers to a close ecological relationship between two different species. These relationships differ along a spectrum from positive to negative interactions.
Symbiosis The phrase symbiotic relationship simply refers to a close ecological relationship between two different species. These relationships differ along a spectrum from positive to negative interactions.
Forensic Science Lesson 3: Trace Evidence Analysis
 Forensic Science Lesson 3: Trace Evidence Analysis History Alphonse Bertillon 1883 Created the first systematic system of individual classification & identification Detailed description of subject, full-length
Forensic Science Lesson 3: Trace Evidence Analysis History Alphonse Bertillon 1883 Created the first systematic system of individual classification & identification Detailed description of subject, full-length
Whale Jenga Food Web Game
 Whale Jenga Food Web Game Baleen whales feed on crustaceans such as amphipods, copepods,and krill, as well as small fish. With changes in ocean temperature, upwelling, acidification and other urban influences,
Whale Jenga Food Web Game Baleen whales feed on crustaceans such as amphipods, copepods,and krill, as well as small fish. With changes in ocean temperature, upwelling, acidification and other urban influences,
Introduction to Animals
 Introduction to Animals Unity and Diversity of Life Q: What characteristics and traits define animals? 25.1 What is an animal? WHAT I KNOW SAMPLE ANSWER: Animals are different from other living things
Introduction to Animals Unity and Diversity of Life Q: What characteristics and traits define animals? 25.1 What is an animal? WHAT I KNOW SAMPLE ANSWER: Animals are different from other living things
Bird Scavenger Hunt Activity
 Bird Scavenger Hunt Activity Materials: Bird questions worksheet (pages 2-3) 18 Bird fact cards (pages 4-8) Tape and scissors Preparation: Print the fact cards on card stock or brightly-colored paper and
Bird Scavenger Hunt Activity Materials: Bird questions worksheet (pages 2-3) 18 Bird fact cards (pages 4-8) Tape and scissors Preparation: Print the fact cards on card stock or brightly-colored paper and
Manatee Anatomy and Physiology
 Manatee Anatomy and Physiology Grade level: Elementary 5 Subject Area: Biology, Anatomy and Physiology, Marine Biology Duration: Teach: 15 minutes, Activity: 20 minutes, Discussion: 20 minutes. Setting:
Manatee Anatomy and Physiology Grade level: Elementary 5 Subject Area: Biology, Anatomy and Physiology, Marine Biology Duration: Teach: 15 minutes, Activity: 20 minutes, Discussion: 20 minutes. Setting:
Right Whale. The Kids Times: Volume II, Issue 6. NOAA s National Marine Fisheries Service, Office of Protected Resources
 NOAA s National Marine Fisheries Service, Office of Protected Resources The Kids Times: Volume II, Issue 6 Right Whale Right whales have no dorsal fin on their backs. How did the right whale get its name?
NOAA s National Marine Fisheries Service, Office of Protected Resources The Kids Times: Volume II, Issue 6 Right Whale Right whales have no dorsal fin on their backs. How did the right whale get its name?
Fish: One-of-a-kind Animals (30 minute activity)
 FISH HEALTH/Activity Fish: One-of-a-kind Animals (30 minute activity) Objectives Materials Background I have known you in your streams and rivers where your fish flashed and danced in the sun, where the
FISH HEALTH/Activity Fish: One-of-a-kind Animals (30 minute activity) Objectives Materials Background I have known you in your streams and rivers where your fish flashed and danced in the sun, where the
A Fishy Tale. Observing the Circulatory System of a Goldfish with a Compound Light Microscope
 A Fishy Tale Observing the Circulatory System of a Goldfish with a Compound Light Microscope A Fishy Tale About this Lesson In this lesson, students will explore a computer animation of the human body
A Fishy Tale Observing the Circulatory System of a Goldfish with a Compound Light Microscope A Fishy Tale About this Lesson In this lesson, students will explore a computer animation of the human body
Legend of the Mermaid by Kelly Hashway
 We ve all heard of mermaids. They are the beautiful half-human, half-fish creatures that live in the sea. They have the head and torso of a human and the tail of a fish. We also know that mermaids only
We ve all heard of mermaids. They are the beautiful half-human, half-fish creatures that live in the sea. They have the head and torso of a human and the tail of a fish. We also know that mermaids only
Theory of Evolution. A. the beginning of life B. the evolution of eukaryotes C. the evolution of archaebacteria D. the beginning of terrestrial life
 Theory of Evolution 1. In 1966, American biologist Lynn Margulis proposed the theory of endosymbiosis, or the idea that mitochondria are the descendents of symbiotic, aerobic eubacteria. What does the
Theory of Evolution 1. In 1966, American biologist Lynn Margulis proposed the theory of endosymbiosis, or the idea that mitochondria are the descendents of symbiotic, aerobic eubacteria. What does the
CRETACEOUS ALBERTA SCIENCE HALL. Changing Earth. What is Palaeontology. Changing Time. 1. This exhibit is based on a discovery made in
 Worksheet Level 2 p. 1 CRETACEOUS ALBERTA 1. This exhibit is based on a discovery made in 2. What type of dinosaur was found at this site and how many individuals were there? 3. What was their age range?
Worksheet Level 2 p. 1 CRETACEOUS ALBERTA 1. This exhibit is based on a discovery made in 2. What type of dinosaur was found at this site and how many individuals were there? 3. What was their age range?
LIFE UNDER THE SEA. (Lesson Plans) Salvador Rodríguez Almendros
 (Lesson Plans) January - March 2009 (Types of marine life: real facts on sea flora and fauna ) 1 1 and 2 - To express opinions and give account of experiences Methodological skills: (Information handling)
(Lesson Plans) January - March 2009 (Types of marine life: real facts on sea flora and fauna ) 1 1 and 2 - To express opinions and give account of experiences Methodological skills: (Information handling)
GRADE 2 DENTAL HEALTH
 GRADE 2 DENTAL HEALTH DENTAL HEALTH GRADE: 2 LESSON: 1 THEME: STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION CONCEPT: PRIMARY TEETH ARE REPLACED BY PERMANENT TEETH IN A SPECIFIC SEQUENCE PREPARATION: 1. Prepare a class set of
GRADE 2 DENTAL HEALTH DENTAL HEALTH GRADE: 2 LESSON: 1 THEME: STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION CONCEPT: PRIMARY TEETH ARE REPLACED BY PERMANENT TEETH IN A SPECIFIC SEQUENCE PREPARATION: 1. Prepare a class set of
Dear Teachers: Welcome to dynamic science
 Educator s Resource Guide GRADES 6 8 Dear Teachers: Welcome to dynamic science activities inspired by the IMAX film. These materials, created by Scholastic Inc., IMAX Corporation, and Warner Bros. Pictures,
Educator s Resource Guide GRADES 6 8 Dear Teachers: Welcome to dynamic science activities inspired by the IMAX film. These materials, created by Scholastic Inc., IMAX Corporation, and Warner Bros. Pictures,
1. Over the past century, several scientists around the world have made the following observations:
 Evolution Keystone Review 1. Over the past century, several scientists around the world have made the following observations: New mitochondria and plastids can only be generated by old mitochondria and
Evolution Keystone Review 1. Over the past century, several scientists around the world have made the following observations: New mitochondria and plastids can only be generated by old mitochondria and
Ecosystems and Food Webs
 Ecosystems and Food Webs How do AIS affect our lakes? Background Information All things on the planet both living and nonliving interact. An Ecosystem is defined as the set of elements, living and nonliving,
Ecosystems and Food Webs How do AIS affect our lakes? Background Information All things on the planet both living and nonliving interact. An Ecosystem is defined as the set of elements, living and nonliving,
Name Class Date WHAT I KNOW. about how organisms have changed. grown in complexity over time.
 History of Life Evolution Q: How do fossils help biologists understand the history of life on Earth? 19.1 How do scientists use fossils to study Earth s history? WHAT I KNOW SAMPLE ANSWER: Fossils give
History of Life Evolution Q: How do fossils help biologists understand the history of life on Earth? 19.1 How do scientists use fossils to study Earth s history? WHAT I KNOW SAMPLE ANSWER: Fossils give
Satellite Pursuit: Tracking Marine Mammals
 : Tracking Marine Mammals Material adapted from: Monterey Bay Research Institute, EARTH: Satellite Tracking OPB NOVA Teachers: Ocean Animal Emergency Teach Engineering: Marine Animal Tracking Introduction:
: Tracking Marine Mammals Material adapted from: Monterey Bay Research Institute, EARTH: Satellite Tracking OPB NOVA Teachers: Ocean Animal Emergency Teach Engineering: Marine Animal Tracking Introduction:
This booklet was prepared by the Conservation Education Department at The National Aquarium in Baltimore.
 This booklet was prepared by the Conservation Education Department at The National Aquarium in Baltimore. Nancy Hotchkiss, Director Dianne Wilkes, Administrative Assistant Susi Ridenour, Librarian Staff:
This booklet was prepared by the Conservation Education Department at The National Aquarium in Baltimore. Nancy Hotchkiss, Director Dianne Wilkes, Administrative Assistant Susi Ridenour, Librarian Staff:
Ground substance is the component of connective tissue between the cells and the fibers
 Connective Tissues Directions: Insert and install your Interactions: Foundations CD. a. Click the "Contents" button. b. Open the Tissue Level of Organization file. c. Click on Anatomy Overviews. d. Work
Connective Tissues Directions: Insert and install your Interactions: Foundations CD. a. Click the "Contents" button. b. Open the Tissue Level of Organization file. c. Click on Anatomy Overviews. d. Work
Dental Bridges. What are they? What are the parts of a typical dental bridge (fixed)? When are dental bridges needed?
 Dental Bridges What are they? Dental bridges are false teeth anchored on neighbouring teeth in order to replace one or more missing teeth. The false tooth is known as a pontic and is fused in between two
Dental Bridges What are they? Dental bridges are false teeth anchored on neighbouring teeth in order to replace one or more missing teeth. The false tooth is known as a pontic and is fused in between two
Activity 1 Exploring Animal Diets and Sizes
 Activity 1 Exploring Animal Diets and Sizes Objective & Overview: Using measurement and books, students will gain a better understanding of animal size, diversity, and diet through the fun study of wildlife.
Activity 1 Exploring Animal Diets and Sizes Objective & Overview: Using measurement and books, students will gain a better understanding of animal size, diversity, and diet through the fun study of wildlife.
