INTRACEREBRAL METASTASIS OF GLIOBLASTOMA MULTIFORME. CASE REPORT AND LITERATURE REVIEW
|
|
|
- Shonda Holmes
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ANNALES ACADEMIAE MEDICAE STETINENSIS ROCZNIKI POMORSKIEJ AKADEMII MEDYCZNEJ W SZCZECINIE 2011, 57, 1, DARIUSZ JEŻEWSKI, DOMINIKA PARAFINIUK, PRZEMYSŁAW NOWACKI 1, IRENEUSZ KOJDER INTRACEREBRAL METASTASIS OF GLIOBLASTOMA MULTIFORME. CASE REPORT AND LITERATURE REVIEW PRZERZUT WEWNĄTRZMÓZGOWY GLIOBLASTOMA MULTIFORME. OPIS PRZYPADKU I PRZEGLĄD PIŚMIENNICTWA Katedra i Klinika Neurochirurgii Pomorskiego Uniwersytetu Medycznego w Szczecinie ul. Unii Lubelskiej 1, Szczecin Kierownik: prof. dr hab. n. med. Ireneusz Kojder 1 Katedra i Klinika Neurologii Pomorskiego Uniwersytetu Medycznego w Szczecinie ul. Unii Lubelskiej 1, Szczecin Kierownik: prof. dr hab. n. med. Przemysław Nowacki Streszczenie Gąbczak wielopostaciowy jest najczęściej występującym guzem mózgu u dorosłych. Cechuje się wysoką złośliwością oraz szybką i częstą tendencją do wznowy miejscowej. Przerzuty odległe rozsiane w mózgu o innym umiejscowieniu w stosunku do zmiany pierwotnej i poza układem nerwowym rzadko są opisywane. Autorzy przedstawili przypadek 53 letniego pacjenta operowanego w 2008 r. z powodu guza o typie gąbczaka wielopostaciowego w lewej okolicy ciemieniowej przykomorowej, u którego wiodącymi objawem były objawy zespołu Gerstmanna, afazja mieszana oraz zaburzenia pamięci. Chory był radykalnie operowany, z następową radioterapią oraz chemioterapią. Dwa lata od operacji u pacjenta doszło do nasilenia afazji oraz pojawiły się serie napadów padaczkowych, co skłoniło do wykonania badania MRI, w którym stwierdzono ognisko guza w lewej okolicy skroniowej przykomorowej, a więc o innej lokalizacji w stosunku do zmiany pierwotnej. Chorego operowano na drodze lobektomii skroniowej. Usunięte w całości ognisko w badaniu histopatologicznym rozpoznano jako Glioblastoma multiforme IV wg WHO. W oparciu o piśmiennictwo, w pracy omówiono cechy guza oraz czynniki wpływające na możliwość pojawienia się przerzutów glioblastoma do innych okolic mózgu. H a s ł a: guz mózgu glejak wysokiego stopnia złośliwości gąbczak wielopostaciowy przerzuty rozsiew droga płynu mózgowo rdzeniowego wznowa guza. Summary Glioblastoma multiforme is the most common primary malignant brain tumor in adults. It s characterized by a high malignancy and rapid, frequent tendency to local recurrence. Distant metastases disseminated in the brain compared to the primary lesion and outside the central nervous system are rarely reported in the literature. The case which is being presented is of a 53 year old man operated in 2008 because of Glioblastoma multiforme IV WHO in the left periventricular parietal region, in which the main symptoms were the Gerstmann syndrome, mixed aphasia and memory disturbance. The patient was operated totally followed by adjuvant radiotherapy and chemotherapy. Two years later epileptic seizures and aphasia were intensified. Due to this adverse symptoms MRI was ordered, which revealed a tumor in the left periventricular temporal region in different location compared to the primary lesion. The patient was operated by temporal lobectomy. Histopathological diagnosis was Glioblastoma multiforme IV WHO. According to the literature we analyzed the natural GBM tumor features and factors responsible for possibility to appear of the same type of tumor in another location of the brain. K e y w o r d s: brain tumor high grade glioma glioblastoma multiforme metastases cerebrospinal fluid dissemination recurrence.
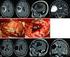
2 60 DARIUSZ JEŻEWSKI, DOMINIKA PARAFINIUK, PRZEMYSŁAW NOWACKI, IRENEUSZ KOJDER Introduction Derived from the glial cells glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) belongs to the most common primary brain tumors in adults which is characterized by the highest level of fourth degrees in malignancy scale according to WHO [1, 2]. The GBM etiology still remains unknown. The observations confirm the influence of ionizing radiation and increased risk of developing a genetically determined syndromes such as Li Fraumeni type [3]. It occurs four times more common in males, mainly in the fourth and fifth decade of life [2, 4]. It localizes predominantly in the frontal lobes and temporal lobes [4]. The tumor is characterized by a tendency to rapid local recurrence and rare distant intracerebral metastases related to the primary tumor localisation as well [5]. Extra cranial metastases, despite the high grade GBM are also rare and occur up to 5% [6, 7, 8]. GBM metastases occur within two years of diagnosis [9] and comprise mainly the regional lymph nodes, lungs, bone and sometimes the liver [6]. Despite the diversity of glioblastoma multiforme in clinical MRI images it has distinctive features. The irregular tumor accompanied by peritumoral oedema have cystic components inside. MRI T1 weighted scans after administration of contrast medium usually reveal ring shaped enhanced borders in the tumor periphery corresponding to increased cell proliferation and pathological angiogenesis. The tumor central compartment corresponds to the hypointensive cystic necrotic changes inside the tumor [7, 10]. Neurological symptoms are characterized by a significant dynamics and correspond to the occupated brain region. Microscope image of GBM diagnosis is not in doubt. There is much increased cytosis, cell polymorphism, atypia and nuclei hiperchromatism, numerous mitotic figures, necrosis, and new angiogenesis. Glioblastoma multiforme shows a positive immunohistochemical reaction with antibodies against GFAP, S 100 protein and wimentine [8, 9, 10]. The standard therapy for high grade gliomas has not changed for several decades. This includes surgical resection, radiotherapy and chemotherapy, and still represents a major challenge for modern medicine [1, 9]. Due to the infiltrative nature of the tumor the neuronavigation seems to be a very useful method supporting intraoperative mapping of the resected tumor [11]. Case report 50 years old right handed caucasian man was admitted to the Department of Neurosurgery and Pediatric Neurosurgery, Pomeranian Medical University in Szczecin (Poland) in November 2008 because of increasing difficulty in self expression, reading, comprehension, counting (Gerstmann syndrome sympthoms) from about one month. On admission, the patient was conscious, breathing and circulatory efficient in difficult verbal contact. No paralysis of limbs and no headache was observed. The neurological examination confirmed sensory aphasia (speech incoherent, multi threaded), alexia, acalculia, body schema disturbances, difficulties in distinguishing between the body sides. T1 weighted with contrast enhanced the brain MRI revealed the presence of tumor in the left parietal periventricular region. Peripheral strong contrast tumor enhencement was observed (fig. 1). T2 weighted and FLAIR signal showed tumor heterogeneity (increased in the peripheral parts, with areas of low signal in the central part, probably of a necrosis). On the base of clinical and radiological sympthoms patient was qualified for surgical treatment. Craniotomy was performed in the left parietal area. With the help of neuronavigated mapping glial tumor involving Fig. 1. T1 weighted MRI scan with contrast enhancement from 2008 revealed tumor in the left periventricular parietal region with heterogenous signal: increased at the periphery, hypointensive in the central region (necrosis) Ryc. 1. Obraz MRI T1 zależny ze wzmocnieniem kontrastowym z 2008 r. wykazuje w lewym płacie ciemieniowym w okolicy przykomorowej obecność guza o niejednorodnym sygnale: podwyższonym w części obwodowej, z hipointensywną częścią centralną (martwica) the left lateral ventricle posterior horn was removed totally. After the operation the patient rapidly developed aphasia and right sided amblyopia. Because of postoperative oedema decompressive craniectomy was performed on third day post operation. Gradual improvement in clinical state was achieved very quickly after decompresion. The tumor was diagnosed histologically as glioblastoma multiforme WHO grade IV (fig. 2). The patient was discharged home on 12 th day. There was no limbs paresis, he was walking alone, with persistent symptoms of Gerstmann syndrome and right sided amblyopia in visual field. Then he underwent teleradiotherapy in maximum dose of 60 Gy/30 cycles and chemotherapy by temozolomide (Temodal) 5 cycles. He still became under neurological and neurosurgical and oncological control.
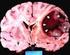
3 INTRACEREBRAL METASTASIS OF GLIOBLASTOMA MULTIFORME 61 Fig. 2. Glioblastoma multiforme IV WHO (2008) characterized by a high increase in glial cellularity and nuclear pleomorphism. There are signs of anaplasia and angiogenesis (H E stained) Ryc. 2. Gąbczak wielopostaciowy IV WHO (2008 r.) wykazuje duży wzrost liczby komórek oraz znaczny pleomorfizm jąder. Widoczne są wyraźne cechy anaplazji komórkowej oraz angiogenezy (barwienie HE) Fig. 4. Glioblastoma multiforme IV WHO (2010) histopathology study results are very similar to results from 2008 revealed a high increase in glial cellularity, nuclear pleomorphism, signs of anaplasia, angiogenesis and necrosis (H E stained) Ryc. 4. Gąbczak wielopostaciowy IV WHO (2010 r.) obraz histopatologiczny zbliżony do badania z 2008 r., wykazujący wzrost liczby komórek, pleomorfizm jąder, cechy anaplazji, angiogenezy oraz martwicy komórkowej (barwienie HE) Two years after surgery and one year after completion of oncological treatment he developed series of seizures and severity of aphasia. The control MRI T1 weighted scans with contrast enhancement revealed hyperintensive ring sheped tumor in the left temporal area occupying ventricular temporal horn surrounded by a brain oedema. It aroused the suspicion of secondary proliferative changes (fig. 3). There was no tumor recurrance in place of previous resection. Patient was qualified to the temporal craniotomy and temporal lobectomy with tumor removal. Intraoperative macroscopic picture showed a tumor of a similar nature as Fig. 3. MRI T1 weighted scan with contrast enhancement from 2010 revealed hyperdensity ring sheped tumor in left temporal periventricular region Ryc. 3. Obraz MRI T1 zależny z 2010 r. ze wzmocnieniem kontrastowym wykazuje obecność w lewym płacie skroniowym przy rogu skroniowym hiperintensywnego pierścieniowatego guza in the first operation, but the different location in relation to the primary focus. This was confirmed histopathologically as the diagnosis of glioblastoma multiforme WHO grade IV (fig. 4). After surgery the patient without seizures, with persistent symptoms of Gerstmann syndrome, especially severe mixed aphasia was sent for further oncological and neurological observation. As we agreed, the patient died suddenly from cardiac arrest in the three months since the last surgery. Discussion Glioblastoma multiforme (grade IV according to WHO) is not a problem either radiological or histopathological. The picture is clear and rarely in doubt. Treatment of this type of neoplasm does not bring satisfactory results, still raises many controversies and questions, in spite of advanced medical progress. Therapy standards developed by Ryo include the maximum safe surgical resection, radiation in the full dose of 60 Gy in 30 cycles, and chemotherapy with temozolomide [1]. According to this schema, therapy is widely accepted and used by highest reference neurooncological centers. Resignation one of these treatment stages or modification of therapy shortens survival by several months [1]. In presented case the treatment was adapted to worldwide standards. Unfortunately, despite aggressive treatment cure or long term remission of cancer can not be achieved in cases of GBM. Median survival ranges from several months to about 2 years. By Ushio et al. survival depends primarily on the size of the tumor resection. The longest survival period of 20 months was achieved by complete removal of the tumor, in a partial resection (cytoreduction), median survival time was 14.2 months, the shortest, for about 8.3 months was
4 62 DARIUSZ JEŻEWSKI, DOMINIKA PARAFINIUK, PRZEMYSŁAW NOWACKI, IRENEUSZ KOJDER associated with the tumor biopsy [4]. In the described case, the total survival time from diagnosis of GBM was already 27 months, when it was interrupted dramatically because of heart failure. Diffuse, infiltrative nature of glioblastoma multiforme do not allow for complete microscopic resection, and the tumor deep location indicates only for the lesion biopsy. It appears that GBM with a diameter of less than 3 cm, with a slight peritumoral oedema distinguishes the small infiltration of adjacent tissues as opposed to changes larger than 6 cm in diameter, with greater infiltration, accompanied by massive oedema [12]. The longest median survival was observed at the frontal lobes GBM location [4]. In the presented patient MRI shown that the tumor dimension did not exceed 3 cm, although it was accompanied by a zone of oedema. Neuronavigation supported surgery allowed for complete removal of the tumor to ensure longer survival despite unfavorable topography in the deep structures of the left periventricular parietal region. Extracranial gliblastoma multiforme metastasis are rare and occur in 0.44% [6, 7] and 0.5% [13] or by other authors in 2% [11] and even 5% [8]. Commonly is accepted opinion that the rare incidence of metastases outside the brain is caused by a really short period of patients survival, the lack of lymphatic vessels in the brain, and the presence of the natural barrier such as the dura mater surrounding venous sinus [6]. GBM metastases rarely extracranially as compared to medulloblastoma (56.3%), germinoma (9.8%), diagnosed in patients under 18 years [13]. They appear about 2 years since the first neurosurgical intervention [9], covering the first lymph nodes, lungs, pleura, bone and liver [6, 7, 14]. In addition, the mechanism of formation of metastatic foci within the central nervous system, as well as intracranial and intrathecal malignant gliomas remains unrecognized. Erlich and Davis have already described in 1978 the first cases of GBM metastases intracranially and into the spinal canal [15]. Cancer cells usually disseminate via the cerebrospinal fluid, but also use the blood vessels [7, 8]. Numerous factors that affect the appearance of extracranial metastases were highlighted. The most important of them is that the interruption continuity of the dura mater after neurosurgical interventions creates the gateway to the spread of cancer cells [6, 7, 8]. Implanted ventriculo peritoneal shunts, and catheters used for brain tumors brachytherapy promote to disseminate GBM cells [7, 8]. Although there are described isolated cases in which there was a dissemination of the tumor without the prior neurosurgery [7]. According to Frank et al. greater invasiveness of glioblastoma cells is associated with the change of gene expression by tumor cells in interaction with the surrounding normal brain tissue [10]. Total removal of GBM, the maximum dose of radiotherapy combined with chemotherapy do not protect against the local recurrence, which occurs in most cases. Increasingly there are reports about the possibility of recurrence of GBM metastases within the brain [5, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20]. That course of the disease we describe in this paper. It is undoubtedly associated with intracranial metastatic tumors process of dissemination by cerebrospinal fluid pathways. It appears that in the group of malignant glioma cerebrospinal fluid circulation spread occurs from 10 to 27%. Ependymomas, germinal cell tumors and PNET have a special affinity. Predisposing factors for dissemination is young age, partial resection or tumor biopsy and mostly open fluid space during neurosurgical intervention [16]. MRI is very useful in the diagnosis of tumor spread through cerebrospinal fluid pathways [17]. Misaki et al. emphasize the greater usefulness, even indispensable, MRI FLAIR images compared to T2 weighted in detecting glioblastoma multiforme metastates in the fluid spaces. FLAIR scans are more legible and more certain. FLAIR sequence also highlights foci located on the brain surface such as inflammation, but has less sensitivity in the detection of intracerebral metastasis compared with the T1 option [17]. Parsa et al. have identified three categories of GBM spreading based on MRI in T1 weighted sequences: type I a single focus with subarachnoid and subependymal spread of tumor, type II multifocal lesion without subarachnoid and subependymal tumor spread, type III multifocal lesion with subarachnoid and subependymal tumor spread [5]. Results of treatment of GBM are compared in the groups including the size and type of resection, adjuvant therapy, epidemiological data and clinical state. Authors emphasize the significant relationship between the various types of metastatic tumors and survival time. The longest survival time occurred in the type I 88 weeks, shorter 42 weeks in the type II and in the shortest 10 weeks in type III. They note that patients with type I spread have no a worse prognosis compared to a single local recurrence. Adjuvant chemotherapy does not affect the results of survival. Our patient presented with single focal primary lesion and a single distant GBM metastasis qualifying for the type I according to the criteria proposed by Parsa et al. survived about 105 weeks after the first resection. There are great difficulties in precisely defining and distinguishing the form of multifocal GBM from intracerebral metastases via cerebrospinal fluid. Czepko et al. on the base of described their patient with GBM metastasis development emphasize the importance of the cerebrospinal fluid pathways in cancer cells dissemination. During the primary lesion operation the posterior horn of the lateral ventricle was opened. In authors opinion it certainly has become a gateway to spread the GBM cells into the cerebrospinal fluid, the more as a second lesion occurred in the temporal lateral ventricle vicinity. They require the special care to behave during the glioma operation to avoid opening fluid space barrier to reduce the possibility of dissemination tumor cells [18]. Our observations relate to the same. In the case described by us the ventricular system was opened during resection of the tumor in the parietal periventricular region as well. It seems to be the cause of GBM cells dissemination via cerebrospinal fluid and the appearance of a new tumor in the temporal lobe near to the temporal horn.
5 INTRACEREBRAL METASTASIS OF GLIOBLASTOMA MULTIFORME 63 According to Cohen et al. there is a correlation between tumor size and the tendency to spread cancer. It often appear that little foci, even detected on autopsy show more aggressiveness to spread by the cerebrospinal fluid [19]. Radiological diagnosis of multifocal GBM poses difficulties for radiologists and oncologist There are strong resemblance GBM to metastatic tumors, especially adenocarcinomas. In spite of all metastases appear as a more regular, ring shaped, with border easier to designate, more common on the border of the cortex and white matter and larger peritumoral oedema compared to the GBM [20]. In presented patient irregular tumor was located in white matter in deep parietal region. Lafitte et al. divided gliomas into two groups 1 policystic and 2 multifocal. Multifocal lesions more frequently predispose to tumor spread [20]. In our case, the policystic but single tumor in MRI diagnosed as glioblastoma multiforme deny expressed by Lafitte et al., observation of distant GBM intracerebral metastasis. Conclusion In conclusion it should be emphasized that high grade gliomas in mostly occur as a single focus, rarely with their distant metastases and intracerebral spread. The spread of cancer cells within the nervous system takes place mainly via cerebrospinal fluid, which causes the appearance of new GBM foci in distant location in relation to the primary lesion. One should note that during the first tumor resection the neurosurgeon should try to avoid opening the cerebrospinal spaces, especially the ventricular system to reduce the risk of intracerebral dissemination. Classification of types of GBM spread allows to specify further prognosis independently to adjuvant methods of treatment. References 1. Ryo N. : Standard Therapy for Glioblastoma a review of where we are. Nerol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2010, 50, Kraft M., Lang F., Braunschweig R., Janzer R.C. : Parotid gland metastasis from glioblastoma multiforme: a case report and review of the literature. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2008, 265 (6), Schlehofer B., Hettinger I., Ryan P., Blettner M., Preston Martin S., Little J. et al.: Occupational risk factors for low grade and high grade glioma: results from international case control study of adult brain tumor. Int J Cancer. 2005, 113, Ushio Y., Kochi M., Hamada J., Kai Y., Nakamura H. : Effect of surgical removal on survival and quality of life in patients with supratentorial glioblastoma. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2005, 45, Parsa A.T., Wachhorst S., Lamborn K.R., Prados M.D., McDermott M.W., Berger M.S. et al.: Prognostic significance of intracranial dissemination of glioblastoma multiforme in adults. J Neurosurg. 2005, 102, Ytsuki S., Tanaka S., Oka H., Iwamoto K., Sagiuchi T., Fujii K.: Glioblastoma multiforme metastasis to the axis. J Neurosurg. 2005, 102, Yasuhara T., Tamiya T., Meguro T., Ichikawa T., Sato Y., Date I.H. et al. : Glioblastoma with metastasis to the spleen. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2003, 43, Esberk Ates L., Bayindir C., Bilgic B., Karasu A. : Glioblastoma with lymph node metastases. Neuropathology. 2003, 23, 2, Didelot A., Taillandier L., Grignon Y., Vespignani H., Beauchesne P. : Concomitant bone marrow metastasis of a glioblastoma multiforme revealed at the diagnosis. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2006, 148, Frank S., Kuhn S., Brodhun M., Mueller U., Romeike B., Kosmehl H. et al.: Metastatic glioblastoma cells use common pathways via blood and lymphatic vessels. Neurol Neurochirur Pol. 2009, 43, 2, Nowacki P., Tabaka J., Jeżewski D., Honczarenko K.: Diagnostyka glejaków mózgu pobranych drogą biopsji stereotaktycznej wspomaganej optycznym systemem neuronawigacji. Neurol Neurochir Pol. 2004, 38 (1), Tamura M., Zama A., Kurihara H., Ono N., Kano T., Imai H. et al. : Correlation between glioblastoma cell infiltration and T2 prolongation on magnetic resonance imaging. Neuropathology. 1997, 17, Yokosuka K., Ishii R., Suzuki Y., Hirano K., Ishii N., Sekihara Y. et al. : Extraneural metastasis of high grade glioma without simultaneos central nervous system recurrance. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2007, 47, Vural G., Hagmar B., Walaas L. : Extracranial metastasis of glioblastoma multiforme diagnosed by fine needle aspiration: a report of two cases and a review of the literature. Diagn Cytopathol. 1999, 15, Erlich S.S., Davis R.L. : Spinal subarachnoid metastasis from primary intracranial glioblastoma multiforme. Cancer. 42, Shetty P.M., Moiyadi A.V. : Florid leptomeningeal dissemination in case of glioblastoma multiforme. Neurol India. 2010, 58, Misaki K., Nakada M., Hayashi Y., Tachibana O., Yamashita J., Ueda F. et al.: Contrast enhanced fluid attenuated inversion recovery MRI is useful to detect the CSF dissemination of glioblastoma. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2001, 25 (6), Czepko R., Kwinta B., Adamek D., Uhl H., Betlej M., Lopatka P. : Multiple cerebral glioma or tumor dissemination via CSF pathways? Case report. Neurol Neurochir Pol. 2003, 37 (6), Cohen Z.R., Hassenbush S.J., Maor M.H., Pfeffer R.M., Ram Z. : Intactable vomiting from glioblastoma metastatic to the fourth ventricle: three case studies. Neuro Oncol. 2002, 4, Lafitte F., Morel Precetti S., Duverneuil N., Guermazi A., Brunet E., Heran F. et al.: Chiras J.: Multiple glioblastomas CT and MR features. Eur Radiol. 2001, 11, Comment Primary brain tumors, like GBM, show a unique pattern of invasion and with rare exceptions do not metastasize outside the brain. These tumors invade widely as single cells anywhere within the brain, showing some tendency to infiltrate along the periphery of blood vessel walls, along the subpial glial space (glia limitans externa), or along white matter tracts such as the optic radiation or corpus callosum. GBM is the most frequent and the most malignant brain tumor, with an incidence 3.55 new cases per 100,000 Caucasians per year. Despite progress in surgical techniques, radiotherapy and chemotherapy, the prognosis remains poor, with a median survival less than one year. GBM is characterized by rapid diffusely infiltrative growth and high level of cellular heterogeneity associated with therapeutic resistance. Glioblastomas are also characterized by multiple genetic alterations. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) amplification and PTEN mutations are typical for primary glioblastomas developing rapidly de novo,
6 64 DARIUSZ JEŻEWSKI, DOMINIKA PARAFINIUK, PRZEMYSŁAW NOWACKI, IRENEUSZ KOJDER whereas TP53 mutations are frequent in the pathway leading to secondary glioblastomas developing usually from lower grade astrocytomas. Loss of heterozygosity (LOH) 10q is the most frequent aberration in both primary and secondary glioblastomas. Recently Carro (Carro M.S. et al.: The transcriptional network for mesenchymal transformation of brain tumours. Nature. 2010, 463, ) has revealed mesenchymal phenotype in GBM as a the hallmark of tumor aggressiveness. From another point of view an extracellular proteolytic enzymes are critical for the invasive properties of malignant neoplasms. Glioma cell invasion is a complex and multistep mechanism involving a large array of molecules and cell cell and cell-ecm (ECM extracellular matrix) interactions. These processes allow individual tumor cells to migrate and invade the healthy surrounding brain. In accordance with Wilson (1992) distribution of GBM into surrounding brain is as follows: 92% of GBM cells is in the centre of tumor, 1.8% GBM cells is in the distance from mm, 0.2% is in the distance more than 40 mm. Maybe in described case GBM metastasis could be a simple consequence of GBM cells invasion? Histopathological features of GBM include magnitude of cellularity, degree of cellular pleomorphism, number of mitoses, prominence of endothelial/pericytic proliferation and necrosis. In the GBM there are positive immunohistocemical reactions against GFAP, S-100 protein and others. These was introduced initially in our Department to clinical practice a method of GBM recurrence control on the basis of biomarkers estimation with anti-5-methylcytosine antibodies in peripheral blood. As authors marked in the paper treatment of GBM does not bring satisfactory results due to diffuse infiltration by tumor. Radical surgery of GBM is insufficient and postoperative radiotherapy and temozolamide are recommended. In spite of these therapies mean survival time is not satisfactory extended. Recently some postsurgery management were developed and implemented. Yet over 30 years ago antiangiogenesis was proposed by Folkman (NEJM 1971) as cancer therapy. He hypothesized that tumor growth is angiogenesis depended. The idea predicted that would be unable to grow beyond a microscopic size of 1 2 mm 3 without continuous recruitment of new capillary blood vessels. However, in 2008 therapy with bevacizumab (humanized monoclonal antibody recombinant developed against VEGF) was introduced in treatment of GBM. Unfortunatelly control MRI in GBM patients revealed multifocal form of tumor recurrences during the therapy with that agent. Encouragingly, more recent strategies using neural stem cells (NSCs) to target disseminated tumor islands showed promising results in animal experiments. NSCs have been shown to be capable of actively migrating and tracking the invading glioma cells within the brain. Lethal cardiac arrest, in patient who had undergone a prior resection of a supratentorial GBM is not an unusual event as it was e.g. indicated by J.M. Ammerman and coworkers, prof. dr hab. n. med. Stanisław Nowak
Brain Cancer. This reference summary will help you understand how brain tumors are diagnosed and what options are available to treat them.
 Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
Glioblastoma (cancer affecting the brain) A guide for journalists on glioblastoma and its treatment
 Glioblastoma (cancer affecting the brain) A guide for journalists on glioblastoma and its treatment Section 1 Glioblastoma Section 2 Epidemiology and prognosis Section 3 Treatment Contents Contents 2 3
Glioblastoma (cancer affecting the brain) A guide for journalists on glioblastoma and its treatment Section 1 Glioblastoma Section 2 Epidemiology and prognosis Section 3 Treatment Contents Contents 2 3
Case Report. Central Neurocytoma. Fotis Souslian, MD; Dino Terzic, MD; Ramachandra Tummala, MD. Department of Neurosurgery, University of Minnesota
 1 Case Report Central Neurocytoma Fotis, MD; Dino Terzic, MD; Ramachandra Tummala, MD Department of Neurosurgery, University of Minnesota Case This is a previously healthy 20 year old female, with 3 months
1 Case Report Central Neurocytoma Fotis, MD; Dino Terzic, MD; Ramachandra Tummala, MD Department of Neurosurgery, University of Minnesota Case This is a previously healthy 20 year old female, with 3 months
What is Glioblastoma? How is GBM classified according to the WHO Grading System? What risk factors pertain to GBM?
 GBM (English) What is Glioblastoma? Glioblastoma or glioblastoma multiforme is one of the most common brain tumors accounting for approximately 12 to 15 percent of all brain tumors. The name of the tumor
GBM (English) What is Glioblastoma? Glioblastoma or glioblastoma multiforme is one of the most common brain tumors accounting for approximately 12 to 15 percent of all brain tumors. The name of the tumor
High-grade glioma in a patient with breast cancer
 Asian Journal of Surgery (2014) 37, 162e166 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-asianjournalsurgery.com CASE REPORT High-grade glioma in a patient with breast cancer Che-Chao
Asian Journal of Surgery (2014) 37, 162e166 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-asianjournalsurgery.com CASE REPORT High-grade glioma in a patient with breast cancer Che-Chao
Understanding Metastatic Disease
 Supported by an unrestricted educational grant from Pfizer Understanding Metastatic Disease Metastatic disease or metastases are phrases that mean the same as Secondary cancer. This means that the cancer
Supported by an unrestricted educational grant from Pfizer Understanding Metastatic Disease Metastatic disease or metastases are phrases that mean the same as Secondary cancer. This means that the cancer
Supportive Care For Patients With High-Grade Glioma (primary brain tumours) Dr Susan Catt & Professor Lesley Fallowfield
 Supportive Care For Patients With High-Grade Glioma (primary brain tumours) Dr Susan Catt & Professor Lesley Fallowfield Partners Mr Giles Critchley Consultant Neurosurgeon Hurstwood Park Neurological
Supportive Care For Patients With High-Grade Glioma (primary brain tumours) Dr Susan Catt & Professor Lesley Fallowfield Partners Mr Giles Critchley Consultant Neurosurgeon Hurstwood Park Neurological
Report series: General cancer information
 Fighting cancer with information Report series: General cancer information Eastern Cancer Registration and Information Centre ECRIC report series: General cancer information Cancer is a general term for
Fighting cancer with information Report series: General cancer information Eastern Cancer Registration and Information Centre ECRIC report series: General cancer information Cancer is a general term for
Brain Tumor 101. Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center
 Brain Tumor 101 Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center Objectives Identify the different parts of the brain Describe how each part of the brain works Connect each part
Brain Tumor 101 Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center Objectives Identify the different parts of the brain Describe how each part of the brain works Connect each part
Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Staging and Prognosis of Three Separate Cases.
 Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Staging and Prognosis of Three Separate Cases. Abstract This paper describes the staging, imaging, treatment, and prognosis of renal cell carcinoma. Three case studies
Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Staging and Prognosis of Three Separate Cases. Abstract This paper describes the staging, imaging, treatment, and prognosis of renal cell carcinoma. Three case studies
What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)?
 What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair 1 What
What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair 1 What
Aggressive lymphomas. Michael Crump Princess Margaret Hospital
 Aggressive lymphomas Michael Crump Princess Margaret Hospital What are the aggressive lymphomas? Diffuse large B cell Mediastinal large B cell Anaplastic large cell Burkitt lymphoma (transformed lymphoma:
Aggressive lymphomas Michael Crump Princess Margaret Hospital What are the aggressive lymphomas? Diffuse large B cell Mediastinal large B cell Anaplastic large cell Burkitt lymphoma (transformed lymphoma:
PRIMARY GLIOMA (oligodendroglioma, astrocytoma, oligodendroglioma, oligoastrocytoma, including anaplastic, gliosarcoma and glioblastoma multiforme)
 Protocol for Planning and Treatment The process to be followed when a course of chemotherapy is required to treat: PRIMARY GLIOMA (oligodendroglioma, astrocytoma, oligodendroglioma, oligoastrocytoma, including
Protocol for Planning and Treatment The process to be followed when a course of chemotherapy is required to treat: PRIMARY GLIOMA (oligodendroglioma, astrocytoma, oligodendroglioma, oligoastrocytoma, including
Brain Tumor Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumor Treatment Brain Tumors Overview A brain tumor is a group of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. Tumors can directly destroy healthy brain cells. They can
Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumor Treatment Brain Tumors Overview A brain tumor is a group of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. Tumors can directly destroy healthy brain cells. They can
Smoking and misuse of certain pain medicines can affect the risk of developing renal cell cancer.
 Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
LYMPHOMA IN DOGS. Diagnosis/Initial evaluation. Treatment and Prognosis
 LYMPHOMA IN DOGS Lymphoma is a relatively common cancer in dogs. It is a cancer of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoid tissue is normally present in many places in the
LYMPHOMA IN DOGS Lymphoma is a relatively common cancer in dogs. It is a cancer of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoid tissue is normally present in many places in the
Lung cancer is not just one disease. There are two main types of lung cancer:
 1. What is lung cancer? 2. How common is lung cancer? 3. What are the risk factors for lung cancer? 4. What are the signs and symptoms of lung cancer? 5. How is lung cancer diagnosed? 6. What are the available
1. What is lung cancer? 2. How common is lung cancer? 3. What are the risk factors for lung cancer? 4. What are the signs and symptoms of lung cancer? 5. How is lung cancer diagnosed? 6. What are the available
New strategies in anticancer therapy
 癌 症 診 療 指 引 簡 介 及 臨 床 應 用 New strategies in anticancer therapy 中 山 醫 學 大 學 附 設 醫 院 腫 瘤 內 科 蔡 明 宏 醫 師 2014/3/29 Anti-Cancer Therapy Surgical Treatment Radiotherapy Chemotherapy Target Therapy Supportive
癌 症 診 療 指 引 簡 介 及 臨 床 應 用 New strategies in anticancer therapy 中 山 醫 學 大 學 附 設 醫 院 腫 瘤 內 科 蔡 明 宏 醫 師 2014/3/29 Anti-Cancer Therapy Surgical Treatment Radiotherapy Chemotherapy Target Therapy Supportive
Lung Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand lung cancer and the treatment options that are available.
 Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
How To Treat Lung Cancer At Cleveland Clinic
 Treatment Guide Lung Cancer Management The Chest Cancer Center at Cleveland Clinic, which includes specialists from the Respiratory Institute, Taussig Cancer Institute and Miller Family Heart & Vascular
Treatment Guide Lung Cancer Management The Chest Cancer Center at Cleveland Clinic, which includes specialists from the Respiratory Institute, Taussig Cancer Institute and Miller Family Heart & Vascular
OBJECTIVES By the end of this segment, the community participant will be able to:
 Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too.
 Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
Objectives. Mylene T. Truong, MD. Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Background
 Imaging of Pleural Tumors Mylene T. Truong, MD Imaging of Pleural Tumours Mylene T. Truong, M. D. University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX Objectives To review tumors involving the
Imaging of Pleural Tumors Mylene T. Truong, MD Imaging of Pleural Tumours Mylene T. Truong, M. D. University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX Objectives To review tumors involving the
THYROID CANCER. I. Introduction
 THYROID CANCER I. Introduction There are over 11,000 new cases of thyroid cancer each year in the US. Females are more likely to have thyroid cancer than men by a ratio of 3:1, and it is more common in
THYROID CANCER I. Introduction There are over 11,000 new cases of thyroid cancer each year in the US. Females are more likely to have thyroid cancer than men by a ratio of 3:1, and it is more common in
New Options to Treat Brain Tumors
 New Options to Treat Brain Tumors Guest Expert: Joachim, MD Associate Professor of Neuro-Oncology Director, Yale Cancer Center Brain Tumor Program www.wnpr.org www.yalecancercenter.org Welcome to Yale
New Options to Treat Brain Tumors Guest Expert: Joachim, MD Associate Professor of Neuro-Oncology Director, Yale Cancer Center Brain Tumor Program www.wnpr.org www.yalecancercenter.org Welcome to Yale
Breast Cancer. Sometimes cells keep dividing and growing without normal controls, causing an abnormal growth called a tumor.
 Breast Cancer Introduction Cancer of the breast is the most common form of cancer that affects women but is no longer the leading cause of cancer deaths. About 1 out of 8 women are diagnosed with breast
Breast Cancer Introduction Cancer of the breast is the most common form of cancer that affects women but is no longer the leading cause of cancer deaths. About 1 out of 8 women are diagnosed with breast
Current Status and Perspectives of Radiation Therapy for Breast Cancer
 Breast Cancer Current Status and Perspectives of Radiation Therapy for Breast Cancer JMAJ 45(10): 434 439, 2002 Masahiro HIRAOKA, Masaki KOKUBO, Chikako YAMAMOTO and Michihide MITSUMORI Department of Therapeutic
Breast Cancer Current Status and Perspectives of Radiation Therapy for Breast Cancer JMAJ 45(10): 434 439, 2002 Masahiro HIRAOKA, Masaki KOKUBO, Chikako YAMAMOTO and Michihide MITSUMORI Department of Therapeutic
AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION. Metastatic Brain Tumors
 AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION Metastatic Brain Tumors AcKnoWLeDGemenTs about the american BRaIn tumor association Founded in 1973, the American Brain Tumor Association (ABTA) was the first national
AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION Metastatic Brain Tumors AcKnoWLeDGemenTs about the american BRaIn tumor association Founded in 1973, the American Brain Tumor Association (ABTA) was the first national
The Brain and Spine CenTer
 The Br ain and Spine Center Choosing the right treatment partner is important for patients facing tumors involving the brain, spine or skull base. The Brain and Spine Center at The University of Texas
The Br ain and Spine Center Choosing the right treatment partner is important for patients facing tumors involving the brain, spine or skull base. The Brain and Spine Center at The University of Texas
Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW
 Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW Kidney cancer is the third most common genitourinary cancer in adults. There are approximately 54,000 new cancer cases each year in the United States, and the incidence of kidney
Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW Kidney cancer is the third most common genitourinary cancer in adults. There are approximately 54,000 new cancer cases each year in the United States, and the incidence of kidney
Glioblastoma, brain metastases, spine metastases
 VOL. III Issue 1 2012 This issue focuses on: Neurologic-Oncology Welcome to the Spring 2012 edition of Oncology News from Memorial Regional Cancer Center. This issue focuses on Neurologic-Oncology. At
VOL. III Issue 1 2012 This issue focuses on: Neurologic-Oncology Welcome to the Spring 2012 edition of Oncology News from Memorial Regional Cancer Center. This issue focuses on Neurologic-Oncology. At
Glioblastoma: Is Survival Possible? By Ben A. Williams Copyright, 2014
 Glioblastoma: Is Survival Possible? By Ben A. Williams Copyright, 2014 Glioblastoma multiforme are among the most deadly neoplasms and continue to be regarded as incurable and universally fatal. This reputation
Glioblastoma: Is Survival Possible? By Ben A. Williams Copyright, 2014 Glioblastoma multiforme are among the most deadly neoplasms and continue to be regarded as incurable and universally fatal. This reputation
YOUR LUNG CANCER PATHOLOGY REPORT
 UNDERSTANDING YOUR LUNG CANCER PATHOLOGY REPORT 1-800-298-2436 LungCancerAlliance.org A GUIDE FOR THE PATIENT 1 CONTENTS What is a Pathology Report?...3 The Basics...4 Sections of a Pathology Report...7
UNDERSTANDING YOUR LUNG CANCER PATHOLOGY REPORT 1-800-298-2436 LungCancerAlliance.org A GUIDE FOR THE PATIENT 1 CONTENTS What is a Pathology Report?...3 The Basics...4 Sections of a Pathology Report...7
CMScript. Member of a medical scheme? Know your guaranteed benefits! Issue 7 of 2014
 Background CMScript Member of a medical scheme? Know your guaranteed benefits! Issue 7 of 2014 Prostate cancer is second only to lung cancer as the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in men. It is
Background CMScript Member of a medical scheme? Know your guaranteed benefits! Issue 7 of 2014 Prostate cancer is second only to lung cancer as the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in men. It is
Targeted Therapy What the Surgeon Needs to Know
 Targeted Therapy What the Surgeon Needs to Know AATS Focus in Thoracic Surgery 2014 David R. Jones, M.D. Professor & Chief, Thoracic Surgery Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center I have no disclosures
Targeted Therapy What the Surgeon Needs to Know AATS Focus in Thoracic Surgery 2014 David R. Jones, M.D. Professor & Chief, Thoracic Surgery Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center I have no disclosures
Radiotherapy in locally advanced & metastatic NSC lung cancer
 Radiotherapy in locally advanced & metastatic NSC lung cancer Dr Raj Hegde. MD. FRANZCR Consultant Radiation Oncologist. William Buckland Radiotherapy Centre. Latrobe Regional Hospital. Locally advanced
Radiotherapy in locally advanced & metastatic NSC lung cancer Dr Raj Hegde. MD. FRANZCR Consultant Radiation Oncologist. William Buckland Radiotherapy Centre. Latrobe Regional Hospital. Locally advanced
Diagnosis and Prognosis of Pancreatic Cancer
 Main Page Risk Factors Reducing Your Risk Screening Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Overview Chemotherapy Radiation Therapy Surgical Procedures Lifestyle Changes Managing Side Effects Talking to Your Doctor
Main Page Risk Factors Reducing Your Risk Screening Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Overview Chemotherapy Radiation Therapy Surgical Procedures Lifestyle Changes Managing Side Effects Talking to Your Doctor
Brain Tumor Center. A Team Approach to Treating Brain Tumors
 Brain Tumor Center A Team Approach to Treating Brain Tumors Introducing Our Brain Tumor Center Making an appointment with the Brain Tumor Center at the Center for Advanced Medicine is the important first
Brain Tumor Center A Team Approach to Treating Brain Tumors Introducing Our Brain Tumor Center Making an appointment with the Brain Tumor Center at the Center for Advanced Medicine is the important first
Primary -Benign - Malignant Secondary
 TUMOURS OF THE LUNG Primary -Benign - Malignant Secondary The incidence of lung cancer has been increasing almost logarithmically and is now reaching epidemic levels. The overall cure rate is very low
TUMOURS OF THE LUNG Primary -Benign - Malignant Secondary The incidence of lung cancer has been increasing almost logarithmically and is now reaching epidemic levels. The overall cure rate is very low
Mesothelioma. 1995-2013, The Patient Education Institute, Inc. www.x-plain.com ocft0101 Last reviewed: 03/21/2013 1
 Mesothelioma Introduction Mesothelioma is a type of cancer. It starts in the tissue that lines your lungs, stomach, heart, and other organs. This tissue is called mesothelium. Most people who get this
Mesothelioma Introduction Mesothelioma is a type of cancer. It starts in the tissue that lines your lungs, stomach, heart, and other organs. This tissue is called mesothelium. Most people who get this
Brain Tumors A HANDBOOK FOR THE NEWLY DIAGNOSED
 Brain Tumors A HANDBOOK FOR THE NEWLY DIAGNOSED INSURANCE CARD Insurance PART ONE: THE DIAGNOSIS Introduction...3 Where do I start?...5 Types of brain tumor treatments...5 Your healthcare team.................
Brain Tumors A HANDBOOK FOR THE NEWLY DIAGNOSED INSURANCE CARD Insurance PART ONE: THE DIAGNOSIS Introduction...3 Where do I start?...5 Types of brain tumor treatments...5 Your healthcare team.................
Hosts. New Methods for Treating Colorectal Cancer
 Hosts Anees Chagpar MD Associate Professor of Surgical Oncology Francine MD Professor of Medical Oncology New Methods for Treating Colorectal Cancer Guest Expert: Scott, MD Associate Professor in the Department
Hosts Anees Chagpar MD Associate Professor of Surgical Oncology Francine MD Professor of Medical Oncology New Methods for Treating Colorectal Cancer Guest Expert: Scott, MD Associate Professor in the Department
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم
 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Updates in Mesothelioma By Samieh Amer, MD Professor of Cardiothoracic Surgery Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University History Wagner and his colleagues (1960) 33 cases of mesothelioma
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Updates in Mesothelioma By Samieh Amer, MD Professor of Cardiothoracic Surgery Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University History Wagner and his colleagues (1960) 33 cases of mesothelioma
Avastin: Glossary of key terms
 Avastin: Glossary of key terms Adenocarcinoma Adenoma Adjuvant therapy Angiogenesis Anti-angiogenics Antibody Antigen Avastin (bevacizumab) Benign A form of carcinoma that originates in glandular tissue.
Avastin: Glossary of key terms Adenocarcinoma Adenoma Adjuvant therapy Angiogenesis Anti-angiogenics Antibody Antigen Avastin (bevacizumab) Benign A form of carcinoma that originates in glandular tissue.
Radiation Therapy in the Treatment of
 Lung Cancer Radiation Therapy in the Treatment of Lung Cancer JMAJ 46(12): 537 541, 2003 Kazushige HAYAKAWA Professor and Chairman, Department of Radiology, Kitasato University School of Medicine Abstract:
Lung Cancer Radiation Therapy in the Treatment of Lung Cancer JMAJ 46(12): 537 541, 2003 Kazushige HAYAKAWA Professor and Chairman, Department of Radiology, Kitasato University School of Medicine Abstract:
Disease/Illness GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER. What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? www.simpsonmillar.co.uk Telephone 0844 858 3200
 GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
Mesothelioma. 1. Introduction. 1.1 General Information and Aetiology
 Mesothelioma 1. Introduction 1.1 General Information and Aetiology Mesotheliomas are tumours that arise from the mesothelial cells of the pleura, peritoneum, pericardium or tunica vaginalis [1]. Most are
Mesothelioma 1. Introduction 1.1 General Information and Aetiology Mesotheliomas are tumours that arise from the mesothelial cells of the pleura, peritoneum, pericardium or tunica vaginalis [1]. Most are
An Introduction to PROSTATE CANCER
 An Introduction to PROSTATE CANCER Being diagnosed with prostate cancer can be a life-altering experience. It requires making some very difficult decisions about treatments that can affect not only the
An Introduction to PROSTATE CANCER Being diagnosed with prostate cancer can be a life-altering experience. It requires making some very difficult decisions about treatments that can affect not only the
Thymus Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand what thymus cancer is and what treatment options are available.
 Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
The following information is only meant for people who have been diagnosed with advanced non-small cell
 Important information for people with advanced non-small cell lung cancer The following information is only meant for people who have been diagnosed with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). NSCLC
Important information for people with advanced non-small cell lung cancer The following information is only meant for people who have been diagnosed with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). NSCLC
AA Life Insurance providing access to Best Doctors. AA Life Insurance is provided by Friends Life and Pensions Limited
 AA Life Insurance is provided by Friends Life and Pensions Limited What would be the first thing you might think about if you were diagnosed with a serious illness? 2 It is very likely that the first thing
AA Life Insurance is provided by Friends Life and Pensions Limited What would be the first thing you might think about if you were diagnosed with a serious illness? 2 It is very likely that the first thing
Small cell lung cancer
 Small cell lung cancer Small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs that are found within
Small cell lung cancer Small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs that are found within
AA Life Insurance providing access to Best Doctors. AA Life Insurance is provided by Friends Life Limited
 AA Life Insurance is provided by Friends Life Limited What would be the first thing you might think about if you were diagnosed with a serious illness? It is very likely that the first thing you might
AA Life Insurance is provided by Friends Life Limited What would be the first thing you might think about if you were diagnosed with a serious illness? It is very likely that the first thing you might
AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION. Ependymoma
 AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION Ependymoma ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ABOUT THE AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION Founded in 1973, the American Brain Tumor Association (ABTA) was the first national nonprofit organization
AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION Ependymoma ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ABOUT THE AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION Founded in 1973, the American Brain Tumor Association (ABTA) was the first national nonprofit organization
MesoPDT. Photodynamic Therapy for malignant pleural mesothelioma ONCO-THAI. Image Assisted Laser Therapy for Oncology
 MesoPDT Photodynamic Therapy for malignant pleural mesothelioma ONCO-THAI Image Assisted Laser Therapy for Oncology Unité Inserm ONCO-THAI «Image Assisted Laser Therapy for Oncology» Inserm ONCO-THAI "Image
MesoPDT Photodynamic Therapy for malignant pleural mesothelioma ONCO-THAI Image Assisted Laser Therapy for Oncology Unité Inserm ONCO-THAI «Image Assisted Laser Therapy for Oncology» Inserm ONCO-THAI "Image
What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms
 What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Interventions Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Radiology Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D.,
What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Interventions Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Radiology Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D.,
Adjuvant Therapy for Breast Cancer: Questions and Answers
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Adjuvant Therapy for Breast
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Adjuvant Therapy for Breast
Update in Hematology Oncology Targeted Therapies. Mark Holguin
 Update in Hematology Oncology Targeted Therapies Mark Holguin 25 years ago Why I chose oncology People How to help people with possibly the most difficult thing they may have to deal with Science Turning
Update in Hematology Oncology Targeted Therapies Mark Holguin 25 years ago Why I chose oncology People How to help people with possibly the most difficult thing they may have to deal with Science Turning
CHAPTER 2. Neoplasms (C00-D49) March 2014. 2014 MVP Health Care, Inc.
 Neoplasms (C00-D49) March 2014 2014 MVP Health Care, Inc. CHAPTER SPECIFIC CATEGORY CODE BLOCKS C00-C14 Malignant neoplasms of lip, oral cavity and pharynx C15-C26 Malignant neoplasms of digestive organs
Neoplasms (C00-D49) March 2014 2014 MVP Health Care, Inc. CHAPTER SPECIFIC CATEGORY CODE BLOCKS C00-C14 Malignant neoplasms of lip, oral cavity and pharynx C15-C26 Malignant neoplasms of digestive organs
Understanding. Brain Tumors. Jana, diagnosed in 1999, with her husband, Paul.
 Understanding Brain Tumors Jana, diagnosed in 1999, with her husband, Paul. What Is a Brain Tumor? A brain tumor, like other tumors, is a collection of cells that multiply at a rapid rate. The tumor may
Understanding Brain Tumors Jana, diagnosed in 1999, with her husband, Paul. What Is a Brain Tumor? A brain tumor, like other tumors, is a collection of cells that multiply at a rapid rate. The tumor may
How common is bowel cancer?
 information Primary Care Society for Gastroenterology Bowel Cancer (1 of 6) How common is bowel cancer? Each year 35,000 people in Britain are diagnosed with cancer of the bowel, that is to say cancer
information Primary Care Society for Gastroenterology Bowel Cancer (1 of 6) How common is bowel cancer? Each year 35,000 people in Britain are diagnosed with cancer of the bowel, that is to say cancer
Lung cancer forms in tissues of the lung, usually in the cells lining air passages.
 Scan for mobile link. Lung Cancer Lung cancer usually forms in the tissue cells lining the air passages within the lungs. The two main types are small-cell lung cancer (usually found in cigarette smokers)
Scan for mobile link. Lung Cancer Lung cancer usually forms in the tissue cells lining the air passages within the lungs. The two main types are small-cell lung cancer (usually found in cigarette smokers)
Diagnostic Challenge. Department of Pathology,
 Cytology of Pleural Fluid as a Diagnostic Challenge Paavo Pääkkö,, MD, PhD Chief Physician and Head of the Department Department of Pathology, Oulu University Hospital,, Finland Oulu University Hospital
Cytology of Pleural Fluid as a Diagnostic Challenge Paavo Pääkkö,, MD, PhD Chief Physician and Head of the Department Department of Pathology, Oulu University Hospital,, Finland Oulu University Hospital
Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment Cancer begins in our cells. Cells are the building blocks of our tissues. Tissues make up the organs of the body.
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment Cancer begins in our cells. Cells are the building blocks of our tissues. Tissues make up the organs of the body.
Malignant Lymphomas and Plasma Cell Myeloma
 Malignant Lymphomas and Plasma Cell Myeloma Dr. Bruce F. Burns Dept. of Pathology and Lab Medicine Overview definitions - lymphoma lymphoproliferative disorder plasma cell myeloma pathogenesis - translocations
Malignant Lymphomas and Plasma Cell Myeloma Dr. Bruce F. Burns Dept. of Pathology and Lab Medicine Overview definitions - lymphoma lymphoproliferative disorder plasma cell myeloma pathogenesis - translocations
Colorectal Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Treatment Colorectal cancer overview Colorectal cancer, also called large bowel cancer, is the term used to describe malignant tumors found in the colon and rectum.
Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Treatment Colorectal cancer overview Colorectal cancer, also called large bowel cancer, is the term used to describe malignant tumors found in the colon and rectum.
These rare variants often act aggressively and may respond differently to therapy than the more common prostate adenocarcinoma.
 Prostate Cancer OVERVIEW Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer diagnosed among American men, accounting for nearly 200,000 new cancer cases in the United States each year. Greater than 65% of
Prostate Cancer OVERVIEW Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer diagnosed among American men, accounting for nearly 200,000 new cancer cases in the United States each year. Greater than 65% of
How To Treat A Uterine Sarcoma
 EVERYONE S GUIDE FOR CANCER THERAPY Malin Dollinger, MD, Ernest H. Rosenbaum, MD, Margaret Tempero, MD, and Sean Mulvihill, MD 4 th Edition 2001 Uterus: Uterine Sarcomas Jeffrey L. Stern, MD Uterine sarcomas
EVERYONE S GUIDE FOR CANCER THERAPY Malin Dollinger, MD, Ernest H. Rosenbaum, MD, Margaret Tempero, MD, and Sean Mulvihill, MD 4 th Edition 2001 Uterus: Uterine Sarcomas Jeffrey L. Stern, MD Uterine sarcomas
Surgery. Wedge resection only part of the lung, not. not a lobe, is removed. Cancer Council NSW
 The treatment you receive will depend on your lung cancer type, for example, whether you have a non-small cell lung cancer Adenocarcinoma or Squamous cell carcinoma, and if this is a sub-type with a mutation.
The treatment you receive will depend on your lung cancer type, for example, whether you have a non-small cell lung cancer Adenocarcinoma or Squamous cell carcinoma, and if this is a sub-type with a mutation.
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ABLATION THERAPY
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ABLATION THERAPY THE DIVISION OF VASCULAR/INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY THE ROBERT WOOD JOHNSON UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL Treatment options for patients with cancer continue to expand, providing
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ABLATION THERAPY THE DIVISION OF VASCULAR/INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY THE ROBERT WOOD JOHNSON UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL Treatment options for patients with cancer continue to expand, providing
The brain structure and function
 The brain structure and function This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding brain tumours. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 5. Contents Introduction
The brain structure and function This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding brain tumours. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 5. Contents Introduction
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Therapies
 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Therapies Guest Expert: Roy, MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Therapeutic Radiology Scott, MD Assistant Professor of Medical Oncology www.wnpr.org www.yalecancercenter.org Welcome
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Therapies Guest Expert: Roy, MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Therapeutic Radiology Scott, MD Assistant Professor of Medical Oncology www.wnpr.org www.yalecancercenter.org Welcome
Access to over 53,000 of the world s leading medical experts, from your first day of cover.
 For customers Friends Life Individual Protection providing access to Best Doctors Access to over 53,000 of the world s leading medical experts, from your first day of cover. A second medical opinion could
For customers Friends Life Individual Protection providing access to Best Doctors Access to over 53,000 of the world s leading medical experts, from your first day of cover. A second medical opinion could
ACUTE MYELOID LEUKEMIA (AML),
 1 ACUTE MYELOID LEUKEMIA (AML), ALSO KNOWN AS ACUTE MYELOGENOUS LEUKEMIA WHAT IS CANCER? The body is made up of hundreds of millions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide, and die in an orderly
1 ACUTE MYELOID LEUKEMIA (AML), ALSO KNOWN AS ACUTE MYELOGENOUS LEUKEMIA WHAT IS CANCER? The body is made up of hundreds of millions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide, and die in an orderly
Clinical Management Guideline Management of locally advanced or recurrent Renal cell carcinoma. Protocol for Planning and Treatment
 Protocol for Planning and Treatment The process to be followed in the management of: LOCALLY ADVANCED OR METASTATIC RENAL CELL CARCINOMA Patient information given at each stage following agreed information
Protocol for Planning and Treatment The process to be followed in the management of: LOCALLY ADVANCED OR METASTATIC RENAL CELL CARCINOMA Patient information given at each stage following agreed information
Case report : pineal metastasis from lung cancer
 Copyright Priory Lodge Education Ltd. 2005 First Published 17 th June 2005 Case report : pineal metastasis from lung cancer Dr. K.W. Lam 1 MRCS, Dr F C Cheung 2 FRCS, FHKAM, Dr K M Ko 1 FRCS, FHKAM Department
Copyright Priory Lodge Education Ltd. 2005 First Published 17 th June 2005 Case report : pineal metastasis from lung cancer Dr. K.W. Lam 1 MRCS, Dr F C Cheung 2 FRCS, FHKAM, Dr K M Ko 1 FRCS, FHKAM Department
Avastin in breast cancer: Summary of clinical data
 Avastin in breast cancer: Summary of clinical data Worldwide, over one million people are diagnosed with breast cancer every year 1. It is the most frequently diagnosed cancer in women 1,2, and the leading
Avastin in breast cancer: Summary of clinical data Worldwide, over one million people are diagnosed with breast cancer every year 1. It is the most frequently diagnosed cancer in women 1,2, and the leading
Understanding. Pancreatic Cancer
 Understanding Pancreatic Cancer Understanding Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreas The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your
Understanding Pancreatic Cancer Understanding Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreas The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your
One out of every two men and one out of every three women will have some type of cancer at some point during their lifetime. 3
 1. What is cancer? 2. What causes cancer?. What causes cancer? 3. Can cancer be prevented? The Facts One out of every two men and one out of every three women will have some type of cancer at some point
1. What is cancer? 2. What causes cancer?. What causes cancer? 3. Can cancer be prevented? The Facts One out of every two men and one out of every three women will have some type of cancer at some point
SUNY DOWNSTATE MEDICAL CENTER SURGERY GRAND ROUNDS February 28, 2013 VERENA LIU, MD ROSEANNA LEE, MD
 SUNY DOWNSTATE MEDICAL CENTER SURGERY GRAND ROUNDS February 28, 2013 VERENA LIU, MD ROSEANNA LEE, MD Case Presentation 35 year old male referred from PMD with an asymptomatic palpable right neck mass PMH/PSH:
SUNY DOWNSTATE MEDICAL CENTER SURGERY GRAND ROUNDS February 28, 2013 VERENA LIU, MD ROSEANNA LEE, MD Case Presentation 35 year old male referred from PMD with an asymptomatic palpable right neck mass PMH/PSH:
1400 Telegraph Bloomfield Hills, MI 48302 248-334-6877-Phone number/248-334-6877-fax Number CANCER TREATMENT
 1400 Telegraph Bloomfield Hills, MI 48302 248-334-6877-Phone number/248-334-6877-fax Number CANCER TREATMENT Learning that your pet has a diagnosis of cancer can be overwhelming. We realize that your pet
1400 Telegraph Bloomfield Hills, MI 48302 248-334-6877-Phone number/248-334-6877-fax Number CANCER TREATMENT Learning that your pet has a diagnosis of cancer can be overwhelming. We realize that your pet
Cavernous Angioma. Cerebral Cavernous Malformation ...
 Cavernous Angioma... Cerebral Cavernous Malformation Information For Patients And Loved Ones 107 Quaker Meeting House Road Williamsburg, Virginia 23188 USA 1-866-HEAL-CCM 1-757-258-3355 www.angiomaalliance.org
Cavernous Angioma... Cerebral Cavernous Malformation Information For Patients And Loved Ones 107 Quaker Meeting House Road Williamsburg, Virginia 23188 USA 1-866-HEAL-CCM 1-757-258-3355 www.angiomaalliance.org
ATLAS OF HEAD AND NECK PATHOLOGY THYROID PAPILLARY CARCINOMA
 Papillary carcinoma is the most common of thyroid malignancies and occurs in all age groups but particularly in women under 45 years of age. There is a high rate of cervical metastatic disease and yet
Papillary carcinoma is the most common of thyroid malignancies and occurs in all age groups but particularly in women under 45 years of age. There is a high rate of cervical metastatic disease and yet
Medullary Renal Cell Carcinoma Case Report
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 27, No. 4, December 2005 Medullary Renal Cell Carcinoma Case Report Mohammed Abdulla Al-Tantawi MBBCH, CABS* Abdul Amir Issa MBBCH, CABS*** Mohammed Abdulla MBBCH, CABS**
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 27, No. 4, December 2005 Medullary Renal Cell Carcinoma Case Report Mohammed Abdulla Al-Tantawi MBBCH, CABS* Abdul Amir Issa MBBCH, CABS*** Mohammed Abdulla MBBCH, CABS**
The Di Bella Method (DBM) improves Survival, Objective Response and Performance Status in Breast Cancer
 BIT's 4th World Cancer Congress 2011 People s Republic of China Dalian The Di Bella Method (DBM) improves Survival, Objective Response and Performance Status in treated with DBM therapy Retrospective observational
BIT's 4th World Cancer Congress 2011 People s Republic of China Dalian The Di Bella Method (DBM) improves Survival, Objective Response and Performance Status in treated with DBM therapy Retrospective observational
NICE Pathways bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic.
 bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published.
bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published.
Breast Cancer: from bedside and grossing room to diagnoses and beyond. Adriana Corben, M.D.
 Breast Cancer: from bedside and grossing room to diagnoses and beyond Adriana Corben, M.D. About breast anatomy Breasts are special organs that develop in women during puberty when female hormones are
Breast Cancer: from bedside and grossing room to diagnoses and beyond Adriana Corben, M.D. About breast anatomy Breasts are special organs that develop in women during puberty when female hormones are
AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION. Meningioma
 AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION Meningioma AcKnoWLeDGemenTs about the american BraIn tumor association Founded in 1973, the American Brain Tumor Association (ABTA) was the first national nonprofit organization
AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION Meningioma AcKnoWLeDGemenTs about the american BraIn tumor association Founded in 1973, the American Brain Tumor Association (ABTA) was the first national nonprofit organization
Management of spinal cord compression
 Management of spinal cord compression (SUMMARY) Main points a) On diagnosis, all patients should receive dexamethasone 10mg IV one dose, then 4mg every 6h. then switched to oral dose and tapered as tolerated
Management of spinal cord compression (SUMMARY) Main points a) On diagnosis, all patients should receive dexamethasone 10mg IV one dose, then 4mg every 6h. then switched to oral dose and tapered as tolerated
PRODYNOV. Targeted Photodynamic Therapy of Ovarian Peritoneal Carcinomatosis ONCO-THAI. Image Assisted Laser Therapy for Oncology
 PRODYNOV Targeted Photodynamic Therapy of Ovarian Peritoneal Carcinomatosis ONCO-THAI Image Assisted Laser Therapy for Oncology Inserm ONCO-THAI «Image Assisted Laser Therapy for Oncology» Inserm ONCO-THAI
PRODYNOV Targeted Photodynamic Therapy of Ovarian Peritoneal Carcinomatosis ONCO-THAI Image Assisted Laser Therapy for Oncology Inserm ONCO-THAI «Image Assisted Laser Therapy for Oncology» Inserm ONCO-THAI
National Cancer Institute. What You Need TM. To Know About. Brain Tumors. U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health
 National Cancer Institute What You Need TM To Know About Brain Tumors U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health For more publications This is only one of many free booklets
National Cancer Institute What You Need TM To Know About Brain Tumors U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health For more publications This is only one of many free booklets
95% of childhood kidney cancer cases are Wilms tumours. Childhood kidney cancer is extremely rare, with only 90 cases a year in
 James Whale Fund for Kidney Cancer Childhood kidney cancer factsheet Kidney cancer rarely afflicts children and about 90 paediatric cases are diagnosed in the UK each year. About 75% of childhood kidney
James Whale Fund for Kidney Cancer Childhood kidney cancer factsheet Kidney cancer rarely afflicts children and about 90 paediatric cases are diagnosed in the UK each year. About 75% of childhood kidney
How Cancer Begins???????? Chithra Manikandan Nov 2009
 Cancer Cancer is one of the most common diseases in the developed world: 1 in 4 deaths are due to cancer 1 in 17 deaths are due to lung cancer Lung cancer is the most common cancer in men Breast cancer
Cancer Cancer is one of the most common diseases in the developed world: 1 in 4 deaths are due to cancer 1 in 17 deaths are due to lung cancer Lung cancer is the most common cancer in men Breast cancer
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER
 GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER BY Ali Shamseddine, MD (Coordinator); as04@aub.edu.lb Fady Geara, MD Bassem Shabb, MD Ghassan Jamaleddine, MD CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER BY Ali Shamseddine, MD (Coordinator); as04@aub.edu.lb Fady Geara, MD Bassem Shabb, MD Ghassan Jamaleddine, MD CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT
Metastatic Breast Cancer...
 DIAGNOSIS: Metastatic Breast Cancer... What Does It Mean For You? A diagnosis of metastatic breast cancer can be frightening. It raises many questions and reminds us of days past when cancer was such a
DIAGNOSIS: Metastatic Breast Cancer... What Does It Mean For You? A diagnosis of metastatic breast cancer can be frightening. It raises many questions and reminds us of days past when cancer was such a
Technology appraisal guidance Published: 27 June 2007 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta121
 Carmustine implants and temozolomide for the treatment of newly diagnosed high-grade glioma Technology appraisal guidance Published: 27 June 2007 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta121 NICE 2007. All rights reserved.
Carmustine implants and temozolomide for the treatment of newly diagnosed high-grade glioma Technology appraisal guidance Published: 27 June 2007 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta121 NICE 2007. All rights reserved.
Avastin in breast cancer: Summary of clinical data
 Avastin in breast cancer: Summary of clinical data Worldwide, over one million people are diagnosed with breast cancer every year 1. It is the most frequently diagnosed cancer in women 1,2, and the leading
Avastin in breast cancer: Summary of clinical data Worldwide, over one million people are diagnosed with breast cancer every year 1. It is the most frequently diagnosed cancer in women 1,2, and the leading
Parts of the Brain. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
Novel Surgery for Inoperable Brain Tumors. A Patient Guide to NeuroBlate
 Novel Surgery for Inoperable Brain Tumors A Patient Guide to NeuroBlate rose ella burkhardt brain tumor and neuro-oncology center Pioneering a Promising Surgical Treatment A brain tumor diagnosis is overwhelming
Novel Surgery for Inoperable Brain Tumors A Patient Guide to NeuroBlate rose ella burkhardt brain tumor and neuro-oncology center Pioneering a Promising Surgical Treatment A brain tumor diagnosis is overwhelming
SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER
 Protocol for Planning and Treatment The process to be followed in the management of: SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER Patient information given at each stage following agreed information pathway 1. DIAGNOSIS New
Protocol for Planning and Treatment The process to be followed in the management of: SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER Patient information given at each stage following agreed information pathway 1. DIAGNOSIS New
