Latitude and Longitude Vocabulary. Equator imaginary line separating the northern and southern hemispheres.
|
|
|
- Rosalyn Manning
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Latitude and Longitude Vocabulary Degrees the unit for measuring distance on a map Equator imaginary line separating the northern and southern hemispheres. Globe a miniature model of the Earth Hemisphere one half of the planet
2 Latitude horizontal lines on a map that run east and west. They measure north and south of the equator. Longitude the vertical lines on a map that run north and south. They measure east and west of the Prime Meridian. Meridian lines of longitude Prime Meridian the line of longitude is starting point for measuring distance of east and west. It is at 0 degrees longitude. Absolute location the exact location of a place using latitude and longitude locations Relative location a location of a place that is close but not exact.
3 Latitude and Longitude Vocabulary Degrees the unit for measuring distance on a map Equator imaginary line separating the northern and southern hemispheres. Globe a miniature model of the Earth Hemisphere one half of the planet
4 Latitude horizontal lines on a map that run east and west. They measure north and south of the equator. Longitude the vertical lines on a map that run north and south. They measure east and west of the Prime Meridian. Meridian lines of longitude Prime Meridian the line of longitude is starting point for measuring distance of east and west. It is at 0 degrees longitude. Absolute location the exact location of a place using latitude and longitude locations Relative location a location of a place that is close but not exact.
5 Latitude and Longitude Vocabulary Degrees the unit for measuring distance on a map Equator imaginary line separating the northern and southern hemispheres. Globe a miniature model of the Earth Hemisphere one half of the planet
6 Latitude horizontal lines on a map that run east and west. They measure north and south of the equator. Longitude the vertical lines on a map that run north and south. They measure east and west of the Prime Meridian. Meridian lines of longitude Prime Meridian the line of longitude is starting point for measuring distance of east and west. It is at 0 degrees longitude. Absolute location the exact location of a place using latitude and longitude locations Relative location a location of a place that is close but not exact.
7 Latitude and Longitude Vocabulary Degrees the unit for measuring distance on a map Equator imaginary line separating the northern and southern hemispheres. Globe a miniature model of the Earth Hemisphere one half of the planet
8 Latitude horizontal lines on a map that run east and west. They measure north and south of the equator. Longitude the vertical lines on a map that run north and south. They measure east and west of the Prime Meridian. Meridian lines of longitude Prime Meridian the line of longitude is starting point for measuring distance of east and west. It is at 0 degrees longitude. Absolute location the exact location of a place using latitude and longitude locations Relative location a location of a place that is close but not exact.
9 Latitude and Longitude Vocabulary Degrees the unit for measuring distance on a map Equator imaginary line separating the northern and southern hemispheres. Globe a miniature model of the Earth Hemisphere one half of the planet
10 Latitude horizontal lines on a map that run east and west. They measure north and south of the equator. Longitude the vertical lines on a map that run north and south. They measure east and west of the Prime Meridian. Meridian lines of longitude Prime Meridian the line of longitude is starting point for measuring distance of east and west. It is at 0 degrees longitude. Absolute location the exact location of a place using latitude and longitude locations Relative location a location of a place that is close but not exact.
11 Latitude and Longitude Vocabulary Degrees the unit for measuring distance on a map Equator imaginary line separating the northern and southern hemispheres. Globe a miniature model of the Earth Hemisphere one half of the planet
12 Latitude horizontal lines on a map that run east and west. They measure north and south of the equator. Longitude the vertical lines on a map that run north and south. They measure east and west of the Prime Meridian. Meridian lines of longitude Prime Meridian the line of longitude is starting point for measuring distance of east and west. It is at 0 degrees longitude. Absolute location the exact location of a place using latitude and longitude locations Relative location a location of a place that is close but not exact.
13 Latitude and Longitude Vocabulary Degrees the unit for measuring distance on a map Equator imaginary line separating the northern and southern hemispheres. Globe a miniature model of the Earth Hemisphere one half of the planet
14 Latitude horizontal lines on a map that run east and west. They measure north and south of the equator. Longitude the vertical lines on a map that run north and south. They measure east and west of the Prime Meridian. Meridian lines of longitude Prime Meridian the line of longitude is starting point for measuring distance of east and west. It is at 0 degrees longitude. Absolute location the exact location of a place using latitude and longitude locations Relative location a location of a place that is close but not exact.
15 Latitude and Longitude Vocabulary Degrees the unit for measuring distance on a map Equator imaginary line separating the northern and southern hemispheres. Globe a miniature model of the Earth Hemisphere one half of the planet
16 Latitude horizontal lines on a map that run east and west. They measure north and south of the equator. Longitude the vertical lines on a map that run north and south. They measure east and west of the Prime Meridian. Meridian lines of longitude Prime Meridian the line of longitude is starting point for measuring distance of east and west. It is at 0 degrees longitude. Absolute location the exact location of a place using latitude and longitude locations Relative location a location of a place that is close but not exact.
17 Latitude and Longitude Vocabulary Degrees the unit for measuring distance on a map Equator imaginary line separating the northern and southern hemispheres. Globe a miniature model of the Earth Hemisphere one half of the planet
18 Latitude horizontal lines on a map that run east and west. They measure north and south of the equator. Longitude the vertical lines on a map that run north and south. They measure east and west of the Prime Meridian. Meridian lines of longitude Prime Meridian the line of longitude is starting point for measuring distance of east and west. It is at 0 degrees longitude. Absolute location the exact location of a place using latitude and longitude locations Relative location a location of a place that is close but not exact.
19 Latitude and Longitude Vocabulary Degrees the unit for measuring distance on a map Equator imaginary line separating the northern and southern hemispheres. Globe a miniature model of the Earth Hemisphere one half of the planet
20 Latitude horizontal lines on a map that run east and west. They measure north and south of the equator. Longitude the vertical lines on a map that run north and south. They measure east and west of the Prime Meridian. Meridian lines of longitude Prime Meridian the line of longitude is starting point for measuring distance of east and west. It is at 0 degrees longitude. Absolute location the exact location of a place using latitude and longitude locations Relative location a location of a place that is close but not exact.
21 Latitude and Longitude Vocabulary Degrees the unit for measuring distance on a map Equator imaginary line separating the northern and southern hemispheres. Globe a miniature model of the Earth Hemisphere one half of the planet
22 Latitude horizontal lines on a map that run east and west. They measure north and south of the equator. Longitude the vertical lines on a map that run north and south. They measure east and west of the Prime Meridian. Meridian lines of longitude Prime Meridian the line of longitude is starting point for measuring distance of east and west. It is at 0 degrees longitude. Absolute location the exact location of a place using latitude and longitude locations Relative location a location of a place that is close but not exact.
23 Latitude and Longitude Vocabulary Degrees the unit for measuring distance on a map Equator imaginary line separating the northern and southern hemispheres. Globe a miniature model of the Earth Hemisphere one half of the planet
24 Latitude horizontal lines on a map that run east and west. They measure north and south of the equator. Longitude the vertical lines on a map that run north and south. They measure east and west of the Prime Meridian. Meridian lines of longitude Prime Meridian the line of longitude is starting point for measuring distance of east and west. It is at 0 degrees longitude. Absolute location the exact location of a place using latitude and longitude locations Relative location a location of a place that is close but not exact.
25 Latitude and Longitude Vocabulary Degrees the unit for measuring distance on a map Equator imaginary line separating the northern and southern hemispheres. Globe a miniature model of the Earth Hemisphere one half of the planet
26 Latitude horizontal lines on a map that run east and west. They measure north and south of the equator. Longitude the vertical lines on a map that run north and south. They measure east and west of the Prime Meridian. Meridian lines of longitude Prime Meridian the line of longitude is starting point for measuring distance of east and west. It is at 0 degrees longitude. Absolute location the exact location of a place using latitude and longitude locations Relative location a location of a place that is close but not exact.
27 Latitude and Longitude Vocabulary Degrees the unit for measuring distance on a map Equator imaginary line separating the northern and southern hemispheres. Globe a miniature model of the Earth Hemisphere one half of the planet
28 Latitude horizontal lines on a map that run east and west. They measure north and south of the equator. Longitude the vertical lines on a map that run north and south. They measure east and west of the Prime Meridian. Meridian lines of longitude Prime Meridian the line of longitude is starting point for measuring distance of east and west. It is at 0 degrees longitude. Absolute location the exact location of a place using latitude and longitude locations Relative location a location of a place that is close but not exact.
29 Latitude and Longitude Vocabulary Degrees the unit for measuring distance on a map Equator imaginary line separating the northern and southern hemispheres. Globe a miniature model of the Earth Hemisphere one half of the planet
30 Latitude horizontal lines on a map that run east and west. They measure north and south of the equator. Longitude the vertical lines on a map that run north and south. They measure east and west of the Prime Meridian. Meridian lines of longitude Prime Meridian the line of longitude is starting point for measuring distance of east and west. It is at 0 degrees longitude. Absolute location the exact location of a place using latitude and longitude locations Relative location a location of a place that is close but not exact.
31 Latitude and Longitude Vocabulary Degrees the unit for measuring distance on a map Equator imaginary line separating the northern and southern hemispheres. Globe a miniature model of the Earth Hemisphere one half of the planet
32 Latitude horizontal lines on a map that run east and west. They measure north and south of the equator. Longitude the vertical lines on a map that run north and south. They measure east and west of the Prime Meridian. Meridian lines of longitude Prime Meridian the line of longitude is starting point for measuring distance of east and west. It is at 0 degrees longitude. Absolute location the exact location of a place using latitude and longitude locations Relative location a location of a place that is close but not exact.
33 Latitude and Longitude Vocabulary Degrees the unit for measuring distance on a map Equator imaginary line separating the northern and southern hemispheres. Globe a miniature model of the Earth Hemisphere one half of the planet
34 Latitude horizontal lines on a map that run east and west. They measure north and south of the equator. Longitude the vertical lines on a map that run north and south. They measure east and west of the Prime Meridian. Meridian lines of longitude Prime Meridian the line of longitude is starting point for measuring distance of east and west. It is at 0 degrees longitude. Absolute location the exact location of a place using latitude and longitude locations Relative location a location of a place that is close but not exact.
35 Latitude and Longitude Vocabulary Degrees the unit for measuring distance on a map Equator imaginary line separating the northern and southern hemispheres. Globe a miniature model of the Earth Hemisphere one half of the planet
36 Latitude horizontal lines on a map that run east and west. They measure north and south of the equator. Longitude the vertical lines on a map that run north and south. They measure east and west of the Prime Meridian. Meridian lines of longitude Prime Meridian the line of longitude is starting point for measuring distance of east and west. It is at 0 degrees longitude. Absolute location the exact location of a place using latitude and longitude locations Relative location a location of a place that is close but not exact.
37 Latitude and Longitude Vocabulary Degrees the unit for measuring distance on a map Equator imaginary line separating the northern and southern hemispheres. Globe a miniature model of the Earth Hemisphere one half of the planet
38 Latitude horizontal lines on a map that run east and west. They measure north and south of the equator. Longitude the vertical lines on a map that run north and south. They measure east and west of the Prime Meridian. Meridian lines of longitude Prime Meridian the line of longitude is starting point for measuring distance of east and west. It is at 0 degrees longitude. Absolute location the exact location of a place using latitude and longitude locations Relative location a location of a place that is close but not exact.
39 Latitude and Longitude Vocabulary Degrees the unit for measuring distance on a map Equator imaginary line separating the northern and southern hemispheres. Globe a miniature model of the Earth Hemisphere one half of the planet
40 Latitude horizontal lines on a map that run east and west. They measure north and south of the equator. Longitude the vertical lines on a map that run north and south. They measure east and west of the Prime Meridian. Meridian lines of longitude Prime Meridian the line of longitude is starting point for measuring distance of east and west. It is at 0 degrees longitude. Absolute location the exact location of a place using latitude and longitude locations Relative location a location of a place that is close but not exact.
41 Latitude and Longitude Vocabulary Degrees the unit for measuring distance on a map Equator imaginary line separating the northern and southern hemispheres. Globe a miniature model of the Earth Hemisphere one half of the planet
42 Latitude horizontal lines on a map that run east and west. They measure north and south of the equator. Longitude the vertical lines on a map that run north and south. They measure east and west of the Prime Meridian. Meridian lines of longitude Prime Meridian the line of longitude is starting point for measuring distance of east and west. It is at 0 degrees longitude. Absolute location the exact location of a place using latitude and longitude locations Relative location a location of a place that is close but not exact.
43 Latitude and Longitude Vocabulary Degrees the unit for measuring distance on a map Equator imaginary line separating the northern and southern hemispheres. Globe a miniature model of the Earth Hemisphere one half of the planet
44 Latitude horizontal lines on a map that run east and west. They measure north and south of the equator. Longitude the vertical lines on a map that run north and south. They measure east and west of the Prime Meridian. Meridian lines of longitude Prime Meridian the line of longitude is starting point for measuring distance of east and west. It is at 0 degrees longitude. Absolute location the exact location of a place using latitude and longitude locations Relative location a location of a place that is close but not exact.
45 Latitude and Longitude Vocabulary Degrees the unit for measuring distance on a map Equator imaginary line separating the northern and southern hemispheres. Globe a miniature model of the Earth Hemisphere one half of the planet
46 Latitude horizontal lines on a map that run east and west. They measure north and south of the equator. Longitude the vertical lines on a map that run north and south. They measure east and west of the Prime Meridian. Meridian lines of longitude Prime Meridian the line of longitude is starting point for measuring distance of east and west. It is at 0 degrees longitude. Absolute location the exact location of a place using latitude and longitude locations Relative location a location of a place that is close but not exact.
Solar Angles and Latitude
 Solar Angles and Latitude Objectives The student will understand that the sun is not directly overhead at noon in most latitudes. The student will research and discover the latitude ir classroom and calculate
Solar Angles and Latitude Objectives The student will understand that the sun is not directly overhead at noon in most latitudes. The student will research and discover the latitude ir classroom and calculate
Lines on Maps and Globes. Cross Curricular Writing Activity Social Studies Grade 4
 Lines on Maps and Globes Cross Curricular Writing Activity Social Studies Grade 4 Fourth Grade Social Studies Standard Map: Chart/Globe The learner will be able to use maps, charts, graphs, and globes
Lines on Maps and Globes Cross Curricular Writing Activity Social Studies Grade 4 Fourth Grade Social Studies Standard Map: Chart/Globe The learner will be able to use maps, charts, graphs, and globes
The Globe Latitudes and Longitudes
 INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT MIDDLE SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE The Globe Latitudes and Longitudes NAME: CLASS VI SEC: ROLL NO: DATE:.04.2015 I NAME THE FOLLOWING: 1. A small spherical model of the Earth:
INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT MIDDLE SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE The Globe Latitudes and Longitudes NAME: CLASS VI SEC: ROLL NO: DATE:.04.2015 I NAME THE FOLLOWING: 1. A small spherical model of the Earth:
Celestial Observations
 Celestial Observations Earth experiences two basic motions: Rotation West-to-East spinning of Earth on its axis (v rot = 1770 km/hr) (v rot Revolution orbit of Earth around the Sun (v orb = 108,000 km/hr)
Celestial Observations Earth experiences two basic motions: Rotation West-to-East spinning of Earth on its axis (v rot = 1770 km/hr) (v rot Revolution orbit of Earth around the Sun (v orb = 108,000 km/hr)
Sun Earth Relationships
 1 ESCI-61 Introduction to Photovoltaic Technology Sun Earth Relationships Ridha Hamidi, Ph.D. Spring (sun aims directly at equator) Winter (northern hemisphere tilts away from sun) 23.5 2 Solar radiation
1 ESCI-61 Introduction to Photovoltaic Technology Sun Earth Relationships Ridha Hamidi, Ph.D. Spring (sun aims directly at equator) Winter (northern hemisphere tilts away from sun) 23.5 2 Solar radiation
Coordinate Systems. Orbits and Rotation
 Coordinate Systems Orbits and Rotation Earth orbit. The earth s orbit around the sun is nearly circular but not quite. It s actually an ellipse whose average distance from the sun is one AU (150 million
Coordinate Systems Orbits and Rotation Earth orbit. The earth s orbit around the sun is nearly circular but not quite. It s actually an ellipse whose average distance from the sun is one AU (150 million
Pre and post-visit activities - Navigating by the stars
 Pre and post-visit activities - Navigating by the stars Vocabulary List Adult Education at Scienceworks Pre-visit Activity 1: What is longitude and latitude? Activity 2: Using the Southern Cross to find
Pre and post-visit activities - Navigating by the stars Vocabulary List Adult Education at Scienceworks Pre-visit Activity 1: What is longitude and latitude? Activity 2: Using the Southern Cross to find
FIRST GRADE 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 FIRST GRADE 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES UNIVERSE CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FIRST GRADE UNIVERSE WEEK 1. PRE: Describing the Universe. LAB: Comparing and contrasting bodies that reflect light. POST: Exploring
FIRST GRADE 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES UNIVERSE CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FIRST GRADE UNIVERSE WEEK 1. PRE: Describing the Universe. LAB: Comparing and contrasting bodies that reflect light. POST: Exploring
Stage 4. Geography. Blackline Masters. By Karen Devine
 1 Devine Educational Consultancy Services Stage 4 Geography Blackline Masters By Karen Devine Updated January 2010 2 This book is intended for the exclusive use in NSW Secondary Schools. It is meant to
1 Devine Educational Consultancy Services Stage 4 Geography Blackline Masters By Karen Devine Updated January 2010 2 This book is intended for the exclusive use in NSW Secondary Schools. It is meant to
The following words and their definitions should be addressed before completion of the reading:
 Seasons Vocabulary: The following words and their definitions should be addressed before completion of the reading: sphere any round object that has a surface that is the same distance from its center
Seasons Vocabulary: The following words and their definitions should be addressed before completion of the reading: sphere any round object that has a surface that is the same distance from its center
Grades 3-5. Benchmark A: Use map elements or coordinates to locate physical and human features of North America.
 Grades 3-5 Students use knowledge of geographic locations, patterns and processes to show the interrelationship between the physical environment and human activity, and to explain the interactions that
Grades 3-5 Students use knowledge of geographic locations, patterns and processes to show the interrelationship between the physical environment and human activity, and to explain the interactions that
Topographic Maps Practice Questions and Answers Revised October 2007
 Topographic Maps Practice Questions and Answers Revised October 2007 1. In the illustration shown below what navigational features are represented by A, B, and C? Note that A is a critical city in defining
Topographic Maps Practice Questions and Answers Revised October 2007 1. In the illustration shown below what navigational features are represented by A, B, and C? Note that A is a critical city in defining
THE UNIVERSAL GRID SYSTEM
 NGA Office of GEOINT Sciences Coordinate Systems Analysis (CSAT) Phone: 314-676-9124 Unclassified Email: coordsys@nga.mil March 2007 THE UNIVERSAL GRID SYSTEM Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) Military
NGA Office of GEOINT Sciences Coordinate Systems Analysis (CSAT) Phone: 314-676-9124 Unclassified Email: coordsys@nga.mil March 2007 THE UNIVERSAL GRID SYSTEM Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) Military
4 The Rhumb Line and the Great Circle in Navigation
 4 The Rhumb Line and the Great Circle in Navigation 4.1 Details on Great Circles In fig. GN 4.1 two Great Circle/Rhumb Line cases are shown, one in each hemisphere. In each case the shorter distance between
4 The Rhumb Line and the Great Circle in Navigation 4.1 Details on Great Circles In fig. GN 4.1 two Great Circle/Rhumb Line cases are shown, one in each hemisphere. In each case the shorter distance between
Introduction to Geography
 High School Unit: 1 Lesson: 1 Suggested Duration: 3 days Introduction to Lesson Synopsis: The purpose of this lesson is to introduce students to geography and geography terminology, to teach students about
High School Unit: 1 Lesson: 1 Suggested Duration: 3 days Introduction to Lesson Synopsis: The purpose of this lesson is to introduce students to geography and geography terminology, to teach students about
Earth Coordinates & Grid Coordinate Systems
 Earth Coordinates & Grid Coordinate Systems How do we model the earth? Datums Datums mathematically describe the surface of the Earth. Accounts for mean sea level, topography, and gravity models. Projections
Earth Coordinates & Grid Coordinate Systems How do we model the earth? Datums Datums mathematically describe the surface of the Earth. Accounts for mean sea level, topography, and gravity models. Projections
IAntarcticaI. IArctic Ocean I. Where in the World? Arctic Ocean. Pacific Ocean. Pacific Ocean. Atlantic Ocean. North America.
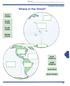 Name ------------------------------ Where in the World? Continents and s Arctic Pacific Pacific Atlantic.1.... 0" o ". North America South America Antarctica Arctic 261 Name Where in the World Continents
Name ------------------------------ Where in the World? Continents and s Arctic Pacific Pacific Atlantic.1.... 0" o ". North America South America Antarctica Arctic 261 Name Where in the World Continents
compass Encyclopedic Entry
 This website would like to remind you: Your browser (Apple Safari 7) is out of date. Update your browser for more security, comfort and the best experience on this site. Encyclopedic Entry compass For
This website would like to remind you: Your browser (Apple Safari 7) is out of date. Update your browser for more security, comfort and the best experience on this site. Encyclopedic Entry compass For
OBJECTIVES. Identify the means by which latitude and longitude were created and the science upon which they are based.
 Name: Key OBJECTIVES Correctly define: isolines, gradient, topographic map, contour interval, hachured lines, profile, latitude, longitude, hydrosphere, lithosphere, atmosphere, elevation, model EARTH
Name: Key OBJECTIVES Correctly define: isolines, gradient, topographic map, contour interval, hachured lines, profile, latitude, longitude, hydrosphere, lithosphere, atmosphere, elevation, model EARTH
6 th Grade Vocabulary-ALL CAMPUSES
 6 th Grade Vocabulary-ALL CAMPUSES 6.1 History. The student understands that historical events influence contemporary events. (B) analyze the historical background of the United States to evaluate relationships
6 th Grade Vocabulary-ALL CAMPUSES 6.1 History. The student understands that historical events influence contemporary events. (B) analyze the historical background of the United States to evaluate relationships
Latitude, Longitude, and Time Zones
 Latitude, Longitude, and Time Zones Typical Graph This is an example of a typical graph. It is made up of points that are connected by a line. Y axis Typical Graph Each point has two values: (4,7) An X
Latitude, Longitude, and Time Zones Typical Graph This is an example of a typical graph. It is made up of points that are connected by a line. Y axis Typical Graph Each point has two values: (4,7) An X
SECOND GRADE 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 SECOND GRADE 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES UNIVERSE CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SECOND GRADE UNIVERSE WEEK 1. PRE: Discovering stars. LAB: Analyzing the geometric pattern of constellations. POST: Exploring
SECOND GRADE 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES UNIVERSE CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SECOND GRADE UNIVERSE WEEK 1. PRE: Discovering stars. LAB: Analyzing the geometric pattern of constellations. POST: Exploring
Unit One Study Guide
 Unit One Study Guide Terms BCE: Before the Common Era. Referring to the time before Christ s birth. CE: Common Era. Referring to the time after Christ s birth. BC: Before Christ. Referring to the time
Unit One Study Guide Terms BCE: Before the Common Era. Referring to the time before Christ s birth. CE: Common Era. Referring to the time after Christ s birth. BC: Before Christ. Referring to the time
Inside Earth Chapter 3
 Name Hour Due Date Inside Earth Chapter Page 1 Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics Page 2 Volcanic Activity Page - Mapping Earthquakes and Volcanoes Page 4 Mapping Earthquakes and Volcanoes table Page 5 - Mapping
Name Hour Due Date Inside Earth Chapter Page 1 Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics Page 2 Volcanic Activity Page - Mapping Earthquakes and Volcanoes Page 4 Mapping Earthquakes and Volcanoes table Page 5 - Mapping
Newton s Law of Gravity
 Gravitational Potential Energy On Earth, depends on: object s mass (m) strength of gravity (g) distance object could potentially fall Gravitational Potential Energy In space, an object or gas cloud has
Gravitational Potential Energy On Earth, depends on: object s mass (m) strength of gravity (g) distance object could potentially fall Gravitational Potential Energy In space, an object or gas cloud has
World Map Lesson 4 - The Global Grid System - Grade 6+
 World Map Lesson 4 - The Global Grid System - Grade 6+ Activity Goal To use the global grid system of latitude and longitude to find specific locations on a world map. Materials Needed: A pencil, a ruler,
World Map Lesson 4 - The Global Grid System - Grade 6+ Activity Goal To use the global grid system of latitude and longitude to find specific locations on a world map. Materials Needed: A pencil, a ruler,
Basic Coordinates & Seasons Student Guide
 Name: Basic Coordinates & Seasons Student Guide There are three main sections to this module: terrestrial coordinates, celestial equatorial coordinates, and understanding how the ecliptic is related to
Name: Basic Coordinates & Seasons Student Guide There are three main sections to this module: terrestrial coordinates, celestial equatorial coordinates, and understanding how the ecliptic is related to
The Celestial Sphere. Questions for Today. The Celestial Sphere 1/18/10
 Lecture 3: Constellations and the Distances to the Stars Astro 2010 Prof. Tom Megeath Questions for Today How do the stars move in the sky? What causes the phases of the moon? What causes the seasons?
Lecture 3: Constellations and the Distances to the Stars Astro 2010 Prof. Tom Megeath Questions for Today How do the stars move in the sky? What causes the phases of the moon? What causes the seasons?
EPSG. Coordinate Reference System Definition - Recommended Practice. Guidance Note Number 5
 European Petroleum Survey Group EPSG Guidance Note Number 5 Coordinate Reference System Definition - Recommended Practice Revision history: Version Date Amendments 1.0 April 1997 First release. 1.1 June
European Petroleum Survey Group EPSG Guidance Note Number 5 Coordinate Reference System Definition - Recommended Practice Revision history: Version Date Amendments 1.0 April 1997 First release. 1.1 June
Tropical Horticulture: Lecture 2
 Lecture 2 Theory of the Tropics Earth & Solar Geometry, Celestial Mechanics The geometrical relationship between the earth and sun is responsible for the earth s climates. The two principal movements of
Lecture 2 Theory of the Tropics Earth & Solar Geometry, Celestial Mechanics The geometrical relationship between the earth and sun is responsible for the earth s climates. The two principal movements of
Measuring Your Latitude from the Angle of the Sun at Noon
 Measuring Your Latitude from the Angle of the Sun at Noon Background: You can measure your latitude in earth's northern hemisphere by finding out the altitude of the celestial equator from the southern
Measuring Your Latitude from the Angle of the Sun at Noon Background: You can measure your latitude in earth's northern hemisphere by finding out the altitude of the celestial equator from the southern
An Introduction to Coordinate Systems in South Africa
 An Introduction to Coordinate Systems in South Africa Centuries ago people believed that the earth was flat and notwithstanding that if this had been true it would have produced serious problems for mariners
An Introduction to Coordinate Systems in South Africa Centuries ago people believed that the earth was flat and notwithstanding that if this had been true it would have produced serious problems for mariners
Satellite Pursuit: Tracking Marine Mammals
 : Tracking Marine Mammals Material adapted from: Monterey Bay Research Institute, EARTH: Satellite Tracking OPB NOVA Teachers: Ocean Animal Emergency Teach Engineering: Marine Animal Tracking Introduction:
: Tracking Marine Mammals Material adapted from: Monterey Bay Research Institute, EARTH: Satellite Tracking OPB NOVA Teachers: Ocean Animal Emergency Teach Engineering: Marine Animal Tracking Introduction:
Follow That Hurricane!
 Discover Your World With NOAA Follow That Hurricane! What You Will Do Devastating damage expected A most Track a hurricane on the same powerful hurricane with unprecedented type of chart used at the strength
Discover Your World With NOAA Follow That Hurricane! What You Will Do Devastating damage expected A most Track a hurricane on the same powerful hurricane with unprecedented type of chart used at the strength
Stellarium a valuable resource for teaching astronomy in the classroom and beyond
 Stellarium 1 Stellarium a valuable resource for teaching astronomy in the classroom and beyond Stephen Hughes Department of Physical and Chemical Sciences, Queensland University of Technology, Gardens
Stellarium 1 Stellarium a valuable resource for teaching astronomy in the classroom and beyond Stephen Hughes Department of Physical and Chemical Sciences, Queensland University of Technology, Gardens
Module 11: The Cruise Ship Sector. Destination #3
 Module 11: The Cruise Ship Sector Destination #3 Cruise Destinations Welcome to your third destination. Use the following resource article to learn about the different oceans and time zones. Seen from
Module 11: The Cruise Ship Sector Destination #3 Cruise Destinations Welcome to your third destination. Use the following resource article to learn about the different oceans and time zones. Seen from
Navigation: Latitude and Longitude
 Sextants and Chronometers Help Sailors Find Their Position at Sea Latitude lines run horizontally across the globe and are used to measure distances north and south of the equator. Sailors used a sextant
Sextants and Chronometers Help Sailors Find Their Position at Sea Latitude lines run horizontally across the globe and are used to measure distances north and south of the equator. Sailors used a sextant
KML EXPORT & 3D CONSTRUCTION POINT TIP SHEET FOR iwitness TM V2
 KML EXPORT & 3D CONSTRUCTION POINT TIP SHEET FOR iwitness TM V2 Working with GPS Coordinates STEP 1. Conduct the iwitness project and assure the scale distance used is set in Meters (Metres). NOTE: there
KML EXPORT & 3D CONSTRUCTION POINT TIP SHEET FOR iwitness TM V2 Working with GPS Coordinates STEP 1. Conduct the iwitness project and assure the scale distance used is set in Meters (Metres). NOTE: there
Measuring the Earth Using a GPS M. Scott Wilkerson & M. Beth Wilkerson, DePauw University, May 10, 2007
 Measuring the Earth Using a GPS M. Scott Wilkerson & M. Beth Wilkerson, DePauw University, May 10, 2007 Modified from: Kerski, J.J., 2007, Measuring the Earth s Circumference with GPS, Copyright ESRI,
Measuring the Earth Using a GPS M. Scott Wilkerson & M. Beth Wilkerson, DePauw University, May 10, 2007 Modified from: Kerski, J.J., 2007, Measuring the Earth s Circumference with GPS, Copyright ESRI,
Calculating Astronomical Unit from Venus Transit
 Calculating Astronomical Unit from Venus Transit A) Background 1) Parallaxes of the Sun (the horizontal parallaxes) By definition the parallaxes of the Sun is the angle β shown below: By trigonometry,
Calculating Astronomical Unit from Venus Transit A) Background 1) Parallaxes of the Sun (the horizontal parallaxes) By definition the parallaxes of the Sun is the angle β shown below: By trigonometry,
CELESTIAL CLOCK - THE SUN, THE MOON, AND THE STARS
 INTRODUCTION CELESTIAL CLOCK - THE SUN, THE MOON, AND THE STARS This is a scientific presentation to provide you with knowledge you can use to understand the sky above in relation to the earth. Before
INTRODUCTION CELESTIAL CLOCK - THE SUN, THE MOON, AND THE STARS This is a scientific presentation to provide you with knowledge you can use to understand the sky above in relation to the earth. Before
Plotting Earthquake Epicenters an activity for seismic discovery
 Plotting Earthquake Epicenters an activity for seismic discovery Tammy K Bravo Anne M Ortiz Plotting Activity adapted from: Larry Braile and Sheryl Braile Department of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences Purdue
Plotting Earthquake Epicenters an activity for seismic discovery Tammy K Bravo Anne M Ortiz Plotting Activity adapted from: Larry Braile and Sheryl Braile Department of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences Purdue
How do you find a place on a globe? How do you look up a place based on latitude and longitude?
 Why are globes tilted? Most Replogle globes are made to tilt at an angle of 23.5º to match the actual tilt of the earth in relationship to our sun. Incidentally, it is this tilting of the earth relative
Why are globes tilted? Most Replogle globes are made to tilt at an angle of 23.5º to match the actual tilt of the earth in relationship to our sun. Incidentally, it is this tilting of the earth relative
ES 106 Laboratory # 3 INTRODUCTION TO OCEANOGRAPHY. Introduction The global ocean covers nearly 75% of Earth s surface and plays a vital role in
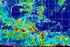 ES 106 Laboratory # 3 INTRODUCTION TO OCEANOGRAPHY 3-1 Introduction The global ocean covers nearly 75% of Earth s surface and plays a vital role in the physical environment of Earth. For these reasons,
ES 106 Laboratory # 3 INTRODUCTION TO OCEANOGRAPHY 3-1 Introduction The global ocean covers nearly 75% of Earth s surface and plays a vital role in the physical environment of Earth. For these reasons,
USING MAPS AND GLOBES
 USING MAPS AND GLOBES Grade Level or Special Area: 4 th Grade Written by: Krystal Kroeker, Colorado Springs Charter Academy, Colorado Springs, CO Length of Unit: Five lessons (approximately one week (five
USING MAPS AND GLOBES Grade Level or Special Area: 4 th Grade Written by: Krystal Kroeker, Colorado Springs Charter Academy, Colorado Springs, CO Length of Unit: Five lessons (approximately one week (five
Full credit for this chapter to Prof. Leonard Bachman of the University of Houston
 Chapter 6: SOLAR GEOMETRY Full credit for this chapter to Prof. Leonard Bachman of the University of Houston SOLAR GEOMETRY AS A DETERMINING FACTOR OF HEAT GAIN, SHADING AND THE POTENTIAL OF DAYLIGHT PENETRATION...
Chapter 6: SOLAR GEOMETRY Full credit for this chapter to Prof. Leonard Bachman of the University of Houston SOLAR GEOMETRY AS A DETERMINING FACTOR OF HEAT GAIN, SHADING AND THE POTENTIAL OF DAYLIGHT PENETRATION...
UTM: Universal Transverse Mercator Coordinate System
 Practical Cartographer s Reference #01 UTM: Universal Transverse Mercator Coordinate System 180 174w 168w 162w 156w 150w 144w 138w 132w 126w 120w 114w 108w 102w 96w 90w 84w 78w 72w 66w 60w 54w 48w 42w
Practical Cartographer s Reference #01 UTM: Universal Transverse Mercator Coordinate System 180 174w 168w 162w 156w 150w 144w 138w 132w 126w 120w 114w 108w 102w 96w 90w 84w 78w 72w 66w 60w 54w 48w 42w
Celestial Sphere. Celestial Coordinates. Lecture 3: Motions of the Sun and Moon. ecliptic (path of Sun) ecliptic (path of Sun)
 Lecture 3: Motions of the and Moon ecliptic (path of ) ecliptic (path of ) The 23.5 degree tilt of Earth s spin axis relative to its orbital axis around the causes the seasons Celestial Sphere Celestial
Lecture 3: Motions of the and Moon ecliptic (path of ) ecliptic (path of ) The 23.5 degree tilt of Earth s spin axis relative to its orbital axis around the causes the seasons Celestial Sphere Celestial
Lab Activity on the Causes of the Seasons
 Lab Activity on the Causes of the Seasons 2002 Ann Bykerk-Kauffman, Dept. of Geological and Environmental Sciences, California State University, Chico * Objectives When you have completed this lab you
Lab Activity on the Causes of the Seasons 2002 Ann Bykerk-Kauffman, Dept. of Geological and Environmental Sciences, California State University, Chico * Objectives When you have completed this lab you
An Analysis of the Rossby Wave Theory
 An Analysis of the Rossby Wave Theory Morgan E. Brown, Elise V. Johnson, Stephen A. Kearney ABSTRACT Large-scale planetary waves are known as Rossby waves. The Rossby wave theory gives us an idealized
An Analysis of the Rossby Wave Theory Morgan E. Brown, Elise V. Johnson, Stephen A. Kearney ABSTRACT Large-scale planetary waves are known as Rossby waves. The Rossby wave theory gives us an idealized
Motion & The Global Positioning System (GPS)
 Grade Level: K - 8 Subject: Motion Prep Time: < 10 minutes Duration: 30 minutes Objective: To learn how to analyze GPS data in order to track an object and derive its velocity from positions and times.
Grade Level: K - 8 Subject: Motion Prep Time: < 10 minutes Duration: 30 minutes Objective: To learn how to analyze GPS data in order to track an object and derive its velocity from positions and times.
SOUTH AMERICA CONTENTS. What s in This Book... 2. Section 1: South America in the World... 3. Section 2: Political Divisions of South America...
 SOUTH CONTENTS What s in This Book 2 Section 1: 3 Section 2: Political Divisions of 1 Section 3: Physical Features of 41 Section 4: Valuable Resources of 67 Section : n Culture 89 Section 6: Assessment
SOUTH CONTENTS What s in This Book 2 Section 1: 3 Section 2: Political Divisions of 1 Section 3: Physical Features of 41 Section 4: Valuable Resources of 67 Section : n Culture 89 Section 6: Assessment
Thought Questions on the Geostrophic Wind and Real Winds Aloft at Midlatitudes
 Thought Questions on the Geostrophic Wind and Real Winds Aloft at Midlatitudes (1) The geostrophic wind is an idealized, imaginary wind that we define at each point in the atmosphere as the wind that blows
Thought Questions on the Geostrophic Wind and Real Winds Aloft at Midlatitudes (1) The geostrophic wind is an idealized, imaginary wind that we define at each point in the atmosphere as the wind that blows
The Observed Calendar of the Second Temple Dates For 2014
 www.120jubilees.com The Observed Calendar of the Second Temple Dates For 2014 The Observed Calendar of the Second Temple Era was used by the official priests of the Second Temple from at least 520 BC to
www.120jubilees.com The Observed Calendar of the Second Temple Dates For 2014 The Observed Calendar of the Second Temple Era was used by the official priests of the Second Temple from at least 520 BC to
WE VE GOT THE WHOLE WORLD IN OUR HANDS: Geography Spatial Sense
 WE VE GOT THE WHOLE WORLD IN OUR HANDS: Geography Spatial Sense Grade Level: Written by: Length of Unit: Third Grade Wendy S. Hyndman, The Classical Academy, Colorado Springs, CO Doreen W. Jennings, Lincoln
WE VE GOT THE WHOLE WORLD IN OUR HANDS: Geography Spatial Sense Grade Level: Written by: Length of Unit: Third Grade Wendy S. Hyndman, The Classical Academy, Colorado Springs, CO Doreen W. Jennings, Lincoln
Maintaining High Accuracy in Modern Geospatial Data
 Maintaining High Accuracy in Modern Geospatial Data Patrick Cunningham President info@bluemarblegeo.com www.bluemarblegeo.com +1 (207) 582 6747 Copyright 2010 Blue Marble Geographics Concepts Geodesy -
Maintaining High Accuracy in Modern Geospatial Data Patrick Cunningham President info@bluemarblegeo.com www.bluemarblegeo.com +1 (207) 582 6747 Copyright 2010 Blue Marble Geographics Concepts Geodesy -
Week 1. Week 2. Week 3
 Week 1 1. What US city has the largest population? 2. Where is Aachen? 3. What is the capitol of Florida? 4. What is the longest mountain range in Spain? 5. What countries border Equador? Week 2 1. What
Week 1 1. What US city has the largest population? 2. Where is Aachen? 3. What is the capitol of Florida? 4. What is the longest mountain range in Spain? 5. What countries border Equador? Week 2 1. What
Today. Solstices & Equinoxes Precession Phases of the Moon Eclipses. Ancient Astronomy. Lunar, Solar FIRST HOMEWORK DUE NEXT TIME
 Today Solstices & Equinoxes Precession Phases of the Moon Eclipses Lunar, Solar Ancient Astronomy FIRST HOMEWORK DUE NEXT TIME The Reason for Seasons Hypothesis check: How would seasons in the northern
Today Solstices & Equinoxes Precession Phases of the Moon Eclipses Lunar, Solar Ancient Astronomy FIRST HOMEWORK DUE NEXT TIME The Reason for Seasons Hypothesis check: How would seasons in the northern
CHAPTER 9 SURVEYING TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS
 CHAPTER 9 SURVEYING TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS Surveying Terms 9-2 Standard Abbreviations 9-6 9-1 A) SURVEYING TERMS Accuracy - The degree of conformity with a standard, or the degree of perfection attained
CHAPTER 9 SURVEYING TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS Surveying Terms 9-2 Standard Abbreviations 9-6 9-1 A) SURVEYING TERMS Accuracy - The degree of conformity with a standard, or the degree of perfection attained
Lines of Latitude and Longitude
 ED 5661 Mathematics & Navigation Teacher Institute Keith Johnson Lesson Plan Lines of Latitude and Longitude Lesson Overview: This lesson plan will introduce students to latitude and longitude along with
ED 5661 Mathematics & Navigation Teacher Institute Keith Johnson Lesson Plan Lines of Latitude and Longitude Lesson Overview: This lesson plan will introduce students to latitude and longitude along with
The ecliptic - Earth s orbital plane
 The ecliptic - Earth s orbital plane The line of nodes descending node The Moon s orbital plane Moon s orbit inclination 5.45º ascending node celestial declination Zero longitude in the ecliptic The orbit
The ecliptic - Earth s orbital plane The line of nodes descending node The Moon s orbital plane Moon s orbit inclination 5.45º ascending node celestial declination Zero longitude in the ecliptic The orbit
Earth In Space Chapter 3
 Earth In Space Chapter 3 Shape of the Earth Ancient Greeks Earth casts a circular shadow on the moon during a lunar eclipse Shape of the Earth Ancient Greeks Ships were observed to disappear below the
Earth In Space Chapter 3 Shape of the Earth Ancient Greeks Earth casts a circular shadow on the moon during a lunar eclipse Shape of the Earth Ancient Greeks Ships were observed to disappear below the
Plotting and Adjusting Your Course: Using Vectors and Trigonometry in Navigation
 Plotting and Adjusting Your Course: Using Vectors and Trigonometry in Navigation ED 5661 Mathematics & Navigation Teacher Institute August 2011 By Serena Gay Target: Precalculus (grades 11 or 12) Lesson
Plotting and Adjusting Your Course: Using Vectors and Trigonometry in Navigation ED 5661 Mathematics & Navigation Teacher Institute August 2011 By Serena Gay Target: Precalculus (grades 11 or 12) Lesson
6. The greatest atmospheric pressure occurs in the 1) troposphere 3) mesosphere 2) stratosphere 4) thermosphere
 1. The best evidence of the Earth's nearly spherical shape is obtained through telescopic observations of other planets photographs of the Earth from an orbiting satellite observations of the Sun's altitude
1. The best evidence of the Earth's nearly spherical shape is obtained through telescopic observations of other planets photographs of the Earth from an orbiting satellite observations of the Sun's altitude
Cycles in the Sky. Teacher Guide: Cycles in the Sky Page 1 of 8 2008 Discovery Communications, LLC
 Cycles in the Sky What is a Fun damental? Each Fun damental is designed to introduce your younger students to some of the basic ideas about one particular area of science. The activities in the Fun damental
Cycles in the Sky What is a Fun damental? Each Fun damental is designed to introduce your younger students to some of the basic ideas about one particular area of science. The activities in the Fun damental
Using Handheld GPS Units in the Field Overview
 Using Handheld GPS Units in the Field Overview Most recently revised 3/13/12 Equipment to have with you in the field PC laptop loaded with: - ESRI ArcMap 10 (get from Tufts GIS Support) - DNR Garmin (freeware
Using Handheld GPS Units in the Field Overview Most recently revised 3/13/12 Equipment to have with you in the field PC laptop loaded with: - ESRI ArcMap 10 (get from Tufts GIS Support) - DNR Garmin (freeware
Reasons for Seasons. Question: TRUE OR FALSE. Question: TRUE OR FALSE? What causes the seasons? What causes the seasons?
 Reasons for Seasons Question: TRUE OR FALSE? Earth is closer to the Sun in summer and farther from the Sun in winter. Question: TRUE OR FALSE? Earth is closer to the Sun in summer and farther from the
Reasons for Seasons Question: TRUE OR FALSE? Earth is closer to the Sun in summer and farther from the Sun in winter. Question: TRUE OR FALSE? Earth is closer to the Sun in summer and farther from the
The Basics of Navigation
 The Basics of Navigation Knowledge of map reading and the use of the compass is an indispensable skill of bushcraft. Without this skill, a walker is a passenger and mere follower on a trip. To become a
The Basics of Navigation Knowledge of map reading and the use of the compass is an indispensable skill of bushcraft. Without this skill, a walker is a passenger and mere follower on a trip. To become a
Heat Transfer. Energy from the Sun. Introduction
 Introduction The sun rises in the east and sets in the west, but its exact path changes over the course of the year, which causes the seasons. In order to use the sun s energy in a building, we need to
Introduction The sun rises in the east and sets in the west, but its exact path changes over the course of the year, which causes the seasons. In order to use the sun s energy in a building, we need to
Earth, Sun and Moon is a set of interactives designed to support the teaching of the QCA primary science scheme of work 5e - 'Earth, Sun and Moon'.
 is a set of interactives designed to support the teaching of the QCA primary science scheme of work 5e - ''. Learning Connections Primary Science Interactives are teaching tools which have been created
is a set of interactives designed to support the teaching of the QCA primary science scheme of work 5e - ''. Learning Connections Primary Science Interactives are teaching tools which have been created
What Causes Climate? Use Target Reading Skills
 Climate and Climate Change Name Date Class Climate and Climate Change Guided Reading and Study What Causes Climate? This section describes factors that determine climate, or the average weather conditions
Climate and Climate Change Name Date Class Climate and Climate Change Guided Reading and Study What Causes Climate? This section describes factors that determine climate, or the average weather conditions
Seasonal & Daily Temperatures. Seasons & Sun's Distance. Solstice & Equinox. Seasons & Solar Intensity
 Seasonal & Daily Temperatures Seasons & Sun's Distance The role of Earth's tilt, revolution, & rotation in causing spatial, seasonal, & daily temperature variations Please read Chapter 3 in Ahrens Figure
Seasonal & Daily Temperatures Seasons & Sun's Distance The role of Earth's tilt, revolution, & rotation in causing spatial, seasonal, & daily temperature variations Please read Chapter 3 in Ahrens Figure
COASTLINING THE ZODIAC
 COASTLINING THE ZODIAC Astronomy books and skywatching guides offer a wide variety of charts for naked-eye observation of the skies. What works best for each person will depend on various factors such
COASTLINING THE ZODIAC Astronomy books and skywatching guides offer a wide variety of charts for naked-eye observation of the skies. What works best for each person will depend on various factors such
Essential Question. Enduring Understanding
 Earth In Space Unit Diagnostic Assessment: Students complete a questionnaire answering questions about their ideas concerning a day, year, the seasons and moon phases: My Ideas About A Day, Year, Seasons
Earth In Space Unit Diagnostic Assessment: Students complete a questionnaire answering questions about their ideas concerning a day, year, the seasons and moon phases: My Ideas About A Day, Year, Seasons
Where in the World is the arctic?
 Where in the World is the arctic? Summary: Students map the arctic in relation to their home in order to learn the location and countries of the arctic. Grade Level: 3-4; 5-8; K-2 Time one class period.
Where in the World is the arctic? Summary: Students map the arctic in relation to their home in order to learn the location and countries of the arctic. Grade Level: 3-4; 5-8; K-2 Time one class period.
Optimum Orientation of Solar Panels
 Optimum Orientation of Solar Panels To get the most from solar panels, point them in the direction that captures the most sun. But there are a number of variables in figuring out the best direction. This
Optimum Orientation of Solar Panels To get the most from solar panels, point them in the direction that captures the most sun. But there are a number of variables in figuring out the best direction. This
The Size & Shape of the Galaxy
 name The Size & Shape of the Galaxy The whole lab consists of plotting two graphs. What s the catch? Aha visualizing and understanding what you have plotted of course! Form the Earth Science Picture of
name The Size & Shape of the Galaxy The whole lab consists of plotting two graphs. What s the catch? Aha visualizing and understanding what you have plotted of course! Form the Earth Science Picture of
II. 2005 Core Knowledge National Conference, Meet the Explorers from Our Past, Connections: 3 rd & 5 th Grade 1
 Meet the Explorers From Our Past Grade Level: Connections_3 rd and 5 th Written by: Michelle Abernathy, Suzanne Gandy, and Staci Lewis Length of Unit: (8 lessons) I. ABSTRACT A. This unit is an exciting
Meet the Explorers From Our Past Grade Level: Connections_3 rd and 5 th Written by: Michelle Abernathy, Suzanne Gandy, and Staci Lewis Length of Unit: (8 lessons) I. ABSTRACT A. This unit is an exciting
Geography I Pre Test #1
 Geography I Pre Test #1 1. The sun is a star in the galaxy. a) Orion b) Milky Way c) Proxima Centauri d) Alpha Centauri e) Betelgeuse 2. The response to earth's rotation is a) an equatorial bulge b) polar
Geography I Pre Test #1 1. The sun is a star in the galaxy. a) Orion b) Milky Way c) Proxima Centauri d) Alpha Centauri e) Betelgeuse 2. The response to earth's rotation is a) an equatorial bulge b) polar
Earth-Sun Relationships. The Reasons for the Seasons
 Earth-Sun Relationships The Reasons for the Seasons Solar Radiation The earth intercepts less than one two-billionth of the energy given off by the sun. However, the radiation is sufficient to provide
Earth-Sun Relationships The Reasons for the Seasons Solar Radiation The earth intercepts less than one two-billionth of the energy given off by the sun. However, the radiation is sufficient to provide
Seasons on Earth LESSON
 LESSON 4 Seasons on Earth On Earth, orange and red autumn leaves stand out against the blue sky. NATIONAL OCEANIC AND ATMOSPHERIC ADMINISTRATION (NOAA) PHOTO LIBRARY/NOAA CENTRAL LIBRARY INTRODUCTION Nearly
LESSON 4 Seasons on Earth On Earth, orange and red autumn leaves stand out against the blue sky. NATIONAL OCEANIC AND ATMOSPHERIC ADMINISTRATION (NOAA) PHOTO LIBRARY/NOAA CENTRAL LIBRARY INTRODUCTION Nearly
How Do Oceans Affect Weather and Climate?
 How Do Oceans Affect Weather and Climate? In Learning Set 2, you explored how water heats up more slowly than land and also cools off more slowly than land. Weather is caused by events in the atmosphere.
How Do Oceans Affect Weather and Climate? In Learning Set 2, you explored how water heats up more slowly than land and also cools off more slowly than land. Weather is caused by events in the atmosphere.
Which month has larger and smaller day time?
 ACTIVITY-1 Which month has larger and smaller day time? Problem: Which month has larger and smaller day time? Aim: Finding out which month has larger and smaller duration of day in the Year 2006. Format
ACTIVITY-1 Which month has larger and smaller day time? Problem: Which month has larger and smaller day time? Aim: Finding out which month has larger and smaller duration of day in the Year 2006. Format
Noon Sun Angle = 90 Zenith Angle
 Noon Sun Angle Worksheet Name Name Date Subsolar Point (Latitude where the sun is overhead at noon) Equinox March 22 nd 0 o Equinox September 22 nd 0 o Solstice June 22 nd 23.5 N Solstice December 22 nd
Noon Sun Angle Worksheet Name Name Date Subsolar Point (Latitude where the sun is overhead at noon) Equinox March 22 nd 0 o Equinox September 22 nd 0 o Solstice June 22 nd 23.5 N Solstice December 22 nd
Calculation of Azimuth, Elevation and Polarization for non-horizontal aligned Antennas
 Calculation of Azimuth, Elevation and Polarization for non-horizontal aligned Antennas Algorithm Description Technical Document TD-1205-a Version 1.1 23.10.2012 In Co-operation with 1 Objective Many SatCom
Calculation of Azimuth, Elevation and Polarization for non-horizontal aligned Antennas Algorithm Description Technical Document TD-1205-a Version 1.1 23.10.2012 In Co-operation with 1 Objective Many SatCom
Orientation to the Sky: Apparent Motions
 Chapter 2 Orientation to the Sky: Apparent Motions 2.1 Purpose The main goal of this lab is for you to gain an understanding of how the sky changes during the night and over the course of a year. We will
Chapter 2 Orientation to the Sky: Apparent Motions 2.1 Purpose The main goal of this lab is for you to gain an understanding of how the sky changes during the night and over the course of a year. We will
Motions of Earth LEARNING GOALS
 2 Patterns in the Sky Motions of Earth The stars first found a special place in legend and mythology as the realm of gods and goddesses, holding sway over the lives of humankind. From these legends and
2 Patterns in the Sky Motions of Earth The stars first found a special place in legend and mythology as the realm of gods and goddesses, holding sway over the lives of humankind. From these legends and
1. In the diagram below, the direct rays of the Sun are striking the Earth's surface at 23 º N. What is the date shown in the diagram?
 1. In the diagram below, the direct rays of the Sun are striking the Earth's surface at 23 º N. What is the date shown in the diagram? 5. During how many days of a calendar year is the Sun directly overhead
1. In the diagram below, the direct rays of the Sun are striking the Earth's surface at 23 º N. What is the date shown in the diagram? 5. During how many days of a calendar year is the Sun directly overhead
ASTRONOMY 161. Introduction to Solar System Astronomy
 ASTRONOMY 161 Introduction to Solar System Astronomy Seasons & Calendars Monday, January 8 Season & Calendars: Key Concepts (1) The cause of the seasons is the tilt of the Earth s rotation axis relative
ASTRONOMY 161 Introduction to Solar System Astronomy Seasons & Calendars Monday, January 8 Season & Calendars: Key Concepts (1) The cause of the seasons is the tilt of the Earth s rotation axis relative
CELESTIAL MOTIONS. In Charlottesville we see Polaris 38 0 above the Northern horizon. Earth. Starry Vault
 CELESTIAL MOTIONS Stars appear to move counterclockwise on the surface of a huge sphere the Starry Vault, in their daily motions about Earth Polaris remains stationary. In Charlottesville we see Polaris
CELESTIAL MOTIONS Stars appear to move counterclockwise on the surface of a huge sphere the Starry Vault, in their daily motions about Earth Polaris remains stationary. In Charlottesville we see Polaris
APPENDIX D: SOLAR RADIATION
 APPENDIX D: SOLAR RADIATION The sun is the source of most energy on the earth and is a primary factor in determining the thermal environment of a locality. It is important for engineers to have a working
APPENDIX D: SOLAR RADIATION The sun is the source of most energy on the earth and is a primary factor in determining the thermal environment of a locality. It is important for engineers to have a working
Earth, Moon, and Sun Study Guide. (Test Date: )
 Earth, Moon, and Sun Study Guide Name: (Test Date: ) Essential Question #1: How are the Earth, Moon, and Sun alike and how are they different? 1. List the Earth, Moon, and Sun, in order from LARGEST to
Earth, Moon, and Sun Study Guide Name: (Test Date: ) Essential Question #1: How are the Earth, Moon, and Sun alike and how are they different? 1. List the Earth, Moon, and Sun, in order from LARGEST to
ใบงานท ๕ เร อง เคร องม อทางภ ม ศาสตร รอบต วเรา และล กษณะสาค ญ
 ใบงานท ๕ เร อง เคร องม อทางภ ม ศาสตร รอบต วเรา และล กษณะสาค ญ ต วช ว ด : ส งท น กเร ยนพ งร และปฏ บ ต ได มฐ. ส ๕.๑ (๑) จ ดประสงค การเร ยนร. ศ กษากระบวนการทางภ ม ศาสตร โดยการเล อกใช เคร องม อทางภ ม ศาสตร
ใบงานท ๕ เร อง เคร องม อทางภ ม ศาสตร รอบต วเรา และล กษณะสาค ญ ต วช ว ด : ส งท น กเร ยนพ งร และปฏ บ ต ได มฐ. ส ๕.๑ (๑) จ ดประสงค การเร ยนร. ศ กษากระบวนการทางภ ม ศาสตร โดยการเล อกใช เคร องม อทางภ ม ศาสตร
MULTI-LEVEL LESSON PLAN GUIDE Earth, Moon, and Beyond
 1 MULTI-LEVEL LESSON PLAN GUIDE Earth, Moon, and Beyond Jeni Gonzales e-mail: JeniLG7@aol.com SED 5600 Dr. Michael Peterson December 18, 2001 1 2 Unit Plan: Multi-level- Earth, Moon, and Beyond Theme:
1 MULTI-LEVEL LESSON PLAN GUIDE Earth, Moon, and Beyond Jeni Gonzales e-mail: JeniLG7@aol.com SED 5600 Dr. Michael Peterson December 18, 2001 1 2 Unit Plan: Multi-level- Earth, Moon, and Beyond Theme:
1 213 Ref: Compass, Boxing, Heading C A vessel heading ENE is on a course of. A. 022.5 C. 067.5 B. 045.0 D. 090.0
 1 213 Ref: Compass, Boxing, Heading C A vessel heading ENE is on a course of. A. 022.5 C. 067.5 B. 045.0 D. 090.0 2 214 Ref: Compass, Boxing, Heading A A vessel heading ESE is on a course of. A. 112.5
1 213 Ref: Compass, Boxing, Heading C A vessel heading ENE is on a course of. A. 022.5 C. 067.5 B. 045.0 D. 090.0 2 214 Ref: Compass, Boxing, Heading A A vessel heading ESE is on a course of. A. 112.5
Where on Earth are the daily solar altitudes higher and lower than Endicott?
 Where on Earth are the daily solar altitudes higher and lower than Endicott? In your notebooks, write RELATIONSHIPS between variables we tested CAUSE FIRST EFFECT SECOND EVIDENCE As you increase the time
Where on Earth are the daily solar altitudes higher and lower than Endicott? In your notebooks, write RELATIONSHIPS between variables we tested CAUSE FIRST EFFECT SECOND EVIDENCE As you increase the time
ORANGE PUBLIC SCHOOLS OFFICE OF CURRICULUM AND INSTRUCTION OFFICE OF SCIENCE. GRADE 6 SCIENCE Post - Assessment
 ORANGE PUBLIC SCHOOLS OFFICE OF CURRICULUM AND INSTRUCTION OFFICE OF SCIENCE GRADE 6 SCIENCE Post - Assessment School Year 2013-2014 Directions for Grade 6 Post-Assessment The Grade 6 Post-Assessment is
ORANGE PUBLIC SCHOOLS OFFICE OF CURRICULUM AND INSTRUCTION OFFICE OF SCIENCE GRADE 6 SCIENCE Post - Assessment School Year 2013-2014 Directions for Grade 6 Post-Assessment The Grade 6 Post-Assessment is
ALGEBRA 2: 4.1 Graph Quadratic Functions in Standard Form
 ALGEBRA 2: 4.1 Graph Quadratic Functions in Standard Form Goal Graph quadratic functions. VOCABULARY Quadratic function A function that can be written in the standard form y = ax 2 + bx+ c where a 0 Parabola
ALGEBRA 2: 4.1 Graph Quadratic Functions in Standard Form Goal Graph quadratic functions. VOCABULARY Quadratic function A function that can be written in the standard form y = ax 2 + bx+ c where a 0 Parabola
Solar Flux and Flux Density. Lecture 3: Global Energy Cycle. Solar Energy Incident On the Earth. Solar Flux Density Reaching Earth
 Lecture 3: Global Energy Cycle Solar Flux and Flux Density Planetary energy balance Greenhouse Effect Vertical energy balance Latitudinal energy balance Seasonal and diurnal cycles Solar Luminosity (L)
Lecture 3: Global Energy Cycle Solar Flux and Flux Density Planetary energy balance Greenhouse Effect Vertical energy balance Latitudinal energy balance Seasonal and diurnal cycles Solar Luminosity (L)
WGS AGD GDA: Selecting the correct datum, coordinate system and projection for north Australian applications
 internal report WGS AGD GDA: Selecting the correct datum, coordinate system and projection for north Australian applications JBC Lowry Hydrological and Ecological Processes Program Environmental Research
internal report WGS AGD GDA: Selecting the correct datum, coordinate system and projection for north Australian applications JBC Lowry Hydrological and Ecological Processes Program Environmental Research
